Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bonding and fractographic characterization of universal adhesives applied to dentin in multimode strategies: an in vitro study
- Samaa M. Morsy, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Naji Kharouf, Ahmed A. Holiel
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e12. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
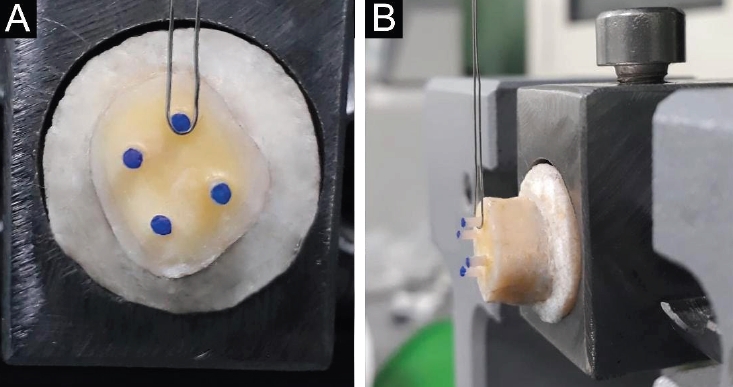
Universal adhesives (UAs) are marketed as versatile systems for both self-etch (SE) and total-etch (TE) modes. While their bond strength has been widely investigated, evidence linking fracture characteristics to bonding performance remains limited. This study evaluated the micro-shear bond strength (μSBS) and failure patterns of three UAs applied in SE and TE modes, complemented by fractographic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
Methods
Eighteen extracted human molars were sectioned to expose mid-coronal dentin and randomly allocated to SE or TE application. Three UAs were tested: Tetric N-Bond Universal, All-Bond Universal, and Single Bond Universal (SBU). Composite micro-rods (n = 72) were bonded, thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5°C and 55°C, and subjected to μSBS testing. Fracture surfaces were examined under SEM and classified as adhesive, cohesive, or mixed. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test, and Spearman correlation (α = 0.05).
Results
In TE mode, SBU demonstrated the highest μSBS (p < 0.001), whereas no significant differences were observed among adhesives in SE mode (p > 0.05). SEM analysis revealed adhesive failures as interfacial fractures, cohesive failures with beach marks, and mixed failures involving crack propagation through both dentin and composite. Adhesive failures correlated negatively with μSBS (rs = –0.77), while mixed failures correlated positively (rs = 0.81).
Conclusions
Both the etching strategy and adhesive formulation significantly affect bond strength and fracture behavior. Fractographic SEM analysis provides critical insights into the mechanical reliability of UAs and informs their clinical application.
- 215 View
- 24 Download

- Effects of dentin surface preparations on bonding of self-etching adhesives under simulated pulpal pressure
- Chantima Siriporananon, Pisol Senawongse, Vanthana Sattabanasuk, Natchalee Srimaneekarn, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e4. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
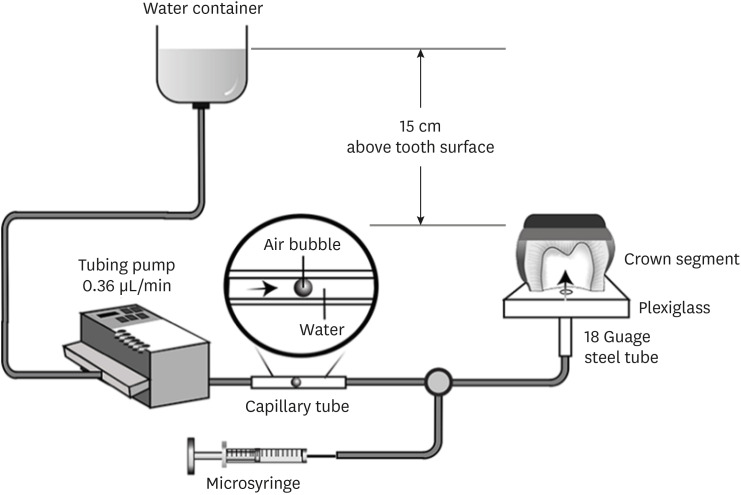
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of different smear layer preparations on the dentin permeability and microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of 2 self-etching adhesives (Clearfil SE Bond [CSE] and Clearfil Tri-S Bond Universal [CTS]) under dynamic pulpal pressure.
Materials and Methods Human third molars were cut into crown segments. The dentin surfaces were prepared using 4 armamentaria: 600-grit SiC paper, coarse diamond burs, superfine diamond burs, and carbide burs. The pulp chamber of each crown segment was connected to a dynamic intra-pulpal pressure simulation apparatus, and the permeability test was done under a pressure of 15 cmH2O. The relative permeability (%P) was evaluated on the smear layer-covered and bonded dentin surfaces. The teeth were bonded to either of the adhesives under pulpal pressure simulation, and cut into sticks after 24 hours water storage for the µTBS test. The resin-dentin interface and nanoleakage observations were performed using a scanning electron microscope. Statistical comparisons were done using analysis of variance and
post hoc tests.Results Only the method of surface preparation had a significant effect on permeability (
p < 0.05). The smear layers created by the carbide and superfine diamond burs yielded the lowest permeability. CSE demonstrated a higher µTBS, with these values in the superfine diamond and carbide bur groups being the highest. Microscopic evaluation of the resin-dentin interface revealed nanoleakage in the coarse diamond bur and SiC paper groups for both adhesives.Conclusions Superfine diamond and carbide burs can be recommended for dentin preparation with the use of 2-step CSE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
Chavakorn Atsavathavornset, Pipop Saikaew, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Hidehiko Sano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Universal adhesive systems in dentistry: A narrative review
Svetlana N. Razumova, Anzhela S. Brago, Oxana R. Ruda, Zoya A. Guryeva, Elvira V. Adzhieva
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2024; 28(5): 512. CrossRef - Delayed light activation of resin composite affects the bond strength of adhesives under dynamic simulated pulpal pressure
Nattaporn Sukprasert, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Pisol Senawongse, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(11): 6743. CrossRef
- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
- 3,122 View
- 48 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Microleakage and characteristics of resin-tooth tissues interface of a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive systems
- Xuan Vinh Tran, Khanh Quang Tran
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e30. Published online May 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
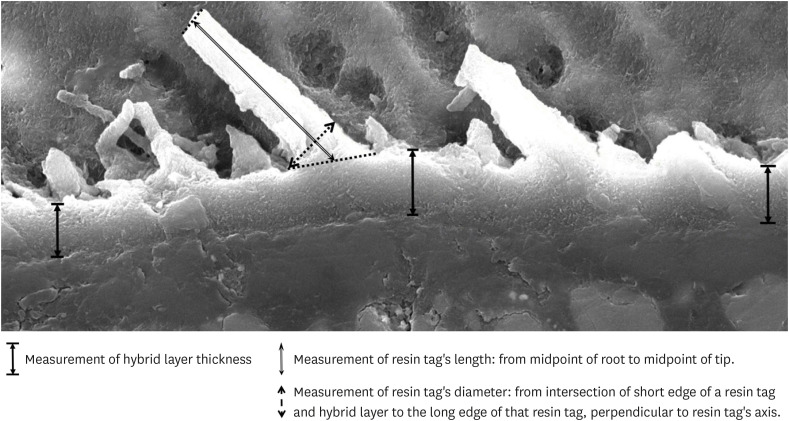
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to compare the microleakage and characteristics of the resin-tooth tissue interface between self-etch and etch-and-rinse adhesive systems after 48 hours and 3 months.
Materials and Methods 40 extracted premolar teeth were randomly divided into 2 groups: 1-step self-etch adhesive system – Optibond™ All-In-One, and 2-step etch-and-rinse adhesive system - Adper™ Single Bond 2. Both groups were subjected to 500 thermocycles (5°C–55°C) before scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis or microleakage trial at 48-hour and 3-month time periods.
Results SEM images showed the hybrid layer thickness, diameter, and length of resin tags of the self-etch adhesive (0.42 ± 0.14 µm; 1.49 ± 0.45 µm; 16.35 ± 14.26 µm) were smaller than those of the etch-and-rinse adhesive (4.39 ± 1.52 µm; 3.49 ± 1 µm; 52.81 ± 35.81 µm). In dentin, the microleakage scores of the 2 adhesives were not different in both time periods (48 hours/3 months). However, the microleakage score of etch-and-rinse adhesive increased significantly after 3 months (0.8 ± 0.63 and 1.9 ± 0.88,
p < 0.05).Conclusions The self-etch adhesive exhibited better long-term sealing ability in dentin when compared to that of the etch-and-rinse adhesive. The greater hybrid layer thickness and dimensions of resin tags did not guarantee reliable, long-lasting sealing in the bonding area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of shear bond strength of sixth- and fourth-generation adhesives in primary teeth
Maryam Hajiahmadi, Najmeh Akhlaghi, Hamid Mosleh, Ehsan Samani, Sheida Bagheri, Zohreh Salehi
Dental Research Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of different adhesive systems in bonding direct resin composite restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ravinder S. Saini, Rajesh Vyas, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Artak Heboyan
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(2): 115. CrossRef - Characterisation of universal adhesive bonded resin-dentin interface after focused ultrasound smear layer conditioning
Cheryl Fu, Peta L. Clode, Amr S. Fawzy
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 142: 104115. CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Pretreatment With Dimethyl Sulfoxide Solution on Interfacial Fracture Toughness of Composite Resin to Wet and Dry Dentin
Fatemeh Molaei, Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Seyedeh Maryam Tavangar, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Resin tags formation by modified Renewal MI formulations in a carious dentine model
Nabih Alkhouri, Wendy Xia, Paul Ashley, Anne Young
Frontiers in Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of propolis added to single‐bottle adhesives on water permeation through the hybrid layer
Lucineide Silva da Rocha, Daniela Ferreira de Oliveira, Cinthya Luna Veloso de Lima, Ticiano Gomes do Nascimento, Johnnatan Duarte de Freitas, Jeniffer Mclaine Duarte de Freitas, Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploration and preliminary clinical investigation of an adhesive approach for primary tooth restoration
Xiangqin Xu, Jiansheng Zhu, May Lei Mei, Huaying Wu, Kaipeng Xie, Shoulin Wang, Yaming Chen
The Journal of Biomedical Research.2023; 37(2): 138. CrossRef - Adhesion to enamel and dentine: an update
Rana Alkattan
Primary Dental Journal.2023; 12(3): 33. CrossRef - Effects of carbodiimide combined with ethanol–wet bonding pretreatment on dentin bonding properties: an in vitro study
Xiaoxiao You, Long Chen, Jie Xu, Sihui Li, Zhenghao Zhang, Ling Guo
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14238. CrossRef - The effects of amalgam contamination and different surface modifications on microleakage of dentin bonded to bulk fill composite when using different adhesive protocols
Nojoud Alshehri, Abdullah Aljamhan, Mohammed Bin-Shuwaish
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of low-shrinkage dental adhesives via blending with spiroorthocarbonate expanding monomer and unsaturated epoxy resin monomer
Zonghua Wang, Xiaoran Zhang, Shuo Yao, Jiaxin Zhao, Chuanjian Zhou, Junling Wu
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 133: 105308. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on the resin-dentin bond strength and antibacterial activity of a self-etch adhesive system
Jia Wang, Wei Jiang, Jingping Liang, Shujun Ran
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(6): 1363.e1. CrossRef
- A systematic review of shear bond strength of sixth- and fourth-generation adhesives in primary teeth
- 2,698 View
- 41 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Effect of smear layer deproteinization on bonding of self-etch adhesives to dentin: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Khaldoan H. Alshaikh, Hamdi H. H. Hamama, Salah H. Mahmoud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e14. Published online March 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this systematic review was to critically analyze previously published studies of the effects of dentin surface pretreatment with deproteinizing agents on the bonding of self-etch (SE) adhesives to dentin. Additionally, a meta-analysis was conducted to quantify the effects of the above-mentioned surface pretreatment methods on the bonding of SE adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods An electronic search was performed using the following databases: Scopus, PubMed and ScienceDirect. The online search was performed using the following keywords: ‘dentin’ or ‘hypochlorous acid’ or ‘sodium hypochlorite’ and ‘self-etch adhesive.’ The following categories were excluded during the assessment process: non-English articles, randomized clinical trials, case reports, animal studies, and review articles. The reviewed studies were subjected to meta-analysis to quantify the effect of the application time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl) deproteinizing agents on bonding to dentin.
Results Only 9 laboratory studies fit the inclusion criteria of this systematic review. The results of the meta-analysis revealed that the pooled average microtensile bond strength values to dentin pre-treated with deproteinizing agents (15.71 MPa) was significantly lower than those of the non-treated control group (20.94 MPa).
Conclusions In light of the currently available scientific evidence, dentin surface pretreatment with deproteinizing agents does not enhance the bonding of SE adhesives to dentin. The HOCl deproteinizing agent exhibited minimal adverse effects on bonding to dentin in comparison with NaOCl solutions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of finishing protocols on dentin surface characteristics and bond strength after tooth preparation for indirect restorations
Paola Bernardes, Amanda das Graças Soares, Bárbara Inácio de Melo, Leandro Maruki Pereira, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Rafael Rocha Pacheco, Marcel Santana Prudente, Luís Henrique Araújo Raposo
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2026; 135(2): 371.e1. CrossRef - Is the Percentage of Collagen in Coronal Dentin Related to Microtensile Strength? An In Vitro Study
Taíssa Cássia de Souza Furtado, Gilberto Antonio Borges, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo-Martins, Bruno Henrique dos Reis Souza Oliveira, Renata Margarida Etchebehere, Sanívia Aparecida de Lima Pereira
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Biomodification on the Survival of Resin Composite Restorations: An Umbrella Review
El Alaoui Nihal, Chala Sanaa, Ghoul Sonia
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(2): 109446. CrossRef - Coronal cavity pretreatment agents and restoration protocols effect on microleakage of endodontically treated teeth
Lena Bal, Cangül Keskin, Aybüke Karaca Sakallı, Osman Fatih Aydın
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2026; 7(1): 40. CrossRef -
Evaluating the remnants of Al
2
O
3
particles on different dentine substrate after sandblasting and various cleaning protocols
Faeze Hamze, Khotan Aflatoonian, Mahshid Mohammadibassir, Mohammad-Bagher Rezvani
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2025; 39(6): 869. CrossRef - Preservation Strategies for Interfacial Integrity in Restorative Dentistry: A Non-Comprehensive Literature Review
Carmem S. Pfeifer, Fernanda S. Lucena, Fernanda M. Tsuzuki
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(2): 42. CrossRef - Outcome of Er, Cr:YSGG laser and antioxidant pretreatments on bonding quality to caries-induced dentin
Lamiaa M. Moharam, Haidy N. Salem, Ahmed Abdou, Rasha H. Afifi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - A comparison of different cleaning approaches for blood contamination after curing universal adhesives on the dentine surface
Ting Liu, Haifeng Xie, Chen Chen
Dental Materials.2024; 40(11): 1786. CrossRef - Effect of fiber-reinforced direct restorative materials on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated mandibular molars restored with a conservative endodontic cavity design
Merve Nezir, Beyza Arslandaş Dinçtürk, Ceyda Sarı, Cemile Kedici Alp, Hanife Altınışık
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the use of bromelain associated with bioactive glass-ceramic on dentin/adhesive interface
Rocio Geng Vivanco, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Viviane de de Cássia Oliveira, Mário Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experimental and Chitosan-Infused Adhesive with Dentin Pretreated with Femtosecond Laser, Methylene Blue-Activated Low-Level Laser, and Phosphoric Acid
Fahad Alkhudhairy
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(10): 634. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effective Bond Strength of Composite Resin to Etched Dentin after Dentin Pretreatment: An In-vitro Study
Muhammed Bilal, Shiraz Pasha, Arathi S. Nair
Journal of the Scientific Society.2024; 51(4): 545. CrossRef - Comparison of Different Dentin Deproteinizing Agents on Bond Strength and Microleakage of Universal Adhesive to Dentin
Fatih Bedir, Gül Yıldız Telatar
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2023; 14(1): 44. CrossRef - Addition of metal chlorides to a HOCl conditioner can enhance bond strength to smear layer deproteinized dentin
Kittisak Sanon, Antonin Tichy, Takashi Hatayama, Ornnicha Thanatvarakorn, Taweesak Prasansuttiporn, Takahiro Wada, Yasushi Shimada, Keiichi Hosaka, Masatoshi Nakajima
Dental Materials.2022; 38(8): 1235. CrossRef - Internal and Marginal Adaptation of Adhesive Resin Cements Used for Luting Inlay Restorations: An In Vitro Micro-CT Study
Linah M. Ashy, Hanadi Marghalani
Materials.2022; 15(17): 6161. CrossRef - Collagen-depletion strategies in dentin as alternatives to the hybrid layer concept and their effect on bond strength: a systematic review
António H. S. Delgado, Madalena Belmar Da Costa, Mário Cruz Polido, Ana Mano Azul, Salvatore Sauro
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - NaOCl Application after Acid Etching and Retention of Cervical Restorations: A 3-Year Randomized Clinical Trial
M Favetti, T Schroeder, AF Montagner, RR Moraes, T Pereira-Cenci, MS Cenci
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 268. CrossRef - Resin infiltrant protects deproteinized dentin against erosive and abrasive wear
Ana Theresa Queiroz de Albuquerque, Bruna Oliveira Bezerra, Isabelly de Carvalho Leal, Maria Denise Rodrigues de Moraes, Mary Anne S. Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bis[2-(Methacryloyloxy) Ethyl] Phosphate as a Primer for Enamel and Dentine
R. Alkattan, G. Koller, S. Banerji, S. Deb
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(10): 1081. CrossRef - Influence of Dentine Pre-Treatment by Sandblasting with Aluminum Oxide in Adhesive Restorations. An In Vitro Study
Bruna Sinjari, Manlio Santilli, Gianmaria D’Addazio, Imena Rexhepi, Alessia Gigante, Sergio Caputi, Tonino Traini
Materials.2020; 13(13): 3026. CrossRef - A novel prime-&-rinse mode using MDP and MMPs inhibitors improves the dentin bond durability of self-etch adhesive
Jingqiu Xu, Mingxing Li, Wenting Wang, Zhifang Wu, Chaoyang Wang, Xiaoting Jin, Ling Zhang, Wenxiang Jiang, Baiping Fu
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 104: 103698. CrossRef - The effects of deproteinization and primer treatment on microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to dentin
In-Hye Bae, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(2): 99. CrossRef - Effect of Papain and Bromelain Enzymes on Shear Bond Strength of Composite to Superficial Dentin in Different Adhesive Systems
Farahnaz Sharafeddin, Mina Safari
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(9): 1077. CrossRef
- Effect of finishing protocols on dentin surface characteristics and bond strength after tooth preparation for indirect restorations
- 2,785 View
- 27 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Comparing the effect of a desensitizing material and a self-etch adhesive on dentin sensitivity after periodontal surgery: a randomized clinical trial
- Hila Hajizadeh, Atefeh Nemati-Karimooy, Sara Majidinia, Amir Moeintaghavi, Marjaneh Ghavamnasiri
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):168-175. Published online July 21, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.168
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the ability of a desensitizing agent and a self-etch adhesive on cervical dentin sensitivity (CDS) after periodontal surgery.
Materials and Methods Ninety hypersensitive teeth of 13 subjects were included in the study. After periodontal surgery, the teeth of each posterior sextant treated with one of the following materials: G1: Clearfil S3 Bond (Kuraray Dental), G2: Gluma Desensitizer (Heraeus Kulzer), and G3: placebo (water). The sensitivity was assessed using evaporative stimuli before treatment (baseline, T0), 1 day after treatment (T1), after 1 week (T2), and after 1 month (T3) according to visual analog scale (VAS).
Results Following the treatment, all the 3 groups showed significant reduction of CDS in T1 compared to T0. Reduction of CDS between T1 and T2 was observed only in G1 but there was no significant difference between T2 and T3 in this group. Although we observed a significant difference in T3 compared to T1 and T2 in G2 and G3, comparison of treatment groups in each assessment time showed a significant difference only in T3. According to paired comparison, this was due to the difference between G2 and G3.
Conclusions Dentin sensitivity following periodontal surgery will decrease spontaneously over time, but treating the sensitive teeth with Gluma Desensitizer and Clearfil S3 Bond can have some benefits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different material protocols on the control of dentin hypersensitivity: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
Júlia Marques Martins, Maria Fernanda Ferreira Nogueira, Guilherme José Pimentel Lopes de Oliveira, Alexandre Coelho Machado, Paulo César de Freitas Santos Filho, Hugo Lemes Carlo, Carlos José Soares, Gisele Rodrigues da Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomineralization reaction from nanosized calcium silicate: A new method for reducing dentin hypersensitivity
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Jeong-Kil Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Yu-Chih Chiang, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(1): 428. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self-etching Adhesive Only Versus in Combination with Gluma Desensitizer for Preventing Post-composite Sensitivity - A Prospective Study
Hemamalini Rath, Shilpa Mahapatra, Sri Priya Narayanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(1): 32. CrossRef - Efficacy of seventh generation bonding agents as desensitizers in patients with dentin hypersensitivity: a randomized clinical trial
Sumaiya Shabbir, Shahbaz Ahmed, Syed Jaffar Abbas Zaidi, Sania Riaz, Huma Sarwar, Muhammad Taqi, Zia ur Rahman Khan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the crystal formation from calcium silicate in human dentinal tubules and the effect of phosphate buffer saline concentration
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jin-Soo Ahn, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2278. CrossRef - The effect of fluoride iontophoresis on seal ability of self-etch adhesive in human dentin in vitro
Kanittha Kijsamanmith, Parintorn Wallanon, Chanya Pitchayasatit, Poonnapha Kittiratanaviwat
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The study of toothpaste desensitizing properties
S. B. Ulitovskiy, O. V. Kalinina, A. A. Leontev, O. V. Khabarova, L. I. Pankrateva, E. S. Soloveva, N. K. Fok
Parodontologiya.2022; 27(1): 81. CrossRef - Effectiveness and cytotoxicity of two desensitizing agents: a dentin permeability measurement and dentin barrier testing in vitro study
Ruodan Jiang, Yongxiang Xu, Feilong Wang, Hong Lin
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A randomized clinical trial of dentin hypersensitivity reduction over one month after a single topical application of comparable materials
Samar Hatem Abuzinadah, Abdulrahman Jafar Alhaddad
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between effectiveness of dentine desensitizer and one bottle self-etch adhesive on dentine hypersensitivity
Muhammad Zohaib Younus, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Azeem Ul Yaqin Syed, Jiand Malik Baloch, Muhammad Ali, Abubakar Sheikh
Technology and Health Care.2021; 29(6): 1153. CrossRef - A long-term evaluation of experimental potassium oxalate concentrations on dentin hypersensitivity reduction: A triple-blind randomized clinical trial
Alexia da Mata Galvão, Livia Fávaro Zeola, Guilherme Faria Moura, Daniela Navarro Ribeiro Teixeira, Ramon Corrêa de Queiroz Gonzaga, Gisele Rodrigues da Silva, Paulo Vinícius Soares
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 89: 103180. CrossRef
- Effect of different material protocols on the control of dentin hypersensitivity: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
- 2,488 View
- 10 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Marginal microleakage of cervical composite resin restorations bonded using etch-and-rinse and self-etch adhesives: two dimensional vs. three dimensional methods
- Maryam Khoroushi, Ailin Ehteshami
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):83-90. Published online April 18, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was evaluated the marginal microleakage of two different adhesive systems before and after aging with two different dye penetration techniques.
Materials and Methods Class V cavities were prepared on the buccal and lingual surfaces of 48 human molars. Clearfil SE Bond and Single Bond (self-etching and etch-and-rinse systems, respectively) were applied, each to half of the prepared cavities, which were restored with composite resin. Half of the specimens in each group underwent 10,000 cycles of thermocycling. Microleakage was evaluated using two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) dye penetration techniques separately for each half of each specimen. Data were analyzed with SPSS 11.5 (SPSS Inc.), using the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests (α = 0.05).
Results The difference between the 2D and 3D microleakage evaluation techniques was significant at the occlusal margins of Single bond groups (
p = 0.002). The differences between 2D and 3D microleakage evaluation techniques were significant at both the occlusal and cervical margins of Clearfil SE Bond groups (p = 0.017 andp = 0.002, respectively). The difference between the 2D and 3D techniques was significant at the occlusal margins of non-aged groups (p = 0.003). The difference between these two techniques was significant at the occlusal margins of the aged groups (p = 0.001). The Mann-Whitney test showed significant differences between the two techniques only at the occlusal margins in all specimens.Conclusions Under the limitations of the present study, it can be concluded that the 3D technique has the capacity to detect occlusal microleakage more precisely than the 2D technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Post‐Gel Polymerization Shrinkage Strain and Marginal Integrity of Repeatedly Preheated Thermo‐Viscous and Matrix‐Modified Bulk‐Fill Resin Composite (Pre‐Clinical Study)
Ahmed Amir, Rasha Zaghlool, Mona Riad
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026; 38(1): 97. CrossRef - The current advancements in chitosan nanoparticles in the management of non-surgical periodontitis treatment
Mehrnaz Sadighi Shamami, Mohammad Ekhlaspour, Jameel M. A. Sulaiman, Radhwan Abdul Kareem, Nahed Mahmood Ahmed Alsultany, Kamyar Nasiri, Naghmeh Shenasa
Nanotoxicology.2025; 19(3): 290. CrossRef - Effect of different types of adhesive systems on the bond strength and marginal integrity of composite restorations in cavities prepared with the erbium laser—a systematic review
Deepti Dua, Ankur Dua, Eugenia Anagnostaki, Riccardo Poli, Steven Parker
Lasers in Medical Science.2022; 37(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparing the Ability of Various Resin-Based Composites and Techniques to Seal Margins in Class-II Cavities
Abdullah Saleh Aljamhan, Sultan Ali Alhazzaa, Abdulrahman Hamoud Albakr, Syed Rashid Habib, Muhammad Sohail Zafar
Polymers.2021; 13(17): 2921. CrossRef - Comparison of the Ability of Two Brands of CBCT with That of SEM to Detect the Marginal Leakage of Class V Composite Resin Restorations
Mitra Karbasi Kheir, Leili Khayam, Mehrbakhsh Nilashi
The Scientific World Journal.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Analysis of microleakage and marginal gap presented by new polymeric systems in class V restorations: An in vitro study
Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Hugo Alberto Vidotti, Lindomar Corrêa Júnior, Alef Vermudt, Mauro de Souza Almeida, Saulo Pamato
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(3): 156. CrossRef - Hydrolysis-resistant and stress-buffering bifunctional polyurethane adhesive for durable dental composite restoration
Jiahui Zhang, Xiaowei Guo, Xiaomeng Zhang, Huimin Wang, Jiufu Zhu, Zuosen Shi, Song Zhu, Zhanchen Cui
Royal Society Open Science.2020; 7(7): 200457. CrossRef - A comparison of the marginal and internal fit of porcelain laminate veneers fabricated by pressing and CAD-CAM milling and cemented with 2 different resin cements
Ziad N. Al-Dwairi, Rana M. Alkhatatbeh, Nadim Z. Baba, Charles J. Goodacre
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(3): 470. CrossRef - Microleakage in class V cavities prepared using conventional method versus Er:YAG laser restored with glass ionomer cement or resin composite
Sertac Peker, Figen Eren Giray, Basak Durmus, Nural Bekiroglu, Betül Kargül, Mutlu Özcan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2017; 31(5): 509. CrossRef
- Post‐Gel Polymerization Shrinkage Strain and Marginal Integrity of Repeatedly Preheated Thermo‐Viscous and Matrix‐Modified Bulk‐Fill Resin Composite (Pre‐Clinical Study)
- 1,620 View
- 9 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of endodontic tri-antibiotic paste on bond strengths of dentin adhesives to coronal dentin
- Parvin Mirzakoucheki, Ricardo Walter, Navid Khalighinejad, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Sanaz Mirsattari, Navid Akbarzadeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):136-142. Published online February 12, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of tri-antibiotic paste (TAP) on microtensile bond strengths (MTBS) of dental adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods Sixty extracted molars had their occlusal surfaces flattened to expose dentin. They were divided into two groups, i.e., control group with no dentin treatment and experimental group with dentin treatment with TAP. After 10 days, specimens were bonded using self-etch (Filtek P90 adhesive) or etch-and-rinse (Adper Single Bond Plus) adhesives and restored with composite resin. Teeth were sectioned into beams, and the specimens were subjected to MTBS test. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey tests.
Results There was a statistically significant interaction between dentin treatment and adhesive on MTBS to coronal dentin (
p = 0.003). Despite a trend towards worse MTBS being noticed in the experimental groups, TAP application showed no significant effect on MTBS (p = 0.064).Conclusions The etch-and-rinse adhesive Adper Single Bond Plus presented higher mean bond strengths than the self-etch adhesive Filtek P90, irrespective of the group. The superior bond performance for Adper Single Bond when compared to Filtek P90 adhesive was confirmed by a fewer number of adhesive failures. The influence of TAP in bond strength is insignificant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efecto antimicrobiano como medicación intraconducto de la pasta triantibiótica.
Paúl Sebastián Ulloa Amores, Diana Álvarez Álvarez, María Elizabeth Moscoso Abad, Magda Zulay Bastidas Calva
Revista de la Asociación Dental Mexicana.2024; 81(4): 211. CrossRef - Effect of Intracanal Medicaments on Push-out Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-based Materials
Hyuntae Jeong, Sunmi Yang, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi, Jaehwan Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(4): 455. CrossRef
- Efecto antimicrobiano como medicación intraconducto de la pasta triantibiótica.
- 1,358 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of additional etching and ethanol-wet bonding on the dentin bond strength of one-step self-etch adhesives
- Joonghee Ahn, Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):68-74. Published online November 18, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.68
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effects of additional acid etching on the dentin bond strength of one-step self-etch adhesives with different compositions and pH. The effect of ethanol wetting on etched dentin bond strength of self-etch adhesives was also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Forty-two human permanent molars were classified into 21 groups according to the adhesive types (Clearfil SE Bond [SE, control]; G-aenial Bond [GB]; Xeno V [XV]; Beauti Bond [BB]; Adper Easy Bond [AE]; Single Bond Universal [SU]; All Bond Universal [AU]), and the dentin conditioning methods. Composite resins were placed on the dentin surfaces, and the teeth were sectioned. The microtensile bond strength was measured, and the failure mode of the fractured specimens was examined. The data were analyzed statistically using two-way ANOVA and Duncan's
post hoc test.Results In GB, XV and SE (pH ≤ 2), the bond strength was decreased significantly when the dentin was etched (
p < 0.05). In BB, AE and SU (pH 2.4 - 2.7), additional etching did not affect the bond strength (p > 0.05). In AU (pH = 3.2), additional etching increased the bond strength significantly (p < 0.05). When adhesives were applied to the acid etched dentin with ethanol-wet bonding, the bond strength was significantly higher than that of the no ethanol-wet bonding groups, and the incidence of cohesive failure was increased.Conclusions The effect of additional acid etching on the dentin bond strength was influenced by the pH of one-step self-etch adhesives. Ethanol wetting on etched dentin could create a stronger bonding performance of one-step self-etch adhesives for acid etched dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Different Application Modes of a Universal Adhesive System on the Bond Strength of Bulk‐Fill Composite Resin to Enamel and Dentin in Primary Teeth
Ali Nozari, Maryam Pakniyat Jahromi, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Zahra Jowkar, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a novel pretreatment on the microtensile bond strength of universal adhesives with dentin
Yixiang Pan, Jiajia Xu, Xue Cai, Xiaodong Li, Xiaoyan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1148. CrossRef - Microfluidic Organ-on-A-chip: A Guide to Biomaterial Choice and Fabrication
Uyen M. N. Cao, Yuli Zhang, Julie Chen, Darren Sayson, Sangeeth Pillai, Simon D. Tran
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3232. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on bond strength and interfacial integrity of universal adhesive to deep dentin
Ahmed Mostafa Attia, Ahmed Fawzy Abo-Elezz, Rehab Khalil Safy
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 116. CrossRef - Microtensile Bond Strength of Total-Etch and Self-Etch Universal Adhesives Containing 10-MDP: A Systematic Review
I. Hisham Ismail, N.A. Abdul Razak, N.D. Mohd Ramzi, M.Y.P. Mohd Yusof
The Journal of Dentists.2022; 10: 12. CrossRef - Biomodification of dentin collagen by primers with crosslinking reagents using ethanol wet bonding technique
Talita Arrais Daniel Mendes, Samuel Chillavert Dias Pascoal, Marcelo Victor Sidou Lemos, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Juliano Sartori Mendonça
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2022; 119: 103254. CrossRef - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef - The effect of additional chlorhexidine and/or ethanol on the bond strength of universal adhesives
Zeynep Buket Kaynar, Magrur Kazak, Nazmiye Donmez, Evrim Eliguzeloglu Dalkilic
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(4): 375. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Microshear Bond Strength of Composite Resin Restorations to Dentin using Different Adhesive Systems and the Effect of Thermocycling
Sara Valizadeh, Elham Farhadi, Aida Moradi, Sedighe S. Hashemikamangar
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 734. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Universal Adhesives to Dentin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Naji Kharouf, Davide Mancino, Maciej Zarow, Natalia Jakubowicz, Youssef Haikel, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez
Polymers.2021; 13(5): 814. CrossRef - Effects of simplified ethanol–wet bonding and hydrophobic coating on resin–dentin bonding properties
Xia Wang, He Li, Liang Chen, Yue Wang, Jianfei Bai, Defei Wang, Hong Liu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(9): 913. CrossRef - Effect of dentin biomodification techniques on the stability of the bonded interface
Nida Mehmood, Rajni Nagpal, UdaiPratap Singh, Meenal Agarwal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 265. CrossRef - Assessment of nanohardness, elastic modulus, and nanoleakage of the adhesive interface using the ethanol-wet-bonding technique
Mauricio Yugo Souza, Jéssica Lopes Andrade, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele, Eduardo Bresciani
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2020; 99: 102572. CrossRef - The improvement of biocompatibility of adhesives
Cigdem Atalayin, Huseyin Tezel, Zeynep Ergucu, Nimet Unlu, Guliz Armagan, Taner Dagci, Timur Kose
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(8): 3213. CrossRef - Comparison of the micro-tensile bond strengths of four different universal adhesives to caries-affected dentin after ER:YAG laser irradiation
Nazmiye DÖNMEZ, Ayça Sarıalioğlu GÜNGÖR, Barış KARABULUT, Şeyda Hergüner SİSO
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(2): 218. CrossRef - Six-month performance of restorations produced with the ethanol-wet-bonding technique: a randomized trial
Maurício Yugo de SOUZA, Ana Luiza Barbosa JUREMA, Taciana Marco Ferraz CANEPPELE, Eduardo BRESCIANI
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of ethanol-wet dentin, adhesive mode of application, and aging on bond strength of universal adhesive
Mauricio Yugo de SOUZA, Rebeca DI NICOLÓ, Eduardo BRESCIANI
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of light curing modes and ethanol-wet bonding on dentin bonding properties
Mu-zi Li, Jin-rui Wang, Hong Liu, Xia Wang, Kang Gan, Xiu-ju Liu, De-li Niu, Xiao-qing Song
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2016; 17(9): 703. CrossRef - Effect of an Er,Cr:YSGG laser preparation on dentin bond strength of a universal adhesive
A. Rüya Yazici, Emel Karaman, Duygu Tuncer, Gizem Berk, Atilla Ertan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(22): 2477. CrossRef - The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
Jayang Kim, Sungok Hong, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 299. CrossRef
- Influence of Different Application Modes of a Universal Adhesive System on the Bond Strength of Bulk‐Fill Composite Resin to Enamel and Dentin in Primary Teeth
- 2,021 View
- 6 Download
- 20 Crossref

- A study on the compatibility between one-bottle dentin adhesives and composite resins using micro-shear bond strength
- Minju Song, Yooseok Shin, Jeong-Won Park, Byoung-Duck Roh
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):30-36. Published online September 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to determine whether the combined use of one-bottle self-etch adhesives and composite resins from same manufacturers have better bond strengths than combinations of adhesive and resins from different manufacturers.
Materials and Methods 25 experimental micro-shear bond test groups were made from combinations of five dentin adhesives and five composite resins with extracted human molars stored in saline for 24 hr. Testing was performed using the wire-loop method and a universal testing machine. Bond strength data was statistically analyzed using two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's
post hoc test.Results Two way ANOVA revealed significant differences for the factors of dentin adhesives and composite resins, and significant interaction effect (
p < 0.001). All combinations with Xeno V (Dentsply De Trey) and Clearfil S3 Bond (Kuraray Dental) adhesives showed no significant differences in micro-shear bond strength, but other adhesives showed significant differences depending on the composite resin (p < 0.05). Contrary to the other adhesives, Xeno V and BondForce (Tokuyama Dental) had higher bond strengths with the same manufacturer's composite resin than other manufacturer's composite resin.Conclusions Not all combinations of adhesive and composite resin by same manufacturers failed to show significantly higher bond strengths than mixed manufacturer combinations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
Stefan Dačić, Milan Miljković, Aleksandar Mitić, Goran Radenković, Marija Anđelković‐Apostolović, Milica Jovanović
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(6): 1212. CrossRef - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef - Dentin bond strengths of all-in-one adhesives combined with different manufacturers’ flowable resin composites
Koichi SHINKAI, Daiki YOSHII, Akira KOIDE, Masaya SUZUKI, Shiro SUZUKI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(5): 1094. CrossRef - DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE ADEZİV SİSTEMLER
Elmas TÜRKER, Buket AYNA
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of EDC on Dentin-Resin Shear Bond Strength and Demineralized Dentin Thermal Properties
Lin Tang, Yi Zhang, Yuhua Liu, Yongsheng Zhou
Materials.2016; 9(11): 920. CrossRef
- Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
- 1,473 View
- 7 Download
- 5 Crossref

-
Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems on
Streptococcus mutans - Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):32-38. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we evaluated the antibacterial activity of self-etching adhesive systems against
Streptococcus mutans using the agar diffusion method.Materials and Methods Three 2-step systems, Clearfil SE Bond (SE, Kuraray), Contax (CT, DMG), and Unifil Bond (UnB, GC), and three 1-step systems, Easy Bond (EB, 3M ESPE), U-Bond (UB, Vericom), and All Bond SE (AB, BISCO) were used. 0.12% chlorhexidine (CHX, Bukwang) and 37% phosphoric acid gel (PA, Vericom) were used as positive controls.
Results The antibacterial activity of CHX and PA was stronger than that of the other groups, except SE. After light activation, the inhibition zone was reduced in the case of all 2-step systems except CT. However, all 1-step systems did not exhibit any inhibition zone upon the light activation.
Conclusions SE may be better than CT or UnB among the 2-step systems with respect to antibacterial activity, however, 1-step systems do not exhibit any antibacterial activity after light curing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Three Universal Bonding Agents Against Streptococcus mutans on Demineralized Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Kirti Rathee, Charu Dayal, Reena Rani, A Anukriti, Anjum Zia, Ankita Sundan, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Incorporation of chlorhexidine in self-adhesive resin cements
Idris M. MEHDAWI, Ranna KITAGAWA, Haruaki KITAGAWA, Satoshi YAMAGUCHI, Nanako HIROSE, Tomoki KOHNO, Satoshi IMAZATO
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 675. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Bonding Properties of Universal Adhesive Dental Polymers Doped with Pyrogallol
Naji Kharouf, Ammar Eid, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Youri Arntz, Hamdi Jmal, Federico Foschi, Salvatore Sauro, Vincent Ball, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1538. CrossRef - Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and Epigallocatechin-3-O-(3-O-methyl)-gallate Enhance the Bonding Stability of an Etch-and-Rinse Adhesive to Dentin
Hao-Han Yu, Ling Zhang, Fan Yu, Fang Li, Zheng-Ya Liu, Ji-Hua Chen
Materials.2017; 10(2): 183. CrossRef - An In vitro Assessment of Antibacterial Activity of Three Self-etching Primers Against Oral Microflora
Sneha Dipak Shinde, Vikram Pai, R. Vijay Naik
APOS Trends in Orthodontics.2017; 7: 181. CrossRef - Functional Dental Restorative Materials That Hinder Oral Biofilm
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Victor Trassi Fernandes da Silva Souza, Rafael Amorim Martins, Ana Carolina Bosco Mendes, Monica Irma Aparecida Valdeci de Souza, Ângela Cristina Cilense Zuanon, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Current Oral Health Reports.2017; 4(1): 22. CrossRef - In vitroantibacterial activity of various adhesive materials against oral streptococci
Emre Ozel, Fetiye Kolayli, Elif Bahar Tuna, Doganhan Er
Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment.2016; 30(1): 121. CrossRef - A systematic review about antibacterial monomers used in dental adhesive systems: Current status and further prospects
Alexandra Rubin Cocco, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Rafael Guerra Lund, Evandro Piva
Dental Materials.2015; 31(11): 1345. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Three Universal Bonding Agents Against Streptococcus mutans on Demineralized Dentin: An In Vitro Study
- 1,522 View
- 5 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of different air-drying time on the microleakage of single-step self-etch adhesives
- Horieh Moosavi, Maryam Forghani, Esmatsadat Managhebi
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):73-78. Published online May 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of three different air-drying times on microleakage of three self-etch adhesive systems.
Materials and Methods Class I cavities were prepared for 108 extracted sound human premolars. The teeth were divided into three main groups based on three different adhesives: Opti Bond All in One (OBAO), Clearfil S3 Bond (CSB), Bond Force (BF). Each main group divided into three subgroups regarding the air-drying time: without application of air stream, following the manufacturer's instruction, for 10 sec more than manufacturer's instruction. After completion of restorations, specimens were thermocycled and then connected to a fluid filtration system to evaluate microleakage. The data were statistically analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Tukey-test (α = 0.05).
Results The microleakage of all adhesives decreased when the air-drying time increased from 0 sec to manufacturer's instruction (
p < 0.001). The microleakage of BF reached its lowest values after increasing the drying time to 10 sec more than the manufacturer's instruction (p < 0.001). Microleakage of OBAO and CSB was significantly lower compared to BF in all three drying time (p < 0.001).Conclusions Increasing in air-drying time of adhesive layer in one-step self-etch adhesives caused reduction of microleakage, but the amount of this reduction may be dependent on the adhesive components of self-etch adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Species profile of volatile organic compounds emission and health risk assessment from typical indoor events in daycare centers
Hailin Zheng, Júlia Csemezová, Marcel Loomans, Shalika Walker, Florent Gauvin, Wim Zeiler
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 918: 170734. CrossRef - Development of Drying Process for Removal of Residual Moisture from Biomass Pretreated with Ethanol and Its Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis
Seo-Young Park, Jin-Hyun Kim
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering.2021; 26(5): 814. CrossRef - Effect of 9.3 μm CO2 and 2.94 μm Er:YAG Laser vs. Bur Preparations on Marginal Adaptation in Enamel and Dentin of Mixed Class V Cavities Restored With Different Restorative Systems
Clara Isabel Anton y Otero, Enrico Di Bella, Ivo Krejci, Tissiana Bortolotto
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Drying Process for Removal of Residual Solvent from Crystalline Vancomycin and Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis Thereof
Tae-Hun Yoon, Jin-Hyun Kim
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering.2020; 25(5): 777. CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef - Optical Evaluation of Enamel Microleakage with One-Step Self-Etch Adhesives
Alaa Turkistani, Maha Almutairi, Nouf Banakhar, Reem Rubehan, Sulafa Mugharbil, Ahmed Jamleh, Adnan Nasir, Turki Bakhsh
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2018; 36(11): 589. CrossRef - Improved drying method for removal of residual solvents from paclitaxel by pre-treatment with ethanol and water
Chung-Gi Lee, Jin-Hyun Kim
Process Biochemistry.2015; 50(6): 1031. CrossRef
- Species profile of volatile organic compounds emission and health risk assessment from typical indoor events in daycare centers
- 1,922 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of chlorhexidine application on the bond strength of resin core to axial dentin in endodontic cavity
- Yun-Hee Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):207-214. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the influence of chlorhexidine (CHX) on the microtensile bonds strength (µTBS) of resin core with two adhesive systems to dentin in endodontic cavities.
Materials and Methods Flat dentinal surfaces in 40 molar endodontic cavities were treated with self-etch adhesive system, Contax (DMG) and total-etch adhesive system, Adper Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE) after the following surface treatments: (1) Priming only (Contax), (2) CHX for 15 sec + rinsing + priming (Contax), (3) Etching with priming (Adper Single Bond 2), (4) Etching + CHX for 15 sec + rinsing + priming (Adper Single Bond 2). Resin composite build-ups were made with LuxaCore (DMG) using a bulk method and polymerized for 40 sec. For each condition, half of specimens were submitted to µTBS after 24 hr storage and half of them were submitted to thermocycling of 10,000 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃ before testing. The data were analyzed using ANOVA and independent
t -test at a significance level of 95%.Results CHX pre-treatment did not affect the bond strength of specimens tested at the immediate testing period, regardless of dentin surface treatments. However, after 10,000 thermocycling, all groups showed reduced bond strength. The amount of reduction was greater in groups without CHX treatments than groups with CHX treatment. These characteristics were the same in both self-etch adhesive system and total-etch adhesive system.
Conclusions 2% CHX application for 15 sec proved to alleviate the decrease of bond strength of dentin bonding systems. No significant difference was shown in µTBS between total-etching system and self-etching system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro Tensile bond strength and microleakage assessment of total-etch and self-etch adhesive bonded to carious affected dentin disinfected with Chlorhexidine, Curcumin, and Malachite green
Zeeshan Qamar, Nishath Sayed Abdul, R Naveen Reddy, Mahesh Shenoy, Saleh Alghufaili, Yousef Alqublan, Ali Barakat
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 43: 103636. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef - Influence of chlorhexidine 2% and sodium hypochlorite 5.25% on micro-tensile bond strength of universal adhesive system (G-Premio Bond)
Nafiseh Fazelian, Abbas Rahimi Dashtaki, MohammadAmin Eftekharian, Batool Amiri
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effects of different methods of post space preparation in primary anterior teeth on the fracture resistance of tooth restorations
Bahman Seraj, Sara Ghadimi, Ebrahim Najafpoor, Fatemeh Abdolalian, razieh khanmohammadi
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 141. CrossRef - Chemical, microbial, and host‐related factors: effects on the integrity of dentin and the dentin–biomaterial interface
Marcela T. Carrilho, Fabiana Piveta, Leo Tjäderhane
Endodontic Topics.2015; 33(1): 50. CrossRef - MMP Inhibitors on Dentin Stability
A.F. Montagner, R. Sarkis-Onofre, T. Pereira-Cenci, M.S. Cenci
Journal of Dental Research.2014; 93(8): 733. CrossRef - Thermal cycling for restorative materials: Does a standardized protocol exist in laboratory testing? A literature review
Anna Lucia Morresi, Maurizio D'Amario, Mario Capogreco, Roberto Gatto, Giuseppe Marzo, Camillo D'Arcangelo, Annalisa Monaco
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 29: 295. CrossRef
- Micro Tensile bond strength and microleakage assessment of total-etch and self-etch adhesive bonded to carious affected dentin disinfected with Chlorhexidine, Curcumin, and Malachite green
- 1,403 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of moisture and drying time on the bond strength of the one-step self-etching adhesive system
- Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):155-159. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To investigate the effect of dentin moisture degree and air-drying time on dentin-bond strength of two different one-step self-etching adhesive systems.
Materials and Methods Twenty-four human third molars were used for microtensile bond strength testing of G-Bond and Clearfil S3 Bond. The dentin surface was either blot-dried or air-dried before applying these adhesive agents. After application of the adhesive agent, three different air drying times were evaluated: 1, 5, and 10 sec. Composite resin was build up to 4 mm thickness and light cured for 40 sec with 2 separate layers. Then the tooth was sectioned and trimmed to measure the microtensile bond strength using a universal testing machine. The measured bond strengths were analyzed with three-way ANOVA and regression analysis was done (
p = 0.05).Results All three factors, materials, dentin wetness and air drying time, showed significant effect on the microtensile bond strength. Clearfil S3 Bond, dry dentin surface and 10 sec air drying time showed higher bond strength.
Conclusions Within the limitation of this experiment, air drying time after the application of the one-step self-etching adhesive agent was the most significant factor affecting the bond strength, followed by the material difference and dentin moisture before applying the adhesive agent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An in vitro study on comparative evaluation of shear bond strength of bioactive composite to tooth structure with various dentin conditioning agents
Priyanka Pokkula, Shaik Mohammed Asif, Abdullah Alqarni, Shahabe Saquib Abullais, Shaik Mohamed Shamsudeen, Syed M Yassin, Abosofyan S. Atta, Wahaj Ahmad Khan
AIP Advances.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Drying Time, Application Mode, and Agitation on the Dentin Bond Strength of a Novel Mesoporous Bioactive Glass-Containing Universal Dentin Adhesive
Jiyoung Kwon, Jungwon Kim, Dongseok Choi, Duck-Su Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(7): 247. CrossRef - The occluding effects of layered calcium phosphate and cyanoacrylate on dentinal tubules: a SEM study
Özge Uzuner Bilgiç, Sühan Gürbüz, Altan Dogan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of two newly marketed self‐adhesive resin cements to different substrates: A light and scanning electron microscopy evaluation
Cansu Atalay, Uzay Koc Vural, Ivana Miletic, Sevil Gurgan
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(5): 1694. CrossRef - The effect of curing mode of dual-cure resin cements on bonding performance of universal adhesives to enamel, dentin and various restorative materials
Erick LUZ MADRIGAL, Antonin TICHY, Keiichi HOSAKA, Masaomi IKEDA, Masatoshi NAKAJIMA, Junji TAGAMI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(2): 446. CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef - Effect of pre-curing of two universal adhesives on the shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia
Ga-Eun Son, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(1): 21. CrossRef - Bonding effectiveness of different dentin conditions on etch-and-rinse mode of two universal adhesives: the confocal laser scanning and shear bond strength
Jounghyun Lee, Ka-Young Cho, Jin-Young Kim, Sungho Park, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yooseok shin
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2017; 31(9): 933. CrossRef - Effect of dentin dehydration and composite resin polymerization mode on bond strength of two self-etch adhesives
Pooran Samimi, Mehdi Alizadeh, Farinaz Shirban, Amin Davoodi, Maryam Khoroushi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2016; 7(1): 16. CrossRef - Effect of different air-drying time on the microleakage of single-step self-etch adhesives
Horieh Moosavi, Maryam Forghani, Esmatsadat Managhebi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(2): 73. CrossRef
- An in vitro study on comparative evaluation of shear bond strength of bioactive composite to tooth structure with various dentin conditioning agents
- 1,573 View
- 9 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
- Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):477-482. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the microshear bond strength (uSBS) to enamel prepared with different burs and to determine what type of bur were chosen when a self-etching primer adhesive was used.
Materials and Methods Enamel of forty-two human molars were used. They were divided into one of six groups (n = 7), Group 1, coarse (125 - 150 µm) diamond bur; Group 2, standard (106 - 125 µm) diamond bur; Group 3, fine (53 - 63 µm) diamond bur; Group 4, extrafine (20 - 30 µm) diamond bur; Group 5, plain-cut carbide bur (no. 245); Group 6, cross-cut carbide bur (no. 557). Clearfil SE Bond and Clearfil AP-X (Kuraray Medical Inc.) was bonded to enamel surface. The bonded specimens were subjected to uSBS testing.
Results The uSBS of Group 4 was the highest among groups and it was significantly higher than that of Groups 1, 2, 3, and 6 (
p < 0.05), but it was not significantly different from that of Group 5.Conclusions Different burs used on enamel surface affected the microshear bond strengths of a self-etching primer adhesive to the enamel surface. In the case of Clearfil SE Bond, extrafine diamond and plain-cut carbide bur are recommended for bonding to enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sixty-month follow up of three different universal adhesives used with a highly-filled flowable resin composite in the restoration of non-carious cervical lesion
Fatma Dilsad Oz, Canan Ozturk, Reza Soleimani, Sevil Gurgan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(8): 5377. CrossRef
- Sixty-month follow up of three different universal adhesives used with a highly-filled flowable resin composite in the restoration of non-carious cervical lesion
- 1,055 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
- Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test,
p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test,p < 0.05).Conclusions When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
- 1,301 View
- 1 Download

- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):203-210. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of various application methods of one-step self-etch adhesives to microtensile resin-dentin bond strength.
Materials and Methods Thirty-six extracted human molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to twelve groups (
n = 15), according to the three different adhesive systems (Clearfil Tri-S Bond, Adper Prompt L-Pop, G-Bond) and application methods. The adhesive systems were applied on the dentin as follows: 1) The single coating, 2) The double coating, 3) Manual agitation, 4) Ultrasonic agitation. Following the adhesive application, light-cure composite resin was constructed. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and prepared 15 specimens per groups. Then microtensile bond strength was measured and the failure mode was examined.Results Manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating and double coating did. Double coating of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating did and there was no significant difference between the manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation group. There was significant difference in microtensile bonding strength among all adhesives and Clearfil Tri-S Bond showed the highest bond strength.
Conclusions In one-step self-etching adhesives, there was significant difference according to application methods and type of adhesives. No matter of the material, the manual or ultrasonic agitation of the adhesive showed significantly higher microtensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
Nuray Zulkadir Ergin, Aslı Seçilmiş
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 16(3): 356. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef
- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
- 2,067 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of 2% chlorhexidine application on microtensile bond strength of resin composite to dentin using one-step self-etch adhesives
- Soon-Ham Jang, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):486-491. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.486
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effect of 2% chlorhexidine on the µTBS of a direct composite restoration using one-step self-etch adhesives on human dentin.
Materials and Methods Twenty-four extracted permanent molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to six groups (
n = 10), according to the adhesive system and application of chlorhexidine. With or without the application of chlorhexidine, each adhesive system was applied to the dentin surface. After the bonding procedure, light-cure composite resin buildups were produced. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and then cut and glued to the jig of the microtensile testing machine. A tensile load was applied until the specimen failed. The failure mode was examined using an operating microscope. The data was analyzed statistically using one-way ANOVA, Student'st -test (p < 0.05) and Scheffé's test.Results Regardless of the application of chlorhexidine, the Clearfil S3 Bond showed the highest µTBS, followed by G-Bond and Xeno V. Adhesive failure was the main failure mode of the dentin bonding agents tested with some samples showing cohesive failure.
Conclusions The application of 2% chlorhexidine did not affect the µTBS of the resin composite to the dentin using a one-step self-etch adhesive.
- 1,473 View
- 3 Download

- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
- Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):134-142. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation with hypersensitivity mode on microtensile bond strength of composite resin. Twenty extracted permanent molars were randomly assigned to six groups, according to the irradiation of Er,Cr:YSGG laser, adhesive system (Optibond FL or Clearfil SE bond) and application time of etchant (15 sec or 20 sec). Then composite resin was build up on each conditioned surface. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 h and twelve specimens for each group were prepared. All specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength and the fracture modes were evaluated. Also, the prepared dentin surface and laser irradiated dentin surface were examined under SEM.
The results were as follows:
The microtensile bond strength of laser irradiated group was lower than that of no laser irradiated group.
Regardless of laser irradiation, the microtensile bond strength of Optibond FL was higher than that of Clearfil SE bond. And the microtensile bond strength of 20 sec etching group was higher than that of 15 sec etching group when using Optibond FL.
The SEM image of laser irradiated dentin surface showed prominent peritubular dentin, opened dentinal tubules and no smear layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 180. CrossRef
- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- 1,535 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
- Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):106-115. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microtensile bond strength (µTBS), failure modes and bonding interfaces of self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin.
Cylindrical composite blocks (Tescera, Bisco Inc.) were luted with resin cements (PA: Panavia F 2.0, Kuraray Medical Inc., RE: RelyX Unicem Clicker, 3M ESPE., MA: Maxem, Kerr Co., BI: BisCem, Bisco Inc.) on the prepared occlusal dentin surfaces of 20 extracted molars. After storage in distilled water for 24 h, 1.0 mm × 1.0 mm composite-dentin beams were prepared. µTBS was tested at a cross-head speed of 0.5 mm/min. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test. Dentin sides of all fractured specimens and interfaces of resin cements-dentin or resin cements-composite were examined at FE-SEM (Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope).
In conclusion, PA and RE showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than MA and BI when indirect composite blocks were luted to dentin using a self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements.
- 1,061 View
- 2 Download

- Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
- Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):13-19. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to dentin prepared with different diamond points, carbide burs and SiC papers, and also to determine which SiC paper yield similar strength to that of dentinal surface prepared with points or burs.
Fifty-six human molar were sectioned to expose the occlusal dentinal surfaces of crowns and slabs of 1.2 mm thick were made. Dentinal surfaces were removed with three diamond points, two carbide burs, and three SiC papers. They were divided into one of eight equal groups (n = 7); Group 1: standard diamond point(TF-12), Group 2: fine diamond point (TF-12F), Group 3: extrafine diamond point (TF-12EF), Group 4: plain-cut carbide bur (no. 245), Group 5: cross-cut carbide bur (no. 557), Group 6 : P 120-grade SiC paper, Group 7: P 220-grade SiC paper, Group 8: P 800-grade SiC paper.
Clearfil SE Bond was applied on dentinal surface and Clearfil AP-X was placed on dentinal surface using Tygon tubes. After the bonded specimens were subjected to uSBS testing, the mean uSBS (n = 20 for each group) was statistically compared using one-way ANOVA and Tukey HSD test.
In conclusion, the use of extrafine diamond point is recommended for improved bonding of Clearfil SE Bond to dentin. Also the use of P 220-grade SiC paper in vitro will be yield the results closer to dentinal surface prepared with fine diamond point or carbide burs
in vivo .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the flexural and repair bond strengths of 3D-printed temporary restorations
Nazmi Dinçer, Şafak Külünk, Seniha Kısakürek, Ibrahim Duran
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of shear bond strength between various temporary prostheses resin blocks fabricated by subtractive and additive manufacturing methods bonded to self-curing reline resin
Hyo-Min Ryu, Jin-Han Lee
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2023; 61(3): 189. CrossRef - The Effect of Aging and Different Surface Treatments on Temporary Cement Bonding of Temporaray Crown Materials
Sebahat FINDIK AYDINER, Nuran YANIKOĞLU, Zeynep YEŞİL DUYMUŞ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(2): 144. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and repair materials on the shear bond strength of CAD/CAM provisional restorations
Ki-Won Jeong, Sung-Hun Kim
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2019; 11(2): 95. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of dental CAD-CAM hybrid restorative materials repaired with composite resin
Yun-Hee Moon, Jonghyuk Lee, Myung-Gu Lee
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2016; 54(3): 193. CrossRef - Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 477. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the flexural and repair bond strengths of 3D-printed temporary restorations
- 1,257 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of the application time of self-etching primers on the bonding of enamel
- Cheol-Hee Jin, Young-Gon Cho, Soo-Mee Kim, Myeong-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):224-234. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.224
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the normal and two times of application time of six self-etching primers applied to enamel using microshear bond strength (uSBS) test and the finding of scanning electronic microscope (SEM).
Crown of sixty human molars were bisected mesiodistally and buccal and lingual enamel of crowns were partially exposed and polished with 600 grit SiC papers. They were divided into one of two equal groups subdivided into one of six equal groups (n = 10) by self-etching primer adhesives.
After the same manufacture's adhesive resin and composites were bonded on the enamel surface of each group, the bonded specimens were subjected to uSBS testing and also observed under SEM.
In conclusion, generally two times of primer application time increased the enamel uSBS, especially with the statistical increase of bond strength in adhesives involving high-pH primers.
- 863 View
- 3 Download

- Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
- Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):133-140. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by several self-etching primers and methacrylate-based root canal sealer. Seventy single-rooted human teeth were used in this study. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down manner with Gate-Glidden drills and .04 Taper Profile to ISO #40. The teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups of 15 teeth each according to root canal filling material and self-etching primers and two control groups (positive and negative) of 5 teeth each as follows: group 1 - gutta percha and AH26® sealer; group 2 - Resilon, RealSeal™ primer and RealSeal™ sealer; group 3 - Resilon, Clearfil SE Bond® primer and RealSeal™ sealer group 4 - Resilon, AdheSe® primer and RealSeal™ sealer. Apical leakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration of roots sectioned longitudinally by diamond disk. Statistical analysis was performed using the One-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe's test. There were no statistical differences in the mean apical dye penetration among the groups 2, 3 and 4 of self-etching primers. And group 1, 2 and 3 had also no statistical difference in apical dye penetration. But, there was statistical difference between group 1 and 4 (p < 0.05). The group 1 showed the least dye penetration. According to the results of this study, Resilon with self-etching primer was not sealed root canal better than gutta precha with AH26® at sealing root canals. And there was no significant difference in apical leakage among the three self-etching primers.
- 821 View
- 1 Download

- Effect of application methods of a self-etching primer adhesive system on enamel bond strength
- Jae-Gu Park, Kwon-Hwan Cho, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):90-97. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of passive or active application of primer and coat times of bond on the shear bond strength when a self-etching primer adhesive (Clearfil SE Bond) was applied to enamel surface.
Crowns of sixteen human molars were selected. Buccal and lingual enamels of crowns were partially exposed and slabs of 1.2 mm thick were made. They were divided into one of four equal groups (n = 8). Group 1: passive application of Primer and 1 coat of Bond, Group 2: active application of Primer and 1 coat of Bond, Group 3: passive application of Primer and 2 coats of Bond, Group 4: active application of Primer and 2 coats of Bond. Clearfil AP-X was bonded to enamel suface of each group using Tygon tubes. The bonded specimens were subjected to microshear bond strength (
u SBS) testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min.The results of this study were as follows;
The
u SBS of Group 1 was the lowest among groups and theu SBS of Group 4 was the highest.There was not statistically significant interaction between enamel
u SBS by application method of Primer and coat time of Bond (p > 0.05).There was not statistically significant difference between enamel
u SBS by passive and active application of Primer (p > 0.05).There was statistically significant difference between enamel
u SBS by one- and two-coat of Bond (p < 0.05).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel Bond Strength of Self-Etch Adhesives with Phototherapy Active Application: a Pilot Study
M. K. Ayar, Ö. Yeşil
Strength of Materials.2024; 56(3): 669. CrossRef - Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 203. CrossRef - The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
Jin-hee Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 526. CrossRef
- Enamel Bond Strength of Self-Etch Adhesives with Phototherapy Active Application: a Pilot Study
- 1,128 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Microleakage of composite resin restoration according to the number of thermocycling
- Chang-Youn Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):377-384. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.377
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Present tooth bonding system can be categorized into total etching bonding system (TE) and self-etching boding system (SE) based on their way of smear layer treatment. The purposes of this study were to compare the effectiveness between these two systems and to evaluate the effect of number of themocycling on microleakage of class V composite resin restorations.
Total forty class V cavities were prepared on the single-rooted bovine teeth and were randomly divided into four experimental groups: two kinds of bonding system and another two kinds of thermocycling groups. Half of the cavities were filled with Z250 follwing the use of TE system, Single Bond and another twenty cavities were filled with Metafil and AQ Bond, SE system. All composite restoratives were cured using light curing unit (XL2500, 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA) for 40 seconds with a light intensity of 600 mW/cm2.
Teeth were stored in distilled water for one day at room temperature and were finished and polished with Sof-Lex system. Half of teeth were thermocycled 500 times and the other half were thermocycled 5,000 times between 5℃ and 55℃ for 30 second at each temperature.
Teeth were isolated with two layers of nail varnish except the restoration surface and 1 mm surrounding margins. Electrical conductivity (µA) was recorded in distilled water by electrochemical method. Microleakage scores were compared and analyzed using two-way ANOVA at 95% level.
From this study, following results were obtained: There was no interaction between variables of bonding system and number of thermocycling (p = 0.485). Microleakage was not affected by the number of thermocycling either (p = 0.814). However, Composite restoration of Metafil and AQ Bond, SE bond system showed less microleakage than composite restoration of Z250 and Single Bond, TE bond system (p = 0.005).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength and Microleakage of Bulk-fill Resin Composites
Hanbyeol Lee, Hyunwoo Seo, Juhyun Lee, Howon Park
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2015; 42(4): 281. CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems
Ji-Hoon Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 333. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength and Microleakage of Bulk-fill Resin Composites
- 1,098 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
- Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):327-334. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of burs on microleakage of Class V resin restorations when a self-etching primer adhesive was used.
Forty Class V cavities were prepared with four different cutting burs on extracted third molars, and divided into one of four equal groups (n = 10); Group 1-plain cut carbide bur (no. 245), Group 2-cross cut carbide bur (no. 557), Group 3-fine diamond bur (TF-21F), Group 4-standard diamond bur (EX-41).
The occlusal and gingival margin of cavities was located in enamel and dentin, respectively. Cavities were treated with Clearfil SE Bond and restored with Clearfil AP-X. Specimens were thermocycled, immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours, and bisected longitudinally. They were observed leakages at enamel and dentinal margins. Data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked test.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. At enamel margin, microleakage of group 4 was statistically higher than those of group 1, 2 and 3 (p < 0.01).
2. At dentinal margin, microleakage of group 4 was statistically higher than group 3 (p < 0.01), but group 1 and 2 were not statistically different with group 3 and 4.
3. Enamel microleakage was statistically higher than dentinal microleakage in group 1, 2 and 3 (p < 0.05), but statistical difference between the microleakage of enamel and dentinal margin was not in group 4.
In conclusion, the use of coarse diamond bur showed high microleakage at both enamel and dentinal margin when Clearfil SE Bond was used in class V cavity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 477. CrossRef - Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 13. CrossRef
- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
- 1,078 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
- Sae-Hee Han, Eun-Soung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):169-179. Published online May 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was to compare the microshear bond strength (µSBS) of light- and chemically cured composites to enamel coupled with four 2-step self-etch adhesives and also to evaluate the incompatibility between 2-step self-etch adhesives and chemically cured composite resin.
Crown segments of extracted human molars were cut mesiodistally, and a 1 mm thickness of specimen was made. They were assigned to four groups by adhesives used: SE group (Clearfil SE Bond), AdheSE group (AdheSE), Tyrian group (Tyrian SPE/One-Step Plus), and Contax group (Contax). Each adhesive was applied to a cut enamel surface as per the manufacturer's instruction. Light-cured (Filtek Z250) or chemically cured composite (Luxacore Smartmix Dual) was bonded to the enamel of each specimen using a Tygon tube. After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, the bonded specimens were subjected to µSBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. The mean µSBS (n=20 for each group) was statistically compared using two-way ANOVA, Tukey HSD, and t test at 95% level. Also the interface of enamel and composite was evaluated under FE-SEM.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The µSBS of the SE Bond group to the enamel was significantly higher than that of the AdheSE group, the Tyrian group, and the Contax group in both the light-cured and the chemically cured composite resin (p < 0.05).
2. There was not a significant difference among the AdheSE group, the Tyrian group, and the Contax group in both the light-cured and the chemically cured composite resin.
3. The µSBS of the light-cured composite resin was significantly higher than that of the chemically cured composite resin when same adhesive was applied to the enamel (p < 0.05).
4. The interface of enamel and all 2-step self-etch adhesives showed close adaptation, and so the incompatibility of the chemically cured composite resin did not show.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 30. CrossRef
- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
- 1,181 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparative enamel bond strength between light- and dual-cured composites bonded by self-etching adhesives
- Young-Gon Cho, Sang-Hoon Yoo
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study compared the microshear bond strength (µSBS) of light-cured and dual-cured composites to enamel bonded with three self-etching adhesives. Crown segments of extracted human molars were cut mesiodistally, and 1 mm thickness of specimen was made. They were assigned to three groups by used adhesives: Xeno group (Xeno III), Adper group (Adper Prompt L-Pop), and AQ group (AQ Bond). Each adhesive was applied to cut enamel surface as per manufacturer's instruction. Light-cured (Filtek Z 250) or dual-cured composite (Luxacore) was bonded to enamel of each specimen using Tygon tube.
After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, the bonded specimens were subjected to µSBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. The mean µSBS (n = 20 for each group) was statistically compared using two-way ANOVA, Tukey HSD, and t test at the 0.05 probability level. The results of this study were as follows;
1. The µSBS of light-cured composite was significantly higher than that of dual-cured composite when same adhesive was applied to enamel.
2. For Z 250, the µSBS of AQ group (9.95 ± 2.51 MPa) to enamel was significantly higher than that of Adper goup (6.74 ± 1.80 MPa), but not significantly different with Xeno group (7.73 ± 2.01 MPa).
3. For Luxacore, the µSBS of Xeno group (5.19 ± 1.32 MPa) to enamel was significantly higher than that of Adper goup (3.41 ± 1.19 MPa), but not significantly different with AQ group (4.50 ± 0.96 MPa).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Bond Strengths Between Dual Cure Resin Cement and Light Cure Resin Cement in Root Surface Indirect Restorations: An In Vitro Analysis Study
Karishma Desai, Karthickraj S M
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef - Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
Sook-Kyung Choi, Ji-Wan Yum, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 397. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Bond Strengths Between Dual Cure Resin Cement and Light Cure Resin Cement in Root Surface Indirect Restorations: An In Vitro Analysis Study
- 1,114 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- THE EFFECT OF THERMOCYCLING ON THE DURABILITY OF DENTIN ADHESIVE SYSTEMS
- Young-Hoon Moon, Jong-Ryul Kim, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):222-235. Published online January 14, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The objectives of this study was to evaluate the effect of thermocycling on the μTBS (microtensile bond strength) to dentin with four different adhesive systems to examine the bonding durability.
Freshly extracted 3rd molar teeth were exposed occlusal dentin surfaces, and randomly distributed into 8 adhesive groups: 3-steps total-etching (Scotchbond Multi-Purpose Plus; SM, All Bond-2; AB), 2-steps total-etching (Single Bond; SB, One Step plus; OS), 2-steps self-etching (Clearfil SE Bond; SE, AdheSE; AD) and single-step self-etching systems (Promp L-Pop; PL, Xeno III; XE). Each adhesive system in 8 adhesives groups was applied on prepared dentin surface as an instruction and resin composite (Z250) was placed incrementally and light-cured. The bonded specimens were sectioned with low-speed diamond saw to obtain 1 × 1 ㎜ sticks after 24 hours of storage at 37 °C distilled water and proceeded thermocycling at the pre-determined cycles of 0, 1,000 and 2,000. The μTBS test was carried out with EZ-tester at 1 mm/min. The results of bond strength test were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA/ Duncan's test at the α〈 0.05 confidence level. Also, the fracture mode of debonded surface and the interface were examined under SEM.
The results of this study were as follows;
3-step total etching adhesives showed stable, but bond strength of 2-step adhesives were decreased as thermocycling stress.
SE showed the highest bond strength, but single step adhesives (PL, XE) had the lowest value both before and after thermocycling.
Most of adhesives showed adhesive failure. The total-etching systems were prone to adhesive failure and the single-step systems were mixed failure after thermocycling.
Within limited results of this study, the bond strength of adhesive system was material specific and the bonding durability was affected by the bonding step/ procedure of adhesive. Simplified bonding procedures do not necessarily imply improved bonding performance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical characterization and bond performance of a non-methacrylate dental adhesive in long-term biochemical and thermal aging models
Zach Gouveia, Rastin Rahiminejad, Lingyun Zhu, Jesse Barker, Yoav Finer, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Quantitative comparison of permeability in the adhesive interface of four adhesive systems
Juhea Chang, Keewook Yi, Hae-Young Kim, In Bog Lee, Byeong Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 51. CrossRef
- Physical characterization and bond performance of a non-methacrylate dental adhesive in long-term biochemical and thermal aging models
- 1,825 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Aging effect on the microtensile bond strength of self-etching adhesives
- JS Park, JS Kim Kim, HH Son, HC Kwon, BH Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):415-426. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.415
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In this study, the changes in the degree of conversion (DC) and the microtensile bond strength (MTBS) of self-etching adhesives to dentin was investigated according to the time after curing. The MTBS of Single Bond (SB, 3M ESPE, USA), Clearfil SE Bond (SE, Kuraray, Japan), Xeno-III (XIII, Dentsply, Germany), and Adper Prompt (AP, 3M ESPE, USA) were measured at 48h, at 1 week and after thermocycling for 5,000 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃. The DC of the adhesives were measured immediately, at 48h and at 7 days after curing using a Fourier Transform Infra-red Spectrometer. The fractured surfaces were also evaluated with scanning electron microscope. The MTBS and DC were significantly increased with time and there was an interaction between the variables of time and material (MTBS, 2-way ANOVA, p = 0.018; DC, Repeated Measures ANOVA, p < 0.001). The low DC was suggested as a cause of the low MTBS of self-etching adhesives, XIII and AP, but the increase in the MTBS of SE and AP after 48h could not be related with the changes in the DC. The microscopic maturation of the adhesive layer might be considered as the cause of increasing bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Plasma Deposition Using Low-Power/Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Promoting Adhesion of Composite Resin to Enamel
Geum-Jun Han, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2014; 34(4): 933. CrossRef - The effect of priming etched dentin with solvent on the microtensile bond strength of hydrophobic dentin adhesive
Eun-Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Bae, Jong-Soon Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, In-Bog Lee, Chang-Keun Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 42. CrossRef - Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 103. CrossRef - Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef - The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
Jin-hee Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 526. CrossRef
- Effect of Plasma Deposition Using Low-Power/Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Promoting Adhesion of Composite Resin to Enamel
- 1,262 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Influence of additional etching on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive system to enamel
- Sun-Jin Yoo, Young-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Won Park, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):263-268. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.263
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Recently, self-etching adhesive system has been introduced to simplify the clinical bonding procedures. It is less acidic compared to the phosphoric acid, thus there is doubt whether this system has enough bond strength to enamel. The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of additional etching on the adhesion of resin composite to enamel.
Ninety extracted bovine permanent anterior teeth were used. The labial surfaces of the crown were ground with 600-grit abrasive paper under wet condition. The teeth were randomly divided into six groups of 15 teeth each. Clearfil SE Bond®, Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE™ were used as self-etching primers. Each self-etching primers were applied in both enamel specimens with and without additional etching. For additional etching groups, enamel surface was pretreated with 32% phosphoric acid (UNI-ETCH, Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA). Hybrid resin composite Clearfil AP-X, (Kuraray Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) was packed into the mold and light-cured for 40 seconds. Twenty-four hours after storage, the specimens were tested in shear bond strength. The data for each group were subjected to independent
t - test atp < 0.01 to make comparisons among the groups.In Clearfil SE Bond®, shear bond strength of additional etching group was higher than no additional etching group (
p < 0.01). In Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE, there were no significant difference between additional etching and non-etching groups (p > 0.01).In conclusion, self-etching adhesive system with weak acid seems to have higher bond strength to enamel with additional etching, while self-etching adhesive system with strong acid seems not.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 23. CrossRef
- Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
- 1,402 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of additional coating of bonding resin on the microtensile bond strength of self-etching adhesives to dentin
- Moon-Kyung Jung, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Young-Chul Han, Sae-Joon Choung
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):103-112. Published online January 14, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract This study investigated the hypothesis that the dentin bond strength of self-etching adhesive (SEA) might be improved by applying additional layer of bonding resin that might alleviate the pH difference between the SEA and the restorative composite resin. Two SEAs were used in this study; Experimental SEA (Exp, pH: 1.96) and Adper Prompt (AP, 3M ESPE, USA, pH: 1.0). In the control groups, they were applied with two sequential coats. In the experimental groups, after applying the first coat of assigned SEAs, the D/E bonding resin of All-Bond 2 (Bisco Inc., USA, pH: 6.9) was applied as the intermediate adhesive. Z-250 (3M ESPE, USA) composite resin was built-up in order to prepare hourglass-shaped specimens. The microtensile bond strength (MTBS) was measured and the effect of the intermediate layer on the bond strength was analyzed for each SEA using t-test. The fracture mode of each specimen was inspected using stereomicroscope and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM). When D/E bonding resin was applied as the second coat, MTBS was significantly higher than that of the control groups. The incidence of the failure between the adhesive and the composite or between the adhesive and dentin decreased and that of the failure within the adhesive layer increased. According to the results, applying the bonding resin of neutral pH can increase the bond strength of SEAs by alleviating the difference in acidity between the SEA and restorative composite resin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
Sook-Kyung Choi, Ji-Wan Yum, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 397. CrossRef - Aging effect on the microtensile bond strength of self-etching adhesives
JS Park, JS Kim, MS Kim, HH Son, HC Kwon, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(6): 415. CrossRef
- Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
- 1,409 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Compatibility of self-etching dentin adhesives with resin luting cements
- Do-Wan Kim, Sang-Jin Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):493-504. Published online November 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.493
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was performed to investigate the compatibility between 4 dentin adhesives and 4 resin luting cements.
Dentin adhesives used in this study were All-Bond 2 (Bisco Inc., Schaumbrug, IL, USA), Clearfil SE-Bond (Kuraray Medical Inc, Osaka, Japan), Prompt L-Pop (3M Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, USA), One-Up Bond F (Tokuyama corp., Tokyo, Japan). Resin luting cements used in this study were Choice (Bisco Inc., Schaumbrug, IL, USA), Panavia F (Kuraray Medical Inc, Osaka, Japan), RelyX ARC (3M Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, USA), Bistite II DC (Tokuyama corp., Tokyo, Japan). Combination of each dentin adhesive and corresponding resin cement was made to 16 experimental groups.
Flat dentin surfaces was created on mid-coronal dentin of extracted mandibular third molars, then dentin surface was polished with 320-grit silicon carbide abrasive papers.
Indirect resin composite block (Tescera, Bisco) was fabricated. Its surface for bonding to tooth was polished with silicon carbide abrasive papers. Each dentin adhesive was treated on tooth surface and resin composite overlay were luted with each resin cement. Each bonded specimen was poured in epoxy resin and sectioned occluso-gingivally into 1.0 mm thick slab, then further sectioned into 1.0 × 1.0 mm2 composite-dentin beams. Microtensile bond strength was tested at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. The data were analysed by one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple comparison tests.
The results of this study were as follows;
2-step self-etching dentin adhesive which has additional bonding resin is more compatible than 1-step self-etching dentin adhesive.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
Tae-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Young-Jung Choi, So-Young Yang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 419. CrossRef - Effect of the additional etching procedure on push-out bond strength of one-step resin cement
Soon-Il Kang, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(5): 443. CrossRef - The study of shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin luting cement to dentin
Hee-Sun In, Jong-Il Park, Jong-In Choi, Hye-Won Cho, Jin-Keun Dong
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2008; 46(5): 535. CrossRef - Comparison of bond strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements
Hyun-A Lee, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 499. CrossRef - The Effect of Temporary Filling Materials on The Adhesion between Dentin Adhesive-coated Surface and Resin Inlay
Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 553. CrossRef - The bonding durability of resin cements
Min-Woo Cho, Sang-Hyuk Park, Jong-Ryul Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 343. CrossRef
- Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
- 1,472 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Microshear bond strength of adhesives according to the direction of enamel rods
- Young-Gon Cho, Jong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):344-351. Published online July 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study compared the microshear bond strength (µSBS) to end and side of enamel rod bonded by four adhesives including two total etch adhesives and two self-etch adhesives.
Crown segments of extracted human molars were cut mesiodistally. The outer buccal or lingual surface was used as specimens cutting the ends of enamel rods, and inner slabs used as specimens cutting the sides of enamel rods.
They were assigned to four groups by used adhesives: Group 1 (All-Bond 2), Group 2 (Single Bond), Group 3 (Tyrian SPE/One-Step Plus), Group 4 (Adper Prompt L-Pop). After each adhesive was applied to enamel surface, three composite cylinders were adhered to it of each specimen using Tygon tube. After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, the bonded specimens were subjected to µSBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. The results of this study were as follows;
1. The µSBS of Group 2 (16.50 ± 2.31 MPa) and Group 4 (15.83 ± 2.33 MPa) to the end of enamel prism was significantly higher than that of Group 1 (11.93 ± 2.25 MPa) and Group 3 (11.97 ± 2.05 MPa) (p < 0.05).
2. The µSBS of Group 2 (13.43 ± 2.93 MPa) to the side of enamel prism was significantly higher than that of Group 1 (8.64 ± 1.53 MPa), Group 3 (9.69 ± 1.80 MPa), and Group 4 (10.56 ± 1.75 MPa) (p < 0.05).
3. The mean µSBS to the end of enamel rod was significantly higher than that to the side of enamel rod in all group (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
Sae-Hee Han, Eun-Soung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 169. CrossRef
- Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
- 1,233 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- THE CHANGE OF ADAPTABILITY CHANGE IN ADHESIVE SYSTEMS TO DENTIN SUBSTRTE ACCORDING TO STORAGE TIME
- Young-Gon Cho, Il-Hwan Ban, Mi-Kyung Yu
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):204-214. Published online January 14, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT This study compared the microtensile bond strength (μTBS) and microscopic change of two 2-step and two 1-step self-etching adhesives to dentin according to storage times in distilled water.
Occlusal dentin was exposed in 48 human molars. They were divided to four groups by different adhesives: SE Bond group (Clearfil SE Bond), AdheSE group (AdheSE), Adper group (Adper Prompt L-Pop), and Xeno group (Xeno III). Each group was stored in 37℃ distilled water for 1, 15, and 30 days.
Resin-bonded specimens were sectioned into beams and subjected to μTBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. For SEM observation, one specimen was selected and sectioned in each group after each stroage time. Resin-dentin interface was observed under FE-SEM.
In all storage times, mean μTBS of SE group was significantly higher than those of other groups (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference between mean μTBS of SE group and AdheSE group among all storage times, but significant difference between 1- and 30-day storage in mean μTBS of Adper group and Xeno group (p < 0.05). For 1-and 15-day storage, all groups showed the close adaptation between resin-dentin interfaces. For 30-day storage, resin-dentin interfaces showed wide gap in Adper group and separate pattern in Xeno III group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 223. CrossRef - The effect of thermocycling on the durability of dentin adhesive systems
Young-Hoon Moon, Jong-Ryul Kim, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 222. CrossRef
- Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
- 1,090 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Priming time and etching effect on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive
- In-Joo Kang, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):185-190. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.185
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of additional etching on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive system to enamel
Sun-Jin Yoo, Young-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Won Park, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(4): 263. CrossRef
- Influence of additional etching on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive system to enamel
- 1,619 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of shear bond strength of different bonding systems on bleached enamel
- Kwang-Keun Kim, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.030
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
Jeong-Lyong Son, Gye-Young Lee, Yu-Mi Kang, Young-Taek Oh, Kwang-Won Lee, Tae-Gun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 406. CrossRef - Effect of vital tooth bleaching agent on dentin bonding
Na-Young Jeong, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 79. CrossRef
- The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
- 1,294 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- INFLUENCE OF APPICATION TIME OF SELF-ETCHING PRIMERS ON DENTINAL MICROTENSILE BOND STRENGTH
- Young-Gon Cho, Young-Gon Lee, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park, Jong-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):430-438. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.430
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT This study evaluated the influence of application time of self-etching primers on microtensile bond strength (μTBS) to dentin using three self-etching primer adhesive systems.
Dentin surfaces were exposed from forty-eight human molars. They were conditioned with three self-etching primers (Clearfil SE Bond [SE], Unifil Bond [UF], Tyrian SPE + One Step Plus [TY]) and different primining times (10s, 20s, 30s and 40s). Composite resins were bonded to dentin surfaces and specimens were made. μTBS was tested and statistically compared using by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s Test.
The results of this study presented that priming time for 10s in SE and UF groups and for 30s and 40s in TY group was highly decreased μTBS to dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The utility of dental health capacity of the first permanent molars as an oral health indicator among children and adolescents
Sun-Ho Lee, Heung-Soo Lee, Hyo-Won Oh, Hyun-Jeong Ju, So-Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2015; 39(3): 174. CrossRef - Logistic regression analysis of factors affecting the survival of first molars in Korean adults
Sung-Suk Chung, Jong-Bae Kim, Young-Sam Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Jin-Sil Hong, Ju-Yeon Kim, Kee-Wan Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2015; 39(2): 88. CrossRef - Dental health capacity of the first permanent molars among children and adolescents in Korea for the year 2010
Sun-Ho Lee, Hyun-Jeong Ju, So-Young Park, Hyo-Won Oh, Heung-Soo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2013; 37(2): 103. CrossRef
- The utility of dental health capacity of the first permanent molars as an oral health indicator among children and adolescents
- 1,174 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

-
IN VITRO MICRO-SHEAR BOND STRENGTH OF FIVE COMPOSITE RESINS TO DENTIN WITH FIVE DIFFERENT DENTIN ADHESIVES - Jin-Ho Chung, Byoung-Duck Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):353-364. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to compare and to evaluate the combination use of 5 kinds of dentin adhesive systems and 5 kinds of composite resins using micro-shear bond test. Five adhesive systems (Prime & Bond NT (PBN), Onecoat bond (OC), Excite (EX), Syntac (SY), Clearfil SE bond (CS)) and five composite resins (Spectrum (SP), Synergy Compact (SC), Tetric Ceram (TC), Clearfil AP-X (CA), Z100 (Z1)) were used for this study (5 × 5 = 25group, n = 14/group). The slices of horizontally sectioned human tooth were bonded with each bonding system and each composite resin, and tested by a micro-shear bond strength test. These results were analyzed statistically. The mean micro-shear bond strength of dentin adhesive systems were in order of CS (22.642 MPa), SY (18.368 MPa), EX (14.599 MPa), OC (13.702 MPa), PBN (12.762 MPa). The mean bond strength of self-etching primer system group (CS, SY) in dentin was higher than that of self-priming adhesive system groups (PBN, EX, OC) significantly (P<0.05). The mean bond strength of composite resins was in order of SP (19.008 MPa), CA (17.532 MPa), SC (15.787 MPa), TC (15.068 MPa), Z1 (14.678 MPa). Micro-shear bond strength of SP was stronger than those of other composite resins significantly (P < 0.05). And those of TC and Z1 were weaker than other composite resins significantly (P < 0.05). No difference was found in micro-shear bond strength of composite resin in self-etching primer adhesive system groups (CS, SY) statistically. However, there was significant difference of micro-shear bond strength of composite resin groups in self-priming adhesive systems group (PBN, EX, OC). The combination of composite resin and dentin adhesive system recommended by manufacturer did not represent positive correlation. It didn’t seem to be a significant factor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 30. CrossRef - Correlation Between the Amount of Linear Polymerization Shrinkage and Cuspal Deflection
S-Y. Lee, S-H. Park
Operative Dentistry.2006; 31(3): 364. CrossRef - Correlation between Linear polymerization shrinkage & tooth cuspal deflection
Soon-Young Lee, Sung-Ho Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(6): 442. CrossRef
- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
- 1,136 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Shear bond strength of self-etching adhesives to dentin and sem analysis
- Young-Gon Cho, Kee-Sun Roh, Soo-Mee Kim, Young-Gon Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Jae Ki
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(3):222-231. Published online May 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare shear bond strength and interfacial pattern of composite bonded to dentin using self-etching adhesive systems.
Sixty extracted human molars with exposed occlusal dentin were divided into four groups and bonded with four adhesives and composites: Single Bond/Filtek Z 250(SB), Tyrian SPE-One-Step Plus/Aelitefil(TY), Prompt L-Pop/Filtek Z 250(LP), and One-Up Bond F/Palfique Toughwell(OU).
The results of this study were as follows;
Shear bond strength for OU was significantly lower than that of other groups(p<0.05). No significant difference was founded among SB, TY, and LP.
Failure modes to dentin showed adhesive and mixed for SB, TY, and LP, but them for OU showed adhesive in all spceimens.
Dentin-resin interface showed close adaptation for SB, TY, and LP, but it showed gap for OU.
The hybrid layers for TY, LP, OU were thinner than that of SB. Adhesive layers were observed between composite and hybrid layer, which were 5 µm thick for TY and 10 µm thick for OU.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- POSITIONING SELF‐ETCHING ADHESIVES: VERSUS OR IN ADDITION TO PHOSPHORIC ACID ETCHING?
Claus‐Peter Ernst
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2004; 16(1): 57. CrossRef
- POSITIONING SELF‐ETCHING ADHESIVES: VERSUS OR IN ADDITION TO PHOSPHORIC ACID ETCHING?
- 1,184 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Self-adhesion of low-viscosity composites to dentin surface
- Tae-Hee Cho, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(3):209-221. Published online May 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.3.209
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objectiveness of this study was to evaluate whether low-viscosity composite can bond effectively to dentin surface without bonding resin. The low-viscosity composites being 50wt% filler content were made by the inclusion of bonding resin of two self-etching systems(Clearfil SE Bond, Unifil Bond) varied with contents as 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50wt%.
Exposed dentin surfaces of extracted 3rd molars are used. Dentin bond strengths were measured. The tests were carried out with a micro-shear device placed testing machine at a CHS of 1mm/min after a low-viscosity composite was filled into an iris cut from micro tygon tubing with internal diameter approximately 0.8mm and height of 1.0mm.
Flexural strength and modulus was increased with the addition of bonding resin.
Micro-shear bond strength to dentin was improved according to content of bonding resin irrespective of applying or not bonding resin in bonding procedure, and that of Clearfil SE Bond groups was higher than Unifil Bond.
There were no significant difference whether use of each bonding resin in bonding procedure for S-40, S-50, U-50(p>0.05).
In SEM examination, resin was well infiltrated into dentin after primed with self-etching primer only for S-50 and U-50 in spite of the formation of thinner hybrid layer.
Low viscosity composite including some functional monomer may be used as dentin bonding resin without an intermediary bonding agent. It makes a simplified bonding procedure and foresees the possibility of self-adhesive restorative material.
- 994 View
- 0 Download

- Microleakage of various composite resin systems
- In-Soo Kim, Kyung-San Min, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):127-133. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The object of this study was to compare the microleakage between various composite resin systems of multistep, one-bottle, and self-etching systems using electrical conductivity.
After making class V cavities (4×3×1.5 mm around CEJ), they were bulk filled with three kinds of resins of A3. Teeth were storaged in a saline solution for one day, after then, they were finished and polished using Sof-Lex system. Another stress of thermocycling was made for 500 times from 5° to 55℃ with each dwelling time of 10 seconds. Electrical conductivity (microamphere, µA) was checked four times: before and after cavity preparation, after filling, after thermocycling.
One-way ANOVA and 95% Scheffe Post Hoc test was used for checking any statistical difference among groups. Another 95% Paired Samples T-test was also used for estimating any significant difference within group after cavity filling or thermocycling.
The results were as follows:
Every specimen showed various range of microleakage after filling.
There was, however, no difference between composite resin systems.
All composite resin systems showed marked increase in microleakage with a thermocycling (p<0.05), there was, however, no difference between composite resin systems.
Although there was no significant difference between groups (p=0.078), one-bottle and self-etching systems seemed to be unstable than multistep system.
Within the limits of this study, it was concluded that much more consideration should be needed when using thermally unstable one-bottle and self-etching systems that have multi-advantages from simplified step. More studies will be needed to solve these kinds of problems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a new resin monomer on the microleakage of composite resin restorations
JH Bae, YK Kim, PY Yoon, MA Lee, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 469. CrossRef - Microhardness and microleakage of composite resin cured by visible light with various band of wavelength
Soo-Man Park, Jae-Yong Lee, Seung-Ryul Han, Sang-Yoon Ha, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2002; 27(4): 403. CrossRef
- Effect of a new resin monomer on the microleakage of composite resin restorations
- 1,111 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Morphological patterns of self-etching primers and self-etching adhesive bonded to tooth structure
- Young-Gon Cho, Seok-Jong Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Lee, Soo-Mee Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):23-33. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.023
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare in vitro interfacial relationship of restorations bonded with three self-etching primer adhesives and one self-etching adhesive.
Class I cavity preparations were prepared on twenty extracted human molars. Prepared teeth were divided into four groups and restored with four adhesives and composites: Clearfil SE Bond/Clearfil™ AP-X (SE), UniFil Bond/UniFil® F (UF), FL Bond/Filtek™ Z 250 (FL) and Prompt L-Pop/Filtek™ Z 250 (LP)
After storing in distilled water of room temperature for 24 hours, the specimens were vertically sectioned and decalcified. Morphological patterns between the enamel/dentin and adhesives were observed under SEM.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. They showed close adaptation between enamel and SE, UF and FL except for LP.
2. The hybrid layer in dentin was 2 µm thick in SE, 1.5 µm thick in UF, and 0.4 µm in both FL and LP. So, the hybrid layers of SE and UF were slightly thicker than that of FL and LP.
3. The lengths and diameters of resin tags in UF and FL were similar, but those of LP were slightly shorter and slenderer than those of SE.
4. The resin tags were long rod shape in SE, and funnel shape in other groups.
Within the limitations of this study, it was concluded that self-etching primer adhesives showed close adaptation on enamel. In addition, the thickness of hybrid layer ranged from 0.4-1.5 µm between adhesives and dentin. The resin tags were long rod or funnel shape, and dimension of them was similar or different among adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of appication time of self-etching primers on dentinal microtensile bond strength
Young-Gon Cho, Young-Gon Lee, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park, Jong-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2004; 29(5): 430. CrossRef
- Influence of appication time of self-etching primers on dentinal microtensile bond strength
- 1,133 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The influence of IRM temporary restorations on marginal microleakage of dentin adhesives
- Young-Gon Cho, Hyun-Kyung Kim, Young-Gon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):1-10. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the influence of IRM on marginal microleakage of 5th generation adhesives. Class V cavities with gingival margins in dentin were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of 60 extracted human molar teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into six groups. Group 1 and 4 received no temporary restoration with IRM. Group 2 and 5 were covered with IRM mixed at P/L ratio(10g/1g). Group 3 and 6 were covered with IRM mixed at P/L ratio(10g/2g). The temporary restorations were removed mechanically with an ultrasonic scaler after one-week storage in distilled water. The cavities were restored using one of two adhesives and composites; Single Bond/Filtek Z 250(Group 1, 2 and 3), UniFil Bond/UniFil F(Group 4, 5 and 6).
Following one day storage in distilled water, the restored teeth were thermocycled for 500 cycles(between 5℃ and 55℃) and immersed in 2% methylene blue for dye penetration testing. The results were analysed using Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked test at a significance level of 0.05.
The results of this study were as follows:
1. Ranking of mean microleakage scores at the enamel margins was Group 1<Group 3<Group 2<Group 4<Group 5<Group 6. The microleakage of Group 6 was significantly higher than that of Groups 1, 2 and 3(p<0.05).
2. At the enamel margins, without regard to pretreatment with IRM, the microleakage of Single Bond was lower than that of UniFil Bond.
3. Ranking of mean microleakage scores at the dentin margins was Group 4<Group 1<Group 5<Group 6<Group 3<Group 2. But there were no significant difference among microleakages of each group(p>0.05).
4. At the dentin margins, the microleakage of the group not pretreated with IRM was lower than that of the group pretreated with IRM. And the microleakage of UniFil Bond was lower than that of Single Bond.
5. Compared with microleakages between the enamel and dentin margins of each groups, Group 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 at dentin margin were higher microleakage than those at enamel margin. There were significant difference between enamel and dentin microleakage of Group 2 and 3(p<0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 327. CrossRef
- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
- 1,168 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Marginal microleakage of self-etching primer adhesives and a self-etching adhesive
- Young-Gon Cho, Kong-Chul Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(5):493-501. Published online September 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.5.493
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the microleakage performance of four self-etcing primer adhesives(Clearfil SE Bond, Clearfil Liner Bond 2, UniFil Bond, and FL Bond) and one self-etching adhesive(Prompt L-Pop). Class V cavity preparations with occlusal margins in enamel and gingival margins in dentin were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of 50 extracted human molar teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into five groups and restored using one of five adhesives and composite resins: Prompt L-Pop/Filtek Z 250(Group 1), Clearfil SE Bond/Clearfil AP-X(Group 2), Clearfil Liner Bond 2/Clearfil AP-X(Group 3), UniFil Bond/UniFil F(Group 4), and FL Bond/Filtek Z 250(Group 5).
Following one day storage in room temperature water, the restored teeth were thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃. Marginal microleakage was assessed by dye penetration using 2% methylene blue dye. After 24 hours, the teeth were sectioned longitudinally and evaluated for microleakage under steromicroscope. The data were statistically analysed by Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked tests.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microleakges at both enamel and dentinal margins were the lowest in group 4, increasing among groups in the following order: group 2, follwed by group 5, follwed by group 1, and the highest in group 3.
2. At the enamel margins, the microleakage of group 3 was significantly higher than those of groups 2, 4 and 5(p<0.05), and also the microleakage of group 1 was statistically higher than those of groups 2 and 5(p<0.05).
3. At the dentinal margins, microleakage of group 3 was significantly higher than microleakages of groups 1, 2, 4 and 5(p<0.05).
4. Compared with microleakages between the enamel and dentinal margins of each group, groups 1, 4 and 5 at enamel margin and group 2 and group 3 at dentinal margin were higher microleakage. But there was no significant difference between enamel and dentinal microleakages of each group(p>0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 13. CrossRef - Comparison of bond strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements
Hyun-A Lee, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 499. CrossRef - Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
Sae-Hee Han, Eun-Soung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 169. CrossRef - Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 327. CrossRef - Influence of appication time of self-etching primers on dentinal microtensile bond strength
Young-Gon Cho, Young-Gon Lee, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park, Jong-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2004; 29(5): 430. CrossRef - Morphological patterns of self-etching primers and self-etching adhesive bonded to tooth structure
Young-Gon Cho, Seok-Jong Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Lee, Soo-Mee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(1): 23. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of self-etching adhesives to dentin and sem analysis
Young-Gon Cho, Kee-Sun Roh, Soo-Mee Kim, Young-Gon Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Jae Ki
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(3): 222. CrossRef - The effect of additional enamel etching on microleakage of the adhesion of self-etching primer system
Jung-Jin Yoon, Kyung-San Min, Chan-Ui Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(5): 363. CrossRef
- Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
- 1,061 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The influence of moisture control on bond strength of composite resin treated with self-etching adhesive system
- Myoung Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Jeong-won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(4):363-369. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.4.363
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different air-drying time on the microleakage of single-step self-etch adhesives
Horieh Moosavi, Maryam Forghani, Esmatsadat Managhebi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(2): 73. CrossRef - Effect of moisture and drying time on the bond strength of the one-step self-etching adhesive system
Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 155. CrossRef - Priming time and etching effect on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive
In-Joo Kang, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2004; 29(2): 185. CrossRef
- Effect of different air-drying time on the microleakage of single-step self-etch adhesives
- 2,492 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


