Most download articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Most download articles
Most-download articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last three month.
- Sample size determination for conducting a pilot study to assess reliability of a questionnaire
- Mohamad Adam Bujang, Evi Diana Omar, Diana Hui Ping Foo, Yoon Khee Hon
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e3. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This article is a narrative review that discusses the recommended sample size requirements to design a pilot study to assess the reliability of a questionnaire. A list of various sample size tables that are based on the kappa agreement test, intra-class correlation test and Cronbach’s alpha test has been compiled together. For all calculations, type I error (alpha) was set at a maximum value of 0.05, and power was set at a minimum value of 80.0%. For the kappa agreement test, intra-class correlation test, and Cronbach’s alpha test, the recommended minimum sample size requirement based on the ideal effect sizes shall be at least 15, 22, and 24 subjects respectively. By making allowances for a non-response rate of 20.0%, a minimum sample size of 30 respondents will be sufficient to assess the reliability of the questionnaire. The clear guideline of minimum sample size requirement for the pilot study to assess the reliability of a questionnaire is discussed and this will ease researchers in preparation for the pilot study. This study provides justification for a minimum requirement of a sample size of 30 respondents specifically to test the reliability of a questionnaire.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preliminary efficacy of an online intervention based on Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for family caregivers of people with dementia: a feasibility study
Golnaz L. Atefi, Rosalie J. M. van Knippenberg, Sara Laureen Bartels, Andrés Losada-Baltar, María Márquez-González, Frans R. J. Verhey, Marjolein E. de Vugt
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy.2026; 55(1): 74. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Adaptation of the Feeling Safe During Surgery Scale
Hatice Çakır, Seda Cansu Yeniğün, Seçil Taylan
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2026; 41(1): 116. CrossRef - Development of immersive radiotherapy clinical learning experience prototype (IRCLEP)
Nur Najihah Binti Hamzaini, Gunalan A.L. Ramachandran, Tavaneethan A.L. Mogan, Nur Liyana Shuib, Abdul Khaliq Mohd Saparudin, Nur Khalis Sukiman, Noraini Ahmad Wahid, Saiful Izzuan Hussin, Nor Aniza Azmi
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences.2026; 57(2): 102167. CrossRef - Developing and validating the augmented reality-enabled e-commerce questionnaire (ARECQ): an extended technology acceptance model for Gen Z
Alfia Sayed, Asish Oommen Mathew, Lewlyn L. R. Rodrigues
Cogent Social Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - School-based interventions of menstrual hygiene management in Indonesia: systematic literature review
Aldilia Wyasti Pratama, Erni Rosita Dewi, Kusmayra Ambarwati
BMC Women's Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Cultural Adaptation and Reliability Testing of the Coeliac Disease Food Attitudes and Behaviours Scale in Brazil
Camila dos Santos Ribeiro, Eduardo Yoshio Nakano, Renata Puppin Zandonadi
Nutrients.2026; 18(1): 162. CrossRef - Pilot study: Training bilingual Hmong caregivers using the pain assessment information visualization tool for effective communication in healthcare
Maichou Lor, Betty Chewning, Linkai Wu
Patient Education and Counseling.2026; 145: 109476. CrossRef - Occupants’ perceived importance and satisfaction towards indoor environmental quality of a Malaysian green campus
Agnes Tien Tien Wong, Shi Yee Wong, Nor Nazihah Chuweni, Chih Siong Wong, Ai Chen Tay
Property Management.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Veterinarians' attitudes, knowledge, and practices about antibiotic use in animals: questionnaire design and reliability
Ana Filipa Pereira, Leonardo de Rago, Jacinta Oliveira Pinho, Ana Isabel Plácido, Adolfo Figueiras, Fátima Roque, Maria Teresa Herdeiro, Ana Cláudia Coelho, Paula Alexandra Oliveira
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing biopsychosocial status in people living with HIV: validity, reliability, and responsiveness of BETY-BQ
Sinan Buran, Orkun Tüfekçi, Erkin Oğuz Sarı, Süreyya Damar-Örenler, Tuba Damar-Çakırca, Ayşen Akgöz, Ayşenur Besler-Tuncer, Yavuz Yakut, Nur Banu Karaca, Mertcan Uzun, Meliha Çağla Sönmezer, Ahmet Çağkan İnkaya, Serhat Ünal, Edibe Ünal
BMC Infectious Diseases.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Pesticide Exposure and Mucocutaneous Symptoms Among Thai Agricultural Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study
Warin Intana, Chime Eden, Weeratian Tawanwongsri
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2026; 23(1): 97. CrossRef - Climate-smart radiography in Ghana: training needs of diagnostic radiographers mapped to the WHO operational framework and UNFCCC Action for Climate Empowerment (ACE)
Christian Ven Emery, Eric Akpabli, Bernard Amedzoame, Tretu Beracah, Jeffery Gameli Amlalo, Hayford Insidey, Isaac Tigbee, Joseph Amihere Ackah, Wuni Abdul-Razak
BMC Health Services Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Longing for Another: Extradyadic Infatuation and Its Associations with Features of the Primary Relationship and Infidelity
Teodora-Elena Huţanu, Andrei Corneliu Holman
Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Level of community collaboration in the implementation of wildlife conservation and management policy in King’wal Wildlife Conservancy, Nandi County, Kenya
Josphat K. Koech, Edmond M. Were, Daniel Rotich Kandagor
African Journal of Empirical Research.2026; 7(1): 215. CrossRef - Patient Adherence to Splint Therapy and Counselling Programmes in Temporomandibular Disorders: Development and Validation of a New Questionnaire
Soaad Tolba Badawy, Amal T. Badawi, Mai Ahmed Haggag
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling sustainable environmental responsibility behavior of students in private university
Shaohua Ben, Wenjun Zheng, Mohamad Bin Bilal Ali
Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management.2026; 34(1): 19. CrossRef - Reliability and validity of stroke self-efficacy questionnaire: a Vietnamese version
Tinh Thi Thanh Nguyen, Thanh Tran Ngoc Dang, Vien Truong Nguyen, Hong Thuy Phuong Huynh
Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Comprehensive mental and cognitive health screening: A novel approach
Sejal K. Vyas
Current Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric testing of the teacher food and nutrition-related health and wellbeing questionnaire
Tammie Jakstas, Andrew Miller, Vanessa A. Shrewsbury, Tamara Bucher, Clare E. Collins
BMC Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioural and Systemic Determinants of Pesticide Waste Disposal Among Nigerian Cocoa Farmers: Insights from Mixed-Methods Research
Oluseye Oludoye, Charles C. Okolo, Opeyemi Adebanjo-Aina, Koleayo Omoyajowo, Lanrewaju Ogunyebi
Pollutants.2026; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Validation of the Iranian version of the work-family guilt scale
Seyedeh-Bahare Safavi, Mahnaz Joukar, Farahnaz Kamali, Khatoon Samsami, Razieh Bagherzadeh
BMC Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Dark triad with green attitude influence green intentions towards employee health and well-being
Mohammed Ashrafunnisa, D. Lakshmi Narasimha Prasad, Karthikeya Gattupalli, Jangili Siva Rama Krishna, Md Asadul Haque, A. V. S. Kamesh, Kirubaharan Boobalan
Discover Sustainability.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Preliminary Validation of a Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Questionnaire Assessing Parental Self-Healthcare for Respiratory Tract Infections in Children With Cerebral Palsy in Malaysia
Riham M. K Abualeinein, Sazlina Kamaralzaman, Nur Zakiah Mohd Saat
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Public perceptions of community pharmacists' evolving role in health promotion and pharmaceutical care: A cross-sectional study in Indonesia
Didiek Hardiyanto Soegiantoro, Fortunata Narwadan, Joyce Nadia Clarita Ndruru, Oktaviana Koa, Yunita Susanti Mahemba, Betriks Utang Palunggu, Debora Olivke, Mikha Adyatama Putra, Nikodemus Yeingo, Gregory Hope Soegiantoro
Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning.2026; 18(5): 102600. CrossRef - A validated Arabic version of the clinical learning evaluation questionnaire for medical students and interns
Ahmed Amir Samir, Kerollos Abdelsayed, Hebatalla Abdelmaksoud Abdelmonsef Ahmed, Ahmed Almahdy Mohamed, Ahmed Reda Bahr, Naji Al-bawah, Ali Malik Tiryag, Alla' Khirfan, Mohamed Yacoub, Ramy Mohamed Ghazy
Medical Education Online.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing Human Emotional Responses to Urban Sound Environments: Evidence from Web Questionnaire and EEG Survey
Neng Zhao, Weishi Li, Xiaoxia Wang, Lin Liu, Qing Wu, Wei Liao
Buildings.2026; 16(4): 874. CrossRef - Assessing active thumb palmar and radial abduction in persons with thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis via intermetacarpal distance methods: an exploration of validity, reliability, and precision
Halil Ibrahim Ergen, Karl Dischinger, Corey W. McGee
Clinical Rheumatology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and validation of a short spirituality scale on a French population: SPI-8
Océane Agli, Christine-Vanessa Cuervo-Lombard, Nathalie Bailly
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics Plus.2026; 3(2): 100265. CrossRef - Determinants of honey production among smallholder beekeepers: evidence from Baringo County, Kenya
Naftali Kiprono, Naomi Chebiwot Chelang’a, Raphael Gitau
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Construct Validity and Reliability of the Effective Early Childhood Physical Literacy Pedagogue (ECE-PLP) Self-Report Instrument
Jaime Barratt, Dean Dudley, Michalis Stylianou, George Thomas, Kai Wheeler, John Cairney
Measurement in Physical Education and Exercise Science.2025; 29(2): 145. CrossRef - Enhancing energy resilience in manufacturing enterprises: A systematic mapping of challenges to strategies
P. Lebepe, T.N.D. Mathaba
Journal of Economy and Technology.2025; 3: 82. CrossRef - Impact of digital device utilization on public health surveillance to enhance city resilience during the public health emergency response: A case study of SARS-CoV-2 response in Thailand (2020–2023)
Watcharaporn Chutarong, Roongaroon Thammalikhit, Rungwasun Kraiklang, Anurak Sawangwong, Orachorn Saechang, Yuqian Guo, Weiwen Zhang
DIGITAL HEALTH.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of Life and the Role of Gender in Patients With Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in Greece
Nikolitsa S Dareioti, Christos Τ Lampropoulos, Balasis B Stavros, Sophia Georgiou, Philippos Gourzis, Nicholas S Mastronikolis
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring public perspectives on solar energy adoption in Mexico
Ana Sofia Andrade-Arias, Golam Kabir, Mehdi Mirmohammadsadeghi, Angappa Gunasekaran, Armando Elizondo-Noriega
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.2025; 212: 115410. CrossRef - Development and Initial Validation of the Psychosocial Stress Scale for Dancers
Yuqianqian Dong, Young-Eun Noh, Siqi Liu, Eliza Hafiz
SSRN Electronic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analyzing factors influencing students’ decisions to adopt smart classrooms in higher education
Long Kim, Rungrawee Jitpakdee, Wasin Praditsilp, Sook Fern Yeo
Education and Information Technologies.2025; 30(10): 14335. CrossRef - Collaborative Working Relationships Between Community Prevention Coalitions and Their Technical Assistance Providers: A Mixed Methods Approach for the Development of an Innovative Implementation Measure
Sarah M. Chilenski, Meg Small, Jochebed G. Gayles, Brittany Rhoades Cooper, Louis D. Brown
Prevention Science.2025; 26(2): 193. CrossRef - Intentions of hospital pharmacists to use digital technology in their daily practice: a cross-sectional survey using the Theory of Planned Behaviour
Kamer Tecen-Yucel, Nesligül Ozdemir-Ayduran, Emre Kara, Kutay Demirkan, Betul Okuyan
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2025; 47(4): 1024. CrossRef - Development and validation of the nurses’ touch comfort evaluation scale in China
Yaohong Liu, Sainan Qiu, Hao Li, Chong Chen, Renhe Yu, Su’e Yuan
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sequential mediator and moderator model of intention for the implementation of chatbots in Malaysian government agencies
Ramizatunnisah Jais, Abdul Hafaz Ngah
Journal of Decision Systems.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Freshmen’s Perceptions of the Effect of Technology on Learning English: A Case Study at the National University of Battambang, Cambodia
Keo Vireak, Sam Rany, Lan Bunrosy, Rouet Wen
Journal of Social Knowledge Education (JSKE).2025; 6(1): 54. CrossRef - Exploring EFL students’ challenges in oral presentations at National University of Battambang
Vireak Keo, Bunrosy Lan, Rany Sam, Wen Rouet
International Journal of Professional Development, Learners and Learning.2025; 7(2): e2513. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Persian Prosthesis Embodiment Scale for Lower Limb Amputees
Alireza Khani, Robin Bekrater-Bodmann, Zahra Fattahi, Vahideh Moradi, Mehdi Rezaee, Taher Babaee
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(20): 5368. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Persian version of the treatment satisfaction questionnaire for medication (TSQM) among Iranian hypertensive patients
Ali Khalooei, Mohadeseh Ghasemi, Sahar Salehi, Farshid Sharifi, Mehran Nakhaeizadeh
Chronic Illness.2025; 21(3): 390. CrossRef - The SCIEPR checklist: A tool for standardizing chest X-ray interpretation in resource-constrained settings – A pilot study
K.M. Sethole, N. Mshunqane
Radiography.2025; 31(3): 102912. CrossRef - Extracurricular physical activities and academic achievement in Saudi female physical education students: the mediating effect of motivation, enjoyment, and BMI
Mohamed Frikha
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frailty as a Predictor of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder After Advance Care Planning Communication Intervention by Trained Care Managers in Long-Term Care Service Users in Japan: A Secondary Analysis
Mariko Miyamichi, Kyoko Oshiro, Shozo Okochi, Noriyasu Takeuchi, Tomoe Nakamura, Terumi Matsushima, Masako Okada, Yoshimi Kudo, Takehiro Ishiyama, Tomoyasu Kinoshita, Hideki Kojima, Mitsunori Nishikawa
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(4): 159. CrossRef - Cross-cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Italian Version of the Revised Perceived Perioperative Competence Scale
Chiara Giammaria, Nicolò Panattoni, Irene Terrenato, Alessandro Spano, Aurora De Leo, Bernardino Tomei, Emanuele Di Simone, Fabrizio Petrone
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2025; 40(5): 1230. CrossRef - Assessing ChatGPT for Clinical Decision-Making in Radiation Oncology, With Open-Ended Questions and Images
Wei-Kai Chuang, Yung-Shuo Kao, Yen-Ting Liu, Cho-Yin Lee
Practical Radiation Oncology.2025; 15(5): e412. CrossRef - Accuracy of a self-report questionnaire to predict peri-implant disease: a pilot study
Drew M. Young, Debora C. Matthews, Haider Al-Waeli
Periodontal and Implant Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sport-specific relationship problems: Turkish adaptation of an evaluation method
Sabriye Ercan, Esma Arslan, Elif Şahi̇n, Esra Şahi̇n, Aydan Örsçeli̇k, Gökhan Büyüklüoğlu, Nihan Büyüklüoğlu, Hasan Kaya
BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidimensional evaluation of the clinical efficacy and potential mechanisms of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training in the treatment of stroke: a study based on multiple evaluation indicators
Jingjun Xie, Jinxia Li, Qi Sun, Jie Jiang
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of Chinese version of the familiar tools use test for assessing limb apraxia in stroke patients
Jinni Wang, Jingxin Wei, Meilian Chen, Lu Gao, Xiaoyan Liao
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Sigortası Okuryazarlığı Düzeyinin Ölçümüne Yönelik Bir Model Çalışması
Doğancan Çavmak
Akademik Araştırmalar ve Çalışmalar Dergisi (AKAD).2025; 17(32): 219. CrossRef - Pain self-efficacy scale for children and adolescents aged 8 to 17 years (SPaSE): Translation, adaptation and psychometric properties into Turkish
Bahar Aksoy, Seda Cansu Yeniğün, Adem Sümen
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 84: 188. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the Box and Block Test for individuals with schizophrenia spectrum disorder
Jing-Wen Su, Hsiang-Yu Chen, Kuan-Yi Li
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Arabic version of the patient education materials assessment tool (PEMAT): translation and validation
Marwan A. Alrasheed, Aliyah Almobarak, Hisham M. Alfayyadh, Abdulelah Alkahtani, Bander Balkhi
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between self-reported and pedometer-measured physical activity in Vietnamese adolescents: A reliability and agreement study
Tram T. N. Truong, Van-Anh N. Huynh, Kien G. To, Julia Robinson
PLOS Global Public Health.2025; 5(6): e0004725. CrossRef - Psychological Burden and Coping Strategies Among Pakistani Adults: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study
Madeeha Malik, Humaira Rehman, Azhar Hussain, Ayisha Hashmi, Khalid Ahmad Al-Sunaidar, Georgina Balogh, Márió Gajdács, Shazia Jamshed
Epidemiologia.2025; 6(3): 30. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of an Iranian instrument for assessing adherence to ethical principles in the use of artificial intelligence among healthcare providers
Mohsen Khosravi, Yasaman Herandi, Sedighe Sadat Tabatabaei Far, Ghasem Rajabi Vasokolaei, Fatemeh Yousefi Nejad, Hossein Bouzarjomehri, Reyhane Izadi, Zahra Zare, Marzie Abdollahzade, Hojjat Rahmani, Milad Ahmadi Marzaleh
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2025; 203: 106019. CrossRef - Development and reproducibility of a questionnaire to assess drivers and barriers to consuming plant-based alternatives to dairy foods
Beatriz Philippi Rosane, Julia Batalha, Eduardo Yoshio Nakano, Derek V. Byrne, Susanne Gjdested Bügel, Barbara Vad Andersen, Renata Puppin Zandonadi, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2025; 41: 101231. CrossRef - Development of the SCI-BodyMap—Measuring Mental Body Representations in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury: Protocol for Item Generation, Reliability, and Validity Testing
Sydney Carpentier, Sara Bottale, Nicole Cenci, Mauro Cracchiolo, Daniele De Patre, Julian Pablo Gorosito, Ilaria Grimaldi, Mara Melo, Bianca Polinelli, Marco Rigoni, Fortunata Romeo, Marina Zernitz, Ann Van de Winckel
JMIR Research Protocols.2025; 14: e72370. CrossRef - Inter-Rater Reliability of Griffiths III in a Multi-lingual Community
Nur Alfreena Alfie, Jeffrey Soon-Yit Lee, Siew-Ming Ting, Teck-Hock Toh
Malaysian Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health.2025; 31(S1): 25. CrossRef - Mediating effects of sustainability-oriented innovation on the relationship between organizational creativity and sustainable performance among Chinese manufacturing SMEs
Xie Qiong, Mohd Hizam Hanafiah, Hu Yang, Roshayati Abdul Hamid, Noor Hasni Juhdi
Multidisciplinary Reviews.2025; 8(12): 2025373. CrossRef - A study of knowledge, awareness and eating habits of Orang Asli children at Sg Rual primary school, Jeli, Kelantan, Malaysia
Muhamad Azahar Abas, Ameer Sabrin Muhammad Shukri, Mohamad Faiz Mohd Amin, Mohd Sukhairi Mat Rasat, Noor Janatun Naim Jemali
Multidisciplinary Reviews.2025; 8(12): 2025344. CrossRef - Quality Management Systems (QMSs): Exploring the Effect of Risk Factors and Developing the Risk Management Framework for QMS Effectiveness in Service Institutions
Simon Emmanuel, Ismail W. R. Taifa
Quality and Reliability Engineering International.2025; 41(7): 3176. CrossRef - Selection of Resin-Based Dental Restorative Materials: A Pilot Study on Professional Characteristics, Knowledge, and Selection Criteria
Anna Kontakou Zoniou, Maria Antoniadou, Sofia Saridou
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 7987. CrossRef - Perceptions and Procedural Errors in the Use of a Patient‐Specific 3D‐Printed Model for MTA Apexification Technique Training
H. Plascencia, M. A. Contreras‐Preciado, J. F. Brito‐Ortiz, M. Díaz, R. Solis, G. Gascón
International Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of eHealth Literacy in Healthcare Service Users: Construction and Validation of a Measurement Instrument
Juan Morales, César Augusto Eguia
Clinical Practice & Epidemiology in Mental Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Sidewalk Built Environment Design Strategies to Promote Walkability in Tropical Humid Climates
Pakin Anuntavachakorn, Purinat Pawarana, Tarid Wongvorachan, Chaniporn Thampanichwat, Suphat Bunyarittikit
Buildings.2025; 15(15): 2659. CrossRef - Impact of freight logistics supply chain management on supply chain robustness and financial performance: Post-COVID-19 era
Valentine Muradzikwa, Chengedzai Mafini, Douglas Zvinowanda
International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147- 4478).2025; 14(5): 32. CrossRef - Management of maxillofacial trauma in patients with alcohol use disorder : a cross-sectional study on awareness, practices and gaps
Elavenil Panneerselvam, Rajkumar Krishnan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptation of the Child Coeliac Disease Food Attitudes and Behaviours Scale (Child CD-FAB) into Brazilian Portuguese: Translation and Evaluation of Reproducibility and Internal Consistency
Marina de Cesaro Schwantes, Heather Maddison-Roberts, Eduardo Yoshio Nakano, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho, Renata Puppin Zandonadi
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2704. CrossRef - Validation of the consumer health activation index (CHAI) among community-dwelling adults in primary care clinics in Singapore
Justin Guang Jie Lee, Qin Xiang Ng, Nan Luo, Gerald Choon Huat Koh, Ling Jie Cheng
Population Health Metrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal satisfaction with childbirth and its implications for maternity care quality: A cross-sectional study
Mirko Prosen, Sabina Ličen
Journal of Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Media in the E-Government Adoption in Morocco: A Diffusion of Innovation and Technology Acceptance Model Perspective Using PLS-SEM
Oumaima El Harim, Nouh El Harmouzi
Digital.2025; 5(3): 39. CrossRef - The effect of segmented-interactive video demonstration on student performance in procedural skills among healthcare students
Nurul Rimadhayanti Hamzah, Mohd Fadzil Abdul Hanid, Mohamad Ikram Zakaria
Advances in Health Sciences Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Purchase intention towards products on wildberries: an empirical study among Gen Z in Russia with customer attitude as mediator
Anna Orelskaia, Arumugam G Sithamparam, Daniel Ruiz De Garibay Ponce, Ruslan V. Ozarnov
Cogent Business & Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Servitization and Digitalization on Firm Competitiveness and Performance: The Moderating Role of Government Support
Hendri Ginting, Hamidah Nayati Utami, Riyadi Riyadi, Benny Hutahayan
Sustainability.2025; 17(19): 8756. CrossRef - Assessing food label literacy: development and validation of a psychometric scale for adults
Güldane Yildirim, Muhammet Ali Çakır
Nutrition & Food Science.2025; 55(8): 1280. CrossRef - Building Resilience in Sandwich-Generation Families: Financial Literacy and Emergency Fund Ownership from an Islamic Socio-Cultural Perspective
Irni Rahmayani Johan, Sifa Nabila Azzahra, Megawati Simanjuntak, Mohamad Fazli Sabri
Fikri : Jurnal Kajian Agama, Sosial dan Budaya.2025; 10(2): 521. CrossRef - Phase one preliminary validation of a psychologically informed scale for faith based organisational effectiveness
Abraham Nyako Jnr, Ramakrushna Mahapatra
Discover Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Home-Based Exercise and Fall Prevention in Older Adults: Development, Validation and Usability of the Mais Equilíbrio Mobile App
Mateus Medeiros Leite, Alessandro de Oliveira Silva, Silvana Schwerz Funghetto, Luciano Ramos de Lima, Samuel Barbosa Mezavila Abdelmur, Hudson Azevedo Pinheiro, Calliandra Maria de Souza Silva, Maurílio Tiradentes Dutra, Marina Morato Stival
JMIR Aging.2025; 8: e80724. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Antenatal Care Attendance among Pregnant Women in Mogadishu, Somalia
Walid Abdulkadir Osman, Aweis Ahmed Moallim Abdullahi, Hassan Muse Ahmed, Khalid Abdukadir Osman, Abdiwali Abdullahi Abdiwali, Ahmed Mohamud Hussein
Sage Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of an instrument measuring artificial intelligence utilization in decision-making domains of healthcare organizations
Zahra Zare, Mohsen Khosravi, Milad Ahmadi Marzaleh, Faride Sadat Jalali, Reyhane Izadi, Homeira Naseh
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of stressors on readiness for clinical practice in novice nursing students: a path analysis
Nur Guven Ozdemir, Berna Kokturk Dalcali, Soner Berse
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the operationalized ICF Core Sets for autism and ADHD: item metrics, reliability, and validity
Lovisa Alehagen, John Hasslinger, Melissa H. Black, Elina Wessman, Sven Bölte
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Sun protection behaviors and knowledge of skin cancer and sun exposure among Emirati undergraduate students
Huda Anshasi, Hajer Almazrouei, Nojoud Rashed, Reem Salem, Mareyah Suhail, Amal Abdulla
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the ASSU Model for Age-Friendly E-Service Quality: An Independent Research Aligned With the ISO 25556:2025 Evidence From Senior Tourists in Guilin, China
Fan Yang, Ahmad Albattat
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of the Adult Interpersonal Acceptance-Rejection Scale to measure parents, best friend, and romantic partner acceptance in Bangladeshi young adults
Rumana Aktar, Mohammad Ifaz Uddin, Md. Imran Hossain, Md. Robiul Hossain
Acta Psychologica.2025; 261: 105899. CrossRef - Bridging the divide between projected hydroclimatic variability and agricultural ecosystem sustainability through Life Cycle Assessment–Geographic Information System
Haseeb Akbar, Shabbir H. Gheewala
Sustainable Production and Consumption.2025; 61: 194. CrossRef - Development and validation of an instrument to assess the maturity of digital transformation in higher education institutions
Carlos Valdivia-Salazar, Oscar Serquén, Laurita Guevara, Jessie Bravo-Jaico, Roger Alarcón, Nilton Germán, Janet Aquino, Gisella Luisa Elena Maquen-Niño, Armando Moreno Heredia
Frontiers in Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship Between Religiosity and Happiness Among Students of the Pancasila and Civic Education Study Program at the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Pamulang University
Adam Sugiarto, Rachmatullah Rusli
Journal of Smart Pedagogy and Education.2025; 1(1): 12. CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of the Osteoporosis Preventing Behaviors Questionnaire (OPBQ) based on pender’s health promotion model
Mahsa Askarian, Ali Baloochi, Fatemeh Vizeshfar, Fatemeh Mohammadizadeh, Mobin Mottahedi, Farzad Abaszadeh
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - From Planting to Participation: Early-Phase Resident Attachment in an Urban Fruit Orchard
Jiri Remr, Jiri Sedlák
Urban Science.2025; 9(12): 492. CrossRef - The risk of occupational anaphylaxis in beekeepers: an educational public health intervention
Tea Močnik, Mihaela Zidarn, Nina Frelih, Sabina Ličen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Financial and Access Factors in Housing Decisions: An Economic Education Perspective from Phnom Penh
Berna Ou, Por Narith, Sario T Pio
Journal of Social Knowledge Education (JSKE).2025; 6(4): 438. CrossRef - Evaluating the quality-of-life for patient surviving with breast cancer diseases
Nor Intan Shamimi Abdul Aziz, Mass Hareeza Ali, Ahmad Taufik Jamil, Yuhanis Ab Aziz
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2025; : 1. CrossRef - ДОСВІД УКРАЇНОМОВНОЇ АДАПТАЦІЇ ОСОБИСТІСНОГО ОПИТУВАЛЬНИКА HEXACO M. C. ASHTON & K. LEE
Зіновія Карпенко , Арсен Климпуш
Psychological Prospects Journal.2025; (46): 39. CrossRef - Prevalence and Contributing Factors of Illicit Drug Use Among Youth Aged 18–24 Years in South Korea
Chaehee Kim, Kihye Han, Jieun Kim, Alison M. Trinkoff, Sihyun Park, Hyejin Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(5): 433. CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding mosquito-borne diseases in an urban sector of southwestern Colombia
Francisco Javier Bedoya-Rodríguez, Carlos Eduardo Guevara-Fletcher, Jonathan S. Pelegrin
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient perspectives on follow-up CT scans after treatment for renal cell carcinoma (RCC): a cross-sectional questionnaire study
Marlin A. A. Reijerink, Jaap Stoker, Patricia J. Zondervan, Shandra Bipat
Abdominal Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Technology Transfer Within the China–Laos Economic Corridor on Industrial SME Performance: A Configurational Approach
Ying Xong Thanongsack, Muhammad Kamil, Souvanhxay Paovangsa, Ke Xing
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Movement and Function Assessment Kit (MFAK) for Children with Specific Learning Disabilities
Nur Sakinah Baharudin, Dzalani Harun, Suhaili Ibrahim, Hanif Farhan Mohd Rasdi, Masne Kadar
Environment-Behaviour Proceedings Journal.2025; 10(SI35): 43. CrossRef - Religiosity and LGBTQ+ Affirmative Practice Among Filipino Mental Health Professionals
Rolf Gian Marcos, John Manuel R. Kliatchko, Marc Eric S. Reyes
Sexuality & Culture.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Cultural Model for Family Caregivers of Older People with Musculoskeletal Pain in East Coast Malaysia: A Pilot Validation Study
Nurin Syafiqah Mohd Jaias, Che Azunie Che Abdullah, Muhammad Kamil Che Hasan, Mohd Khairul Zul Hasymi Firdaus, Nur Ain Mahat
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CARE SCHOLARS .2025; 8(3): 64. CrossRef - MRI safety knowledge and attitudes among nursing students in the UAE
Mohamed Zakaria El-Sayed, Mohammad Rawashdeh, Mohammed Muhussin, Ayesha Bibi, Magdi A. Ali
Health Education.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Development and Pilot Validation of the Sexual Satisfaction and Emotional Impact After Cesarean Section Scale (SSEI-CS-24): A Pilot Study
Ana-Maria Brezeanu, Dragos Brezeanu, Stase Simona, Dan Cozmei, Vlad I Tica
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Procurement Skills and Organizational Performance of the Procurement Department of the County Government of Nakuru, Kenya.
Teresiah Wanjiru Kibe, Duncan Nyakundi Nyaberi
International Journal of Social Science and Humanities Research (IJSSHR) ISSN 2959-7056 (o); 2959-7048 (p).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of Luxury Train Seat Integrating Emotional Perception and Local Wisdom Approaches
Afif Hakim, Bambang Suhardi, Pringgo Widyo Laksono, Mirwan Ushada, Jafri Mohd Rohani
Jurnal Optimasi Sistem Industri.2025; 24(2): 234. CrossRef - Psychometric of the Ferrer-Urbina multidimensional scale of sexual self concept (MSSSC) in the Iranian population
Yeganeh Dadashzadeh Sangary, Mohammad Hassan Asayesh, Ali Asgharzadeh, Zahra Naghsh
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Content validity, practicality and testing of the reliability of various tools for the detection and screening of delirium in residents with dementia in German nursing homes: a study protocol
Johanna Christina Seiters, Vincent Molitor, Alessandro Morandi, Tania Zieschang, Martin N Dichter, Burkhard Haastert, Maria Erdmann, Falk Hoffmann, Rebecca Palm
BMJ Open.2025; 15(12): e112357. CrossRef - Development and validation of Transtheoretical model-based questionnaire on micronutrients for adolescents: Psychometric properties
Priyanka Pareek, Aparna Thorat, Chethana Chandrasekar, Poonam Khanna, Rashmi Kulkarni, Shravya Karkera
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Critical success factors for digital transformation in government organizations using a structural model approach
Abdalla Al Maazmi, Zehra Canan Araci, Sujan Piya
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of the Thai Halitosis Associated Life-Quality Test (T-HALT): an evaluation of psychometric properties
Yodhathai Satravaha, Katkarn Thitiwatpalakarn, Supakit Peanchitlertkajorn, Supatchai Boonpratham, Chaiyapol Chaweewannakorn, Kawin Sipiyaruk
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing and validating a culturally tailored questionnaire to assess COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Israel’s ultraorthodox Jewish population
Imanuel Ber, Wasef Na’amnih, Saritte Perlman, Ben Kasstan, Yehuda Lerman, Khitam Muhsen
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Blood Lead Level Determinants in Refinery Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study
Luay M Mohammed , Manoochehr Karami, Yadollah Mehrabi , Seyed S Hashemi, Somayeh Farhang Dehghan, Mohammed Rafiee, Hasan Baiee
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of intervention by trained care managers on advance care planning engagement among long-term care service users in Japan: a pre- and post-pilot comparative study across multiple institutions
Shozo Okochi, Kyoko Oshiro, Noriyasu Takeuchi, Mariko Miyamichi, Tomoe Nakamura, Terumi Matsushima, Masako Okada, Yoshimi Kudo, Takehiro Ishiyama, Tomoyasu Kinoshita, Hideki Kojima, Mitsunori Nishikawa
Palliative Care and Social Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Arabic version of the knee and hip health-related quality of life (Mini-OAKHQOL) questionnaire in male Saudi patients with osteoarthritis: a methodological observational design
Madi Talal Alharbi, Mahamed Ateef, Ahmad Alanazi, Msaad Alzhrani
PeerJ.2024; 12: e18122. CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the parents' perception of satisfaction with care from pediatric nurse practitioners instrument
Dilek Demir Kösem, Şenay Demir, Murat Bektaş, Frances DiAnna Kinder
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 78: e75. CrossRef - Advanced Work Packaging (AWP): Implementation and Challenges in the Malaysian Oil and Gas Sector
Muhammad Ali Musarat, Wesam Salah Alaloul, Mohd Al-Azahary bin Abdullah Sani, Ng Wei Chong
Sustainability.2024; 16(23): 10234. CrossRef - The assessment of reliability and validity of the Thai Versions of the Thirst Distress Scale for patients with Heart Failure and the Simplified Nutritional Appetite Questionnaire in heart failure patients
Jenjiratchaya Thanapholsart, Ehsan Khan, Satit Janwanishstaporn, Porntipa Thongma, Saowanee Naowapanich, Pornpoj Pramyothin, Srisakul Chirakarnjanakorn, Porntera Sethalao, Thitipong Tankumpuan, Nana Waldréus, Geraldine A. Lee
Journal of Research in Nursing.2024; 29(8): 622. CrossRef - Measuring internalized health-related stigma across health conditions: development and validation of the I-HEARTS Scale
Rebecca L. Pearl, Yulin Li, Laurie C. Groshon, Marian Hernandez, Danielle Saunders, Miriam Sheynblyum, Kimberly A. Driscoll, Joel M. Gelfand, Preeti Manavalan, Marjorie Montanez-Wiscovich, Deidre B. Pereira, Rebecca M. Puhl, Thomas A. Wadden, Lori B. Waxe
BMC Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Modular XR Collaborative Platform for Occupational Safety and Health Training: A Case Study in Circular Logistics Facilities
Ali Vatankhah Barenji, Jorge E. Garcia, Benoit Montreuil
Information.2024; 15(9): 570. CrossRef
- Preliminary efficacy of an online intervention based on Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for family caregivers of people with dementia: a feasibility study
- 57,835 View
- 2,041 Download
- 103 Web of Science
- 124 Crossref

- Marginal adaptation of three root-end filling materials in cavities prepared with laser and ultrasonic tips: an in vitro comparative study
- Busra Zengin, Seda Aydemir, Nicholas Paul Chandler
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e32. Published online September 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e32

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
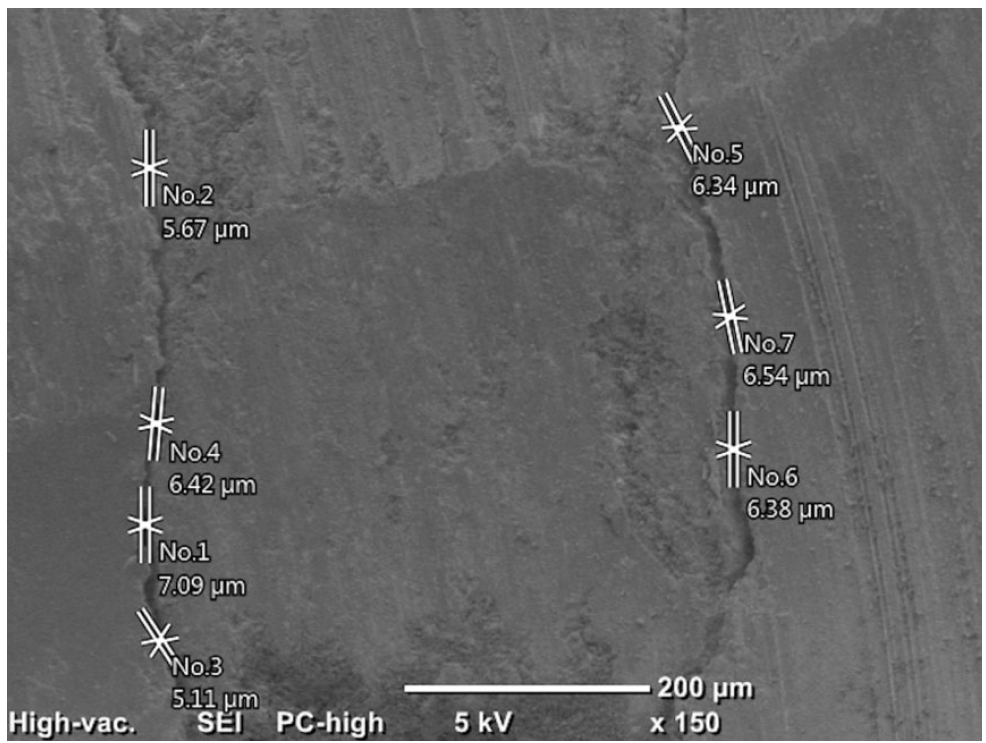
This study evaluated the marginal adaptation of ProRoot MTA (Dentsply Tulsa Dental), Biodentine (Septodont), and TotalFill BC RRM (FKG) placed in root-end cavities prepared with ultrasonic or Er,Cr:YSGG laser tips, using scanning electron microscopy.
Methods
The canals of 90 extracted maxillary central incisors were prepared and obturated and their roots resected. Six groups of 15 specimens were allocated as follows: ultrasonic + ProRoot MTA, ultrasonic + Biodentine, ultrasonic + TotalFill, laser + ProRoot MTA, laser + Biodentine, and laser + TotalFill. Roots were sectioned longitudinally to expose the filling material. Apical and coronal micrographs were taken, and the greatest distance between dentin and filling material was measured. The total gap area was also calculated using further micrographs.
Results
Cavities prepared with the ultrasonic tips and filled with Biodentine showed significantly greater gap dimensions compared with TotalFill (p < 0.001) and ProRoot MTA (p = 0.007) in the apical region. The ultrasonic group showed significantly higher void values compared to the laser group for ProRoot MTA (p = 0.026), when comparing the total values of void. The Biodentine group was significantly higher than the TotalFill group in root-end cavities prepared with ultrasonic tips (p < 0.001). The Biodentine group was significantly higher than the ProRoot MTA group in root-end cavities prepared with the laser tip (p = 0.002).
Conclusions
Under the conditions of this study, it was determined that the root-end cavity preparation technique had an effect on the amount of gaps formed between the dentin and the three filling materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Marginal Adaptability of Harvard MTA and Biodentine Used as Root-End Filling Material: A Comparative SEM Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Materials.2025; 18(19): 4598. CrossRef
- Marginal Adaptability of Harvard MTA and Biodentine Used as Root-End Filling Material: A Comparative SEM Study
- 3,013 View
- 251 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

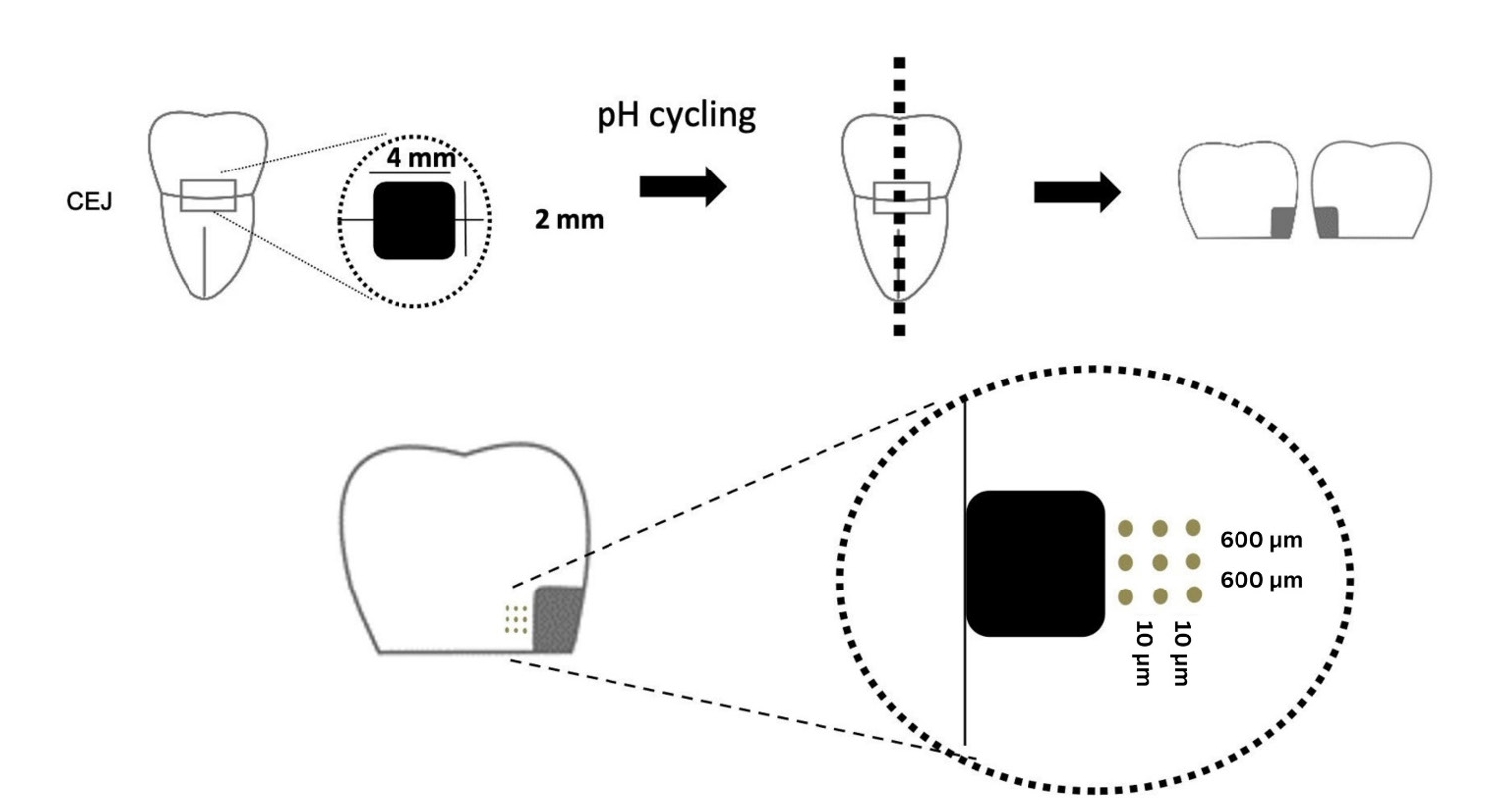
- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,861 View
- 215 Download

- Cone-beam computed tomography in endodontics: from the specific technical considerations of acquisition parameters and interpretation to advanced clinical applications
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Sara Quijano-Guauque, Sandra Briñez-Rodríguez, Gustavo Velasco-Flechas, Antonieta Muñoz-Solís, Carlos Chávez, Rafael Fernandez-Grisales
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e1. Published online December 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e1
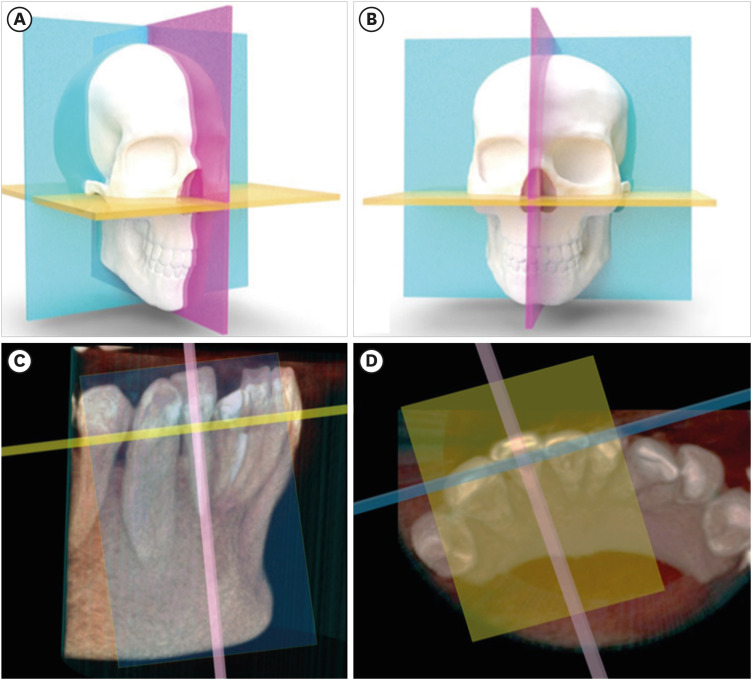
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The implementation of imaging methods that enable sensitive and specific observation of anatomical structures has been a constant in the evolution of endodontic therapy. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) enables 3-dimensional (3D) spatial anatomical navigation in the 3 volumetric planes (sagittal, coronal and axial) which translates into great accuracy for the identification of endodontic pathologies/conditions. CBCT interpretation consists of 2 main components: (i) the generation of specific tasks of the image and (ii) the subsequent interpretation report. A systematic and reproducible method to review CBCT scans can improve the accuracy of the interpretation process, translating into greater precision in terms of diagnosis and planning of endodontic clinical procedures. MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, Google Scholar, Embase and Scopus were searched from inception to March 2023. This narrative review addresses the theoretical concepts, elements of interpretation and applications of the CBCT scan in endodontics. In addition, the contents and rationale for reporting 3D endodontic imaging are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
Aishwarya Talakeri, Pravin Kumar, Soundharrajan P, Vinay Kumar Chugh , Rajat Sharma, Arun Patnana
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and morphometric assessment of the middle mesial canal in mandibular first molars in a turkish population: A CBCT study
Elif Solakoğlu, Özge Kurt
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Pathologies in Children and Adolescents with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study
Ayşe Çelik, Nilüfer Ersan, Senem Selvi-Kuvvetli
The Cleft Palate Craniofacial Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - Early diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia utilizing clinical, radiographic, and dental age indicators
Rehab F Ghouraba, Shaimaa S. EL-Desouky, Mohamed R. El-Shanshory, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Nancy M. Metwally
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of apexogenesis with human treated dentin matrix in young permanent molars: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
Nora M. Abo Shanady, Nahed A. Abo Hamila, Gamal M. El Maghraby, Rehab F. Ghouraba
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Integration of Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality in Dental Diagnostics, Surgical Planning, and Education: A Narrative Review
Aida Meto, Gerta Halilaj
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(11): 6308. CrossRef - Healing Outcomes of Through‐And‐Through Bone Defects in Periapical Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Bibi Fatima, Farhan Raza Khan, Syeda Abeerah Tanveer
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 518. CrossRef - Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of cone beam computed tomography on exfoliated epithelial cells in different age groups
Maged Bakr, Fatma Ata, Asmaa Saleh Elmahdy, Bassant Mowafey
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bridging the gap in aberrant root canal systems: Case series
Seethalakshmi Tamizhselvan, Diana Davidson, Srinivasan Manali Ramakrishnan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 833. CrossRef - IMAGING TECHNIQUES IN ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Mihaela Salceanu, Anca Melian , Tudor Hamburda , Cristina Antohi , Corina Concita , Claudiu Topoliceanu , Cristian Levente Giuroiu
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(1): 705. CrossRef - A Three-rooted Deciduous Second Molar in a 13-year-old Caucasian Female
Daniel Traub, Robert Walsh, Colleen Ahern
International Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025; 4(3): 51. CrossRef - Critical success factors for digital transformation in government organizations using a structural model approach
Abdalla Al Maazmi, Zehra Canan Araci, Sujan Piya
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - AGE ESTIMATION BASED ON PULP / TOOTH VOLUME BY CONE BEAM COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGE
Ramadhan Rasheed, Salah Faraj
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 288. CrossRef - Clinical Benefits and Limitations of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontic Practice: A Contemporary Evidence-Based Review
Jasmine Wong, Chengfei Zhang, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3117. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bildgebung im ZMK-Bereich – aber in welcher Reihenfolge?
Rainer Lutz
Zahnmedizin up2date.2024; 18(04): 297. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of shaping ability of kedo-S square and fanta AF™ baby rotary files compared to manual K-files in root canal preparation of primary anterior teeth
Shaimaa S. El-Desouky, Bassem N. El Fahl, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Shimaa M. Hadwa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Endodontic Successes and Failures in the Removal of Fractured Endodontic Instruments during Retreatment: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Corrado Dello Russo, Filippo Scarano, Fariba Esperouz, Andrea Ballini, Diego Sovereto, Mario Alovisi, Angelo Martella, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Healthcare.2024; 12(14): 1390. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
- 17,180 View
- 706 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

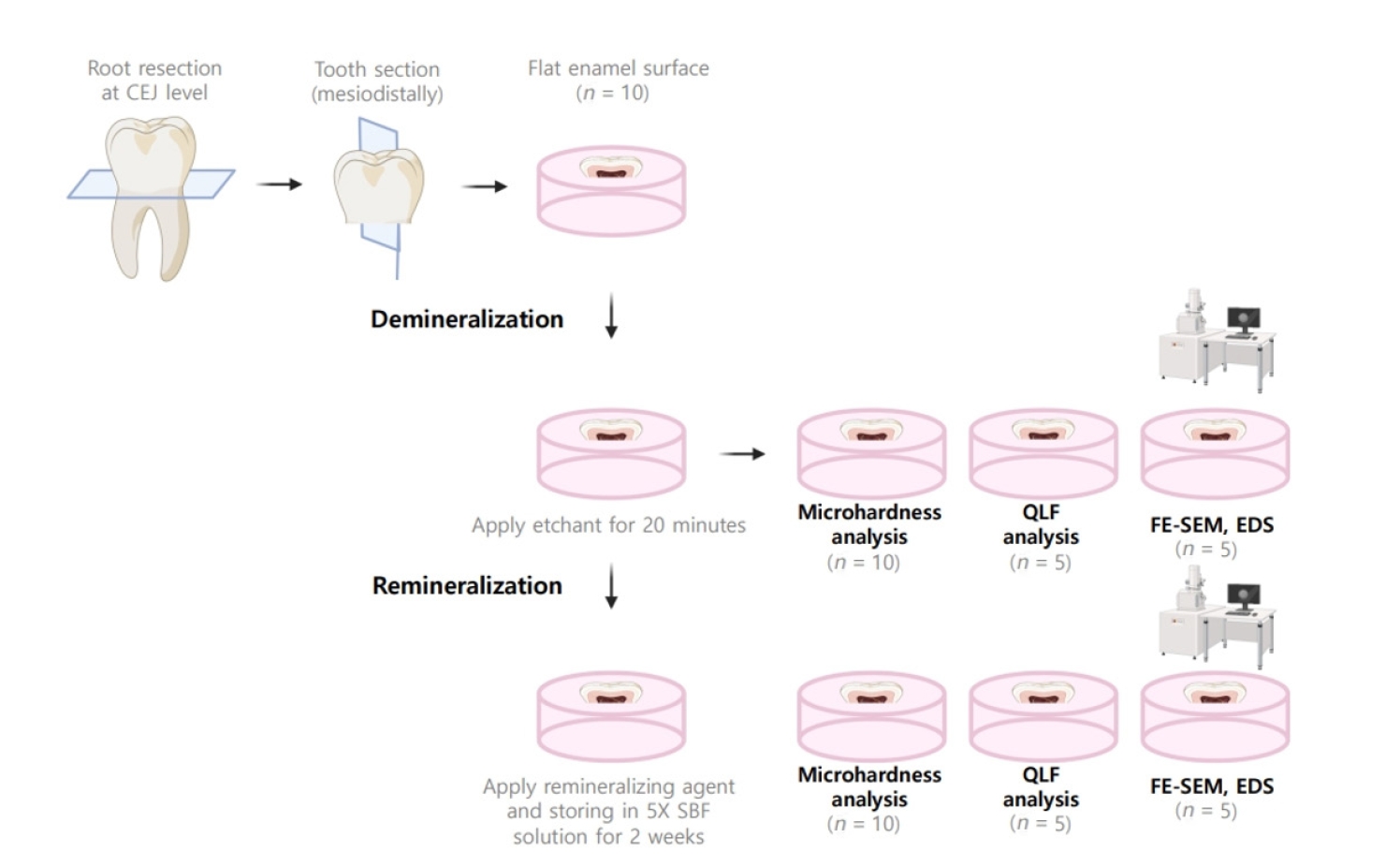
- The influence of bioactive glass (BGS-7) on enamel remineralization: an in vitro study
- Chaeyoung Lee, Eunseon Jeong, Kun-Hwa Sung, Su-Jung Park, Yoorina Choi
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e33. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare the remineralizing capacity of bioactive glass (BGS-7, CGBIO) with other agents.
Methods
Twenty caries-free third molars were sectioned and demineralized. Specimens were divided into four groups: (1) control, (2) Clinpro XT varnish (Solventum), (3) 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel, and (4) a new type of CaO-SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 system of bioactive glass ceramics (BGS-7). Agents were applied and stored in simulated body fluid at 37℃ for 2 weeks. Microhardness was measured using the Vickers hardness testing method. Five specimens per group were analyzed using quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF) to assess mineral loss. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) were used to examine the surface morphology and elemental composition. Data were analyzed using paired t-test and one-way analysis of variance (p < 0.05).
Results
BGS-7 showed the highest microhardness values and the greatest recovery in QLF analysis (p < 0.05). FE-SEM revealed granular precipitates on demineralized enamel in the BGS-7 group. EDS confirmed the presence of newly formed silicon and fluoride layers.
Conclusions
BGS-7 demonstrated superior remineralization capacity compared to other agents, suggesting its potential as an effective remineralizing material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
Helal F. Hetta, Ibraheem M. Mwafey, Noura H. Abd Ellah, Fawaz E. Alanazi, Yasmin N. Ramadan
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
- 1,696 View
- 194 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- An elaboration on sample size determination for correlations based on effect sizes and confidence interval width: a guide for researchers
- Mohamad Adam Bujang
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e21. Published online May 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This paper aims to serve as a useful guide for sample size determination for various correlation analyses that are based on effect sizes and confidence interval width.
Materials and Methods Sample size determinations are calculated for Pearson’s correlation, Spearman’s rank correlation, and Kendall’s Tau-b correlation. Examples of sample size statements and their justification are also included.
Results Using the same effect sizes, there are differences between the sample size determination of the 3 statistical tests. Based on an empirical calculation, a minimum sample size of 149 is usually adequate for performing both parametric and non-parametric correlation analysis to determine at least a moderate to an excellent degree of correlation with acceptable confidence interval width.
Conclusions Determining data assumption(s) is one of the challenges to offering a valid technique to estimate the required sample size for correlation analyses. Sample size tables are provided and these will help researchers to estimate a minimum sample size requirement based on correlation analyses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Model Selection Challenges in Non-Stationary Precipitation Estimation: The Role of AIC, BIC, and Covariate Choice
Murat Yegin, Gulsah Karakaya, Elcin Kentel
Water Resources Management.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Sampling Methods and Sample Size Determination in Clinical Research: An Educational Review
Azzam Zrineh, Maysa Al‐Usta, Abdallah Alwawi
Journal of General and Family Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef -
Phytochemical investigation of
Calophyllum sundaicum
P.F.Stevens: isolation, structure elucidation, and biological potential
Mas Atikah Lizazman, Vivien Yi Mian Jong, Nor Hisam Zamakshshari, Yiizamy Suffian, Mohamad Izwan Bin Ismail, Enis Nadia Md Yusof, Nurr Maria Ulfa Binti Seruji
Natural Product Research.2026; : 1. CrossRef - How Participants Are Selected in Intelligent Vehicle Human-Machine Interaction Usability Evaluation: A Systematic Review of Current Practices
Xiaofang Yuan, Datao Zhou, Yidi Sun, Yu Wu
International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction.2026; : 1. CrossRef - A long-term exploratory study of source code quality issues in open-source Python projects
Liviu-Marian Berciu, Simona Claudia Motogna, Arthur-Jozsef Molnar
Software Quality Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Apego entre iguales y su relación con la percepción del sexismo en adolescentes
Azucena Prado-Espinoza, Jesus Chavez-Parillo, Rosario Castelo-Collado, Ruth Soto-Yana, Juan Coaquira-Mamani, Magnolia Sierra-Delgado
Revista Estudios Psicológicos.2026; 6(1): 7. CrossRef - Return to work in young and middle-aged colorectal cancer survivors: Factors influencing self-efficacy, fear, resilience, and financial toxicity
Dan Hu, Yue Li, Hua Zhang, Lian-Lian Wang, Wen-Wen Liu, Xin Yang, Ming-Zhao Xiao, Hao-Ling Zhang, Juan Li
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Return to work in young and middle-aged colorectal cancer survivors: Factors influencing self-efficacy, fear, resilience, and financial toxicity
Dan Hu, Yue Li, Hua Zhang, Lian-Lian Wang, Wen-Wen Liu, Xin Yang, Ming-Zhao Xiao, Hao-Ling Zhang, Juan Li
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive validity of obstacle-crossing test variations in identifying fallers after inpatient rehabilitation for stroke
Prudence Plummer, Megan E. Schliep, Lina Jallad, Ehsan Sinaei, Jody A. Feld, Vicki S. Mercer
Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation.2025; 32(6): 631. CrossRef - Global NDVI-LST Correlation: Temporal and Spatial Patterns from 2000 to 2024
Ehsan Rahimi, Pinliang Dong, Chuleui Jung
Environments.2025; 12(2): 67. CrossRef - Increased functional connectivity of motor regions and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in musicians with focal hand dystonia
Stine Alpheis, Christopher Sinke, Julian Burek, Tillmann H. C. Krüger, Eckart Altenmüller, Daniel S. Scholz
Journal of Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanded span of control, leadership and management performance, work-related stress, and job satisfaction among first-line managers: A repeated cross-sectional study
Jonas Svanström, Bernice Skytt, Maria Lindberg, Magnus Lindberg
WORK: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment & Rehabilitation.2025; 81(3): 2952. CrossRef - The Dilemma and Wisdom in Translating p Values: A Collaborative Approach to Strengthening Scientific Validity
Mohamad Adam Bujang, Suyan Tian
BioMed Research International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Condylar Position Discrepancies Assessed Using an Optical Jaw Tracking System and a Conventional Condylar Position Indicator
Joana Silva, Eugénio Martins, Alberto Canabez, Domingo Martin, Conchita Martin
Prosthesis.2025; 7(2): 40. CrossRef - Examining the link between intensive care unit nurses’ burnout and perceived quality of life: a multicenter cross-sectional study
Hazel Novela Villagracia, Tajah Ali Akhdair, Salwa Abd El Gawad Sallam, Rico William A. Villagracia, Bushra Alshammari, Awatif M. Alrasheeday, Shaimaa Mohamed Nageeb, Lea L. Dando, Odeta A. Nacubuan, Turki Ahmed Alsaif, Sage Mesias Raguindin, Ingrid Jacin
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Microstructural Engineering of Porous Polymethylsilsesquioxane via Solvothermal Synthesis in Diverse Solvents
Stefanie Beatrice Hauser, Gabriella Saraiva, Chiara Hasenfratz, Mengmeng Li, Zahra Mazrouei-Sebdani, Wim J. Malfait, Shanyu Zhao
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.2025; 17(17): 25634. CrossRef - Playfulness of Preschool-Aged Children With Autism in a Sensory Integration Room
Sinem Kars, Esra Aki
Clinical Pediatrics.2025; 64(11): 1538. CrossRef - Fish community responses to habitat alteration: Interactions, biomass shifts, and the value of imperfect data
Eric A. Bonk, Robert H. Hanner, Adrienne J. Bartlett, Gerald R. Tetreault
Environmental Biology of Fishes.2025; 108(7): 1047. CrossRef - Osteoprotegerin and its ligands RANKL and TRAIL in falciparum, vivax, and knowlesi malaria
Arya Sheela Nair, John Woodford, Jessica Loughland, Dean Andrew, Kim Piera, Fiona Amante, Timothy William, Matthew J. Grigg, James S. McCarthy, Nicholas M. Anstey, Michelle J. Boyle, Bridget E. Barber
iScience.2025; 28(6): 112768. CrossRef - Text Analysis of Corporate Cryptocurrency Disclosures in Varying Market Conditions
Ramy Elitzur, Wendy Rotenberg
Journal of Alternative Finance.2025; 2(3): 302. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Influence of Intervention Tools Used in Nutrition Education Programs: A Mixed Approach
Luca Muzzioli, Costanza Gimbo, Maria Pintavalle, Silvia Migliaccio, Lorenzo M. Donini
Nutrients.2025; 17(15): 2460. CrossRef - Path Analysis Reveals Plant Pod Number as the Key Trait for Indirect Selection in Segregating Generations For Pigeonpea Grain Yield
Carlos Antonio Fernandes Santos, Antonio Elton da Silva Costa
Revista de Gestão Social e Ambiental.2025; 19(8): e013079. CrossRef - Analysis of the current status of attitudes toward aging and its influencing factors in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients in remote areas: a cross-sectional study
Hao-jie Zeng, Zheng-juan Shi, Mei-ying Shen, Sheng-jing Li, Xiang Peng
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 65: 103553. CrossRef - Exploratory Data Analysis of a North American Whole Building Life Cycle Assessment datasets
Yang Shen, Brad Benke, Milad Ashtiani, Monica Huang, Kathrina Simonen
Building and Environment.2025; 286: 113655. CrossRef - Dengue disease severity in humans is augmented by waning Japanese encephalitis virus immunity
Sidharth Malhotra, Birendra P. Gupta, Surendra Uranw, Chinmay Kumar Mantri, Abhay P.S. Rathore, Ashley L. St. John
Science Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of Anthropogenic and Emerging Contaminants in Sinkholes (Cenotes) of the Great Mayan Aquifer, Yucatán Peninsula
Sarah Kopczynski, Rayna Nolen, David Hala, Fernanda Lases-Hernández, Wendy Escobedo-Hinojosa, Flor Arcega-Cabrera, Ismael Oceguera-Vargas, Antonietta Quigg
Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology.2025; 89(3): 279. CrossRef - Bahasa Indonesia version of Weight Stigma Exposure Inventory (WeSEI): Translation and validation among young adults
Kamolthip Ruckwongpatr, Jian-An Su, I-Hua Chen, Nadia Bevan, Ira Nurmala, Muthmainnah Muthmainnah, Lutfi Agus Salim, Asma Nadia, Musheer A. Aljaberi, Mark D. Griffiths, Chung-Ying Lin
Acta Psychologica.2025; 261: 105748. CrossRef - Clinician-Caregiver Engagement in Older Adult Care. Development of a Validated Caregiver Experience Survey to Inform the Optimization of the Caregiver Role
Ronaye T Gilsenan, Rhonda E Schwartz, Iris A Gutmanis
Journal of Patient Experience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the quantity and spatial density of macrophage-like cells in patients with retinal vascular disease and healthy subjects via non-invasive retinal imaging
Farhad Ghaseminejad, Thomas J. van Rijssen, Parsa Khatami, Pedro L. Rissoli, Ricky Chen, Yudan Chen, Brendan Tao, Myeong Jin Ju, Faisal Beg, Eduardo V. Navajas
International Journal of Retina and Vitreous.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sperm DNA Fragmentation in Normozoospermic Men Is Associated with Blastocyst Formation and Quality in Conventional In Vitro Fertilization
Yusaku Mori, Linji Chen, Shogo Nishii, Miwa Sakamoto, Makoto Ohara, Akihiko Sekizawa, Sho-Ichi Yamagishi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8892. CrossRef - The Impact of Depression on Defense Mechanisms in Adults: The Moderating Role of Attachment Style
Andra-Iuliana Tanase, Amelia-Damiana Trifu, Simona Trifu
Behavioral Sciences.2025; 16(1): 57. CrossRef - The Role of the Basophil Activation Test in the Diagnosis of Drug-Induced Anaphylaxis
Maria Czarnobilska, Małgorzata Bulanda, Ewa Czarnobilska, Wojciech Dyga, Marcel Mazur
Diagnostics.2024; 14(18): 2036. CrossRef - Food insecurity impacts diet quality and adherence to the gluten‐free diet in youth with celiac disease
Xinyi Wang, Sven Anders, Zhiqian Jiang, Marcia Bruce, Dominica Gidrewicz, Margaret Marcon, Justine M. Turner, Diana R. Mager
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.2024; 79(6): 1180. CrossRef - Fuel Load Models for Different Tree Vegetation Types in Sichuan Province Based on Machine Learning
Hongrong Wang, Haoquan Chen, Hanmin Sheng, Kai Chen, Chen Dong, Zhiqiang Min
Forests.2024; 16(1): 42. CrossRef
- Model Selection Challenges in Non-Stationary Precipitation Estimation: The Role of AIC, BIC, and Covariate Choice
- 14,904 View
- 402 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref

- Fracture resistance and failure modes of endodontically-treated permanent teeth restored with Ribbond posts vs other post systems: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- Meghana Aditya Vartak, Vibha Rahul Hegde, Sanitra Rahul Hegde, Ushaina Fanibunda
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e5. Published online February 17, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e5

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This systematic review aimed to investigate the fracture resistance and mode of failure of endodontically-treated permanent teeth restored with Ribbond posts (Ribbond, Inc.) compared with endodontically-treated permanent teeth restored with other post systems.
Methods
A comprehensive, systematic literature search was carried out using several electronic databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library. Two separate researchers were appointed to identify the studies meeting the eligibility criteria, and to perform the data extraction, risk of bias, and quality assessment.
Results
Twelve studies were included in the quantitative analysis. Meta-analysis was performed with 11 of the 12 included articles. The meta-analysis showed that Ribbond posts have a fracture strength less than prefabricated metal posts, cast metal posts, and prefabricated fiber posts and greater than custom e-glass fiber posts. Mode of failure analysis revealed that Ribbond posts have the most favorable non-catastrophic fractures.
Conclusions
Although Ribbond posts have lower fracture resistance, their favorable mode of failure makes them potentially the most biomimetic post system. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Short and Long Fiber-Reinforced Composite Resins Used as Post and Core on Fracture Resistance of Premolars: An in vitro Study
Manal Hussian Abd-alla, Tuqa Jameel Ebrahim, Ahmed Sleibi Mustafa
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2026; 10(1): 66. CrossRef - Análise comparativa dos aspectos biomecânicos dos pinos de fibra de vidro e fibra de polietileno (RIBBOND) - revisão de literatura
Ana Kamily da Cunha Silva, Tânia Regina Carvalho de Sá, Livia Duarte Santos Lopes de Carvalho, Lilian Gomes Soares Pires, Marconi Raphael de Siqueira Rego, Matheus Araújo Brito Santos Lopes
RCMOS - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar O Saber.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomimetic Strategies for the Rehabilitation of Compromised Anterior Teeth
Aakansha Puri, M.S. Prathap
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2025; 16(3): 218. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Nonmetallic Customized Post-and-Core Systems: A Systematic Review
Jonathan Jun Xian Yuen, Yew Hin Beh, Zhi Kuan Saw, Hock Siang Chua
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of fracture resistance and crack propensity of bulk-fill composite restorations reinforced by polyethylene fiber
Ayşe Aslı Şenol, Aybike Manav, Bengü Doğu Kaya, Pınar Yılmaz Atalı, Erkut Kahramanoğlu, Bilge Tarçın, Cafer Türkmen
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Fracture Resistance of CAD/CAM–Fabricated Single‐Piece Post‐Crowns
Ali Erdem, Mehmet Selim Bilgin, Ibrahim Ersoy, Erhan Dilber, Ebru Nur Işık, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Extensively Compromised Anterior Teeth Restored With Fiberglass Posts and Biomimetic Protocols: An In Vitro Study
Chiu Tzyy Haur, Emanuel Ewerton Mendonça Vasconcelos, Natália Gomes de Oliveira, Gabriela Queiroz de Melo Monteiro, Luís Felipe Espíndola‐Castro
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CAD/CAM Technologies in Post and Core Restoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth: Current Evidence, Clinical Applications, and Interdisciplinary Perspectives
Rawabi Abdulrahman Ahmed, Faris Ali Aseri, Ahmed Saleh Alammari, Zaher Saleh Asiri, Fahad Oudah Al Matir, Sami Safar Al Shahrani, Abdullah Ali Alharthi, Abdulaziz Ahmed Alfaifi, Hassan Yahya Hassan Asiri, Hassan Manea Ali Al Fotais, Amal Mali Almutairi, A
Journal of Clinical Practice and Medical Research.2025; 1(3): 178. CrossRef
- Effect of Short and Long Fiber-Reinforced Composite Resins Used as Post and Core on Fracture Resistance of Premolars: An in vitro Study
- 12,880 View
- 518 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Success rate of direct pulp capping on permanent teeth using bioactive materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Karem Paula Pinto, Gabriela Ribeiro da Silva, Cláudio Malizia Alves Ferreira, Luciana Moura Sassone, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e34. Published online September 6, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the success rate of direct pulp capping (DPC) on permanent teeth, comparing the use of MTA with calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate-based cements. A systematic search was carried out in 4 databases until July 2023. The selection was based on PICOS criteria and only randomized clinical trials were included. The risk of bias was assessed using RoB-2 tool, and meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The overall quality of evidence was determined using the GRADE tool. Thirteen studies were included. Meta-analyses indicated significantly higher success rate for DPC using MTA compared to calcium hydroxide, while no significant difference was observed between MTA and Biodentine, showing a success rate from 80% to 100% even after 3 years of follow-up. Five studies were classified as having high risk of bias and the GRADE assessment revealed low certainty of evidence. DPC is highly effective for permanent teeth when using MTA or Biodentine. There is a need for future well-designed randomized clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of DPC using newer bioceramic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
Njwan Fadhel SHEHAB
Dental Materials Journal.2026; 45(1): 92. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation-assisted pulp capping using nano-hydroxyapatite and mineral trioxide aggregate: Report of two cases
Priya Pal, Rhythm Bains, Promila Verma, Vivek Kumar Bains
Journal of Healthcare Research and Education.2026; 2: 2. CrossRef - Histological Tissue Response to Calcium Silicate-Based Cements Assessed in Human Tooth Culture Models: A Systematic Review
Alberto Cabrera-Fernández, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Aránzazu Díaz-Cuenca, Juan J. Segura-Egea, Jenifer Martín-González, João Peça, Diana B. Sequeira, João Miguel Marques dos Santos
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 78. CrossRef - Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics consensus statement on deep caries management
Deepak Kumar Sharma, R. S. Mohan Kumar, Shishir Singh, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Meenal Nithin Gulve, Dipali Y. Shah, Sathish Abraham, Shruthi Nagaraja, Raksha Bhat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 714. CrossRef
- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
- 19,360 View
- 570 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

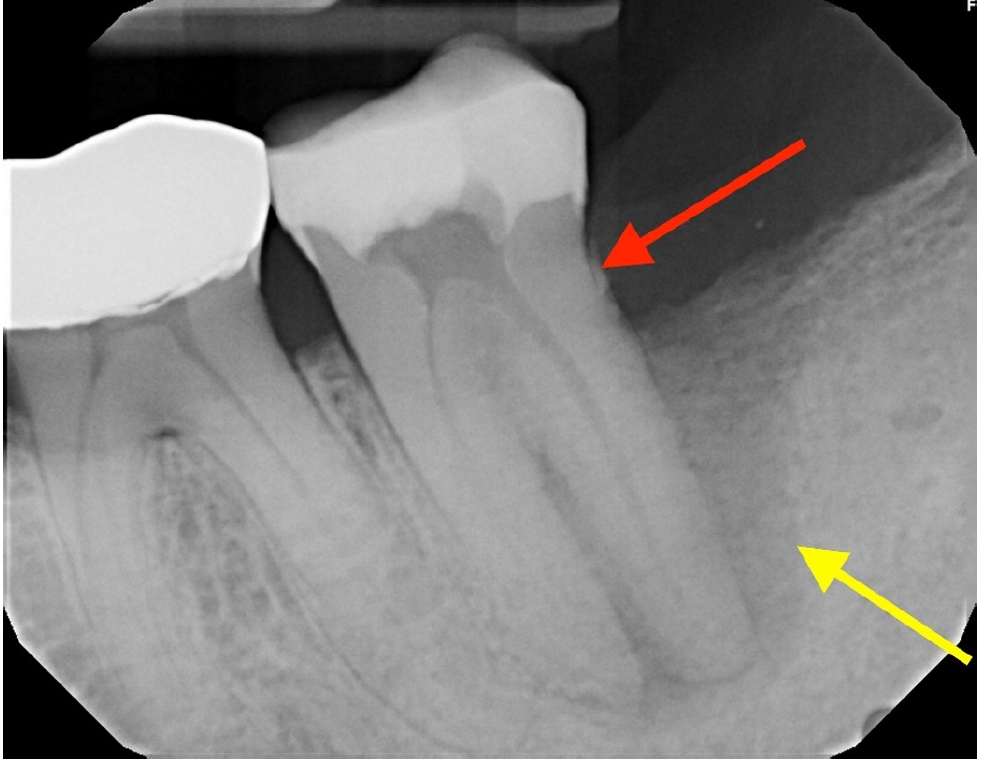
- Multidisciplinary management of an endo-perio lesion complicated by a cemental tear: a case report
- Nishanth D. Sadhak, Akshaya Pallod, Shreyas Oza
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e31. Published online August 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Endodontic-periodontal lesions (EPLs) complicated by cemental tears present a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. This case report describes the successful management of a 66-year-old male patient with a mandibular second molar (#18) exhibiting an EPL complicated by a cemental tear. Clinical examination revealed a draining sinus tract, deep periodontal pockets, and radiographic evidence of a “J-shaped” lesion and a radiopaque cemental fragment. The tooth had previously initiated endodontic treatment. A multidisciplinary approach involving endodontic treatment and surgical removal of the cemental tear was implemented. At 24-month follow-up, clinical and radiographic examination revealed significant improvement in periodontal health, bone regeneration, and resolution of the lesion. This case highlights the importance of considering cemental tears in the differential diagnosis of EPLs and demonstrates the efficacy of a combined endodontic-periodontal approach for achieving predictable outcomes.
- 3,366 View
- 248 Download

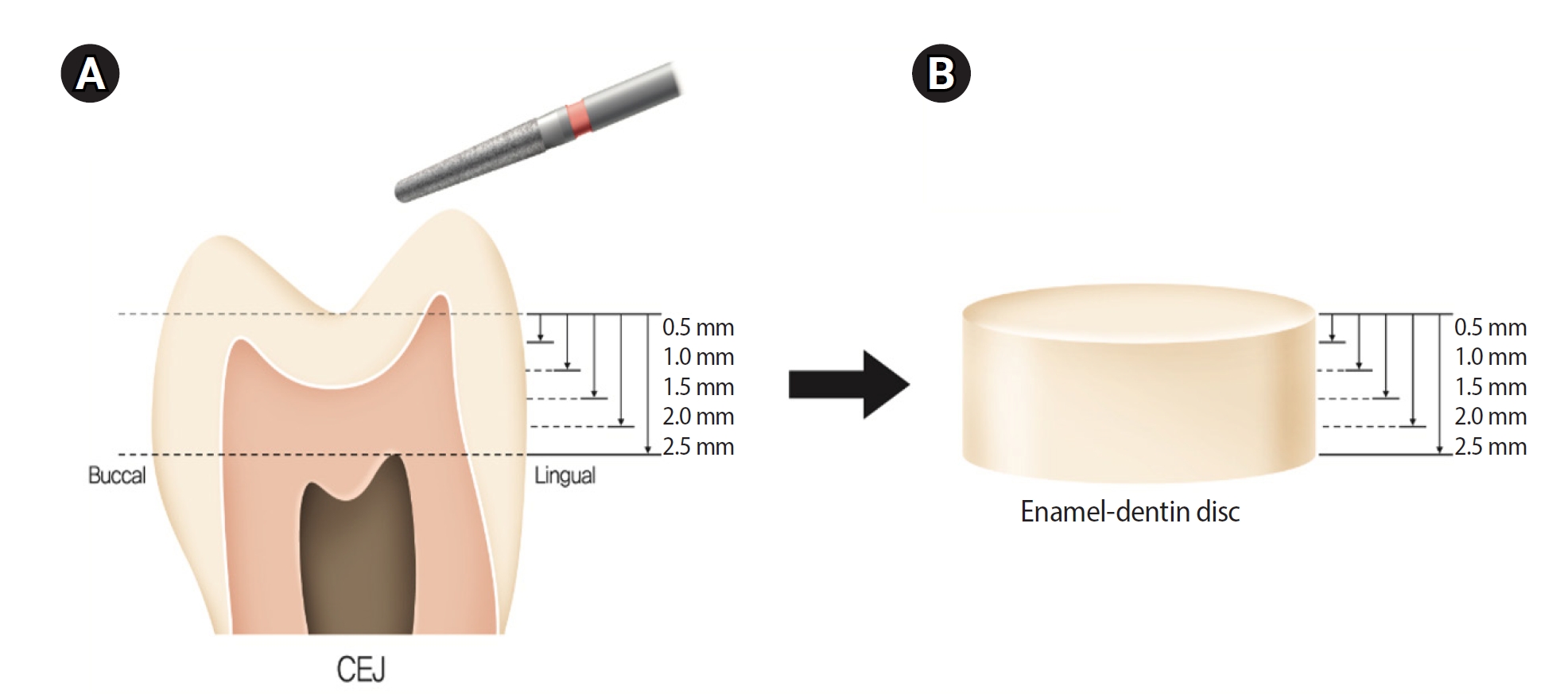
- Difference in light transmittance and depth of cure of flowable composite depending on tooth thickness: an in vitro experimental study
- Seong-Pyo Bae, Myung-Jin Lee, Kyung-San Min, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e39. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to quantify light attenuation through varying tooth thicknesses and its impact on the depth of cure of composite resin.
Methods
Twenty extracted premolars were used to create enamel-dentin discs that were sanded progressively in 0.5 mm increments from 2.5 mm to 0.5 mm. Light irradiance was measured with and without tooth specimens to evaluate light transmittance. Resin was cured beneath different thicknesses, and the depth of cure was assessed using the Vickers hardness test.
Results
The results demonstrated that light transmittance significantly decreased as tooth thickness increased (p < 0.01), leading to reduced resin polymerization. In the 2.0-mm and 2.5-mm tooth thickness groups, the depth of cure was significantly lower than in the control group without tooth specimens (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Ultimately, for tooth structures exceeding 2 mm, self-cure or dual-cure resin polymerization is thought to be more efficient than light polymerization.
- 1,264 View
- 122 Download

- In vitro experimental study comparing continuous and intermittent irrigation protocols: influence of sodium hypochlorite volume and contact time on tissue dissolution
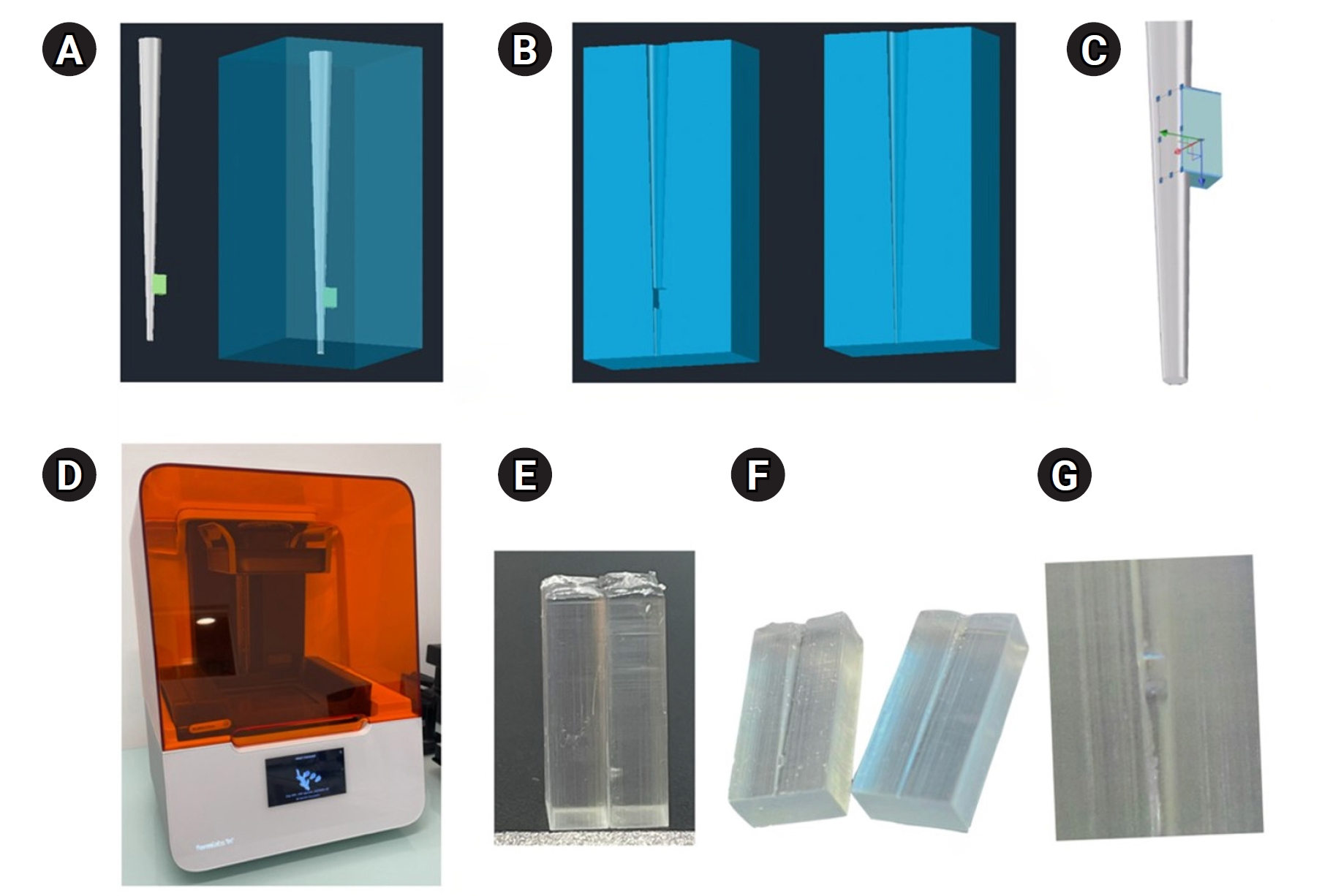
- Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Gwenael Rolin, Camille Coussens, Aurelian Louvrier, Felipe G Belladonna, Edouard Euvrard, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e36. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate whether continuous irrigation with larger volumes or allowing sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) resting time is more critical for pulp tissue dissolution using a controlled artificial root canal system.
Methods
A three-dimensional printed artificial root canal with a lateral canal in the apical third was fabricated. Standardized bovine pulp tissue specimens were inserted, and three irrigation protocols were tested: group A (continuous NaOCl irrigation at 1 mL/min via syringe pump), group B (intermittent NaOCl irrigation with 0.1 mL and a 3-minute resting period), and group C (control, saline irrigation). The time for complete dissolution and the total NaOCl volume were recorded.
Results
Complete dissolution occurred in groups A and B, with significant differences in NaOCl volume and time (p < 0.05). In group A, complete dissolution was consistently observed after the 6th irrigation cycle, corresponding to a total NaOCl volume of 6.0 ± 0.66 mL per test. The average time required for complete dissolution in this group was 6 ± 0.66 minutes. In group B, complete dissolution occurred after the 4th cycle, with a total NaOCl volume of 0.4 ± 0.06 mL per test and a mean dissolution time of 12.6 ± 1.8 minutes.
Conclusions
NaOCl volume and exposure time significantly influence pulp tissue dissolution.
- 1,590 View
- 161 Download

- Evaluation of platelet concentrates in regenerative endodontics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Anna Tsiolaki, Dimitrios Theocharis, Nikolaos Tsitsipas, Anastasia Fardi, Konstantinos Kodonas
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e38. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this systematic review is to compare the effectiveness of advanced platelet concentrates as regenerative endodontic therapeutic alternatives to blood clot (BC) revascularization in immature permanent necrotic teeth.
Methods
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing regenerative endodontic therapies using platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), or platelet pellet (PP) with the BC revascularization approach in immature permanent necrotic teeth were systematically searched in PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science until May 2025. Data was extracted and analyzed both qualitatively and quantitatively. Study quality was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. A meta-analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS software (version 29.0), with success rates expressed as risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
The initial search yielded 4,917 studies. After removing duplicates and applying eligibility criteria, 15 RCTs were included. Meta-analysis indicated no significant difference in the risk ratio (RR), as the BC method has similar success rates with PRP (10 studies; RR = 1.01; 95% CI, 0.94–1.09; p = 0.76) and PRF (8 studies; RR = 0.98; 95% CI, 0.89–1.08; p = 0.65) at 12 months. The primary outcomes evaluated were based on clinical and radiographic success.
Conclusions
Current evidence suggests PRP, PRF, and BC are all effective in treating immature permanent necrotic teeth with similar success rates. However, further research is needed to assess long-term outcomes.
- 1,443 View
- 85 Download

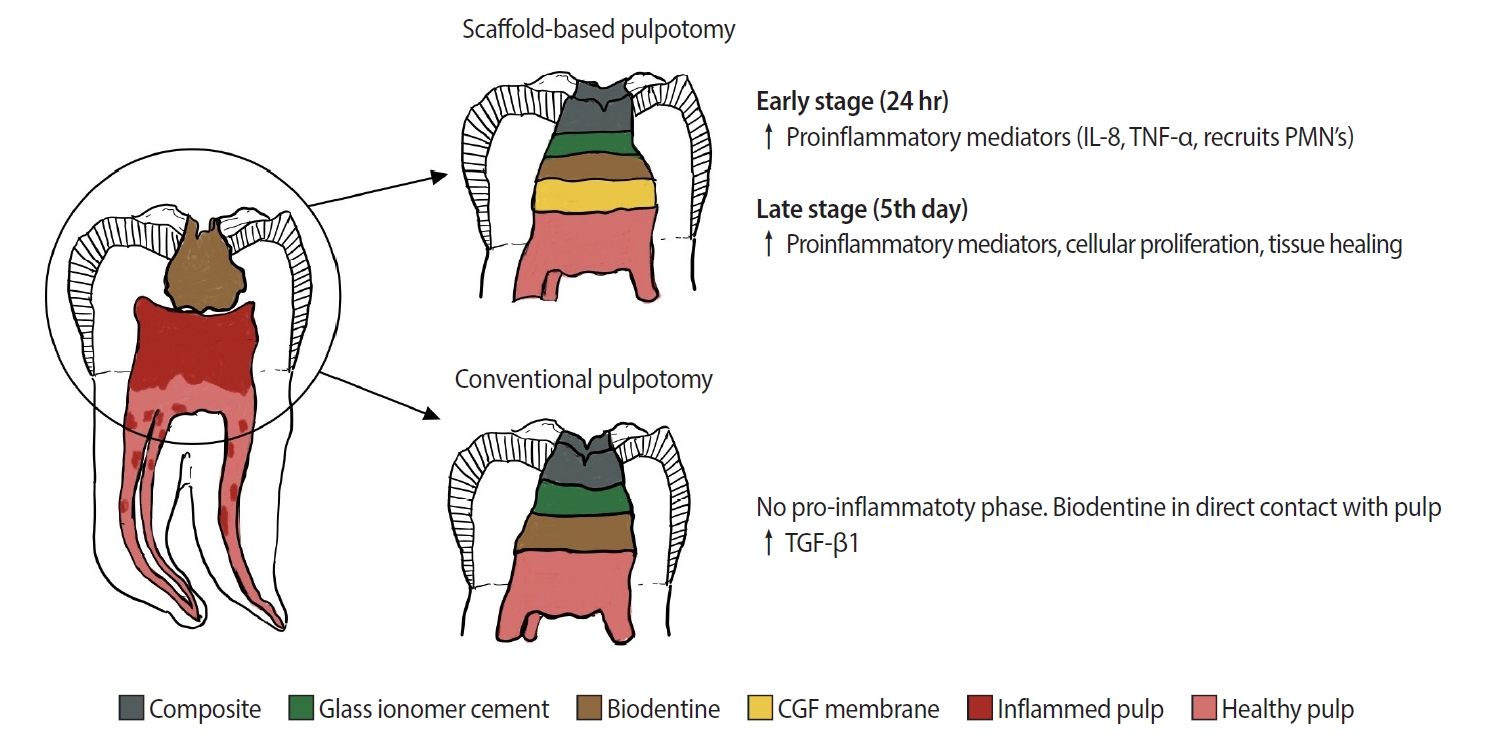
- Concentrated growth factor scaffold-based pulpotomy of permanent molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
- Arthi K. Harith, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Dinesh Kowsky, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, Suresh Nandini
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e1. Published online January 17, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to retain the vitality of the radicular pulp by removing the inflamed coronal pulp tissue. This case series presents the successful management of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis by pulpotomy with concentrated growth factor (CGF) scaffolds.
Methods
Six permanent mandibular molars with a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis were included. Under Local anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, caries were excavated using high-speed bur under coolant. Full coronal pulpotomy was done and hemostasis was achieved. CGF membrane was prepared and placed over the radicular pulp and layered with Biodentine (Septodont). Final restoration of type IX glass ionomer cement and bulk fill composite resin was placed. Patients were assessed for various clinical and radiographic parameters at intervals of 1 week and 3, 6, and 12 months. Five patients fulfilled the success criteria at the end of 1 year.
Results
Pulpotomy is considered an alternative treatment modality for root canal treatment in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis aiming at alleviating symptoms and maintaining vitality. CGF scaffold when used as a capping material acts as a reservoir for growth factors with anti-inflammatory properties and enhances healing.
Conclusions
Scaffold-based pulpotomy can be considered a biological approach to healing inflamed pulp.
- 4,602 View
- 472 Download

- Fifty-year follow-up of dens invaginatus treated by nonsurgical and surgical endodontic treatments: a case report
- Qais Arow, Eyal Rosen, Galit Sela, Shlomo Elbahary, Igor Tsesis
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e1. Published online December 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e1
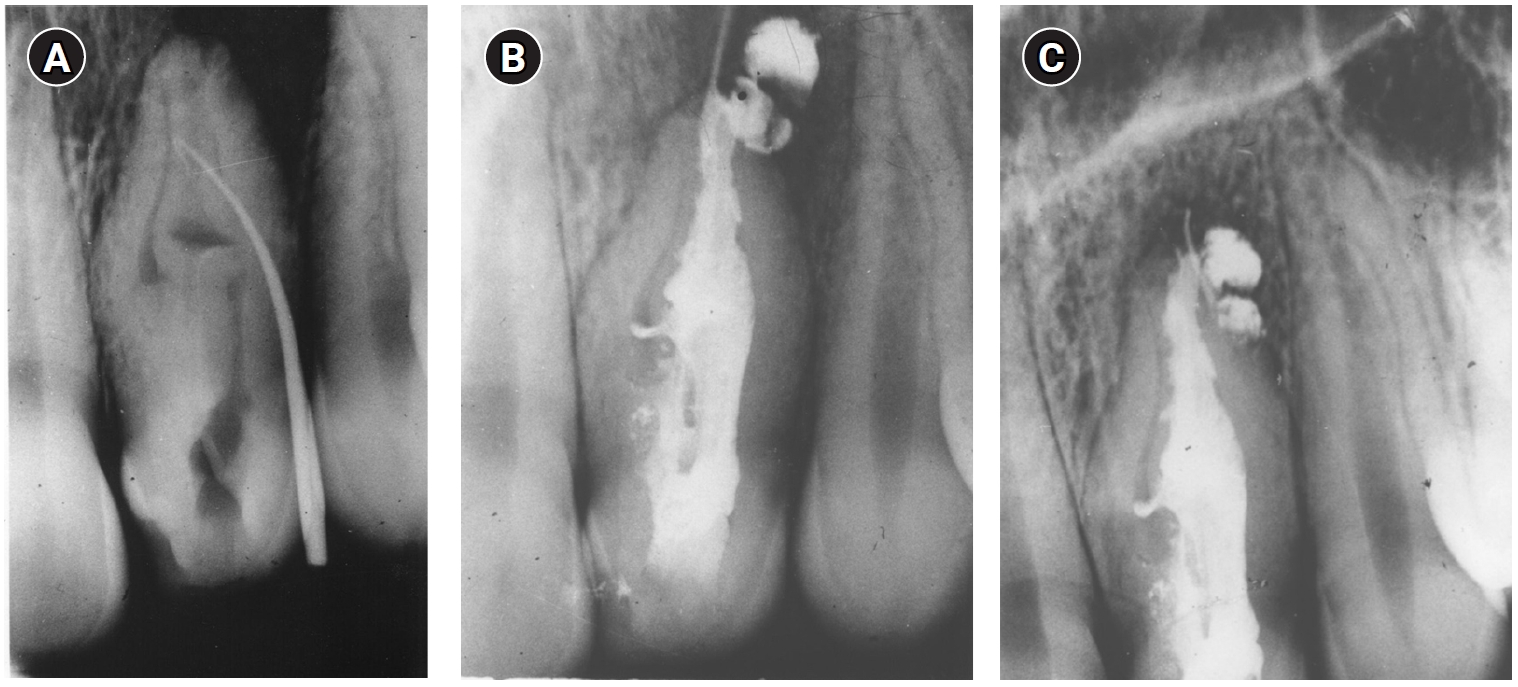
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - This case report presents a lateral maxillary incisor with dens invaginatus (DI) type IIIb that was treated both nonsurgically and surgically over 50 years. Treatment of teeth with DI can be challenging. Suggested options may include nonsurgical root canal treatment, endodontic surgery, or extraction. In this case report, a 13-year-old patient with a lateral maxillary incisor with DI type IIIb was treated by nonsurgical root canal treatment, modern endodontic surgery, and reoperation over the course of 50 years. There was complete healing at the last follow-up, 11 years after the reoperation. Correct diagnosis and proper treatment using modern endodontic techniques can enable teeth with DI to survive throughout the life span of the patient.
- 784 View
- 68 Download

- Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule occlusion by desensitizing agents after tooth bleaching: an in vitro study
- Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Spyros Papageorgiou, Kosmas Tolidis
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e8. Published online February 10, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of three commercially available desensitizing agents in occluding dentinal tubules, which may help reduce tooth sensitivity following a bleaching treatment.
Methods
Twenty healthy human third molars were utilized in this investigation. The samples were prepared by transversely sectioning 2.5 mm of the crowns to expose the dentin. They were initially treated with 15% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid gel for 4 minutes, followed by application of Perfect Bleach (VOCO GmbH) bleaching agent (16% carbamide peroxide) for 2 hours. The samples were randomly allocated into four groups (n = 5), each receiving one of the following treatments: group 1: No treatment (control), group 2: treated with UltraEZ (Ultradent Products Inc.,), containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride, group 3: treated with Perfect Protect (VOCO GmbH), also containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride and group 4: treated with TheraSol Whitening & Sensitive (ABC Kinitron IKE), containing strontium acetate and sodium monofluorophosphate. Subsequently, the specimens were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy to evaluate dentin tubule occlusion.
Results
SEM observations showed no occlusion of dentin tubules in the control group, whereas groups 2 to 4 exhibited significant occlusion. The most effective treatment was Perfect Protect (p < 0.05), while UltraEZ and TheraSol Whitening & Sensitive demonstrated similar effectiveness, with no statistically significant difference between them (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
The tested desensitizing agents effectively occluded dentin tubules to a considerable extent. Differences in their effectiveness were attributed to variations in their formulations.
- 485 View
- 47 Download

- Neuropeptide Y regulation of dental pulp neurogenic inflammation provoked by tooth bleaching agents: a descriptive comparative clinical study
- Javier Caviedes-Bucheli, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Mario Pérez-Villota, Karolina Aucú-Miño, Diana Escobar-Mafla, Hernán Darío Muñoz-Alvear, José Francisco Gomez-Sosa, Luis Diaz-Barrera, Edgar Güiza – Cristancho, Hugo Roberto Munoz
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e10. Published online February 13, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in human dental pulp after tooth bleaching with three in-office hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-based systems.
Methods
Forty pulps were collected from premolars scheduled for extraction and divided into four groups (n = 10): Control (no bleaching; basal NPY values); Pola Office (35% H2O2, 8 minutes); Opalescence Boost (40% H2O2, 20 minutes); and Zoom (25% H2O2 + cold blue light, 15 minutes). After extraction, pulps were fixed in 4% formaldehyde and processed. NPY levels were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data distribution was assessed with the Shapiro-Wilk test. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc test with Bonferroni correction were applied (p < 0.05).
Results
NPY expression differed significantly among groups (p = 0.0097). The control group showed the lowest mean expression (0.026 ± 0.002 pmol/mg of pulp tissue), followed by Zoom (0.031 ± 0.005 pmol/mg), Pola Office (0.040 ± 0.004 pmol/mg), and Opalescence Boost, which exhibited the highest NPY expression (0.044 ± 0.004 pmol/mg). Post-hoc analysis revealed a statistically significant difference between the control and Opalescence Boost groups (p = 0.0122).
Conclusions
The increase in NPY expression—particularly with Opalescence Boost—indicates that in-office bleaching agents can elicit measurable neurobiological responses in pulp tissue after a single application. The significant difference between the control and Opalescence Boost groups suggests a possible H2O2 concentration- or formulation-dependent effect on pulpal neuropeptide activity, underscoring the need for further research on the biological impact of bleaching treatments.
- 495 View
- 46 Download

- Effect of combined application of premixed bioceramic paste and diode laser in vital pulp therapy: an immunohistochemical randomized controlled split-mouth in vivo animal experiment
- Mo’men A. Salama, Dalia M. Fayyad, Mohamed I. Rabie, Manar A. A. Selim, Mahmoud F. Ahmed
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e4. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e4
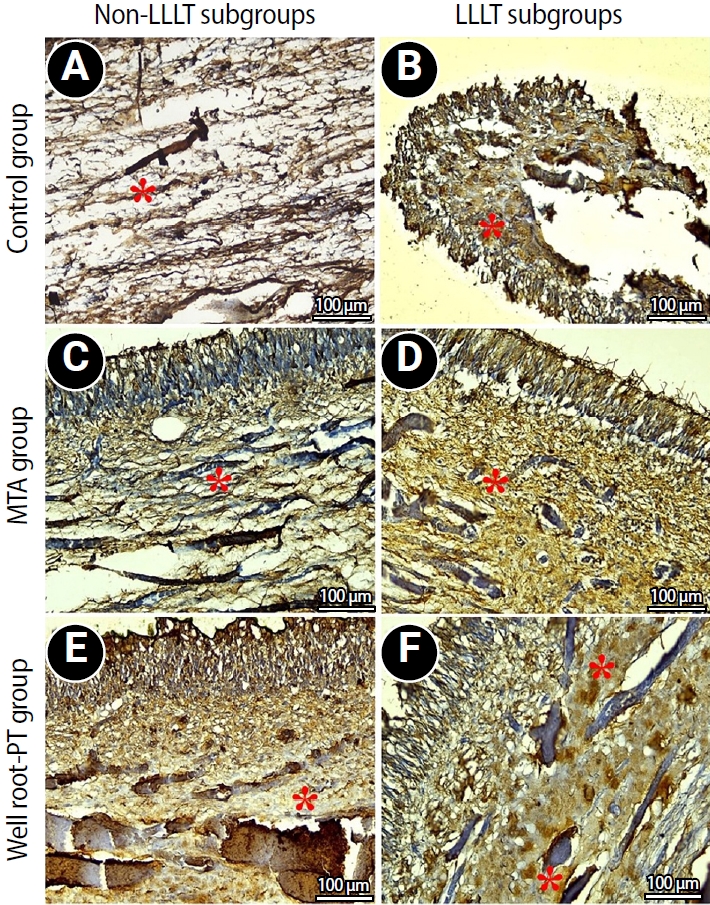
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of premixed bioceramic paste (Well-Root PT; Vericom) compared to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on the expression of the mineralization-related marker dentin sialoprotein (DSP) in dental pulp following direct pulp capping, with or without prior diode laser application.
Methods
Direct pulp exposures were performed in the upper and lower incisors of eight dogs (n = 96 teeth). Cavities (Class V) were created and received pulp capping with either Well-Root PT (n = 32), MTA (n = 32), or no capping material (polytetrafluoroethylene disc only) (n = 32), with or without the application of a diode laser. Immunohistochemical analysis of DSP expression was conducted and quantified as the mean area percentage using ImageJ software at 2 and 8 weeks posttreatment.
Results
Both the Well-Root PT and MTA groups showed significantly increased DSP expression compared to the control group at both 2 and 8 weeks (p < 0.05). No significant difference in the mean area percentage of DSP expression was found between the Well-Root PT and MTA groups. The diode laser application did not produce a significant effect on DSP expression. Within-group comparison revealed a significant increase in DSP expression between the 2- and 8-week follow-up periods (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Well-Root PT demonstrated comparable efficacy to MTA in promoting DSP expression, supporting its use as an effective direct pulp capping material. Diode laser application prior to capping had no effect on DSP expression in this experimental model.
- 660 View
- 46 Download

- Enhancing antimicrobial properties of a resin-based material via incorporation of a powdered phytotherapeutic extract: an in vitro experimental study
- Rodolfo Xavier de Sousa-Lima, Maria Eduarda Lima do Nascimento Marinho, Janielly Cristina Costa da Silva, Moan Jéfter Fernandes Costa, Pedro Henrique Sette-de-Souza, Giana da Silveira Lima, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e2. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e2
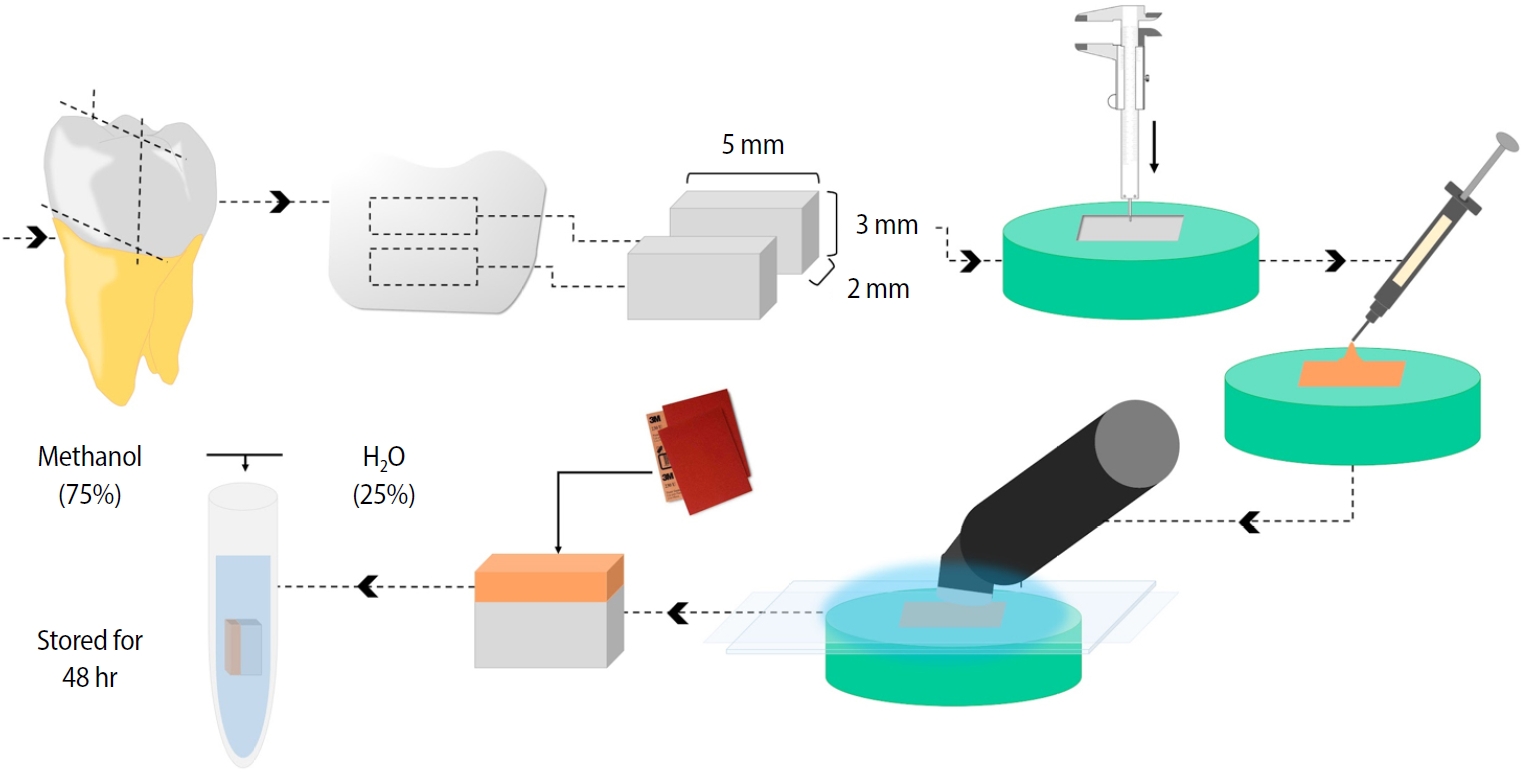
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the degree of conversion (DC), immediate enamel bond strength (IEBS), antimicrobial activity, and release of the active principle of a resin-based material (RBM) enriched with the powdered Schinopsis brasiliensis (Braúna) stem antibacterial extract.
Methods
The RBM was enriched with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 wt% powdered Braúna extract. The DC (n = 7) was assessed using micro-Raman spectroscopy. The IEBS (n = 7) was determined through the microshear test until failure, and failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. The antimicrobial activity (n = 15) was assessed by quantifying colony-forming units, and the release of the active principle was determined using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. One-way analysis of variance/Tukey and Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn tests were utilized to analyze the data (p < 0.05).
Results
Materials with 10 wt% and 20 wt% extract showed the lowest DC statistically. However, for IEBS, there were no statistically significant differences among the different groups. All materials released the active principle, but only those with 20 wt% and 10 wt% extract could inhibit biofilm formation similarly to 0.12% chlorhexidine.
Conclusions
Adding powdered Braúna extract between 10 wt% and 20 wt% is a promising alternative to provide an antimicrobial function to RBMs.
- 660 View
- 45 Download

- Analysis of temperature change during polymerization according to resin thickness: an in vitro experimental study
- Kkot-Byeol Bae, Eun-Young Noh, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e34. Published online November 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e34
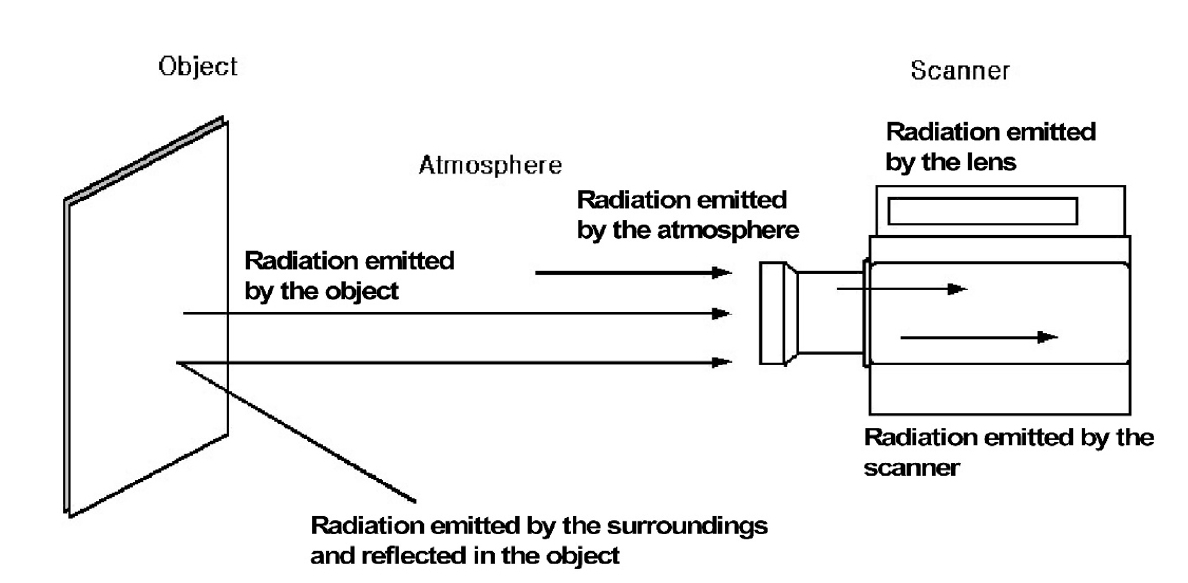
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the temperature changes during the light curing of conventional flowable composite resin and bulk-fill composite resin of various thicknesses using an infrared thermographic camera.
Methods
Flowable composite resin (G-aenial Flo, GC Co.) and bulk-fill composite resin (SDR, Dentsply Caulk) were used. Specimens with thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 5.0 mm were prepared. The infrared thermographic camera measured the temperature changes at the maximum temperature rise point during light curing. The data were analyzed for maximum temperature, time to peak temperature, and temperature rise patterns.
Results
For G-aenial Flo, the maximum temperature tended to decrease with increasing thickness, whereas for SDR, the maximum temperature decreased up to 2.0 mm and then remained relatively consistent from 2.0 mm to 5.0 mm. At thicknesses of 1.5 mm or less, both resins showed a rapid temperature increase within the first 5 seconds, followed by a reduced rate of increase up to 80 seconds. At thicknesses of 2.0 mm or greater, the temperature peaked and then gradually decreased. Across all thicknesses, SDR was observed to reach peak temperature more rapidly than G-aenial Flo.
Conclusions
Observable differences in polymerization dynamics were identified between the two resin types, particularly at greater thicknesses. Although no statistical analysis was performed, these descriptive findings suggest that infrared thermographic cameras may be useful for indirectly assessing polymerization dynamics during resin polymerization.
- 1,329 View
- 88 Download

- Biological mechanisms underlying the inflammatory radicular cyst formation-focus on epithelial proliferation: a systematic review of experimental cell and tissue models
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Sandra Briñez-Rodríguez, David Betancur-Calle, Marggie Grajales, Óscar Mauricio Jiménez-Peña, Mario Guerrero-Torres, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e7. Published online February 12, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e7
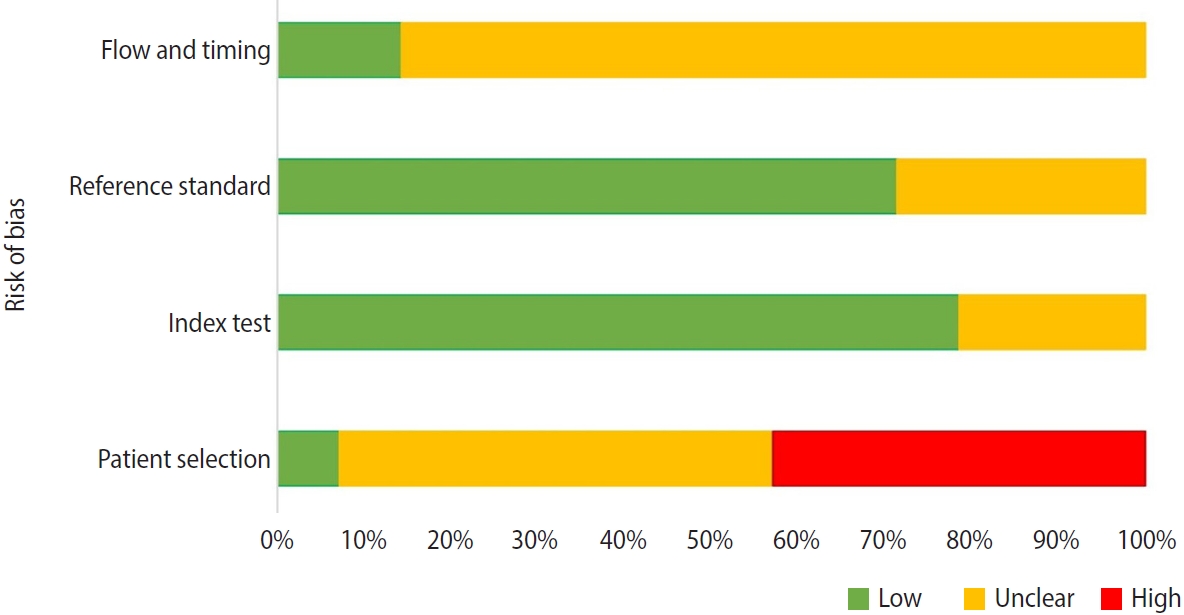
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in the epithelial proliferation that leads to the transformation of periapical granulomas (PGs) into inflammatory radicular cysts (IRCs).
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted in three databases. Experimental, observational, or descriptive studies using human or animal tissue samples, or epithelial cell cultures that assessed the molecular and/or cellular mechanisms driving the proliferation of epithelial rests of Malassez and their role in the transformation of PGs into IRCs were included. The risk of bias and applicability of the included studies were assessed using the QUADAS-2.
Results
Fourteen studies (including 399 samples) met the inclusion criteria for qualitative synthesis. The studies highlight the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6), growth factors (EGF, KGF, TGF-β, and IGF), and signaling pathways (NF-κB, MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and Smad) in the progression of PG to IRC. Biomarkers of epithelial proliferation, such as Ki-67, PCNA, and CD34, are consistently associated with this process, while MMP-13 emerges as a key regulator of epithelial behavior and matrix remodeling.
Conclusions
IRC development arises from a transition from homeostatic to pathological signaling, in which pro-inflammatory mediator levels inside the periapical chronic inflammation override regulatory checkpoints.
- 697 View
- 43 Download

- Influence of adjacent restorative material and distance on the accuracy of inlay cavity impressions with intraoral scanner: an in vitro study
- So-Yeon Lee, Sung-Ae Son, Jae-Hoon Kim, Deog-Gyu Seo, Jeong-Kil Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e6. Published online January 23, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e6
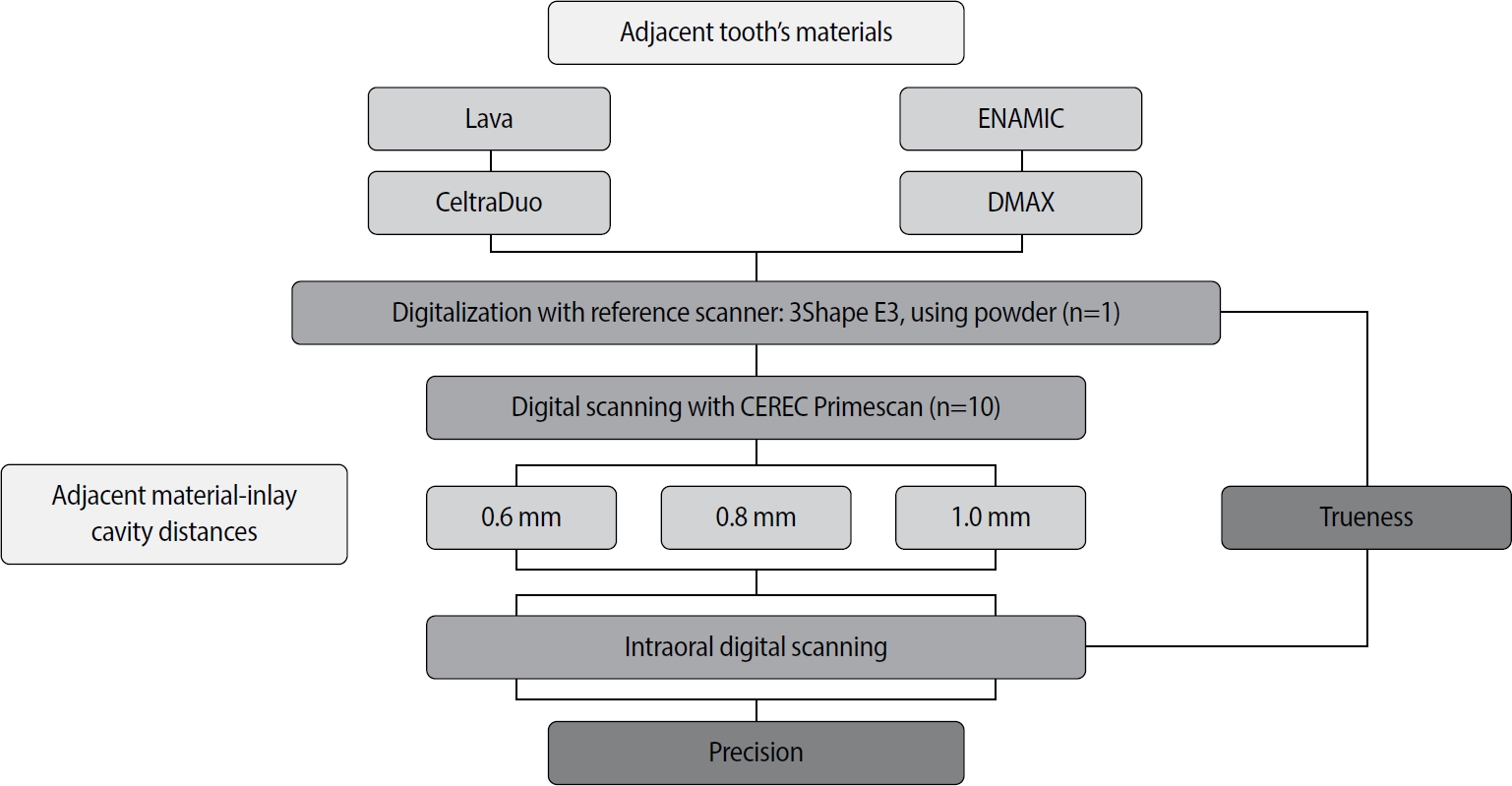
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of adjacent restorative material and interproximal distance on the accuracy of digital impressions of inlay cavities obtained using an intraoral scanner.
Methods
A disto-occlusal inlay cavity was prepared on a mandibular right first molar model, and digital scans were performed using a CEREC Primescan (Dentsply Sirona). The adjacent restorative materials used were Lava (3M ESPE), ENAMIC (VITA Zahnfabrik), Celtra Duo (Dentsply Sirona), and DMAX (DMAX), and the interproximal distances were set to 0.6 mm, 0.8 mm, and 1.0 mm. The obtained scan data were analyzed using GOM Inspect software (GOM GmbH).
Results
Trueness, maximum positive and negative deviations, and precision were significantly influenced by both the adjacent restorative material and the interproximal distance, while their interaction showed a significant effect only on precision. Celtra Duo demonstrated the highest trueness, with mean deviation values decreasing from 7.8 μm at a 0.6 mm interproximal distance to 7.3 μm at 1.0 mm. ENAMIC showed the best precision, presenting mean deviations of 2.6 μm at 0.6 mm, 2.9 μm at 0.8 mm, and 2.4 μm at 1.0 mm. A narrow interproximal distance of 0.6 mm resulted in lower trueness, measured at 8.3 μm, and the highest precision deviation of 3.4 μm. In contrast, an interproximal distance of 1.0 mm yielded improved scan accuracy, with increased trueness and reduced precision variation.
Conclusions
Digital impression accuracy of inlay cavities was influenced by adjacent restorative material and interproximal distance, suggesting clinical consideration is needed in CAD/CAM workflows to optimize restoration fit.
- 690 View
- 43 Download

- Ex vivo comparative analysis of retrievability among four calcium silicate-based sealers for regaining apical patency
- Darian Shomali, Timothy Kirkpatrick, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Ji Wook Jeong
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e3. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e3
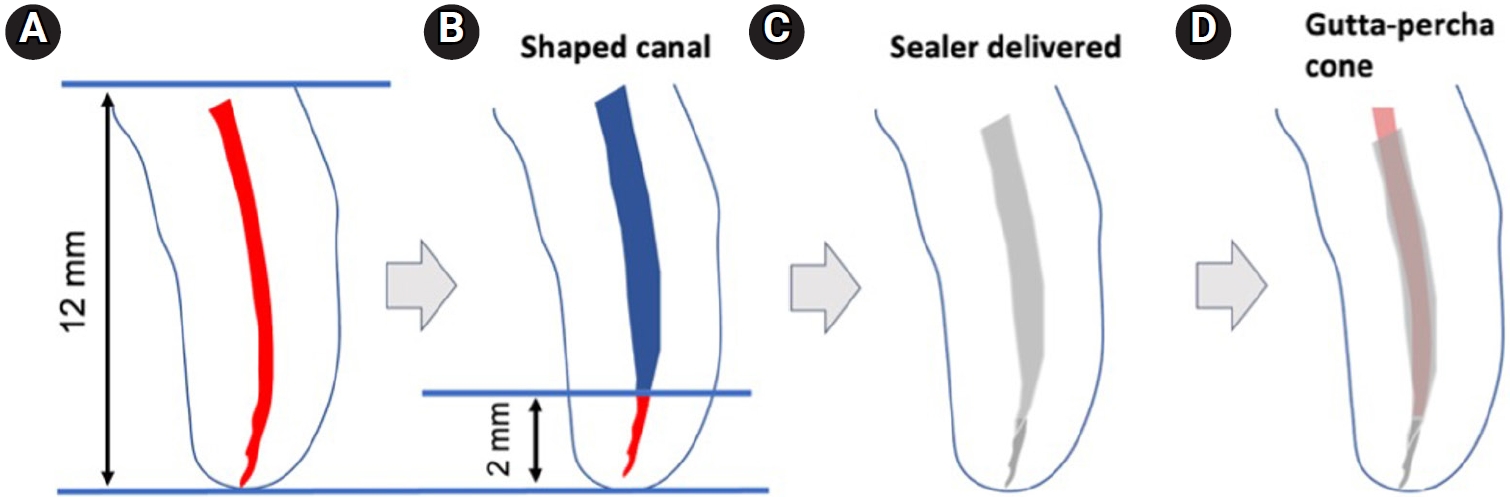
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Efficient retrievability is a key requirement for endodontic sealers. This study evaluated the retrievability of four different calcium silicate-based sealers (CSS).
Methods
A total of 153 single-rooted human teeth with straight canals were decoronated to a standardized working length of 12 mm. The canals were negotiated to working length using K files up to size 15/.02, followed by rotary instrumentation up to 35/.04, 2 mm short of working length. The teeth were randomly assigned to five groups: NeoSEALER Flo (NEO; Avalon Biomed), Ceraseal (CS; Meta Biomed), Endosequence BC Sealer (BC; Brasseler USA), AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer (AHB; Dentsply Sirona), and a negative control group. Sealer application and obturation with a 35/.04 gutta-percha cone were performed. After incubation at 37°C in 100% humidity for 7 days, retreatment was performed until apical patency was obtained, with retrievability assessed by regaining apical patency. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey contrast test were used to determine whether there was a significant difference among the four different CSS (p < 0.05).
Results
Success rates in regaining apical patency were NEO (79.4%), CS (37.0%), BC (50.0%), and AHB (69.7%). NEO demonstrated the highest retrievability, while CS had the lowest (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
The type of CSS used has a considerable impact on retreatment difficulty. Among the tested sealers, Neo- SEALER Flo showed the highest retrievability, making it the most retrievable CSS in terms of retreatment efficacy.
- 637 View
- 43 Download

- Effect of moisture and pH on setting time and microhardness of three premixed calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: an in vitro experimental study
- Sooyoun Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e41. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e41
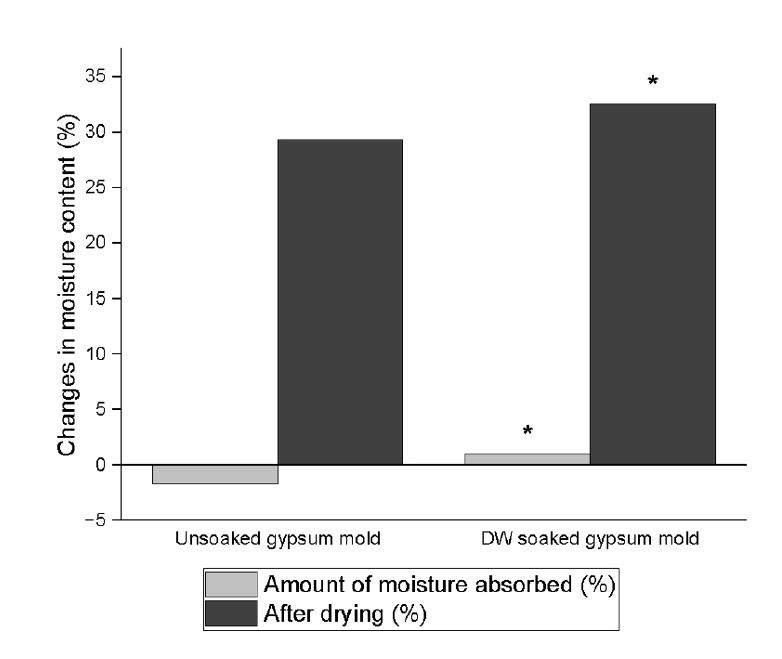
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to investigate how environmental conditions impact the setting time and microhardness of premixed calcium silicate-based sealers.
Methods
The setting time and microhardness of three sealers (Endoseal MTA [MARUCHI], One-Fil [MEDICLUS], and Well-Root ST [VERICOM]) were evaluated under four environmental conditions: unsoaked, distilled water-soaked, phosphate-buffered saline-soaked, and pH 5-soaked gypsum molds (n = 12/group/condition). The setting time was measured with Gilmore needles, and microhardness was assessed using a Vickers tester after 3 days. Welch’s analysis of variance and Games-Howell post hoc tests were used for statistical analysis.
Results
The sealer type and environmental conditions significantly influenced setting time and microhardness (p < 0.001). The initial and final setting times were the shortest in the unsoaked samples. For Endoseal MTA and One-Fil, the unsoaked condition exhibited significantly shorter setting times than the soaked conditions. Well-Root ST exhibited significantly longer setting times in acidic conditions. Surface microhardness was highest in the unsoaked group (p < 0.001). Among the soaked groups, the phosphate-buffered saline-soaked group had the lowest hardness for Endoseal MTA, whereas the pH 5-soaked group exhibited the lowest hardness for One-Fil and Well-Root ST. Endoseal MTA consistently demonstrated a lower microhardness than the other sealers (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Moisture, pH, and solution chemistry influenced the setting time and microhardness of premixed calcium silicate sealers. Although acidic conditions generally prolong the setting time and reduce hardness, the effects vary based on the sealers used and the setting environment.
- 1,020 View
- 71 Download

- Pattern of endodontic instrument separation and factors affecting its retrieval: a 10-year retrospective observational study in a postgraduate institute
- Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Aswathi Varghese, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Srinivasan Narasimhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e7. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e7
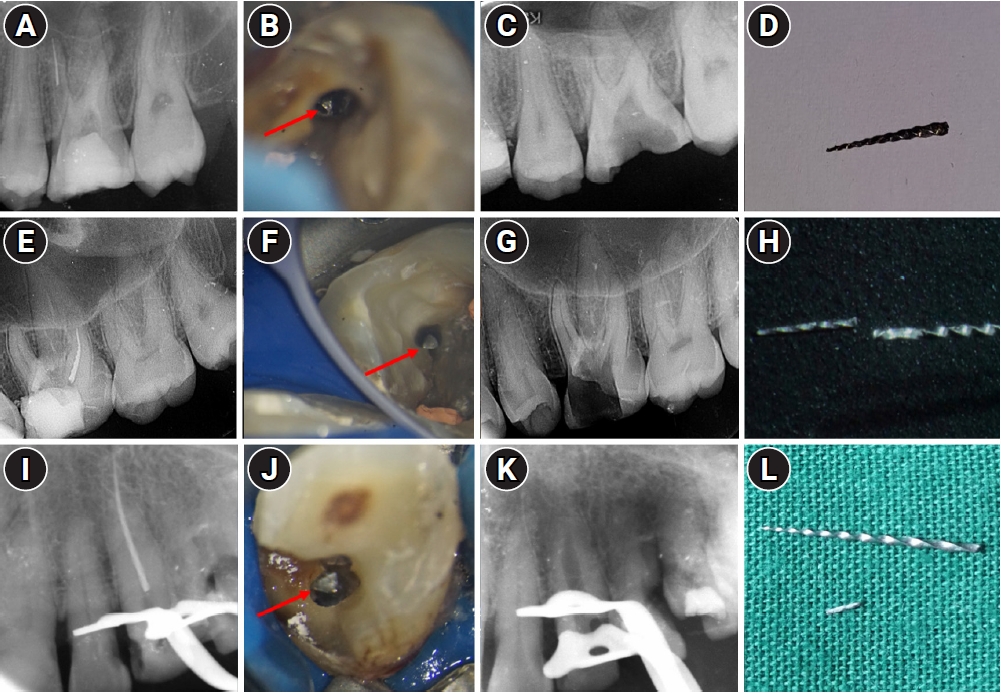
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the pattern of endodontic instrument separation, their retrievability, and factors affecting its retrieval, in a postgraduate institute.
Methods
Cases referred for the management of separated endodontic instruments (SEI) from 2013 to 2023 were considered for this study. Data related to demographics, tooth type, file type, and retrieval were documented in an Excel sheet. Eight prognostic factors assumed to influence the retrieval were analyzed in this study. The secondary aim was to compare the pattern of SEI and retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. Retrieval was attempted by a senior endodontist under the dental operating microscope. Various ultrasonic tips and a Broken Tool Removal loop system were used during retrieval. Simple descriptive statistics were performed. Binomial logistic regression was done to identify the effect of the eight prognostic factors on the retrieval outcome.
Results
A total of 190 SEI was reported. SEI occurred more often in posterior teeth than anterior teeth, mandibular arch than maxillary arch, and in larger files than smaller files. Separation occurred more often in the apical third compared to the other levels. Retrieval was attempted in 88 cases and successful in 70 cases (79.5%). The larger taper and apical position of the SEI negatively influenced the retrieval by 1.4 and 8.7 times, respectively.
Conclusions
Retrieval of SEI was successful in the majority of the cases. An increase in taper and apically placed SEI negatively impacted the retrieval. There was no difference in the pattern of separation nor retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Le Zhao, WangYu Luo, Yue Shen, WanNing Yu, Liu Yang, Xiaolei Zhang
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of microscope-assisted root canal treatment in permanent posterior teeth: A retrospective cohort study
Ya-Ching Chang, Ting-Ya Wang
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 157: 105771. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Nildem İnönü, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, Kaan Orhan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(14): 1744. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF INTRACANAL SEPARATED INSTRUMENTS: FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO ENDODONTIC FILE SEPARATION — A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Tareq Hajaj, Paul Freiman , Serban Talpos Niculescu , Mihai Rominu , Tiberiu Hosszu , Ioana Veja
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(2): 993. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
- 7,802 View
- 370 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Guided endodontics, precision and predictability: a case series of mineralized anterior teeth with follow-up cone-beam computed tomography
- Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Javier Rojas-Gutierrez, Pamela Mejía, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Néstor Ríos-Osorio
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e4. Published online January 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e4
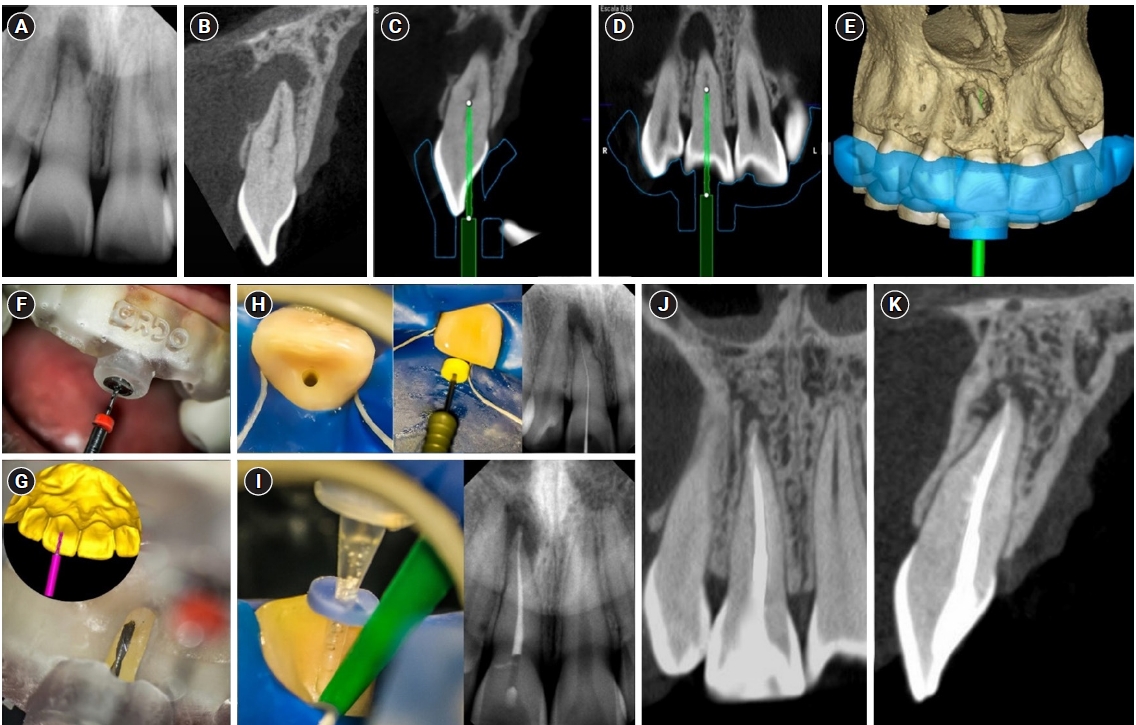
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Pulp chamber and root canal obliteration (PCO/RCO) presents a challenge for clinicians when nonsurgical endodontic treatment is indicated. Guided endodontics (GE) aims to precisely locate the root canal (RC) system while preserving as much pericervical dentin as possible. GE involves integrating cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) of the affected tooth with a digital impression of the maxillary/mandibular arch, allowing for careful planning of the drilling path to the RC system through a three-dimensional (3D) static guide. This article reports four cases of teeth with PCO/RCO, accompanied by additional diagnoses of internal and external root resorption and horizontal tooth fracture, all successfully treated with GE. These cases highlight the clinical and radiographic success of GE treatments using CBCT, establishing this technique as a predictable approach for managing mineralized teeth.
- 4,179 View
- 345 Download

- An unusual case of dens invaginatus on a mandibular second molar: a case report
- Davide Mancino, Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Fabien Bornert, Youssef Haïkel
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e2. Published online January 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e2

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - The present case report describes the endodontic treatment of a type III B dens invaginatus (DI) in a three-rooted mandibular second molar since the invagination invades the root and extends apically. Clinical and cone-beam computed tomography examination of the mandibular second molar showed a broadened coronal morphology, DI, a third root, periapical radiolucency, and compression of a distal root canal by the invagination, which developed an atypical semilunar shape. The tooth was diagnosed with pulpal necrosis, symptomatic apical, and peri-invagination periodontitis. Consequently, three-dimensional virtual reconstruction was conducted to improve anatomical interpretation and case planning and accelerate the intraoperative phase by reducing operator stress and minimizing intraoperative variables. The present case report aims to raise awareness of the existence of DI on the mandibular second molar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dens Invaginatus—Mandibular Second Molar—Case Report
Krystyna Pietrzycka, Natalia Lutomska, Cornelis H. Pameijer, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(1): 27. CrossRef - Type IIIb dens invaginatus in a maxillary second molar and its microscopic anatomical features: a case report
Mingming Li, Zhiwu Wu, Shaoying Duan, Yuling Zuo
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dens Invaginatus—Mandibular Second Molar—Case Report
- 3,321 View
- 240 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Supplement of the 3rd Meeting of the Asian-Oceanian Federation of Conservative Dentistry (ConsAsia 2025) August 28-31, 2025 · Chennai, India
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(Suppl):S1-S101. Published online October 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.Supplement
- 521 View
- 328 Download

- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
- Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e20. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e20
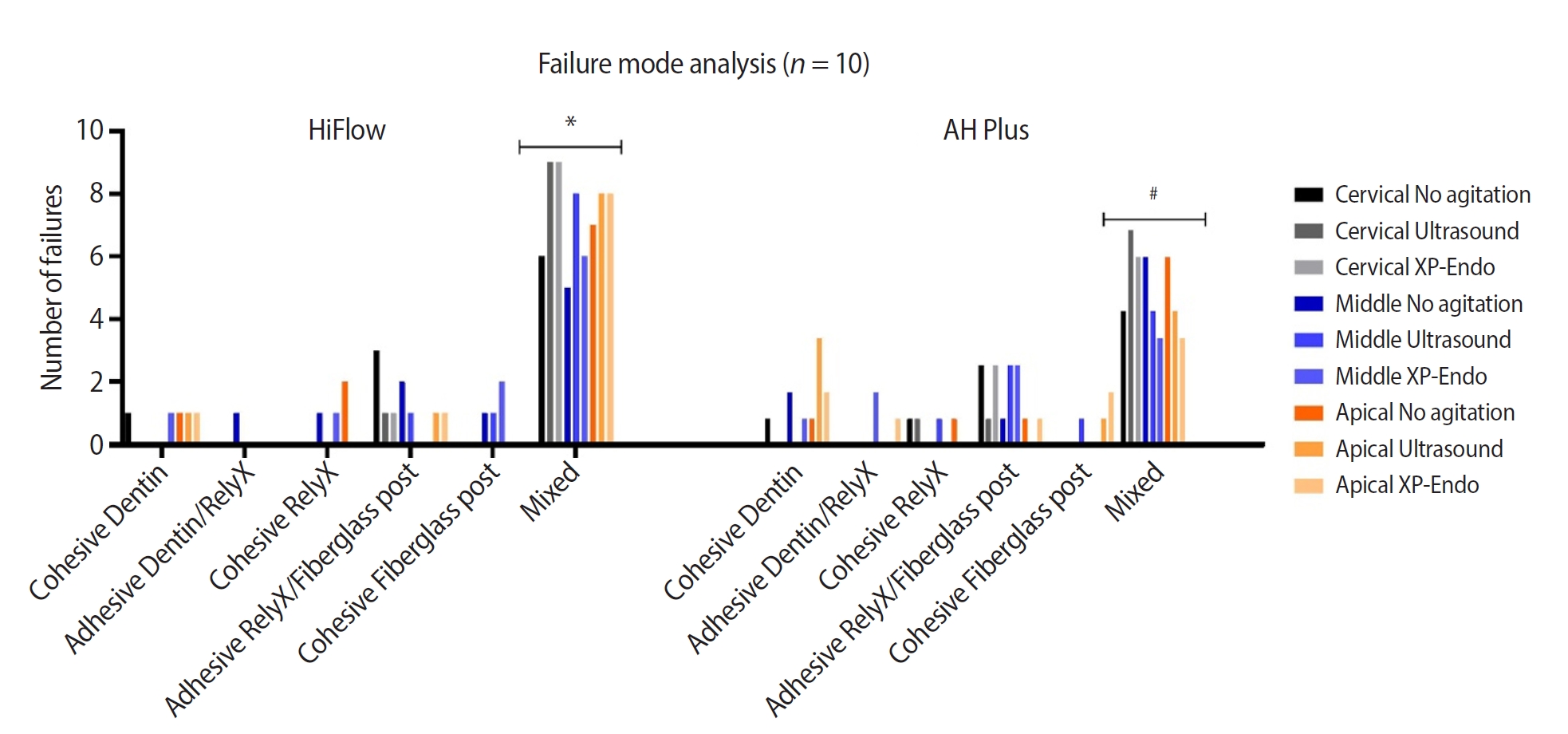
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate whether the agitation protocols using ultrasonic inserts or the XP-endo Finisher R file improved the removal of two different endodontic sealer remnants and the bond strength of fiberglass posts to dentin.
Methods
Seventy-two human teeth were selected. The canals were prepared with Reciproc 50 and Easy ProDesign 30/.10 and root filled according to the endodontic sealer groups: AH Plus or EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow. The samples were kept at 37ºC and 95% humidity for 28 days. During the post space preparation, the obturation was removed with Largo burs, and the groups were divided according to the irrigant agitation protocols (n = 12): no agitation, agitation with R1-Clearsonic associated with E1-Irrisonic ultrasonic inserts, or agitation with XP-endo Finisher R file. The fiberglass posts were cemented with RelyX ARC. The roots were sectioned into slices and submitted to the push-out test. Micro-computed tomography analysis was used to check the effectiveness of irrigating solution agitation in the elimination of remnants.
Results
The cleaning protocols with agitation were more effective in increasing the bond strength of posts to dentin for both sealer groups compared to non-agitation (p < 0.05). There was no difference between the same cleaning protocols for the different sealers. Among the different thirds, there was no statistical difference for the same sealer in the different cleaning protocols (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Both agitation protocols effectively clean root-filled canals sealed with resin-based and calcium silicate-based sealers during fiberglass post space preparation. These protocols result in improved bond strength compared to non-agitation methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cleaning efficacy and bond interaction of glycine-based air polishing and glass microparticles abrasion on dentin impregnated with premixed bioceramic sealer
Ândresson Aurélio Fernandes Martins, Maria Carolina Sidonio Alves, Bruno Martins Maciel, José Rodolfo Estruc Verbicário, João Felipe Besegato, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante-Otárola, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 147: 104277. CrossRef - Effect of Endodontic Sealers on the Bond Strength of Glass Fibre Posts: A Systematic Review
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana D. Bronzato, Vanessa Gallego Arias Pecorari, Jennifer Santos Pereira, Talita Tartari, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cleaning efficacy and bond interaction of glycine-based air polishing and glass microparticles abrasion on dentin impregnated with premixed bioceramic sealer
- 4,008 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of different curing methods on the color stability of composite resins
- Massimo Pisano, Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Andrea Chiacchio, Marzio Galdi, Stefano Martina
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e33. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the effects of different polymerization strategies and the effectiveness of finishing and polishing procedures of composite resins on color stability.
Materials and Methods The samples were divided into 4 main groups according to the polymerization strategy, and all groups except the control group received surface treatment. Each group was subsequently divided into 3 subgroups respectively: Kuraray Clearfil Majesty ES-2 Classic, Premium and Universal. Approximately 24 hours after preparation of the samples, they were immersed for 7 days in a coffee solution. A first color measurement was performed after the preparation of the samples, the second measurement was performed after 7 days in the coffee solution. All measurements were carried out using a dental spectrophotometer to assess the CIE
L *a *b * color parameters.Results There was a statistically significant difference between ΔE values for different procedures (
p = 0.003); in particular, the differences were found only between the groups that received surface treatment and the control group. In addition, a statistically significant difference was observed between the values of ΔE for different composites in the different procedure groups.Conclusions Spectrophotometric analysis showed that the additional photopolymerization and oxygen inhibition procedures did not yield better results in relation to color stability. In addition, finishing and polishing provided better color stability compared to not performing these procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026; 32(1): 94. CrossRef - Abrasiveness and Bleaching Level of Toothpastes on Composite Resins: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Novel Brushing Simulator
Simge Meseli, Elif Alkan, Bora Korkut, Ozlem Kanar, Dilek Tagtekin
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(5): 2314. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Direct and Indirect Composite Restorations in Class II Tooth Preparations - An In vivo Study
Akshun Gupta, Garima Arora, Aprajita Mehta, Satish Sane, Siddhi Nevrekar, Apurva Nagrale
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 550. CrossRef - Micro- and Nanoplastics and the Oral Cavity: Implications for Oral and Systemic Health, Dental Practice, and the Environment—A Narrative Review
Federica Di Spirito, Veronica Folliero, Maria Pia Di Palo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Leonardo Aulisio, Stefano Martina, Luca Rinaldi, Gianluigi Franci
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 332. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 6,345 View
- 345 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Analysis of the reciprocating kinematics of the VDW Silver Reciproc, E-Connect Pro, Ecom, and Endopen endodontic motors: an in vitro experimental study
- Cristielly França, Juliana D. Bronzato, Dieimes Braambati, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Carla C. R. B. Félix, Michelle A. N. S. Ferreira, Marcos Frozoni
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e5. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e5

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the actual parameters of four endodontic motors, each adjusted for reciprocating motion, and compare them to the manufacturers’ declared values.
Methods
The motors used were the VDW Silver Reciproc (VDW GmbH), E-Connect Pro (MK Life), Ecom (Woodpecker), and Endopen (Schuster Woodpecker). A custom optical target was attached to the motor contra-angle, the movements were recorded with a high-resolution camera, and the images were analyzed. Engagement, disengagement, net angles, and speed for each operation cycle, duration of clockwise (CW) and counter-clockwise (CCW) movement, duration of standstill after CW and CCW movement, and the number of cycles to complete a full rotation were analyzed. The data were statistically analyzed at a significance level of 5%. The replicability of all reciprocal parameters analyzed was statistically different from that reported by the manufacturers.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference between the VDW Silver Reciproc, Ecom, and Endopen for the engagement angle. The E-Connect Pro was the least reliable at the 150°/30° settings for both angle parameters. There was no significant difference between the set and actual cycle net angles for the VDW Silver Reciproc (p = 0.493). While the actual values for the Ecom and E-Connect Pro were significantly higher than the set (p < 0.001), the actual values for the Endopen were significantly lower than the set (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Experiments on four commercially available reciprocating endodontic motors revealed that the actual motor values differed significantly from the set values.
- 675 View
- 28 Download

- Success rates comparison of endodontic microsurgery and single implants with comprehensive and explicit criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Min Jung Ko, Ju Hyun Park, Na Rae Lee, Joon-Ho Yoon, Young-Taek Kim, Sin-Yeon Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e8. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e8
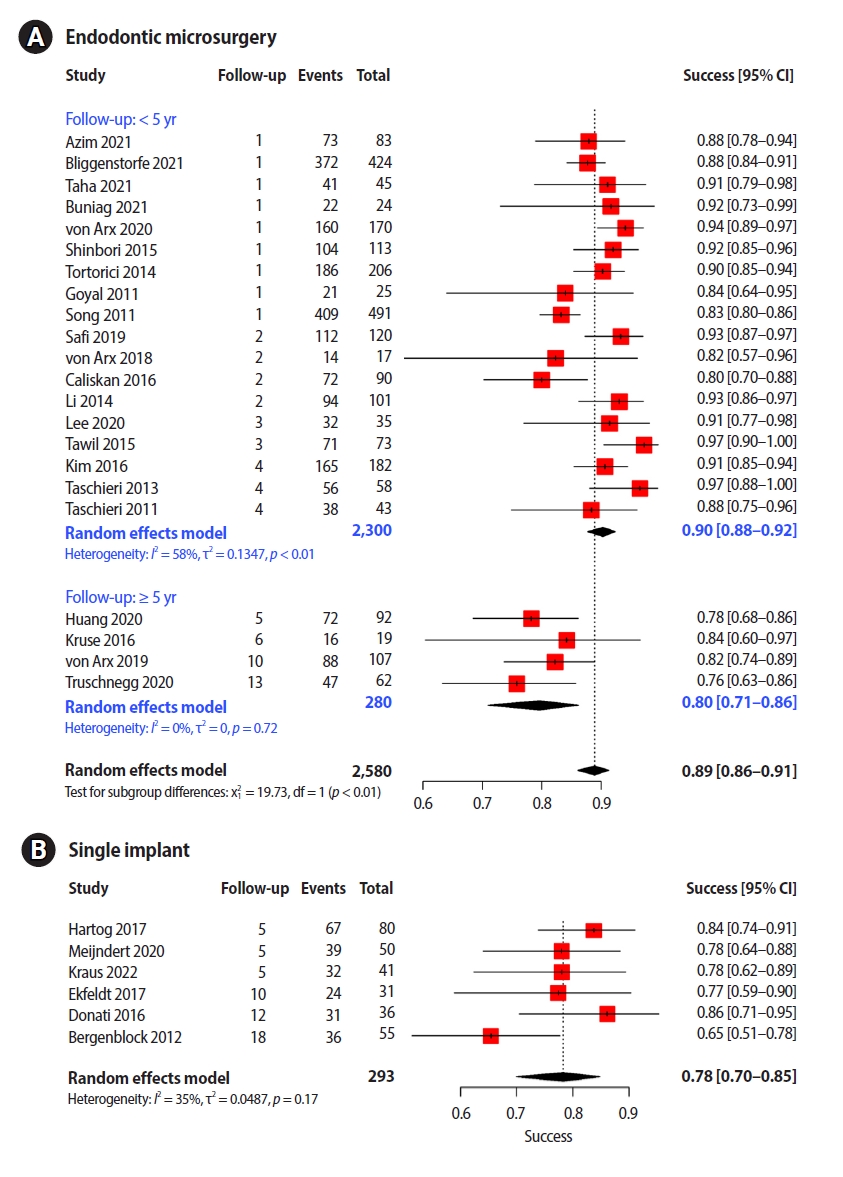
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
While the success criteria of endodontic microsurgery (EMS) have been consistently defined and widely accepted, the success criteria of dental implants are outdated and focus only on the implant fixture and surrounding bone. This study aimed to evaluate the outcomes of EMS and single implants (SIs) with explicit criteria.
Methods
We searched for articles published from January 2010 to February 2022 and discussed them and consulted with a clinical advisory committee composed of four dental specialists and one epidemiologist during article selection and data extraction.
Results
Twenty-two EMS studies and six SI studies were included in the meta-analysis. Teeth treated using EMS had a pooled success rate of 89% (90% at <5-year follow-up and 80% at ≥5-year follow-up) and the pooled success rate of SI was 78%.
Conclusions
The success rates of the two procedures with similar follow-up periods were comparable. Subgroup analysis found no other variable that significantly influenced study heterogeneity. Considering the treatment sequence and the similar success rates, it would be advantageous to consider EMS, rather than implants, first in a situation where both procedures are applicable. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Management of a Separated Instrument and Radicular Cyst: A Nine-Month Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Follow-up
Dipti Chauhan, Hemant Yadav, Anshu Minocha, Vishal Sharma
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness of Endodontic Retreatment vs Implants: A 5-year Retrospective Analysis in India
Pramod Kumar, Himanshu Sharma
Journal of Clinical Insights and Research in Dentistry.2025; 1(3): 121. CrossRef
- Surgical Management of a Separated Instrument and Radicular Cyst: A Nine-Month Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Follow-up
- 8,800 View
- 168 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparative study of the effectiveness of different bleaching agents on blood-colored extracted teeth and investigation of recoloring after bleaching: an in vitro experimental study
- Gülşen Arslan, Akın Aladağ, Ayşegül Demirbaş, Murat Türkün
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e22. Published online July 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e22
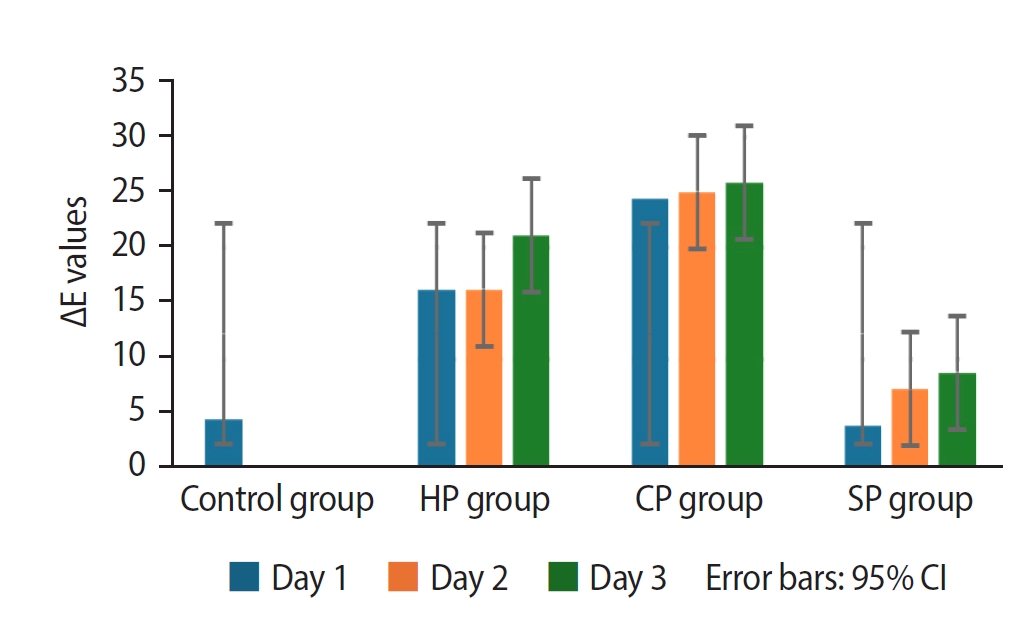
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the efficacy of three distinct bleaching agents over time on blood-stained, devitalized teeth. Furthermore, the recoloring subsequent to bleaching will be monitored.
Methods
The study was conducted on 60 caries-free, unfilled, upper human incisors. The Freccia and Peters blood staining technique was employed, and four groups (n = 15) were identified: control, 35% hydrogen peroxide-treated, 37% carbamide peroxide-treated, and sodium perborate-treated groups. Color differences were measured using ΔE00, ΔWID, L*, a*, and b* values. To investigate tooth discoloration after bleaching, 10 unbleached teeth with three groups of 10 bleached teeth were compared by vine staining. The group of bleached teeth was restored immediately, another group waited one week, and the third group had sodium ascorbate applied and analyzed using one-way analysis of variance tests (p < 0.05).
Results
Among the groups, carbamide peroxide exhibited the most significant whitening during the 6-day bleaching process, followed by hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate. Subsequent examination of the wine recoloring of post-bleaching samples demonstrated that bleached teeth exhibited a heightened propensity for recoloration in contrast to unbleached teeth. Notably, sodium ascorbate treatments for hydrogen peroxide neutralization and the wait-and-restore approach were not statistically significant in terms of preventing recoloration.
Conclusions
Sodium perborate is less effective and more time-consuming than hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide for bleaching purposes. Carbamide peroxide is the most effective bleaching agent. The sodium ascorbate treatment and the wait-and-restore approach are ineffective in preventing recoloring. Bleached teeth have more discoloration than unbleached teeth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Adhesive Systems on Shade Matching of Composite Veneer
Fadak Al Marar, Raghad Aljarboua, Fatimah M. Alatiyyah, Shahad AlGhamdi, Faraz Ahmed Farooqi, Lama Almuhanna, Rasha AlSheikh, Abdul Samad Khan
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(2): 85. CrossRef
- The Effect of Adhesive Systems on Shade Matching of Composite Veneer
- 3,324 View
- 244 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical management of maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin after reestablishing maxillary sinus floor healing through a nonsurgical approach: a case report
- Eun-Sook Kang, Min-Kyeong Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e12. Published online April 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e12
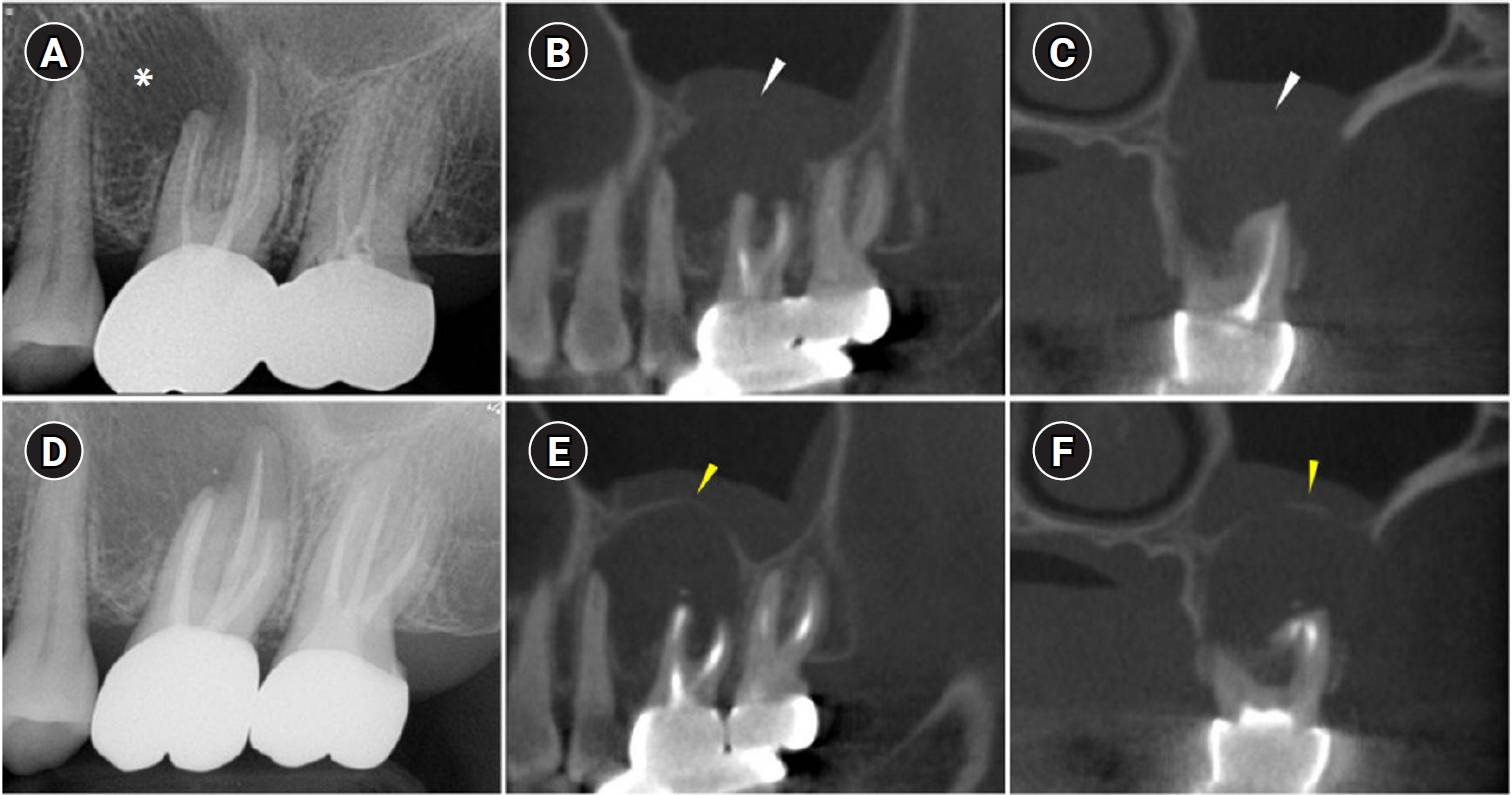
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - When root canal infections breach the maxillary sinus floor (MSF), maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin (MSEO) can result. This case illustrates the surgical management of MSEO following the nonsurgical reestablishment of the MSF. A 55-year-old woman presented with left facial pain and was diagnosed with MSEO originating from the left upper first molar. Despite undergoing nonsurgical root canal treatment, there was no evidence of bony healing after 6 months. However, cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) scans revealed the reestablishment of MSF. Subsequently, surgical intervention was carried out using a dental operating microscope. Two years after surgery, CBCT images indicated that the mucosal edema had resolved, and the MSF was well reestablished. Preserving the MSF is crucial for the success of endodontic surgery. When MSEO is present, the integrity of the MSF must be assessed to determine appropriate treatment options.
- 4,151 View
- 211 Download

- Can carbamide peroxide be as effective as hydrogen peroxide for in-office tooth bleaching and cause less sensitivity? A systematic review
- Patrick Wesley Marques de Boa, Kaiza de Sousa Santos, Francisca Jennifer Duarte de Oliveira, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e14. Published online March 20, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e14
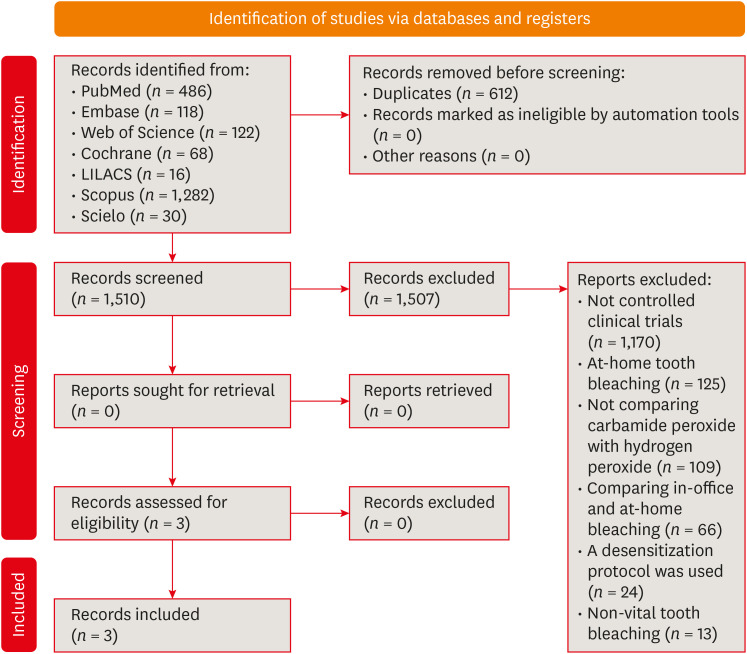
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to answer the question through a systematic review: Can carbamide peroxide be as effective as hydrogen peroxide and cause less in-office bleaching sensitivity? A literature survey was performed in PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, and gray literature. Primary clinical trials that compared the efficacy or the in-office bleaching sensitivity between carbamide and hydrogen peroxides were included. The risk of bias was evaluated using the RoB2. The certainty of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE approach. DPI training significantly improved the mean scores of the dental undergraduates from 7.53 in the pre-DPI-training test to 9.01 in the post-DPI-training test (
p < 0.001). After 6 weeks, the mean scores decreased marginally to 8.87 in the retention test (p = 0.563). DPI training increased their confidence level from 5.68 pre-DPI training to 7.09 post-DPI training. The limited evidence suggests that the 37% carbamide peroxide may be similarly effective to the 35% hydrogen peroxide for bleaching teeth in-office and causes less bleaching sensitivity. However, more well-designed split-mouth clinical trials are necessary to strengthen the evidence.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of nanostructured additives in tooth bleaching agents on enhancing color change and reducing side effects: a scoping review
Patrick Wesley Marques de Boa, Kaiza de Sousa Santos, Aleph Matthews da Silva Souza, Arnóbio Antônio da Silva-Júnior, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Enamel Surface Roughness Following High-Concentration Peroxide Bleaching: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Mamnoon Ghafir, Nida Mehmood, Leeza Bharati, Shreya Bhukal, Ritika Sethi, Aanchal Chaudhary, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Using violet light during in-office tooth bleaching to enhance the efficacy of carbamide peroxide without increasing bleaching sensitivity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mariana Silva de Bessa, Kaiza de Sousa Santos, Patrick Wesley Marques de Boa, Francisca Jennifer Duarte de Oliveira, Bárbara Faria de Sá Barbosa, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Different Light-Activated Bleaching Gels on Pulp Chamber Temperature: An In Vitro Study
Mandana Karimi, Elmira Ataee, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani, Mahdi Abbasi, Elham Ahmadi
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(4): 225. CrossRef
- Impact of nanostructured additives in tooth bleaching agents on enhancing color change and reducing side effects: a scoping review
- 11,360 View
- 162 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Bonding and fractographic characterization of universal adhesives applied to dentin in multimode strategies: an in vitro study
- Samaa M. Morsy, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Naji Kharouf, Ahmed A. Holiel
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e12. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e12
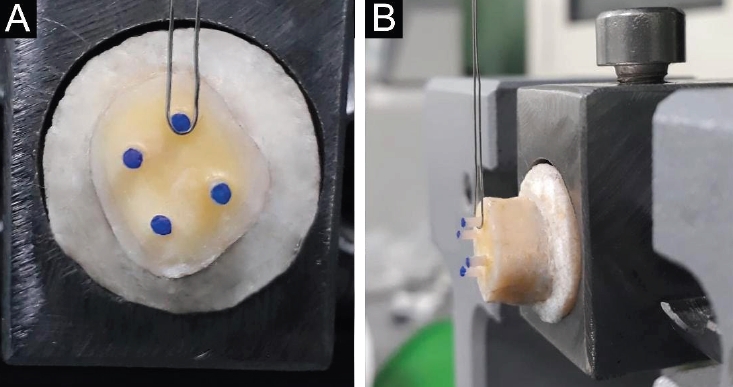
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Universal adhesives (UAs) are marketed as versatile systems for both self-etch (SE) and total-etch (TE) modes. While their bond strength has been widely investigated, evidence linking fracture characteristics to bonding performance remains limited. This study evaluated the micro-shear bond strength (μSBS) and failure patterns of three UAs applied in SE and TE modes, complemented by fractographic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
Methods
Eighteen extracted human molars were sectioned to expose mid-coronal dentin and randomly allocated to SE or TE application. Three UAs were tested: Tetric N-Bond Universal, All-Bond Universal, and Single Bond Universal (SBU). Composite micro-rods (n = 72) were bonded, thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5°C and 55°C, and subjected to μSBS testing. Fracture surfaces were examined under SEM and classified as adhesive, cohesive, or mixed. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test, and Spearman correlation (α = 0.05).
Results
In TE mode, SBU demonstrated the highest μSBS (p < 0.001), whereas no significant differences were observed among adhesives in SE mode (p > 0.05). SEM analysis revealed adhesive failures as interfacial fractures, cohesive failures with beach marks, and mixed failures involving crack propagation through both dentin and composite. Adhesive failures correlated negatively with μSBS (rs = –0.77), while mixed failures correlated positively (rs = 0.81).
Conclusions
Both the etching strategy and adhesive formulation significantly affect bond strength and fracture behavior. Fractographic SEM analysis provides critical insights into the mechanical reliability of UAs and informs their clinical application.
- 215 View
- 24 Download

- Phase transformation temperatures influence the reduction ratio of fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium reciprocating files at body temperature: an in vitro experimental study
- Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Lola Pedèches, Sylvie Lê, Marie Georgelin-Gurgel, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Franck Diemer
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e35. Published online November 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e35
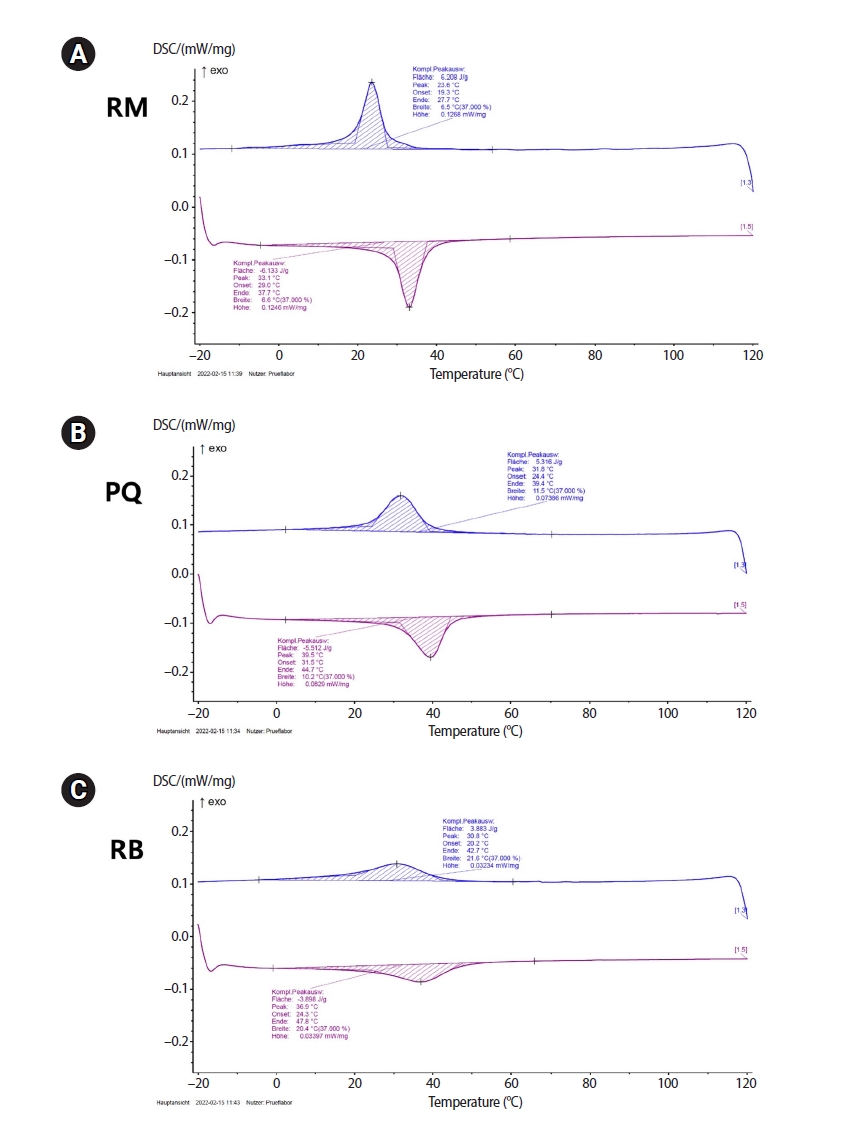
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of transformational temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance at body temperature of reciprocating file systems: R motion (RM), Procodile Q (PQ), and Reciproc Blue.
Methods
Resistance test was done in a custom-made device at room (20°C ± 1°C) and body (37°C ± 1°C) temperatures within a 60° angle of curvature and 5 mm radius of the artificial canal. The time to fracture (TTF) was recorded. The scanning electron microscope observation and differential scanning calorimetry analyses were performed. Two-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc comparison were applied at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
The results showed a significant influence of temperature on instrumental breakage, regardless of the file systems (p < 0.05). The TTF is significantly decreased at body temperature (p < 0.05). PQ showed the longest TTF in both temperature conditions (p < 0.05). RM demonstrated a significantly higher TTF reduction ratio compared to the other files (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Within the limitations of this study, the heat-treated files with reciprocating kinetics may have different reduction ratios of the fatigue resistance of the file systems under different temperature conditions. This characteristic is an important point of consideration when clinicians select the file system to reduce potential file fracture.
- 1,545 View
- 64 Download

- Effect of surface treatment on glass ionomers in sandwich restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory studies
- Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e13. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e13
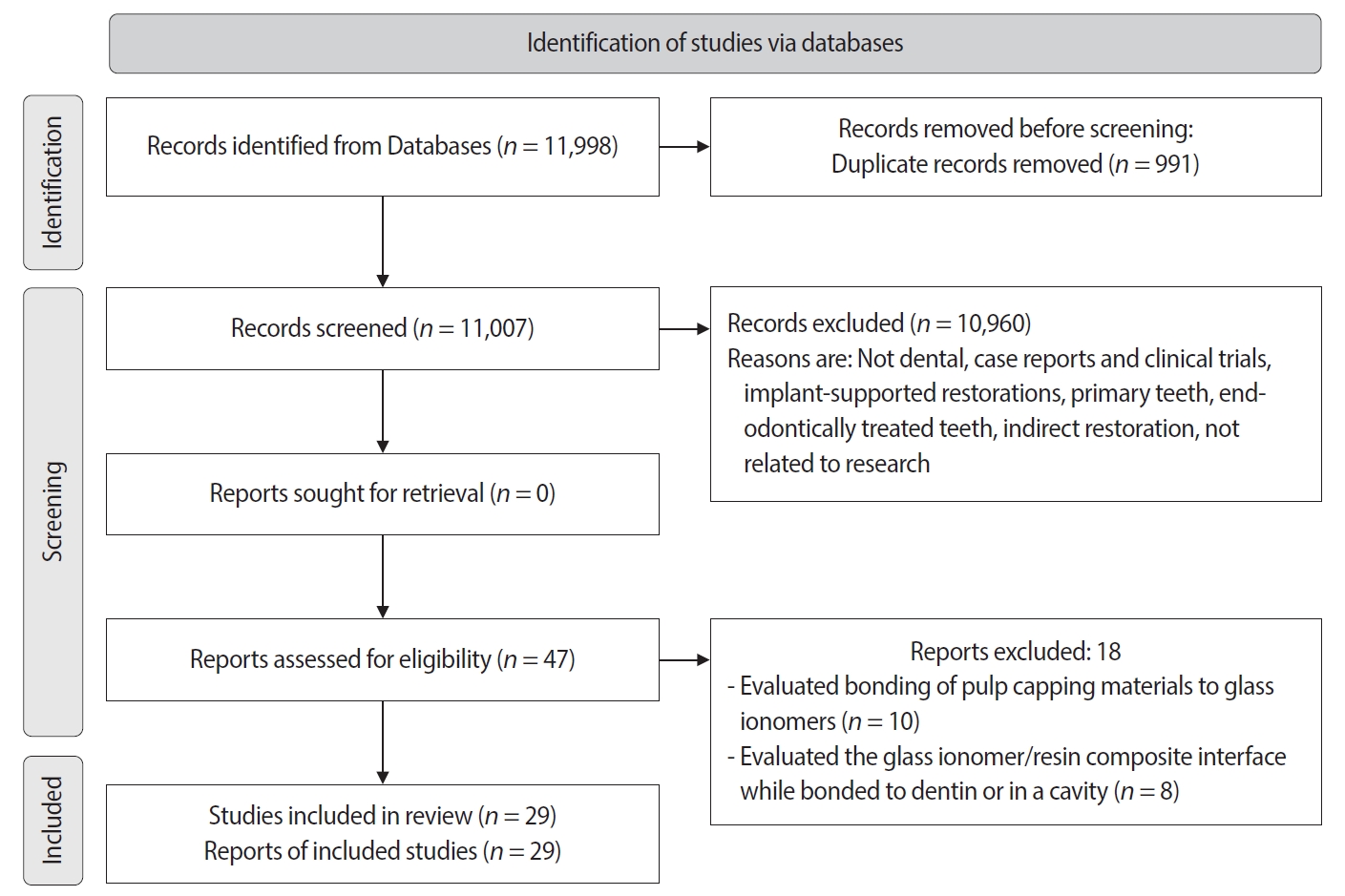
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of different surface treatments on the bond strength between new or aged glass ionomers (GI) and resin composites in sandwich restorations.
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted in three databases to identify studies focusing on the bond strength of new or aged GIs and resin composites in laboratory settings. The selected studies were assessed for potential biases based on predetermined criteria. Additionally, a meta-analysis was performed using three studies.
Results
A total of 29 studies were included, with 24 investigating the bond strength of new GIs and five focusing on GI repair. Three studies were included in the meta-analysis (with a 95% confidence interval) which revealed no significant difference in the mean MPa values of resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) treated with phosphoric acid or Er,Cr:YSGG laser before the application of an etch-and-rinse adhesive. Surface treatment was found to be crucial for achieving optimal bonding between GI and resin composite, regardless of the GI’s condition.
Conclusions
The combination of mechanical and chemical surface treatments does not significantly affect the bond strength between new RMGI and composite. However, for GI repair, it is recommended to use both treatments to enhance the bond strength. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
Rashid El Abed, Amre R. Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Anas Al Jadaa, Hamza El-Faraj, Abdel Rahman Bani Amer, Taher Al Omari
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
- 8,716 View
- 218 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
- Jia Min Ng, Yan Yee Lee, Prashanti Chippagiri, Elaheh Ahanin, Abhishek Parolia
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e3. Published online January 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e3
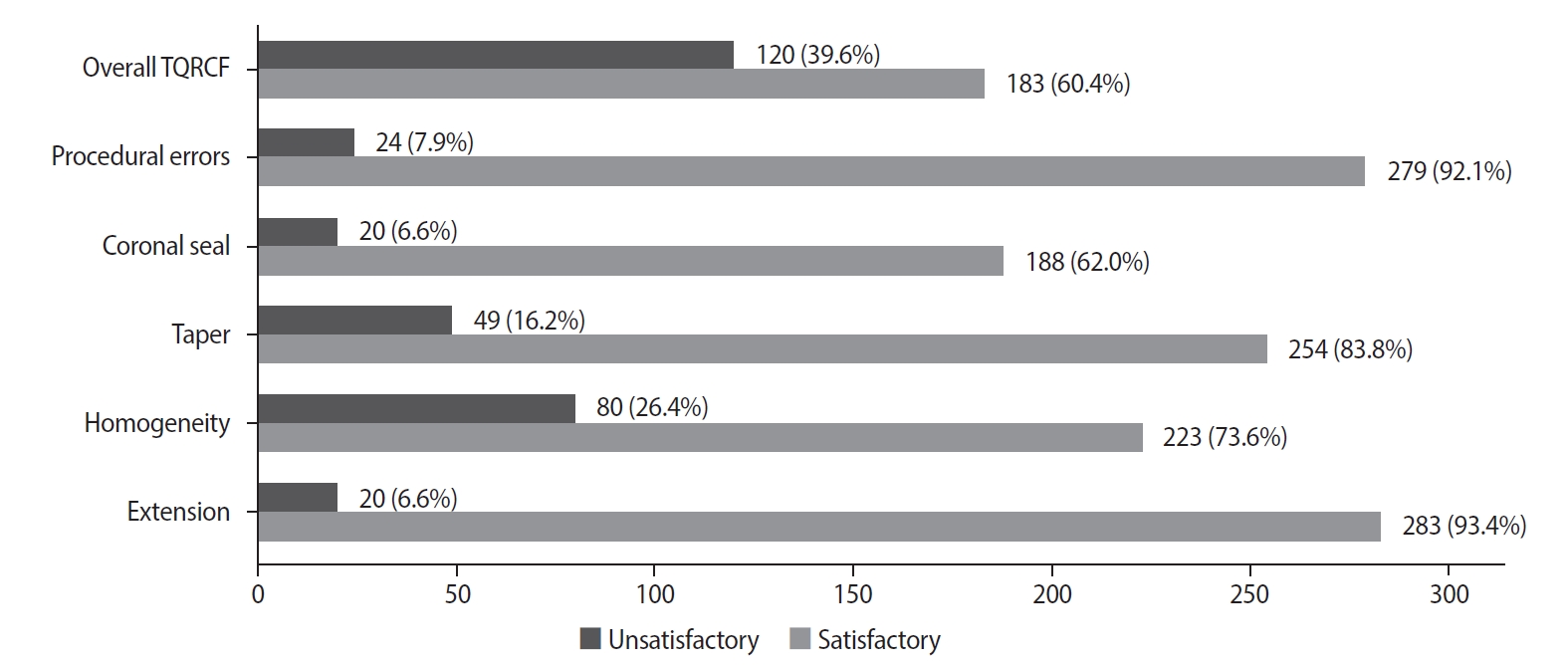
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the number and quality of working length (WL) and master cone (MC) radiographs taken during root canal treatment by dental undergraduates, and their associations with the technical quality of root canal fillings (TQRCF) and endodontic outcomes (EO).
Methods
A retrospective evaluation of radiographs from 303 root canal-treated teeth in 231 patients was conducted, with 72 patients attending recall visits to assess EO. The chi-square and one-way analysis of variance tests were performed.
Results
A total of 505 WL and 557 MC radiographs were reviewed, with 72.9% and 75% deemed satisfactory, respectively. Satisfactory TQRCF was achieved in 60.4% of cases. Significant associations were found between the extension of the file in WL and gutta-percha in MC radiographs and TQRCF (p = 0.000). Misinterpretation of these radiographs resulted in poor TQRCF. Furthermore, 64.2% of teeth had satisfactory EO. A significant relationship was noted between the quality of MC radiographs and both TQRCF (p = 0.043) and EO (p = 0.003).
Conclusions
Unsatisfactory MC radiographs were linked to poor TQRCF and unfavorable EO. Regular radiographic training is recommended to enhance EO. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of radiographic errors and repetition rates in undergraduate endodontic education: a retrospective clinical study
Marwa Ameen, Abdul Rahman Saleh, Dunia Alhadi, Manal Almaslamani
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Periapical Radiography in Root Canal Treatment: A Literature Review
Jennifer Lois Violita Malau, Keizha Allysia Nabila, Widiani Harrista, Regina Amara Ginting, Tassa Kusuma Arya Putri, Jatu Rachel Keshena
Acta Odontologica Indonesia.2025; 1(2): 49. CrossRef
- Assessment of radiographic errors and repetition rates in undergraduate endodontic education: a retrospective clinical study
- 11,690 View
- 265 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Restorative Dentistry and Endodontics 2025 annual highlights: gratitude to our reviewers and achievement of the first journal impact factor
- Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e14. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e14
- 405 View
- 21 Download

- Analysis of thermal profiles on tooth structure and insert during one-piece or adapter-coupled ultrasonic insert use: an in vitro experimental study
- Gabriela Loewen Brotto, Bruno Monguilhott Crozeta, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Alysson Nunes Diógenes, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e24. Published online July 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e24
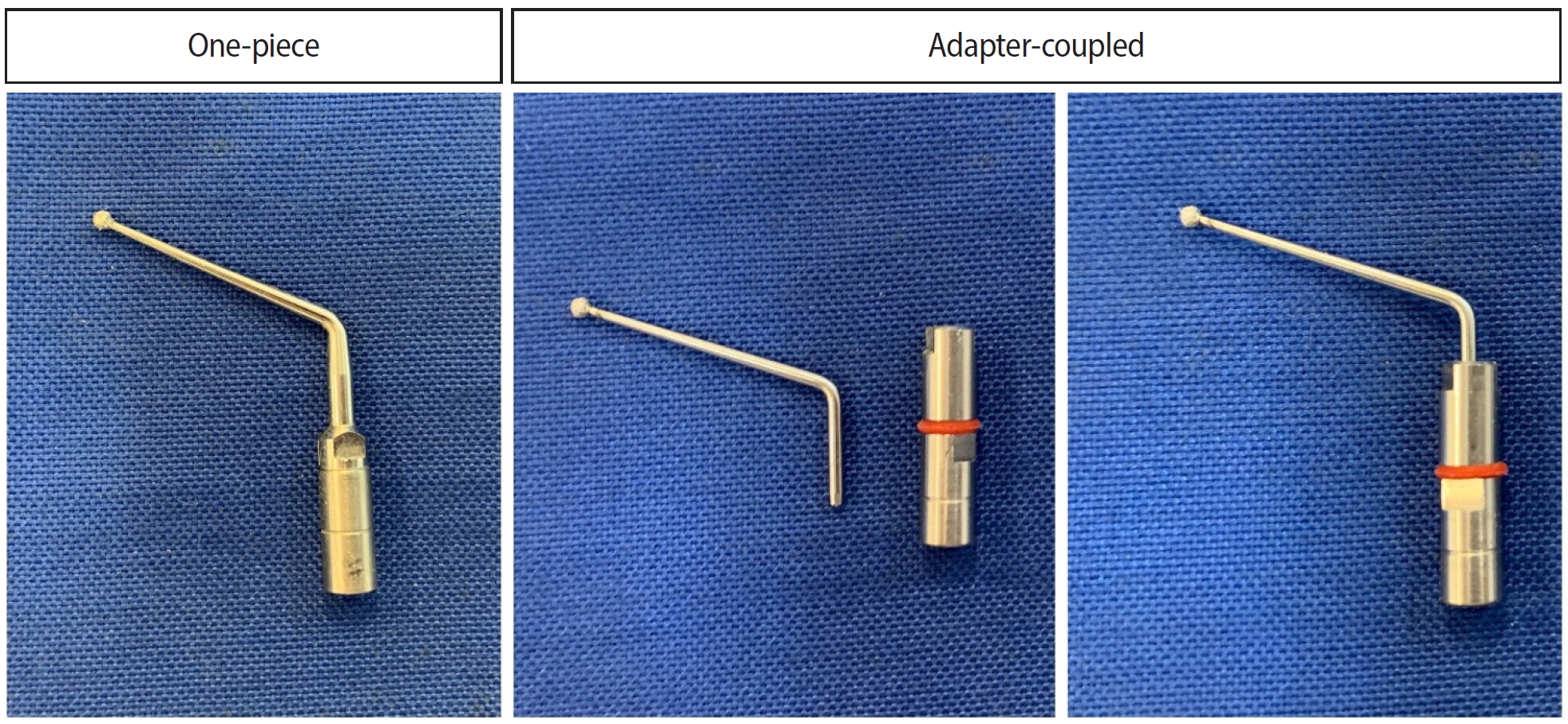
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate temperature variation on the external surface of mandibular molars and within ultrasonic inserts when using adapter-coupled versus one-piece inserts.
Methods
Twenty-four extracted human mandibular molars were divided into two groups based on the type of ultrasonic insert used: adapter-coupled and one-piece inserts. Temperature on the external surface of each tooth was measured with a thermocouple probe positioned in the furcation area, capturing data continuously. The temperature of the ultrasonic inserts was monitored in real-time using a thermal imaging camera. Measurements were taken in a controlled environment without cooling for over 120 seconds. Statistical analysis was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-way ANOVA with repeated measures to evaluate temperature variations between groups and over time, with significance set at 5%.
Results
In the external tooth surface temperature measurements, no significant differences were observed between the groups during the initial 15 seconds (p = 0.185) and 30 seconds (p = 0.067). However, significant differences emerged at 60 seconds (p = 0.025), 90 seconds (p = 0.024), and 120 seconds (p = 0.020), with the one-piece insert group demonstrating higher temperatures in the furcation region. Thermal imaging of the inserts revealed a significant difference at all time points (p < 0.001), with adapter-coupled inserts showing greater heating.
Conclusions
The use of ultrasonic inserts leads to a gradual rise in temperature on the external tooth surface. One-piece inserts generated higher temperatures on the tooth, while adapter-coupled inserts exhibited greater heating within the insert.
- 1,832 View
- 96 Download

- Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
- Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e13. Published online March 18, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e13
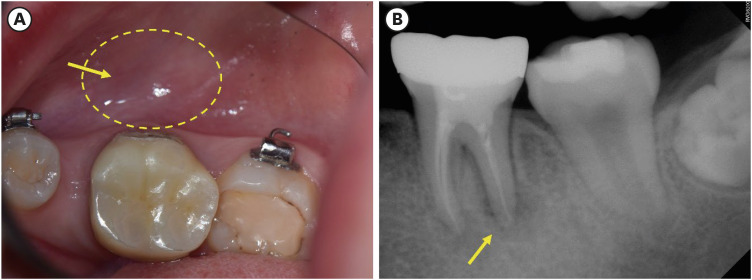
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Chronic osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis, known as Garre’s osteomyelitis, is a type of osteomyelitis characterized by a distinctive gross thickening of the periosteum of bones. Peripheral reactive bone formation can be caused by mild irritation or infection. Garre’s osteomyelitis is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and the mandible is more affected than the maxilla. The following is a case report of a 12-year-old female patient with Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible due to an infection of a root canal-treated tooth. Without surgical intervention, the patient’s symptoms were relieved through nonsurgical root canal re-treatment with long-term calcium hydroxide placement. A cone-beam computed tomography image obtained 6 months after treatment completion displayed complete healing of the periapical lesion and resolution of the peripheral reactive buccal bone. Due to the clinical features of Garre's osteomyelitis, which is characterized by thickening of the periosteum, it can be mistaken for other diseases such as fibrous dysplasia. It is important to correctly diagnose Garre's osteomyelitis based on its distinctive clinical features to avoid unnecessary surgical intervention, and it can lead to minimally invasive treatment options.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Focal osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis
Zarah Yakoob
South African Dental Journal.2025; 79(09): 508. CrossRef - Garré’s osteomyelitis of the mandible in an adolescent: a case report
Wiem Feki, Imen Haddar, Marwa Bahloul, Zeineb Mnif, Thouraya Kammoun, Ines Maaloul
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Garré’s Chronic Sclerosing Osteomyelitis: An Overview of Clinical and Radiologic Features
Mohamed Fadil, Ayman Farouki, Rachida Saouab, Hassan En-nouali, Jamal El Fenni, Zakariya Toufga
Oxford Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Focal osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis
- 8,110 View
- 197 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Does the use of different root canal sealers and adhesive resin cements impact the bond strength of glass fiber posts?
- Ália Regina Neves de Paula Porto, Rudá França Moreira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e29. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e29
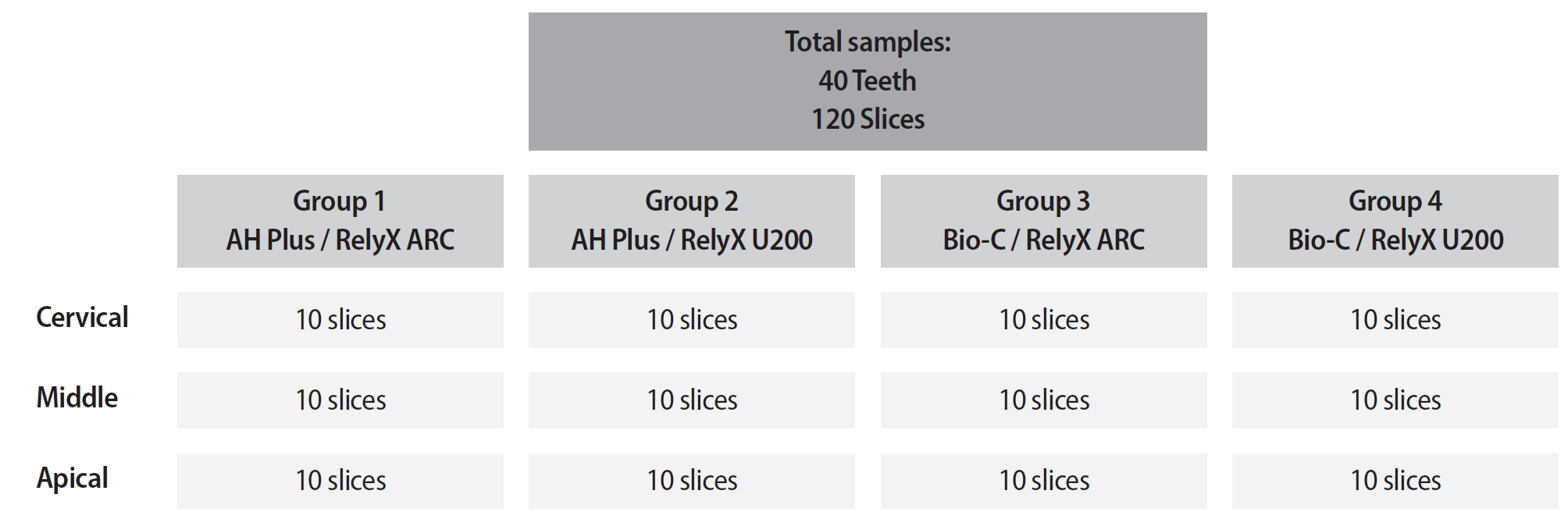
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the influence of two endodontic sealers on the bond strength of glass fiber posts using conventional and self-adhesive resin cement through a push-out test. Methods: Forty central human incisors were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) based on sealer (epoxy resin- based or calcium silicate-based) and cement (conventional and self-adhesive resin) types: AH Plus (Dentsply De- Trey)/RelyX ARC (3M ESPE), AH Plus/RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), Bio-C Sealer (Angelus)/RelyX ARC, and Bio-C Sealer/RelyX U200. After canal filling and post cementation, roots were sectioned to obtain one specimen per root third. A pushout test and failure pattern assessment were conducted, with bond strength analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test. Results: AH Plus/RelyX ARC showed the highest bond strength values, with a significant difference in the middle third. The most common failure was mixed (55%), while adhesive failures made up 45%, with 23.5% at the cement/post interface and 21.5% at the cement/dentin interface. Conclusions: AH Plus/RelyX ARC provided the highest bond strength values for glass fiber posts to dentin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Endodontic Sealers on the Bond Strength of Glass Fibre Posts: A Systematic Review
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana D. Bronzato, Vanessa Gallego Arias Pecorari, Jennifer Santos Pereira, Talita Tartari, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of Endodontic Sealers on the Bond Strength of Glass Fibre Posts: A Systematic Review
- 1,852 View
- 147 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of limonene extract on the adhesion of different endodontic cements to root dentin: an in vitro experimental study
- Nayara Lima Ferraz Aguiar, Eduardo José Soares, Guilherme Nilson Alves dos Santos, Anna Luísa Araújo Pimenta, Laryssa Karla Romano, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e16. Published online May 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e16
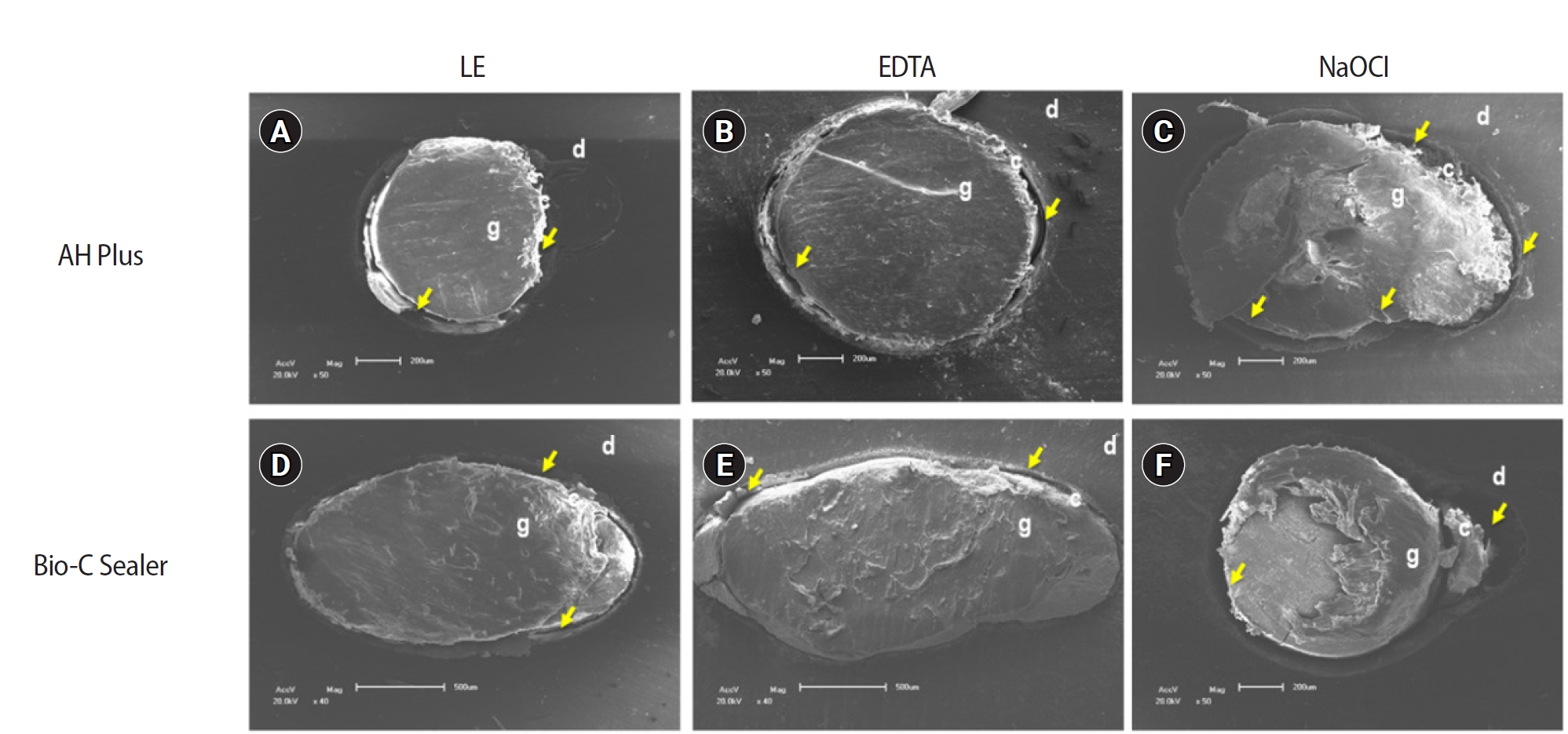
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to evaluate the effect of limonene extract (LE) on push-out bond strength (BS) to root dentin in endodontically treated teeth.
Methods
Single-rooted teeth were selected and instrumented using the reciprocating technique, then divided into three groups based on the final irrigating solution: 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and 5% LE. The roots were further divided (n = 12) and obturated using the single-cone technique with epoxy resin-based (ERB) or bioceramic sealer (Bio-C). After 3 days, the roots were sectioned into 2-mm slices, obtaining two slices from each root third. Push-out BS testing was conducted at 0.5 mm/min, followed by failure pattern and adhesive interface analysis using scanning electron microscopy. Push-out BS data were analyzed by three-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
Results
ERB showed higher BS when irrigated with EDTA (5.0 ± 2.3 MPa) compared to NaOCl (1.8 ± 1.1 MPa) (p = 0.0005), particularly in the cervical third. LE yielded intermediate values without significant differences from the other irrigants (3.5 ± 1.9 MPa) (p > 0.05). For Bio-C, the highest BS was observed in the apical third, especially with LE (9.4 ± 5.0 MPa), differing from other thirds and final irrigating solutions (p < 0.05). Mixed failure patterns were most prevalent, regardless of the irrigant solutions.
Conclusions
The combination of LE with Bio-C demonstrated superior BS in the apical third, suggesting its potential as a final irrigating solution in endodontic treatments.
- 2,527 View
- 223 Download

- Surface properties and susceptibility to staining of a resin composite after brushing with different whitening toothpastes
- Aline da Silva Barros, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Junior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e6. Published online February 26, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e6
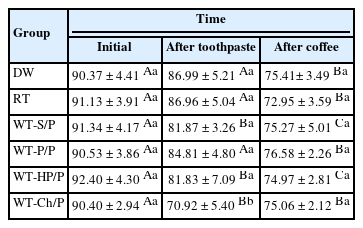
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study investigated the effects of different whitening toothpaste (WT) on the surface properties and staining susceptibility of a resin composite.
Methods
Cylindrical samples were prepared with a micro-hybrid resin composite and were randomized into groups according to the toothpaste (n = 12): distilled water (DW), regular toothpaste (RT), WT with silica + pyrophosphate (WT-S/P), WT with pentaphosphate and pyrophosphate (WT-P/P), WT with hydrogen peroxide and pyrophosphate (WT-HP/P) and WT with charcoal and pyrophosphate (WT-Ch/P). The samples were brushed for 825 cycles in an automatic brushing machine, simulating 30 days of brushing. After that, an immersion in coffee (10 mL/sample) was performed for 30 minutes for 30 days. The analyses of color, surface microhardness (SMH), and surface roughness (Ra) were performed at the initial time, after brushing with toothpaste and after immersion in coffee. The ΔL*, Δa*, Δb*, ΔEab, Δand E00 values were calculated comparing after toothpaste with initial time and after coffee with after toothpaste. Data were analyzed using a mixed linear model for repeated measures (SMH), Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Friedman, and Nemenyi tests, with α = 0.05.
Results
For ΔL*, the WT-Ch/P group had the lowest values and differed from the other groups comparing the after toothpaste with the initial time interval (p < 0.001). The WT-Ch/P group had the lowest SMH values in after-toothpaste time (p < 0.001). In after-toothpaste time and after coffee time, the WT-S/P group had the highest Ra values and differed from the groups except the WT-Ch/P group (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The toothpaste composition affects the surface characteristics and susceptibility to staining of the resin composite. The charcoal-based toothpaste had the worst performance for the color analyses and SMH.
- 5,049 View
- 167 Download

- Resolvin E1 incorporated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold accelerates repair of dental pulp stem cells under inflammatory conditions: a laboratory investigation
- Hemalatha P Balasubramanian, Nandini Suresh, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e40. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e40
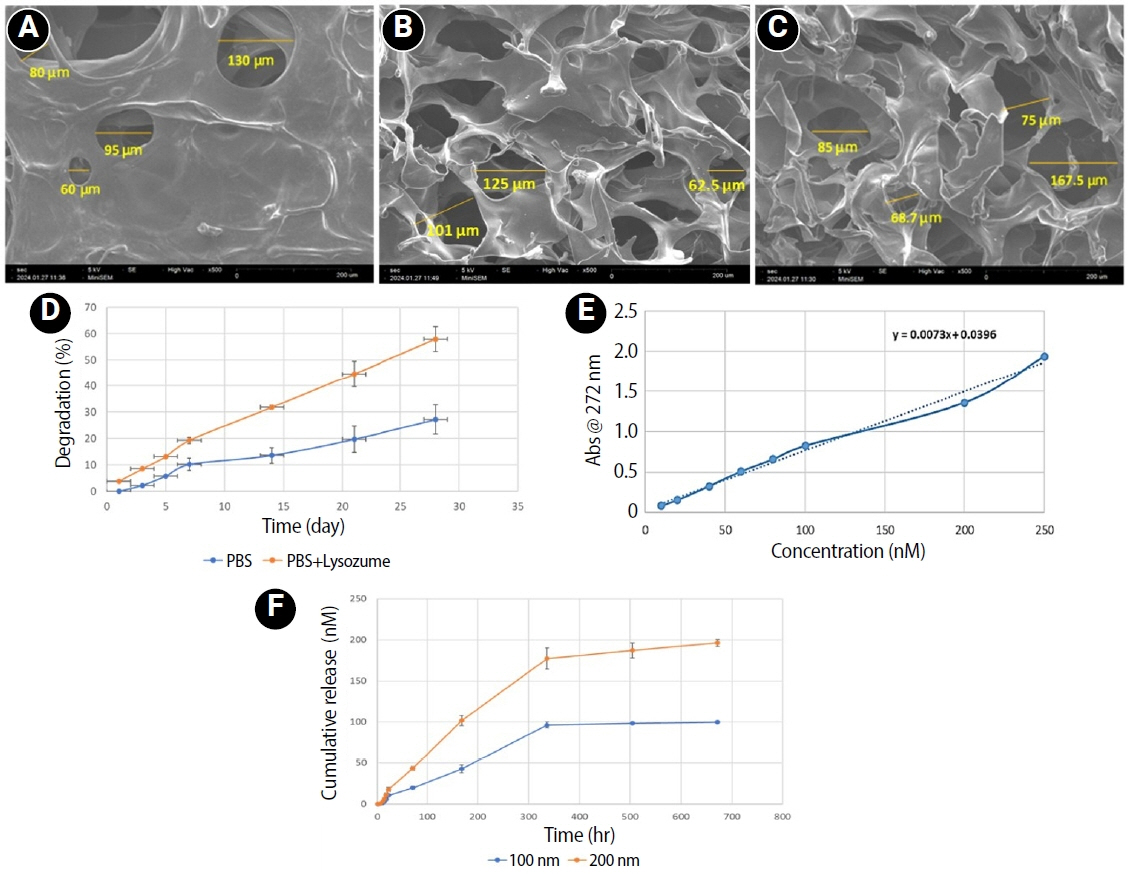
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study fabricated and characterized a resolvin E1 (RvE1)-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) scaffold and determined its cytotoxicity and mineralization potential on inflamed human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Methods
CMC scaffold incorporated with two concentrations of RvE1 (100 and 200 nM) was fabricated and characterized. The scaffolds’ porosity, drug release kinetics, and degradation were assessed. The impact of RvE1 on inflamed hDPSCs proliferation, proinflammatory gene expression (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), alkaline phosphatase activity, and alizarin red S staining was evaluated.
Results
Scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated a highly porous interconnected microstructure. Release kinetics showed gradual RvE1 release peaking at day 14. Cumulative degradation of the CMC scaffold at 28 days was 57.35%. Inflamed hDPSCs exposed to 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold exhibited significantly improved viability compared to 100 nM. Both RvE1-CMC scaffolds significantly suppressed the expression of TNF-α at 7 days. Alkaline phosphatase activity was enhanced by both RvE1 concentrations on days 7 and 14. Alizarin red staining revealed superior mineralization potential of 200 nM RvE1 on days 14 and 21.
Conclusions
This study concludes 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold is a promising therapy for inflamed pulp conditions, enhancing cell proliferation and biomineralization potential in inflamed hDPSCs.
- 767 View
- 37 Download

- Evaluation of the effects of different file systems and apical functions of integrated endodontic motors on debris extrusion: an ex vivo experimental study
- Sıla Nur Usta, Antonio Magan-Fernandez, Cumhur Aydın
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e14. Published online April 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e14
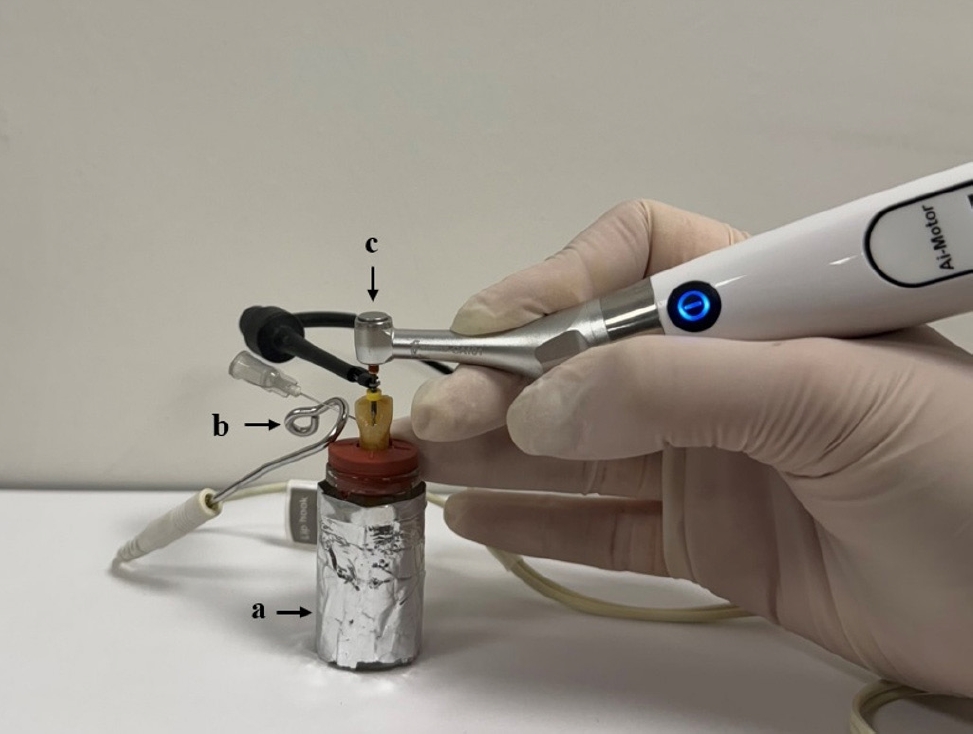
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of two different file systems operated with three apical functions of an endodontic motor integrated with an electronic apex locator on debris extrusion.
Methods
Sixty single-rooted teeth were prepared and divided into two main groups and three subgroups based on the file system (OneShape [Micro-Mega SA] and WaveOne [Dentsply Maillefer]) and apical function of the endodontic motor used (auto apical stop [AAS], auto apical reverse [AAR], and auto apical slowdown [ASD]). The teeth were mounted in pre-weighed glass tubes filled with 0.9% sodium chloride to complete the circuit with the apex locator. Files were advanced until the respective apical function (stop, reverse, or slowdown) was activated. The extruded debris was collected, dried, and weighed by subtracting pre-weighed values from post-weighed values. Preparation time was also recorded. Statistical analyses were performed to compare the groups.
Results
OneShape was associated with significantly less debris extrusion compared to WaveOne, regardless of the apical function (p < 0.05). The ASD function resulted in the least debris extrusion compared to AAS and AAR (p < 0.05). Preparation time was significantly longer in the ASD function (p < 0.05), while no differences were observed between the file systems (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
The OneShape file system and the ASD function produced the least amount of apical debris. While the ASD function requires more preparation time, its potential to minimize debris extrusion suggests it may reduce postoperative symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammatory Mediator Levels and Postoperative Pain Following Root Canal Shaping with Different Apical Actions: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Oğuz Karalar, Huriye Erbak Yılmaz, Emrah Karataşlıoğlu
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammatory Mediator Levels and Postoperative Pain Following Root Canal Shaping with Different Apical Actions: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 4,443 View
- 228 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Straightforward replication of digital wax-up design into direct composite resin restorations in adolescents using a custom 3-dimensionally printed index
- Ra’fat Ibrahim Farah, Sanaa Najeh Al-Haj Ali, Abdullah Alharbi, Bandar Alresheedi
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e36. Published online October 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e36
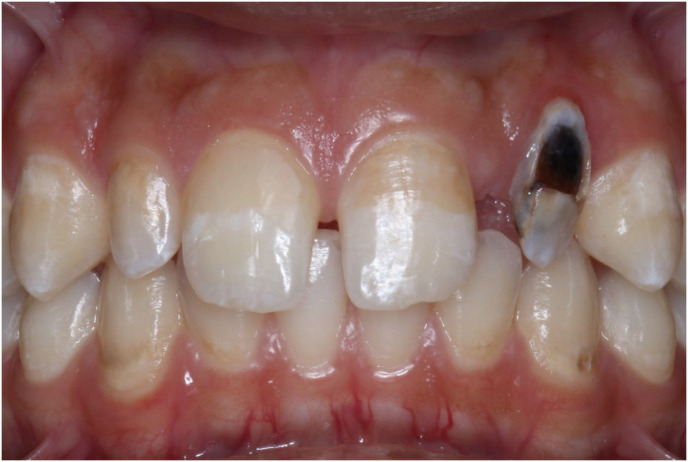
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report introduces a straightforward, noninvasive approach for the esthetic rehabilitation of malformed anterior teeth in adolescents using direct composite restorations. The universal composite resin restorations are applied within a transparent 3-dimensionally printed rigid-resin index, which is individually customized from a digital wax-up. Compared to other methods, this technique streamlines the restoration process, significantly reducing chairside time while enhancing the predictability, accuracy, and patient acceptance of the aesthetic outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diastema closure and esthetic rehabilitation with peg-shaped laterals: A case series
Afsana Ansari, Dipika Yadav
The Saint's International Dental Journal.2024; 8(2): 48. CrossRef
- Diastema closure and esthetic rehabilitation with peg-shaped laterals: A case series
- 4,776 View
- 249 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A global overview of enamel microabrasion for white spot lesions: a bibliometric review
- Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Karina Cardoso, Michely Cristina Goebel, Pablo Silveira Santos, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Juliana Silva Ribeiro, Carla Miranda Santana, Mariane Cardoso
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e29. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e29
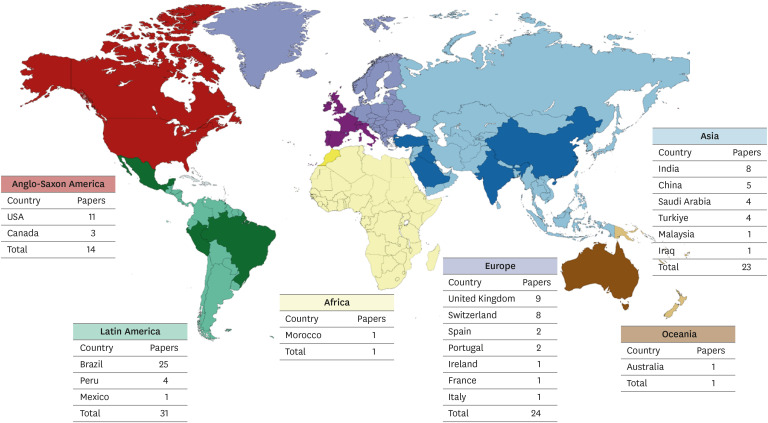
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to identify and analyze articles on enamel microabrasion for the treatment of white spot lesions. A search was conducted on the Web of Science. The following parameters were recorded and analyzed: number of citations, year, journal, impact factor, study design, theme, country and continent, institution, authors, and keywords. Data was analyzed using VOSviewer software. The initial search resulted in 1,126 documents, of which 94 articles were included. The highest number of citations an article received was 65. The oldest article was published in 1975, and the most recent in 2023. The most frequent study design was case report (
n = 42). Regarding the themes, it was observed that the main objective of the studies was to evaluate the clinical performance of enamel microabrasion (n = 75), primarily using Opalustre (Ultradent Products Inc., South Jordan, UT, USA) (n = 37) for treating white stains caused by dental fluorosis (n = 41). Most articles originated from Latin America (n = 31), mainly from Brazil (n = 26). The most frequent author was Sundfeld RH (n = 10). This study reveals research trends in the field of enamel microabrasion. The publications were mainly case reports/series using Opalustre for the removal of fluorosis stains.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
Michael Willian Favoreto, Leticia Condolo, Camila Mendes Camargo, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Karol Carrillo, Abraham Lincoln Calixto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105655. CrossRef - Micro- and Macroabrasion in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review and Case Study
Jose Villalobos-Tinoco, Carlos A. Jurado, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Nechama S. Citrin, Staley Colvert, Jose Luis Gutierrez-Quintero, Salwa Mekled
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(5): 183. CrossRef - Evaluation of demineralization changes in molar tissues in vitro using electrical impedance spectroscopy
V. D. Goncharov, M. A. Gorelikova, K. V. Shadrina, L. Yu. Orekhova, V. D. Berezkin, E. S. Nemovskaya, A. A. Petrov
Parodontologiya.2025; 30(3): 254. CrossRef
- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
- 5,544 View
- 149 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of maxillary premolar canal anatomy: Ahmed’s versus Vertucci’s classifications in a Jordanian cohort
- Raidan Ba-Hattab, Muna M. Shaweesh, Nessrin A. Taha, Elham S. Abu Alhaija
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e11. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study analyzed the root and canal configurations of maxillary premolars in a Jordanian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and classified them based on Vertucci’s and Ahmed’s systems.
Methods
Two hundred CBCT scans of 800 maxillary premolars were retrospectively assessed for root morphology, canal configurations, and root canal divergence and merging. Data was statistically analyzed.
Results
The study included 70 males and 130 females. Most right and left maxillary first premolars (RFPM, LFPM) had two roots (59.0% and 58.5%), with a significant association between sex and root number for RFPM and LFPM (p < 0.05). In contrast, the right and left maxillary second premolars (RSPM, LSPM) mostly had a single root (87.5% and 88.5%), with no association with sex. Vertucci’s classification showed type IV as the predominant configuration in first premolars (RFPM, 65.0% and LFPM, 67.0%) and type I in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%). A significant sex association was found only with RSPM. Ahmed’s classification revealed that maxillary premolar with two separated roots and two separated canals (2MP B1 P1) was mostly found in first premolars (RFPM, 58.0% and LFPM, 56.0%), and maxillary premolar with one root and one canal (1MP1) in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%), with a significant sex association for RSPM and LSPM (p < 0.05). Age had no impact, and symmetry was observed between the right and left sides. Three-rooted premolars were identified in four cases. Almost all of Vertucci’s types and numerous codes from Ahmed’s classification were documented.
Conclusions
CBCT revealed diverse anatomical variations in the Jordanian subpopulation, with Ahmed’s classification providing more detailed canal configurations than Vertucci’s, uncovering previously overlooked variations.
- 209 View
- 18 Download

- Shaping ability and cyclic fatigue resistance between Genius ProFlex, ZenFlex, and TruNatomy rotary systems: an experimental study
- Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Pedro Cesar Gomes Titato, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Carlos Alberto Spironelli Ramos, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e9. Published online February 13, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of three newly introduced rotary endodontic systems: Genius ProFlex (Medidenta), TruNatomy (Dentsply Maillefer), and ZenFlex (Kerr).
Methods
Forty-five mandibular molars with root canal curvatures <5° were utilized. Micro-computed tomography scans were performed pre- and post-preparation to assess apical transportation, centralization, percentage of dentin wear, and canal volume alterations. Eight instruments of each diameter underwent cyclic fatigue testing.
Results
The percentage of dentin wear on mesial and distal walls showed no significant differences among ZenFlex, TruNatomy, and Genius ProFlex at 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm from the apical foramen and root canal orifice (p > 0.05). Centering ability varied in the mesiolingual canal (p < 0.05). No notable differences were observed in transportation (p > 0.05). Genius ProFlex demonstrated lower volumetric changes (p < 0.05). There were significant differences in cyclic fatigue, with higher values for Genius ProFlex and lower values for TruNatomy (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The three nickel-titanium rotary instruments are safe and efficient for root canal preparation, with Genius ProFlex exhibiting superior cyclic fatigue resistance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Shaping Ability and Apical Debris Extrusion Using 4 Different Nickel–Titanium Single‐File Systems
Siyu Li, Mengzhen Tang, Xi Wang, Jian Yang, Hyun-Do Jung
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of Shaping Ability and Apical Debris Extrusion Using 4 Different Nickel–Titanium Single‐File Systems
- 3,136 View
- 175 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


