-
Ex vivo comparative analysis of retrievability among four calcium silicate-based sealers for regaining apical patency
-
Darian Shomali, Timothy Kirkpatrick, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Ji Wook Jeong
-
Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e3. Published online January 14, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e3
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
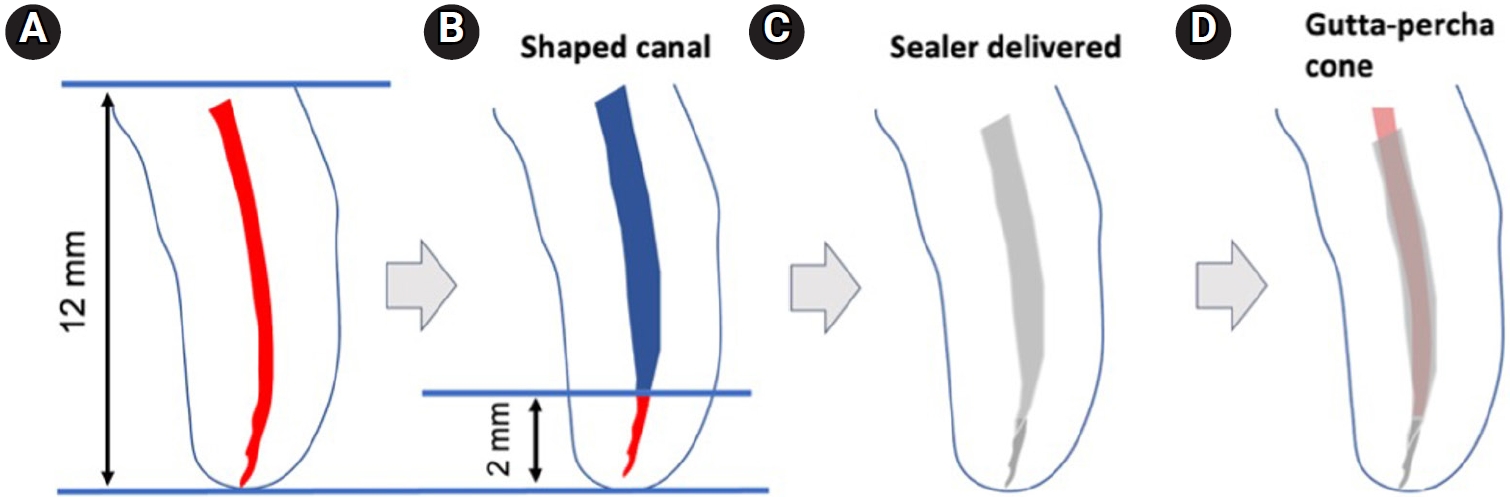
Efficient retrievability is a key requirement for endodontic sealers. This study evaluated the retrievability of four different calcium silicate-based sealers (CSS).
Methods
A total of 153 single-rooted human teeth with straight canals were decoronated to a standardized working length of 12 mm. The canals were negotiated to working length using K files up to size 15/.02, followed by rotary instrumentation up to 35/.04, 2 mm short of working length. The teeth were randomly assigned to five groups: NeoSEALER Flo (NEO; Avalon Biomed), Ceraseal (CS; Meta Biomed), Endosequence BC Sealer (BC; Brasseler USA), AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer (AHB; Dentsply Sirona), and a negative control group. Sealer application and obturation with a 35/.04 gutta-percha cone were performed. After incubation at 37°C in 100% humidity for 7 days, retreatment was performed until apical patency was obtained, with retrievability assessed by regaining apical patency. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey contrast test were used to determine whether there was a significant difference among the four different CSS (p < 0.05).
Results
Success rates in regaining apical patency were NEO (79.4%), CS (37.0%), BC (50.0%), and AHB (69.7%). NEO demonstrated the highest retrievability, while CS had the lowest (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
The type of CSS used has a considerable impact on retreatment difficulty. Among the tested sealers, Neo- SEALER Flo showed the highest retrievability, making it the most retrievable CSS in terms of retreatment efficacy.
-
Phase transformation temperatures influence the reduction ratio of fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium reciprocating files at body temperature: an in vitro experimental study
-
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Lola Pedèches, Sylvie Lê, Marie Georgelin-Gurgel, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Franck Diemer
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e35. Published online November 5, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e35
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
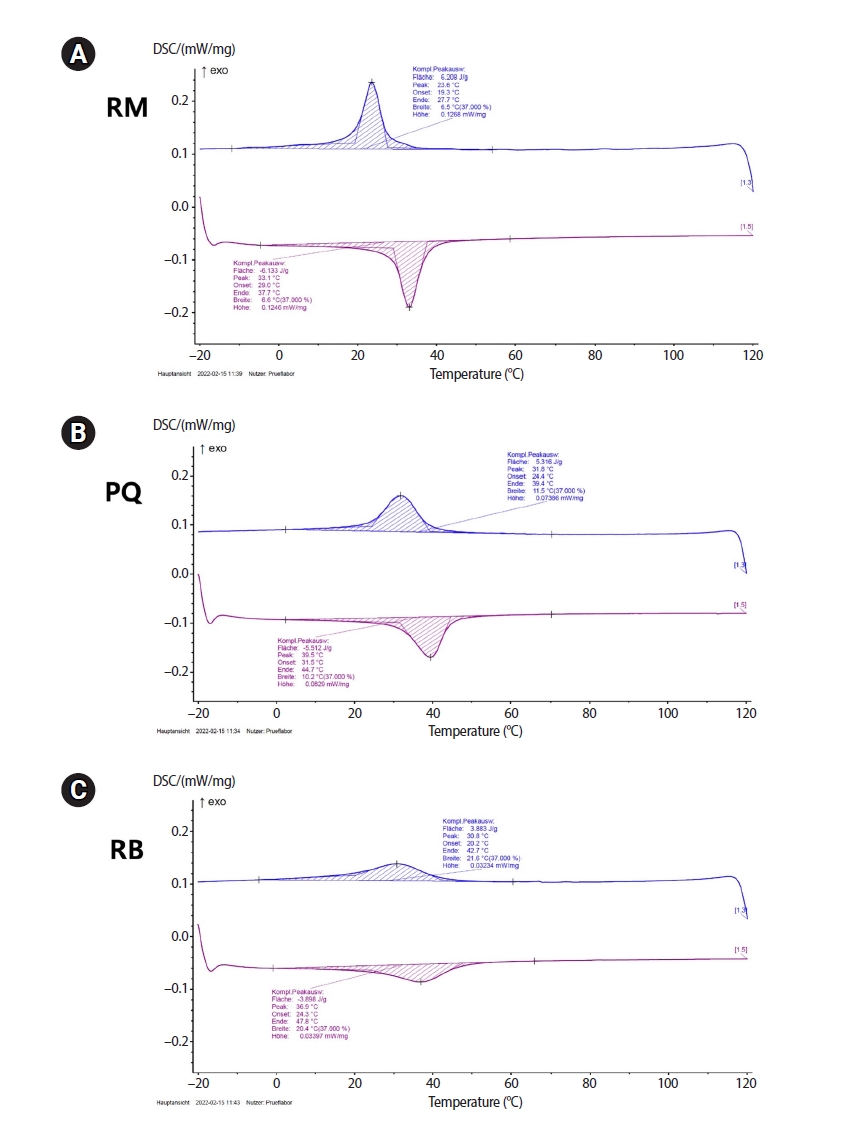
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of transformational temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance at body temperature of reciprocating file systems: R motion (RM), Procodile Q (PQ), and Reciproc Blue.
Methods
Resistance test was done in a custom-made device at room (20°C ± 1°C) and body (37°C ± 1°C) temperatures within a 60° angle of curvature and 5 mm radius of the artificial canal. The time to fracture (TTF) was recorded. The scanning electron microscope observation and differential scanning calorimetry analyses were performed. Two-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc comparison were applied at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
The results showed a significant influence of temperature on instrumental breakage, regardless of the file systems (p < 0.05). The TTF is significantly decreased at body temperature (p < 0.05). PQ showed the longest TTF in both temperature conditions (p < 0.05). RM demonstrated a significantly higher TTF reduction ratio compared to the other files (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Within the limitations of this study, the heat-treated files with reciprocating kinetics may have different reduction ratios of the fatigue resistance of the file systems under different temperature conditions. This characteristic is an important point of consideration when clinicians select the file system to reduce potential file fracture.
-
Shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen to the mandibular premolars in an Indian sub-population: a retrospective CBCT analysis
-
Komal Sheth, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, James L. Gutmann, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e1. Published online December 13, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
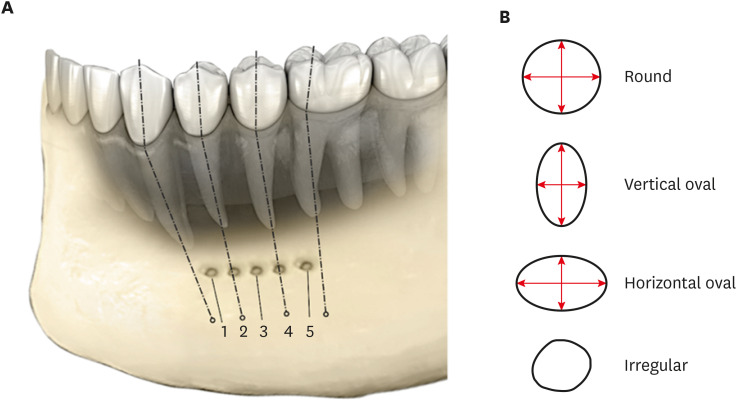
This study assessed the shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen (MF) to mandibular posterior teeth in an Indian sub-population. Materials and MethodsIn total, 475 existing cone-beam computed tomography records exhibiting 950 MFs and including the bilateral presence of mandibular premolars and first molars were assessed. Images were evaluated 3-dimensionally to ascertain the position, shape, and anatomical proximity of MFs to mandibular teeth. The position and shape of MFs were measured and calculated. The Pythagorean theorem was used to calculate the distance between the root apex of the mandibular teeth and the MF. ResultsMFs exhibited a predominantly round shape (left: 67% and right: 65%) followed by oval (left: 30% and right: 31%) in both males and females and in different age groups. The root apices of mandibular second premolars (left: 71% and right: 62%) were closest to the MF, followed by distal to the first premolars and mesial to the second premolars. The mean vertical distance between the MF and the nearest tooth apex calculated on sagittal sections was 2.20 mm on the right side and 2.32 mm on the left side; no significant difference was found according to sex or age. The distance between the apices of the teeth and the MF was ≥ 4 mm (left; 4.09 ± 1.27 mm and right; 4.01 ± 1.15 mm). ConclusionsThese findings highlight the need for clinicians to be aware of the location of the MF in treatment planning and while performing non-surgical and surgical endodontic procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Anatomical and radiographic assessment of variations of the mental foramen and their impact on success of local anaesthesia administration
Isratul Jannat, M. Ummay Salma, Nipu Rani Chowdhury, Kulsum Nahar, Dilruba Binte Mostafa, Khandokar Emanuzzaman Emon, Shahela Sarmin
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2026; 14(3): 823. CrossRef - Clinical Implications of the Localization and Morphological Variability of the Mental Foramen—A Systematic Review
Mariola Krzykawska-Krupska, Janusz Pach, Piotr Regulski, Jacek Tomczyk, Izabela Strużycka, Kazimierz Szopiński, Katarzyna Osipowicz, Anna Pogorzelska
Diagnostics.2026; 16(5): 779. CrossRef - Optimising Treatment Strategies: Labial versus Labio-inferior Plating Using Three-dimensional Miniplates for Mandibular Symphysis and Parasymphysis Fractures
Akash P Muralidharan, Kalyani Bhate, K Mithun Nilgiri, Sumithra S Nair, Lakshmi Shetty, Rose Johnson
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(2): 242. CrossRef - Morphometric analysis of mental foramen in retained cadaveric specimens of mandibles of Sri Lankan population
Dadallage Tharanga De Silva, Usliyanage Clifford Priyantha Perera
Anatomical Science International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional CBCT Study of Anterior Loop, Accessory Mental Foramen, and Lingual Foramina in Patients’ Mandibles: Implications for Safer Implant Planning
Abbas Shokri, Mohammad Mahdi Maleki, Leili Tapak
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiographic Recognition of Mental Nerve for Secured Dental Implant Placement by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Mosul City Population
Asmaa B. Al-Saffar, Mekdad H. Alrigbo, Rawaa Y. Al-Rawee
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(7): 2049. CrossRef - Accuracy of Implant Size Prediction Based on Edentulous Ridge Dimension on Cone-beam Computed Tomography - A Retrospective Study
Hunter R. Jolicoeur, Gerard A. Camargo, Tamara G. Stephenson, Wenjian Zhang
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Mental Foramenin Panoramik Radyografi ve Konik Işınlı Bilgisayarlı Tomografi Görüntüleri Üzerinde Morfolojik Analizi
Ezgi UZUN, Burak Kerem APAYDIN, Ayşen TİL
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(3): 540. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Possible Relationship between the Curvature and
Horizontal Course of the Inferior Alveolar Canal
Cansu G. Koca, M. Fatih Çiçek, Sanaz Sadry, Ozan Yenidünya, Fatma Akkoca Kaplan, Aras Erdil
Current Medical Imaging Formerly Current Medical Imaging Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,047
View
-
51
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
9
Crossref
-
Efficacy of reciprocating and rotary retreatment nickel-titanium file systems for removing filling materials with a complementary cleaning method in oval canals
-
Said Dhaimy, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Lamyae Bedida, Imane Benkiran
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e13. Published online February 3, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e13
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate and compare the efficacy of the S1 reciprocating system and the D-Race retreatment rotary system for filling material removal and the apical extrusion of debris. Materials and MethodsSixty-four freshly extracted maxillary canines were shaped with size 10 and size 15 K-files, instrumented using ProTaper Gold under irrigation with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), obturated according to the principle of thermo-mechanical condensation with gutta-percha and zinc oxide eugenol sealer, and allowed to set for 3 weeks at 37°C. Subsequently, the teeth were divided into a control group (n = 4), the D-Race rotary instrument group (n = 30), and the S1 reciprocating instrument group (n = 30). After classical retreatment, the canals were subjected to a complementary approach with the XP-Endo Shaper. Desocclusol was used as a solvent, and irrigation with 2.5% NaOCl was performed. Each group was divided into subgroups according to the timing of radiographic readings. The images were imported into a software program to measure the remaining filling material, the apical extrusion, and the root canal space. The data were statistically analyzed using the Z-test and JASP graphics software. ResultsNo significant differences were found between the D-Race and S1 groups for primary retreatment; however, using a complementary cleaning method increased the removal of remnant filling (p < 0.05). ConclusionsClassical removal of canal filling material may not be sufficient for root canal disinfection, although a complementary finishing approach improved the results. Nevertheless, all systems left some debris and caused apical extrusion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness of different supplementary protocols for remaining filling material removal in endodontic reintervention: an integrative review
Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Bruna Venzke Fischer, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Anna Victoria Costa Serique, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Odontology.2024; 112(1): 51. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Economic analysis of the different endodontic instrumentation techniques used in the Unified Health System
Laura Paredes Merchan, Livia Fernandes Probst, Ana Clara Correa Duarte Simões, Augusto Cesar Santos Raimundo, Yuri Wanderley Cavalcanti, Denise de Fátima Barros Cavalcante, João Victor Frazão Câmara, Antonio Carlos Pereira
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabrication of a Potential Electrodeposited Nanocomposite for Dental Applications
Chun-Wei Chang, Chen-Han Tsou, Bai-Hung Huang, Kuo-Sheng Hung, Yung-Chieh Cho, Takashi Saito, Chi-Hsun Tsai, Chia-Chien Hsieh, Chung-Ming Liu, Wen-Chien Lan
Inorganics.2022; 10(10): 165. CrossRef - Influence of Filling Material Remnants on the Diffusion of Hydroxyl Ions in Endodontically Retreated Teeth: An Ex Vivo Study
Vania Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Marilisa Carneiro Leao Gabardo, Natanael Henrique Ribeiro Mattos, Camila Paiva Perin, Liliane Roskamp, Cristiano Miranda de Araújo, Luiz Fernando Fariniuk, Flares Baratto–Filho
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(8): 768. CrossRef - Efficacy of Removing Thermafil and GuttaCore from Straight Root Canal Systems Using a Novel Non-Surgical Root Canal Re-Treatment System: A Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis
Vicente Faus-Llácer, Rubén Linero Pérez, Ignacio Faus-Matoses, Celia Ruiz-Sánchez, Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Salvatore Sauro, Vicente Faus-Matoses
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(6): 1266. CrossRef
-
2,099
View
-
37
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
-
Age-dependent root canal instrumentation techniques: a comprehensive narrative review
-
Michael Solomonov, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Avi Hadad, Dan Henry Levy, Joe Ben Itzhak, Oleg Levinson, Hadas Azizi
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e21. Published online March 4, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this article was to review age-dependent clinical recommendations for appropriate root canal instrumentation techniques. A comprehensive narrative review of canal morphology, the structural characteristics of dentin, and endodontic outcomes at different ages was undertaken instead of a systematic review. An electronic literature search was carried out, including the Medline (Ovid), PubMed, and Web of Science databases. The searches used controlled vocabulary and free-text terms, as follows: ‘age-related root canal treatment,’ ‘age-related instrumentation,’ ‘age-related chemo-mechanical preparation,’ ‘age-related endodontic clinical recommendations,’ ‘root canal instrumentation at different ages,’ ‘geriatric root canal treatment,’ and ‘pediatric root canal treatment.’ Due to the lack of literature with practical age-based clinical recommendations for an appropriate root canal instrumentation technique, a narrative review was conducted to suggest a clinical algorithm for choosing the most appropriate instrumentation technique during root canal treatment. Based on the evidence found through the narrative review, an age-related clinical algorithm for choosing appropriate instrumentation during root canal treatment was proposed. Age affects the morphology of the root canal system and the structural characteristics of dentin. The clinician’s awareness of root canal morphology and dentin characteristics can influence the choice of instruments for root canal treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Challenges Faced by Undergraduate Dental Students During Root Canal Treatment (RCT) and the Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients After RCT
Mubashir Baig Mirza, Abdullah Bajran Almuteb, Abdulaziz Tariq Alsheddi, Qamar Hashem, Mohammed Ali Abuelqomsan, Ahmed AlMokhatieb, Shahad AlBader, Abdullah AlShehri
Medicina.2025; 61(2): 215. CrossRef - OUTCOMES OF COMBINED ENDODONTIC TREATMENT AND APICAL SURGERY IN MANAGING LARGE PERIAPICAL CYSTS: A CLINICAL STUDY
Sapna Pandey, P Nihar, Amit Kumar, Nitin Bhagat, Vikram Karande, Zameer Pasha, Anukriti Kumari
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 329. CrossRef - El Uso del hipoclorito de sodio en endodoncia: concentración, temperatura y activación
Ábilson Josue Fabiani Ticona, Fernanda Camargo Espejo
Revista de investigación e información en salud.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Anatomical Dentin Thickness in Mandibular First Molar: An In Vivo Cone‐Beam Computed Tomographic Study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Jerry Jose, Mariangela Cernera, Parisa Soltani, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral Health Concerns of the ‘Sunset Age’
Pradnya V. Kakodkar, Amandeep Kaur, Shivasakthy Manivasakan, Sounyala Rayannavar, Revati Deshmukh, Smita Athavale
Journal of Medical Evidence.2023; 4(2): 141. CrossRef - Root canal treatment of a six-canal first mandibular molar with extensive periapical lesion: A case report
Xin Li, Shuyu Sun, Tengyi Zheng
Medicine.2023; 102(30): e34336. CrossRef - Endodontic Dentistry: Analysis of Dentinal Stress and Strain Development during Shaping of Curved Root Canals
Laura Iosif, Bogdan Dimitriu, Dan Florin Niţoi, Oana Amza
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2918. CrossRef - Mechanisms of age-related changes in the morphology of the pulp system of the first lower molars
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, V.A. Venediktova
Stomatologiya.2022; 101(2): 19. CrossRef
-
3,316
View
-
37
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Dentinal defects induced by 6 different endodontic files when used for oval root canals: an in vitro comparative study
-
Ajinkya M Pawar, Bhagyashree Thakur, Anda Kfir, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e31. Published online July 29, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e31
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
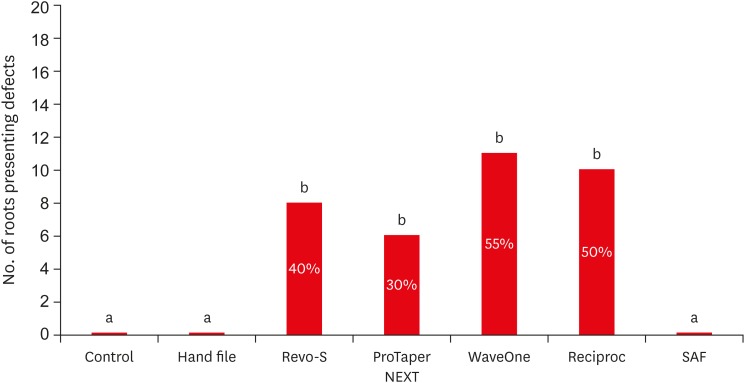
To compare the formation of dentinal defects using stainless-steel hand K-files (HFs), rotary files, reciprocating files, and Self-Adjusting File (SAF), when used for oval root canals. Materials and MethodsOne hundred and forty extracted human mandibular premolar with single root and oval canal were selected for this study. Oval canals were confirmed by exposing to mesio-distal and bucco-lingual radiographs. Teeth with open apices or anatomic irregularities were excluded. All selected teeth were de-coronated perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth, leaving roots segments approximately of 16 mm in length. Twenty teeth were left unprepared (control), and the remaining 120 teeth were divided into 6 groups (n = 20) and instrumented using HF (size 40/0.02), Revo-S (RS; size 40/0.06), ProTaper NEXT (PTN; size 40/0.06), WaveOne (WO; size 40/0.09), RECIPROC (RC; size 40/0.06), and the SAF (2 mm). Roots were then sectioned 3, 6, and 9 mm from the apex, and observed under stereomicroscope, for presence of dentinal defects. “No defect” was defined as root dentin that presented with no visible microcracks or fractures. “Defect” was defined by microcracks or fractures in the root dentin. ResultsThe control, HF, and SAF did not exhibit any dentinal defects. In roots instrumented by RS, PTN, WO, and RC files exhibited microcracks (incomplete or complete) in 40%, 30%, 55%, and 50%, respectively. ConclusionsThe motor-driven root canal instrumentation with rotary and reciprocating files may create microcracks in radicular dentine, whereas the stainless-steel hand file instrumentation, and the SAF produce minimal or less cracks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of dentinal crack formation during post space preparation using different fiber post systems with micro-computed tomography
Ayşe Nur Kuşuçar, Damla Kırıcı
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Computational Insights into Root Canal Treatment: A Survey of Selected Methods in Imaging, Segmentation, Morphological Analysis, and Clinical Management
Jianning Li, Kerstin Bitter, Anh Duc Nguyen, Hagay Shemesh, Paul Zaslansky, Stefan Zachow
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(12): 579. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using three different endodontic retreatment systems – An in vitro study
S. Aarthi, J. S. Sivakumar, A. Andamuthu Sivakumar, J. Saravanapriyan Soundappan, M. Chittrarasu, G. Jayanthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 262. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dentin Cracks by Stereomicroscope after Preparation of Mesiobuccal Canal of Maxillary First Molars Using Edge Taper Platinum and ProTaper Gold Rotary Files: A Laboratory Study
Narjes Hoshyari, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Eghlima Malakan, Abolfazl Hosseinnataj, Azam Haddadi Kohsar
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2023; 15(4): 167. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of dentinal defects after root canal preparation with different rotary and reciprocal systems
Ece Yakın, Berna Aslan, Emine Odabaşı Tezer
Northwestern Medical Journal.2023; 3(3): 147. CrossRef - Comparison of Dentinal Defects Induced by Rotary, Reciprocating, and Hand Files in Oval Shaped Root Canal - An In-Vitro Study
Harakh Chand Branawal, Neelam Mittal, Prachi Rani, Aiyman Ayubi, Silviya Samad
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2023; 34(4): 433. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using hand, rotary, and reciprocating files: An ex vivo study
Debanjan Das, Sudipto Barai, Rohit Kumar, Sourav Bhattacharyya, AsimB Maity, Pushpa Shankarappa
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(1): 78. CrossRef - Effect of XP‐endo Shaper versus conventional rotary files on postoperative pain and bacterial reduction in oval canals with necrotic pulps: a randomized clinical study
R. S. Emara, S. I. Gawdat, H. M. M. El‐Far
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1026. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Formation by Single Reciprocating File Systems: An In Vitro Study
Baby James, A Devadathan, Manuja Nair, Ashitha T Kulangara, Jose Jacob
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2020; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - The potential effect of instrumentation with different nickel titanium rotary systems on dentinal crack formation—An in vitro study
Márk Fráter, András Jakab, Gábor Braunitzer, Zsolt Tóth, Katalin Nagy, Andrej M. Kielbassa
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238790. CrossRef
-
2,014
View
-
24
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
The top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured instruments: a bibliometric analysis
-
Lora Mishra, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Priti Pragati Rath
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e2. Published online December 26, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e2
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this research was to identify the top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured or broken instruments and to perform a bibliometric analysis thereof. Materials and MethodsPublished articles related to fractured instruments were screened from online databases, such as Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect, and highly cited papers, with at least 50 citations since publication, were identified. The most-cited articles were selected and analysed with regard to publication title, authorship, the journal of publication, year, institution, country of origin, article type, and number of citations. ResultsThe top 10 most-cited articles were from various journals. Most were published in the Journal of Endodontics, followed by the International Endodontic Journal, and Dental Traumatology. The leading countries were Australia, Israel, Switzerland, the USA, and Germany, and the leading institution was the University of Melbourne. The majority of articles among the top 10 articles were clinical research studies (n = 8), followed by a basic research article and a non-systematic review article. ConclusionsThis bibliometric analysis revealed interesting information about scientific progress in endodontics regarding fractured instruments. Overall, clinical research studies and basic research articles published in high-impact endodontic journals had the highest citation rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Endodontide Mikro-Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Kullanımı Konusunda Yayımlanan Makalelerin Bibliyometrik Analizi: Nicel Araştırma
Özge Kurt, Emine Şimşek
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 18(3): 309. CrossRef - A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Top-Cited Articles on Vertical Root Fractures
Pillai Arun Gopinathan , Ikram UI Haq, Nawaf Alfahad, Saleh Alwatban, Abdullah Alghamdi, Amal Alamri, Kiran Iyer
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most‐cited case reports and case series in Endodontic journals
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Jelena Jacimovic, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(3): 185. CrossRef - The Most Highly Cited Publications on Basketball Originate From English-Speaking Countries, Are Published After 2000, Are Focused on Medicine-Related Topics, and Are Level III Evidence
Zachary D. Griffin, Jordan R. Pollock, M. Lane Moore, Kade S. McQuivey, Jaymeson R. Arthur, Anikar Chhabra
Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation.2022; 4(3): e891. CrossRef - Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Publication trends in micro‐CT endodontic research: a bibliometric analysis over a 25‐year period
U. Aksoy, M. Küçük, M. A. Versiani, K. Orhan
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(3): 343. CrossRef
-
1,634
View
-
10
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an in vitro study
-
Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):316-323. Published online October 31, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.316
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study compared the amount of apically extruded bacteria during the glide-path preparation by using multi-file and single-file glide-path establishing nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary systems. Materials and MethodsSixty mandibular first molar teeth were used to prepare the test apparatus. They were decoronated, blocked into glass vials, sterilized in ethylene oxide gas, infected with a pure culture of Enterococcus faecalis, randomly assigned to 5 experimental groups, and then prepared using manual stainless-steel files (group KF) and glide-path establishing NiTi rotary files (group PF with PathFiles, group GF with G-Files, group PG with ProGlider, and group OG with One G). At the end of canal preparation, 0.01 mL NaCl solution was taken from the experimental vials. The suspension was plated on brain heart infusion agar and colonies of bacteria were counted, and the results were given as number of colony-forming units (CFU). ResultsThe manual instrumentation technique tested in group KF extruded the highest number of bacteria compared to the other 4 groups (p < 0.05). The 4 groups using rotary glide-path establishing instruments extruded similar amounts of bacteria. ConclusionsAll glide-path establishment instrument systems tested caused a measurable apical extrusion of bacteria. The manual glide-path preparation showed the highest number of bacteria extruded compared to the other NiTi glide-path establishing instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Warley O. Silva, Jeferson O. Marques, Ana Carolina S.P. Guerra, Flávio R.F. Alves
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 866. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Multiple Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Severely Curved Mesial Roots of Mandibular Molars: An In Vitro Study
Niranjan Desai, Ashish S Bhadane, Nishant K Vyavahare, Dipali Y Shah, Akash S Kale, Simran K Chaudhari
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Impact of Different Glidepath Techniques on the Overall Performance of WaveOne Gold in an Artificial S-Shape Canal
Vlad Mircea Lup, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Carlo Gaeta, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 182. CrossRef - Influence of different irrigant activation methods on apical debris extrusion and bacterial elimination from infected root canals
KSadia Ada, Shibani Shetty, KB Jayalakshmi, PrasannaLatha Nadig, PG Manje Gowda, ArulK Selvan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of glide path files with different metallurgy on intracanal bacterial extrusion by HyFlex electrical discharge machining file
Priyanka Soni, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja, Anshi Jain
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 168. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris using Three Rotary and One Reciprocating Instrumentation Ni-Ti Systems
Maha Adnan Habeeb
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2022; 14(2): 93. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of a glide path creation necessity at the initial stages of endodontic treatment
Z. S. Khabadze, Yu. A. Generalova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Apically extruded debris produced during glide path preparation using R‐Pilot, WaveOne Gold Glider and ProGlider in curved root canals
Cangül Keskin, Özlem Sivas Yilmaz, Uğur Inan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(3): 439. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Glide Path Preparation Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Joo-Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(2): 199. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Postoperative pain after glide path preparation using manual, reciprocating and continuous rotary instruments: a randomized clinical trial
C. Keskin, Ö. Sivas Yilmaz, U. Inan, Ö. Özdemir
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(5): 579. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef - Effects of Different Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Curved Root Canals
Betul Gunes, Kubra Yesildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1191. CrossRef
-
1,690
View
-
13
Download
-
23
Crossref
-
Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
-
Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):216-223. Published online June 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.216
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare the mechanical properties of various nickel-titanium (NiTi) files with similar tapers and cross-sectional areas depending on whether they were surface-treated. Materials and MethodsThree NiTi file systems with a similar convex triangular cross-section and the same ISO #25 tip size were selected for this study: G6 (G6), ProTaper Universal (PTU), and Dia-PT (DPT). To test torsional resistance, 5 mm of the straightened file's tip was fixed between polycarbonate blocks (n = 15/group) and continuous clockwise rotation until fracture was conducted using a customized device. To evaluate cyclic fatigue resistance, files were rotated in an artificial curved canal until fracture in a dynamic mode (n = 15/group). The torsional data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey post-hoc comparison test, while the cyclic fatigue data were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test at a significance level of 95%. ResultsPTU showed significantly greater toughness, followed by DPT and G6 (p < 0.05). G6 showed the lowest resistance in ultimate torsional strength, while it showed a higher fracture angle than the other files (p < 0.05). In the cyclic fatigue test, DPT showed a significantly higher number of cycles to failure than PTU or G6 (p < 0.05). ConclusionsWithin the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that the torsional resistance of NiTi files was affected by the cross-sectional area, while the cyclic fatigue resistance of NiTi files was influenced by the surface treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
Abdulkadir ÖZŞAHİN, Meltem DARTAR ÖZTAN, Emine ODABAŞI TEZER
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Heat Treatment and Surface Treatment of Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Ya Shen, He Liu, Zhejun Wang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Markus Haapasalo
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,341
View
-
6
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
-
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):304-309. Published online November 8, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.304
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare the maximum screw-in forces generated during the movement of various Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) file systems. Materials and MethodsForty simulated canals in resin blocks were randomly divided into 4 groups for the following instruments: Mtwo size 25/0.07 (MTW, VDW GmbH), Reciproc R25 (RPR, VDW GmbH), ProTaper Universal F2 (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Next X2 (PTN, Dentsply Maillefer, n = 10). All the artificial canals were prepared to obtain a standardized lumen by using ProTaper Universal F1. Screw-in forces were measured using a custom-made experimental device (AEndoS-k, DMJ system) during instrumentation with each NiTi file system using the designated movement. The rotation speed was set at 350 rpm with an automatic 4 mm pecking motion at a speed of 1 mm/sec. The pecking depth was increased by 1 mm for each pecking motion until the file reach the working length. Forces were recorded during file movement, and the maximum force was extracted from the data. Maximum screw-in forces were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc comparison at a significance level of 95%. ResultsReciproc and ProTaper Universal files generated the highest maximum screw-in forces among all the instruments while M-two and ProTaper Next showed the lowest (p < 0.05). ConclusionsGeometrical differences rather than shaping motion and alloys may affect the screw-in force during canal instrumentation. To reduce screw-in forces, the use of NiTi files with smaller cross-sectional area for higher flexibility is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Restoration of teeth lacking complete ferrules using cast precious metal alloy post-and-cores and knife-edged crowns: A retrospective clinical study
Fangyue Xiang, Keying Shi, Haoyang Hua, Jing Zhao, Yuanna Zheng
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(5): 1729. CrossRef - Comparison of mechanical properties and shaping performance of ProGlider and ProTaper ultimate slider
Jeyi Song, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Treatment Prevents Effects of Downward Loads on the Screw-In Force Generation and Canal-Centering Ability of Nickel–Titanium Rotary Instruments
Keiichiro Maki, Arata Ebihara, Yanshan Luo, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Satoshi Omori, Shunsuke Kimura, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2025; 18(15): 3610. CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of rotation and insertion speeds of rotary Ni-Ti file on the vertical force and torque during root canal preparation: by a new automatic root canal shaping simulation method
Hyungwoo Lee, In-Bog Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(4): 221. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Effect of Core Mass and Alloy on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Different Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Instruments in Matching Artificial Canals
Sebastian Bürklein, Lennart Zupanc, David Donnermeyer, Karsten Tegtmeyer, Edgar Schäfer
Materials.2021; 14(19): 5734. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of torque and apical force to assess the cutting behaviour of ProTaper Next and ProTaper Universal endodontic instruments
Gustavo de Cristofaro Almeida, Diego Pinheiro Aun, Pedro Damas Resende, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Vicente Tadeu Lopes Buono, Maria Guiomar de Azevedo Bahia
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 52. CrossRef - Enhanced root canal-centering ability and reduced screw-in force generation of reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments with a post-machining thermal treatment
Keiichiro MAKI, Arata EBIHARA, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Kana MIYARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(2): 251. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Evaluation of stress distribution in nickel-titanium rotary instruments with different geometrical designs subjected to bending and torsional load: a finite element study
Manar Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of mechanical properties of WaveOne Gold Primary reciprocating instruments
Tong FANGLI, Keiichiro MAKI, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(3): 490. CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Gripping the Gripped: Removal of Foreign Bodies from Root Canal System
Shweta Jain, Sachin Jain, Shikha Jain, Sophia Thakur
Dental Research and Management.2019; : 13. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Orifice Preflaring Nickel-titanium Rotary Instrument Heat Treated Using T-Wire Technology
Maamoun Ataya, Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Rashid El Abed, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1867. CrossRef - How biomechanics can affect the endodontic treated teeth and their restorative procedures?
Carlos José Soares, Monise de Paula Rodrigues, André Luis Faria-e-Silva, Paulo Cesar Freitas Santos-Filho, Crisnicaw Veríssimo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Antheunis Versluis
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Nickel–titanium instruments in endodontics: a concise review of the state of the art
Giulio Gavini, Marcelo dos Santos, Celso Luis Caldeira, Manoel Eduardo de Lima Machado, Laila Gonzales Freire, Elaine Faga Iglecias, Ove Andrea Peters, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef
-
1,599
View
-
11
Download
-
27
Crossref
-
Preference of undergraduate students after first experience on nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
-
Sang Won Kwak, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):176-181. Published online June 23, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.176
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to compare two nickel-titanium systems (rotary vs. reciprocating) for their acceptance by undergraduate students who experienced nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments for the first time. Materials and MethodsEighty-one sophomore dental students were first taught on manual root canal preparation with stainless-steel files. After that, they were instructed on the use of ProTaper Universal system (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), then the WaveOne (WO, Dentsply Maillefer). They practiced with each system on 2 extracted molars, before using those files to shape the buccal or mesial canals of additional first molars. A questionnaire was completed after using each file system, seeking students' perception about 'Ease of use', 'Flexibility', 'Cutting-efficiency', 'Screwing-effect', 'Feeling-safety', and 'Instrumentation-time' of the NiTi files, relative to stainless-steel instrumentation, on a 5-point Likert-type scale. They were also requested to indicate their preference between the two systems. Data was compared between groups using t-test, and with Chi-square test for correlation of each perception value with the preferred choice (p = 0.05). ResultsAmong the 81 students, 55 indicated their preferred file system as WO and 22 as PTU. All scores were greater than 4 (better) for both systems, compared with stainless-steel files, except for 'Screwing-effect' for PTU. The scores for WO in the categories of 'Flexibility', 'Screwing-effect', and 'Feeling-safety' were significantly higher scores than those of PTU. A significant association between the 'Screwing-effect' and students' preference for WO was observed. ConclusionsNovice operators preferred nickel-titanium instruments to stainless-steel, and majority of them opted for reciprocating file instead of continuous rotating system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
B. Baracco, N. Escribano, D. Da Silva, V. Belliard, L. Ceballos, V. Fuentes
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Technical Quality and Students' Perception of Endodontic Preclinical Training Using Natural or LikeReal Artificial Teeth
Gabriela Biagioni, Fernanda Comodo, Marcelo Santos Coelho
European Journal of Dental Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Procedural Errors and Associated Factors among Undergraduate Dental Students: A Cross-sectional Study
Vivek Padmanabhan, Md Sofiqul Islam, Mohamed A Elsayed, Duaa R Saleh, Amal M Alnahdi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 24(12): 998. CrossRef - Clinicians’ perspectives, inducements, preferences, and clinical experiences regarding the use of electronic apex locator and apex locator integrated engine-driven instrumentation: a cross-sectional study
Sena Kaşıkçı, Sena Kolunsağ Özbek, Ebru Şirinoğlu, Olcay Özdemir
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Comparison of Manual and Mechanical Endodontic Instrumentation Completed by Undergraduate Dental Students on Endodontic Blocks
António Ginjeira, Abayomi O. Baruwa, Karla Baumotte
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(11): 363. CrossRef - The first experiences of preclinical dentistry students with rotary instruments: A pilot study
Işıl Kaya Büyükbayram, Gizem Çolakoğlu, Sana Mahroos Al-Shammari, Katia Stoicefidis
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 205. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Manual vs. Rotary/Reciprocating NiTi Instrumentation by Novice Dental Students on Simulated Root Canals
Ethan Smith, Olivia Davis
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2024; 4(2): 82. CrossRef - First Experience of an Undergraduate Dental Student with a Reciprocating System in Simulated Root Canals—A Pilot Study
Ana Rita Arede, Inês Ferreira, Ana Cristina Braga, Irene Pina-Vaz
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(8): 4848. CrossRef - Effect on undergraduate student self-confidence in using 3D printed primary molars for root canal treatment simulation training
C. Delfosse, T. Marquillier, S. Ndoye, P.-Y. Cousson, M. Hennequin, C. Catteau
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(1): 105. CrossRef - Influence of operator expertise on glide path and root canal preparation of curved root canals with rotary and reciprocating motions
Ana Belén Dablanca‐Blanco, Ana Arias, María José Ginzo‐Villamayor, María Consuelo Pérez, Pablo Castelo‐Baz, Benjamín Martín‐Biedma
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 37. CrossRef - Quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate students using nickel‐titanium reciprocating versus hand instruments
Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Pelin Güneri, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
Journal of Dental Education.2022; 86(12): 1662. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of endodontic mishaps in an undergraduate student clinic: a 2-year retrospective study
Manal Matoug-Elwerfelli, Ahmed Abdou, Wejdan Almutairi, Malak Alhuthayli, Shaikhah Aloyaynaa, Rahaf Almohareb
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13858. CrossRef - Ex vivo shaping ability of reciprocating instruments operated by new users: Reciproc versus WaveOne
Mary S. H. Lam, Jeffrey W. W. Chang, Gary S. P. Cheung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2791. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Undergraduate Students’ Acceptance of a Reciprocating One-File System for Endodontic Treatment
Benjamin Mahmoodi, Adriano Azaripour, Kawe Sagheb, Keyvan Sagheb, Brita Willershausen, Jens Weusmann
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(03): 393. CrossRef - Fracture of endodontic instruments - Part 1: Literature review on factors that influence instrument breakage
Maheshan Pillay, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2020; 75(10): 553. CrossRef - A comparative study of root canal shaping using protaper universal and protaper next rotary files in preclinical dental education
Gül Çelik, Feyza Özdemir Kısacık, Emir Faruk Yılmaz, Arife Mersinlioğlu, İhsan Furkan Ertuğrul, Hikmet Orhan
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7419. CrossRef - Undergraduate dentistry students’ perception of difficulties regarding endodontic treatment
Lorrane G. Tavares, Stella M. F. Lima, Miriane G. Lima, Marcos P. Arruda, Thiago C. Menegazzi, Taia M. B. Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 98. CrossRef - First Experience of Rotary Nickel Titanium Root Canal Instrumentation Performed by Undergraduate Students and General Dentists
marwa sharaan, Noreen Kamel, Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Care.2017; 3(2): 1. CrossRef
-
1,622
View
-
10
Download
-
19
Crossref
-
Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
-
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):123-127. Published online January 7, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.123
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Glide path preparation is recommended to reduce torsional failure of nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary instruments and to prevent root canal transportation. This study evaluated whether the repetitive insertions of G-files to the working length maintain the apical size as well as provide sufficient lumen as a glide path for subsequent instrumentation. Materials and MethodsThe G-file system (Micro-Mega) composed of G1 and G2 files for glide path preparation was used with the J-shaped, simulated resin canals. After inserting a G1 file twice, a G2 file was inserted to the working length 1, 4, 7, or 10 times for four each experimental group, respectively (n = 10). Then the canals were cleaned by copious irrigation, and lubricated with a separating gel medium. Canal replicas were made using silicone impression material, and the diameter of the replicas was measured at working length (D0) and 1 mm level (D1) under a scanning electron microscope. Data was analysed by one-way ANOVA and post-hoc tests (p = 0.05). ResultsThe diameter at D0 level did not show any significant difference between the 1, 2, 4, and 10 times of repetitive pecking insertions of G2 files at working length. However, 10 times of pecking motion with G2 file resulted in significantly larger canal diameter at D1 (p < 0.05). ConclusionsUnder the limitations of this study, the repetitive insertion of a G2 file up to 10 times at working length created an adequate lumen for subsequent apical shaping with other rotary files bigger than International Organization for Standardization (ISO) size 20, without apical transportation at D0 level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
Mahima Bharat Mehta, Anupam Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Ashwini A. Narayanan
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 101. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive up-and-down movements on torque/force generation, surface defects and shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: an ex vivo study
Moe Sandar Kyaw, Arata Ebihara, Yoshiko Iino, Myint Thu, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Pyae Hein Htun, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Number of Pecking Motions at Working Length on the Shaping Ability of Single-file Systems in Long Oval-shaped Curved Canals
Lixiao Wang, Ruitian Lin, Hui Chen, Zihan Li, Franklin R. Tay, Lisha Gu
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(4): 548. CrossRef - Influence of pecking frequency at working length on the volume of apically extruded debris: A micro-computed tomography analysis
Li-Xiao Wang, Hui Chen, Rui-Tian Lin, Li-Sha Gu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(3): 1274. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef
-
1,531
View
-
7
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
-
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):270-275. Published online July 16, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.270
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study compared the mechanical properties of various instruments for canal exploration and glide-path preparations. Materials and MethodsThe buckling resistance, bending stiffness, ultimate torsional strength, and fracture angle under torsional load were compared for C+ file (CP, Dentsply Maillefer), M access K-file (MA, Dentsply Maillefer), Mani K-file (MN, Mani), and NiTiFlex K-file (NT, Dentsply Maillefer). The files of ISO size #15 and a shaft length of 25 mm were selected. For measuring buckling resistance (n = 10), the files were loaded in the axial direction of the shaft, and the maximum load was measured during the files' deflection. The files (n = 10) were fixed at 3-mm from the tip and then bent 45° with respect to their long axis, while the bending force was recorded by a load cell. For measuring the torsional properties, the files (n = 10) were also fixed at 3-mm, and clockwise rotations (2-rpm) were applied to the files in a straight state. The torsional load and the distortion angle were recorded until the files succumbed to the torque. ResultsThe CP was shown to require the highest load to buckle and bend the files, and the NT showed the least. While MA and MN showed similar buckling resistances, MN showed higher bending stiffness than MA. The NT had the lowest bending stiffness and ultimate torsional strength (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe tested instruments showed different mechanical properties depending on the evaluated parameters. CP and NT files were revealed to be the stiffest and the most flexible instruments, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparison of torsional, bending, and buckling resistances of different nickel-titanium glide path files
Feyyaz Çeliker, İrem Çetinkaya
Matéria (Rio de Janeiro).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic 0.15 Stainless-Steel K-Files: Exploring Design, Composition, and Mechanical Performance
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(2): 29. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic ISO Size 06, 08, and 10 Stainless Steel K-Files Used for Glide Path Procedures
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 98. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Shaping Ability and Buckling Resistance of TruNatomy, WaveOne gold, and XP-Endo Shaper Single-File Systems
Neveen Ali Shaheen, Nahla Gamal Eldin Elhelbawy
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(3): 261. CrossRef - A comparison of different hand and rotary endodontic glide path files for buckling resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Pramod Mohite, Suvarna Patil, Nandita Bansal
Endodontology.2021; 33(2): 102. CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on color and flexibility of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
Bernardo Corrêa de ALMEIDA, Carlos Nelson ELIAS
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of buckling resistance of Proglider and One-G file: An in vitro study
Priyanka Himmatrao Patil, Meenal Nitin Gulve, Swapnil Janardan Kolhe
Endodontology.2018; 30(1): 21. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
-
2,554
View
-
46
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Cutting efficiency of apical preparation using ultrasonic tips with microprojections: confocal laser scanning microscopy study
-
Sang-Won Kwak, Young-Mi Moon, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):276-281. Published online July 22, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.276
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare the cutting efficiency of a newly developed microprojection tip and a diamond-coated tip under two different engine powers. Materials and MethodsThe apical 3-mm of each root was resected, and root-end preparation was performed with upward and downward pressure using one of the ultrasonic tips, KIS-1D (Obtura Spartan) or JT-5B (B&L Biotech Ltd.). The ultrasonic engine was set to power-1 or -4. Forty teeth were randomly divided into four groups: K1 (KIS-1D / Power-1), J1 (JT-5B / Power-1), K4 (KIS-1D / Power-4), and J4 (JT-5B / Power-4). The total time required for root-end preparation was recorded. All teeth were resected and the apical parts were evaluated for the number and length of cracks using a confocal scanning micrscope. The size of the root-end cavity and the width of the remaining dentin were recorded. The data were statistically analyzed using two-way analysis of variance and a Mann-Whitney test. ResultsThere was no significant difference in the time required between the instrument groups, but the power-4 groups showed reduced preparation time for both instrument groups (p < 0.05). The K4 and J4 groups with a power-4 showed a significantly higher crack formation and a longer crack irrespective of the instruments. There was no significant difference in the remaining dentin thickness or any of the parameters after preparation. ConclusionsUltrasonic tips with microprojections would be an option to substitute for the conventional ultrasonic tips with a diamond coating with the same clinical efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
-
1,545
View
-
9
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
-
Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):146-153. Published online August 23, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.146
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Aluminum step wedge (ASW) equivalent radiodensity (eRD) has been used to quantify restorative material's radiodensity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of image acquisition control (IAC) of a digital X-ray system on the radiodensity quantification under different exposure time settings. Materials and MethodsThree 1-mm thick restorative material samples with various opacities were prepared. Samples were radiographed alongside an ASW using one of three digital radiographic modes (linear mapping (L), nonlinear mapping (N), and nonlinear mapping and automatic exposure control activated (E)) under 3 exposure time settings (underexposure, normal-exposure, and overexposure). The ASW eRD of restorative materials, attenuation coefficients and contrasts of ASW, and the correlation coefficient of linear relationship between logarithms of gray-scale value and thicknesses of ASW were compared under 9 conditions. ResultsThe ASW eRD measurements of restorative materials by three digital radiographic modes were statistically different (p = 0.049) but clinically similar. The relationship between logarithms of background corrected grey scale value and thickness of ASW was highly linear but attenuation coefficients and contrasts varied significantly among 3 radiographic modes. Varying exposure times did not affect ASW eRD significantly. ConclusionsEven though different digital radiographic modes induced large variation on attenuation of coefficient and contrast of ASW, E mode improved diagnostic quality of the image significantly under the under-exposure condition by improving contrasts, while maintaining ASW eRDs of restorative materials similar. Under the condition of this study, underexposure time may be acceptable clinically with digital X-ray system using automatic gain control that reduces radiation exposure for patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Is the radiopacity of CAD/CAM aesthetic materials sufficient?
Rua S. Babaier, Modi S. Aldeeb, Nick Silikas, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2022; 38(6): 1072. CrossRef
-
1,662
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Multivariate analysis of the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation techniques in the canal and isthmus of mandibular posterior teeth
-
Yeon-Jee Yoo, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):154-159. Published online August 23, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.154
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation regimens in canal and isthmus of mandibular molars, and to evaluate the influence of related variables on cleaning efficacy of the irrigation systems. Materials and MethodsMesial root canals from 60 mandibular molars were prepared and divided into 4 experimental groups according to the final irrigation technique: Group C, syringe irrigation; Group U, ultrasonics activation; Group SC, VPro StreamClean irrigation; Group EV, EndoVac irrigation. Cross-sections at 1, 3 and 5 mm levels from the apex were examined to calculate remaining debris area in the canal and isthmus spaces. Statistical analysis was completed by using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test for comparison among groups, and multivariate linear analysis to identify the significant variables (regular replenishment of irrigant, vapor lock management, and ultrasonic activation of irrigant) affecting the cleaning efficacy of the experimental groups. ResultsGroup SC and EV showed significantly higher canal cleanliness values than group C and U at 1 mm level (p < 0.05), and higher isthmus cleanliness values than group U at 3 mm and all levels of group C (p < 0.05). Multivariate linear regression analysis demonstrated that all variables had independent positive correlation at 1 mm level of canal and at all levels of isthmus with statistical significances. ConclusionsBoth VPro StreamClean and EndoVac system showed favorable result as final irrigation regimens for cleaning debris in the complicated root canal system having curved canal and/or isthmus. The debridement of the isthmi significantly depends on the variables rather than the canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Efficacy of different irrigant activation techniques for cleaning root canal anastomosis
O. K. Montaser, D. M. Fayyad, N. Abdelsalam
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Heated distilled water with or without continuous ultrasonic irrigation improves final irrigation efficacy and reduces dentine erosion
Michelli Cássia dos Santos, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Bruno Henriques, Franklin R. Tay, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 103: 103507. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation during Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Petruţa E. Căpută, Anastasios Retsas, Lydwien Kuijk, Luis E. Chávez de Paz, Christos Boutsioukis
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 31. CrossRef - Irrigation effectiveness of continuous ultrasonic irrigation system: An ex vivo study
Ahmed JAMLEH, Hideaki SUDA, Carlos G. ADORNO
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure irrigation versus syringe irrigation: a systematic review of cleaning and disinfection of the root canal system
E. Konstantinidi, Z. Psimma, L. E. Chávez de Paz, C. Boutsioukis
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(11): 1034. CrossRef - Effect of Different Agitation Techniques on the Penetration of Irrigant and Sealer into Dentinal Tubules
Yu Gu, Hiran Perinpanayagam, David J.W. Jin, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Jin-Sun Jeong, Sang-Min Lim, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2017; 35(2): 71. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Sonic, Ultrasonic, and Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming Activation of NaOCl on Filling Material Removal Following Retreatment in Oval Canal Anatomy
Shan Jiang, Ting Zou, Dongxia Li, Jeffery W.W. Chang, Xiaojing Huang, Chengfei Zhang
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2016; 34(1): 3. CrossRef -
Efficacy of Needle, Ultrasonic, and Endoactivator Irrigation and Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming in Removing Calcium Hydroxide from the Main Canal and Isthmus: An
In Vitro
Micro-Computed Tomography and Scanning
Dongxia Li, Shan Jiang, Xingzhe Yin, Jeffrey Wen Wei Chang, Jie Ke, Chengfei Zhang
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2015; 33(6): 330. CrossRef - Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 143. CrossRef
-
1,303
View
-
1
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Comparison of the centering ability of Wave·One and Reciproc nickel-titanium instruments in simulated curved canals
-
Young-Jun Lim, Su-Jung Park, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):21-25. Published online February 26, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of newly marketed single-file instruments, Wave·One (Dentsply-Maillefer) and Reciproc (VDW GmbH), in terms of maintaining the original root canal configuration and curvature, with or without a glide-path. Materials and MethodsAccording to the instruments used, the blocks were divided into 4 groups (n = 10): Group 1, no glide-path / Wave·One; Group 2, no glide-path / Reciproc; Group 3, #15 K-file / Wave·One; Group 4, #15 K-file / Reciproc. Pre- and post-instrumented images were scanned and the canal deviation was assessed. The cyclic fatigue stress was loaded to examine the cross-sectional shape of the fractured surface. The broken fragments were evaluated under the scanning electron microscope (SEM) for topographic features of the cross-section. Statistically analysis of the data was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test (α = 0.05). ResultsThe ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1 and 2 mm levels was significantly lower in Group 1 (p < 0.05). The centering ratio at 3, 5, and 7 mm level were not significantly different. ConclusionsThe Wave·One file should be used following establishment of a glide-path larger than #15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of ProTaper, Mtwo, WaveOne, and Reciproc Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: In Vitro Study
M Remya, Asha Joseph, Prabath Singh, Anju Varughese, Pallavi Chandran, Deepthy Subramanian, S Vijay Kumar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(6): 589. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Canal transportation and centering ability of root canals prepared using rotary and reciprocating systems with and without PathFiles in cone-beam computed tomography-based three-dimensional molar prototypes
MSruthi Sunildath, Josey Mathew, Liza George, RV Vineet, Priya Thomas, Dhanya John
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 246. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciproc R25 File and Mtwo System Used in Continuous and Reciprocating Motion
Vincenzo Campanella, Leonardo Gianni, Antonio Libonati, Gianni Gallusi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(2): 171. CrossRef - Canal shaping with a reciprocating system is easy to learn
E. Muñoz, L. Forner, S. Garcet, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, C. Llena
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1244. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of HyFlex EDM and ProTaper Next Rotary Instruments in Curved Root Canals: A Micro-CT Study
Ahmed K Turkistani, Madiha M Gomaa, Lubna A Shafei, Loai Alsofi, Abdul Majeed, Emad AlShwaimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(6): 680. CrossRef - Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of ProTaper Next and 2Shape nickel–titanium files in simulated severe curved canals
Simone Staffoli, Taha Özyürek, Avi Hadad, Alex Lvovsky, Michael Solomonov, Hadas Azizi, Joe Ben Itzhak, Maurizo Bossù, Nicola M. Grande, Gianluca Plotino, Antonella Polimeni
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2018; 32(2): 52. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Rotary endodontics in primary teeth – A review
Sageena George, S. Anandaraj, Jyoti S. Issac, Sheen A. John, Anoop Harris
The Saudi Dental Journal.2016; 28(1): 12. CrossRef - Performance of Three Single Instrument Systems in the Preparation of Long Oval Canals
Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Fredson Marcio Acris de Carvalho, Flares Baratto-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2016; 27(2): 217. CrossRef - Quantitative transportation assessment in curved canals prepared with an off-centered rectangular design system
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal SILVA, Vania Cristina Gomes VIEIRA, Michele Dias Nunes TAMEIRÃO, Felipe Gonçalves BELLADONNA, Aline de Almeida NEVES, Erick Miranda SOUZA, Gustavo DE-DEUS
Brazilian Oral Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Cervical and Apical Enlargement Associated with the WaveOne System on the Transportation and Centralization of Endodontic Preparations
Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Kauhanna Vianna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 626. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Brushing Motion on the Cutting Behavior of 3 Reciprocating Files in Oval-shaped Canals
Shereen Alattar, Walid Nehme, Franck Diemer, Alfred Naaman
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 703. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue of instruments for endodontic glide path
Gianluca Gambarini, Gianluca Plotino, GianPaolo Sannino, Nicola Maria Grande, Alessio Giansiracusa, Lucila Piasecki, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Dina Al-Sudani, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2015; 103(1): 56. CrossRef - Influence of the glide path on various parameters of root canal prepared with WaveOne reciprocating file using cone beam computed tomography
Anil Dhingra, Nidhi Nagar, Vipul Sapra
Dental Research Journal.2015; 12(6): 534. CrossRef - Apical Transportation, Centering Ability, and Cleaning Effectiveness of Reciprocating Single-file System Associated with Different Glide Path Techniques
Guilherme Moreira de Carvalho, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Junior, Angela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido, Raphael Carlos Comelli Lia, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, André Augusto Franco Marques
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 2045. CrossRef - Influence of cervical preflaring on apical transportation in curved root canals instrumented by reciprocating file systems
Neisiana Barbieri, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marina Samara Baechtold, Gisele Maria Correr, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, João César Zielak, Flares Baratto-Filho
BMC Oral Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Assessment of Reciprocation in Endodontic Preparation: A Comprehensive Review—Part II: Properties and Effectiveness
Gianluca Plotino, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Nicola Maria Grande, Stephen Cohen, Frédéric Bukiet
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 1939. CrossRef - Influence of flexion angle of files on the decentralization of oval canals during instrumentation
Maria Antonieta Veloso Carvalho de OLIVEIRA, Letícia Duarte ALVES, Analice Giovani PEREIRA, Luís Henrique Araújo RAPOSO, João Carlos Gabrielli BIFFI
Brazilian Oral Research.2015; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Quantitative Transportation Assessment in Simulated Curved Canals Prepared with an Adaptive Movement System
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Michele Dias Nunes Tameirão, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1125. CrossRef - Efficacy of reciprocating and rotary systems for removing root filling material: A micro-computed tomography study
D. Helvacioglu-Yigit, A. Yilmaz, G. Kiziltas-Sendur, O. S. Aslan, P. V. Abbott
Scanning.2014; 36(6): 576. CrossRef - Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 104. CrossRef - Performance of RaCe Instrumentation System in Curved Root Canals: A Comprehensive Analysis by Three Study Methods
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Gilson Blitzkow Sydney, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Flares Baratto-Filho, Samantha Schaffer Pugsley Baratto, Paulo Sergio Cerri
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 230. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 167. CrossRef
-
1,661
View
-
8
Download
-
29
Crossref
-
Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
-
Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):31-35. Published online February 26, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.31
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium (NiTi) files obtained in a conventional test using a simulated canal with a newly developed method that allows the application of constant fatigue load conditions. Materials and MethodsProFile and K3 files of #25/.06, #30/.06, and #40/.04 were selected. Two types of testing devices were built to test their fatigue performance. The first (conventional) device prescribed curvature inside a simulated canal (C-test), the second new device exerted a constant load (L-test) whilst allowing any resulting curvature. Ten new instruments of each size and brand were tested with each device. The files were rotated until fracture and the number of cycles to failure (NCF) was determined. The NCF were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Duncan's post-hoc test for each method. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was computed to examine any association between methods. ResultsSpearman's rank correlation coefficient (ρ = -0.905) showed a significant negative correlation between methods. Groups with significant difference after the L-test divided into 4 clusters, whilst the C-test gave just 2 clusters. From the L-test, considering the negative correlation of NCF, K3 gave a significantly lower fatigue resistance than ProFile as in the C-test. K3 #30/.06 showed a lower fatigue resistance than K3 #25/.06, which was not found by the C-test. Variation in fatigue test methodology resulted in different cyclic fatigue resistance rankings for various NiTi files. ConclusionsThe new methodology standardized the load during fatigue testing, allowing determination fatigue behavior under constant load conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fracture Resistance of Heat-treated NiTi Instruments by the Load of Mechanical Preparation According to Tooth Type and Canal Number
Badria AlAli, Amre Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Fatemeh Ahmad, Amar H. Khamis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Rashid El Abed
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - File-Specific Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of NiTi Instruments After Repeated Use in Simulated Canals: Patterns Compatible with Potential Stress-Induced Martensite Transformation Effects
Hyeonu Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2026; 19(5): 866. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeFile X7, 2Shape, and F-one nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
ArkanH Al-Amidi, HikmetAbdul-Rahim Al-Gharrawi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 26. CrossRef - Investigation of cyclic fatigue of rotary endodontic instruments
Z. S. Khabadze, F. R. Ismailov
Endodontics Today.2022; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Instruments under Different Temperature Conditions
Hyo Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2021; 14(18): 5295. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 216. CrossRef - Effect from Rotational Speed on Torsional Resistance of the Nickel-titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung Kyo Kim, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 443. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Conditioning of root canal anatomy on static and dynamics of nickel-titanium rotary instruments
Italo Di Giuseppe, Davide Di Giuseppe, Vito Antonio Malagnino, Enrico Paolo Silla, Francesco Somma
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 58. CrossRef - Effect from surface treatment of nickel‐titanium rotary files on the fracture resistance
Bo Hoon Kim, Jung‐Hong Ha, Woo Cheol Lee, Sang‐Won Kwak, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of alloy type on the life‐time of torsion‐preloaded nickel‐titanium endodontic instruments
Jung‐Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Gary Shun‐Pan Cheung, Seong Hwa Jeong, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(3): 172. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Elastic Limits in Torsion of Reciprocating Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Seo-Ryeong Kim, Antheunis Versluis, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jin-Woon Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 715. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Safety of the Factory Preset Rotation Angle of Reciprocating Instruments
Jin-Woon Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Antheunis Versluis, Sang-Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(10): 1671. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals
Oscar Faciola Pessoa, Juliana Melo da Silva, Giulio Gavini
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(2): 117. CrossRef - Methods and models to study nickel–titanium instruments
Ya Shen, Gary S.P. Cheung
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 18. CrossRef - An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
Huimin Zhou, Bin Peng, Yu‐Feng Zheng
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 42. CrossRef
-
1,645
View
-
5
Download
-
19
Crossref
-
A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
-
WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):201-206. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.201
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose was to investigate the preference and usage technique of NiTi rotary instruments and to retrieve data on the frequency of re-use and the estimated incidence of file separation in the clinical practice among general dentists. Materials and MethodsA survey was disseminated via e-mail and on-site to 673 general dentists. The correlation between the operator's experience or preferred technique and frequency of re-use or incidence of file fracture was assessed. ResultsA total of 348 dentists (51.7%) responded. The most frequently used NiTi instruments was ProFile (39.8%) followed by ProTaper. The most preferred preparation technique was crown-down (44.6%). 54.3% of the respondents re-used NiTi files more than 10 times. There was a significant correlation between experience with NiTi files and the number of reuses (p = 0.0025). 54.6% of the respondents estimated experiencing file separation less than 5 times per year. The frequency of separation was significantly correlated with the instrumentation technique (p = 0.0003). ConclusionsA large number of general dentists in Korea prefer to re-use NiTi rotary files. As their experience with NiTi files increased, the number of re-uses increased, while the frequency of breakage decreased. Operators who adopt the hybrid technique showed less tendency of separation even with the increased number of re-use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
Chiaki Akiba Katz, Misaki Fujimoto, Hidetaka Kuroda, Koichiro Muromachi
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 321. CrossRef - Adoption of rotary instrumentation among general practitioners in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey
Badi B. Alotaibi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Undergraduate Endodontic Training and Its Relation to Contemporary Practice: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia
Fahda N. Algahtani, Reem M. Barakat, Lujain M. Alqarni, Alanoud F. Alqabbani, Manal F. Alkadi, Rahaf A. Almohareb, André Luiz Ferreira Costa
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Fracture Incidence of Kedo-S Square Pediatric Rotary Files: A Prospective Clinical Study
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Satish Vishwanathaiah
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 594. CrossRef - Prevention and management of fractured instruments in endodontic treatment
Wei-Rong Tang
World Journal of Surgical Procedures.2015; 5(1): 82. CrossRef - Influence of operator's experience level on lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in extracted teeth
Abdulrahman Mohammed Saleh, Saeid Tavanafar, Pouyan Vakili-Gilani, Noor Jamal Al Sammerraie, Faahim Rashid
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 222. CrossRef
-
2,062
View
-
11
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
-
Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):203-210. Published online May 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.203
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of various application methods of one-step self-etch adhesives to microtensile resin-dentin bond strength.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-six extracted human molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to twelve groups (n = 15), according to the three different adhesive systems (Clearfil Tri-S Bond, Adper Prompt L-Pop, G-Bond) and application methods. The adhesive systems were applied on the dentin as follows: 1) The single coating, 2) The double coating, 3) Manual agitation, 4) Ultrasonic agitation. Following the adhesive application, light-cure composite resin was constructed. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and prepared 15 specimens per groups. Then microtensile bond strength was measured and the failure mode was examined.
Results
Manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating and double coating did. Double coating of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating did and there was no significant difference between the manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation group. There was significant difference in microtensile bonding strength among all adhesives and Clearfil Tri-S Bond showed the highest bond strength.
Conclusions
In one-step self-etching adhesives, there was significant difference according to application methods and type of adhesives. No matter of the material, the manual or ultrasonic agitation of the adhesive showed significantly higher microtensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
Nuray Zulkadir Ergin, Aslı Seçilmiş
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 16(3): 356. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef
-
2,064
View
-
13
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Effect of the difference in spectral outputs of the single and dual-peak LEDs on the microhardness and the color stability of resin composites
-
Hye-Jung Park, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):108-113. Published online March 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.108
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
To determine the effect of the spectral output of single and dual-peak light emitting diode (LED) curing lights on the microhardness and color stability of commercial resin composites formulated with camphorquinone and alternative photoinitiators in combination.
Materials and Methods
Three light-polymerized resin composites (Z100 (3M ESPE), Tetric Ceram (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Aelite LS Posterior (Bisco)) with different photoinitiator systems were used. The resin composites were packed into a Teflon mold (8 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness) on a cover glass. After packing the composites, they were light cured with single-peak and dual-peak LEDs. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and color difference (ΔE) for 30 days were measured. The data was analyzed statistically using a student's t-test (p < 0.05).
Results
All resin composites showed improved microhardness when a third-generation dual-peak LED light was used. The color stability was also higher for all resin composites with dual-peak LEDs. However, there was a significant difference only for Aelite LS Posterior.
Conclusions
The dual-peak LEDs have a beneficial effect on the microhardness and color stability of resin composites formulated with a combination of camphorquinone and alternative photoinitiators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of irradiance from curing units on the microhardness of composite - a systematic review
Neenu Francis, Rakesh R. Rajan, Vijay Kumar, Anju Varughese, Vineetha Karuveetil, C. M. Sapna
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography evaluation of volumetric polymerization shrinkage and degree of conversion of composites cured by various light power outputs
Pablo J. ATRIA, Camila S. SAMPAIO, Eduardo CÁCERES, Jessica FERNÁNDEZ, Andre F. REIS, Marcelo GIANNINI, Paulo G. COELHO, Ronaldo HIRATA
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(1): 33. CrossRef - Effect of the irradiance distribution from light curing units on the local micro-hardness of the surface of dental resins
Thomas Haenel, Berenika Hausnerová, Johannes Steinhaus, Richard B.T. Price, Braden Sullivan, Bernhard Moeginger
Dental Materials.2015; 31(2): 93. CrossRef - 1,3-Butadiene as an Adhesion Promoter Between Composite Resin and Dental Ceramic in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Jet
Geum-Jun Han, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Kyu Hwan Oh, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2013; 33(2): 539. CrossRef - Optimal combination of 3-component photoinitiation system to increase the degree of conversion of resin monomers
Chang-Gyu Kim, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 313. CrossRef
-
1,342
View
-
3
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
-
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):1-11. Published online January 14, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
Introduction:
The aim of this paper is to discuss the mechanical and geometric features of Nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files and its clinical effects. NiTi rotary files have been introduced to the markets with their own geometries and claims that they have better ability for the root canal shaping than their competitors. The contents of this paper include the (possible) interrelationship between the geometries of NiTi file (eg. tip, taper, helical angle, etc) and clinical performance of the files as follows;
- Fracture modes of NiTi rotary files
- Non-cutting guiding tip and glide path
- Taper and clinical effects
- Cross-sectional area and clinical effects
- Heat treatments and surface characteristics
- Screw-in effect and preservation of root dentin integrity
- Designs for reducing screw-in effect
Conclusions:
Based on the reviewed contents, clinicians may have an advice to use various brands of NiTi rotary instruments regarding their advantages which would fit for clinical situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 31. CrossRef
-
2,939
View
-
80
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Management of white spots: resin infiltration technique and microabrasion
-
Jeong-Hye Son, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):66-71. Published online January 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.66
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This case report compared the effectiveness of resin infiltration technique (Icon, DMG) with microabrasion (Opalustre, Ultradent Products, Inc.) in management of white spot lesions. It demonstrates that although neither microabrasion nor resin infiltration technique can remove white spot lesions completely, resin infiltration technique seems to be more effective than microabrasion. Therefore resin infiltration technique can be chosen preferentially for management of white spot lesions and caution should be taken for case selection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Resin Infiltration for the Esthetic Improvement of Dental Fluorosis and White Spots: A Case Report
Sumayyah L Alkhudhayri, Shahad L Alhassani, Nada A AbdelAleem
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - White spot lesions in fixed orthodontic treatment: Etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and future research perspectives
Suma Shankarappa, Jerusha Titus Burk, Pradeep Subbaiah, Raghunath Nagasundara Rao, Vidya Gowdappa Doddawad
Journal of Orthodontic Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - White Spot Lesions in Fixed Orthodontics: A Literature Review on Etiology, Prevention, and Treatment
Deem Al-Blaihed, Omar El Meligy, Khlood Baghlaf, Rabab A Aljawi, Shahad Abudawood
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of low-viscosity resin infiltration (Icon) on color change of enamel white spot lesions: 1-year follow-up clinical study
Mohamed. H. Zaazou, Reham S. Saleh, Shahinaz N. Hassan, Ali Abdelnabi, Zeinab M. Zaki, Tamer M. Hamdy, Dalia Y. Zaki, Lamiaa M. Moharam
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual tooth segmentation in human teeth images using pseudo edge-region obtained by deep neural networks
Seongeun Kim, Chang-Ock Lee
Signal Processing: Image Communication.2024; 120: 117076. CrossRef - Surface topography and spectrophotometric assessment of white spot lesions restored with nano-hydroxyapatite-containing universal adhesive resin: an in-vitro study
Neven S. Aref, Rahaf M. Alsdrani
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Infiltrating Resins, Noninvasive Treatment of White Spot Lesions: A Case Report
Rubén Darío Miranda-Carreño, Jacqueline Adelina Rodríguez-Chávez, Abigailt Flores-Ledesma
Journal of Oral Health and Community Dentistry.2023; 17(2): 75. CrossRef - Management of Turner's Hypoplasia Using Resin Infiltration: A Case Report
Dhruvi Solanki, Punit Fulzele, Nilima Thosar, Unnati Shirbhate
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study)
Abdulaziz Alhotan, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Saleh Alhijji, Merry Angelyn Tan De Vera, Aref Sufyan, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Tamer M. Hamdy
Polymers.2023; 15(14): 3068. CrossRef - Effect of Resin Infiltration and Microabrasion on the Microhardness of the Artificial White Spot Lesions (An in Vitro Study)
Reem Majeed H.J. Al-Mamoori, Aseel Haidar M.J. Al Haidar
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2022; 34(1): 44. CrossRef - Effect of sodium fluoride plus tricalcium phosphate with and without CO2 laser on remineralization of white spot lesions
Nouran M. Eissa, Eman M. Elshourbagy, Nahla E. Gomaa
Heliyon.2022; 8(10): e10752. CrossRef - Efficacy of Resin Infiltration and Fluoride Casein Phosphopeptide Amorphous Calcium Phosphate Varnish on Non-cavitated Active White Spot Lesions in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Mohit Dhamija, Rish Tyagi, Namita Kalra, Amit Khatri
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual Tooth Segmentation in Human Teeth Images Using Pseudo Edge-Region Obtained by Deep Neural Networks
Seongeun Kim, Chang-Ock Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro, Influence Of In-Office Dental Whitening On The Color Of Teeth Treated With Resin Infiltration
Basil Almutairi, Mohammed Al-Refai, Bander AL-Meshary, Abdulrahman Al-Asim, Fahad Al-Sharidah, Abdullah Alshehri
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(4): 6. CrossRef - Evaluation of color changes of white spot lesions treated with three different treatment approaches: an in-vitro study
Shaza M. Hammad, Noha A. El-Wassefy, Mohamed A. Alsayed
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(1): 26. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric Evaluation of Color Change in Tooth Enamel Defects Using Resin Infiltrate: An In Vivo Study
Anil Gupta, Shikha Dogra, Sakshi Joshi, Vimanyu Kataria, Jyotika Saini, Monika Nagpal, Payal Narula
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(2): 150. CrossRef - Erosion Infiltration in the Management of Molar‐Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH) Defects
Rym Mabrouk, Souha Yahia, Afef Oueslati, Nadia Frih, Yuk Kwan Chen
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pediatric Dentists’ Educational Experiences, Attitudes, and Professional Behavior Concerning Resin Infiltration: Implications for Dental Education
Michael Jordan Halcomb, Marita R. Inglehart, Elisabeta Karl
Journal of Dental Education.2020; 84(3): 290. CrossRef - Esthetic improvements of postorthodontic white-spot lesions treated with resin infiltration and microabrasion: A split-mouth, randomized clinical trial
Xi Gu, Lin Yang, Deqin Yang, Yuan Gao, Xiaolei Duan, Xin Zhu, He Yuan, Jiyao Li
The Angle Orthodontist.2019; 89(3): 372. CrossRef - Effect of resin infiltration on the color and microhardness of bleached white‐spot lesions in bovine enamel (an in vitro study)
Sidika Aynur Horuztepe, Meserret Baseren
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2017; 29(5): 378. CrossRef - Effect of Resin Infiltration on Artificial Caries: Anin vitroEvaluation of Resin Penetration and Microhardness
Deepesh Prajapati, Rashmi Nayak, Deepika Pai, Nagraj Upadhya, Vipin K Bhaskar, Pujan Kamath
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef - Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry
Hee-Jin Kim, Lorena Karanxha, Su-Jung Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 236. CrossRef - Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 90. CrossRef
-
4,429
View
-
39
Download
-
24
Crossref
-
Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
-
Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):445-452. Published online November 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.445
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare apical sealing ability and physical properties of MTA, MTA - AH-plus mixture (AMTA) and experimental Portland cement - Epoxy resin mixture (EPPC) for a development of a novel retro-filling material.
Materials and Methods
Forty-nine extracted roots were instrumented and filled with gutta-percha. Apical root was resected at 3 mm and the retro-filling cavity was prepared for 3 mm depth. Roots were randomly divided into 3 groups of 15 roots each. The retro-filling was done using MTA, AMTA, and EPPC as the groups divided. Four roots were used as control groups. After setting in humid condition for 24 hours, the roots were immersed in 1% methylene blue dye solution for 72 hours to test the apical leakage. After immersion, the roots were vertically sectioned and photos were taken to evaluate microleakage. Setting times were measured with Vicat apparatus and digital radiographs were taken to evaluate aluminum equivalent thickness using aluminum step wedge. The results of microleakage and setting time were compared between groups using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's post-hoc comparison at the significance level of 95%.
Results
AMTA and EPPC showed less microleakage than MTA group (p < 0.05). AMTA showed the highest radio-opacity than other groups and the novel EPPC showed 5 mm aluminum thickness radio-opacity. EPPC showed the shortest initial and final setting times than other groups while the MTA showed the longest (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Under the condition of this study, the novel composite using Portland cement-Epoxy resin mixture may useful for retro-filling with the properties of favorable leakage resistance, radio-opacity and short setting time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
Jing-Ling Che, Jae-Hwan Kim, Seon-Mi Kim, Nam-ki Choi, Hyun-Joo Moon, Moon-Jin Hwang, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(1): 61. CrossRef - Biological Effects and Washout Resistance of a Newly Developed Fast-setting Pozzolan Cement
Yoorina Choi, Su-Jung Park, Seoung-Hoon Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(4): 467. CrossRef
-
1,251
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Effect of 2% chlorhexidine application on microtensile bond strength of resin composite to dentin using one-step self-etch adhesives
-
Soon-Ham Jang, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):486-491. Published online November 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.486
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study examined the effect of 2% chlorhexidine on the µTBS of a direct composite restoration using one-step self-etch adhesives on human dentin.
Materials and Methods
Twenty-four extracted permanent molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to six groups (n = 10), according to the adhesive system and application of chlorhexidine. With or without the application of chlorhexidine, each adhesive system was applied to the dentin surface. After the bonding procedure, light-cure composite resin buildups were produced. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and then cut and glued to the jig of the microtensile testing machine. A tensile load was applied until the specimen failed. The failure mode was examined using an operating microscope. The data was analyzed statistically using one-way ANOVA, Student's t-test (p < 0.05) and Scheffé's test.
Results
Regardless of the application of chlorhexidine, the Clearfil S3 Bond showed the highest µTBS, followed by G-Bond and Xeno V. Adhesive failure was the main failure mode of the dentin bonding agents tested with some samples showing cohesive failure.
Conclusions
The application of 2% chlorhexidine did not affect the µTBS of the resin composite to the dentin using a one-step self-etch adhesive.
-
Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
-
Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):479-485. Published online November 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.479
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare the push-out bond strengths of resin cement/fiber post systems to post space dentin using different application methods of resin cement.
Materials and Methods
Thirty extracted human premolars were selected and randomly divided into 3 groups according to the technique used to place the cement into root canal: using lentulo-spiral instrument (group Lentulo), applying the cement onto the post surface (group Direct), and injecting the material using a specific elongation tip (group Elongation tip). After shaping and filling of the root canal, post space was drilled using Rely-X post drill. Rely-X fiber post was seated using Rely-X Unicem and resin cement was light polymerized. The root specimens were embedded in an acrylic resin and the specimens were sectioned perpendicularly to the long axis using a low-speed saw. Three slices per each root containing cross-sections of coronal, middle and apical part of the bonded fiber posts were obtained by sectioning. The push-out bond strength was measured using Universal Testing Machine. Specimens after bond failure were examined using operating microscope to evaluate the failure modes.
Results
Push-out bond strengths were statistically influenced by the root regions. Group using the elongation tip showed significantly higher bond strength than other ways. Most failures occurred at the cement/dentin interface or in a mixed mode.
Conclusions
The use of an elongation tip seems to reduce the number of imperfections within the self-adhesive cement interface compared to the techniques such as direct applying with the post and lentulo-spiral technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
Abdulaziz A. Al-Kheraif, Badreldin A. Mohamed, Aref Othman Hasan Sufyan, Aftab Ahmed Khan, Darshan Devang Divakar
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 36: 102526. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography analysis of gap and void formation in different prefabricated fiber post cementation materials and techniques
Aws ArRejaie, Saleh A. Alsuliman, Mohammed O. Aljohani, Hesham A. Altamimi, Emad Alshwaimi, Ahmad M. Al-Thobity
The Saudi Dental Journal.2019; 31(2): 236. CrossRef - Micro-computerized tomography analysis of cement voids and pull-out strength of glass fiber posts luted with self-adhesive and glass-ionomer cements in the root canal
Serkan Sarıdağ, Dilek Helvacıoğlu-Yiğit, Mutlu Özcan, Egemen Avcu, Güllü Kızıltaş
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(14): 1585. CrossRef - Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 95. CrossRef - Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef
-
1,297
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
-
Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):134-142. Published online March 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.134
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation with hypersensitivity mode on microtensile bond strength of composite resin. Twenty extracted permanent molars were randomly assigned to six groups, according to the irradiation of Er,Cr:YSGG laser, adhesive system (Optibond FL or Clearfil SE bond) and application time of etchant (15 sec or 20 sec). Then composite resin was build up on each conditioned surface. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 h and twelve specimens for each group were prepared. All specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength and the fracture modes were evaluated. Also, the prepared dentin surface and laser irradiated dentin surface were examined under SEM.
The results were as follows:
The microtensile bond strength of laser irradiated group was lower than that of no laser irradiated group.
Regardless of laser irradiation, the microtensile bond strength of Optibond FL was higher than that of Clearfil SE bond. And the microtensile bond strength of 20 sec etching group was higher than that of 15 sec etching group when using Optibond FL.
The SEM image of laser irradiated dentin surface showed prominent peritubular dentin, opened dentinal tubules and no smear layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 180. CrossRef
-
1,535
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
-
Sook-Kyung Choi, Ji-Wan Yum, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(5):397-405. Published online September 30, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.397
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study compared the effect of an activator, intermediate bonding resin and low-viscosity flowable resin on the microtensile bond strength of a self-curing composite resin used with two-step total etching adhesives. Twenty extracted permanent molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to nine groups (n=10) according to the adhesive system and application of additional methods (activator, intermediate adhesive, flowable resin). The bonding agents and additional applications of each group were applied to the dentin surfaces. Self-curing composite resin buildups were made for each tooth to form a core, 5mm in height. The restored teeth were then stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24h before sectioning. The microtensile bond strength of all specimens was examined. The data was analyzed statistically by one-way ANOVA and a Scheffe's test. The application of an intermediate bonding resin (Optibond FL adhesive) and low-viscosity flowable resin (Tetric N-flow) produced higher bond strength than that with the activator in all groups. Regardless of the method selected, Optibond solo plus produced the lowest µTBS to dentin. The failure modes of the tested dentin bonding agents were mostly adhesive failure but there were some cases showed cohesive failure in the resin.
-
Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
-
Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):208-214. Published online May 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.208
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the dye leakage of MTA (mineral trioxide aggregate) apical plug produced by two orthograde placement techniques (hand condensation technique and ultrasonically assisted hand condensation technique).
To simulate straight canal, 60 transparent acrylic blocks with straight canal were fabricated. These transparent acrylic blocks were divided into 2 groups (Group C; hand condensation technique (HC) and Group U; ultrasonically assisted hand condensation technique (UAHC)) of 30 blocks with each MTA application method. Each group was divided into 2 subgroups (n = 15) with different canal size of #70 (subgroup C70 and subgroup U70) and #120 (subgroup C120 and subgroup U120). After apical plug was created, a wet paper point was placed over the MTA plug and specimen was kept in a humid condition at room temperature to allow MTA to set. After 24 hours, remaining canal space was backfilled using Obtura II. All specimens were transferred to floral form socked by 0.2% rhodamine B solution and stored in 100% humidity at room temperature. After 48 hours, resin block specimens were washed and scanned using a scanner. The maximum length of microleakage was measured from the scanned images of four surfaces of each resin block using Photoshop 6.0.
Statistical analysis was performed with Mann-Whitney U test. Group U of UAHC had significantly lower leakage than Group C of HC in #70-size canal (subgroup U70) (p < 0.05).
-
Stress distribution for NiTi files of triangular based and rectangular based cross-sections using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
-
Hyun-Ju Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.001
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the stress distributions of NiTi rotary instruments based on their cross-sectional geometries of triangular shape-based cross-sectional design, S-shaped cross-sectional design and modified rectangular shape-based one using 3D FE models.
NiTi rotary files of S-shaped and modified rectangular design of cross-section such as Mtwo or NRT showed larger stress change while file rotation during simulated shaping.
The stress of files with rectangular cross-section design such as Mtwo, NRT was distributed as an intermittent pattern along the long axis of file. On the other hand, the stress of files with triangular cross-section design was distributed continuously.
When the residual stresses which could increase the risk of file fatigue fracture were analyzed after their withdrawal, the NRT and Mtwo model also presented higher residual stresses.
From this result, it can be inferred that S-shaped and modified rectangular shape-based files were more susceptible to file fracture than the files having triangular shape-based one. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Autogenous teeth used for bone grafting: a comparison with traditional grafting materials
Young-Kyun Kim, Su-Gwan Kim, Pil-Young Yun, In-Sung Yeo, Seung-Chan Jin, Ji-Su Oh, Heung-Joong Kim, Sun-Kyoung Yu, Sook-Young Lee, Jae-Sung Kim, In-Woong Um, Mi-Ae Jeong, Gyung-Wook Kim
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2014; 117(1): e39. CrossRef - Analysis of crystalline structure of autogenous tooth bone graft material: X-Ray diffraction analysis
Gyung-Wook Kim, In-Sung Yeo, Su-Gwan Kim, In-Woong Um, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2011; 37(3): 225. CrossRef
-
1,466
View
-
6
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary second premolars restored with different methods: Three-dimensional finite element analysis
-
Dong-Yeol Lim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):69-79. Published online January 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.069
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of elastic modulus of restorative materials and the number of interfaces of post and core systems on the stress distribution of three differently restored endodontically treated maxillary second premolars using 3D FE analysis. Model 1, 2 was restored with a stainless steel or glass fiber post and direct composite resin. A PFG or a sintered alumina crown was considered. Model 3 was restored by EndoCrown. An oblique 500 N was applied on the buccal (Load A) and palatal (Load B) cusp. The von Mises stresses in the coronal and root structure of each model were analyzed using ANSYS. The elastic modulus of the definitive restorations rather than the type of post and core system was the primary factor that influenced the stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary premolars. The stress concentration at the coronal structure could be lowered through the use of definitive restoration of high elastic modulus. The stress concentration at the root structure could be lowered through the use of definitive restoration of low elastic modulus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - How loss of tooth structure impacts the biomechanical behavior of a single-rooted maxillary premolar: FEA
Roaa Abdelwahab Abdelfattah, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Engy M. Kataia, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber
Odontology.2024; 112(1): 279. CrossRef - Effect of Proximal Caries-driven Access on the Biomechanical Behavior of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Premolars
Nawar Naguib Nawar, Roaa Abdelwahab Abdelfattah, Mohamed Kataia, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Engy Medhat Kataia, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(10): 1337. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - Influence of Cavity Design on Stress Distribution in Second Premolar Tooth Using Finite Element Analysis
Z. Parlar, E.U. Gökçek, K. Yildirim, A. Kahyaoglu
Acta Physica Polonica A.2017; 132(3-II): 949. CrossRef - Influence of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in the immature tooth model
Jong-Hyun Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Il-Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 257. CrossRef
-
1,782
View
-
8
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Effect of restoration type on the stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary premolars; Three-dimensional finite element study
-
Heun-Sook Jung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):8-19. Published online January 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.008
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of four restorative materials under various occlusal loading conditions on the stress distribution at the CEJ of buccal, palatal surface and central groove of occlusal surface of endodontically treated maxillary second premolar, using a 3D finte element analysis.
A 3D finite element model of human maxillary second premolar was endodontically treated. After endodontic treatment, access cavity was filled with Amalgam, resin, ceramic or gold of different mechanical properties. A static 500N forces were applied at the buccal (Load-1) and palatal cusp (Load-2) and a static 170N forces were applied at the mesial marginal ridge and palatal cusp simultaneously as centric occlusion (Load-3). Under 3-type Loading condition, the value of tensile stress was analyzed after 4-type restoration at the CEJ of buccal and palatal surface and central groove of occlusal surface
Excessive high tensile stresses were observed along the palatal CEJ in Load-1 case and buccal CEJ in Load-2 in all of the restorations. There was no difference in magnitude of stress in relation to the type of restorations. Heavy tensile stress concentrations were observed around the loading point and along the central groove of occlusal surface in all of the restorations. There was slight difference in magnitude of stress between different types of restorations. High tensile stress concentrations around the loading points were observed and there was no difference in magnitude of stress between different types of restorations in Load-3.
-
The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
-
Jin-hee Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):526-536. Published online November 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.526
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of various dentin bonding systems on microtensile bond strength of immediate dentin sealing (IDS) and delayed dentin sealing (DDS). Eighteen extracted permanent molars were used in this study. The teeth for DDS group were restored with a provisional restorations, and immersed in saline solution for 1 week, and divided into 3 subgroups according to various dentin bonding adhesives; SB subgroup (3 step total-etch adhesive), SE subgroup (2 step self-etch adhesive), XE subgroup (1 step self-etch adhesive). In IDS group, the teeth were divided into 3 subgroups, and applied with bonding adhesives as in DDS group. The teeth were restored with provisional restorations, and immersed in saline solution for 1 week. Indirect composite disc was cemented with resin cement, and all specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength. The data were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Student t-test.
The results were as follows:
The IDS group showed significantly higher µTBS than DDS group in 3 step total-etch and 2 step self-etch adhesive (p < 0.05).
In IDS and DDS group, 3 step total-etch adhesive showed the highest µTBS value, followed by 2 step self-etch, and 1 step self-etch adhesive. In IDS group, the µTBS value for 1 step self-etch adhesive was significantly different from those of the other subgroups (p < 0.05), and in DDS group, there were statistical differences in all subgroup (p < 0.05).
Failure modes of tested dentin bonding adhesives were mostly mixed failure and only 1 step self-etch adhesive showed adhesive failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 134. CrossRef
-
1,704
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Stress analysis of maxillary premolars with composite resin restoration of notch-shaped class V cavity and access cavity; Three-dimensional finite element study
-
Seon-Hwa Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):570-579. Published online November 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.570
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate the distribution of tensile stress of canal obturated maxillary second premolar with access cavity and notch-shaped class V cavity restored with composite resin using a 3D finite element analysis.
The tested groups were classified as 8 situations by only access cavity or access cavity with notch-shaped class VS cavity (S or N), loading condition (L1 or L2), and with or without glass ionomer cement base (R1 or R2). A static load of 500 N was applied at buccal and palatal cusps. Notch-shaped cavity and access cavity were filled microhybrid composite resin (Z100) with or without GIC base (Fuji II LC). The tensile stresses presented in the buccal cervical area, palatal cervical area and occlusal surface were analyzed using ANSYS.
Tensile stress distributions were similar regardless of base. When the load was applied on the buccal cusp, excessive high tensile stress was concentrated around the loading point and along the central groove of occlusal surface. The tensile stress values of the tooth with class V cavity were slightly higher than that of the tooth without class V cavity. When the load was applied the palatal cusp, excessive high tensile stress was concentrated around the loading point and along the central groove of occlusal surface. The tensile stress values of the tooth without class V cavity were slightly higher than that of the tooth with class V cavity.
-
EFFECT OF THE ADDITIONAL ETCHING PROCEDURE ON PUSH-OUT BOND STRENGTH OF ONE-STEP RESIN CEMENT
-
Soon-Il Kang, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):443-451. Published online January 14, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.443
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of additional etching procedure prior to Maxcem resin cement application in indirect restoration cementation using push-out bonding strength.
One hundred and two extracted human molars were used to make indirect resin restorations of gold inlay and Synfony. These restorations were cemented using Maxcem and Variolink II. Additional etching procedures were done for one group with Maxcem. Three groups have 17 specimens in both restoration types. Push-out bond strength was measured using multi-purpose tester and calculated for bonding strength per sqaure-millimeter area. The mean bonding strength values were compared using SPSS 12.0K program for one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's Test with 95% significance.
Under the condition of this study, the additional etching procedure prior to usage of Maxcem resulted in reduced bond strength for both of restoration types.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
-
1,079
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
-
Tae-Oh Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):323-331. Published online July 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.323
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Flexibility and fracture properties determine the performance of NiTi rotary instruments. The purpose of this study was to evaluate how geometrical differences between three NiTi instruments affect the deformation and stress distributions under bending and torsional conditions using finite element analysis.
Three NiTi files (ProFile .06 / #30, F3 of ProTaper and ProTaper Universal) were scanned using a Micro-CT. The obtained structural geometries were meshed with linear, eight-noded hexahedral elements. The mechanical behavior (deformation and von Mises equivalent stress) of the three endodontic instruments were analyzed under four bending and rotational conditions using ABAQUS finite element analysis software. The nonlinear mechanical behavior of the NiTi was taken into account.
The U-shaped cross sectional geometry of ProFile showed the highest flexibility of the three file models. The ProTaper, which has a convex triangular cross-section, was the most stiff file model. For the same deflection, the ProTaper required more force to reach the same deflection as the other models, and needed more torque than other models for the same amount of rotation. The highest von Mises stress value was found at the groove area in the cross-section of the ProTaper Universal.
Under torsion, all files showed highest stresses at their groove area. The ProFile showed highest von Mises stress value under the same torsional moment while the ProTaper Universal showed the highest value under same rotational angle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in .06 taper ProFile
Hye-Rim Jung, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 79. CrossRef
-
1,450
View
-
8
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparative analysis of various corrosive environmental conditions for NiTi rotary files
-
Ji-Wan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):377-388. Published online July 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.377
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of the present study is to compare the corrosion tendency using two kinds of NiTi files in the various environmental conditions through the visual examination and electrochemical analysis. ProTaper Universal S2, 21 mm (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and Hero 642, 0.06 tapers, size 25, 21 mm (Micromega, Besancon, France) rotary instruments were tested. The instruments were randomly divided into eighteen groups (n = 5) by the immersion temperature, the type of solution, the brand of NiTi rotary instrument and the presence of mechanical loading. Each file was examined at various magnifications using Scanning Electron Microscope (JEOL, Akishima, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDX). EDX was used to determine the components of the endodontic file alloy in corroded and noncorroded areas. The corrosion resistance of unused and used NiTi files after repeated uses in the human teeth was evaluated electrochemically by potentiodynamic polarization test using a potentiostat (Applied Corrosion Monitoring, Cark-in-Cartmel, UK).
Solution temperature and chloride ion concentration may affect on passivity of NiTi files. Under the conditions of this in vitro study, the corrosion resistance is slightly increased after clinical use. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A novel approach to assess surface roughness and EDX profiling of blue rotary NiTi files following dynamic immersion in various hypochlorite concentrations
Hebatullah Ahmad Safwat, Nesreen Y. Mohammed, Asmaa Abd El-Hady
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Free Recovery Transformation Temperature of NiTi Endodontic Single-File Systems Using a Novel Testing Setup
Emad Youssef, Holger Jungbluth, Søren Jepsen, Manfred Gruener, Christoph Bourauel
Materials.2024; 17(3): 566. CrossRef - The Determination of the Corrosion Rates of Rotary Ni-Ti Instruments in Various Irrigation Solutions
Tolga Özcan, Bade Sonat, Meltem Dartar Öztan, Fatma Basmaci, Umut Aksoy
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2023; 8(2): 136. CrossRef - A Nonlinear Probabilistic Pitting Corrosion Model of Ni–Ti Alloy Immersed in Shallow Seawater
Špiro Ivošević, Gyöngyi Vastag, Nataša Kovač, Peter Majerič, Rebeka Rudolf
Micromachines.2022; 13(7): 1031. CrossRef - Corrosion resistance assessment of nickel-titanium endodontic files with and without heat treatment
Tatiana Dias Costa, Elison da Fonseca e Silva, Paula Liparini Caetano, Marcio José da Silva Campos, Leandro Marques Resende, André Guimarães Machado, Antônio Márcio Resende do Carmo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite, EDTA, and Chitosan Solution on Corrosion and Quantity of Extruded Nickel Ions Using Two Rotary Instruments (In Vitro)
Eltica Oktavia, Trimurni Abidin
World Journal of Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 207. CrossRef
-
1,717
View
-
6
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
The influence of occlusal loads on stress distribution of cervical composite resin restorations: A three-dimensional finite element study
-
Chan-Seok Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):246-257. Published online May 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.246
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of various occlusal loading sites and directions on the stress distribution of the cervical composite resin restorations of maxillary second premolar, using 3 dimensional (3D) finite element (FE) analysis. Extracted maxillary second premolar was scanned serially with Micro-CT (SkyScan1072; SkyScan, Aartselaar, Belgium). The 3D images were processed by 3D-DOCTOR (Able Software Co., Lexington, MA, USA). HyperMesh (Altair Engineering, Inc., Troy, USA) and ANSYS (Swanson Analysis Systems, Inc., Houston, USA) was used to mesh and analyze 3D FE model. Notch shaped cavity was filled with hybrid (Z100, 3M Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, USA) or flowable resin (Tetric Flow, Vivadent Ets., FL-9494-Schaan, Liechtenstein) and each restoration was simulated with adhesive layer thickness (40 µm). A static load of 200 N was applied on the three points of the buccal incline of the palatal cusp and oriented in 20° increments, from vertical (long axis of the tooth) to oblique 40° direction towards the buccal. The maximum principal stresses in the occlusal and cervical cavosurface margin and vertical section of buccal surfaces of notch-shaped class V cavity were analyzed using ANSYS. As the angle of loading direction increased, tensile stress increased. Loading site had little effect on it. Under same loading condition, Tetric Flow showed relatively lower stress than Z100 overall, except both point angles. Loading direction and the elastic modulus of restorative material seem to be important factor on the cervical restoration. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of bonding protocols and physical-mechanical properties of composite on durability and failure rate of fixed orthodontic retainers: a systematic review of laboratory studies
Maciej Jedliński, Marta Mazur, Claudia Salerno, Katarzyna Grocholewicz, Joanna Janiszewska-Olszowska
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Finite element analysis of maxillary central incisors restored with various post-and-core applications
MinSeock Seo, WonJun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 324. CrossRef
-
1,997
View
-
12
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The effect of different bonding systems on shear bond strength of repaired composite resin
-
Eun-Mi Seon, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):125-132. Published online March 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.125
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to compare the shear bond strength of repaired composite resin with different bonding agents and evaluate the effect of bonding agents on composite repair strength. Forty composite specimens (Z-250) were prepared and aged for 1week by thermocycling between 5 and 55℃ with a dwell time of 30s. After air abrasion with 50 µm aluminum oxide, following different bonding agents were applied (n = 10); SB group: Scotchbond multipurpose adhesive (3 step Total-Etch system); SE group: Clearfil SE bond (2 step Self-Etch system); XP group: XP bond (2 step Total-Etch system); XE group: XenoIII (1 step Self-Etch system). After bonding procedure was completed, new composite resin (Z-250) was applied to the mold and cured. For control group, 10 specimens were prepared. Seven days after repair, shear bond strength was measured. Data was statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey's test (p < 0.05). The means and standard deviations of shear bond strength (MPa ± S.D.) per group were as follows: SB group: 17.06; SE group: 19.10; XP group: 14.44; XE group: 13.57; Control Group: 19.40. No significant difference found in each group. Within the limit of this study, it was concluded that the different type of bonding system was not affect on the shear bond strength of repaired composite resin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Smart Biomaterials: An Evolving Paradigm in Dentistry
Harsha P Rathi, Manoj Chandak, Amit Reche, Abhilasha Dass, Swayangprabha Sarangi, Samiksha R Thawri
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,546
View
-
7
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparison of apical sealing efficacies using different plugging depth in continuous wave of obturation technique
-
Sang-Jin Lee, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):491-497. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.491
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare apical sealing ability of continuous wave canal filling technique according to various heat source plugging depths.
Eighty one extracted human premolars with straight root were cleaned and shaped to size 35 using .06 taper rotary NiTi file. After cleansing and shaping, the teeth were divided into 5 groups following the heat source probing depths from the apex; 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 mm. All specimens were filled using E&Q plus with #35 / .06 tapered gutta-percha cone. The positive control teeth were not filled. All teeth were coated with nail varnish except the apical 1 mm around the apical foramen. Negative control teeth were completely sealed include the apical foramen. All specimens were immersed in 1% methylene blue solution for 72 hours. Then the specimens were sectioned horizontally at 1, 2 and 3 mm from the root apex. Each sectioned surface was photographed using a digital camera attached to the stereomicroscope at 12.5 × 2.5 fold magnification. All points at 1, 2 and 3 mm were summed as final score of one specimen. Statistical analysis of the collected data was performed.
Under the condition of this study, there was no significant difference between the heat source plugging depths of 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 mm in apical sealing ability. All of apical heat source plugging depth from 3 to 7 mm including Buchanan's protocol -from 5 to 7 mm- seems to be acceptable in clinical application.
-
Comparison of apical sealing ability of continuous wave of obturation technique using EndoTwinn and System B
-
Hyun-Ju Shin, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):522-529. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.522
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the apical leakage of the root canal filled with the System B and the EndoTwinn (the combined application of heat and ultrasonic vibration).
Sixty extracted premolars with straight root were cleaned and shaped to size 35. Group SB was obturated using System B and Group ET was filled with EndoTwinn. A size 35 of 0.06 tapered gutta-percha and Adseal were used and the plugger which could be introduced to 4 mm short of working length was selected in the obturation procedure. As the positive control, Group PC was not filled. In Group SB, ET and PC, all external surfaces of each tooth were coated with nail varnish leaving only 1 mm area around the apical foramen. In the negative control of Group NSB and Group NET, all of external tooth surface including apical foramen was coated with the nail varnish. The specimens were immersed in methylene blue dye solution for 2 days. Then the specimens were sectioned at each 1 mm from apex to 5 mm level. The final score of one specimen was given by summing up of the points at all levels.
The dye leakage of Group ET was significantly less than that observed in Group SB (p < 0.05). And the frequency of gutta-percha pulling out from root canal when the plugger was removed was more often with the System B than with EndoTwinn but there was no significant difference.
-
Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
-
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):530-541. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.530
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Currently, various Nickel-Titanium rotary files are used in endodontic treatment, but there is no one perfect system that can be applied to any clinical situation. Therefore, the combined uses of various file systems which can emphasize the advantages of each system are introduced as hybrid instrumentation.
The ProTaper system is efficient in body shaping and apical pre-enlargement but is reported to have more possibility of transportation and produce more aberrations and deformation in more or less severe curved canals. Recently, new ProTaper system (ProTaper Universal) with different configuration and cross-sectional design to overcome the week points of ProTaper have been marketed.
The purpose of this study was to compare and evaluate the shaping abilities of ProTaper, ProTaper Universal system, and two hybrid methods using S-series of ProTaper Universal and Hero Shaper or ProFile.
The time lapses for instrumentation were measured and the used files were inspected for distortion. The pre- and post-instrumented root canals were scanned and superimposed to evaluate the aberrations and reduction of root canal curvature and change of radius of canal curvature. The increased canal width and apical centering ratio were calculated at 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm levels from apical foramen.
Under the conditions of this study, the ProTaper Universal seems to have better shaping ability than ProTaper in terms of instrumented width and instrumentation time. It may be suggested that the ProTaper Universal system is efficient as much as hybrid instrumentation using ProTaper and other constant-tapered NiTi file systems in highly experienced operators. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 201. CrossRef - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
-
1,434
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Surface roughness and color stability of various composite resins
-
Sung-Yi Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):542-549. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.542
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the difference in the surface roughness after polishing and to evaluate the difference in color stability after immersion in a dye solution among four types of composite resin materials. Four light-polymerized composite resins (Shade A2) with different sized filler content (a nanofilled, a hybrid, a microfilled, a flowble) were used. Average surface roughness (Ra) was measured with a surface roughness tester (Surftest Formtracer) before and after polishing with aluminum oxide abrasive discs (Super-Snap). Color of specimens before and after staining with 2% methylene blue solution were measured using spectrophotometer (CM-3700d) with SCI geometries. The results of Ra and ΔE were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), a Scheffe multiple comparison test and Student t-test (p = 0.05). After polishing, Ra values were decreased regardless of type of composite resins. In surface roughness after polishing and color stability after staining, nanofilled composite resin was not different with other composite resins except flowable resins. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of contemporary polishing systems on hardness and roughness of one-shaded dental composites
Kivanc Dulger, Gencaga Purcek
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2025; 61(3): 841. CrossRef - Physicomechanical properties and polymerization shrinkage of the newly developed radiopaque flowable composite derived from rice husk
Nor Ain Fatihah Azlisham, Yanti Johari, Dasmawati Mohamad, Mohd Firdaus Yhaya, Zuliani Mahmood
Polymer Composites.2025; 46(7): 5924. CrossRef - Highly Filled Flowable Composite Resins as Sole Restorative Materials: A Systematic Review
Konstantinos Tzimas, Eftychia Pappa, Maria Fostiropoulou, Efstratios Papazoglou, Christos Rahiotis
Materials.2025; 18(14): 3370. CrossRef - Effect of immersion and thermocycling in different beverages on the surface roughness of single- and multi-shade resin composites
Aiah A. El-Rashidy, Omar Shaalan, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Nour A. Habib
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Degree of conversion and physicomechanical properties of newly developed flowable composite derived from rice husk using urethane dimethacrylate monomer
Nor Ain Fatihah Azlisham, Yanti Johari, Dasmawati Mohamad, Mohd Firdaus Yhaya, Zuliani Mahmood
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2023; 237(12): 1339. CrossRef - Translucency and Color Stability of a Simplified Shade Nanohybrid Composite after Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing
Ksenia Babina, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Alexandr Zaytsev, Elena E. Nikonova, Gleb S. Budylin, Evgeny A. Shirshin, Christian Tantardini, Nina Novozhilova
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(24): 4465. CrossRef - Surface properties and color stability of dental flowable composites influenced by simulated toothbrushing
Guangyun LAI, Liya ZHAO, Jun WANG, Karl-Heinz KUNZELMANN
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(5): 717. CrossRef - Topography and surface roughness of fluid resins used as bioprotectors of mini-implants
Rogério Lacerda-Santos, Mirella de Fátima Liberato de Moura, Fabíola Galbiatti Carvalho, Hugo Lemes Carlo, Matheus Melo Pithon, Bruno Alessandro Silva Guedes de Lima, Tibério Andrade dos Passos
Applied Adhesion Science.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,545
View
-
19
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Comparison of shaping ability between single length technique and crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file
-
Yoo-Kyoung Lim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):385-396. Published online July 31, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.385
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aims of this study were to compare the shaping effect and safety between single length technique recommended by manufacturer and crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file and to present a modified method in use of Mtwo file.
Sixty simulated root canal resin blocks were used. The canals were divided into three groups according to instrument and the manner of using methods. Each group had 20 specimens. Group MT was instrumented with single length technique of Mtwo, group MC was instrumented with crowndown technique of Mtwo and group PT was instrumented with crown-down technique of ProTaper. All of the rotary files used in this study were operated by an electric motor. The scanned canal images of before and after preparation were superimposed. These superimposed images were evaluated at apical 1 to 8 mm levels. Angle changes were calculated. The preparation time, weight loss, instrument failure and binding, canal aberrations, and centering ratio were measured. Statistical analysis of the three experimental groups was performed with ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range tests for post-hoc comparison and Fisher's exact test was done for the frequency comparison.
In total preparation time, group MT and group MC were less than group PT. In the aberrations, group MT had more elbows than those of group MC and group PT. The binding of group MC was least and group MT was less than group PT (P < 0.05).
Under the condition of this study, crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file is better and safer method than single length technique recommended by the manufacturer.
-
The influence of composite resin restoration on the stress distribution of notch shaped noncarious cervical lesion; A three dimensional finite element analysis study
-
Chae-Kyung Lee, Jeong-Kil Park, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung-Gwan Woo, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Bock Hur
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):69-79. Published online January 31, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.069
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of composite resin restorations on the stress distribution of notch shaped noncarious cervical lesion using three-dimensional (3D) finite element analysis (FEA).
Extracted maxillary second premolar was scanned serially with Micro-CT (SkyScan1072; SkyScan, Aartselaar, Belgium). The 3D images were processed by 3D-DOCTOR (Able Software Co., Lexington, MA, USA). ANSYS (Swanson Analysis Systems, Inc., Houston, USA) was used to mesh and analyze 3D FE model. Notch shaped cavity was filled with hybrid or flowable resin and each restoration was simulated with adhesive layer thickness (40 µM). A static load of 500 N was applied on a point load condition at buccal cusp (loading A) and palatal cusp (loading B). The principal stresses in the lesion apex (internal line angle of cavity) and middle vertical wall were analyzed using ANSYS.
The results were as follows
1. Under loading A, compressive stress is created in the unrestored and restored cavity. Under loading B, tensile stress is created. And the peak stress concentration is seen at near mesial corner of the cavity under each load condition.
2. Compared to the unrestored cavity, the principal stresses at the cemeto-enamel junction (CEJ) and internal line angle of the cavity were more reduced in the restored cavity on both load conditions.
3. In teeth restored with hybrid composite, the principal stresses at the CEJ and internal line angle of the cavity were more reduced than flowable resin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The influence of occlusal loads on stress distribution of cervical composite resin restorations: A three-dimensional finite element study
Chan-Seok Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(3): 246. CrossRef
-
1,521
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The effect of adhesive thickness on microtensile bond strength to the cavity wall
-
Hwa-Eon Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):9-18. Published online January 31, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.009
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purposes of this study were to examine the variability of adhesive thickness on the different site of the cavity wall when used total-etch system without filler and simplified self-etch system with filler and to evaluate the relationship between variable adhesive thickness and microtensile bond strength to the cavity wall.
A class I cavity in six human molars was prepared to expose all dentinal walls. Three teeth were bonded with a filled adhesive, Clearfil™ SE bond and the other three teeth were bonded with unfilled adhesives, Scotchbond™ Multi Purpose. Morphology and thickness of adhesive layer were examined using fluorescence microscope. Bonding agent thickness was measured at three points along the axial cavity wall, edge of cavity margin (rim), halfway down each cavity wall (hlf), internal angle of the cavity (ang). After reproducing the adhesive thickness at rim, hlf and ang, micro-tensile bond strength were evaluated.
For both bonding agents, adhesive thickness of ang was significantly thicker than that of rim and hlf (P < 0.05). As reproduced the adhesive thickness, microtensile bond strength was increased as adhesive thickness was increased in two bonding agents.
Adhesive thickness of internal angle of the cavity was significantly thicker than that of the cavity margin and the halfway cavity wall for both bonding agents. Microtensile bond strength of the thick adhesive layer at the internal angle of the cavity was higher than that of the thin adhesive layer at the cavity margin and the halfway cavity in the two bonding systems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Bond strength of a 3-step total-etch bonding system to dentine – An improved approach
H. Hassan Elnadif, W. Palin, M.A. Hadis, B.W. Darvell
Dental Materials.2025; 41(5): 483. CrossRef - Evaluation of bonding effectiveness of a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive resin to un-treated and Er:Yag laser treated dentin using mini-interfacial fracture toughness test
Marjan Behroozibakhsh, Sotoudeh Davaie, Abbas Monzavi, Tayebeh Abazari, Sima Shahabi, Maryam Pirmoradian
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2019; 33(11): 1201. CrossRef - The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 134. CrossRef
-
1,861
View
-
7
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Effects of occlusal load on the cervical stress distribution: A three-dimensional finite element study
-
Hyeong-Mo Lee, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung-Gwan Woo, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):427-436. Published online November 30, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.427
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of various occlusal loads on the stress distribution of the buccal cervical region of a normal maxillary second premolar, using a three dimensional finite element analysis (3D FEA).
After 3D FE modeling of maxillary second premolar, a static load of 500N of three load cases was applied. Stress analysis was performed using ANSYS (Swanson Analysis Systems, Inc., Houston, USA). The maximum principal stresses and minimum principal stresses were sampled at thirteen nodal points in the buccal cervical enamel for each four horizontal planes, 1.0 mm above CEJ, 0.5 mm above CEJ, CEJ, 0.5 mm under CEJ.
The results were as follows
1. The peak stress was seen at the cervical enamel surface of the mesiobuccal line angle area, asymmetrically.
2. The values of compressive stresses were within the range of the failure stress of enamel. But the values of tensile stresses exceeded the range of the failure stress of enamel.
3. The tensile stresses from the perpendicular load at the buccal incline of palatal cusp may be shown to be the primary etiological factors of the NCCLs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Biomechanical and Occlusal Factors Influencing the Longevity of Single-Unit Restorations: A Comprehensive Review
Wedad S Alaida, Safa A Gadi, Rokia E Al-Ghannam, Moayad F Alamri, Feras I Mirdad, Ruba M Argaibeh, Bushra A Alqahtani, Abdulrahman M Alqahtani, Abdulelah A Al Jaban, Turki M Alkuraydimi, Abdulrahman S Alamari
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of restoration type on the stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary premolars; Three-dimensional finite element study
Heun-Sook Jung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 8. CrossRef - Stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary second premolars restored with different methods: Three-dimensional finite element analysis
Dong-Yeol Lim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 69. CrossRef
-
1,797
View
-
5
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Effects of one or two applications of all-in-one adhesive on microtensile bond strength to unground enamel
-
Chang-Yong Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):445-451. Published online November 30, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.445
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purposes of this study were to compare the effects of one or two applications of all-in-one adhesives on microtensile bond strengths (µTBS) to unground enamel and to investigate the morphological changes in enamel surfaces treated with these adhesives using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Twenty-five noncarious, unrestored human mandibular molars were used. The unground enamel surfaces were cleansed with pumice. The following adhesives were applied to lingual, mid-coronal surfaces according to manufacture's directions; Clearfil SE bond in SE group, Adper Prompt L-Pop™1 coat in LP1 group, 2 coats in LP2 group, Xeno® III 1 coat in XN1 group, and 2 coats in XN2 group. After application of the adhesives, a hybrid light-activated resin composite was built up on the unground enamel. Each tooth was sectioned to make a cross-sectional area of approximately 1.0 mm2 for each stick. The microtensile bond strength was determined. Each specimen was observed under SEM to examine the morphological changes. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microtensile bond strength values were; SE (19.77±2.44 MPa), LP1 (13.88±3.67 MPa), LP2 (14.50±2.52 MPa), XN1 (14.42±2.51 MPa) and XN2 (15.28±2.79 MPa). SE was significantly higher than the other groups in bond strength (p < 0.05). All groups except SE were not significantly different in bond strength (p < 0.05).
2. All groups were characterized as shallow and irregular etching patterns. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
Jin-hee Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 526. CrossRef
-
1,378
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparison of screw-in effect of three NiTi file systems used by undergraduates
-
Seung-Hei Oh, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):477-484. Published online November 30, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.477
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purposes of this study were to compare the apical terminus width of simulated curved root canal prepared with three NiTi file systems used by undergraduates for evaluation the effects of flute angle and pitch or radial land on reducing screw-in effect and to determine more safe NiTi file system for inexperienced operators.
Fifty inexperienced undergraduate students prepared 150 simulated curved root canals in resin blocks with three NiTi file systems ; ProFile®, Hero Shaper®, K3™. The electric motor set at a speed of 300 rpm and torque of 30 in a 16 : 1 reduction handpiece was used. The simulated root canal was prepared to ISO #25 sizes with each file system. The scanned images of pre- and post-instrumented canal of resin block were superimposed. To evaluate the screw-in effect of three NiTi file systems, apical terminus width of root canal was measured from superimposed images and statistical analysis was performed.
There were significant differences in three NiTi file systems. ProFile® had significantly smaller width than Hero Shaper® and K3™ (P < 0.05), but no significant difference was observed between K3™ and Hero Shaper®.
Under the condition of this study, active file system (Hero Shaper®, K3™) with variable pitch and helical angle had more screw-in effect than passive file system (ProFile®) with constant pitch and helical angle. It seems that the radial lands play more important role in reducing screw-in effect. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 267. CrossRef - Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Hye-Jin Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 380. CrossRef - Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 374. CrossRef
-
1,561
View
-
2
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Effects of occlusal load on the stress distribution of four cavity configurations of noncarious cervical lesions: A three-dimensional finite element analysis study
-
Sang-Je Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung-Gwan Woo, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Bock Hur
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):359-370. Published online January 14, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.359
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of excessive occlusal loading on stress distribution on four type of cervical lesion, using a three dimensional finite element analysis (3D FEA).
The extracted maxillary second premolar was scanned serially with Micro-CT. The 3D images were processed by 3D-DOCTOR. ANSYS was used to mesh and analyze 3D FE model. Four different lesion configurations representative of the various types observed clinically for teeth were studied. A static point load of 500N was applied to the buccal and lingual cusp (Load A and B). The principal stresses in lesion apex, and vertical sectioned margin of cervical wall were analyzed.
The results were as follows
The patterns of stress distribution were similar but the magnitude was different in four types of lesion.
The peak stress was observed at mesial corner and also stresses concentrated at lesion apex.
The compressive stress under load A and the tensile stress under load B were dominant stress.
Under the load, lesion can be increased and harmful to tooth structure unless restored.
-
In vitro comparison of measurement accuracy in pre-enlarged and enlarged canals with four apex locators
-
Sang-Yup Sung, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):371-377. Published online September 30, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.371
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purposes of this study were to assess the accuracy of measurements in pre-enlarged canals with small instruments and to compare the accuracies, in enlarged canal, with small size instruments and instruments that match the actual canal diameter using Root ZX, Bingo1020, SmarPex, and e-Magic Finder. Ten extracted teeth were embedded in an alginate model made for testing apex locators. A size 10 file was placed into the root canal until the tip of the file reached the plane of the major diameter of the foramen under a dental operating microscope at the 25 × magnification. The measurement was done with digital caliper and defined as actual length. Electronic length measurement with a size 10 file in pre-enlarged canal was done by reading the index indicating Apex of each device to gain a definite value. After completion of canal enlargement to a size 45 file, each difference between actual length and electric measurement value with a size 10 and 40 files in enlarged canal was recorded as L10 and L40. The one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's multiple range tests were computed for analyze the differences among the four apex locators in the same group. The Student's t-test between L10 and L40 of each locator was done. The accuracies of electronic measurements were significantly different among the 4 devices. The file size made no difference on the accuracy of electronic measurement in enlarged canal with same device. The e-Magic Finder was the most accurate device among the 4 apex locators used in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Working Length Determination Using Two Fifth-Generation Apex Locators With Radiovisiography: An In vivo Study
H. K. Shwetha, C. N. Vijay Kumar, Arun J. Kumar, Ashwini Bhaskar, M Kavyashree, S Amrita
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(2): 69. CrossRef
-
1,304
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparison of shaping ability of rotary Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates
-
Mun-Seong Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):1-10. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.001
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the shaping ability of three Ni-Ti file systems used by dental students or the experts and consequently to aid in choosing a proper systems for educational courses of dental students and beginners.
Fifty students and ten dentists who have clinical experience over two years prepared 180 simulated root canals in resin blocks with three Ni-Ti systems; ProFile® (PF), HeroShaper® (HS), K3TM (K3).
After preparation, the Ni-Ti files were evaluated for distortion and canal preparation time was recorded. The images of pre- and post-instrumented canals were scanned and superimposed. Amounts of increased canal widths, deviation, and centering ratio were calculated at apical 1, 3 and 5 mm levels and statistical analysis was performed.
The results were as follows:
HS showed the shortest preparation time and instrumented canal width in K3 was significantly larger than other groups (P < 0.05).
At 1 and 3 mm levels, all groups had outward deviation. In student group, at the 1 mm level, PF had the least deviation (P < 0.05).
In the centering ratio, the PF had the best centering ability compared to the others at 5 mm level. At 1 and 3 mm levels, HS and PF had better abilities than K3. Student group had better ratio than the expert at 3 mm level with PF (P < 0.05).
Based on the results, it is surmised that the ProFile® is the safest and most ideal instrument for students and beginners. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A comparative study of root canal shaping using protaper universal and protaper next rotary files in preclinical dental education
Gül Çelik, Feyza Özdemir Kısacık, Emir Faruk Yılmaz, Arife Mersinlioğlu, İhsan Furkan Ertuğrul, Hikmet Orhan
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7419. CrossRef
-
1,209
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparison of shaping ability between various hybrid instrumentation methods with ProTaper
-
Eun-Sook Hong, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):11-19. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.011
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare and evaluate the shaping abilities of various hybrid instrumentation method using constant tapered file systems with ProTaper® S1 and the difference between experts and inexperienced clinicians in use of NiTi file.
Three hybrid methods used in this study were composed of ProTaper® S1 and K-Flexofile® (group S), ProTaper® S1 and HeroShaper® (group H), and ProTaper® S1 and ProFile® (group P), respectively. The ProTaper®-alone method (group C) was introduced as a control group.
After canal preparation, the lapse of time was recorded. The images of pre- and post-operative canal were scanned and superimposed. Amounts of instrumented canal widths and centering ratio were measured at apical 1, 2 and 3 mm levels and statistical analysis was performed.
In this study, both of the group C and S took more time to prepare canals than other groups. Inexperienced operators required more time for the entire preparation with the groups C and H than the experienced (p < 0.05). And the centering ratio of group P were preferable to ProTaper®-alone method or the hybrid technique using stainless steel files. As such, within experienced operators, group H also showed better results in addition to the group P.
Under these condition, the hybrid methods of each the ProFile® system and HeroShaper® with ProTaper® are recommendable comparative to ProTaper®-alone method. According to the results, the hybrid instrumentation method is a more appropriate method of canal preparation than single file system for narrow or curved canals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of Forces Generated During Root Canal Shaping and Residual Stresses of Three Nickel–Titanium Rotary Files by Using a Three-Dimensional Finite-element Analysis
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Soon-Il Kang
Journal of Endodontics.2008; 34(6): 743. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between single length technique and crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file
Yoo-Kyoung Lim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 385. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef
-
1,603
View
-
3
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
The effect of restorative materials on the stress distribution of class V composite resin restorations - a 3D finite element investigation
-
Hyoung-Ryoul Ahn, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Huh, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):20-29. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.020
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to analyze the stress distribution aspect of unrestored and restored combined shape (wedge shape occlusally and saucer shape gingivally) class V cavity, which found frequently in clinical cases.
A maxillary second premolar restored with a combined shape class V composite restorations were modeled using the three dimensional finite element method. Static occlusal load of 170 N was applied on lingual incline of buccal cusp at the angle of 45° with the longitudinal axis of the tooth. And three dimensional finite element analysis was taken by ANSYS (Version 6.0, Swanson Analysis System Co., Houston, U.S.A) program which represent the stress distribution on unrestored and restored cavity wall and margin.
The conclusions were as follows.
Compared to the unrestored cavity, Von Mises stress at the cementoenamel junction and line angle of the cavity base were reduced and in restored cavity.
Von Mises stress at the occlusal and cervical cavity margin and wall were increased in restored cavity in comparison with the unrestored cavity.
In the hybrid and hybrid/flowable composite resin restoration, Von Mises stress at the cementoenamel junction and line angle of the cavity base were reduced more than in the flowable restoration.
In the hybrid and hybrid/flowable composite resin restoration, Von Mises stress at the occlusal and cervical cavity margin and wall were increased more than in the flowable restoration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of marginal microleakage between low and high flowable resins in class V cavity
Sang-Bae Bae, Young-Gon Cho, Myeong-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 477. CrossRef
-
1,235
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Step by step analysis of root canal instrumentation with ProTaper®
-
Mi-Hee Kim, Bock Huh, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):50-57. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.050
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate influence of each file step of ProTaper® system on canal transportation.
Twenty simulated canals were prepared with either engine-driven ProTaper® or manual ProTaper®. Group R-resin blocks were instrumented with rotary ProTaper® and group M-resin blocks were instrumented with manual ProTaper®. Pre-operative resin blocks and post-operative resin blocks after each file step preparation were scanned. Original canal image and the image after using each file step were superimposed for calculation of centering ratio. The image after using each file step and image after using previous file step were superimposed for calculation of the amount of deviation. Measurements were taken horizontally at five different levels (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm) from the level of apical foramen.
In rotary ProTaper® instrumentation group, centering ratio and the amount of deviation of each step at all levels were not significantly different (p > 0.05). In manual ProTaper® instrumentation group, centering ratio and the amount of deviation of each step at all levels except of 1 mm were not significantly different (p > 0.05). At the level of 1 mm, F2 file step had significantly large centering ratio and the amount of deviation (p < 0.05).
Under the condition of this study, F2 file step of manual ProTaper® tended to transport the apical part of the canals than that of rotary ProTaper®.
-
The effect of different flute design and torque-controlled motor on the shaping ability of simulated resin root canals
-
Hyoung-Mee Roh, Bock Huh, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):486-492. Published online November 30, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.486
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the shaping ability of the two different Ni-Ti file systems and the two different engine systems in simulated canals.
A total of four groups of each 10 were tested. Each group was instrumented with HeroShaper®and Endo-Mate2® (Group HE), HeroShaper® and Tecnika® (Group HT), ProFile® and Endo-Mate2® (Group PE), and ProFile® and Tecnika® (Group PT).
Canal preparation time was recorded. The images of pre- and post-instrumented root canals were scanned and superimposed. The amounts of increased width and centering ratio were measured and calculated at apical 1, 3 and 5 mm levels.
These data were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test
The results of this study were as follows;
1. Canal preparation time of HT group was the shortest (p < 0.05).
2. The amount of increased canal width in HE group was significantly larger than PT group at apical 1 mm level (p < 0.05). At apical 3 mm level, PT group was significantly smaller than other groups (p < 0.05). At apical 5 mm level, PE group was significantly larger than PT group (p < 0.05).
3. The amount of centering ratio in HE group was significantly larger than other groups (p < 0.05). At apical 5 mm level, HT group was significantly larger than PE group and PT group (p < 0.05).
Under the condition of this study, torque-controlled endodontic motor is safer than no torque controlled motor, especially when the active file is used.
-
Relative efficacy of three Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates
-
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):38-48. Published online January 31, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.038
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare and evaluate the shaping ability of the three different Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduate students.
Fifty undergraduate students prepared 150 simulated curved root canals in resin blocks with three Ni-Ti file systems - ProFile® (PF), Manual ProTaper® (MPT), Rotary ProTape® (RPT). Every student prepared 3 simulated root canals with each system respectively. After root canal preparation, the Ni-Ti files were evaluated for distortion or breakage. Assessments were made according to the presence of various types of canal aberrations. The pre- and post-instrumented canal images were attained and superimposed. The instrumented root canal width were measured and calculated for the net transportation (deviation) and the centering ratio.
Under the condition of this study, both ProTaper® systems allowed significantly more removal of root canal wall than the ProFile® system. In the important other aspects such as the centering ratio, there was no significant differences between the systems. Novice dental students were able to prepare curved root canals with any kinds of Ni-Ti file systems with little aberration and great conservation of tooth structure. Students want to learn effective methods and at the same time simple rotary procedures. The rotary ProTaper® systems were one of the most compatible to these students from the point of view of cutting ability. The ProFile® system was also compatible in safe and gentle shaping. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Prognostic factors influencing clinical outcome of nonsurgical endodontic treatment
Seonah Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 436. CrossRef - Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
T. O. Kim, G. S. P. Cheung, J. M. Lee, B. M. Kim, B. Hur, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2009; 42(1): 14. CrossRef - Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
Tae-Oh Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 323. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between single length technique and crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file
Yoo-Kyoung Lim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 385. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of rotary Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates
Mun-Seong Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between various hybrid instrumentation methods with ProTaper
Eun-Sook Hong, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 11. CrossRef
-
1,196
View
-
0
Download
-
7
Crossref
-
Microtensile bond strength of all-in-one adhesive to caries-affected dentin
-
Ji-Deok Moon, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):49-57. Published online January 31, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.049
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of multiple application of all-in-one dentin adhesive system on microtensile bond strength to caries-affected dentin.
Twenty one extracted human molars with occlusal caries extending into mid-dentin were prepared by grinding the occlusal surface flat. The carious lesions were excavated with the aid of caries detector dye. The following adhesives were applied to caries-affected dentin according to manufacturer's directions; Scotchbond™ Multi-Purpose in SM group, Adper Prompt L-Pop™ 1 coat in LP1 group, 2 coats in LP2 group, 3 coats in LP3 group, Xeno® III 1 coat in XN1 group, 2 coats in XN2 group, and 3 coats in XN3 group. After application of the adhesives, a cylinder of resin-based composite was built up on the occlusal surface. Each tooth was sectioned vertically to obtain the 1 × 1 mm2 sticks. The microtensile bond strength was determined. Each specimen was observed under SEM to examine the failure mode. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microtensile bond strength values were; SM (14.38 ± 2.01 MPa), LP1 (9.15 ± 1.81 MPa), LP2 (14.08 ± 1.75 MPa), LP3 (14.06 ± 1.45 MPa), XN1 (13.65 ± 1.95 MPa), XN2 (13.98 ± 1.60 MPa), XN3 (13.88 ± 1.66 MPa). LP1 was significantly lower than the other groups in bond strength (p < 0.05). All groups except LP1 were not significantly different in bond strength (p > 0.05).
2. In LP1, there were a higher number of specimens showing adhesive failure. Most specimens of all groups except LP1 showed mixed failure.
-
A comparison of shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals
-
So-Youn Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):58-65. Published online January 31, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.058
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals.
Thirty resin blocks were divided into 3 groups with 10 canals each. Each group was instrumented with manual ProTaper® (Group M), rotary ProTaper® (Group R), and hybrid technique (Group H). Canal preparation time was recorded. The images of pre- and post-instrumented root canals were scanned and superimposed. The amounts of canal deviation, total canal width, inner canal width, outer canal width and centering ratio were measured at apical 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 mm levels.
1. Canal preparation time was the shortest in R group (p < 0.05).
2. The amounts of total canal width in R group was generally larger than the other groups, but no significant differences were observed except at the 1, 3 mm levels (p > 0.05).
3. The amounts of inner canal width in R group was larger than M group at the 1 mm level and H group was larger than R group at the 6 mm level (p < 0.05). The amounts of outer canal width in R group was larger than H group only at the 1 mm level (p < 0.05).
4. The direction of canal deviation in H, R group at the 1, 2, 3 mm levels was outward and that in M group at the 1, 2 mm levels was inward. The amounts of canal deviation in H group was larger than R group at the 6 mm level (p < 0.05).
5. The amounts of centering ratio in H group was larger than R group at the 6 mm level (p < 0.05).
-
The etching effects and microtensile bond strength of total etching and self-etching adhesive system on unground enamel
-
Sun-Kyong Oh, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):273-280. Published online May 31, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.273
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the etching effects and bond strength of total etching and self-etching adhesive system on unground enamel using scanning electron microscopy and microtensile bond strength test.
The buccal coronal unground enamel from human extracted molars were prepared using low-speed diamond saw. Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (group SM), Clearfil SE Bond (group SE), or Adper Prompt L-Pop (group LP) were applied to the prepared teeth, and the blocks of resin composite (Filtek Z250) were built up incrementally. Resin tag formation was evaluated by scanning electron microscopy, after removal of enamel surface by acid dissolution and dehydration. For microtensile bond strength test, resin-bonded teeth were sectioned to give a bonded surface area of 1mm2. Microtensile bond strength test was perfomed.
The results of this study were as follows.
1. A definite etching pattern was observed in Scotchbond Multi-Purpose group.
2. Self-etching groups were characterized as shallow and irregular etching patterns.
3. The results (mean) of microtensile bond strength were SM; 26.55 MPa, SE; 18.15 MPa, LP; 15.57 MPa. SM had significantly higher microtensile bond strength than SE and PL (p < 0.05), but there was no significant differance between SE and PL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on lithium disilicate ceramic and dentin
Hye-Jin Shin, Chang-Kyu Song, Se-Hee Partk, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 184. CrossRef - Effects of one or two applications of all-in-one adhesive on microtensile bond strength to unground enamel
Chang-Yong Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(6): 445. CrossRef
-
1,054
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Crossref
|