Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Nanoleakage of apical sealing using a calcium silicate-based sealer according to canal drying methods
- Yoon-Joo Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e20. Published online April 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e20

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the nanoleakage of root canal obturations using calcium silicate-based sealer according to different drying methods.
Materials and Methods Fifty-two extracted mandibular premolars with a single root canal and straight root were selected for this study. After canal preparation with a nickel-titanium rotary file system, the specimens were randomly divided into 4 groups according to canal drying methods (1: complete drying, 2: blot drying/distilled water, 3: blot drying/NaOCl, 4: aspiration only). The root canals were obturated using a single-cone filling technique with a calcium silicate–based sealer. Nanoleakage was evaluated using a nanoflow device after 24 hours, 1 week, and 1 month. Data were collected twice per second at the nanoscale and measured in nanoliters per second. Data were statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann–Whitney
U -tests (p < 0.05).Results The mean flow rate measured after 24 hours showed the highest value among the time periods in all groups. However, the difference in the flow rate between 1 week and 1 month was not significant. The mean flow rate of the complete drying group was the highest at all time points. After 1 month, the mean flow rate in the blot drying group and the aspiration group was not significantly different.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, the canal drying method had a significant effect on leakage and sealing ability in root canal obturations using a calcium silicate-based sealer. Thus, a proper drying procedure is critical in endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
- 2,514 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of vibration characteristics of file systems for root canal shaping according to file length
- Seong-Jun Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Hyo-Jin Ji, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e51. Published online October 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives No studies have yet assessed vibration characteristics according to endodontic file length. Accordingly, the objective of the present study was to examine the vibration characteristics according to nickel-titanium file length and to compare these characteristics between different file systems.
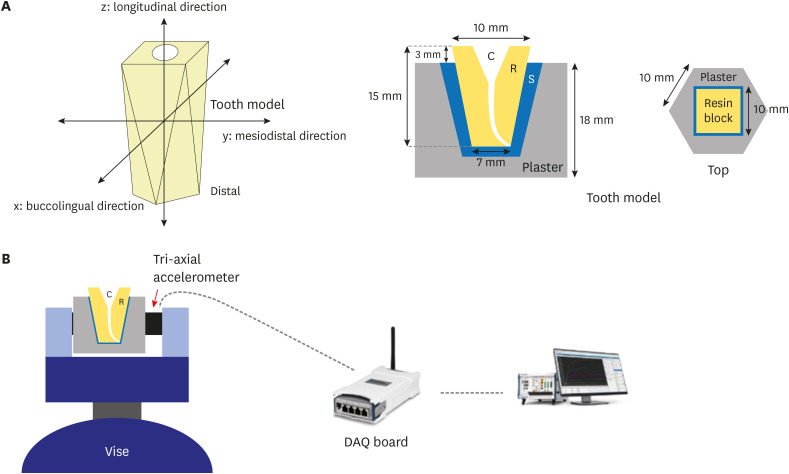
Materials and Methods A total of 45 root canal models were divided into 3 experimental groups (
n = 15 each) based on the file system used (ProTaper Gold [PTG], ProTaper Next, or WaveOne Gold [WOG]). Each experimental group was further divided into 3 subgroups according to file length (21, 25, or 31 mm). An electric motor (X-SMART PLUS) was used in the experiment. For each file system, vibrations generated when using a size 25 file were measured and used to calculate the average vibration acceleration. The differences in vibrations were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Scheffépost hoc test with a confidence interval of 95%.Results In the PTG file system, significantly lower vibration acceleration was observed when using a 21-mm file than when using a 31-mm file. In the WOG file system, significantly stronger vibration acceleration was observed when using a 31-mm file than when using 21- or 25-mm files. Regardless of the file length, the WOG group exhibited significantly stronger vibration acceleration than the other 2 experimental groups.
Conclusions In clinical practice, choosing a file with the shortest length possible could help reduce vibrations. Additionally, consideration should be given to vibrations that could be generated when using WOG files with reciprocating motion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison vibration characteristics of several wireless endodontic handpieces
Bo-Kyung Lee, Yoon Lee, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2022; 38(2): 81. CrossRef
- Comparison vibration characteristics of several wireless endodontic handpieces
- 1,498 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A cone-beam computed tomography study of the prevalence and location of the second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars
- Seong-Ju Lee, Eun-Hye Lee, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e46. Published online September 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e46
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
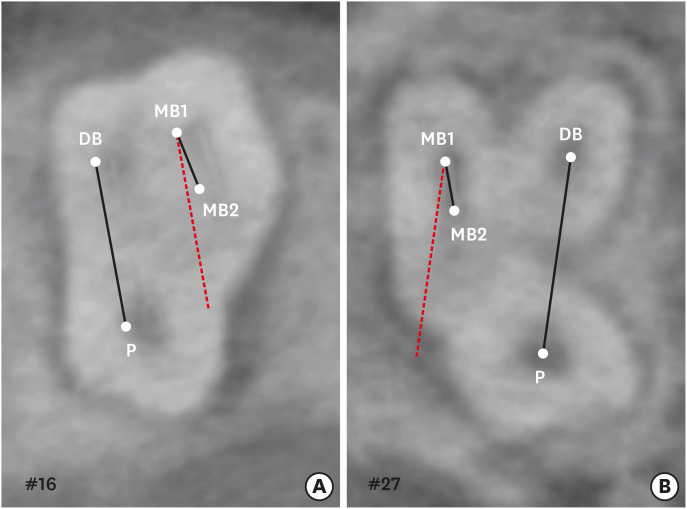
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the incidence and location of the second mesiobuccal root (MB2) canal in maxillary molars with the aid of various measuring points and lines using cone-beam computed tomography (CT).
Materials and Methods A total of 205 images of patients who underwent cone-beam CT examinations between 2011 and 2015 as part of their dental diagnosis and treatment were included. There were 76 images of the maxillary first molar and 135 images of the maxillary second molar. Canal orifices were detected at −1 mm from the top of the pulpal floor on cone-beam CT images. Image assessment was performed by 2 observers in reformatted image planes using software. Assessments included measurement of the distance between the MB1 and MB2 canals, and the angles between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and distobuccal (DB)-palatal (P) canals. The data were analyzed using the student's
t -test.Results The prevalence of the MB2 canal was 86.8% in the first molar and 28.9% in the second molar. The angle between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and DB-P canals was 2.3° ± 5.7° in the first molar and −3.95° ± 7.73° in the second molar. The distance between the MB1 and MB2 canals was 2.1 ± 0.44 mm in the first molar and 1.98 ± 0.42 mm in the second molar.
Conclusions The angles between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and DB-P canals was almost parallel. These findings may aid in the prediction of the location of the MB2 canal orifice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Position of Second Mesiobuccal Canal Relative to Distobuccal and Palatal Canals of Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population
Sina Mosadeghian, Azadeh Torkzadeh, Parisa Ranjbarian, Roya Asaadi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - EVALUATION OF THE PREVALENCE AND LOCATION OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANALS IN 2100 UPPER FIRST AND SECOND MOLAR TEETH: A CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY STUDY
Bahar Kaplan, Özkan Adıgüzel, Ayşe Gül Öner Talmaç, Elif Meltem Aslan
İnönü Üniversitesi Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi.2025; 13(3): 752. CrossRef - A novel method for the precise second mesiobuccal canal orifice location: A combined strategy for enhanced clinical practice
Yuhan Wang, Lingyun Li, Lu Zhang, Xiaoyan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the Geometric Location Method of the Danger Zone in the Mesial Roots of Mandibular First Molars
Jinjie Yan, Yuanling Peng, Jing Yang, Jie Liu, Linxian Wang, Tingyuan Zhao, Jian Zhang, Kehua Que
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Correlation between Intraorifice Distance and the Anatomical Characteristics of the Second Mesiobuccal Canal of Maxillary Molars: A CBCT Study
Isabella Perondi, Silvio Taschieri, Martino Baruffaldi, Roberto Fornara, Luca Francetti, Stefano Corbella, Deepa Gurunathan
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of type I maxillary first molar with two palatal roots using cone-beam computed tomography
Nuha Alghamdi
Dental Journal.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - 3D geometric analysis of second mesiobuccal canal in permanent maxillary first molar tooth
Indrani Khadilkar, Divya Nangia, Amrita Chawla, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Shalini Gupta, Ajay Logani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 140. CrossRef - Prevalence of mesiobuccal-2 canals in maxillary first and second molars among the Bruneian population—CBCT analysis
Hui Yi Onn, Malissa Siao Yun Abdullah Sikun, Hanif Abdul Rahman, Jagjit Singh Dhaliwal
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Location angle of second mesio-buccal canal in maxillary molars of an Indian population: an in vivo retrospective CBCT evaluation and proposal of a new classification
Kishor Vhorkate, Kulvinder Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Shugufta Mir, Suraj Arora, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Anuj Bhardwaj, Alexander Maniangat Luke
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14234. CrossRef - Maxillary molar root and canal morphology of Neolithic and modern Chinese
H.Y. Ren, K.Y. Kum, Y.S. Zhao, Y.J. Yoo, J.S. Jeong, Hiran Perinpanayagam, X.Y. Wang, G.J. Li, F. Wang, H. Fang, Y. Gu
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 131: 105272. CrossRef
- Position of Second Mesiobuccal Canal Relative to Distobuccal and Palatal Canals of Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population
- 4,100 View
- 45 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Fiber-reinforced composite resin bridges: an alternative method to treat root-fractured teeth
- Gun Heo, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e8. Published online December 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The replacement of missing teeth, especially in the anterior region, is an essential part of dental practice. Fiber-reinforced composite resin bridges are a conservative alternative to conventional fixed dental prostheses or implants. It is a minimally invasive, reversible technique that can be completed in a single visit. The two cases presented herein exemplify the treatment of root-fractured anterior teeth with a natural pontic immediately after extraction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prosthodontic Aspects of Splinting the Mandibular Anterior Teeth by Fiber Reinforced Composites
Hrelja Miroslav, Laškarin Mirko, Čimić Samir, Kraljević Sonja, Dulčić Nikša, Badel Tomislav
Journal of Dental Problems and Solutions.2025; 12(1): 004. CrossRef - Current Evidence on the Fiber-reinforced Composite Bridges
Ramesh Chowdhary, Sunil Kumar Mishra
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 12(4): 159. CrossRef - Bridging the Gap: A Case Report of Tooth Replacement using Resin-Bonded Fiber- Reinforced Composite Resin
Vineet Sharma, Sumit Bhansali, Sonal Priya Bhansali
Journal of Pierre Fauchard Academy (India Section).2023; : 66. CrossRef - Reconstruction of Natural Smile and Splinting with Natural Tooth Pontic Fiber‐Reinforced Composite Bridge
Maryam S. Tavangar, Fatemeh Aghaei, Massoumeh Nowrouzi, Andrea Scribante
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prosthodontic Aspects of Splinting the Mandibular Anterior Teeth by Fiber Reinforced Composites
- 2,077 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Plugger temperature of cordless heat carriers according to the time elapsed
- Hoon-Sang Chang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e12. Published online February 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e12

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
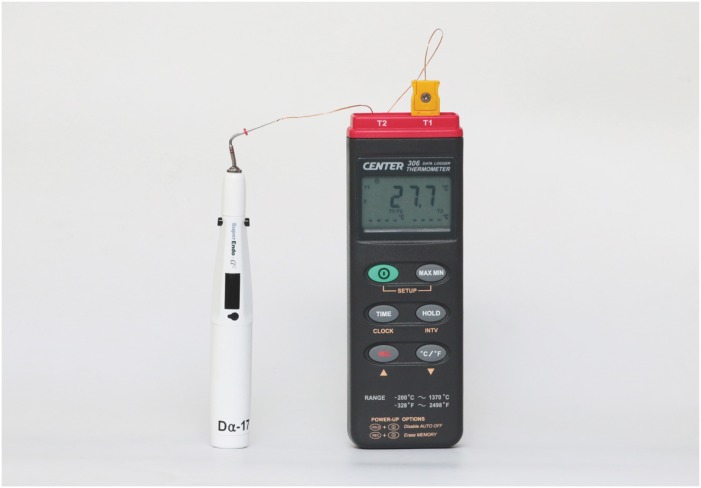
ePub Objective The purpose of this study was to measure the temperature of the plugger tip of 3 cordless heat carriers set at 200°C.
Materials and Methods Pluggers of the same taper (0.06, 0.08, 0.10) and similar tip sizes (sizes of 50 and 55) from 3 cordless heat carriers, namely SuperEndo-α2 (B & L Biotech), Friendo (DXM), and Dia-Pen (Diadent), were used and an electric heat carrier, System B (SybronEndo), was used as the control. The plugger tips were covered with customized copper sleeves, heated for 10 seconds, and the temperature was recorded with a computerized measurement system attached to a K-type thermometer at room temperature (
n = 10). The data were analyzed with 2-way analysis of variance at a 5% level of significance.Results The peak temperature of the plugger tips was significantly affected by the plugger taper and by the heat carrier brand (
p < 0.05). The peak temperature of the plugger tips was between 177°C and 325°C. The temperature peaked at 207°C–231°C for the 0.06 taper pluggers, 195°C–313°C for the 0.08 taper pluggers, and 177°C–325°C for the 0.10 taper pluggers. Only 5 of the 12 plugger tips showed a temperature of 200°C ± 10°C. The time required to reach the highest temperature or 200°C ± 10°C was at least 4 seconds.Conclusion When using cordless heat carriers, clinicians should pay attention to the temperature setting and to the activation time needed to reach the intended temperature of the pluggers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Temperature Variation with Three Continuous Wave Obturation Systems in Endodontics: An In Vitro Study
Jesús Mena-Álvarez, Maria Ruiz-Barrio, Norberto Quispe-López, Ana de Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6229. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Softening versus Ultrasonic Removal of Root-End Gutta-Percha on the Quality of Root-End Preparation for Endodontic Microsurgery
Zhiting Ling, Ziting Zheng, Yuting Zeng, Lifang Jiang, Yuan Wu, Buling Wu, Wenjuan Yan, Lavinia C. Ardelean
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Temperature Variation with Three Continuous Wave Obturation Systems in Endodontics: An In Vitro Study
- 1,299 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Differential diagnosis of periapical cyst using collagen birefringence pattern of the cyst wall
- Hyo Jin Ji, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Suk Keun Lee, Jin Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):111-117. Published online February 9, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Periapical lesions, including periapical cyst (PC), periapical granuloma (PG), and periapical abscess (PA), are frequently affected by chemical/physical damage during root canal treatment or severe bacterial infection, and thus, the differential diagnosis of periapical lesions may be difficult due to the presence of severe inflammatory reaction. The aim of this study was to make differential diagnosis among PC, PG, and PA under polarizing microscope.
Materials and Methods The collagen birefringence patterns of 319 cases of PC (
n = 122), PG (n = 158), and PA (n = 39) obtained using a polarizing microscope were compared. In addition, 6 cases of periodontal fibroma (PF) were used as positive controls.Results Collagen birefringence was condensed with a thick, linear band-like pattern in PC, but was short and irregularly scattered in PG, and scarce or absent in PA. PF showed intense collagen birefringence with a short, palisading pattern but no continuous band-like pattern. The linear band-like birefringence in PC was ascribed to pre-existing expansile tensile stress of the cyst wall.
Conclusions In this study all PCs (
n = 122) were distinguishable from PGs and PAs by their characteristic birefringence, despite the absence of lining epithelium (n = 20). Therefore, the authors suggest that the presence of linear band-like collagen birefringence of the cyst wall aids the diagnostic differentiation of PC from PG and PA.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interplay of collagen and mast cells in periapical granulomas and periapical cysts: a comparative polarizing microscopic and immunohistochemical study
Deepty Bansal, Mala Kamboj, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi, Nisha Marwah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interplay of collagen and mast cells in periapical granulomas and periapical cysts: a comparative polarizing microscopic and immunohistochemical study
- 1,977 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Phosphoric acid etching for multi-mode universal adhesive
- Kyung-Mo Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):157-158. Published online April 5, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.157
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Nd:YAG laser irradiation on microtensile bond strength of universal adhesives to dentin
Shiva Jafarnia, Javad Zeinaddini Meymand, Fateme Zandkarimi, Sogol Saberi, Alireza Valanezhad, Sima Shahabi
Laser Physics.2021; 31(5): 055602. CrossRef
- Effect of Nd:YAG laser irradiation on microtensile bond strength of universal adhesives to dentin
- 1,298 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
- Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):7-11. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) rotary files and verify the size conformity.
Materials and Methods ProFile (Dentsply Maillefer), RaCe (FKG Dentaire), and TF file (SybronEndo) #25 with a 0.04 and 0.06 taper were investigated, with 10 in each group for a total of 60 files. Digital images of Ni-Ti files were captured under light microscope (SZX16, Olympus) at 32×. Taper and diameter at D1 to D16 of each files were calculated digitally with AnalySIS TS Materials (OLYMPUS Soft Imaging Solutions). Differences in taper, the diameter of each level (D1 to D16) at 1 mm interval from (ANSI/ADA) specification No. 101 were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's
post-hoc test at 95% confidence level.Results TF was the only group not conform to the nominal taper in both tapers (
p < 0.05). All groups except 0.06 taper ProFile showed significant difference from the nominal diameter (p < 0.05).Conclusions Actual size of Ni-Ti file, especially TF, was different from the manufacturer's statements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ex Vivo Evaluation of the Fit of Matched Gutta Percha Points in Human Root Canals Prepared With the Corresponding Nickel‐Titanium Files
Samuel Deng, Paul V. Abbott
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 684. CrossRef - Diameter and Taper Variability of Single-file Instrumentation Systems and Their Corresponding Gutta-percha Cones
Franziska Haupt, Miriam Seidel, Marta Rizk, Hans-Georg Sydow, Annette Wiegand, Tina Rödig
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(9): 1436. CrossRef
- Ex Vivo Evaluation of the Fit of Matched Gutta Percha Points in Human Root Canals Prepared With the Corresponding Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,550 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Chronic maxillary sinusitis caused by root canal overfilling of Calcipex II
- Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Soh-Ra Park, Sang-Shin Lee, Suk-Keun Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):63-67. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.63
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This is a case report of chronic maxillary sinusitis caused by root canal overfilling of Calcipex II (Techno-Dent). A 60 year-old male complained of dull pain in the right maxillary molar area after complicated endodontic treatment using Calcipex II paste and was finally diagnosed with a chronic maxillary sinusitis through a clinical and radiological observation. In the biopsy examination, the periapical granuloma contained a lot of dark and translucent Calcipex II granules which were not stained with hematoxylin and eosin. They were usually engulfed by macrophages but rarely resorbed, resulting in scattering and migrating into antral mucosa. Most of the Calcipex II granules were also accumulated in the cytoplasms of secretory columnar epithelial cells, and small amount of Calcipex II granules were gradually secreted into sinus lumen by exocytosis. However, chronic granulomatous inflammation occurred without the additional recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and lymphocytes, and many macrophages which engulfed the Calcipex II granules were finally destroyed in the processes of cellular apoptosis. It is presumed that Calcipex II granules are likely to have a causative role to induce the granulomatous foreign body inflammation in the periapical region, and subsequently to exacerbate the chronic maxillary sinusitis in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
Dohee Kim, Young Kim, Jeong Joon Han
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic effects of reduced graphene oxide on the antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments containing different vehicles
Mi-Ah Kim, Min-Kyeong Kim, Eun-Sook Kang, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - The effect of extrusion of the filling material on the periapical status
M. Yu. Pokrovsky, T. P. Goryacheva, A. М. Pokrovskiy, O. А. Aleshina
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 31. CrossRef - Rheological properties and handling characteristics of four injectable calcium hydroxide pastes
Min-Jung KIM, In-Bog LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 796. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of jet dispenser versus direct syringe injection for calcium hydroxide paste placement in artificial root canals
Youngwook Song, Hwichan Ham, WooCheol Lee, Ryan Jin Young Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A white cloud in the antrum: Maxillary sinusitis following an endodontic treatment
Kamis Gaballah, Mawada Hassan
Asian Journal of Surgery.2023; 46(4): 1690. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The significance of diagnosis and treatment planning in periapical lesion overfilled with calcium hydroxide paste
Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Eun-Young Kwon, Youn-Kyung Choi, So-Yeun Kim, Hye-Mi Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(2): 95. CrossRef - Maxillary antroliths detected by cone-beam computed tomography in an adult dental population
Bong-Hae Cho, Yun-Hoa Jung, Jae-Joon Hwang
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2019; 49(1): 59. CrossRef - Influence of the Maxillary Sinus on the Accuracy of the Root ZX Apex Locator: An Ex Vivo Study
Roula El Hachem, Elie Wassef, Nadim Mokbel, Richard Abboud, Carla Zogheib, Nada El Osta, Alfred Naaman
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(1): 3. CrossRef - Removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a calcium hydroxide paste using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone as a vehicle
Myung-Jin Lim, Hyun-Jin Jang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 290. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef - Maxillary Sinus Impaction of a Core Carrier Causing Sustained Apical Periodontitis, Sinusitis, and Nasal Stenosis: A 3-year Follow-up
Lars Bjørndal, Catharina Amaloo, Merete Markvart, Vibe Rud, Klaus Qvortrup, Camilla Stavnsbjerg, Thomas Bjarnsholt
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(12): 1851. CrossRef - Proximity of Posterior Teeth to the Maxillary Sinus and Buccal Bone Thickness: A Biometric Assessment Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Sung Hyun Kang, Bom Sahn Kim, Yemi Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1839. CrossRef
- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
- 2,284 View
- 8 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Accuracy of Root ZX in teeth with simulated root perforation in the presence of gel or liquid type endodontic irrigant
- Hyeong-Soon Shin, Won-Kyung Yang, Mi-Ri Kim, Hyun-Jung Ko, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):149-154. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the accuracy of the Root ZX in teeth with simulated root perforation in the presence of gel or liquid type endodontic irrigants, such as saline, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine liquid, 2% chlorhexidine gel, and RC-Prep, and also to determine the electrical conductivities of these endodontic irrigants.
Materials and Methods A root perforation was simulated on twenty freshly extracted teeth by means of a small perforation made on the proximal surface of the root at 4 mm from the anatomic apex. Root ZX was used to locate root perforation and measure the electronic working lengths. The results obtained were compared with the actual working length (AWL) and the actual location of perforations (AP), allowing tolerances of 0.5 or 1.0 mm. Measurements within these limits were considered as acceptable. Chi-square test or the Fisher's exact test was used to evaluate significance. Electrical conductivities of each irrigant were also measured with an electrical conductivity tester.
Results The accuracies of the Root ZX in perforated teeth were significantly different between liquid types (saline, NaOCl) and gel types (chlorhexidine gel, RC-Prep). The accuracies of electronic working lengths in perforated teeth were higher in gel types than in liquid types. The accuracy in locating root perforation was higher in liquid types than gel types. 5.25% NaOCl had the highest electrical conductivity, whereas 2% chlorhexidine gel and RC-Prep gel had the lowest electrical conductivities among the five irrigants.
Conclusions Different canal irrigants with different electrical conductivities may affect the accuracy of the Root ZX in perforated teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vivo and In Vitro Accuracy and Precision Evaluations of Mini Electronic Apex Locators
Özlem Kara, Rüstem Kemal Sübay
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 329. CrossRef - Effect of different kinematics and perforation diameter on integrated electronic apex locator accuracy in detecting root canal perforations
Ecenur Tuzcu, Safa Kurnaz
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of precipitate formation in the root canal on the accuracy of electronic apex locators
Kürşat Er, Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Ömer Kesmez, Feride Demir, Eszther Borbely
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(4): 161. CrossRef - Effect of Different Electroconductive Root Canal Irrigations on the Accuracy of Different Apex Locators: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Eman M. Yahya, Ashraf S. Alchalabi, Emad Farhan Alkhalidi
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2024; 14(3): 211. CrossRef - The precision of radiographic and electronic working length estimation methods in endodontics: A systematic review of clinical studies
Anithakumari Rangappa, Buvaneshwari Arul, Jayalakshmi Somasundaram, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Accuracy and Reliability of Three Electronic Apex Locators in Determining the Apical Constriction of Molar Canals: A Micro-CT Evaluation
Reem M. Barakat, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Arwa O. Alharbi, Asma Alhazmi, Reem Alomar
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(17): 5199. CrossRef - Accuracy of the integrated electronic apex locator in locating simulated perforation under various irrigating solutions in an in vitro study
Chintan Joshi, Surabhi Joshi, Urooj Desai, Sweety Thumar, Aashray Patel, Ankita Khunt
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e241118. CrossRef - The Accuracy of Different Apex Locator Systems in Detecting Root Perforations in the Presence of Different Irrigation Solutions
Oğuz Burhan Çetinkaya, Emre Çulha, Uğur Aydın
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 30(1): 39. CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of the Accuracy of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scanning and Electronic Apex Locators in Detection of Simulated Root Perforations in Different Localizations
Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç, Alper Kuştarcı
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(12): 1676. CrossRef - Accuracy of different electronic apex locators in determination of minimum Root perforation diameter
Simay Koç, Alper Kuştarcı, Kürşat Er
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 179. CrossRef - The influence of MTAD and QMix on the accuracy of electronic apex locator in locating simulated perforations
A Dumani, AA Ates, CS Ucan, S Yilmaz, I Unal, O Yoldas
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(3): 281. CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of grafted xanthan gum as a drug carrier in developing lornoxicam gel formulations
SandipAshok Murtale, PrakashS Goudanavar, NRaghavendra Naveen, WalaaF Alsanie, Majid Alhomrani, AbdulhakeemS Alamri, SyedMohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, MdKhalid Anwer, Nagaraja Sreeharsha, MazenAl Gharsan, Santosh Fattepur
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - KOMBİNE İRRİGASYON SOLÜSYONLARININ ELEKTRİKSEL İLETKENLİĞİNİN KARŞILAŞTIRILMASI
Ayşin DUMANİ, Şehnaz YILMAZ, Oğuz YOLDAŞ, Güray KILINÇÇEKER
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Accuracy of Different Apex Locators: Propex IQ, Raypex 6, Root ZX, and Apex ID with CBCT and Periapical Radiograph—In Vitro Study
Okba Mahmoud, Mawada Hassan Awad Abdelmagied, Ahmad Hisham Dandashi, Bakr Nssaief Jasim, Hussam Alddin Tawfik Kayali, Saaid Al Shehadat, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Temperature Increase From Joule Heat in Numerical Tooth Model by Applying 500 kHz Current for Apical Periodontitis Treatment—Effect of Applied Voltage and Tooth Conductivity
Hiroo Tarao, Masatake Akutagawa, Takahiro Emoto, Amane Takei, Hiromichi Yumoto, Toshihiko Tominaga, Toshitaka Ikehara, Yosuke Kinouchi
Bioelectromagnetics.2021; 42(3): 224. CrossRef - Confort visual en oficinas, factor temporal en la evaluación de deslumbramiento
J. Yamin, A. Pattini, E. Colombo
Informes de la Construcción.2020; 72(557): e329. CrossRef - The influence of two forms of chlorhexidine on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators
Ewa Marek, Ryta Łagocka, Katarzyna Kot, Krzysztof Woźniak, Mariusz Lipski
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of an integrated apex locator in determining working length in various irrigating solutions: An in vivo study
RakeshReddy Chukka, MalatiDevi Bellam, NarenderReddy Marukala, Sainath Dinapadu, NareshKumar Konda, Jithender Nagilla
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2020; 12(5): 410. CrossRef - Accuracy of two electronic apex locators in locating root perforations in curved canals in dry and wet conditions: A comparative in vitro study
MonishaParshotam Khatri, SheetalB Ghivari, Madhu Pujar, Reshma Faras, Pallavi Gopeshetti, Amulya Vanti
Dental Research Journal.2019; 16(6): 407. CrossRef - Consistency of electronic measurements of endodontic working length when using multiple devices from the same manufacturer—an in vitro study
Franziska Haupt, M Hülsmann
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(9): 3107. CrossRef - The Influence of Various Irrigants on the Accuracy of 2 Electronic Apex Locators in Locating Simulated Root Perforations
Demet Altunbaş, Alper Kuştarcı, Mustafa Toyoğlu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 439. CrossRef - Accuracy and Repeatability of 3 Apex Locators in Locating Root Canal Perforations: An Ex Vivo Study
Fábio Luiz Cunha D'Assunção, Julio Cézar Nascimento Sousa, Kayo César Amaro Felinto, Thiago Clístines de Medeiros, Diego Tavares Leite, Raissa Bezerra de Lucena, Joab de Oliveira Lima
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1241. CrossRef
- In Vivo and In Vitro Accuracy and Precision Evaluations of Mini Electronic Apex Locators
- 1,418 View
- 7 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in .06 taper ProFile
- Hye-Rim Jung, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):79-83. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relation between intentionally induced internal stress and cyclic fatigue failure of .06 taper ProFile.
Materials and Methods Length 25 mm, .06 taper ProFile (Dentsply Maillefer), and size 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 were used in this study. To give the internal stress, the rotary NiTi files were put into the .02 taper, Endo-Training-Bloc (Dentsply Maillefer) until auto-stop by torque controlled motor. Rotary NiTi files were grouped by the number of induced internal stress and randomly distributed among one control group and three experimental groups (
n = 10, Stress 0 [control], Stress 1, Stress 2 and Stress 3). For cyclic fatigue measurement, time for separation of the rotary NiTi files was recorded. The fractured surfaces were observed by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, SU-70, Hitachi). The time for separation was statistically analyzed using two-way ANOVA andpost-hoc Scheffe test at 95% level.Results In .06 taper ProFile size 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40, there were statistically significant difference on time for separation between control group and the other groups (
p < 0.05).Conclusion In the limitation of this study, cyclic fatigue failure of .06 taper ProFile is influenced by internal stress accumulated in the files.
- 772 View
- 4 Download

- Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in K3
- Jun-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):74-78. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the cyclic fatigue of a K3 file and internal stress intentionally induced until the activation of the auto-stop function of the torque-controlled motor.
Materials and Methods K3 (Sybron Endo) .04 and .06 taper, size 25, 30, 35, 40 and 45 were used in this study. To give the internal stress, the K3 files were put into the .02 taper Endo-Training-Bloc (Dentsply Maillefer) until the activation of the auto-stop function of the torque-controlled motor. The rotation speed was 300 rpm and torque value was 1.0 N·cm. K3 were grouped by the number of induced internal stress and randomly distributed to 4 experimental groups (
n = 10, Stress 0 [control], Stress 1, Stress 2 and Stress 3). For measuring the cyclic fatigue failure, the K3 files were worked against a sloped glass block and time for file separation was recorded. Data was statistically analyzed Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA and Duncan post-hoc test atp < 0.05 level.Results Except .04 taper size 30 in Stress 1 group, there were statistically significant differences in time for file separation between control and all experimental groups. K3 with .04 taper showed higher cyclic fatigue resistance than those of .06 taper.
Conclusion In the limitation of this study, the cyclic fatigue of the K3 file was influenced by the accumulated internal stress from use until the auto-stop function was activated by the torque-controlled motor. Therefore, clinicians should avoid the reuse of the K3 file that has undergone auto-stops.
- 858 View
- 1 Download

- Currently there are so many fiber reinforced composite posts in the market. Some products are factory silanated but some products are not. Should I use silane for surface treatment of fiber reinforced composite posts?
- Kyung-Mo Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):127-127. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.127
- 839 View
- 1 Download

- Treatment of a lateral incisor anatomically complicated with palatogingival groove
- Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):238-242. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Palatogingival groove is a developmental anomaly that starts near the cingulum of the tooth and runs down the cementoenamel junction in apical direction, terminating at various depths along the roots. While frequently associated with periodontal pockets and bone loss, pulpal necrosis of these teeth may precipitate a combined endodontic-periodontal lesion. This case presents a case of a lateral incisor anatomically complicated with palatogingival groove.
Methods Two patients with lesion associated with the palatogingival groove were chosen for this report. Palatogingival grooves were treated with different restoration materials with endodontic treatment.
Conclusions Maxillary lateral incisor with a palatogingival groove may occur the periodontal disease with pulpal involvement. Elimination of groove may facilitate the periodontal re-attachment and prevent the recurrence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
- 1,161 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
- Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):132-138. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate curing degree of three dual-cure resin cements with the elapsed time in self-cure and dual-cure mode by means of the repeated measure of micro-hardness.
Materials and Methods Two dual-cure self-adhesive resin cements studied were Maxcem Elite (Kerr), Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE) and one conventional dual-cure resin cement was Rely-X ARC resin cement (3M ESPE). Twenty specimens for each cements were made in Teflon mould and divided equally by self-cure and dual-cure mode and left in dark, 36℃, 100% relative humidity conditional-micro-hardness was measured at 10 min, 30 min, 1 hr, 3 hr, 6 hr, 12 hr and 24 hr after baseline. The results of micro-hardness value were statistically analyzed using independent samples
t -test and one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons using Scheffe's test.Results The micro-hardness values were increased with time in every test groups. Dual-cure mode obtained higher micro-hardness value than self-cure mode except after one hour of Maxcem. Self-cured Rely-X Unicem showed lowest value and dual-cured Rely-X Unicem showed highest value in every measuring time.
Conclusions Sufficient light curing to dual-cure resin cements should provided for achieve maximum curing.
- 1,040 View
- 9 Download

- Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
- Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):125-131. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements.
Materials and Methods Pre-surface treated LuxaPost (DMG), Rely-X Fiber Post (3M ESPE) and self adhesive resin cement Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE), conventional resin cement Rely-X ARC (3M ESPE), and Rely-X Ceramic Primer (3M ESPE) were used. After completing the surface treatments of the posts, posts and resin cement were placed in clear molds and photo-activation was performed. The specimens were sectioned perpendicular to the FRC-Post into 2 mm-thick segments, and push-out strength were measured. The results of bond strength value were statistically analyzed using independent samples
t -test and one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons using Scheffe's test.Results Silanization of posts affect to the bond strength in LuxaPost, and did not affect in Rely-X Fiber Post. Rely-X ARC showed higher value than Rely-X Unicem.
Conclusions Silanization is needed to enhance the bond strength between LuxaPost and resin cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of fracture resistance and push-out bond strength of glass fiber post with composite core and single-unit post and core system luted with two different resin cements: An in vitro study
Ishika Garg, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 240. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite resin posts according to cement thickness
Jun-Seong Park, Jeong-Sub Lee, Jeong-Won Park, Won-Gyun Chung, Eun-Hee Choi, Yoon Lee
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2017; 118(3): 372. CrossRef - Currently there are so many fiber reinforced composite posts in the market. Some products are factory silanated but some products are not. Should I use silane for surface treatment of fiber reinforced composite posts?
Kyung-Mo Cho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 127. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of fracture resistance and push-out bond strength of glass fiber post with composite core and single-unit post and core system luted with two different resin cements: An in vitro study
- 1,138 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Evaluation of radiopacity and discriminability of various fiber reinforced composite posts
- Eun-Hye Lee, Hang-Moon Choi, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):188-197. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare radiopacity and radiographic discriminability of various FRC-Posts.
Six FRC-Posts were investigated ; 1) FRC Postec Plus (Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein), 2) Snowlight (Carbotech, Lewis center, OH, USA), 3) Dentin Post (Komet Brasseler, Lamgo, Germany), 4) Rely-X Fiber Post (3M ESPE, St.paul, MN, USA), 5) D.T.-Light Post (BISCO, Schaumburg, IL,USA), 6) Luxapost (DMG, Hamburg, Germany)
The radiographs of each post with a reference 1 mm / 2 mm aluminum step-wedge was taken using digital sensor. The optical density were calculated by gray value of 10 × 10 pixel and compared in mm Al equivalent at five points.
Six maxillary incisors of similar radiopacity were used. Radiographs of posts in Mx. incisors of lingual side of dry mandible were taken.
We showed radiographs and asked the questionnaire to 3 radiologists, 3 endodontists, 3 general practitioners. The questionnaire was comprised of choices of the highest, lowest radiopaque individual post and the choices of best discriminable post at apical, coronal area.
The following results were obtained.
Each post system showed various radiopacity.
There was change of discriminability between each post and simulated specimens regardless of examiner.
Although each post showed various radiopacity, the difference of radiopacity did not affect on discriminability.
- 1,011 View
- 4 Download

- The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
- Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):80-87. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.080
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the different canal irrigation methods to prevent the formation of precipitate between sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and chlorhexidine (CHX).
Extracted 50 human single-rooted teeth were used. The root canals were instrumented using NiTi rotary file (Profile .04/#40) with 2.5% NaOCl and 17% EDTA as irrigants. Teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups and one control group as follows; Control group: 2.5% NaOCl only, Group 1: 2.5% NaOCl + 2% CHX, Group 2: 2.5% NaOCl + paper points + 2% CHX, Group 3: 2.5% NaOCl + preparation with one large sized-file + 2% CHX, Group 4: 2.5% NaOCl +95% alcohol+ 2% CHX.
The teeth were split in bucco-lingual aspect and the specimens were observed using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope. The percentages of remaining debris and patent dentinal tubules were determined. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Energy Dispersive x-ray Spectroscopy was used for analyzing the occluded materials in dentinal tubule for elementary analysis.
There were no significant differences in percentage of remaining debris and patent tubules between all experimental groups at all levels (p > .05).
In elementary analysis, the most occluded materials in dentinal tubule were dentin debris. NaOCl/CHX precipitate was detected in one tooth specimen of Group 1.
In conclusion, there were no significant precipitate on root canal, but suspected material was detected on Group 1. The irrigation system used in this study could be prevent the precipitate formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 295. CrossRef
- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
- 1,732 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Mouthguard for relief of repeated clenching stress to cervical restorations during exercises
- Sung-Young Yoon, Chang-Kyu Song, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):20-23. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.020
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mouthguards were used to protect boxers from lip lacerations and other soft tissue injuries in the late 19th century. Now they are used various parts of dental treatment, which are sports protective aid, bleaching tray, orthodontic retainer, implant insertion guide tray, splint and so on.
Repeated dislodgement of Class V restoration due to habitual clenching stress should be restored with stress control. Mouthguard can be used as stress relief device.
This case describes methods that can relieve occlusal force to teeth by using mouthguard.
Satisfactory results can be obtained by using mouthguard for retention of repeated dislodgement Class V restorations.
If patients suffered from repeated restorations of Class V due to clenching, mouthguard can be used additional device to relieve the occlusal stress in conservative dentistry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of the Effects of Teeth Clenching Due to Weight Training on Oral Health
Sang Min Lee, Eun Chae Lee, Juwon Gong, Chae Eun Jang, Young Sun Hwang
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(3): 152. CrossRef - Sports-Related Oral and Maxillofacial Injuries: A 5-Year Retrospective Study, Pusan National University Dental Hospital
Han-Kyul Park, Jin-Young Park, Na-Rae Choi, Uk-Kyu Kim, Dae-Seok Hwang
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2021; 79(1): 203.e1. CrossRef - Influencing factors on oral and maxillofacial trauma prevention education experience of students majoring in physical education
Kyeung-Ae Jang
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2014; 14(6): 915. CrossRef - Correlation between maxillofacial injury, use of mouth guards and stress in physical education majoring male students
Jong-Hwa Jang, Jee-Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Emergency Medical Services.2013; 17(2): 89. CrossRef
- Investigation of the Effects of Teeth Clenching Due to Weight Training on Oral Health
- 1,097 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Management of fibrous hyperplasia in oral mucosa
- Sun-Young Ham, Chang-Kyu Song, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):340-345. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.340
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are a number of situations where the oral mucosa can be sucked or pressed to produce relatively banal but clinical distinctive changes. The labial and buccal mucosa and tongue may develop protuberances in areas where a tooth is missing or extra space is present. The mucosa is pressed and sucked into these spaces, thus leading to the development of a fibrous hyperplasia.
This case report describes the management of fibrous hyperplasia in oral mucosa.
Fibrous hyperplasia can be formed by habitual pressure or suction in oral mucosa. Treatment of fibrous hyperplasia consists of simple excision and, if feasible, elimination of the cause. And habit control is a important factor for preventing recurrence.
- 1,101 View
- 5 Download

- Physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on lithium disilicate ceramic and dentin
- Hye-Jin Shin, Chang-Kyu Song, Se-Hee Partk, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):184-191. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on dentin and lithium disilicate ceramic and compare these result with that of conventional resin cement. For this study, four self-adhesive resin cements (Rely-X Unicem, Embrace Wetbond, Mexcem, BisCem), one conventional resin cement (Rely-X ARC) and one restorative resin composite (Z-350) were used. In order to evaluate the physical properties, compressive strength, diametral tensile strength and flexural strength were measured. To evaluate the shear bond strength on dentin, each cement was adhered to buccal dentinal surface of extracted human lower molars. Dentin bonding agent was applied after acid etching for groups of Rely-X ARC and Z-350. In order to evaluate the shear bond strength on ceramic, lithium disilicate glass ceramic (IPS Empress 2) disks were prepared. Only Rely-X ARC and Z-350 groups were pretreated with hydrofluoric acid and silane. And then each resin cement was adhered to ceramic surface in 2 mm diameter. Physical properties and shear bond strengths were measured using a universal testing machine.
Results were as follows
1. BisCem showed the lowest compressive strength, diametral tensile strength and flexural strength. (
P <0.05)2. Self-adhesive resin cements showed significantly lower shear bond strength on the dentin and lithium disilicate ceramic than Rely-X ARC and Z-350 (
P <0.05)In conclusion, self-adhesive resin cements represent the lower physical properties and shear bond strength than a conventional resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Compressive Strength Evaluation in Brazed ZrO2/Ti6Al4V Joints Using Finite Element Analysis
Ashutosh Sharma, Se Ho Kee, Flora Jung, Yongku Heo, Jae Pil Jung
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2016; 25(5): 1722. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef - The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 139. CrossRef
- Compressive Strength Evaluation in Brazed ZrO2/Ti6Al4V Joints Using Finite Element Analysis
- 1,295 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
- Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):95-102. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of light energy on the tooth whitening effect of bleaching agent in vitro. Extracted human mandibular molars were sectioned to 2 fragments(mesial, distal) and lingual portions of crown were used in this study. All specimens were stained using a red wine for 24 hours and immersed in artificial saliva. Specimens divided into four groups, group 1 and 2 light-activated by LumaCool (LED, LumaLite, Inc., Spring Valley, USA), group 3 and 4 light-activated by FlipoWhite2 (Plasma acr lamp, Lokki, Australia). Group 1 and 3 bleached with LumaWhite(LumaLite, Inc., Spring Valley, USA), group 2 and 4 bleached with Polaoffice(SDI, Victoria, Australia). Bleaching treatment performed during 10 minutes every 24 hours and repeated 6 times. During bleaching treatment , distal fragments was light-activated(L) but mesial fragments was not(NL). Shade assessment employed before and after bleaching treatment using spectrophotometer. The results of the change in shade was compared and analysed between NL and L by using paired-sample T test with 95% level of confidence.
There were no significant differences between NL and L with a few exceptions. In group 2, a* value more change in L, in group 3, b* value more change in L, in group 4, a* value less change in L. After bleaching, L* value and ΔE increased in all groups and the value of a* and b* decreased in all groups.
Within the limitation of this test conditions, the results of this study indicate that the light energy has no obvious improving impact on the tooth whitening effect of a bleaching agent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Tooth-whitening Apparatus
Young-Jin Lee, Jong-Hoo Paik, Jeong-Bae Lee, Seung-Jae Choi
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2013; 14(5): 268. CrossRef - Clinical assessment of whitening efficacy and safety of in-office tooth whitening system containing 15% hydrogen peroxide with or without light activation
Young-Suk Noh, Young-Jee Rho, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hyang-Ok Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Hyun-Jeong Kweon, Yeun Kim, Seong-Yeon Park, Hee-Young Yoon, Jung-Hyun Lee, Chan-Hee Lee, So-Ram Oh, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 306. CrossRef
- Development of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Tooth-whitening Apparatus
- 1,313 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Iatrogenic chemical burn on facial skin by 37% phosphoric acid etchant
- Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):38-41. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub When we use the total-etch dentin adhesive system for composite resin restorations, gel or liquid acid etchant such as 37% phosphoric acid is commonly used. Thirty seven percentage phosphoric acid is very powerful erosive agent, and can cause severe harmful effects when it contacts with an oral mucosa and facial skin.
This case describes iatrogenic chemical burn on facial skin caused by phosphoric acid which was happened during composite resin restorative procedure.
Chemical burn by acid etchant can be evoked by careless handling of remnant and syringe. In order to prevent these iatrogenic injuries, we should check the complete removal of the etching agent both in intra and extra-oral environments after etching and rinsing procedure and it is necessary to use of the rubber dam or isolation instruments.
If accidental burn were occurred, immediate wash with copious water. And bring the patient to the dermatologist as soon as possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytotoxicity of V-Prep Versus Phosphoric Acid Etchant on Oral Gingival Fibroblasts
Victor Ghoubril, Sylvie Changotade, Didier Lutomski, Joseph Ghoubril, Carole Chakar, Maher Abboud, Louis Hardan, Naji Kharouf, Elie Khoury
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 266. CrossRef - Effects of dental acid etchants in oral epithelial cells
Do-kyeong Kim, Jae-won Kwak, Ryeong-mi Jo, Da-som Jung, Da-young Youn, Na-yeon Oh, Ji-hye Jang
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(4): 299. CrossRef
- Cytotoxicity of V-Prep Versus Phosphoric Acid Etchant on Oral Gingival Fibroblasts
- 3,995 View
- 61 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A COMPARISON OF THE IRRIGATION SYSTEMS IN CALCIUM HYDROXIDE REMOVAL
- Jae-Seung Eun, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):508-514. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.508
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purposes of this study were to compare the efficacy of irrigation systems by removing a calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) paste from the apical third of the root canal and the effect of the patency file. Sixty single rooted human teeth were used in this study. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down manner with .04 taper ProFile to ISO #35. Ca(OH)2 and distilled water were mixed and placed inside the root canals. The teeth were divided into 6 groups according to the root canal irrigation system and the use of patency file as follows: group 1 - conventional method; group 2 - EndoActivator®; group 3 - EndoVac®; group 4 - conventional method, patency; group 4 - EndoActivator®, patency; group 6 - EndoVac®, patency. All teeth were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. After the root canal irrigation, the teeth were split in bucco-lingual aspect. Percentage of the root canal surface coverage with residual Ca(OH)2 until 3 mm from working length was analyzed using Image Pro Plus ver. 4.0. Statistical analysis was performed using the One-way ANOVA, t-test and Scheffe's post-hoc test. Conventional groups had significantly more Ca(OH)2 debris than EndoActivator®, EndoVac® groups. There was no significant difference between EndoActivator® and EndoVac® groups. Groups with patency file showed more effective in removing Ca(OH)2 paste than no patency groups, but, it was no significant difference. This study showed that EndoActivator® and EndoVac® systems were more effective in removing Ca(OH)2 paste from the apical third of the root canal than conventional method.
- 953 View
- 3 Download

-
EVALUATION OF
ENTEROCOCCUS FAECALIS REMOVAL EFFICACY OF THE ENDOVAC® AND ENDOACTIVATOR® INTRACANAL IRRIGATION METHODS - Seung-Gon Song, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(5):390-396. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The aim of this study was to evaluate endodontic irrigation methods with EndoVac® and EndoActivator® in the elimination of
Enterococcus faecalis from the root canals. Extracted 70 human single-rooted teeth were used. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down technique with .04 taper ProFile to ISO size 40. After the teeth were autoclaved, the canals were inoculated withE. faecalis and incubated for 48 h. The teeth were randomly divided into three experimental groups of 20 teeth each according to canal irrigation methods and two control groups as follows: group 1 - EndoVac®; group 2 - EndoActivator®; group 3 - Conventional needle irrigation method. After canal irrigation using 2.5% NaOCl, first samples (S1) were taken using sterile paper point. And the canals were filled with sterile brain heart infusion (BHI) broth and incubated for 24 h, then second samples (S2) were taken. The samples were cultured on BHI agar plate to determine the numbers of colony forming units (CFU). In first sampling (S1), only one canal of conventional method among the all experimental groups was positive cultured. In second sampling (S2), EndoVac® group showed the least positive culture numbers ofE. faecalis . There was statistically significant difference between the EndoVac® and conventional needle irrigation methods in the mean value of Log CFU. According to the results of this study, EndoVac® showed better efficacy than conventional needle irrigation method in the elimination ofE. faecalis from the root canal.
- 841 View
- 8 Download

- EFFECT OF DENTIN SURFACE WETNESS ON TENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
- Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):113-119. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to compare the tensile bond strength of several self-adhesive resin cements bonded to dentin surfaces with different wet conditions.
Three self-adhesive resin cements; Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA), Embrace Wetbond (Pulpdent, Oakland, MA, USA), Maxcem (Kerr, Orange, CA, USA) were used. Extracted sixty human molars were used. Each self-adhesive resin cement was adhered to the dentin specimens (two rectangular sticks from each molar) in different wet conditions.
Tensile bond strength were measured using universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu corporation, Kyoto, Japan) at a crosshead speed of 1.0mm/min. After the testing, bonding failures of specimens were observed by Operative microscope (OPMI pro, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). T-test was used to evaluate the effect of dentin surface wetness. One-way ANOVA test was used to evaluate the tensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements in the same condition. Scheffe's test was used for statistical analyzing at the 95% level of confidence.
The result showed that wetness of dentin surface didn't affect tensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements and Maxcem showed the lowest tensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overdried Preparation and Thermocycling on the Fracture of CAD–CAM Hybrid Ceramic Occlusal Veneer Restorations
Daranee Tantbirojn, Antheunis Versluis, Paul D Edgerley, David R Cagna
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 9(2): 38. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef - 'Wet or Dry tooth surface?' - for self-adhesive resin cement
Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 249. CrossRef
- Impact of Overdried Preparation and Thermocycling on the Fracture of CAD–CAM Hybrid Ceramic Occlusal Veneer Restorations
- 1,347 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Microleakage of resilon by methacrylate-based sealer and self-adhesive resin cement
- Sun-Young Ham, Jin-Woo Kim, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):204-212. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by methacrylate-based root canal sealer or 2 different self-adhesive resin cements. Seventy single-rooted extracted human teeth were sectioned at the CEJ perpendicular to the long axis of the roots with diamond disk. Canal preparation was performed with crown-down technique using Profile NiTi rotary instruments and GG drill. Each canal was prepared to ISO size 40, .04 taper and 1 mm short from the apex. The prepared roots were randomly divided into 4 experimental groups of 15 roots each and 5 roots each for positive and negative control group. The root canals were filled by lateral condensation as follows. Group 1: Guttapercha with AH-26, Group 2: Resilon with RealSeal primer & sealer, Group 3: Resilon with Rely-X Unicem, Group 4: Resilon with BisCem. After stored in 37℃, 100% humidity chamber for 7 days, the roots were coated with 2 layers of nail varnish except apical 3 mm. The roots were then immersed in 1% methylene blue dye for 7 days. Apical microleakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration after roots were separated longitudinally. One way ANOVA and Scheffe's post-hoc test were performed for statistical analysis. Group 1 showed the least apical leakage and there was no statistical significance between Group 2, 3, 4. According to the results, the self adhesive resin cement is possible to use as sealer instead of primer & sealant when root canal filled by Resilon.
- 834 View
- 1 Download

- Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
- Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):133-140. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by several self-etching primers and methacrylate-based root canal sealer. Seventy single-rooted human teeth were used in this study. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down manner with Gate-Glidden drills and .04 Taper Profile to ISO #40. The teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups of 15 teeth each according to root canal filling material and self-etching primers and two control groups (positive and negative) of 5 teeth each as follows: group 1 - gutta percha and AH26® sealer; group 2 - Resilon, RealSeal™ primer and RealSeal™ sealer; group 3 - Resilon, Clearfil SE Bond® primer and RealSeal™ sealer group 4 - Resilon, AdheSe® primer and RealSeal™ sealer. Apical leakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration of roots sectioned longitudinally by diamond disk. Statistical analysis was performed using the One-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe's test. There were no statistical differences in the mean apical dye penetration among the groups 2, 3 and 4 of self-etching primers. And group 1, 2 and 3 had also no statistical difference in apical dye penetration. But, there was statistical difference between group 1 and 4 (p < 0.05). The group 1 showed the least dye penetration. According to the results of this study, Resilon with self-etching primer was not sealed root canal better than gutta precha with AH26® at sealing root canals. And there was no significant difference in apical leakage among the three self-etching primers.
- 804 View
- 1 Download

-
Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) on
Enterococcus faecalis in the root canal - Hye-Jeong Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):121-129. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to assess the antibacterial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC), sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), and chlorhexidine (CHX) on
Enterococcus faecalis and to evaluate and to compare the time-dependant antimicrobial effect of NaDCC with NaOCl and CHX in the root canalin vitro before and after instrumentation.Extracted human single teeth were prepared by serial instrumentation technique. The samples were autoclaved and contaminated for 3 days with
E. faecalis monocultures. The teeth were then divided into 4 groups. Each group was irrigated and inserted with 2% NaOCl, 2% NaDCC, 2% CHX and sterilized saline. After 6, 12, 24, 72h, and 1 week incubation, sterilized paper point was inserted into the root canal. Paper points containing root canal contents were then placed on the agar plate. And then each root canal was prepared with #4 and #5 GG (Gates-Glidden) drill. The debris were collected in the sterilized microtube and the plates were incubated at 37℃ in an increased CO2 atmosphere. After 24h incubation the growth of bacteria around the paper points were measured.NaOCl and NaDCC solution shows similar antimicrobial effect for
E. faecalis at 6, 12, 24, 72h and 1 week. In control group, irrigated with sterilized saline, no antimicrobial effect was observed.The results are in agreement with other investigators, who have shown the bactericidal property and possibility of NaDCC as a root canal irrigation solution. Thus it seems that NaDCC solutions can be clinically applied into the root canal within 1 week after dilution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary toxicity of sodium dichloroisocyanurate after intratracheal instillation in sprague-dawley rats
Jean Yoo, Haewon Kim, Yeon-Mi Lim, Byung-Il Yoon, Pilje Kim, Ig-Chun Eom, Ilseob Shim
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis in endodontic infections: antibiotic resistance profile and susceptibility to photodynamic therapy
Ana Carolina Chipoletti Prado, Patrícia Pimentel De Barros, Jéssica Diane Dos Santos, Luciane Dias De Oliveira, Claudio Antônio Talge Carvalho, Marcia Carneiro Valera, Antonio Olavo Cardoso Jorge, Juliana Campos Junqueira
Lasers in Dental Science.2017; 1(2-4): 91. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Disease Control Efficacy of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) Against Major Strawberry Diseases
Da-Ran Kim, Gun-Hye Gang, Hyun-Ji Cho, Hae-Suk Yoon, Youn-Sig Kwak
The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science.2015; 19(1): 47. CrossRef - Effect of Gamma Irradiation and Its Convergent Treatments on Lily Leaf Blight Pathogen, Botrytis elliptica, and the Disease Development
Ji-Hoon Kim, Sung-Chul Yun
Research in Plant Disease.2014; 20(2): 71. CrossRef - Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 258. CrossRef - Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 295. CrossRef - The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 80. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 500. CrossRef - Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
Seung-Gon Song, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 390. CrossRef - The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 397. CrossRef
- Pulmonary toxicity of sodium dichloroisocyanurate after intratracheal instillation in sprague-dawley rats
- 2,012 View
- 14 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Polymerization shrinkage of composite resins cured by variable light intensities
- Mi-Young Lim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Chan-Ui Hong
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):28-36. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.028
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of exponential curing method with conventional curing and soft start curing method on polymerization shrinkage of composite resins.
Three brands of composite resins (Synergy Duo Shade, Z250, Filtek Supreme) and three brands of light curing units (Spectrum 800, Elipar Highlight, Elipar Trilight) were used. 40 seconds curing time was given. The shrinkage was measured using linometer for 90 seconds.
The effect of time on polymerization shrinkage was analysed by one-way ANOVA and the effect of curing modes and materials on polymerization shrinkage at the time of 90s were analysed by two-way ANOVA. The shrinkage ratios at the time of 20s to 90s were taken and analysed the same way. The results were as follows:
1. All the groups except Supreme shrank almost within 20s. Supreme cured by soft start and exponential curing had no further shrinkage after 30s (p < 0.05).
2. Statistical analysis revealed that polymerization shrinkage varied among materials (p = 0.000) and curing modes (p = 0.003). There was no significant interaction between material and curing mode.
3. The groups cured by exponential curing showed the statistically lower polymerization shrinkage at 90s than the groups cured by conventional curing and soft start curing (p < 0.05).
4. The initial shrinkage ratios of soft start and exponential curing were statistically lower than conventional curing (p < 0.05).
From this study, the use of low initial light intensities may reduce the polymerization rate and, as a result, reduce the stress of polymerization shrinkage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Degree of Conversion and Polymerization Shrinkage of Low and High Viscosity Bulk-Fill Giomer-based and Resin-based composites
Heera Kim, Jaesik Lee, Hyunjung Kim, Taeyub Kwon, Soonhyeun Nam
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2019; 46(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
So-Rae Seong, Duck-kyu Seo, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 125. CrossRef
- Degree of Conversion and Polymerization Shrinkage of Low and High Viscosity Bulk-Fill Giomer-based and Resin-based composites
- 1,526 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
The effects of tooth bleaching agents on microhardness of enamel
in situ - Yoon-Woo Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):470-476. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.470
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this
in situ study was to evaluate the effects of whitening strip (Claren, LG Household & Health Care Ltd, 2.6% hydrogen peroxide) and gel (Opalescence, Ultradent, 10% carbamide peroxide) on microhardness of enamel in comparison with untreated control. Extracted twenty human upper incisors were disinfected, cleaned, and labial side of each incisor sectioned into 3 fragments by 2 × 2 mm size. After sectioning, labial sides of fragments were flattened and fixed to orthodontic bracket using flowable composite resin. Specimens prepared from each tooth were attached to the labial side of upper incisors of twenty volunteers one by one and treated by three different methods: (1) untreated control (2) treated with whitening strip for 14 days (3) treated with whitening gel for 14 days.Microhardness (Microhardness tester, Zwick) of each specimen was measured at the baseline of pre-treatment, immediate after bleaching treatment, 14 days after bleaching treatment and Knoop Hardness Number was determined. Microhardness changes of experimental groups were compared.
The results show that tooth whitening strip and gel used in this study does not effect the micro-hardness of enamel during bleaching procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Damage and Bleaching Effect according to the Application Type of Home Tooth Bleaching Applicants
Na-Yeoun Tak, Do-Seon Lim, Hee-Jung Lim, Im-Hee Jung
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2020; 20(4): 252. CrossRef - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef
- Surface Damage and Bleaching Effect according to the Application Type of Home Tooth Bleaching Applicants
- 2,983 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Management of separated file in the root canal
- Hye-Jeong Kim, Hoon-Sang Jang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):161-168. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub During root canal preparation procedures, the potential for instrument separation is always present. Files, a lentulo, a Gates-Glidden (GG) bur or any manufactured obstruction can be left behind in the canal. Nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files are in common usage in these days. Despite their undeniable advantages, there is a potential risk of separation within the canals. It is very rapid, unpredictable, and creates a great deal of stress for the practitioner.
When an endodontic instrument separates, the best option is to remove it. Ultrasonic instruments and microscopes have improved the success rate for removing separated instruments. But it is difficult and not always possible. Therefore prevention is the key.
In this case report, several management methods of separated file in the canal are presented.
- 953 View
- 4 Download

- Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
- Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):327-334. Published online July 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile.
Thirty six resin blocks were divided equally into three groups by instrumentation motions: anticurvature filing motion, circumferential filing motion and straight up-and-down motion. Each resin block was sectioned at 8 mm level from the apex and at the greatest curvature of the canal and reassembled in metal mold by a modified Bramante technique. All groups were instrumented with the ProFile system. At each levels, image of sectioned surface were taken using CCD camera under a stereomicroscope at ×40 magnification and stored. Distances of transportation at the inner and outer area of curvature and the centering ratio were determined and compared by statistical analysis, along with the assessment of the increase of root canal cross-sectional area.
The results were as follows;
1. In all groups, there was no statistical difference in the mean increase of root canal cross-sectional area, the centering ratio, and the mean distances of transportation at the inner area of curvature at each level.
2. At 8 mm level from the apex, the mean distances of transportation at the outer area of curvature decreases in following order anticurvature filing motion, circumferential filing motion, straight up-and-down motion but, no significant difference at the greatest curvature of the canal among three groups.
Effect of anticurvature filing motion using ProFile does not seem to be different from other instrumentation motions at the inner area of curvature in curved root canal.
- 1,402 View
- 12 Download

- Lifetime and fracture patterns of NiTi rotary files in molars
- Jin-Woo Kim, Byung-Doo Ahn, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):184-192. Published online May 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Intracanal separation of the rotary files is a serious concern in modern endodontic practice. The objective of this study was to compare the life span and fracture patterns of three NiTi rotary files in molar teeth.
Mesiobuccal roots of upper molar (n = 150) and mesial roots of lower molar (n = 150) were divided into three groups and each group was prepared with Profile, ProTaper, and K3 respectively. Every file was used until separation and/or deterioration of the cutting blade was happened, and then the number of canals to separation and/or unwinding were recorded. Radiographs and Scanning electon microscope (SEM) photographs were taken to evaluate the patterns of separation.
The results were as follows :
1. There were no significant differences in numbers of canals to separation and/or unwinding among the groups.
2. Comparing between flaring files, K3 showed significant lower numbers of canals to separation and/or unwinding (p < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between shaping files
3. Separations of instruments were occurred at the midpoint of curvatures within the canals.
4. In SEM observations, ductile fractures were seen in most of cases, characterized by shallow dimples.
Additional researches is needed to provide a new guideline that informs the appropriate number of times to use NiTi files.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing evidence-based clinical imaging guidelines for the diagnosis of vertically fractured teeth
Ki-Hong Kim, Jo-Eun Kim, Sam-Sun Lee, Chena Lee, Miyoung Choi, Hwan Seok Yong, Seung Eun Jung, Min-Suk Heo, Kyung-Hoe Huh
Oral Radiology.2024; 40(4): 471. CrossRef
- Developing evidence-based clinical imaging guidelines for the diagnosis of vertically fractured teeth
- 1,001 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A NEW POST REMOVAL TECHNIQUE USING ATD TUGGING DEVICE
- Yun-Woo Park, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):215-220. Published online January 14, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT It is common for clinicians to encounter endodontically treated teeth that contain posts within their roots. If endodontic treatment is failed, these posts must be removed to facilitate successful nonsurgical retreatment.
There have been many techniques such as ultrasonic instrument, Ruddle post removal system, Eggler post remover and Masserann kit developed to facilitate removal of posts from the root canal space. But these methods may be disadvantageous because long length of time required for post removal and fracture of post or teeth. In now days new post removal technique using ATD automatic bridge remover was introduced. Advantages of this method are simple and short time consuming compare to others.
This article served as a successful case report of post removal using ATD automatic bridge remover.
- 996 View
- 5 Download

- The influence of different access cavity designs on the fracture strength in endodontically treated mandibular anterior teeth
- Young-Gyun Lee, Hye-Jin Shin, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(6):515-519. Published online November 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.515
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Straight access cavity design allows the operator to locate all canals, helps in proper cleaning and shaping, ultimately facilitates the obturation of the canal system. However, change in the fracture strength according to the access cavity designs was not clearly demonstrated yet. The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of different access cavity designs on the fracture strength in endodontically treated mandibular anterior teeth.
Recently extracted mandibular anterior teeth that have no caries, cervical abrasion, and fracture were divided into three groups (Group 1 : conventional lingual access cavity, Group 2 : straight access cavity, Group 3 : extended straight access cavity) according to the cavity designs. After conventional endodontic treatment, cavities were filled with resin core material. Compressive loads parallel to the long axis of the teeth were applied at a crosshead speed of 2mm/min until the fracture occurred. The fracture strength analyzed with ANOVA and the Scheffe test at the 95% confidence level.
The results of this study were as follows :
1. The mean fracture strength decrease in following sequence Group 1 (558.90 ± 77.40 N), Group 2 (494.07 ± 123.98 N) and Group 3 (267.33 ± 27.02 N).
2. There was significant difference between Group 3 and other groups (P = 0.00).
Considering advantage of direct access to apical third and results of this study, straight access cavity is recommended for access cavity form of the mandibular anterior teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fracture resistance of crown-root fractured teeth repaired with dual-cured composite resin and horizontal posts
Seok-Woo Chang, Yong-Keun Lee, Seung-Hyun Kyung, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Tae-Seok Oh, Dong-Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 383. CrossRef
- Fracture resistance of crown-root fractured teeth repaired with dual-cured composite resin and horizontal posts
- 1,132 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of various commercially available bleaching agents on the microshear bond strength of composite resin to enamel
- Hoon-Sang Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):219-225. Published online May 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.219
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the microshear bond strength of composte resin to teeth bleached with commercial whitening strips and compared with those bleached with home bleaching gel. Twelve extracted human central incisors were cut into pieces and central four segments were chosen from each tooth and embedded in acrylic resin. Four blocks with 12 tooth segments embedded in acrylic resin were acquired and numbered from group one to group four. Group 1 was bleached with Crest Whitestrips, group 2 with Claren, group 3 with Opalescence tooth whitening gel (10% carbamide peroxide). Group 4 was used as control. The bleaching procedure was conducted for 14 days according to the manufacturer's instructions; the bleaching strips twice a day for 30 min and the bleaching gel once a day for 2 hr. After bleaching, composite resin (Filtek Supreme) was bonded to the enamel surfaces with a self-etching adhesive (Adper Prompt L-Pop) using Tygon tube. Microshear bond strength was tested with a universal testing machine (EZ-test). The data were statistically analysed by one-way ANOVA. The study resulted in no statistical differences in microshear bond strength between the tooth segments bleached with 2 different whitening strips and bleaching gel. It can be concluded that the effect of bleaching with either commercial whitening strips or bleaching gel on enamel is minimal in bonding with self-etching adhesive to composite resin.
- 1,155 View
- 2 Download

- A study of contraction shrinkage of composite resins and ormocers with various curing times
- Yeon-Chung Chung, Kyung-San Min, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Yong-Bum Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(4):326-333. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.4.326
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Ormocer has organic-inorganic compound polymers. One of advantages of ormocer is reduced polymerization shrinkage. The purpose of this study was to compare the amount of contraction shrinkage of composite resins and ormocers. Additionally, the time of each material when there is no further change of contraction shrinkage was analysed.
Four brands of composite resins (P-60, Surefil, Z-250 and Denfil) and two brands of ormocers (Definite and Admira) were used. 20 seconds, 40 seconds and 60 seconds of curing times were given. Contraction shrinkage of them were measured using a linometer for 80 seconds.
The effect of material and curing time to contraction shrinkage at the time of 80 seconds was analysed by two-way ANOVA. The effect of time to contraction shrinkage was analysed by one-way ANOVA, and the time when there was no further change of the contraction shrinkage was analysed. The results are as follows :
P-60, Definite, Z-250 and Denfil had no further change of contraction shrinkage from the time of 20 seconds, and Surefil and Admira had no further change of contraction shrinkage from the time of 10 seconds.
Statistical analysis revealed volumetric shrinkage varied among material (p<0.05). No significant difference of contraction shrinkage among different curing times was found, and there was no effect of interaction between materials and curing times to contraction shrinkage.
Definite and Admira showed the statistically same contraction shrinkage with those of Z-250 and P-60, which is higher than that of Surefil and lower than that of Denfil (p<0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Polymerization shrinkage and stress analysis during dental restoration observed by digital image correlation method
Jung-Hoon Park, Nak-Sam Choi
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2021; 35(12): 5435. CrossRef - Acoustic emission characteristics of methacrylate-based composite and silorane-based composite during dental restoration according to a variety of C-factor
Jung-Hoon Park, Ja-Uk Gu, Nak-Sam Choi
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2017; 31(9): 4067. CrossRef - Behavior of Polymerization Shrinkage Stress of Methacrylate-based Composite and Silorane-based Composite during Dental Restoration
Jung-Hoon Park, Nak-Sam Choi
Composites Research.2015; 28(1): 6. CrossRef
- Polymerization shrinkage and stress analysis during dental restoration observed by digital image correlation method
- 1,264 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Polymerization ability of several light curing sources on composite resin
- Hye-Jin Shin, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):156-161. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the polymerization ability of three different light sources by microhardness test. Stainless steel molds of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm in thickness of 7 mm in diameter were prepared. The hybrid composite Z100 was packed into the hole of the mold and curing light was activated for designated time. Three different light sources, conventional halogen, light emitting diode, and plasma arc, were used for curing of composite. Two different curing times applied; one is to follow the manufacturer's recommendation and the other is to extend the curing time of LED and plasma arc for balancing the light energy with halogen. Immediately after curing, the Vickers hardness was measured at the bottom of specimen.
The results were as follows.
The composite cured with LED showed equal to higher microhardnesss than halogen.
The composite was cured with plasma arc by manufacturer's recommendation showed lowest microhardness at all thickness. However, when curing time was extended, microhardness was higher than the others.
In conclusion, this study suggested that plasma arc needs properly extended curing time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- 1,171 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The efficiency of the Ni-Ti rotary files in curved simulated canals shaped by novice operators
- Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):146-155. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.146
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
T. O. Kim, G. S. P. Cheung, J. M. Lee, B. M. Kim, B. Hur, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2009; 42(1): 14. CrossRef - Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
Tae-Oh Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 323. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between various hybrid instrumentation methods with ProTaper
Eun-Sook Hong, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 11. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of rotary Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates
Mun-Seong Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef
- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
- 1,566 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of various canal preparation techniques using rotary nickel-titanium files on the maintenance of canal curvature
- Cheol-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Chan-Ui Hong
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):41-49. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are increasing usage of Nickel-Titanium rotary files in modern clinical endodontic treatment because it is effective and faster than hand filing due to reduced step.
This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of canal preparations using 3 different rotary Nickel-Titanium files that has different cross sectional shape and taper on the maintenance of canal curvature. Simulated resin block were instrumented with Profile(Dentsply, USA), GT rotary files(Dentsply, USA), Hero 642(Micro-Mega, France), and Pro-Taper(Dentsply, USA).
The image of Pre-instrumentation and Post-instrumentation were acquired using digital camera and overspreaded in the computer. Then the total differences of canal diameter, deviation at the outer portion of curvature, deviation at the inner portion of curvature, movement of center of the canal and the centering ratio at the pre-determined level from the apex were measured.
Results were statistically analyzed by means of ANOVA, followed by Scheffe test at a significance level of 0.05.
The results were as follows;
1. Deviation at the outer portion of curvature, deviation at the inner portion of curvature were showed largest in Pro-Taper, so also did in the total differences of canal diameter(p<0.05).
2. All the groups showed movements of center. Profile combined with GT rotary files and Hero 642 has no difference but Pro-Taper showed the most deviation(p<0.05).
3. At the 1, 2, 3mm level from the apex movements of center directed toward the outer portion of curvature, but in 4, 5 mm level directed toward the inner portion of curvature(p<0.05).
As a results of this study, it could be concluded that combined use of other Nickel-Titanium rotary files is strongly recommended when use Pro-Taper file because it could be remove too much canal structure and also made more deviation of canal curvature than others.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
T. O. Kim, G. S. P. Cheung, J. M. Lee, B. M. Kim, B. Hur, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2009; 42(1): 14. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - A study of insertion depth of buchanan plugger after shaping using NI-TI rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Youn-Sik Park, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 125. CrossRef - Step by step analysis of root canal instrumentation with ProTaper®
Mi-Hee Kim, Bock Huh, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 50. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef - A comparison of shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals
So-Youn Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(1): 58. CrossRef
- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
- 1,103 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- A comparison of thermoplasticized injectable gutta-percha techniques in ribbon-shaped canals : adaptation to canal walls
- Hyun-sook Hwang, Kyung-mo Cho, Jin-woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(4):411-420. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.4.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study is to compare the adaptability of thermoplasticized injectable gutta-percha technique to the canal walls in ribbon-shaped canals.
Thirty resin models simulated ribbon-shape canals were instrumented to #40 using .06 taper Profile systems. Three groups of each 10 resin models were obturated by the lateral condensation technique(LC) and the two thermoplasticized injectable gutta-percha technique; Ultrafil Endoset+Obtura II(EO) and Ultrafil Firmset(UF), respectively.
After resin model were kept at room temperature for 4 days, they were resected horizontally with microtome at 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5mm levels from apex. At each levels, image of resected surface were taken using CCD camera under a stereomicroscope at ×40 magnification and stored. Ratio of the area of gutta-percha was obtained by calculating area of gutta-percha cone to the total area of canal using digitized image-analyzing program. The data were collected then analyzed statistically using One-way ANOVA.
The results were as follows.
1. At 1mm levels, there was no statistically significant difference in the mean ratio of gutta-percha among the groups.
2. At 2mm level, EO showed the highest mean ratio of gutta-percha (p<0.05) and there was no significant difference between LC and UF.
3. At 3, 4, 5mm levels, EO and UF had significantly greater mean ratio of gutta-percha than LC(p<0.05) and there was no significant difference between EO and UF.
In conclusion, the thermoplasticized injectable gutta-percha techniques demonstrated relatively favorable adaptability to canal walls than lateral condensation technique in ribbon-shaped canals except for 1mm level.
- 902 View
- 1 Download

- Comparison of warm gutta-percha condensation techniques in ribbon shaped canal: weight of filled gutta-percha
- Hyun-Hee Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(3):277-283. Published online May 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.3.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the two warm gutta-percha filling techniques by measuring the weight changes of resin blocks before and after canal filling in ribbon shaped canal. Simulated ribbon shaped root canals in 30 transparent resin blocks were instrumented to #40 using .06 taper Profile. 15 resin blocks were obturated with gutta-percha using cold lateral condensation. Warm lateral condensation using the Endotec II was then accomplished on the same 15 blocks. Another 15 resin blocks were obturated using the System B. All canals were obturated without sealer. The resin blocks were weighed after canal preparation and after each subsequent obturation, and then weight changes of the resin blocks were calculated.
The results were as follows.
1. Warm lateral condensation using Endotec II and continuous wave of condensation using System B produced a denser obturation of gutta-percha compared with conventional cold lateral condensation (p<0.01).
2. There was no significant difference between warm lateral condensation and continuous wave condensation.
In conclusion, the warm gutta-percha condensation techniques like warm lateral condensation and continuous wave condensation can be expected to bring favorable canal obturation results in ribbon shaped canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Maxillary and Mandibular Premolars in an Emirati Sub-Population
Hanadi Almehrzi, Summaya Khawajah, Nouf Alharbi, Rashid El Abed, Mohamed Jamal
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1864. CrossRef - Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e18. CrossRef - Aetiology, incidence and morphology of the C‐shaped root canal system and its impact on clinical endodontics
A. Kato, A. Ziegler, N. Higuchi, K. Nakata, H. Nakamura, N. Ohno
International Endodontic Journal.2014; 47(11): 1012. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Maxillary and Mandibular Premolars in an Emirati Sub-Population
- 2,105 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


