Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 35(3); 2010 > Article
- Basic Research Evaluation of radiopacity and discriminability of various fiber reinforced composite posts
- Eun-Hye Lee1, Hang-Moon Choi2, Se-Hee Park1, Jin-Woo Kim1, Kyung-Mo Cho1
-
2010;35(3):-197.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.188
Published online: May 31, 2010
1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
2Department of Oral and maxillofacial radiology, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- Correspondence to: Kyung-Mo Cho. Department of Conservative Dentistry College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University 123 Chibyon-dong Gangwon-do, 210-702, Korea. Tel: 82-33-640-2467, Fax: 82-33-642-6410, drbozon@gwnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,027 Views
- 4 Download
Abstract
-
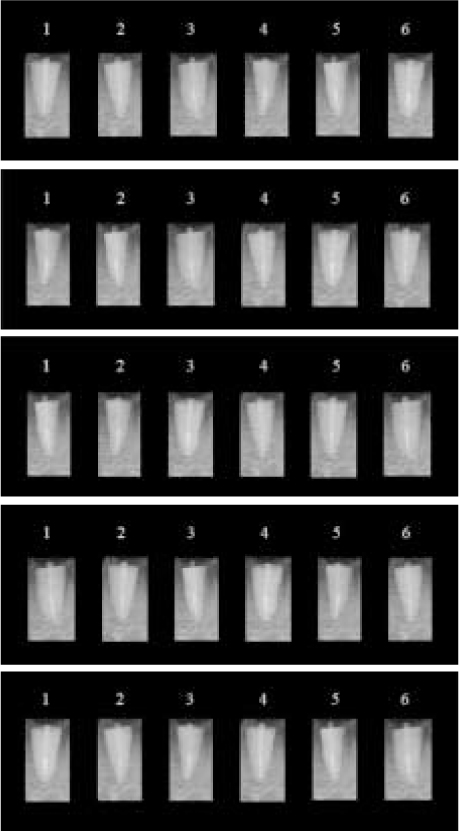
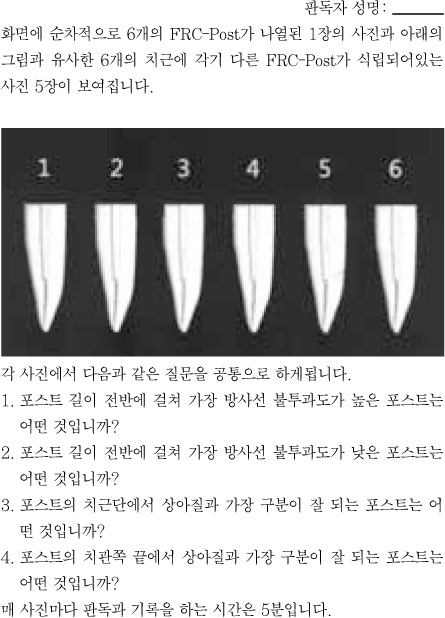
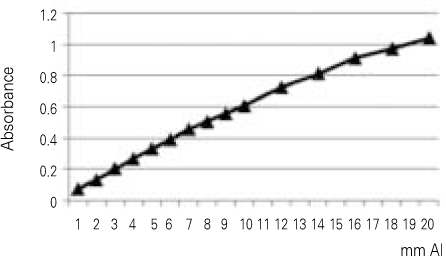
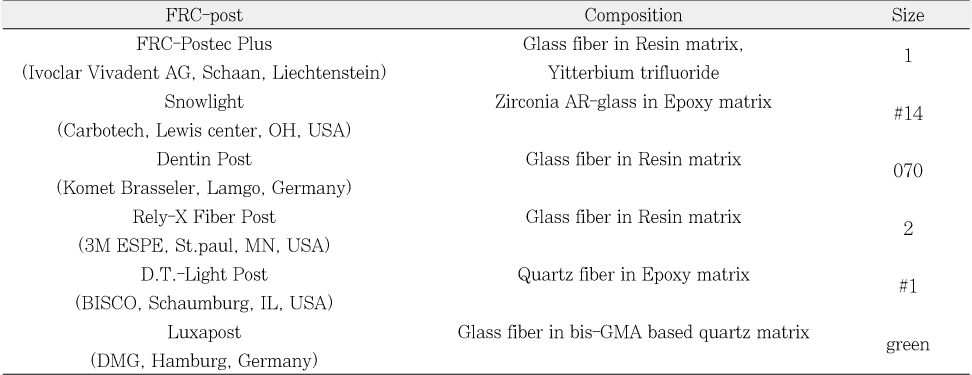
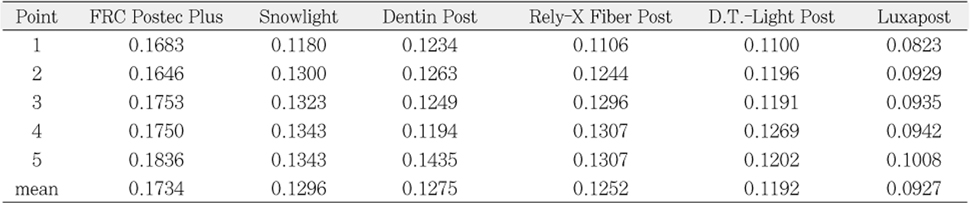
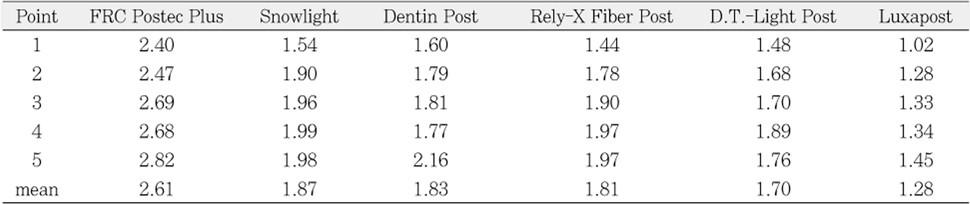
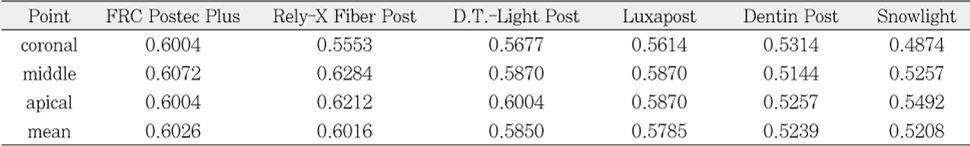
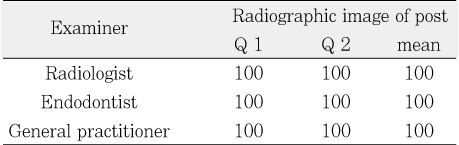
The purpose of this study was to compare radiopacity and radiographic discriminability of various FRC-Posts.Six FRC-Posts were investigated ; 1) FRC Postec Plus (Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein), 2) Snowlight (Carbotech, Lewis center, OH, USA), 3) Dentin Post (Komet Brasseler, Lamgo, Germany), 4) Rely-X Fiber Post (3M ESPE, St.paul, MN, USA), 5) D.T.-Light Post (BISCO, Schaumburg, IL,USA), 6) Luxapost (DMG, Hamburg, Germany)The radiographs of each post with a reference 1 mm / 2 mm aluminum step-wedge was taken using digital sensor. The optical density were calculated by gray value of 10 × 10 pixel and compared in mm Al equivalent at five points.Six maxillary incisors of similar radiopacity were used. Radiographs of posts in Mx. incisors of lingual side of dry mandible were taken.We showed radiographs and asked the questionnaire to 3 radiologists, 3 endodontists, 3 general practitioners. The questionnaire was comprised of choices of the highest, lowest radiopaque individual post and the choices of best discriminable post at apical, coronal area.The following results were obtained.Although each post showed various radiopacity, the difference of radiopacity did not affect on discriminability.
- 1. Elíasson ST, Haasken B. Radiopacity of impression materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1979;47(5):485-491.ArticlePubMed
- 2. International Standards Organization. Dentistry-polymer-based filling, restorative and luting materials. 2000;3rd Ed. ISO 4049.
- 3. O'Rourke B, Walls AWG, Wassell RW. Radiographic detection overhangs formed by resin composite luting agents. J Dent. 1995;23(6):353-357.PubMed
- 4. Soares CJ, Mistsui FHO, Neto FH, Marchi GMM, Martins LRM. Radiodensity evaluation of seven root post systems. Am J Dent. 2005;18(1):57-60.PubMed
- 5. Rasimick BJ, Steven G, Allan SD, Barry LM. Measuring the radiopacity of luting cements, dowels, and core build-up materials with a digital radiography system using a CCD sensor. J Prosthodont. 2007;16(5):357-364.PubMed
- 6. Ibrahim H, El-Mowafy O, Brown JW. Radiopacity of nonmetallic root canal posts. Int J Prosthodont. 2006;19(1):101-102.PubMed
- 7. Finger WJ, Ahlstrand WM, Fritz UB. Radiopacity of fiber-reinforced resin posts. Am J Dent. 2002;15(2):81-84.PubMed
- 8. Bouschlicher MR, Cobb DS, Boyer DB. Radiopacity of compomers, flowable and conventional resin composites for posterior restorations. Oper Dent. 1999;24(1):20-25.PubMed
- 9. Schwartz RS, Robbins JW. Post placement and restoration of endodontically treated teeth: A literature review. J Endod. 2004;30(5):289-301.PubMed
- 10. Goracci C, Gorciolani G, Vichi A, Ferrari M. Light-transmitting ability of marketed fiber posts. J Dent Res. 2008;87(12):1122-1126.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Al-Hazaimeh N, Gutteridge DL. An in vitro study into the effect of the ferrule preparation on the fracture resistance of crowned teeth incorporating prefabricated post and composite core restorations. Int Endod J. 2001;34(1):40-46.PubMed
- 12. Akkayan B. An in vitro study evaluating the effect of ferrule length on fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth restored with fiber-reinforced and zirconia dowel systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2004;92(2):155-162.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Naumann M, Preuss A, Frankenberger R. Reinforcement effect of adhesively luted fiber reinforced composite versus titanium posts. Dent Mater. 2007;23(2):138-144.PubMed
- 14. Shah PMM, Sidhu SK, Chong BS, Pitt Ford TR. Radiopacity of resin-modified glass ionomer liners and bases. J Prosthet Dent. 1997;77(3):239-242.PubMed
- 15. Marouf N, Sidhu SK. A study on the radiopacity of different shades of resin-modified glass-ionomer restorative materials. Oper Dent. 1998;23(1):10-14.PubMed
- 16. Akerboom HBM, Kreulen CM, Amerongen WE, Mol A. Radiopacity of posterior composite resins, composite resin luting cements, and glass ionomer lining cements. J Prosthet Dent. 1993;70(4):351-355.PubMed
- 17. Turgut MD, Attar N, Onen A. Radiopacity of direct esthetic restorative materials. Oper Dent. 2003;28(5):508-514.PubMed
- 18. Gu S, Rasimick BJ, Deutsch AS, Musikant BL. Radiopacity of dental materials using a digital X-ray system. Dent Mater. 2006;22(8):765-770.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Rasimick BJ, Shah RP, Musikant BL, Deutsch AS. Radiopacity of endodontic materials on film and a digital sensor. J Endod. 2007;33(9):1098-1101.PubMed
- 20. Tagger M, Katz A. Radiopacity of endodontic sealers: development of a new method for direct measurement. J Endod. 2003;29(11):751-755.PubMed
- 21. Yoshiura K, Kawazu T, Chikui T. Assessment of image quality in dental radiographypart 1. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999;87(1):115-122.PubMed
- 22. Carvalho-Junior JR, Correr-Sobrinho L, Correr AB, Sinhoreti MA, Consani S, Sousa-Neto MD. Radiopacity of root filling materials using digital radiography. Int Endod J. 2007;40(7):514-520.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Sabbagh J, Vreven J, Leloup G. Radiopacity of resin based materials measured in film radiographs and storage phosphor plate. Oper Dent. 2004;29(6):677-684.PubMed
- 24. Kim HJ, Kim SK. Radiopacity comparison of tooth colored restorative materials with digital radigraphy. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2000;25(4):499-508.
- 25. Kleier DJ, Shibilski K, Averbach RE. Radiographic appearance of titanium posts in endodontically treated teeth. J Endod. 1999;25(2):128-131.PubMed
- 26. Tagger M, Katz A. Radiopacity of endodontic sealers development of a new method for direct measurement. J Endod. 2003;29(11):751-755.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Tasdemir T, Yesilyurt C, Yildirim T, Er K. Evaluation of the radiopacity of new root canal paste/sealers by digital radiography. J Endod. 2008;34(11):1388-1390.PubMed
- 28. Baksi BG, Sen BH, Eyuboglu TF. Differences in aluminum equivalent values of endodontic sealers: conventional versus digital radiography. J Endod. 2008;34(9):1101-1104.PubMed
- 29. Kim CK, Ryu HW, Chang HS, Lee BD, Min KS, Hong CU. Evaluation of the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of resinous root canal sealers. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007;32(5):419-425.
- 30. Kim TM, Kim SK, Hwang IN, Hwang YC, Kang BC, Yoon SJ, Lee JS, Oh WM. A comparative study on radipacity of root canal sealers. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2009;34(1):61-68.Article
- 31. Rud J, Rud V, Munksgaard EC. Retrograde root filling with dentin-bonded modified resin composite. J Endod. 1996;22(9):477-480.PubMed
- 32. Niederman R, Theodosopoulou JN. A systematic review of in vivo retrograde obturation materials. Int Endod J. 2003;36(9):577-585.PubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

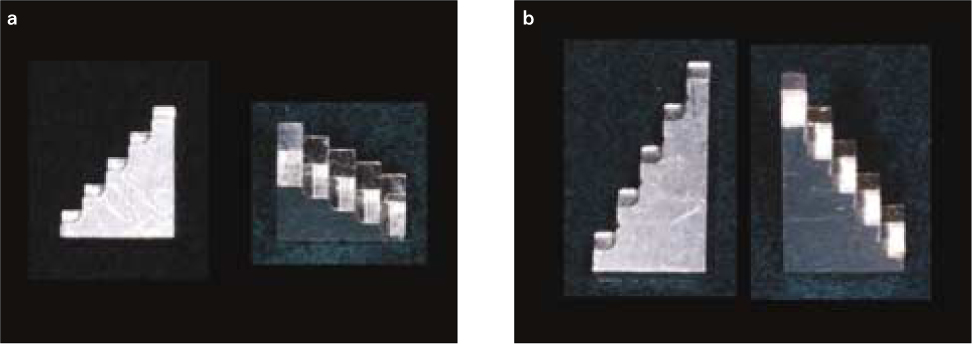
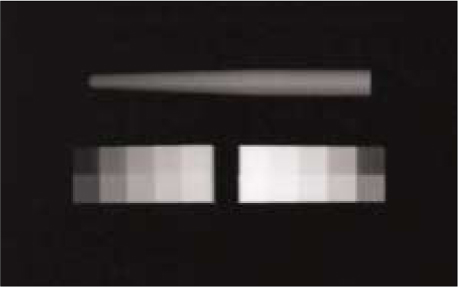
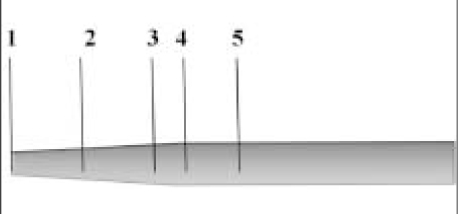

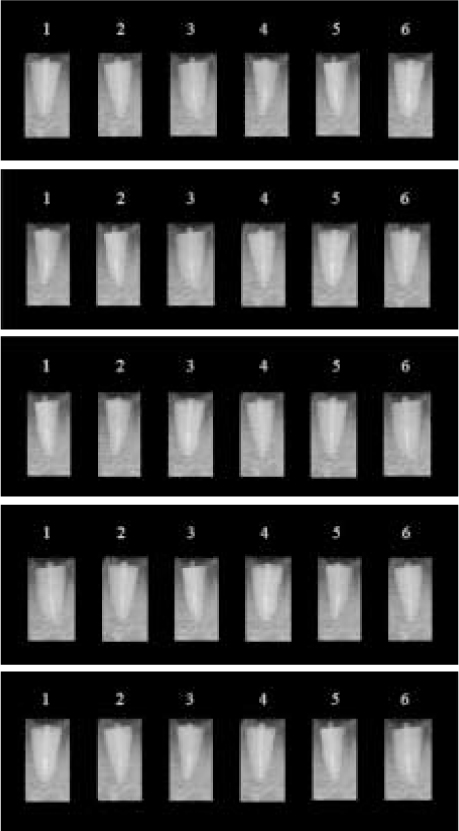
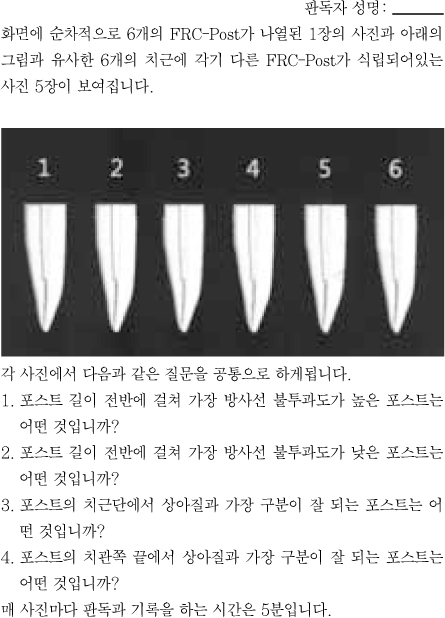
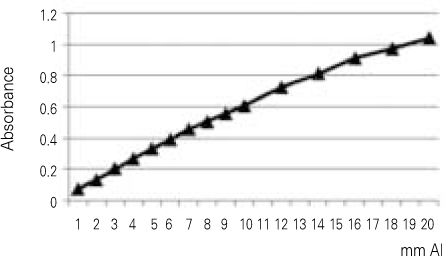
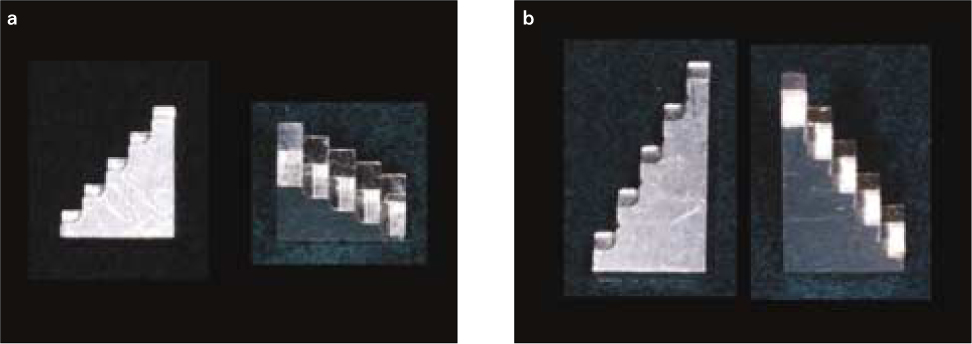
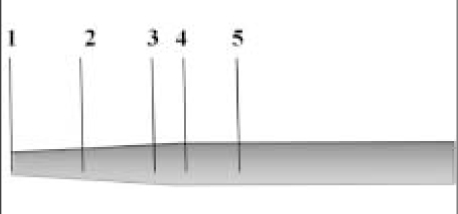
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Composition of FRC-Post
The value of radiopacity at each measuring point of post (absorbance/mm post)
The value of radiopacity at each measuring point of post (mm Al/mm post)
The value of radiographic images of simulated specimens (absorbance)
Difference of radiopacity between dentin and post at apical area (absorbance)
Difference of radiopacity between dentin and post at coronal area (absorbance)
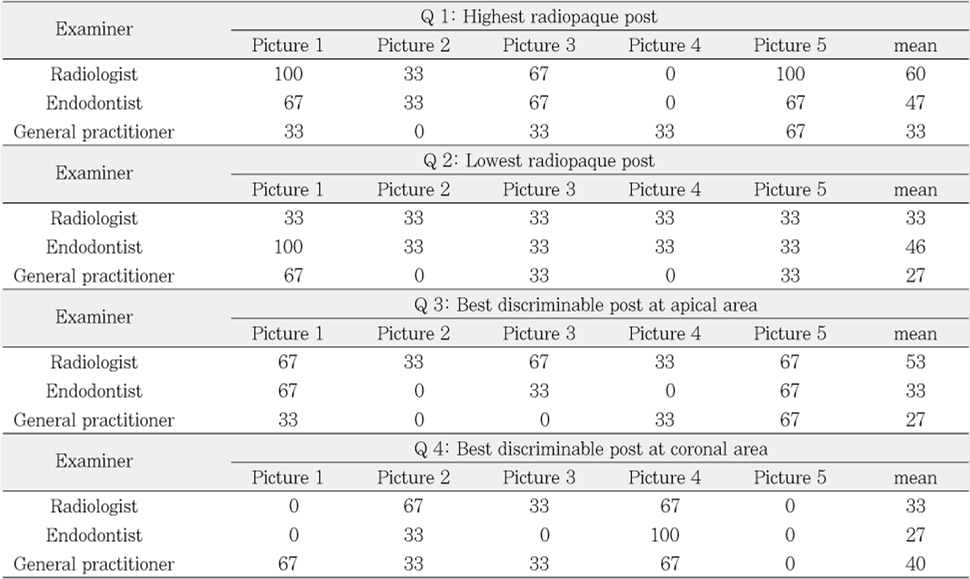
The percentage of correct answers in radiographic image of post (%)
The percentage of correct answers in radiographic image of simulated specimens (%)

 KACD
KACD




 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

