Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Does the use of different root canal sealers and adhesive resin cements impact the bond strength of glass fiber posts?
- Ália Regina Neves de Paula Porto, Rudá França Moreira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e29. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
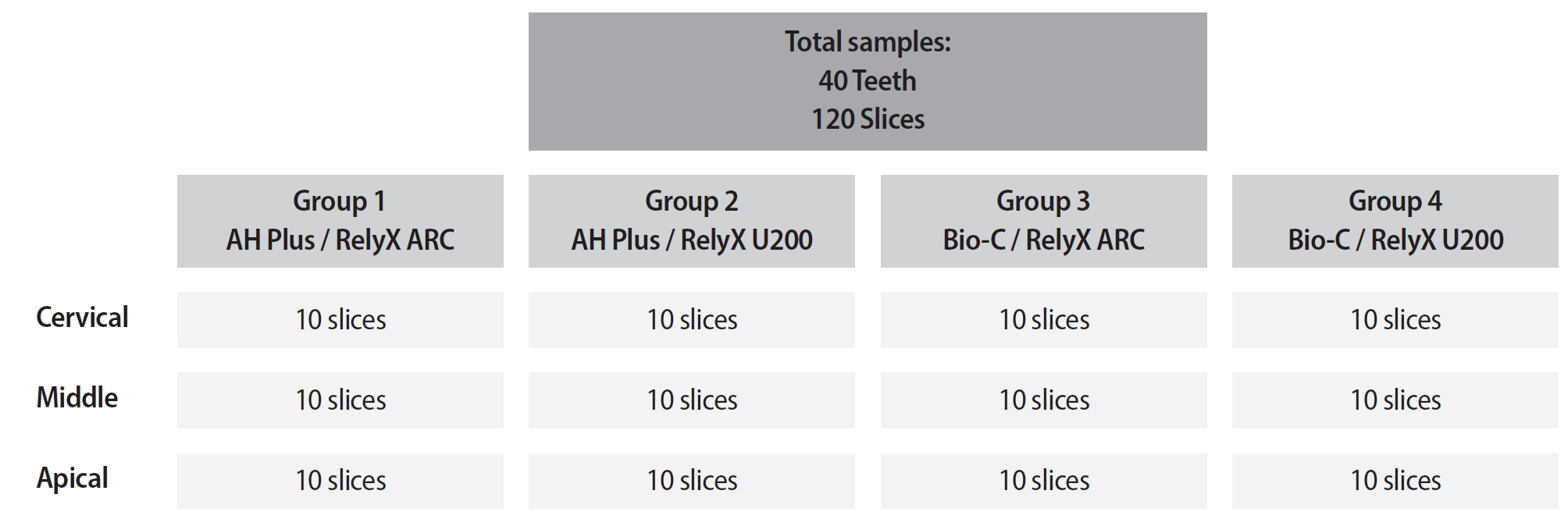
This study aimed to assess the influence of two endodontic sealers on the bond strength of glass fiber posts using conventional and self-adhesive resin cement through a push-out test. Methods: Forty central human incisors were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) based on sealer (epoxy resin- based or calcium silicate-based) and cement (conventional and self-adhesive resin) types: AH Plus (Dentsply De- Trey)/RelyX ARC (3M ESPE), AH Plus/RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), Bio-C Sealer (Angelus)/RelyX ARC, and Bio-C Sealer/RelyX U200. After canal filling and post cementation, roots were sectioned to obtain one specimen per root third. A pushout test and failure pattern assessment were conducted, with bond strength analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test. Results: AH Plus/RelyX ARC showed the highest bond strength values, with a significant difference in the middle third. The most common failure was mixed (55%), while adhesive failures made up 45%, with 23.5% at the cement/post interface and 21.5% at the cement/dentin interface. Conclusions: AH Plus/RelyX ARC provided the highest bond strength values for glass fiber posts to dentin.
- 1,819 View
- 146 Download

- Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
- Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e18. Published online March 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of relined and non-relined fiberglass posts when cemented to root canal dentin using a conventional dual-cure resin cement or a self-adhesive resin cement.
Materials and Methods Two types of resin cements were utilized: conventional and self-adhesive. Additionally, 2 cementation protocols were employed, involving relined and non-relined fiberglass posts. In total, 72 bovine incisors were cemented and subjected to push-out bond strength testing (
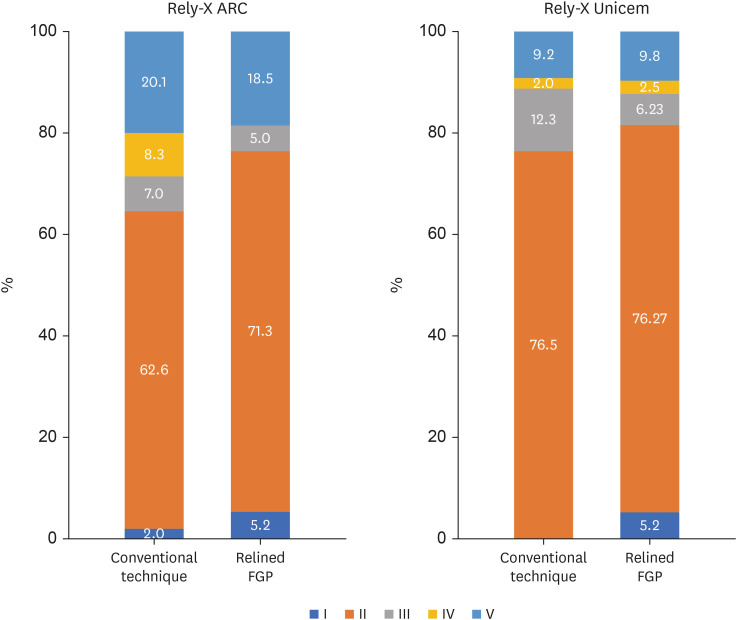
n = 10) followed by failure mode analysis. The cross-sectional microhardness (n = 5) was assessed along the root canal, and interface analyses (n = 3) were conducted using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data from the push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness tests were analyzed via 3-way analysis of variance and the Bonferronipost-hoc test (α = 0.05).Results For non-relined fiberglass posts, conventional resin cement exhibited higher push-out bond strength than self-adhesive cement. Relined fiberglass posts yielded comparable results between the resin cements. Type II failure was the most common failure mode for both resin cements, regardless of cementation protocol. The use of relined fiberglass posts improved the cross-sectional microhardness values for both cements. SEM images revealed voids and bubbles in the incisors with non-relined fiberglass posts.
Conclusions Mechanical properties were impacted by the cementation protocol. Relined fiberglass posts presented the highest push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness values, regardless of the resin cement used (conventional dual-cure or self-adhesive). Conversely, for non-relined fiberglass posts, the conventional dual-cure resin cement yielded superior results to the self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 5,100 View
- 133 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Giovanna Corrêa Denucci, Gabriela Soffner, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e32. Published online July 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements (SARCs).
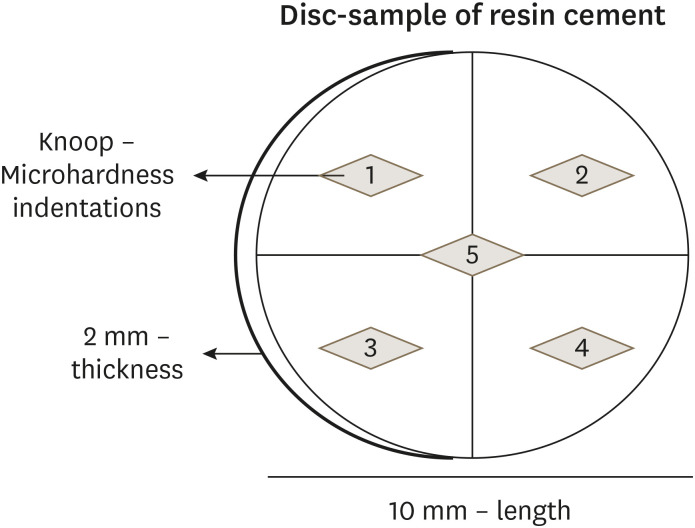
Materials and Methods Three SARCs including RelyX Unicem-2 (RUN), Maxcem Elite (MAX), and Calibra Universal (CAL) were tested. Rectangular bar-shaped specimens were prepared for flexural strength (FS) and flexural modulus (FM) and determined by a 3-point bending test. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and top/bottom microhardness ratio (%KHN) were conducted on the top and bottom faces of disc-shaped samples. Sorption (Wsp) and solubility (Wsl) were evaluated after 24 hours of water immersion. Filler morphology was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). FS, FM, %KHN, Wsp, Wsl, and EDS results were submitted to 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s
post-hoc test, and KHN also to pairedt -test (α = 0.05).Results SARC-CAL presented the highest FS value, and SARC-RUN presented the highest FM. SARC-MAX and RUN showed the lowest Wsp and Wsl values. KHN values decreased from top to bottom and the SARCs did not differ statistically. Also, all resin cements presented carbon, aluminum, and silica in their composition. SARC-MAX and RUN showed irregular and splintered particles while CAL presented small and regular size particles.
Conclusions A higher mechanical strength can be achieved by a reduced spread in grit size and the filler morphology can influence the KHN, as well as photoinitiators in the composition. Wsp and Wsl can be correlated with ions diffusion of inorganic particles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Assessment of fit accuracy and retentive strength of additively manufactured zirconia crowns luted to Ti‐base abutments with different resin cements: An in vitro study
Rafat Sasany, Sultan Merve Uçar, Burak Yilmaz
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Resin Cement Color Stability and Restoration Thickness as Determinants of the Final Shade in a Glass–Ceramic CAD/CAM Material
Hanin E. Yeslam, Alaa Turkistani
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 319. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Resin-Based Luting Materials—Review
Aleksandra Maletin, Milica Jeremić Knežević, Daniela Đurović Koprivica, Tanja Veljović, Tatjana Puškar, Bojana Milekić, Ivan Ristić
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4156. CrossRef - A Scoping Review on the Polymerization of Resin-Matrix Cements Used in Restorative Dentistry
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Orlanda Torres, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva, Susana O. Catarino, Mutlu Özcan, Júlio C. M. Souza
Materials.2023; 16(4): 1560. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
- 2,188 View
- 23 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Cytotoxicity of two self-adhesive resin cements and their interference in the phagocytic activity of murine macrophages
- Danilo Couto da Silva, Leonardo Gomes Vaz, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares, Leda Quercia Vieira, Ricardo Reis de Oliveira, Antônio Paulino Ribeiro Sobrinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e31. Published online July 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate
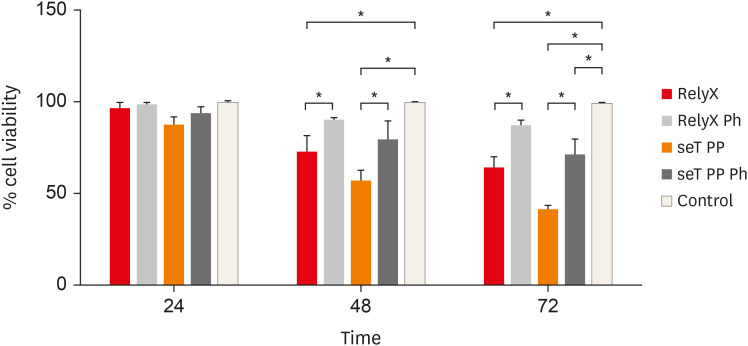
in vitro the effects of the self-adhesive resin cements RelyX U200 (3M ESPE) and seT PP (SDI Limited) on murine macrophages and the interference of the photoactivation.Materials and Methods Cell viability assays, cell adherence, yeast phagocytosis of
Saccharomyces boulardii and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were performed in the presence of capillaries containing the respective self-adhesive cement when photoactivated or not.Results After long periods of contact, both types of cements, when not photoactivated, are more cytotoxic for macrophages. The seT PP cement when only chemically activated seems to interfere more negatively in the process of phagocytosis of yeasts
S. boulardii. Both types of cements interfere in the cell adhesion process, independent of photoactivation. None of the types of cements tested was able to induce the production of ROS.Conclusions Our results highlight the great importance of the photoactivation of self-adhesive resin cements in the dental clinic, since RelyX U200, when photoactivated, presented the best results within the evaluated parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Preheating Self-Adhesive Cements on the Degree of Conversion, Cell Migration, and Cell Viability
Henrique Cantarelli, Fernando Antonio Costa Xavier, Fernando Freitas Portella, Keiichi Hosaka, Eduardo Galia Reston, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Celso Afonso Klein-Junior
Applied Mechanics.2024; 5(3): 553. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef
- Influence of Preheating Self-Adhesive Cements on the Degree of Conversion, Cell Migration, and Cell Viability
- 1,943 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of 10-MDP concentration on the adhesion and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Kazuhiko Shibuya, Naoko Ohara, Serina Ono, Kumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Yoshiyama
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e45. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e45
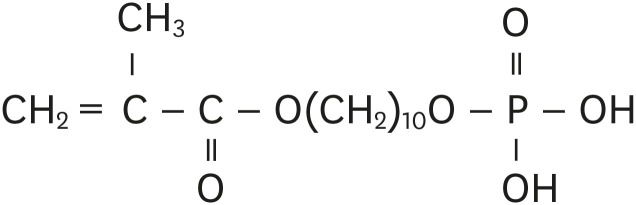
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Self-adhesive resin cements contain functional monomers that enable them to adhere to the tooth structure without a separate adhesive or etchant. One of the most stable functional monomers used for chemical bonding to calcium in hydroxyapatite is 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the10-MDP concentration on the bond strength and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods We used experimental resin cements containing 3 different concentrations of 10-MDP: 3.3 wt% (RC1), 6.6 wt% (RC2), or 9.9 wt% (RC3). The micro-tensile bond strength of each resin cement to dentin and a hybrid resin block (Estenia C&B, Kuraray Noritake Dental) was measured, and the fractured surface morphology was analyzed. Further, the flexural strength of the resin cements was measured using the three-point bending test. The water sorption and solubility of the cements following 30 days of immersion in water were measured.
Results The bond strength of RC2 was significantly higher than that of RC1. There was no significant difference between the bond strength of RC2 and that of RC3. The water sorption of RC3 was higher than that of any other cement. There were no significant differences in the three-point bending strength or water solubility among all three types of cements.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it is suggested that 6.6 wt% 10-MDP showed superior properties than 3.3 wt% or 9.9 wt% 10-MDP in self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Sofia Bignotto de Carvalho, Lívia Maiumi Uehara, João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104260. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Influence of temperature and curing modes on polymerization of self-adhesive resin cements
Hae-In Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(3): 143. CrossRef - Clinical Performance and Retention of Partial Implant Restorations Cemented with Fuji Plus® and DentoTemp™: A Retrospective Clinical Study with Mechanical Validation
Sergiu-Manuel Antonie, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Ioan-Achim Borsanu, Remus Christian Bratu, Emanuel-Adrian Bratu
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2183. CrossRef - A thorough assessment of 10-MDP primers in modern dental adhesive systems
Ahmed A Abduljawad, Harraa SM Salih, Omar F Tawfiq
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 79. CrossRef - Material properties and finite element analysis of adhesive cements used for zirconia crowns on dental implants
Megha Satpathy, Hai Pham, Shreya Shah
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Clinical reliability of self-adhesive luting resins compared to other adhesive procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammed Ahmed Alghauli, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 129: 104394. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization on bond strength between zirconia frameworks and Ti-base abutments using different resin cements
Reinhold Lang, Karl-Anton Hiller, Lena Kienböck, Katrin Friedl, Karl-Heinz Friedl
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(4): 617.e1. CrossRef - Varying 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP) level improves polymerisation kinetics and flexural strength in self-adhesive, remineralising composites
António H.S. Delgado, Nazanin Owji, Paul Ashley, Anne M. Young
Dental Materials.2021; 37(9): 1366. CrossRef - Investigating a Commercial Functional Adhesive with 12-MDPB and Reactive Filler to Strengthen the Adhesive Interface in Eroded Dentin
Madalena Belmar da Costa, António HS Delgado, Tomás Amorim Afonso, Luís Proença, Ana Sofia Ramos, Ana Mano Azul
Polymers.2021; 13(20): 3562. CrossRef
- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- 2,801 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of CAD/CAM-fabricated polymer-ceramics to different adhesive resin cements
- Leyla Sadighpour, Farideh Geramipanah, Zahra Ghasri, Mehrnoosh Neshatian
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e40. Published online September 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of polymer-ceramic and indirect composite resin with 3 classes of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Two computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated polymer-ceramics (Enamic [ENA; Vita] and Lava Ultimate [LAV; 3M ESPE]) and a laboratory indirect composite resin (Gradia [GRA; GC Corp.]) were equally divided into 6 groups (
n = 18) with 3 classes of resin cements: Variolink N (VAR; Vivadent), RelyX U200 (RXU; 3M ESPE), and Panavia F2 (PAN; Kuraray). The μTBS values were compared between groups by 2-way analysis of variance and thepost hoc Tamhane test (α = 0.05).Results Restorative materials and resin cements significantly influenced µTBS (
p < 0.05). In the GRA group, the highest μTBS was found with RXU (27.40 ± 5.39 N) and the lowest with VAR (13.54 ± 6.04 N) (p < 0.05). Similar trends were observed in the ENA group. In the LAV group, the highest μTBS was observed with VAR (27.45 ± 5.84 N) and the lowest with PAN (10.67 ± 4.37 N) (p < 0.05). PAN had comparable results to those of ENA and GRA, whereas the μTBS values were significantly lower with LAV (p = 0.001). The highest bond strength of RXU was found with GRA (27.40 ± 5.39 N,p = 0.001). PAN showed the lowest µTBS with LAV (10.67 ± 4.37 N;p < 0.001).Conclusions When applied according to the manufacturers' recommendations, the µTBS of polymer-ceramic CAD/CAM materials and indirect composites is influenced by the luting cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
Mohamed F. Haridy, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Shehabeldin Saber, Edgar Schafer, Samar Elsayed Swelam, Youssef M. Haridy, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrofluoric acid and self-etch ceramic primers on the flexural strength and fatigue resistance of glass ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Paulo Matias Moreira, Gabriela Luiza Moreira Carvalho, Rodrigo de Castro Albuquerque, Carolina Bosso André
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 198. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on the mechanical properties of permanent composite-based CAD-CAM restorative materials produced by additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques
Tuğba Temizci, Hatice Nalan Bozoğulları
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on resin-matrix CAD/CAM ceramics bonding to dentin: in vitro study
Hanan Fathy, Hamdi H. Hamama, Noha El-Wassefy, Salah H. Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital image analysis of fluorescence of ceramic veneers with different ceramic materials and resin cements
Jiao ZHANG, Qing YU
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 868. CrossRef - Fatigue Behavior of Monolithic Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramic Restorations: Effects of Conditionings of the Intaglio Surface and the Resin Cements
F Dalla-Nora, LF Guilardi, CP Zucuni, LF Valandro, MP Rippe
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): 316. CrossRef
- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
- 2,113 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Light transmittance of CAD/CAM ceramics with different shades and thicknesses and microhardness of the underlying light-cured resin cement
- Zahra Jafari, Homayoon Alaghehmand, Yasaman Samani, Mina Mahdian, Soraya Khafri
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e27. Published online June 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the effects of the thickness and shade of 3 types of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials.Materials and Methods A total of 120 specimens of 2 shades (A1 and A3) and 2 thicknesses (1 and 2 mm) were fabricated using VITA Mark II (VM; VITA Zahnfabrik), IPS e.max CAD (IE; IvoclarVivadent), and VITA Suprinity (VS; VITA Zahnfabrik) (
n = 10 per subgroup). The amount of light transmission through the ceramic specimens was measured by a radiometer (Optilux, Kerr). Light-cured resin cement samples (Choice 2, Bisco) were fabricated in a Teflon mold and activated through the various ceramics with different shades and thicknesses using an LED unit (Bluephase, IvoclarVivadent). In the control group, the resin cement sample was directly light-cured without any ceramic. Vickers microhardness indentations were made on the resin surfaces (KoopaPazhoohesh) after 24 hours of dark storage in a 37°C incubator. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance followed by the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05).Results Ceramic thickness and shade had significant effects on light transmission and the microhardness of all specimens (
p < 0.05). The mean values of light transmittance and microhardness of the resin cement in the VM group were significantly higher than those observed in the IE and VS groups. The lowest microhardness was observed in the VS group, due to the lowest level of light transmission (p < 0.05).Conclusion Greater thickness and darker shades of the 3 types of CAD/CAM ceramics significantly decreased the microhardness of the underlying resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
Shervin Reybod, Fariba Ezoji, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenouz, Behnaz Esmaeili
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Ultrasonic Scaling on Microleakage in Lithium Disilicate Crowns Luted With Different Resin Cements
Waleed AL-Mutairi, Marwa Eltayeb I. Elagra, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Polymerization through Glass-ceramics: Influence of Light-polymerizing Unit’s Emitted Power and Restoration Parameters (Shade, Translucency, and Thickness) on Transmitted Radiant Power
Ra’fat I. Farah, Ibrahim A. Alblihed, Alhareth A. Aljuoie, Bandar Alresheedi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 35. CrossRef - Effect of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing bleach shade ceramic thickness on its light transmittance and microhardness of light-cured resin cement
Pardis Sheibani, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenous, Behnaz Esmaeili, Ali Bijani
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of shade and thickness on the translucency parameter of anatomic-contour zirconia, transmitted light intensity, and degree of conversion of the resin cement
Noppamath Supornpun, Molly Oster, Kamolphob Phasuk, Tien-Min G. Chu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 129(1): 213. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Color Stabilities of Lithium Disilicate Material
Onur Doğan DAĞ, Göknil ALKAN DEMETOĞLU, Ayşegül KURT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(2): 395. CrossRef - Effect of thickness of CAD/CAM materials on light transmission and resin cement polymerization using a blue light‐emitting diode light‐curing unit
Eduardo Fernandes de Castro, Bruna Marin Fronza, Jorge Soto‐Montero, Marcelo Giannini, Carlos Tadeu dos‐Santos‐Dias, Richard Bengt Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(2): 368. CrossRef - Effect of Optical Properties of Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramics and Light-Curing Protocols on the Curing Performance of Resin Cement
Kejing Meng, Lu Wang, Jintao Wang, Zhuoqun Yan, Bin Zhao, Bing Li
Coatings.2022; 12(6): 715. CrossRef - Effect of the thickness of CAD‐CAM materials on the shear bond strength of light‐polymerized resin cement
Yener Okutan, Banucicek Kandemir, Mustafa Borga Donmez, Munir Tolga Yucel
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inhomogeneity of the polymerization light beam on the microhardness of resin cement under a CAD-CAM block
Yu-Ra Go, Kwang-Man Kim, Sung-Ho Park
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(5): 802.e1. CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness and water sorption/solubility of dual-cure resin cement through monolithic zirconia in different shades
Elham Ansarifard, Zahra Panbehzan, Rashin Giti
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(1): 50. CrossRef - Comparison between Different Shades of Monolithic Zirconia over Microhardness and Water Solubility and Sorption of Dual-cure Resin Cement
Sarika Sharma, Soni Kumari, Nikita Raman, Ashish K Srivastava, Gunja LNU, Arunendra S Chauhan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1019. CrossRef - Effect of light intensity, light-curing unit exposure time, and porcelain thickness of ips e.max press and vintage LD press on the hardness of resin cement
Silvia Naliani, Suzan Elias, Rosalina Tjandrawinata
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(1): 21. CrossRef
- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
- 2,047 View
- 8 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of air-abrasion pressure on the resin bond strength to zirconia: a combined cyclic loading and thermocycling aging study
- Eman Z. Al-Shehri, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Alaa H. Sabrah, Sarah S. Al-Angari, Laila Al Dehailan, George J. Eckert, Mutlu Özcan, Jeffrey A. Platt, Marco C. Bottino
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):206-215. Published online June 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the combined effect of fatigue cyclic loading and thermocycling (CLTC) on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a resin cement to zirconia surfaces that were previously air-abraded with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) particles at different pressures.
Materials and Methods Seventy-two cuboid zirconia specimens were prepared and randomly assigned to 3 groups according to the air-abrasion pressures (1, 2, and 2.8 bar), and each group was further divided into 2 groups depending on aging parameters (
n = 12). Panavia F 2.0 was placed on pre-conditioned zirconia surfaces, and SBS testing was performed either after 24 hours or 10,000 fatigue cycles (cyclic loading) and 5,000 thermocycles. Non-contact profilometry was used to measure surface roughness. Failure modes were evaluated under optical and scanning electron microscopy. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and χ2 tests (α = 0.05).Results The 2.8 bar group showed significantly higher surface roughness compared to the 1 bar group (
p < 0.05). The interaction between pressure and time/cycling was not significant on SBS, and pressure did not have a significant effect either. SBS was significantly higher (p = 0.006) for 24 hours storage compared to CLTC. The 2 bar-CLTC group presented significantly higher percentage of pre-test failure during fatigue compared to the other groups. Mixed-failure mode was more frequent than adhesive failure.Conclusions CLTC significantly decreased the SBS values regardless of the air-abrasion pressure used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
Yanru Shen, Xiang Wang, Chen Yang, Ying Jiang, Feng Wang, Li Peng, Yongsheng Zhou, Yuchun Sun
Surfaces and Interfaces.2024; 54: 105153. CrossRef - Multiscale analysis of the compressive behaviour of polymer-based composites reinforced by hybrid Al2O3/Al fibres
Hao Tang, Jiaqi Xu, Constantinos Soutis, Aleksey Yerokhin
Composites Science and Technology.2024; 255: 110718. CrossRef - An Advanced Surface Treatment Technique for Coating Three-Dimensional-Printed Polyamide 12 by Hydroxyapatite
Abdulaziz Alhotan, Saleh Alhijji, Sahar Ahmed Abdalbary, Rania E. Bayoumi, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Tamer M. Hamdy, Rasha M. Abdelraouf
Coatings.2024; 14(9): 1181. CrossRef -
Does incorporation of TiO
2
nanotubes in air-abraded high translucent zirconia influence shear bond strength?*
Bahadır Ezmek, Osman Cumhur Sipahi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(22): 3206. CrossRef - Effects of aging and light-curing unit type on the volume and internal porosity of bulk-fill resin composite restoration
Afnan O. Al-Zain, Elaf A. Alboloshi, Walaa A. Amir, Maryam A. Alghilan, Eliseu A. Münchow
The Saudi Dental Journal.2022; 34(3): 243. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and cyclic fatigue on subsurface defects and mechanical properties of zirconia frameworks
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Nikolaos Silikas, Moustafa Aboushelib
Dental Materials.2021; 37(5): 905. CrossRef - Effects of low-temperature degradation on the surface roughness of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hui Yang, Yi-Li Xu, Guang Hong, Hao Yu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(2): 222. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on repair strength, roughness and morphology in aged metal-free crowns
Yançanã Luizy Gruber, Thaís Emanuelle Bakaus, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, João Carlos Gomes, Alessandra Reis, Giovana Mongruel Gomes
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 19: e206155. CrossRef - Retentive Force of Glass-Ceramic Soldered Customized Zirconia Abutment Copings with Prefabricated Titanium Bases
Jeremias Hey, Monika Kasaliyska, Andreas Kiesow, Ramona Schweyen, Christin Arnold
Materials.2020; 13(14): 3193. CrossRef - Solvent-aided direct adhesion of a metal/polymer joint using micro/nano hierarchical structures
Gyosik Jun, Jeong-Won Lee, Younghun Shin, Kihwan Kim, Woonbong Hwang
Journal of Materials Processing Technology.2020; 285: 116744. CrossRef - Study of physicochemical properties and effects on bonding to zirconia ceramics of five resin cements
Xiuju Liu, Zhaoying Liu, Xuan Li, Han Wang, Gaigai Yu, Song Zhu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(18): 2031. CrossRef - The effect of air-particle abrasion and a zirconia primer application on resin cement bonding strength to zirconia
Alana M. Dantas, Fernanda Campos, Sarina M. Pereira, Elis J. dos Santos, Laudenice L. Pereira, Dayanne M. Moura, Rodrigo O. Souza
Minerva Stomatologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on Shear Bond Strength between Y-TZP and Self-Adhesive Resin Cement
Dae-Sung Kim, Jong-Ju Ahn, Eun-Bin Bae, Gyoo-Cheon Kim, Chang-Mo Jeong, Jung-Bo Huh, So-Hyoun Lee
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3321. CrossRef - Effect of airborne particle abrasion and sintering order on the surface roughness and shear bond strength between Y-TZP ceramic and resin cement
Yener OKUTAN, Munir Tolga YUCEL, Tugce GEZER, Mustafa Borga DONMEZ
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(2): 241. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
- 2,260 View
- 13 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Bonding of the silane containing multi-mode universal adhesive for lithium disilicate ceramics
- Hyun-Young Lee, Geum-Jun Han, Juhea Chang, Ho-Hyun Son
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):95-104. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the influence of a multi-mode universal adhesive (MUA) containing silane (Single Bond Universal, 3M EPSE) on the bonding of resin cement to lithium disilicate.
Materials and Methods Thirty IPS e.max CAD specimens (Ivoclar Vivadent) were fabricated. The surfaces were treated as follows: Group A, adhesive that did not contain silane (ANS, Porcelain Bonding Resin, Bisco); Group B, silane (S) and ANS; Group C, hydrofluoric acid (HF), S, and ANS; Group D, MUA; Group E, HF and MUA. Dual-cure resin cement (NX3, Kerr) was applied and composite resin cylinders of 0.8 mm in diameter were placed on it before light polymerization. Bonded specimens were stored in water for 24 hours or underwent a 10,000 thermocycling process prior to microshear bond strength testing. The data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of variance (
p < 0.05).Results Bond strength varied significantly among the groups (
p < 0.05), except for Groups A and D. Group C showed the highest initial bond strength (27.1 ± 6.9 MPa), followed by Group E, Group B, Group D, and Group A. Thermocycling significantly reduced bond strength in Groups B, C, and E (p < 0.05). Bond strength in Group C was the highest regardless of the storage conditions (p < 0.05).Conclusions Surface treatment of lithium disilicate using HF and silane increased the bond strength of resin cement. However, after thermocycling, the silane in MUA did not help achieve durable bond strength between lithium disilicate and resin cement, even when HF was applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Roles of Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Bonding Materials
Maria Arampatzi, Ellas Spyratou, Iosif Sifakakis, Efstathios P. Efstathopoulos
Applied Sciences.2026; 16(4): 1996. CrossRef - The influence of different factors on the bond strength of lithium disilicate-reinforced glass–ceramics to Resin: a machine learning analysis
Jiawen Liu, Suqing Tu, Mingjuan Wang, Du Chen, Chen Chen, Haifeng Xie
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different primers and adhesive system combinations on the durability of resin bonding to lithium disilicate
Christine Yazigi, Shila Alawi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(3): 749. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength and Finite Element Stress Analysis of Composite Repair Using Various Adhesive Strategies With and Without Silane Application
Elif Ercan Devrimci, Hande Kemaloglu, Cem Peskersoy, Tijen Pamir, Murat Turkun
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(15): 8159. CrossRef - Effect of multiple firings on mechanical and optical properties of CAD/CAM lithium disilicate-based glass ceramics
Chawal Padunglappisit, Pitsucha Charoensakthanakul, Sintwo Wongthongdee, Kan Wongkamhaeng
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of universal adhesives and self-etch ceramic primers on bond strength to glass-ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Renally Bezerra Wanderley Lima, Isis de Araújo Ferreira Muniz, Débora e Silva Campos, Fabián Murillo-Gómez, Ana Karina Maciel de Andrade, Rosângela Marques Duarte, Grace Mendonça de Souza
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(3): 392. CrossRef - Effect of the difference water amounts and hydrolysis times of silane coupling agent on the shear bond strength between lithium disilicate glass ceramic and composite resin
Pimchanok OSOTPRASIT, Sasipin LAUVAHUTANON, Yosnarong SIRIMETHAWONG, Patcharanun CHAIAMORNSUP, Pornpot JIANGKONGKHO
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(3): 375. CrossRef - Is additional silane application necessary for a new silane‐containing universal adhesive to bond to glass ceramics?
Priscila Luciane da Silva, Hélio Radke Bittencourt, Luiz Henrique Burnett, Ana Maria Spohr
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(10): 1452. CrossRef - The Effect of Various Lasers on the Bond Strength Between Orthodontic Brackets and Dental Ceramics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Jaafar Abduo, Mehrnaz Zakizade, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Ahmed Hussain
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(1): 20. CrossRef - Long-Term Bonding Performance of One-Bottle vs. Two-Bottle Bonding Agents to Lithium Disilicate Ceramics
Masao Irie, Masahiro Okada, Yukinori Maruo, Goro Nishigawa, Takuya Matsumoto
Polymers.2024; 16(16): 2266. CrossRef - Bond strength to different CAD/CAM lithium disilicate reinforced ceramics
Mona Alhomuod, Jin‐Ho Phark, Sillas Duarte
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(1): 129. CrossRef - Surface Treatment Effect on Shear Bond Strength between Lithium Disilicate Glass-Ceramic and Resin Cement
Siripan Simasetha, Awiruth Klaisiri, Tool Sriamporn, Kraisorn Sappayatosok, Niyom Thamrongananskul
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(02): 373. CrossRef - Bonding of Clear Aligner Composite Attachments to Ceramic Materials: An In Vitro Study
Bashair A. Alsaud, Maher S. Hajjaj, Ahmad I. Masoud, Ensanya A. Abou Neel, Dalia A. Abuelenain, Amal I. Linjawi
Materials.2022; 15(12): 4145. CrossRef - Bonding of different resin luting materials to composite, polymer-infiltrated and feldspathic ceramic CAD/CAM blocks
Burcu Dikici, Esra Can Say
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2022; 36(14): 1572. CrossRef - Influence of mechanical and chemical pre-treatments on the repair of a hybrid ceramic
Sascha Niklas Jung, Stefan Rüttermann
Dental Materials.2022; 38(7): 1140. CrossRef - Effect of Silane-Containing Universal Adhesives on the Bonding Strength of Lithium Disilicate
Yu-Ri Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3976. CrossRef - Ceramics in dentistry: which material is appropriate for the anterior or posterior Dentition? Part 1: materials science
Loo Chien Win, Peter Sands, Stephen J Bonsor, FJ Trevor Burke
Dental Update.2021; 48(8): 680. CrossRef - The effect of different ceramic surface treatments on the repair bond strength of resin composite to lithium disilicate ceramic
Nanako UEDA, Tomohiro TAKAGAKI, Toru NIKAIDO, Rena TAKAHASHI, Masaomi IKEDA, Junji TAGAMI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(5): 1073. CrossRef - Bonding Strength of Universal Adhesives to Indirect Substrates: A Meta‐Analysis of in Vitro Studies
Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suárez, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Rafael Pino Vitti, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Evandro Piva
Journal of Prosthodontics.2020; 29(4): 298. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments and multimode adhesive application on the Weibull characteristics, wettability, surface topography and adhesion to CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramic
Karina Barbosa Souza, Dayanne Monielle Duarte Moura, Sarah Emille Gomes da Silva, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Rafael de Almeida Spinelli Pinto, Fabíola Pessôa Pereira Leite, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the ratio of silane to 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogenphosphate (MDP) in primer on bonding performance of silica-based and zirconia ceramics
Minkhant Koko, Tomohiro Takagaki, Ahmed Abdou, Masanao Inokoshi, Masaomi Ikeda, Takahiro Wada, Motohiro Uo, Toru Nikaido, Junji Tagami
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 112: 104026. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and repair materials on the shear bond strength of CAD/CAM provisional restorations
Ki-Won Jeong, Sung-Hun Kim
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2019; 11(2): 95. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strengths of adhesively bonded polymer-based CAD/CAM materials to dentin
Nuray CAPA, Esra CAN SAY, Cansin CELEBI, Ayca CASUR
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(1): 75. CrossRef - Simplified Surface Treatments for Ceramic Cementation: Use of Universal Adhesive and Self-Etching Ceramic Primer
Heloísa A. B. Guimarães, Paula C. Cardoso, Rafael A. Decurcio, Lúcio J. E. Monteiro, Letícia N. de Almeida, Wellington F. Martins, Ana Paula R. Magalhães
International Journal of Biomaterials.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Effects of surface treatments on repair bond strength of a new CAD/CAM ZLS glass ceramic and two different types of CAD/CAM ceramics
Ayse Seda Ataol, Gulfem Ergun
Journal of Oral Science.2018; 60(2): 201. CrossRef - An in vitro evaluation of fracture load of implant‐supported zirconia‐based prostheses fabricated with different veneer materials
Hiroki Takata, Futoshi Komine, Junichi Honda, Markus B. Blatz, Hideo Matsumura
Clinical Oral Implants Research.2018; 29(4): 396. CrossRef - Effects of multiple firings on mechanical properties and resin bonding of lithium disilicate glass-ceramic
Hongliang Meng, Haifeng Xie, Lu Yang, Bingzhuo Chen, Ying Chen, Huaiqin Zhang, Chen Chen
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2018; 88: 362. CrossRef
- Clinical Roles of Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Bonding Materials
- 4,068 View
- 22 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Effects of radiant exposure and wavelength spectrum of light-curing units on chemical and physical properties of resin cements
- Adriano Fonseca Lima, Stephanie Ellen Ferreira Formaggio, Lígia França Aires Zambelli, Alan Rodrigo Muniz Palialol, Giselle Maria Marchi, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Marcelo Tavares de Oliveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):271-277. Published online September 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we evaluated the influence of different radiant exposures provided by single-peak and polywave light-curing units (LCUs) on the degree of conversion (DC) and the mechanical properties of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Six experimental groups were established for each cement (RelyX ARC, 3M ESPE; LuxaCore Dual, Ivoclar Vivadent; Variolink, DMG), according to the different radiant exposures (5, 10, and 20 J/cm2) and two LCUs (single-peak and polywave). The specimens were made (7 mm in length × 2 mm in width × 1 mm in height) using silicone molds. After 24 hours of preparation, DC measurement was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. The same specimens were used for the evaluation of mechanical properties (flexural strength, FS; elastic modulus,
E ) by a three-point bending test. Data were assessed for normality, after which two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey's test were performed.Results No properties of the Variolink cement were influenced by any of the considered experimental conditions. In the case of the RelyX ARC cement, DC was higher when polywave LCU was used; FS and E were not influenced by the conditions evaluated. The LuxaCore cement showed greater sensitivity to the different protocols.
Conclusions On the basis of these results, both the spectrum of light emitted and the radiant exposure used could affect the properties of resin cements. However, the influence was material-dependent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
Eduardo Fernández Godoy, Alain Chaple Gil, Rodrigo Caviedes Thomas, Cristian Bersezio Miranda, Javier Martín Casielles, Gonzalo Rodríguez Martínez, Pablo Angel Aguirre
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Transmittance and Depth of Cure of a Bulk Fill Composite Based on the Exposure Reciprocity Law
Mateus Garcia Rocha, Jean-François Roulet, Mario Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Américo Bortolazzo Correr, Dayane Oliveira
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(1): 78. CrossRef
- Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
- 1,833 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility of Zirconia (Y-TZP) posts with various dental cements
- Hyeongsoon Shin, Hyunjung Ko, Miri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):167-175. Published online May 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Endodontically treated teeth with insufficient tooth structure are often restored with esthetic restorations. This study evaluated the cytotoxicity and biological effects of yttria partially stabilized zirconia (Y-TZP) blocks in combination with several dental cements.
Materials and Methods Pairs of zirconia cylinders with medium alone or cemented with three types of dental cement including RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), FujiCEM 2 (GC), and Panavia F 2.0 (Kuraray) were incubated in medium for 14 days. The cytotoxicity of each supernatant was determined using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays on L929 fibroblasts and MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. The levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA were evaluated by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and IL-6 protein was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey
post-hoc tests. Ap < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results The MTT assays showed that MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts were more susceptible to dental cements than L929 fibroblasts. The resin based dental cements increased IL-6 expression in L929 cells, but reduced IL-6 expression in MC3T3-E1 cells.
Conclusions Zirconia alone or blocks cemented with dental cement showed acceptable biocompatibilities. The results showed resin-modified glass-ionomer based cement less produced inflammatory cytokines than other self-adhesive resin-based cements. Furthermore, osteoblasts were more susceptible than fibroblasts to the biological effects of dental cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital light processing 3D printing of yttria stabilized zirconia ceramics: microstructures, characterizations, and cytocompatibility
Luke Wadle, Mena Asha Krishnan, Ryan Wall, Lanh Trinh, Bin Duan, Bai Cui
Emergent Materials.2025; 8(2): 1023. CrossRef - Doping of casted silk fibroin membranes with extracellular vesicles for regenerative therapy: a proof of concept
Sandra Fuest, Amanda Salviano-Silva, Cecile L. Maire, Yong Xu, Christian Apel, Audrey Laure Céline Grust, Arianna Delle Coste, Martin Gosau, Franz L. Ricklefs, Ralf Smeets
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 3D printing of ceramics: Advantages, challenges, applications, and perspectives
Susmita Bose, Enver Koray Akdogan, Vamsi K. Balla, Sushant Ciliveri, Paolo Colombo, Giorgia Franchin, Nicholas Ku, Priya Kushram, Fangyong Niu, Joshua Pelz, Andrew Rosenberger, Ahmad Safari, Zachary Seeley, Rodney W. Trice, Lionel Vargas‐Gonzalez, Jeffrey
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2024; 107(12): 7879. CrossRef - A Review on Biocompatibility of Dental Restorative and Reconstruction Materials
Pune Nina Paqué, Mutlu Özcan
Current Oral Health Reports.2024; 11(1): 68. CrossRef - Enhancement of Human Gingival Fibroblasts Bioactivity and Proliferation on Plasma Sprayed Yttria-Stabilised Zirconia/TiO2 Surface Coating of Titanium Alloys: An In-Vitro Study
Afida Jemat, Masfueh Razali, Yuichi Otsuka, Mariyam Jameelah Ghazali
Coatings.2023; 13(10): 1746. CrossRef - Material extrusion-based additive manufacturing of zirconia toughened alumina: Machinability, mechanical properties and biocompatibility
Tianyu Yu, Xiaolong Zhu, Hongwei Yu, Pan Wu, Chun Li, Xiaoxiao Han, Mingjun Chen
Journal of Manufacturing Processes.2023; 94: 120. CrossRef - Green synthesis and characterization of zirconium nanoparticlefor dental implant applications
Mohammad Asaduzzaman Chowdhury, Nayem Hossain, Md. Golam Mostofa, Md. Riyad Mia, Md. Tushar, Md. Masud Rana, Md. Helal Hossain
Heliyon.2023; 9(1): e12711. CrossRef - The role of Y2O3 in the bioactivity of YSZ/PLLA composites
Elia Marin, Giada Bassi, Orion Yoshikawa, Francesco Boschetto, Wenliang Zhu, Arianna Rossi, Alex Lanzutti, Huaizhong Xu, Monica Montesi, Silvia Panseri, Giuseppe Pezzotti
Journal of Materials Science.2023; 58(27): 11218. CrossRef - Nano-β-tricalcium phosphate incorporated root dentin adhesive in the bonding interface of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline post
Amal S. Al-Qahtani, Huda I. Tulbah, Mashael Binhasan, Mai M. Alhamdan, Imran Farooq, Fahim Vohra, Tariq Abduljabbar
Applied Nanoscience.2022; 12(11): 3489. CrossRef - Outcome of teeth restored with CAD/CAM zirconium dioxide post-cores: a retrospective study with a follow-up period of 3–6 years
Shunv Ying, Song Chen, Siyuan Wang, Lingli Xu, Xiaofeng Wang, Fuming He, Wei Liu
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of Physical, Mechanical, and Biological Characteristics of 3D-Printed Bioceramic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications
Mahendran Thangavel, Renold Elsen Selvam
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2022; 8(12): 5060. CrossRef - Comparison of Regular and Speed Sintering on Low-Temperature Degradation and Fatigue Resistance of Translucent Zirconia Crowns for Implants: An In Vitro Study
Suchada Kongkiatkamon, Chaimongkon Peampring
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 281. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Bonding Property of Bioinspired Nacre-like Ceramic-Polymer Composites
Hui Sun, Kefeng Gao, Zhe Yi, Chengwei Han, Zengqian Liu, Qiang Wang, Qing Zhou, Zhefeng Zhang
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterisation of Selected Materials in Medical Applications
Kacper Kroczek, Paweł Turek, Damian Mazur, Jacek Szczygielski, Damian Filip, Robert Brodowski, Krzysztof Balawender, Łukasz Przeszłowski, Bogumił Lewandowski, Stanisław Orkisz, Artur Mazur, Grzegorz Budzik, Józef Cebulski, Mariusz Oleksy
Polymers.2022; 14(8): 1526. CrossRef - Adhesive bond integrity of Y‐TZP post with calcium fluoride infiltrated resin dentin adhesive: An SEM, EDX, FTIR and micro‐Raman study
Eman M. AlHamdan, Samar Al‐Saleh, Mohammad H. AlRefeai, Imran Farooq, Eisha Abrar, Fahim Vohra, Tariq Abduljabbar
Surface and Interface Analysis.2021; 53(11): 956. CrossRef - Additive Manufacturing (3D PRINTING) Methods and Applications in Dentistry
Elif DEMİRALP, Gülsüm DOĞRU, Handan YILMAZ
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(1): 182. CrossRef - Interleukin-1β activity in gingival crevicular fluid of abutment teeth with temporary fixed restorations versus final fixed restorations: Prospective observational study
Amal Abdallah A. Abo-Elmagd, Dina Sabry, Ebtehal Mohammed
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(6): 322. CrossRef - Change in the Microhardness of Composite Ceramics at the CaO–ZrO2/CaO–ZrO2 + Al2O3 Interface
A. A. Dmitrievskiy, D. G. Zhigacheva, G. V. Grigoriev, P. N. Ovchinnikov
Journal of Surface Investigation: X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques.2021; 15(S1): S137. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of two self-adhesive flowable composites on bovine dental pulp-derived cells
Firdevs KAHVECİOĞLU, Türkay KÖLÜŞ, Fatma SAĞ GÜNGÖR, Hayriye Esra ÜLKER
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2021; 4(2): 209. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility of high mol% yttria containing zirconia
Gulsan Ara Sathi Kazi, Ryo Yamagiwa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytotoxic effects of different self-adhesive resin cements: Cell viability and induction of apoptosis
Soner Şişmanoğlu, Mustafa Demirci, Helmut Schweikl, Gunes Ozen-Eroglu, Esin Cetin-Aktas, Serap Kuruca, Safa Tuncer, Neslihan Tekce
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(2): 89. CrossRef - Effects of nano-zirconia fillers conditioned with phosphate ester monomers on the conversion and mechanical properties of Bis-GMA- and UDMA-based resin composites
Jiaxue Yang, Jiadi Shen, Xinyi Wu, Feng He, Haifeng Xie, Chen Chen
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 94: 103306. CrossRef - Effect of APTES- or MPTS-Conditioned Nanozirconia Fillers on Mechanical Properties of Bis-GMA-Based Resin Composites
Jiaxue Yang, Mengyuan Liao, Gaoying Hong, Shiqi Dai, Jiadi Shen, Haifeng Xie, Chen Chen
ACS Omega.2020; 5(50): 32540. CrossRef - In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Self-Adhesive Dual-Cured Resin Cement Polymerized Beneath Three Different Cusp Inclinations of Zirconia
Chang-Yuan Zhang, Yi-Ling Cheng, Xin-Wen Tong, Hao Yu, Hui Cheng
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Investigations on the corrosion behaviour and biocompatibility of magnesium alloy surface composites AZ91D-ZrO2 fabricated by friction stir processing
R. Vaira Vignesh, R. Padmanaban, M. Govindaraju, G. Suganya Priyadharshini
Transactions of the IMF.2019; 97(5): 261. CrossRef - Microwave assisted synthesis and antimicrobial activity of Fe3O4-doped ZrO2 nanoparticles
M. Imran, Saira Riaz, Ifra Sanaullah, Usman Khan, Anjum N. Sabri, Shahzad Naseem
Ceramics International.2019; 45(8): 10106. CrossRef - Additive manufacturing of ceramics for dental applications: A review
Raquel Galante, Celio G. Figueiredo-Pina, Ana Paula Serro
Dental Materials.2019; 35(6): 825. CrossRef - Reinforcement of dental resin composite via zirconium hydroxide coating and phosphate ester monomer conditioning of nano-zirconia fillers
Xinyi Wu, Shiqi Dai, Ying Chen, Feng He, Haifeng Xie, Chen Chen
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 94: 32. CrossRef - Effects of TiO2 on microstructural, mechanical properties and in-vitro bioactivity of plasma sprayed yttria stabilised zirconia coatings for dental application
A. Jemat, M.J. Ghazali, M. Razali, Y. Otsuka, A. Rajabi
Ceramics International.2018; 44(4): 4271. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of different self-adhesive resin cements
Necla Demir, Firdevs Kahvecioğlu, Muhammet Karcı, Hayriye Esra Ülker, Nuray Günaydın
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital light processing 3D printing of yttria stabilized zirconia ceramics: microstructures, characterizations, and cytocompatibility
- 2,490 View
- 18 Download
- 30 Crossref

- Effect of antioxidants on push-out bond strength of hydrogen peroxide treated glass fiber posts bonded with two types of resin cement
- Maryam Khoroushi, Hamid Mazaheri, Pardis Tarighi, Pouran Samimi, Navid Khalighinejad
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):303-309. Published online September 2, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) surface treatment of fiber posts has been reported to increase bond strength of fiber posts to resin cements. However, residual oxygen radicals might jeopardize the bonding procedure. This study examined the effect of three antioxidant agents on the bond strength of fiber posts to conventional and self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods Post spaces were prepared in forty human maxillary second premolars. Posts were divided into five groups of 8 each: G1 (control), no pre-treatment; G2, 10% H2O2 pre-treatment; G3, G4 and G5. After H2O2 application, Hesperidin (HES), Sodium Ascorbate (SA) or Rosmarinic acid (RA) was applied on each group respectively. In each group four posts were cemented with Duo-Link conventional resin cement and the others with self-adhesive BisCem cement. Push-out test was performed and data were analyzed using 2-way ANOVA and tukey's
post-hoc test (α = 0.05).Results There was a statistically significant interaction between the cement type and post surface treatment on push-out bond strength of fiber posts (
p < 0.001, F = 16). Also it was shown that different posts' surface treatments significantly affect the push-out bond strength of fiber posts (p = 0.001). H2O2 treated posts (G2) and control posts (G1) cemented with Duo-link showed the highest (15.96 ± 5.07MPa) and lowest bond strengths (6.79 ± 3.94) respectively.Conclusions It was concluded that H2O2 surface treatment might enhance the bond strength of fiber posts cemented with conventional resin cements. The effect of antioxidants as post's surface treatment agents depends on the characteristics of resin cements used for bonding procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatments on the adhesion of fiber post to resin composite core material
Jiyoon KWON, Hyo Jin JO, Jeong Hun LEE, Young Kyung KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2025; 44(6): 697. CrossRef - Comparison of the push-out bond strength of AH Plus sealer to dentin after using different herbal irrigation solutions as the final rinse
Mohammadreza Nabavizadeh, Fereshte Sobhnamayan, Mahdi Sedigh-Shams, Sepideh Liaghat, Ajinkya M. Pawar
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0276666. CrossRef - The influence of different treatments on fiber post and root canal to bond strength of fiber post
Deli Niu, Jinfang Xie, Chang Liu, Shanling Ni, Hong Liu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(9): 928. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on the dislocation resistance of prefabricated esthetic fiber posts bonded with self-adhesive resin cement: A systematic review and meta-analysis
ShwetaElizabeth Jacob, SabahMohd Zubair, ManuelSebastian Thomas, Vinod Jathanna, Ramya Shenoy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(2): 113. CrossRef - Dentin pretreatment with Er:YAG laser and sodium ascorbate to improve the bond strength of glass fiber post
Laís Lima Pelozo, Reinaldo Dias Silva-Neto, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel
Lasers in Medical Science.2019; 34(1): 47. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Effects of hydrogen peroxide pretreatment and heat activation of silane on the shear bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite posts to resin cement
Jung-Hoon Pyun, Tae-Bong Shin, Joo-Hee Lee, Kang-Min Ahn, Tae-Hyung Kim, Hyun-Suk Cha
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2016; 8(2): 94. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatments on the adhesion of fiber post to resin composite core material
- 1,653 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Bond strength of resin cement to CO2 and Er:YAG laser-treated zirconia ceramic
- Shahin Kasraei, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Bijan Heidari, Fariborz Vafaee
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):296-302. Published online August 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It is difficult to achieve adhesion between resin cement and zirconia ceramics using routine surface preparation methods. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of CO2 and Er:YAG laser treatment on the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics.
Materials and Methods In this
in-vitro study 45 zirconia disks (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) were assigned to 3 groups (n = 15). In control group (CNT) no laser treatment was used. In groups COL and EYL, CO2 and Er:YAG lasers were used for pretreatment of zirconia surface, respectively. Composite resin disks were cemented on zirconia disk using dual-curing resin cement. Shear bond strength tests were performed at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min after 24 hr distilled water storage. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA andpost hoc Tukey's HSD tests.Results The means and standard deviations of shear bond strength values in the EYL, COL and CNT groups were 8.65 ± 1.75, 12.12 ± 3.02, and 5.97 ± 1.14 MPa, respectively. Data showed that application of CO2 and Er:YAG lasers resulted in a significant higher shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics (
p < 0.0001). The highest bond strength was recorded in the COL group (p < 0.0001). In the CNT group all the failures were adhesive. However, in the laser groups, 80% of the failures were of the adhesive type.Conclusions Pretreatment of zirconia ceramic via CO2 and Er:YAG laser improves the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic, with higher bond strength values in the CO2 laser treated samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Er:YAG Laser Irradiation on the Flexural Fatigue Strength of a 4YSZ Ceramic
Duvan Cala Castillo, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Gabriela Carrão Aragonez, Bibiana Vogel Peres Riesgo, Natália de Freitas Daudt, Marilia Pivetta Rippe, Mutlu Özcan, Liliana Gressler May, Luiz Felipe Valandro, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Sandblasting, Tribochemical Silica Coating, CO2 Laser, and Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition on Surface Characteristics and Shear Bond Strength of 3Y-TZP Zirconia
Mohammed A. Alrabiah, Fahad Alkhudhairy
Crystals.2026; 16(1): 59. CrossRef - The Impact of Surface Roughness and Different Pre-treatments on the Shear Bond Strength of Super-translucent Multi-layered Zirconia to Adhesive Resin Cement: An In Vitro Study
Manar Almousli
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Surface Roughening Techniques on Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Monolithic Zirconia: In Vitro Study
Nehal F Albelasy, Ahmad M Hafez, Abdullah S Alhunayni
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(12): 1104. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of etching with ytterbium fiber laser on the bond strength, color stability, and fracture analysis of lithium disilicate ceramics to bovine teeth: an in vitro study
Göknil Alkan Demetoğlu, Esra Talay Çevlïk
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear bond strength of multilayered zirconia to adhesive resin cement after CO2 laser surface treatment (an in vitro study)
Abdelrahman Badran, Reem Gabr
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Different surface treatments and adhesive monomers for zirconia-resin bonds: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Xinyang Li, Shengjie Liang, Masanao Inokoshi, Shikai Zhao, Guang Hong, Chenmin Yao, Cui Huang
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 175. CrossRef - The impact of CO2 laser on the bond strength of translucent zirconia and traditional zirconia with the resin cement: In vitro study
Rima Saker, Bashar Zleik
Balkan Journal of Dental Medicine.2024; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Evaluation of Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Prepared with Different Surface Roughening Methods: An In Vitro Study
Marwa A Tawfik, Abdullah M Fayyadh, Mohammed A Elbialy
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(8): 766. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser and sllica-coating on zirconia framework-veneering ceramic bonding, surface chemistry and crystallographic changes
Tevfik Yavuz, Muhammed Ali Aslan, Yusuf Ziya Akpinar, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Nadin Al-Haj Husain, Mutlu Özcan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(6): 1059. CrossRef - In vitro comparative study between adhesion forces obtained on zirconia ceramic micromechanically treated with femtosecond laser (1027 nm), carbon dioxide laser (10,600 nm), and aluminum-oxide particles
Ignasi Piulachs, Luis Giner-Tarrida, Antoni España-Tost, Josep Arnabat-Dominguez, Camilo Florian
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating in Combination with Physical Modifications on Microshear Bond Strength of Zirconia to Resin Cement
Faezeh Atri, Vanya Rasaie, Sakineh Nikzad Jamnani, Saba Mohammadi, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Zirconia Surface Treatment with CO2 and Nd:YAG Lasers on Shear Bond Strength between Zirconia Frameworks and Porcelain Veneers
Bijan Heidari, Hadi Ranjzad, Farzane Ostovar Rad, Amirreza Hendi, Zahra Ghorbani
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(10): 1026. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Three Surface Treatments on the Bond Strength of Zirconia to Resin-luting Agents: An In Vitro Study
Abhinav Sharma, Arka Swarnakar, Angana Pal Swarnakar, Himadri Sekhar Pal, Shivani Tyagi, Pragati Rawat
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 883. CrossRef - Surface modification of zirconia or lithium disilicate-reinforced glass ceramic by laser texturing to increase the adhesion of prosthetic surfaces to resin cements: an integrative review
Júlio C. M. Souza, Angelo Raffaele-Esposito, Oscar Carvalho, Filipe Silva, Mutlu Özcan, Bruno Henriques
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3331. CrossRef - A Shift to Synergistic Surface Treatment Using Laser to Enhance the Bonding of Zirconia to Veneering Ceramic: An In Vitro Study
N Kiran Kumar, Anoop Nair, Savitha B Naik, Annie Swathisha, CH Laxmi Priya, HS Preetham, V Shylaja
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(1): 37. CrossRef - Effects of cold atmospheric plasma treatment on resin bonding to high-translucency zirconia ceramics
Xin-Yi YE, Ming-Yue LIU, Jing LI, Xiao-Qiang LIU, Yu LIAO, Ling-Lu ZHAN, Xiao-Ming ZHU, He-Ping LI, Jianguo TAN
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 896. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser zirconia surface treatment on cement shear bond strength
Elif Yeğin, Tevfik Yavuz, Muhammed Ali Aslan, Mustafa Hayati Atala, John A. Sorensen, Hamdi Şükür Kılıç
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2022; 36(18): 1951. CrossRef - Effects of different frequencies of Er:YAG laser on the bonding properties of zirconia ceramic
Hong Zhu, Hui-hui Tao, Meng Wei, Pan Liu, Lu Yuan, Yan-nan Zhang, Bo Wang, Jian-feng Chen
Lasers in Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on Repair Bond Strength of CAD/CAM Resin-Matrix Ceramics
Semih Arkoy, Mutahhar Ulusoy
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6314. CrossRef - Effect of different laser treatments on the shear bond strength of zirconia ceramic to resin cement
Mahnaz Hatami, Mohammadhossein Lotfi-Kamran, Abdolrahim Davari, Meisam Molazem
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 56. CrossRef - Effect of laser irradiation on bond strength between zirconia and resin cement or veneer ceramic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
SandroBasso Bitencourt, LetíciaChaves Ferreira, LeticiaCerri Mazza, DanielaMicheline dos Santos, AldierisAlves Pesqueira, LeticiaHelena Theodoro
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(2): 125. CrossRef - Effect of laser irradiation on the adhesion of resin-based materials to zirconia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato, Oscar Carvalho, Mutlu Özcan, Márcio Celso Fredel, Filipe Samuel Silva
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(10): 1035. CrossRef - Laser surface texturing of zirconia-based ceramics for dental applications: A review
Jide Han, Fei Zhang, Bart Van Meerbeek, Jozef Vleugels, Annabel Braem, Sylvie Castagne
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 123: 112034. CrossRef - Effect of Nd:YAG, Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation, and Adjunctive Photodynamic Therapy on Push‐Out Bond Strength of Zirconia Posts to Radicular Dentin
Freah Alshammary, Mohmed I. Karobari, Ali A. Assiry, Anand Marya, Gul M. Shaikh, Ammar A. Siddiqui, Mohammad K. Alam, Iole Vozza
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser and silica coating on the bond strength of zirconia ceramic
Hongbo Zhou, Chen Yu, Cheng Qi, Dingxiang Qiu, Shusen Zhang, Jilin Li, Youwang Hu
Advances in Applied Ceramics.2020; 119(5-6): 276. CrossRef - Laser-Milled Microslits Improve the Bonding Strength of Acrylic Resin to Zirconia Ceramics
Saiji Shimoe, Tzu-Yu Peng, Yuki Wakabayashi, Hiroto Takenaka, Shogo Iwaguro, Masato Kaku
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 817. CrossRef - Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal/resin luting agent bond strength: Influence of Titanium dioxide nanotubes addition in both materials
Ana Paula Rodrigues Magalhães, Carla Müller Ramos-Tonello, Mateus Zamora Galli, Orisson Ponce Gomes, Leandro Edgar Pacheco, Carlos Alberto Fortulan, Paulo Noronha Lisboa-Filho, Rafael Francisco Lia Mondelli, Adilson Yoshio Furuse, Ana Flávia Sanches Borge
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2020; 64(4): 408. CrossRef - Exploring the use of pulsed erbium lasers to retrieve a zirconia crown from a zirconia implant abutment
Ahmed Elkharashi, Kinga Grzech-Leśniak, Janina Golob Deeb, Aous A. Abdulmajeed, Sompop Bencharit, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(6): e0233536. CrossRef - Evaluation of zirconia surface roughness after aluminum oxide airborne-particle abrasion and the erbium-YAG, neodymium-doped YAG, or CO2 lasers: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Felipe V. Martins, Cláudia T. Mattos, Wayne J.B. Cordeiro, Edgard M. Fonseca
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(6): 895. CrossRef - Effect of thermal and mechanical cycles on shear bond strength of zirconia core to porcelain veneer under different surface treatments
Tahereh Ghaffari, Elnaz Moslehifard, Mehrnaz Motiei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(3): 227. CrossRef - Ultrashort-pulse laser as a surface treatment for bonding between zirconia and resin cement
Mahmood Abu Ruja, Grace M. De Souza, Yoav Finer
Dental Materials.2019; 35(11): 1545. CrossRef - Adhesion behavior of conventional and high‐translucent zirconia: Effect of surface conditioning methods and aging using an experimental methodology
Edwin Ruales‐Carrera, Paulo F. Cesar, Bruno Henriques, Márcio C. Fredel, Mutlu Özcan, Claudia A. M. Volpato
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 31(4): 388. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Resin Cement and Glass Ionomer to Nd:YAG Laser‐Treated Zirconia Ceramics
Nafiseh Asadzadeh, Foojan Ghorbanian, Farzaneh Ahrary, Hamidreza Rajati Haghi, Reza Karamad, Amir Yari, Abdollah Javan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Zirconia and Glass Fiber Posts with Radicular Dentin
Raneem S. Alofi, Ibraheem F. Alshiddi, Yasser F. AlFawaz, Abdulaziz Alsahhaf, Khulud Abdulrahman Al-Aali, Tariq Abduljabbar, Fahim Vohra
International Journal of Biomaterials.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG Laser, Sandblast and Several Types of Universal Bonding on Shear Bond Strength of Zirconia Ceramic to Composite Resin
Mahdi Akbarzadeh, Loghman R Sofi, Reza Fekrazad, Marjan Maleki
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(10): 1246. CrossRef - The effects of lasers on bond strength to ceramic materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Verónica García-Sanz, Vanessa Paredes-Gallardo, Omel Mendoza-Yero, Miguel Carbonell-Leal, Alberto Albaladejo, José María Montiel-Company, Carlos Bellot-Arcís, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(1): e0190736. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on the shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic and metal alloy
Munir Tolga Yucel, Ismail Kilic, Yener Okutan, Elif Sumeyye Tobi, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Abdullah Kepceoglu, Mustafa Borga Donmez
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2018; 32(20): 2232. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser beam angle and formed shape on surface roughness and shear bond strength between zirconia and resin cement
Munir Tolga Yucel, Ismail Kilic, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Yasemin Gundogdu, Yener Okutan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2018; 32(12): 1265. CrossRef - The effect of subpressure on the bond strength of resin to zirconia ceramic
Yong-Mei Li, Rui-Shen Zhuge, Zu-Tai Zhang, Yue-Ming Tian, Ning Ding, Dengshun Miao
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(6): e0179668. CrossRef - Effects of Laser Treatment on the Bond Strength of Differently Sintered Zirconia Ceramics
Doğu Ömür Dede, Murat Yenisey, Nergiz Rona, Figen Öngöz Dede
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2016; 34(7): 276. CrossRef - Zirconia based ceramics, some clinical and biological aspects: Review
Ossama Saleh Abd El-Ghany, Ashraf Husein Sherief
Future Dental Journal.2016; 2(2): 55. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - The Effect of Femtosecond Laser Treatment on the Effectiveness of Resin-Zirconia Adhesive: An In Vitro Study
María Vicente Prieto, Ana Luisa Caseiro Gomes, Javier Montero Martín, Alfonso Alvarado Lorenzo, Vicente Seoane Mato, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2016; 7(4): 214. CrossRef - Adhesion to Zirconium Dioxide Used for Dental Reconstructions: Surface Conditioning Concepts, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Mutlu Özcan, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
Current Oral Health Reports.2015; 2(4): 190. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of MDP-Containing Self-Adhesive Resin Cement and Y-TZP Ceramics: Effect of Phosphate Monomer-Containing Primers
Jin-Soo Ahn, Young-Ah Yi, Yoon Lee, Deog-Gyu Seo
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Preliminary studies on the effects of in situ synthesized polycrystalline particulates on the bonding strength of resin to zirconia ceramic surface
Yueming Tian, Lingling Zhang, Zutai Zhang, Ning Ding, Yan Liu, Guozhong Tian
Applied Surface Science.2015; 357: 961. CrossRef
- Effect of Er:YAG Laser Irradiation on the Flexural Fatigue Strength of a 4YSZ Ceramic
- 1,919 View
- 12 Download
- 47 Crossref

- Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
- Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):95-103. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of three antioxidizing agents on pull-out bond strengths of dentin treated with sodium hypochlorite.
Materials and Methods Root canals of 75 single-rooted human teeth were prepared. Fifteen teeth were irrigated with normal saline for a negative control group, and the remaining 60 teeth (groups 2 - 5) with 2.5% NaOCl. The teeth in group 2 served as a positive control. Prior to post cementation, the root canals in groups 3 - 5 were irrigated with three antioxidizing agents including 10% rosmarinic acid (RA, Baridge essence), 10% hesperidin (HPN, Sigma), and 10% sodium ascorbate hydrogel (SA, AppliChem). Seventy-five spreaders (#55, taper .02, Produits Dentaires S.A) were coated with silica and silanized with the Rocatec system and ceramic bond. All the prepared spreaders were cemented with a self-adhesive resin cement (Bifix SE, Voco Gmbh) in the prepared canals. After storage in distilled water (24 h/37℃), the spreaders were pulled out in a universal testing machine at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. Pull-out strength values were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test (α = 0.05).
Results There were significant differences between study groups (
p = 0.016). The highest pull-out strength was related to the SA group. The lowest strength was obtained in the positive control group.Conclusions Irrigation with NaOCl during canal preparation decreased bond strength of resin cement to root dentin. Amongst the antioxidants tested, SA had superior results in reversing the diminishing effect of NaOCl irrigation on the bond strength to root dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of passive ultrasonic irrigation on the bond strength of two different self-etch adhesives to human pulp chamber dentine: a laboratory investigation
Mohammed Turky, Jukka Matinlinna, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul M. H. Dummer, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Nermin Alsayed Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of cavity design on the mechanical behavior of endo-crown restorations: an ex-vivo study
Mohamed Gomaa Altamimi, Omaima El Mahallawi, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Mohammed Turky
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Irrigants on Push-Out Bond Strength in Resin Cementation Protocols for Fiber Posts in Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Sandra García-Varela, João Carlos Ramos, María José Ginzo-Villamayor, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Ramón Méndez-Díaz, Marcos Aníbal Anache-D’Abate, Tania Gancedo-Gancedo, Manuel Ruíz-Piñón, Soledad Mareque-Bueno, Benjamín José Martín-Biedma
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1432. CrossRef - A facile method for rejuvenating the bonding efficacy of root canal sealer-smeared dentine
Wenqing Lin, Yuan Gao, Surong Chen, Yan Yang, Weihu Ye, Diana Tran, Brian E. Bergeron, Franklin R. Tay, Jingzhi Ma
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 136: 104591. CrossRef - The Effect of Antioxidants on Dentin Bond Strength after Application of Common Endodontic Irrigants: A Systematic Review
Regina Gascón, Leopoldo Forner, Carmen Llena
Materials.2023; 16(6): 2260. CrossRef - Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and thermal cycling on the bond strength of resin cements to the root dentin
Danielle Cristine Messias, Moisés Franco Barbosa da Silva, Natália Spadini de Faria, Tatiane Rocco Dias-Arnez, Fuad Jacob Rached-Júnior, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 854. CrossRef - Effect of Er
Horieh Moosavi, Farzaneh Ahrari, Maryam Zanjani
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 17. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite on adhesive charactersitics of dentin: A systematic review of laboratory-based testing
Ensanya A. Abou Neel, Jonathan C. Knowles, Laurent Bozec
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 95: 102419. CrossRef - Effect of irrigant neutralizing reducing agents on the compromised dislocation resistance of an epoxy resin and a methacrylate resin-based root canal sealer in vitro
Pallavi Reddy, Prasanna Neelakantan, Kavitha Sanjeev, Jukka Pekka Matinlinna
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2018; 82: 206. CrossRef - Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigation and Its Effect on Bond Strength to Dentin
Tariq S. Abuhaimed, Ensanya A. Abou Neel
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Impact of conditioning regimens and time on adhesion of a fiber post to root dentin using two resin cements
P. Neelakantan, R. Mohanraj, E. Chua, S. Belli
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2015; 29(4): 337. CrossRef - Effect of antioxidants on push-out bond strength of hydrogen peroxide treated glass fiber posts bonded with two types of resin cement
Maryam Khoroushi, Hamid Mazaheri, Pardis Tarighi, Pouran Samimi, Navid Khalighinejad
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 303. CrossRef
- Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,871 View
- 10 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to composite submitted to different surface pretreatments
- Victor Hugo dos Santos, Sandro Griza, Rafael Ratto de Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):12-16. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Extensively destroyed teeth are commonly restored with composite resin before cavity preparation for indirect restorations. The longevity of the restoration can be related to the proper bonding of the resin cement to the composite. This study aimed to evaluate the microshear bond strength of two self-adhesive resin cements to composite resin.
Materials and Methods Composite discs were subject to one of six different surface pretreatments: none (control), 35% phosphoric acid etching for 30 seconds (PA), application of silane (silane), PA + silane, PA + adhesive, or PA + silane + adhesive (
n = 6). A silicone mold containing a cylindrical orifice (1 mm2 diameter) was placed over the composite resin. RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE) or BisCem (Bisco Inc.) self-adhesive resin cement was inserted into the orifices and light-cured. Self-adhesive cement cylinders were submitted to shear loading. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's test (p < 0.05).Results Independent of the cement used, the PA + Silane + Adhesive group showed higher microshear bond strength than those of the PA and PA + Silane groups. There was no difference among the other treatments. Unicem presented higher bond strength than BisCem for all experimental conditions.
Conclusions Pretreatments of the composite resin surface might have an effect on the bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to this substrate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
Yugandhar Garlapati, Sampath Krishna Veni, Jashva Vamsi Kogila, Polisetty Siva Krishna, K. N. Anand Kumar
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2025; 59(3): 279. CrossRef - Effect of Cement Type on Marginal Microleakage of Zirconia Crowns with or without Cervical Margin Relocation: An In Vitro Study
RI Farah
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(2): 194. CrossRef - Challenges faced when masking a single discoloured tooth - Part 2: indirect restoration procedures
May Aljanahi, Argwan Alhussin, Haitham Elbishari
British Dental Journal.2025; 239(1): 25. CrossRef - Influence of mechanochemical treatment and oxygen inhibited layer on the adhesion of self-adhesive resin cement to bulk-fill composite resin
Sreya Dutta, Samikhya Priyadarsani Sahu, Anushka Arora, Srikant Natarajan, Abhishek Parolia, Manuel Thomas
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2024; 27(2): 79. CrossRef - Substrate Rigidity Effect on CAD/CAM Restorations at Different Thicknesses
César Rogério Pucci, Ana Paula Valente Pinho Mafetano, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Cornelis J. Kleverlaan, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(04): 1020. CrossRef - Microgap Formation between a Dental Resin-Matrix Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing Ceramic Restorative and Dentin after Various Surface Treatments and Artificial Aging
Alexandros Galanopoulos, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Constantinos Papadopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Kosmas Tolidis
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(4): 2335. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef - Effect of full-step versus simplified resin cement luting strategies on the push-out bond strength of indirect resin composite restorations bonded to dentin
Bianca Cristina Dantas da Silva, Isabelle Helena Gurgel de Carvalho, Taciana Emília Leite Vila-Nova, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges, Marília Regalado Galvão Rabelo Caldas, Isauremi Vieira de Assunção, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(24): 3552. CrossRef - Effect of various polymerization protocols on the cytotoxicity of conventional and self-adhesive resin-based luting cements
Ece Irem Oguz, Ufuk Hasanreisoglu, Sadullah Uctasli, Mutlu Özcan, Mehmet Kiyan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1161. CrossRef - Repair bond strength of resin composite to three aged CAD/CAM blocks using different repair systems
Pinar Gul, Latife Altınok-Uygun
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 131. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Surface Characteristics of Dental CAD/CAM Materials after Different Surface Treatments
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Kimon Pahinis, Kyriaki Saltidou, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Effrosyni Tsitrou
Materials.2020; 13(4): 981. CrossRef - Adhesive Systems Used in Indirect Restorations Cementation: Review of the Literature
Cristian Abad-Coronel, Belén Naranjo, Pamela Valdiviezo
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(3): 71. CrossRef - Effects of different etching methods and bonding procedures on shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets applied to different CAD/CAM ceramic materials
S. Kutalmış Buyuk, Ahmet Serkan Kucukekenci
The Angle Orthodontist.2018; 88(2): 221. CrossRef - Ceramic repairs with resins: silanization protocols
Teresa Cristina Vasconcelos dos Santos
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different surface treatments on bond strength of novel CAD/CAM restorative materials to resin cement
Meltem Bektaş Kömürcüoğlu, Elçin Sağırkaya, Ayça Tulga
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(6): 439. CrossRef - Adhesive bonding to polymer infiltrated ceramic
Judith SCHWENTER, Fredy SCHMIDLI, Roland WEIGER, Jens FISCHER
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(5): 796. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of Silanization on Microtensile Bond Strength of Different Resin Cements to a Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramic
Cristina Parise Gré, Renan C de Ré Silveira, Shizuma Shibata, Carlo TR Lago, Luiz CC Vieira
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2016; 17(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of air abrasion with alumina or glass beads on surface characteristics of CAD/CAM composite materials and the bond strength of resin cements
ARAO Nobuaki, YOSHIDA Keiichi, SAWASE Takashi
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2015; 23(6): 629. CrossRef - Resin cement to indirect composite resin bonding: Effect of various surface treatments
Omer Kirmali, Cagatay Barutcugil, Osman Harorli, Alper Kapdan, Kursat Er
Scanning.2015; 37(2): 89. CrossRef - Impact of different adhesives on work of adhesion between CAD/CAM polymers and resin composite cements
Christine Keul, Manuel Müller-Hahl, Marlis Eichberger, Anja Liebermann, Malgorzata Roos, Daniel Edelhoff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Journal of Dentistry.2014; 42(9): 1105. CrossRef - Effect of Plasma Deposition Using Low-Power/Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Promoting Adhesion of Composite Resin to Enamel
Geum-Jun Han, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2014; 34(4): 933. CrossRef - Bonding efficacy of a self-adhesive resin cement to enamel and dentin
Linhu Wang, Haixing Xu, Songyang Li, Bin Shi, Rong Li, Mingfu Ye, Jing Yang
Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed..2014; 29(6): 1307. CrossRef
- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
- 1,787 View
- 8 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):234-240. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of intraradicular moisture on the pushout bond strength of a fibre post luted with several self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods Endodontically treated root canals were treated with one of three luting cements: (1) RelyX U100, (2) Clearfil SA, and (3) G-Cem. Roots were then divided into four subgroups according to the moisture condition tested: (I) dry: excess water removed with paper points followed by dehydration with 95% ethanol, (II) normal moisture: canals blot-dried with paper points until appearing dry, (III) moist: canals dried by low vacuum using a Luer adapter, and (IV) wet: canals remained totally flooded. Two 1-mm-thick slices were obtained from each root sample and bond strength was measured using a push-out test setup. The data were analysed using a two-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni
post hoc test withp = 0.05.Results Statistical analysis demonstrated that moisture levels had a significant effect on the bond strength of luting cements (
p < 0.05), with the exception of G-Cem. RelyX U100 displayed the highest bond strength under moist conditions (III). Clearfil SA had the highest bond strength under normal moisture conditions (II). Statistical ranking of bond strength values was as follows: RelyX U100 > Clearfil SA > G-Cem.Conclusions The degree of residual moisture significantly affected the adhesion of luting cements to radicular dentine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Dentin bond strength of resin luting agents under a simulated intra-oral environment
Takashi Washino, Hanemi Tsuruta, Masaomi Ikeda, Michael F. Burrow, Toru Nikaido
Asian Pacific Journal of Dentistry.2024; 24(2): 13. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of dentin moisture on the adhesive properties of luting fiber posts using adhesive strategies
Renata Terumi JITUMORI, Rafaela Caroline RODRIGUES, Alessandra REIS, João Carlos GOMES, Giovana Mongruel GOMES
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different intraradicular chemical pretreatments on the bond strength of adhesive interface between dentine and fiber post cements: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Ana Luiza Barbosa Jurema, Ayla Macyelle de Oliveira Correia, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SELF ADEZİV REZİN SİMANLAR / SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
Kübra AMAÇ, Engin ESENTÜRK, Bilge TURHAN BAL
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Development and characterization of biological bovine dentin posts
Alice Gonçalves Penelas, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Laiza Tatiana Poskus, Amanda Cypriano Alves, Isis Ingrid Nogueira Simões, Viviane Hass, José Guilherme Antunes Guimarães
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 92: 197. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite on the bond strength of glass fibre post
Beau Knight, Robert M. Love, Roy George
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(3): 267. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Is the bonding of self-adhesive cement sensitive to root region and curing mode?
Thaynara Faelly BOING, Giovana Mongruel GOMES, João Carlos GOMES, Alessandra REIS, Osnara Maria Mongruel GOMES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(1): 2. CrossRef - A Twofold Comparison between Dual Cure Resin Modified Cement and Glass Ionomer Cement for Orthodontic Band Cementation
Hanaa El Attar, Omnia Elhiny, Ghada Salem, Ahmed Abdelrahman, Mazen Attia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2016; 4(4): 695. CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of various self-adhesive resin cements between bovine dentin and 4 types of adherends
Ah-Jin Kim, Da-Ryeong Park, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(4): 365. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 1,775 View
- 4 Download
- 13 Crossref

-
Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: an
in vitro study - Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):215-221. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the retentive strength and failure mode of undercut composite post, glass fiber post and polyethylene fiber post luted with flowable composite resin and resin-cement.
Materials and Methods Coronal parts of 120 primary canine teeth were sectioned and specimens were treated endodontically. The teeth were randomly divided into 6 groups (
n = 20). Prepared root canals received intracanal retainers with a short composite post, undercut composite post, glass fiber post luted with flowable resin or resin-cement, and polyethylene fiber post luted with flowable resin or resin-cement. After crown reconstruction, samples were tested for retentive strength and failure mode. Statistical analysis was done with one-way ANOVA and Tukey tests (p < 0.05).Results There were statistically significant differences between groups (
p = 0.001). Mean bond strength in the undercut group was significantly greater than in the short composite post (p = 0.030), and the glass fiber post (p = 0.001) and the polyethylene fiber post group luted with resin-cement (p = 0.008). However, the differences between the undercut group and the groups with flowable composite as the luting agent were not significant (p = 0.068,p = 0.557). Adhesive failure was more frequent in the fiber post groups.Conclusions Although the composite post with undercutting showed the greatest resistance to dislodgement, fiber posts cemented with flowable composite resin provided acceptable results in terms of retentive strength and fracture mode.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of fracture resistance of three types of post utilized in restoration of root canal treated primary anterior teeth (an in-vitro study)
Doaa K. Hassan, Nagwa A. Ghoname, Arafa M. Khatab, Samy M. El Safty, Nahed S. Shoker
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(1): 172. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Compressive Strength and Modes of Failure of Unpolymerized Glass Fiber Post, Polyethylene Fiber Post, and Short Composite Post Used in Endodontically Treated Primary Anterior Teeth: An In Vitro Experimental Study
Gouri R Reddy, Bharath KP, Tejashree Rajanna, Praveen KS Bali, Nagaveni NB, Nivedita Bhovi
Dental Journal of Advance Studies.2025; 13(3): 120. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties and Clinical Success of Intracanal Posts in Primary Maxillary Anterior Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Selvakumar Haridoss, MS Muthu, Kavitha Swaminathan, Yamuna Shanmugam, Aksshaya Raghu, Krishnapillai Chandrababu Vignesh, Sunil Babu Kotha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 16(S3): S293. CrossRef - Comparison of shear bond strength of different types of intracanal posts in restoring extensively damaged primary anterior teeth
Shabnam Asghari Mollabashi, Shima Nourmohamadi, Afrooz Nakhostin
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2024; 18(2): 95. CrossRef - Effects of glass fibers reinforced and non-reinforced composite resin on fracture behavior of severely destructed primary incisors and restored with post and core system
Rizk El Agamy
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(3): 451. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effects of Different Types of Resin Cement Systems on the Push-Out Bond Strength of the Fiber Post to Intracanal Dentin in Anterior Primary Teeth
Ali Nozari, Boshra Rasoolzade, Zahra Jowkar, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi, Mohammad Jowkar, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the Pull-Out Resistance of Grossly Decayed Primary Anterior Teeth Restored With Two Different Intracanal Posts: An In Vitro Study
Ayham Hijaz, Mohamed K Altinawi, Imad Katbeh, Eyad Gergos, Gharawi Alhamzah
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of fracture resistance of primary incisor teeth restored with glass fiber post and reversed-oriented metal post – an in vitro study
Hamideh Barghi, Samira Sharifi
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic comparative study to evaluate the efficacy of restoring destroyed primary incisors using two different techniques—A pilot study
Seba Ibrahim, Abdul Wahab Nourallah
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2020; 6(5): 537. CrossRef - Coronal Microleakage of Teeth Restored with Cast Posts and Cores Cemented with Four Different Luting Agents after Thermocycling
Maryam Mohajerfar, Kaveh Nadizadeh, Tabasom Hooshmand, Elaheh Beyabanaki, Hamid Neshandar Asli, Siamak Sabour
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of different post materials and adhesive systems on the bonding strength of short‐post technique for primary teeth
Nihal Beldüz Kara, Tunahan Kanyilmaz, Soner Çankaya, Cankat Kara
International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 28(2): 239. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal
Anny Carine Barros Aguiar, Daniely Amorim de Meireles, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Angela Delfina Bitencourt Garrido, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 265. CrossRef
- Evaluation of fracture resistance of three types of post utilized in restoration of root canal treated primary anterior teeth (an in-vitro study)
- 2,060 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Evaluation of the rat tissue reaction to experimental new resin cement and mineral trioxide aggregate cement
- Won-Kyung Yang, Hyun-Jung Ko, Mi-Ri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):194-200. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives New resin cement (NRC) has been developed as a root repairing material and the material is composed of organic resin matrix and inorganic powders. The aim of this study was to compare the rat subcutaneous tissue response to NRC and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) cement and to investigate the tissue toxicity of both materials.
Materials and Methods Sixty rats received two polyethylene tube-implants in dorsal subcutaneous regions, MTA and NRC specimens. Twenty rats were sacrificed respectively at 1, 4 and 8 wk after implantation and sectioned to 5 µm thickness and stained with Hematoxylin-Eosin (H-E) or von-Kossa staining. The condition of tissue adjacent to the implanted materials and the extent of inflammation to each implant were evaluated by two examiners who were unaware of the type of implanted materials in the tissues. Data were statistically analyzed with paired
t -test (p < 0.05).Results In specimens implanted with both NRC and MTA, severe inflammatory reactions were present at one wk, which decreased with time. At eighth wk, MTA implanted tissue showed mild inflammatory reaction, while there were moderate inflammatory reactions in NRC implanted tissue, respectively. In NRC group, von-Kossa staining showed more calcification materials than MTA group at eighth wk.
Conclusions It was concluded that the calcium reservoir capability of NRC may contribute to mineralization of the tissues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
Ranjdar Mahmood Talabani, Balkees Taha Garib, Reza Masaeli, Kavosh Zandsalimi, Farinaz Ketabat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotoxicity of root canal sealers: a literature review
Fábio Miguel dos Santos Costa, Maria Helena Fernandes, Silvia Regina Batistuzzo de Medeiros
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(10): 3347. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation, solubility and biocompatibility of TheraCal LC compared with MTA-angelus and biodentine as a furcation perforation repair material
M. A. Alazrag, A. M. Abu-Seida, K. M. El-Batouty, S. H. El Ashry
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation in vivo of biocompatibility of differents resin-modified cements for bonding orthodontic bands
JANAINA A. MESQUITA, ROGÉRIO LACERDA-SANTOS, GÊISA A.M. SAMPAIO, GUSTAVO P. GODOY, CASSIANO F.W. NONAKA, POLLIANNA M. ALVES
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências.2017; 89(3 suppl): 2433. CrossRef - A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 227. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef
- Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
- 1,367 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
- Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):132-138. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate curing degree of three dual-cure resin cements with the elapsed time in self-cure and dual-cure mode by means of the repeated measure of micro-hardness.
Materials and Methods Two dual-cure self-adhesive resin cements studied were Maxcem Elite (Kerr), Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE) and one conventional dual-cure resin cement was Rely-X ARC resin cement (3M ESPE). Twenty specimens for each cements were made in Teflon mould and divided equally by self-cure and dual-cure mode and left in dark, 36℃, 100% relative humidity conditional-micro-hardness was measured at 10 min, 30 min, 1 hr, 3 hr, 6 hr, 12 hr and 24 hr after baseline. The results of micro-hardness value were statistically analyzed using independent samples
t -test and one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons using Scheffe's test.Results The micro-hardness values were increased with time in every test groups. Dual-cure mode obtained higher micro-hardness value than self-cure mode except after one hour of Maxcem. Self-cured Rely-X Unicem showed lowest value and dual-cured Rely-X Unicem showed highest value in every measuring time.
Conclusions Sufficient light curing to dual-cure resin cements should provided for achieve maximum curing.
- 1,036 View
- 9 Download

- Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
- Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):125-131. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements.
Materials and Methods Pre-surface treated LuxaPost (DMG), Rely-X Fiber Post (3M ESPE) and self adhesive resin cement Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE), conventional resin cement Rely-X ARC (3M ESPE), and Rely-X Ceramic Primer (3M ESPE) were used. After completing the surface treatments of the posts, posts and resin cement were placed in clear molds and photo-activation was performed. The specimens were sectioned perpendicular to the FRC-Post into 2 mm-thick segments, and push-out strength were measured. The results of bond strength value were statistically analyzed using independent samples
t -test and one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons using Scheffe's test.Results Silanization of posts affect to the bond strength in LuxaPost, and did not affect in Rely-X Fiber Post. Rely-X ARC showed higher value than Rely-X Unicem.
Conclusions Silanization is needed to enhance the bond strength between LuxaPost and resin cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of fracture resistance and push-out bond strength of glass fiber post with composite core and single-unit post and core system luted with two different resin cements: An in vitro study
Ishika Garg, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 240. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite resin posts according to cement thickness
Jun-Seong Park, Jeong-Sub Lee, Jeong-Won Park, Won-Gyun Chung, Eun-Hee Choi, Yoon Lee
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2017; 118(3): 372. CrossRef - Currently there are so many fiber reinforced composite posts in the market. Some products are factory silanated but some products are not. Should I use silane for surface treatment of fiber reinforced composite posts?
Kyung-Mo Cho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 127. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of fracture resistance and push-out bond strength of glass fiber post with composite core and single-unit post and core system luted with two different resin cements: An in vitro study
- 1,135 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
- Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):479-485. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the push-out bond strengths of resin cement/fiber post systems to post space dentin using different application methods of resin cement.
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human premolars were selected and randomly divided into 3 groups according to the technique used to place the cement into root canal: using lentulo-spiral instrument (group Lentulo), applying the cement onto the post surface (group Direct), and injecting the material using a specific elongation tip (group Elongation tip). After shaping and filling of the root canal, post space was drilled using Rely-X post drill. Rely-X fiber post was seated using Rely-X Unicem and resin cement was light polymerized. The root specimens were embedded in an acrylic resin and the specimens were sectioned perpendicularly to the long axis using a low-speed saw. Three slices per each root containing cross-sections of coronal, middle and apical part of the bonded fiber posts were obtained by sectioning. The push-out bond strength was measured using Universal Testing Machine. Specimens after bond failure were examined using operating microscope to evaluate the failure modes.
Results Push-out bond strengths were statistically influenced by the root regions. Group using the elongation tip showed significantly higher bond strength than other ways. Most failures occurred at the cement/dentin interface or in a mixed mode.
Conclusions The use of an elongation tip seems to reduce the number of imperfections within the self-adhesive cement interface compared to the techniques such as direct applying with the post and lentulo-spiral technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
Abdulaziz A. Al-Kheraif, Badreldin A. Mohamed, Aref Othman Hasan Sufyan, Aftab Ahmed Khan, Darshan Devang Divakar
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 36: 102526. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography analysis of gap and void formation in different prefabricated fiber post cementation materials and techniques
Aws ArRejaie, Saleh A. Alsuliman, Mohammed O. Aljohani, Hesham A. Altamimi, Emad Alshwaimi, Ahmad M. Al-Thobity
The Saudi Dental Journal.2019; 31(2): 236. CrossRef - Micro-computerized tomography analysis of cement voids and pull-out strength of glass fiber posts luted with self-adhesive and glass-ionomer cements in the root canal
Serkan Sarıdağ, Dilek Helvacıoğlu-Yiğit, Mutlu Özcan, Egemen Avcu, Güllü Kızıltaş
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(14): 1585. CrossRef - Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 95. CrossRef - Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef
- Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
- 1,264 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
- Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):106-115. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microtensile bond strength (µTBS), failure modes and bonding interfaces of self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin.
Cylindrical composite blocks (Tescera, Bisco Inc.) were luted with resin cements (PA: Panavia F 2.0, Kuraray Medical Inc., RE: RelyX Unicem Clicker, 3M ESPE., MA: Maxem, Kerr Co., BI: BisCem, Bisco Inc.) on the prepared occlusal dentin surfaces of 20 extracted molars. After storage in distilled water for 24 h, 1.0 mm × 1.0 mm composite-dentin beams were prepared. µTBS was tested at a cross-head speed of 0.5 mm/min. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test. Dentin sides of all fractured specimens and interfaces of resin cements-dentin or resin cements-composite were examined at FE-SEM (Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope).
In conclusion, PA and RE showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than MA and BI when indirect composite blocks were luted to dentin using a self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements.
- 1,036 View
- 2 Download

- Effect of film thickness of resin cement on bonding efficiency in indirect composite restoration
- Sang-Hyuck Lee, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):69-79. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of film thickness of various resin cements on bonding efficiency in indirect composite restoration by measurement of microtensile bond strength, polymerization shrinkage, flexural strength and modulus, fractographic FE-SEM analysis. Experimental groups were divided according to film thickness (< 50 µm-control, 50 µm-T50, 100 µm-T100, 150 µm-T150) using composite-based resin cements (Variolink II, Duo-Link) and adhesive-based resin cements (Panavia F, Rely X Unicem). The data was analyzed using ANOVA and Duncan's multiple comparison test (p < 0.05).
The results were as follows;
Variolink II showed higher microtensile bond strength than that of adhesive-based resin cements in all film thickness (p < 0.05) but Duo-Link did not show significant difference except control group (p < 0.05).
Microtensile bond strength of composite-based resin cements were decreased significantly according to increasing film thickness (p < 0.05) but adhesive-based resin cements did not show significant difference among film thickness (p > 0.05).
Panavia F showed significantly lower polymerization shrinkage than other resin cements (p < 0.05).
Composite-based resin cements showed significantly higher flexural strength and modulus than adhesive-based resin cements (p < 0.05).
FE-SEM examination showed uniform adhesive layer and well developed resin tags in composite-based resin cements but unclear adhesive layer and poorly developed resin tags in adhesive-based resin cements. In debonded surface examination, composite-based resin cements showed mixed failures but adhesive-based resin cements showed adhesive failures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Full mapping tensile bond strength of luting in search for differences due to centripetal curing shrinkage
José C. de la Macorra, Beatriz Romero
Dental Materials.2022; 38(4): e69. CrossRef
- Full mapping tensile bond strength of luting in search for differences due to centripetal curing shrinkage
- 1,592 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on lithium disilicate ceramic and dentin
- Hye-Jin Shin, Chang-Kyu Song, Se-Hee Partk, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):184-191. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on dentin and lithium disilicate ceramic and compare these result with that of conventional resin cement. For this study, four self-adhesive resin cements (Rely-X Unicem, Embrace Wetbond, Mexcem, BisCem), one conventional resin cement (Rely-X ARC) and one restorative resin composite (Z-350) were used. In order to evaluate the physical properties, compressive strength, diametral tensile strength and flexural strength were measured. To evaluate the shear bond strength on dentin, each cement was adhered to buccal dentinal surface of extracted human lower molars. Dentin bonding agent was applied after acid etching for groups of Rely-X ARC and Z-350. In order to evaluate the shear bond strength on ceramic, lithium disilicate glass ceramic (IPS Empress 2) disks were prepared. Only Rely-X ARC and Z-350 groups were pretreated with hydrofluoric acid and silane. And then each resin cement was adhered to ceramic surface in 2 mm diameter. Physical properties and shear bond strengths were measured using a universal testing machine.
Results were as follows
1. BisCem showed the lowest compressive strength, diametral tensile strength and flexural strength. (
P <0.05)2. Self-adhesive resin cements showed significantly lower shear bond strength on the dentin and lithium disilicate ceramic than Rely-X ARC and Z-350 (
P <0.05)In conclusion, self-adhesive resin cements represent the lower physical properties and shear bond strength than a conventional resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Compressive Strength Evaluation in Brazed ZrO2/Ti6Al4V Joints Using Finite Element Analysis
Ashutosh Sharma, Se Ho Kee, Flora Jung, Yongku Heo, Jae Pil Jung
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2016; 25(5): 1722. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef - The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 139. CrossRef
- Compressive Strength Evaluation in Brazed ZrO2/Ti6Al4V Joints Using Finite Element Analysis
- 1,286 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
- Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):103-112. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of curing methods of adhesive resins and resin cements in the root canal. Crown portions of 32 single-rooted mandibular premolars were removed. Routine endodontic treatment was done, and 9 mm deep post spaces were prepared within root canals. No. 3 FRC Postec posts (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Liechtenstein) were cemented in the post spaces by self-(SC) or light-curing (LC) using two dual-cured adhesives (Adper Scotchbond multi-purpose plus and Exite DSC )and resin cements (RelyX ARC and Variolink II). They were assigned to 4 groups (n=8); R-SC, R-LC, V-SC, V-LC group.
After stored in distilled water for 24 hours, each root was transversally sectioned with 1.5 mm thick and made three slices. The specimens were subjected to push-out test in a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu Co., Japan) with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. The data were analyzed with repeated ANOVA and one-way.
ANOVA. Also the interface of post-resin cement and resin cement-canal wall of each group was observed under FE-SEM.
When fiber posts were cemented into the root canal using total-etch adhesives, the bond strength and adaptation between post and root canal dentin was affected by curing method. Self-cure of adhesives and resin cements showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than light-cure of them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 125. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 479. CrossRef
- Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
- 1,126 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- EFFECT OF DENTIN SURFACE WETNESS ON TENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
- Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):113-119. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to compare the tensile bond strength of several self-adhesive resin cements bonded to dentin surfaces with different wet conditions.
Three self-adhesive resin cements; Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA), Embrace Wetbond (Pulpdent, Oakland, MA, USA), Maxcem (Kerr, Orange, CA, USA) were used. Extracted sixty human molars were used. Each self-adhesive resin cement was adhered to the dentin specimens (two rectangular sticks from each molar) in different wet conditions.
Tensile bond strength were measured using universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu corporation, Kyoto, Japan) at a crosshead speed of 1.0mm/min. After the testing, bonding failures of specimens were observed by Operative microscope (OPMI pro, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). T-test was used to evaluate the effect of dentin surface wetness. One-way ANOVA test was used to evaluate the tensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements in the same condition. Scheffe's test was used for statistical analyzing at the 95% level of confidence.
The result showed that wetness of dentin surface didn't affect tensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements and Maxcem showed the lowest tensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overdried Preparation and Thermocycling on the Fracture of CAD–CAM Hybrid Ceramic Occlusal Veneer Restorations
Daranee Tantbirojn, Antheunis Versluis, Paul D Edgerley, David R Cagna
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 9(2): 38. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef - 'Wet or Dry tooth surface?' - for self-adhesive resin cement
Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 249. CrossRef
- Impact of Overdried Preparation and Thermocycling on the Fracture of CAD–CAM Hybrid Ceramic Occlusal Veneer Restorations
- 1,340 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of bond strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements
- Hyun-A Lee, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):499-506. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.499
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the push-out strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements. Newly extracted 36 human mandibular premolars which had single root canal were selected and their crown portions were removed. The root canal was instrumented using PROTAPER™ system and obturated using continuous wave technique. In each root, a 9-mm deep post space was prepared. #2 translucent fiber post (DT Light post, Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A.) was cemented using injection technique with Uni-dose needle tip (Bisco) and six different resin cements. The tested resin cements were Duo-Link (Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A.), Variolink II (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Schann, Liechtenstein), Panavia F (Kuraray Medical Inc., Okayama, Japan), Multilink Automix (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Schann, Liechtenstein), RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.), and Maxcem (Kerr Co., CA, U.S.A.). After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, each root was transversally sectioned into approximately 1-mm thick sections. This procedure resulted in 6 serial sections per root. Push-out test was performed using a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu Co.) with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. The data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey HSD (p=0.05).
The push-out strength of the groups which cemented fiber post with Panavia F and Multilink Automix were lower than those of the other groups. But, there were no statistically significant difference among groups at a probability level of 0.05.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 479. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
- 1,171 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Influence of adhesive application on shear bond strength of the resin cement to indirect resin composite
- Mi-Hae Song, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):419-427. Published online September 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study analyzed the influence of dental adhesive/primer on the bond strength between indirect resin composite and the resin cement.
Seventy disc specimens of indirect resin composite (Tescera Dentin, Bisco) were fabricated. And bonding area of all specimens were sandblasted and silane treated for one minute. The resin cements were used with or without application of adhesive/primer to bonding area of indirect resin restoration: Variolink-II (Ivoclar-Vivadent): Exite DSC, Panavia-F (Kuraray): ED-Primer, RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE): Single-Bond, Duolink (Bisco): One-step, Mulitlink (Ivoclar-Vivadent): Multilinh Primer.
Shear bond strength was measured by Instron universal testing machine.
Adhesive application improved shear bond strength (p < 0.05). But Variolink II and Panavia-F showed no statistically significant difference according to the adhesive application.
With the above results, when resin inlay is luted by resin cement it seems that application of dental adhesive/primer is necessary in order to improve the bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 223. CrossRef - Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 103. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
- 1,188 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Color stability of the resin cements with accelerated aging
- Ha-Jeung Song, Su-Jung Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):389-396. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the color stability of resin cements with accelerated test. Four dual curing resin cements: Panavia-F (KURARAY), Duolink (BISCO), Variolink-II (Ivoclar Vivadent), and RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE) and 1 self curing resin cement: Resiment CE (j. l. Blosser) were used in this study. In control group, Gradia Anterior (GC) composite resin and Tescera Dentin (Bisco) indirect composite were used. Ten disk shape specimens were made from each resin cement. The specimens were subjected to an accelerated aging process in a refrigerated bath circulator at 60℃ for 15 and 30 days. Spectrophotometric analyses were made before and after 15 days and 30 days of accelerated aging time.
The color characteristics (L*, a*, b*) and the color difference (ΔE*) of the specimens before and after immersion were measured and computed.
Regardless of type of the resin cements, L* value was decreased and a* value was increased, but there were no significant difference. But b* value was increased significantly (p < 0.05). Tescera inlay showed least color change (p < 0.05), but Gradia showed notable color change after 15 days.
After 30 days on accelerated aging, ΔE* value was increased (Panavia-F < Variolink-II < Resiment CE < Duolink < Unicem) (p < 0.05), but there were no significant difference among Panavia-F, Variolink-II, and Resiment CE groups. After 30 days of accelerated aging, ΔE* value of all resin cements were greater than 3.0 and could be perceived by the human eye.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of light-curing on the translucence change and color stability of amine-free dual-cured resin cements
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Bo-Ram Lee, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(3): 165. CrossRef - Effect of Accelerated Aging on the Color Stability of Dual-Cured Self-Adhesive Resin Cements
Ah-Rang Kim, Yong-Chan Jeon, Chang-Mo Jeong, Mi-Jung Yun, Jung-Bo Huh
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2015; 8(2): 49. CrossRef
- Influence of light-curing on the translucence change and color stability of amine-free dual-cured resin cements
- 1,338 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Microleakage of resilon by methacrylate-based sealer and self-adhesive resin cement
- Sun-Young Ham, Jin-Woo Kim, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):204-212. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by methacrylate-based root canal sealer or 2 different self-adhesive resin cements. Seventy single-rooted extracted human teeth were sectioned at the CEJ perpendicular to the long axis of the roots with diamond disk. Canal preparation was performed with crown-down technique using Profile NiTi rotary instruments and GG drill. Each canal was prepared to ISO size 40, .04 taper and 1 mm short from the apex. The prepared roots were randomly divided into 4 experimental groups of 15 roots each and 5 roots each for positive and negative control group. The root canals were filled by lateral condensation as follows. Group 1: Guttapercha with AH-26, Group 2: Resilon with RealSeal primer & sealer, Group 3: Resilon with Rely-X Unicem, Group 4: Resilon with BisCem. After stored in 37℃, 100% humidity chamber for 7 days, the roots were coated with 2 layers of nail varnish except apical 3 mm. The roots were then immersed in 1% methylene blue dye for 7 days. Apical microleakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration after roots were separated longitudinally. One way ANOVA and Scheffe's post-hoc test were performed for statistical analysis. Group 1 showed the least apical leakage and there was no statistical significance between Group 2, 3, 4. According to the results, the self adhesive resin cement is possible to use as sealer instead of primer & sealant when root canal filled by Resilon.
- 831 View
- 1 Download

- EFFECT OF THE ADDITIONAL ETCHING PROCEDURE ON PUSH-OUT BOND STRENGTH OF ONE-STEP RESIN CEMENT
- Soon-Il Kang, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):443-451. Published online January 14, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of additional etching procedure prior to Maxcem resin cement application in indirect restoration cementation using push-out bonding strength.
One hundred and two extracted human molars were used to make indirect resin restorations of gold inlay and Synfony. These restorations were cemented using Maxcem and Variolink II. Additional etching procedures were done for one group with Maxcem. Three groups have 17 specimens in both restoration types. Push-out bond strength was measured using multi-purpose tester and calculated for bonding strength per sqaure-millimeter area. The mean bonding strength values were compared using SPSS 12.0K program for one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's Test with 95% significance.
Under the condition of this study, the additional etching procedure prior to usage of Maxcem resulted in reduced bond strength for both of restoration types.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
- 1,055 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The bonding durability of resin cements
- Min-Woo Cho, Sang-Hyuk Park, Jong-Ryul Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):343-355. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.343
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objectives of this study was to evaluate the durability of 4 resin cements by means of microtensile bond strength test combined with thermocycling method and fractographic FE-SEM analysis.
Experimental groups were prepared according to thermocycling (0, 1,000, 5,000) and the kind of resin cements, those were Variolink II, Multilink, Panavia F 2.0, Rely X Unicem. Flat dentin surfaces were created on mid-coronal dentin of extracted third molars. Then fresh dentin surface was grounded with 320-grit silicon carbide abrasive papers to create uniform smear layers. Indirect composite block (Tescera, Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA) was fabricated (12 × 12 × 6 mm3). It's surface for bonding to tooth was grounded with silicon carbide abrasive papers from 180- to 600-grit serially, then sandblasted with 20 - 50 µm alumina oxide. According to each manufacturer's instruction, dentin surface was treated and indirect composite block was luted on it using each resin cement. For Rely X Unicem, dentin surface was not treated. The bonded tooth-resin block were stored in distilled water at 37℃ for 24 hours. After thermocycling, the bonded tooth-resin block was sectioned occluso-gingivally to 1.0 mm thick serial slabs using an Isomet slow-speed saw (Isomet, Buehler Ltd, Lake Bluff, IL, USA). These sectioned slabs were further sectioned to 1.0 × 1.0 mm2 composite-dentin beams. The specimens were tested with universal testing machine (EZ-Test, Shimadzu, Japan) at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min with maximum load of 500 N. The data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple comparison test at p ≤ 0.05 level.
Within the limited results, we conclude as follows;
1. The bond strength of Variolink II was evaluated the highest among experimental groups and was significantly decreased after 1,000 thermocycling (p < 0.05).
2. The bond strength of Multilink was more affected by thermocycling than the other experimental groups and significantly decreased after 1,000 thermocycling (p < 0.05).
3. Panavia F 2.0 and Rely X Unicem showed the gradually decreased tendency of microtensile bond strength according to thermocycling but there was no significant difference (p > 0.05).
4. Adhesive based-resin cements showed lower bond strength with or without thermocycling than composite based-resin cements.
5. Variolink II & Multilink showed high bond strength and mixed failure, which was occurred with a thin layer of luting resin cement before thermocycling and gradually increased adhesive failure along the dentin surface after thermocycling.
The bonding performance of resin cement can be affected by application procedure and chemical composition. Composite based-resin cement showed higher bond strength and durability than adhesive based-resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 125. CrossRef - Physical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements and their shear bond strength on lithium disilicate ceramic and dentin
Hye-Jin Shin, Chang-Kyu Song, Se-Hee Partk, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 184. CrossRef - Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 223. CrossRef - Effect of the additional etching procedure on push-out bond strength of one-step resin cement
Soon-Il Kang, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(5): 443. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
- 1,276 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Comparative evaluation of micro-shear bond strength between two different luting methods of resin cement to dentin
- Yoon-Jeong Lee, Sang-Jin Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):283-293. Published online January 14, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of dual bonding technique by comparing micro-shear bond strength between two different luting methods of resin cement to tooth dentin. Three dentin bonding systems(All-Bond 2, One-Step, Clearfil SE Bond), two temporary cements (Propac, Freegenol) were used in this study.
In groups used conventional luting procedure, dentin surfaces were left untreated. In groups used dual bonding technique, three dentin bonding systems were applied to each dentin surface. All specimens were covered with each temporary cement. The temporary cements were removed and each group was treated using one of three different dentin bonding system. A resin cement was applied to the glass cylinder surface and the cylinder was bonded to the dentin surface. Then, micro-shear bond strength test was performed. For the evaluation of the morphology at the resin/dentin interface, SEM examination was also performed.
Conventional luting procedure showed higher micro-shear bond strengths than dual boning technique. However, there were no significant differences.
Freegenol showed higher micro-shear bond strengths than Propac, but there were no significant differences.
In groups used dual bonding technique, SE Bond showed significantly higher micro-shear bond strengths in One-Step and All-Bond 2 (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between One-Step and All-Bond 2.
In SEM observation, with the use of All-Bond 2 and One-Step, very long and numerous resin tags were observed. This study suggests that there were no findings that the dual bonding technique would be better than the conventional luting procedure.
- 963 View
- 1 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


