-
Anatomical analysis of the resected roots of mandibular first molars after failed non-surgical retreatment
-
Jiyoung Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Jihyun Bae, Yonghoon Choi
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e16. Published online March 5, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e16
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
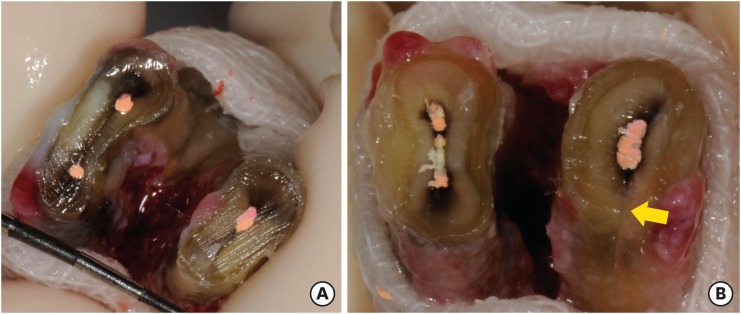
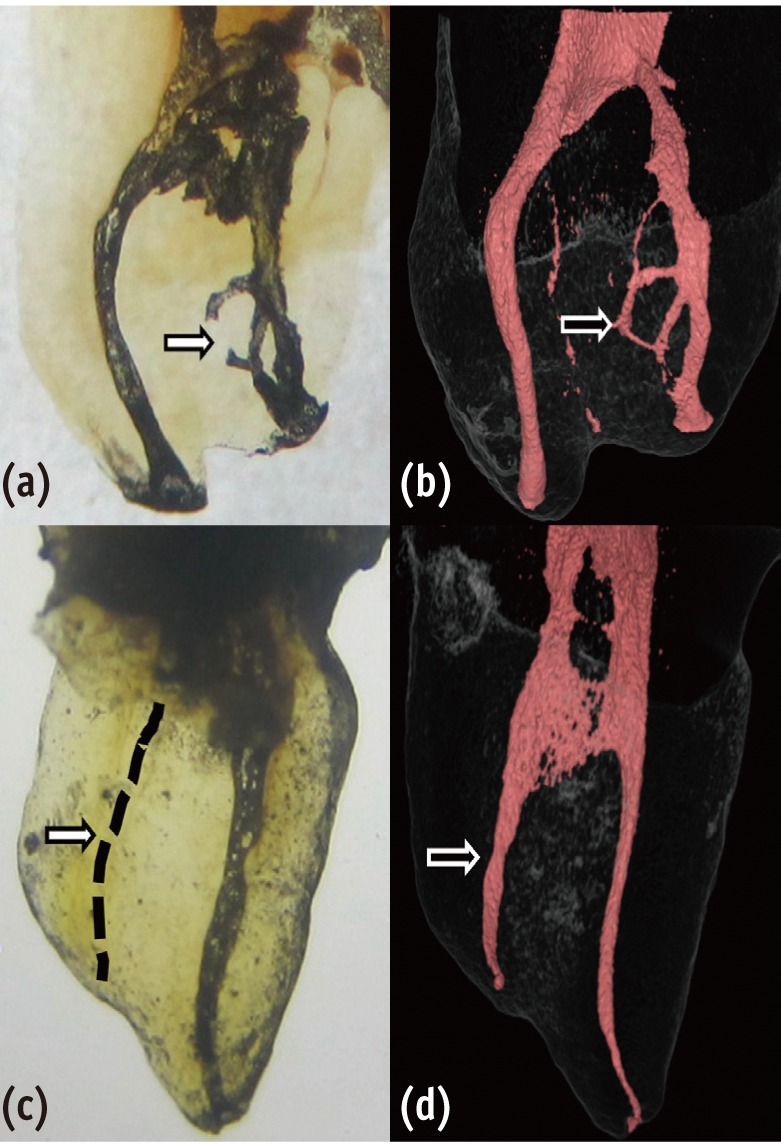
Understanding the reason for an unsuccessful non-surgical endodontic treatment outcome, as well as the complex anatomy of the root canal system, is very important. This study examined the cross-sectional root canal structure of mandibular first molars confirmed to have failed non-surgical root canal treatment using digital images obtained during intentional replantation surgery, as well as the causative factors of the failed conventional endodontic treatments. Materials and MethodsThis study evaluated 115 mandibular first molars. Digital photographic images of the resected surface were taken at the apical 3 mm level and examined. The discolored dentin area around the root canal was investigated by measuring the total surface area, the treated areas as determined by the endodontic filling material, and the discolored dentin area. ResultsForty 2-rooted teeth showed discolored root dentin in both the mesial and distal roots. Compared to the original filled area, significant expansion of root dentin discoloration was observed. Moreover, the mesial roots were significantly more discolored than the distal roots. Of the 115 molars, 92 had 2 roots. Among the mesial roots of the 2-rooted teeth, 95.7% of the roots had 2 canals and 79.4% had partial/complete isthmuses and/or accessory canals. ConclusionsDentin discoloration that was not visible on periapical radiographs and cone-beam computed tomography was frequently found in mandibular first molars that failed endodontic treatment. The complex anatomy of the mesial roots of the mandibular first molars is another reason for the failure of conventional endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In vitro evaluation of the sealing ability of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling
Xu Dong, Qian Xie, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2969. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical diagnostic approach in the treatment of chronic periodontitis in mandibular molars: Clinical cases
M. A. Postnikov, A. M. Golovachev, S. E. Chigarina, D. N. Kudryashov, I. A. Zakharova, S. A. Burakshaev
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2023; 30(5): 100. CrossRef - Evaluation of interorifice distance in permanent mandibular first molar with middle mesial canal in Bengaluru city, Karnataka: A cone-beam computed tomography study
Shruthika Mahajan, N. Meena, Anithakumari Rangappa, Ali Mohammed Mashood, Chethana Murthy, M. Lokapriya
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 100. CrossRef - A comparative study of the effects of gutta‐percha solvents on human osteoblasts and murine fibroblasts
Gul Ipek Gundogan, Sare Durmus, Gulgun Cansu Ozturk, Nazmi Kucukyesil, Yasin Talat Acar, Rumeysa Balaban, Cenk Kig
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 569. CrossRef - Endodontic retreatment of curved root canals using the dual wavelength erbium, chromium:yttrium, scandium, gallium, garnet, and diode 940-nm lasers and the XP-Endoshaper/finisher technique
Riman Nasher, Ralf-Dieter Hilgers, Norbert Gutknecht
Lasers in Dental Science.2020; 4(4): 211. CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef
-
1,640
View
-
10
Download
-
7
Crossref
-
Marginal and internal fit of nano-composite CAD/CAM restorations
-
So-Hyun Park, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Yoo-Jin Shin, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Ho Baek
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):37-43. Published online January 19, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare the marginal and internal fit of nano-composite CAD-CAM restorations. Materials and MethodsA full veneer crown and an mesio-occluso-distal (MOD) inlay cavity, which were prepared on extracted human molars, were used as templates of epoxy resin replicas. The prepared teeth were scanned and CAD-CAM restorations were milled using Lava Ultimate (LU) and experimental nano-composite CAD/CAM blocks (EB) under the same milling parameters. To assess the marginal and internal fit, the restorations were cemented to replicas and were embedded in an acrylic mold for sectioning at 0.5 mm intervals. The measured gap data were pooled according to the block types and measuring points for statistical analysis. ResultsBoth the block type and measuring point significantly affected gap values, and their interaction was significant (p = 0.000). In crowns and inlays made from the two blocks, gap values were significantly larger in the occlusal area than in the axial area, while gap values in the marginal area were smallest (p < 0.001). Among the blocks, the restorations milled from EB had a significantly larger gap at all measuring points than those milled from LU (p = 0.000). ConclusionsThe marginal and internal gaps of the two nano-composite CAD/CAM blocks differed according to the measuring points. Among the internal area of the two nano-composite CAD/CAM restorations, occlusal gap data were significantly larger than axial gap data. The EB crowns and inlays had significantly larger gaps than LU restorations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Dimensional accuracy of additive and subtractive manufactured ceramic-reinforced hybrid composite inlays: a CBCT-based in vitro study
Arwa Daghrery, Thilla Sekar Vinothkumar, Hissah Majrashi, Ghadah Faqihi, Rahaf Gofshi, Shroog Almasoudi, Rehaf Madkhali, Walter Yu Hang Lam, Honey Lunkad, Hemant Chourasia, Akhilanand Chaurasia
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Modern Light-Cured Restorative Composites as Luting Agents: The Effect of Preheating on Conversion and Film Thickness
Maria Dimitriadi, Aikaterini Petropoulou, Ioannis Papathanasiou, Spiros Zinelis, George Eliades
Materials.2025; 18(16): 3721. CrossRef - Benchmarking deep learning-designed inlay restorations across operator experience: An in vitro comparison of time efficiency, contact intensity, and contour quality
Jun-Ho Cho, Hyung-In Yoon, Burak Yilmaz, Martin Schimmel
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 162: 106083. CrossRef - The Influence of Extra-Fine Milling Protocol on the Internal Fit of CAD/CAM Composite and Ceramic Crowns
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Fatema Hosseini, Rafaela Oliveira Pilecco, Carlos Manuel Serrano, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva
Materials.2024; 17(22): 5601. CrossRef - Marginal fit of three different nanocomposite inlays fabricated with computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology: a comparative study
Hyunsuk Choi, Jae-Young Jo, Min-Ho Hong
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2024; 41(2): 80. CrossRef - Clinical comparison of marginal fit of ceramic inlays between digital and conventional impressions
Franklin Guillermo Vargas-Corral, Américo Ernesto Vargas-Corral, Miguel Angel Rodríguez-Valverde, Manuel Bravo, Juan Ignacio Rosales-Leal
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2024; 16(1): 57. CrossRef - Evaluation of Fitness and Accuracy of Milled and Three-Dimensionally Printed Inlays
Yoen Ah Lim, Jeong Mi Kim, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(04): 1029. CrossRef - Microscopic Inspection of the Adhesive Interface of Composite Onlays after Cementation on Low Loading: An In Vitro Study
Tiago Magalhães, Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Orlanda Torres, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva, Bruno Henriques, Mutlu Özcan, Júlio C. M. Souza
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(3): 148. CrossRef - Triple scan evaluation of internal and marginal adaptation of overlays using different restorative materials
Cynthia Kassis, Carina Mehanna, Pierre Khoury, Hani Tohme, Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suárez, Rim Bourgi, Monika Lukomska‐Szymanska, Louis Hardan
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(3): 493. CrossRef - Effect of Bonding Protocols on the Performance of Luting Agents Applied to CAD–CAM Composites
Bruna Hilgemberg, Fabiana Suelen Figuerêdo de Siqueira, Andres Felipe Millan Cardenas, Josiane Loch Ribeiro, Andrés Dávila-Sánchez, Salvatore Sauro, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio, Cesar Augusto Galvao Arrais
Materials.2022; 15(17): 6004. CrossRef - Marginal and internal fit and fracture resistance of three‐unit provisional restorations fabricated by additive, subtractive, and conventional methods
Mehran Falahchai, Samiye Rahimabadi, Ghazaleh Khabazkar, Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Hamid Neshandar Asli
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(6): 1404. CrossRef - Analysis of Cosmetic Effect of Nanocomposite Resin on Anterior Teeth
Yubo Wang, Junfu Li, Daiyun Chen, Li Li, Tao Huang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Microleakage and Marginal Integrity of Direct and Indirect Composite Resin Restorations in MOD Cavities After Thermo-Mechanical Loading
Ayşe Aslı ŞENOL, Pınar YILMAZ ATALI, Erkut KAHRAMANOĞLU
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(3): 564. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of different hybrid ceramic inlays after thermal cycling
Kun Qian, Xin Yang, Hailan Feng, Yihong Liu
Advances in Applied Ceramics.2020; 119(5-6): 284. CrossRef - BİLGİSAYAR DESTEKLİ TASARIM-BİLGİSAYAR DESTEKLİ ÜRETİM SİSTEMLERİNİN FARKLI DENTAL RESTORASYONLARIN KENAR VE İÇ YÜZEY UYUMLARINA ETKİSİNİN DEĞERLENDİRİLMESİ: İN-VİTRO ÇALIŞMA
Merve BENLİ, Bilge GÖKÇEN-ROHLİG
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - BİLGİSAYAR DESTEKLİ TASARIM-BİLGİSAYAR DESTEKLİ ÜRETİM SİSTEMLERİNİN FARKLI DENTAL RESTORASYONLARIN KENAR VE İÇ YÜZEY UYUMLARINA ETKİSİNİN DEĞERLENDİRİLMESİ: İN-VİTRO ÇALIŞMA
Merve BENLİ, Bilge GÖKÇEN-ROHLİG
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Marginal and internal fit of CAD-CAM inlay/onlay restorations: A systematic review of in vitro studies
Alexis Goujat, Hazem Abouelleil, Pierre Colon, Christophe Jeannin, Nelly Pradelle, Dominique Seux, Brigitte Grosgogeat
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(4): 590. CrossRef - Effect of alumina-blasting pressure on adhesion of CAD/CAM resin block to dentin
Yuki NARUSE, Tomohiro TAKAGAKI, Naoko MATSUI, Takaaki SATO, Alghamdi ALI, Masaomi IKEDA, Toru NIKAIDO, Junji TAGAMI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(5): 805. CrossRef - Comparison between direct chairside and digitally fabricated temporary crowns
Adil O. ABDULLAH, Sarah POLLINGTON, Yi LIU
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(6): 957. CrossRef - Edge strength of CAD/CAM materials
Maria Pfeilschifter, Verena Preis, Michael Behr, Martin Rosentritt
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 74: 95. CrossRef - Influence of preparation, fitting, and cementation on the vitro performance and fracture resistance of CAD/CAM crowns
Martin Rosentritt, Verena Preis, Michael Behr, Sebastian Hahnel
Journal of Dentistry.2017; 65: 70. CrossRef
-
2,144
View
-
23
Download
-
21
Crossref
-
Evaluation of electrical impedance ratio measurements in accuracy of electronic apex locators
-
Pil-Jong Kim, Hong-Gee Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):113-122. Published online December 26, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.113
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this paper was evaluating the ratios of electrical impedance measurements reported in previous studies through a correlation analysis in order to explicit it as the contributing factor to the accuracy of electronic apex locator (EAL). Materials and MethodsThe literature regarding electrical property measurements of EALs was screened using Medline and Embase. All data acquired were plotted to identify correlations between impedance and log-scaled frequency. The accuracy of the impedance ratio method used to detect the apical constriction (APC) in most EALs was evaluated using linear ramp function fitting. Changes of impedance ratios for various frequencies were evaluated for a variety of file positions. ResultsAmong the ten papers selected in the search process, the first-order equations between log-scaled frequency and impedance were in the negative direction. When the model for the ratios was assumed to be a linear ramp function, the ratio values decreased if the file went deeper and the average ratio values of the left and right horizontal zones were significantly different in 8 out of 9 studies. The APC was located within the interval of linear relation between the left and right horizontal zones of the linear ramp model. ConclusionsUsing the ratio method, the APC was located within a linear interval. Therefore, using the impedance ratio between electrical impedance measurements at different frequencies was a robust method for detection of the APC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of Anatomical Parameters on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in C-shaped Canals: A Novel Micro-CT Analysis Incorporating Feret Diameter
Kuan-Wei Tung, Hajime Sasaki, Bruno Cavalcanti, Richard Gardner, Neville McDonald
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(1): 134. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence techniques for ground fault line selection in power systems: State-of-the-art and research challenges
Fuhua Wang, Zongdong Zhang, Kai Wu, Dongxiang Jian, Qiang Chen, Chao Zhang, Yanling Dong, Xiaotong He, Lin Dong
Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering.2023; 20(8): 14518. CrossRef - Anin vitroevaluation of the accuracy of four electronic apex locators using stainless-steel and nickel-titanium hand files
Paras Mull Gehlot, Vinutha Manjunath, Mysore Krishnaswamy Manjunath
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 6. CrossRef
-
1,867
View
-
17
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Epigenetics: general characteristics and implications for oral health
-
Ji-Yun Seo, Yoon-Jung Park, Young-Ah Yi, Ji-Yun Hwang, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Deog-Gyu Seo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):14-22. Published online November 13, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.14
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Genetic information such as DNA sequences has been limited to fully explain mechanisms of gene regulation and disease process. Epigenetic mechanisms, which include DNA methylation, histone modification and non-coding RNAs, can regulate gene expression and affect progression of disease. Although studies focused on epigenetics are being actively investigated in the field of medicine and biology, epigenetics in dental research is at the early stages. However, studies on epigenetics in dentistry deserve attention because epigenetic mechanisms play important roles in gene expression during tooth development and may affect oral diseases. In addition, understanding of epigenetic alteration is important for developing new therapeutic methods. This review article aims to outline the general features of epigenetic mechanisms and describe its future implications in the field of dentistry. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Embracing change: Chemical modifications of nucleic acid bases as epigenetic marks
Nishu Nain, Shoaib Khan, Priyanka Phogat, Aparna Bansal, Shrikant Kukreti
Next Research.2026; 5: 101292. CrossRef - Conversation between skin microbiota and the host: from early life to adulthood
Jimin Cha, Tae-Gyun Kim, Ji-Hwan Ryu
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2025; 57(4): 703. CrossRef - Identification of two novel variants in homeodomain of
MSX1 associated with oligodontia
Ting Zeng, Xiuyou Wang, Li Xu, Xin Dong, Xili Qiu, Zhiyuan Deng, Saimin Pei, Rong Lei, Yuehong Wang, Ling Peng
Oral Science and Homeostatic Medicine.2025; 1(2): 9610029. CrossRef - DNA Methylation of COX‐2, IFN‐γ, TNF‐α, and LINE‐1 in Clinically Stable Periodontal Tissues Following Periodontal Therapy
Giulio Rasperini, Koki Yoshida, Alessandro Martinotti, Valentina Bollati, Letizia Tarantini, Farah Asa'ad
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Long Non-coding RNA and DNA Methylation on Gene Expression in Dental Fluorosis
Xiaoyan Hu, Huiru Li, Minzhi Yang, Yujiong Chen, Ailin Zeng, Jiayuan Wu, Jian Zhang, Yuan Tian, Jing Tang, Shengyan Qian, Mingsong Wu
Biological Trace Element Research.2024; 202(1): 221. CrossRef - MicroRNAs: Mighty Mite RNAs in Oral Diseases
Devapriya Appukuttan, P. S. G. Prakash
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2024; 14(3): 145. CrossRef - Role of epigenetics in OSCC: an understanding above genetics
Priyanka P. Vatsa, Yogita Jindal, Janhavi Bhadwalkar, Ambika Chamoli, Vinal Upadhyay, Amit Mandoli
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Downregulation of miRNA‐26 in chronic periodontitis interferes with innate immune responses and cell migration by targeting phospholipase C beta 1
Juhi R. Uttamani, Afsar R. Naqvi, Araceli Maria Valverde Estepa, Varun Kulkarni, Maria F. Brambila, Gloria Martínez, Gabriela Chapa, Christine D. Wu, Wei Li, Sona Rivas‐Tumanyan, Salvador Nares
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2023; 50(1): 102. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Epigenetic Modifications on Different Facets in the Periodontal Pathogenesis
Samuel Laberge, Daniel Akoum, Piotr Wlodarczyk, Jean-Daniel Massé, Dominique Fournier, Abdelhabib Semlali
Genes.2023; 14(6): 1202. CrossRef - The Role of Histone Acetylation Modification in Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Odontogenesis
Haoling Chen, Zijing Huang, Chuxiao Chen
Cellular Reprogramming.2023; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Your health is in your mouth: A comprehensive view to promote general wellness
Antonia Barranca-Enríquez, Tania Romo-González
Frontiers in Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Brief Landscape of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Dental Pathologies
Wojciech Tynior, Joanna Katarzyna Strzelczyk
Cytology and Genetics.2022; 56(5): 475. CrossRef - Influence of epigenetics on periodontitis and peri‐implantitis pathogenesis
Lena Larsson, Nolan M. Kavanagh, Trang V. N. Nguyen, Rogerio M. Castilho, Tord Berglundh, William V. Giannobile
Periodontology 2000.2022; 90(1): 125. CrossRef - DNA methylation alterations and their potential influence on macrophage in periodontitis
Yiyang Jiang, Jingfei Fu, Juan Du, Zhenhua Luo, Lijia Guo, Junji Xu, Yi Liu
Oral Diseases.2022; 28(2): 249. CrossRef - Stabilizing and Anti-Repressor Elements Effectively Increases Transgene Expression in Transfected CHO Cells
Qin Li, Rui-Fang Yan, Yong-Xiao Yang, Chun-liu Mi, Yan-long Jia, Tian-Yun Wang
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis and Anticancer Potential of New Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Chemotherapeutic Agents
Işıl Nihan Korkmaz, Hasan Özdemir
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.2022; 194(12): 6349. CrossRef - Impact of Epigenetic Alterations in the Development of Oral Diseases
Rodopi Emfietzoglou, Evangelos Pachymanolis, Christina Piperi
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 28(6): 1091. CrossRef - Basics of Epigenetics and Role of Epigenetics in Diabetic Complications
Andamuthu Yamunadevi, Ramani Pratibha, Muthusamy Rajmohan, Sengottaiyan Mahendraperumal, Nalliappan Ganapathy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S336. CrossRef - Effects of Epigenetic Regulation on Cancer
Muhammet Mesut Nezir ENGİN, Esra ÖZEN ENGİN, Recep ERÖZ, Gorkem DULGER, Hüseyin YÜCE
Journal of Biotechnology and Strategic Health Research.2021; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation therapy improves human dental pulp stem cell viability and migration in vitro associated to upregulation of histone acetylation
Ivana M. Zaccara, Letícia B. Mestieri, Emily F. S. Pilar, Maria S. Moreira, Fabiana S. Grecca, Manoela D. Martins, Patrícia Maria Poli Kopper
Lasers in Medical Science.2020; 35(3): 741. CrossRef - The Biology of Social Adversity Applied to Oral Health
N. Gomaa, H. Tenenbaum, M. Glogauer, C. Quiñonez
Journal of Dental Research.2019; 98(13): 1442. CrossRef - The effect of DNA methylation on the miRNA expression pattern in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in human dental pulp cells
Zehuan Mo, Qimeng Li, Luhui Cai, Minkang Zhan, Qiong Xu
Molecular Immunology.2019; 111: 11. CrossRef - One-Carbon Metabolism Links Nutrition Intake to Embryonic Development via Epigenetic Mechanisms
Si Wu, Jun Zhang, Feifei Li, Wei Du, Xin Zhou, Mian Wan, Yi Fan, Xin Xu, Xuedong Zhou, Liwei Zheng, Yachuan Zhou
Stem Cells International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation in dental pulp inflammation
T Hui, C Wang, D Chen, L Zheng, D Huang, L Ye
Oral Diseases.2017; 23(1): 22. CrossRef - Current Concepts of Epigenetics and Its Role in Periodontitis
Lena Larsson
Current Oral Health Reports.2017; 4(4): 286. CrossRef - The periodontal war: microbes and immunity
Jeffrey L. Ebersole, Dolph Dawson, Pinar Emecen‐Huja, Radhakrishnan Nagarajan, Katherine Howard, Martha E. Grady, Katherine Thompson, Rebecca Peyyala, Ahmad Al‐Attar, Kathryn Lethbridge, Sreenatha Kirakodu, Octavio A. Gonzalez
Periodontology 2000.2017; 75(1): 52. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulatory elements: Recent advances in understanding their mode of action and use for recombinant protein production in mammalian cells
Niamh Harraghy, David Calabrese, Igor Fisch, Pierre‐Alain Girod, Valérie LeFourn, Alexandre Regamey, Nicolas Mermod
Biotechnology Journal.2015; 10(7): 967. CrossRef - Protocol for assessing maternal, environmental and epigenetic risk factors for dental caries in children
Surani Fernando, David J. Speicher, Mahmoud M. Bakr, Miles C. Benton, Rodney A. Lea, Paul A. Scuffham, Gabor Mihala, Newell W. Johnson
BMC Oral Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,630
View
-
27
Download
-
28
Crossref
-
Thermal irritation of teeth during dental treatment procedures
-
Su-Jung Kwon, Yoon-Jung Park, Sang-Ho Jun, Jin-Soo Ahn, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Deog-Gyu Seo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):105-112. Published online August 23, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.105
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
While it is reasonably well known that certain dental procedures increase the temperature of the tooth's surface, of greater interest is their potential damaging effect on the pulp and tooth-supporting tissues. Previous studies have investigated the responses of the pulp, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone to thermal irritation and the temperature at which thermal damage is initiated. There are also many in vitro studies that have measured the temperature increase of the pulp and tooth-supporting tissues during restorative and endodontic procedures. This review article provides an overview of studies measuring temperature increases in tooth structures during several restorative and endodontic procedures, and proposes clinical guidelines for reducing potential thermal hazards to the pulp and supporting tissues. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of Various Sleeve Materials on Temperature Variations During Guided Endodontic Access Cavity Preparation Utilizing Finite‐Element Analysis
Anna Muryani, Wandi Prasetia, Dudi Aripin, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Zainul Ahmad Rajion, Satrio Wicaksono
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of microcrack formation and fracture resistance of root dentin with the use of three different rotary files: An in vitro study
Paridhi Maheshwari, Sayantan Mukherjee, Ipsita Maity, Paromita Mazumdar
Journal of Oral Research and Review.2026; 18(1): 59. CrossRef - Infrared thermographic evaluation of root surface during warm vertical compaction technique
Aysenur Oncu, Ecem Ozgur, Merve Sarı, Pelin Tufenkci, Berkan Celikten
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - External Root Temperature and Its Relationship With Dentin Thickness During Gutta-Percha Removal Procedures With Ultrasound. An Ex Vivo Study
Juan Ramon Salazar-Silva, Carlos Emilio Paschoal, Daniela de Fatima Teixeira da Silva, Denise Maria Zezell, Fábio Luiz Cunha D'Assuncao, Celso Luiz Caldeira
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(3): 340. CrossRef - Temperature Changes of NaOCl after Irrigation Using Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation, Easy Clean, and XP-Endo Finisher: A Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial
Geraldo Edson Freitas Athayde de Moraes, Daniel Guimarães Pedro Rocha, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Índia Olinta De Azevedo Queiroz, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 660. CrossRef - Real‐Time Analysis of Changes in Internal and External Root Temperatures Using Different Systems for Activating the Irrigation Solution
Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Julia Menezes Savaris, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Tamer Ferreira Schmidt, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Behaviour of Teeth With Internal Root Resorption During Obturation and Enhancing Thermal Simulations: A Finite-Element Analysis
Alper Kabakci, Ayca Yilmaz, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(6): 103903. CrossRef - Determination of a safe protocol for using laser ablation with indocyanine green dye in endodontic treatment. In vitro, in vivo and human study
Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Mirtha Perdomo, Marcelo Costa Perdomo, María Betania Acevedo Giménez, Celso Kenji Nishiyama, Fernando Accorsi Orosco, Arturo Javier Aranda Garcia, Carolina Sayuri Wajima, Cristiane Cantiga-Silva, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Flávio
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial PEEK-Ag Surfaces: Development and In Vitro Evaluation Against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Flávio Rodrigues, Mariana Fernandes, Filipe Samuel Silva, Óscar Carvalho, Sara Madeira
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(10): 388. CrossRef - The effect of di̇fferent preheati̇ng methods on the intrapulpal temperature of bulk-fi̇ll composi̇te resi̇ns
Hilal Ateş, Merve İşcan Yapar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of increase in temperature on the external root surface of teeth during retrieval of broken NiTi instrument using two ultrasonic tips and two power settings: An in vitro study
Ashish K. Jain, Rishabhkumar Jain, Rahul Rao, Prajakta Rao, Pooja Yadav, Vinayak Thorat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 634. CrossRef - Dental health concerns for patients suffering from facial, peri-oral burns, and inhalation injury: A persistent yet underappreciated challenge
Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, Isabelle Rennekampff, Mayer Tenenhaus
Burns.2024; 50(9): 107224. CrossRef - Recent advances in the pathogenesis and prevention strategies of dental calculus
Yu Wei, Gao-peng Dang, Zhao-yang Ren, Mei-chen Wan, Chen-yu Wang, Hong-bo Li, Tong Zhang, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Root Surface Temperature Using Different Endodontic Filling Techniques
Lea Külzer, Theresia Saban, Andreas Braun, Johannes-S. Wenzler
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9830. CrossRef - Accuracy comparison of single- and double-sleeve endodontic guides for fiber post removal
Omid Dianat, Mandana Naseri, Yaser Safi, Ali Modaberi, Nazanin Zargar, Ove A. Peters, Mehran Farajollahi
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Water Coolant and Bur Type on Pulp Temperature When Removing Tooth Structure and Restorative Dental Materials
C Mafrici, M Kingston, R Grice, PV Abbott
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(1): 91. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Temperature Variations in Incisor Root Surfaces During Root Canal Preparation Using Various Rotary Systems and Irrigation Protocols
Mihai Paven, Adrian-George Marinescu, Osama Abuabboud, Laura-Elena Cirligeriu, Luminita Maria Nica, Vlad Tiberiu Alexa, Ruxandra Sava Rosianu, Atena Galuscan, Roxana Oancea
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(23): 7484. CrossRef - The Effect of Restoration Polymerization and Residual Dentine Thickness on Thermal Changes of Pulp Chamber of Immature Permanent Teeth
Kevser Kolçakoğlu, Merve Aksoy, Cenkhan Bal, Akif Demirel, Firdevs Tulga Öz
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of pulpotomy in managing irreversible pulpitis in mature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuanyuan Li, Wenying Wang, Qian Zeng, Michelle Tang, Joshua Massey, Brian E. Bergeron, Lisha Gu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 144: 104923. CrossRef - Evaluation of diamond rotary instruments marketed for removing zirconia restorations
Severin Hunziker, Lea Thorpe, Nicola U. Zitzmann, Nadja Rohr
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(5): 895. CrossRef - Influence of different cutting instruments and rotational speeds on heat generation and cutting efficiency when sectioning different types of zirconia
Lisa Türp, Frank Lehmann, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 160: 106715. CrossRef - Loss of pulp vitality correlated with the duration of the interim restoration and the experience of the dentist: A retrospective study
Göran Nilsson, Stefan Ellner, Liselott Arnebrant, Lars Brudin, Christel Larsson
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(6): 833. CrossRef - Thermal Sensing of Photo-Activated Dental Resin Composites Using Infrared Thermography
Turki A. Bakhsh, Abdulaziz Alfaifi, Yousef Alghamdi, Mohannad Nassar, Roaa A. Abuljadyel
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4117. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation acid solutions on cleaning and bond strength to post‐space dentin
C. de Melo Alencar, J. Ferrari Zaniboni, J. Felipe Besegato, A. Patricia Oliveira Barros, M. Bena Gélio, L Garcia Belizário, E. Maximiliano Fernandez Godoy, M. Carlos Kuga
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Intermediate Irrigation on Temperature Rise during Broken NiTi File Removal Using Ultrasonic Device
László Pintér, Károly Krajczár, Fanni Őry, József Szalma, Edina Lempel
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9761. CrossRef - Top tips for improving crown preparations
James Baker, Ewen McColl, Christopher Tredwin
British Dental Journal.2023; 234(1): 16. CrossRef - Evaluation of knowledge and awareness of pediatric oral health among school teachers of Hazaribag before and after oral health education.
Vipin Ahuja, Annapurna Ahuja, Nilima Thosar
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1292. CrossRef - Applications of single laser pulse from Nd:doped lasers for cleaning of small diameter carious lesions. Modelling and analytical study
T Uzunov, M Deneva, P Uzunova, M Nenchev
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2023; 2487(1): 012022. CrossRef - Accuracy of a 3D printed sleeveless guide system used for fiber post removal: An in vitro study
Siyi Mo, Yongwei Xu, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104367. CrossRef - Heat generated during dental treatments affecting intrapulpal temperature: a review
Xin Er Lau, Xiaoyun Liu, Helene Chua, Wendy Jingwen Wang, Maykon Dias, Joanne Jung Eun Choi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2277. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature rise in light-cure bonding of brackets with and without primer, in intact versus restored teeth
Gabriela Cenci SCHMITZ, Fernanda de Souza HENKIN, Mauricio MEZOMO, Mariana MARQUEZAN, Gabriela BONACINA, Maximiliano Schünke GOMES, Eduardo Martinelli Santayana de LIMA
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature Rise in Curing Modes of Two Different Dental Light-Curing Units: The Importance of Heating Rate
Ahmad Soori, Faezeh Soori, Farshad Kowsary, Shahin Kasraei
International Journal of Thermophysics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effective application of suitable single pulse of Nd:doped lasers for cleaning of initial carious lesions of human teeth. Experimental study
T Uzunov, M Deneva, V Kazakov, P Uzunova, N Kaimakanova, M Nenchev
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2023; 2487(1): 012021. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Intrapulpal Thermal Changes during the Polymerization of Different Adhesive Resin Materials: An In Vitro Study
Pavithra K Ramanna, Suneel V Vadavadagi, Konsam Bidya Devi, Pawankumar Kamalapurkar, Shreeshail Indi, Vineetha Chakravarthy Srinivas
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(5): 539. CrossRef - Anesthetic-, irrigation- and pain-free dentistry? The case for a femtosecond laser enabled intraoral robotic device
Ludovic Rapp, Steve Madden, Andrei V. Rode, Laurence J. Walsh, Heiko Spallek, Quan Nguyen, Van Dau, Peter Woodfield, Dzung Dao, Omar Zuaiter, Alaa Habeb, Timothy R. Hirst
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - 4D Printing of Shape‐Memory Semi‐Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Based On Aromatic Heterochain Polymers
Kseniia N. Bardakova, Bato Ch. Kholkhoev, Ivan A. Farion, Evgenii O. Epifanov, Olga S. Korkunova, Yuri M. Efremov, Nikita V. Minaev, Anna B. Solovieva, Peter S. Timashev, Vitaliy F. Burdukovskii
Advanced Materials Technologies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How does indirect air-cooling influence pulp chamber temperature in different volume teeth and absence/presence of resin-based composite during light curing?
Mathieu Mouhat, Lina Stangvaltaite-Mouhat, Emil Finnäs, Amani Andersen, Anneli Lirhus Evertsen, Bo W. Nilsen
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intrapulpal temperature changes during the cementation of ceramic veneers
Edina Lempel, Dóra Kincses, Donát Szebeni, Dóra Jordáki, Bálint Viktor Lovász, József Szalma
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Femtosecond laser dentistry for precise and efficient cavity preparation in teeth
Ludovic Rapp, Steve Madden, Julia Brand, Laurence J. Walsh, Heiko Spallek, Omar Zuaiter, Alaa Habeb, Timothy R. Hirst, Andrei V. Rode
Biomedical Optics Express.2022; 13(9): 4559. CrossRef - Three Dimensional mapping of the root apex: distances between apexes and anatomical structures and external cortical plates
Carlos Henrique FERRARI, Amjad ABU HASNA, Frederico Canato MARTINHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of 9,300 nm Carbon Dioxide Laser on Dental Hard Tissue: A Concise Review
Vicky Wenqing Xue, Irene Shuping Zhao, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, John Yun Niu, Edward Chin Man Lo, Chun Hung Chu
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2021; Volume 13: 155. CrossRef - PHOTOPOLYMERIZED COMPOSITIONS AND LIGHT SOURCES FOR DENTAL PRACTICE (REVIEW)
A. M. Lalatovich, M. A. Vaniev, N. V. Sidorenko, Y. A. Makedonova, D. Yu. Dyachenko, S. V. Dyachenko
IZVESTIA VOLGOGRAD STATE TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY.2021; (12(259)): 7. CrossRef - Spray mist reduction by means of a high-volume evacuation system—Results of an experimental study
Martin Koch, Christian Graetz, Essam Al-Moraissi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(9): e0257137. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature changes during orthodontic bonding – an in vitro study
Aysegul Ayhan Bani, Burcu Balos Tuncer, Cumhur Tuncer
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(2): 157. CrossRef - Thermal Behavior of Teeth During Restoration Procedure With Composite: Experimental Tests and Numerical Simulation
M. Potenza, P. Coppa, L. Cerroni, G. Bovesecchi
Journal of Heat Transfer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Thermal Alterations on External Root Surface during Mechanical Instrumentation and Thermoplasticized Gutta-percha Obturation: An Ex Vivo Study
Rohit Sharma, Atul Jain, Madhurima Sharma, Shivani Chauhan, Abhinay Agarwal
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(5): 367. CrossRef - Degree of conversion and in vitro temperature rise of pulp chamber during polymerization of flowable and sculptable conventional, bulk-fill and short-fibre reinforced resin composites
Edina Lempel, Zsuzsanna Őri, Dóra Kincses, Bálint Viktor Lovász, Sándor Kunsági-Máté, József Szalma
Dental Materials.2021; 37(6): 983. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature changes during orthodontic bonding – an in vitro study
Aysegul Ayhan Bani, Burcu Balos Tuncer, Cumhur Tuncer
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(2): 157. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature Dependence of Specific Heat of Human Enamel and Dentin: An Experimental Study
Ahmad Soori, Farshad Kowsary, Shahin Kasraei
International Journal of Thermophysics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prosthodontic Applications of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): An Update
Muhammad Sohail Zafar
Polymers.2020; 12(10): 2299. CrossRef - The effect of halogen bulb and light-emitting diode light curing units on temperature increase and fibroblast viability
Georgia Memari Trava, Juliane Almeida Santos, Lucas Paula Ramos, Pamela Beatriz Rosário Estevam dos Santos, Amjad Abu Hasna, Karen Cristina Yui, Adriano Bressane, Luciane Dias de Oliveira, Marianne Spalding
F1000Research.2020; 9: 1369. CrossRef - A Study on Temperature Changes during Bone Scaling and Cutting of Dental Ultrasonic Scaling/Surgery System
Min-Woo Sa, Tae-Jo Ko, Jong Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2020; 19(2): 1. CrossRef - Controlling In Vivo, Human Pulp Temperature Rise Caused by LED Curing Light Exposure
DC Zarpellon, P Runnacles, C Maucoski, U Coelho, FA Rueggeberg, CAG Arrais
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(3): 235. CrossRef - Pulp Temperature Rise Induced by Light-Emitting Diode Light-Curing Units Using an Ex Vivo Model
Alexandra Vinagre, João Ramos, Clara Rebelo, José Basto, Ana Messias, Nélia Alberto, Rogério Nogueira
Materials.2019; 12(3): 411. CrossRef - The cooling efficiency of different dental high-speed handpiece coolant port designs
Helene Chua, Joanne Jung Eun Choi, Rishi Sanjay Ramani, Ritu Ganjigatti, John Neil Waddell
Heliyon.2019; 5(8): e02185. CrossRef - Polymerisation Shrinkage Profiling of Dental Composites using Optical Fibre Sensing and their Correlation with Degree of Conversion and Curing Rate
Ginu Rajan, Raju Raju, Sagar Jinachandran, Paul Farrar, Jiangtao Xi, B. Gangadhara Prusty
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth sectioning for coronectomy: how to perform?
József Szalma, László Vajta, Lajos Olasz, Edina Lempel
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(2): 519. CrossRef - Dentistry Applications of Fiber Bragg Gratings: Irradiation Protocols for Bulk Fill Flow Dental Composites
Ana Paula Gebert de Oliveira Franco, Manoella Maria Machado Costa, Leandro Zen Karam, Osnara Maria Mongruel Gomes, Hypolito Jose Kalinowski
Journal of Lightwave Technology.2019; 37(18): 4881. CrossRef - In Vitro Analysis of Techniques that Alter the Surface Hardness of a Glass Ionomer Restorative Material
Riaan Mulder, Naeemah Noordien, Shaun Rossouw, Luzaan van Zyl
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(12): 1362. CrossRef - Changes in the radicular pulp-dentine complex in healthy intact teeth and in response to deep caries or restorations: A histological and histobacteriological study
Domenico Ricucci, Simona Loghin, Li-na Niu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 73: 76. CrossRef - Effect of Irradiance and Exposure Duration on Temperature and Degree of Conversion of Dual-Cure Resin Cement for Ceramic Restorations
JS Shim, SH Han, N Jha, ST Hwang, W Ahn, JY Lee, JJ Ryu
Operative Dentistry.2018; 43(6): E280. CrossRef - Protective Effects of Base Cements against Intrapulpal Temperature Rise during Curing of Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study by Pulpal Blood Microcirculation Model
Ihsan F Ertugrul, Basak Yazkan, Ceylan Ç Ertugrul
International Journal of Experimental Dental Science.2018; 7(2): 85. CrossRef - Thermal imaging of the pulp during residual adhesive removal
Gökmen Kurt, Nisa Gül, Özgür Er, Gülşen Çakmak, Emre Bendeş, Veysel Aslantaş
Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopädie.2017; 78(4): 330. CrossRef - Influence of the material for preformed moulds on the polymerization temperature of resin materials for temporary FPDs
Philipp-Cornelius Pott, Hans Schmitz-Wätjen, Meike Stiesch, Michael Eisenburger
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(4): 294. CrossRef - Light curing in dentistry and clinical implications: a literature review
Frederick Allen RUEGGEBERG, Marcelo GIANNINI, Cesar Augusto Galvão ARRAIS, Richard Bengt Thomas PRICE
Brazilian Oral Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Intrapulpal temperature changes during curing of different bulk-fill restorative materials
Elif YASA, Cigdem ATALAYIN, Gamze KARACOLAK, Tugrul SARI, L. Sebnem TURKUN
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(5): 566. CrossRef - Can Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Nanoparticulate EndoSequence Root Repair Material Produce Injurious Effects to Rat Subcutaneous Tissues?
Wafaa A. Khalil, Siham K. Abunasef
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1151. CrossRef - Comparison of photopolymerization temperature increases in internal and external positions of composite and tooth cavities in real time: Incremental fillings of microhybrid composite vs. bulk filling of bulk fill composite
Ryan Jin-Young Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Ji-Yun Hwang, In-Bog Lee, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1093. CrossRef - Real-Time Analysis of Temperature Changes in Composite Increments and Pulp Chamber during Photopolymerization
Ryan Jin-Young Kim, In-Bog Lee, Jin-Young Yoo, Su-Jung Park, Sin-Young Kim, Young-Ah Yi, Ji-Yun Hwang, Deog-Gyu Seo
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Maryam Khoroushi, Mohammadreza Moharreri, Mohammad Atai
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 155. CrossRef - Comparison of Exothermic Release during the Polymerization of Four Materials used to fabricate Provisional Restorations
Minu Raju
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2014; 4(1): 1. CrossRef
-
5,405
View
-
37
Download
-
72
Crossref
-
The effect of clinical performance on the survival estimates of direct restorations
-
Kyou-Li Kim, Cheol Namgung, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):11-20. Published online February 26, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.11
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
In most retrospective studies, the clinical performance of restorations had not been considered in survival analysis. This study investigated the effect of including the clinically unacceptable cases according to modified United States Public Health Service (USPHS) criteria into the failed data on the survival analysis of direct restorations as to the longevity and prognostic variables. Materials and MethodsNine hundred and sixty-seven direct restorations were evaluated. The data of 204 retreated restorations were collected from the records, and clinical performance of 763 restorations in function was evaluated according to modified USPHS criteria by two observers. The longevity and prognostic variables of the restorations were compared with a factor of involving clinically unacceptable cases into the failures using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard model. ResultsThe median survival times of amalgam, composite resin and glass ionomer were 11.8, 11.0 and 6.8 years, respectively. Glass ionomer showed significantly lower longevity than composite resin and amalgam. When clinically unacceptable restorations were included into the failure, the median survival times of them decreased to 8.9, 9.7 and 6.4 years, respectively. ConclusionsAfter considering the clinical performance, composite resin was the only material that showed a difference in the longevity (p < 0.05) and the significantly higher relative risk of student group than professor group disappeared in operator groups. Even in the design of retrospective study, clinical evaluation needs to be included.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
Ömer Hatipoğlu, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Nessrin Taha, Thiyezen Abdullah Aldhelai, Daoud M. Ayyad, Ahmed A. Madfa, Benjamin Martin‐Biedma, Rafael Fernández‐Grisales, Bakhyt A. Omarova, Wen Yi Lim, Suha Alfirjani, Kacper Nijak
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 977. CrossRef - Clinical Performance of Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Veneers Cemented With Light-Cured Resin Cements: An Observational Study
Nguyen Thi Minh Hien, Tran Hung Lam, Do Thi Thao, Hoang Viet
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Failure Risk of Composite Resin and Amalgam Restorations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Woroud Al-Sulimmani, Asmaa Al-Rasheed, Hebah Al-Daraan, Muna Al-Mutairi, Yash Brahmbhatt, Hesham Al-Hazmi, Hend Al-Qaderi
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(4): 100871. CrossRef - The Effect of Polishing on the Clinical Performance of Amalgam Restorations Using the Mahler’s Scale and Modified United States Public Health Service Criteria: A Prospective Clinical Study
Soham Suraj Wadke, Dipali Y. Shah
Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry.2025; 23(3): 282. CrossRef - Navigating the practical-knowledge gap in deep margin elevation: A step towards a structured case selection – a review
Eman H. Ismail, Saba S. Ghazal, Rahaf D. Alshehri, Hajar N. Albisher, Rana S. Albishri, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(5): 674. CrossRef - A review of dental antibacterial agents and antibacterial modification of composite resins and dentin adhesives
Hojin Moon
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 189. CrossRef - Er:YAG laser in selective caries removal and dentin treatment with chitosan: a randomized clinical trial in primary molars
Rai Matheus Carvalho Santos, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Sérgio Luiz de Souza Salvador, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Longevity of composite restorations is definitely not only about materials
Flávio Fernando Demarco, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Anelise Fernandes Montagner, Verônica Pereira de Lima, Marcos Britto Correa, Rafael R. Moraes, Niek J.M. Opdam
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of different adhesive systems on dental defects and sensitivity to teeth in composite resin restoration: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Keda Fang, Kenan Chen, Mengqi Shi, Liang Wang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2495. CrossRef - Survival of direct resin composite onlays and indirect tooth-coloured adhesive onlays in posterior teeth: a systematic review
Colin E. McGrath, Stephen J. Bonsor
British Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A 2-year clinical evaluation of direct and semi-direct resin composite restorations in non-carious cervical lesions: a randomized clinical study
Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele, Laura Célia Fernandes Meirelles, Rafael Santos Rocha, Lucélia Lemes Gonçalves, Daniele Mara Silva Ávila, Sérgio Eduardo de Paiva Gonçalves, Eduardo Bresciani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1321. CrossRef - Treatment options for large posterior restorations: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Bruna M. Vetromilla, Niek J. Opdam, Ferdinan L. Leida, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, Flavio F. Demarco, Mark P.J. van der Loo, Maximiliano S. Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(8): 614. CrossRef - Effect of a novel prime‐and‐rinse approach on short‐ and long‐term dentin bond strength of self‐etch adhesives
Mingxing Li, Jingqiu Xu, Ling Zhang, Chaoyang Wang, Xiaoting Jin, Yan Hong, Baiping Fu, Matthias Hannig
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 127(6): 547. CrossRef - Longevity of resin-bonded fixed partial dental prostheses made with metal alloys
Naomi Tanoue
Clinical Oral Investigations.2016; 20(6): 1329. CrossRef - Amalgam vs Composite Restoration, Survival, and Secondary Caries
Muhanad Alhareky, Mary Tavares
Journal of Evidence Based Dental Practice.2016; 16(2): 107. CrossRef - Seal, replacement or monitoring amalgam restorations with occlusal marginal defects? Results of a 10-year clinical trial
G. Moncada, E. Fernández, K. Mena, J. Martin, P. Vildósola, O.B. De Oliveira, J. Estay, I.A. Mjör, V.V. Gordan
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(11): 1371. CrossRef - Longitudinal Results of a 10-year Clinical Trial of Repair of Amalgam Restorations
G Moncada, P Vildósola, E Fernández, J Estay, OB de Oliveira Júnior, MF de Andrade, J Martin, IA Mjör, VV Gordan
Operative Dentistry.2015; 40(1): 34. CrossRef - Amalgam and resin composite longevity of posterior restorations: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Vittorio Moraschini, Cheung Ka Fai, Raphael Monte Alto, Gustavo Oliveira dos Santos
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1043. CrossRef - Aumento de longevidad de restauraciones de resinas compuestas y de su unión adhesiva. Revisión de tema
Gustavo Moncada, Patricio Vildósola, Eduardo Fernandez, Juan Estay, Osmir B de Oliveira Junior, Javier Martin
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of resin-modified glass-ionomer and resin composite polymerisation shrinkage stress in a wet environment
Joshua J. Cheetham, Joseph E.A. Palamara, Martin J. Tyas, Michael F. Burrow
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 29: 33. CrossRef - Factors affecting the placement or replacement of direct restorations in a dental school
Samara Silvani, Roberta Ferreira Trivelato, Ruchele Dias Nogueira, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo-Martins
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2014; 5(1): 54. CrossRef
-
1,715
View
-
4
Download
-
21
Crossref
-
Early caries detection using optical coherence tomography: a review of the literature
-
Young-Seok Park, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Pyo Lee, Won-Jun Shon
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):367-376. Published online September 14, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.367
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
Early detection of carious lesions increases the possibility of treatment without the need for surgical intervention. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an emerging three-dimensional imaging technique that has been successfully used in other medical fields, such as ophthalmology for optical biopsy, and is a prospective candidate for early caries detection. The technique is based on low coherence interferometry and is advantageous in that it is non-invasive, does not use ionizing radiation, and can render three-dimensional images. A brief history of the development of this technique and its principles are discussed in this paper. There have been numerous studies on caries detection, which were mostly in vitro or ex vivo experiments. Through these studies, the feasibility of OCT for caries detection was confirmed. However, further research should be performed, including in vivo studies of OCT applications, in order to prove the clinical usefulness of this technique. In addition, some technological problems must be resolved in the near future to allow for the use of OCT in everyday practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Differential diagnosis of periapical cyst using collagen birefringence pattern of the cyst wall
Hyo Jin Ji, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Suk Keun Lee, Jin Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 111. CrossRef - How to designin situstudies: an evaluation of experimental protocols
Young-Hye Sung, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 164. CrossRef
-
2,510
View
-
18
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
-
Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods
Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results
The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.05).
Conclusions
When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
-
Effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion and flexural strength
-
Ji-A Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):324-335. Published online July 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.324
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study investigated the effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion (DC) and biaxial flexural strength (FS).
Materials and Methods
Four enamel shades (A1, A2, A3, A4) and two dentin shades (A2O, A3O) of Premisa (Kerr Co.) and Denfil (Vericom Co.) were evaluated on their CIE L*, a*, b* color components using the spectrophotometer before curing, after curing and at 7 day. The DC of same specimens were measured with Near-infrared spectrometer (Nexus, Thermo Nicolet Co.) at 2 hr after cure and at 7 day. Finally, the FS was obtained after all the other measurements were completed at 7 day. The correlations between each color component and DC and FS were evaluated.
Results
The light-curing of composite resin resulted in color changes of Premisa in red-blue direction and Denfil in green-blue direction. The DC and FS were affected by product, time and shade (3-way ANOVA, p < 0.05) and product and shade (2-way ANOVA, p < 0.05), respectively. Premisa only showed a significant correlation between the DC and CIE a* component - before and after polymerization (Pearson product moment correlation, p < 0.05). The FS of Premisa showed significant negative correlations with CIE a* and CIE b* components.
Conclusions
The DC and FS of the light-curing composite resin were affected by the color components of the material before and after polymerization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Color Stability according to Shade of Temporary Crown Resin Using Digital Spectrophotometer: In Vitro Study
Hye-min Ku, Mi-Kyoung Jun
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2022; 22(3): 139. CrossRef - The properties of UDMA dental composite resin with novel photosensitizers
Gum Ju Sun
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2013; 35(3): 209. CrossRef
-
1,516
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
-
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):139-148. Published online March 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.139
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study investigated the effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of adhesives on the bond strength to dentin. The experimental adhesives containing various ratios of hydrophobic, low-viscosity Bis-M-GMA, with Bis-GMA and TEGDMA, were made and evaluated on the mechanical properties and bond strength to dentin.
Materials and Methods
Five experimental adhesives formulated with various Bis-GMA/Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA ratios were evaluated on their viscosity, degree of conversion (DC), flexural strength (FS), and microtensile bond strength (MTBS). The bonded interfaces were evaluated with SEM and the solubility parameter was calculated to understand the wetting characteristics of the adhesives.
Results
Although there were no significant differences in the DC between the experimental adhesives at 48 hr after curing (p > 0.05), the experimental adhesives that did not contain Bis-GMA exhibited a lower FS than did those containing Bis-GMA (p < 0.05). The experimental adhesives that had very little to no TEGDMA showed significantly lower MTBS than did those containing a higher content of TEGDMA (p < 0.05). The formers exhibited gaps at the interface between the adhesive layer and the hybrid layer. The solubility parameter of TEGDMA approximated those of the components of the primed dentin, rather than Bis-GMA and Bis-M-GMA.
Conclusions
To achieve a good dentin bond, a strong base monomer, such as Bis-GMA, cannot be completely replaced by Bis-M-GMA for maintaining mechanical strength. For compatible copolymerization between the adhesive and the primed dentin as well as dense cross-linking of the adhesive layer, at least 30% fraction of TEGDMA is also needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Equivalence study of the resin-dentine interface of internal tunnel restorations when using an enamel infiltrant resin with ethanol-wet dentine bonding
Andrej M. Kielbassa, Sabrina Summer, Wilhelm Frank, Edward Lynch, Julia-Susanne Batzer
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole
Yasaman Delaviz, Timothy W. Liu, Ashley R. Deonarain, Yoav Finer, Babak Shokati, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): 229. CrossRef
-
2,201
View
-
7
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
-
Mi-Ae Lee, Duck-Kyu Seo, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):164-172. Published online May 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.164
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
During a composite resin restoration, an anticipating contraction gap is usually tried to seal with low-viscosity resin after successive polishing, etching, rinsing and drying steps, which as a whole is called rebonding procedure. However, the gap might already have been filled with water or debris before applying the sealing resin. We hypothesized that microleakage would decrease if the rebonding agent was applied before the polishing step, i.e., immediately after curing composite resin. On the buccal and lingual surfaces of 35 extracted human molar teeth, class V cavities were prepared withthe occlusal margin in enamel and the gingival margin in dentin. They were restored with a hybrid composite resin Z250 (3M ESPE, USA) using an adhesive AdperTM Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE). As rebonding agents, BisCover LV (Bisco, USA), ScotchBond Multi-Purpose adhesive (3M ESPE) and an experimental adhesive were applied on the restoration margins before polishing step or after successive polishing and etching steps. The infiltration depth of 2% methylene blue into the margin was measured using an optical stereomicroscope. The correlation between viscosity of rebonding agents and mciroleakage was also evaluated. There were no statistically significant differences in the microleakage within the rebonding procedures, within the rebonding agents, and within the margins. However, when the restorations were not rebonded, the microleakage at gingival margin was significantly higher than those groups rebonded with 3 agents (p < 0.05). The difference was not observed at the occlusal margin. No significant correlation was found between viscosity of rebonding agents and microleakage, except very weak correlation in case of rebonding after polishing and etching at gingival margin (r = -0.326, p = 0.041). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef
-
1,239
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
-
So-Rae Seong, Duck-kyu Seo, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):125-133. Published online March 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.125
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
Rapid polymerization of overlying composite resin causes high polymerization shrinkage stress at the adhesive layer. In order to alleviate the shrinkage stress, increasing the light intensity over the first 5 seconds was suggested as an exponential curing mode by an LED light curing unit (Elipar FreeLight2, 3M ESPE). In this study, the effectiveness of the exponential curing mode on reducing stress was evaluated with measuring microtensile bond strength of three adhesives after the overlying composite resin was polymerized with either continuous or exponential curing mode.
Methods
Scotchbond Multipurpose Plus (MP, 3M ESPE), Single Bond 2 (SB, 3M ESPE), and Adper Prompt (AP, 3M ESPE) were applied onto the flat occlusal dentin of extracted human molar. The overlying hybrid composite (Denfil, Vericom, Korea) was cured under one of two exposing modes of the curing unit. At 48h from bonding, microtensile bond strength was measured at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. The fractured surfaces were observed under FE-SEM.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference in the microtensile bond strengths of each adhesive between curing methods (Two-way ANOVA, p > 0.05). The microtensile bond strengths of MP and SB were significantly higher than that of AP (p < 0.05). Mixed failures were observed in most of the fractured surfaces, and differences in the failure mode were not observed among groups.
Conclusion
The exponential curing method had no beneficial effect on the microtensile dentin bond strengths of three adhesives compared to continuous curing method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 139. CrossRef
-
1,206
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The effect of the amount of interdental spacing on the stress distribution in maxillary central incisors restored with porcelain laminate veneer and composite resin: A 3D-finite element analysis
-
Junbae Hong, Seung-Min Tak, Seung-Ho Baek, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):30-39. Published online January 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.030
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study evaluated the influence of the type of restoration and the amount of interdental spacing on the stress distribution in maxillary central incisors restored by means of porcelain laminate veneers and direct composite resin restorations.
Three-dimensional finite element models were fabricated to represent different types of restorations. Four clinical situations were considered. Type I, closing diastema using composite resin. Labial border of composite resin was extended just enough to cover the interdental space; Type II, closing diastema using composite resin without reduction of labial surface. Labial border of composite resin was extended distally to cover the half of the total labial surface; Type III, closing diastema using composite resin with reduction of labial surface. Labial border of the preparation and restored composite resin was extended distally two-thirds of the total labial surface; Type IV, closing diastema using porcelain laminate veneer with a feathered-edge preparation technique. Four different interdental spaces (1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 mm) were applied for each type of restorations.
For all types of restoration, adding the width of free extension of the porcelain laminate veneer and composite resin increased the stress occurred at the bonding layer. The maximum stress values observed at the bonding layer of Type IV were higher than that of Type I, II and III. However, the increasing rate of maximum stress value of Type IV was lower than that of Type I, II and III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Revamping the Peg Smile: An Art of Rehabilitation of Peg Laterals with Ceramic Veneers and Composite Restorations—A Case Report
Mahendran Kavitha, Ramdhas Annapurani, Pasupathy Shakunthala, Jayavel Nandhakumar
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022; 6(2): 69. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Diastema Restoration with Prefabricated Sectional Veneers
Claudio Novelli, Andrea Scribante
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(2): 60. CrossRef
-
1,383
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Pulp response of beagle dog to direct pulp capping materials: Histological study
-
Ji-Hyun Bae, Young-Gyun Kim, Pil-Young Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Yong-Hoon Choi
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):5-12. Published online January 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.005
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the pulp tissue reaction to direct pulp capping of mechanically exposed beagle dogs'pulp with several capping materials. A total of 36 teeth of 2 healthy beagle dongs were used. The mechanically exposed pulps were capped with one of the followings: (1) Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA: ProRoot® MTA, Dentsply, Tulsa, USA), (2) Clearfil SE Bond (Dentin adhesive system: Kuraray, Osaka, Japan), (3) Ultra-Blend (Photo-polymerized Calcium hydroxide: Ultradent, South Jordan, USA), (4) Dycal (Quick setting Calcium hydroxide: LD Caulk Co., Milford, USA) at 7, 30, and 90 days before sacrificing. The cavities were restored with Z350 flowable composite resin (3M ESPE, St. Paul. MN, USA). After the beagle dogs were sacrificed, the extracted teeth were fixed, decalcified, prepared for histological examination and stained with HE stain. The pulpal tissue responses to direct pulp capping materials were assessed.
In MTA, calcium hydroxide, and photo-polymerized calcium hydroxide groups, initial mild inflammatory cell infiltration, newly formed odontoblast-like cell layer and hard tissue bridge formation were observed. Compared with dentin adhesive system, these materials were biocompatible and good for pulp tissue regeneration.
In dentin adhesive system group, severe inflammatory cell infiltration, pulp tissue degeneration and pulp tissue necrosis were observed. It seemed evident that application of dentin adhesive system in direct pulp capping of beagle dog teeth cannot lead to acceptable repair of the pulp tissue with dentine bridge formation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Experimental Study of Pulp Capping Using Xenogenic Demineralized Dentin Paste
Ji-Young Yun, Yong-Hoon Choi, Young-Kyun Kim, In-Woong Um, Joo-Cheol Park, Ji-Yoon Kim
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2016; 25(3): 321. CrossRef - Comparison of gene expression profiles of human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 397. CrossRef - Gene expression profiling in human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 152. CrossRef - Histology of dental pulp healing after tooth replantation in rats
Eun-Jin Go, Han-Seong Jung, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 273. CrossRef
-
1,344
View
-
11
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Real-time measurement of dentinal tubular fluid flow during and after amalgam and composite restorations
-
Sun-Young Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Ho Baek, Bum-Sun Lim, In-Bog Lee
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):467-476. Published online November 30, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.467
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to measure the dentinal tubular fluid flow (DFF) during and after amalgam and composite restorations. A newly designed fluid flow measurement instrument was made. A third molar cut at 3 mm apical from the CEJ was connected to the flow measuring device under a hydrostatic pressure of 15 cmH2O. Class I cavity was prepared and restored with either amalgam (Copalite varnish and Bestaloy) or composite (Z-250 with ScotchBond MultiPurpose: MP, Single Bond 2: SB, Clearfil SE Bond: CE and Easy Bond: EB as bonding systems). The DFF was measured from the intact tooth state through restoration procedures to 30 minutes after restoration, and re-measured at 3 and 7days after restoration.
Inward fluid flow (IF) during cavity preparation was followed by outward flow (OF) after preparation. In amalgam restoration, the OF changed to IF during amalgam filling and slight OF followed after finishing.
In composite restoration, application CE and EB showed a continuous OF and air-dry increased rapidly the OF until light-curing, whereas in MP and SB, rinse and dry caused IF and OF, respectively. Application of hydrophobic bonding resin in MP and CE caused a decrease in flow rate or even slight IF. Light-curing of adhesive and composite showed an abrupt IF. There was no statistically significant difference in the reduction of DFF among the materials at 30 min, 3 and 7 days after restoration (P > 0.05). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Real-time measurement of dentinal fluid flow during desensitizing agent application
Sun-Young Kim, Eun-Joo Kim, In-Bog Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 313. CrossRef
-
1,167
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Finite element analysis of maxillary central incisors restored with various post-and-core applications
-
MinSeock Seo, WonJun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Ho Baek
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):324-332. Published online July 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.324
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of rigidity of post core systems on stress distribution by the theoretical technique, finite element stress-analysis method. Three-dimensional finite element models simulating an endodontically treated maxillary central incisor restored with a zirconia ceramic crown were prepared and 1.5 mm ferrule height was provided. Each model contained cortical bone, trabecular bone, periodontal ligament, 4 mm apical root canal filling, and post-and-core. Six combinations of three parallel type post (zirconia ceramic, glass fiber, and stainless steel) and two core (Paracore and Tetric ceram) materials were evaluated, respectively. A 50 N static occlusal load was applied to the palatal surface of the crown with a 60° angle to the long axis of the tooth. The differences in stress transfer characteristics of the models were analyzed. von Mises stresses were chosen for presentation of results and maximum displacement and hydrostatic pressure were also calculated. An increase of the elastic modulus of the post material increased the stress, but shifted the maximum stress location from the dentin surface to the post material. Buccal side of cervical region (junction of core and crown) of the glass fiber post restored tooth was subjected to the highest stress concentration. Maximum von Mises stress in the remaining radicular tooth structure for low elastic modulus resin core (29.21 MPa) was slightly higher than that for high elastic modulus resin core (29.14 MPa) in case of glass fiber post. Maximum displacement of glass fiber post restored tooth was higher than that of zirconia ceramic or stainless steel post restored tooth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of stress distribution on an endodontically treated maxillary central tooth with lesion restored with different crown materials: A finite element analysis
Ömer Kirmali, Gülsah Icen, H. Kursat Celik, Allan E.W. Rennie
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e25829. CrossRef - The mechanical and physical properties of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC)/sisal/PMMA hybrid composites for dental applications
Harini Sosiati, Arif Muhammad Rizky, Aldi Lukman Maulana Latief, Rahmad Kuncoro Adi, Sinin Hamdan
Materials Research Express.2023; 10(3): 035301. CrossRef - Influence of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in the immature tooth model
Jong-Hyun Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Il-Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 257. CrossRef
-
1,620
View
-
7
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Histological evaluation of direct pulp capping with DSP-derived synthetic peptide in beagle dog
-
Jae-Hoon Kim, Jun-Bae Hong, Bum-Soon Lim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):120-129. Published online January 14, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.120
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the pulpal response to direct pulp capping with dentin sialo-protein (DSP) -derived synthetic peptide in teeth of dogs, and to compare its efficacy to capping substances Ca(OH)2 and white mineral trioxide aggregate (WMTA). A total of 72 teeth of 6 healthy male beagle dogs were used. The mechanically exposed pulps were capped with one of the following: (1) DSP-derived synthetic peptide (PEP group); (2) Ca(OH)2 (CH group); (3) a mixture paste of peptide and Ca(OH)2 (PEP+CH group); or (4) white MTA (WMTA group). The access cavity was restored with a reinforced glass ionomer cement. Two dogs were sacrificed at each pre-determined intervals (2 weeks, 1 month, and 3 months). After the specimens were prepared for standard histological processing, sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Under a light microscope, inflammatory response and hard tissue formation were evaluated in a blind manner by 2 observers. In the PEP group, only 3 of 17 specimens showed hard tissue formation, indication that the DSP-derived synthetic peptide did not induce proper healing of the pulp. Compared with the CH group, the PEP group demonstrated an increased inflammatory response and poor hard tissue formation. The CH and WMTA groups showed similar results for direct pulp capping in mechanically exposed teeth of dogs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Tubular Dentin Regeneration Using a CPNE7-Derived Functional Peptide
Yoon Lee, Yeoung-Hyun Park, Dong-Seol Lee, You-Mi Seo, Ji-Hyun Lee, Joo-Hwang Park, Han-Wool Choung, So-Hyun Park, Won Shon, Joo-Cheol Park
Materials.2020; 13(20): 4618. CrossRef - Pulp response of beagle dog to direct pulp capping materials: Histological study
Ji-Hyun Bae, Young-Gyun Kim, Pil-Young Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Yong-Hoon Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 5. CrossRef
-
1,592
View
-
7
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
A survey on the use of composite resin in Class II restoration in Korea
-
Dong-Ho Shin, Se-Eun Park, In-Seok Yang, Juhea Chang, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):87-94. Published online March 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.087
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to assess the current materials, methods and difficulties according to the year of licence and educational background of Korean dentists in Class II direct composite resin restorations.
Total 17 questions were included in the questionnaire. Questions were broadly divided into two parts; first, operator's information, and second, the materials and methods used in Class II posterior composite restoration. The questionnaire was sent to dentists enrolled in Korean Dental Association via e-mail. Total 12,193 e-mails were distributed to dentists, 2,612 e-mails were opened, and 840 mails (32.2%) were received from respondents. The data was statically analyzed by chi-square test using SPSS(v. 12.0.1, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
Male dentists among respondents was 79%. 60.3% of the respondents acquired their licences recently (1998-2007), and 77% practiced in private offices. 83.4% have acquired their knowledge through school lectures, conferences and seminars.
For the Class II restorations, gold inlays were preferred by 65.7% of respondents, while direct composite resin restorations were used by 12.1% amalgam users were only 4.4% of respondents.
For the restorative technique, 74.4% of respondents didn't use rubber dam as needed. For the matrix, mylar strip (53.4%), metal matrix (33.8%) and Palodent system (6.5%) were used. 99.6% of respondents restored the Class II cavity by incremental layering.
Obtaining of the tight interproximal contact was considered as the most difficult procedure (57.2%) followed by field isolation (21%).
Among various bonding systems, 22.6% of respondents preferred SE Bond and 20.2% used Single Bond. Z-250 was used most frequently among a variety of composite resins. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A review of dental antibacterial agents and antibacterial modification of composite resins and dentin adhesives
Hojin Moon
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 189. CrossRef - Comparison of operative techniques between female and male dentists in class 2 and class 5 resin composite restorations
Juhea Chang, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 116. CrossRef
-
1,421
View
-
5
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
THE EFFECT OF PRIMING ETCHED DENTIN WITH SOLVENT ON THE MICROTENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF HYDROPHOBIC DENTIN ADHESIVE
-
Eun-Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Bae, Jong-Soon Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, In-Bog Lee, Chang-Keun Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):42-50. Published online January 14, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.042
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
Deterioration of long-term dentin adhesion durability is thought to occur by hydrolytic degradation within hydrophilic domains of the adhesive and hybrid layers. This study investigated the hypothesis that priming the collagen network with an organic solvent displace water without collapse and thereby obtain good bond strength with an adhesive made of hydrophobic monomers and organic solvents. Three experimental adhesives were prepared by dissolving two hydrophobic monomers, bisphenol-A-glycidylmethacrylate (Bis-GMA) and triethylenegly-col dimethacrylate (TEGDMA), into acetone, ethanol or methanol. After an etching and rinsing procedure, the adhesives were applied onto either wet dentin surfaces (wet bonding) or dentin surfaces primed with the same solvent (solvent-primed bonding). Microtensile bond strength (MTBS) was measured at 48 hrs, 1 month and after 10,000 times of thermocycles. The bonded interfaces were evaluated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Regardless of bonding protocols, well-developed hybrid layers were observed at the bonded interface in most specimens. The highest mean MTBS was observed in the adhesive containing ethanol at 48 hrs. With solvent-primed bonding, increased MTBS tendencies were seen with thermocycling in the adhesives containing ethanol or methanol. However, in the case of wet bonding, no increase in MTBS was observed with aging.
-
Is an oxygen inhibition layer essential for the interfacial bonding between resin composite layers?
-
Sun-Young Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Bog Lee
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):405-412. Published online July 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.405
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study was aimed to investigate whether an oxygen inhibition layer (OIL) is essential for the interfacial bonding between resin composite layers or not.
A composite (Z-250, 3M ESPE) was filled in two layers using two aluminum plate molds with a hole of 3.7 mm diameter. The surface of first layer of cured composite was prepared by one of five methods as followings, thereafter second layer of composite was filled and cured: Group 1 - OIL is allowed to remain on the surface of cured composite; Group 2 - OIL was removed by rubbing with acetone-soaked cotton; Group 3 - formation of the OIL was inhibited using a Mylar strip; Group 4 - OIL was covered with glycerin and light-cured; Group 5 (control) - composite was bulk-filled in a layer. The interfacial shear bond strength between two layers was tested and the fracture modes were observed. To investigate the propagation of polymerization reaction from active area having a photo-initiator to inactive area without the initiator, a flowable composite (Aelite Flow) or an adhesive resin (Adhesive of ScotchBond Multipurpose) was placed over an experimental composite (Exp_Com) which does not include a photoinitiator and light-cured. After sectioning the specimen, the cured thickness of the Exp_Com was measured.
The bond strength of group 2, 3 and 4 did not show statistically significant difference with group 1. Groups 3 and 4 were not statistically significant different with control group 5. The cured thicknesses of Exp_Com under the flowable resin and adhesive resin were 20.95 (0.90) um and 42.13 (2.09), respectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Finishing and Polishing of Composite Restoration: Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Among Various Dental Professionals in India
Sankar Vishwanath, Sadasiva Kadandale, Senthil kumar Kumarappan, Anupama Ramachandran, Manu Unnikrishnan, Honap manjiri Nagesh
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Surface Roughness of Composite, Compomer and Carbomer After Curing Through Mylar Strip and Glycerin: A Comparative Study
Asli Topaloglu-Ak, Dilara Çayırgan, Melisa Uslu
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2020; 11(1): 12. CrossRef - Effect of glycerin on the surface hardness of composites after curing
Hyun-Hee Park, In-Bog Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 483. CrossRef
-
2,124
View
-
15
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Shear bond strength of dentin bonding agents cured with a Plasma Arc curing light
-
Youngchul Kwon, Sun-Young Kim, Sae-Joon Chung, Young-Chul Han, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):213-223. Published online May 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.213
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The objective of this study was to compare dentin shear bond strength (DSBS) of dentin bonding agents (DBAs) cured with a plasma arc (PAC) light curing unit (LCU) and those cured with a light emitting diode (LED) LCU. Optical properties were also analyzed for Elipar freelight 2 (3M ESPE); LED LCU, Apollo 95E (DMT Systems); PAC LCU and VIP Junior (Bisco); Halogen LCU. The DBAs used for DSBS test were Scotchbond Multipurpose (3M ESPE), Singlebond 2 (3M ESPE) and Clearfil SE Bond (Kuraray). After DSBS testing, fractured specimens were analyzed for failure modes with SEM.
The total irradiance and irradiance between 450 nm and 490 nm of the LCUs were different. LED LCU showed narrow spectral distribution around its peak at 462 nm whereas PAC and Halogen LCU showed a broad spectrum. There were no significant differences in mean shear bond strength among different LCUs (P > 0.05) but were significant differences among different DBAs (P < 0.001) -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Maryam Khoroushi, Mohammadreza Moharreri, Mohammad Atai
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 155. CrossRef
-
1,317
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The nanoleakage patterns of experimental hydrophobic adhesives after load cycling
-
Suh-Jin Sohn, Ju-Hae Chang, Suk-Ho Kang, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):9-19. Published online January 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.009
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was: (1) to compare nanoleakage patterns of a conventional 3-step etch and rinse adhesive system and two experimental hydrophobic adhesive systems and (2) to investigate the change of the nanoleakage patterns after load cycling. Two kinds of hydrophobic experimental adhesives, ethanol containing adhesive (EA) and methanol containing adhesive (MA), were prepared. Thirty extracted human molars were embedded in resin blocks and occlusal thirds of the crowns were removed. The polished dentin surfaces were etched with a 35% phosphoric acid etching gel and rinsed with water. Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (MP), EA and MA were used for bonding procedure. Z-250 composite resin was built-up on the adhesive-treated surfaces. Five teeth of each dentin adhesive group were subjected to mechanical load cycling. The teeth were sectioned into 2 mm thick slabs and then stained with 50% ammoniacal silver nitrate. Ten specimens for each group were examined under scanning electron microscope in backscattering electron mode. All photographs were analyzed using image analysis software. Three regions of each specimen were used for evaluation of the silver uptake within the hybrid layer. The area of silver deposition was calculated and expressed in gray value. Data were statistically analyzed by two-way ANOVA and post-hoc testing of multiple comparisons was done with the Scheffe's test. Silver particles were observed in all the groups. However, silver particles were more sparsely distributed in the EA group and the MA group than in the MP group (p < .0001). There were no changes in nanoleakage patterns after load cycling. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of the removal of chondroitin sulfate on bond strength of dentin adhesives and collagen architecture
Jong-Ryul Kim, Sang-Jin Park, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 211. CrossRef - The effect of priming etched dentin with solvent on the microtensile bond strength of hydrophobic dentin adhesive
Eun-Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Bae, Jong-Soon Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, In-Bog Lee, Chang-Keun Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 42. CrossRef
-
2,126
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
A clinical evaluation of a bleaching strip containing 2.9% hydrogen peroxide
-
Eun-Sook Park, So-Rae Seong, Seong-Tae Hong, Ji-Eun Kim, So-Young Lee, Soo-Youn Hwang, Shin-Jae Lee, Bo-Hyoung Jin, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):269-281. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.269
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study evaluated the effectiveness and safety of an experimental bleaching strip (Medison dental whitening strip, Samsung medical Co., Anyang, Korea) containing 2.9% hydrogen peroxide. Twenty-three volunteers used the bleaching strips for one and a half hour daily for 2 weeks. As control group, the same strips in which hydrogen peroxide was not included were used by 24 volunteers with the same protocol. The shade change (ΔE*, color difference) of twelve anterior teeth was measured using Shade Vision (X-Rite Inc., S.W. Grandville, MI, USA), Chroma Meter (Minolta Co., Ltd. Osaka, Japan) and Vitapan classical shade guide (Vita Zahnfabrik, Germany). The shade change of overall teeth in the experimental group was significantly greater than that in the control group (p < 0.05) and was easily perceivable. The change resulted from the increase of lightness (CIE L* value) and the decrease of redness (CIE a* value) and yellowness (CIE b* value). The shade change of individual tooth was greatest in canine, and smallest in central incisor. The safety of the bleaching strip was also confirmed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of at-home agents and concentrations on bleaching efficacy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Renata Maria Oleniki Terra, Michael Willian Favoreto, Tom Morris, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105857. CrossRef - Effects of Citrus limon Extract on Oxidative Stress-Induced Nitric Oxide Generation and Bovine Teeth Bleaching
Soon-Jeong Jeong
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(2): 96. CrossRef - Efficacy of a self - applied paint - on whitening gel combined with wrap
Soo-Yeon Kim, Jae-Hyun Ahn, Ji-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2018; 34(3): 175. CrossRef - Effects of a whitening strip combined with a desensitizing primer on tooth color
Hae-Eun Shin, Sang-Uk Im, Eun-Kyung Kim, Jong-Hun Kim, Jae-Hyun Ahn, Youn-Hee Choi, Keun-Bae Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(1): 31. CrossRef - A clinical evaluation of efficacy of an office bleaching gel containing 30% hydrogen peroxide
Sin-Young Kim, Je-Uk Park, Chang-Hyen Kim, Sung-Eun Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 40. CrossRef - The evaluation of clinical efficacy and longevity of home bleaching without combined application of In-office bleaching
Byunk-Gyu Shin, Sung-Eun Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 387. CrossRef - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef - Clinical study of shade improvement and safety of polymer-based pen type BlancTic Forte whitening agent containing 8.3% Carbamide peroxide
Jin-Kyung Lee, Sun-Hong Min, Sung-Tae Hong, So-Ram Oh, Shin-Hye Chung, Young-Hye Hwang, Sung-Yeop You, Kwang-Shik Bae, Seung-Ho Baek, Woo-Cheol Lee, Won-Jun Son, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 154. CrossRef
-
1,615
View
-
3
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Prospective clinical evaluation of three different bonding systems in class V resin restorations with or without mechanical retention
-
Kyung-Wook Lee, Sae-Joon Choung, Young-Chul Han, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Myoung-Hwan Oh, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):300-311. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.300
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to evaluate prospectively the effect of different bonding systems and retention grooves on the clinical performance of resin restorations in non-carious cervical lesions (NCCLs). Thirty-nine healthy adults who had at least 2 NCCLs in their premolar areas were included in this study. One hundred and fifty teeth were equally assigned to six groups: (A) Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (SBMP, 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA, 4th generation bonding system) without retention grooves; (B) SBMP with retention grooves; (C) BC Plus (Vericom Co., Anyang, Gyeonggido, Korea, 5th generation bonding system) without retention grooves; (D) BC Plus with retention grooves; (E) Adper Prompt (3M ESPE, Seefeld, Germany, 6th generation bonding system) without retention grooves; (F) Adper Prompt with retention grooves. All cavities were filled with a hybrid composite resin, Denfil (Vericom Co., Anyang, Gyeonggido, Korea) by one operator. Restorations were evaluated at baseline and at 6-month recall, according to the modified USPHS (United States Public Health Service) criteria. Additionally, clinical photographs were taken and epoxy resin replicas were made for SEM evaluation. At 6-month recall, there were some differences in the number of alpha ratings among the experimental groups. But, despite the differences in the number of alpha ratings, there was no significant difference among the 3 adhesive systems (p > 0.05). There was also no significant difference between the groups with or without mechanical retention (p > 0.05). Follow-ups for longer periods than 6 months are needed to verify the clinical performance of different bonding systems and retention grooves. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of marginal microleakage between low and high flowable resins in class V cavity
Sang-Bae Bae, Young-Gon Cho, Myeong-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 477. CrossRef
-
1,770
View
-
11
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effect of additional coating of bonding resin on the microtensile bond strength of self-etching adhesives to dentin
-
Moon-Kyung Jung, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Young-Chul Han, Sae-Joon Choung
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):103-112. Published online January 14, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.103
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
This study investigated the hypothesis that the dentin bond strength of self-etching adhesive (SEA) might be improved by applying additional layer of bonding resin that might alleviate the pH difference between the SEA and the restorative composite resin. Two SEAs were used in this study; Experimental SEA (Exp, pH: 1.96) and Adper Prompt (AP, 3M ESPE, USA, pH: 1.0). In the control groups, they were applied with two sequential coats. In the experimental groups, after applying the first coat of assigned SEAs, the D/E bonding resin of All-Bond 2 (Bisco Inc., USA, pH: 6.9) was applied as the intermediate adhesive. Z-250 (3M ESPE, USA) composite resin was built-up in order to prepare hourglass-shaped specimens. The microtensile bond strength (MTBS) was measured and the effect of the intermediate layer on the bond strength was analyzed for each SEA using t-test. The fracture mode of each specimen was inspected using stereomicroscope and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM). When D/E bonding resin was applied as the second coat, MTBS was significantly higher than that of the control groups. The incidence of the failure between the adhesive and the composite or between the adhesive and dentin decreased and that of the failure within the adhesive layer increased. According to the results, applying the bonding resin of neutral pH can increase the bond strength of SEAs by alleviating the difference in acidity between the SEA and restorative composite resin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
Sook-Kyung Choi, Ji-Wan Yum, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 397. CrossRef - Aging effect on the microtensile bond strength of self-etching adhesives
JS Park, JS Kim, MS Kim, HH Son, HC Kwon, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(6): 415. CrossRef
-
1,409
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Effect of cavity shape, bond quality and volume on dentin bond strength
-
Hyo-Jin Lee, Jong-Soon Kim, Shin-Jae Lee, Bum-Soon Lim, Seung-Ho Baek, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):450-460. Published online November 30, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.450
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of cavity shape, bond quality of bonding agent and volume of resin composite on shrinkage stress developed at the cavity floor. This was done by measuring the shear bond strength with respect to iris materials (cavity shape; adhesive-coated dentin as a high C-factor and Teflon-coated metal as a low C-factor), bonding agents (bond quality; Scotchbond™ Multi-purpose and Xeno®III) and iris hole diameters (volume; 1 mm or 3 mm in diameter × 1.5 mm in thickness). Ninety-six molars were randomly divided into 8 groups (2 × 2 × 2 experimental setup). In order to simulate a Class I cavity, shear bond strength was measured on the flat occlusal dentin surface with irises. The iris hole was filled with Z250 restorative resin composite in a bulk-filling manner. The data was analyzed using three-way ANOVA and the Tukey test. Fracture mode analysis was also done. When the cavity had high C-factor, good bond quality and large volume, the bond strength decreased significantly. The volume of resin composite restricted within the well-bonded cavity walls is also be suggested to be included in the concept of C-factor, as well as the cavity shape and bond quality. Since the bond quality and volume can exaggerate the effect of cavity shape on the shrinkage stress developed at the resin-dentin bond, resin composites must be filled in a method, which minimizes the volume that can increase the C-factor.
-
Dentin bond strength of bonding agents cured with Light Emitting Diode
-
Sun-Young Kim, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Chung-Moon Um
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(6):504-514. Published online January 14, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.504
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- ABSTRACT
This study compared the dentin shear bond strengths of currently used dentin bonding agents that were irradiated with an LED (Elipar FreeLight, 3M-ESPE) and a halogen light (VIP, BISCO). The optical characteristics of two light curing units were evaluated. Extracted human third molars were prepared to expose the occlusal dentin and the bonding procedures were performed under the irradiation with each light curing unit. The dentin bonding agents used in this study were Scotchbond Multipurpose (3M ESPE), Single Bond (3M ESPE), One-Step (Bisco), Clearfil SE bond (Kuraray), and Adper Prompt (3M ESPE). The shear test was performed by employing the design of a chisel-on-iris supported with a Teflon wall. The fractured dentin surface was observed with SEM to determine the failure mode.
The spectral appearance of the LED light curing unit was different from that of the halogen light curing unit in terms of maximum peak and distribution. The LED LCU (maximum peak in 465 ㎚) shows a narrower spectral distribution than the halogen LCU (maximum peak in 487 ㎚). With the exception of the Clearfil SE bond (P < 0.05), each 4 dentin bonding agents showed no significant difference between the halogen light-cured group and the LED light-cured group in the mean shear bond strength (P > 0.05).
The results can be explained by the strong correlation between the absorption spectrum of cam-phoroquinone and the narrow emission spectrum of LED.
-
MMP-1 and TIMP-1 production in MG-63 cells stimulated with Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharide
-
Won-Kyung Yang, Mi-Ri Kim, Won-Jun Shon, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Chung-Moon Um, Ho-Hyun Son
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):470-478. Published online September 30, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.470
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to monitor the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) produced by human osteosarcoma cell line (MG63) stimulated with Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and to compare the level of secretion before and after the treatment of calcium hydroxide on P. nigrescens LPS.
LPS was extracted and purified from anaerobically cultured P. nigrescens. MG63 cells were stimulated by the LPS (0, 1, 10 µg/ml) or LPS (10 µg/ml) pretreated with 12.5 mg/ml of Ca(OH)2 for 3 days.
Total RNA was isolated from the cell, and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed for quantification of MMP-1 and TIMP-1.
The results were as follows.
1. MMP-1 mRNA expression at 48 hr was highly increased by stimulation with P. nigrescens LPS. The increase was dose-dependent.
2. When stimulated with 1 µg/ml of LPS, TIMP-1 mRNA expression was highly increased at 24 hr and 48 hr. However, TIMP-1 expression was suppressed at higher concentration (10 µg/ml).
3. When P. nigrescens LPS was pretreated with Ca(OH)2, MMP-1 and TIMP-1 gene expression was downregulated.
The results of this study suggest that transcriptional regulation of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 by P. nigrescens LPS could be one of the important mechanisms in bone resorption of periapical inflammation. The result of calcium hydroxide on MMP-1 and TIMP-1 gene expression suppression shows that calcium hydroxide detoxified bacterial LPS and thus should be used the medication of choice for intracanal dressings in root canal infected with black-pigmented bacteria.
-
The effect of cavity wall property on the shear bond strength test using iris method
-
Dong-Hwan Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho, In-Bog Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Hyun-Mi Ryu, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Hyuck-Choon Kwon
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):170-176. Published online March 31, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.170
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
In the unique metal iris method, the developing interfacial gap at the cavity floor resulting from the cavity wall property during polymerizing composite resin might affect the nominal shear bond strength values. The aim of this study is to evaluate that the iris method reduces the cohesive failure in the substrates and the cavity wall property effects on the shear bond strength tests using iris method.
Materials and Methods
The occlusal dentin of 64 extracted human molars were randomly divided into 4 groups to simulate two different levels of cavity wall property (metal and dentin iris) and two different materials (ONE-STEP® and ALL-BOND® 2) for each wall property. After positioning the iris on the dentin surface, composite resin was packed and light-cured. After 24 hours the shear bond strength was measured at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min. Fracture analysis was performed using a microscope and SEM. The data was analyzed statistically by a two-way ANOVA and t-test.
Results
The shear bond strength with metal iris was significant higher than those with dentin iris (p = 0.034). Using ONE-STEP®, the shear bond strength with metal iris was significant higher than those with dentin iris (p = 0.005), but not in ALL-BOND® 2 (p = 0.774). The incidence of cohesive failure was very lower than other shear bond strength tests that did not use iris method.
Conclusions
The iris method may significantly reduce the cohesive failures in the substrates. According to the bonding agent systems, the shear bond strength was affected by the cavity wall property.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of infection control barrier thickness on light curing units
Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Ryun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Chang-Kyu Song, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 368. CrossRef
-
1,419
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Influence of the curing time for the adhesive on the oxygen-inhibited layer thickness and the shear bond strength to dentin
-
Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae, Ho-Hyun Son, In-Bog Lee, Chung-Moon Um, Seung-Ho Baek, Oh-Young Kim, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):177-184. Published online January 14, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.177
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- ABSTRACT
Objectives:
This study investigated the hypothesis that increasing light-curing time would leave the oxygen-inhibited layer (OIL) of the adhesive thinner, and in turn, result in lower shear bond strength (SBS) than those obtained by the routine curing procedures.
Methods:
120 human extracted posterior teeth were randomly divided into three groups for bonding with three adhesives: All Bond 2®, One Step®, and Adper Prompt®. They were subsequently divided into four subgourps with different light-curing time (10, 20, 30 and 60 s). The assigned adhesives were applied on superficial occlusal dentin according to the manufacturer’s instructions and cured with one of the four curing times. Composite resin cylinder, 2.35 mm in diameter, were built on the cured adhesive and light-cured for 40 s. SBS were measured after 24 h from the bonding using a universal testing machine (crosshead speed 1.0 mm/min). The relative thickness of the OIL and the degree of conversion (DC) were determined from the adhesive on a slide glass using FT-NIR in an absorbance mode. Data were analysed with One-way ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple test (p < 0.05).
Results:
With increasing cure time, although there were no significant difference in th SBS of One-step and Adper Prompt (p > 0.05), those of All Bond 2 decreased significantly (p < 0.05). The relative thicknesses of the OIL on each adhesive were not affected by the cure time (p > 0.05). Although the DC of All-Bond 2 were statistically not different with increasing cure time (p > 0.05), those of One-Step and Adper Prompt showed an increasing trends with increasing cure time (p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
Increasing light-curing time did not affect on the relative thickness of the OIL of the adhesives, and in turn, on the SBS to dentin.
-
The effect of viscosity, specimen geometry and adhesion on the linear polymerization shrinkage measurement of light cured composites
-
In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Hyuk-Chun Kwon, Chung-Moon Um, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):457-466. Published online November 30, 2003
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.457
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of study was to investigate the effect of flow, specimen geometry and adhesion on the measurement of linear polymerization shrinkage of light cured composite resins using linear shrinkage measuring device.
Methods
Four commercially available composites - an anterior posterior hybrid composite Z100, a posterior packable composite P60 and two flowable composites, Filtek flow and Tetric flow - were studied. The linear polymerization shrinkage of composites was determined using 'bonded disc method' and 'non-bonded' free shrinkage method at varying C-factor in the range of 1~8 by changing specimen geometry. These measured linear shrinkage values were compared with free volumetric shrinkage values.
The viscosity and flow of composites were determined and compared by measuring the dropping speed of metal rod under constant load.
Results
In non-bonded method, the linear shrinkage approximated one third of true volumetric shrinkage by isotropic contraction. However, in bonded disc method, as the bonded surface increased the linear shrinkage increased up to volumetric shrinkage value by anisotropic contraction. The linear shrinkage value increased with increasing C-factor and approximated true volumetric shrinkage and reached plateau at about C-factor 5~6. The more flow the composite was, reduced linear shrinkage was measured by compensation radial flow.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of cavity size and restoration methods on the cusp deflection in composite restoration
Mi-Ra Lee, In-Bog Lee, Chang-In Seok, Sang-Tag Lee, Chung-Moon Um
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2004; 29(6): 532. CrossRef
-
1,282
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effect of light intensity on the polymerization rate of composite resin using real-time measurement of volumetric change
-
Sung-Ho La, In-Bog Lee, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Kwang-Won Lee, Ho-Hyun Son
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):135-141. Published online March 31, 2002
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.135
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of light intensity variation on the polymerization rate of composite resin using IB system (the experimental equipment designed by Dr. IB Lee) by which real-time volumetric change of composite can be measured.
Methods
Three commercial composite resins [Z100(Z1), AeliteFil(AF), SureFil(SF)] were photopolymerized with Variable Intensity Polymerizer unit (Bisco, U.S.A.) under the variable light intensity (75/150/225/300/375/450mW2) during 20 sec. Polymerization shrinkage of samples was detected continuously by IB system during 110 sec and the rate of polymerization shrinkage was obtained by its shrinkage data. Peak time(P.T.) showing the maximum rate of polymerization shrinkage was used to compare the polymerization rate.
Results
Peak time decreased with increasing light intensity(p<0.05). Maximum rate of polymerization shrinkage increased with increasing light intensity(p<0.05). Statistical analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between peak time and inverse square root of the light intensity (AF:R=0.965, Z1:R=0.974, SF:R=0.927). Statistical analysis revealed a significant negative correlation between the maximum rate of polymerization shrinkage and peak time(AF:R=-0.933, Z1:R=-0.892, SF:R=-0.883), and a significant positive correlation between the maximum rate of polymerization shrinkage and square root of the light intensity (AF:R=0.988, Z1:R=0.974, SF:R=0.946).
Discussion and Conclusions
The polymerization rate of composite resins used in this study was proportional to the square root of light intensity. Maximum rate of polymerization shrinkage as well as peak time can be used to compare the polymerization rate. Real-time volume method using IB system can be a simple, alternative method to obtain the polymerization rate of composite resins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of instrument compliance on the polymerization shrinkage stress measurements of dental resin composites
Deog-Gyu Seo, Sun-Hong Min, In-Bog Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 145. CrossRef
-
1,221
View
-
3
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Microleakage of microfill and flowable composite resins in class V cavity after load cycling
-
Suk-Ho Kang, Oh-young Kim, Myung-Hwan Oh, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Chung-Moon Um, Hyuk-Choon Kwon, Ho-Hyun Son
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):142-149. Published online March 31, 2002
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.142
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Low-viscosity composite resins may produce better sealed margins than stiffer compositions (Kemp-Scholte and Davidson, 1988; Crim, 1989). Flowable composites have been recommended for use in Class V cavities but it is also controversial because of its high rates of shrinkage. On the other hand, in the study comparing elastic moduli and leakage, the microfill had the least leakage (Rundle et al. 1997). Furthermore, in the 1996 survey of the Reality Editorial Team, microfills were the clear choice for abfraction lesions.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microleakage of 6 compostite resins (2 hybrids, 2 microfills, and 2 flowable composites) with and without load cycling.
Notch-shaped Class V cavities were prepared on buccal surface of 180 extracted human upper premolars on cementum margin. The teeth were randomly divided into non-load cycling group (group 1) and load cycling group (group 2) of 90 teeth each. The experimental teeth of each group were randomly divided into 6 subgroups of 15 samples. All preparations were etched, and Single bond was applied. Preparations were restored with the following materials (n=15): hybrid composite resin [Z250(3M Dental Products Inc. St.Paul, USA), Denfil(Vericom, Ahnyang, Korea)], microfill [Heliomolar RO(Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein), Micronew(Bisco Inc. Schaumburg, IL, USA)], and flowable composite [AeliteFlo(Bisco Inc. Schaumburg, IL, USA), Revolution(Kerr Corp. Orange, CA, USA)]. Teeth of group 2 were subjected to occlusal load (100N for 50,000 cycles) using chewing simulator(MTS 858 Mini Bionix II system, MTS Systems Corp., Minn. USA). All samples were coated with nail polish 1mm short of the restoration, placed in 2% methylene blue for 24 hours, and sectioned with a diamond wheel. Enamel and dentin/cementum margins were analyzed for microleakage on a sclale of 0 (no leakage) to 3 (3/3 of wall). Results were statistically analyzed by Kruscal-Wallis One way analysis, Mann-Whitney U-test, and Student-Newmann-Keuls method. (p=0.05)
Results
1. There was significantly less microleage in enamel margins than dentinal margins of all groups. (p<0.05)
2. There was no significant difference between six composite resin in enamel margin of group 1.
3. In dentin margin of group 1, flowable composite had more microleakage than others but not of significant differences.
4. There was no significant difference between six composite resin in enamel margin of group 2.
5. In dentin margin of group 2, the microleakage were R>A=H=M>D>Z. But there was no significant differences.
6. In enamel margins, load cycling did not affect the marginal microleakage in significant degree.
7. In dentin margins, load cycling did affect the marginal microleakage only in Revolution. (p<0.05)
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of a new resin monomer on the microleakage of composite resin restorations
JH Bae, YK Kim, PY Yoon, MA Lee, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 469. CrossRef
-
1,188
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effects of filler addition to bonding agents on shear bond strength
-
Young Oh, Myung-Hwan Oh, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Hyuk-Choon Kwon, Chung-Moon Um
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(1):44-53. Published online January 31, 2002
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.1.044
-
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Hybrid Layer, Shear Bond Strength, and Fracture Patterns of Titanium Dioxide–Doped Phosphate Glass–Filled Universal Dental Adhesives
Adam bin Husein, Sana Mhd. Fouad Seoudi, Hatem Mostafa El-Damanhoury, Ibrahim Mahmood Aziz, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(01): 044. CrossRef
-
1,859
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Crossref
|