Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Determination of optimal horizontal beam angulations for canal separation in mandibular molars using cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective image-based analysis
- Benedikt Schneider, Tamina Tepe, Daniel Rapp, Wilhelm Frank, Maria Lessani, Constantin von See, Sebastian Fitzek, Jörg Philipp Tchorz
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e9. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
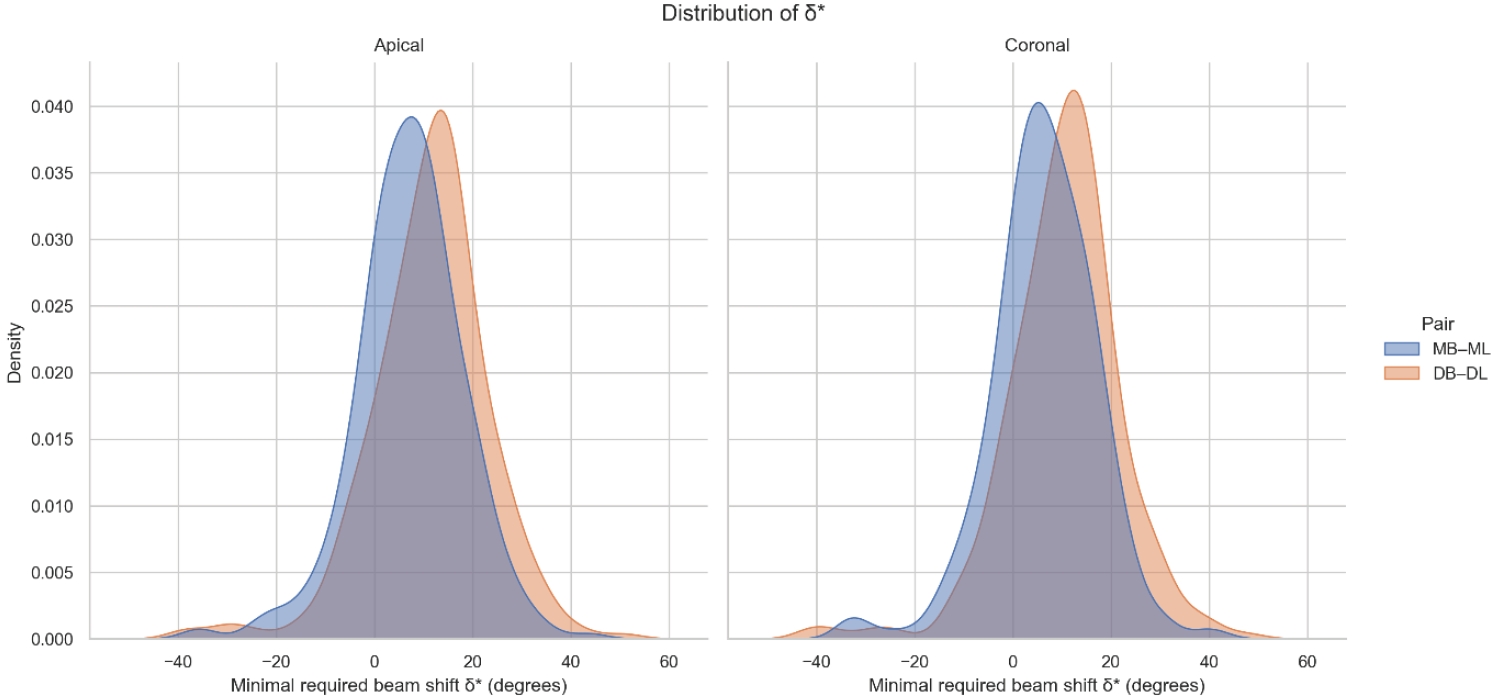
Two-dimensional intraoral radiographs often obscure canals due to superimposition, especially in mandibular molars with complex anatomy. This cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) study identified the horizontal beam angles at which first and second molar canals overlap and derived clinically applicable angulations for enhanced canal separation.
Methods
Eighty-five CBCT datasets from 100 patients met the inclusion criteria, yielding 318 mandibular molars (160 first, 158 second). Using ImageJ, absolute horizontal overlap angles (α) were measured to determine the corresponding theoretical separation angles defined as δ* = 90° – α. Separability was modeled across horizontal beam angulation increments from −45° to +45° in five steps, and Wilson’s 95% confidence intervals were computed. Group comparisons used the Mann-Whitney U and independent t-tests (p ≤ 0.05)
Results
Minimal mesial beam angulations for effective canal separability (δ* = 90° − α) ranged from approximately 7° to 15° for mesial roots and approximately 10° to 13° for distal roots. No significant mesial differences were observed between first and second molars (p > 0.30). Distal roots of second molars exhibited significantly higher angulations (p = 0.003 coronal, p < 0.001 apical). Mesial canals achieved ≥95% separability at approximately 25° and ≥99% at approximately 35°; distal canals required approximately 30° and approximately 40°.
Conclusions
A mesial beam angulation of 30° to 35° provides probable canal differentiation in mandibular molars, separating mesial canals in ≥99% and distal canals in ≥95% of cases. This range refines previous recommendations and supports the as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) principle.
- 377 View
- 14 Download

- Bonding and fractographic characterization of universal adhesives applied to dentin in multimode strategies: an in vitro study
- Samaa M. Morsy, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Naji Kharouf, Ahmed A. Holiel
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e12. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Universal adhesives (UAs) are marketed as versatile systems for both self-etch (SE) and total-etch (TE) modes. While their bond strength has been widely investigated, evidence linking fracture characteristics to bonding performance remains limited. This study evaluated the micro-shear bond strength (μSBS) and failure patterns of three UAs applied in SE and TE modes, complemented by fractographic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
Methods
Eighteen extracted human molars were sectioned to expose mid-coronal dentin and randomly allocated to SE or TE application. Three UAs were tested: Tetric N-Bond Universal, All-Bond Universal, and Single Bond Universal (SBU). Composite micro-rods (n = 72) were bonded, thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5°C and 55°C, and subjected to μSBS testing. Fracture surfaces were examined under SEM and classified as adhesive, cohesive, or mixed. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test, and Spearman correlation (α = 0.05).
Results
In TE mode, SBU demonstrated the highest μSBS (p < 0.001), whereas no significant differences were observed among adhesives in SE mode (p > 0.05). SEM analysis revealed adhesive failures as interfacial fractures, cohesive failures with beach marks, and mixed failures involving crack propagation through both dentin and composite. Adhesive failures correlated negatively with μSBS (rs = –0.77), while mixed failures correlated positively (rs = 0.81).
Conclusions
Both the etching strategy and adhesive formulation significantly affect bond strength and fracture behavior. Fractographic SEM analysis provides critical insights into the mechanical reliability of UAs and informs their clinical application.
- 174 View
- 17 Download

- Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of maxillary premolar canal anatomy: Ahmed’s versus Vertucci’s classifications in a Jordanian cohort
- Raidan Ba-Hattab, Muna M. Shaweesh, Nessrin A. Taha, Elham S. Abu Alhaija
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e11. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
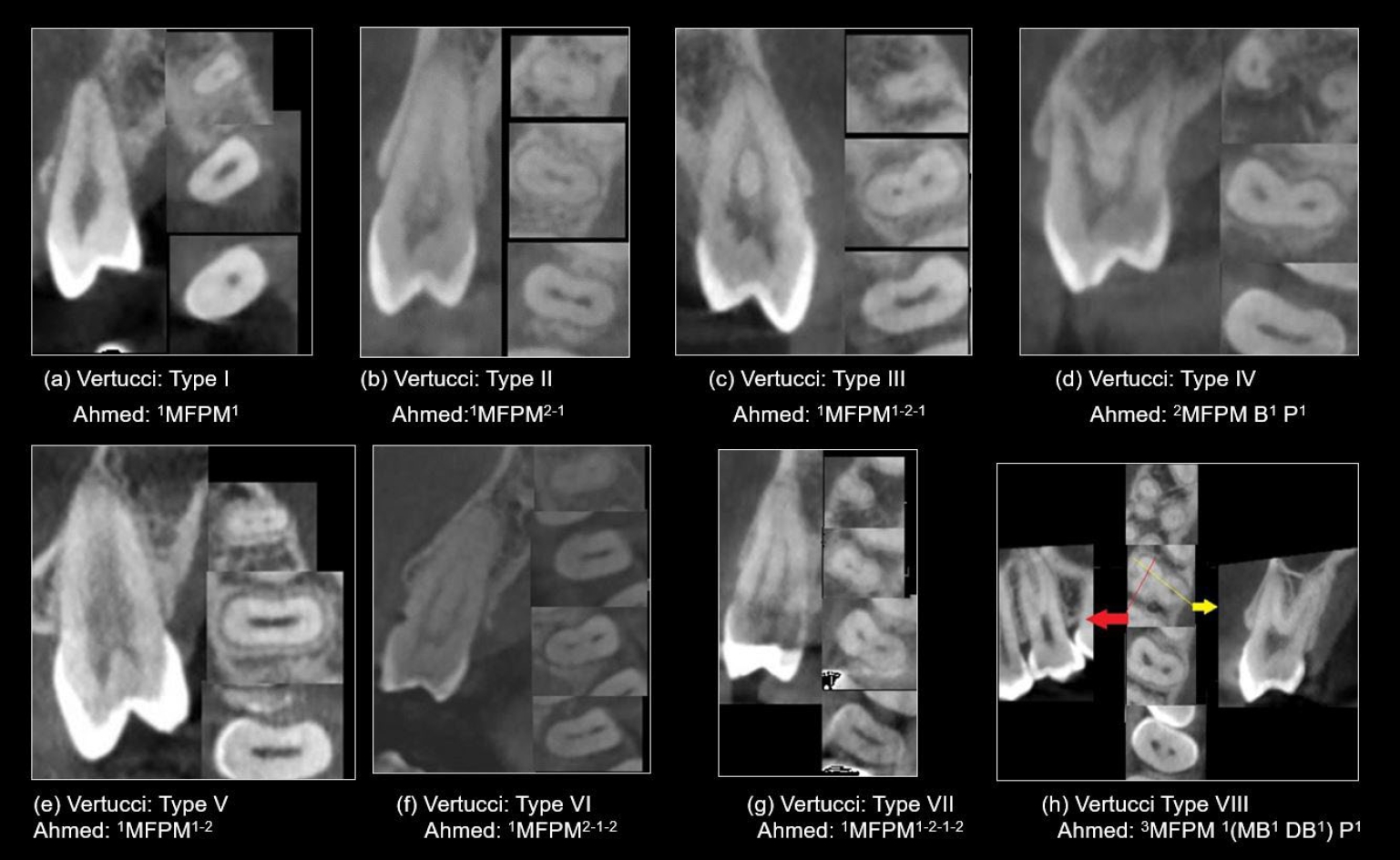
This study analyzed the root and canal configurations of maxillary premolars in a Jordanian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and classified them based on Vertucci’s and Ahmed’s systems.
Methods
Two hundred CBCT scans of 800 maxillary premolars were retrospectively assessed for root morphology, canal configurations, and root canal divergence and merging. Data was statistically analyzed.
Results
The study included 70 males and 130 females. Most right and left maxillary first premolars (RFPM, LFPM) had two roots (59.0% and 58.5%), with a significant association between sex and root number for RFPM and LFPM (p < 0.05). In contrast, the right and left maxillary second premolars (RSPM, LSPM) mostly had a single root (87.5% and 88.5%), with no association with sex. Vertucci’s classification showed type IV as the predominant configuration in first premolars (RFPM, 65.0% and LFPM, 67.0%) and type I in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%). A significant sex association was found only with RSPM. Ahmed’s classification revealed that maxillary premolar with two separated roots and two separated canals (2MP B1 P1) was mostly found in first premolars (RFPM, 58.0% and LFPM, 56.0%), and maxillary premolar with one root and one canal (1MP1) in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%), with a significant sex association for RSPM and LSPM (p < 0.05). Age had no impact, and symmetry was observed between the right and left sides. Three-rooted premolars were identified in four cases. Almost all of Vertucci’s types and numerous codes from Ahmed’s classification were documented.
Conclusions
CBCT revealed diverse anatomical variations in the Jordanian subpopulation, with Ahmed’s classification providing more detailed canal configurations than Vertucci’s, uncovering previously overlooked variations.
- 166 View
- 16 Download

- Enhancing antimicrobial properties of a resin-based material via incorporation of a powdered phytotherapeutic extract: an in vitro experimental study
- Rodolfo Xavier de Sousa-Lima, Maria Eduarda Lima do Nascimento Marinho, Janielly Cristina Costa da Silva, Moan Jéfter Fernandes Costa, Pedro Henrique Sette-de-Souza, Giana da Silveira Lima, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e2. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the degree of conversion (DC), immediate enamel bond strength (IEBS), antimicrobial activity, and release of the active principle of a resin-based material (RBM) enriched with the powdered Schinopsis brasiliensis (Braúna) stem antibacterial extract.
Methods
The RBM was enriched with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 wt% powdered Braúna extract. The DC (n = 7) was assessed using micro-Raman spectroscopy. The IEBS (n = 7) was determined through the microshear test until failure, and failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. The antimicrobial activity (n = 15) was assessed by quantifying colony-forming units, and the release of the active principle was determined using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. One-way analysis of variance/Tukey and Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn tests were utilized to analyze the data (p < 0.05).
Results
Materials with 10 wt% and 20 wt% extract showed the lowest DC statistically. However, for IEBS, there were no statistically significant differences among the different groups. All materials released the active principle, but only those with 20 wt% and 10 wt% extract could inhibit biofilm formation similarly to 0.12% chlorhexidine.
Conclusions
Adding powdered Braúna extract between 10 wt% and 20 wt% is a promising alternative to provide an antimicrobial function to RBMs.
- 520 View
- 28 Download

- Analysis of temperature change during polymerization according to resin thickness: an in vitro experimental study
- Kkot-Byeol Bae, Eun-Young Noh, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e34. Published online November 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the temperature changes during the light curing of conventional flowable composite resin and bulk-fill composite resin of various thicknesses using an infrared thermographic camera.
Methods
Flowable composite resin (G-aenial Flo, GC Co.) and bulk-fill composite resin (SDR, Dentsply Caulk) were used. Specimens with thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 5.0 mm were prepared. The infrared thermographic camera measured the temperature changes at the maximum temperature rise point during light curing. The data were analyzed for maximum temperature, time to peak temperature, and temperature rise patterns.
Results
For G-aenial Flo, the maximum temperature tended to decrease with increasing thickness, whereas for SDR, the maximum temperature decreased up to 2.0 mm and then remained relatively consistent from 2.0 mm to 5.0 mm. At thicknesses of 1.5 mm or less, both resins showed a rapid temperature increase within the first 5 seconds, followed by a reduced rate of increase up to 80 seconds. At thicknesses of 2.0 mm or greater, the temperature peaked and then gradually decreased. Across all thicknesses, SDR was observed to reach peak temperature more rapidly than G-aenial Flo.
Conclusions
Observable differences in polymerization dynamics were identified between the two resin types, particularly at greater thicknesses. Although no statistical analysis was performed, these descriptive findings suggest that infrared thermographic cameras may be useful for indirectly assessing polymerization dynamics during resin polymerization.
- 1,293 View
- 86 Download

- How protocol, posts, and experience affect fracture detection in multi-rooted teeth using cone-beam computed tomography: an ex vivo experimental study
- Gleica Dal’ Ongaro Savegnago, Gabriela Marzullo de Abreu, Carolina Baumgratz Spiger, Lucas Machado Maracci, Wislem Miranda de Mello, Gabriela Salatino Liedke
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e23. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) acquisition protocol, the presence of intraradicular metal post, and examiner experience on the detection of complete root fractures in multi-rooted teeth.
Methods
Twenty human molar teeth filled with gutta-percha were placed into artificial alveoli created in bovine ribs. The sample was divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of intraradicular posts in the distal roots. CBCT scans were obtained using four acquisition protocols with varying voxel sizes (0.28, 0.2, 0.125, and 0.80 mm). Following the creation of controlled fractures using a chisel and hammer, CBCT imaging was repeated, resulting in 160 images. Five examiners assessed the images using OnDemand software (KaVo Dental GmbH). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were calculated for each examiner, CBCT protocol, and post-condition. Statistical comparisons were performed using Cochran’s Q test and McNemar test, and a significance level of 5%.
Results
In teeth without metallic posts, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy values exceeded 0.70, 0.70, and 0.80, respectively. However, the presence of metallic posts significantly reduced diagnostic performance, particularly in low-resolution protocols evaluated by less-experienced examiners.
Conclusions
CBCT acquisition protocols should be selected based on the presence of metallic posts to optimize root fracture detection in multi-rooted teeth. Examiner experience also plays a critical role in diagnostic accuracy.
- 2,363 View
- 101 Download

- Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
- Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e18. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to measure the dentin thickness of C-shaped canals in mandibular first and second premolars at coronal, middle, and apical root levels using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Dentin thicknesses of buccal, lingual, mesial, and distal root walls of 41 C-shaped premolars were measured at three different root levels on axial CBCT slices. The measurements were made at the midpoint of each third, along with 1 mm below and above the midpoint. C-shape configurations of the premolar root canals were also recorded. Analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis, and the independent samples t-tests were used for the comparisons (p = 0.05).
Results
The thickest walls for both premolars were buccal and lingual walls at all three root levels (p < 0.05). The thinnest walls for the first premolar teeth were mesial and distal walls of the lingual canal, while it was the mesial end of the buccal and lingual canals for the second premolars (p < 0.05). Dentin wall thicknesses at the mesial end of buccal and lingual canals of C1-shaped first premolars were thinner than C2-shaped first premolars at the apical level (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Danger zones for C-shaped mandibular first and second premolars are predominantly mesial walls facing the radicular groove and distal wall of the lingual canal. CBCT imaging during endodontic treatment is recommended to avoid complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
- 3,559 View
- 135 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
- Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
- 4,012 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical management of maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin after reestablishing maxillary sinus floor healing through a nonsurgical approach: a case report
- Eun-Sook Kang, Min-Kyeong Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e12. Published online April 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
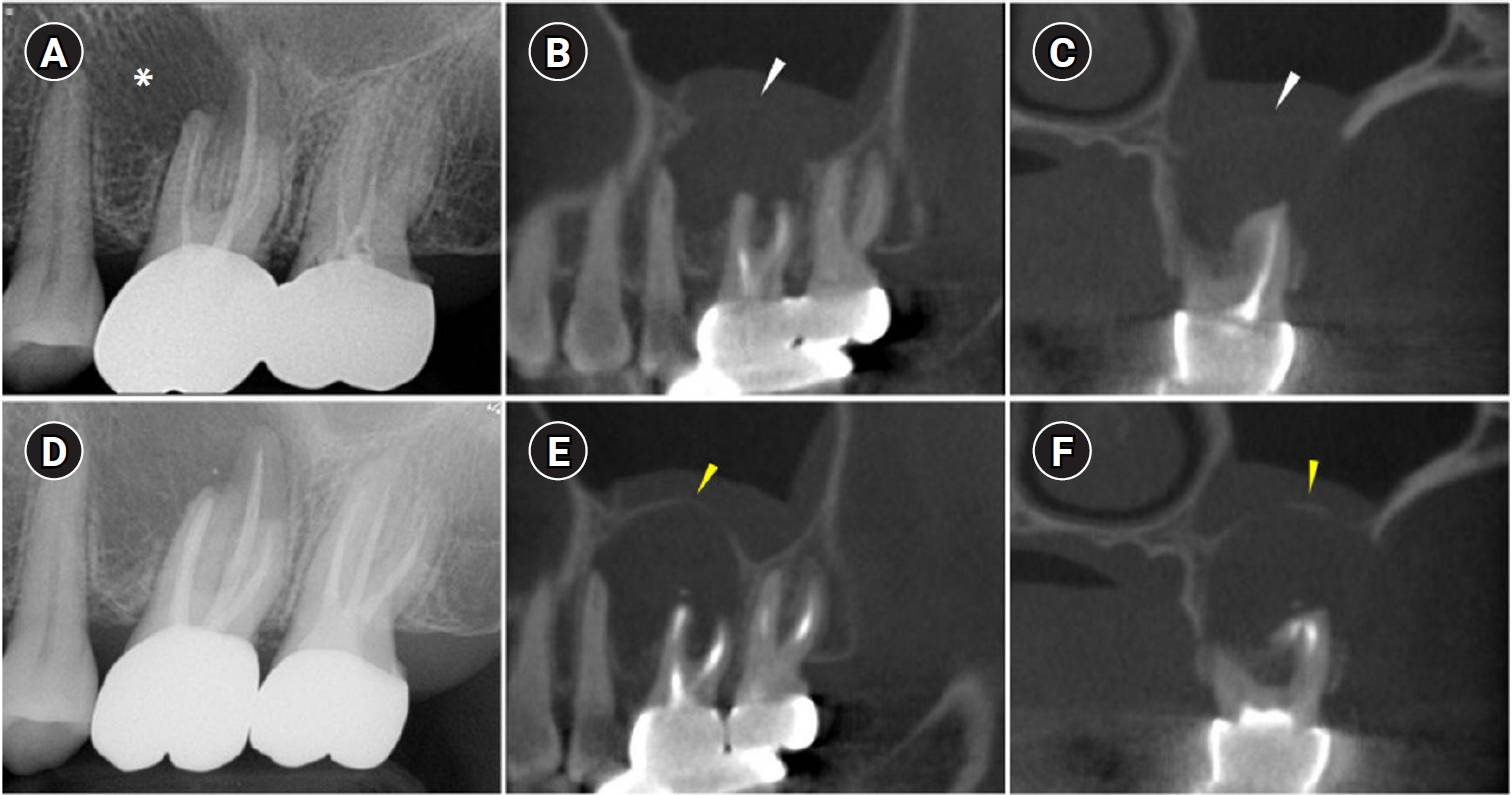
ePub - When root canal infections breach the maxillary sinus floor (MSF), maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin (MSEO) can result. This case illustrates the surgical management of MSEO following the nonsurgical reestablishment of the MSF. A 55-year-old woman presented with left facial pain and was diagnosed with MSEO originating from the left upper first molar. Despite undergoing nonsurgical root canal treatment, there was no evidence of bony healing after 6 months. However, cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) scans revealed the reestablishment of MSF. Subsequently, surgical intervention was carried out using a dental operating microscope. Two years after surgery, CBCT images indicated that the mucosal edema had resolved, and the MSF was well reestablished. Preserving the MSF is crucial for the success of endodontic surgery. When MSEO is present, the integrity of the MSF must be assessed to determine appropriate treatment options.
- 4,091 View
- 208 Download

- An unusual case of dens invaginatus on a mandibular second molar: a case report
- Davide Mancino, Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Fabien Bornert, Youssef Haïkel
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e2. Published online January 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e2

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - The present case report describes the endodontic treatment of a type III B dens invaginatus (DI) in a three-rooted mandibular second molar since the invagination invades the root and extends apically. Clinical and cone-beam computed tomography examination of the mandibular second molar showed a broadened coronal morphology, DI, a third root, periapical radiolucency, and compression of a distal root canal by the invagination, which developed an atypical semilunar shape. The tooth was diagnosed with pulpal necrosis, symptomatic apical, and peri-invagination periodontitis. Consequently, three-dimensional virtual reconstruction was conducted to improve anatomical interpretation and case planning and accelerate the intraoperative phase by reducing operator stress and minimizing intraoperative variables. The present case report aims to raise awareness of the existence of DI on the mandibular second molar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dens Invaginatus—Mandibular Second Molar—Case Report
Krystyna Pietrzycka, Natalia Lutomska, Cornelis H. Pameijer, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(1): 27. CrossRef - Type IIIb dens invaginatus in a maxillary second molar and its microscopic anatomical features: a case report
Mingming Li, Zhiwu Wu, Shaoying Duan, Yuling Zuo
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dens Invaginatus—Mandibular Second Molar—Case Report
- 3,290 View
- 238 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
- Jia Min Ng, Yan Yee Lee, Prashanti Chippagiri, Elaheh Ahanin, Abhishek Parolia
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e3. Published online January 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the number and quality of working length (WL) and master cone (MC) radiographs taken during root canal treatment by dental undergraduates, and their associations with the technical quality of root canal fillings (TQRCF) and endodontic outcomes (EO).
Methods
A retrospective evaluation of radiographs from 303 root canal-treated teeth in 231 patients was conducted, with 72 patients attending recall visits to assess EO. The chi-square and one-way analysis of variance tests were performed.
Results
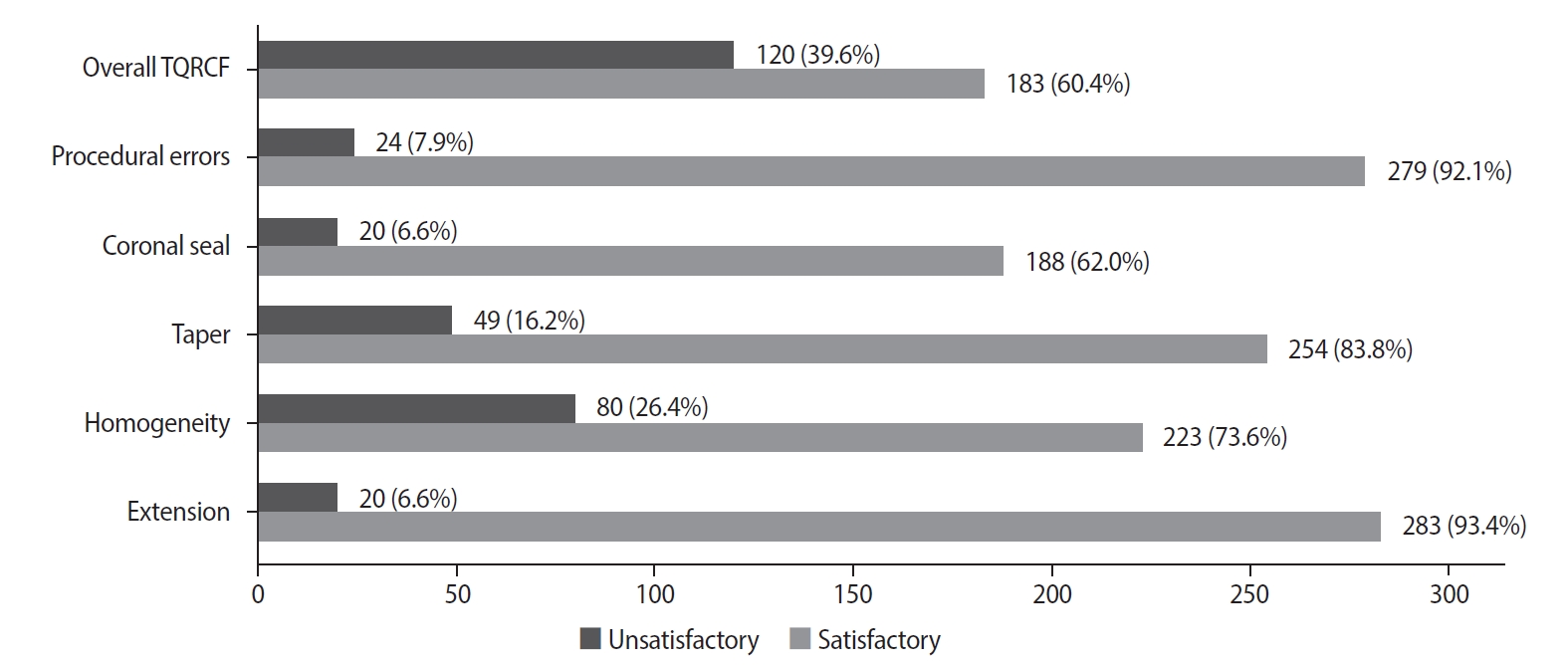
A total of 505 WL and 557 MC radiographs were reviewed, with 72.9% and 75% deemed satisfactory, respectively. Satisfactory TQRCF was achieved in 60.4% of cases. Significant associations were found between the extension of the file in WL and gutta-percha in MC radiographs and TQRCF (p = 0.000). Misinterpretation of these radiographs resulted in poor TQRCF. Furthermore, 64.2% of teeth had satisfactory EO. A significant relationship was noted between the quality of MC radiographs and both TQRCF (p = 0.043) and EO (p = 0.003).
Conclusions
Unsatisfactory MC radiographs were linked to poor TQRCF and unfavorable EO. Regular radiographic training is recommended to enhance EO. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of radiographic errors and repetition rates in undergraduate endodontic education: a retrospective clinical study
Marwa Ameen, Abdul Rahman Saleh, Dunia Alhadi, Manal Almaslamani
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Periapical Radiography in Root Canal Treatment: A Literature Review
Jennifer Lois Violita Malau, Keizha Allysia Nabila, Widiani Harrista, Regina Amara Ginting, Tassa Kusuma Arya Putri, Jatu Rachel Keshena
Acta Odontologica Indonesia.2025; 1(2): 49. CrossRef
- Assessment of radiographic errors and repetition rates in undergraduate endodontic education: a retrospective clinical study
- 11,631 View
- 264 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Guided endodontics, precision and predictability: a case series of mineralized anterior teeth with follow-up cone-beam computed tomography
- Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Javier Rojas-Gutierrez, Pamela Mejía, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Néstor Ríos-Osorio
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e4. Published online January 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
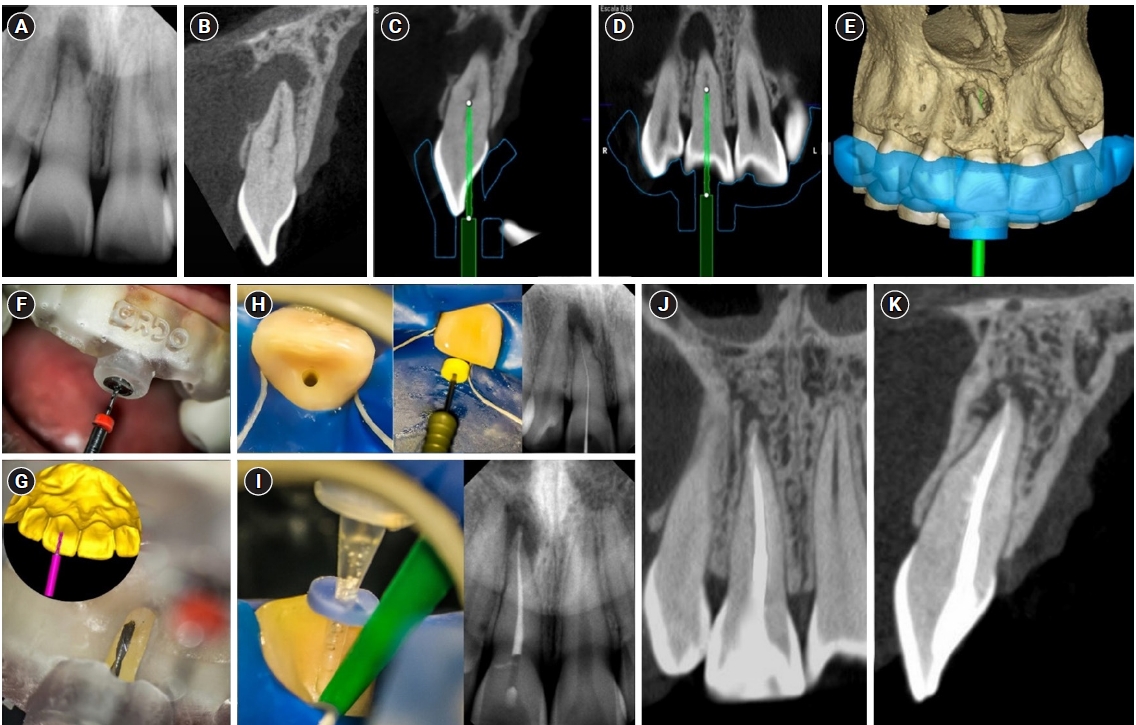
ePub - Pulp chamber and root canal obliteration (PCO/RCO) presents a challenge for clinicians when nonsurgical endodontic treatment is indicated. Guided endodontics (GE) aims to precisely locate the root canal (RC) system while preserving as much pericervical dentin as possible. GE involves integrating cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) of the affected tooth with a digital impression of the maxillary/mandibular arch, allowing for careful planning of the drilling path to the RC system through a three-dimensional (3D) static guide. This article reports four cases of teeth with PCO/RCO, accompanied by additional diagnoses of internal and external root resorption and horizontal tooth fracture, all successfully treated with GE. These cases highlight the clinical and radiographic success of GE treatments using CBCT, establishing this technique as a predictable approach for managing mineralized teeth.
- 4,122 View
- 339 Download

- Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
- Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e37. Published online October 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the physical-mechanical, chemical, and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements (GICs).
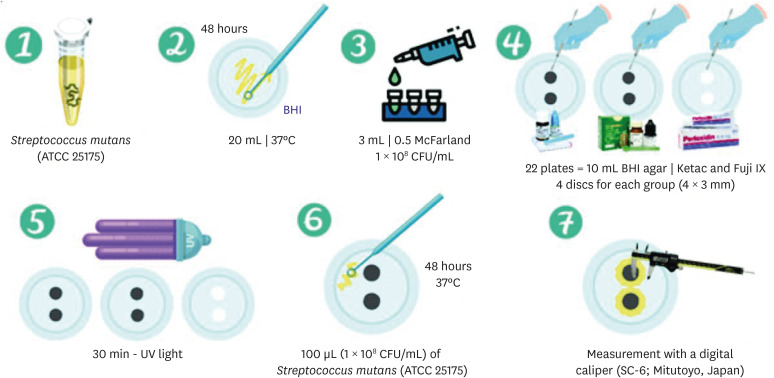
Materials and Methods Different proportions of graphene powder were incorporated into 2 high-viscosity self-curing GIC, Ketac Molar (GKetac) and Fuji IX (GFuji), in 4 different concentrations: 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 5%. The control groups included the GICs without graphene. Experiments were performed to analyze linear (Ra) and volumetric roughness (Sa), antimicrobial activity, radiopacity, fluoride release, microhardness, solubility, and water sorption. Data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis, Mann-Whitney, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance, and Tukey’s test (
p ≤ 0.05).Results The GKetac 0% and GFuji0% groups presented higher Ra (4.05 and 2.72) and Sa (4.76 and 5.16), respectively. No inhibition zone was observed, and the incorporation of graphene reduced radiopacity. Moreover, there was no influence on the solubility and water sorption after 21 days. A greater fluoride release was observed in the period of 7 days for most of the groups. After 21 days, GKetac 5%, 2%, and 1% presented higher releasing than 0% and 0.5% (
p ≤ 0.05).Conclusions The graphene incorporation improved the microhardness of GICs in lower concentrations. Graphene incorporation to GICs modified some physical-mechanical, and chemical, but not affected biological properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laboratory-based additive modifications in glass ionomer cements: A scoping review using a systematic data mining and trend analysis framework (2015-2024)
Kenta Tsuchiya, Sharanbir K Sidhu, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, James Kit Hon Tsoi, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106349. CrossRef
- Laboratory-based additive modifications in glass ionomer cements: A scoping review using a systematic data mining and trend analysis framework (2015-2024)
- 2,832 View
- 177 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of different curing methods on the color stability of composite resins
- Massimo Pisano, Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Andrea Chiacchio, Marzio Galdi, Stefano Martina
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e33. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
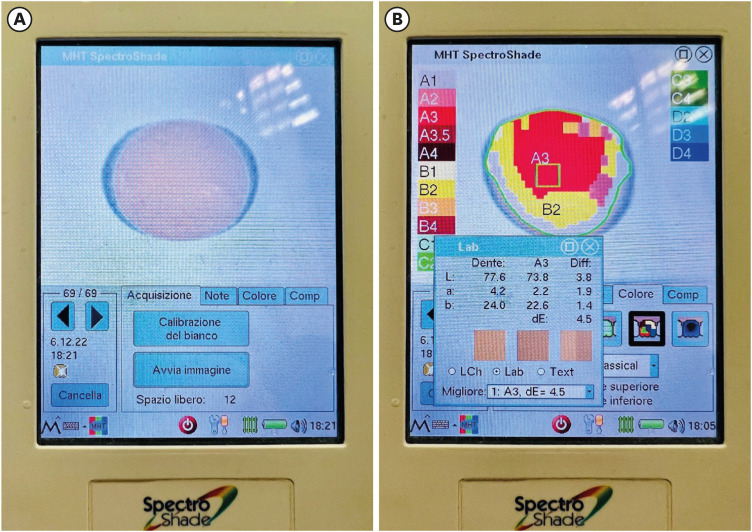
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the effects of different polymerization strategies and the effectiveness of finishing and polishing procedures of composite resins on color stability.
Materials and Methods The samples were divided into 4 main groups according to the polymerization strategy, and all groups except the control group received surface treatment. Each group was subsequently divided into 3 subgroups respectively: Kuraray Clearfil Majesty ES-2 Classic, Premium and Universal. Approximately 24 hours after preparation of the samples, they were immersed for 7 days in a coffee solution. A first color measurement was performed after the preparation of the samples, the second measurement was performed after 7 days in the coffee solution. All measurements were carried out using a dental spectrophotometer to assess the CIE
L *a *b * color parameters.Results There was a statistically significant difference between ΔE values for different procedures (
p = 0.003); in particular, the differences were found only between the groups that received surface treatment and the control group. In addition, a statistically significant difference was observed between the values of ΔE for different composites in the different procedure groups.Conclusions Spectrophotometric analysis showed that the additional photopolymerization and oxygen inhibition procedures did not yield better results in relation to color stability. In addition, finishing and polishing provided better color stability compared to not performing these procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026; 32(1): 94. CrossRef - Abrasiveness and Bleaching Level of Toothpastes on Composite Resins: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Novel Brushing Simulator
Simge Meseli, Elif Alkan, Bora Korkut, Ozlem Kanar, Dilek Tagtekin
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(5): 2314. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Direct and Indirect Composite Restorations in Class II Tooth Preparations - An In vivo Study
Akshun Gupta, Garima Arora, Aprajita Mehta, Satish Sane, Siddhi Nevrekar, Apurva Nagrale
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 550. CrossRef - Micro- and Nanoplastics and the Oral Cavity: Implications for Oral and Systemic Health, Dental Practice, and the Environment—A Narrative Review
Federica Di Spirito, Veronica Folliero, Maria Pia Di Palo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Leonardo Aulisio, Stefano Martina, Luca Rinaldi, Gianluigi Franci
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 332. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 6,305 View
- 343 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of surface sealant on the color stability and whiteness index of single-shade resin composites after staining and bleaching
- Muhammet Fidan, Özhan Yağcı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e30. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
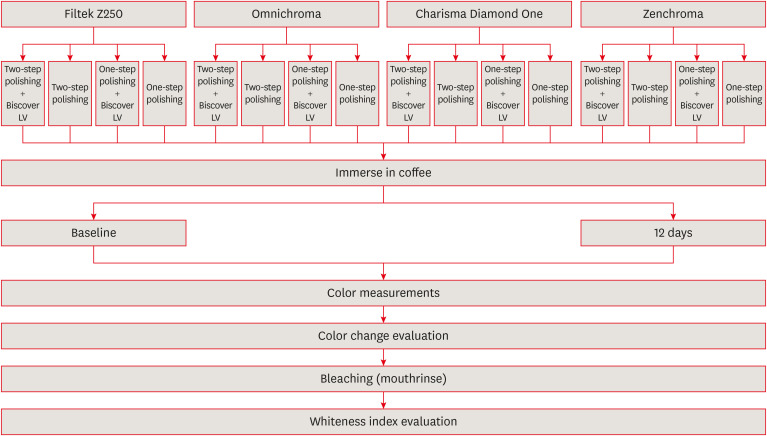
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study was to evaluate the effect of polishing systems and surface sealant on the color stability and whiteness index of single-shade resin composites after staining and bleaching.
Materials and Methods Three single-shade (Omnichroma, Charisma Diamond One, Zenchroma) and one multi-shade (Filtek Z250) materials were tested. From each resin composite, 40 specimens were prepared. The specimens were divided into 4 subgroups (
n = 10) according to the surface treatments: 1-step polishing, 1-step + Biscover LV, 2-step polishing, and 2-step polishing + Biscover LV. Color differences (ΔE00) were calculated after being immersed in the coffee solution for 12 days. After the staining, the specimens were immersed in a whitening mouthrinse (Crest-3D White) for 12 hours. Whiteness index differences (∆WID = WID after staining − WID after bleaching) values were recorded. The generalized linear model was used for analysis (p < 0.05).Results The lowest and highest ΔE00 values were found for Zenchroma and Charisma Diamond One respectively. Sealed groups indicated higher ΔE00 values than nonsealed groups with significant differences (
p = 0.008). The lowest and highest ΔWID values were found for Zenchroma and Charisma Diamond One respectively. Sealed groups indicated lower ΔWID values than nonsealed groups with significant differences (p = 0.022).Conclusions The use of surface sealant increased the discoloration and showed less whiteness change in resin materials. When the 1-step was compared with the 2-step polishing, the effects on the color stability and whiteness index values of the resin materials were similar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color and surface properties of conventional, injectable, and 3D-printed resin composites for anterior restorations: influence of a surface sealant
Soner Sismanoglu
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the effects of bleaching on color stability and surface roughness in single-shade and multi-shade resin composites
Hatice Tepe, Özge Çeliksöz, Zeynep Biçer, Batucan Yaman
Anatolian Current Medical Journal.2024; 6(6): 372. CrossRef
- Color and surface properties of conventional, injectable, and 3D-printed resin composites for anterior restorations: influence of a surface sealant
- 2,954 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

-
Procedural errors detected by cone beam tomography in cases with indication for retreatment:
in vivo cross-sectional study - Henry Paul Valverde Haro, Carmen Rosa Garcia Rupaya, Flávio R. F. Alves
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e26. Published online June 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the frequency and type of endodontic procedural errors in cases indicated for retreatment through cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) analysis.
Materials and Methods The sample consisted of 96 CBCT scans, encompassing 122 permanent teeth with fully formed roots. Errors included perforation, instrument fracture, canal transportation, missed canals, and inadequate apical limit of filling. Additionally, potential risk factors were analyzed and subjected to statistical modeling.
Results The most frequent procedural error observed was the inadequate apical limit of filling, followed by canal transportation, perforation, missed canal, and instrument fracture. Statistically significant associations were identified between various procedural errors and specific factors. These include canal transportation and root canal wall, with the buccal wall being the most commonly affected; missed canal and tooth type, particularly the palatine and second mesiobuccal canal canals; inadequate apical limit of filling and root curvature, showing a higher deviation to the mesial direction in severely curved canals; inadequate apical limit of filling and the presence of calcifications, with underfilling being the most frequent; canal transportation and periapical lesion, notably with deviation to the buccal direction; and the direction of perforation and periapical lesion, most frequently occurring to buccal direction.
Conclusions CBCT emerges as a valuable tool in identifying procedural errors and associated factors, crucial for their prevention and management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
Ariana Esperanza Apolo Aguilar, Maria Soledad Peñaherrera Manosalvas, Henry Paul Valverde Haro
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1007. CrossRef - Impact of Downward Load and Rotational Kinematics on Root Canal Instrumentation with a Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Rotary Instrument
Risako Yamamoto, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Satoshi Omori, Keiko Hirano, Arata Ebihara, Yoshio Yahata, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2025; 19(1): 108. CrossRef - ANALYSIS OF THE QUALITY OF ROOT CANAL OBTURATION AND PREVALENCE OF APICAL PERIODONTITIS IN ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH
Cristina Coralia Nistor, Ioana Suciu , Elena Zabrac , Ruxandra Ioana Bartok , Bogdan Dimitriu , Andreea Baluta
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(4): 311. CrossRef
- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
- 3,031 View
- 121 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Prevalence of apical periodontitis and quality of root canal treatment in an adult Kuwaiti sub-population: a cross-sectional study
- Abdulrahman A. Alhailaa, Saad A Al-Nazhan, Mazen A Aldosimani
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e16. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This cross-sectional study evaluated the prevalence of apical periodontitis (AP) and the technical quality of root canal fillings in an adult Kuwaiti subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Materials and Methods Two experienced examiners analyzed 250 CBCT images obtained from Kuwaiti patients aged 15–65 years who attended government dental specialist clinics between January 2019 and September 2020. The assessment followed the radiographic scoring criteria proposed by De Moor for periapical status and the technical quality of root canal filling. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used for statistical analysis, with significance level set at
p < 0.05.Results Among the 2,762 examined teeth, 191 (6.91%) exhibited radiographic signs of AP, and 176 (6.37%) had undergone root canal filling. AP prevalence in root canal-treated teeth was 32.38%, with a significant difference between males and females. Most of the endodontically treated teeth exhibited adequate root canal filling (71.5%).
Conclusions The study demonstrated a comparable prevalence of AP and satisfactory execution of root canal treatment compared to similar studies in different countries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- RISK FACTORS FOR CHRONIC APICAL PERIODONTITIS ACCORDING TO THE CASE-CONTROL STUDY
N. Bagryantseva
Vrach.2026; : 43. CrossRef - A Retrospective Study of CBCT-Based Detection of Endodontic Failures and Periapical Lesions in a Romanian Cohort
Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Anca Gabriela Gheorghe, Mihaela Jana Țuculină, Maria Cristina Munteanu, Cătălina Alexandra Iacov, Virginia Maria Rădulescu, Mihaela Ionescu, Adina Andreea Mirea, Carina Alexandra Bănică
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6364. CrossRef
- RISK FACTORS FOR CHRONIC APICAL PERIODONTITIS ACCORDING TO THE CASE-CONTROL STUDY
- 4,958 View
- 87 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
- Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e7. Published online January 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
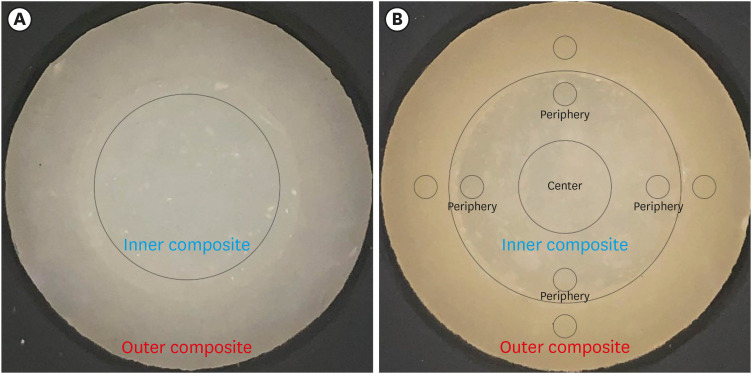
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the impact of substrate color and interface distance on the color adjustment of 2 single-shade composites, Vittra APS Unique and Charisma Diamond One.
Materials and Methods Dual disc-shaped specimens were created using Vittra APS Unique or Charisma Diamond One as the center composite, surrounded by shaded composites (A1 or A3). Color measurements were taken with a spectrophotometer against a gray background, recording the color coordinates in the CIELAB color space. Illumination with a light-correcting device and image acquisition using a polarizing filter-equipped cell phone were performed on specimens over the same background. Image processing software was used to measure the color coordinates in the center and periphery of the inner composite and in the outer composite. The color data were then converted to CIELAB coordinates and adjusted using data from the spectrophotometer. Color differences (ΔE00) between the center/periphery of single-shade and outer composites were calculated, along with color changes in single-shade composites caused by different outer composites. Color differences for the inner composites surrounded by A1 and A3 were also calculated. Data were analyzed using repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05).
Results The results showed that color discrepancies were lowest near the interface and when the outer composite was whiter (A1). Additionally, Charisma Diamond One exhibited better color adjustment ability than Vittra APS Unique.
Conclusions Color discrepancies between the investigated single-shade composites diminished towards the interface with the surrounding composite, particularly when the latter exhibited a lighter shade.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Staining Resistance of Two Single-Shade Composites in Coffee and Chlorhexidine: A Spectrophotometric Analysis
Unmesh Khanvilkar, Shrinath D Kulkarni, Siddhesh Bandekar, Ved M Talathi, Oshin Baghel, Priyanka Razdan, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Implications of Color Adjustment in Single-Shade Resins Post-Dental Bleaching: A Systematic Review
Samille Biasi Miranda, Caroline de Farias Charamba Leal, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Antonio Japiassu Resende Montes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(9): 3194. CrossRef - Accuracy and Reliability of Smartphone Versus Mirrorless Camera Images-Assisted Digital Shade Guides: An In Vitro Study
Soo Teng Chew, Suet Yeo Soo, Mohd Zulkifli Kassim, Khai Yin Lim, In Meei Tew
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 8070. CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,355 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

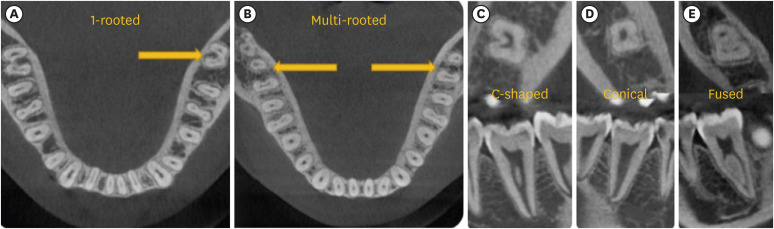
- Predictor factors of 1-rooted mandibular second molars on complicated root and canal anatomies of other mandibular teeth
- Hakan Aydın, Hatice Harorlı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e2. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to determine the effects of 1-rooted mandibular second molar (MnSM) teeth on root canal anatomy complexities of the mandibular central incisor (MnCI), mandibular lateral incisor (MnLI), mandibular canine (MnCn), mandibular first premolar (MnFP), mandibular second premolar (MnSP), and mandibular first molar (MnFM) teeth.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography images of 600 patients with full lower dentition were examined. Individuals with 1-rooted MnSMs were determined, and the complexity of root canal anatomy of other teeth was compared with individuals without 1-rooted MnSMs (Group-1; subjects with at least one 1-rooted MnSM, Group-2; subjects with more than a single root in both MnSMs). A second canal in MnCIs, MnLIs, MnCns, MnFPs, and MnSPs indicated a complicated root canal. The presence of a third root in MnFMs was recorded as complicated.
Results The prevalence of 1-rooted MnSMs was 12.2%, with the C-shaped root type being the most prevalent (9%). There were fewer complicated root canals in MnCIs (
p = 0.02), MnLIs (p < 0.001), and MnFPs (p < 0.001) in Group 1. The other teeth showed no difference between the groups (p > 0.05). According to logistic regression analysis, 1-rooted right MnSMs had a negative effect on having complex canal systems of MnLIs and MnFPs. Left MnSMs were explanatory variables on left MnLIs and both MnFPs.Conclusions In individuals with single-rooted MnSMs, a less complicated root canal system was observed in all teeth except the MnFMs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
Ariana Esperanza Apolo Aguilar, Maria Soledad Peñaherrera Manosalvas, Henry Paul Valverde Haro
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1007. CrossRef
- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
- 1,930 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

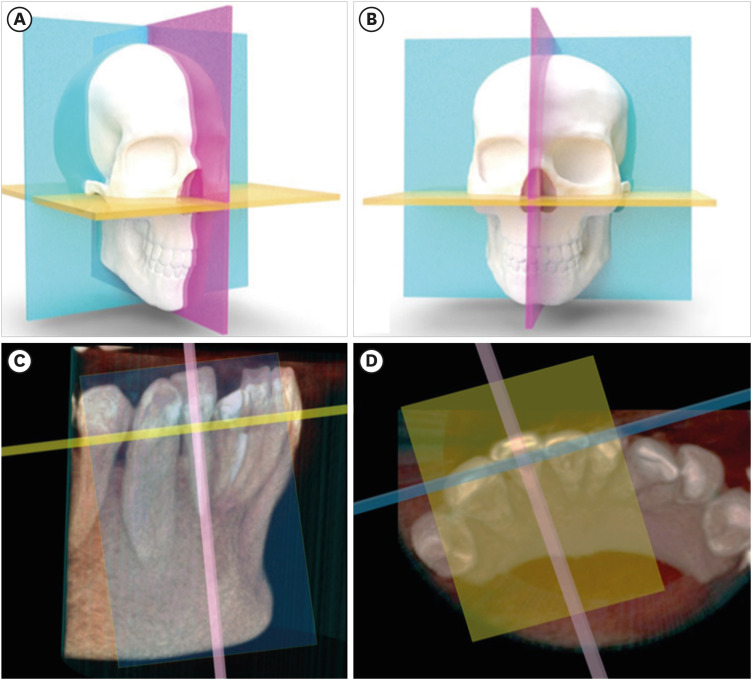
- Cone-beam computed tomography in endodontics: from the specific technical considerations of acquisition parameters and interpretation to advanced clinical applications
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Sara Quijano-Guauque, Sandra Briñez-Rodríguez, Gustavo Velasco-Flechas, Antonieta Muñoz-Solís, Carlos Chávez, Rafael Fernandez-Grisales
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e1. Published online December 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The implementation of imaging methods that enable sensitive and specific observation of anatomical structures has been a constant in the evolution of endodontic therapy. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) enables 3-dimensional (3D) spatial anatomical navigation in the 3 volumetric planes (sagittal, coronal and axial) which translates into great accuracy for the identification of endodontic pathologies/conditions. CBCT interpretation consists of 2 main components: (i) the generation of specific tasks of the image and (ii) the subsequent interpretation report. A systematic and reproducible method to review CBCT scans can improve the accuracy of the interpretation process, translating into greater precision in terms of diagnosis and planning of endodontic clinical procedures. MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, Google Scholar, Embase and Scopus were searched from inception to March 2023. This narrative review addresses the theoretical concepts, elements of interpretation and applications of the CBCT scan in endodontics. In addition, the contents and rationale for reporting 3D endodontic imaging are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
Aishwarya Talakeri, Pravin Kumar, Soundharrajan P, Vinay Kumar Chugh , Rajat Sharma, Arun Patnana
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and morphometric assessment of the middle mesial canal in mandibular first molars in a turkish population: A CBCT study
Elif Solakoğlu, Özge Kurt
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Pathologies in Children and Adolescents with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study
Ayşe Çelik, Nilüfer Ersan, Senem Selvi-Kuvvetli
The Cleft Palate Craniofacial Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - Early diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia utilizing clinical, radiographic, and dental age indicators
Rehab F Ghouraba, Shaimaa S. EL-Desouky, Mohamed R. El-Shanshory, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Nancy M. Metwally
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of apexogenesis with human treated dentin matrix in young permanent molars: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
Nora M. Abo Shanady, Nahed A. Abo Hamila, Gamal M. El Maghraby, Rehab F. Ghouraba
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Integration of Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality in Dental Diagnostics, Surgical Planning, and Education: A Narrative Review
Aida Meto, Gerta Halilaj
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(11): 6308. CrossRef - Healing Outcomes of Through‐And‐Through Bone Defects in Periapical Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Bibi Fatima, Farhan Raza Khan, Syeda Abeerah Tanveer
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 518. CrossRef - Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of cone beam computed tomography on exfoliated epithelial cells in different age groups
Maged Bakr, Fatma Ata, Asmaa Saleh Elmahdy, Bassant Mowafey
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bridging the gap in aberrant root canal systems: Case series
Seethalakshmi Tamizhselvan, Diana Davidson, Srinivasan Manali Ramakrishnan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 833. CrossRef - IMAGING TECHNIQUES IN ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Mihaela Salceanu, Anca Melian , Tudor Hamburda , Cristina Antohi , Corina Concita , Claudiu Topoliceanu , Cristian Levente Giuroiu
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(1): 705. CrossRef - A Three-rooted Deciduous Second Molar in a 13-year-old Caucasian Female
Daniel Traub, Robert Walsh, Colleen Ahern
International Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025; 4(3): 51. CrossRef - Critical success factors for digital transformation in government organizations using a structural model approach
Abdalla Al Maazmi, Zehra Canan Araci, Sujan Piya
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - AGE ESTIMATION BASED ON PULP / TOOTH VOLUME BY CONE BEAM COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGE
Ramadhan Rasheed, Salah Faraj
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 288. CrossRef - Clinical Benefits and Limitations of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontic Practice: A Contemporary Evidence-Based Review
Jasmine Wong, Chengfei Zhang, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3117. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bildgebung im ZMK-Bereich – aber in welcher Reihenfolge?
Rainer Lutz
Zahnmedizin up2date.2024; 18(04): 297. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of shaping ability of kedo-S square and fanta AF™ baby rotary files compared to manual K-files in root canal preparation of primary anterior teeth
Shaimaa S. El-Desouky, Bassem N. El Fahl, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Shimaa M. Hadwa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Endodontic Successes and Failures in the Removal of Fractured Endodontic Instruments during Retreatment: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Corrado Dello Russo, Filippo Scarano, Fariba Esperouz, Andrea Ballini, Diego Sovereto, Mario Alovisi, Angelo Martella, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Healthcare.2024; 12(14): 1390. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
- 16,884 View
- 694 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

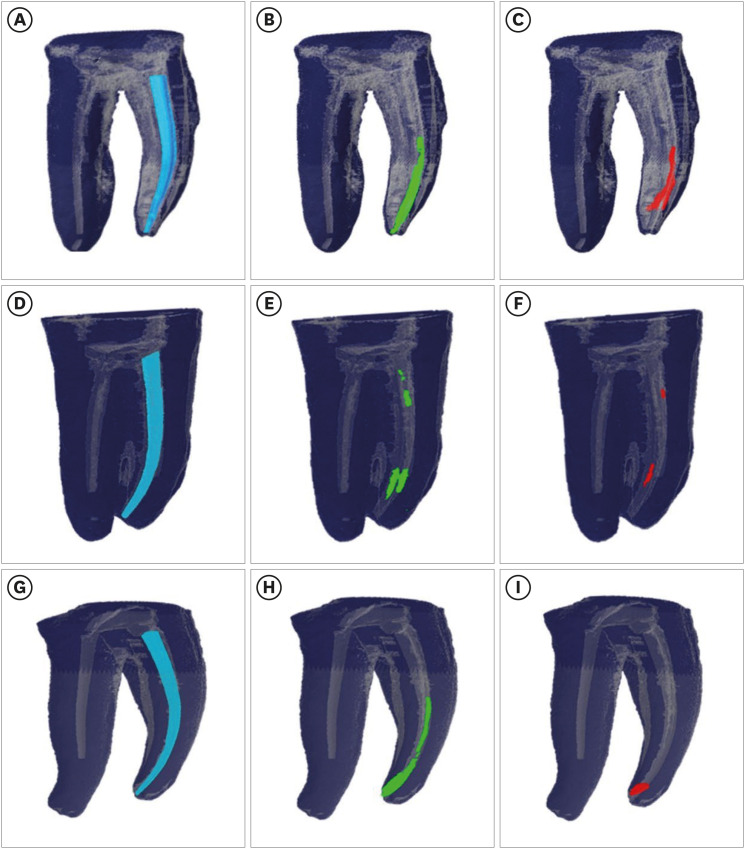
- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
- Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e36. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of a single-file reciprocating system (WaveOne Gold, WOG) and a multi-file rotary system (ProTaper Universal Retreatment, PTUR) in removing canal filling from severely curved canals and to evaluate the possible adjunctive effects of XP-Endo Finisher (XPF), the Self-Adjusting File (SAF), and an erbium, chromium: yttrium, scandium, gallium garnet (Er,Cr:YSGG) laser using micro-computed tomography (μCT).
Materials and Methods Sixty-six curved mandibular molars were divided into 2 groups based on the retreatment technique and then into 3 based on the supplementary method. The residual filling volumes and root canals were evaluated with μCT before and after retreatment, and after the supplementary steps. The data were statistically analyzed with the
t -test, Mann-WhitneyU test, analysis of covariance, and factorial analysis of variance (p < 0.05).Results PTUR and WOG showed no significant difference in removing filling materials (
p > 0.05). The supplementary techniques were significantly more effective than reciprocating or rotary systems only (p < 0.01). The supplementary steps showed no significant differences in canal filling removal effectiveness (p > 0.05), but XPF showed less dentin reduction than the SAF and Er,Cr:YSGG laser (p < 0.01).Conclusions The supplementary methods significantly decreased the volume of residual filling materials. XPF caused minimal changes in root canal volume and might be preferred for retreatment in curved root canals. Supplementary approaches after retreatment procedures may improve root canal cleanliness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology
Kıvanç Kamburoğlu
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrieval of AH Plus Bioceramic and Ceraseal Versus AH Plus in Endodontic Retreatment
Eurok Shim, Jee Woo Son, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(6): 1826. CrossRef - Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP‐Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
Sarah M. Alkahtany, Rana Alfadhel, Aseel AlOmair, Sarah Bin Durayhim, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the filling technique on the filling removal from oval-shaped canals
Lislaine Valerio, Lisa Yurie Oda, Felipe Andretta Copelli, Clarissa Teles Rodrigues, Everdan Carneiro, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology
- 4,093 View
- 97 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Does photobiomodulation on the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth? A systematic review of animal studies
- Theodoro Weissheimer, Karolina Frick Bischoff, Carolina Horn Troian Michel, Bruna Barcelos Só, Manoela Domingues Martins, Matheus Albino Souza, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e24. Published online June 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This review aimed to answer the following question “Does photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth?” Electronic searches were performed in the MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Grey Literature Report databases. Risk of bias was evaluated using SYRCLE Risk of Bias tool. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) tool was used to assess the certainty of evidence. In total, 6 studies were included. Five studies reported a reduced occurrence of root resorption in teeth that received photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation. Only 1 study reported contradictory results. The photobiomodulation parameters varied widely among studies. GRADE assessment showed a low certainty of evidence. It can be inferred that photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation of teeth can reduce the occurrence of root resorption. Nonetheless, further clinical studies are needed.
Trial Registration PROSPERO Identifier: CRD42022349891
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
Noriaki Yoshihashi
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 85. CrossRef - Evidence Mapping and Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews in Dental Traumatology: A 54 Months Update
Nitesh Tewari, Pavithra Devi, Hemlata Nehta, Ekta Wadhwani, Rigzen Tamchos, Georgios Tsilingaridis, Vijay Prakash Mathur, Morankar Rahul
Dental Traumatology.2025; 41(6): 727. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Literature Watch September 2023
James D. Carroll
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(7): 498. CrossRef
- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
- 2,874 View
- 44 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

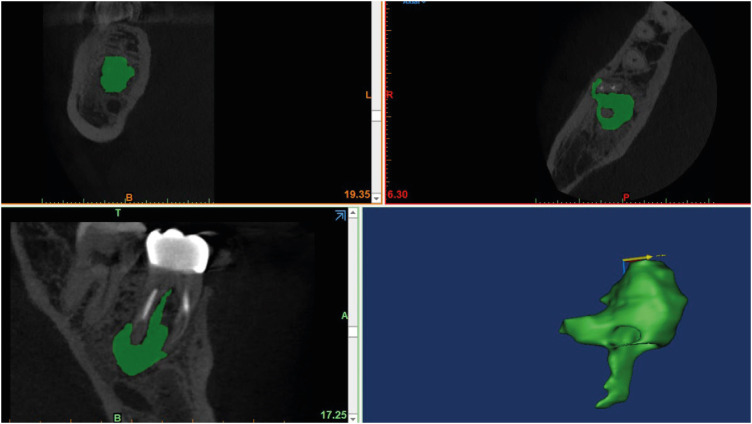
- Radiographic patterns of periosteal bone reactions associated with endodontic lesions
- Poorya Jalali, Jessica Riccobono, Robert A. Augsburger, Mehrnaz Tahmasbi-Arashlow
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e23. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The formation of new bone by periosteum due to an insult is called periosteal bone reaction (PBR). This study assessed the cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) patterns of periosteal bone reactions associated with periapical inflammatory lesion (apical periodontitis/periapical rarefying osteitis).
Materials and Methods Twenty-two small field of view CBCT images of patients with PBR were selected from a database of a private practice limited to endodontics. The volume of the periapical inflammatory lesion, the presence of cortical fenestration, the distance of the root apices to the affected cortex, and the location, pattern, and longest diameter of the periosteal reaction were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed using Wilcoxon Ranksum, Fischer’s exact, Spearman Correlation Coefficient, and paired
t -test.Results In all cases, periosteal bone reaction manifested as either parallel (90.9%) or irregular (9.1%). No correlation was found between periapical inflammatory lesion volume and the periosteal reaction's longest diameter (
p > 0.05). Cortical fenestration was noted in 72.7% of the cases. In addition, the findings showed that periosteal reactions were located mostly on the buccal and were present 53.8% and 100% of the time in the mandible and maxilla, respectively.Conclusions The periosteal reactions of endodontic origin had a nonaggressive form (
i.e ., parallel or irregular), and none of the lesions resulted in a periosteal reaction with an ominous Codman’s triangle or spicule pattern.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ENDODONTIA E INTERCORRÊNCIAS: COMPREENDENDO OS ACIDENTES E OTIMIZANDO O PROGNÓSTICO
Ana Paula Oliveira Rocha, Flávia Cordeiro Antunes , Millena Alberto Luna , Raissa Danielle Muniz Da Silva , Gustavo Henrique Palma Durães , Juliano Magno de Valadares Bicalho , Lorena Miranda Lima , Barbara Quadros Tonelli
REMUNOM.2026; 2(03): 1. CrossRef - The influence of endodontic treatment quality on periapical lesions' architecture in cone‐beam computed tomography
Ewa Mackiewicz, Tobias Bonsmann, Krzysztof Safranow, Patrycja Nowicka, Janusz Kołecki, Alicja Nowicka
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(1): 36. CrossRef - Novel radiographic pattern of maxillary periostitis induced by endodontic inflammation: A case report
Pai-Chun Huang, I-Hao Su, Meng-Ling Chiang, Jyh-Kwei Chen
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(3): 1982. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- ENDODONTIA E INTERCORRÊNCIAS: COMPREENDENDO OS ACIDENTES E OTIMIZANDO O PROGNÓSTICO
- 5,250 View
- 85 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

-
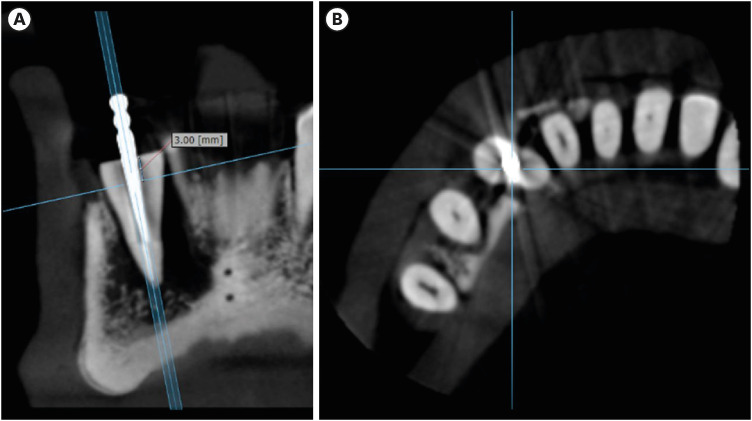
Influence of CBCT parameters on image quality and the diagnosis of vertical root fractures in teeth with metallic posts: an
ex vivo study - Larissa Pereira Lagos de Melo, Polyane Mazucatto Queiroz, Larissa Moreira-Souza, Mariana Rocha Nadaes, Gustavo Machado Santaella, Matheus Lima Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e16. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of peak kilovoltage (kVp) and a metal artifact reduction (MAR) tool on image quality and the diagnosis of vertical root fracture (VRF) in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Materials and Methods Twenty single-rooted human teeth filled with an intracanal metal post were divided into 2 groups: control (
n = 10) and VRF (n = 10). Each tooth was placed into the socket of a dry mandible, and CBCT scans were acquired using a Picasso Trio varying the kVp (70, 80, 90, or 99), and the use of MAR (with or without). The examinations were assessed by 5 examiners for the diagnosis of VRF using a 5-point scale. A subjective evaluation of the expression of artifacts was done by comparing random axial images of the studied protocols. The results of the diagnoses were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and the Tukeypost hoc test, the subjective evaluations were compared using the Friedman test, and intra-examiner reproducibility was evaluated using the weighted kappa test (α = 5%).Results The kVp and MAR did not influence the diagnosis of VRF (
p > 0.05). According to the subjective classification, the 99 kVp protocol with MAR demonstrated the least expression of artifacts, while the 70 kVp protocol without MAR led to the most artifacts.Conclusions Protocols with higher kVp combined with MAR improved the image quality of CBCT examinations. However, those factors did not lead to an improvement in the diagnosis of VRF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital Dentistry Society Quality Forum: Clinical recommendations on cone-beam computed tomography for the digital dentistry workflow
Hugo Gaêta-Araujo, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Reinhilde Jacobs
Digital Dentistry Journal.2026; 3(1): 100065. CrossRef - Photon‐Counting CT for Diagnosing Vertical Root Fractures in Teeth With Metal Posts: An Ex Vivo Comparative Analysis With Four CBCT Devices
Renata M. S. Leal, Fernanda B. Fagundes, Maria F. S. A. Bortoletto, Samuel C. Kluthcovsky, Walter Coudyzer, Bruno C. Cavenago, Reinhilde Jacobs, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele
International Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Iterative Reconstruction of Cone-beam Computed Tomography for Detecting Vertical Root Fractures in the Presence of Metal Artifacts
Matheus Barros-Costa, Gustavo Santaella, Christiano Oliveira-Santos, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, William C. Scarfe, Francisco Carlos Groppo
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(6): 715. CrossRef - Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Laser-Enhanced Disinfection in Endodontic Therapy
Janos Kantor, Sorana Maria Bucur, Eugen Silviu Bud, Victor Nimigean, Ioana Maria Crișan, Mariana Păcurar
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4055. CrossRef - Exploring Diagnostic Reliability of CBCT for Vertical Root Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analytical Approach
Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Adriana Pinto Bezerra, Marcio Correa, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Stefano Corbella
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning for dentomaxillofacial cone-beam computed tomography image quality enhancement: A pilot study
Ali Nazari, Seyed Mohammad Yousef Najafi, Reza Abbasi, Hossein Mohammad-Rahimi, Parisa Motie, Mina Iranparvar Alamdari, Mehdi Hosseinzadeh, Ruben Pauwels, Falk Schwendicke
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2025; 55(3): 271. CrossRef - Diagnostic Accuracy of Intraoral, Extraoral and Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)-Generated Bitewings for Detecting Approximal Caries and Periodontal Bone Loss
Jyoti Mago, Alan G Lurie, Aadarsh Gopalakrishna, Aditya Tadinada
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vertical root fracture diagnosis in teeth with metallic posts: Impact of metal artifact reduction and sharpening filters
Débora Costa Ruiz, Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Amanda Farias-Gomes, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2024; 54(2): 139. CrossRef - Comparing standard- and low-dose CBCT in diagnosis and treatment decisions for impacted mandibular third molars: a non-inferiority randomised clinical study
Kuo Feng Hung, Andy Wai Kan Yeung, May Chun Mei Wong, Michael M. Bornstein, Yiu Yan Leung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital Dentistry Society Quality Forum: Clinical recommendations on cone-beam computed tomography for the digital dentistry workflow
- 3,211 View
- 53 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

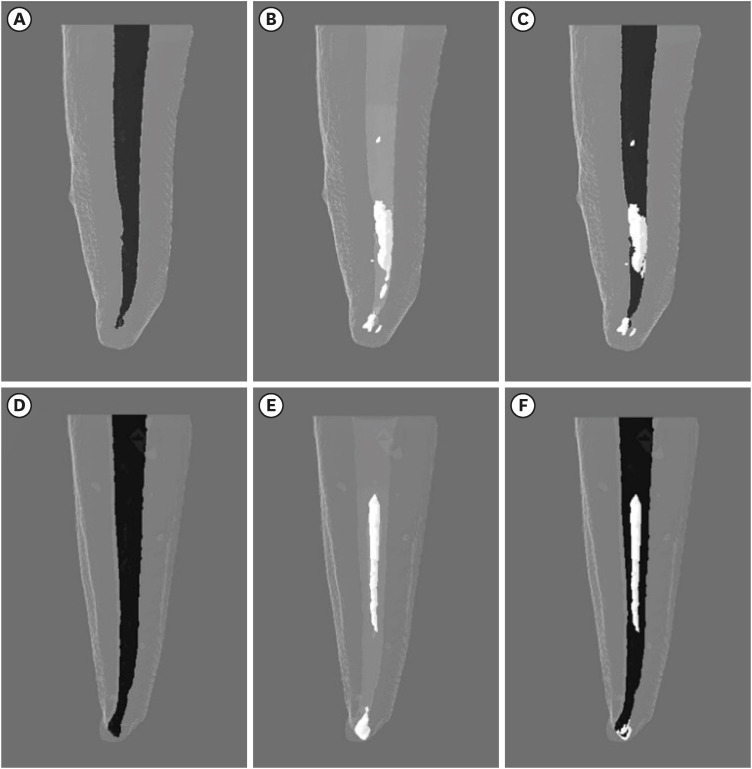
- Effectiveness of endodontic retreatment using WaveOne Primary files in reciprocating and rotary motions
- Patricia Marton Costa, Renata Maíra de Souza Leal, Guilherme Hiroshi Yamanari, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e15. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the efficiency of WaveOne Primary files (Dentsply Sirona) for removing root canal fillings with 2 types of movement: reciprocating (RCP) and continuous counterclockwise rotation (CCR).
Materials and Methods Twenty mandibular incisors were prepared with a RCP instrument (25.08) and filled using the Tagger hybrid obturation technique. The teeth were retreated with a WaveOne Primary file and randomly allocated to 2 experimental retreatment groups (
n = 10) according to movement type: RCP and CCR. The root canals were emptied of filling material in the first 3 steps of insertion, until reaching the working length. The timing of retreatment and procedure errors were recorded for all samples. The specimens were scanned before and after the retreatment procedure with micro-computed tomography to calculate the percentage and volume (mm3) of the residual filling material. The results were statistically evaluated using paired and independentt -tests, with a significance level set at 5%.Results No significant difference was found in the timing of filling removal between the groups, with a mean of 322 seconds (RCP) and 327 seconds (CCR) (
p < 0.05). There were 6 instrument fractures: 1 in a RCP motion file and 5 in continuous rotation files. The volumes of residual filling material were similar (9.94% for RCP and 15.94% for CCR;p > 0.05).Conclusions The WaveOne Primary files used in retreatment performed similarly in both RCP and CCR movements. Neither movement type completely removed the obturation material, but the RCP movement provided greater safety.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
- 2,542 View
- 57 Download
- 1 Crossref

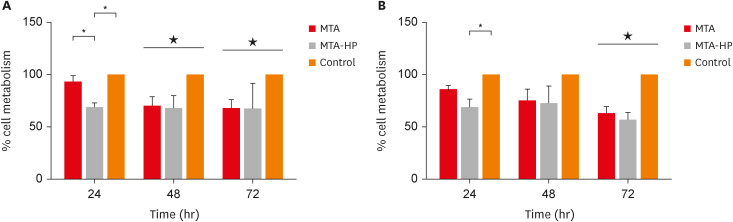
- High-plasticity mineral trioxide aggregate and its effects on M1 and M2 macrophage viability and adherence, phagocyte activity, production of reactive oxygen species, and cytokines
- Betânia Canal Vasconcellos, Layara Cristine Tomaz Tavares, Danilo Couto da Silva, Francielen Oliveira Fonseca, Francine Benetti, Antônio Paulino Ribeiro Sobrinho, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e6. Published online December 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of high-plasticity mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA-HP) on the activity of M1 and M2 macrophages, compared to white MTA (Angelus).
Materials and Methods Peritoneal inflammatory M1 (from C57BL/6 mice) and M2 (from BALB/c mice) macrophages were cultured in the presence of the tested materials. Cell viability (MTT and trypan blue assays), adhesion, phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β production were evaluated. Parametric analysis of variance and the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test were used. Results were considered significant when
p < 0.05.Results The MTT assay revealed a significant decrease in M1 metabolism with MTA-HP at 24 hours, and with MTA and MTA-HP later. The trypan blue assay showed significantly fewer live M1 at 48 hours and live M2 at 48 and 72 hours with MTA-HP, compared to MTA. M1 and M2 adherence and phagocytosis showed no significant differences compared to control for both materials. Zymosan A stimulated ROS production by macrophages. In the absence of interferon-γ, TNF-α production by M1 did not significantly differ between groups. For M2, both materials showed higher TNF-α production in the presence of the stimulus, but without significant between-group differences. Likewise, TGF-β production by M1 and M2 macrophages was not significantly different between the groups.
Conclusions M1 and M2 macrophages presented different viability in response to MTA and MTA-HP at different time points. Introducing a plasticizer into the MTA vehicle did not interfere with the activity of M1 and M2 macrophages.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Local Immune Response to Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Narrative Review
Shankargouda Patil, Shilpa Bhandi, Oladapo T Okareh
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(4): 382. CrossRef
- Local Immune Response to Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Narrative Review
- 2,159 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Physicochemical properties of a calcium aluminate cement containing nanoparticles of zinc oxide
- Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Thuany Schmitz Amaral, Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Taynara Santos Goulart, Hebert Luís Rossetto, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e3. Published online December 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
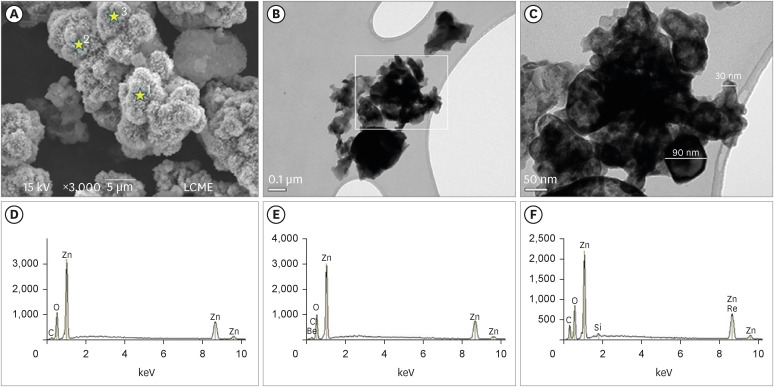
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of different nanoparticulated zinc oxide (nano-ZnO) and conventional-ZnO ratios on the physicochemical properties of calcium aluminate cement (CAC).
Materials and Methods The conventional-ZnO and nano-ZnO were added to the cement powder in the following proportions: G1 (20% conventional-ZnO), G2 (15% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO), G3 (12% conventional-ZnO + 3% nano-ZnO) and G4 (10% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO). The radiopacity (Rad), setting time (Set), dimensional change (Dc), solubility (Sol), compressive strength (Cst), and pH were evaluated. The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO were also assessed using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Radiopacity data were analyzed by the 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni tests (
p < 0.05). The data of the other properties were analyzed by the ANOVA, Tukey, and Fisher tests (p < 0.05).Results The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO powders presented particles with few impurities and nanometric and micrometric sizes, respectively. G1 had the highest Rad mean value (
p < 0.05). When compared to G1, groups containing nano-ZnO had a significant reduction in the Set (p < 0.05) and lower values of Dc at 24 hours (p < 0.05). The Cst was higher for G4, with a significant difference for the other groups (p < 0.05). The Sol did not present significant differences among groups (p > 0.05).Conclusions The addition of nano-ZnO to CAC improved its dimensional change, setting time, and compressive strength, which may be promising for the clinical performance of this cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
Sara Ghorbani, Rahim Naghizadeh, Ebrahim Ghasemi, Hamidreza Rezaie
Advances in Cement Research.2025; 37(4): 269. CrossRef - Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design
Hongyin Hu, Fufei Wu, Jiao Chen, Shuangshuang Guan, Peng Qu, Hongqin Zhang, Yuyi Chen, Zirun Xu, Chuanteng Huang, Shuang Pu
Materials.2025; 18(7): 1515. CrossRef - Radiographic, mechanical, and chemical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate from nanosilica and clam shell calcium carbonate
Leny Yuliatun, Muhammad Adly Rahandi Lubis, Muhammad Khaliim Jati Kusala, Lia Destiarti, Ratna Betriani, Jolang Budiarta, Mariyam Mariyam
Polyhedron.2025; 278: 117590. CrossRef - Application of Calcium Aluminate-Based Materials for Direct Pulp Capping – In Vivo Study
Ognjenka Janković, Smiljana Paraš, Tijana Adamović, Ljiljana Tadić Latinović, Radmila Arbutina, Igor Đukić, Saša Marin, Marko Bulajić, Karolina Vukoje, Vukoman Jokanović, Verica Pavlić
Acta Veterinaria.2025; 75(2): 212. CrossRef - Nanotechnology for calcium aluminate cement: thematic analysis
Lapyote Prasittisopin
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
- 2,109 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- The prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption based on cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: a cross-sectional study
- Matheus Diniz Ferreira, Matheus Barros-Costa, Felipe Ferreira Costa, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e39. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
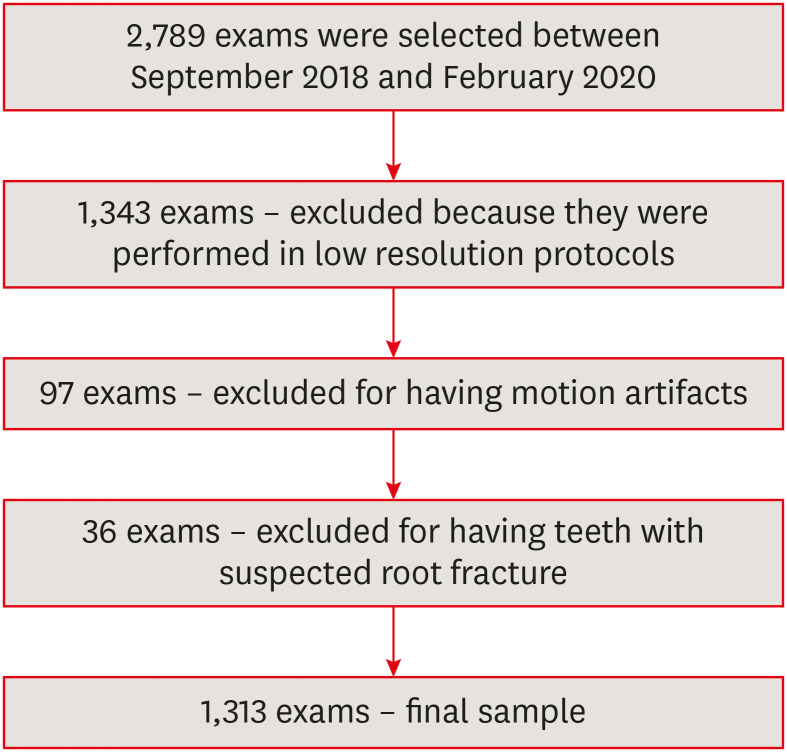
ePub Objectives This study investigated the prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption (ECR) regarding sex, age, tooth, stages of progression, and portal of entry, using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
Materials and Methods CBCT scans of 1,313 patients from a Brazilian subpopulation comprising 883 female and 430 male patients (mean age, 55.2 years), acquired using a PreXion 3D CBCT unit, were evaluated. All permanent teeth included in the scans were evaluated for the presence of ECR according to the 3-dimensional classification and the portal of entry. The association between the presence of ECR and the factors studied was assessed using the χ2 test. Intra-observer agreement was analyzed with the kappa test (
α = 0.05).Results In total, 6,240 teeth were analyzed, of which 84 (1.35%) were affected by ECR. A significant association was found between the presence of ECR and sex, with a higher prevalence in male patients (
p = 0.002). The most frequently affected teeth were the mandibular and maxillary central incisors. The most common height was the mid-third of the root. For the portal of entry, 44% of cases were on the proximal surfaces, 40.5% on the lingual/palatal surface and 15.5% on the buccal surface. Intra-observer agreement was excellent.Conclusions The prevalence of ECR was 1.35%, with a higher prevalence in male patients and a wide age distribution. The mandibular and maxillary central incisors were the most commonly affected teeth, and cases of ECR most frequently showed a height into the mid-third of the root and proximal entry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
Terrell F. Pannkuk
Dental Traumatology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prise en charge des lésions cervicales
C. Mocquot, L. Detzen, I. Fontanille, B. Orlik, F. Decup
EMC - Médecine buccale.2025; 18(3): 1. CrossRef - Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characterization of External Cervical Resorption Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Isadora Carneiro Pereira Machado, Marilia Oliveira Morais, Adriana Lustosa Pereira Bicalho, Patricia Helena Pereira Ferrari, Juliano Martins Bueno, José Luiz Cintra Junqueira, Mariana Quirino Silveira Soares
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 164. CrossRef - Influence of tube current and metal artifact reduction on the diagnosis of external cervical resorption in teeth adjacent to a dental implant in CBCT: an ex-vivo study
Thamiles Gonzalez-Passos, Matheus Barros-Costa, Matheus L Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maxillary anterior teeth with extensive root resorption treated with multidisciplinary approach: A case report
Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho, Carollyne Souza Campello, Juliana Pires Abdelnur, Vivian Ronquete, Carlos Henrique Sardenberg Pereira, Marilia F Marceliano-Alves
International Journal of Case Reports and Images.2023; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic features of external cervical resorption – An observational study
Shanon Patel, Francesc Abella, Kreena Patel, Paul Lambrechts, Nassr Al‐Nuaimi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(12): 1475. CrossRef
- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
- 3,726 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
- Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e38. Published online October 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the cytotoxicity, radiopacity, pH, and dentinal tubule penetration of a paste of 1.0% calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals (ZnO:1.0Ca) combined with propylene glycol (PRG) or polyethylene glycol and propylene glycol (PEG-PRG).
Materials and Methods The pastes were prepared by mixing calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] or ZnO:1.0Ca with PRG or a PEG-PRG mixture. The pH was evaluated after 24 and 96 hours of storage in deionized water. Digital radiographs were acquired for radiopacity analysis and bubble counting of each material. The materials were labeled with 0.1% fluorescein and applied to root canals, and images of their dentinal tubule penetration were obtained using confocal laser scanning microscopy. RAW264.7 macrophages were placed in different dilutions of culture media previously exposed to the materials for 24 and 96 hours and tested for cell viability using the MTT assay. Analysis of variance and the Tukey test (
α = 0.05) were performed.Results ZnO:1.0Ca materials showed lower viability at 1:1 and 1:2 dilutions than Ca(OH)2 materials (
p < 0.0001). Ca(OH)2 had higher pH values than ZnO:1.0Ca at 24 and 96 hours, regardless of the vehicle (p < 0.05). ZnO:1.0Ca pastes showed higher radiopacity than Ca(OH)2 pastes (p < 0.01). No between-material differences were found in bubble counting (p = 0.0902). The ZnO:1.0Ca pastes had a greater penetration depth than Ca(OH)2 in the apical third (p < 0.0001).Conclusions ZnO:1.0Ca medicaments presented higher penetrability, cell viability, and radiopacity than Ca(OH)2. Higher values of cell viability and pH were present in Ca(OH)2 than in ZnO:1.0Ca.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Nano calcium zincate-assisted synthesis of benzo[
d
]thiazol-2-yl phenylisoxazoles: quantum computational,
in silico
molecular docking simulations and DNA interaction
A. K. Smitha, V. Srinivasa Murthy, B. Vinay Kumar, M. Sennappan, A. H. Shridhar, Lohit Naik, K. Yogendra, N. Madhusudhana
Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids.2026; 45(3): 261. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-Enhanced Dentistry: A Clinical Perspective
Selvam Manoj, Radhakrishnan Sreena, Rajkumar Divya, Starlin Ebinesh, Shenbagaraman Akshaya, Srikumar Sugantha Angel, Arputharaj Joseph Nathanael
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2025; 11(8): 4671. CrossRef
-
Nano calcium zincate-assisted synthesis of benzo[
d
]thiazol-2-yl phenylisoxazoles: quantum computational,
in silico
molecular docking simulations and DNA interaction
- 2,078 View
- 24 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Apical periodontitis in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: influence of anatomy and quality of root canal treatment, a CBCT study
- Samantha Jannone Carrion, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e37. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of apical periodontitis (AP) in the mesiobuccal roots of root canal-treated maxillary molars.
Materials and Methods One thousand cone-beam computed tomography images of the teeth were examined by 2 dental specialists in oral radiology and endodontics. The internal anatomy of the roots, Vertucci’s classification, quality of root canal treatment, and presence of missed canals were evaluated; additionally, the correlation between these variables and AP was ascertained.
Results A total of 1,000 roots (692 first molars and 308 second molars) encompassing 1,549 canals were assessed, and the quality of the root canal filling in the majority (56.9%) of the canals was satisfactory. AP was observed in 54.4% of the teeth. A mesiolingual canal in the mesiobuccal root (MB2 canal) was observed in 54.9% of the images, and the majority (83.5%) of these canals were not filled. Significant associations were observed between the presence of an MB2 canal and the quality of the root canal filling and the presence of AP.
Conclusions AP was detected in more than half of the images. The MB2 canals were frequently missed or poorly filled.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical Configuration of the MB2 Canal Using High-Resolution Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Luciana Magrin Blank-Gonçalves, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Monikelly do Carmo Chagas Nascimento, Ana Grasiela Limoeiro, Luiz Roberto Coutinho Manhães-Jr
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(5): 609. CrossRef - The Effect of Age and Gender on the Distance Between the Maxillary Sinus Cortical Bone and Maxillary Molars: A Cone-Beam Tomography Analysis
Thaysa Menezes Constantino, Marília Fagury Videira Marceliano-Alves, Vivian Ronquete, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Pablo Andres Amoroso-Silva, Mariano Simon Pedano, Tchilalo Boukpessi, Fábio Vidal, Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho
Sinusitis.2025; 9(1): 9. CrossRef - Retrospective study of the morphology of third maxillary molars among the population of Lower Silesia based on analysis of cone beam computed tomography
Anna Olczyk, Barbara Malicka, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299123. CrossRef - Relationship between apical periodontitis and missed canals in mesio-buccal roots of maxillary molars: CBCT study
Badi B. Alotaibi, Kiran I. Khan, Muhammad Q. Javed, Smita D. Dutta, Safia S. Shaikh, Nawaf M. Almutairi
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2024; 19(1): 18. CrossRef - APICAL PERIODONTITIS IN MAXILLARY MOLARS WITH MISSED SECOND MESIO-BUCCAL ROOT CANAL: A CBCT STUDY
Cristina Coralia Nistor, Ioana Suciu , Ecaterina Ionescu , Anca Dragomirescu , Elena Coculescu , Andreea Baluta
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(3): 100. CrossRef - Anatomic Comparison of Contralateral Maxillary Second Molars Using High-Resolution Micro-CT
Ghassan Dandache, Umut Aksoy, Mehmet Birol Ozel, Kaan Orhan
Symmetry.2023; 15(2): 420. CrossRef
- Anatomical Configuration of the MB2 Canal Using High-Resolution Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
- 3,411 View
- 51 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Giovanna Corrêa Denucci, Gabriela Soffner, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e32. Published online July 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements (SARCs).
Materials and Methods Three SARCs including RelyX Unicem-2 (RUN), Maxcem Elite (MAX), and Calibra Universal (CAL) were tested. Rectangular bar-shaped specimens were prepared for flexural strength (FS) and flexural modulus (FM) and determined by a 3-point bending test. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and top/bottom microhardness ratio (%KHN) were conducted on the top and bottom faces of disc-shaped samples. Sorption (Wsp) and solubility (Wsl) were evaluated after 24 hours of water immersion. Filler morphology was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). FS, FM, %KHN, Wsp, Wsl, and EDS results were submitted to 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s
post-hoc test, and KHN also to pairedt -test (α = 0.05).Results SARC-CAL presented the highest FS value, and SARC-RUN presented the highest FM. SARC-MAX and RUN showed the lowest Wsp and Wsl values. KHN values decreased from top to bottom and the SARCs did not differ statistically. Also, all resin cements presented carbon, aluminum, and silica in their composition. SARC-MAX and RUN showed irregular and splintered particles while CAL presented small and regular size particles.
Conclusions A higher mechanical strength can be achieved by a reduced spread in grit size and the filler morphology can influence the KHN, as well as photoinitiators in the composition. Wsp and Wsl can be correlated with ions diffusion of inorganic particles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Assessment of fit accuracy and retentive strength of additively manufactured zirconia crowns luted to Ti‐base abutments with different resin cements: An in vitro study
Rafat Sasany, Sultan Merve Uçar, Burak Yilmaz
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Resin Cement Color Stability and Restoration Thickness as Determinants of the Final Shade in a Glass–Ceramic CAD/CAM Material
Hanin E. Yeslam, Alaa Turkistani
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 319. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Resin-Based Luting Materials—Review
Aleksandra Maletin, Milica Jeremić Knežević, Daniela Đurović Koprivica, Tanja Veljović, Tatjana Puškar, Bojana Milekić, Ivan Ristić
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4156. CrossRef - A Scoping Review on the Polymerization of Resin-Matrix Cements Used in Restorative Dentistry
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Orlanda Torres, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva, Susana O. Catarino, Mutlu Özcan, Júlio C. M. Souza
Materials.2023; 16(4): 1560. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
- 2,190 View
- 23 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Cytotoxicity of two self-adhesive resin cements and their interference in the phagocytic activity of murine macrophages
- Danilo Couto da Silva, Leonardo Gomes Vaz, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares, Leda Quercia Vieira, Ricardo Reis de Oliveira, Antônio Paulino Ribeiro Sobrinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e31. Published online July 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e31
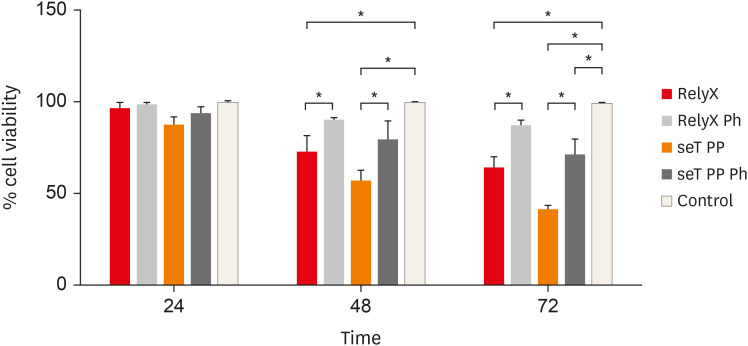
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate
in vitro the effects of the self-adhesive resin cements RelyX U200 (3M ESPE) and seT PP (SDI Limited) on murine macrophages and the interference of the photoactivation.Materials and Methods Cell viability assays, cell adherence, yeast phagocytosis of
Saccharomyces boulardii and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were performed in the presence of capillaries containing the respective self-adhesive cement when photoactivated or not.Results After long periods of contact, both types of cements, when not photoactivated, are more cytotoxic for macrophages. The seT PP cement when only chemically activated seems to interfere more negatively in the process of phagocytosis of yeasts
S. boulardii. Both types of cements interfere in the cell adhesion process, independent of photoactivation. None of the types of cements tested was able to induce the production of ROS.Conclusions Our results highlight the great importance of the photoactivation of self-adhesive resin cements in the dental clinic, since RelyX U200, when photoactivated, presented the best results within the evaluated parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Preheating Self-Adhesive Cements on the Degree of Conversion, Cell Migration, and Cell Viability
Henrique Cantarelli, Fernando Antonio Costa Xavier, Fernando Freitas Portella, Keiichi Hosaka, Eduardo Galia Reston, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Celso Afonso Klein-Junior
Applied Mechanics.2024; 5(3): 553. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef
- Influence of Preheating Self-Adhesive Cements on the Degree of Conversion, Cell Migration, and Cell Viability
- 1,947 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Morphotypes of the apical constriction of maxillary molars: a micro-computed tomographic evaluation
- Jeffrey Wen-Wei Chang, Kuzhanchinathan Manigandan, Lakshman Samaranayake, Chellapandian NandhaKumar, Pazhamalai AdhityaVasun, Johny Diji, Angambakkam Rajasekharan PradeepKumar
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e19. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e19
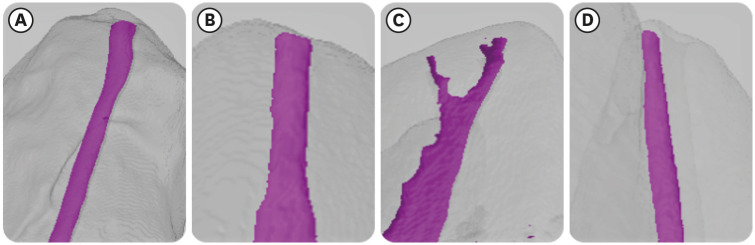
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the apical constriction (AC) and apical canal morphology of maxillary first and second molars, using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
Materials and Methods The anatomical features of 313 root canals from 41 maxillary first molars and 57 maxillary second molars of patients with known age and sex were evaluated using micro-CT, with a resolution of 26.7 µm. The factors evaluated were the presence or absence of AC, the morphotypes, bucco-lingual dimension, mesio-distal dimension, and the profile (shape) of AC and the apical root canal. The apical root canal dimensions, location of the apical foramen (AF), AC to AF distance, and presence of accessory canals in the apical 5 mm were also assessed. Descriptive and analytical statistics were used for data evaluation.
Results AC was present in all 313 root canals. Patients’ age and sex did not significantly impact either AC or the apical canal dimensions. The most common AC morphotype detected was the traditional (single) constriction (52%), followed by the parallel (29%) morphotype. The mean AC dimensions in maxillary first molars were not significantly different from those in maxillary second molars. Sixty percent of AF were located within 0.5 mm from the anatomic apex.
Conclusions The most common morphotype of AC detected was the traditional constriction. Neither patients’ age nor sex had a significant impact on the dimensions of the AC or the apical root canal. The majority of AF (60%) were located within 0.5 mm from the anatomic apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vivo and In Vitro Accuracy and Precision Evaluations of Mini Electronic Apex Locators
Özlem Kara, Rüstem Kemal Sübay
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 329. CrossRef - Effect of Coronal Flaring on Initial Apical File Size Estimation in Curved Canals Using Three Distinct Rotary Instruments: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Vinodhini Varatharajan, Muhammed Abdul Rahman Thazhathveedan, Mohammed Salman Kuttikkodan, Ismail Puzhangaraillath Mundanatayil, Amrutha Ravindran Thazhe Mangool, Ashraf Karumbil
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Accuracy of Three Electronic Apex Locators Using Different Sodium Hypochlorite Concentrations
Sanda Ileana Cîmpean, Radu Marcel Chisnoiu, Adela Loredana Colceriu Burtea, Rareș Rotaru, Marius Gheorghe Bud, Ada Gabriela Delean, Ioana-Sofia Pop-Ciutrilă
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 918. CrossRef - Cone beam computed tomography analysis of the root and canal morphology of the maxillary second molars in a Hail province of the Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al-Zubaidi, Albandari H. Alghurayes, Safanah D. AlDAkhayel, Fatemah I. Alzoori, Taif F. Alshammari, Abrar M. Aldakhil
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19477. CrossRef
- In Vivo and In Vitro Accuracy and Precision Evaluations of Mini Electronic Apex Locators
- 2,365 View
- 47 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Efficacy of reciprocating instruments and final irrigant activation protocols on retreatment of mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: a micro-CT analysis
- Lilian Tietz, Renan Diego Furlan, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Theodoro Weissheimer, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e13. Published online February 15, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e13
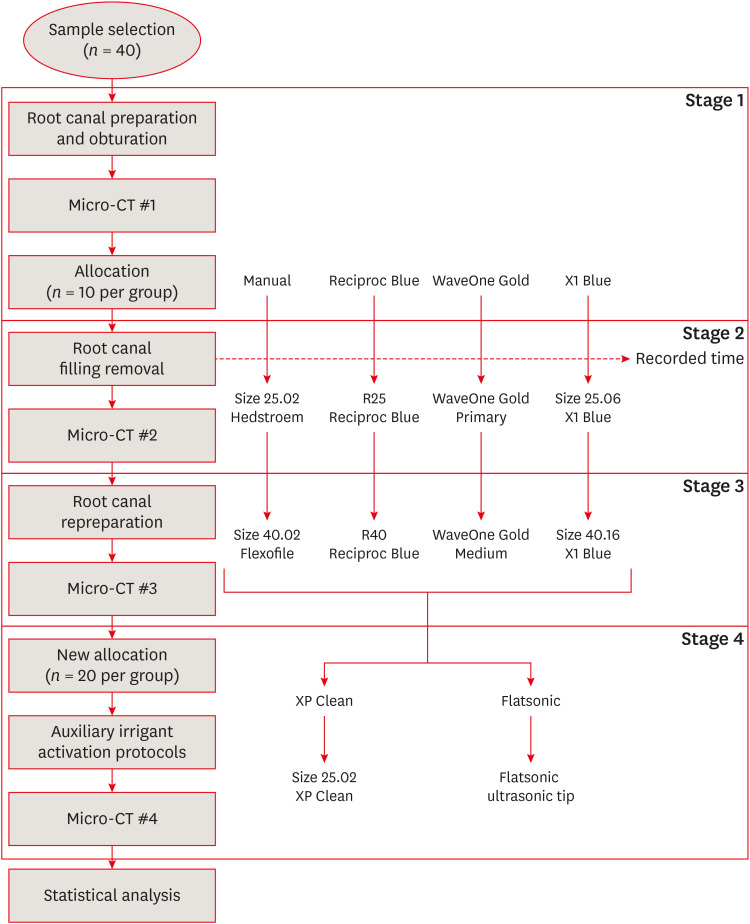
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the efficacy of 3 reciprocating systems and the effects of 2 instruments for irrigant activation on filling material removal.
Materials and Methods Forty mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared up to size 25.06 and obturated. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) examination #1 was performed. Teeth were then divided into 4 groups (
n = 10), according to the retreatment protocol: (1) manual, (2) Reciproc Blue, (3) WaveOne Gold, and (4) X1 Blue. Micro-CT examinations #2 and #3 were performed after filling removal and repreparation, respectively. Next, all teeth were divided into 2 new groups (n = 20) according to the irrigant activation protocol: XP Clean (XP Clean size 25.02) and Flatsonic (Flatsonic ultrasonic tip). Micro-CT examination #4 was performed after irrigant activation. Statistical analysis was performed with a significance level set at 5%.Results WaveOne Gold removed a significantly greater amount of filling material than the manual group (
p < 0.05). The time to reach the WL was similar for all reciprocating systems (p > 0.05). X1 Blue was faster than the manual group (p < 0.05). Only manual group improved the filling material removal after the repreparation stage (p < 0.05). Both activation protocols significantly improved the filling material removal (p < 0.05), without differences between them (p > 0.05).Conclusions None of the tested instruments completely removed the filling material. X1 Blue size 25.06 reached the working length in the shortest time. XP Clean and Flatsonic improved the filling material removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Supplementary instrumentation did not enhance the removal of residual gutta-percha: a micro-computed tomography study
Selin Nur Ayaz, Meltem Kucuk, Deniz Yanık Nalbantoğlu, Ali Keles, Amine Yigit, Fugen Dagli Comert Tasman, Bekir Karabucak
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Ability of 3 Reciprocating Instruments to Remove Obturation Material: A Micro–Computed Tomography Study
Fábio Luiz Cecagno, Alexandre Sigrist De Martin, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Wayne Martins Nascimento, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 376. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cleaning efficiency of single file NiTi rotary system during root canal treatment procedure - A scanning electron microscope study
Ruchi Vashisht, Umesh Kumar, Swaty Jhamb, Ruchi Singla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 316. CrossRef - Influence of rotary and reciprocating kinematics on the accuracy of an integrated apex locator
Verônica de Almeida Gardelin, Júlia Itzel Acosta Moreno Vinholes, Renata Grazziotin‐Soares, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Fernando Branco Barletta
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 202. CrossRef
- Supplementary instrumentation did not enhance the removal of residual gutta-percha: a micro-computed tomography study
- 2,469 View
- 39 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effect of irrigants on the color stability, solubility, and surface characteristics of calcium-silicate based cements
- Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Hacer Aksel, Şenay Canay, Duygu Karasan
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e10. Published online February 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e10

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the color stability, solubility, and surface characteristics of 3 calcium silicate-based cements (CSCs) after immersion in different solutions.
Materials and Methods ProRoot white mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and Endosequence Root Repair Material (ERRM) were placed in cylindrical molds and stored at 37°C for 24 hours. Each specimen was immersed in distilled water, 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine, or 0.1% octenidine hydrochloride (OCT) for 24 hours. Color changes were measured with a spectrophotometer. Solubility was determined using an analytical balance with 10−5 g accuracy. The surface characteristics were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectroscopy. Data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance, the Tukey test, and the paired
t -test.Results MTA exhibited significant discoloration in contact with NaOCl (
p < 0.05). White precipitation occurred on the surfaces of Biodentine and ERRM after contact with the solutions, and none of the materials presented dark brown discoloration. All materials showed significant solubility after immersion in the solutions (p < 0.05), irrespective of the solution type (p > 0.05). The surface topography and elemental composition of the samples showed different patterns of crystal formation and precipitation depending on the solution type.Conclusions All materials presented some amount of solubility and showed crystal precipitation after contact with the solutions. Biodentine and ERRM are suitable alternatives to ProRoot MTA as they do not exhibit discoloration. The use of OCT can be considered safe for CSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
Laila Mohamed Mohamed Kenawi, Mohamed Fattouh, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Abla Arafa
The Open Dentistry Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical and in vivo analyses of calcium silicate‐based materials in bone and connective tissues
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Matheus Barros‐Costa, Isabela Alvarenga Maciel dos Santos, Fábio Roberto de Souza Batista, Juliana de Aguiar Silveira Meira, Mariza Akemi Ma
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(3): 484. CrossRef - Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi, Eva Habazaj, Kleves Elezi, Rialda Xhizdari, Nevila Alliu
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bismuth release from endodontic materials: Proposed mechanisms for systemic circulation and organ accumulation
Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Benjamin Hewitt, Rodrigo Bueno de Oliveira, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Débora C. Coraça-Huber, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Marina Angélica Marciano
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2025; 494: 138580. CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Data about application of chlorhexidine as a periodontal irrigant –
Systematic Review.
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi , Eva Habazaj , Kristi Sulanjaku , Nevila Alliu
Acta Stomatologica Marisiensis Journal.2025; 8(1): 6. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Cement MTA FlowTM on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells In Vitro
Paulius Tušas, Josette Camilleri, Milda Alksnė, Egidijus Šimoliūnas, Saulius Drukteinis, Eglė Marija Urbonė, Virginija Bukelskienė, Vygandas Rutkūnas, Vytautė Pečiulienė
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(7): 252. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effects of Different Irrigation Solutions on MTA and Dentin Microhardness
Gokay Buyukcolpan, İdil Özden, Hesna Sazak Öveçoğlu
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 524. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Intratubular Penetration Ability of Two Retrograde Obturation Techniques in Micro-Endodontic Surgical Procedure: An In Vitro Study with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Alberto Casino Alegre, Michell Ramírez López, Manuel Monterde Hernández, Susana Aranda Verdú, Jorge Rubio Climent, Antonio Pallarés Sabater
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(11): 509. CrossRef - The outcome of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling in endodontic microsurgery: a randomized controlled trial
Xu Dong, Qin Su, Wen Li, Jinbo Yang, Dongzhe Song, Jing Yang, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions
Sıla Nur Usta, Cangül Keskin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of various irrigation solutions on the color stabilities of five calcium silicate cement: an in-vitro study
Aslı Soğukpınar Onsuren, Onur Kesici, Elif Uğurbekler Hündü
Selcuk Dental Journal.2024; 11(3): 313. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers on tooth color: A 3-year in vitro experimental study
Carmen Llena, Ana Herrero, Sandra Lloret, Martha Barraza, Jose Luis Sanz
Heliyon.2023; 9(2): e13237. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Four Bioceramic Materials with Different Restorative Materials and Timings
Abeer S. Alqahtani, Ayman M. Sulimany, Abdullah S. Alayad, Abdulaziz S. Alqahtani, Omar A. Bawazir
Materials.2022; 15(13): 4668. CrossRef
- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
- 2,167 View
- 37 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref

- Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
- Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e8. Published online February 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e8
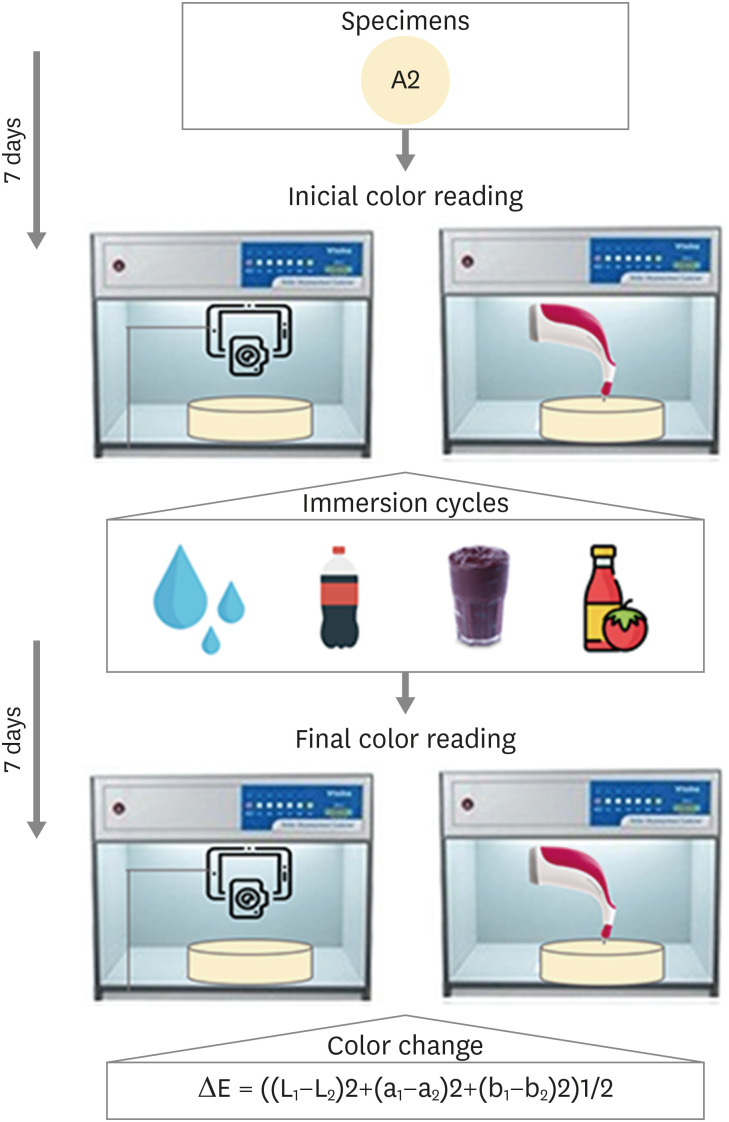
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the color change of the Giomer resin composite (Beautifil-Bulk) by using photographs obtained with a smartphone (iPhone 6S) associated with Adobe Photoshop software (digital method), with the spectrophotometric method (Vita Easyshade) after immersion in different pigment solutions.
Materials and Methods Twenty resin composite samples with a diameter of 15.0 mm and thickness of 1.0 mm were confectioned in A2 color (
n = 5). Photographs and initial color readings were performed with a smartphone and spectrophotometer, respectively. Then, samples were randomly divided and subjected to cycles of immersion in distilled water (control), açai, Coke, and tomato sauce, 3 times a day, 20 minutes for 7 days. Later, new photographs and color readings were taken.Results The analysis (2-way analysis of variance, Holm-Sidak,
p < 0.05) demonstrated no statistical difference (p < 0.005) between the methods in all groups. Similar color changes were observed for all pigment solutions when using the spectrophotometric method. For the digital method, all color changes were clinically unacceptable, with distilled water and tomato sauce similar to each other and with statistical differences (p < 0.005) for Coke and açai.Conclusions Only the tomato sauce produced a color change above the acceptability threshold using both methods of color assessment. The spectrophotometric and digital methods produce different patterns of color change. According to our results, the spectrophotometric method is more recommended in color change assessment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
Jamieson Wong, Constance Yeo, Michelle The, Filip Taneski, Uros Josic, Lorenzo Breschi, Vesna Miletic
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026; 38(1): 70. CrossRef - The effects of mechanical and chemical degradation on the surface roughness, gloss, and color stability of bulk-fill resin composites
Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Esra Özyurt, Naz Bayar, Mediha Büyükgöze Dindar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef
- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
- 2,756 View
- 39 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Morphological characteristics of the mesiobuccal root in the presence of a second mesiobuccal canal: a micro-CT study
- Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Matheus Lima Oliveira, Karla Rovaris, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, Frederico Sampaio Neves
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e6. Published online January 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the internal morphology of mesiobuccal (MB) roots of maxillary molars with a second mesiobuccal (MB2) canal.
Materials and Methods Forty-seven maxillary first or second molars from Brazilians were scanned using micro-computed tomography. The following measurements were obtained from the MB roots: root thickness, root width, and dentin thickness of the buccal aspect of the first mesiobuccal (MB1) canal, between the MB1 and MB2 canals, and the palatal aspect of the MB2 and MB1 canals at 3 mm from the root apex and in the furcation region. For statistical analysis, the Student’s
t -test and analysis of variance with thepost-hoc Tukey test were used (α = 0.05).Results In maxillary molars with an MB2 canal, MB roots were significantly thicker (
p = 0.0014) and narrower (p = 0.0016) than in maxillary molars without an MB2 canal. The dentin thickness of the palatal aspect of the MB1 canal was also significantly greater than that of MB roots without an MB2 canal at 3 mm from the root apex (p = 0.0007) and in the furcation region (p < 0.0001). In the furcation region of maxillary molars with an MB2 canal, the dentin thickness between the MB1 and MB2 canals was significantly smaller than that in the buccal and palatal aspects (p < 0.0001).Conclusions The internal morphology of MB roots of maxillary molars with an MB2 canal revealed differences in dentin thickness, root diameter, and distance between the canals when compared with maxillary molars without an MB2 canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of three NiTi systems in endodontic retreatment of MB1 and MB2 root canals: a micro-CT and CBCT combined analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Pedro Luis Busto Rosim, Andréa Gonçalves, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of root and canal morphology of maxillary molars in a Chinese kazakh population
Shuchun Yang, Chenye Li, Hui Shi, Ming Liu, Xu Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Can maxillary molar dimensions predict the presence of the second mesiobuccal canal?
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, Karla Rovaris, Matheus L. Oliveira, Frederico Sampaio Neves
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(3): 482. CrossRef - Can the detection of second mesiobuccal canals be enhanced based on the volume of adjacent canals?
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Deborah Q. Freitas, Karla Rovaris, Matheus L. Oliveira, Frederico S. Neves
Archives of Oral Biology.2023; 146: 105604. CrossRef - Assessment of the coronal root canal morphology of permanent maxillary first molars using digital 3D-reconstruction technology based on micro-computed tomography data
Mudan Wang, Yuxuan Gao, Qi Deng, Yuan Gao, Dongzhe Song, Dingming Huang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(2): 586. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of three NiTi systems in endodontic retreatment of MB1 and MB2 root canals: a micro-CT and CBCT combined analysis
- 1,805 View
- 36 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e2. Published online December 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the impact of micro-computed tomography (micro-CT)-based voxel size on the analysis of material/dentin interface voids and thickness of different endodontic cements.
Materials and Methods Following root-end resection and apical preparation, maxillary premolars were filled with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and intermediate restorative material (IRM) (
n = 24). The samples were scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272; Bruker) and the cement/dentin interface and thickness of materials were evaluated at voxel sizes of 5, 10, and 20 µm. Analysis of variance and the Tukey test were conducted, and the degree of agreement between different voxel sizes was evaluated using the Bland and Altman method (p < 0.05).Results All materials showed an increase in thickness from 5 to 10 and 20 µm (
p < 0.05). When evaluating the interface voids, materials were similar at 5 µm (p > 0.05), while at 10 and 20 µm Biodentine showed the lowest percentage of voids (p < 0.05). A decrease in the interface voids was observed for MTA and IRM at 20 µm, while Biodentine showed differences among all voxel sizes (p < 0.05). The Bland-Altman plots for comparisons among voxel sizes showed the largest deviations when comparing images between 5 and 20 µm.Conclusions Voxel size had an impact on the micro-CT evaluation of thickness and interface voids of endodontic materials. All cements exhibited an increase in thickness and a decrease in the void percentage as the voxel size increased, especially when evaluating images at 20 µm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
Shuting Feng, Weiqing Zhou, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1380. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef
- Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
- 2,117 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Porosity and pore size distribution in high-viscosity and conventional glass ionomer cements: a micro-computed tomography study
- Aline Borburema Neves, Laísa Inara Gracindo Lopes, Tamiris Gomes Bergstrom, Aline Saddock Sá da Silva, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Aline de Almeida Neves
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e57. Published online October 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare and evaluate the porosity and pore size distribution of high-viscosity glass ionomer cements (HVGICs) and conventional glass ionomer cements (GICs) using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
Materials and Methods Forty cylindrical specimens (
n = 10) were produced in standardized molds using HVGICs and conventional GICs (Ketac Molar Easymix, Vitro Molar, MaxxionR, and Riva Self-Cure). The specimens were prepared according to ISO 9917-1 standards, scanned in a high-energy micro-CT device, and reconstructed using specific parameters. After reconstruction, segmentation procedures, and image analysis, total porosity and pore size distribution were obtained for specimens in each group. After checking the normality of the data distribution, the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test was used to detect differences in porosity among the experimental groups with a 5% significance level.Results Ketac Molar Easymix showed statistically significantly lower total porosity (0.15%) than MaxxionR (0.62%), Riva (0.42%), and Vitro Molar (0.57%). The pore size in all experimental cements was within the small-size range (< 0.01 mm3), but Vitro Molar showed statistically significantly more pores/defects with a larger size (> 0.01 mm3).
Conclusions Major differences in porosity and pore size were identified among the evaluated GICs. Among these, the Ketac Molar Easymix HVGIC showed the lowest porosity and void size.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of contouring instruments on immediate quality and porosity of direct restorations
Carlos Soler-Tornero, Pekka Toivonen, Jaakko Suorsa, Sakari S. Karhula, Simo Saarakkala, Vuokko Anttonen, Jukka Leinonen
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Human Blood Contamination on Microhardness of Glass-Ionomer Cements and Glass-Hybrid Material
Katarina Franić, Ana Brundić, Jurica Matijević, Ana Ivanišević, Ivana Miletić, Anja Baraba
Materials.2025; 18(17): 4075. CrossRef - Effect of crown seating methods on the remnant cement in the subgingival region of a cement-retained implant crown
Fanghui Ji, Ji Suk Shim, Jeongyol Lee, Hwiseong Oh, Jae Jun Ryu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing Wear Resistance in Glass Ionomer Cement through Green-mediated Chitosan-, Titanium-, Zirconium-, and Hydroxyapatite-based Nanocomposites: An Analysis before and after Chewing Simulator Endurance
Jessy Paulraj, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Subhabrata Maiti, Srinavasa Surya Sitaram
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(11): 1229. CrossRef - The effect of mesoporous silica doped with silver nanoparticles on glass ionomer cements; physiochemical, mechanical and ion release analysis
Syed Saad Bin Qasim, Ali Bmuajdad
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperbaric Pressure Effect on Dental Luting Cements
Secil OZKAN ATA, Nazım ATA, Rıfat UGURLUTAN
Journal of Basic and Clinical Health Sciences.2023; 7(1): 464. CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum
Hyun-Jin Kim, Jun-Seok Lee, Dong-Hoon Gwak, Yong-Seok Ko, Chun-Il Lim, Seung-Youl Lee
Materials.2023; 17(1): 35. CrossRef - Adhesion and Surface Roughness of Apatite-Containing Carbomer and Improved Ionically Bioactive Resin Compared to Glass Ionomers
Handan Yıldırım Işık, Aylin Çilingir
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(7): 367. CrossRef - An influence of finishing procedures and protective coating on the ultrastructure of conventional and hybrid glass ionomer cement restorations
Antonije Stankovic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Nikolic, Aleksandar Mitic, Nenad Stosic, Radomir Barac, Aleksandra Milovanovic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2023; 70(3): 138. CrossRef - Effect of aging on mechanical and antibacterial properties of fluorinated graphene reinforced glass ionomer: In vitro study
Suzan Khaled Arafa, Dalia Ibrahim Sherief, Mohamed Salah Nassif
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2023; 142: 105803. CrossRef
- The effect of contouring instruments on immediate quality and porosity of direct restorations
- 2,600 View
- 17 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
- Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e56. Published online October 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated 2 nickel-titanium rotary systems and a complementary protocol with an ultrasonic tip and a small-diameter instrument in flattened root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty-two human maxillary second premolars with flattened canals (buccolingual diameter ≥4 times larger than the mesiodistal diameter) at 9 mm from the radiographic apex were selected. The root canals were prepared by ProDesign Logic (PDL) 30/0.01 and 30/0.05 or Hyflex EDM (HEDM) 10/0.05 and 25/0.08 (
n = 16), followed by application of the Flatsonic ultrasonic tip in the cervical and middle thirds and a PDL 25/0.03 file in the apical third (FPDL). The teeth were scanned using micro-computed tomography before and after the procedures. The percentage of volume increase, debris, and uninstrumented surface area were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance/Tukey, and paired and unpairedt -tests (α = 0.05).Results No significant difference was found in the volume increase and uninstrumented surface area between PDL and HEDM (
p > 0.05). PDL had a higher percentage of debris than HEDM in the middle and apical thirds (p < 0.05). The FPDL protocol resulted in less debris and uninstrumented surface area for PDL and HEDM (p < 0.05). This protocol, with HEDM, reduced debris in the middle and apical thirds and uninstrumented surface area in the apical third (p < 0.05).Conclusions High percentages of debris and uninstrumented surface area were observed after preparation of flattened root canals. The HEDM, Flatsonic tip, and 25/0.03 instrument protocol enhanced cleaning in flattened root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
Ayşenur Kızıltaş Gül, Turan Mert Hisar, Seniha Miçooğulları
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(1): 157. CrossRef - Flatsonic Ultrasonic Tip Optimizes the Removal of Remaining Filling Material in Flattened Root Canals: A Micro–computed Tomographic Analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 612. CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heat-treated NiTi instruments and final irrigation protocols for biomechanical preparation of flattened canals
Kleber Kildare Teodoro CARVALHO, Igor Bassi Ferreira PETEAN, Alice Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Rafael Verardino CAMARGO, Jardel Francisco MAZZI-CHAVES, Yara Terezinha Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Manoel Damião SOUSA-NETO
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
- 1,830 View
- 26 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
- Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e54. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e54
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to quantify phase transformation after hydrofluoric acid (HF) etching at various concentrations on the surface of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), and to evaluate changes in bonding strength before and after thermal cycling.
Materials and Methods A group whose Y-TZP surface was treated with tribochemical silica abrasion (TS) was used as the control. Y-TZP specimens from each experimental group were etched with 5%, 10%, 20%, and 40% HF solutions at room temperature for 10 minutes. First, to quantify the phase transformation, Y-TZP specimens (
n = 5) treated with TS, 5%, 10%, 20% and 40% HF solutions were subjected to X-ray diffraction. Second, to evaluate the change in bond strength before and after thermal cycling, zirconia primer and MDP-containing resin cement were sequentially applied to the Y-TZP specimen. After 5,000 thermal cycles for half of the Y-TZP specimens, shear bond strength was measured for all experimental groups (n = 10).Results The monoclinic phase content in the 40% HF-treated group was higher than that of the 5%, 10%, and 20% HF-treated groups, but lower than that of TS-treated group (
p < 0.05). The 40% HF-treated group showed significantly higher bonding strength than the TS, 5%, and 10% HF-treated groups, even after thermal cycling (p < 0.05).Conclusions Through this experiment, the group treated with SiO2 containing air-borne abrasion on the Y-TZP surface showed higher phase transformation and higher reduction in bonding strength after thermal cycling compared to the group treated with high concentration HF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase transition regulation and enhancement of optical properties in YPO4:Eu3+ through the influence of alkali metal ions
Junwei Zhan, Liusai Yang, Yaoxian Zhu, Yifan Zhu, Jianlei Liu, Siyan Peng, Jianping Zou
Journal of Molecular Structure.2026; 1352: 144420. CrossRef - Etchability of zirconia ceramics and its effect on adhesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Anina Sieber, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104303. CrossRef - Effect of BaTiO particle size and distribution on the BaTiO-3Y-TZP interface reactivity of bioactive ceramic composites
João Pinto, Michael Gasik, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva
Ceramics International.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving the Clinical Performance of Dental Implants Through Advanced Surface Treatments: The Case of Ti and ZrO2 Coatings
Mohamed Aissi, Qanita Tayyaba, Azzedine Er-Ramly, Hendra Hermawan, Nadia Merzouk
Metals.2025; 15(3): 320. CrossRef - Enhancing the bonding of zirconia to resin by constructing a graded zirconia-glass composite surface
Zhiqi Yan, Jiale Li, Jing Chen, Zhe Zhao, Fan Li, Ling Zhang, Jihua Chen, Fu Wang
Surfaces and Interfaces.2025; 64: 106374. CrossRef - Surface property changes observed in zirconia during etching with high-concentration hydrofluoric acid over various immersion times
Ga-Eul YOU, Myung-Jin LIM, Kyung-San MIN, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(1): 52. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength for different generation of zirconia CAD/CAM blocks
Man-Jong Cho, Sunwoong Song, Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park, Bum-Soon Lim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(3): 157. CrossRef - Is zirconia surface etching a viable alternative to airborne particle abrasion? A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Carlo D'Alessandro, Uros Josic, Claudia Mazzitelli, Tatjana Maravic, Laurel Graham, Carlo Barausse, Annalisa Mazzoni, Lorenzo Breschi, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105394. CrossRef - Exploring Zirconia Adhesion: Pre and Postsintering Physical Surface Treatment, Chemical Treatment, and Cement Interactions
Flávia Gonçalves, Mirko Dennys Ayala-Perez, Francisco Carlos dos Santos Reis, Walter Gomes Miranda-Júnior, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 3Y-TZP electrostatic painting to increase bond strength to dentin and dental prostheses
Alessandro Brito Thomaz, Carlos Nelson Elias, Heraldo Elias Salomão dos Santos, Celso Renato de Souza Resende, Claudinei dos Santos
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 26: 9063. CrossRef - Effect of surface topography and wettability on shear bond strength of Y-TZP ceramic
Suriyakul Wongsue, Ornnicha Thanatvarakorn, Taweesak Prasansuttiporn, Piyarat Nimmanpipug, Thanapat Sastraruji, Keiichi Hosaka, Richard M. Foxton, Masatoshi Nakajima
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesive Cementation of Zirconia Based Ceramics-Surface Modification Methods Literature Review
Magdalena Szawioła-Kirejczyk, Karolina Chmura, Krzysztof Gronkiewicz, Andrzej Gala, Jolanta E. Loster, Wojciech Ryniewicz
Coatings.2022; 12(8): 1067. CrossRef - Y-TZP Physicochemical Properties Conditioned with ZrO2 and SiO2 Nanofilms and Bond Strength to Dual Resin Cement
Ricardo Faria Ribeiro, Danilo Flamini Oliveira, Camila Bussola Tovani, Ana Paula Ramos, Ana Flavia Sanches Borges, Adriana Claudia Lapria Faria, Rossana Pereira de Almeida, Renata Cristina Silveira Rodrigues
Materials.2022; 15(22): 7905. CrossRef - Enhanced osteogenic activity of titania-modified zirconia implant by ultraviolet irradiation
Shuang Tang, Yan Wang, Zhenyu Zong, Ning Ding, Zutai Zhang
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Phase transition regulation and enhancement of optical properties in YPO4:Eu3+ through the influence of alkali metal ions
- 2,094 View
- 22 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

- Which factors related to apical radiolucency may influence its radiographic detection? A study using CBCT as reference standard
- Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Eduarda Helena Leandro Nascimento, Hugo Gaêta-Araujo, Laís Oliveira de Araujo Cardelli, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e43. Published online July 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the detection rate of apical radiolucencies in 2-dimensional images using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) as the reference standard, and to determine which factors related to the apical radiolucencies and the teeth could influence its detection.
Materials and Methods The sample consisted of exams of patients who had panoramic (PAN) and/or periapical (PERI) radiography and CBCT. The exams were assessed by 2 oral radiologists and divided into PAN+CBCT (227 teeth–285 roots) and PERI+CBCT (94 teeth–115 roots). Radiographic images were evaluated for the presence of apical radiolucency, while CBCT images were assessed for presence, size, location, and involvement of the cortical bone (thinning, expansion, and destruction). Diagnostic values were obtained for PERI and PAN.
Results PERI and PAN presented high accuracy (0.83 and 0.77, respectively) and specificity (0.89 and 0.91, respectively), but low sensitivity, especially for PAN (0.40 vs. 0.65 of PERI). The size of the apical radiolucency was positively correlated with its detection in PERI and PAN (
p < 0.001). For PAN, apical radiolucencies were 3.93 times more frequently detected when related to single-rooted teeth (p = 0.038). The other factors did not influence apical radiolucency detection (p > 0.05).Conclusions PERI presents slightly better accuracy than PAN for the detection of apical radiolucency. The size is the only factor related to radiolucency that influences its detection, for both radiographic exams. For PAN, apical radiolucency is most often detected in single-rooted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiomics-based classification of pediatric dental trauma in periapical radiographs: a preliminary study
Mengtian Peng, Bin Yu, Juan Hu, Xiaoxin Xie, Jihong He
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Diagnostic Acumen in Endodontics
Shilpa Thakkar, Dana Mominkhan
Dental Clinics of North America.2025; 69(4): 479. CrossRef - Three-dimensional clinical assessment for MRONJ risk in oncologic patients following tooth extractions
Catalina Moreno Rabie, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Nicolly Oliveira Santos, Fernanda Nogueira Reis, Tim Van den Wyngaert, Reinhilde Jacobs
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of techniques used to assess clinical outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment in necrotic mature teeth
Roy George
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022; 23(3): 98. CrossRef
- Radiomics-based classification of pediatric dental trauma in periapical radiographs: a preliminary study
- 2,939 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

-
Comparative evaluation of
Emblica officinalis as an etchant and an MMP inhibitor with orthophosphoric acid and chlorhexidine on the microshear bond strength of composite resin: anex vivo study - Divya Sangeetha Rajkumar, Annapoorna Ballagere Mariswamy
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e36. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate
Emblica officinalis (Indian gooseberry or amla) as an acid etchant and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, and to compare its effect on the microshear bond strength of composite resin with orthophosphoric acid (OPA) and 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) as an acid etchant and MMP inhibitor, respectively.Materials and Methods The etching effect and MMP-inhibiting action of amla on dentin samples were confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and gelatin zymography, respectively. Dentinal slabs (3 mm thick) from 80 extracted human molars were divided into 10 and 20 samples to form 2 control groups and 3 experimental groups. Groups 1, 2, and 4 were etched with OPA and groups 3 and 5 with amla juice. An MMP inhibitor was then applied: CHX for group 2 and amla extract for groups 4 and 5. Groups 1 and 3 received no MMP inhibitor. All specimens received a standardized bonding protocol and composite resin build-up, and were subjected to microshear bond strength testing. The force at which the fracture occurred was recorded and statistically analyzed.
Results Amla juice had a similar etching effect as a self-etch adhesive in SEM and 100% amla extract was found to inhibit MMP-9 by gelatin zymography. The microshear bond strength values of amla were lower than those obtained for OPA and CHX, but the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusions Amla has a promising role as an acid etchant and MMP inhibitor, but further studies are necessary to substantiate its efficacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro assessment of anti-glioblastoma potential of Emblica officinalis methanolic fruit extract and green nanoparticles in U87-MG cells
Kokkonda Jackson Sugunakara Chary, Anuradha Sharma, Amrita Singh
Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Eco-conscious synthesis of novel 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as potent Anti-microbial agent and comparative study of cell viability and cytotoxicity in HEK-293 cell line utilizing Indian gooseberry (Phyllanthus emblica) fruit extract
Bhaktiben R. Bhatt, Kamalkishor Pandey, Tarosh Patel, Anupama Modi, Chandani Halpani, Vaibhav D. Bhatt, Bharat C. Dixit
Bioorganic Chemistry.2024; 153: 107936. CrossRef - Cell mediated ECM-degradation as an emerging tool for anti-fibrotic strategy
Peng Zhao, Tian Sun, Cheng Lyu, Kaini Liang, Yanan Du
Cell Regeneration.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into the development of versatile dentin bonding agents to increase the durability of the bonding interface
Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto, Teresa de Lisieux Guedes Ferreira Lôbo, Raphaela Farias Rodrigues, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Aurélio Bomfim da Silva
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- In vitro assessment of anti-glioblastoma potential of Emblica officinalis methanolic fruit extract and green nanoparticles in U87-MG cells
- 1,833 View
- 20 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Evaluation of the relation between the pulp stones and direct restorations using cone beam computed tomography in a Turkish subpopulation
- Güzide Pelin Sezgin, Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e34. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e34
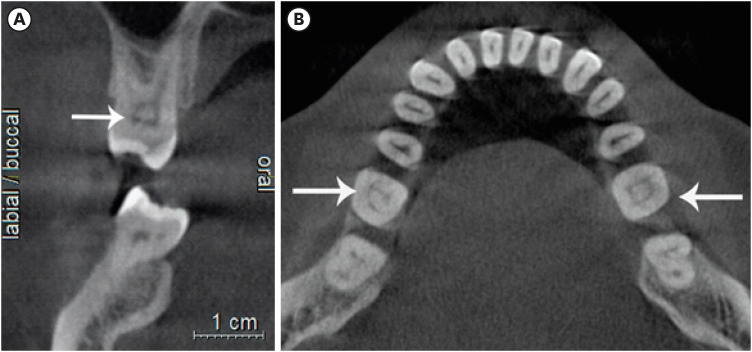
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the presence of pulp stones through an examination of cone beam computed tomography images and correlate their prevalence with age, sex, dental arch and side, tooth type, and restoration type and depth.
Materials and Methods Cone beam computed tomography images obtained from 673 patients and archival data on 11,494 teeth were evaluated. The associations of pulp stones with age, sex, dental arch and side, tooth type, and restoration type and depth were noted. All the measurements were subjected to a χ2 test and one sample χ2 test (
p < 0.05).Results In the study group, 163 (24.2%) patients and 379 (3.3%) teeth had at least one pulp stone. The pulp stone frequency in those aged 30–39 years was significantly greater than in those aged 18–29 and ≥ 60 years, and the frequency was higher in females than in males (
p < 0.05). The highest prevalence of pulp stones was found in maxillary dental arches and molar teeth (p < 0.05). Pulp stones were significantly more common in medium-depth restorations (p < 0.05).Conclusions Maxillary molar teeth, medium-depth restorations, individuals aged 30–39 years and females had a greater percentage of pulp stones.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Assessment of the Prevalence and Association of Pulp Calcification with Dental and Periodontal Pathology: A Descriptive Study
José Luis Sanz, Lucía Callado, Stefana Mantale, Jenifer Nicolás, James Ghilotti, Carmen Llena
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(4): 1373. CrossRef - Prevalence of mineralization in the pulp chamber in patients according to CBCT data
V. A. Molokova, I. N. Antonova, V. A. Osipova
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(2): 188. CrossRef - Could carotid artery calcifications and pulp stones be an alarm sign for diabetes mellitus? A retrospective observational study
Motahare Baghestani, Mohadese Faregh, Seyed Hossein Razavi, Fatemeh Owlia
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution and influencing factors of pulp stones based on CBCT: a retrospective observational study from southwest China
Wantong Zhang, Yao Wang, Lin Ye, Yan Zhou
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Association of Calcified Pulp Stones with Periodontitis: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study in Saudi Arabian Population
Abdullah Saad Alqahtani
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S644. CrossRef - The Prevalence And Distribution Of Pulp Stones: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study İn A Group Of Turkish Patients
Mujgan Firincioglulari, Seçil Aksoy, Melis Gülbeş, Umut Aksoy, Kaan Orhan
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 13(3): 496. CrossRef - Radiographical examination of pulp stone distribution by cone beam computed tomography
Fatma Tunç, Emre Çulha, Muazzez Naz Baştürk
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2024; 7(4): 472. CrossRef - Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Based Investigation of the Prevalence and Distribution of Pulp Stones and Their Relation to Local and Systemic Factors in the Makkah Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Laila M Kenawi, Haytham S Jaha, Mashael M Alzahrani, Jihan I Alharbi, Shahad F Alharbi, Taif A Almuqati, Rehab A Alsubhi, Wahdan M Elkwatehy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone beam computed tomography assessment of the prevalence and association of pulp calcification with periodontitis
Lingling Xiang, Botao Wang, Yuan Zhang, Jintao Wang, Peipei Wu, Jian Zhang, Liangjun Zhong, Rui He
Odontology.2023; 111(1): 248. CrossRef - Three-dimensional analysis for detection of pulp stones in a Saudi population using cone beam computed tomography
Hassan H. Kaabi, Abdullah M. Riyahi, Nassr S. Al-Maflehi, Saleh F. Alrumayyan, Abdullah K. Bakrman, Yazeed A. Almutaw
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 257. CrossRef
- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Assessment of the Prevalence and Association of Pulp Calcification with Dental and Periodontal Pathology: A Descriptive Study
- 2,246 View
- 26 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
- Shashirekha Govind, Amit Jena, Satabdi Pattanaik, Mahaprasad Anarasi, Satyajit Mohapatra, Vinay Shivagange
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e33. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of ionic and non-ionic-based contrast media (
in vitro study) and the combinatorial effect of chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution (CERS) (in vivo study) for visualization of the root canal anatomy.Materials and Methods In vitr o study (120 teeth): The root canal of maxillary premolars and molars (in vitro group 1 and 2 respectively,n = 60 each) were analyzed using 4 different contrast media (subgroups: Omnipaque 350, Iopamidol, Xenetix 350, and Urografin 76;n = 15 each) in combination with 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Based on the results of thein vitro study,in vivo study (80 teeth) was done to compare Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl with CERS (in vivo group 1 and 2 respectively,n = 40 each) on maxillary and mandibular premolars and molars. Two endodontists used radiovisiography to assess the depth of ingress and identify the aberrant root anatomy after access cavity preparation, and after initial cleaning and shaping of canals. Kruskal-Wallis test was used forin vitro comparison (p < 0.05), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Mann-WhitneyU test forin vivo analysis (p < 0.01).Results In vitro study, Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl facilitated a significant higher visualization (p < 0.05). Forin vivo study, CERS had a statistically significant depth of ingress (p < 0.01), and was efficient in identifying the aberrant root canal anatomy of premolars and molars.Conclusions CERS facilitates better visualization of the root canal anatomy of human premolars and molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Improving Endodontic Radiograph Interpretation with TV-CLAHE for Enhanced Root Canal Detection
Barbara Obuchowicz, Joanna Zarzecka, Michał Strzelecki, Marzena Jakubowska, Rafał Obuchowicz, Adam Piórkowski, Elżbieta Zarzecka-Francica, Julia Lasek
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(15): 5554. CrossRef - Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation on irrigant penetration in different tapered preparations: An in vitro study
M. Rama Sowmya, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Pradeep Solete, Sahil Choudhari, S Delphine Priscilla Antony, Mohammed Mustafa
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 370. CrossRef - Analysis of the value of visualized root canal technique in the clinical treatment of endodontics
Nana SUN, Nannan WANG, Xin QIAN
Panminerva Medica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
- 1,767 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Color assessment of resin composite by using cellphone images compared with a spectrophotometer
- Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Ratto Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e23. Published online April 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study assessed the reliability of digital color measurements using images of resin composite specimens captured with a cellphone.
Materials and Methods The reference color of cylindrical specimens built-up with the use of resin composite (shades A1, A2, A3, and A4) was measured with a portable spectrophotometer (CIELab). Images of the specimens were obtained individually or pairwise (compared shades in the same photograph) under standardized parameters. The color of the specimens was measured in the images using RGB system and converted to CIELab system using image processing software. Whiteness index (WID) and color differences (ΔE00) were calculated for each color measurement method. For the cellphone, the ΔE00 was calculated between the pairs of shades in separate images and in the same image. Data were analyzed using 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05). Linear regression models were used to predict the reference ΔE00 values of those calculated using color measured in the images.
Results Images captured with the cellphone resulted in different WID values from the spectrophotometer only for shades A3 and A4. No difference to the reference ΔE00 was observed when individual images were used. In general, a similar ranking of ΔE00 among resin composite shades was observed for all methods. Stronger correlation coefficients with the reference ΔE00 were observed using individual than pairwise images.
Conclusions This study showed that the use of cellphone images to measure the color difference seems to be a feasible alternative providing outcomes similar to those obtained with the spectrophotometer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How the Translucency and Color Stability of Single-Shade Universal Resin Composites Are Affected by Coffee?
Büşra Özdemir, Betül Kübra Kurucu Karadeniz, Seyit Bilal Özdemir, Ömer Akbulut
Current Research in Dental Sciences.2024; 34(4): 270. CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of VITA Shade Guide and Various Composite Shades Using Spectrophotometer, Digital Single-lens Reflex, and Cellphone: An In Vitro Study
Aman Verma, Sonali Taneja, Surabhi Ghosh
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 803. CrossRef - Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,625 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Shaping ability and apical debris extrusion after root canal preparation with rotary or reciprocating instruments: a micro-CT study
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Sara Gomes de Moura, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Waleska Florentino Misael, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Luciana Moura Sassone
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e16. Published online February 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e16

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems and the apical extrusion of debris after root canal instrumentation. The ProTaper Universal system was used as a reference for comparison.
Materials and Methods Thirty-three mandibular premolars with a single canal were scanned using micro-computed tomography and were matched into 3 groups (
n = 11) according to the instrumentation system: TruShape, Reciproc Blue and ProTaper Universal. The teeth were accessed and mounted in an apparatus with agarose gel, which simulated apical resistance provided by the periapical tissue and enabled the collection of apically extruded debris. During root canal preparation, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite was used as an irrigant. The samples were scanned again after instrumentation. The percentage of unprepared area, removed dentin, and volume of apically extruded debris were analyzed. The data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test for multiple comparisons at a 5% significance level.Results No significant differences in the percentage of unprepared area were observed among the systems (
p > 0.05). ProTaper Universal presented a higher percentage of dentin removal than the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems (p < 0.05). The systems produced similar volumes of apically extruded debris (p > 0.05).Conclusions All systems caused apically extruded debris, without any significant differences among them. TruShape, Reciproc Blue, and ProTaper Universal presented similar percentages of unprepared area after root canal instrumentation; however, ProTaper Universal was associated with higher dentin removal than the other systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endomotor integration, file kinematics impact on apical debris extrusion in severely curved canals
Anshika Saxena, Vineeta Nikhil
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 87. CrossRef - Comparison of post-operative pain prevalence after single visit endodontic treatment with two NiTi rotary files - a randomized clinical trial
M. E. Khallaf, Yousra Aly, Amira Ibrahim Mohamed
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Silver-Ion-Coated Rotary Nickel Titanium Files - An In Vitro Study
Jhanvi H. Sadaria, Kondas V. Venkatesh, Dhanasekaran Sihivahanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(3): 344. CrossRef - A quantitative comparison of apically extruded debris during root canal preparation using NiTi full-sequence rotary and single-file rotary systems: An in vitro study
Pallavi Goel, R. Vikram, R. Anithakumari, M. S. Adarsha, M. E. Sudhanva
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 235. CrossRef - Extrusion of Sodium Hypochlorite in Oval-Shaped Canals: A Comparative Study of the Potential of Four Final Agitation Approaches Employing Agarose-Embedded Mandibular First Premolars
Aalisha Parkar, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Alexander Maniangat Luke
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(10): 2748. CrossRef - Shaping Efficiency of Rotary and Reciprocating Kinematics of Engine-driven Nickel-Titanium Instruments in Moderate and Severely curved Root Canals Using Microcomputed Tomography: A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Claudiu Călin, Ana-Maria Focșăneanu, Friedrich Paulsen, Andreea C. Didilescu, Tiberiu Niță
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 907. CrossRef - Intracanal removal and apical extrusion of filling material after retreatment using rotary or reciprocating instruments: A new approach using human cadavers
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Victor O. Cortes‐Cid, Marilia F. V. Marceliano‐Alves, Andrea F. Campello, Luan F. Bastos, Ricardo T. Lopes, José F. Siqueira, Flávio R. F. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(1): 100. CrossRef - Assessment of debris extrusion on using automated irrigation device with conventional needle irrigation – An ex vivo study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Raja Kumar, Sindhu Ramesh
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 263. CrossRef - Postoperative pain perception and associated risk factors in children after continuous rotation versus reciprocating kinematics: A randomised prospective clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Dania Ibrahem Sermani, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 345. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of new reciprocating or rotary instruments with two cross‐sectional designs: An ex vivo study
Isabela G. Guedes, Renata C. V. Rodrigues, Marília F. Marceliano‐Alves, Flávio R. F. Alves, Isabela N. Rôças, José F. Siqueira
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Endomotor integration, file kinematics impact on apical debris extrusion in severely curved canals
- 2,739 View
- 50 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- The effect of different confluence confirmation strategies on the obturation of Vertucci type II canal: micro-CT analysis
- Seungjae Do, Min-Seock Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e12. Published online January 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The present study aims to compare the obturation quality of 2 confluence confirmation techniques in artificial maxillary first premolars showing Vertucci type II root canal configuration.
Materials and Methods Thirty artificial maxillary premolars having Vertucci type II root canal configuration were made. They were divided into 3 groups according to the confluence confirmation technique as follows. Gutta-percha indentation (GPI) group (confluence confirmation using a gutta-percha cone and a K file); electronic apex locator (EAL) group (confluence confirmation using K files and EAL); and no confluence detection (NCD) group. In the GPI group and the EAL group, shaping and obturation were performed with the modified working length (WL). In the NCD group, shaping was performed without WL adjustment and obturation was carried out with an adjusted master cone. Micro-computed tomography was used before preparation and after obturation to calculate the percentage of gutta-percha occupied volume (%GPv) and the volume increase in the apical 4 mm. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and
post hoc Tukey's test.Results Statistically significant difference was not found in terms of the %GPv from the apex to apical 4 mm. However, the NCD group showed a statistically significant volume increase compared with the EAL group (
p < 0.05).Conclusions In terms of gutta-percha occupied volume, no significant difference was observed among the 3 groups. Confluence confirmation using an EAL in teeth with Vertucci type II configuration showed less volume increase during canal shaping compared with no confluence confirmation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ANALISE TOMOGRÁFICA DAS TERMINAÇÕES APICAIS DOS CONDUTOS MV1 e MV2 EM MOLARES SUPERIORES
Milena Matos Borges, Giulio César Moreira Manzi, Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Izabella Lucas de Abreu Lima, Diogo de Azevedo Miranda, Flávio Ricardo Manzi
ARACÊ .2026; 8(1): e11921. CrossRef - Root and root canal morphology of mandibular first and second molars in a Jordanian subpopulation: a cross-sectional cone-beam computed tomography study
Rawan Abu Zaghlan, Laith Abu Qdais, Farouq Mansour, Faisal Mansour, Faleh Sawair
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Can the addition of surfactants to NaOCl irrigation impact on the percentage of voids of root canal filling?
Laise Pena Braga Monteiro, Marcella Yasmin Reis Guerreiro, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Juliana Melo da Silva Brandão
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 260. CrossRef
- ANALISE TOMOGRÁFICA DAS TERMINAÇÕES APICAIS DOS CONDUTOS MV1 e MV2 EM MOLARES SUPERIORES
- 2,187 View
- 46 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e2. Published online December 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives New premixed bioceramic root repair materials require moisture for setting. Using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), this study evaluated the filling ability and volumetric changes of calcium silicate-based repair materials (mineral trioxide aggregate repair high-plasticity [MTA HP] and Bio-C Repair, Angelus), in comparison with a zinc oxide and eugenol-based material (intermediate restorative material [IRM]; Dentsply DeTrey).
Materials and Methods Gypsum models with cavities 3 mm deep and 1 mm in diameter were manufactured and scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272. Bruker). The cavities were filled with the cements and scanned again to evaluate their filling capacity. Another scan was performed after immersing the samples in distilled water for 7 days to assess the volumetric changes of the cements. The statistical significance of differences in the data was evaluated using analysis of variance and the Tukey test with a 5% significance level.
Results Bio-C Repair had a greater filling ability than MTA HP (
p < 0.05). IRM was similar to Bio-C and MTA HP (p > 0.05). MTA HP presented the largest volumetric change (p < 0.05), showing more volume loss than Bio-C and IRM, which were similar (p > 0.05).Conclusions Bio-C Repair is a new endodontic material with excellent filling capacity and low volumetric change. The gypsum model proposed for evaluating filling ability and volumetric changes by micro-CT had appropriate and reproducible results. This model may enhance the physicochemical evaluation of premixed bioceramic materials, which need moisture for setting.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of sealing potential of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine, and bio-C repair in furcation perforations: A glucose penetration study
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira Anjum Sultana, A. Srirekha, C. Champa, Suditi Pal, V. Sahithi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 144. CrossRef - Evaluation of volumetric and surface stability of calcium silicate-based repair cements at different pHs
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Débora Leticia Bittencourt Leite Alves, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Nilvan Alves da Silva, Matheus Barros-Costa, Luciano Augusto Cano Martins, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marina Angélica Marciano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and periodontal ligament stem cell response to NeoMTA 2
Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Ariadne Letra, Renato Menezes Silva, Letícia Chaves de Souza, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Condensation Time on Void Formation and Microhardness of Well-RootTM PT Apical Plugs in 3D-Printed Immature Teeth
Krasimir Hristov, Ralitsa Bogovska-Gigova
Materials.2025; 18(21): 4835. CrossRef - Effect of pH on the solubility and volumetric change of ready-to-use Bio-C Repair bioceramic material
Luana Raphael da SILVA, Jader Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of blood and artificial saliva contamination on marginal adaptation and sealing ability of different retrograde filling materials: A comparative analysis
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(7): 743. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Volumetric change of calcium silicate-based repair materials in a simulated inflammatory environment: A micro-computed tomography study
Giovanna da Cunha Mendonça, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(8): 817. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, bioactivity, porosity, and sealer/dentin interface of bioceramic ready-to-use sealers using a dentin-tube model
Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Camila Soares Lopes, Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Juliane Maria Guerreiro–Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing the Open Apex: A Case Report on Innovative Apexogenesis of a Maxillary Molar Using Bio-C Repair
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira A Sultana, Keerthan B V, Nithin S Reddy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, bioactive potential, porosity, and interface analysis calcium silicate repair cements in a dentin tube model
Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Camila Soares Lopes, Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3839. CrossRef - A new proposal for evaluating of the solubility of bioceramic materials in dentin tubes after immersion in PBS: a laboratory investigation
Giovanna da Cunha MENDONÇA, Karina Ines Medina Carita TAVARES, Airton Oliveira SANTOS-JUNIOR, Jáder Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of sealing potential of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine, and bio-C repair in furcation perforations: A glucose penetration study
- 2,390 View
- 32 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

-
Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an
in vitro study - Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e50. Published online October 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we investigated the potential of amoxicillin-loaded polymeric microspheres to be delivered to tooth root infection sites via a bioactive reparative cement.
Materials and Methods Amoxicillin-loaded microspheres were synthesized by a spray-dray method and incorporated at 2.5% and 5% into a mineral trioxide aggregate cement clinically used to induce a mineralized barrier at the root tip of young permanent teeth with incomplete root development and necrotic pulp. The formulations were modified in liquid:powder ratios and in composition by the microspheres. The optimized formulations were evaluated
in vitro for physical and mechanical eligibility. The morphology of microspheres was observed under scanning electron microscopy.Results The optimized cement formulation containing microspheres at 5% exhibited a delayed-release response and maintained its fundamental functional properties. When mixed with amoxicillin-loaded microspheres, the setting times of both test materials significantly increased. The diametral tensile strength of cement containing microspheres at 5% was similar to control. However, phytic acid had no effect on this outcome (
p > 0.05). When mixed with modified liquid:powder ratio, the setting time was significantly longer than that original liquid:powder ratio (p < 0.05).Conclusions Lack of optimal concentrations of antibiotics at anatomical sites of the dental tissues is a hallmark of recurrent endodontic infections. Therefore, targeting the controlled release of broad-spectrum antibiotics may improve the therapeutic outcomes of current treatments. Overall, these results indicate that the carry of amoxicillin by microspheres could provide an alternative strategy for the local delivery of antibiotics for the management of tooth infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Local drug delivery for regeneration and disinfection in endodontics: A narrative review
Anu Elsa Swaroop, Sylvia Mathew, P. Harshini, Shruthi Nagaraja
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 119. CrossRef - Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate—A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements
C. Pushpalatha, Vismaya Dhareshwar, S. V. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Thilla Sekar Vinothkumar, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Amal Shaiban, Ateet Kakti, Shilpa H. Bhandi, Alok Dubey, Amulya V. Rai, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Local drug delivery for regeneration and disinfection in endodontics: A narrative review
- 1,877 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


