Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- In vitro experimental study comparing continuous and intermittent irrigation protocols: influence of sodium hypochlorite volume and contact time on tissue dissolution
- Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Gwenael Rolin, Camille Coussens, Aurelian Louvrier, Felipe G Belladonna, Edouard Euvrard, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e36. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
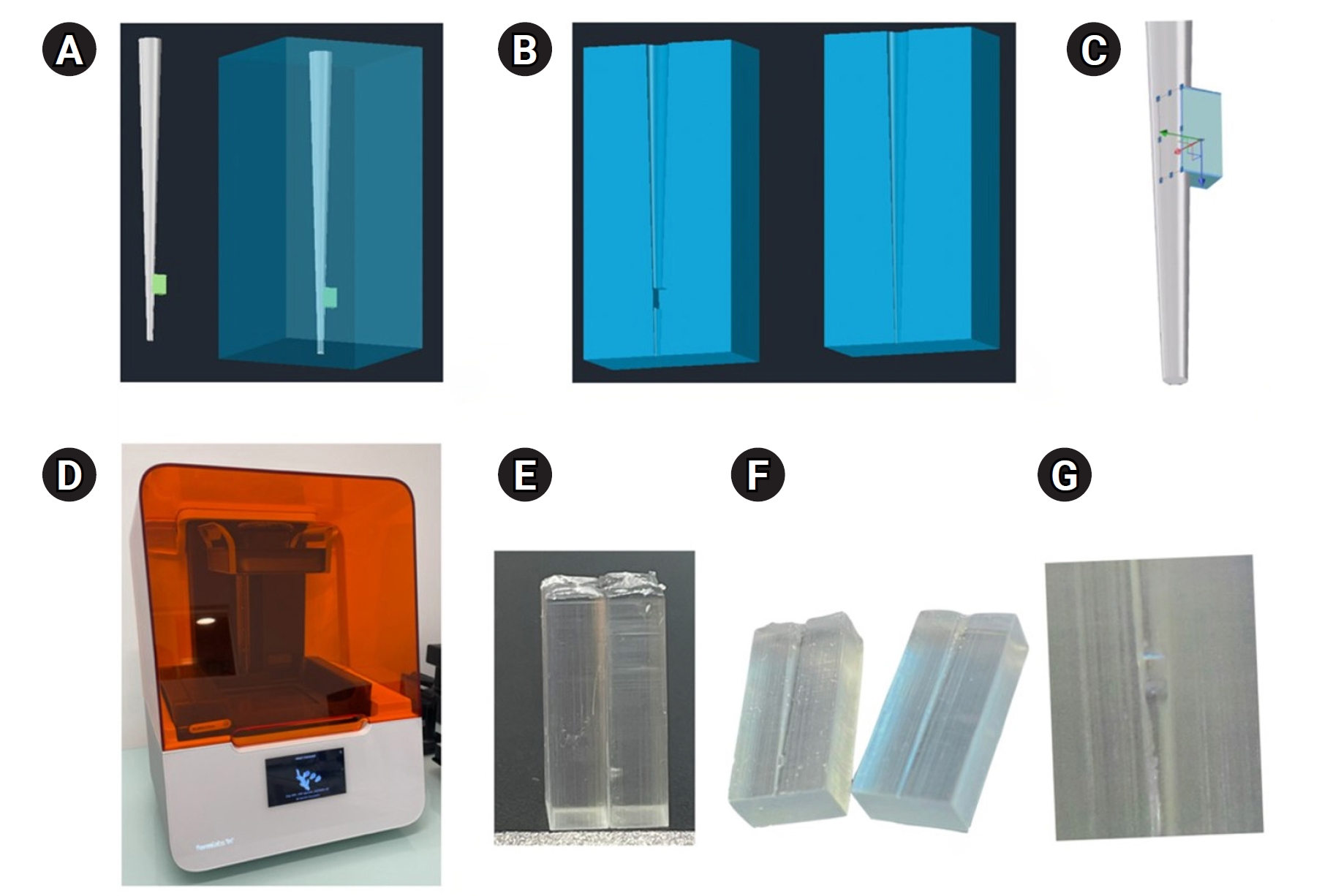
This study aimed to evaluate whether continuous irrigation with larger volumes or allowing sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) resting time is more critical for pulp tissue dissolution using a controlled artificial root canal system.
Methods
A three-dimensional printed artificial root canal with a lateral canal in the apical third was fabricated. Standardized bovine pulp tissue specimens were inserted, and three irrigation protocols were tested: group A (continuous NaOCl irrigation at 1 mL/min via syringe pump), group B (intermittent NaOCl irrigation with 0.1 mL and a 3-minute resting period), and group C (control, saline irrigation). The time for complete dissolution and the total NaOCl volume were recorded.
Results
Complete dissolution occurred in groups A and B, with significant differences in NaOCl volume and time (p < 0.05). In group A, complete dissolution was consistently observed after the 6th irrigation cycle, corresponding to a total NaOCl volume of 6.0 ± 0.66 mL per test. The average time required for complete dissolution in this group was 6 ± 0.66 minutes. In group B, complete dissolution occurred after the 4th cycle, with a total NaOCl volume of 0.4 ± 0.06 mL per test and a mean dissolution time of 12.6 ± 1.8 minutes.
Conclusions
NaOCl volume and exposure time significantly influence pulp tissue dissolution.
- 1,549 View
- 159 Download

- Color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions
- Sıla Nur Usta, Cangül Keskin
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e25. Published online June 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e25

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions.
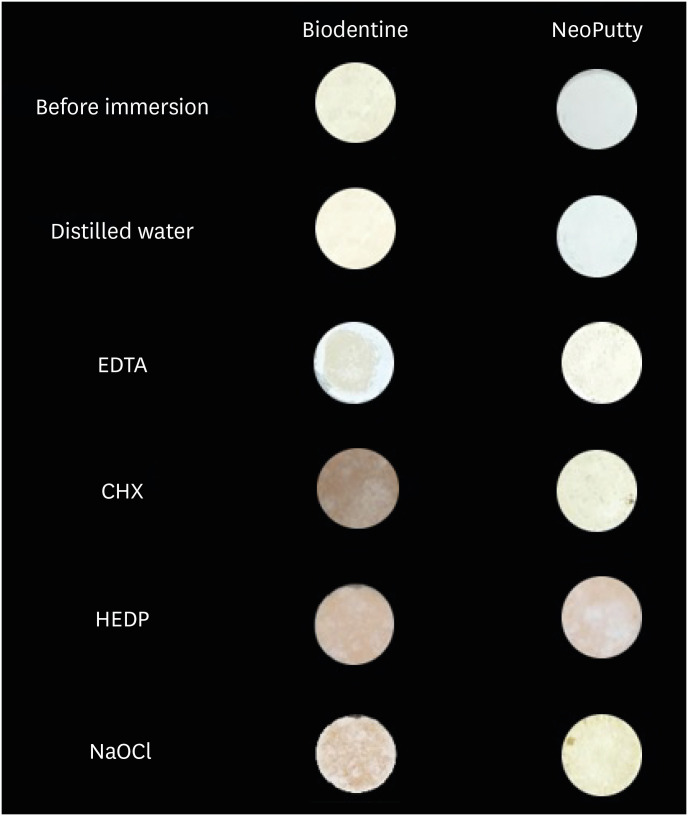
Materials and Methods Biodentine and NeoPutty were set in cylindrical molds with 7 mm diameter and 1.5 mm high and immersed in distilled water, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 2% chlorhexidine (CHX), 9% 1-hydroxyethylidene 1,1-diphosphonate (HEDP), and 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) solutions for 24 hours. The color change was measured with a spectrophotometer. The solubility values were calculated as the mass loss was expressed as a percentage of the original mass using an analytical balance with 10−4 g accuracy. Data were analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis followed by Mann-Whitney
U tests, and 2-way analysis of variance test followed by Bonferroni corrections for pairwise comparisons for solubility and color stability with a 5% significance threshold, respectively.Results Biodentine exhibited higher color changes compared to the NeoPutty contact with all solutions except distilled water (
p < 0.05). Both hydraulic cements (HCs) showed higher discoloration values immersion in CHX followed by NaOCl. No statistically significant difference was found between Biodentine and NeoPutty regardless of irrigation solution in terms of solubility (p > 0.05). Solubility values were lower in the distilled water group compared to EDTA and CHX (p < 0.05).Conclusions Tested HCs showed solubility and color changes at various rates. NeoPutty could be an appropriate material in aesthetic areas. The usage of HEDP as an irrigant solution can be considered suitable for various endodontic treatments due to its relatively lower solubility and discoloration values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sealing ability of Biodentine, zirconia reinforced glass ionomer cement and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as furcation perforation repair materials: an in vitro analysis
Sumita Panwar, Yajuvender Singh Hada
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2026; 13: 21. CrossRef
- Sealing ability of Biodentine, zirconia reinforced glass ionomer cement and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as furcation perforation repair materials: an in vitro analysis
- 2,811 View
- 154 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Disinfectant effectiveness of chlorhexidine gel compared to sodium hypochlorite: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- Theodoro Weissheimer, Karem Paula Pinto, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e37. Published online October 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to compare the disinfectant ability of chlorhexidine (CHX) gel and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Systematic searches were conducted from inception until December 8th, 2022 (MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and Grey Literature databases). Only randomized clinical trials were included. The revised Cochrane risk of bias tools for randomized trials were used to assess the quality of studies. Meta-analyses were performed. The overall quality of evidence was assessed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation tool. Six studies were included. Five had a low risk of bias and 1 had some concerns. Three studies assessed bacterial reduction. Two were included in the meta-analysis for bacterial reduction (mean difference, 75.03 [confidence interval, CI, −271.15, 421.22],
p = 0.67;I 2 = 74%); and 3 in the meta-analysis for cultivable bacteria after chemomechanical preparation (odds ratio, 1.03 [CI, 0.20, 5.31],P = 0.98;I 2 = 49%). Five studies assessed endotoxin reduction. Three were included in a meta-analysis (mean difference, 20.59 [CI, −36.41, 77.59],p = 0.48;I 2 = 74%). There seems to be no difference in the disinfectant ability of CHX gel and NaOCl, but further research is necessary.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- REGENERATIVE ENDODONTIC PROCEDURES: MAPPING AND CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF CLINICAL TRIAL EVIDENCE
Felipe Oliveira Nunes, Eduardo Borges Sollim, Carolynne Ferreira dos Santos, Maria Karolina Martins Ferreira, João Daniel Mendonça Moura, Juliana Melo Brandão, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Paulo Jorge Palma, Rafael Rodrigues Lima
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Bactericidal Effects of Ultraviolet-C Light-Emitting Diode Prototype Device Through Thin Optical Fiber
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Deog-Gyu Seo
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4504. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Irrigation Protocols in Endodontic Therapy: An Umbrella Review
Manuel J. Orozco-Gallego, Eliana L. Pineda-Vélez, Wilder J. Rojas-Gutiérrez, Martha L. Rincón-Rodríguez, Andrés A. Agudelo-Suárez
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 273. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Disinfectants on Gutta-Percha Cones: Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans
Tringa Kelmendi, Donika Bajrami Shabani, Aida Meto, Hani Ounsi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 6846. CrossRef - Preparing porcine lens to mimic human lens capsule
Yajing Pei, Shaofeng Han, Mingfeng Lu, Yang Yang, Ke Ma
Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery.2024; 50(9): 963. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Disinfection Protocols for Dental Impressions in Prosthodontics
Subhash Sonkesriya, Ghanshyam Gaur, Akanksha Maheshwari, Arun Kumar Ashahiya, Simran Kaur Aulakh, Amit Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- REGENERATIVE ENDODONTIC PROCEDURES: MAPPING AND CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF CLINICAL TRIAL EVIDENCE
- 6,409 View
- 124 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Dentinal tubule penetration of sodium hypochlorite in root canals with and without mechanical preparation and different irrigant activation methods
- Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Matheus Albino Souza, Rodrigo Gonçalves Ribeiro, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e1. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the dentinal penetration depth of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) in root canals with and without preparation and different irrigant activation protocols.
Materials and Methods Sixty-three bovine mandibular incisors were randomly allocated to 6 groups (
n = 10): G1, preparation + conventional needle irrigation (CNI); G2, preparation + passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI); G3, preparation + Odous Clean (OC); G4, no preparation + CNI; G5, no preparation + PUI; G6, no preparation + OC; and CG (negative control;n = 3). Samples were filled with crystal violet for 72 hours. Irrigant activation was performed. Samples were sectioned perpendicularly along the long axis, 3 mm and 7 mm from the apex. Images of the root thirds of each block were captured with a stereomicroscope and analyzed with an image analysis software. One-way analysis of variance, followed by the Tukeypost hoc test, and the Student’st -test were used for data analysis, with a significance level of 5%.Results The NaOCl penetration depth was similar when preparation was performed, regardless of the method of irrigation activation (
p > 0.05). In the groups without preparation, G6 showed greater NaOCl penetration depth (p < 0.05). The groups without preparation had a greater NaOCl penetration depth than those with preparation (p = 0.0019).Conclusions The NaOCl penetration depth was similar in groups with root canal preparation. Without root canal preparation, OC allowed deeper NaOCl penetration. The groups without preparation had greater NaOCl penetration than those undergoing root canal preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Novel approaches involving curcumin in endodontic and periodontal diseases: a scoping review
Yuxi Xing, Yanbing Zhu, Yukai Shen, Yuou Xu, Ziman Xu, Mengxue Wang, Xudong Ma, Lehua Liu, Shu Chen
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of passive ultrasonic irrigation cycles on the penetration depth of sodium hypochlorite into root dentin
Hüseyin Gündüz, Esin Özlek, Züleyha Baş
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the Effects of Various Antioxidants on Dentinal Tubule Penetrability of a Resin-Based Sealer: A Confocal Laser Microscopic Study
Sanjeev Srivastava, Shijita Sinha, Abhishek Singh, Aditya Singh, Pragyan Paliwal, Syed H Mehdii
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different activation procedures on sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after endodontic retreatment via confocal laser scanning microscopy
Betul Gunes, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter, Yasin Altay
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Debridement ability of the WaveOne Gold and TruNatomy systems in the apical third of root canals: ex vivo assessment
Sara Carvalho Avelar de Oliveira, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Carolina Pessoa Stringheta
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined effect of electrical energy and graphene oxide on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Myung-Jin LEE, Mi-Ah KIM, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 844. CrossRef
- Novel approaches involving curcumin in endodontic and periodontal diseases: a scoping review
- 2,624 View
- 69 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

-
The influence of sodium hypochlorite concentration on the fibrin structure of human blood clots and transforming growth factor-beta 1 release: an
ex vivo study - Anisha Mishra, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e42. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This study investigated the effects of various concentrations of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) on human whole-blood clotting kinetics, the structure of the blood clots formed, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 release.
Materials and Methods Human whole blood was collected from 5 healthy volunteers and divided into 4 groups: CG (control, 0.5 mL of blood), BN0.5 (0.5 mL of blood with 0.5 mL of 0.5% NaOCl), BN3 (0.5 mL of blood with 0.5 mL of 3% NaOCl), and BN5.25 (0.5 mL of blood with 0.5 mL of 5.25% NaOCl). The effects of NaOCl on clotting kinetics, structure of fibrin and cells, and release of TGF-β1 were assessed using thromboelastography (TEG), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and enzyme-linked immunosobent assay, respectively. Statistical analysis was conducted using the Kruskal Wallis and Mann-Whitney
U tests, followed by thepost hoc Dunn test. Ap value < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.Results The blood samples in BN0.5 and BN3 did not clot, whereas the TEG of BN5.25 showed altered clot formation. Samples from the CG and BN3 groups could only be processed with SEM, which showed that the latter lacked fibrin formation and branching of fibers, as well as clumping of red blood cells with surface roughening and distortion. TGF-β1 release was significantly highest in BN3 when all groups were compared to CG (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Each concentration of NaOCl affected the release of TGF-β1 from blood clots and altered the clotting mechanism of blood by affecting clotting kinetics and cell structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytotoxic Effects of Synthetic and Herbal Endodontic Irrigants on Human Red Blood Cells: An In Vitro Study
Panna Mangat, Bhaviya Chandel, Mampi Biswas, Sara Trivedy, Akshata Gupta, Nayan Shree, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cytotoxic Effects of Synthetic and Herbal Endodontic Irrigants on Human Red Blood Cells: An In Vitro Study
- 2,019 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref

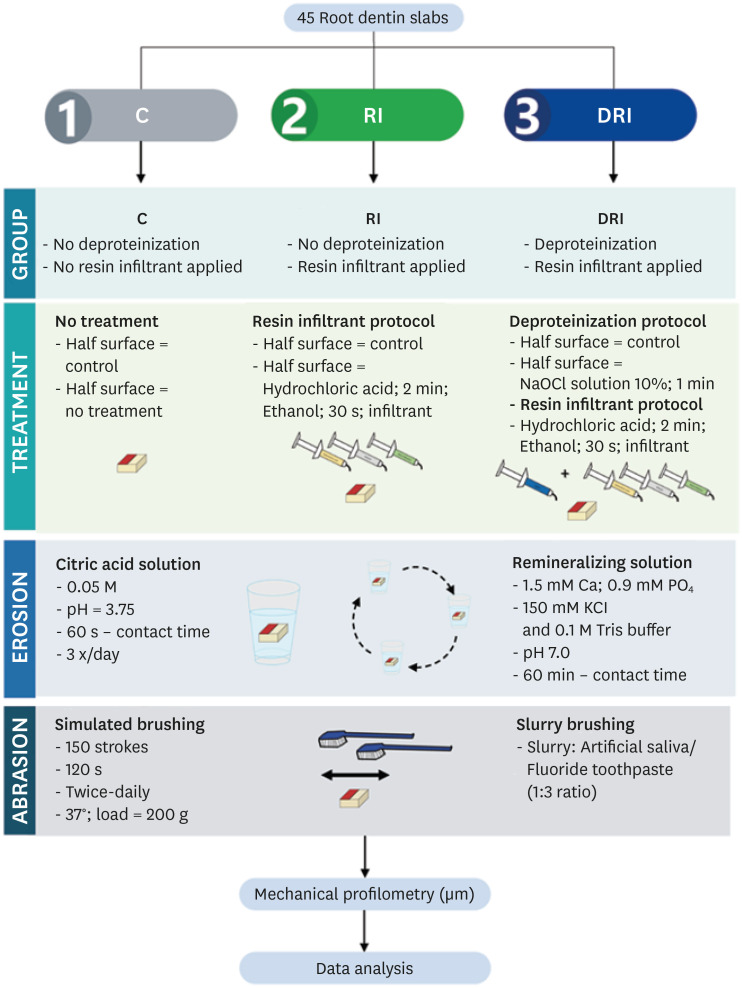
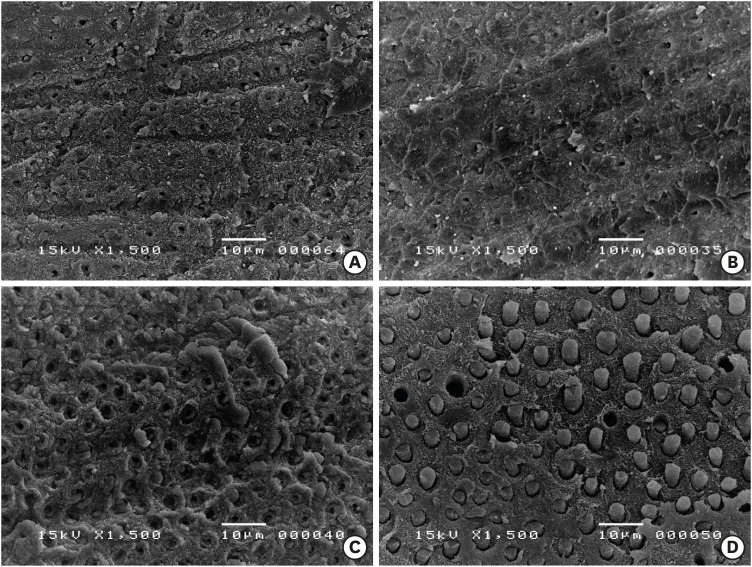
- Resin infiltrant protects deproteinized dentin against erosive and abrasive wear
- Ana Theresa Queiroz de Albuquerque, Bruna Oliveira Bezerra, Isabelly de Carvalho Leal, Maria Denise Rodrigues de Moraes, Mary Anne S. Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e29. Published online July 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the anti-erosive/abrasive effect of resin infiltration of previous deproteinized dentin.
Materials and Methods Dentin slabs were randomly assigned to 3 groups (
n = 15): Control (no deproteinization; no resin infiltrant applied), RI (no deproteinization; resin infiltrant applied), and DRI (deproteinization; resin infiltrant applied). After undergoing the assigned treatment, all slabs were subjected to anin vitro cycling model for 5 days. The specimens were immersed in citric acid (0.05 M, pH = 3.75; 60 seconds; 3 times/day) and brushed (150 strokes). Between the challenges, the specimens were exposed to a remineralizing solution (60 minutes). The morphological alterations were analyzed by mechanical profilometry (µm) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were submitted to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey tests (p < 0.05).Results Control and RI groups presented mineral wear and did not significantly differ from each other (
p = 0.063). DRI maintained a protective layer preserving the dentin (p < 0.001). After erosive/abrasive cycles, it was observed that in group RI, only 25% of the slabs partially evidenced the presence of the infiltrating, while, in the DRI group, 80% of the slabs presented the treated surface entirely covered by a resin-component layer protecting the dentin surface as observed in SEM images.Conclusions The removal of the organic content allows the resin infiltrant to efficiently protect the dentin surface against erosive/abrasive lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acidic/abrasive challenges on simulated non-carious cervical lesions development and morphology
Giovanna C. Denucci, Ian Towle, Cecilia P. Turssi, George J. Eckert, Anderson T. Hara
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 169: 106120. CrossRef - Physio‐Mechanic and Microscopic Analyses of Bioactive Glass‐Based Resin Infiltrants
Syed Zubairuddin Ahmed, Abdul Samad Khan, Wejdan Waleed Nasser, Methayel Abdulrahman Alrushaid, Zahrah Mohammed Alfaraj, Moayad Mohammed Aljeshi, Asma Tufail Shah, Budi Aslinie Md Sabri, Sultan Akhtar, Mohamed Ibrahim Abu Hassan
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(2): 595. CrossRef - Resin Infiltration Treatment of Developmental Enamel Defects in a Patient With Hydrocephalus and Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report on the Impact on the Maternal Caregiver
Eduarda Martins Fontes Cantarella de Almeida, Anna Luísa Araujo Pimenta, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula‐Silva, Fabricio Kitazono de Carvalho, Laurindo Borelli‐Neto, Susanne Effenberger, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona, K
Special Care in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Acidic/abrasive challenges on simulated non-carious cervical lesions development and morphology
- 2,320 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Clinical efficacy of activated irrigation in endodontics: a focused review
- Amelia Wan Tin Cheung, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Gary Shun Pan Cheung
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e10. Published online January 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Root canal debridement, which includes the removal of infected tissues and microbial biofilms, is considered the corner stone of root canal treatment. Chemical adjuncts play a multitude of functions in this regard, as tissue solvents, antimicrobial agents and for removing the smear layer. These adjuncts (irrigants) are usually delivered using a syringe and needle. With increasing knowledge of the complexity of root canal anatomy and tenacity of microbial biofilms, the need for strategies that potentiate the action of these irrigants within the root canal system cannot be overemphasized. Several such activated irrigation strategies exist. The aim of this review is to comprehensively discuss the different irrigant activation methods from the context of clinical studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of Er: YAG, continuous-wave, and pulsed diode laser-activated irrigation on smear layer removal: a comparative microscopic study
Muhammad Mahmoud Abaza, Tarek Abdel Hamid Harhash, Ahmed Abbas Zaky
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite accident approach with photobiomodulation during an endodontic procedure: a case report
Johanna Hernandez La Rotta, Marggie Grajales
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium dichloroisocyanurate and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid intracanal medicaments on Enterococcus faecalis: A comparative in-vitro study
Rasmina K. Nizar, Anju Varughese, M. Remya, V.P. Prabath Singh, Gayathri Usha, Gayathri Presannakumar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(5): 1149. CrossRef - ВПЛИВ ХІМІЧНИХ ІРИГАНТІВ НА СТАН БІОПЛІВКИ КОРЕНЕВОГО КАНАЛУ ПРИ ЛІКУВАННІ ПЕРІОДОНТИТІВ
Р. І. Новосядлий, М. М. Рожко
Art of Medicine.2025; : 33. CrossRef - REVOLUCIONANDO LA ENDODONCIA: LA IMPORTANCIA DE IRRIGANTES MÚLTIPLES PARA UNA DESINFECCIÓN EFECTIVA DEL SISTEMA DE CONDUCTOS RADICULARES UNA REVISIÓN NARRATIVA
Irving Pablo Fernandez Calle, Edwin Macias Limachi , Abigail Marisol Vargas Ticona , Jenny Paula Aguilar Avalos , Marivel Irene Condori Escobar, Alcides Ramber Maldonado Huaycho , Jenny Claudia Apaza Cayo , Miguel Angel Espinoza Vega , Jesús Alejan
RECIMA21 - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar - ISSN 2675-6218.2024; 5(11): e5115929. CrossRef - Cleaning and disinfection of the root canal system provided by four active supplementary irrigation methods
Alessandra Timponi Goes Cruz, Adriane Antoniw Klemz, Edvaldo Antônio Ribeiro Rosa, Fabiana Soares Grecca, Bianca Mattos, Lucila Piasecki, Ricardo Machado, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Postendodontic Pain Using Single File System with Different Irrigation Protocols in Single-visit Root Canal Treatment: A Randomized Control Trial
Kiran Patel, Kailash Attur, Nishtha Patel, Kamal M Bagda, Karthik P Venkataraghavan, Mohammed B Mustafa, Shylaja K Attur
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(2): 180. CrossRef - Bacteria debridement efficacy of two sonic root canal irrigant activation systems
Chang Zeng, Pei Hu, Colin P. Egan, Brian E. Bergeron, Franklin Tay, Jingzhi Ma
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 140: 104770. CrossRef - Evaluation of different activated irrigation protocols on debridement quality in various access cavity designs
Urvashi M. Ujariya, Mitul Lallubhai Gangani, Rajendra P. Bharatiya, Anjali K. Kothari
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 400. CrossRef - Synergistic antimicrobial potential of EGCG and fosfomycin against biofilms associated with endodontic infections
Cristiane DUQUE, Amanda Caselato Andolfatto SOUZA, Kelly Limi AIDA, Jesse Augusto PEREIRA, Karina Sampaio CAIAFFA, Vanessa Rodrigues dos SANTOS, Leopoldo COSME-SILVA, Anuradha PRAKKI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insights of fluid dynamics in an optimally shaped root canal system
Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Krishnamachari Janani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 216. CrossRef - Diamond–coated ultrasonic tip decreases debris and uninstrumented surface after preparation of curved canals with isthmus
Maria Luiza GIOSTER–RAMOS, Mariana Mena Barreto PIVOTO–JOÃO, Jáder Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO–TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU–FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation Protocols in Simulated Complex Root Canal Cavities
Flávia A. Plazza, Renan Dal-Fabbro, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Paulo C. T. Duarte, Caroline Loureiro, Vitória Z. Custódio, Luciano T. A. Cintra, Marco A. H. Duarte, João Eduardo Gomes-Filho
Oral.2022; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of sealer penetration of sonic activation versus conventional needle irrigation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Li Tan, Qiong Liu, Yun Chen, Ya-Qiong Zhao, Jie Zhao, Marie Aimee Dusenge, Yao Feng, Qin Ye, Jing Hu, Ze-Yue Ou-Yang, Ying-Hui Zhou, Yue Guo, Yun-Zhi Feng
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Photoinduced Photoacoustic Streaming and Diode Laser Irrigation Techniques on Smear Layer Removal, Sealer Penetration and Push-out Bond Strength
Latifa Mohamed Abdelgawad, Nancy Attia Ahmed ElShafei, Somaia Abdlatif Eissa, Dalia Yahia Ibrahim
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2022; 13(1): e12. CrossRef - Microbiological Aspects of Root Canal Infections and Disinfection Strategies: An Update Review on the Current Knowledge and Challenges
Jasmine Wong, Daniel Manoil, Peggy Näsman, Georgios N. Belibasakis, Prasanna Neelakantan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of efficacy of two endodontic sonic-powered irrigant agitation systems in killing single-species intracanal biofilms
Chang Zeng, Joseph Everett, Stephanie Sidow, Brian E. Bergeron, Fucong Tian, Jingzhi Ma, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 115: 103859. CrossRef - A novel three‐dimensionally printed model to assess biofilm removal by ultrasonically activated irrigation
Min‐Ji Choi, Mi‐Ah Kim, Yoorina Choi, Prasanna Neelakantan, Mi‐Kyung Yu, Kyung‐San Min
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(10): 1871. CrossRef
- Efficacy of Er: YAG, continuous-wave, and pulsed diode laser-activated irrigation on smear layer removal: a comparative microscopic study
- 7,414 View
- 123 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Physicochemical properties, cytotoxicity and penetration into dentinal tubules of sodium hypochlorite with and without surfactants
- Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Isadora Barbieri, Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Ana Paula Ramos, Gisele Faria
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e47. Published online September 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to assess the physicochemical properties, cytotoxicity and penetration into dentinal tubules of ChlorCid™ Surf (3% sodium hypochlorite [NaOCl] with surfactant) in comparison to ChlorCid™ (3% NaOCl without surfactant).
Materials and Methods The physicochemical properties evaluated were pH, surface tension, free available chlorine (FAC) and contact angle. Cytotoxicity was evaluated in L929 fibroblasts exposed to the solutions by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide and neutral red assays. Assessment of penetration into dentinal tubules was performed by staining single-rooted permanent human teeth with crystal violet (
n = 9), which were irrigated with the solutions and analyzed in cervical, middle and apical segments. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey'spost -test, 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni'spost -test ort -test (α = 0.05).Results ChlorCid™ Surf and ChlorCid™ FAC values were close to those indicated by the manufacturer. ChlorCid™ Surf showed lower surface tension and contact angle on dentin, and higher pH than ChlorCid™ (
p < 0.05). The penetration of ChlorCid™ Surf was higher in cervical and middle segments, compared with ChlorCid™ (p < 0.05). There was no difference in irrigant cytotoxicity (p > 0.05).Conclusions ChlorCid™ Surf showed lower surface tension, lower contact angle on root canal dentin, higher penetration into dentinal tubules and more alkaline pH, compared with ChlorCid™. However, both solutions showed similar cytotoxicity and FAC content.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of penetration enhancers on the performance of irrigants for root canal disinfection
Yi Luo, Runze Liu, Pei Liu, Mengting Duan, Wei Fan, Bing Fan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical and Biological Properties of the “All-In-One” Endodontic Irrigant Triton
Jesus Aranda, Elda Olivia Nobre de Souza, Arturo Javier Aranda Garcia, Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Ana Paula Ramos, Giampiero Rossi-Fedele, Gisele Faria
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of post space disinfection protocols on the push-out bond strength of fiber posts luted with self-adhesive cement
Satheesh B. Haralur, Salem Ali Alqahtani, Khalid Salem Alqahtani, Mohammed A. Al-Qarni, Saeed M. AlQahtani
AIP Advances.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research methods assessing sodium hypochlorite cytotoxicity: A scoping review
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Luana Raphael da Silva, Gisele Faria
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23060. CrossRef - Amelioration in the sodium hypochlorite as root canal irrigant – A review
Preety Sehrawat
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 12(2): 65. CrossRef - Sonic-assisted antibacterial photodynamic therapy: a strategy for enhancing lateral canal disinfection
Yanhuang Wang, Lishan Lei, Jing Huang, Zhiyu Cai, Xiaojing Huang
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Contact Angle and Depth of Penetration of Sodium Hypochlorite With Various Surfactants: An In Vitro Study
Shubhashini N, Krithika D, Akhilesh Gowda , Shruthi Nagaraja , Rhea S Mathew, Nivaskumar G A, Vinaychandra R
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, and hypochlorous acid on dentinal surfaces infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Aysenur Oncu, Berkan Celikten, Betül Aydın, Gulin Amasya, Erkan Tuncay, Gamze Guney Eskiler, Leyla Açık, Fatma Semra Sevimay
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(9): 2094. CrossRef - Advances in the Role of Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigant in Chemical Preparation of Root Canal Treatment
Chen Cai, Xuan Chen, Yang Li, Qianzhou Jiang, Yeliz Guven
BioMed Research International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite-based formulations on the adhesion interface after fiber post cementation
Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes COSTA, Tatiane Miranda MANZOLI, João Felipe BESEGATO, Joissi Ferrari ZANIBONI, Eliane Cristina Gulin DE OLIVEIRA, Lucas David GALVANI, Andréa Abi Rached DANTAS, Luis Geraldo VAZ, Milton Carlos KUGA
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 878. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and penetration into dentinal tubules of calcium hypochlorite with surfactants
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Julia da Silva Toledo, Ana Paula Ramos, Gisele Faria
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 1. CrossRef
- Effects of penetration enhancers on the performance of irrigants for root canal disinfection
- 2,643 View
- 32 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effect of phytic acid as an endodontic chelator on resin adhesion to sodium hypochlorite-treated dentin
- Mohannad Nassar, Noriko Hiraishi, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Maria JRH. Romero, Masayuki Otsuki, Junji Tagami
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e44. Published online August 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Phytic acid (IP6), a naturally occurring agent, has been previously reported as a potential alternative to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). However, its effect on adhesion to sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)-treated dentin and its interactions with NaOCl have not been previously reported. Thus, in this study, the effects of IP6 on resin adhesion to NaOCl-treated dentin and the failure mode were investigated and the interactions between the used agents were analyzed.
Materials and Methods Micro-tensile bond strength (µTBS) testing was performed until failure on dentin treated with either distilled water (control), 5% NaOCl, or 5% NaOCl followed with chelators: 17% EDTA for 1 minute or 1% IP6 for 30 seconds or 1 minute. The failed specimens were assessed under a scanning electron microscope. The reaction of NaOCl with EDTA or IP6 was analyzed in terms of temperature, pH, effervescence, and chlorine odor, and the effects of the resulting mixtures on the color of a stained paper were recorded.
Results The µTBS values of the control and NaOCl with chelator groups were not significantly different, but were all significantly higher than that of the group treated with NaOCl only. In the failure analysis, a distinctive feature was the presence of resin tags in samples conditioned with IP6 after treatment with NaOCl. The reaction of 1% IP6 with 5% NaOCl was less aggressive than the reaction of the latter with 17% EDTA.
Conclusions IP6 reversed the adverse effects of NaOCl on resin-dentin adhesion without the chlorine-depleting effect of EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
Md Sofiqul Islam, Shadi El Bahra, Smriti Aryal A C, Vivek Padmanabhan, Abdulaziz Al Tawil, Ihab Saleh, Muhammed Mustahsen Rahman, Upoma Guha
Polymers.2025; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part I: Impact of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on the Chemical Composition and Structural Integrity of Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Sara Fateixa, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1848. CrossRef - Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - Effects of phytic acid and etidronic acid using continuous and sequential chelation on the removal of smear layer, dentin microhardness, and push-out bond strength of calcium silicate-based cement
Ecehan Hazar, Ahmet Hazar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of free available chlorine in sodium hypochlorite solutions admixed with novel chelating agents
Somya Tyagi, Sonali Taneja, Kandasamy Nagarajan, Divya Chowdhary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 188. CrossRef - Effect of different chelating agents, with and without activation, including XP-endo Finisher, on root dentin microhardness: An in vitro study
Mahmoud Mohamed A. Sherif, Mai Hamdy Ragab, Marwa ElSayed Sharaan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(3): 282. CrossRef - Oracle of phytic acid in dental panacea – Insight into properties, therapeutic effect, regeneration, materials interaction and oral physiology
Ummey Salma, C. Pushpalatha, SV. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shilpa Bhandi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(8): 1093. CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Is a mix – A fix? “A microscopic analysis of depth of penetration of three combinations of irrigants”
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Nadimpalli Mahendra Varma, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(2): 186. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on dentinal collagen solubilization and its binding and debinding potentials to dentin
Diletta Forgione, Mohannad Nassar, Roda Seseogullari-Dirihan, Ahmed Jamleh, Arzu Tezvergil-Mutluay
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104361. CrossRef - Application of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol in Dental Medicine: An Overview
Ana Druzijanic, Mare Kovic, Marija Roguljic, Livia Cigic, Martina Majstorovic, Ivana Vucenik
Biomolecules.2023; 13(6): 913. CrossRef - Ex-vivo study about antimicrobial effectiveness of phytic acid against Enterococcus faecalis into root canals
Giulia BOSCHI, Giorgio PICCINELLI, Carlo BONFANTI, Stefano A. SALGARELLO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on bond strength and interfacial integrity of universal adhesive to deep dentin
Ahmed Mostafa Attia, Ahmed Fawzy Abo-Elezz, Rehab Khalil Safy
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 116. CrossRef - Resin-Based Cement Applied to Enamel and Dentin Pre-Treated with Phytic Acid: An In Vitro Study
Mohannad Nassar, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Smriti Aryal A C, Hatem Mostafa El-Damanhoury, Salvatore Sauro, Noriko Hiraishi
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11976. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Phytic Acid: Properties and Potential Applications in Dentistry
Mohannad Nassar, Rania Nassar, Husain Maki, Abdullah Al-Yagoob, Mahmood Hachim, Abiola Senok, David Williams, Noriko Hiraishi
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
- 2,334 View
- 19 Download
- 17 Crossref

- The effect of root canal irrigants on dentin: a focused review
- Priti Pragati Rath, Cynthia Kar Yung Yiu, Jukka Pekka Matinlinna, Anil Kishen, Prasanna Neelakantan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e39. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Despite the vast literature on the effects of root canal irrigants on the dentin characteristics, the precise effects of clinically relevant irrigation sequences remain unclear. In this review, we systematically dissect the role of different sequential irrigation approaches that are used in clinical endodontics. Using a systematic search strategy, we attempt to answer the question: ‘Which irrigating sequence has the most deleterious effects on dentin structure and properties?’ The effect of irrigants on the dentin composition and mechanical properties have been reviewed. A wide variety of concentrations, duration and techniques have been employed to characterize the effects of chemicals on dentin properties, thus making it impossible to draw guidelines or recommendations of irrigant sequences to be followed clinically. It was apparent that all the studied irrigation sequences potentially result in some deleterious effects on dentin such as decrease in the flexural strength, microhardness, modulus of elasticity and inorganic content and organic-inorganic ratio of the dentin. However, the literature still lacks comprehensive investigations to compare the deleterious effect of different irrigation sequences, using a wide variety of qualitative and quantitative methods. Such investigations are essential to make clinical recommendations and strategize efforts to minimize chemically-induced damage to dentin characteristics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- OZONIOTERAPIA NA ENDODONTIA: ANÁLISE CRÍTICA DO POTENCIAL E APLICAÇÕES DO O3 GASOSO, AQUOSO, OLEOSO
Cíntia Bueno de Paula, Fernanda dos Santos Lacerda, Eduarda Calisto de Almeida, Sandra Regina Fernandes Albuquerque
Revista Contemporânea.2026; 6(2): e10259. CrossRef - Optimised clinical protocol for root canal obturation using single cone and hydraulic cement sealer
Sweta Surana Bhandari, William M. Palin, Sarah A. Kuehne, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of 980 nm diode laser irradiation in comparison with conventional irrigation on smear layer removal from radicular dentin—an in vitro experimental study
Syeda Abeerah Tanveer, Robia Ghafoor, Adil Omerson
BDJ Open.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Properties of 50% Grape Seed Extract, N-acetyl Cysteine and 5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite against Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 19433) – An In vitro Study
Nikita Vishweshwar Kurtkoti, Madhura Vivek Pawar, Vaishnavi Ketan Mathawala, Shraddha Mahadeo Shirsat
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(2): 237. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Pulp Dissolution and Smear Layer Removal Properties of Various Herbal Extracts: An in vitro Study
Suleman Abbas Khan, Harshal Gaidhane, Saumya Navit, Meenakshi Upadhyay, Sujeet Shriram Pal, Nishi Grover
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 496. CrossRef - Exploring a new Portland cement-free calcium silicate cement —Part 1: Synthesis of dicalcium and tricalcium silicate
Tomomi ITOH, Kohei SHINTANI, Takashi HORIGUCHI, Norihiro SASAMOTO, Katsushi OKUYAMA, Yukimichi TAMAKI, Takeshi SUWABE, Satoshi YOKOSE, Satoshi KAWANO
Dental Materials Journal.2025; 44(2): 140. CrossRef - Effect of phthalocyanine, methylene blue and toluidine blue photosensitizers on the adhesive interface of fiber posts: a confocal laser microscopy study
Tuba Gök, Gamze Er Karaoglu, Hulde Korucu
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial effect of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irradiated with the 445 Nm diode laser against bacterial biofilms in root canal - in vitro pilot study
Ivan Katalinić, Antonija Pranjić, Ana Budimir, Lucija Kanižaj, Ivona Bago, Valentina Rajić
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - When oral health affects overall health: biofilms, dental infections, and emerging antimicrobial strategies
Ahmed Adel Abdelaziz, Ahmed S. Doghish, Akram N. Salah, Reda M. Mansour, Yasser M. Moustafa, Sherif S. Abdel Mageed, Hebatallah Ahmed Mohamed Moustafa, Walaa A. El-Dakroury, Sama A. Doghish, Osama A. Mohammed, Mustafa Ahmed Abdel-Reheim, Shaimaa O. Abbass
Infection.2025; 53(5): 1603. CrossRef - Enhanced Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface of Resin‐Based Sealer to Root Dentine Using a Novel Single Multifunctional Endodontic Irrigant Solution
Paulo Oliveira Silva, Julia Godoi Lopes, Iago Ramirez, Helena Cristina de Assis, Vinícius Leite Rosa‐e‐Silva, Gustavo Alexandre de Castro‐Vasconcelos, Antonio Miranda da Cruz‐Filho, Renato Roperto, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Benedetta Ghezzi, Fabiane Ca
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 423. CrossRef - Enhanced Cleaning, Enhanced Healing: A Systematic Review of Advances in Endodontic Irrigation
Shubhi Gupta, Karunakaran Venkataraman Jeyaraman, M. Deepthi, Rohan Shinkre, Neha Singh, Sagar Shah
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 2): S1845. CrossRef - ВПЛИВ ХІМІЧНИХ ІРИГАНТІВ НА СТАН БІОПЛІВКИ КОРЕНЕВОГО КАНАЛУ ПРИ ЛІКУВАННІ ПЕРІОДОНТИТІВ
Р. І. Новосядлий, М. М. Рожко
Art of Medicine.2025; : 33. CrossRef - Dual- or single rinse? The tubular sealer penetration of endodontic chelating agents
Beliz Ozel, Tuba Ayhan, Figen Kaptan, Fikrettin Sahin, Meriç Karapınar-Kazandağ, Ajinkya M. Pawar
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(6): e0303377. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of simulated dentin caries treated with metal cations and l-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Julia Vakhnovetsky, Amir Abdolmaleki, Elham Samadi, Fatereh Samadi, Salvatore Napoli, Michael Conte, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2024; 112(2): 489. CrossRef - The advancement in irrigation solution within the field of endodontics, A Review
Fatima Fahad , Raghad A Al-Hashimi , Munther J Hussain
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 54. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
Aparna Palekar, Piyush Mantri, Minal Awinashe, Basawaraj Biradar, Mukund Singh
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of herbal irrigants on surface roughness of intraradicular dentin using quantitative method of 3D surface texture analysis
Sabah M. Sobhy, Heba Abdelfatah, Hanaa M. Elgamily, Nesreen Y. Mohammed
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of different root canal irrigants on surface roughness and microhardness of Biodentine combined with triple antibiotic paste: An in vitro study
Rahul Halkai, S. Syed Ishaq, Kiran R. Halkai, Syeda Uzma Mahveen
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(5): 508. CrossRef - Bacteria debridement efficacy of two sonic root canal irrigant activation systems
Chang Zeng, Pei Hu, Colin P. Egan, Brian E. Bergeron, Franklin Tay, Jingzhi Ma
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 140: 104770. CrossRef - Effects of endodontic irrigation solutions on structural, chemical, and mechanical properties of coronal dentin: A scoping review
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, João Miguel Santos, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(4): 606. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic and Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation protocol on dual-species root canal biofilm removal: An in vitro study
Venkata Divya Durga Datla, Lakshman Varma Uppalapati, Hema Prakash Kumari Pilli, Jyothi Mandava, Sirisha Kantheti, Sri Naagaja Krishnaveni Komireddy, Vedamani Chandolu
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 613. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Dental Pulp Tissue Dissolution Ability of Sapindus mukorossi and Sodium Hypochlorite
Sriram Kaliamoorthy, Sreeram Rayar, Shanmugapriya SundarRaj, Sugantha Priya Sayeeram, V.V. Premkumar, Sapna C Muddappa, Venkatraman Muthukumaran, Kanmani Raju, Agila Samidorai
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Irrigating Solutions on Root Canal Dentin Microhardness—A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Sunidhi Agarwal, Lora Mishra, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Rini Behera, Manoj Kumar, Ravishankar Nagaraja, Krzysztof Sokolowski, Barbara Lapinska
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(5): 132. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Herbal Irrigant on Microhardness of Root Dentin: An in vitro Study
Anuya Ravindra Koparde, Anupam Sandeep Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Madhura A. Jadhav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 170. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Endodontic irrigants from a comprehensive perspective
Rayana Duarte Khoury, Lara Steffany de Carvalho, Mauro Felipe Rios do Nascimento, Fadi Alhussain, Amjad Abu Hasna
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(21): 4460. CrossRef - Exploring Periostracum as an Alternative Root Canal Irrigant: Insights From Zebrafish Embryo Experiments
Annie Sylvea Valan, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta, Ajay Guru
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Systematic Review of the Comparative Efficacy of Lactobacillus Probiotics and Sodium Hypochlorite as Intracanal Irrigants Against Enterococcus faecalis
Mrinalini Mrinalini, Alpa Gupta, Dax Abraham, Arun Kumar Duraisamy, Rajat Sharma
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid activated by laser and ultrasonic energy on surface morphology and chemical composition of intracanal dentin
Adriana Katunarić, Sandra Flinčec Grgac, Dragana Gabrić, Božidar Pavelić, Ivona Bago
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(4): 818. CrossRef - Impact of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on the bond-strength and penetration of endodontic sealers: A systematic review
Khalid H Almadi
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 41: 103249. CrossRef - In Vitro Assessment of SWEEPS and Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy Alone or in Combination for Eradicating Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm in Root Canals
Ali Shahi Ardakani, Shima Afrasiabi, Pegah Sarraf, Stefano Benedicenti, Luca Solimei, Nasim Chiniforush
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(11): 2628. CrossRef - Effects of traditional and novel proteolytic agents on tissue dissolution and dentine microhardness
Shwetha Elizabeth Jacob, Niharika Prasad, Sreya Dutta, Vasavi Kumblekar, Srikant Natarajan, Kukkila Jayaprakash, Manuel Sebastian Thomas
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(2): 287. CrossRef - Push-Out Bond Strength of EndoSeal Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and AH Plus Sealers after Using Three Different Irrigation Protocols
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Fatimah Alkhalifa, Ghofran AlQuraini, Zahraa Alsalman, Zahraa Alwesaibi, Noha Taymour
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(01): 076. CrossRef - Can natural irrigants replace sodium hypochlorite? A systematic review
Anand Venkatraman Susila, Shamini Sai, Nikita Sharma, Arthi Balasubramaniam, Aruna Kumari Veronica, Sureshbabu Nivedhitha
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 1831. CrossRef - Advances in the Role of Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigant in Chemical Preparation of Root Canal Treatment
Chen Cai, Xuan Chen, Yang Li, Qianzhou Jiang, Yeliz Guven
BioMed Research International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A laboratory investigation on the effect of biguanide‐ and pyridine‐derived antiseptics on the adhesion of resin composites to dentin
Arzu Yağmur Uçar, Türkay Kölüş, D. Alperen Bozkurt, Prasanna Neelakantan, Islam A. A. Ali, Sema Belli
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 599. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Disinfection of radicular dentin using Riboflavin, Rose Bengal, Curcumin, and Porfimer sodium on extrusion bond strength of fiber post to radicular dentin
Sami A Alturaiki, Ahmed A. Bamanie, Mohammed A. Albulowey, Abdullah A. Al Daafas, Abdullah Almalki, Ali Alqerban
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 37: 102625. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Minimally invasive root canal preparation and periradicular surgery
Prasanna Neelakantan, Vijetha Vishwanath, Silvio Taschieri, Stefano Corbella
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S4): 845. CrossRef - Ex Vivo Effect of Novel Lipophosphonoxins on Root Canal Biofilm Produced by Enterococcus faecalis: Pilot Study
Yuliya Morozova, Iva Voborná, Radovan Žižka, Kateřina Bogdanová, Renata Večeřová, Dominik Rejman, Milan Kolář, Duy Dinh Do Pham, Pavel Holík, Roman Moštěk, Matej Rosa, Lenka Pospíšilová
Life.2022; 12(1): 129. CrossRef - Irrigating Solutions and Activation Methods Used in Clinical Endodontics: A Systematic Review
Riccardo Tonini, Matteo Salvadori, Elisabetta Audino, Salvatore Sauro, Maria Luisa Garo, Stefano Salgarello
Frontiers in Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Effects of Various Irrigating Solutions on Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin Using FTIR, SEM, and EDS: An In Vitro Study
Indu Padmakumar, Dharam Hinduja, Abdul Mujeeb, Raghu Kachenahalli Narasimhaiah, Ashwini Kumar Saraswathi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ali Robaian, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Giuseppe Alessandro Scardina
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 197. CrossRef - Final irrigation protocols affect radicular dentin DMP1-CT expression, microhardness, and biochemical composition
Cristina Retana-Lobo, Tatiana Ramírez-Mora, Fabian Murillo-Gómez, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Jessie Reyes-Carmona
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(8): 5491. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Formulations of Septilin and Triphala with Conventional 2% Chlorhexidine on Root Canal and Oral Commensal Bacteria using Kirby Bauer Method
Shadab Ahmed, Kamil Shahnawaz, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Mamnoon Ghafir, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Gaurav Vishal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 383. CrossRef - Adjunctive procedure with solvent mixtures in non-surgical endodontic retreatment: does it affect root dentin hardness?
Inês Ferreira, Ana Cristina Braga, Maria Ascensão Lopes, Irene Pina-Vaz
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 812. CrossRef
- OZONIOTERAPIA NA ENDODONTIA: ANÁLISE CRÍTICA DO POTENCIAL E APLICAÇÕES DO O3 GASOSO, AQUOSO, OLEOSO
- 5,127 View
- 104 Download
- 45 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of octenidine as an antimicrobial agent againstStaphylococcus epidermidis in disinfecting the root canal system - Jia Da Chum, Darryl Jun Zhi Lim, Sultan Omer Sheriff, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Anand Suresh, Fabian Davamani
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e8. Published online February 8, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
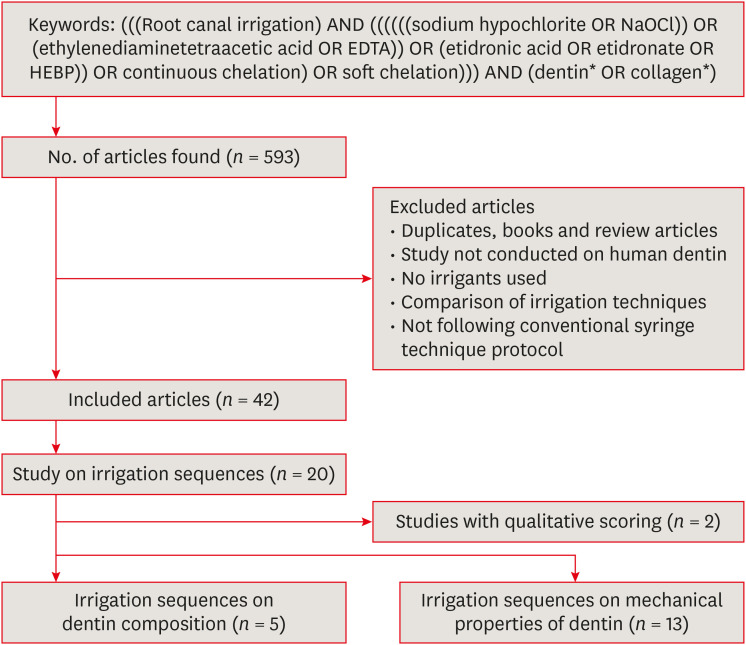
ePub Objectives Irrigants are imperative in endodontic therapy for the elimination of pathogens from the infected root canal. The present study compared the antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride (OCT) with chlorhexidine (CHX) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) against
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis ) for root canal disinfection.Materials and Methods The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was obtained using serial dilution method. The agar diffusion method was then used to determine the zones of inhibition for each irrigant. Lastly, forty 6-mm dentin blocks were prepared from human mandibular premolars and inoculated with
S. epidermidis . Samples were randomly divided into 4 groups of 10 blocks and irrigated for 3 minutes with saline (control), 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, or 0.1% OCT. Dentin samples were then collected immediately for microbial analysis, including an analysis of colony-forming units (CFUs).Results The MICs of each tested irrigant were 0.05% for CHX, 0.25% for NaOCl, and 0.0125% for OCT. All tested irrigants showed concentration-dependent increase in zones of inhibition, and 3% NaOCl showed the largest zone of inhibition amongst all tested irrigants (
p < 0.05). There were no significant differences among the CFU measurements of 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, and 0.1% OCT showing complete elimination ofS. epidermidis in all samples.Conclusions This study showed that OCT was comparable to or even more effective than CHX and NaOCl, demonstrating antimicrobial activity at low concentrations against
S. epidermidis .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Gülgün Atay Yılmaz, Nihan Şengül, Ahmet Keleş, Selen Küçükkaya Eren
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Substantivity of different antiseptic oral gels. An In vitro study
Nirit Tagger Green, Roni Kolerman, Carlos Nemcovsky, Shlomo Matalon, Dan Gaukhman, Liat Chaushu
Heliyon.2025; : e42654. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of crustacean-derived chitosan against Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes
Sivainesh Devi Remesh, Pratheep Sandrasaigaran, Santhaniswarman Remesh, Veeradasan Perumal, Joshua Yap Lip Vun, Sivasangkary Gandhi, Hanan Hasan
Food Bioscience.2025; : 106697. CrossRef - Glycerol-Enhanced Gum Karaya Hydrogel Films with a Sandwich-like Structure Enriched with Octenidine for Antibacterial Action against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Eva Černá, Vilém Neděla, Eva Tihlařiková, Jana Brtníková, Zdenka Fohlerová, Břetislav Lipový, Lukáš Vacek, Filip Růžička, Jana Matulová, Lucy Vojtová
ACS Omega.2025; 10(27): 29530. CrossRef - Effect of Mouth Rinsing and Antiseptic Solutions on Periodontitis Bacteria in an In Vitro Oral Human Biofilm Model
Jan Tinson Strenge, Ralf Smeets, Maria Geffken, Thomas Beikler, Ewa Klara Stuermer
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 324. CrossRef - In Vitro Investigation of the Effects of Octenidine Dihydrochloride on Nasal Septum Squamous Carcinoma Cells
Ihsan Hakki Ciftci, Asuman Deveci Ozkan, Gulay Erman, Elmas Pinar Kahraman Kilbas, Mehmet Koroglu
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2668. CrossRef - Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein-S as a Dual-Action Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Agent Against Staphylococcus aureus
Priya Verma, Priyanka Swaroop, Surabhi Pandit, Ved Prakash, Surender Kumar Sharawat, T. P. Singh, Sujata Sharma, Pradeep Sharma
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Effects of Endodontic Irrigants Containing Disodium Edetate and Chlorhexidine Gluconate, Octenidine Dihydrochloride, and Benzalkonium Bromide Against Intracanal Enterococcus faecalis
Anna Siemińska, Katarzyna Kot, Ewa Marek, Agnieszka Chamarczuk, Magdalena Kaczała, Joanna Rasławska-Socha, Laurentia Schuster, Till Dammaschke, Liliana Szyszka-Sommerfeld, Mariusz Lipski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 7100. CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain in endodontic retreatment with apical periodontitis using ozonated 2% chlorhexidine and 0.1% octenidine application: A randomized clinical trial
Nidhi Sinha, Geeta Asthana, Girish Parmar, Akshayraj Langaliya, Jinali Shah, Bijay Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 654. CrossRef - Research on NiTi instruments combined with ultrasonic irrigation and multiantibiotic paste in root canal therapy of periapical inflammation in deciduous teeth
Zongxia Zhu, Guangli Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride, superoxidized solution, ozonated water, 0.1% silver nanoparticle solution, and Q mix™ 2 in 1 in root canals infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Mahenaz Salam Inamdar, Dayanand G. Chole, Shrinivas S. Bakle, Preeti B. Vaprani, Neha P. Gandhi, Nikhil R. Hatte
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(10): 1059. CrossRef - Causal relationship, shared genes between rheumatoid arthritis and pulp and periapical disease: evidence from GWAS and transcriptome data
Huili Wu, Lijuan Wang, Chenjie Qiu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of octenidine dihydrochloride on the antibacterial activity of a formulated resin composite: an in vitro study
Mahitab Mansour, Tarek Salah, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between pulp and periapical disease with type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Yuqiang Wang, Jiakang Zhu, Ying Tang, Cui Huang
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 566. CrossRef - New Insights Regarding the Use of Relevant Synthetic Compounds in Dentistry
Stefania-Irina Dumitrel, Anamaria Matichescu, Stefania Dinu, Roxana Buzatu, Ramona Popovici, Dorin Dinu, Dana Bratu
Molecules.2024; 29(16): 3802. CrossRef - Formulation and Characterization of a Novel Palm-Oil-Based α-Mangostin Nano-Emulsion (PO-AMNE) as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant: An In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Haresh Kumar A/L Kantilal, Khoo Suan Phaik, Hira Choudhury, Fabian Davamani
Processes.2023; 11(3): 798. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Formulations of Septilin and Triphala with Conventional 2% Chlorhexidine on Root Canal and Oral Commensal Bacteria using Kirby Bauer Method
Shadab Ahmed, Kamil Shahnawaz, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Mamnoon Ghafir, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Gaurav Vishal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 383. CrossRef - A comparative assessment of pomegranate extract, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, Myrrh (Commiphora molmol), tulsi extract against Enterococcus faecalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Staphylococci epidermidis
Mallwika Sisodiya, Shadab Ahmed, Ranjan Sengupta, Priyanka, Ankit Kumar Saha, Gourav Verma
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2021; 25(2): 369. CrossRef - Effects of Octenidine on the Formation and Disruption of Dental Biofilms: An Exploratory In Situ Study in Healthy Subjects
B. Reda, J. Dudek, M. Martínez-Hernández, M. Hannig
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(9): 950. CrossRef - Does Cavity Disinfectant Affect Sealing Ability of Universal Self-etch Adhesive?
S Lata, Prasanti Kumari Pradhan, Gaurav Patri, Subhasmita Bhol, Kanhu C Sahoo, Khushboo Ghosh
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 273. CrossRef - Effect of duration and dilution on antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine hydrochloride as an intracanal medicament with chitosan carrier against Enterococcus faecalis – A modified direct contact test
VinayaSusan Varghese, Nirmal Kurian
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2020; 23(5): 463. CrossRef
- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
- 2,564 View
- 20 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Effect of smear layer deproteinization on bonding of self-etch adhesives to dentin: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Khaldoan H. Alshaikh, Hamdi H. H. Hamama, Salah H. Mahmoud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e14. Published online March 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
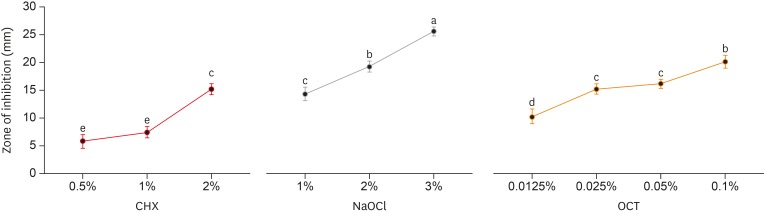
ePub Objectives The aim of this systematic review was to critically analyze previously published studies of the effects of dentin surface pretreatment with deproteinizing agents on the bonding of self-etch (SE) adhesives to dentin. Additionally, a meta-analysis was conducted to quantify the effects of the above-mentioned surface pretreatment methods on the bonding of SE adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods An electronic search was performed using the following databases: Scopus, PubMed and ScienceDirect. The online search was performed using the following keywords: ‘dentin’ or ‘hypochlorous acid’ or ‘sodium hypochlorite’ and ‘self-etch adhesive.’ The following categories were excluded during the assessment process: non-English articles, randomized clinical trials, case reports, animal studies, and review articles. The reviewed studies were subjected to meta-analysis to quantify the effect of the application time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl) deproteinizing agents on bonding to dentin.
Results Only 9 laboratory studies fit the inclusion criteria of this systematic review. The results of the meta-analysis revealed that the pooled average microtensile bond strength values to dentin pre-treated with deproteinizing agents (15.71 MPa) was significantly lower than those of the non-treated control group (20.94 MPa).
Conclusions In light of the currently available scientific evidence, dentin surface pretreatment with deproteinizing agents does not enhance the bonding of SE adhesives to dentin. The HOCl deproteinizing agent exhibited minimal adverse effects on bonding to dentin in comparison with NaOCl solutions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of finishing protocols on dentin surface characteristics and bond strength after tooth preparation for indirect restorations
Paola Bernardes, Amanda das Graças Soares, Bárbara Inácio de Melo, Leandro Maruki Pereira, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Rafael Rocha Pacheco, Marcel Santana Prudente, Luís Henrique Araújo Raposo
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2026; 135(2): 371.e1. CrossRef - Is the Percentage of Collagen in Coronal Dentin Related to Microtensile Strength? An In Vitro Study
Taíssa Cássia de Souza Furtado, Gilberto Antonio Borges, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo-Martins, Bruno Henrique dos Reis Souza Oliveira, Renata Margarida Etchebehere, Sanívia Aparecida de Lima Pereira
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Biomodification on the Survival of Resin Composite Restorations: An Umbrella Review
El Alaoui Nihal, Chala Sanaa, Ghoul Sonia
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(2): 109446. CrossRef - Coronal cavity pretreatment agents and restoration protocols effect on microleakage of endodontically treated teeth
Lena Bal, Cangül Keskin, Aybüke Karaca Sakallı, Osman Fatih Aydın
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2026; 7(1): 40. CrossRef -
Evaluating the remnants of Al
2
O
3
particles on different dentine substrate after sandblasting and various cleaning protocols
Faeze Hamze, Khotan Aflatoonian, Mahshid Mohammadibassir, Mohammad-Bagher Rezvani
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2025; 39(6): 869. CrossRef - Preservation Strategies for Interfacial Integrity in Restorative Dentistry: A Non-Comprehensive Literature Review
Carmem S. Pfeifer, Fernanda S. Lucena, Fernanda M. Tsuzuki
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(2): 42. CrossRef - Outcome of Er, Cr:YSGG laser and antioxidant pretreatments on bonding quality to caries-induced dentin
Lamiaa M. Moharam, Haidy N. Salem, Ahmed Abdou, Rasha H. Afifi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - A comparison of different cleaning approaches for blood contamination after curing universal adhesives on the dentine surface
Ting Liu, Haifeng Xie, Chen Chen
Dental Materials.2024; 40(11): 1786. CrossRef - Effect of fiber-reinforced direct restorative materials on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated mandibular molars restored with a conservative endodontic cavity design
Merve Nezir, Beyza Arslandaş Dinçtürk, Ceyda Sarı, Cemile Kedici Alp, Hanife Altınışık
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the use of bromelain associated with bioactive glass-ceramic on dentin/adhesive interface
Rocio Geng Vivanco, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Viviane de de Cássia Oliveira, Mário Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experimental and Chitosan-Infused Adhesive with Dentin Pretreated with Femtosecond Laser, Methylene Blue-Activated Low-Level Laser, and Phosphoric Acid
Fahad Alkhudhairy
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(10): 634. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effective Bond Strength of Composite Resin to Etched Dentin after Dentin Pretreatment: An In-vitro Study
Muhammed Bilal, Shiraz Pasha, Arathi S. Nair
Journal of the Scientific Society.2024; 51(4): 545. CrossRef - Comparison of Different Dentin Deproteinizing Agents on Bond Strength and Microleakage of Universal Adhesive to Dentin
Fatih Bedir, Gül Yıldız Telatar
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2023; 14(1): 44. CrossRef - Addition of metal chlorides to a HOCl conditioner can enhance bond strength to smear layer deproteinized dentin
Kittisak Sanon, Antonin Tichy, Takashi Hatayama, Ornnicha Thanatvarakorn, Taweesak Prasansuttiporn, Takahiro Wada, Yasushi Shimada, Keiichi Hosaka, Masatoshi Nakajima
Dental Materials.2022; 38(8): 1235. CrossRef - Internal and Marginal Adaptation of Adhesive Resin Cements Used for Luting Inlay Restorations: An In Vitro Micro-CT Study
Linah M. Ashy, Hanadi Marghalani
Materials.2022; 15(17): 6161. CrossRef - Collagen-depletion strategies in dentin as alternatives to the hybrid layer concept and their effect on bond strength: a systematic review
António H. S. Delgado, Madalena Belmar Da Costa, Mário Cruz Polido, Ana Mano Azul, Salvatore Sauro
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - NaOCl Application after Acid Etching and Retention of Cervical Restorations: A 3-Year Randomized Clinical Trial
M Favetti, T Schroeder, AF Montagner, RR Moraes, T Pereira-Cenci, MS Cenci
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 268. CrossRef - Resin infiltrant protects deproteinized dentin against erosive and abrasive wear
Ana Theresa Queiroz de Albuquerque, Bruna Oliveira Bezerra, Isabelly de Carvalho Leal, Maria Denise Rodrigues de Moraes, Mary Anne S. Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bis[2-(Methacryloyloxy) Ethyl] Phosphate as a Primer for Enamel and Dentine
R. Alkattan, G. Koller, S. Banerji, S. Deb
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(10): 1081. CrossRef - Influence of Dentine Pre-Treatment by Sandblasting with Aluminum Oxide in Adhesive Restorations. An In Vitro Study
Bruna Sinjari, Manlio Santilli, Gianmaria D’Addazio, Imena Rexhepi, Alessia Gigante, Sergio Caputi, Tonino Traini
Materials.2020; 13(13): 3026. CrossRef - A novel prime-&-rinse mode using MDP and MMPs inhibitors improves the dentin bond durability of self-etch adhesive
Jingqiu Xu, Mingxing Li, Wenting Wang, Zhifang Wu, Chaoyang Wang, Xiaoting Jin, Ling Zhang, Wenxiang Jiang, Baiping Fu
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 104: 103698. CrossRef - The effects of deproteinization and primer treatment on microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to dentin
In-Hye Bae, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(2): 99. CrossRef - Effect of Papain and Bromelain Enzymes on Shear Bond Strength of Composite to Superficial Dentin in Different Adhesive Systems
Farahnaz Sharafeddin, Mina Safari
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(9): 1077. CrossRef
- Effect of finishing protocols on dentin surface characteristics and bond strength after tooth preparation for indirect restorations
- 2,739 View
- 26 Download
- 24 Crossref

-
Root canal irrigants influence the hydrophobicity and adherence of
Staphylococcus epidermidis to root canal dentin: anin vitro study - Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Omer Sheriff Sultan, Sreedharan Kannathasan, Amir Shahreza Patel, Ebenezer Chitra, Prasanna Neelakantan, Fabian Davamani
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e1. Published online December 7, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
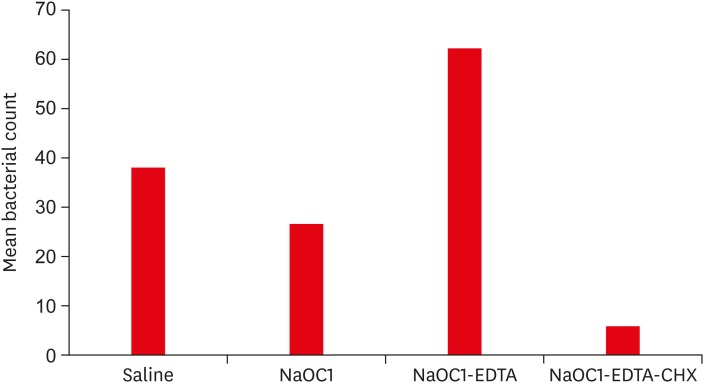
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of root canal irrigants on the hydrophobicity and adherence of
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis ) to root canal dentinin vitro .Materials and Methods Root dentin blocks (
n = 60) were randomly divided into 4 groups based on the irrigation regimen: group 1, saline; group 2, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); group 3, 5.25% NaOCl followed by 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA); group 4, same as group 3 followed by 2% chlorhexidine (CHX). The hydrophobicity ofS. epidermidis to root dentin was calculated by cell surface hydrophobicity while the adherence was observed by fluorescence microscopy, and bacteria were quantified using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health). Statistical analysis of the data was done using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-WhitneyU test (p = 0.05).Results The hydrophobicity and adherence of
S. epidermidis to dentin were significantly increased after irrigating with group 3 (NaOCl-EDTA) (p < 0.05), whereas in group 4 (NaOCl-EDTA-CHX) both hydrophobicity and adherence were significantly reduced (p < 0.05).Conclusions The adherence of
S. epidermidis to dentin was influenced differently by root canal irrigants. Final irrigation with CHX reduces the bacterial adherence and may impact biofilm formation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quaternary ammonium silane (k21) based intracanal medicament triggers biofilm destruction
Esther Sook Kuan Kok, Xian Jin Lim, Soo Xiong Chew, Shu Fen Ong, Lok Yin See, Siao Hua Lim, Ling Ang Wong, Fabian Davamani, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Amr Fawzy, Umer Daood
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Quaternary ammonium silane (k21) based intracanal medicament triggers biofilm destruction
- 1,433 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
Antibacterial effect of urushiol on
E. faecalis as a root canal irrigant - Sang-Wan Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):54-59. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.54

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the antibacterial activity of urushiol against
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) to that of NaOCl.Materials and Methods The canals of thirty two single rooted human teeth were instrumented with Ni-Ti files (ProTaper Next X1, X2, X3, Dentsply). A pure culture of
E. faecalis ATCC 19433 was prepared in sterile brain heart infusion (BHI) broth. The teeth were submerged in the suspension ofE. faecalis and were incubated at 37℃ for 7 days to allow biofilm formation. The teeth were randomly divided into three experimental groups according to the irrigant used, and a negative control group where no irrigant was used (n = 8). Group 1 used physiologic normal saline, group 2 used 6% NaOCl, and group 3 used 10 wt% urushiol solution. After canal irrigation, each sample was collected by the sequential placement of 2 sterile paper points (ProTaper NEXT paper points, size X3, Dentsply). Ten-fold serial dilutions on each vials, and 100 µL were cultured on a BHI agar plate for 8 hours, and colony forming unit (CFU) analysis was done. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-whitney U tests.Results Saline group exhibited no difference in the CFU counts with control group, while NaOCl and urushiol groups showed significantly less CFU counts than saline and control groups (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The result of this study suggests 10% urushiol and 6% NaOCl solution had powerful antibacterial activity against
E. faecalis when they were used as root canal irrigants.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A critical review on innovative targets for signal disruption in Enterococcus faecalis infection management
Kayeen Vadakkan, Gajanan Sampatrao Ghodake, Chin Wei Lai, Selvaraj Vijayanand, Janarthanam Hemapriya
Microbial Pathogenesis.2025; 207: 107876. CrossRef - Effect of proanthocyanidins application on push-out bond strength of root canal filling after different final irrigation procedures
Funda Fundaoğlu Küçükekenci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Silver-Ion-Coated Rotary Nickel Titanium Files - An In Vitro Study
Jhanvi H. Sadaria, Kondas V. Venkatesh, Dhanasekaran Sihivahanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(3): 344. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of natural-based endodontic solutions: a systematic review with a network meta-analysis
Danilo Cassiano FERRAZ, Anahi de Paula MELO, Felipe de Souza MATOS, Luiz Renato PARANHOS, Camilla Christian Gomes MOURA, Cauane BLUMENBERG, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Irrigants and irrigation activation systems in Endodontics
Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Emelly Aveiro, Anil Kishen
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(4): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite gel and solutions in endodontics: A systematic review
Sourabh Barbhi, SR Srinidhi, Rajesh Shetty, Poonam Joshi, Vini Mehta, Sanket Aras
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 290. CrossRef - Antibiofilm activity of phytochemicals against Enterococcus faecalis: A literature review
Islam A. A. Ali, Prasanna Neelakantan
Phytotherapy Research.2022; 36(7): 2824. CrossRef - Chemical compounds Anti-bacterial of Citrus aurantifolia Ethanol Extract to Inhibit the Early Biofilm Formation and Growth of Enterococcus faecalis Root Canal Isolate
Nur Asmah, Dewi Fatma Suniarti, Endang Winiati Bachtiar, Dewi Angraini Margono, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2667. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of silver diamine fluoride as a root canal irrigant
Ebtissam M. Al‐Madi, Manar A. Al‐Jamie, Noura M. Al‐Owaid, Amal A. Almohaimede, Albandary M. Al‐Owid
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2019; 5(5): 551. CrossRef
- A critical review on innovative targets for signal disruption in Enterococcus faecalis infection management
- 2,065 View
- 19 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effect of dentin treatment on proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells
- Minjeong Park, Nan-Sim Pang, Il-Young Jung
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):290-298. Published online September 23, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) is an excellent bactericidal agent, but it is detrimental to stem cell survival, whereas intracanal medicaments such as calcium hydroxide (Ca[OH]2) promote the survival and proliferation of stem cells. This study evaluated the effect of sequential NaOCl and Ca[OH]2 application on the attachment and differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs).
Materials and Methods DPSCs were obtained from human third molars. All dentin specimens were treated with 5.25% NaOCl for 30 min. DPSCs were seeded on the dentin specimens and processed with additional 1 mg/mL Ca[OH]2, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment, file instrumentation, or a combination of these methods. After 7 day of culture, we examined DPSC morphology using scanning electron microscopy and determined the cell survival rate with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. We measured cell adhesion gene expression levels after 4 day of culture and odontogenic differentiation gene expression levels after 4 wk using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results DPSCs did not attach to the dentin in the NaOCl-treated group. The gene expression levels of fibronectin-1 and secreted phosphoprotein-1 gene in both the Ca[OH]2- and the EDTA-treated groups were significantly higher than those in the other groups. All Ca[OH]2-treated groups showed higher expression levels of dentin matrix protein-1 than that of the control. The dentin sialophosphoprotein level was significantly higher in the groups treated with both Ca[OH]2 and EDTA.
Conclusions The application of Ca[OH]2 and additional treatment such as EDTA or instrumentation promoted the attachment and differentiation of DPSCs after NaOCl treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Intracanal Medications on the Viability of Human Periodontal Ligament‐Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Arian Braido, Walbert de Andrade Vieira, Bruno Cazotti Pereira, Karina Gonzales Silvério, Paulo Henrique Gabriel, Aline Cristine Gomes Matta, Emerson Alves Martins, Adriana de Jesus Soares
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of erbium yttrium aluminium garnet laser dentin conditioning on dental pulp stem cells viability
Aryan Jafari, Mehdi Vatanpour, Nooshin Barikrow, Pouyan Razavi, Sohrab Tour Savadkouhi
Heliyon.2024; 10(5): e26954. CrossRef - Comparison of the effect of NaOCL, curcumin, and EDTA on differentiation, proliferation, and adhesion of dental pulp stem cells
Vahid Zand, Amin Salem Milani, Carolyn Primus, Marzie Aghazade, Hadi Mokhtari, Sabete Bagheri Sabzevar, Pardis Tehranchi
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(2): 347. CrossRef - Differential Effects of Extracellular Matrix Glycoproteins Fibronectin and Laminin-5 on Dental Pulp Stem Cell Phenotypes and Responsiveness
Hyungbin Lee, Allen Bae, John Kim, Karl Kingsley
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(2): 91. CrossRef - Assessment of the Influence of Various Concentrations of Sodium Hypochlorite on Stem Cell Derived From Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth (SHED) Proliferation and Differentiation
Viral Maru, Ashwini KB, Manisha Madkaikar, R K Sarada Devi, Ashita Gada, Salil Bapat
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on proliferation, osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation, and mechanosensitive gene expression of human dental pulp stem cells
Yuejun Li, Changlong Jin, Shouliang Zhao, Han Xie
Tissue and Cell.2022; 79: 101955. CrossRef - Influence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on regenerative endodontics: A systematic review
Alexandre H. dos Reis‐Prado, Lucas G. Abreu, Rogéria R. Fagundes, Sabrina de C. Oliveira, Marco C. Bottino, Antônio P. Ribeiro‐Sobrinho, Francine Benetti
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(6): 579. CrossRef - An in-vitro Comparative Evaluation of Quantitative Release of Transforming Growth Factor β-1 from Dentin upon the Action of Endodontic Irrigants, Medicaments, Ultrasonic Activation, and Low-Level Laser Irradiation
Anilkumar Akhila, V. P. Prabath Singh, Kerala R. Varma, Senthil V. Vasudevan, V. Sukhithasri, Salu Sasikumar
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2021; 17(2): 34. CrossRef - Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma-Conditioned Root Dentin Promotes Attraction and Attachment of Primary Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Real-Time Ex Vivo
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Min-Ji Kang, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Joo-Cheol Park, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6836. CrossRef - The Effects of Intracanal Irrigants and Medicaments on Dental-Derived Stem Cells Fate in Regenerative Endodontics: An update
Sara Ayoub, Ali Cheayto, Sanaa Bassam, Mehdi Najar, Antoine Berbéri, Mohammad Fayyad-Kazan
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(4): 650. CrossRef - An Immunofluorescence Study to Analyze Wound Healing Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontics in an Immature Premolar with Chronic Apical Abscess
Jeen Nee Lui, Wen Yi Lim, Domenico Ricucci
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(5): 627. CrossRef - Dynamic Irrigation Promotes Apical Papilla Cell Attachment in an Ex Vivo Immature Root Canal Model
Sanupong Prompreecha, Thanapat Sastraruji, Phumisak Louwakul, Tanida Srisuwan
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 744. CrossRef - Odontoblast-like differentiation and mineral formation of pulpsphere derived cells on human root canal dentin in vitro
Jörg Neunzehn, Sandra Pötschke, Christian Hannig, Hans-Peter Wiesmann, Marie-Theres Weber
Head & Face Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate, an Antibacterial Cross-linking Agent, on Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells Cultured in Collagen Scaffolds
Young-Sun Kwon, Hee-Jin Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Vinicius Rosa, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(2): 289. CrossRef
- Effect of Intracanal Medications on the Viability of Human Periodontal Ligament‐Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- 1,797 View
- 6 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
- Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):143-148. Published online February 11, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the maximum depth and percentage of irrigant penetration into dentinal tubules by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human teeth were instrumented and divided into three groups. According to final irrigation regimen, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (Group A, NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine (Group B, CHX) and saline solution (Group C, control group) were applied with Irrisafe 20 tips (Acteon) and PUI. Irrigant was mixed with 0.1% rhodamine B. Sections at 2 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm from the apex were examined with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The percentage and maximum depth of irrigant penetration were measured. Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test were performed for overall comparison between groups at each level and for pairwise comparison, respectively. Within a group, Wilcoxon test was performed among different levels.
p values less than 0.05 were considered significant.Results In all groups, highest penetration depth and percentage of penetration were observed at the 8 mm level. At 2 mm level, Groups A and B had significantly greater depths and percentages in penetration than Group C (
p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences between Groups A and B. At 5 mm level, penetration depths and percentage of penetration was not significantly different among the groups.Conclusions NaOCl and CHX applied by PUI showed similar depth and percentage of penetration at all evaluated levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
Anjali Meena, Nidhi Sharma, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Sarita Singh, Anu Dhawan, Neha Verma
Endodontology.2025; 37(1): 80. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Sonic versus ultrasonic activation for the cleaning of the root canal after post space preparation: an in vitro study.
René Carrasco, Ricardo Román, Makarena Ojeda, Carolina Vergara
Journal Oral Of Research.2015; 4(4): 255. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
- 1,613 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Crossref

-
Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of
Ferula gummosa plant essential oil compared to NaOCl and CHX: a preliminaryin vitro study - Abbas Abbaszadegan, Ahmad Gholami, Hosein Mirhadi, Mina Saliminasab, Aboozar Kazemi, Mahmood Reza Moein
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):50-57. Published online December 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The usage of medicinal plants as natural antimicrobial agents has grown in many fields including dental medicine. The aim of this
in vitro study was three-fold: (i) to determine the chemical compositions of theFerula gummosa essential oil (FGEO), (ii) to compare the antimicrobial efficacy of the oil with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and chlorhexidine (CHX), (iii) to assess the toxic behavior of FGEO in different concentrations compared to 5% NaOCl and 0.2% CHX.Materials and Methods Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used to determine the chemical compositions of the oil. The disk diffusion method and a broth micro-dilution susceptibility assay were exploited to assess the antimicrobial efficacy against
Enterococcus faecalis ,Staphylococcus aureus ,Streptococcus mitis , andCandida albicans . The cytocompatibility of the FGEO was assessed on L929 fibroblasts, and compared to that of NaOCl and CHX.Results Twenty-seven constituents were recognized in FGEO. The major component of the oil was β-pinene (51.83%). All three irrigants significantly inhibited the growth of all examined microorganisms compared to the negative control group. FGEO at 50 µg/mL was effective in lower concentration against
Enterococcus faecalis than 5% NaOCl and 0.2% CHX, and was also more potent than 0.2% CHX againstCandida albicans andStaphylococcus aureus . FGEO was a cytocompatible solution, and had significantly lower toxicity compared to 5% NaOCl and 0.2% CHX.Conclusions FGEO showed a promising biological potency as a root canal disinfectant. More investigations are required on the effectiveness of this oil on intracanal bacterial biofilms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Isolation, characterization and control of Botrytis spp. pathogenic on strawberry in Iran
Fatemeh Maghsoodi, Parissa Taheri, Saeed Tarighi
Heliyon.2025; 11(2): e42037. CrossRef - Novel chitosan-alginate dressings with UIO-66-NH2 nanoparticles and ferula gummosa extracts for effective wound healing
Fatemeh Mojtahedi, Mohammad Reza Nasiri, Saba Naeimaei Ali, Azadeh Mohammadgholi, Shekoufe Mohebbi, Zahra Shahbazi, Reza Behfar, Saina Namazifard, Hassan Noorbazargan, Fahimeh Baghbani-Arani
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects.2025; 719: 137004. CrossRef -
Phytochemical analysis and bioactivity assessment of
Ferula longipes
Coss. ex Bonn. &Maury. methanolic extract: insights into antioxidant, and anti-corrosive properties
Abada Faten, Boulkroune Mina, Bicha Sabrina, Atalar Mehmet Nuri, Bensouici Chawki, Akkal Salah
Natural Product Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Investigation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of a hydroxyapatite-enhanced nanocomposite for dental applications
Xin Yan, Ali ebrahimi, Reza Mohammadi, Mona Mohajeri Tehrani, Pardis Chaboki, Mohammed Mustafa, Almustafa Alhumadi, I. B. Sapaev, Ahmed Hjazi, Khadije Yousefi, Mojdeh Yousefi
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Phytochemical Profiling of Ferula varia Extract and Its Antibiofilm Activity Against Streptococcus mutans
Marlen K. Smagulov, Yana K. Levaya, Karakoz Zh. Badekova, Svetlana A. Ivasenko, Gayane A. Atazhanova, Vika Gabe, Margarita Yu. Ishmuratova, Tomas Kacergius
Molecules.2025; 30(21): 4178. CrossRef - Chemical compositions and antibacterial activity of essential oil from Ferula lapidosa korovin flowers
Kholida Khasanova, Anarbay Babekov, Komila Eshbakova, Kurbonazar Juraev, Usmonov Kamoliddin, Jaxongir Tursunov, Bokhodir Mamarasulov
Medicinal Plants - International Journal of Phytomedicines and Related Industries.2025; 17(1): 91. CrossRef - Research methods assessing sodium hypochlorite cytotoxicity: A scoping review
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Luana Raphael da Silva, Gisele Faria
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23060. CrossRef - Comparison the effect of Ferula gummosa and Chlorhexidine on dental cariogenic bacteria
bahareh nazemi salman, ali Yazdi Nejad, fakhri haghi, mahtab Mohammadi Gheydari, samira basir shabestari
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(2): 125. CrossRef - Use of irrigating substances of natural origin in Endodontics
Yoneisy Abraham-Millán, Rosa María Montano-Silva, Yaima Pupo-Martínez
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias.2023; 2: 591. CrossRef - Comparison effects of Ferula gummosa essential oil and Beta-pinene Alginate nanoparticles on human melanoma and breast cancer cells proliferation and apoptotic index in short term normobaric hyperoxic model
Mahmoud Osanloo, Somayyeh Pishamad, Ali ghanbariasad, Elham Zarenezhad, Media Alipanah, Hiva Alipanah
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A promising insight into the inhibition of lipid oxidation, protein degradation and biogenic amine accumulation in postmortem fish: Functional glazing layers of modified bio-polymer
Xiaodan Hui, Yu Wan, Hao Dong, Jian Peng, Weiliang Wu, Xingfen Yang, Qi He
LWT.2023; 177: 114575. CrossRef -
Efficacy of hypochlorous acid as an alternative oral antimicrobial agent on human gingival fibroblasts,
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
, and
Candida albicans
biofilms
in vitro
Gözdem Bayraktar, Ayşe Mine Yılmaz Göler, Burak Aksu, Hafize Öztürk Özener
Biofouling.2023; 39(9-10): 980. CrossRef - Molecular Docking and Antibacterial Assessment of Monocyclic β‐Lactams against Broad‐Spectrum and Nosocomial Multidrug‐Resistant Pathogens
Elham Riazimontazer, Roghayeh Heiran, Aliasghar Jarrahpour, Ahmad Gholami, Zahra Hashemi, Aboozar Kazemi
ChemistrySelect.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant and antimicrobial characteristics of chitosan and galbanum gum composite coating incorporated with cumin essential oil on the shelf life of chicken fillets
Leila Aghababaei, Maryam Hasani, Peyman Mahasti Shotorbani, Afshin Akhondzadeh Basti, Hassan Hamedi
Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization.2022; 16(3): 1820. CrossRef - Assessing edible composite coating of sodium alginate–galbanum gum impregnated with nettle extract on improving the shelf life of rainbow trout fillet
Maliheh Zarandi, Maryam Hasani, Peyman Mahasti Shotorbani, Afshin Akhondzadeh Basti, Hassan Hamedi
Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization.2022; 16(4): 2556. CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils against Oral Pathogens
Thaís A. S. Oliveira, Mariana B. Santiago, Valmore H. P. Santos, Eliane O. Silva, Carlos H. G. Martins, Antônio E. M. Crotti
Chemistry & Biodiversity.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Profile, Bioactivities, and Variations in the Chemical Constituents of Essential Oils of the Ferula Genus (Apiaceae)
Priyankaraj Sonigra, Mukesh Meena
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Gene Expression Changes of a Novel Homeopathic Antiseptic Oral Rinse in Comparison to Chlorhexidine in Gingival Fibroblasts
Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi, Benoit Schaller, Michael A. Pikos, Anton Sculean, Richard J. Miron
Materials.2020; 13(14): 3190. CrossRef - Current herbal medicine as an alternative treatment in dentistry: In vitro, in vivo and clinical studies
Ehsan Tafazoli Moghadam, Mohsen Yazdanian, Elahe Tahmasebi, Hamid Tebyanian, Reza Ranjbar, Alireza Yazdanian, Alexander Seifalian, Ali Tafazoli
European Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 889: 173665. CrossRef - A review of Ferula species: Biochemical characteristics, pharmaceutical and industrial applications, and suggestions for biotechnologists
Maryam Salehi, Mohammad Reza Naghavi, Moslem Bahmankar
Industrial Crops and Products.2019; 139: 111511. CrossRef - Investigation effects of extracted compounds from shell and cluster of pistachio nut on the inactivation of free radicals
Morteza Mohammadi, Mohammad Ghorbani, Adel Beigbabaei, Samira Yeganehzad, Alireza Sadeghi-Mahoonak
Heliyon.2019; 5(9): e02438. CrossRef - Effect of Irrigation Time of Antiseptic Solutions on Bone Cell Viability and Growth Factor Release
Kosaku Sawada, Ken Nakahara, Maiko Haga-Tsujimura, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi, Tateyuki Iizuka, Richard J. Miron
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2018; 29(2): 376. CrossRef - Mining Ferula gummosa transcriptome to identify miRNAs involved in the regulation and biosynthesis of terpenes
Ahmad Sobhani Najafabadi, Mohammad Reza Naghavi
Gene.2018; 645: 41. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Persea major Kopp (Lauraceae) extract against Enterococcus faecalis: a preliminary in vitro study
Lusiane Volpato, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Paulo Henrique Tomazinho, Leila Teresinha Maranho, Flares Baratto-Filho
BMC Research Notes.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate, an Antibacterial Cross-linking Agent, on Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells Cultured in Collagen Scaffolds
Young-Sun Kwon, Hee-Jin Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Vinicius Rosa, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(2): 289. CrossRef - A novel bioactive edible coating based on sodium alginate and galbanum gum incorporated with essential oil of Ziziphora persica: The antioxidant and antimicrobial activity, and application in food model
Hassan Hamedi, Mina Kargozari, Peyman Mahasti Shotorbani, Nima Babolani Mogadam, Maryam Fahimdanesh
Food Hydrocolloids.2017; 72: 35. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Calcium Hydroxide, and Triple Antibiotic Paste as Root Canal Dressing Materials
Abbas Abbaszadegan, Sahar Dadolahi, Ahmad Gholami, Mahmoud Reza Moein, Shahram Hamedani, Younes Ghasemi, Paul Vincent Abbott
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2016; 17(2): 105. CrossRef - Natural Therapeutic Options in Endodontics - A Review
Nagendrababu Venkateshbabu, Suresh Anand, Mohan Abarajithan, Sultan O. Sheriff, Pulikkotil S. Jacob, Nath Sonia
The Open Dentistry Journal.2016; 10(1): 214. CrossRef - Ferula gummosa, a Traditional Medicine with Novel Applications
Mohaddese Mahboubi
Journal of Dietary Supplements.2016; 13(6): 700. CrossRef - Effects of Antiseptic Solutions Commonly Used in Dentistry on Bone Viability, Bone Morphology, and Release of Growth Factors
Kosaku Sawada, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi, Eizaburo Kobayashi, Benoit Schaller, Richard J. Miron
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2016; 74(2): 247. CrossRef - Antiseptic solutions modulate the paracrine‐like activity of bone chips: differential impact of chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite
Kosaku Sawada, Jordi Caballé‐Serrano, Dieter D. Bosshardt, Benoit Schaller, Richard J. Miron, Daniel Buser, Reinhard Gruber
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2015; 42(9): 883. CrossRef - Tributyl tetradecyl phosphonium chloride for biofouling control in reverse osmosis processes
Taek-Seung Kim, Hee-Deung Park
Desalination.2015; 372: 39. CrossRef
- Isolation, characterization and control of Botrytis spp. pathogenic on strawberry in Iran
- 2,336 View
- 10 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Calcium hydroxide dressing residues after different removal techniques affect the accuracy of Root-ZX apex locator
- Emel Uzunoglu, Ayhan Eymirli, Mehmet Özgür Uyanik, Semra Çalt, Emre Nagas
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):44-49. Published online November 5, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the ability of several techniques to remove calcium hydroxide (CH) from the root canal and determined the influence of CH residues on the accuracy of the electronic apex locator.
Materials and Methods Root canals of 90 human maxillary lateral incisors with confirmed true working length (TWL) were prepared and filled with CH. The teeth were randomly assigned to one of the experimental groups according to the CH removal technique (
n = 14): 0.9% saline; 0.9% saline + master apical file (MAF); 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA); 17% EDTA + MAF; 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); 5.25% NaOCl + MAF. Six teeth were used as negative control. After CH removal, the electronic working length was measured using Root-ZX (Morita Corp.) and compared with TWL to evaluate Root-ZX accuracy. All specimens were sectioned longitudinally, and the area of remaining CH (CH) and total canal area were measured using imaging software.Results The EDTA + MAF and NaOCl + MAF groups showed better CH removal than other groups (
p < 0.05). Root-ZX reliability to prevent overestimated working length to be > 85% within a tolerance of ± 1.0 mm (p < 0.05). There was strong negative correlation between amount of CH residues and EAL accuracy (r = -0.800 for ± 0.5 mm;r = -0.940 for ± 1.0 mm).Conclusions The mechanical instrumentation improves the CH removal of irrigation solutions although none of the techniques removed the dressing completely. Residues of CH medication in root canals affected the accuracy of Root-ZX adversely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Kürs¸at Er
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluation of heated sodium hypochlorite’s effect on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators: an in vitro study
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
Shayan Golkar, Abbasali Khademi, Amin Saatchi, Amir Ghorani, Pedram Iranmanesh
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a new irrigation solution -RISA- on removing calcium hydroxide from artificial standardized grooves in root canals - an in vitro study
İpek Eraslan Akyüz, Salih Düzgün, Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Apical Patency, Coronal Preflaring and Calcium Hydroxide on the Accuracy of Root ZX Apex Locator for Working Length Determination: An In Vitro Study
Mostafa Godiny, Reza Hatam, Roya Safari-Faramani, Atefeh Khavid, Mohammad Reza Rezaei
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(1): 38. CrossRef - Endodontic cement penetration after removal of calcium hydroxide dressing using XP-endo finisher
Alyssa Sales dos Santos, Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Eduardo Nunes
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of glycolic acid for the removal of calcium hydroxide from simulated internal Resorption cavities
Cangül Keskin, Ali Keleş, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4407. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Farklı Kanal İçi Ortamların Apeks Bulucuların Doğruluğu Üzerine Etkisi
Asena OKUR, Tuğrul ASLAN, Burak SAĞSEN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 859. CrossRef - Evaluation of the accuracy of different apex locators in determiningthe working length during root canal retreatment
Pelin Tufenkci, Aylin Kalaycı
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 125. CrossRef - Influence of calcium hydroxide residues after using different irrigants on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators: An in vitro study
NooshinSadat Shojaee, Zahra Zaeri, MohammadMehdi Shokouhi, Fereshteh Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl
Dental Research Journal.2020; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and File Sızes on the Accuracy of the Electronic Apex Locator in Simulated Immature Teeth
Leyla AYRANCİ, Ahmet ÇETİNKAYA, Serkan ÖZKAN
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2019; 5(3): 273. CrossRef - The Effect of File Size and Type and Irrigation Solutions on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators: AnIn VitroStudy on Canine Teeth
Maciej Janeczek, Piotr Kosior, Dagmara Piesiak-Pańczyszyn, Krzysztof Dudek, Aleksander Chrószcz, Agnieszka Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz, Małgorzata Kowalczyk-Zając, Aleksandra Gabren-Syller, Karol Kirstein, Aleksandra Skalec, Ewelina Bryła, Maciej Dobrzyński
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
- 1,662 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
- Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):295-301. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.295
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purposes of this study were firstly to investigate the any formation of precipitate after interaction between ALX and NaOCL and secondarily to analyze the PCA formation by using time of flight secondary ion mass (TOF-SIM) spectrometry. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed for the mixture of 0.5% ALX and 5.25% NaOCl. As controls, 2.5% CHX with 5.25% NaOCl and 1% PCA solutions were used. Any formation of precipitates in 10 tested solutions was evaluated by naked eye. Results of mass spectrum showed that the typical peak of PCA was not detected in mixed solution of ALX and NaOCl, whereas CHX/NaOCl mixture showed the same peak that found in the PCA spectrum. Precipitate formation was only observed in CHX/NaOCL mixture. The present TOF-SIM spectrometry results indicated that ALX can be a useful root canal irrigant combined with NaOCl during canal instrumentation. Further study is necessary to confirm the antimicrobial effect of ALX against endodontic pathogen before its clinical application as an endodontic irrigant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chemical Interaction of Alexidine and Sodium Hypochlorite
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Qiang Zhu, Seung-Ho Baek, Il-Young Jung, Won-Jun Son, Seok-Woo Chang, Woocheol Lee, Yu Gu, Yoon Lee, Sung-Tae Hong, Kwang-Shik Bae, Ji-Woong Kim, Kun Cho, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2012; 38(1): 112. CrossRef
- Chemical Interaction of Alexidine and Sodium Hypochlorite
- 1,852 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
- Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):80-87. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.080
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the different canal irrigation methods to prevent the formation of precipitate between sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and chlorhexidine (CHX).
Extracted 50 human single-rooted teeth were used. The root canals were instrumented using NiTi rotary file (Profile .04/#40) with 2.5% NaOCl and 17% EDTA as irrigants. Teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups and one control group as follows; Control group: 2.5% NaOCl only, Group 1: 2.5% NaOCl + 2% CHX, Group 2: 2.5% NaOCl + paper points + 2% CHX, Group 3: 2.5% NaOCl + preparation with one large sized-file + 2% CHX, Group 4: 2.5% NaOCl +95% alcohol+ 2% CHX.
The teeth were split in bucco-lingual aspect and the specimens were observed using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope. The percentages of remaining debris and patent dentinal tubules were determined. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Energy Dispersive x-ray Spectroscopy was used for analyzing the occluded materials in dentinal tubule for elementary analysis.
There were no significant differences in percentage of remaining debris and patent tubules between all experimental groups at all levels (p > .05).
In elementary analysis, the most occluded materials in dentinal tubule were dentin debris. NaOCl/CHX precipitate was detected in one tooth specimen of Group 1.
In conclusion, there were no significant precipitate on root canal, but suspected material was detected on Group 1. The irrigation system used in this study could be prevent the precipitate formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 295. CrossRef
- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
- 1,726 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- CYCLIC FATIGUE OF THE SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE TREATED AND /OR STEAM AUTOCLAVED NICKEL-TITANIUM ENDODONTIC FILES
- Hye-Young Cho, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):54-65. Published online January 14, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of sodium hypochlorite and steam autoclaving on the cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium endodontic files.
Two types of files with a .06 taper and #30 were used, K3® (SybronEndo, Glendora, California, USA) and Hero642®(Micro-Mega, Besançon, France).
The files were divided into 6 experimental groups containing 10 files each group depending the soaking time in 6% sodium hypochlorite solution and number of cycles of steam autoclave. After sterilization, a cyclic fatigue test was performed on each file, and the fracture time was recorded in seconds. The control group underwent the cyclic fatigue test only. After the test, the surface characteristics of the files were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
All groups containing the Hero 642® files showed a similar cyclic fatigue fracture time. However, the cyclic fatigue fracture time with the K3® files was significantly shorter in groups which were treated with sodium hypochlorite than in the control group (P < 0.05). SEM revealed both Hero642® and K3® files to have significant corrosion on the file surface in groups treated with sodium hypochlorite, compared with the sharp and regular blades of the control group. K3® files showed more corrosion than the Hero642® files. Bluntness of the blades of the K3® file was observed in groups treated with steam autoclave. Although there was no obvious destruction on the surface of steam autoclaved Hero642® files, slight bluntness was observed.
Sterilizing with a steam autoclave is much less destructive to K3® files than sodium hypochlorite. The longer time exposed to sodium hypochlorite, the more destructive pattern was shown on the blades of the files. Therefore, when using sodium hypochlorite solution, the exposure time should be as short as possible in order to prevent corrosion and increase the cyclic fatigue fracture time.
- 870 View
- 1 Download

-
Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) on
Enterococcus faecalis in the root canal - Hye-Jeong Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):121-129. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to assess the antibacterial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC), sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), and chlorhexidine (CHX) on
Enterococcus faecalis and to evaluate and to compare the time-dependant antimicrobial effect of NaDCC with NaOCl and CHX in the root canalin vitro before and after instrumentation.Extracted human single teeth were prepared by serial instrumentation technique. The samples were autoclaved and contaminated for 3 days with
E. faecalis monocultures. The teeth were then divided into 4 groups. Each group was irrigated and inserted with 2% NaOCl, 2% NaDCC, 2% CHX and sterilized saline. After 6, 12, 24, 72h, and 1 week incubation, sterilized paper point was inserted into the root canal. Paper points containing root canal contents were then placed on the agar plate. And then each root canal was prepared with #4 and #5 GG (Gates-Glidden) drill. The debris were collected in the sterilized microtube and the plates were incubated at 37℃ in an increased CO2 atmosphere. After 24h incubation the growth of bacteria around the paper points were measured.NaOCl and NaDCC solution shows similar antimicrobial effect for
E. faecalis at 6, 12, 24, 72h and 1 week. In control group, irrigated with sterilized saline, no antimicrobial effect was observed.The results are in agreement with other investigators, who have shown the bactericidal property and possibility of NaDCC as a root canal irrigation solution. Thus it seems that NaDCC solutions can be clinically applied into the root canal within 1 week after dilution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary toxicity of sodium dichloroisocyanurate after intratracheal instillation in sprague-dawley rats
Jean Yoo, Haewon Kim, Yeon-Mi Lim, Byung-Il Yoon, Pilje Kim, Ig-Chun Eom, Ilseob Shim
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis in endodontic infections: antibiotic resistance profile and susceptibility to photodynamic therapy
Ana Carolina Chipoletti Prado, Patrícia Pimentel De Barros, Jéssica Diane Dos Santos, Luciane Dias De Oliveira, Claudio Antônio Talge Carvalho, Marcia Carneiro Valera, Antonio Olavo Cardoso Jorge, Juliana Campos Junqueira
Lasers in Dental Science.2017; 1(2-4): 91. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Disease Control Efficacy of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) Against Major Strawberry Diseases
Da-Ran Kim, Gun-Hye Gang, Hyun-Ji Cho, Hae-Suk Yoon, Youn-Sig Kwak
The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science.2015; 19(1): 47. CrossRef - Effect of Gamma Irradiation and Its Convergent Treatments on Lily Leaf Blight Pathogen, Botrytis elliptica, and the Disease Development
Ji-Hoon Kim, Sung-Chul Yun
Research in Plant Disease.2014; 20(2): 71. CrossRef - Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 258. CrossRef - Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 295. CrossRef - The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 80. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 500. CrossRef - Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
Seung-Gon Song, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 390. CrossRef - The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 397. CrossRef
- Pulmonary toxicity of sodium dichloroisocyanurate after intratracheal instillation in sprague-dawley rats
- 1,995 View
- 13 Download
- 10 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


