Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of irrigation protocols on smear layer removal, bond strength and nanoleakage of fiber posts using a self-adhesive resin cement
- Rodrigo Stadler Alessi, Renata Terumi Jitumori, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, Giovana Mongruel Gomes, João Carlos Gomes
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e28. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
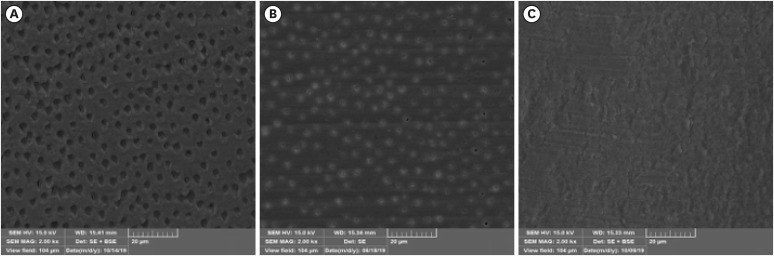
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the effect of the application method of 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) and its influence on the adhesion of fiberglass posts cemented with a self-adhesive resin cement.
Materials and Methods Sixty human mandibular premolars were endodontically treated and divided into 5 groups (
n = 12), according to the canal irrigant and its application method: 2 groups with conventional syringe irrigation (CSI)—2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) (control) and 2% CHX— and 3 groups with 2% CHX irrigation/activation—by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), Easy Clean file, and XP-Endo Finisher file. Two roots per group were evaluated for smear layer (SL) removal by scanning electron microscopy. For other roots, fiber posts were luted using a self-adhesive resin cement. The roots were sectioned into 6 slices for push-out bond strength (BS) (7/group) and nanoleakage (NL) (3/group). Data from SL removal were submitted to Kruskal-Wallis and Student-Newman-Keuls tests (α = 0.05). Data from BS and NL were evaluated by 2-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).Results For SL removal and BS, the CHX irrigation/activation promoted better values than CSI with CHX (
p < 0.05), but it was not significantly different from CSI with NaOCl (p > 0.05). For NL, the lowest values were obtained by the chlorhexidine irrigation/activation groups (p < 0.05).Conclusions Active 2% CHX irrigation can be used to improve the post space cleaning and adhesion before fiber post cementation with self-adhesive resin cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
Lívia Ribeiro, Luíz Carlos de Lima Dias-Júnior, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Paulo Marcelo Rodrigues, Vicente Ribeiro Netto, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Renata Gondo Machado, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Luc
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104252. CrossRef - Laser‐Activated Irrigation via Photon‐Induced Photoacoustic Streaming and Shock Wave Enhanced Emission on Smear Layer Removal Efficacy, Pushout Bond Strength, and Sealer Adaptation: A SEM Assessment
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(6): 1806. CrossRef - The impact of passive ultrasonic irrigation on the bond strength of two different self-etch adhesives to human pulp chamber dentine: a laboratory investigation
Mohammed Turky, Jukka Matinlinna, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul M. H. Dummer, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Nermin Alsayed Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of nanoparticles incorporation titanium dioxide and zirconium oxide within self-adhesive resin cement on the push-out bond strength of the fiber post to the radicular dentin: An in vitro study
Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori, Maha Anwer AL-Murad
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 162. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Post Space Conditioning Procedures and Different Endodontic Sealers on the Push-Out Bond Strengths of Fiber Posts
Leyla Ayranci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci, Fatih Sarı, Ahmet Çetinkaya
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 620. CrossRef - Evaluation of Microleakage Using Different Luting Cements in Kedo Zirconia Crowns: An In Vitro Assessment
Guru Vishnu, Ganesh Jeevanandan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
- 3,463 View
- 69 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Microleakage and characteristics of resin-tooth tissues interface of a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive systems
- Xuan Vinh Tran, Khanh Quang Tran
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e30. Published online May 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
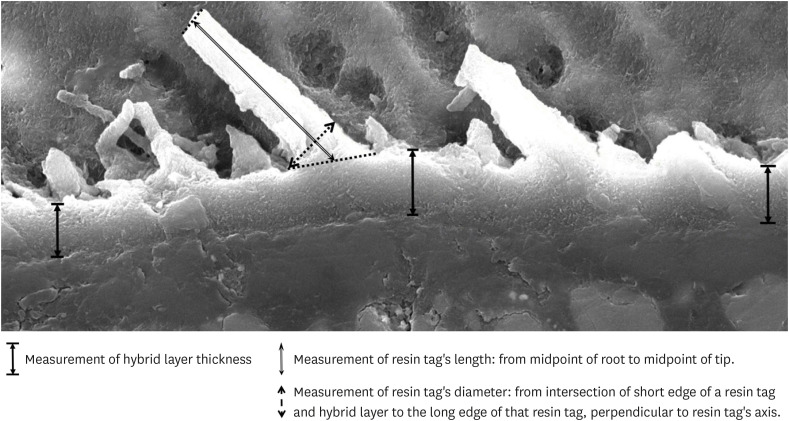
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to compare the microleakage and characteristics of the resin-tooth tissue interface between self-etch and etch-and-rinse adhesive systems after 48 hours and 3 months.
Materials and Methods 40 extracted premolar teeth were randomly divided into 2 groups: 1-step self-etch adhesive system – Optibond™ All-In-One, and 2-step etch-and-rinse adhesive system - Adper™ Single Bond 2. Both groups were subjected to 500 thermocycles (5°C–55°C) before scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis or microleakage trial at 48-hour and 3-month time periods.
Results SEM images showed the hybrid layer thickness, diameter, and length of resin tags of the self-etch adhesive (0.42 ± 0.14 µm; 1.49 ± 0.45 µm; 16.35 ± 14.26 µm) were smaller than those of the etch-and-rinse adhesive (4.39 ± 1.52 µm; 3.49 ± 1 µm; 52.81 ± 35.81 µm). In dentin, the microleakage scores of the 2 adhesives were not different in both time periods (48 hours/3 months). However, the microleakage score of etch-and-rinse adhesive increased significantly after 3 months (0.8 ± 0.63 and 1.9 ± 0.88,
p < 0.05).Conclusions The self-etch adhesive exhibited better long-term sealing ability in dentin when compared to that of the etch-and-rinse adhesive. The greater hybrid layer thickness and dimensions of resin tags did not guarantee reliable, long-lasting sealing in the bonding area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of shear bond strength of sixth- and fourth-generation adhesives in primary teeth
Maryam Hajiahmadi, Najmeh Akhlaghi, Hamid Mosleh, Ehsan Samani, Sheida Bagheri, Zohreh Salehi
Dental Research Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of different adhesive systems in bonding direct resin composite restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ravinder S. Saini, Rajesh Vyas, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Artak Heboyan
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(2): 115. CrossRef - Characterisation of universal adhesive bonded resin-dentin interface after focused ultrasound smear layer conditioning
Cheryl Fu, Peta L. Clode, Amr S. Fawzy
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 142: 104115. CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Pretreatment With Dimethyl Sulfoxide Solution on Interfacial Fracture Toughness of Composite Resin to Wet and Dry Dentin
Fatemeh Molaei, Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Seyedeh Maryam Tavangar, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Resin tags formation by modified Renewal MI formulations in a carious dentine model
Nabih Alkhouri, Wendy Xia, Paul Ashley, Anne Young
Frontiers in Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of propolis added to single‐bottle adhesives on water permeation through the hybrid layer
Lucineide Silva da Rocha, Daniela Ferreira de Oliveira, Cinthya Luna Veloso de Lima, Ticiano Gomes do Nascimento, Johnnatan Duarte de Freitas, Jeniffer Mclaine Duarte de Freitas, Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploration and preliminary clinical investigation of an adhesive approach for primary tooth restoration
Xiangqin Xu, Jiansheng Zhu, May Lei Mei, Huaying Wu, Kaipeng Xie, Shoulin Wang, Yaming Chen
The Journal of Biomedical Research.2023; 37(2): 138. CrossRef - Adhesion to enamel and dentine: an update
Rana Alkattan
Primary Dental Journal.2023; 12(3): 33. CrossRef - Effects of carbodiimide combined with ethanol–wet bonding pretreatment on dentin bonding properties: an in vitro study
Xiaoxiao You, Long Chen, Jie Xu, Sihui Li, Zhenghao Zhang, Ling Guo
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14238. CrossRef - The effects of amalgam contamination and different surface modifications on microleakage of dentin bonded to bulk fill composite when using different adhesive protocols
Nojoud Alshehri, Abdullah Aljamhan, Mohammed Bin-Shuwaish
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of low-shrinkage dental adhesives via blending with spiroorthocarbonate expanding monomer and unsaturated epoxy resin monomer
Zonghua Wang, Xiaoran Zhang, Shuo Yao, Jiaxin Zhao, Chuanjian Zhou, Junling Wu
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 133: 105308. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on the resin-dentin bond strength and antibacterial activity of a self-etch adhesive system
Jia Wang, Wei Jiang, Jingping Liang, Shujun Ran
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(6): 1363.e1. CrossRef
- A systematic review of shear bond strength of sixth- and fourth-generation adhesives in primary teeth
- 2,644 View
- 41 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Interface between calcium silicate cement and adhesive systems according to adhesive families and cement maturation
- Nelly Pradelle-Plasse, Caroline Mocquot, Katherine Semennikova, Pierre Colon, Brigitte Grosgogeat
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e3. Published online December 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
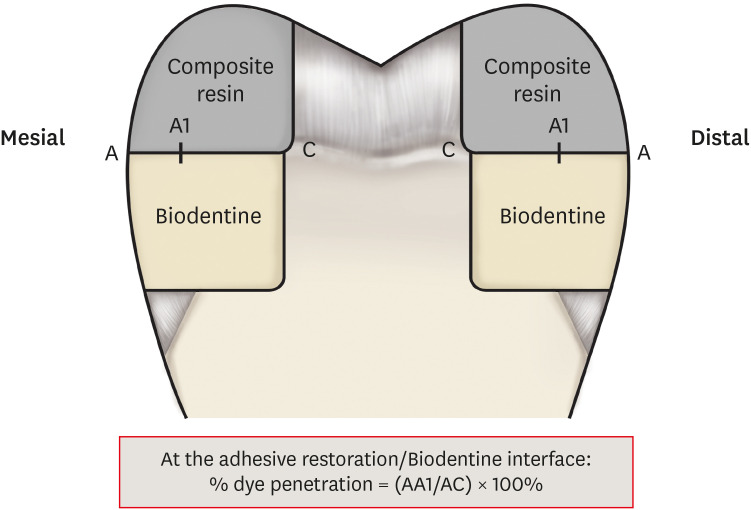
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the interface between a calcium silicate cement (CSC), Biodentine and dental adhesives in terms of sealing ability.
Materials and Methods Microleakage test: 160 standardized class II cavities were prepared on 80 extracted human molars. The cavities were filled with Biodentine and then divided into 2 experimental groups according to the time of restoration: composite resin obturation 15 minutes after Biodentine handling (D0); restoration after 7 days (D7). Each group was then divided into 8 subgroups (
n = 5) according to the adhesive system used: etch-and-rinse adhesive (Prime & Bond); self-etch adhesive 2 steps (Optibond XTR and Clearfil SE Bond); self-etch adhesive 1 step (Xeno III, G-aenial Bond, and Clearfil Tri-S Bond); and universal used as etch-and-rinse or self-etch (ScotchBond Universal ER or SE). After thermocycling, the teeth were immersed in a silver nitrate solution, stained, longitudinally sectioned, and the Biodentine/adhesive percolation was quantified. Scanning electron microscopic observations: Biodentine/adhesive interfaces were observed.Results A tendency towards less microleakage was observed when Biodentine was etched (2.47%) and when restorations were done without delay (D0: 4.31%, D7: 6.78%), but this was not significant. The adhesives containing 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate monomer showed the most stable results at both times studied. All Biodentine/adhesive interfaces were homogeneous and regular.
Conclusions The good sealing of the CSC/adhesive interface is not a function of the system adhesive family used or the cement maturation before restoration. Biodentine can be used as a dentine substitute.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of compressive strength, surface microhardness, and surface microstructure of different types of bioceramics following varying surface treatments
Zeynep Hale Keleş, Vasfiye Işık, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er Cr YSGG laser etching procedure on the bond strength of different calcium silicate cements
Yesim Sesen Uslu, Hakan Yasin Gönder, Pinar Sesen, Gizem Gunduz Bektaş
Lasers in Dental Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Resistance of Natural Molars vs. Additive-Manufactured Simulators Treated with Pulpotomy and Endocrown
Marie-Laure Munoz-Sanchez, Alexis Gravier, Olivier Francois, Emmanuel Nicolas, Martine Hennequin, Nicolas Decerle
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(9): 444. CrossRef - Characterisation of the calcium silicate‐based cement–composite interface and the bonding strength with total‐etch or single/two‐stage self‐etch adhesive systems
Abidin Talha Mutluay, Merve Mutluay
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 501. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Adhesive Systems to Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
Louis Hardan, Davide Mancino, Rim Bourgi, Alejandra Alvarado-Orozco, Laura Emma Rodríguez-Vilchis, Abigailt Flores-Ledesma, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Ammar Eid, Maya-Line Danhache, Maryline Minoux, Youssef Haïkel, Naji Kharo
Gels.2022; 8(5): 311. CrossRef
- Comparison of compressive strength, surface microhardness, and surface microstructure of different types of bioceramics following varying surface treatments
- 2,877 View
- 50 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Bacterial leakage and micro-computed tomography evaluation in round-shaped canals obturated with bioceramic cone and sealer using matched single cone technique
- Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Ratchapin Laovanitch Srisatjaluk
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e30. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
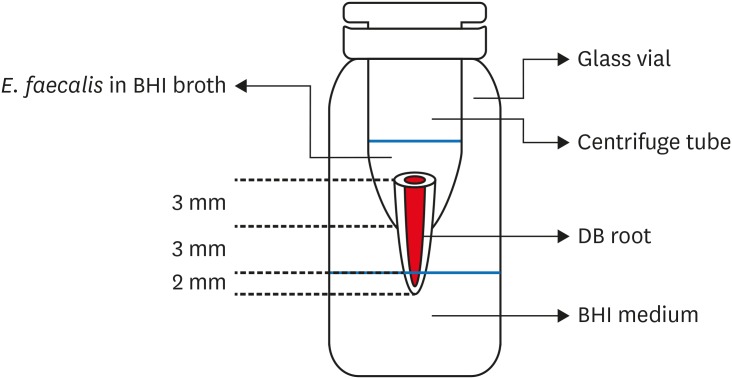
ePub Objectives To evaluate sealing ability of root canals obturated with bioceramic-impregnated gutta percha cone (BCC) or gutta percha (GP), with bioceramic sealer (BCS) or AH Plus (AH; Dentsply-Maillefer), in roundly-prepared canals using matched single-cone technique, based on bacterial leakage test, and to analyze obturation quality using micro-computed tomography (CT) analysis.
Materials and Methods Ninety-two distobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared using nickel-titanium files to apical size 40/0.06. The roots were divided into 4 groups (
n = 20) that were obturated with a master cone and sealer: GP/AH, BCC/AH, GP/BCS, and BCC/BCS. Bacterial leakage model usingEnterococcus faecalis was used to evaluate sealing ability for 60-day period. Obturated samples from each group (n = 4) were analyzed using micro-CT.Results All groups showed bacterial leakage at 20%–45% of samples with mean leakage times of 42–52 days. There were no significant differences in bacterial leakage among the groups. Micro-CT showed minimal gaps and voids in all groups at less than 1%.
Conclusions In roundly-prepared canals, the single cone obturation with BCC/BCS was comparable to GP/AH for bacterial leakage at 60 days.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-Dependent Volumetric and Porosity Changes of Bioceramic, Silicone Bioactive Glass-Based, and Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Micro-CT Analysis
Thanh Quang Nguyen, Chantida Pawaputanon Na Mahasarakham, Pinpana Thaweesit, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Angsana Jainaen
European Journal of Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - Synthesis, physical properties, and root canal sealing of experimental MTA- and salicylate-based root canal sealers
Rafael Pino Vitti, Kusai Baroudi, Tarun Walia, Raghavandra M. Shetty, Flávia Goulart da Rosa Cardoso, Flávia de Moura Pereira, Evandro Piva, Cesar Henrique Zanchi, Gabriel Flores Abuna, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Flávio
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0329476. CrossRef - Impact of cone system compatibility on single cone bioceramic obturation in canals prepared with variable taper NiTi rotary files
Reem M. Barakat, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Njoom Aleid, Hoor Almowais, Aljawhara Alharbi, Meshal Al-Sharafa, Ali Alrahlah
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio de la obturación con selladores biocerámicos de conductos radiculares de premolares inferiores
Alicia Beatriz Bonafé, Cecilia Inés Rourera, Carla Pedraza, Yamila Victoria Zanoni, Soledad Salduna, Cecilia Noemi De Caso, Gabriela Martín
Methodo Investigación Aplicada a las Ciencias Biológicas.2025; 10(3): 31. CrossRef - Sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate: A scoping review of laboratory assessment methods
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Deepak Mehta, Kyung‐San Min, Atsushi Tomokiyo
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial Leakage Testing in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Review on Methods, Models, and Clinical Relevance
Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Sukhamoy Gorai
Scientifica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro comparative evaluation of apical leakage using a bioceramic sealer with three different obturating techniques: A glucose leakage model
Tanvi S Agrawal, Shishir Singh, Rajesh S Podar, Gaurav Kulkarni, Anuprita Gadkari, Navin Agarwal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 76. CrossRef - In Vitro Microscopical and Microbiological Assessment of the Sealing Ability of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karin Christine Huth, Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Leander Benz, Stefan Kist, Maximilian Kollmuss
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 341. CrossRef - Comparison between AH plus sealer and total fill bioceramic sealer performance in previously untreated and retreatment cases of maxillary incisors with large-sized periapical lesion: a randomized controlled trial
Eisa Wahbi, Hassan Achour, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial sealing ability of calcium silicate-based sealer for endodontic surgery: an in-vitro study
Mai M. Mansour, Sybel M. Moussa, Marwa A. Meheissen, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Assessment of Bacterial Sealing Ability of Two Different Bio-Ceramic Sealers in Single-Rooted Teeth Using Single Cone Obturation Technique: An In Vitro Study
Doaa M. AlEraky, Ahmed M. Rahoma, Hatem M. Abuohashish, Abdullh AlQasser, Abbas AlHamali, Hussain M. AlHussain, Hussain M. AlShoalah, Zakrya AlSaghah, Abdulrahman Khattar, Shimaa Rifaat
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(5): 2906. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Morse taper implant design on microleakage at implant-healing abutment interface
Soyeon KIM, Joo Won LEE, Jae-Heon KIM, Van Mai TRUONG, Young-Seok PARK
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 767. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - Comparison of Sealing Ability of Bioceramic Sealer, AH Plus, and GuttaFlow in Conservatively Prepared Curved Root Canals Obturated with Single-Cone Technique: An In vitro Study
Shalan Kaul, Ajay Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani, Laxmi Sukhtankar, M. Madhumitha, Amit Kumar
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S857. CrossRef - Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Root Canal Obturation Techniques
Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Amin Mortaheb, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Brett E. Gilbert, Marilena Vivona
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Both Fiber Post/Core Resin Construction System and Root Canal Sealer on the Material Interface in Deep Areas of Root Canal
Hiroki Miura, Shinji Yoshii, Masataka Fujimoto, Ayako Washio, Takahiko Morotomi, Hiroshi Ikeda, Chiaki Kitamura
Materials.2021; 14(4): 982. CrossRef - Sealing ability and microbial leakage of root-end filling materials: MTA versus epoxy resin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Giancarlo Malagnino, Michele Di Cosola, Angela Pia Cazzolla, Luigi Laino, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Heliyon.2021; 7(7): e07494. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - BIOCERAMIC-BASED ROOT CANAL SEALERS
L Somolová, Z Zapletalová, M Rosa, B Novotná, I Voborná, Y Morozova
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2021; 121(4): 116. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Physico-Chemical Properties of Calcium-Silicate vs. Resin Based Sealers—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory-Based Studies
Viresh Chopra, Graham Davis, Aylin Baysan
Materials.2021; 15(1): 229. CrossRef - Comparison of apical sealing ability of bioceramic sealer and epoxy resin-based sealer using the fluid filtration technique and scanning electron microscopy
Widcha Asawaworarit, Thitapa Pinyosopon, Kanittha Kijsamanmith
Journal of Dental Sciences.2020; 15(2): 186. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer
Jong Cheon Kim, Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sealing ability of gutta percha and resilon as root canal filling materials- a systematic review
Pragya Pandey, Himanshi Aggarwal, A.P. Tikku, Arpit Singh, Rhythm Bains, Shambhavi Mishra
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 220. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Root fillings with a matched-taper single cone and two calcium silicate–based sealers: an analysis of voids using micro-computed tomography
Eugenio Pedullà, Roula S. Abiad, Gianluca Conte, Giusy R. M. La Rosa, Ernesto Rapisarda, Prasanna Neelakantan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(12): 4487. CrossRef - Influence of different disinfection protocols on gutta-percha cones surface roughness assessed by two different methods
A.M. Nunes, J.P. Gouvea, L. da Silva
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2019; 8(6): 5464. CrossRef - Endodontic sealers based on calcium silicates: a systematic review
David Donnermeyer, Sebastian Bürklein, Till Dammaschke, Edgar Schäfer
Odontology.2019; 107(4): 421. CrossRef
- Time-Dependent Volumetric and Porosity Changes of Bioceramic, Silicone Bioactive Glass-Based, and Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Micro-CT Analysis
- 2,804 View
- 36 Download
- 33 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of a newly produced resin-based endodontic sealer - Yoo-Seok Song, Yoorina Choi, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Chan-Ui Hong, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):189-195. Published online July 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives A variety of root canal sealers were recently launched to the market. This study evaluated physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability of a newly launched resin-based sealer (Dia-Proseal, Diadent) compared to the existing root canal sealers (AHplus, Dentsply DeTrey and ADseal, Metabiomed).
Materials and Methods The physicochemical properties of the tested sealers including pH, solubility, dimensional change, and radiopacity were evaluated. Biocompatibility was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For microleakage test, single-rooted teeth were instrumented, and obturated with gutta-percha and one of the sealers (
n = 10). After immersion in 1% methylene blue solution for 2 weeks, the specimens were split longitudinally. Then, the maximum length of staining was measured. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey test (p = 0.05).Results Dia-Proseal showed the highest pH value among the tested sealers (
p < 0.05). ADseal showed higher dimensional change compared to AHplus and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The solubility values of AHplus and Dia-Proseal were similar, whereas ADseal had the lowest solubility value (p < 0.05). The flow values of sealer in increasing order were AHplus, DiaProseal, and ADseal (p < 0.05). The radiopacity of AHplus was higher than those of ADseal and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The cell viability of the tested materials was statistically similar throughout the experimental period. There were no significant differences in microleakage values among the tested samples.Conclusions The present study indicates that Dia-Proseal has acceptable physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Comparison of Apical Sealing Ability of Different Endodontic Sealers – An In Vitro Study
Supriya Patil, Rahul Singh, B Jyothi Lekshmi, Sameer Ahmed Khan, H Shalini, Prashanth Kumar Katta
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S513. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of ICON resin infiltration and bioactive glass adhesive for managing initial caries lesions using quantitative light-induced fluorescence: a randomized clinical trial
Zakereyya S.M. Albashaireh, Susan N. Al-Khateeb, Malak K. Altallaq
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 159: 105853. CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparison of Epoxy Resin Sealer Removal During Endodontic Retreatment
Prashant A Bondarde, Aditi S Patkar, Aishwarya R Pawar, Rukmini Pande, Akshata Deshpande, Rachana S Agrawal, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereomicroscopic evaluation of sealing ability of four different root canal sealers: an in-vitro study
Sonam Sah, Panna Mangat, Ajay Kumar, Neha Sah, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Marco Di Blasio, Gabriele Cervino, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological investigation of resinous endodontic sealers containing calcium hydroxide
Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Francine Benetti, Marina Tolomei Sandoval Cury, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Ana Cláudia Rodrigues da Silva, Rogério de Castilho Jacinto, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, E
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0287890. CrossRef - Comparison of the apical seal obtained by Adseal, Proseal, and AH26 sealers in root canal obturation with lateral compaction technique
Akam Saeidi, Romina Hajipour, Elham Mahmoudi, Farideh Feizi, Soraya Khafri
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Calcium Silicate-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Sealers: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Nezar Boreak, Mazen Ahmed Qadi, Faisal Hadi Khormi, Luay Mutaen Faqiri, Sadeem Omar Zaylai, Yaser Ali Jad, Bassam Ali Hamdi, Asayil Juraybi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(8): 610. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength of bioceramic and epoxy sealers after using various final irrigants: An in vitro study
Chandrasekhar Veeramachaneni, Swathi Aravelli, Sreeja Dundigalla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(2): 145. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Reinforcement Using MTA-based, Epoxy Resin-based, and Silicone-based Endodontic Sealers in Canals Instrumented with Single-file Rotary System: An In Vitro Study
Reshma Rajasekhar, Varsha Maria Sebastian, Farhat Nasreen, Pramod Junjanna, Azeem Hassan, Venkidesh Hari Maratt
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1098. CrossRef - The Short-Term Antibacterial Activity of Three Selected Endodontic Sealers against Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Culture
Matej Rosa, Yuliya Morozova, Roman Moštěk, Pavel Holík, Lucia Somolová, Barbora Novotná, Soňa Zábojníková, Kateřina Bogdanová, Kateřina Langová, Iva Voborná, Lenka Pospíšilová, Josef Paul Kovařík
Life.2022; 12(2): 158. CrossRef - Antimicrobial potential of AH Plus supplemented with bismuth lipophilic nanoparticles on E. faecalis isolated from clinical isolates
Jesús Alejandro Torres-Betancourt, Rene Hernandez-Delgadillo, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Juan Manuel Solís-Soto, Nayely Pineda-Aguilar, Maria Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Rosa Isela Sánchez-Nájera, Shankararaman Chellam, Claudio Cabral-Romero
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry Analysis and Radiopacity of Five Different Root Canal Sealers
Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Burcu Serefoglu, Pelin Güneri, Michael Hülsmann, Mehmet Kemal Caliskan
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(5): 1. CrossRef - Ultrasonic vibration and thermo‐hydrodynamic technique for filling root canals: Technical overview and a case series
Yong‐Sik Cho
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1668. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Two Generations of MTA-Based Root Canal Sealers
Sawsan Abu Zeid, Hadeel Yaseen Edrees, Abeer Abdulaziz Mokeem Saleh, Osama S. Alothmani
Materials.2021; 14(20): 5911. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiopacity of endodontic materials using two models for conversion to millimeters of aluminum
Victor Manuel OCHOA-RODRÍGUEZ, Jorge Homero WILCHES-VISBAL, Barbara ROMA, Hernán COAGUILA-LLERENA, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO, Andréa GONÇALVES, Rubens SPIN-NETO, Gisele FARIA
Brazilian Oral Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - SELECTED PROPERTIES OF CONTEMPORARY ENDODONTIC SEALERS: PART 1
M Rosa, Y Morozova, R Moštěk, A Jusku, V Kováčová, L Somolová, I Voborná, T Kovalský
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2020; 120(4): 107. CrossRef - Calcium phosphates as fillers for methacrylate-based sealer
Flávia Veronezi Rostirolla, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Fabio Rocha Bohns, Fernando Freitas Portella, Susana Maria Werner Samuel, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(12): 4417. CrossRef - Do in vitro solubility studies on endodontic sealers demonstrate a high level of evidence? A systematic review
Ankur Razdan, Ana Raquel Benetti, Lars Bjørndal
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(4): 253. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of two epoxy resin-based sealants: Topseal® and Adseal™. a comparative study
Julio César Cardona-Hidalgo, José Manuel González-Carreño, Julio César Avendaño-Rueda
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Materials.2019; 12(15): 2411. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Epoxy Resin-Based and Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
- 2,049 View
- 21 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Marginal microleakage of cervical composite resin restorations bonded using etch-and-rinse and self-etch adhesives: two dimensional vs. three dimensional methods
- Maryam Khoroushi, Ailin Ehteshami
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):83-90. Published online April 18, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was evaluated the marginal microleakage of two different adhesive systems before and after aging with two different dye penetration techniques.
Materials and Methods Class V cavities were prepared on the buccal and lingual surfaces of 48 human molars. Clearfil SE Bond and Single Bond (self-etching and etch-and-rinse systems, respectively) were applied, each to half of the prepared cavities, which were restored with composite resin. Half of the specimens in each group underwent 10,000 cycles of thermocycling. Microleakage was evaluated using two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) dye penetration techniques separately for each half of each specimen. Data were analyzed with SPSS 11.5 (SPSS Inc.), using the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests (α = 0.05).
Results The difference between the 2D and 3D microleakage evaluation techniques was significant at the occlusal margins of Single bond groups (
p = 0.002). The differences between 2D and 3D microleakage evaluation techniques were significant at both the occlusal and cervical margins of Clearfil SE Bond groups (p = 0.017 andp = 0.002, respectively). The difference between the 2D and 3D techniques was significant at the occlusal margins of non-aged groups (p = 0.003). The difference between these two techniques was significant at the occlusal margins of the aged groups (p = 0.001). The Mann-Whitney test showed significant differences between the two techniques only at the occlusal margins in all specimens.Conclusions Under the limitations of the present study, it can be concluded that the 3D technique has the capacity to detect occlusal microleakage more precisely than the 2D technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Post‐Gel Polymerization Shrinkage Strain and Marginal Integrity of Repeatedly Preheated Thermo‐Viscous and Matrix‐Modified Bulk‐Fill Resin Composite (Pre‐Clinical Study)
Ahmed Amir, Rasha Zaghlool, Mona Riad
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026; 38(1): 97. CrossRef - The current advancements in chitosan nanoparticles in the management of non-surgical periodontitis treatment
Mehrnaz Sadighi Shamami, Mohammad Ekhlaspour, Jameel M. A. Sulaiman, Radhwan Abdul Kareem, Nahed Mahmood Ahmed Alsultany, Kamyar Nasiri, Naghmeh Shenasa
Nanotoxicology.2025; 19(3): 290. CrossRef - Effect of different types of adhesive systems on the bond strength and marginal integrity of composite restorations in cavities prepared with the erbium laser—a systematic review
Deepti Dua, Ankur Dua, Eugenia Anagnostaki, Riccardo Poli, Steven Parker
Lasers in Medical Science.2022; 37(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparing the Ability of Various Resin-Based Composites and Techniques to Seal Margins in Class-II Cavities
Abdullah Saleh Aljamhan, Sultan Ali Alhazzaa, Abdulrahman Hamoud Albakr, Syed Rashid Habib, Muhammad Sohail Zafar
Polymers.2021; 13(17): 2921. CrossRef - Comparison of the Ability of Two Brands of CBCT with That of SEM to Detect the Marginal Leakage of Class V Composite Resin Restorations
Mitra Karbasi Kheir, Leili Khayam, Mehrbakhsh Nilashi
The Scientific World Journal.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Analysis of microleakage and marginal gap presented by new polymeric systems in class V restorations: An in vitro study
Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Hugo Alberto Vidotti, Lindomar Corrêa Júnior, Alef Vermudt, Mauro de Souza Almeida, Saulo Pamato
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(3): 156. CrossRef - Hydrolysis-resistant and stress-buffering bifunctional polyurethane adhesive for durable dental composite restoration
Jiahui Zhang, Xiaowei Guo, Xiaomeng Zhang, Huimin Wang, Jiufu Zhu, Zuosen Shi, Song Zhu, Zhanchen Cui
Royal Society Open Science.2020; 7(7): 200457. CrossRef - A comparison of the marginal and internal fit of porcelain laminate veneers fabricated by pressing and CAD-CAM milling and cemented with 2 different resin cements
Ziad N. Al-Dwairi, Rana M. Alkhatatbeh, Nadim Z. Baba, Charles J. Goodacre
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(3): 470. CrossRef - Microleakage in class V cavities prepared using conventional method versus Er:YAG laser restored with glass ionomer cement or resin composite
Sertac Peker, Figen Eren Giray, Basak Durmus, Nural Bekiroglu, Betül Kargül, Mutlu Özcan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2017; 31(5): 509. CrossRef
- Post‐Gel Polymerization Shrinkage Strain and Marginal Integrity of Repeatedly Preheated Thermo‐Viscous and Matrix‐Modified Bulk‐Fill Resin Composite (Pre‐Clinical Study)
- 1,596 View
- 9 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Current perspectives of bio-ceramic technology in endodontics: calcium enriched mixture cement - review of its composition, properties and applications
- Shivani Utneja, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, Mahesh Verma
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):1-13. Published online November 3, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Advancements in bio-ceramic technology has revolutionised endodontic material science by enhancing the treatment outcome for patients. This class of dental materials conciliates excellent biocompatibility with high osseoconductivity that render them ideal for endodontic care. Few recently introduced bio-ceramic materials have shown considerable clinical success over their early generations in terms of good handling characteristics. Calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement, Endosequence sealer, and root repair materials, Biodentine and BioAggregate are the new classes of bio-ceramic materials. The aim of this literature review is to present investigations regarding properties and applications of CEM cement in endodontics. A review of the existing literature was performed by using electronic and hand searching methods for CEM cement from January 2006 to December 2013. CEM cement has a different chemical composition from that of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) but has similar clinical applications. It combines the biocompatibility of MTA with more efficient characteristics, such as significantly shorter setting time, good handling characteristics, no staining of tooth and effective seal against bacterial leakage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CBCT‐Assisted Microsurgical Management of Dual Periapical Lesions Involving Vital and Previously Endodontically Treated Maxillary Molars: A Case Report
Saeed Asgary
Clinical Case Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of calcium-enriched mixture and mineral trioxide aggregate in vital pulp therapy of molars: A systematic review
Aarti Ravishankar Lamb, Sheetal Ghivari, Rishikesh Meshram, Ambar Raut, Maithilee Sapkal, Saniya Rege
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2026; 29(2): 127. CrossRef - Antibacterial Efficacy of Graphene Nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis: In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Preena Sidhu, Kiran Rehman, Thiagrajan Madheswaran, Amalraj Fabian Davamani
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 103. CrossRef - Biomineralization reaction from nanosized calcium silicate: A new method for reducing dentin hypersensitivity
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Jeong-Kil Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Yu-Chih Chiang, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(1): 428. CrossRef - How to Deal with Pulpitis: An Overview of New Approaches
Jakub Fiegler-Rudol, Wojciech Niemczyk, Katarzyna Janik, Anna Zawilska, Małgorzata Kępa, Marta Tanasiewicz
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(1): 25. CrossRef - Effect of Manipulation Methods and Storage Environments on the Microstructural, Chemical, and Mechanical Properties of Calcium‐Enriched Mixture Cement
Leyla Roghanizadeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Ardavan Parhizkar, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Saeed Asgary, Luca Fiorillo
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in 3D Bioprinting of Scaffolds for Dental Tissue Engineering and Regeneration
Senyao Chen, Jianwei Sun, Wenzhi Wu, Zhuo Chen
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vital Pulpa Tedavilerinde Biyoseramik Materyallerin Kullanımı: Sistematik Derleme
Duygu Bal, Gül Keskin
Türk Diş Hekimliği Araştırma Dergisi.2025; 4(2): 103. CrossRef - Bioactive Materials in Pediatric Endodontics: Current Applications and Future Directions
Abdulrahman S Alshalan, Fai A Almutiri, Ali H Al-battat, Abdulrahman M Alqahtani, Khalid A Binzamil, Reem M Alabdan, Khalidah K Alrabghi, Asma M Aldohailan, Eman A Alshammari, Abdulrahman S Khurayniq, Mazen T Alshahrani
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative clinical success of direct pulp capping materials: A network meta-regression of randomized clinical trials
Ömer Hatipoğlu, Elif Varlı Tekingür, Fatma Pertek Hatipoğlu
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 162: 106073. CrossRef - Pharmacopée intracanalaire
J. Davril, R. Balthazard, R. Giess, M. Vincent, E. Mortier
EMC - Odontologie.2025; 41(4): 1. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of four different calcium-based medicaments as an indirect pulp capping agent: An in vivo study
Ray Anuja Awadhesh, Nitin Kararia, Deepak Kumar Sharma, Shyam Agrawal, Rachit Mathur, Jyotirmoyee Bhanja
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1013. CrossRef - Calcium Phosphate Incorporated Polymeric Fibrous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review
Parvathy GH, Nidhish Kumar P, Swapna YV, Mathew CT, Jijimon K Thomas
Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part B.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Investigation of the crystal formation from calcium silicate in human dentinal tubules and the effect of phosphate buffer saline concentration
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jin-Soo Ahn, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2278. CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentinal tubule penetration following ultrasonic, sonic, and single-cone technique of a biosealer: An ex vivo study
Dina Abdellatif, Massimo Pisano, Renato Gullà, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Shishir Singh, Francesco Giordano, Alessio Buonavoglia, Alfredo Iandolo
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 331. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of silicate tricalcium-based cement for use as pulp capping or repair material
Suyane Maria LUNA-CRUZ, Bernardo Almeida AGUIAR, Pierre Basílio Almeida FECHINE, Marco Antônio Húngaro DUARTE, Bruno Carvalho de VASCONCELOS, Juliano Sartori MENDONÇA
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful Tampon Pulpotomy in a Molar With an Endodontic Lesion: A Case Report
Saeed Asgary
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluations of shear bond strength of mineral trioxide aggregate, Biodentine, and calcium-enriched mixture to bulk-fill flowable composite using three different adhesive systems: An in vitro study
Asmat Fatima, Huma İftekhar, Sharique Alam, Rajendra Kumar Tewari, Mukhtar Un Nisar Andrabi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(7): 706. CrossRef - Comparative in vitro analysis of the antifungal activity of different calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers
Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Fernando Peña-Bengoa, Sven Eric Niklander, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Daniel Guimarães Pedro Rocha
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243355. CrossRef - Enhancing pH Modulation and Calcium Ions Release in External Resorption Artificial Defects
Azadeh Kheradyar, Mamak Adel, Majid Sirati-Sabet, Alireza Kolahdouzan, Sahar Shafagh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of pulpotomy for permanent teeth with carious pulp exposure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wenjun Li, Bo Yang, Jing Shi, Carlos Alberto Antunes Viegas
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(7): e0305218. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cervical pulpotomy and pulpectomy for primary molars with irreversible pulpitis: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
S. Sabbagh, Z. Bahrololoomi, A. Sarraf Shirazi, F. Zarebidoki, S. Salajegheh, F. Fotouhi, A. Akbarzadeh Baghban, S. Asgary
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2024; 25(2): 255. CrossRef - Bioceramic Materials: A Boon in Pediatric Dentistry: A Literature Review
Sheenam Ayub, Sonal Gupta, Menia Gumro
Journal of Primary Care Dentistry and Oral Health.2024; 5(1): 3. CrossRef - Peptide KN-17-Loaded Supramolecular Hydrogel Induces the Regeneration of the Pulp-Dentin Complex
Borui Zhao, Qian Zhang, Houzhi Yang, Shuipeng Yu, Rui Fu, Shurui Shi, Yuanyuan Wang, Wei Zhou, Yange Cui, Qingxiang Guo, Xi Zhang
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2024; 10(4): 2523. CrossRef - Cimentos biocerâmicos na endodontia: atualizações sobre as propriedades regenerativas e antibacterianas
Víctor Lucas Ribeiro Lopes, Even Herlany Pereira Alves, Hélio Mateus Silva Nascimento, Maria de Fátima Leal de Sousa, Daniel Fernando Pereira Vasconcelos, Francisca Meire Soares de Freitas Portela
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2024; 16(8): e5259. CrossRef - ZrO2 and ZnO nanoparticles effect on setting time, microhardness, and compressive strength of calcium-enriched-mixture cement
Faezeh Sadat Razavi, Fatemeh Mahmoudi Afsah, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Hasan Torabzadeh, Saeed Asgary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e244482. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Bioceramics in endodontics – A review
Chris Cherian Geogi, Ananya Rawat, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 7(4): 163. CrossRef - Exploring the Most Effective Apical Seal for Contemporary Bioceramic and Conventional Endodontic Sealers Using Three Obturation Techniques
Hira Akhtar, Farah Naz, Arshad Hasan, Anum Tanwir, Danish Shahnawaz, Umair Wahid, Fariha Irfan, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Khalid H. Almadi, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Tariq Abduljabbar, Fahim Vohra
Medicina.2023; 59(3): 567. CrossRef - Tissue Response to a Heat Resistant Silicate-Based and an Epoxy Resin-Based Endodontic Sealer Implanted in Rat Tibias
Osvaldo Zmener, Cornelis H. Pameijer, Roberto Della Porta, Romina de Lucca
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(18): 10075. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of a Third Molar to Replace an Adjacent Unrestorable Tooth: A Case Report
Saeed Asgary
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Molars With Simulated Strip Perforation Repaired With Different Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Alaa Kabtoleh, Ossama Aljabban, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of Endodontic-Treated Teeth Obturated with Bioceramic Sealers in Combination with Warm Gutta-Percha Obturation Techniques: A Prospective Clinical Study
Denise Irene Karin Pontoriero, Edoardo Ferrari Cagidiaco, Valerio Maccagnola, Daniele Manfredini, Marco Ferrari
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2867. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of the effect of three intracanal medicaments – chlorhexidine gel, triple antibiotic paste, and calcium hydroxide paste on the push-out bond strength of MTA Plus, Biodentine, and calcium-enriched mixture
Gouthami Datta, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Gautham P Manjunath, Dishant Patel, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Effects of CEM cement and emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla: a comparative in vitro study
Elham Khoshbin, Leila Ghasemi, Rezvan Najafi, Hamed Karkehabadi
Biotechnology Letters.2023; 45(1): 69. CrossRef - Ceramic nanomaterials: Preparation and applications in osteoporosis and bone tissue regeneration
Anish John, Apurva M. Shetty, Kshema Salian, Samantha Neha Sequeria, P. R. Sumukh, Dewi Sukmawati, Gowtham Menon, Shajan Abraham, Jayachandran Venkatesan, V. Anoop Narayanan
Journal of Materials Research.2023; 38(17): 4023. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Endodontic Diagnosis and Modern Treatment Plans
Alfredo Iandolo
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2786. CrossRef - Outcome of pulpotomy in permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Amber Ather, Biraj Patel, Jonathan A. L. Gelfond, Nikita B. Ruparel
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Coronal Discoloration Induced by White MTA and CEM Cement
Mamak Adel, Sareh Aflaki, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Alireza Darvish, Amanda Mandana Golshiri, Nima Moradi Majd, Rodolfo Reda, Maryam Tofangchiha, Alessio Zanza, Luca Testarelli
Journal of Composites Science.2022; 6(12): 371. CrossRef - Current trends and future perspectives on dental nanomaterials – An overview of nanotechnology strategies in dentistry
Vidhya Rekha Umapathy, Prabhu Manickam Natarajan, C. SumathiJones, Bhuminathan Swamikannu, W.M.S. Johnson, V. Alagarsamy, Ashequr Rahman Milon
Journal of King Saud University - Science.2022; 34(7): 102231. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability and Bond Strength of Two Endodontic Root Canal Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Manuel Marques Ferreira, José Pedro Martinho, Inês Duarte, Diogo Mendonça, Ana Catarina Craveiro, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Ana Coelho, Anabela Paula, Siri Paulo, Nuno Chichorro, Ana Margarida Abrantes
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(11): 201. CrossRef - Outcomes of root canal therapy or full pulpotomy using two endodontic biomaterials in mature permanent teeth: a randomized controlled trial
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Arash Shahravan, Eshaghali Saberi, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Ardavan Parhizkar
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(3): 3287. CrossRef - Trends of calcium silicate biomaterials in medical research and applications: A bibliometric analysis from 1990 to 2020
Hua Yin, Xiaoli Yang, Lisi Peng, Chuanchao Xia, Deyu Zhang, Fang Cui, Haojie Huang, Zhaoshen Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Different types of bioceramics as dental pulp capping materials: A systematic review
Sotoudeh Davaie, Tabassom Hooshmand, Sajjad Ansarifard
Ceramics International.2021; 47(15): 20781. CrossRef - Effect of MTA versus CEM apical plugs on fracture resistance of endodontically treated simulated immature teeth restored with cast metal posts: an in-vitro study
Ensieh Grayli, Abbas Dashtban, Leyla Shadan, Naser Behnampour, Elham Afshari
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - Pediatric Endodontic Treatment of Adolescent Patients
Adriana Modesto Vieira, Herbert L. Ray
Dental Clinics of North America.2021; 65(4): 775. CrossRef - Management of primary molars with irreversible pulpitis employing tampon pulpotomy: Report of three cases with 34‐month mean follow‐up
Saeed Asgary, Alireza Sarraf Shirazi, Sedigheh Sabbagh
Clinical Case Reports.2021; 9(4): 2289. CrossRef - Effects of various liquid-to-powder ratios on the compressive strength of calcium enriched mixture: Original research
Mohammad Forough Reyhani, Sheida Hosseinian Ahangarnezhad, Negin Ghasemi, Amin Salem Milani
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(2): 129. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Use of Bioceramics in Endodontic Management, Literature Review
Wejdan Ali Alkaabinah, Bashayr Faisal Alanazi, Amlak Munahi Albaqami, Bashayer Mohammed Almutiry, Maram Saleh A Alkhamis, Ali Abdullah Alhejailan, Ibrahim Owaidh M Almutairi, Bassel Hamad Aldahman, Alhanoof Falah Alanazi
Pharmacophore.2021; 12(3): 87. CrossRef - Bioactive Glass Modified Calcium Phosphate Cement with Improved Bioactive Properties: A Potential Material for Dental Pulp-Capping Approaches
Sotoudeh Davaie, Sima Shahabi, Marjan Behroozibakhsh, Sanaz Vali, Farhood Najafi
Journal of Biomimetics, Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering.2021; 51: 1. CrossRef - Intratubular penetration of endodontic sealers depends on the fluorophore used for CLSM assessment
Taiane Correa Furtado, Igor Abreu de Bem, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(2): 305. CrossRef - From the Desk of the Editor: The New-Age Bioceramic Root Canal Sealers
Shishir Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 413. CrossRef - Influence of Blood Contamination on Push-Out Bond Strength of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Cristina Rodrigues Paulo, Joana A. Marques, Diana B. Sequeira, Patrícia Diogo, Rui Paiva, Paulo J. Palma, João Miguel Santos
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6849. CrossRef - Comparison of the Success Rate of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Endosequence Bioceramic Root Repair Material, and Calcium Hydroxide for Apexification of Immature Permanent Teeth: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Izaz Shaik, Bhargavi Dasari, Rashmi Kolichala, Mina Doos, Fida Qadri, Jenefer Loveline Arokiyasamy, Rahul Vinay Chandra Tiwari
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S43. CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Toughening of Bioceramic Composites for Bone Regeneration
Zahid Abbas, Massimiliano Dapporto, Anna Tampieri, Simone Sprio
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(10): 259. CrossRef - Performance of Bioceramic-based Root Filling Material with Artifact Reduction Properties in the Detection of Vertical Root Fractures Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Ali Bahmani, Hamed Karkehabadi, Abbas Shokri, Maryam Farhadian
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 170. CrossRef - The effect of partial pulpotomy with iRoot BP Plus in traumatized immature permanent teeth: A randomized prospective controlled trial
YingTing Yang, Bin Xia, Zheng Xu, Guili Dou, Yue Lei, Wei Yong
Dental Traumatology.2020; 36(5): 518. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic cleaning on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic root canal sealer
Fernando Peña Bengoa, Maria Consuelo Magasich Arze, Cristobal Macchiavello Noguera, Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo Da Silveira Bueno
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Silico-Aluminophosphate and Alkali-Aluminosilicate Geopolymers: A Comparative Review
Yan-Shuai Wang, Yazan Alrefaei, Jian-Guo Dai
Frontiers in Materials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of mineral trioxide aggregate and propolis promotes odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through ERK signaling pathway
Jae-Hwan Kim, Soo-Yung Kim, Su-Mi Woo, Ha-Na Jeong, Ji-Yeon Jung, Seon-Mi Kim, Hae-Soon Lim
Food Science and Biotechnology.2019; 28(6): 1801. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Novel Calcium-enriched Mixture Root Cement to Decelerate Replacement Resorption in Replanted Teeth: A Case Report
Nasil Sakkir, Tony Francis, Sonal B Joshi
World Journal of Dentistry.2019; 10(6): 457. CrossRef - Which procedures and materials could be applied for full pulpotomy in permanent mature teeth? A systematic review
M. Zanini, M. Hennequin, PY. Cousson
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(7): 541. CrossRef - Microstructure and chemical analysis of four calcium silicate-based cements in different environmental conditions
K. Ashofteh Yazdi, Sh. Ghabraei, B. Bolhari, M. Kafili, N. Meraji, M. H. Nekoofar, P. M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - Treatment Outcomes of 4 Vital Pulp Therapies in Mature Molars
Saeed Asgary, Raheleh Hassanizadeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - Sectional Fixed Orthodontic Extrusion Technique in Management of Teeth with Complicated Crown-Root Fractures: Report of Two Cases
S. Nagarajan M. P. Sockalingam, Katherine Kong Loh Seu, Halimah Mohamed Noor, Ahmad Shuhud Irfani Zakaria
Case Reports in Dentistry.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of New Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer
Aline Teixeira Mendes, Paula Barcellos da Silva, Bruna Barcelos Só, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marco Antonio Húngaro Duarte, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(6): 536. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management and 2-year Follow-up by means of Cone Beam Computed Tomography of an Invasive Cervical Resorption in a Molar
Esam Halboub, Hemant R Chourasia, Rafael A Roges
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(9): 1152. CrossRef - Management of merged external/internal root resorption using CEM cement: a case report.
Hesam Mirmohammadi, Saeed Asgary
Journal of Oral Research.2018; 7(8): 318. CrossRef - Maturogenesis of an Immature Dens Evaginatus Nonvital Premolar with an Apically Placed Bioceramic Material (EndoSequence Root Repair Material®): An Unexpected Finding
S. Nagarajan M. P. Sockalingam, Mohd Safwani Affan Alli Awang Talip, Ahmad Shuhud Irfani Zakaria
Case Reports in Dentistry.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - The implications and applications of nanotechnology in dentistry: A review
Rawan N. AlKahtani
The Saudi Dental Journal.2018; 30(2): 107. CrossRef - Calcium silicate‐based cements: composition, properties, and clinical applications
Alaa E. Dawood, Peter Parashos, Rebecca H.K. Wong, Eric C. Reynolds, David J. Manton
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility of three new calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealers on human periodontal ligament stem cells
M. Collado‐González, D. García‐Bernal, R. E. Oñate‐Sánchez, P. S. Ortolani‐Seltenerich, A. Lozano, L. Forner, C. Llena, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(9): 875. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and bioactivity of various pulpotomy materials on stem cells from human exfoliated primary teeth
M. Collado‐González, D. García‐Bernal, R. E. Oñate‐Sánchez, P. S. Ortolani‐Seltenerich, T. Álvarez‐Muro, A. Lozano, L. Forner, C. Llena, J. M. Moraleda, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano
International Endodontic Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Three Different Biomaterials on Proliferation and Viability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells (In-vitro Study)
Dalia A. Mohamed, Maha I. Abdelfattah, Eman H. A. Aboulezz
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2017; 5(5): 657. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - Comparison of mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide for apexification of immature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jia-Cheng Lin, Jia-Xuan Lu, Qian Zeng, Wei Zhao, Wen-Qing Li, Jun-Qi Ling
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2016; 115(7): 523. CrossRef - Cytotoxic effects of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium enrichedmixture cement, Biodentine and octacalcium pohosphate onhuman gingival fibroblasts
Eshagh A. Saberi, Narges Farhadmollashahi, Faroogh Ghotbi, Hamed Karkeabadi, Roholla Havaei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2016; 10(2): 75. CrossRef - Influence of Biodentine® - A Dentine Substitute - On Collagen Type I Synthesis in Pulp Fibroblasts In Vitro
Frangis Nikfarjam, Kim Beyer, Anke König, Matthias Hofmann, Manuel Butting, Eva Valesky, Stefan Kippenberger, Roland Kaufmann, Detlef Heidemann, August Bernd, Nadja Nicole Zöller, Dimitrios Karamichos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167633. CrossRef - Challenges in developing valid techniques for equine endodontic treatment of apically infected cheek teeth
R. M. Baratt
Equine Veterinary Education.2016; 28(11): 609. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Procedure in Korean Children and Adolescents: A Case Report
So-Youn An, Jin-Kyoung Kim, Youn-Soo Shim
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(4): 317. CrossRef
- CBCT‐Assisted Microsurgical Management of Dual Periapical Lesions Involving Vital and Previously Endodontically Treated Maxillary Molars: A Case Report
- 3,666 View
- 30 Download
- 85 Crossref

- Effect of 38% carbamide peroxide on the microleakage of silorane-based versus methacrylate-based composite restorations
- Sedighe Sadat Hashemi Kamangar, Maryam Ghavam, Nazanin Mahinfar, Seyed Jalal Pourhashemi
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):172-179. Published online May 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the effect of 38% carbamide peroxide on the microleakage of class V cavities restored with either a silorane-based composite or two methacrylate-based composites.
Materials and Methods A total of 96 class V cavities were prepared on the buccal surface of extracted human teeth with both enamel and dentin margins and were randomly assigned into three groups of Filtek P90 (3M-ESPE) + P90 system adhesive (3M-ESPE)(group A), Filtek Z250 (3M-ESPE) + Adper Prompt L-Pop (3M-ESPE)(group B) and Filtek Z350XT (3M-ESPE) + Adper Prompt L-Pop (group C). Half of the teeth were randomly underwent bleaching (38% carbamide peroxide, Day White, Discus Dental, applying for 15 min, twice a day for 14 day) while the remaining half (control) were not bleached. Dye penetration was measured following immersion in basic fuchsine. Data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests at a level of 0.05.
Results No significant differences were found between composites in the control groups in enamel (
p = 0.171) or dentin (p = 0.094) margins. After bleaching, microleakage of Z250 (in enamel [p = 0.867] or dentin [p = 0.590] margins) and Z350 (in enamel [p = 0.445] or dentin [p = 0.591] margins) did not change significantly, but the microleakage of P90 significantly increased in both enamel (p = 0.042) and dentin (p = 0.002) margins.Conclusions No significant differences were noted between the bleached and control subgroups of two methacrylate-based composites in enamel or dentin margins. Microleakage of silorane-based composite significantly increased after bleaching.
- 1,142 View
- 3 Download

- Micro-CT evaluation of internal adaptation in resin fillings with different dentin adhesives
- Seung-Hoon Han, Sung-Ho Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):24-31. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of present study was to evaluate the internal adaptation of composite restorations using different adhesive systems.
Materials and Methods Typical class I cavities were prepared in 32 human third molars. The teeth were divided into the following four groups: 3-step etch-and-rinse, 2-step etch-and-rinse, 2-step self-etch and 1-step self-etch system were used. After the dentin adhesives were applied, composite resins were filled and light-cured in two layers. Then, silver nitrate solution was infiltrated, and all of the samples were scanned by micro-CT before and after thermo-mechanical load cycling. For each image, the length to which silver nitrate infiltrated, as a percentage of the whole pulpal floor length, was calculated (%SP). To evaluate the internal adaptation using conventional method, the samples were cut into 3 pieces by two sectioning at an interval of 1 mm in the middle of the cavity and they were dyed with Rhodamine-B. The cross sections of the specimens were examined by stereomicroscope. The lengths of the parts where actual leakage was shown were measured and calculated as a percentage of real leakage (%RP). The values for %SP and %RP were compared.
Results After thermo-mechanical loading, all specimens showed significantly increased %SP compared to before thermo-mechanical loading and 1-step self-etch system had the highest %SP (
p < 0.05). There was a tendency for %SP and %RP to show similar microleakage percentage depending on its sectioning.Conclusions After thermo-mechanical load cycling, there were differences in internal adaptation among the groups using different adhesive systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different factors on microleakage and fracture strength of CAD‐CAM produced inlays
Meryem Gülce Subaşı, Gürel Pekkan, Meral Arslan Malkoç, Hilal Ekşi Özsoy
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Destructive In Vitro Evaluation of an Internal Adaptation of Recent Pulp-Capping Materials in Permanent Teeth Using OCT and Micro-CT
Ahmed Y. Alzahrani, Amani A. Al Tuwirqi, Nada O. Bamashmous, Turki A. Bakhsh, Eman A. El Ashiry
Children.2023; 10(8): 1318. CrossRef - Internal Adaptation of Cusp-weakened Class I Preparations Restored with Bulk-fill, Bi-layered, and Incremental Restorative Techniques: A Micro-CT Analysis
DH Floriani, RN Rached, SA Ignácio, EM Souza
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(5): 527. CrossRef - An in vitro micro-CT assessment of bioactive restorative materials interfacial adaptation to dentin
Priyanka Angadala, Jyothi Mandava, Ravichandra Ravi, KoteswarRao Hanumanthu, Prasanthi Penmatsa, Hema Pulidindi
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 56. CrossRef - Tomographic Evaluation of the Internal Adaptation for Recent Calcium Silicate‐Based Pulp Capping Materials in Primary Teeth
A. A. Al Tuwirqi, E. A. El Ashiry, A. Y. Alzahrani, N. Bamashmous, T. A. Bakhsh, Iole Vozza
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef - Validation of a method of quantifying 3D leakage in dental restorations
Fabio A.P. Rizzante, Rana A.F. Sedky, Adilson Y. Furuse, Sorin Teich, Sérgio K. Ishikiriama, Gustavo Mendonça
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2020; 123(6): 839. CrossRef - Comparison of micro-CT and conventional dye penetration for microleakage assessment after different aging conditions
Rayssa Ferreira Zanatta, Annette Wiegand, Christian Dullin, Alessandra Bühler Borges, Carlos Rocha Gomes Torres, Marta Rizk
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 89: 161. CrossRef - Comparison of Internal Adaptation of Bulk-fill and Increment-fill Resin Composite Materials
FS Alqudaihi, NB Cook, KE Diefenderfer, MC Bottino, JA Platt
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(1): E32. CrossRef - Effects of occlusal cavity configuration on 3D shrinkage vectors in a flowable composite
Dalia Kaisarly, Moataz El Gezawi, Guangyun Lai, Jian Jin, Peter Rösch, Karl-Heinz Kunzelmann
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(5): 2047. CrossRef - Bonding Strategies of Resin Cement to Er, Cr:YSGG Lased Dentin: Micro-CT Evaluation and Microshear Bond Strength Testing
Gökçe Meriç, Simge Taşar, Kaan Orhan
The International Journal of Artificial Organs.2016; 39(2): 72. CrossRef - Calcium hypochlorite as a dentin deproteinization agent: Microleakage, scanning electron microscopy and elemental analysis
Michele Bortoluzzi de Conto Ferreira, Bruno Carlini Júnior, Daniel Galafassi, Delton Luiz Gobbi
Microscopy Research and Technique.2015; 78(8): 676. CrossRef
- Effect of different factors on microleakage and fracture strength of CAD‐CAM produced inlays
- 1,458 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Effect of different air-drying time on the microleakage of single-step self-etch adhesives
- Horieh Moosavi, Maryam Forghani, Esmatsadat Managhebi
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):73-78. Published online May 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of three different air-drying times on microleakage of three self-etch adhesive systems.
Materials and Methods Class I cavities were prepared for 108 extracted sound human premolars. The teeth were divided into three main groups based on three different adhesives: Opti Bond All in One (OBAO), Clearfil S3 Bond (CSB), Bond Force (BF). Each main group divided into three subgroups regarding the air-drying time: without application of air stream, following the manufacturer's instruction, for 10 sec more than manufacturer's instruction. After completion of restorations, specimens were thermocycled and then connected to a fluid filtration system to evaluate microleakage. The data were statistically analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Tukey-test (α = 0.05).
Results The microleakage of all adhesives decreased when the air-drying time increased from 0 sec to manufacturer's instruction (
p < 0.001). The microleakage of BF reached its lowest values after increasing the drying time to 10 sec more than the manufacturer's instruction (p < 0.001). Microleakage of OBAO and CSB was significantly lower compared to BF in all three drying time (p < 0.001).Conclusions Increasing in air-drying time of adhesive layer in one-step self-etch adhesives caused reduction of microleakage, but the amount of this reduction may be dependent on the adhesive components of self-etch adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Species profile of volatile organic compounds emission and health risk assessment from typical indoor events in daycare centers
Hailin Zheng, Júlia Csemezová, Marcel Loomans, Shalika Walker, Florent Gauvin, Wim Zeiler
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 918: 170734. CrossRef - Development of Drying Process for Removal of Residual Moisture from Biomass Pretreated with Ethanol and Its Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis
Seo-Young Park, Jin-Hyun Kim
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering.2021; 26(5): 814. CrossRef - Effect of 9.3 μm CO2 and 2.94 μm Er:YAG Laser vs. Bur Preparations on Marginal Adaptation in Enamel and Dentin of Mixed Class V Cavities Restored With Different Restorative Systems
Clara Isabel Anton y Otero, Enrico Di Bella, Ivo Krejci, Tissiana Bortolotto
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Drying Process for Removal of Residual Solvent from Crystalline Vancomycin and Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis Thereof
Tae-Hun Yoon, Jin-Hyun Kim
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering.2020; 25(5): 777. CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef - Optical Evaluation of Enamel Microleakage with One-Step Self-Etch Adhesives
Alaa Turkistani, Maha Almutairi, Nouf Banakhar, Reem Rubehan, Sulafa Mugharbil, Ahmed Jamleh, Adnan Nasir, Turki Bakhsh
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2018; 36(11): 589. CrossRef - Improved drying method for removal of residual solvents from paclitaxel by pre-treatment with ethanol and water
Chung-Gi Lee, Jin-Hyun Kim
Process Biochemistry.2015; 50(6): 1031. CrossRef
- Species profile of volatile organic compounds emission and health risk assessment from typical indoor events in daycare centers
- 1,894 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effective application duration of sodium ascorbate antioxidant in reducing microleakage of bonded composite restoration in intracoronally-bleached teeth
- Jae-Young Park, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young-Kyung Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):43-47. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to determine an appropriate application duration of sodium ascorbate (SA) antioxidant gel in reducing microleakage of bonded composite restoration in intracoronally-bleached teeth.
Materials and Methods Eighty endodontically-treated human incisors were randomly divided into eight groups: control, no bleaching; IB and DB, immediate and delayed bonding after bleaching, respectively; S10m, S60m, S24h, S3d and S7d, bleaching + SA gel for 10 min, 60 min, 24 hr, 3 day and 7 day, respectively. For bleaching, a mixture of 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate was applied for 7 day. All access cavities were restored using One-Step adhesive (Bisco Inc.) and then Aelite LS Packable composite (Bisco Inc.). The bonded specimens were subjected to 500 thermal cycles, immersed in 1% methylene blue for 8 hr, and longitudinally sectioned. Microleakage was assessed with a 0 - 4 scoring system and analyzed using nonparametric statistical methods (α = 0.05).
Results Group IB showed a significantly higher microleakge than the control group (
p = 0.006) and group DB a statistically similar score to the control group (p > 0.999). Although groups S10m, S60m, and S24h exhibited significantly higher scores than group DB (p < 0.05), the microleakage in groups S3d and S7d was statistically similar to that in group DB (p = 0.771,p > 0.999).Conclusions Application of SA gel for 3 day after nonvital bleaching was effective in reducing microleakage of composite restoration in intracoronally-bleached teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Effect of Herbal Antioxidant on Push-out Bond Strength of Resin-based Composite to Dentin after Intracoronal Bleaching: An
in vitro
Study
Parinitha MS, Akshay G, Vidya G. Doddawad, Ashwini Tumkur Shivakumar, Sowmya Halasabalu Kalgeri
Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics.2025; 16(4): 439. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of the application of Quercus cerris extract and the use of fluoride bonding material on the bonding strength of orthodontic brackets after tooth bleaching with hydrogen peroxide
Ezgi Ay, Derya Dursun
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19335. CrossRef - Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming Activation of the Postbleaching Antioxidant Application Rapidly Improves Bonding to Pulp Chamber Dentin
Nasibe Aycan Yilmaz, Hicran Dönmez Özkan
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2021; 39(4): 289. CrossRef - Hypericum perforatum L.: A Potent Antioxidant Source for the Treatment of Oxidized Dentin: An Experimental In Vitro Study
Nasibe Aycan Yilmaz, Rukiye Yavaser, Arife Alev Karagozler
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2021; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - Influence of a short‐time antioxidant application on the dentin bond strength after intracoronal bleaching
Muhammet Karadas, Sezer Demirbuga
Microscopy Research and Technique.2019; 82(10): 1720. CrossRef - Composite resin shear bond strength on bleached dentin increased by 35% sodium ascorbate application
Tunjung Nugraheni, N Nuryono, Siti Sunarintyas, Ema Mulyawati
Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi).2017; 50(4): 178. CrossRef - Antioxidant therapy enhances pulpal healing in bleached teeth
Adriano Fonseca Lima, Marcelo Rocha Marques, Diana Gabriela Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Giselle Maria Marchi, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 44. CrossRef - Influence of Ethanol Pretreatment on the Bonding of Resin Composite to Bleached Dentin
Ga-Eun Son, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(4): 279. CrossRef - Effect of 35% Sodium Ascorbate Treatment on Microtensile Bond Strength after Nonvital Bleaching
Jason R. Hansen, Kenneth J. Frick, Mary P. Walker
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(10): 1668. CrossRef - Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 95. CrossRef
-
Effect of Herbal Antioxidant on Push-out Bond Strength of Resin-based Composite to Dentin after Intracoronal Bleaching: An
in vitro
Study
- 1,638 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
- Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):29-33. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microleakage of 4 temporary materials in teeth with Class II-type endodontic access preparations by using a glucose penetration model.
Materials and Methods Glucose reaction test was performed to rule out the presence of any reaction between glucose and temporary material. Class II-type endodontic access preparations were made in extracted human premolars with a single root (
n = 10). Each experimental group was restored with Caviton (GC), Spacer (Vericom), IRM (Dentsply-Caulk), or Fuji II(GC). Microleakage of four materials used as temporary restorative materials was evaluated by using a glucose penetration model. Data were analyzed by the one-way analysis of variance followed by a multiple-comparison Tukey test. The interface between materials and tooth were examined under a scanning electron microscope (SEM).Results There was no significant reaction between glucose and temporary materials used in this study. Microleakage was significantly lower for Caviton and Spacer than for Fuji II and IRM. SEM observation showed more intimate adaptation of tooth-restoration interfaces in Caviton and Spacer than in IRM and Fuji II.
Conclusions Compared to IRM and Fuji II, Caviton and Spacer can be considered better temporary sealing materials in Class II-type endodontic access cavities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Sealing Ability, Water Absorption, and Solubility of Three Temporary Restorative Materials: An in vitro Study
AR Prabhakar, N Shantha Rani
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(2): 136. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef
- Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
- 2,089 View
- 11 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
- Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test,
p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test,p < 0.05).Conclusions When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
- 1,275 View
- 1 Download

- Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
- Mi-Ae Lee, Duck-Kyu Seo, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):164-172. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub During a composite resin restoration, an anticipating contraction gap is usually tried to seal with low-viscosity resin after successive polishing, etching, rinsing and drying steps, which as a whole is called rebonding procedure. However, the gap might already have been filled with water or debris before applying the sealing resin. We hypothesized that microleakage would decrease if the rebonding agent was applied before the polishing step, i.e., immediately after curing composite resin. On the buccal and lingual surfaces of 35 extracted human molar teeth, class V cavities were prepared withthe occlusal margin in enamel and the gingival margin in dentin. They were restored with a hybrid composite resin Z250 (3M ESPE, USA) using an adhesive AdperTM Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE). As rebonding agents, BisCover LV (Bisco, USA), ScotchBond Multi-Purpose adhesive (3M ESPE) and an experimental adhesive were applied on the restoration margins before polishing step or after successive polishing and etching steps. The infiltration depth of 2% methylene blue into the margin was measured using an optical stereomicroscope. The correlation between viscosity of rebonding agents and mciroleakage was also evaluated. There were no statistically significant differences in the microleakage within the rebonding procedures, within the rebonding agents, and within the margins. However, when the restorations were not rebonded, the microleakage at gingival margin was significantly higher than those groups rebonded with 3 agents (p < 0.05). The difference was not observed at the occlusal margin. No significant correlation was found between viscosity of rebonding agents and microleakage, except very weak correlation in case of rebonding after polishing and etching at gingival margin (r = -0.326, p = 0.041).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef
- Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
- 1,212 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):484-490. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.484
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of soft chelating irrigant on the sealing ability of root fillings by using a glucose leakage test.
A total of 45 single-rooted teeth were selected for the study. The teeth were decoronated leaving a total length of 13mm. The root canals prepared using K3 NiTi rotary instruments to an apical dimension of size 45(0.06 taper). The specimens were then randomly divided into 3 experimental groups of 13 roots each and 2 control groups of 3 roots each. Specimen in each group were prepared with different irrigation protocols : group 1, 2.5% NaOCl; group 2, 2.5% NaOCl and 17% EDTA; group 3, 2.5% NaOCl and 15% HEBP. The root canals were filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer using lateral condensation. After 7 days in 37℃, 100% humidity, the coronal-to-apical microleakage was evaluated quantitatively using a glucose leakage model. The leaked glucose concentration was measured with spectrophotometry at 1, 4, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days.
There was a tendency of increase in leakage in all experimental groups during experimental period. HEBP-treated dentin showed no significant difference with EDTA-treated dentin during experimental period. From the 21th day onward, HEBP-treated dentin showed significantly lower leakage than smear-covered dentin. HEBP-treated dentin displayed a similar sealing pattern to EDTA-treated dentin and a better sealing ability than smear-covered dentin. Consequently, a soft chelator(HEBP) could be considered as the possible alternative to EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 335. CrossRef
- Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
- 1,164 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of marginal microleakage between low and high flowable resins in class V cavity
- Sang-Bae Bae, Young-Gon Cho, Myeong-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):477-483. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the microleakage of low and high viscosity flowable resins in class V cavities applied with 1-step adhesives.
Forty class V cavities were prepared on the cervices of buccal and lingual surfaces of extracted molar teeth and divided into four groups (n=8). Cavities were restored with AQ Bond Plus/Metafil Flo α, G-Bond/UniFil LoFlo Plus (Low flow groups), AQ Bond Plus/Metafil Flo and G-Bond/UniFil Flow (High flow group), respectively.
Specimens were immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours, and bisected longitudinally. They were observed microleakages at the enamel and dentinal margins.
In conclusion, the low viscosity flowable resins showed lower marginal microleakage than do the high viscosity flowable resins in class V cavities.
- 888 View
- 6 Download

- Apical microleakage of MTA with 4-META/MMA & TBB resin as a root-end filling material
- Jin-Cheol Kim, Mi-Ri Kim, Hyun-Jung Ko, Won-Kyung Yang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):371-376. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.371
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub We evaluated
in vitro microleakage of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) powder with 4-methacryloxyethyl trimellitate anhydride (4-META) / methyl methacrylate (MMA) & tri-n-butylborane (TBB) resin as a retrograde filling material by using methylene blue dye method.Fifty-two single rooted, extracted teeth were instrumented and obturated with gutta percha and AH plus sealer. The apical 3mm of each root was resected and 3mm deep ultrasonic root end preparation was done. External surface of roots was coated with nail varnish. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into five groups; Negative control: completely covered with nail varnish; Positive control: coated with nail varnish except for apical foramen; Group 1 (retrofilled with Portland cement); Group 2 (retrofilled with MTA); Group 3 (retrofilled with MTA powder mixed with 4-META/MMA & TBB resin). Immediately after completion of root-end filling, all specimens were submerged in methylene blue dye for 72 hours in 37℃ incubator. The roots were longitudinally sectioned and measured for extent of dye penetration by three different examiners under microscope (×10). The results were statistically analyzed using one way ANOVA and Turkey's HSD test. No leakage was evident in negative control and complete leakage in positive control group. Group 3 showed significantly less leakage than group 1 and 2 (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference between group 1 and 2 (p > 0.01).
It was concluded that MTA powder with 4-META/MMA & TBB resin was excellent in reducing initial apical microleakage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of novel root-end filling material using epoxy resin and Portland cement
Sang-Jin Lee, Jin Chung, Hee-Sam Na, Eun-Joo Park, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Clinical Oral Investigations.2013; 17(3): 1009. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef - Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 445. CrossRef
- Characteristics of novel root-end filling material using epoxy resin and Portland cement
- 1,230 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems
- Ji-Hoon Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):333-339. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was done to determine if there is any difference in microleakage between experimental composite resins, in which various proportions of three component photoinitiators (Camphoroquinone, OPPI, Amine) were included.
Four kinds of experimental composite resin were made by mixing 3.2% silanated barium glass (78 wt.%, average size; 1 µm) with each monomer system including variously proportioned photoinitiator systems used for photoinitiating BisGMA/BisEMA/TEGDMA monomer blend (37.5:37.5:25 wt.%). The weight percentage of each component were as follows (in sequence Camphoroquinone, OPPI, Amine): Group A - 0.5%, 0%, 1% / Group B - 2%, 0.2%, 2% / Group C - 0.2%, 1%, 0.2% / Group D - 1%, 1%, 2%.
Each composite resin was used as a filling material for round class V cavities (diameter: 2/3 of mesiodistal width; depth: 1.5 mm) made on extracted human premolars and they were polymerized using curing light unit (XL 2500, 3M ESPE) for 40 s with an intensity of 600 mW/cm2. Teeth were thermocycled five-hundred times between 50℃ and 550℃ for 30s at each temperature.
Electrical conductivity (µA) was recorded two times (just after thermocycling and after three-month storage in saline solution) by electrochemical method.
Microleakage scores of each group according to evaluation time were as follows [Group: at first record / at second record; unit (µA)]: A: 3.80 (0.69) / 13.22 (4.48), B: 3.42 (1.33) / 18.84 (5.53), C: 4.18 (2.55) / 28.08 (7.75), D: 4.12 (1.86) / 7.41 (3.41).
Just after thermocycling, there was no difference in microleakage between groups, however, group C showed the largest score after three-month storage. Although there seems to be no difference in microleakage between groups just after thermocycling, composite resin with highly concentrated initiation system or classical design (Camphoroquinone and Amine system) would be more desirable for minimizing microleakage after three-month storage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of polymerization shrinkage of dual-cure core build-up resin according to shade and curing mode
Yoorina Choi, Karl Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(4): 243. CrossRef - Optimal combination of 3-component photoinitiation system to increase the degree of conversion of resin monomers
Chang-Gyu Kim, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 313. CrossRef
- Comparison of polymerization shrinkage of dual-cure core build-up resin according to shade and curing mode
- 980 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
- Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):397-404. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.397
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of MTAD, EDTA and sodium hypochlorite(NaOCl) as final irrigants on coronal leakage resistance to
Enterococcus faecalis . Forty extracted human maxillary molars were used in this experiment. The teeth were randomly divided into positive control group (Group 1; n = 5), negative control group (Group 2; n = 5) and three experimental groups (n = 30). In Group 3 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. In Group 4 (n = 10) and 5 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite and rinsed with EDTA and MTAD, respectively. The teeth in each group were cleaned and shaped to #40 profile with .04 taper, and obturated with gutta-percha and AH-26 root canal sealer. The coronal portion of each tooth was placed in contact with inoculum ofEnterococcus faecalis in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) culture media. Each root tip was placed in a vial containing sterile culture media. The vials were placed in anaerobic chamber and observed everyday for turbidity for 180 days. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher's Exact Test. After 180 days, Group 3, 4, and 5 showed 7, 4 and 5 leaking samples respectively. The differences in leakage resistance were not statistically significant among Group 3, 4 and 5.
- 2,035 View
- 6 Download

- Microleakage of resilon by methacrylate-based sealer and self-adhesive resin cement
- Sun-Young Ham, Jin-Woo Kim, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):204-212. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by methacrylate-based root canal sealer or 2 different self-adhesive resin cements. Seventy single-rooted extracted human teeth were sectioned at the CEJ perpendicular to the long axis of the roots with diamond disk. Canal preparation was performed with crown-down technique using Profile NiTi rotary instruments and GG drill. Each canal was prepared to ISO size 40, .04 taper and 1 mm short from the apex. The prepared roots were randomly divided into 4 experimental groups of 15 roots each and 5 roots each for positive and negative control group. The root canals were filled by lateral condensation as follows. Group 1: Guttapercha with AH-26, Group 2: Resilon with RealSeal primer & sealer, Group 3: Resilon with Rely-X Unicem, Group 4: Resilon with BisCem. After stored in 37℃, 100% humidity chamber for 7 days, the roots were coated with 2 layers of nail varnish except apical 3 mm. The roots were then immersed in 1% methylene blue dye for 7 days. Apical microleakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration after roots were separated longitudinally. One way ANOVA and Scheffe's post-hoc test were performed for statistical analysis. Group 1 showed the least apical leakage and there was no statistical significance between Group 2, 3, 4. According to the results, the self adhesive resin cement is possible to use as sealer instead of primer & sealant when root canal filled by Resilon.
- 831 View
- 1 Download

- Microleakage of endodontic temporary restorative materials under dynamic loading
- Dong-Ho Jung, Young-Sin Noh, Hae-Doo Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Kyung-San Min
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):198-203. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.198
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the sealing abilities of four endodontic temporary restorative materials using a methylene blue dye penetration test under dynamic loading. Standardized access cavities were prepared in forty-four intact human permanent molar teeth, and the cavities were restored with Caviton, MD-Temp, IRM, or ZOE. After thermocycling, an intermittent load of 98 N at 1 Hz was applied for 1,000 cycles to the long axis of the functional cusp of each of the teeth, which were immersed in a 1% methylene blue solution. The teeth were split in half, and the linear depth of dye penetration was evaluated according to the criteria. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (p = 0.05) and Duncan's multiple range test. The results demonstrated that Caviton and MD-Temp showed significantly lower microleakage than IRM and ZOE. It was concluded that Caviton and MD-Temp exhibited better sealing ability than IRM and ZOE under dynamic loading.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 29. CrossRef
- Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
- 2,055 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
- Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):133-140. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical microleakage in root canal filled with Resilon by several self-etching primers and methacrylate-based root canal sealer. Seventy single-rooted human teeth were used in this study. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down manner with Gate-Glidden drills and .04 Taper Profile to ISO #40. The teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups of 15 teeth each according to root canal filling material and self-etching primers and two control groups (positive and negative) of 5 teeth each as follows: group 1 - gutta percha and AH26® sealer; group 2 - Resilon, RealSeal™ primer and RealSeal™ sealer; group 3 - Resilon, Clearfil SE Bond® primer and RealSeal™ sealer group 4 - Resilon, AdheSe® primer and RealSeal™ sealer. Apical leakage was measured by a maximum length of linear dye penetration of roots sectioned longitudinally by diamond disk. Statistical analysis was performed using the One-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe's test. There were no statistical differences in the mean apical dye penetration among the groups 2, 3 and 4 of self-etching primers. And group 1, 2 and 3 had also no statistical difference in apical dye penetration. But, there was statistical difference between group 1 and 4 (p < 0.05). The group 1 showed the least dye penetration. According to the results of this study, Resilon with self-etching primer was not sealed root canal better than gutta precha with AH26® at sealing root canals. And there was no significant difference in apical leakage among the three self-etching primers.
- 799 View
- 1 Download

- Polymerization shrinkage, hygroscopic expansion and microleakage of resin-based temporary filling materials
- Nak Yeon Cho, In-Bog Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):115-124. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to measure the polymerization shrinkage and hygroscopic expansion of resin-based temporary filling materials and to evaluate microleakage at the interface between the materials and cavity wall.
Five resin-based temporary filing materials were investigated: Fermit (Vivadent), Quicks (Dentkist), Provifil (Promedica), Spacer (Vericom), Clip (Voco). Caviton (GC) was also included for comparison. Polymerization shrinkage of five resin-based temporary filling materials was measured using the bonded disc method. For the measurement of hygroscopic expansion, the discs of six cured temporary filling materials were immersed in saline and a LVDT displacement sensor was used to measure the expansion for 7 days. For estimating of microleakage, Class I cavities were prepared on 120 extracted human molars and randomly assigned to 6 groups of 20 each. The cavities in each group were filled with six temporary filling materials. All specimens were submitted to 1000 thermo-cycles, with temperature varying from 5℃/55℃. Microleakage was determined using a dye penetration test.
The results were as follows:
Fermit had significantly less polymerization shrinkage than the other resin-based temporary filling materials. Fermit (0.22 %) < Spacer (0.38 %) < Quicks (0.64 %), Provifil (0.67 %), Clip (0.67 %)
Resin-based temporary filling materials showed 0.43 - 1.1 % expansion in 7 days.
Fermit showed the greatest leakage, while Quicks exhibited the least leakage.
There are no correlation between polymerization shrinkage or hygroscopic expansion and microleakage of resin-based temporary filling materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of color stability, gloss, mechanical and physical properties according to dental temporary filling materials type
Ji-Won Choi, You-Young Shin, Song-Yi Yang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2022; 49(3): 97. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of strain according to two wavelengths of light source and constant temperature bath deposition in ultraviolet-curing resin for dental three-dimensional printing
Dong-Yeon Kim, Gwang-Young Lee, Hoo-Won Kang, Cheon-Seung Yang
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2020; 42(3): 208. CrossRef - Effect of cavity disinfectants on antibacterial activity and microtensile bond strength in class I cavity
Bo-Ram KIM, Man-Hwan OH, Dong-Hoon SHIN
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(3): 368. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 29. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
Tae-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Young-Jung Choi, So-Young Yang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 419. CrossRef - The Effect of Temporary Filling Materials on The Adhesion between Dentin Adhesive-coated Surface and Resin Inlay
Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 553. CrossRef
- Comparison of color stability, gloss, mechanical and physical properties according to dental temporary filling materials type
- 1,333 View
- 9 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Evaluation of the influence of apical sizes on the apical sealing ability of the modified continuous wave technique
- Muhyun Ryu, Ilyoung Jung, Seungjong Lee, Sujung Shin, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):66-75. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study examined the influence of the apical sizes on the sealing ability of a root canal filling.
Thirty-six single rooted teeth with a single canal were divided into 3 groups (n = 12) and instrumented with either the Profile® or LightSpeed® system to achieve three different apical sizes (master apical file [MAF] of #25, #40, or #60). The teeth were filled with gutta percha using a modified continuous wave technique. The level of microleakage was determined by immersing ten teeth from each group into India ink for 1 week followed by clearing with nitric acid, ethyl-alcohol, and methylsalicylate. The microleakage was measured using vernier calipers. The data was analyzed statistically using Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA and a Student-Newman-Keuls Method. Two teeth from each group were sectioned horizontally at 1, 2, 3 and 4 mm from the apex in order to observe a cross section.
The apical size was significantly (p < .05) influenced the level of microleakage. In the Student-Newman-Deuls Method, MAF sizes of #25 and #40; and MAF sizes of #25 and #60, respectively showed a statistically significant difference. There was no significant difference between #40 and #60. In most cross sections, oval-shaped canals were observed, and the irregularity of the internal surface increased with decreasing apical size. There was also an increase in the area of recess, which is the area where the canal space is not filled with either gutta-percha or sealer.
When the root canals are filled using a modified continuous wave technique, canal filling with more consistent and predictable outcome may be expected as the apical preparation size is increased.
- 1,082 View
- 9 Download

- The nanoleakage patterns of experimental hydrophobic adhesives after load cycling
- Suh-Jin Sohn, Ju-Hae Chang, Suk-Ho Kang, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):9-19. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was: (1) to compare nanoleakage patterns of a conventional 3-step etch and rinse adhesive system and two experimental hydrophobic adhesive systems and (2) to investigate the change of the nanoleakage patterns after load cycling. Two kinds of hydrophobic experimental adhesives, ethanol containing adhesive (EA) and methanol containing adhesive (MA), were prepared. Thirty extracted human molars were embedded in resin blocks and occlusal thirds of the crowns were removed. The polished dentin surfaces were etched with a 35% phosphoric acid etching gel and rinsed with water. Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (MP), EA and MA were used for bonding procedure. Z-250 composite resin was built-up on the adhesive-treated surfaces. Five teeth of each dentin adhesive group were subjected to mechanical load cycling. The teeth were sectioned into 2 mm thick slabs and then stained with 50% ammoniacal silver nitrate. Ten specimens for each group were examined under scanning electron microscope in backscattering electron mode. All photographs were analyzed using image analysis software. Three regions of each specimen were used for evaluation of the silver uptake within the hybrid layer. The area of silver deposition was calculated and expressed in gray value. Data were statistically analyzed by two-way ANOVA and post-hoc testing of multiple comparisons was done with the Scheffe's test. Silver particles were observed in all the groups. However, silver particles were more sparsely distributed in the EA group and the MA group than in the MP group (p < .0001). There were no changes in nanoleakage patterns after load cycling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of the removal of chondroitin sulfate on bond strength of dentin adhesives and collagen architecture
Jong-Ryul Kim, Sang-Jin Park, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 211. CrossRef - The effect of priming etched dentin with solvent on the microtensile bond strength of hydrophobic dentin adhesive
Eun-Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Bae, Jong-Soon Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, In-Bog Lee, Chang-Keun Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 42. CrossRef
- The effect of the removal of chondroitin sulfate on bond strength of dentin adhesives and collagen architecture
- 2,102 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparison of apical sealing ability of continuous wave of obturation technique using EndoTwinn and System B
- Hyun-Ju Shin, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):522-529. Published online November 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.522
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the apical leakage of the root canal filled with the System B and the EndoTwinn (the combined application of heat and ultrasonic vibration).
Sixty extracted premolars with straight root were cleaned and shaped to size 35. Group SB was obturated using System B and Group ET was filled with EndoTwinn. A size 35 of 0.06 tapered gutta-percha and Adseal were used and the plugger which could be introduced to 4 mm short of working length was selected in the obturation procedure. As the positive control, Group PC was not filled. In Group SB, ET and PC, all external surfaces of each tooth were coated with nail varnish leaving only 1 mm area around the apical foramen. In the negative control of Group NSB and Group NET, all of external tooth surface including apical foramen was coated with the nail varnish. The specimens were immersed in methylene blue dye solution for 2 days. Then the specimens were sectioned at each 1 mm from apex to 5 mm level. The final score of one specimen was given by summing up of the points at all levels.
The dye leakage of Group ET was significantly less than that observed in Group SB (p < 0.05). And the frequency of gutta-percha pulling out from root canal when the plugger was removed was more often with the System B than with EndoTwinn but there was no significant difference.
- 986 View
- 2 Download

- Comparison of apical sealing efficacies using different plugging depth in continuous wave of obturation technique
- Sang-Jin Lee, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):491-497. Published online November 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.491
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare apical sealing ability of continuous wave canal filling technique according to various heat source plugging depths.
Eighty one extracted human premolars with straight root were cleaned and shaped to size 35 using .06 taper rotary NiTi file. After cleansing and shaping, the teeth were divided into 5 groups following the heat source probing depths from the apex; 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 mm. All specimens were filled using E&Q plus with #35 / .06 tapered gutta-percha cone. The positive control teeth were not filled. All teeth were coated with nail varnish except the apical 1 mm around the apical foramen. Negative control teeth were completely sealed include the apical foramen. All specimens were immersed in 1% methylene blue solution for 72 hours. Then the specimens were sectioned horizontally at 1, 2 and 3 mm from the root apex. Each sectioned surface was photographed using a digital camera attached to the stereomicroscope at 12.5 × 2.5 fold magnification. All points at 1, 2 and 3 mm were summed as final score of one specimen. Statistical analysis of the collected data was performed.
Under the condition of this study, there was no significant difference between the heat source plugging depths of 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 mm in apical sealing ability. All of apical heat source plugging depth from 3 to 7 mm including Buchanan's protocol -from 5 to 7 mm- seems to be acceptable in clinical application.
- 810 View
- 2 Download

- Effect of a new resin monomer on the microleakage of composite resin restorations
- JH Bae, YK Kim, PY Yoon, MA Lee, BH Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):469-475. Published online September 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.469
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a new resin monomer on the microleakage of composite resin restorations. By adding new methoxylated Bis-GMA (Bis-M-GMA, 2,2-bis[4-(2-methoxy-3-methacryloyloxy propoxy) phenyl] propane) having low viscosity, the content of TEGDMA which has adverse effects on polymerization shrinkage might be decreased. As a result, microleakage might be improved.
2 mm × 2 mm × 2 mm cavities with occlusal margins in enamel and gingival margins in dentin were prepared on buccal and lingual surfaces of 40 extracted human premolars. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into four groups and restored with Clearfil SE bond (Kuraray, Japan) and one of experimental composite resins; EX1, Experimental composite resin1 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 40 nm nanofillers); EX2, Experimental composite resin2 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 20 nm nanofillers); EX3, Experimental composite resin3 (Bis-GMA/TEGDMA = 70/30 wt%, 40 nm nanofillers); and Filtek Z250 (3M ESPE, USA) was filled as a control group. The restored teeth were thermocycled, and immersed in 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours. The teeth were sectioned buccolingually with a low speed diamond saw and evaluated for microleakage under stereomicroscope. The data were statistically analyzed by Pearson Chi-Square test and Fisher Exact test (p = 0.05).
The microleakage scores seen at the enamel margin were significantly lower than those of dentin margin (p = 0.007). There were no significant differences among the composite resins in the microleakage scores within each margin (p > 0.05). Bis-M-GMA, a new resin monomer having low viscosity, might in part replace high viscous Bis-GMA and might improve the quality of composite resin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef - Surface roughness of experimental composite resins using confocal laser scanning microscope
JH Bae, MA Lee, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(1): 1. CrossRef
- Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
- 1,282 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Microleakage of 2-step adhesive systems in diamond-prepared cavity
- Myung-Goo Lee, Kwon-Hwan Cho, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):437-444. Published online September 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.437
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the marginal microleakage of different 2-step adhesive systems in Class V cavities prepared with different diamond points.
Forty Class V cavities were prepared with two different (coarse or fine) diamond points on cervical third of extracted molars. The occlusal and gingival margin of cavities was located in enamel and dentin, respectively. They were divided into one of four equal groups (n = 10) and ; Group 1-prepared with coarse diamond point (EX-41), restored with Single Bond and Z 250, Group 2-prepared with fine diamond piont (TF-21F), restored with Single Bond and Z 250, Group 3-prepared with coarse diamond point (EX-41), restored with Clearfil SE Bond and Clearfil AP-X, Group 4-prepared with fine diamond point (TF-21F), restored with Clearfil SE Bond and Clearfil AP-X.
Specimens were thermocycled, immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours, and bisected longitudinally. They were observed leakages at enamel and dentinal margins. Data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked test.
In this study, marginal microleakage of Single Bond was not affected by type of diamond points. But Clearfil SE Bond showed higher marginal microleakage at both enamel and dentinal margin when Class V cavity was prepared with coarse diamond point.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 477. CrossRef - Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 13. CrossRef
- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
- 990 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of bonding resin on bond strength of dual-cure resin cements
- Duck-Su Kim, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):426-436. Published online September 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.426
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this study is to evaluate the effect of an additional application of bonding resin on the bond strength of resin luting cements in both the light-cure (LC) and self-cure (SC) modes by means of the µTBS tests.
Three combinations of One-Step Plus with Choice, Single Bond with Rely X ARC, and One-Up Bond F with Bistite II were used. D/E resin and Pre-Bond resin were used for the additional application. Twelve experimental groups were made. Three mandibular 3rd molars were used in each group. Indirect composite blocks were cemented on the tooth surface. 1 × 1 mm2 dentin-composite beam for µTBS testing were made and tested.
When total-etching dentin adhesives were used, an additional application of the bonding resin increased the bond strength (
P < 0.05). However, this additional application didn't influence the bond strength of self-etching dentin adhesives (P > 0.05).In conclusion, the results suggest that an additional application of the bonding resin increases bond strength and enhances quality of bonding when using total-etching dentin adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 95. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 103. CrossRef - Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 223. CrossRef
- Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
- 2,230 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Microleakage of composite resin restoration according to the number of thermocycling
- Chang-Youn Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):377-384. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.377
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Present tooth bonding system can be categorized into total etching bonding system (TE) and self-etching boding system (SE) based on their way of smear layer treatment. The purposes of this study were to compare the effectiveness between these two systems and to evaluate the effect of number of themocycling on microleakage of class V composite resin restorations.
Total forty class V cavities were prepared on the single-rooted bovine teeth and were randomly divided into four experimental groups: two kinds of bonding system and another two kinds of thermocycling groups. Half of the cavities were filled with Z250 follwing the use of TE system, Single Bond and another twenty cavities were filled with Metafil and AQ Bond, SE system. All composite restoratives were cured using light curing unit (XL2500, 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA) for 40 seconds with a light intensity of 600 mW/cm2.
Teeth were stored in distilled water for one day at room temperature and were finished and polished with Sof-Lex system. Half of teeth were thermocycled 500 times and the other half were thermocycled 5,000 times between 5℃ and 55℃ for 30 second at each temperature.
Teeth were isolated with two layers of nail varnish except the restoration surface and 1 mm surrounding margins. Electrical conductivity (µA) was recorded in distilled water by electrochemical method. Microleakage scores were compared and analyzed using two-way ANOVA at 95% level.
From this study, following results were obtained: There was no interaction between variables of bonding system and number of thermocycling (p = 0.485). Microleakage was not affected by the number of thermocycling either (p = 0.814). However, Composite restoration of Metafil and AQ Bond, SE bond system showed less microleakage than composite restoration of Z250 and Single Bond, TE bond system (p = 0.005).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength and Microleakage of Bulk-fill Resin Composites
Hanbyeol Lee, Hyunwoo Seo, Juhyun Lee, Howon Park
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2015; 42(4): 281. CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems
Ji-Hoon Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 333. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength and Microleakage of Bulk-fill Resin Composites
- 1,074 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
- Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):327-334. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of burs on microleakage of Class V resin restorations when a self-etching primer adhesive was used.
Forty Class V cavities were prepared with four different cutting burs on extracted third molars, and divided into one of four equal groups (n = 10); Group 1-plain cut carbide bur (no. 245), Group 2-cross cut carbide bur (no. 557), Group 3-fine diamond bur (TF-21F), Group 4-standard diamond bur (EX-41).
The occlusal and gingival margin of cavities was located in enamel and dentin, respectively. Cavities were treated with Clearfil SE Bond and restored with Clearfil AP-X. Specimens were thermocycled, immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours, and bisected longitudinally. They were observed leakages at enamel and dentinal margins. Data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked test.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. At enamel margin, microleakage of group 4 was statistically higher than those of group 1, 2 and 3 (p < 0.01).
2. At dentinal margin, microleakage of group 4 was statistically higher than group 3 (p < 0.01), but group 1 and 2 were not statistically different with group 3 and 4.
3. Enamel microleakage was statistically higher than dentinal microleakage in group 1, 2 and 3 (p < 0.05), but statistical difference between the microleakage of enamel and dentinal margin was not in group 4.
In conclusion, the use of coarse diamond bur showed high microleakage at both enamel and dentinal margin when Clearfil SE Bond was used in class V cavity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 477. CrossRef - Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 13. CrossRef
- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
- 1,053 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of C-factor and volume on microleakage of composite resin restorations with enamel margins
- Bong-Joo Koo, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):452-459. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.452
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Competition will usually develop between the opposing walls as the restorative resin shrinks during polymerization. Magnitude of this phenomenon may be depended upon cavity configuration and volume.
The purpose of this sturdy was to evaluate the effect of cavity configuration and volume on microleakage of composite resin restoration that has margins on the enamel site only.
The labial enamel of forty bovine teeth was ground using a model trimmer to expose a flat enamel surface. Four groups with cylindrical cavities were defined, according to volume and configuration factor (Depth × Diameter / C-factor) - Group I: 1.5 mm × 2.0 mm / 4.0, Group II: 1.5 mm × 6.0 mm / 2.0, Group III: 2.0 mm × 1.72 mm / 5.62, Group IV: 2.0 mm × 5.23 mm / 2.54.
After treating with fifth-generation one-bottle adhesive - BC Plus™ (Vericom, AnYang, Korea), cavities were bulk filled with microhybrid composite resin - Denfill™ (Vericom). Teeth were stored in distilled water for one day at room temperature and were finished and polished with Sof-Lex system. Specimens were thermocycled 500 times between 5℃ and 55℃ for 30 second at each temperature.
Teeth were isolated with two layers of nail varnish except the restoration surface and 1 mm surrounding margins. Electrical conductivity (µA) was recorded in distilled water by electrochemical method. Microleakage scores were compared and analyzed using two-way ANOVA at 95% level.
The results were as follows:
1. Small cavity volume showed lower microleakage score than large one, however, there was no statistically significant difference.
2. There was no relationship between cavity configuration and microleakage.
Factors of cavity configuration and volume did not affect on microleakage of resin restorations with enamel margins only.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
Mi-Ae Lee, Duck-Kyu Seo, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 164. CrossRef - Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems
Ji-Hoon Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 333. CrossRef - A survey on the use of composite resin in Class II restoration in Korea
Dong-Ho Shin, Se-Eun Park, In-Seok Yang, Juhea Chang, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 87. CrossRef - Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef
- Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
- 1,347 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Estimation of relation between techniques of dye penetration for microleakage and SEM evaluation for marginal adaptation of the restoration
- Soon-Joo Hwang, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):337-343. Published online September 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.337
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to estimate the relation between techniques used for microleakage from dye penetration and for marginal adaptation from SEM evaluation of the restoration.
Using high speed #330 bur, class V cavities (4 × 3 × 1.5 mm around CEJ) were prepared on the buccal surface of 20 extracted human molars. Six dimples as reference points for SEM and dye penetration evaluation were made with 1/2 round bur. Cavity was bulk filled with microhybrid composite resin (Esthet X) and all-in-one adhesive (Xeno III). Teeth were stored in saline solution for one day, after then, they were finished and polished using Sof-Lex system.
Fifty percent silver nitrate dye solution was used for the evaluation of microleakage and resin replica was used for marginal adaptation. All of these were done after 1000 times thermocycling between 5 and 55℃.
Vertical sections were made through three dimples of restoration to obtain samples for the evaluation of dye penetration and inner marginal adaptation. Outer adaptational estimation was done with an intact restoration before sectioning. Dye penetration was determined in three degrees and percentage of outer and inner leaky margin was estimated from SEM image.
The data were analysed statistically: Spearman's rho test were used to check relationships between two methods.
The result were as follows:
There were significant relationships between degree of dye penetration and inner and outer marginal adaptations each (p < 0.01).
However, there was no significant relationship between the results of inner and outer marginal adaptation.
Within the results of this study, relationship between the percentage of marginal adaptation and microleakage shows significant relationship. However, inner and outer marginal adaptation did not show any significant relationship mutually.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength and Microleakage of Bulk-fill Resin Composites
Hanbyeol Lee, Hyunwoo Seo, Juhyun Lee, Howon Park
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2015; 42(4): 281. CrossRef - Comparison of marginal microleakage between low and high flowable resins in class V cavity
Sang-Bae Bae, Young-Gon Cho, Myeong-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 477. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength and Microleakage of Bulk-fill Resin Composites
- 1,151 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of resin sealants on the reduction of microleakage in composite restorations
- Young-Gon Cho, Mun-Hong Kim, Myung-Goo Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):282-289. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the ability of three resin surface sealants to prevent microleakage in Class V composite resin restorations. Forty Class V cavities with the occlusal margin in enamel and gingival margin in dentin were prepared on the buccal surfaces of sound extracted molars, and restored with composite resin. Restorations were randomly assigned into one of four equal groups (n = 10): a control group, without resin sealing, and three experimental groups in which margins were sealed with Fortify Plus, Biscover and Permaseal, respectively. Specimens were thermocycled, immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 4 hours, sectioned longitudinally, and observed the leakage at the occlusal and gingival margins. The result was analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis test, Mann-Whitney test and Wilcoxon signed rank test.
In conclusion, the ability to reduce microleakage at occlusal margins was similar in all of three sealants. However at gingival margin, it depended on the type of used resin surface sealant. At gingival margin, control and Fortify Plus group showed statistically higher microleakage than PermaSeal group, and Fortify Plus group also showed higher microleakage than BisCover group (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
Mi-Ae Lee, Duck-Kyu Seo, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 164. CrossRef - A survey on the use of composite resin in Class II restoration in Korea
Dong-Ho Shin, Se-Eun Park, In-Seok Yang, Juhea Chang, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 87. CrossRef - Microleakage of 2-step adhesive systems in diamond-prepared cavity
Myung-Goo Lee, Kwon-Hwan Cho, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 437. CrossRef
- Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
- 1,100 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of two different calcium hydroxide paste removal techniques on apical leakage: an electrochemical study
- Chan-Je Park, Kyung-A Jeon, Ho-Beom Kwon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):186-191. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the effect of two different calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) paste removal techniques on the apical leakage of canals obturated with gutta percha cones and sealer after removing a Ca(OH)2 dressing using an electrochemical method.
Seventy extracted single-rooted teeth were instrumented on with Profile rotary files under NaOCl irrigation. Fifty-eight canals were filled with calcium hydroxide paste, which was then removed using one of the following two techniques. In group A, calcium hydroxide was removed using only NaOCl irrigation, and in group B, the canals were re-prepared with a Profile rotary files-one size larger than the previous instrument and were irrigated with NaOCl. In both groups, the root surfaces were coated twice with nail varnish from CEJ to an area 4 mm away from the apex after canal obturation. Apical leakage was measured using an electrochemical method for 24 days.
All the specimens showed leakage that increased markedly in the first three days. There was no significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05). The effect of two calcium hydroxide paste removal techniques on the apical leakage was not different during a short period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of the irrigation systems in calcium hydroxide removal
Jae-Seung Eun, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 508. CrossRef
- A Comparison of the irrigation systems in calcium hydroxide removal
- 1,378 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of MTAD on the apical leakage of obturated root canals: an electrochemical study
- Dong-Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):119-124. Published online March 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of newly developed endodontic root canal cleanser (MTAD) on the apical leakage of obturated root canal using an electrochemical method.
Canals of 60 extracted single-rooted human teeth were prepared by using a crown-down technique with rotary nickel-titanium files. In Group 1 (positive control group) and 2 (negative control group), 5.25% NaOCl was used as a canal irrigant and no canal wall treatment was done. In group 3, only 5.25% NaOCl were used as canal irrigant, canal wall treatment and final rinse. In group 4, specimens were irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl, treated with 5
ml of 17% EDTA for 5 minutes and final rinsed with 5.25% NaOCl. Specimens of group 5 were irrigated with 1.3% NaOCl and treated with 5 ml of MTAD for 5 minutes. All root canals are dried with paper points and obtuated with gutta-percha and AH plus as a sealer using a continuous wave of condensation technique except in the group 1. The electrical resistance between the standard and experimental electrodes in canals was measured over a period of 10 days. Rising of apical leakage with time was observed for all the groups. Group 4 and 5 showed lower apical leakage than group 3 but differences between the group 3, 4 and 5 were no statistical significance at any measurement time.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 484. CrossRef
- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- 1,201 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- THE EFFECT OF SMEAR LAYER TREATMENT ON THE MICROLEAKAGE
- Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):378-389. Published online January 14, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.378
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to compare the sealing ability of root canal obturation with or without the treatment of smear layer. Eighty extracted human teeth with one canal were selected. Instrumentation was performed with crown-down technique. After instrumentation, root canals of the NaOCl group and NaOCl-6 group were irrigated with 3% NaOCl. EDTA group and EDTA-6 group were irrigated with 17% EDTA. Then all teeth were obturated using continuous wave obturation technique.
NaOCl group and EDTA group were immersed in methylene blue solution for 84hours. NaOCl-6 group and EDTA-6 group were immersed in methylene blue solution for 6months. The teeth were sectioned at 1.5 mm (Level 1), 3.0 mm (Level 2) and 4.5 mm (Level 3) from the root apex. The length of dye-penetrated interface and the circumferential length of canal at each level were measured using Sigma-Scan Pro 5.0.
The mean leakage ratio was decreased cervically.
NaOCl group showed higher mean leakage ratio than EDTA group at each level. But there was significant difference at level 1 only (p < 0.05).
NaOCl-6 group showed higher mean leakage ratio than EDTA-6 group at each level. But there was significant difference at level 1 only (p < 0.05).
NaOCl-6 group showed higher mean leakage ratio than NaOCl group at each level. But there was significant difference at level 1 only (p < 0.05).
EDTA-6 group showed higher mean leakage ratio than EDTA group at each level. But there was no significant difference.
In NaOCl group and NaOCl-6 group, scanning electron micrographs of tooth sections generally covered with smear layer. In EDTA group and EDTA-6 group, tooth sections showing the penetration of sealers to opened dentinal tubules. The results suggest that removal of smear layer was effective to reduce the apical microleakage of the root canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 484. CrossRef - The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 397. CrossRef
- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- 1,109 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of marginal microleakge according to thickness of flowable resin
- Gi-Gang Song, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):363-371. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the effect of thickness of flowable resin lining on marginal leakage in class II composite restorations. 80 experimental teeth were prepared with class II preparations with enamel margin or dentin margin. Each group was devided into four groups according to flowable resin lining thickness ; Control group - no flowable resin lining, Group 1 - 0.5 mm flowable resin lining, Group 2 - 1 mm flowable resin lining, Group 3 - 2 mm flowable resin lining. The cavities were restored using Scotchbond Multi-Purpose adhesive system, Filtek Flow and Filtek Z 250 composite resin.
Following one day storage in distilled water, the restored teeth were thermocycled for 500 cycles and immersed in 2% methylene blue for 24 hours.
The results of this study were as follows:
1. Ranking of mean microleakage scores at the enamel margins was Group 1 < Control = Group 2 < Group 3. The microleakage of Group 3 was significantly higher than that of Control, Group 1 and Group 2 (p < 0.05).
2. Ranking of mean microleakage scores at the dentin margins was Group 1 < Group 2 < Control < Group 3. The microleakage of Group 3 was significantly higher than that of Control, Group 1 (p < 0.05).
3. Compared with microleakage between the enamel and dentin margins, enamel margin group were significantly lower than dentin margin group.
- 670 View
- 0 Download

- Effect of biscover on the marginal microleakage of composite resin restoration
- Young-Gon Cho, Hee-Young Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):355-362. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.355
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect on marginal leakage of a resin surface sealant (Biscover) applied before or after polymerization of composite resin to unsealed composite restorations. Thirty Class V cavities with the occlusal margin in enamel and cervical margin in dentin or cementum were prepared on the buccal surfaces of sound extracted molars and restored with a microfilled light-cured composite resin (Micronew). Restorations were randomly assigned into one of three equal groups (n = 10): a control group - no surface sealing, group 1 - applied Biscover after polymerization of the composite resin, and group 2 - applied Biscover before polymerization of the composite resin. Specimens were thermocycled, immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 4 hours, sectioned longitudinally, and analyzed for leakage at the occlusal and gingival margins. The results of this study were as follows;
1. In sealed group, group 2 showed higher microleakage than group 1 at both occlusal and gingival margins, but there was no significant difference between two groups (p > 0.05).
2. Unsealed control group showed a little higher microleakage than sealed group at occlusal margins, and a little higher or similar microleakage than sealed group at gingival margins (p > 0.05).
3. Control group and group 2 showed significantly less microleakage at the occlusal margins, but group 1 showed no significantly difference between microleakage at the occlusal and gingival margins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of surface-sealant application on bond effectiveness of all-in-one self-etch adhesives
Safa Tuncer, Neslihan Tekçe, Mustafa Demirci, Canan Baydemir
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2017; 31(6): 677. CrossRef - Influence of rebonding procedures on microleakage of composite resin restorations
Mi-Ae Lee, Duck-Kyu Seo, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 164. CrossRef - The Effect of Three Surface Sealants on Microleakage of Class V Composite Resin Restorations
Won Cheol Lee, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2009; 47(2): 182. CrossRef - Evaluation on the abrasion resistance of a surface sealant
Soo-Mee Kim, Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 180. CrossRef
- The role of surface-sealant application on bond effectiveness of all-in-one self-etch adhesives
- 1,075 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Microleakage of the class V cavity according to restoration site and cavity size using SEM and three-dimensional reconstruction techniques
- In-Seo Yang, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(2):112-120. Published online March 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was done to evaluate whether there were any differences in microleakage of class V composite restorations according to restoration site and cavity size.
Total sixty-four restorations were made in molar teeth using Esthet-X. Small (2 × 2 × 1.5 mm) and large (4 × 2 × 1.5 mm) restorations were made at the buccal/lingual surface and the proximal surface each. After 1,000 times of thermocycling (5℃ - 55℃), resin replica was made and the percentage of marginal gap to the whole periphery of the restoration was estimated from SEM evaluation.
Thermocycled tooth was dye penetrated with 50% silver nitrate solution. After imbedding in an auto-curing resin, it was serially ground with a thickness of 0.25 mm. Volumetric microleakage was estimated after reconstructing three dimensionally.
Two-way ANOVA and independent T-test for dye volume, Mann-Whitney U test for the percentage of marginal gap, Spearman's rho test for the relationship between two techniques were used.
The results were as follows:
1. The site and size of the restoration affected on the microleakage of restoration. Namely, much more leakage was seen in the proximal and the large restorations rather than the buccal/lingual and the small restorations.
2. Close relationship was found between two techniques (Correlation coefficient = 0.614 / P = 0.000).
Within the limits of this study, it was noted that proximal and the large restorations leaked more than buccal/lingual and the small restorations. Therefore, it should be strictly recommended large exposure of margins should be avoided by reducing unnecessary tooth reduction.
- 981 View
- 5 Download

- Surface roughness and microleakage of class V composite restorations : Effect of surface sealing
- Min-Jeong Kim, Mi-Jeong Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Soo-Joung Park, Kwang-Won Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):22-30. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.022
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of surface sealing materials on microleakage and surface roughness in Class V composite restorations.
Twenty five standardized Class V cavity preparations were made on the facial surface of human premolars and were randomly assigned to 5 groups. The teeth were restored with Z-250 after applying Single Bond. Following 7 days storage in distilled water at 37℃, the restorations were sealed as following systems : No sealing ; Single Bond Adhesive ; Biscover ; Fortify ; Optiguard. Then, toothbrush abrasion test was conducted using a wear testing machine.
Surface roughness was measured by means of profilometer before and after toothbrushing and the results were statistically analysed by using a paired t-test and ANOVA. The bonded interfaces and the changes of surface roughness were examined by SEM.
For microleakage test, specimens were stained in a 2% methylene blue solution, then longitudinally sectioned and analyzed for leakage at occlusal and cervical interfaces using stereomicroscope. The results were statistically analysed by using a Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U test.
Surface roughness was increasing in all groups after toothbrushing, but no statistically significant differences. In SEM observation, surface sealant was partially retained and partially detached in bonded interfaces. Especially, microgap was identified in cervical margins. In microleakage test, there was better seal in the enamel region and a significant difference between groups at occlusal margin. Control group and Single Bond group had significantly better marginal seal at enamel margin than cervical margin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microleakage of 2-step adhesive systems in diamond-prepared cavity
Myung-Goo Lee, Kwon-Hwan Cho, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 437. CrossRef
- Microleakage of 2-step adhesive systems in diamond-prepared cavity
- 1,004 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
Bacteriologic
in vitro coronal leakage study of before and after post space preparation - Hyo-An Lee, Eui-Seong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):16-21. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of present study was to compare the speed of coronal leakage before and after post space preparation using
Streptococcus mutans .Forty straight extracted human teeth were selected. The crowns were removed to a uniform remaining root length 14 mm. Canals were enlarged by 06 taper Profiles® to a size #40 as a master apical file. And these were filled with gutta percha point and Tubuliseal® sealer, using continuous wave technique. Groupings are as follows.
Group 1 - These teeth were obturated without sealer.
Group 2 - These teeth were obturated and covered the surface of the root completely with sticky wax.
Group 3 - These teeth were obturated.
Group 4 - These teeth were obturated and prepared for post space remaining 5 mm of gutta percha.
The teeth were suspended in plastic tubes. The upper chamber received the bacterial suspension everyday to simulate clinical situation. The lower chamber consisted of BHI added Andrade's indicator.
All roots in the positive control group (Group 1) turned yellow within 24 h and those of negative control group (Group 2) remained red throughout the experimental period (70 days). The samples of group 3 were contaminated within an average of 27.2 days. The samples of group 4 were contaminated within an average of 15.7 days, ranging from 9 to 22 days.
There was significant difference between group 3 and group 4 statistically (p < 0.05).
- 833 View
- 1 Download

- COMPARISON OF APICAL SEAL WITH OR WITHOUT THE USE OF DENTIN ADHESIVE SYSTEM
- Min-Jo Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):7-15. Published online January 14, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to compare the sealing ability of root canal obturation with or without the use of dentin adhesive system. Forty extracted human teeth with one canal were selected and decoronated. The teeth were divided into two Groups. The obturation procedure of Group 1 was the same as that of Group 2 with the exception of dentin adhesive system. Group 2 were obturated with dentin adhesive system, AH-26, and gutta-percha.
After obturation, the teeth were immersed in methylene blue solution for 84 hours. The teeth were sectioned horizontally at 1.5 mm (Level 1), 2.0 mm (Level 2), 2.5 mm (Level 3) from the root apex using a low speed microtome. Distance of dye-penetrated surface and total dentinal surface were measured using SigmaScan Pro 5.0, and the ratio of dye-penetrated distance to the total dentinal distance was analyzed statistically by Mann-Whitney U-test.
In both groups, the mean leakage ratio was decreased cervically.
At level 1, there was no significant difference between group 1 and grpup 2 (p > 0.05).
At level 2 and 3, group 1 showed significantly higher mean leakage ratio than group 2 (p < 0.05). The results suggest that using dentin adhesive system in root canal obturation procedure reduces the apical microleakage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Application over Time for Each Type of Blending Tea on Bovine Tooth Coloration
Se-Won Bae, Im-Hee Jung, Min-Ha Hong, Eun-Jin Kwon, Ji-Hyeon Kim, Ji-Hyeon Lee, Hee-Jung Lim, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2022; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(2): 133. CrossRef
- Effect of Application over Time for Each Type of Blending Tea on Bovine Tooth Coloration
- 1,100 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- New quantitative measuring technique for microleakage of the restored tooth through 3D reconstruction
- Sang-Yoon Ha, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):413-422. Published online September 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.413
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Established microleakage tests have their own disadvantages. In this study, 3D reconstruction method was tried to overcome these disadvantages.
Four types of microleakage tests were used and relationships among them were estimated: penetrated dye volume; marginal adaptability; degree of dye penetration and relative penetrated length to cavity wall.
Twenty-four Class V cavities were bulk filled with composite (Esthet X) following surface treatments: N group (no treatment); E group (etching only); T group (etching + Prime & Bond NT). 50% silver nitrate was used as a dye solution after thermocycling (5℃ & 55℃, 1,000 times). Teeth were serially ground with a thickness of 0.2 mm. Volume of dye penetration was estimated from a three-dimensionally reconstructed image with a software (3D-DOCTOR). Percentage of margin without gap was estimated from SEM and degree of dye penetration and the relative length of dye penetration to overall cavity wall were also estimated.
ANOVA and Scheffe test for dye volume, Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney test for marginal quality, Spearman's rho test for checking of relationships among methods were used.
The results were as follows:
1. Dye penetration could be seen from several directions, furthermore, its volumetric estimation was possible.
2. Reverse relationship was found between dye volume and marginal quality (r = -0.881 / p = 0.004).
3. Very low relationship was seen between dye volume and two-dimensional tests (degree of dye penetration and relative length). However, 2D evaluation methods showed high relationship (p = 0.002-0.054) each other.
4. Three times vertical section could be recommended as a 2D test.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimation of relation between techniques of dye penetration for microleakage and SEM evaluation for marginal adaptation of the restoration
Soon-Joo Hwang, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(5): 337. CrossRef - Microleakage of the class V cavity according to restoration site and cavity size using SEM and three-dimensional reconstruction techniques
In-Seo Yang, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(2): 112. CrossRef
- Estimation of relation between techniques of dye penetration for microleakage and SEM evaluation for marginal adaptation of the restoration
- 1,149 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- An electrochemical study of the sealing ability of three retrofilling materials
- Dong-Sung Park, Suh-Jin Sohn, Tae-Seok Oh, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Chan-Je Park, Soon-Ho Yim, Young-Kyoo Lee, Seung-Bum Kye
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):365-369. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.365
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the apical sealing ability of Super-EBA, MTA and Dyract-flow as retrofilling materials. Forty-eight extracted human teeth with straight and single root canal were used in this study. The root canals were prepared to a #40 apical canal size and obturated with gutter-percha. Apicoectomies were performed and root end cavities were prepared to a depth of 3mm using an ultrasonic device. The root end cavities were filled with Super-EBA, MTA or Dyract-flow. Leakage was measured using an electrochemical technique for 4 weeks.
According to this study, the results were as follows.
1. Increasing leakage with time was observed in all groups.
2. No significant difference was noted among the 3 groups with time (p = 0.216).
3. No significant difference was noted among the 3 groups when measured within the same time interval (p = 0.814).
The results of this study suggest that the sealing ability of Dyract-flow is equal to that of Super-EBA and MTA, and Dyract-flow may be an alternative to other materials for root-end filling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Sealing Effect and Working Time of Root Canal Filling MTA Materials
Hyojin Kim, Youngjin Kim, Soonhyeun Nam, Kwon Taeyub, Hyunjung Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2016; 43(2): 129. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Sealing Effect and Working Time of Root Canal Filling MTA Materials
- 1,555 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of wetness on the enamel bonding
- Keun-Ho Ko, Young-Gon Cho, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park, Young-Jae Ki, Hee-Young Choi, Jong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):205-211. Published online May 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.205
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the microleakage and interfacial gap between enamel and composite resin under the dry and wet condition of the enamel surface. V shaped class 5 cavities were prepared on the occlusal portion of extracted human molars. Samples were divided into three groups: D group (air dry for 10-15 s), BD group (blot dry with moist cotton pellet), and DR group (air dry for 10-15 s and rewet with Aqua-Prep F for 20 s).
Cavities were filled using Aelitefil composite resin after applied One-Step. Microleakage was tested by 2% methylene blue dye solution and the data were statistically analysed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test. Also Enamel-resin interface was observed under SEM. Group BD showed statistically lower microleakage than group D (p < 0.05), but there was no statistically significant difference between group BD and DR (p > 0.05). At the enamel-resin interface, group D showed the gap of 2 µm thickness, but group BD and DR showed close adaptation.
In conclusion, the use of blot dry and rewetting agent (Aqua-Prep F) resulted in decreased microleakage and improved adhesion between enamel and resin when using One-Step.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
Sook-Kyung Choi, Ji-Wan Yum, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 397. CrossRef
- Effect of an intermediate bonding resin and flowable resin on the compatibility of two-step total etching adhesives with a self-curing composite resin
- 1,089 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A study on the material properties of various composite resins for core build-up
- Soo-Il Shin, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):191-199. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purposes of this study were to estimate the material properties of the recently developed domestic composite resins for core filling material (Chemical, Dual A, Dual B; Vericom, Korea) and to compare them with other marketed foreign products (CorePaste, Den-Mat, USA; Ti-Core, Essential Dental Systems, USA; Support, SCI-Pharm, USA). Six assessments were made; working time, setting time, depth of polymerization, flexural strength, bonding strength, and marginal leakage. All items were compared to ISO standards.
All domestic products satisfied the minimum requirements from ISO standards (working time: above 90 seconds, setting time: within 5 minutes), and showed significantly higher flexural strength than Core Paste. Dual A and B could, especially, reduce the setting time to 60 seconds when cured with 600 mW/cm2 light intensity. All experimental materials showed 6 mm depth of polymerization.
Bond strengths of Ti-Core and Dual B materials were significantly higher than the other materials. Furthermore, three domestic products and Ti-Core could reduce the microleakage effectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
- 1,246 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Marginal microleakage of single step adhesives
- Young-Gon Cho, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Jae Ki, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):162-169. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the marginal microleakage of five single step adhesives. Class V cavity preparations with occlusal margins in enamel and gingival margins in dentin were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of extracted human molar teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into five groups and restored using one of the single step adhesives and composite resins: Prompt L-Pop/Filtek Z-250 (Group 1), AQ Bond/Metafil CX (Group 2), One-Up Bond F/Palfique Toughwell (Group 3), Futurabond/Admira (Group 4), Xeno III/Spectrum TPH (Group 5).
The restored teeth were thermocycled. Microleakage was assessed by dye penetration using 2% methylene blue dye solution. The teeth were bisected buccolingually and evaluated for microleakage under steromicroscope. The data were statistically analysed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney tests.
The results of this study were as follows;
Microleakage of enamel margins in group 3 was statistically higher than that in groups 1, 2, 4, 5 (p < 0.05).
Microleakage of dentin margins in group 1 was statistically higher than that in groups 2, 5, and that in group 3 was statistically higher than that in groups 2, 4, 5 (p < 0.05).
Dentin marginal microleakage was higher than enamel marginal microleakage in all experimental groups.
In conclusion, Prompt L-Pop showed the least leakage at enamel margin, and AQ Bond showed at dentin margin in this study. Marginal miroleakage in dentin was higher than that in enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microtensile bond strength of single step adhesives to dentin
Young-Gon Cho, Young-Jae Kee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 312. CrossRef - Comparative bond strength of single step adhesives to different dentinal depths
Young-Gon Cho, Cheol-Hee Jin, Jung-Bum Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 319. CrossRef
- Microtensile bond strength of single step adhesives to dentin
- 1,058 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A quantitative analysis about microleakage of all-in-one adhesives
- Yong-Hee Kang, Soo-Il Shin, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):66-72. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub All-in-one adhesives were recently developed for reducing the techique sensitivity and chair time, but lots of concerns were made on bondability, longevity, and microleakage.
The object of this study was to evaluate microleakage and marginal quality of all-in-one adhesives using electrochemical method and SEM analysis quantitatively.
After making Class V cavities, they were bulk filled with Heliomolar(#A1) after surface treatment with three adhesives: Adper Prompt (Group A), One up bond F (Group O), Xeno III (Group X). Electrical conductivity (microamphere, µA) was checked two times: before and after cavity filling.
Percentage of leaky margin was estimated from SEM image (×1,000).
The data were statistically analysed: ANOVA and Paired T test for electrical conductivity, Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney test for marginal quality, Spearman's rho test for checking of relationships between 2 methods.
The result were as follows:
1. There was no difference in microleakage between adhesive systems and every specimen showed some of microleakage after filling.
2. Microleakage was reduced about 70% with composite resin filling.
3. Marginal quality was the best in group A, decreasing among groups in the following order: group O, followed by group X. There were significant differences between group A and group X (p=0.015), and between group O and group X (p=0.019).
4. There was no relationship between the microleakage measured by electrochemical method and marginal quality measured by SEM analysis.
Within the results of this study, there was no difference in microleakage among groups by electrical conductivity. However, significant difference in marginal quality was seen among groups. It was believed that these dissimilar results might be induced because of their own characteristics. Analysis of microleakage needs various methods for accuracy.
- 956 View
- 1 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


