Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 34(6); 2009 > Article
- Original Article Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
-
2009;34(6):-490.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.484
Published online: November 30, 2009
Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Mi-Kyung Yu. Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, Geumam-Dong, Deokjin-Gu, Jeonju, Jeonbuk 561-712, Korea. Tel: 82-63-250-2045, Fax: 82-63-250-2049, mkyou102@hanmail.net
• Received: June 24, 2009 • Revised: September 25, 2009 • Accepted: October 14, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,182 Views
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
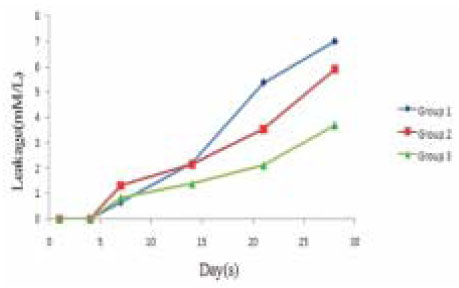
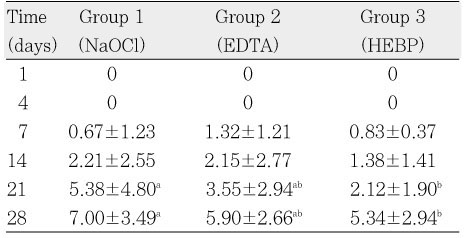
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of soft chelating irrigant on the sealing ability of root fillings by using a glucose leakage test.A total of 45 single-rooted teeth were selected for the study. The teeth were decoronated leaving a total length of 13mm. The root canals prepared using K3 NiTi rotary instruments to an apical dimension of size 45(0.06 taper). The specimens were then randomly divided into 3 experimental groups of 13 roots each and 2 control groups of 3 roots each. Specimen in each group were prepared with different irrigation protocols : group 1, 2.5% NaOCl; group 2, 2.5% NaOCl and 17% EDTA; group 3, 2.5% NaOCl and 15% HEBP. The root canals were filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer using lateral condensation. After 7 days in 37℃, 100% humidity, the coronal-to-apical microleakage was evaluated quantitatively using a glucose leakage model. The leaked glucose concentration was measured with spectrophotometry at 1, 4, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days.There was a tendency of increase in leakage in all experimental groups during experimental period. HEBP-treated dentin showed no significant difference with EDTA-treated dentin during experimental period. From the 21th day onward, HEBP-treated dentin showed significantly lower leakage than smear-covered dentin. HEBP-treated dentin displayed a similar sealing pattern to EDTA-treated dentin and a better sealing ability than smear-covered dentin. Consequently, a soft chelator(HEBP) could be considered as the possible alternative to EDTA.
- 1. Czonstkowsky M, Wilson EG, Holstein FA. The smear layer in endodontics. Dent Clin North Am. 1990;34: 13-25.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Pashley DH, Michelich V, Kehl TJ. Dentin permeability: effects of smear layer removal. J Prosthet Dent. 1981;46: 531-537.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Pashley DH. Smear layer: Physiological considerations. Oper Dent Suppl. 1984;3: 13-29.PubMed
- 4. Foster KH, Kulild JC, Weller RN. Effect of smear layer removal on the diffusion of calcium hydroxide through radicular dentin. J Endod. 1993;19: 136-140.ArticlePubMed
- 5. White RR, Goldman M, Lin PS. The influence of the smeared layer upon dentinal tubule penetration by plastic filling materials. J Endod. 1984;10: 558-562.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Okşan T, Aktener BO, Sen BH, Tezel H. The penetration of root canal sealers into dentinal tubules. Int Endod J. 1993;26: 301-305.PubMed
- 7. Economides N, Liolios E, Kolokuris I, Beltes P. Long-term evaluation of the influence of smear layer removal on the sealing ability of different sealers. J Endod. 1999;25: 123-125.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Lee JM, Park SH, Choi KW. The Effect of Smear Layer Treatment on the Microleakage. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006;31: 378-389.Article
- 9. Johnson WT, Gutmann JL. In: Cohen S, Hargreaves KM, editors. Obturation of the cleaned and shaped root canal system. Pathways of the Pulp. 2005;9th edn. St Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier; 358-399.Article
- 10. Shahravan A, Haghdoost AA, Adl A, Rahimi H, Shadifar F. Effect of smear layer on sealing ability of canal obturation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endod. 2007;33: 96-105.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Lester KS, Boyde A. Scanning electron microscopy of instrumented, irrigated and filled root canals. Br Dent J. 1977;143: 359-367.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Hulsmann N, Heckendorff M, Lennon A. Chelating agents in root canal treatment: mode of action and indications for their use. Int Endod J. 2003;36: 810-830.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Zehnder M, Schmidlin P, Sener B, Waltimo T. Chelation in root canal therapy reconsidered. J Endod. 2005;31: 817-820.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Grawehr M, Sener B, Waltimo T, Zehnder M. Interaction of ethylenediamine tetracetic acid with sodium hypochlorite in aqueous solutions. Int Endod J. 2003;36: 411-415.PubMed
- 15. Baumgartner JC, Marder CL. A scanning electron microscopic evaluation of four root canal irrigation regimens. J Endod. 1987;13: 147-157.ArticlePubMed
- 16. De-Deus G, Zehnder M, Reis C, Fidel S, Fidel RA, Galan J Jr, Paciornik S. Longitudinal co-site optical microscopy study on the chelating ability of etidronate and EDTA using a comparative single-tooth model. J Endod. 2008;34: 71-75.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Ari H, Erdemir A, Belli S. Evaluation of the effect of endodontic irrigation solution on the microhardness and the roughness of root canal dentin. J Endod. 2004;30: 792-795.PubMed
- 18. De-Deus G, Namen F, Galan J Jr, Zehnder M. Soft chelating irrigation protocol optimizes bonding quality of Resilon/Epiphany root fillings. J Endod. 2008;34: 703-705.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Russell RG, Gogers MJ. Bisphosphonates: from the laboratory to the clinic and back again. Bone. 1999;25: 97-106.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Xu Q, Fan MW, Fan B, Cheung GS, Hu HL. A new quantitative method using glucose for analysis of endodontic leakage. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99: 107-111.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Shemesh H, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. Leakage along apical root fillings with and without smear layer usting two different leakage models: a two-month longitudinal ex vivo study. Int Endod J. 2006;39: 968-976.PubMed
- 22. Wu MK, Wesselink PR. Endodontic leakage studies reconsidered. Part I. Methodology, Application and relevance. Int endod J. 1993;26: 37-43.ArticlePubMed
- 23. AliGhamdi A, Wennberg A. Testing of sealing ability of endodontic filling materials. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1994;10: 249-255.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Pommel L, Camps J. Effects of pressure and measurement time on the fluid filtration method in endodontics. J Endod. 2001;27: 256-258.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Rao P, Pattabiraman TN. Reevaluation of the phenol-sulfuric acid reaction for the estimation of hexoses and pentoses. Anal Biochem. 1989;181: 18-22.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Eldeniz AU, Erdemir A, Belli S. Shear bond strengths of three resin based sealers to dentin with and without the smear layer. J Endod. 2005;31: 293-296.PubMed
- 27. Behrend GD, Cutler CW, Gutmann JL. An in-vitro study of smear layer removal and microbial leakage along root-canal fiilings. Int Endod J. 1996;29: 99-107.PubMed
- 28. De-Deus G, Soares J, Leal F, Luna AS, Fidel S, Fidel RA. Similar glucose leakage pattern on smear-covered, EDTA-treated and BioPure MTAD-treated dentin. J Endod. 2008;34: 459-462.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Park DS. The effect of MTAD on the apical leakage of obturated root canals: an electrochemical study. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006;31: 119-124.Article
- 30. Shemesh H, Wu M-K, Wesselink PR. Leakage along apical root fillings with and without smear layer using two different leakage models:a two-month longitudinal ex vivo study. Int Endod J. 2006;39: 968-976.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Calt S, Serper A. Smear layer removal by EGTA. J Endod. 2000;26: 459-461.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Eldeniz AU, Erdemir A, Belli S. Effect of EDTA and citric acid solutions on the microhardness and the roughness of human root canal dentin. J Endod. 2005;31: 107-110.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Schwartz R. Adhesive dentistry and endodontics. Part 2: Bonding in the root canal system-The promise and the problems: A review. J Endod. 2006;32: 1125-1134.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Pashley DH, Tay FR, Yiu C, Hashimoto M, Breschi L, Carvalho RM, Ito S. Collagen degradation by host-derived enzymes during aging. J Dent Res. 2004;83: 216-221.PubMed
- 35. Eldeniz AU, Erdemir A, Belli S. Shear bond strength of three resin based sealers to dentin with and without the smear layer. J Endod. 2005;31: 293-296.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Mamootil K, Messer HH. Penetration of dentinal tubules by endodontic sealer cements in extracted teeth and in vivo. Int endod J. 2007;40: 873-881.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Tay FR, Hosoya Y, Loushine RJ, Pashley DH, Weller RN. Ultrastructure of intraradicular dentin after irrigation with BioPure MTAD. II. The consequence of obturation with an epoxy resin-based sealer. J Endod. 2006;32: 473-477.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 335. CrossRef
Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
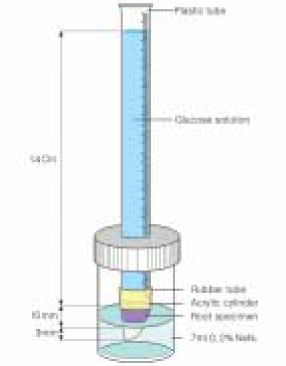
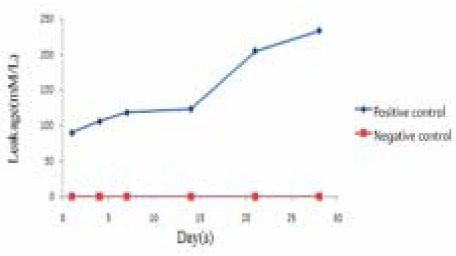
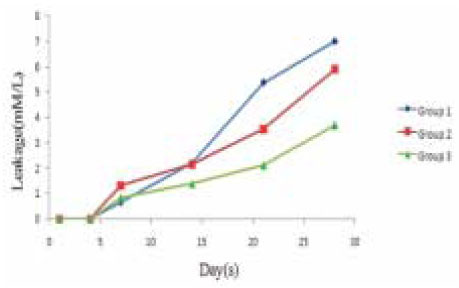
Figure 1
Glucose leakage model.
Figure 2
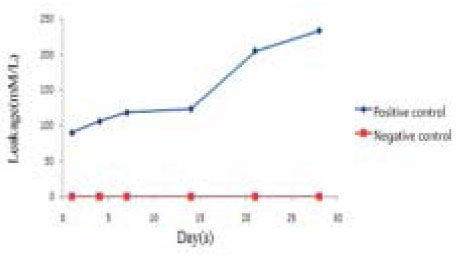
Leakage of positive and negative control groups.
Figure 3
Glucose microleakage of experimental groups.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
Microleakage of glucose in experimental groups (mM/L)
Table 1
Microleakage of glucose in experimental groups (mM/L)

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

