Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Determination of optimal horizontal beam angulations for canal separation in mandibular molars using cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective image-based analysis
- Benedikt Schneider, Tamina Tepe, Daniel Rapp, Wilhelm Frank, Maria Lessani, Constantin von See, Sebastian Fitzek, Jörg Philipp Tchorz
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e9. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
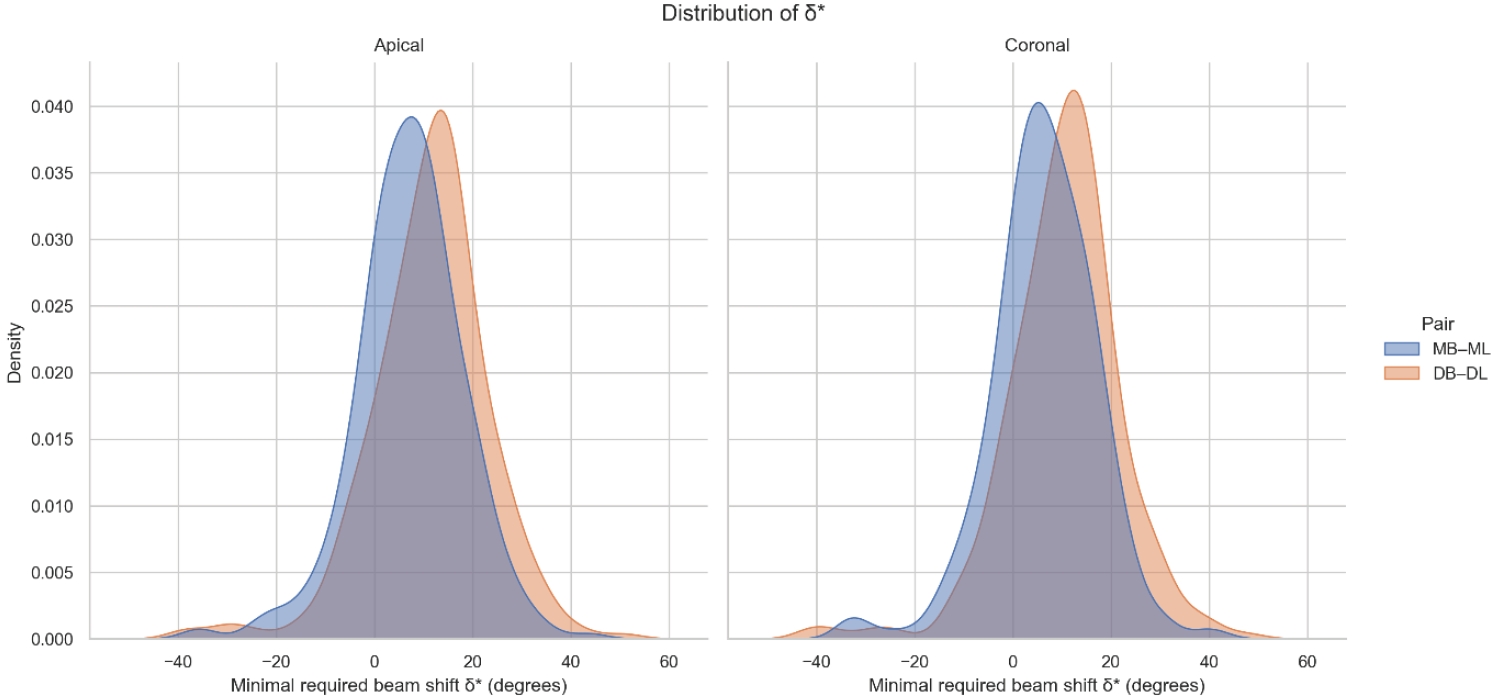
Two-dimensional intraoral radiographs often obscure canals due to superimposition, especially in mandibular molars with complex anatomy. This cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) study identified the horizontal beam angles at which first and second molar canals overlap and derived clinically applicable angulations for enhanced canal separation.
Methods
Eighty-five CBCT datasets from 100 patients met the inclusion criteria, yielding 318 mandibular molars (160 first, 158 second). Using ImageJ, absolute horizontal overlap angles (α) were measured to determine the corresponding theoretical separation angles defined as δ* = 90° – α. Separability was modeled across horizontal beam angulation increments from −45° to +45° in five steps, and Wilson’s 95% confidence intervals were computed. Group comparisons used the Mann-Whitney U and independent t-tests (p ≤ 0.05)
Results
Minimal mesial beam angulations for effective canal separability (δ* = 90° − α) ranged from approximately 7° to 15° for mesial roots and approximately 10° to 13° for distal roots. No significant mesial differences were observed between first and second molars (p > 0.30). Distal roots of second molars exhibited significantly higher angulations (p = 0.003 coronal, p < 0.001 apical). Mesial canals achieved ≥95% separability at approximately 25° and ≥99% at approximately 35°; distal canals required approximately 30° and approximately 40°.
Conclusions
A mesial beam angulation of 30° to 35° provides probable canal differentiation in mandibular molars, separating mesial canals in ≥99% and distal canals in ≥95% of cases. This range refines previous recommendations and supports the as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) principle.
- 375 View
- 13 Download

- Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of maxillary premolar canal anatomy: Ahmed’s versus Vertucci’s classifications in a Jordanian cohort
- Raidan Ba-Hattab, Muna M. Shaweesh, Nessrin A. Taha, Elham S. Abu Alhaija
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e11. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
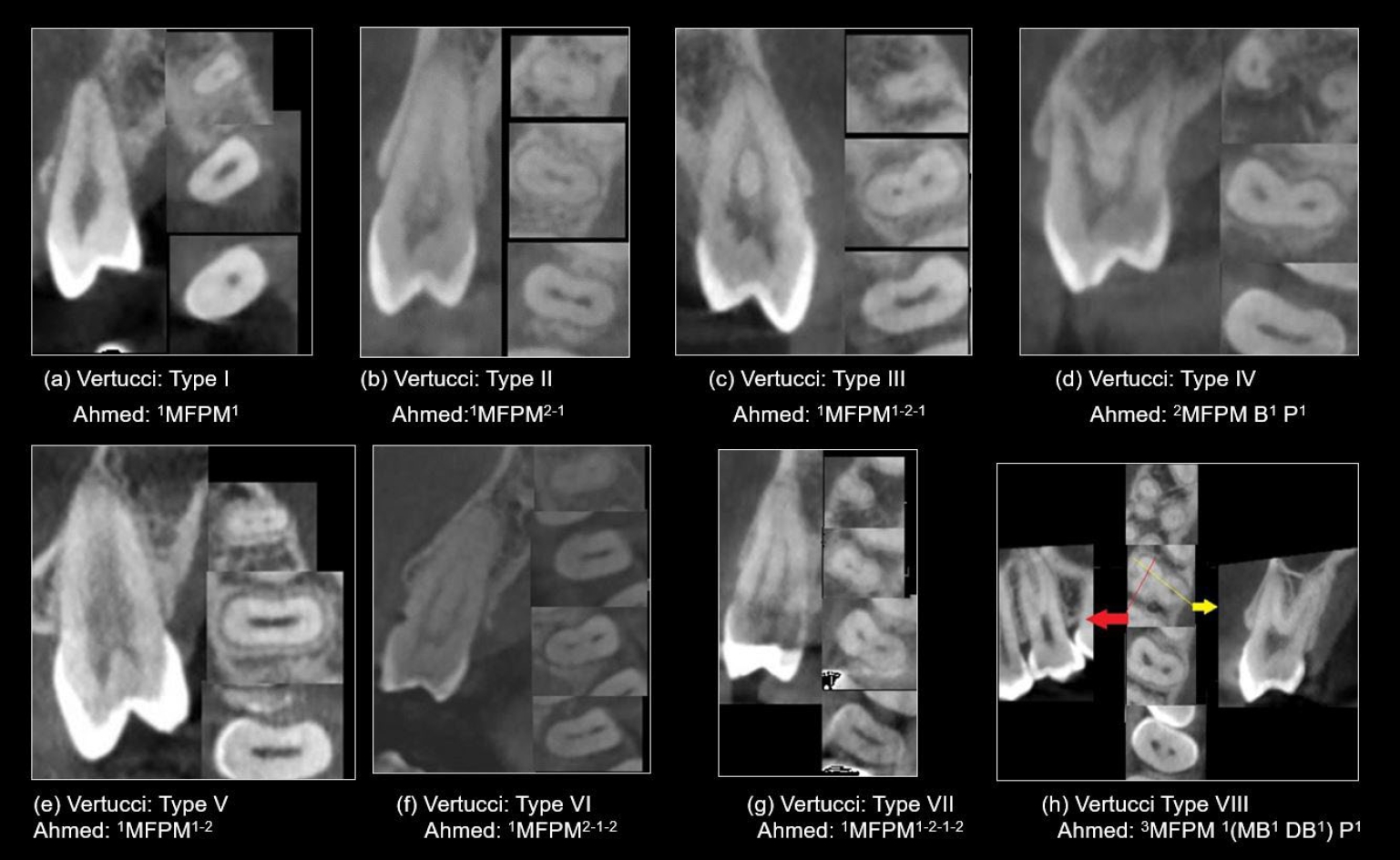
This study analyzed the root and canal configurations of maxillary premolars in a Jordanian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and classified them based on Vertucci’s and Ahmed’s systems.
Methods
Two hundred CBCT scans of 800 maxillary premolars were retrospectively assessed for root morphology, canal configurations, and root canal divergence and merging. Data was statistically analyzed.
Results
The study included 70 males and 130 females. Most right and left maxillary first premolars (RFPM, LFPM) had two roots (59.0% and 58.5%), with a significant association between sex and root number for RFPM and LFPM (p < 0.05). In contrast, the right and left maxillary second premolars (RSPM, LSPM) mostly had a single root (87.5% and 88.5%), with no association with sex. Vertucci’s classification showed type IV as the predominant configuration in first premolars (RFPM, 65.0% and LFPM, 67.0%) and type I in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%). A significant sex association was found only with RSPM. Ahmed’s classification revealed that maxillary premolar with two separated roots and two separated canals (2MP B1 P1) was mostly found in first premolars (RFPM, 58.0% and LFPM, 56.0%), and maxillary premolar with one root and one canal (1MP1) in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%), with a significant sex association for RSPM and LSPM (p < 0.05). Age had no impact, and symmetry was observed between the right and left sides. Three-rooted premolars were identified in four cases. Almost all of Vertucci’s types and numerous codes from Ahmed’s classification were documented.
Conclusions
CBCT revealed diverse anatomical variations in the Jordanian subpopulation, with Ahmed’s classification providing more detailed canal configurations than Vertucci’s, uncovering previously overlooked variations.
- 166 View
- 16 Download

- How protocol, posts, and experience affect fracture detection in multi-rooted teeth using cone-beam computed tomography: an ex vivo experimental study
- Gleica Dal’ Ongaro Savegnago, Gabriela Marzullo de Abreu, Carolina Baumgratz Spiger, Lucas Machado Maracci, Wislem Miranda de Mello, Gabriela Salatino Liedke
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e23. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) acquisition protocol, the presence of intraradicular metal post, and examiner experience on the detection of complete root fractures in multi-rooted teeth.
Methods
Twenty human molar teeth filled with gutta-percha were placed into artificial alveoli created in bovine ribs. The sample was divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of intraradicular posts in the distal roots. CBCT scans were obtained using four acquisition protocols with varying voxel sizes (0.28, 0.2, 0.125, and 0.80 mm). Following the creation of controlled fractures using a chisel and hammer, CBCT imaging was repeated, resulting in 160 images. Five examiners assessed the images using OnDemand software (KaVo Dental GmbH). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were calculated for each examiner, CBCT protocol, and post-condition. Statistical comparisons were performed using Cochran’s Q test and McNemar test, and a significance level of 5%.
Results
In teeth without metallic posts, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy values exceeded 0.70, 0.70, and 0.80, respectively. However, the presence of metallic posts significantly reduced diagnostic performance, particularly in low-resolution protocols evaluated by less-experienced examiners.
Conclusions
CBCT acquisition protocols should be selected based on the presence of metallic posts to optimize root fracture detection in multi-rooted teeth. Examiner experience also plays a critical role in diagnostic accuracy.
- 2,362 View
- 101 Download

- Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
- Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e18. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
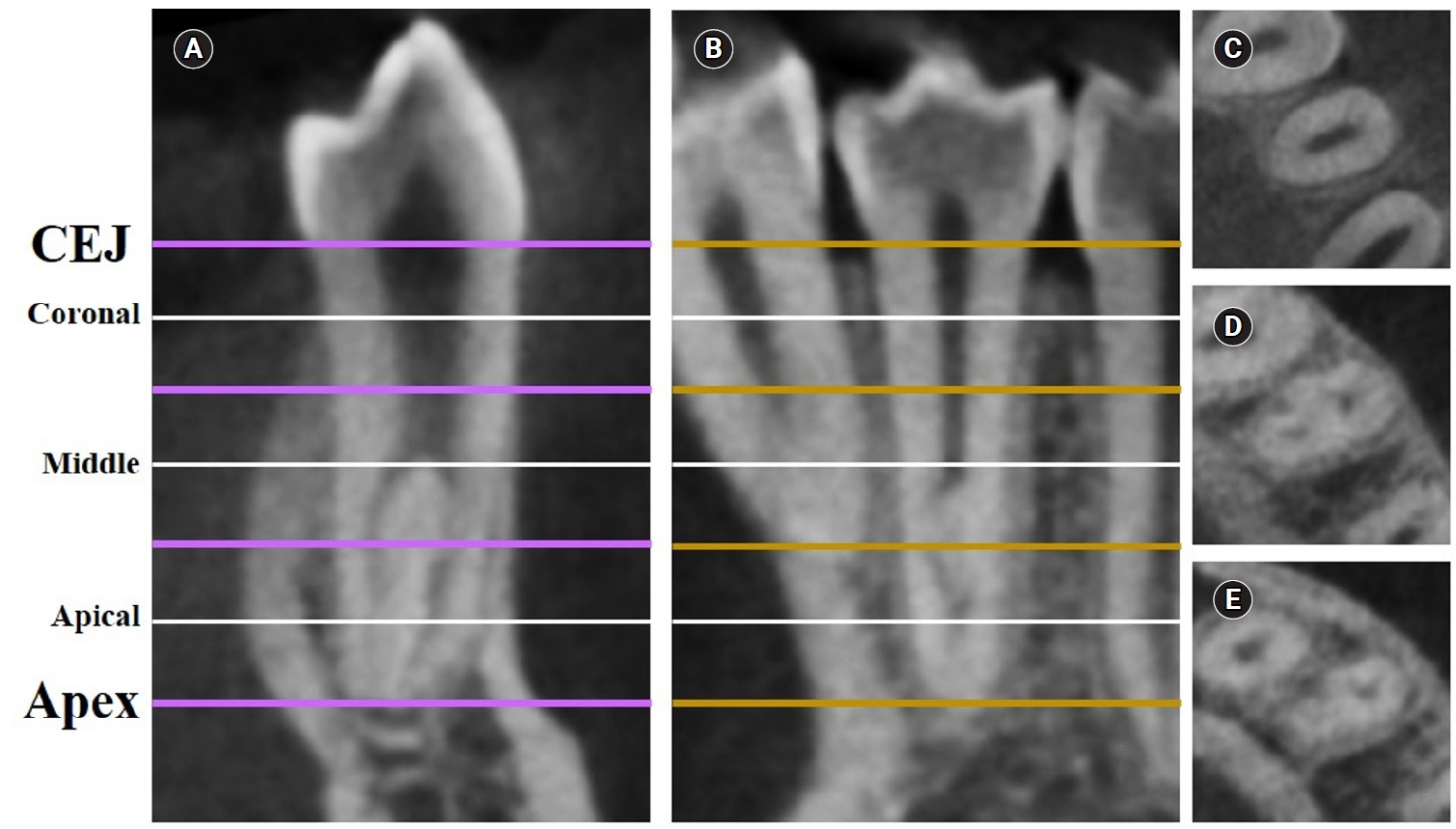
This study aimed to measure the dentin thickness of C-shaped canals in mandibular first and second premolars at coronal, middle, and apical root levels using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Dentin thicknesses of buccal, lingual, mesial, and distal root walls of 41 C-shaped premolars were measured at three different root levels on axial CBCT slices. The measurements were made at the midpoint of each third, along with 1 mm below and above the midpoint. C-shape configurations of the premolar root canals were also recorded. Analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis, and the independent samples t-tests were used for the comparisons (p = 0.05).
Results
The thickest walls for both premolars were buccal and lingual walls at all three root levels (p < 0.05). The thinnest walls for the first premolar teeth were mesial and distal walls of the lingual canal, while it was the mesial end of the buccal and lingual canals for the second premolars (p < 0.05). Dentin wall thicknesses at the mesial end of buccal and lingual canals of C1-shaped first premolars were thinner than C2-shaped first premolars at the apical level (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Danger zones for C-shaped mandibular first and second premolars are predominantly mesial walls facing the radicular groove and distal wall of the lingual canal. CBCT imaging during endodontic treatment is recommended to avoid complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
- 3,556 View
- 135 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

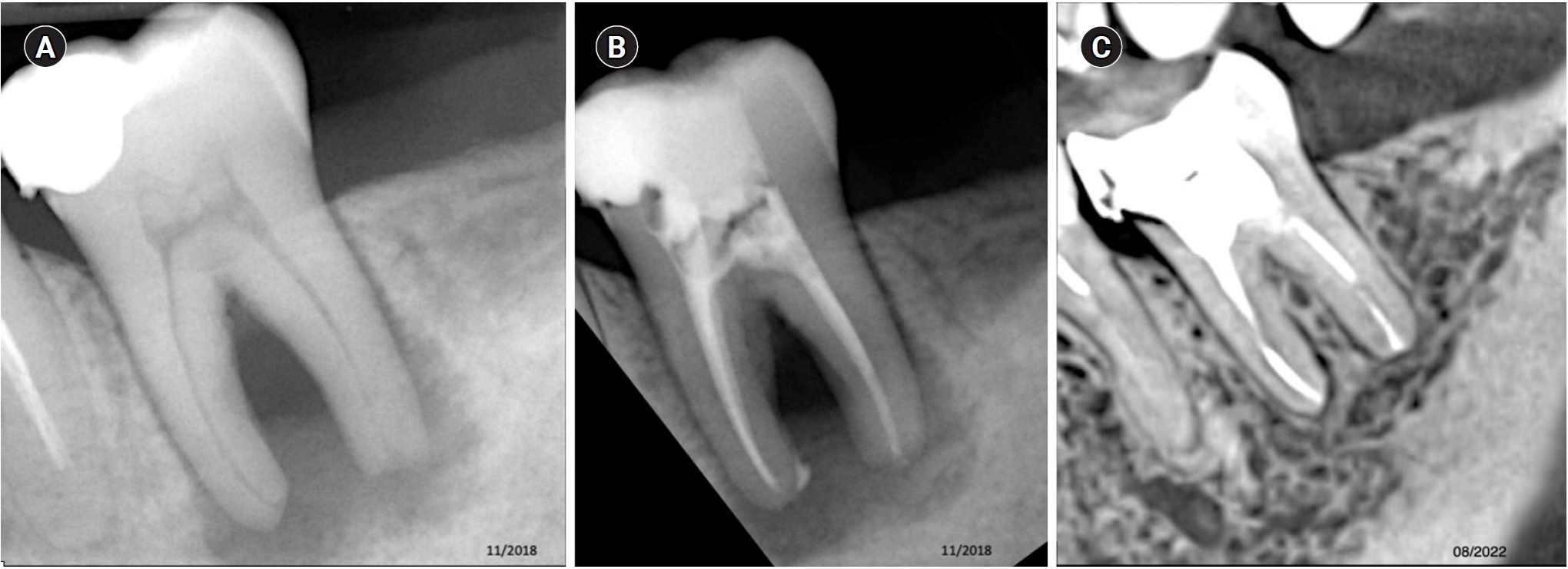
- Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
- Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
- 4,012 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

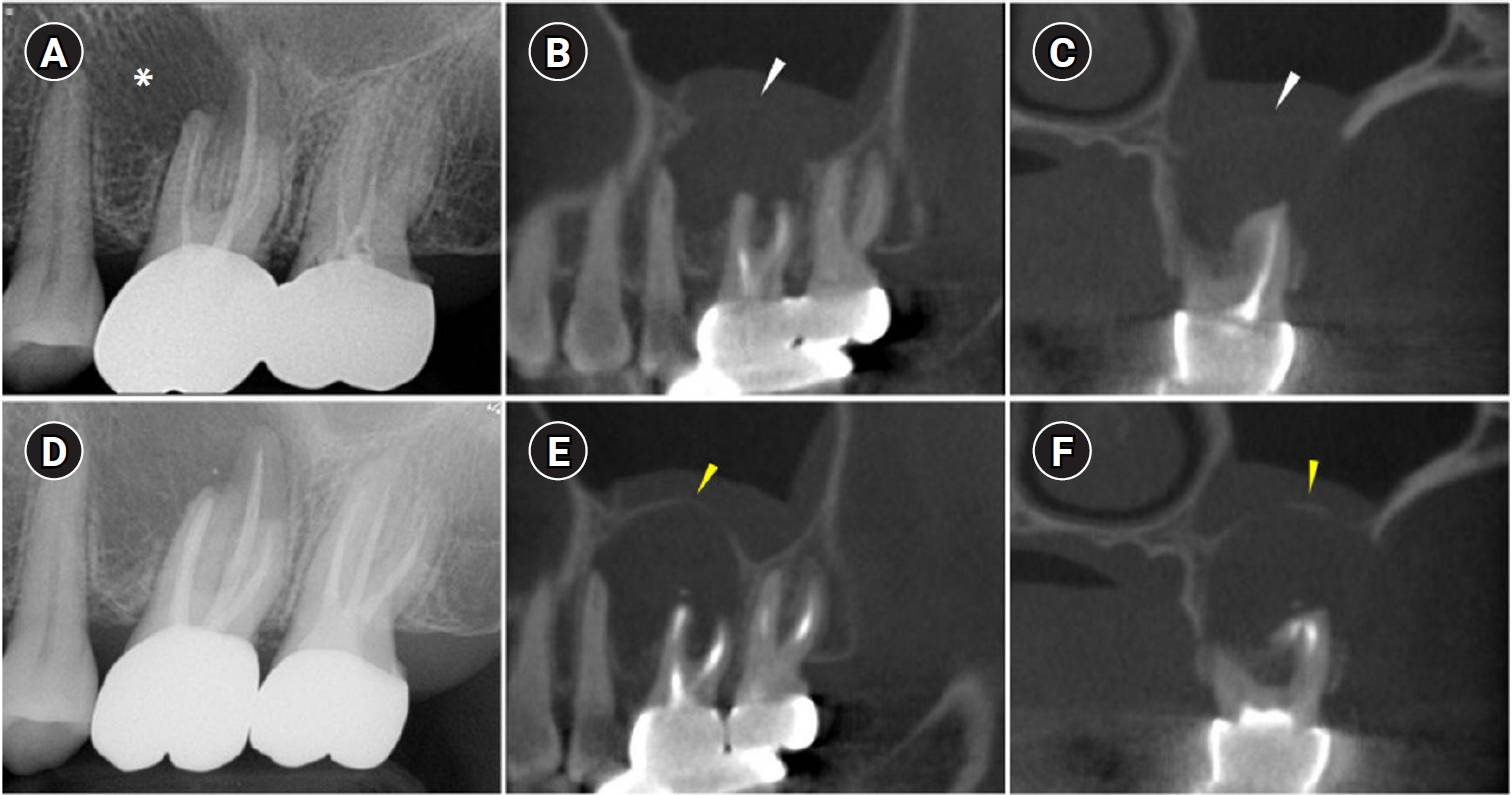
- Surgical management of maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin after reestablishing maxillary sinus floor healing through a nonsurgical approach: a case report
- Eun-Sook Kang, Min-Kyeong Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e12. Published online April 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - When root canal infections breach the maxillary sinus floor (MSF), maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin (MSEO) can result. This case illustrates the surgical management of MSEO following the nonsurgical reestablishment of the MSF. A 55-year-old woman presented with left facial pain and was diagnosed with MSEO originating from the left upper first molar. Despite undergoing nonsurgical root canal treatment, there was no evidence of bony healing after 6 months. However, cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) scans revealed the reestablishment of MSF. Subsequently, surgical intervention was carried out using a dental operating microscope. Two years after surgery, CBCT images indicated that the mucosal edema had resolved, and the MSF was well reestablished. Preserving the MSF is crucial for the success of endodontic surgery. When MSEO is present, the integrity of the MSF must be assessed to determine appropriate treatment options.
- 4,091 View
- 208 Download

- An unusual case of dens invaginatus on a mandibular second molar: a case report
- Davide Mancino, Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Fabien Bornert, Youssef Haïkel
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e2. Published online January 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e2

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - The present case report describes the endodontic treatment of a type III B dens invaginatus (DI) in a three-rooted mandibular second molar since the invagination invades the root and extends apically. Clinical and cone-beam computed tomography examination of the mandibular second molar showed a broadened coronal morphology, DI, a third root, periapical radiolucency, and compression of a distal root canal by the invagination, which developed an atypical semilunar shape. The tooth was diagnosed with pulpal necrosis, symptomatic apical, and peri-invagination periodontitis. Consequently, three-dimensional virtual reconstruction was conducted to improve anatomical interpretation and case planning and accelerate the intraoperative phase by reducing operator stress and minimizing intraoperative variables. The present case report aims to raise awareness of the existence of DI on the mandibular second molar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dens Invaginatus—Mandibular Second Molar—Case Report
Krystyna Pietrzycka, Natalia Lutomska, Cornelis H. Pameijer, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(1): 27. CrossRef - Type IIIb dens invaginatus in a maxillary second molar and its microscopic anatomical features: a case report
Mingming Li, Zhiwu Wu, Shaoying Duan, Yuling Zuo
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dens Invaginatus—Mandibular Second Molar—Case Report
- 3,289 View
- 238 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

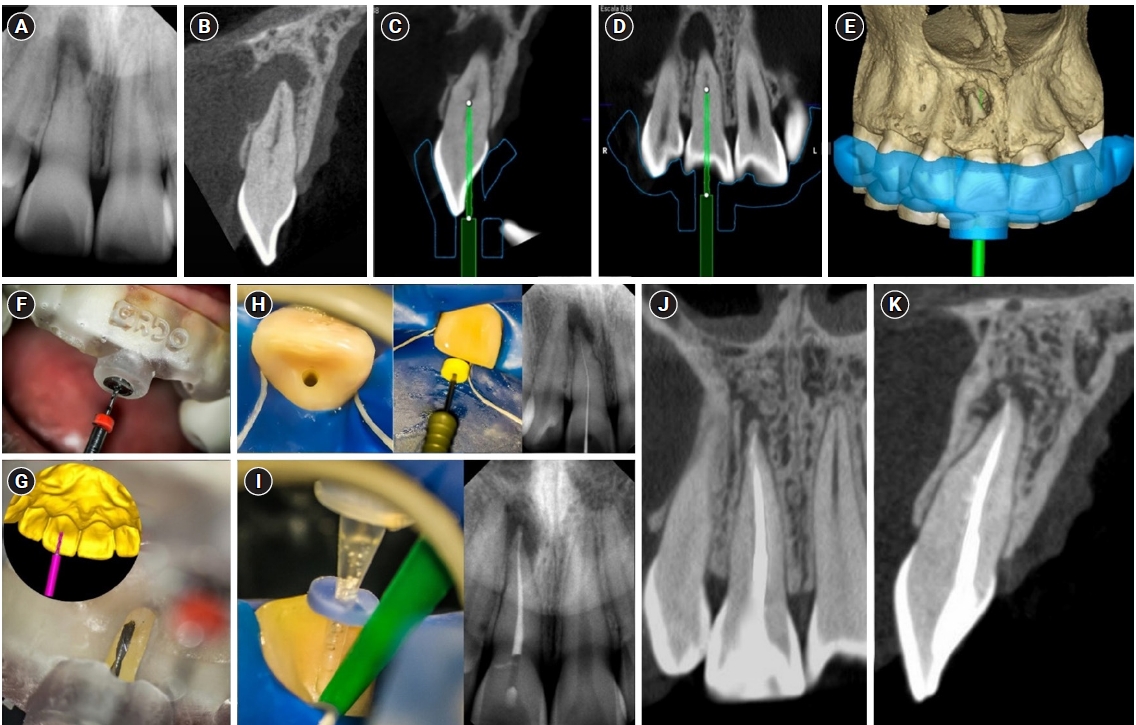
- Guided endodontics, precision and predictability: a case series of mineralized anterior teeth with follow-up cone-beam computed tomography
- Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Javier Rojas-Gutierrez, Pamela Mejía, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Néstor Ríos-Osorio
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e4. Published online January 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Pulp chamber and root canal obliteration (PCO/RCO) presents a challenge for clinicians when nonsurgical endodontic treatment is indicated. Guided endodontics (GE) aims to precisely locate the root canal (RC) system while preserving as much pericervical dentin as possible. GE involves integrating cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) of the affected tooth with a digital impression of the maxillary/mandibular arch, allowing for careful planning of the drilling path to the RC system through a three-dimensional (3D) static guide. This article reports four cases of teeth with PCO/RCO, accompanied by additional diagnoses of internal and external root resorption and horizontal tooth fracture, all successfully treated with GE. These cases highlight the clinical and radiographic success of GE treatments using CBCT, establishing this technique as a predictable approach for managing mineralized teeth.
- 4,121 View
- 339 Download

- Prevalence of apical periodontitis and quality of root canal treatment in an adult Kuwaiti sub-population: a cross-sectional study
- Abdulrahman A. Alhailaa, Saad A Al-Nazhan, Mazen A Aldosimani
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e16. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This cross-sectional study evaluated the prevalence of apical periodontitis (AP) and the technical quality of root canal fillings in an adult Kuwaiti subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Materials and Methods Two experienced examiners analyzed 250 CBCT images obtained from Kuwaiti patients aged 15–65 years who attended government dental specialist clinics between January 2019 and September 2020. The assessment followed the radiographic scoring criteria proposed by De Moor for periapical status and the technical quality of root canal filling. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used for statistical analysis, with significance level set at
p < 0.05.Results Among the 2,762 examined teeth, 191 (6.91%) exhibited radiographic signs of AP, and 176 (6.37%) had undergone root canal filling. AP prevalence in root canal-treated teeth was 32.38%, with a significant difference between males and females. Most of the endodontically treated teeth exhibited adequate root canal filling (71.5%).
Conclusions The study demonstrated a comparable prevalence of AP and satisfactory execution of root canal treatment compared to similar studies in different countries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- RISK FACTORS FOR CHRONIC APICAL PERIODONTITIS ACCORDING TO THE CASE-CONTROL STUDY
N. Bagryantseva
Vrach.2026; : 43. CrossRef - A Retrospective Study of CBCT-Based Detection of Endodontic Failures and Periapical Lesions in a Romanian Cohort
Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Anca Gabriela Gheorghe, Mihaela Jana Țuculină, Maria Cristina Munteanu, Cătălina Alexandra Iacov, Virginia Maria Rădulescu, Mihaela Ionescu, Adina Andreea Mirea, Carina Alexandra Bănică
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6364. CrossRef
- RISK FACTORS FOR CHRONIC APICAL PERIODONTITIS ACCORDING TO THE CASE-CONTROL STUDY
- 4,958 View
- 87 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

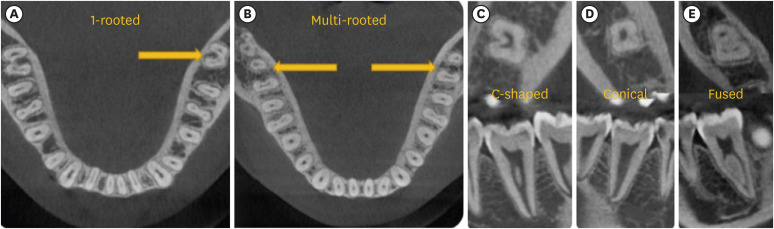
- Predictor factors of 1-rooted mandibular second molars on complicated root and canal anatomies of other mandibular teeth
- Hakan Aydın, Hatice Harorlı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e2. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to determine the effects of 1-rooted mandibular second molar (MnSM) teeth on root canal anatomy complexities of the mandibular central incisor (MnCI), mandibular lateral incisor (MnLI), mandibular canine (MnCn), mandibular first premolar (MnFP), mandibular second premolar (MnSP), and mandibular first molar (MnFM) teeth.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography images of 600 patients with full lower dentition were examined. Individuals with 1-rooted MnSMs were determined, and the complexity of root canal anatomy of other teeth was compared with individuals without 1-rooted MnSMs (Group-1; subjects with at least one 1-rooted MnSM, Group-2; subjects with more than a single root in both MnSMs). A second canal in MnCIs, MnLIs, MnCns, MnFPs, and MnSPs indicated a complicated root canal. The presence of a third root in MnFMs was recorded as complicated.
Results The prevalence of 1-rooted MnSMs was 12.2%, with the C-shaped root type being the most prevalent (9%). There were fewer complicated root canals in MnCIs (
p = 0.02), MnLIs (p < 0.001), and MnFPs (p < 0.001) in Group 1. The other teeth showed no difference between the groups (p > 0.05). According to logistic regression analysis, 1-rooted right MnSMs had a negative effect on having complex canal systems of MnLIs and MnFPs. Left MnSMs were explanatory variables on left MnLIs and both MnFPs.Conclusions In individuals with single-rooted MnSMs, a less complicated root canal system was observed in all teeth except the MnFMs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
Ariana Esperanza Apolo Aguilar, Maria Soledad Peñaherrera Manosalvas, Henry Paul Valverde Haro
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1007. CrossRef
- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
- 1,926 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

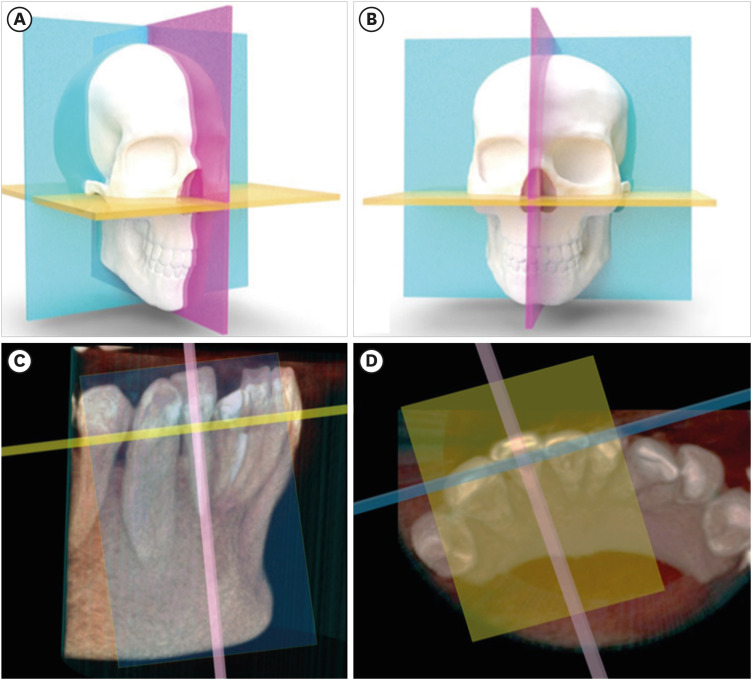
- Cone-beam computed tomography in endodontics: from the specific technical considerations of acquisition parameters and interpretation to advanced clinical applications
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Sara Quijano-Guauque, Sandra Briñez-Rodríguez, Gustavo Velasco-Flechas, Antonieta Muñoz-Solís, Carlos Chávez, Rafael Fernandez-Grisales
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e1. Published online December 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The implementation of imaging methods that enable sensitive and specific observation of anatomical structures has been a constant in the evolution of endodontic therapy. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) enables 3-dimensional (3D) spatial anatomical navigation in the 3 volumetric planes (sagittal, coronal and axial) which translates into great accuracy for the identification of endodontic pathologies/conditions. CBCT interpretation consists of 2 main components: (i) the generation of specific tasks of the image and (ii) the subsequent interpretation report. A systematic and reproducible method to review CBCT scans can improve the accuracy of the interpretation process, translating into greater precision in terms of diagnosis and planning of endodontic clinical procedures. MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, Google Scholar, Embase and Scopus were searched from inception to March 2023. This narrative review addresses the theoretical concepts, elements of interpretation and applications of the CBCT scan in endodontics. In addition, the contents and rationale for reporting 3D endodontic imaging are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
Aishwarya Talakeri, Pravin Kumar, Soundharrajan P, Vinay Kumar Chugh , Rajat Sharma, Arun Patnana
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and morphometric assessment of the middle mesial canal in mandibular first molars in a turkish population: A CBCT study
Elif Solakoğlu, Özge Kurt
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Pathologies in Children and Adolescents with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study
Ayşe Çelik, Nilüfer Ersan, Senem Selvi-Kuvvetli
The Cleft Palate Craniofacial Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - Early diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia utilizing clinical, radiographic, and dental age indicators
Rehab F Ghouraba, Shaimaa S. EL-Desouky, Mohamed R. El-Shanshory, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Nancy M. Metwally
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of apexogenesis with human treated dentin matrix in young permanent molars: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
Nora M. Abo Shanady, Nahed A. Abo Hamila, Gamal M. El Maghraby, Rehab F. Ghouraba
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Integration of Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality in Dental Diagnostics, Surgical Planning, and Education: A Narrative Review
Aida Meto, Gerta Halilaj
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(11): 6308. CrossRef - Healing Outcomes of Through‐And‐Through Bone Defects in Periapical Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Bibi Fatima, Farhan Raza Khan, Syeda Abeerah Tanveer
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 518. CrossRef - Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of cone beam computed tomography on exfoliated epithelial cells in different age groups
Maged Bakr, Fatma Ata, Asmaa Saleh Elmahdy, Bassant Mowafey
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bridging the gap in aberrant root canal systems: Case series
Seethalakshmi Tamizhselvan, Diana Davidson, Srinivasan Manali Ramakrishnan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 833. CrossRef - IMAGING TECHNIQUES IN ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Mihaela Salceanu, Anca Melian , Tudor Hamburda , Cristina Antohi , Corina Concita , Claudiu Topoliceanu , Cristian Levente Giuroiu
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(1): 705. CrossRef - A Three-rooted Deciduous Second Molar in a 13-year-old Caucasian Female
Daniel Traub, Robert Walsh, Colleen Ahern
International Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025; 4(3): 51. CrossRef - Critical success factors for digital transformation in government organizations using a structural model approach
Abdalla Al Maazmi, Zehra Canan Araci, Sujan Piya
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - AGE ESTIMATION BASED ON PULP / TOOTH VOLUME BY CONE BEAM COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGE
Ramadhan Rasheed, Salah Faraj
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 288. CrossRef - Clinical Benefits and Limitations of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontic Practice: A Contemporary Evidence-Based Review
Jasmine Wong, Chengfei Zhang, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3117. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bildgebung im ZMK-Bereich – aber in welcher Reihenfolge?
Rainer Lutz
Zahnmedizin up2date.2024; 18(04): 297. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of shaping ability of kedo-S square and fanta AF™ baby rotary files compared to manual K-files in root canal preparation of primary anterior teeth
Shaimaa S. El-Desouky, Bassem N. El Fahl, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Shimaa M. Hadwa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Endodontic Successes and Failures in the Removal of Fractured Endodontic Instruments during Retreatment: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Corrado Dello Russo, Filippo Scarano, Fariba Esperouz, Andrea Ballini, Diego Sovereto, Mario Alovisi, Angelo Martella, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Healthcare.2024; 12(14): 1390. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
- 16,873 View
- 694 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

-
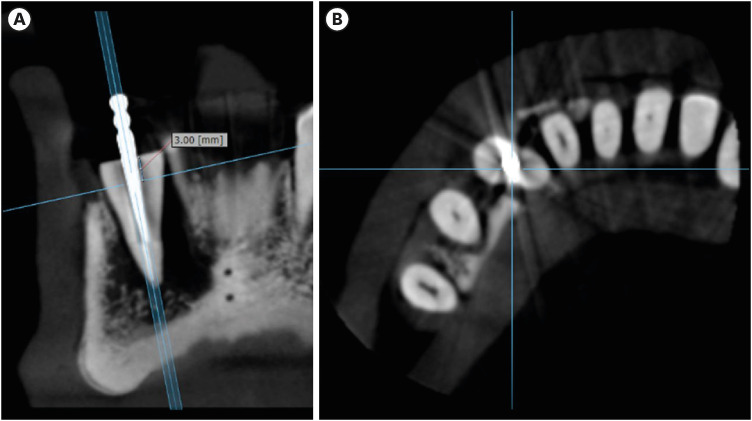
Influence of CBCT parameters on image quality and the diagnosis of vertical root fractures in teeth with metallic posts: an
ex vivo study - Larissa Pereira Lagos de Melo, Polyane Mazucatto Queiroz, Larissa Moreira-Souza, Mariana Rocha Nadaes, Gustavo Machado Santaella, Matheus Lima Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e16. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of peak kilovoltage (kVp) and a metal artifact reduction (MAR) tool on image quality and the diagnosis of vertical root fracture (VRF) in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Materials and Methods Twenty single-rooted human teeth filled with an intracanal metal post were divided into 2 groups: control (
n = 10) and VRF (n = 10). Each tooth was placed into the socket of a dry mandible, and CBCT scans were acquired using a Picasso Trio varying the kVp (70, 80, 90, or 99), and the use of MAR (with or without). The examinations were assessed by 5 examiners for the diagnosis of VRF using a 5-point scale. A subjective evaluation of the expression of artifacts was done by comparing random axial images of the studied protocols. The results of the diagnoses were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and the Tukeypost hoc test, the subjective evaluations were compared using the Friedman test, and intra-examiner reproducibility was evaluated using the weighted kappa test (α = 5%).Results The kVp and MAR did not influence the diagnosis of VRF (
p > 0.05). According to the subjective classification, the 99 kVp protocol with MAR demonstrated the least expression of artifacts, while the 70 kVp protocol without MAR led to the most artifacts.Conclusions Protocols with higher kVp combined with MAR improved the image quality of CBCT examinations. However, those factors did not lead to an improvement in the diagnosis of VRF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital Dentistry Society Quality Forum: Clinical recommendations on cone-beam computed tomography for the digital dentistry workflow
Hugo Gaêta-Araujo, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Reinhilde Jacobs
Digital Dentistry Journal.2026; 3(1): 100065. CrossRef - Photon‐Counting CT for Diagnosing Vertical Root Fractures in Teeth With Metal Posts: An Ex Vivo Comparative Analysis With Four CBCT Devices
Renata M. S. Leal, Fernanda B. Fagundes, Maria F. S. A. Bortoletto, Samuel C. Kluthcovsky, Walter Coudyzer, Bruno C. Cavenago, Reinhilde Jacobs, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele
International Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Iterative Reconstruction of Cone-beam Computed Tomography for Detecting Vertical Root Fractures in the Presence of Metal Artifacts
Matheus Barros-Costa, Gustavo Santaella, Christiano Oliveira-Santos, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, William C. Scarfe, Francisco Carlos Groppo
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(6): 715. CrossRef - Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Laser-Enhanced Disinfection in Endodontic Therapy
Janos Kantor, Sorana Maria Bucur, Eugen Silviu Bud, Victor Nimigean, Ioana Maria Crișan, Mariana Păcurar
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4055. CrossRef - Exploring Diagnostic Reliability of CBCT for Vertical Root Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analytical Approach
Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Adriana Pinto Bezerra, Marcio Correa, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Stefano Corbella
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning for dentomaxillofacial cone-beam computed tomography image quality enhancement: A pilot study
Ali Nazari, Seyed Mohammad Yousef Najafi, Reza Abbasi, Hossein Mohammad-Rahimi, Parisa Motie, Mina Iranparvar Alamdari, Mehdi Hosseinzadeh, Ruben Pauwels, Falk Schwendicke
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2025; 55(3): 271. CrossRef - Diagnostic Accuracy of Intraoral, Extraoral and Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)-Generated Bitewings for Detecting Approximal Caries and Periodontal Bone Loss
Jyoti Mago, Alan G Lurie, Aadarsh Gopalakrishna, Aditya Tadinada
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vertical root fracture diagnosis in teeth with metallic posts: Impact of metal artifact reduction and sharpening filters
Débora Costa Ruiz, Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Amanda Farias-Gomes, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2024; 54(2): 139. CrossRef - Comparing standard- and low-dose CBCT in diagnosis and treatment decisions for impacted mandibular third molars: a non-inferiority randomised clinical study
Kuo Feng Hung, Andy Wai Kan Yeung, May Chun Mei Wong, Michael M. Bornstein, Yiu Yan Leung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital Dentistry Society Quality Forum: Clinical recommendations on cone-beam computed tomography for the digital dentistry workflow
- 3,211 View
- 53 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

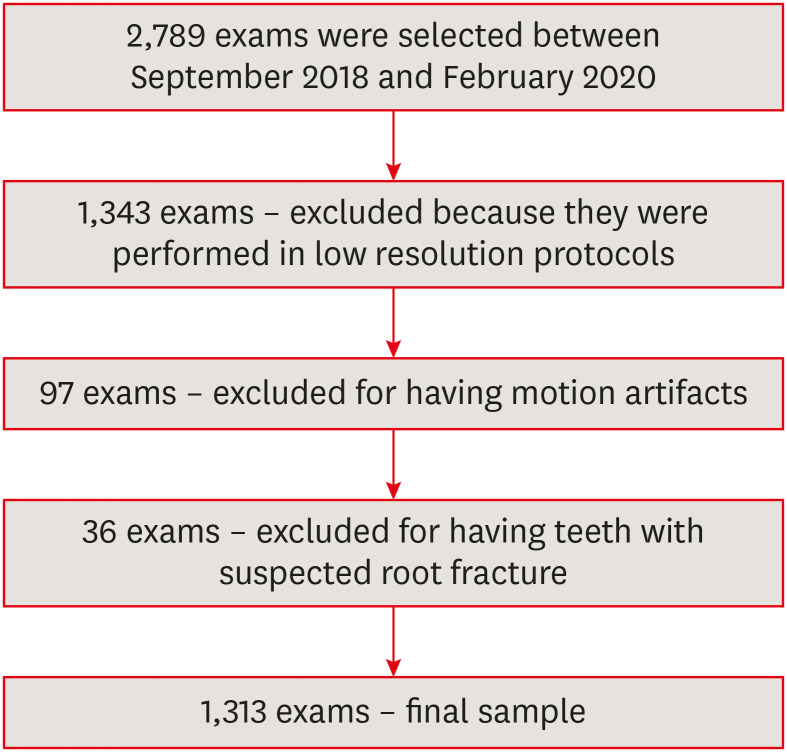
- The prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption based on cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: a cross-sectional study
- Matheus Diniz Ferreira, Matheus Barros-Costa, Felipe Ferreira Costa, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e39. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption (ECR) regarding sex, age, tooth, stages of progression, and portal of entry, using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
Materials and Methods CBCT scans of 1,313 patients from a Brazilian subpopulation comprising 883 female and 430 male patients (mean age, 55.2 years), acquired using a PreXion 3D CBCT unit, were evaluated. All permanent teeth included in the scans were evaluated for the presence of ECR according to the 3-dimensional classification and the portal of entry. The association between the presence of ECR and the factors studied was assessed using the χ2 test. Intra-observer agreement was analyzed with the kappa test (
α = 0.05).Results In total, 6,240 teeth were analyzed, of which 84 (1.35%) were affected by ECR. A significant association was found between the presence of ECR and sex, with a higher prevalence in male patients (
p = 0.002). The most frequently affected teeth were the mandibular and maxillary central incisors. The most common height was the mid-third of the root. For the portal of entry, 44% of cases were on the proximal surfaces, 40.5% on the lingual/palatal surface and 15.5% on the buccal surface. Intra-observer agreement was excellent.Conclusions The prevalence of ECR was 1.35%, with a higher prevalence in male patients and a wide age distribution. The mandibular and maxillary central incisors were the most commonly affected teeth, and cases of ECR most frequently showed a height into the mid-third of the root and proximal entry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
Terrell F. Pannkuk
Dental Traumatology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prise en charge des lésions cervicales
C. Mocquot, L. Detzen, I. Fontanille, B. Orlik, F. Decup
EMC - Médecine buccale.2025; 18(3): 1. CrossRef - Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characterization of External Cervical Resorption Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Isadora Carneiro Pereira Machado, Marilia Oliveira Morais, Adriana Lustosa Pereira Bicalho, Patricia Helena Pereira Ferrari, Juliano Martins Bueno, José Luiz Cintra Junqueira, Mariana Quirino Silveira Soares
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 164. CrossRef - Influence of tube current and metal artifact reduction on the diagnosis of external cervical resorption in teeth adjacent to a dental implant in CBCT: an ex-vivo study
Thamiles Gonzalez-Passos, Matheus Barros-Costa, Matheus L Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maxillary anterior teeth with extensive root resorption treated with multidisciplinary approach: A case report
Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho, Carollyne Souza Campello, Juliana Pires Abdelnur, Vivian Ronquete, Carlos Henrique Sardenberg Pereira, Marilia F Marceliano-Alves
International Journal of Case Reports and Images.2023; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic features of external cervical resorption – An observational study
Shanon Patel, Francesc Abella, Kreena Patel, Paul Lambrechts, Nassr Al‐Nuaimi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(12): 1475. CrossRef
- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
- 3,719 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

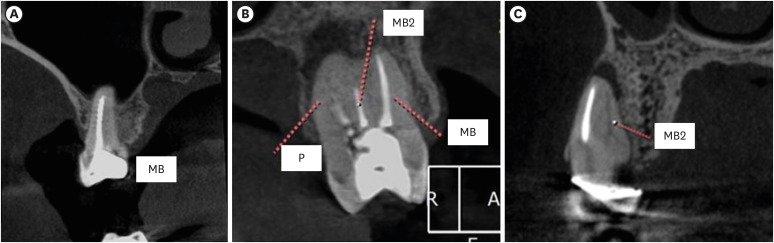
- Apical periodontitis in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: influence of anatomy and quality of root canal treatment, a CBCT study
- Samantha Jannone Carrion, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e37. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of apical periodontitis (AP) in the mesiobuccal roots of root canal-treated maxillary molars.
Materials and Methods One thousand cone-beam computed tomography images of the teeth were examined by 2 dental specialists in oral radiology and endodontics. The internal anatomy of the roots, Vertucci’s classification, quality of root canal treatment, and presence of missed canals were evaluated; additionally, the correlation between these variables and AP was ascertained.
Results A total of 1,000 roots (692 first molars and 308 second molars) encompassing 1,549 canals were assessed, and the quality of the root canal filling in the majority (56.9%) of the canals was satisfactory. AP was observed in 54.4% of the teeth. A mesiolingual canal in the mesiobuccal root (MB2 canal) was observed in 54.9% of the images, and the majority (83.5%) of these canals were not filled. Significant associations were observed between the presence of an MB2 canal and the quality of the root canal filling and the presence of AP.
Conclusions AP was detected in more than half of the images. The MB2 canals were frequently missed or poorly filled.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical Configuration of the MB2 Canal Using High-Resolution Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Luciana Magrin Blank-Gonçalves, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Monikelly do Carmo Chagas Nascimento, Ana Grasiela Limoeiro, Luiz Roberto Coutinho Manhães-Jr
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(5): 609. CrossRef - The Effect of Age and Gender on the Distance Between the Maxillary Sinus Cortical Bone and Maxillary Molars: A Cone-Beam Tomography Analysis
Thaysa Menezes Constantino, Marília Fagury Videira Marceliano-Alves, Vivian Ronquete, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Pablo Andres Amoroso-Silva, Mariano Simon Pedano, Tchilalo Boukpessi, Fábio Vidal, Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho
Sinusitis.2025; 9(1): 9. CrossRef - Retrospective study of the morphology of third maxillary molars among the population of Lower Silesia based on analysis of cone beam computed tomography
Anna Olczyk, Barbara Malicka, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299123. CrossRef - Relationship between apical periodontitis and missed canals in mesio-buccal roots of maxillary molars: CBCT study
Badi B. Alotaibi, Kiran I. Khan, Muhammad Q. Javed, Smita D. Dutta, Safia S. Shaikh, Nawaf M. Almutairi
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2024; 19(1): 18. CrossRef - APICAL PERIODONTITIS IN MAXILLARY MOLARS WITH MISSED SECOND MESIO-BUCCAL ROOT CANAL: A CBCT STUDY
Cristina Coralia Nistor, Ioana Suciu , Ecaterina Ionescu , Anca Dragomirescu , Elena Coculescu , Andreea Baluta
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(3): 100. CrossRef - Anatomic Comparison of Contralateral Maxillary Second Molars Using High-Resolution Micro-CT
Ghassan Dandache, Umut Aksoy, Mehmet Birol Ozel, Kaan Orhan
Symmetry.2023; 15(2): 420. CrossRef
- Anatomical Configuration of the MB2 Canal Using High-Resolution Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
- 3,407 View
- 51 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

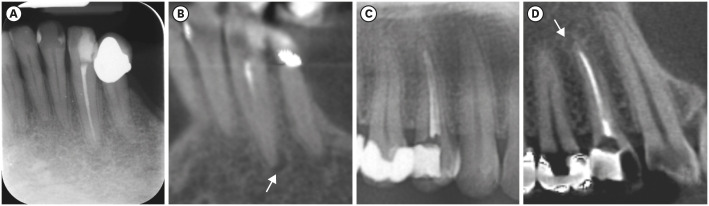
- Which factors related to apical radiolucency may influence its radiographic detection? A study using CBCT as reference standard
- Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Eduarda Helena Leandro Nascimento, Hugo Gaêta-Araujo, Laís Oliveira de Araujo Cardelli, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e43. Published online July 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the detection rate of apical radiolucencies in 2-dimensional images using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) as the reference standard, and to determine which factors related to the apical radiolucencies and the teeth could influence its detection.
Materials and Methods The sample consisted of exams of patients who had panoramic (PAN) and/or periapical (PERI) radiography and CBCT. The exams were assessed by 2 oral radiologists and divided into PAN+CBCT (227 teeth–285 roots) and PERI+CBCT (94 teeth–115 roots). Radiographic images were evaluated for the presence of apical radiolucency, while CBCT images were assessed for presence, size, location, and involvement of the cortical bone (thinning, expansion, and destruction). Diagnostic values were obtained for PERI and PAN.
Results PERI and PAN presented high accuracy (0.83 and 0.77, respectively) and specificity (0.89 and 0.91, respectively), but low sensitivity, especially for PAN (0.40 vs. 0.65 of PERI). The size of the apical radiolucency was positively correlated with its detection in PERI and PAN (
p < 0.001). For PAN, apical radiolucencies were 3.93 times more frequently detected when related to single-rooted teeth (p = 0.038). The other factors did not influence apical radiolucency detection (p > 0.05).Conclusions PERI presents slightly better accuracy than PAN for the detection of apical radiolucency. The size is the only factor related to radiolucency that influences its detection, for both radiographic exams. For PAN, apical radiolucency is most often detected in single-rooted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiomics-based classification of pediatric dental trauma in periapical radiographs: a preliminary study
Mengtian Peng, Bin Yu, Juan Hu, Xiaoxin Xie, Jihong He
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Diagnostic Acumen in Endodontics
Shilpa Thakkar, Dana Mominkhan
Dental Clinics of North America.2025; 69(4): 479. CrossRef - Three-dimensional clinical assessment for MRONJ risk in oncologic patients following tooth extractions
Catalina Moreno Rabie, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Nicolly Oliveira Santos, Fernanda Nogueira Reis, Tim Van den Wyngaert, Reinhilde Jacobs
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of techniques used to assess clinical outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment in necrotic mature teeth
Roy George
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022; 23(3): 98. CrossRef
- Radiomics-based classification of pediatric dental trauma in periapical radiographs: a preliminary study
- 2,938 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

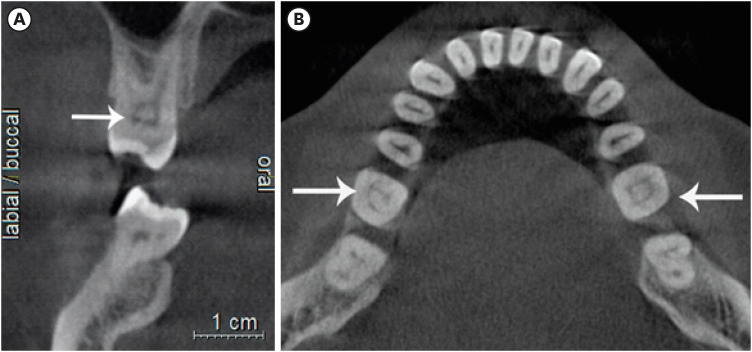
- Evaluation of the relation between the pulp stones and direct restorations using cone beam computed tomography in a Turkish subpopulation
- Güzide Pelin Sezgin, Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e34. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the presence of pulp stones through an examination of cone beam computed tomography images and correlate their prevalence with age, sex, dental arch and side, tooth type, and restoration type and depth.
Materials and Methods Cone beam computed tomography images obtained from 673 patients and archival data on 11,494 teeth were evaluated. The associations of pulp stones with age, sex, dental arch and side, tooth type, and restoration type and depth were noted. All the measurements were subjected to a χ2 test and one sample χ2 test (
p < 0.05).Results In the study group, 163 (24.2%) patients and 379 (3.3%) teeth had at least one pulp stone. The pulp stone frequency in those aged 30–39 years was significantly greater than in those aged 18–29 and ≥ 60 years, and the frequency was higher in females than in males (
p < 0.05). The highest prevalence of pulp stones was found in maxillary dental arches and molar teeth (p < 0.05). Pulp stones were significantly more common in medium-depth restorations (p < 0.05).Conclusions Maxillary molar teeth, medium-depth restorations, individuals aged 30–39 years and females had a greater percentage of pulp stones.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Assessment of the Prevalence and Association of Pulp Calcification with Dental and Periodontal Pathology: A Descriptive Study
José Luis Sanz, Lucía Callado, Stefana Mantale, Jenifer Nicolás, James Ghilotti, Carmen Llena
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(4): 1373. CrossRef - Prevalence of mineralization in the pulp chamber in patients according to CBCT data
V. A. Molokova, I. N. Antonova, V. A. Osipova
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(2): 188. CrossRef - Could carotid artery calcifications and pulp stones be an alarm sign for diabetes mellitus? A retrospective observational study
Motahare Baghestani, Mohadese Faregh, Seyed Hossein Razavi, Fatemeh Owlia
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution and influencing factors of pulp stones based on CBCT: a retrospective observational study from southwest China
Wantong Zhang, Yao Wang, Lin Ye, Yan Zhou
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Association of Calcified Pulp Stones with Periodontitis: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study in Saudi Arabian Population
Abdullah Saad Alqahtani
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S644. CrossRef - The Prevalence And Distribution Of Pulp Stones: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study İn A Group Of Turkish Patients
Mujgan Firincioglulari, Seçil Aksoy, Melis Gülbeş, Umut Aksoy, Kaan Orhan
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 13(3): 496. CrossRef - Radiographical examination of pulp stone distribution by cone beam computed tomography
Fatma Tunç, Emre Çulha, Muazzez Naz Baştürk
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2024; 7(4): 472. CrossRef - Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Based Investigation of the Prevalence and Distribution of Pulp Stones and Their Relation to Local and Systemic Factors in the Makkah Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Laila M Kenawi, Haytham S Jaha, Mashael M Alzahrani, Jihan I Alharbi, Shahad F Alharbi, Taif A Almuqati, Rehab A Alsubhi, Wahdan M Elkwatehy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone beam computed tomography assessment of the prevalence and association of pulp calcification with periodontitis
Lingling Xiang, Botao Wang, Yuan Zhang, Jintao Wang, Peipei Wu, Jian Zhang, Liangjun Zhong, Rui He
Odontology.2023; 111(1): 248. CrossRef - Three-dimensional analysis for detection of pulp stones in a Saudi population using cone beam computed tomography
Hassan H. Kaabi, Abdullah M. Riyahi, Nassr S. Al-Maflehi, Saleh F. Alrumayyan, Abdullah K. Bakrman, Yazeed A. Almutaw
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 257. CrossRef
- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Assessment of the Prevalence and Association of Pulp Calcification with Dental and Periodontal Pathology: A Descriptive Study
- 2,245 View
- 26 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

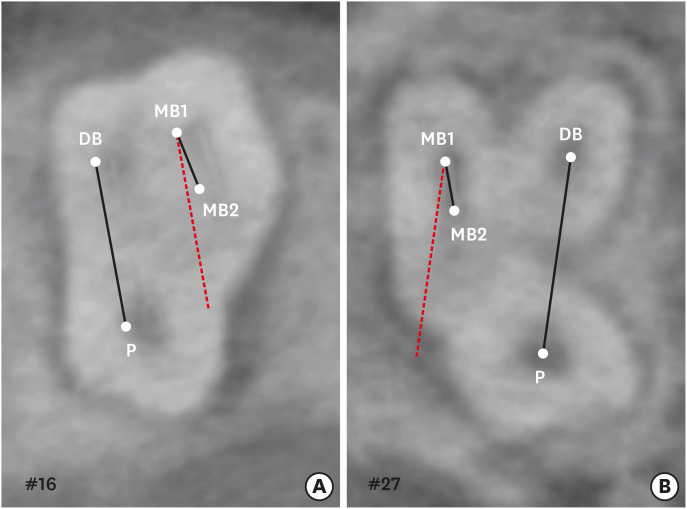
- A cone-beam computed tomography study of the prevalence and location of the second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars
- Seong-Ju Lee, Eun-Hye Lee, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e46. Published online September 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e46
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the incidence and location of the second mesiobuccal root (MB2) canal in maxillary molars with the aid of various measuring points and lines using cone-beam computed tomography (CT).
Materials and Methods A total of 205 images of patients who underwent cone-beam CT examinations between 2011 and 2015 as part of their dental diagnosis and treatment were included. There were 76 images of the maxillary first molar and 135 images of the maxillary second molar. Canal orifices were detected at −1 mm from the top of the pulpal floor on cone-beam CT images. Image assessment was performed by 2 observers in reformatted image planes using software. Assessments included measurement of the distance between the MB1 and MB2 canals, and the angles between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and distobuccal (DB)-palatal (P) canals. The data were analyzed using the student's
t -test.Results The prevalence of the MB2 canal was 86.8% in the first molar and 28.9% in the second molar. The angle between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and DB-P canals was 2.3° ± 5.7° in the first molar and −3.95° ± 7.73° in the second molar. The distance between the MB1 and MB2 canals was 2.1 ± 0.44 mm in the first molar and 1.98 ± 0.42 mm in the second molar.
Conclusions The angles between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and DB-P canals was almost parallel. These findings may aid in the prediction of the location of the MB2 canal orifice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Position of Second Mesiobuccal Canal Relative to Distobuccal and Palatal Canals of Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population
Sina Mosadeghian, Azadeh Torkzadeh, Parisa Ranjbarian, Roya Asaadi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - EVALUATION OF THE PREVALENCE AND LOCATION OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANALS IN 2100 UPPER FIRST AND SECOND MOLAR TEETH: A CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY STUDY
Bahar Kaplan, Özkan Adıgüzel, Ayşe Gül Öner Talmaç, Elif Meltem Aslan
İnönü Üniversitesi Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi.2025; 13(3): 752. CrossRef - A novel method for the precise second mesiobuccal canal orifice location: A combined strategy for enhanced clinical practice
Yuhan Wang, Lingyun Li, Lu Zhang, Xiaoyan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the Geometric Location Method of the Danger Zone in the Mesial Roots of Mandibular First Molars
Jinjie Yan, Yuanling Peng, Jing Yang, Jie Liu, Linxian Wang, Tingyuan Zhao, Jian Zhang, Kehua Que
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Correlation between Intraorifice Distance and the Anatomical Characteristics of the Second Mesiobuccal Canal of Maxillary Molars: A CBCT Study
Isabella Perondi, Silvio Taschieri, Martino Baruffaldi, Roberto Fornara, Luca Francetti, Stefano Corbella, Deepa Gurunathan
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of type I maxillary first molar with two palatal roots using cone-beam computed tomography
Nuha Alghamdi
Dental Journal.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - 3D geometric analysis of second mesiobuccal canal in permanent maxillary first molar tooth
Indrani Khadilkar, Divya Nangia, Amrita Chawla, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Shalini Gupta, Ajay Logani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 140. CrossRef - Prevalence of mesiobuccal-2 canals in maxillary first and second molars among the Bruneian population—CBCT analysis
Hui Yi Onn, Malissa Siao Yun Abdullah Sikun, Hanif Abdul Rahman, Jagjit Singh Dhaliwal
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Location angle of second mesio-buccal canal in maxillary molars of an Indian population: an in vivo retrospective CBCT evaluation and proposal of a new classification
Kishor Vhorkate, Kulvinder Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Shugufta Mir, Suraj Arora, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Anuj Bhardwaj, Alexander Maniangat Luke
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14234. CrossRef - Maxillary molar root and canal morphology of Neolithic and modern Chinese
H.Y. Ren, K.Y. Kum, Y.S. Zhao, Y.J. Yoo, J.S. Jeong, Hiran Perinpanayagam, X.Y. Wang, G.J. Li, F. Wang, H. Fang, Y. Gu
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 131: 105272. CrossRef
- Position of Second Mesiobuccal Canal Relative to Distobuccal and Palatal Canals of Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population
- 4,086 View
- 45 Download
- 11 Crossref

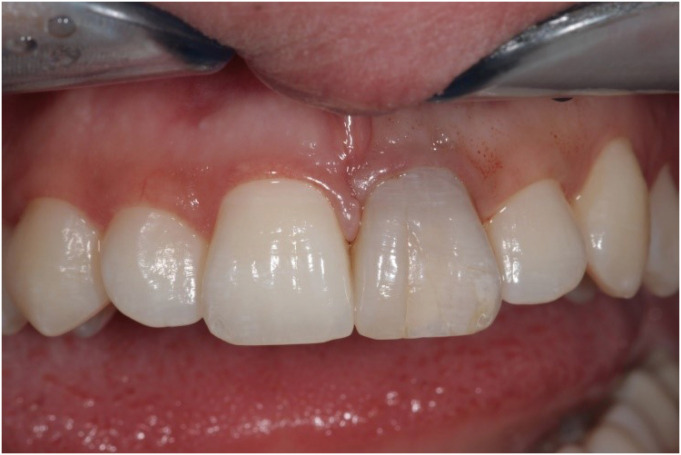
- Bioblock technique to treat severe internal resorption with subsequent periapical pathology: a case report
- Márk Fráter, Tekla Sáry, Sufyan Garoushi
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e43. Published online August 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub A variety of therapeutic modalities can be used for the endodontic treatment of a traumatized tooth with internal root resorption (IRR). The authors present a case report of the successful restoration of a traumatized upper central incisor that was weakened due to severe IRR and subsequent periapical lesion formation. A 20-year-old female patient was referred to our clinic with severe internal resorption and subsequent periapical pathosis destroying the buccal bone wall. Root canal treatment had been initiated previously at another dental practice, but at that time, the patient's condition could not be managed even with several treatments. After cone-beam computed tomography imaging and proper chemomechanical cleaning, the tooth was managed with a mineral trioxide aggregate plug followed by root canal filling using short fiber-reinforced composite, known as the Bioblock technique. This report is the first documentation of the use of the Bioblock technique in the restoration of a traumatized tooth. The Bioblock technique appears to be ideal for restoring wide irregular root canals, as in cases of severe internal resorption, because it can uniquely fill out the hollow irregularities of the canal. However, further long-term clinical investigations are required to provide additional information about this new technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Üvegszálas fogászati kompozit tömőanyag keménysége a gyökércsatornában: nanoindentációs vizsgálat
András Jakab, Kata Lilla Vánkay, Tamás Tarjányi, Gábor Gulyás, Krisztián Bali, Pál Patrik Dézsi, Márton Sámi, Márk Fráter
Fogorvosi Szemle.2024; 117(2): 47. CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness of short fiber-reinforced composites inside the root canal after different light curing methods – An in vitro study
Márk Fráter, János Grosz, András Jakab, Gábor Braunitzer, Tamás Tarjányi, Gábor Gulyás, Krisztián Bali, Paula Andrea Villa-Machado, Sufyan Garoushi, András Forster
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106324. CrossRef - Imaging techniques and various treatment modalities used in the management of internal root resorption: A systematic review
R. S Digholkar, S D Aggarwal, P S Kurtarkar, P. B Dhatavkar, V L Neil, D N Agarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 85. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatigue performance of endodontically treated premolars restored with direct and indirect cuspal coverage restorations utilizing fiber-reinforced cores
Márk Fráter, Tekla Sáry, Janka Molnár, Gábor Braunitzer, Lippo Lassila, Pekka K. Vallittu, Sufyan Garoushi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(4): 3501. CrossRef
- Üvegszálas fogászati kompozit tömőanyag keménysége a gyökércsatornában: nanoindentációs vizsgálat
- 3,633 View
- 99 Download
- 5 Crossref

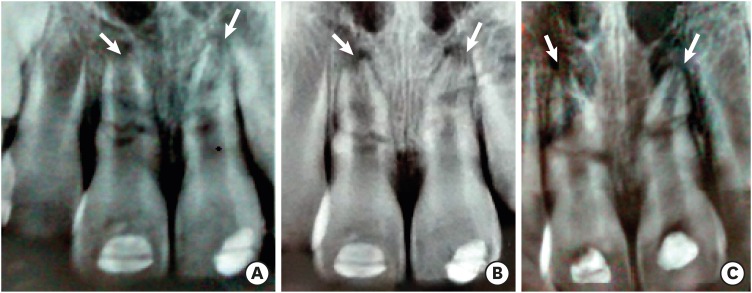
- Pulp revascularization with and without platelet-rich plasma in two anterior teeth with horizontal radicular fractures: a case report
- Edison Arango-Gómez, Javier Laureano Nino-Barrera, Gustavo Nino, Freddy Jordan, Henry Sossa-Rojas
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e35. Published online August 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Pulp revascularization is an alternative treatment in immature traumatized teeth with necrotic pulp. However, this procedure has not been reported in horizontal root fractures. This is a case report of a 9-year-old patient with multiple horizontal root fractures in 2 upper central incisors that were successfully treated with pulp revascularization. The patient presented for treatment 2 years after the initial trauma, and revascularization was attempted after the initial treatment with calcium hydroxide had failed. Prior to pulp revascularization, cone-beam computed tomography and autoradiograms demonstrated multiple horizontal fractures in the middle and apical thirds of the roots of the 2 affected teeth. Revascularization was performed in both teeth; platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was used in one tooth (#11) and the conventional method (blood clot) was used in the other tooth (#21). Clinical and radiographic follow-up over 4 years demonstrated pulp calcification in the PRP-treated tooth. Neither of the 2 teeth were lost, and the root canal calcification of tooth #11 was greater than that of tooth #21. This case suggests that PRP-based pulp revascularization may be an alternative for horizontal root fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Permanent Incisors: Two Case Reports with 6 Years of Follow-Up
María Biedma-Perea, Marcela Arenas-González, María José Barra-Soto, Carolina Caleza-Jiménez, David Ribas-Pérez
Children.2026; 13(2): 246. CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Endodontics: A Scoping Review
Simão Rebimbas Guerreiro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Anabela Paula, Joana Rita de Azevedo Pereira, Eunice Carrilho, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Siri Vicente Paulo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5479. CrossRef - Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells-response to fibrin hydrogel reveals ITGA2 and MMPs expression
David Tong, Stéphanie Gobert, Alicia Reuzeau, Jean-Christophe Farges, Marianne Leveque, Marie Bolon, Arthur Costantini, Marielle Pasdeloup, Jérôme Lafont, Maxime Ducret, Mourad Bekhouche
Heliyon.2024; 10(13): e32891. CrossRef - Pulp regeneration treatment using different bioactive materials in permanent teeth of pediatric subjects
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Francesco Giordano, Davide Mancino, Edouard Euvrard, Massimo Pisano
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(5): 458. CrossRef - Retreatment of a Failed Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in an Immature Tooth with a Horizontal Root Fracture: A Case Report
Zaher Marjy, Iris Slutzky-Goldberg
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(10): 1168. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain and healing following regenerative endodontics using platelet‐rich plasma versus conventional endodontic treatment in necrotic mature mandibular molars with chronic periapical periodontitis. A randomized clinical trial
Yassmin Elsayed Ahmed, Geraldine Mohamed Ahmed, Angie Galal Ghoneim
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 404. CrossRef - Regenerative endodontic procedures for two traumatized mature anterior teeth with transverse root fractures
Jing Lu, Bill Kahler
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Are platelet concentrate scaffolds superior to traditional blood clot scaffolds in regeneration therapy of necrotic immature permanent teeth? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Qianwei Tang, Hua Jin, Song Lin, Long Ma, Tingyu Tian, Xiurong Qin
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Fibrin Used as a Scaffold in Pulp Regeneration: Case Series
Ceren ÇİMEN, Selin ŞEN, Elif ŞENAY, Tuğba BEZGİN
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2021; 24(1): 113. CrossRef - Plasma rico en plaquetas en Odontología: Revisión de la literatura
Hugo Anthony Rosas Rozas, Hugo Leoncio Rosas Cisneros
Yachay - Revista Científico Cultural.2021; 10(1): 536. CrossRef
- Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Permanent Incisors: Two Case Reports with 6 Years of Follow-Up
- 2,726 View
- 42 Download
- 11 Crossref

-
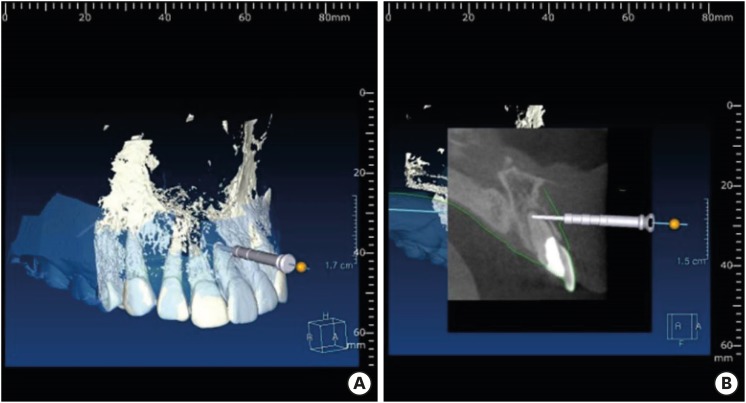
A new minimally invasive guided endodontic microsurgery by cone beam computed tomography and 3-dimensional printing technology

- Jong-Eun Kim, June-Sung Shim, Yooseok Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e29. Published online July 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Endodontic microsurgery is defined as the treatment performed on the root apices of an infected tooth, which was unresolved with conventional root canal therapy. Recently, the advanced technology in 3-dimensional model reconstruction based on computed tomography such as cone beam computed tomography has opened a new avenue in application of personalized, accurate diagnosis and has been increasingly used in the field of dentistry. Nevertheless, direct intra-oral localization of root apex based on the 3-dimensional information is extremely difficult and significant amount of bone removal is inevitable when freehand surgical procedure was employed. Moreover, gingival flap and alveolar bone fenestration are usually required, which leads to prolonged time of surgery, thereby increasing the chance of trauma as well as the risk of infection. The purpose of this case report is to present endodontic microsurgery using the guide template that can accurately target the position of apex for the treatment of an anterior tooth with calcified canal which was untreatable with conventional root canal therapy and unable to track the position of the apex due to the absence of fistula.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
Yinghua Fu, Zhixin Zhang, Xiaoping Tang, Jiangling Su
Medicine.2025; 104(3): e41033. CrossRef - Segmentation algorithms of dental CT images: A comprehensive review from classical to deep learning trend
Dianhao Wu, Jingang Jiang, Jinke Wang, Zhuming Bi, Guang Yu
Expert Systems with Applications.2025; 275: 126853. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Removal of Extraradicular Separated Instrument by Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery Using the 3D‐Printed Guide and Trephine: A Case Report
Lin Yang, Liang Chen
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Augmented Reality-Assisted Micro-Invasive Apicectomy with Markerless Visual–Inertial Odometry: An In Vivo Pilot Study
Marco Farronato, Davide Farronato, Federico Michelini, Giulio Rasperini
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12588. CrossRef - 3D finite element analysis of stress distribution on the shape of resected root-end or with/without bone graft of a maxillary premolar during endodontic microsurgery
Aein Mon, Mi-El Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Ho-Beom Kwon
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 837. CrossRef - TREATMENT OF YATROGENIC POST-TRAUMATIC NEUROPATHY ASSOCIATED WITH
ENDODONTIC THERAPY USING 3D TECHNOLOGIES
Karen Sevterteryan, Vladislav Tarasenok, Lyudmila Tatintsyan
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2024; : 73. CrossRef - Advancements in guided surgical endodontics: A scoping review of case report and case series and research implications
Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Matteo Peditto, Andrea Venticinque, Antonia Marcianò, Alberto Bianchi, Eugenio Pedullà
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 397. CrossRef - Comparison of a Novel Static Computer-aided Surgical and Freehand Techniques for Osteotomy and Root-end Resection
Kyle Westbrook, Corey Rollor, Sara A. Aldahmash, Guadalupe G. Fay, Elias Rivera, Jeffery B. Price, Ina Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik, Frederico C. Martinho
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(5): 528. CrossRef - Comparison of the Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Guided Apicoectomy Performed with a Drill or a Trephine: An In Vitro Study
Ramóna Kiscsatári, Eszter Nagy, Máté Szabó, Gábor Braunitzer, József Piffkó, Márk Fráter, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9642. CrossRef - Review of “Outcome of Endodontic Surgery: A Meta- Analysis of the Literature—Part 1: Comparison
of Traditional Root-End Surgery and Endodontic Microsurgery” by Setzer and Colleagues in J Endod 36(11):1757-1765, 2010
Oleksandr Nozhenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 41. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Exploratory In Vitro Microcomputed Tomographic Investigation of the Efficacy of Semicircular Apicoectomy Performed with Trephine Bur
Eszter Nagy, Brigitta Vőneki, Lívia Vásárhelyi, Imre Szenti, Márk Fráter, Ákos Kukovecz, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(16): 9431. CrossRef - The Time Has Come: Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery: A First Peer-Reviewed Open Access Publication Focused on Microsurgery in Endodontics
Ievgen Fesenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prefabricated Grid-guided Endodontic Microsurgery: A Pilot Study
Cruz Nishanthine, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Ravi Devi, Kadhar Begam Farjana, Dasarathan Duraivel
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022; 6(2): 58. CrossRef - Guided osteotomy
Saini Rashmi, Saini V Kr
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(3): 172. CrossRef - Accuracy of digitally planned, guided apicoectomy with a conventional trephine and a custom-made endodontic trephine: An in vitro comparative study
Eszter Nagy, Gábor Braunitzer, Dániel Gerhard Gryschka, Ibrahim Barrak, Mark Adam Antal
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 123(4): 388. CrossRef - Stress Distribution on Trephine-Resected Root-end in Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery: A Finite Element Analysis
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Miel Kim, Qiang Zhu, Seung-Ho Baek, Ho-Beom Kwon, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(12): 1517. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef - When to consider the use of CBCT in endodontic treatment planning in adults
Nisha Patel, Andrew Gemmell, David Edwards
Dental Update.2021; 48(11): 932. CrossRef
- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
- 2,443 View
- 31 Download
- 21 Crossref

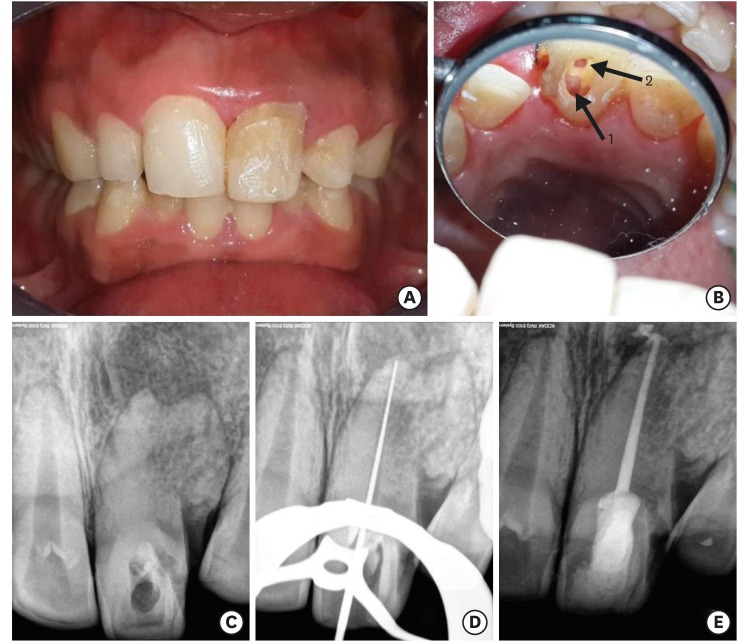
- Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
- Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Ameya Parlikar
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e44. Published online October 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Fusion and gemination are developmental anomalies of teeth that may require endodontic treatment. Fusion may cause various clinical problems related to esthetics, tooth spacing, and other periodontal complications. Additional diagnostic tools are required for the diagnosis and the treatment planning of fused tooth. The present case report describes a case of unilateral fusion of a supernumerary root to an upper permanent central incisor with large periapical lesion in which a conservative approach was used without extraction of supernumerary tooth and obturated with mineral trioxide aggregate to reach a favorable outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of fusion between a third molar and a distomolar: case report
G. M. Almeida, M.A. H. Duarte, J. R. Carvalho-Junior, R.M. C. Travassos, G. F. Silva, M.F. V. Marceliano-Alves, A. G. Limoeiro, M. P. Alcalde
Endodontics Today.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontics and Decompression-Based Management of Extensive Periapical Cystic-Like Lesions: A Comparative and Radiological Study with A Two-Year Follow-Up
Roxana Talpoș-Niculescu, Ioana Veja, Carina Sonia Neagu, Laura Cristina Rusu, Șerban Talpoș-Niculescu, Mălina Popa, Luminița Maria Nica
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(17): 6127. CrossRef - Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
Tatsuya Akitomo, Satoru Kusaka, Momoko Usuda, Mariko Kametani, Ami Kaneki, Taku Nishimura, Masashi Ogawa, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Children.2023; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Approche multidisciplinaire d’un cas de fusion incisive centrale maxillaire avec un « talon cusp »
Sonia Terbeche, Kheira Yousfi, Samia Saddat, Souad Larbi Messaoudi, Noureddine Ahmed Fouatih, G. Mer, O. Weissenbach
Revue d'Orthopédie Dento-Faciale.2022; 56(2): 205. CrossRef
- A rare case of fusion between a third molar and a distomolar: case report
- 2,671 View
- 23 Download
- 4 Crossref

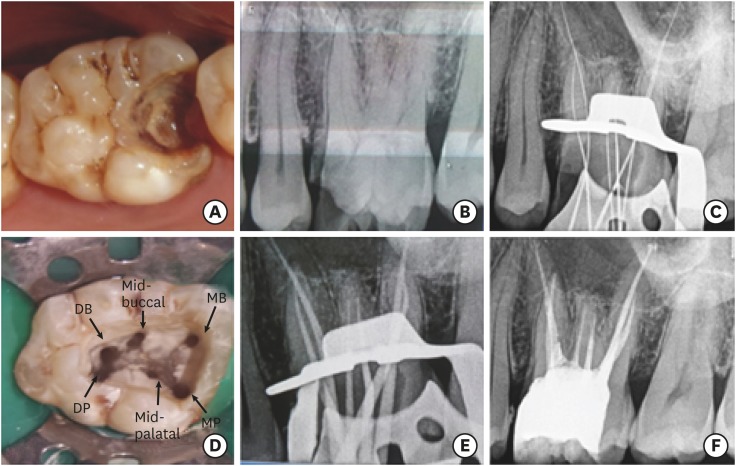
- Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report
- Prateeksha Chowdhry, Pallavi Reddy, Mamta Kaushik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e35. Published online August 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this article was to showcase the endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with an unusual crown and root anatomy. Clinical diagnosis of the roots and root canal configuration was confirmed by a cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and the detection of the canals was made using a dental operating microscope. CBCT images revealed the presence of 5 roots with Vertucci type I canal configuration in all, except, in the middle root which had 2 canals with type IV configuration. The 6 canal orifices were clinically visualized under the dental operating microscope. Clinicians should familiarize themselves with the latest technologies to get additional information in endodontic practice in order to enhance the outcomes of endodontic therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic management of maxillary first molar with unusual anatomy
MadhuriSai Battula, Mamta Kaushik, Neha Mehra, Ankeeta Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 569. CrossRef - Diversity of root canal morphology of maxillary first molars
Juhász Kincső-Réka, Kovács Mónika, Pop Mihai, Pop Silvia, Kerekes-Máthé Bernadette
Bulletin of Medical Sciences.2021; 94(1): 63. CrossRef
- Endodontic management of maxillary first molar with unusual anatomy
- 1,570 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- CBCT study of mandibular first molars with a distolingual root in Koreans
- Hee-Ho Kim, Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e33. Published online July 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of a separate distolingual root and to measure the thickness of the buccal cortical bone in mandibular first molars in Koreans using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Materials and Methods High-quality CBCT data from 432 patients were analyzed in this study. The prevalence of a separate distolingual root of the mandibular first molar was investigated. The distance from the distobuccal and distolingual root apices to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was measured. We also evaluated the thickness of the buccal cortical bone.
Results The prevalence of a separate distolingual root (2 separate distal roots with 1 canal in each root; 2R2C) was 23.26%. In mandibular first molars with 2R2C, the distance from the distobuccal root apex to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was 5.51 mm. Furthermore, the distance from the distolingual root apex to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was 12.09 mm. In mandibular first molars with 2R2C morphology, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone at the distobuccal root apex of the mandibular first molar was 3.30 mm. The buccal cortical bone at the distobuccal root apex was significantly thicker in the right side (3.38 mm) than the left side (3.09 mm) (
p < 0.05).Conclusions A separate distolingual root is not rare in mandibular first molars in the Korean population. Anatomic and morphologic knowledge of the mandibular first molar can be useful in treatment planning, including surgical endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between complex root canal morphology of mandibular anteriors and distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Turkish population
Özge Kurt, Elif Solakoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radix molaris is a hidden truth of mandibular first permanent molars: A descriptive- analytic study using cone beam computed tomography
Mohammed A. Alobaid, Saurabh Chaturvedi, Ebtihal Mobarak S. Alshahrani, Ebtsam M. Alshehri, Amal S. Shaiban, Mohamed Khaled Addas, Giuseppe Minervini
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1957. CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris in India and its comparison with the rest of the world
Sumit MOHAN, Jyoti THAKUR
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of laboratory and clinical research methods to study root and canal anatomy
Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 229. CrossRef - Three‐Rooted Permanent Mandibular First Molars: A Meta‐Analysis of Prevalence
Nyan M. Aung, Kyaw K. Myint, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Reproducibilidad en el diagnóstico imagenológico de periodontitis apical a partir de CBCT
Sandra Milena Buitrago Rojas, Yeny Zulay Castellanos Dominguez, Jhonny Alexander Contreras Vargas, Yosdi Tomás Solano Diaz, Eder Fabián Gutierrez Argote
Acta Odontológica Colombiana.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Root and Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Molars using CBCT
Yoomin Choi, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography
Hassan AL-Alawi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Mazen A. Aldosimani, Mohammed Nabil Zahid, Ghadeer N. Shihabi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Evaluation of roots and canal systems of mandibular first molars in a vietnamese subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography
KhoaVan Pham, AnhHoang Lan Le
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2019; 9(4): 356. CrossRef
- The association between complex root canal morphology of mandibular anteriors and distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Turkish population
- 1,886 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
- Evaldo Rodrigues, Antônio Henrique Braitt, Bruno Ferraz Galvão, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):60-64. Published online August 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.60

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Root canal anatomy is complex, and the recognition of anatomic variations could be a challenge for clinicians. This case report describes the importance of cone beam computed tomographyic (CBCT) imaging during endodontic treatment. A 23 year old woman was referred by her general dental practitioner with the chief complaint of spontaneous pain in her right posterior maxilla. From the clinical and radiographic findings, a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis was made and endodontic treatment was suggested to the patient. The patient underwent CBCT examination, and CBCT scan slices revealed seven canals: three mesiobuccal (MB1, MB2, and MB3), two distobuccal (DB1 and DB2), and two palatal (P1 and P2). Canals were successfully treated with reciprocating files and filled using single-cone filling technique. Precise knowledge of root canal morphology and its variation is important during root canal treatment. CBCT examination is an excellent tool for identifying and managing these complex root canal systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- KONİK IŞINLI BİLGİSAYARLI TOMOGRAFİ İLE DOĞRULANMIŞ OLAĞANDIŞI ÜST BİRİNCİ BÜYÜK AZI DİŞİN ENDODONTİK TEDAVİSİ
Didem Seda Gültekin, Funda Kont Çobankara
Journal of International Dental Sciences.2025; 11(1): 46. CrossRef - Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Somayeh Majidi, Vlaho Brailo
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Unusual Case of Maxillary First Molar: A Case Report
Reetu Shrestha
International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT).2024; : 1330. CrossRef - Root canal therapy of maxillary first molar with seven canals diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography – a case report
Saini Rashmi, Saini V. Kumar
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(3): 169. CrossRef - Four-Rooted Maxillary First Molars: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gabriel Magnucki, Sven V. K. Mietling, Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of various palatal roots in maxillary molars
Chengshi Wei, Keyi Li, Lili Shen, Guangliang Bai, Xiufen Tian
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2021; 152(12): 1044. CrossRef - Diversity of root canal morphology of maxillary first molars
Juhász Kincső-Réka, Kovács Mónika, Pop Mihai, Pop Silvia, Kerekes-Máthé Bernadette
Bulletin of Medical Sciences.2021; 94(1): 63. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Maxillary First Molar with Seven Root Canals Diagnosed Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ravindranath Megha, Venkatachalam Prakash
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 89. CrossRef - Endodontic management of the maxillary first molar with special root canals: A case report and review of the literature
Zhi-Hui Zhang, Hai-Lin Yao, Yan Zhang, Xiao Wang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(12): 2590. CrossRef - Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report
Prateeksha Chowdhry, Pallavi Reddy, Mamta Kaushik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of cone beam computed tomography in perplexing endodontic cases
Amandeep Kaur, Ajay Logani
Endodontology.2018; 30(2): 187. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with seven root canal systems evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography scanning
VijayReddy Venumuddala, Sridhar Moturi, SV Satish, BKalyan Chakravarthy, Sudhakar Malapati
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2017; 7(5): 297. CrossRef
- KONİK IŞINLI BİLGİSAYARLI TOMOGRAFİ İLE DOĞRULANMIŞ OLAĞANDIŞI ÜST BİRİNCİ BÜYÜK AZI DİŞİN ENDODONTİK TEDAVİSİ
- 2,429 View
- 15 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
- Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT.
Results The second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (
p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01).Conclusions For apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
- 2,223 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using cone-beam computed tomography
- Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):55-62. Published online January 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.55

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the incidence of root fusion and C-shaped root canals in maxillary molars, and to classify the types of C-shaped canal by analyzing cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in a Korean population.
Materials and Methods Digitized CBCT images from 911 subjects were obtained in Chosun University Dental Hospital between February 2010 and July 2012 for orthodontic treatment. Among them, a total of selected 3,553 data of maxillary molars were analyzed retrospectively. Tomography sections in the axial, coronal, and sagittal planes were displayed by PiViewstar and Rapidia MPR software (Infinitt Co.). The incidence and types of root fusion and C-shaped root canals were evaluated and the incidence between the first and the second molar was compared using Chi-square test.
Results Root fusion was present in 3.2% of the first molars and 19.5% of the second molars, and fusion of mesiobuccal and palatal root was dominant. C-shaped root canals were present in 0.8% of the first molars and 2.7% of the second molars. The frequency of root fusion and C-shaped canal was significantly higher in the second molar than the first molar (
p < 0.001).Conclusions In a Korean population, maxillary molars showed total 11.3% of root fusion and 1.8% of C-shaped root canals. Furthermore, root fusion and C-shaped root canals were seen more frequently in the maxillary second molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Amin Salem Milani, Shahin Namvar Asl Amirkhizi, Tahmineh Razi, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Pouya Sabanik, Nikhat Kaura
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of c-shaped canal morphology in premolar and molar teeth assessed by cone-beam computed tomography: systematic review and meta-analysis
Faezeh Yousefi, Younes Mohammadi, Elham Shokri
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of C‐Shaped Canal Configuration in Maxillary Molars Among an Iranian Population
Nafiseh Nikkerdar, Mohammad Moslehi, Amin Golshah, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of a C‐shaped mandibular second molar with narrow dentinal thickness: A case report
Mina Mehrjouei, Hamid Jafarzadeh, Pourya Esmaeelpour, Maryam Khorasanchi
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of 2- and 3-dimensional anatomic parameters of C-shaped root canals with cone beam computed tomography, microcomputed tomography, and nanocomputed tomography
Miguel Angel Ventura Molina, Giovane Oliveira Silva, Amanda Pelegrin Candemil, Rafael Verardino de Camargo, Ruben Pauwels, Reinhilde Jacobs, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2023; 136(6): 759. CrossRef - Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Analysis of an Unusual Configuration of the Upper First Molar With a C-shaped Canal With Apically Fused Roots: A Case Report
Kapil D Wahane, Anand V Bansod, Sudha mattigatti, Rushikesh Mahaparale, Yuvraj B Rote, Mayur B Wanjari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Root and canal-specific features of maxillary first molars with fused roots
Katarina Beljic-Ivanovic, Branislav Karadzic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2022; 79(11): 1092. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of maxillary molar with abnormality
Kkot-Byeol Bae, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Oral Biology Research.2022; 46(4): 195. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of the maxillary first molar with palatal canal variations: A case report and review of literature
Kai Chen, Xing Ran, Yan Wang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(32): 12036. CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canals in maxillary molars in a Chinese population using CBCT
Yuyan Qian, Yamei Li, Jukun Song, Ping Zhang, Zhu Chen
BMC Medical Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al‑Zubaidi, Abdulmjeed S. Enizy, Ahmed A. Madfa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canal configuration in maxillary molars: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study
Emre KÖSE, Rüya AK
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(3): 444. CrossRef - Maxillary First Molars with Two Palatal Root Canals
Kun-Hwa Sung, Ho-Keel Hwang, Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Konstantinos Michalakis
Case Reports in Dentistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Evaluation of root and root canal morphology of elderly Korean patients maxillary molars using cone-beam computed tomography
Tae-Yong Lee, Mi-Yeon Kim, Sun-Ho Kim, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2020; 58(2): 95. CrossRef - Second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars—A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence studies using cone beam computed tomography
Jorge N.R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 113: 104589. CrossRef - Prevalência estimada de canais “C- Shaped”: Uma revisão sistemática e meta-análise
Natália Pereira da Silva Falcão, Sandro Junio de Oliveira Tavares, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Katherine Azevedo Batistela Rodrigues Thuller, Leonardo dos Santos Antunes, Estefano Borgo Sarmento, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azevedo, Cinthya Cristina Gomes, Ca
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 91. CrossRef - Evaluation of the internal anatomy of paramolar tubercles using cone-beam computed tomography
G. Colakoglu, I. Kaya Buyukbayram, M. A. Elcin, M. Kazak, H. Sezer
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2020; 42(1): 15. CrossRef - Analysis of Prevalence of Pyramidal Molars in Adolescent
Woojin Kwon, Hyung-Jun Choi, Jaeho Lee, Je Seon Song
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(4): 389. CrossRef - Prevalence Studies on Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Imaging: A Systematic Review
Jorge N.R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(4): 372. CrossRef - Fused roots of maxillary molars: characterization and prevalence in a Latin American sub-population: a cone beam computed tomography study
Maytté Marcano-Caldera, Jose Luis Mejia-Cardona, María del Pilar Blanco-Uribe, Elena Carolina Chaverra-Mesa, Didier Rodríguez-Lezama, Jose Hernán Parra-Sánchez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - An original micro‐CT study and meta‐analysis of the internal and external anatomy of maxillary molars—implications for endodontic treatment
Iwona M. Tomaszewska, Anna Jarzębska, Bendik Skinningsrud, Przemysław A. Pękala, Sebastian Wroński, Joe Iwanaga
Clinical Anatomy.2018; 31(6): 838. CrossRef - A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Study of Root and Canal Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Permanent Molars in a Thai Population
Roserin Ratanajirasut, Anchana Panichuttra, Soontra Panmekiate
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(1): 56. CrossRef - Retrospective Assessment of Healing Outcome of Endodontic Treatment for Mandibular Molars with C-shaped Root Canal
Kishore Kumar Majety, Basanta Kumar Choudhury, Anika Bansal, Achla Sethi, Jaina Panjabi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(7): 591. CrossRef - The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a polish population
Katarzyna Olczak, Halina Pawlicka
BMC Medical Imaging.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
- 1,915 View
- 14 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
- Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):161-165. Published online December 4, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans appears to be a valuable method for assessing pulp canal configuration. The aim of this report is to describe endodontic treatment of a mandibular second premolar with aberrant pulp canal morphology detected by CBCT and confirmed by 3D modeling. An accessory canal was suspected during endodontic treatment of the mandibular left second premolar in a 21 year old woman with a chief complaint of pulsating pain. Axial cross-sectional CBCT scans revealed that the pulp canal divided into mesiobuccal, lingual, and buccal canals in the middle third and ended as four separate foramina. 3D modeling confirmed the anomalous configuration of the fused root with a deep lingual groove. Endodontic treatment of the tooth was completed in two appointments. The root canals were obturated using lateral compaction of gutta-percha and root canal sealer. The tooth remained asymptomatic and did not develop periapical pathology until 12 months postoperatively. CBCT and 3D modeling enable preoperative evaluation of aberrant root canal systems and facilitate endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Technological Progress in Three-Dimensional Imaging for Root Canal Treatments: A Systematic Review
Kanwalpreet Kaur, Ravinder S. Saini, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Vishwanath Gurumurthy, Shan Sainudeen, Vinod Babu Mathew, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Aida Mokhlesi, Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Artak Heboyan
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1097. CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment of Oehlers Type III Dens Invaginatus in Maxillary Lateral Incisor and Remote Sinus Tract Using Dental Surgical Microscope and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Rie Fujii, Tomohiro Asai, Masashi Yamada, Ryo Sako, Yoshiki Tamiya, Masahiro Furusawa
The Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College.2023; 64(2): 67. CrossRef - CBCT and Micro-CT analysis of the mandibular first premolars with C-shaped canal system in a Chinese population author
Yimeng Zhang, Xunben Weng, Yu Fu, Xuekai Qi, Yihuai Pan, Yu Zhao
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring Technological Progress in Three-Dimensional Imaging for Root Canal Treatments: A Systematic Review
- 1,425 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Clinical management of a fused upper premolar with supernumerary tooth: a case report
- Kyu-Min Cho, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang-Hyuk Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):319-323. Published online July 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.319
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In dentistry, the term 'fusion' is used to describe a developmental disorder of dental hard tissues. In the permanent dentition, fusion of a normal tooth and a supernumerary tooth usually involves the incisors or canines. However, a few cases of fusion involving premolars have also been reported to date. We present a rare case in which fusion of the maxillary left second premolar and a supernumerary tooth in a 13-year-old girl was diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT, Alphard-3030, Asahi Roentgen Ind. Co., Ltd.). The tooth was bicuspidized after routine nonsurgical root canal treatment, and the separated teeth underwent appropriate restoration procedures. The second premolar and supernumerary tooth remained asymptomatic without any signs of inflammation after a follow-up period of 9 years. Identification of anatomical anomalies is important for treatment in cases involving fusion with supernumerary tooth, and therefore the microscopic examinations and CBCT are essential for the diagnosis. Fused teeth can be effectively managed by the comprehensive treatment which includes both endodontic and periodontal procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
Tatsuya Akitomo, Satoru Kusaka, Momoko Usuda, Mariko Kametani, Ami Kaneki, Taku Nishimura, Masashi Ogawa, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Children.2023; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Malformed Teeth and Their Endodontic Implications
Annapoorna Annapoorna, Manjunatha M, Shubhashini N, Swetha H. B.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(04): 245. CrossRef - Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Ameya Parlikar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Common dental diseases in children and malocclusion
Jing Zou, Mingmei Meng, Clarice S Law, Yale Rao, Xuedong Zhou
International Journal of Oral Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary Central Incisor fused to a Supernumerary Tooth using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Unusual Clinical Presentation
Thilla S Vinothkumar, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Ganesh Arathi, Sathishkumar Ramkumar, Gnanasekaran Felsypremila
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(6): 522. CrossRef - Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report
Miguel Agostinho Beco Pinto Cardoso, Rita Brandão Noites, Miguel André Duarte Martins, Manuel Pedro da Fonseca Paulo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 148. CrossRef
- Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
- 2,033 View
- 22 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
- Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):132-136. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The presence of radix entomolaris (RE) in a mandibular first molar is a common occurrence in certain ethnic groups, but the presence of RE in a mandibular second molar is a rare occurrence. In the present case, RE was identified from preoperative radiographs and confirmed using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The access cavity was modified to locate the RE. Cleaning and shaping were performed with nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Obturation was completed with gutta-percha cones using AH Plus (Dentsply Detrey GmbH) as sealer. From the CBCT axial images, the RE was determined to have a Type III curvature by the De Moor classification, Type B separate RE by the Carlsen and Alexandersen classification, and radiographically, a Type i image by the Wang classification. The presence of RE in the mandibular second molar makes it essential to anticipate and treat the distolingual root canal. This case report highlights the usefulness of CBCT for assessing RE in the mandibular second molar, which can help the clinician in making a confirmatory diagnosis and assessing the morphology of the root canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Three-Dimensional Observation and Classification of Root and Root Canal Morphology in Japanese Mandibular Third Molars
Tomoyuki Inose, Satoru Matsunaga, Norio Kasahara, Masashi Yamada, Shinichi Abe, Masahiro Furusawa
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2026; 35(1): 7. CrossRef - Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular Second Molar Featuring Vertucci Type V Configuration in the Distal Root: A Case Report
He Liu, Ya Shen
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of a case of radix entomolaris: A case report
Priyanka Shorey, Kitty Sidhu
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2022; 7(1): 39. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of tooth with morphological anomalies using cone-beam computed tomography
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Na-Kyung Yoon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Bin-Na Lee
Oral Biology Research.2018; 42(1): 53. CrossRef - Unusual root morphology in second mandibular molar with a radix entomolaris, and comparison between cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiography: a case report
Elisardo López-Rosales, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Roland De Moor, Manuel Ruíz-Piñón, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, Purificación Varela-Patiño
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Three-Dimensional Observation and Classification of Root and Root Canal Morphology in Japanese Mandibular Third Molars
- 2,196 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
- Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):50-53. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is a useful diagnostic tool for identification of both internal and external root configurations. This case report describes the endodontic management of a lateral incisor with both dens invaginatus and external root irregularity by using CBCT. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment was performed on the lateral incisor with dens invaginatus. A perforation through the dens invaginatus and external concavity was repaired using mineral trioxide aggregate. After 18 mon of follow-up, there were no clinical symptoms. Recall radiographs appeared normal and showed healing of the periapical pathosis. The understanding of both internal root canal configuration and external root irregularity using CBCT can ensure predictable and successful results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cone-beam computed tomography for assessment of dens invaginatus in the Polish population
T. Katarzyna Różyło, Ingrid Różyło-Kalinowska, Magdalena Piskórz
Oral Radiology.2018; 34(2): 136. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of a Molar-Incisor Malformation-affected Mandibular First Molar: A Case Report
Wonyoung Yue, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 664. CrossRef - Three-year follow-up: Healing of a large periapical lesion related to a maxillary central incisor and two canalled lateral incisor after a single visit root canal treatment
Abu Mostafa Ammar
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Hygiene.2015; 7(4): 40. CrossRef - Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 172. CrossRef - Management of root canal perforation by using cone-beam computed tomography
Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 55. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
- Cone-beam computed tomography for assessment of dens invaginatus in the Polish population
- 1,542 View
- 10 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


