Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bonding and fractographic characterization of universal adhesives applied to dentin in multimode strategies: an in vitro study
- Samaa M. Morsy, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Naji Kharouf, Ahmed A. Holiel
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e12. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Universal adhesives (UAs) are marketed as versatile systems for both self-etch (SE) and total-etch (TE) modes. While their bond strength has been widely investigated, evidence linking fracture characteristics to bonding performance remains limited. This study evaluated the micro-shear bond strength (μSBS) and failure patterns of three UAs applied in SE and TE modes, complemented by fractographic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
Methods
Eighteen extracted human molars were sectioned to expose mid-coronal dentin and randomly allocated to SE or TE application. Three UAs were tested: Tetric N-Bond Universal, All-Bond Universal, and Single Bond Universal (SBU). Composite micro-rods (n = 72) were bonded, thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5°C and 55°C, and subjected to μSBS testing. Fracture surfaces were examined under SEM and classified as adhesive, cohesive, or mixed. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test, and Spearman correlation (α = 0.05).
Results
In TE mode, SBU demonstrated the highest μSBS (p < 0.001), whereas no significant differences were observed among adhesives in SE mode (p > 0.05). SEM analysis revealed adhesive failures as interfacial fractures, cohesive failures with beach marks, and mixed failures involving crack propagation through both dentin and composite. Adhesive failures correlated negatively with μSBS (rs = –0.77), while mixed failures correlated positively (rs = 0.81).
Conclusions
Both the etching strategy and adhesive formulation significantly affect bond strength and fracture behavior. Fractographic SEM analysis provides critical insights into the mechanical reliability of UAs and informs their clinical application.
- 174 View
- 17 Download

- Does the use of different root canal sealers and adhesive resin cements impact the bond strength of glass fiber posts?
- Ália Regina Neves de Paula Porto, Rudá França Moreira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e29. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
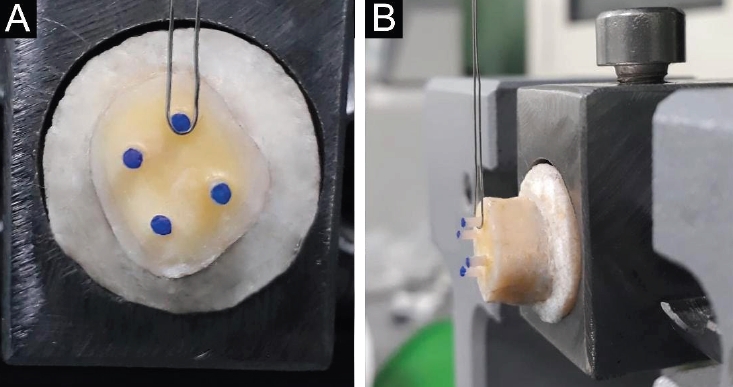
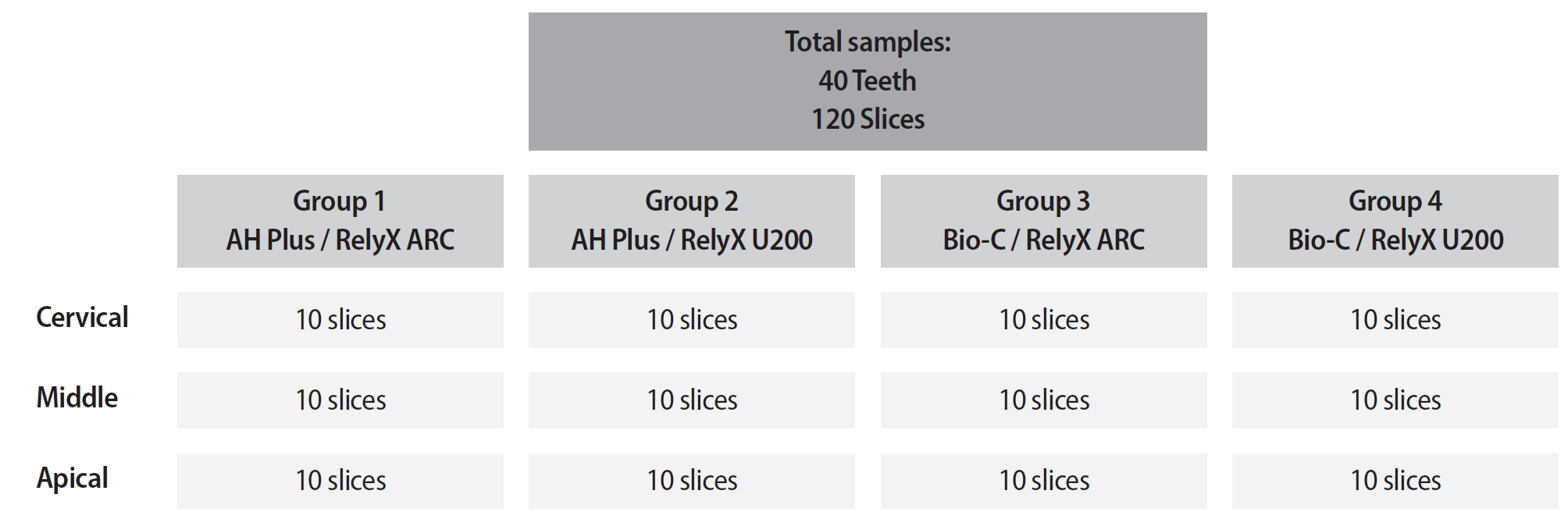
This study aimed to assess the influence of two endodontic sealers on the bond strength of glass fiber posts using conventional and self-adhesive resin cement through a push-out test. Methods: Forty central human incisors were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) based on sealer (epoxy resin- based or calcium silicate-based) and cement (conventional and self-adhesive resin) types: AH Plus (Dentsply De- Trey)/RelyX ARC (3M ESPE), AH Plus/RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), Bio-C Sealer (Angelus)/RelyX ARC, and Bio-C Sealer/RelyX U200. After canal filling and post cementation, roots were sectioned to obtain one specimen per root third. A pushout test and failure pattern assessment were conducted, with bond strength analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test. Results: AH Plus/RelyX ARC showed the highest bond strength values, with a significant difference in the middle third. The most common failure was mixed (55%), while adhesive failures made up 45%, with 23.5% at the cement/post interface and 21.5% at the cement/dentin interface. Conclusions: AH Plus/RelyX ARC provided the highest bond strength values for glass fiber posts to dentin.
- 1,815 View
- 146 Download

- Effect of surface treatment on glass ionomers in sandwich restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory studies
- Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e13. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of different surface treatments on the bond strength between new or aged glass ionomers (GI) and resin composites in sandwich restorations.
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted in three databases to identify studies focusing on the bond strength of new or aged GIs and resin composites in laboratory settings. The selected studies were assessed for potential biases based on predetermined criteria. Additionally, a meta-analysis was performed using three studies.
Results
A total of 29 studies were included, with 24 investigating the bond strength of new GIs and five focusing on GI repair. Three studies were included in the meta-analysis (with a 95% confidence interval) which revealed no significant difference in the mean MPa values of resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) treated with phosphoric acid or Er,Cr:YSGG laser before the application of an etch-and-rinse adhesive. Surface treatment was found to be crucial for achieving optimal bonding between GI and resin composite, regardless of the GI’s condition.
Conclusions
The combination of mechanical and chemical surface treatments does not significantly affect the bond strength between new RMGI and composite. However, for GI repair, it is recommended to use both treatments to enhance the bond strength. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
Rashid El Abed, Amre R. Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Anas Al Jadaa, Hamza El-Faraj, Abdel Rahman Bani Amer, Taher Al Omari
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
- 8,659 View
- 217 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison between a bulk-fill resin-based composite and three luting materials on the cementation of fiberglass-reinforced posts
- Carlos Alberto Kenji Shimokawa, Paula Mendes Acatauassú Carneiro, Tamile Rocha da Silva Lobo, Roberto Ruggiero Braga, Míriam Lacalle Turbino, Adriana Bona Matos
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e30. Published online August 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
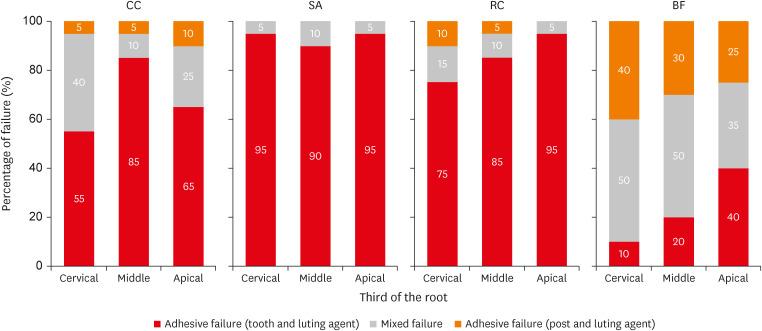
ePub Objectives This study verified the possibility of cementing fiberglass-reinforced posts using a flowable bulk-fill composite (BF), comparing its push-out bond strength and microhardness with these properties of 3 luting materials.
Materials and Methods Sixty endodontically treated bovine roots were used. Posts were cemented using conventional dual-cured cement (CC); self-adhesive cement (SA); dual-cured composite (RC); and BF. Push-out bond strength (
n = 10) and microhardness (n = 5) tests were performed after 1 week and 4 months of storage. Two-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA), 1-way ANOVA,t -test, and Tukeypost-hoc tests were applied for the push-out bond strength and microhardness results; and Pearson correlation test was applied to verify the correlation between push-out bond strength and microhardness results (α = 0.05).Results BF presented higher push-out bond strength than CC and SA in the cervical third before aging (
p < 0.01). No differences were found between push-out bond strength before and after aging for all the luting materials (p = 0.84). Regarding hardness, only SA presented higher values measured before than after aging (p < 0.01). RC and BF did not present 80% of the maximum hardness at the apical regions. A strong positive correlation was found between the luting materials' push-out bond strength and microhardness (p < 0.01, R2 = 0.7912).Conclusions The BF presented comparable or higher push-out bond strength and microhardness than the luting materials, which indicates that it could be used for cementing resin posts in situations where adequate light curing is possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
- 2,186 View
- 42 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of irrigation protocols on smear layer removal, bond strength and nanoleakage of fiber posts using a self-adhesive resin cement
- Rodrigo Stadler Alessi, Renata Terumi Jitumori, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, Giovana Mongruel Gomes, João Carlos Gomes
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e28. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the effect of the application method of 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) and its influence on the adhesion of fiberglass posts cemented with a self-adhesive resin cement.
Materials and Methods Sixty human mandibular premolars were endodontically treated and divided into 5 groups (
n = 12), according to the canal irrigant and its application method: 2 groups with conventional syringe irrigation (CSI)—2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) (control) and 2% CHX— and 3 groups with 2% CHX irrigation/activation—by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), Easy Clean file, and XP-Endo Finisher file. Two roots per group were evaluated for smear layer (SL) removal by scanning electron microscopy. For other roots, fiber posts were luted using a self-adhesive resin cement. The roots were sectioned into 6 slices for push-out bond strength (BS) (7/group) and nanoleakage (NL) (3/group). Data from SL removal were submitted to Kruskal-Wallis and Student-Newman-Keuls tests (α = 0.05). Data from BS and NL were evaluated by 2-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).Results For SL removal and BS, the CHX irrigation/activation promoted better values than CSI with CHX (
p < 0.05), but it was not significantly different from CSI with NaOCl (p > 0.05). For NL, the lowest values were obtained by the chlorhexidine irrigation/activation groups (p < 0.05).Conclusions Active 2% CHX irrigation can be used to improve the post space cleaning and adhesion before fiber post cementation with self-adhesive resin cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
Lívia Ribeiro, Luíz Carlos de Lima Dias-Júnior, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Paulo Marcelo Rodrigues, Vicente Ribeiro Netto, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Renata Gondo Machado, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Luc
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104252. CrossRef - Laser‐Activated Irrigation via Photon‐Induced Photoacoustic Streaming and Shock Wave Enhanced Emission on Smear Layer Removal Efficacy, Pushout Bond Strength, and Sealer Adaptation: A SEM Assessment
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(6): 1806. CrossRef - The impact of passive ultrasonic irrigation on the bond strength of two different self-etch adhesives to human pulp chamber dentine: a laboratory investigation
Mohammed Turky, Jukka Matinlinna, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul M. H. Dummer, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Nermin Alsayed Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of nanoparticles incorporation titanium dioxide and zirconium oxide within self-adhesive resin cement on the push-out bond strength of the fiber post to the radicular dentin: An in vitro study
Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori, Maha Anwer AL-Murad
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 162. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Post Space Conditioning Procedures and Different Endodontic Sealers on the Push-Out Bond Strengths of Fiber Posts
Leyla Ayranci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci, Fatih Sarı, Ahmet Çetinkaya
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 620. CrossRef - Evaluation of Microleakage Using Different Luting Cements in Kedo Zirconia Crowns: An In Vitro Assessment
Guru Vishnu, Ganesh Jeevanandan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
- 3,461 View
- 69 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent on the dentin shear bond strength of a universal adhesive
- Sujin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e14. Published online March 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
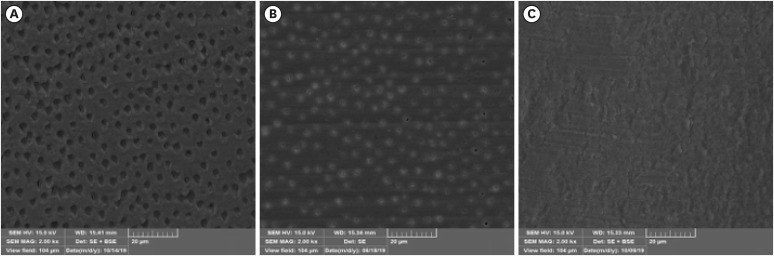
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effect of an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a universal adhesive to dentin.
Materials and Methods Eighty extracted human molars were trimmed at the occlusal dentin surfaces and divided mesiodistally. According to hemostatic agent application, specimens were randomly allocated into control (C) and hemostatic agent (Traxodent; H) groups. Each group was divided into 4 subgroups according to the adhesive system (
n = 20): Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (SBER), Clearfil SE Bond (CLSE), All-Bond Universal etch-and-rinse mode (ALER), and All-Bond Universal self-etch mode (ALSE). SBS was measured for half of the specimens at 24 hours, and the other half were thermocycled in water baths (group T). Fracture surfaces were examined to determine the failure mode. The SBS was measured, and data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance, the Student’st -test, and the Tukey honestly significant difference test (p = 0.05).Results No significant differences in SBS were found between groups C and H for any adhesive system at 24 hours. After thermocycling, a statistically significant difference was observed between CT+ALSE and HT+ALSE (
p < 0.05). When All-Bond Universal was applied to hemostatic agent-contaminated dentin, the SBS of H+ALSE was significantly lower than that of H+ALER (p < 0.05). The SBER subgroups showed no significant differences in SBS regardless of treatment and thermocycling.Conclusions When exposed dentin was contaminated by an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent before dentin adhesive treatment, application of All-Bond Universal in etch-and-rinse mode was superior to self-etch mode.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nature-driven blue-emissive N, S-CDs: Harnessing sequential "switch-off-on" fluorescence signals for detection of chrysin and Al³⁺ along with cellular imaging versatility
Maha Mohammad Abdel-Monem, Mohamed I. Walash, Asmaa Kamal El-Deen
Talanta Open.2025; : 100466. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Self-Adhesive and Glass Ionomer Cement to Dentin After Removal of Hemostatic Agents Using Different Cleansing Protocols: An In Vitro Study
Hemashree Namburajan, Mathew Chalakuzhiyil Abraham, Vidhyasankari N, Rajkumar K, Abhinayaa Suthagar, Vishnupriya Venkatasubramanian, Sindhuja Nagarajan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Emalje- og dentinadhesiver: Avgjørende faser i klinisk behandling
Torgils Lægreid, Tom Paulseth, Arne Lund
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2024; 134(8): 604. CrossRef
- Nature-driven blue-emissive N, S-CDs: Harnessing sequential "switch-off-on" fluorescence signals for detection of chrysin and Al³⁺ along with cellular imaging versatility
- 3,285 View
- 70 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Comparative analysis of bond strength to root dentin and compression of bioceramic cements used in regenerative endodontic procedures
- Maykely Naara Morais Rodrigues, Kely Firmino Bruno, Ana Helena Gonçalves de Alencar, Julyana Dumas Santos Silva, Patrícia Correia de Siqueira, Daniel de Almeida Decurcio, Carlos Estrela
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e59. Published online November 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the Biodentine, MTA Repair HP, and Bio-C Repair bioceramics in terms of bond strength to dentin, failure mode, and compression.
Materials and Methods Fifty-four slices obtained from the cervical third of 18 single-rooted human mandibular premolars were randomly distributed (
n = 18). After insertion of the bioceramic materials, the push-out test was performed. The failure mode was analyzed using stereomicroscopy. Another set of cylindrically-shaped bioceramic samples (n = 10) was prepared for compressive strength testing. The normality of data distribution was analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Kruskal-Wallis and Friedman tests were used for the push-out test data, while compressive strength was analyzed with analysis of variance and the Tukey test, considering a significance level of 0.05.Results Biodentine presented a higher median bond strength value (14.79 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (8.84 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (3.48 MPa), with a significant difference only between Biodentine and Bio-C Repair. In the Biodentine group, the most frequent failure mode was mixed (61%), while in the MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair groups, it was adhesive (94% and 72%, respectively). Biodentine showed greater resistance to compression (29.59 ± 8.47 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (18.68 ± 7.40 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (19.96 ± 3.96 MPa) (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Biodentine showed greater compressive strength than MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair, and greater bond strength than Bio-C Repair. The most frequent failure mode of Biodentine was mixed, while that of MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair was adhesive.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Obturation quality analysis of furcation perforations repaired with different magnifications and biomaterials
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Merve Işık Aydın, Ali Keleş
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparación de la resistencia compresiva entre el Agregado Trióxido Mineral y BiodentineTM en perforaciones de furca de molares inferiores permanentes
Jheymy Gerardo Huatuco-Granda, John Paul Torres-Navarro, Rosa Josefina Roncal-Espinoza
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Dentin Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Natalia Radulica, José Luis Sanz, Adrián Lozano
Applied Sciences.2023; 14(1): 104. CrossRef - Evaluation Of The Push-out Bond Strength Of The Bio-C Repair And Compare It With The Mineral Trioxide Aggregate And Amalgam When Used As Root-end Filling Material
Fatimah R. Hammadi, Zainab M Abdul-Ameer
Dental Hypotheses.2023; 14(2): 62. CrossRef - Effect of different root canal irrigants on push-out bond strength of two novel root-end filling materials
Nada Omar, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Tamer M. Hamdy
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of irrigation systems on the bond strength of calcium-silicate-based cement used as pulp barrier in regenerative endodontic treatment
Cihan Hascizmeci, Burak Buldur
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(23): 3393. CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 3,296 View
- 73 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

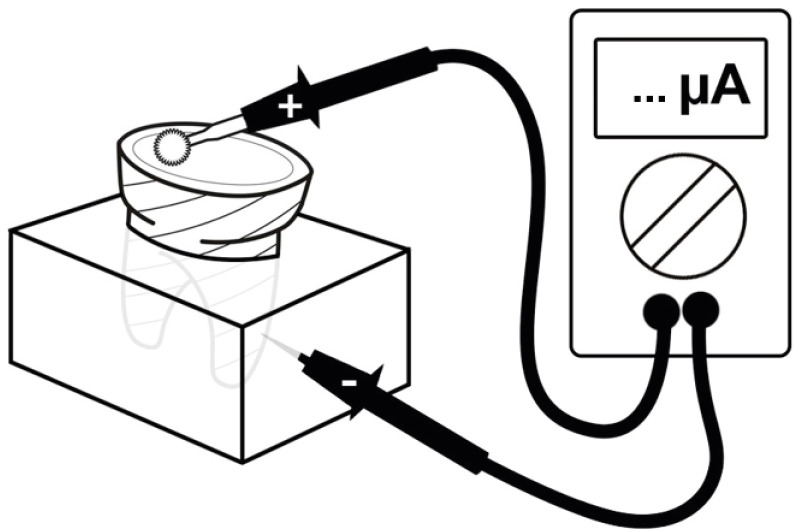
- Adhesive systems applied to dentin substrate under electric current: systematic review
- Carolina Menezes Maciel, Tatiane Cristina Vieira Souto, Bárbara de Almeida Pinto, Laís Regiane Silva-Concilio, Kusai Baroudi, Rafael Pino Vitti
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e55. Published online November 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this systematic review was to collect and discuss the technique of adhesive systems application on dentin substrate under electric current.
Materials and Methods The first search strategy was based on data available at PubMed, LILACS, Scielo, Scopus, and Cochrane Library, using a combination of descriptors such as “dentin bond agents OR adhesive system AND electric current OR electrobond” or “dentin bonding agents OR dentin bonding agent application OR adhesive system AND electric current OR electrobond”, with no limit regarding the publication year. The second search strategy was based on the articles' references found previously. An additional search strategy was applied that concerned the proposed theme in the SBU-UNICAMP (Unicamp's Library System Institutional Repository).
Results Twelve studies published between 2006 and 2020 were found. The analyses of the selected studies showed that the use of electric current during adhesive systems application on dentin, whether conventional or self-conditioning, increases resinous monomer infiltration in the dentin substrate, which improves the hybridization processes and the bond strength of the restorative material to dentin.
Conclusions Despite the favorable results related to the use of this technique, there is still no specific protocol for the application of adhesive systems under electric current.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
Rim Bourgi
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Iontophoresis effects of two-step self-etch and total-etch systems on dentin permeability and sealing of composite restoration under simulated pulpal pressure
Orapin Ajcharanukul, Peeraya Santikulluk, Palat Sasingha, Sirithorn Sabpawat, Kanokporn Sukyanan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
- 2,021 View
- 14 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
- Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e54. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e54
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
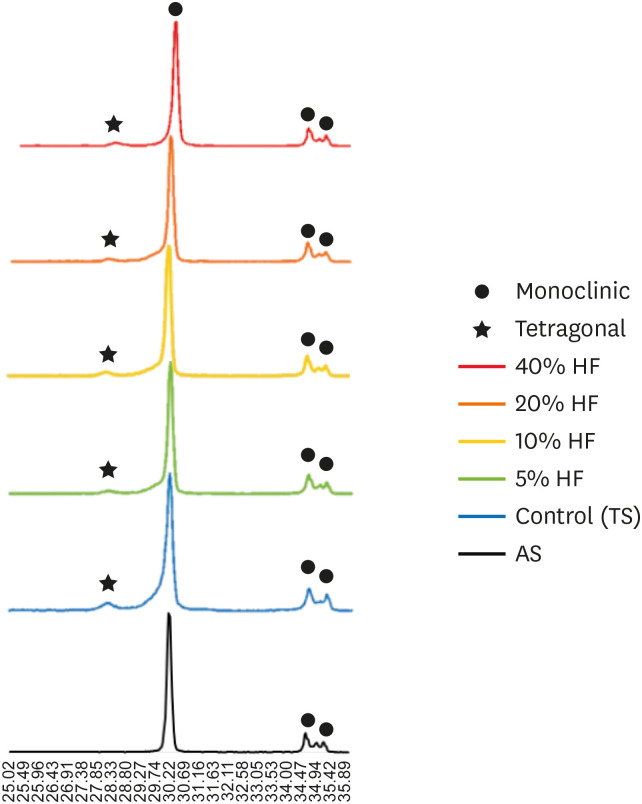
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to quantify phase transformation after hydrofluoric acid (HF) etching at various concentrations on the surface of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), and to evaluate changes in bonding strength before and after thermal cycling.
Materials and Methods A group whose Y-TZP surface was treated with tribochemical silica abrasion (TS) was used as the control. Y-TZP specimens from each experimental group were etched with 5%, 10%, 20%, and 40% HF solutions at room temperature for 10 minutes. First, to quantify the phase transformation, Y-TZP specimens (
n = 5) treated with TS, 5%, 10%, 20% and 40% HF solutions were subjected to X-ray diffraction. Second, to evaluate the change in bond strength before and after thermal cycling, zirconia primer and MDP-containing resin cement were sequentially applied to the Y-TZP specimen. After 5,000 thermal cycles for half of the Y-TZP specimens, shear bond strength was measured for all experimental groups (n = 10).Results The monoclinic phase content in the 40% HF-treated group was higher than that of the 5%, 10%, and 20% HF-treated groups, but lower than that of TS-treated group (
p < 0.05). The 40% HF-treated group showed significantly higher bonding strength than the TS, 5%, and 10% HF-treated groups, even after thermal cycling (p < 0.05).Conclusions Through this experiment, the group treated with SiO2 containing air-borne abrasion on the Y-TZP surface showed higher phase transformation and higher reduction in bonding strength after thermal cycling compared to the group treated with high concentration HF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase transition regulation and enhancement of optical properties in YPO4:Eu3+ through the influence of alkali metal ions
Junwei Zhan, Liusai Yang, Yaoxian Zhu, Yifan Zhu, Jianlei Liu, Siyan Peng, Jianping Zou
Journal of Molecular Structure.2026; 1352: 144420. CrossRef - Etchability of zirconia ceramics and its effect on adhesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Anina Sieber, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104303. CrossRef - Effect of BaTiO particle size and distribution on the BaTiO-3Y-TZP interface reactivity of bioactive ceramic composites
João Pinto, Michael Gasik, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva
Ceramics International.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving the Clinical Performance of Dental Implants Through Advanced Surface Treatments: The Case of Ti and ZrO2 Coatings
Mohamed Aissi, Qanita Tayyaba, Azzedine Er-Ramly, Hendra Hermawan, Nadia Merzouk
Metals.2025; 15(3): 320. CrossRef - Enhancing the bonding of zirconia to resin by constructing a graded zirconia-glass composite surface
Zhiqi Yan, Jiale Li, Jing Chen, Zhe Zhao, Fan Li, Ling Zhang, Jihua Chen, Fu Wang
Surfaces and Interfaces.2025; 64: 106374. CrossRef - Surface property changes observed in zirconia during etching with high-concentration hydrofluoric acid over various immersion times
Ga-Eul YOU, Myung-Jin LIM, Kyung-San MIN, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(1): 52. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength for different generation of zirconia CAD/CAM blocks
Man-Jong Cho, Sunwoong Song, Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park, Bum-Soon Lim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(3): 157. CrossRef - Is zirconia surface etching a viable alternative to airborne particle abrasion? A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Carlo D'Alessandro, Uros Josic, Claudia Mazzitelli, Tatjana Maravic, Laurel Graham, Carlo Barausse, Annalisa Mazzoni, Lorenzo Breschi, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105394. CrossRef - Exploring Zirconia Adhesion: Pre and Postsintering Physical Surface Treatment, Chemical Treatment, and Cement Interactions
Flávia Gonçalves, Mirko Dennys Ayala-Perez, Francisco Carlos dos Santos Reis, Walter Gomes Miranda-Júnior, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 3Y-TZP electrostatic painting to increase bond strength to dentin and dental prostheses
Alessandro Brito Thomaz, Carlos Nelson Elias, Heraldo Elias Salomão dos Santos, Celso Renato de Souza Resende, Claudinei dos Santos
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 26: 9063. CrossRef - Effect of surface topography and wettability on shear bond strength of Y-TZP ceramic
Suriyakul Wongsue, Ornnicha Thanatvarakorn, Taweesak Prasansuttiporn, Piyarat Nimmanpipug, Thanapat Sastraruji, Keiichi Hosaka, Richard M. Foxton, Masatoshi Nakajima
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesive Cementation of Zirconia Based Ceramics-Surface Modification Methods Literature Review
Magdalena Szawioła-Kirejczyk, Karolina Chmura, Krzysztof Gronkiewicz, Andrzej Gala, Jolanta E. Loster, Wojciech Ryniewicz
Coatings.2022; 12(8): 1067. CrossRef - Y-TZP Physicochemical Properties Conditioned with ZrO2 and SiO2 Nanofilms and Bond Strength to Dual Resin Cement
Ricardo Faria Ribeiro, Danilo Flamini Oliveira, Camila Bussola Tovani, Ana Paula Ramos, Ana Flavia Sanches Borges, Adriana Claudia Lapria Faria, Rossana Pereira de Almeida, Renata Cristina Silveira Rodrigues
Materials.2022; 15(22): 7905. CrossRef - Enhanced osteogenic activity of titania-modified zirconia implant by ultraviolet irradiation
Shuang Tang, Yan Wang, Zhenyu Zong, Ning Ding, Zutai Zhang
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Phase transition regulation and enhancement of optical properties in YPO4:Eu3+ through the influence of alkali metal ions
- 2,090 View
- 22 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

- Push-out bond strength and marginal adaptation of apical plugs with bioactive endodontic cements in simulated immature teeth
- Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Eduardo Nunes, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Manoel Brito Júnior, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Stephen Cohen, Frank Ferreira Silveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e53. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
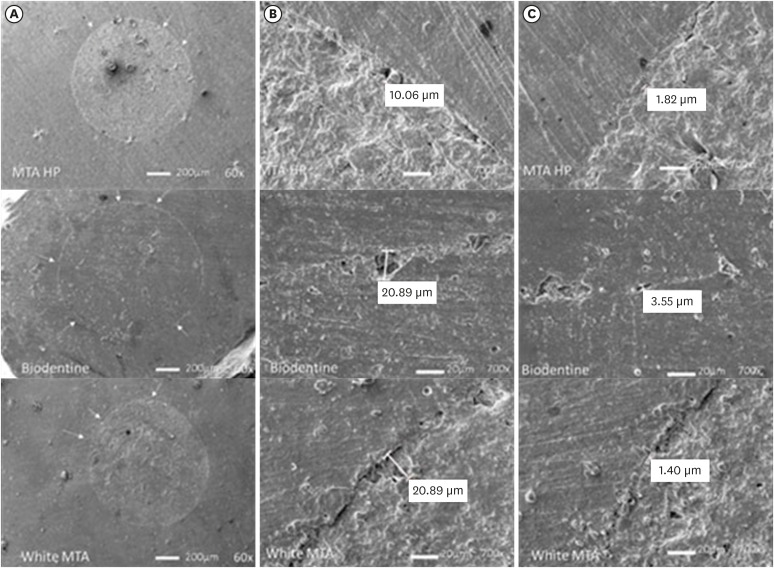
ePub Objectives This study evaluates the bond strength and marginal adaptation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) Repair HP and Biodentine used as apical plugs; MTA was used as reference material for comparison.
Materials and Methods A total of 30 single-rooted teeth with standardized, artificially created open apices were randomly divided into 3 groups (
n = 10 per group), according to the material used to form 6-mm-thick apical plugs: group 1 (MTA Repair HP); group 2 (Biodentine); and group 3 (white MTA). Subsequently, the specimens were transversely sectioned to obtain 2 (cervical and apical) 2.5-mm-thick slices per root. Epoxy resin replicas were observed under a scanning electron microscope to measure the gap size at the material/dentin interface (the largest and smaller gaps were recorded for each replica). The bond strength of the investigated materials to dentin was determined using the push-out test. The variable bond strengths and gap sizes were evaluated independently at the apical and cervical root dentin slices. Data were analyzed using descriptive and analytic statistics.Results The comparison between the groups regarding the variables' bond strengths and gap sizes showed no statistical difference (
p > 0.05) except for a single difference in the smallest gap at the cervical root dentin slice, which was higher in group 3 than in group 1 (p < 0.05).Conclusions The bond strength and marginal adaptation to root canal walls of MTA HP and Biodentine cement were comparable to white MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Biodentine for Apexification of Immature Teeth of Children: A Scoping Review
Liz M Gerard, Sumit Gaur
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(5): 573. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-Out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, a Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, and Two Novel Antibacterial-Enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Arokia Rajkumar Shancy Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Rajalakshmanan Eswaramoorthy, Abirami Arthanari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push out bond strength of hydraulic cements used at different thicknesses
C. Ruiz Durán, Dra L. Gancedo-Caravia, V. Vera González, C. González Losada
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,520 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

-
Comparative evaluation of
Emblica officinalis as an etchant and an MMP inhibitor with orthophosphoric acid and chlorhexidine on the microshear bond strength of composite resin: anex vivo study - Divya Sangeetha Rajkumar, Annapoorna Ballagere Mariswamy
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e36. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
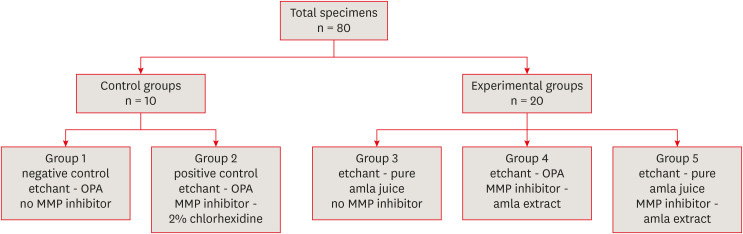
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate
Emblica officinalis (Indian gooseberry or amla) as an acid etchant and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, and to compare its effect on the microshear bond strength of composite resin with orthophosphoric acid (OPA) and 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) as an acid etchant and MMP inhibitor, respectively.Materials and Methods The etching effect and MMP-inhibiting action of amla on dentin samples were confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and gelatin zymography, respectively. Dentinal slabs (3 mm thick) from 80 extracted human molars were divided into 10 and 20 samples to form 2 control groups and 3 experimental groups. Groups 1, 2, and 4 were etched with OPA and groups 3 and 5 with amla juice. An MMP inhibitor was then applied: CHX for group 2 and amla extract for groups 4 and 5. Groups 1 and 3 received no MMP inhibitor. All specimens received a standardized bonding protocol and composite resin build-up, and were subjected to microshear bond strength testing. The force at which the fracture occurred was recorded and statistically analyzed.
Results Amla juice had a similar etching effect as a self-etch adhesive in SEM and 100% amla extract was found to inhibit MMP-9 by gelatin zymography. The microshear bond strength values of amla were lower than those obtained for OPA and CHX, but the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusions Amla has a promising role as an acid etchant and MMP inhibitor, but further studies are necessary to substantiate its efficacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro assessment of anti-glioblastoma potential of Emblica officinalis methanolic fruit extract and green nanoparticles in U87-MG cells
Kokkonda Jackson Sugunakara Chary, Anuradha Sharma, Amrita Singh
Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Eco-conscious synthesis of novel 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as potent Anti-microbial agent and comparative study of cell viability and cytotoxicity in HEK-293 cell line utilizing Indian gooseberry (Phyllanthus emblica) fruit extract
Bhaktiben R. Bhatt, Kamalkishor Pandey, Tarosh Patel, Anupama Modi, Chandani Halpani, Vaibhav D. Bhatt, Bharat C. Dixit
Bioorganic Chemistry.2024; 153: 107936. CrossRef - Cell mediated ECM-degradation as an emerging tool for anti-fibrotic strategy
Peng Zhao, Tian Sun, Cheng Lyu, Kaini Liang, Yanan Du
Cell Regeneration.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into the development of versatile dentin bonding agents to increase the durability of the bonding interface
Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto, Teresa de Lisieux Guedes Ferreira Lôbo, Raphaela Farias Rodrigues, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Aurélio Bomfim da Silva
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- In vitro assessment of anti-glioblastoma potential of Emblica officinalis methanolic fruit extract and green nanoparticles in U87-MG cells
- 1,830 View
- 20 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of adhesive application method on repair bond strength of composite
- Hee Kyeong Oh, Dong Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e32. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
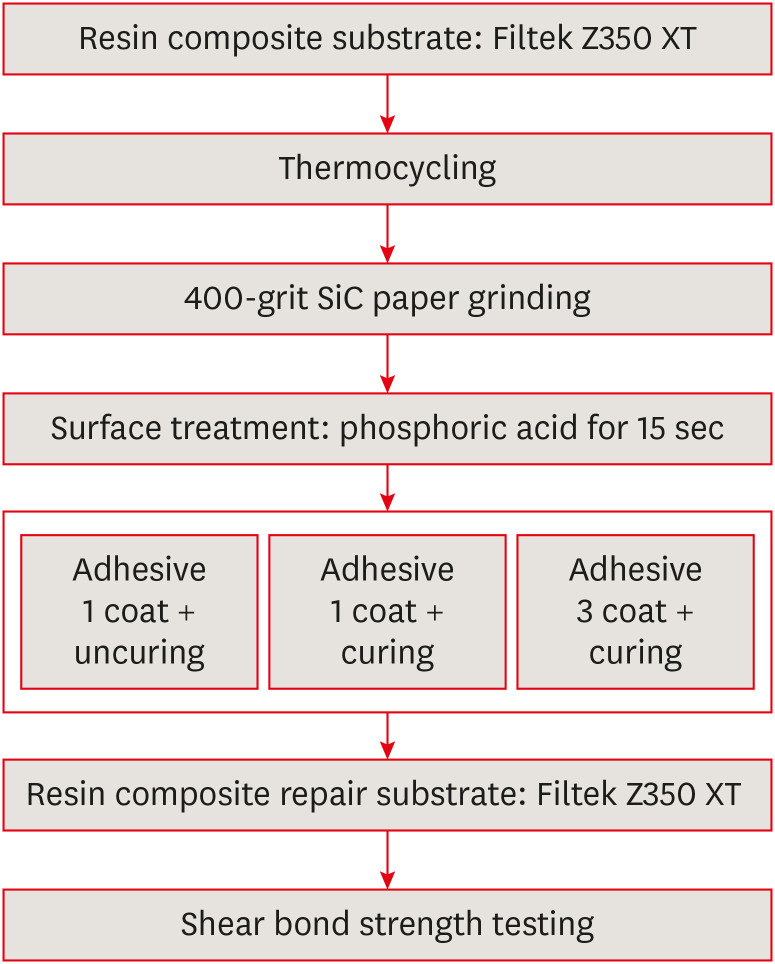
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of the application method of universal adhesives on the shear bond strength (SBS) of repaired composites, applied with different thicknesses.
Materials and Methods The 84 specimens (Filtek Z350 XT) were prepared, stored in distilled water for a week and thermocycled (5,000 cycles, 5°C to 55°C). They were roughened using 400-grit sandpapers and etched with phosphoric acid. Then, specimens were equally divided into 2 groups; Single Bond Universal (SU) and Prime&Bond Universal (PB). Each group was subdivided into 3 subgroups according to application methods (
n = 14); UC: 1 coat + uncuring, 1C: 1 coat + curing, 3C: 3 coats + curing. After storage of the repaired composite for 24 hours, specimens were subjected to the SBS test and the data were statistically analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance and independentt -tests. Specimens were examined with a stereomicroscope to analyze fracture mode and a scanning electron microscope to observe the interface.Results Adhesive material was a significant factor (
p = 0.001). Bond strengths with SU were higher than PB. The highest strength was obtained from the 1C group with SU. Bonding in multiple layers increased adhesive thicknesses, but there was no significant difference in SBS values (p = 0.255). Failure mode was predominantly cohesive in old composites.Conclusions The application of an adequate bonding system plays an important role in repairing composite resin. SU showed higher SBS than PB and the additional layers increased the adhesive thickness without affecting SBS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different surface treatments and adhesive systems on shear bond strength in universal nanohybrid composite resin repair
Merve Kütük Ömeroğlu, Melek Çam, Işıl Doğruer, Zeynep Buket Kaynar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Universal Adhesive Etching Mode on Shear Bond Strength of Pulp Capping Materials to Deep Dentin
Shahram Amirifar, Saba Tohidkhah, Seyedeh Mahsa Sheikh-Al-Eslamian, Mahdi Abbasi, Fatemeh Farshad, Elham Ahmadi, Carlos M. Ardila
BioMed Research International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength and Finite Element Stress Analysis of Composite Repair Using Various Adhesive Strategies With and Without Silane Application
Elif Ercan Devrimci, Hande Kemaloglu, Cem Peskersoy, Tijen Pamir, Murat Turkun
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(15): 8159. CrossRef
- The effect of different surface treatments and adhesive systems on shear bond strength in universal nanohybrid composite resin repair
- 3,797 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of radiation therapy on the dislocation resistance of root canal sealers applied to dentin and the sealer-dentin interface: a pilot study
- Pallavi Yaduka, Rubi Kataki, Debosmita Roy, Lima Das, Shachindra Goswami
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e22. Published online March 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated and compared the effects of radiation therapy on the dislocation resistance of AH Plus and BioRoot RCS applied to dentin and the sealer-dentin interface.
Materials and Methods Thirty single-rooted teeth were randomly assigned to 2 groups (
n = 15 each): AH Plus (Dentsply DeTrey) and BioRoot RCS (Septodont). Each group was subdivided into control and experimental groups. The experimental group was subjected to a total radiation dose of 60 Gy. The root canals of all samples were cleaned, shaped, and obturated using the single-cone technique. Dentin slices (1 mm) were sectioned from each root third for the push-out test and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was done to examine the sealer-dentin interface. The failure mode was determined using stereomicroscopy. Bond strength data were analyzed by the independentt -test, 1-way analysis of variance, and the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05).Results Significantly lower bond strength was observed in irradiated teeth than non-irradiated teeth in the AH Plus group (
p < 0.05). The BioRoot RCS group showed no significant reduction in bond strength after irradiation (p > 0.05) and showed a higher post-irradiation bond strength (209.92 ± 172.26 MPa) than the AH Plus group. SEM revealed slightly larger gap-containing regions in irradiated specimens from both groups.Conclusions The dislocation resistance of BioRoot RCS was not significantly changed by irradiation and was higher than that of AH Plus. BioRoot RCS may be the sealer of choice for root canal treatment in patients undergoing radiation therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of radiotherapy on endodontic treatment: a scoping review
Guilherme Pauletto, Giovanna Isabel Mittmann Voigt, Sidnei Flores de Pellegrin, Yasmin Padoin, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier
Odontology.2026; 114(1): 24. CrossRef - Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
Lívia Ribeiro, Luíz Carlos de Lima Dias-Júnior, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Paulo Marcelo Rodrigues, Vicente Ribeiro Netto, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Renata Gondo Machado, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Luc
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104252. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of bioceramic-based sealers following different irrigation activation techniques
Fatma Begüm Peker, Hümeyra Çapkın, Ahsen Narbay
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of radiation therapy regimen on the dislodgement resistance of endodontic sealers: A micro push-out test
Marcos Testa Magoga, Rafaela Lourdes de Sousa, Luiz Carlos Lima Dias-Junior, Rayssa Sabino-Silva, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Paulo Marcelo Rodrigues, Vicente Ribeiro Netto, Ricardo Machado, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garci
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 136: 103894. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Effects of radiotherapy dose and application time on the load-to-failure values of teeth filled with different sealers
Ozgun Gulderen, Esma Saricam, Sedef Gökhan Açikgöz, Yılmaz Tezcan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasonic activation of the endodontic sealer enhances its intratubular penetration and bond strength to irradiated root dentin
Luana Duart Jordani, Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Julia Menezes Savaris, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Luciano Roberto da Silva, Marcio Toshio Umeda Takashima, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas d
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 917. CrossRef - Effect of the timing of primary endodontic treatment and dosage of radiation therapy on the filling material removal
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias‐Junior, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Cristiane Maria Almeida, Luciano Roberto da Silva, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 321. CrossRef - Does radiation therapy affect adhesion of tricalcium silicate cements to root dentin?
Lochan KHULLAR, Nidambur Vasudev BALLAL, Tan Fırat EYÜBOĞLU, Mutlu ÖZCAN
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the timing of radiation therapy on the push‐out strength of resin cement to root dentine
Patrícia da Agostim Cancelier, Renata Gondo Machado, Júlia Menezes Savaris, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Paulo Marcelo Rodrigues, Vicente Ribeiro Netto, Kamile Leonardi Dutra‐Horstmann, Lucas da
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 122. CrossRef - Influence of irrigation and laser assisted root canal disinfection protocols on dislocation resistance of a bioceramic sealer
Ivona Bago, Ana Sandrić, Katarina Beljic-Ivanovic, Boris Pažin
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 40: 103067. CrossRef - Influence of 2% chlorhexidine on the dislodgement resistance of AH plus, bioroot RCS, and GuttaFlow 2 sealer to dentin and sealer-dentin interface
Debosmita Roy, Rubi Kataki, Lima Das, Khushboo Jain
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(6): 642. CrossRef
- The impact of radiotherapy on endodontic treatment: a scoping review
- 2,392 View
- 24 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Effect of phytic acid as an endodontic chelator on resin adhesion to sodium hypochlorite-treated dentin
- Mohannad Nassar, Noriko Hiraishi, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Maria JRH. Romero, Masayuki Otsuki, Junji Tagami
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e44. Published online August 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Phytic acid (IP6), a naturally occurring agent, has been previously reported as a potential alternative to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). However, its effect on adhesion to sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)-treated dentin and its interactions with NaOCl have not been previously reported. Thus, in this study, the effects of IP6 on resin adhesion to NaOCl-treated dentin and the failure mode were investigated and the interactions between the used agents were analyzed.
Materials and Methods Micro-tensile bond strength (µTBS) testing was performed until failure on dentin treated with either distilled water (control), 5% NaOCl, or 5% NaOCl followed with chelators: 17% EDTA for 1 minute or 1% IP6 for 30 seconds or 1 minute. The failed specimens were assessed under a scanning electron microscope. The reaction of NaOCl with EDTA or IP6 was analyzed in terms of temperature, pH, effervescence, and chlorine odor, and the effects of the resulting mixtures on the color of a stained paper were recorded.
Results The µTBS values of the control and NaOCl with chelator groups were not significantly different, but were all significantly higher than that of the group treated with NaOCl only. In the failure analysis, a distinctive feature was the presence of resin tags in samples conditioned with IP6 after treatment with NaOCl. The reaction of 1% IP6 with 5% NaOCl was less aggressive than the reaction of the latter with 17% EDTA.
Conclusions IP6 reversed the adverse effects of NaOCl on resin-dentin adhesion without the chlorine-depleting effect of EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
Md Sofiqul Islam, Shadi El Bahra, Smriti Aryal A C, Vivek Padmanabhan, Abdulaziz Al Tawil, Ihab Saleh, Muhammed Mustahsen Rahman, Upoma Guha
Polymers.2025; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part I: Impact of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on the Chemical Composition and Structural Integrity of Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Sara Fateixa, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1848. CrossRef - Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - Effects of phytic acid and etidronic acid using continuous and sequential chelation on the removal of smear layer, dentin microhardness, and push-out bond strength of calcium silicate-based cement
Ecehan Hazar, Ahmet Hazar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of free available chlorine in sodium hypochlorite solutions admixed with novel chelating agents
Somya Tyagi, Sonali Taneja, Kandasamy Nagarajan, Divya Chowdhary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 188. CrossRef - Effect of different chelating agents, with and without activation, including XP-endo Finisher, on root dentin microhardness: An in vitro study
Mahmoud Mohamed A. Sherif, Mai Hamdy Ragab, Marwa ElSayed Sharaan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(3): 282. CrossRef - Oracle of phytic acid in dental panacea – Insight into properties, therapeutic effect, regeneration, materials interaction and oral physiology
Ummey Salma, C. Pushpalatha, SV. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shilpa Bhandi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(8): 1093. CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Is a mix – A fix? “A microscopic analysis of depth of penetration of three combinations of irrigants”
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Nadimpalli Mahendra Varma, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(2): 186. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on dentinal collagen solubilization and its binding and debinding potentials to dentin
Diletta Forgione, Mohannad Nassar, Roda Seseogullari-Dirihan, Ahmed Jamleh, Arzu Tezvergil-Mutluay
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104361. CrossRef - Application of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol in Dental Medicine: An Overview
Ana Druzijanic, Mare Kovic, Marija Roguljic, Livia Cigic, Martina Majstorovic, Ivana Vucenik
Biomolecules.2023; 13(6): 913. CrossRef - Ex-vivo study about antimicrobial effectiveness of phytic acid against Enterococcus faecalis into root canals
Giulia BOSCHI, Giorgio PICCINELLI, Carlo BONFANTI, Stefano A. SALGARELLO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on bond strength and interfacial integrity of universal adhesive to deep dentin
Ahmed Mostafa Attia, Ahmed Fawzy Abo-Elezz, Rehab Khalil Safy
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 116. CrossRef - Resin-Based Cement Applied to Enamel and Dentin Pre-Treated with Phytic Acid: An In Vitro Study
Mohannad Nassar, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Smriti Aryal A C, Hatem Mostafa El-Damanhoury, Salvatore Sauro, Noriko Hiraishi
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11976. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Phytic Acid: Properties and Potential Applications in Dentistry
Mohannad Nassar, Rania Nassar, Husain Maki, Abdullah Al-Yagoob, Mahmood Hachim, Abiola Senok, David Williams, Noriko Hiraishi
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
- 2,334 View
- 19 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Bonding of a resin-modified glass ionomer cement to dentin using universal adhesives
- Muhittin Ugurlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e36. Published online June 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aims to assess the effect of universal adhesives pretreatment on the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement to dentin.
Materials and Methods Fifty caries-free human third molars were employed. The teeth were randomly assigned into five groups (
n = 10) based on dentin surface pretreatments: Single Bond Universal (3M Oral Care), Gluma Bond Universal (Heraeus Kulzer), Prime&Bond Elect (Dentsply), Cavity Conditioner (GC) and control (no surface treatment). After Fuji II LC (GC) was bonded to the dentin surfaces, the specimens were stored for 7 days at 37°C. The specimens were segmented into microspecimens, and the microspecimens were subjugated to microtensile bond strength testing (1.0 mm/min). The modes of failure analyzed using a stereomicroscope and scanning electron microscopy. Data were statistically analyzed with one-way analysis of variance and Duncan tests (p = 0.05).Results The surface pretreatments with the universal adhesives and conditioner increased the bond strength of Fuji II LC to dentin (
p < 0.05). Single Bond Universal and Gluma Bond Universal provided higher bond strength to Fuji II LC than Cavity Conditioner (p < 0.05). The bond strengths obtained from Prime&Bond Elect and Cavity Conditioner were not statistically different (p > 0.05).Conclusions The universal adhesives and polyacrylic acid conditioner could increase the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) to dentin. The use of universal adhesives before the application of RMGIC may be more beneficial in improving bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of nanochitosan incorporation on the performance of resin-modified glass ionomer luting cement: a comprehensive in vitro study
Mostafa A. Abdelshafi, Nesma Elgohary, Ahmed Shams
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronal cavity pretreatment agents and restoration protocols effect on microleakage of endodontically treated teeth
Lena Bal, Cangül Keskin, Aybüke Karaca Sakallı, Osman Fatih Aydın
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2026; 7(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of effect of natural collagen cross-linker and silver diamine fluoride pre-treatment before resin-modified glass ionomer cement restoration on dentin of primary teeth: An in vitro study
Mrunal Pawar, N. D. Shashikiran, Sachin Chandrashekar Gugwad, Namrata Gaonkar, Savita Hadakar, Pali Nikose, Sonali Kisan Waghmode, Ankita Maurya
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2026; 44(1): 132. CrossRef - Clinical evaluation of giomer-based injectable resin composite versus resin-modified glass ionomer in class V carious lesions over 18 months: A randomized clinical trial
Reham Hendam, Rania Mosallam, Dina Kamal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(1): 50. CrossRef - Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Bioactive restorative materials in dentistry: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, clinical applications, and future directions
Dina Abozaid, Amr Azab, Mohammad A. Bahnsawy, Mohamed Eldebawy, Abdullah Ayad, Romesa soomro, Enas Elwakeel, Maged Ahmed Mohamed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Leakage and Shear Bond Strength of Cention N, Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cement (RMGIC), and Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC): An In Vitro Study
Khushboo Singh, Debapriya Pradhan, Saurabh Tiwari, Raksha Thakur, Priyamvada Sharma, Devika Agrawal, Mahima Singh, Devshree Jawalikar, Delphina Michael Kapoor, Jyoti Priiya Kodimela
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Nanosilver Fluoride Application on the Microtensile Bond Strength of Glass Ionomer Cement and Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement on Primary Carious Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Ila Srinivasan, Yuthi Milit, Anushka Das, Neeraja Ramamurthy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(5): 565. CrossRef - Effect of Surface Treatments on Shear-bond Strength of Glass Ionomer Cements to Silver Diamine Fluoride-treated Simulated Carious Dentin
WT Koh, OT Yeoh, NA Yahya, AU Yap
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 714. CrossRef - Desensitizing agents’ post-bleaching effect on orthodontic bracket bond strength
Gufa Bagus Pamungkas, Dyah Karunia, Sri Suparwitri
Dental Journal.2024; 57(1): 45. CrossRef - Successful Rehabilitation of Traumatized Immature Teeth by Different Vital Pulp Therapies in Pediatric Patients
Mohammad Kamran Khan
Journal of the Scientific Society.2023; 50(1): 111. CrossRef - Do bioactive materials show greater retention rates in restoring permanent teeth than non-bioactive materials? A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Juliana Benace Fernandes, Sheila Mondragón Contreras, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Graziela Ribeiro Batista, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of tooth preparation on the microleakage of fissure sealant
Gesti Kartiko Sari, Sri Kuswandari, Putri Kusuma Wardani Mahendra
Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi).2022; 55(2): 67. CrossRef - Rheological Properties, Surface Microhardness, and Dentin Shear Bond Strength of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements Containing Methacrylate-Functionalized Polyacids and Spherical Pre-Reacted Glass Fillers
Whithipa Thepveera, Wisitsin Potiprapanpong, Arnit Toneluck, Somruethai Channasanon, Chutikarn Khamsuk, Naruporn Monmaturapoj, Siriporn Tanodekaew, Piyaphong Panpisut
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2021; 12(3): 42. CrossRef
- Impact of nanochitosan incorporation on the performance of resin-modified glass ionomer luting cement: a comprehensive in vitro study
- 4,491 View
- 45 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
- Miyoung Lim, Chanyong Jung, Dong-Hoon Shin, Yong-bum Cho, Minju Song
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e35. Published online June 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Epoxy resin-based sealers are currently widely used, and several studies have considered AH Plus to be the gold-standard sealer. However, it still has limitations, including possible mutagenicity, cytotoxicity, inflammatory response, and hydrophobicity. Drawing upon the advantages of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium silicate-based sealers were introduced with high levels of biocompatibility and hydrophilicity. Because of the hydrophilic environment in root canals, water resorption and solubility of root canal sealers are important factors contributing to their stability. Sealers displaying lower microleakage and stronger push-out bond strength are also needed to endure the dynamic tooth environment. Although the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers meet International Organization for Standardization recommendations, and they have consistently reported to be biocompatible, they have not overcome conventional resin-based sealers in actual practice. Therefore, further studies aiming to improve the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
Lokhasudhan Govindaraju, Rajeswari Kalaiselvam, Mathan Rajan Rajendran, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Jelena Jacimovic, Henry F. Duncan, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2026; 59(3): 341. CrossRef - Evidence synthesis of postoperative pain with bioceramic vs. epoxy resin sealers: umbrella review of randomized trials within existing systematic reviews
Mrunali Dahikar, Ashish Mandwe, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Suraj Arora, Unmesh Khanvilkar, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical and mechanical properties of a strontium silicate-based sealer
Shannon Wong, Xiaofei Zhu, Tun-Yi Hsu, Sami Chogle, Russell A. Giordano, Yuwei Fan
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of bioceramic-based sealers following different irrigation activation techniques
Fatma Begüm Peker, Hümeyra Çapkın, Ahsen Narbay
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Tapered Gutta-Percha Points on Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Root Canal Sealers
Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanothum
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 285. CrossRef - Effect of Electrical Heat Carrier Temperature on Bacterial Leakage of Endodontically Treated Teeth Using a Bioceramic Sealer
Mir Ahmad Nabavi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Pedram Fattahi, Saber Khazaei
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Assessing the antimicrobial properties of bioceramic sealers enhanced with herbal extracts against E. faecalis
KS Sachin, K Shibani Shetty, KB Jeyalakshmi, S Harishma, S Harshini
Folia Medica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio comparativo de la solubilidad de dos selladores endodónticos biocerámicos y un sellador a base de resinas
//Comparative study of the solubility of two bioceramic endodontic sealers and one epoxi-resin based sealer
Alejandro Leonhardt, Nicolás Paduli, Osvaldo Zmener, Miguel Chantiri
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Bioceramic Endodontic Sealers in HepG2 and V79 Cell Lines: An In Vitro Study Using the Comet and Micronucleus Assays
Antonija Tadin, Marija Badrov, Danijela Juric Kacunic, Nada Galic, Matea Macan, Ivan Kovacic, Davor Zeljezic
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 169. CrossRef - In Vitro Apatite-Forming Ability of Different Root Canal Sealers (A Comparative Study)
Raghad A Al-Askary, Wiaam M. O. Al-Ashou, Sawsan H. Al-Jubori
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(2): 173. CrossRef - Microstructural and elemental characterization of novel bioactive glass bioceramic sealer using Fourier transform infrared and X-ray diffraction analysis
Poulomi Guha, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Antony, Nishitha Arun, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Surendar Ramamoorthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(5): 412. CrossRef - Microstructural and Elemental Characterization of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Ireneusz Piwonski, Tomasz Szmechtyk, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(10): 756. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure-enhanced sealer infiltration for obturating long oval-shaped root canals with the single-cone technique
Yaxu Feng, Brian E. Bergeron, Shijin Zhang, Danyang Sun, Kole Fisher, Franklin R. Tay, Bing Fan
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105909. CrossRef - Effects of different apical preparation sizes and root canal sealers on the fracture resistance of roots aged for 12 months in endodontically retreated mandibular premolars
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Sevda Durust Baris, Ali Turkyilmaz, Ali Erdemir
British Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different endodontic treatment protocols on tooth survival: A retrospective cohort study with multistate analysis and group balancing
Ahmed Elmaasarawi, Mohamed Mekhemar, Andreas Bartols
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(10): 1529. CrossRef - Evaluation of 2,6-xylidine precipitate on sealer penetration of calcium silicate-based sealer and resin-based sealer: An in vitro study
M. B. Kalpana, Divya Shetty, Rajaram Naik
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 183. CrossRef - Translational Advances in Regenerative Dentistry: Functional Biomaterials and Emerging Technologies
Seher Yaylacı, Hacer Eberliköse, Hakan Ceylan
Current Oral Health Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of heat and non-heat compatible bioceramic sealers in warm obturation: an in vitro SEM study
Thanomsuk Jearanaiphaisarn, Thanida Leelayuttakarn, Panisara Amatamahuthana, Pinmanus Chenpairojsakul, Keskanya Subbalekha, Pavena Chivatxaranukul
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
Steven K. Uttech, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Maria Martell, Bruno Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1764. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of adhesion abilities between AH Plus® Bioceramic, Ceraseal® and AH Plus® on root canal dentine surfaces
Ike Dwi Maharti, Indira Larasputri, Nendar Herdianto, Anggraini Margono, Riesma Tasomara, Romilda Rosseti
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(9): 881. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of single-cone bioceramic obturation versus traditional techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Firas Elmsmari, Yousef Elsayed, Abdelrahman Aboubakr, Mahdi Kaafarani, Osama Nour, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(6): 1422. CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation Solutions on the Setting Time, Solubility, and pH of Three Types of Premixed Bioceramic‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Kitichai Singharat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Zhengrui Li
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteogenic Potential of Various Premixed Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers on Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Na-Hyun You, Donghee Lee, Yemi Kim, Sieun Nam, Sin-Young Kim
Materials.2025; 18(23): 5326. CrossRef - Polydopamine‐Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Root Canal Sealer: Characterization, Biological, and Physicochemical Properties
Arul Nayagi Raj, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Giuseppe Ciccarella
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of rarely seen internal tunnelling root resorption associated with a maxillary permanent incisor
Kirsty A. Carney, Thibault N. E. Colloc, Julie K. Kilgariff
British Dental Journal.2024; 236(12): 955. CrossRef - Top tips for treatment planning: tooth-by-tooth prognosis - Part 3: endodontic prognosis
Prashanti Eachempati, Andrew Harris, Guy Lambourn, Tony Francis, Ewen McColl
British Dental Journal.2024; 237(9): 686. CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate-based sealers based on micro-computed tomographic evaluation − A systematic review
Sundus Mohammed Bukhary
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1278. CrossRef - Evaluation of Setting Time, Flowability, Film Thickness, and Radiopacity of Experimental Monocalcium Silicate‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Sukanya Juntha, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Carlos M. Ardila
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment and Demand for Continuing Education among Thai Dental Practitioners
Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Pakit Tungsawat, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanotham
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic sealers after exposure to chlorhexidine digluconate: An assessment of physicochemical properties
Vasileios Kapralos, Josette Camilleri, Andreas Koutroulis, Håkon Valen, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Dental Materials.2024; 40(3): 420. CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Interfacial adaptation of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2024; 18(2): 115. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Solubility of Endoseal and AH26 Root Canal Sealers
Nooshin Fakhari, Ali Reza Mirjani, Abbas Bagheri, Jalil Modaresi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2024; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Novel bioactive nanospheres show effective antibacterial effect against multiple endodontic pathogens
Jin Liu, Haoze Wu, Jun Qiu, Sirui Yang, Doudou Xiang, Xinhua Zhang, Jinxin Kuang, Min Xiao, Qing Yu, Xiaogang Cheng
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28266. CrossRef - Evaluation of canal patency and cleanliness following retreatment of bioceramic sealer‐obturated root canals using three different irrigant activation protocols
Daiasharailang Lyngdoh, Sharique Alam, Huma Iftekhar, Surendra Kumar Mishra
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 475. CrossRef - Antibiofilm Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Based Endodontic Sealers
Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Vsevolod Fedoseev, Carmen Solana, Cecilia Muñoz-Sandoval, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3937. CrossRef - Enhancing the Biological Properties of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Calcium Silicate Cements: An In Vitro Study
Minji Choi, Jiyoung Kwon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Duck-Su Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 337. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and cell migration evaluation of a strontium silicate-based root canal sealer on stem cells from rat apical papilla: an in vitro study
Guanglei Zhou, Yu Zhao, Liangjing Cai, Liwei Liu, Xu Li, Lu Sun, Jiayin Deng
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Analysis of Physico–Mechanical Properties of Commercial and Experimental Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Abdulmajeed Kashaf, Faisal Alonaizan, Khalid S. Almulhim, Dana Almohazey, Deemah Abdullah Alotaibi, Sultan Akhtar, Ashwin C. Shetty, Abdul Samad Khan
Bioengineering.2024; 11(11): 1079. CrossRef - Chemical, Antibacterial, and Cytotoxic Properties of Four Different Endodontic Sealer Leachates Over Time
Jo-Hsun Chen, Veksina Raman, Sarah A. Kuehne, Josette Camilleri, Josefine Hirschfeld
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(11): 1612. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Fracture Resistance of Endodontic Sealer Types and Filling Methods
Yun Song, Kee-Deog Kim, Bock-Young Jung, Wonse Park, Nan-Sim Pang
Materials.2024; 18(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Removal of Bioceramic Sealers Using Rotary Retreatment Files Supplemented with Passive Ultrasonic Activation: An In Vitro Study
Anuradha B Patil, Amrut Bambawale, Pooja R Barghare, Sumanthini V Margasahayam, Divya Naik, Jayeeta S Verma
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 292. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of Nonperforating Internal Root Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor: A Case Report with a 4-Year Follow-Up
Paras M. Gehlot, Divya S. Rajkumar, Annapoorna B. Mariswamy, Upendra Natha N. Reddy, Chaitanya Chappidi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S3005. CrossRef - Evaluating the Sealing Performance of Endodontic Sealers: Insights Into Achieving Complete Sealing
Ajay Chhabra, Ramya K P., Saravana Prathap, Priyanka Yadav, Himani Mehra, Sona J Parvathy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vehicles on the physical properties and biocompatibility of premixed calcium silicate cements
Gitae SON, Gyeung Mi SEON, Sang Hoon CHOI, Hyeong-Cheol YANG
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(2): 276. CrossRef - Comparative cytotoxicity study of putty- and powder-type calcium silicate cements
Sora Park, Dohyun Cho, Ji Hyeon Yoon, Yeonjoo Kang, Quang Canh Vo, Gitae Son, Hongjoo Park, Hyeong-Cheol Yang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 259. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Dentinal Tubule Penetrability and Bond Strength of Two Novel Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karissa Shieh, Jack Yang, Elsa Heng Zhu, Ove Andreas Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour
Materials.2023; 16(9): 3309. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Activity of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers Compared to Conventional Resin-Based Sealer in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells
Mohammad Shokrzadeh, Farzaneh Sadat Motafeghi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Mohammad Ghorbani, Azam Haddadi Kohsar, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of three different photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy on bond strength of a calcium silicate‐based sealer to radicular dentin
Cihan Küden, Seda Nur Karakaş
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 265. CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealer on postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis
Cynthia Maria Chaves Monteiro, Ana Cristina Rodrigues Martins, Alessandra Reis, Juliana Larocca de Geus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Activity of Five Calcium Silicate Based Root Canal Sealers against a Multispecies Engineered Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Carla Zogheib, Issam Khalil, Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, Germain Sfeir, May Mallah, Roula El Hachem
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 707. CrossRef - Calcium silicate sealers in endodontics
Archana Chavan, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2023; 39(87): 2624. CrossRef - Assessing the Sealing Performance and Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Treatment in Patients with Chronic Apical Periodontitis Using Epoxy Resin and Calcium Salicylate Seals
Razvan Mihai Horhat, Bogdan Andrei Bumbu, Laura Orel, Oana Velea-Barta, Laura Cirligeriu, Gratiana Nicoleta Chicin, Marius Pricop, Mircea Rivis, Stefania Dinu, Delia Ioana Horhat, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Rodica Anamaria Negrean, Luminita
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1137. CrossRef -
In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Potential of an Endodontic Bioceramic Material
Soumya Sheela, Mohannad Nassar, Fatma M. AlGhalban, Mehmet O. Gorduysus
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(02): 548. CrossRef - Dislodgment Resistance, Adhesive Pattern, and Dentinal Tubule Penetration of a Novel Experimental Algin Biopolymer-Incorporated Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealer
Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Norhayati Luddin, Huwaina Abd Ghani, Josephine Chang Hui Lai, Tahir Yusuf Noorani
Polymers.2023; 15(5): 1317. CrossRef - Impact of Final Irrigation Protocol on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Types of Endodontic Sealers
Germain Sfeir, Frédéric Bukiet, Wajih Hage, Roula El Hachem, Carla Zogheib
Materials.2023; 16(5): 1761. CrossRef - Clinical Approaches to the Three-Dimensional Endodontic Obturation Protocol for Teeth with Periapical Bone Lesions
Angela Gusiyska, Elena Dyulgerova
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9755. CrossRef - Evaluating the bioactivity of endodontic sealers with respect to their thermo-nanomechanical properties
Andreea Marica, Luminita Fritea, Florin Banica, Iosif Hulka, Gerlinde Rusu, Cosmin Sinescu, Traian Octavian Costea, Simona Cavalu
Materials Science-Poland.2023; 41(3): 126. CrossRef - Advances and challenges in regenerative dentistry: A systematic review of calcium phosphate and silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells
B. Christie, N. Musri, N. Djustiana, V. Takarini, N. Tuygunov, M.N. Zakaria, A. Cahyanto
Materials Today Bio.2023; 23: 100815. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - Biodentine Inhibits the Initial Microbial Adhesion of Oral Microbiota In Vivo
Ali Al-Ahmad, Michael Haendel, Markus Altenburger, Lamprini Karygianni, Elmar Hellwig, Karl Wrbas, Kirstin Vach, Christian Tennert
Antibiotics.2022; 12(1): 4. CrossRef - Pilot Evaluation of Sealer-Based Root Canal Obturation Using Epoxy-Resin-Based and Calcium-Silicate-Based Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Minju Song, Min-Gyu Park, Sang-Won Kwak, Ruben H. Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2022; 15(15): 5146. CrossRef - The antibacterial activity of mineral trioxide aggregate containing calcium fluoride
Miyoung Lim, Seunghoon Yoo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(2): 836. CrossRef - Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Premixed Calcium Silicate and Resin Sealers
Naji Kharouf, Salvatore Sauro, Ammar Eid, Jihed Zghal, Hamdi Jmal, Anta Seck, Valentina Macaluso, Frédéric Addiego, Francesco Inchingolo, Christine Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, Florent Meyer, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 14(1): 9. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Resistance between Single-cone and Warm Vertical Compaction Technique Using Bio-C Sealer® in Mandibular Incisors: An In Vitro Study
Raphael Lichaa, George Deeb, Rami Mhanna, Carla Zogheib
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - In vitro physicochemical characterization of five root canal sealers and their influence on an ex vivo oral multi‐species biofilm community
Flavia M. Saavedra, Lauter E. Pelepenko, William S. Boyle, Anqi Zhang, Christopher Staley, Mark C. Herzberg, Marina A. Marciano, Bruno P. Lima
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 772. CrossRef - Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealer Reinforced with Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles to Improve Biological Properties
Min-Kyung Jung, So-Chung Park, Yu-Jin Kim, Jong-Tae Park, Jonathan C. Knowles, Jeong-Hui Park, Khandmaa Dashnyam, Soo-Kyung Jun, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jung-Hwan Lee
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1903. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - The influence of humidity on bond strength of AH Plus, BioRoot RCS, and Nanoseal-S sealers
Sunanda Laxman Gaddalay, Damini Vilas Patil, Ramchandra Kabir
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 202. CrossRef - The Effect of Bioceramic HiFlow and EndoSequence Bioceramic Sealers on Increasing the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Mohamad Khir Abdulsamad Alskaf, Hassan Achour, Hasan Alzoubi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unravelling the effects of ibuprofen-acetaminophen infused copper-bioglass towards the creation of root canal sealant
Chitra S, Riju Chandran, Ramya R, Durgalakshmi D, Balakumar S
Biomedical Materials.2022; 17(3): 035001. CrossRef - A Micro-CT Analysis of Initial and Long-Term Pores Volume and Porosity of Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Michal Leski, Adam K. Puszkarz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2403. CrossRef - A comprehensive in vitro comparison of the biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive root canal sealers
Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Christian Diegritz, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth, Maximilian Kollmuss
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(10): 6209. CrossRef - Stability and solubility test of endodontic materials
Ivan Matovic, Jelena Vucetic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(4): 169. CrossRef - Antimicrobial effectiveness of root canal sealers againstEnterococcus faecalis
Paola Castillo-Villagomez, Elizabeth Madla-Cruz, Fanny Lopez-Martinez, Idalia Rodriguez-Delgado, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Guadalupe Ismael Malagon-Santiago, Myriam Angelica de La Garza-Ramos
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2022; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Influence of variations in the environmental pH on the solubility and water sorption of a calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer
E. J. N. L. Silva, C. M. Ferreira, K. P. Pinto, A. F. A. Barbosa, M. V. Colaço, L. M. Sassone
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1394. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Calcium-Silicate Nanobioceramics with Magnesium: Effect of Heat Treatment on Biological, Physical and Chemical Properties
Konstantina Kazeli, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Anna Theocharidou, Lamprini Malletzidou, Jonathan Rhoades, Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Eleni Likotrafiti, Konstantinos Chrissafis, Theodoros Lialiaris, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Eleana Kontonasaki, Evgenia Lymperaki
Ceramics.2021; 4(4): 628. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - In Vitro Microleakage Evaluation of Bioceramic and Zinc-Eugenol Sealers with Two Obturation Techniques
Francesco De Angelis, Camillo D’Arcangelo, Matteo Buonvivere, Rachele Argentino, Mirco Vadini
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 727. CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef - Apical Sealing Ability of Two Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers Using a Radioactive Isotope Method: An In Vitro Apexification Model
Inês Raquel Pereira, Catarina Carvalho, Siri Paulo, José Pedro Martinho, Ana Sofia Coelho, Anabela Baptista Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho, Maria Filomena Botelho, Ana Margarida Abrantes, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6456. CrossRef
- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
- 13,685 View
- 249 Download
- 100 Crossref

- Dentin moisture conditions strongly influence its interactions with bioactive root canal sealers
- Esin Ozlek, Hüseyin Gündüz, Elif Akkol, Prasanna Neelakantan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e24. Published online March 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It is known that bioactive materials interact with the dentin to undergo biomineralization. The exact role of moisture in this interaction is unknown. Here, we investigate the effects of dentin moisture conditions on the dislocation resistance of two bioactive root canal sealers (MTA Fillapex [Angelus Solucoes Odontologicas] and GuttaFlow BioSeal [Colténe/Whaledent AG]) at 3 weeks and 3 months after obturation.
Materials and Methods Mandibular premolars (
n = 120) were prepared and randomly divided into 3 groups based on the dentin condition: group 1, dry dentin; group 2, moist dentin; group 3, wet dentin. Each group was divided into 2 subgroups for root canal filling: MTA Fillapex and GuttaFlow BioSeal. Dislocation resistance was evaluated by measuring the push-out bond strength at 3 weeks and 3 months. Failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. Data were statistically analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test with a significance level of 5%.Results Moist dentin resulted in higher bond strength values for both materials at both time points. This was significantly higher than wet and dry dentin for both the sealers at the 3 months (
p < 0.05), while at 3 weeks it was significant only for GuttaFlow Bioseal. The different moisture conditions demonstrated similar trends in their effects on the dislocation resistance of the 2 root canal sealers.Conclusions The dentin moisture conditions had a significant impact on its interaction with the bioactive materials tested. Maintaining moist dentin, but not dry or wet dentin, may be advantageous before the filling root canals with bioactive sealers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of moisture conditions and canal morphologies on the filling quality of iRoot SP with single-cone technique in root canals: an ex-vivo study
Jing Yang, Xiran Xu, Jian Zhang, Kehua Que
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(7): 1989. CrossRef - Evaluation of apical seal and tubular penetration of a novel bioactive glass sealer, bioceramic sealer and resin–based sealer: an In-Vitro study
M. Bilal, S. Pasha, S. Kumar, S. Arif, S. Taj, A. Saleem
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 39. CrossRef - Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Post Space Conditioning Procedures and Different Endodontic Sealers on the Push-Out Bond Strengths of Fiber Posts
Leyla Ayranci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci, Fatih Sarı, Ahmet Çetinkaya
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 620. CrossRef - Evaluation of the retreatability of bioceramic root canal sealers with various formulations in simulated grooves
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Abdulaziz Bakhsh, Hakan Arslan
PeerJ.2025; 13: e20398. CrossRef - Preparation and characterization of novel nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based root canal sealer
Nawal Atiya Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 90. CrossRef - The flow behavior and sealing ability of calcium silicate root canal cement containing dimethyl sulfoxide: An in vitro study
Bokyung Shin, Ji-Hwan Seo, Wonjung Kim, Yu Jin Ahn, Ho-Young Kim, Won-Jun Shon
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106156. CrossRef - Nanoleakage of apical sealing using a calcium silicate-based sealer according to canal drying methods
Yoon-Joo Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of operators’ proficiency level and patients’ related factors on possible complications, using a high frequency polyamide sonic intracanal irrigation device: A prospective clinical cohort study
Tobias Hahn, David W. Christofzik, Karim Fawzy El-Sayed, Sandra Freitag-Wolf, Jonas Conrad, Christian Graetz, Birte Größner-Schreiber, Christof Dörfer, Artak Heboyan
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(5): e0285492. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Biocompatibility analysis in subcutaneous tissue and physico-chemical analysis of pre-mixed calcium silicate–based sealers
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Juliana Minto Boldieri, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Nilvan Alves da Silva, Ivo Milton Raimundo, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2221. CrossRef - Canal Drying Protocols to Use with Calcium Silicate–based Sealer: Effect on Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface
Lais Lima Pelozo, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Guilherme Nilson Alves dos Santos, Rafael Verardino Camargo, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(9): 1154. CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength of endodontic sealers after root canal drying with different techniques
Ahmadreza Sarrafan, Ali Soleymani, Tasnim Bagheri Chenari, Seyedali Seyedmajidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2023; 9(2): 314. CrossRef - Designing Calcium Silicate Cements with On-Demand Properties for Precision Endodontics
A. Cahyanto, P. Rath, T.X. Teo, S.S. Tong, R. Malhotra, B.N. Cavalcanti, L.Z. Lim, K.S. Min, D. Ho, W.F. Lu, V. Rosa
Journal of Dental Research.2023; 102(13): 1425. CrossRef - Outcome of root canal treatment using warm vertical compaction with bioceramic and resin‐based sealers: A randomised clinical trial
Jinghao Hu, Yunjie Zhu, Shuli Deng, Zeji Wang, Fuming He
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 170. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability and Bond Strength of Two Endodontic Root Canal Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Manuel Marques Ferreira, José Pedro Martinho, Inês Duarte, Diogo Mendonça, Ana Catarina Craveiro, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Ana Coelho, Anabela Paula, Siri Paulo, Nuno Chichorro, Ana Margarida Abrantes
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(11): 201. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of using calcium-silicate and silicone based root canal sealers in bulk or with main core material on bond strength
Gizem Kadı, Esin Özlek, Yousef Saed
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2022; 16(4): 229. CrossRef - Physico-chemical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers in powder/liquid and ready-to-use forms
Ana C P Janini, Lauter E Pelepenko, Brenda P F A Gomes, Marina A Marciano
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 18. CrossRef - Influence of dentin moisture conditions on the wetting action of different endodontic sealers using Rame-Hart goniometer: An in vitro study
Sivaji Kauravi, ShruthiH Attavar, GyanendraPratap Singh
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(6): 624. CrossRef - Heating stability, physical and chemical analysis of calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealers
T. B. M. Antunes, A. C. P. Janini, L. E. Pelepenko, G. F. Abuna, E. M. Paiva, M. A. C. Sinhoreti, I. M. Raimundo, B. P. F. A. Gomes, A. de‐Jesus‐Soares, M. A. Marciano
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1175. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
- The effect of moisture conditions and canal morphologies on the filling quality of iRoot SP with single-cone technique in root canals: an ex-vivo study
- 2,204 View
- 32 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic cleaning on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic root canal sealer
- Fernando Peña Bengoa, Maria Consuelo Magasich Arze, Cristobal Macchiavello Noguera, Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo Da Silveira Bueno
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e19. Published online February 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e19
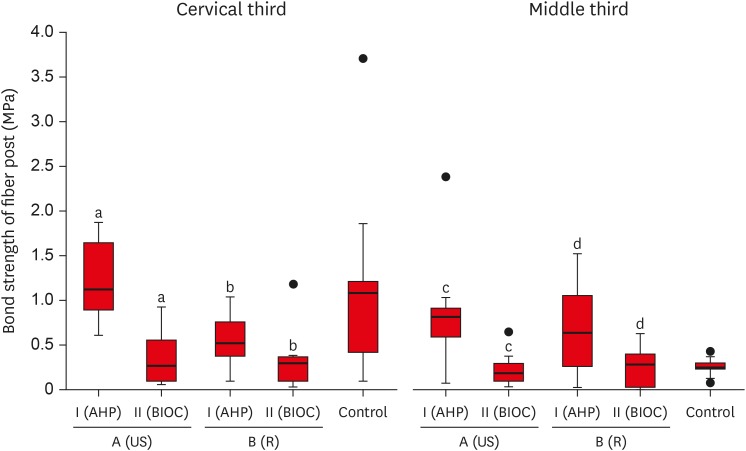
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This study aimed to evaluate the effect of ultrasonic cleaning of the intracanal post space on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic (Bio-C Sealer [BIOC]) root canal sealer.
Materials and Methods Fifty premolars were endodontically prepared and divided into 5 groups (
n = 10), based on the type of root canal filling material used and the post space cleaning protocol. A1: gutta-percha + AH Plus (AHP) and post space preparation with ultrasonic cleaning, A2: gutta-percha + BIOC and post space preparation with ultrasonic cleaning, B1: gutta-percha + AHP and post space preparation, B2: gutta-percha + BIOC and post space preparation, C: control group. Fiber posts were cemented with a self-adhesive luting material, and 1 mm thick slices were sectioned from the middle and cervical third to evaluate the remaining filling material microscopically. The samples were subjected to a push-out test to analyze the bond strength of the fiber post, and the results were analyzed with the Shapiro-Wilk, Bonferroni, Kruskal-Wallis, and Mann-Whitney tests (p < 0.05). Failure modes were evaluated using optical microscopy.Results The results showed that the fiber posts cemented in canals sealed with BIOC had lower bond strength than those sealed with AHP. The ultrasonic cleaning of the post space improved the bond strength of fiber posts in canals sealed with AHP, but not with BIOC.
Conclusions BIOC decreased the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals, regardless of ultrasonic cleaning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e20. CrossRef - In Vitro Effect of Using Endo‐Activator on Pushout Bond Strength of Radicular Dentin to Prefabricated Fiber Post in Using Natural Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors
Nadia Elyassi Gorji, Homayoun Alaghemand, Faraneh Mokhtarpour, Elham Mahmodnia
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of different mechanical cleaning protocols associated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in the removal of residues from the post space
Matheus Sousa Vitória, Eran Nair Mesquita de Almeida, Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Eliane Cristina Gulin de Oliveira, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Andrea Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 274. CrossRef - Fiber post cemented using different adhesive strategies to root canal dentin obturated with calcium silicate-based sealer
Lalita Patthanawijit, Kallaya Yanpiset, Pipop Saikaew, Jeeraphat Jantarat
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealers on push-out bond strength of CAD-CAM or prefabricated fiber glass posts
Andréa Pereira de Souza PINTO, Fabiana Mantovani Gomes FRANÇA, Roberta Tarkany BASTING, Cecilia Pedroso TURSSI, José Joatan RODRIGUES JÚNIOR, Flávia Lucisano Botelho AMARAL
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of mechanical cleaning protocols in the fiber post space on the adhesive interface between universal adhesive and root dentin
Gabriela Mariana Castro‐Núnez, José Rodolfo Estruc Verbicário dos Santos, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante‐Otárola, Thiago Soares Porto, Milton Carlos Kuga
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(6): 2131. CrossRef - Effect of bioceramic root canal sealers on the bond strength of fiber posts cemented with resin cements
Rafael Nesello, Isadora Ames Silva, Igor Abreu De Bem, Karolina Bischoff, Matheus Albino Souza, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu Da Rosa
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols on root canal wall after post preparation: a micro-CT and microhardness study
Camila Maria Peres de Rosatto, Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Lilian Vieira Oliveira, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira Soares, Carlos José Soares, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
- 2,214 View
- 27 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of hydrofluoric acid-based etchant at an elevated temperature on the bond strength and surface topography of Y-TZP ceramics
- Mi-Kyung Yu, Myung-Jin Lim, Noo-Ri Na, Kwang-Won Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e6. Published online December 3, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effects of a hydrofluoric acid (HA; solution of hydrogen fluoride [HF] in water)-based smart etching (SE) solution at an elevated temperature on yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) ceramics in terms of bond strength and morphological changes.
Materials and Methods Eighty sintered Y-TZP specimens were prepared for shear bond strength (SBS) testing. The bonding surface of the Y-TZP specimens was treated with 37% phosphoric acid etching at 20°C–25°C, 4% HA etching at 20°C–25°C, or HA-based SE at 70°C–80°C. In all groups, zirconia primers were applied to the bonding surface of Y-TZP. For each group, 2 types of resin cement (with or without methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate [MDP]) were used. SBS testing was performed. Topographic changes of the etched Y-TZP surface were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The results were analyzed and compared using 2-way analysis of variance.
Results Regardless of the type of resin cement, the highest bond strength was measured in the SE group, with significant differences compared to the other groups (
p < 0.05). In all groups, MDP-containing resin cement yielded significantly higher bond strength values than MDP-free resin cement (p < 0.05). It was also shown that the Y-TZP surface was etched by the SE solution, causing a large change in the surface topography.Conclusions Bond strength significantly improved when a heated HA-based SE solution was applied to the Y-TZP surface, and the etched Y-TZP surface was more irregular and had higher surface roughness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Etchability of zirconia ceramics and its effect on adhesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Anina Sieber, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Surface Roughening Techniques on Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Monolithic Zirconia: In Vitro Study
Nehal F Albelasy, Ahmad M Hafez, Abdullah S Alhunayni
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(12): 1104. CrossRef - Effect of Acid Surface Treatments on the Shear Bond Strength of Metal Bracket to Zirconia Ceramics
Punchanit Wongrachit, Bancha Samruajbenjakun, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon, Tanapat Jearanai, Supontep Teerakanok, Pannapat Chanmanee
Ceramics.2024; 7(2): 689. CrossRef - Exploring Zirconia Adhesion: Pre and Postsintering Physical Surface Treatment, Chemical Treatment, and Cement Interactions
Flávia Gonçalves, Mirko Dennys Ayala-Perez, Francisco Carlos dos Santos Reis, Walter Gomes Miranda-Júnior, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of zirconia surfaces and shear bond strength after acid–etching with ultrasonic vibration
Xiaozhen Zhang, Hepeng Nie, Jiaxin Lv, Shanshan Yuan, Juan Wang, Kunzhan Cai, Jin Wu, Qingqing Zhang, Chunbo Tang
Materials Research Express.2024; 11(2): 025401. CrossRef - Effects of Surface-Etching Systems on the Shear Bond Strength of Dual-Polymerized Resin Cement and Zirconia
Sang-Hyun Kim, Kyung Chul Oh, Hong-Seok Moon
Materials.2024; 17(13): 3096. CrossRef - Zirconia bond strength durability following artificial aging: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Athanasios E. Rigos, Katia Sarafidou, Eleana Kontonasaki
Japanese Dental Science Review.2023; 59: 138. CrossRef - Y-TZP Physicochemical Properties Conditioned with ZrO2 and SiO2 Nanofilms and Bond Strength to Dual Resin Cement
Ricardo Faria Ribeiro, Danilo Flamini Oliveira, Camila Bussola Tovani, Ana Paula Ramos, Ana Flavia Sanches Borges, Adriana Claudia Lapria Faria, Rossana Pereira de Almeida, Renata Cristina Silveira Rodrigues
Materials.2022; 15(22): 7905. CrossRef - Effect of the nanofilm-coated zirconia ceramic on resin cement bond strength
Viviane Maria Gonçalves de Figueiredo, Alecsandro de Moura Silva, Marcos Massi, Argemiro Soares da Silva Sobrinho, José Renato Cavalcanti de Queiroz, João Paulo Barros Machado, Renata Falchete do Prado, Lafayette Nogueira Junior
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2022; 16(3): 170. CrossRef - Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Bond Strength and Topography for Y-TZP Etched with Hydrofluoric Acid Depending on Concentration and Temperature Conditions
Hyo-Eun Kim, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
Medicina.2020; 56(11): 568. CrossRef - Do different sintering conditions influence bond strength between the resin cements and a currently used esthetic zirconia?
Fatma Ayse Sanal, Hamiyet Kilinc
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(16): 1809. CrossRef
- Etchability of zirconia ceramics and its effect on adhesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,204 View
- 11 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Influence of 10-MDP concentration on the adhesion and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Kazuhiko Shibuya, Naoko Ohara, Serina Ono, Kumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Yoshiyama
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e45. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Self-adhesive resin cements contain functional monomers that enable them to adhere to the tooth structure without a separate adhesive or etchant. One of the most stable functional monomers used for chemical bonding to calcium in hydroxyapatite is 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the10-MDP concentration on the bond strength and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods We used experimental resin cements containing 3 different concentrations of 10-MDP: 3.3 wt% (RC1), 6.6 wt% (RC2), or 9.9 wt% (RC3). The micro-tensile bond strength of each resin cement to dentin and a hybrid resin block (Estenia C&B, Kuraray Noritake Dental) was measured, and the fractured surface morphology was analyzed. Further, the flexural strength of the resin cements was measured using the three-point bending test. The water sorption and solubility of the cements following 30 days of immersion in water were measured.
Results The bond strength of RC2 was significantly higher than that of RC1. There was no significant difference between the bond strength of RC2 and that of RC3. The water sorption of RC3 was higher than that of any other cement. There were no significant differences in the three-point bending strength or water solubility among all three types of cements.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it is suggested that 6.6 wt% 10-MDP showed superior properties than 3.3 wt% or 9.9 wt% 10-MDP in self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Sofia Bignotto de Carvalho, Lívia Maiumi Uehara, João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104260. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Influence of temperature and curing modes on polymerization of self-adhesive resin cements
Hae-In Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(3): 143. CrossRef - Clinical Performance and Retention of Partial Implant Restorations Cemented with Fuji Plus® and DentoTemp™: A Retrospective Clinical Study with Mechanical Validation
Sergiu-Manuel Antonie, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Ioan-Achim Borsanu, Remus Christian Bratu, Emanuel-Adrian Bratu
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2183. CrossRef - A thorough assessment of 10-MDP primers in modern dental adhesive systems
Ahmed A Abduljawad, Harraa SM Salih, Omar F Tawfiq
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 79. CrossRef - Material properties and finite element analysis of adhesive cements used for zirconia crowns on dental implants
Megha Satpathy, Hai Pham, Shreya Shah
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Clinical reliability of self-adhesive luting resins compared to other adhesive procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammed Ahmed Alghauli, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 129: 104394. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization on bond strength between zirconia frameworks and Ti-base abutments using different resin cements
Reinhold Lang, Karl-Anton Hiller, Lena Kienböck, Katrin Friedl, Karl-Heinz Friedl
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(4): 617.e1. CrossRef - Varying 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP) level improves polymerisation kinetics and flexural strength in self-adhesive, remineralising composites
António H.S. Delgado, Nazanin Owji, Paul Ashley, Anne M. Young
Dental Materials.2021; 37(9): 1366. CrossRef - Investigating a Commercial Functional Adhesive with 12-MDPB and Reactive Filler to Strengthen the Adhesive Interface in Eroded Dentin
Madalena Belmar da Costa, António HS Delgado, Tomás Amorim Afonso, Luís Proença, Ana Sofia Ramos, Ana Mano Azul
Polymers.2021; 13(20): 3562. CrossRef
- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- 2,799 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Influence of silver nanoparticles on resin-dentin bond strength durability in a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive system
- Zahra Jowkar, Fereshteh Shafiei, Elham Asadmanesh, Fatemeh Koohpeima
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e13. Published online March 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of dentin pretreatment with silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and chlorhexidine (CHX) on the microshear bond strength (µSBS) durability of different adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods Occlusal surfaces of 120 human molars were ground to expose flat dentin surfaces. The specimens were randomly assigned to six groups (
n = 20). Three groups (A, B, and C) were bonded with Adper Single Bond 2 (SB) and the other groups (D, E, and F) were bonded with Clearfil SE Bond (SEB). Dentin was pretreated with CHX in groups B and E, and with SNPs in groups C and F. The specimens were restored with Z250 composite. Half of the bonded surfaces in each group underwent µSBS testing after 24 hours and the other half was tested after 6 months of water storage.Results SNP application was associated with a higher µSBS than was observed in the CHX and control groups for SEB after 24 hours (
p < 0.05). A significantly lower µSBS was observed when no dentin pretreatment was applied compared to dentin pretreatment with CHX and SNPs for SB after 24 hours (p < 0.05). The µSBS values of the 6-month specimens were significantly lower than those obtained from the 24-hour specimens for all groups (p < 0.05). This decrease was much more pronounced when both adhesives were used without any dentin pretreatment (p < 0.05).Conclusions SNPs and CHX reduced the degradation of resin-dentin bonds over a 6-month period for both adhesive systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Nanoparticle-enhanced dental adhesives: improving dentin bond strength through multifunctional nanotechnology
Suleiman Ibrahim Mohammad, Asokan Vasudevan, Lashin Saad Ali, Wenchang Chen
The Journal of Adhesion.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer: An In Vitro Study
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Dalal AlDabeeb
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9817. CrossRef - Performance of self-etching adhesives on caries-affected primary dentin treated with glutaraldehyde or silver diamine fluoride
Marcelly Tupan Christoffoli Wolowski, Andressa Mioto Stabile Grenier, Victória Alícia de Oliveira, Caroline Anselmi, Mariana Sversut Gibin, Lidiane Vizioli de Castro-Hoshino, Francielle Sato, Cristina Perez, Régis Henke Scheffel, Josimeri Hebling, Mauro L
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106293. CrossRef - The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles on Dentinal Tubule Penetration of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealer
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Amal Almohaimede, Nourah Alkhayatt, Shahad Alsulaiman, Salma Alohali
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11639. CrossRef - Effect of silver diamine fluoride on the longevity of the bonding properties to caries-affected dentine
LP Muniz, M Wendlinger, GD Cochinski, PHA Moreira, AFM Cardenas, TS Carvalho, AD Loguercio, A Reis, FSF Siqueira
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 143: 104897. CrossRef - Evaluation of Chitosan-Oleuropein Nanoparticles on the Durability of Dentin Bonding
Shuya Zhao, Yunyang Zhang, Yun Chen, Xianghui Xing, Yu Wang, Guofeng Wu
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2023; Volume 17: 167. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on the resin-dentin bond strength and antibacterial activity of a self-etch adhesive system
Jia Wang, Wei Jiang, Jingping Liang, Shujun Ran
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(6): 1363.e1. CrossRef - Marginal Integrity of Composite Restoration with and without Surface Pretreatment by Gold and Silver Nanoparticles vs Chlorhexidine: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Aya AEM Nemt-Allah, Shereen H Ibrahim, Amira F El-Zoghby
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1087. CrossRef - Effect of Cavity Disinfectants on Dentin Bond Strength and Clinical Success of Composite Restorations—A Systematic Review of In Vitro, In Situ and Clinical Studies
Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Beatriz Rascão, Inês Marcelino, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 22(1): 353. CrossRef
- An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
- 1,536 View
- 13 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The push-out bond strength of BIOfactor mineral trioxide aggregate, a novel root repair material
- Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Durmus Alperen Bozkurt, Arslan Terlemez, Melek Akman
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e5. Published online January 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the push-out bond strength of a novel calcium silicate-based root repair material-BIOfactor MTA to root canal dentin in comparison with white MTA-Angelus (Angelus) and Biodentine (Septodont).Materials and Methods The coronal parts of 12 central incisors were removed and the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. Midroot dentin of each sample was horizontally sectioned into 1.1 mm slices and 3 slices were obtained from each root. Three canal-like standardized holes having 1 mm in diameter were created parallel to the root canal on each dentin slice with a diamond bur. The holes were filled with MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, or BIOfactor MTA. Wet gauze was placed over the specimens and samples were stored in an incubator at 37°C for 7 days to allow complete setting. Then samples were subjected to the push-out test method using a universal test machine with the loading speed of 1 mm/min. Data was statistically analyzed using Friedman test and
post hoc Wilcoxon signed rank test with Bonferroni correction.Results There were no significant differences among the push-out bond strength values of MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA (
p > 0.017). Most of the specimens exhibited cohesive failure in all groups, with the highest rate found in Biodentine group.Conclusions Based on the results of this study, MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA showed similar resistances to the push-out testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Examination of the Bond Strength of Retrograde Filling in Teeth with Failed Apical Resection After Retreatment
Sevda Tok, Leyla Benan Ayranci
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(7): 3441. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Physicocomechanical Properties of MTA and Biodentine with Addition of Graphene Oxide to MTA and Biodentine: An In-vitro Study
Tanvi Arvind Jagtap, Budhabhushan A. Sonvane, Guruprasad Handal, Jayashri Nimba Bhangare, Kedar Vilas Saraf, Abhishek Mulay
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S608. CrossRef - Influence of Incubation Duration on Bond Strength and Microhardness of Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials
Emine Şimşek, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 438. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength after root perforation repair using recently introduced bioceramic and calcium silicate-based materials – An in vitro study
Gurinder Kaur, Deepak Kurup, Deepyanti Dubey, Ajit Hindlekar, Ganesh Ranganath Jadhav, Priya Mittal, Siddharth Shinde
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 194. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, and Two Novel Antibacterial-enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Sanjeev Khanagar, Suman Panda, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Satish Vishwanathaiah, Ather A Syed, Sara Kalagi, Arokia RS Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Aram AlShehri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(2): 168. CrossRef - Influence of Phase Composition and Morphology on the Calcium Ion Release of Several Classical and Hybrid Endodontic Cements
Ivanka Dimitrova, Galia Gentscheva, Ivanka Spassova, Daniela Kovacheva
Materials.2024; 17(22): 5568. CrossRef - The Effect of Two Different MTA (Mineral Trioxide Aggregate) On Thermal Insulation
Gizem Akkus, Ecem Salmaz, Didem Oner Ozdas
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength and apical microleakage of different calcium silicate‐based cements after using EDTA, chitosan and phytic acid irrigations
Tutku Koçak Şahin, Murat Ünal
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(9): 2072. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the physical characteristics and push-out bond strength of new experimental nano-MTA
Nada Omar, Yousra Aly, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interfacial characteristics of BIOfactor MTA and Biodentine with dentin
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Şeref Nur Mutlu, Mehmet Ali Soylu, Emine Şimşek
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(2): 258. CrossRef - Systemic effect of calcium silicate-based cements with different radiopacifiers-histopathological analysis in rats
Osman Ataş, Kubra Bılge, Semsettin Yıldız, Serkan Dundar, Ilknur Calik, Asime Gezer Ataş, Alihan Bozoglan
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15376. CrossRef - The push-out bond strength of three root canal materials used in primary teeth: in vitro study
Hazal Özer, Merve Abaklı İnci, Sevcihan Açar Tuzluca
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different irrigation protocols on push-out bond strength of pre-mixed calcium silicate-based cements
Sabiha Ceren İlisulu, Aliye Tugce Gürcan, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2023; 59(5): 1381. CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Sealing Quality and Bond Strength of Different MTA Apical Plugs
Taibe Tokgöz Kaplan, Murat Selim Botsalı
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Kan kontaminasyonunun farklı kök ucu dolgu materyallerinin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Şeyma Nur GERÇEKCİOĞLU, Melike BAYRAM, Emre BAYRAM
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2023; 40(1): 9. CrossRef - Tooth Discoloration Effect of BIOfactor Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A 6-Month In Vitro Study
Şeref Nur Mutlu, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(15): 8914. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Push-Out Bond Strength of Root-End Filling Materials by Using Different Condensation Methods
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Sevinç Sevgi, Ayşenur Öncü, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Berkan Çelikten
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Different Adhesive Strategies on the Microshear Bond Strength of Calcium-Silicate-Based Materials
Aliye Tuğçe Gürcan, Soner Şişmanoğlu, Görkem Sengez
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 191. CrossRef - BIOfactor MTA’nın Radyoopasitesinin Dijital Radyografi ile Değerlendirilmesi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Bilge AKBULUT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 520. CrossRef - Morphological and Chemical Analysis of Different Types of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements
Okba Mahmoud, Nashwan Abdullah Al-Afifi, Mohideen Salihu Farook, Maysara Adnan Ibrahim, Saaid Al Shehadat, Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Blood Contamination on Push-Out Bond Strength of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Cristina Rodrigues Paulo, Joana A. Marques, Diana B. Sequeira, Patrícia Diogo, Rui Paiva, Paulo J. Palma, João Miguel Santos
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6849. CrossRef - An In vitro comparative evaluation of effect of novel irrigant Qmix and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the push-out bond strength of biodentine and endosequence bioceramic root repair material
VandanaJ Gade, Aparajita Gangrade, JaykumarR Gade, Neelam Rahul
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 124. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,058 View
- 12 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of CAD/CAM-fabricated polymer-ceramics to different adhesive resin cements
- Leyla Sadighpour, Farideh Geramipanah, Zahra Ghasri, Mehrnoosh Neshatian
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e40. Published online September 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e40
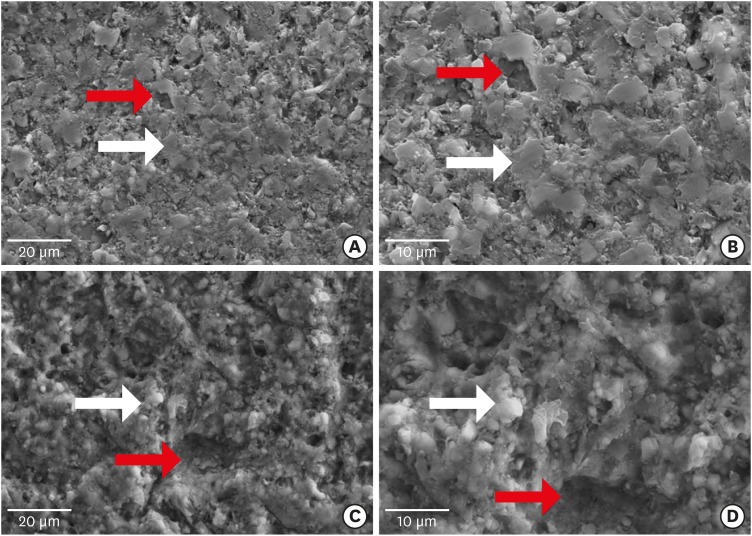
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of polymer-ceramic and indirect composite resin with 3 classes of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Two computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated polymer-ceramics (Enamic [ENA; Vita] and Lava Ultimate [LAV; 3M ESPE]) and a laboratory indirect composite resin (Gradia [GRA; GC Corp.]) were equally divided into 6 groups (
n = 18) with 3 classes of resin cements: Variolink N (VAR; Vivadent), RelyX U200 (RXU; 3M ESPE), and Panavia F2 (PAN; Kuraray). The μTBS values were compared between groups by 2-way analysis of variance and thepost hoc Tamhane test (α = 0.05).Results Restorative materials and resin cements significantly influenced µTBS (
p < 0.05). In the GRA group, the highest μTBS was found with RXU (27.40 ± 5.39 N) and the lowest with VAR (13.54 ± 6.04 N) (p < 0.05). Similar trends were observed in the ENA group. In the LAV group, the highest μTBS was observed with VAR (27.45 ± 5.84 N) and the lowest with PAN (10.67 ± 4.37 N) (p < 0.05). PAN had comparable results to those of ENA and GRA, whereas the μTBS values were significantly lower with LAV (p = 0.001). The highest bond strength of RXU was found with GRA (27.40 ± 5.39 N,p = 0.001). PAN showed the lowest µTBS with LAV (10.67 ± 4.37 N;p < 0.001).Conclusions When applied according to the manufacturers' recommendations, the µTBS of polymer-ceramic CAD/CAM materials and indirect composites is influenced by the luting cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
Mohamed F. Haridy, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Shehabeldin Saber, Edgar Schafer, Samar Elsayed Swelam, Youssef M. Haridy, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrofluoric acid and self-etch ceramic primers on the flexural strength and fatigue resistance of glass ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Paulo Matias Moreira, Gabriela Luiza Moreira Carvalho, Rodrigo de Castro Albuquerque, Carolina Bosso André
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 198. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on the mechanical properties of permanent composite-based CAD-CAM restorative materials produced by additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques
Tuğba Temizci, Hatice Nalan Bozoğulları
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on resin-matrix CAD/CAM ceramics bonding to dentin: in vitro study
Hanan Fathy, Hamdi H. Hamama, Noha El-Wassefy, Salah H. Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital image analysis of fluorescence of ceramic veneers with different ceramic materials and resin cements
Jiao ZHANG, Qing YU
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 868. CrossRef - Fatigue Behavior of Monolithic Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramic Restorations: Effects of Conditionings of the Intaglio Surface and the Resin Cements
F Dalla-Nora, LF Guilardi, CP Zucuni, LF Valandro, MP Rippe
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): 316. CrossRef
- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
- 2,112 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of air-abrasion pressure on the resin bond strength to zirconia: a combined cyclic loading and thermocycling aging study
- Eman Z. Al-Shehri, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Alaa H. Sabrah, Sarah S. Al-Angari, Laila Al Dehailan, George J. Eckert, Mutlu Özcan, Jeffrey A. Platt, Marco C. Bottino
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):206-215. Published online June 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the combined effect of fatigue cyclic loading and thermocycling (CLTC) on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a resin cement to zirconia surfaces that were previously air-abraded with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) particles at different pressures.
Materials and Methods Seventy-two cuboid zirconia specimens were prepared and randomly assigned to 3 groups according to the air-abrasion pressures (1, 2, and 2.8 bar), and each group was further divided into 2 groups depending on aging parameters (
n = 12). Panavia F 2.0 was placed on pre-conditioned zirconia surfaces, and SBS testing was performed either after 24 hours or 10,000 fatigue cycles (cyclic loading) and 5,000 thermocycles. Non-contact profilometry was used to measure surface roughness. Failure modes were evaluated under optical and scanning electron microscopy. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and χ2 tests (α = 0.05).Results The 2.8 bar group showed significantly higher surface roughness compared to the 1 bar group (
p < 0.05). The interaction between pressure and time/cycling was not significant on SBS, and pressure did not have a significant effect either. SBS was significantly higher (p = 0.006) for 24 hours storage compared to CLTC. The 2 bar-CLTC group presented significantly higher percentage of pre-test failure during fatigue compared to the other groups. Mixed-failure mode was more frequent than adhesive failure.Conclusions CLTC significantly decreased the SBS values regardless of the air-abrasion pressure used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
Yanru Shen, Xiang Wang, Chen Yang, Ying Jiang, Feng Wang, Li Peng, Yongsheng Zhou, Yuchun Sun
Surfaces and Interfaces.2024; 54: 105153. CrossRef - Multiscale analysis of the compressive behaviour of polymer-based composites reinforced by hybrid Al2O3/Al fibres
Hao Tang, Jiaqi Xu, Constantinos Soutis, Aleksey Yerokhin
Composites Science and Technology.2024; 255: 110718. CrossRef - An Advanced Surface Treatment Technique for Coating Three-Dimensional-Printed Polyamide 12 by Hydroxyapatite
Abdulaziz Alhotan, Saleh Alhijji, Sahar Ahmed Abdalbary, Rania E. Bayoumi, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Tamer M. Hamdy, Rasha M. Abdelraouf
Coatings.2024; 14(9): 1181. CrossRef -
Does incorporation of TiO
2
nanotubes in air-abraded high translucent zirconia influence shear bond strength?*
Bahadır Ezmek, Osman Cumhur Sipahi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(22): 3206. CrossRef - Effects of aging and light-curing unit type on the volume and internal porosity of bulk-fill resin composite restoration
Afnan O. Al-Zain, Elaf A. Alboloshi, Walaa A. Amir, Maryam A. Alghilan, Eliseu A. Münchow
The Saudi Dental Journal.2022; 34(3): 243. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and cyclic fatigue on subsurface defects and mechanical properties of zirconia frameworks
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Nikolaos Silikas, Moustafa Aboushelib
Dental Materials.2021; 37(5): 905. CrossRef - Effects of low-temperature degradation on the surface roughness of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hui Yang, Yi-Li Xu, Guang Hong, Hao Yu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(2): 222. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on repair strength, roughness and morphology in aged metal-free crowns
Yançanã Luizy Gruber, Thaís Emanuelle Bakaus, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, João Carlos Gomes, Alessandra Reis, Giovana Mongruel Gomes
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 19: e206155. CrossRef - Retentive Force of Glass-Ceramic Soldered Customized Zirconia Abutment Copings with Prefabricated Titanium Bases
Jeremias Hey, Monika Kasaliyska, Andreas Kiesow, Ramona Schweyen, Christin Arnold
Materials.2020; 13(14): 3193. CrossRef - Solvent-aided direct adhesion of a metal/polymer joint using micro/nano hierarchical structures
Gyosik Jun, Jeong-Won Lee, Younghun Shin, Kihwan Kim, Woonbong Hwang
Journal of Materials Processing Technology.2020; 285: 116744. CrossRef - Study of physicochemical properties and effects on bonding to zirconia ceramics of five resin cements
Xiuju Liu, Zhaoying Liu, Xuan Li, Han Wang, Gaigai Yu, Song Zhu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(18): 2031. CrossRef - The effect of air-particle abrasion and a zirconia primer application on resin cement bonding strength to zirconia
Alana M. Dantas, Fernanda Campos, Sarina M. Pereira, Elis J. dos Santos, Laudenice L. Pereira, Dayanne M. Moura, Rodrigo O. Souza
Minerva Stomatologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on Shear Bond Strength between Y-TZP and Self-Adhesive Resin Cement
Dae-Sung Kim, Jong-Ju Ahn, Eun-Bin Bae, Gyoo-Cheon Kim, Chang-Mo Jeong, Jung-Bo Huh, So-Hyoun Lee
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3321. CrossRef - Effect of airborne particle abrasion and sintering order on the surface roughness and shear bond strength between Y-TZP ceramic and resin cement
Yener OKUTAN, Munir Tolga YUCEL, Tugce GEZER, Mustafa Borga DONMEZ
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(2): 241. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
- 2,258 View
- 13 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Bonding of the silane containing multi-mode universal adhesive for lithium disilicate ceramics
- Hyun-Young Lee, Geum-Jun Han, Juhea Chang, Ho-Hyun Son
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):95-104. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the influence of a multi-mode universal adhesive (MUA) containing silane (Single Bond Universal, 3M EPSE) on the bonding of resin cement to lithium disilicate.
Materials and Methods Thirty IPS e.max CAD specimens (Ivoclar Vivadent) were fabricated. The surfaces were treated as follows: Group A, adhesive that did not contain silane (ANS, Porcelain Bonding Resin, Bisco); Group B, silane (S) and ANS; Group C, hydrofluoric acid (HF), S, and ANS; Group D, MUA; Group E, HF and MUA. Dual-cure resin cement (NX3, Kerr) was applied and composite resin cylinders of 0.8 mm in diameter were placed on it before light polymerization. Bonded specimens were stored in water for 24 hours or underwent a 10,000 thermocycling process prior to microshear bond strength testing. The data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of variance (
p < 0.05).Results Bond strength varied significantly among the groups (
p < 0.05), except for Groups A and D. Group C showed the highest initial bond strength (27.1 ± 6.9 MPa), followed by Group E, Group B, Group D, and Group A. Thermocycling significantly reduced bond strength in Groups B, C, and E (p < 0.05). Bond strength in Group C was the highest regardless of the storage conditions (p < 0.05).Conclusions Surface treatment of lithium disilicate using HF and silane increased the bond strength of resin cement. However, after thermocycling, the silane in MUA did not help achieve durable bond strength between lithium disilicate and resin cement, even when HF was applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Roles of Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Bonding Materials
Maria Arampatzi, Ellas Spyratou, Iosif Sifakakis, Efstathios P. Efstathopoulos
Applied Sciences.2026; 16(4): 1996. CrossRef - The influence of different factors on the bond strength of lithium disilicate-reinforced glass–ceramics to Resin: a machine learning analysis
Jiawen Liu, Suqing Tu, Mingjuan Wang, Du Chen, Chen Chen, Haifeng Xie
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different primers and adhesive system combinations on the durability of resin bonding to lithium disilicate
Christine Yazigi, Shila Alawi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(3): 749. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength and Finite Element Stress Analysis of Composite Repair Using Various Adhesive Strategies With and Without Silane Application
Elif Ercan Devrimci, Hande Kemaloglu, Cem Peskersoy, Tijen Pamir, Murat Turkun
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(15): 8159. CrossRef - Effect of multiple firings on mechanical and optical properties of CAD/CAM lithium disilicate-based glass ceramics
Chawal Padunglappisit, Pitsucha Charoensakthanakul, Sintwo Wongthongdee, Kan Wongkamhaeng
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of universal adhesives and self-etch ceramic primers on bond strength to glass-ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Renally Bezerra Wanderley Lima, Isis de Araújo Ferreira Muniz, Débora e Silva Campos, Fabián Murillo-Gómez, Ana Karina Maciel de Andrade, Rosângela Marques Duarte, Grace Mendonça de Souza
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(3): 392. CrossRef - Effect of the difference water amounts and hydrolysis times of silane coupling agent on the shear bond strength between lithium disilicate glass ceramic and composite resin
Pimchanok OSOTPRASIT, Sasipin LAUVAHUTANON, Yosnarong SIRIMETHAWONG, Patcharanun CHAIAMORNSUP, Pornpot JIANGKONGKHO
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(3): 375. CrossRef - Is additional silane application necessary for a new silane‐containing universal adhesive to bond to glass ceramics?
Priscila Luciane da Silva, Hélio Radke Bittencourt, Luiz Henrique Burnett, Ana Maria Spohr
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(10): 1452. CrossRef - The Effect of Various Lasers on the Bond Strength Between Orthodontic Brackets and Dental Ceramics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Jaafar Abduo, Mehrnaz Zakizade, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Ahmed Hussain
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(1): 20. CrossRef - Long-Term Bonding Performance of One-Bottle vs. Two-Bottle Bonding Agents to Lithium Disilicate Ceramics
Masao Irie, Masahiro Okada, Yukinori Maruo, Goro Nishigawa, Takuya Matsumoto
Polymers.2024; 16(16): 2266. CrossRef - Bond strength to different CAD/CAM lithium disilicate reinforced ceramics
Mona Alhomuod, Jin‐Ho Phark, Sillas Duarte
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(1): 129. CrossRef - Surface Treatment Effect on Shear Bond Strength between Lithium Disilicate Glass-Ceramic and Resin Cement
Siripan Simasetha, Awiruth Klaisiri, Tool Sriamporn, Kraisorn Sappayatosok, Niyom Thamrongananskul
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(02): 373. CrossRef - Bonding of Clear Aligner Composite Attachments to Ceramic Materials: An In Vitro Study
Bashair A. Alsaud, Maher S. Hajjaj, Ahmad I. Masoud, Ensanya A. Abou Neel, Dalia A. Abuelenain, Amal I. Linjawi
Materials.2022; 15(12): 4145. CrossRef - Bonding of different resin luting materials to composite, polymer-infiltrated and feldspathic ceramic CAD/CAM blocks
Burcu Dikici, Esra Can Say
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2022; 36(14): 1572. CrossRef - Influence of mechanical and chemical pre-treatments on the repair of a hybrid ceramic
Sascha Niklas Jung, Stefan Rüttermann
Dental Materials.2022; 38(7): 1140. CrossRef - Effect of Silane-Containing Universal Adhesives on the Bonding Strength of Lithium Disilicate
Yu-Ri Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3976. CrossRef - Ceramics in dentistry: which material is appropriate for the anterior or posterior Dentition? Part 1: materials science
Loo Chien Win, Peter Sands, Stephen J Bonsor, FJ Trevor Burke
Dental Update.2021; 48(8): 680. CrossRef - The effect of different ceramic surface treatments on the repair bond strength of resin composite to lithium disilicate ceramic
Nanako UEDA, Tomohiro TAKAGAKI, Toru NIKAIDO, Rena TAKAHASHI, Masaomi IKEDA, Junji TAGAMI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(5): 1073. CrossRef - Bonding Strength of Universal Adhesives to Indirect Substrates: A Meta‐Analysis of in Vitro Studies
Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suárez, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Rafael Pino Vitti, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Evandro Piva
Journal of Prosthodontics.2020; 29(4): 298. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments and multimode adhesive application on the Weibull characteristics, wettability, surface topography and adhesion to CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramic
Karina Barbosa Souza, Dayanne Monielle Duarte Moura, Sarah Emille Gomes da Silva, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Rafael de Almeida Spinelli Pinto, Fabíola Pessôa Pereira Leite, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the ratio of silane to 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogenphosphate (MDP) in primer on bonding performance of silica-based and zirconia ceramics
Minkhant Koko, Tomohiro Takagaki, Ahmed Abdou, Masanao Inokoshi, Masaomi Ikeda, Takahiro Wada, Motohiro Uo, Toru Nikaido, Junji Tagami
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 112: 104026. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and repair materials on the shear bond strength of CAD/CAM provisional restorations
Ki-Won Jeong, Sung-Hun Kim
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2019; 11(2): 95. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strengths of adhesively bonded polymer-based CAD/CAM materials to dentin
Nuray CAPA, Esra CAN SAY, Cansin CELEBI, Ayca CASUR
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(1): 75. CrossRef - Simplified Surface Treatments for Ceramic Cementation: Use of Universal Adhesive and Self-Etching Ceramic Primer
Heloísa A. B. Guimarães, Paula C. Cardoso, Rafael A. Decurcio, Lúcio J. E. Monteiro, Letícia N. de Almeida, Wellington F. Martins, Ana Paula R. Magalhães
International Journal of Biomaterials.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Effects of surface treatments on repair bond strength of a new CAD/CAM ZLS glass ceramic and two different types of CAD/CAM ceramics
Ayse Seda Ataol, Gulfem Ergun
Journal of Oral Science.2018; 60(2): 201. CrossRef - An in vitro evaluation of fracture load of implant‐supported zirconia‐based prostheses fabricated with different veneer materials
Hiroki Takata, Futoshi Komine, Junichi Honda, Markus B. Blatz, Hideo Matsumura
Clinical Oral Implants Research.2018; 29(4): 396. CrossRef - Effects of multiple firings on mechanical properties and resin bonding of lithium disilicate glass-ceramic
Hongliang Meng, Haifeng Xie, Lu Yang, Bingzhuo Chen, Ying Chen, Huaiqin Zhang, Chen Chen
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2018; 88: 362. CrossRef
- Clinical Roles of Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Bonding Materials
- 4,068 View
- 22 Download
- 27 Crossref

- The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
- Jayang Kim, Sungok Hong, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):299-305. Published online October 2, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.299
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of multiple decontamination procedures for salivary contamination after curing of a universal adhesive on dentin bond strength according to its etch modes.
Materials and Methods Forty-two extracted bovine incisors were trimmed by exposing the labial dentin surfaces and embedded in cylindrical molds. A universal adhesive (All-Bond Universal, Bisco) was used. The teeth were randomly divided into groups according to etch mode and decontamination procedure. The adhesive was applied according to the manufacturer's instructions for a given etch mode. With the exception of the control groups, the cured adhesive was contaminated with saliva for 20 sec. In the self-etch group, the teeth were divided into three groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive. In the etch-and-rinse group, the teeth were divided into four groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive. A composite resin (Filtek Z350XT, 3M ESPE) was used for filling and was cured on the treated surfaces. Shear bond strength was measured, and failure modes were evaluated. The data were subjected to one-way analysis of variation and Tukey's HSD test.
Results The etch-and-rinse subgroup that was decontaminated by rinse, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive showed a significantly higher bond strength.
Conclusions When salivary contamination occurs after curing of the universal adhesive, additional etching improves the bond strength to dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of different methods of saliva decontamination on microshear bond strength of composite to composite: An in vitro study
Sara Ordooei Javan, Reza Movahedian, Somayeh Hosseini Tabatabaei
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
Rim Bourgi
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of contamination and decontamination methods on the bond strength of adhesive systems to dentin: A systematic review
Rim Bourgi, Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suarez, Walter Devoto, Ana Josefina Monjarás‐Ávila, Paulo Monteiro, Khalil Kharma, Monika Lukomska‐Szymanska, Louis Hardan
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1218. CrossRef - Universal adhesive application to contaminated/non-contaminated dentin with three different protocols: An in vitro shear bond strength and SEM analysis
Tuğçe BALOGLU GONCU, Nasibe Aycan YILMAZ
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(4): 633. CrossRef - Tükürük kontaminasyon/dekontaminasyonunun üniversal adezivlerin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Cansu ATALAY, Aybüke USLU, Ece MERAL, Ayşe YAZICI, A. Atila ERTAN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 611. CrossRef - Bioactive glass ceramic can improve the bond strength of sealant/enamel?
R. E. Silveira, R. G. Vivanco, R. C. de Morais, G. Da Col dos Santos Pinto, F. de C. P. Pires-de-Souza
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2019; 20(4): 325. CrossRef - Universal dental adhesives: Current status, laboratory testing, and clinical performance
Sanket Nagarkar, Nicole Theis‐Mahon, Jorge Perdigão
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2019; 107(6): 2121. CrossRef - Effect of Saliva Decontamination on Bond Strength of 1-step Self-etching Adhesives to Dentin of Primary Posterior Teeth
Junhee Lee, Shin Kim, Taesung Jeong, Jonghyun Shin, Eungyung Lee, Jiyeon Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2019; 46(3): 274. CrossRef - Polymeric materials and films in dentistry: An overview
Dinesh Rokaya, Viritpon Srimaneepong, Janak Sapkota, Jiaqian Qin, Krisana Siraleartmukul, Vilailuck Siriwongrungson
Journal of Advanced Research.2018; 14: 25. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of Light-Cured Dental Materials according to Different Sample Preparation Methods
Myung-Jin Lee, Mi-Joo Kim, Jae-Sung Kwon, Sang-Bae Lee, Kwang-Mahn Kim
Materials.2017; 10(3): 288. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of different methods of saliva decontamination on microshear bond strength of composite to composite: An in vitro study
- 2,793 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of solvent volatilization time on the bond strength of etch-and-rinse adhesive to dentin using conventional or deproteinization bonding techniques
- José Aginaldo de Sousa Júnior, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):202-208. Published online March 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study determined the effect of the air-stream application time and the bonding technique on the dentin bond strength of adhesives with different solvents. Furthermore, the content and volatilization rate of the solvents contained in the adhesives were also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Three adhesive systems with different solvents (Stae, SDI, acetone; XP Bond, Dentsply De Trey, butanol; Ambar, FGM, ethanol) were evaluated. The concentrations and evaporation rates of each adhesive were measured using an analytical balance. After acid-etching and rinsing, medium occlusal dentin surfaces of human molars were kept moist (conventional) or were treated with 10% sodium hypochlorite for deproteinization. After applying adhesives over the dentin, slight air-stream was applied for 10, 30 or 60 sec. Composite cylinders were built up and submitted to shear testing. The data were submitted to ANOVA and Tukey's test (α = 0.05).
Results Stae showed the highest solvent content and Ambar the lowest. Acetone presented the highest evaporation rate, followed by butanol. Shear bond strengths were significantly affected only by the factors of 'adhesive' and 'bonding technique' (
p < 0.05), while the factor 'duration of air-stream' was not significant. Deproteinization of dentin increased the bond strength (p < 0.05). Stae showed the lowest bond strength values (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was observed between XP Bond and Ambar.Conclusions Despite the differences in content and evaporation rate of the solvents, the duration of air-stream application did not affect the bond strength to dentin irrespective of the bonding technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of solvent evaporation and photo-irradiation strategy of contact-cure adhesive system on bonding to root canal
Wahyuni Suci Dwiandhany, Kittisak Sanon, Yasushi Shimada, Ahmed Abdou
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef
- Effect of solvent evaporation and photo-irradiation strategy of contact-cure adhesive system on bonding to root canal
- 1,644 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of endodontic tri-antibiotic paste on bond strengths of dentin adhesives to coronal dentin
- Parvin Mirzakoucheki, Ricardo Walter, Navid Khalighinejad, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Sanaz Mirsattari, Navid Akbarzadeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):136-142. Published online February 12, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of tri-antibiotic paste (TAP) on microtensile bond strengths (MTBS) of dental adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods Sixty extracted molars had their occlusal surfaces flattened to expose dentin. They were divided into two groups, i.e., control group with no dentin treatment and experimental group with dentin treatment with TAP. After 10 days, specimens were bonded using self-etch (Filtek P90 adhesive) or etch-and-rinse (Adper Single Bond Plus) adhesives and restored with composite resin. Teeth were sectioned into beams, and the specimens were subjected to MTBS test. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey tests.
Results There was a statistically significant interaction between dentin treatment and adhesive on MTBS to coronal dentin (
p = 0.003). Despite a trend towards worse MTBS being noticed in the experimental groups, TAP application showed no significant effect on MTBS (p = 0.064).Conclusions The etch-and-rinse adhesive Adper Single Bond Plus presented higher mean bond strengths than the self-etch adhesive Filtek P90, irrespective of the group. The superior bond performance for Adper Single Bond when compared to Filtek P90 adhesive was confirmed by a fewer number of adhesive failures. The influence of TAP in bond strength is insignificant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efecto antimicrobiano como medicación intraconducto de la pasta triantibiótica.
Paúl Sebastián Ulloa Amores, Diana Álvarez Álvarez, María Elizabeth Moscoso Abad, Magda Zulay Bastidas Calva
Revista de la Asociación Dental Mexicana.2024; 81(4): 211. CrossRef - Effect of Intracanal Medicaments on Push-out Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-based Materials
Hyuntae Jeong, Sunmi Yang, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi, Jaehwan Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(4): 455. CrossRef
- Efecto antimicrobiano como medicación intraconducto de la pasta triantibiótica.
- 1,335 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
- Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):23-29. Published online August 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of pre-etching on the bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system to dentin.
Materials and Methods Thirty human molars were randomly divided into 5 groups according to the different bonding strategies. For teeth restored with silorane-based composite (Filtek Silorane, 3M ESPE), the specific self-etching adhesive system (Adhesive System P90, 3M ESPE) was used with and without pre-etching (Pre-etching/Silorane and Silorane groups). Teeth restored with methacrylate based-composite (Filtek Z250, 3M ESPE) were hybridized with the two-step self-etching system (Clearfil SE Bond, Kuraray), with and without pre-etching (Pre-etching/Methacrylate and Methacrylate groups), or three-step adhesive system (Adper Scotchbond Multi-Purpose, 3M ESPE) (Three-step/Methacrylate group) (
n = 6). The restored teeth were sectioned into stick-shaped test specimens (1.0 × 1.0 mm), and coupled to a universal test machine (0.5 mm/min) to perform microtensile testing.Results Pre-etching/Methacrylate group presented the highest bond strength values, with significant difference from Silorane and Three-step/Methacrylate groups (
p < 0.05). However, it was not significantly different from Preetching/Silorane and Methacrylate groups.Conclusions Pre-etching increased bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system to dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef
- Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- 1,421 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Push-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement used as endodontic sealer
- Eduardo Diogo Gurgel-Filho, Felipe Coelho Lima, Vicente de Paula Aragão Saboia, Tauby de Souza Coutinho-Filho, Aline de Almeida Neves, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):282-287. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of the present study was to investigate the bond strength of RelyX Unicem (3M) to root canal dentin when used as an endodontic sealer.
Materials and Methods Samples of 24 single-rooted teeth were prepared with Gates Glidden drills and K3 files. After that, the roots were randomly assigned to three experimental groups (
n = 8) according to the filling material, (1) AH Plus (Dentsply De Trey GmbH)/Gutta-Percha cone; (2) Epiphany SE (Pentron)/Resilon cone; (3) RelyX Unicem/Gutta-Percha cone. All roots were filled using a single cone technique associated to vertical condensation. After the filling procedures, each tooth was prepared for a push-out bond strenght test by cutting 1 mm-thick root slices. Loading was performed on a universal testing machine at a speed of 0.5 mm/min. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey test for multiple comparisons were used to compare the results among the experimental groups.Results Epiphany SE/Resilon showed significantly lower push-out bond strength than both AH Plus/Gutta-Percha and RelyX Unicem/Gutta-Percha (
p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in bond strength between AH Plus/Gutta-Percha and RelyX Unicem/Gutta-Percha (p > 0.05).Conclusions Under the present
in vitro conditions, bond strength to root dentin promoted by RelyX Unicem was similar to AH Plus. Epiphany SE/Resilon resulted in lower bond strength values when compared to both materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro comparative evaluation of physicochemical and mechanical properties, cytocompatibility, and antimicrobial efficacy of various bioceramic root canal sealers
Fushi Wang, Jiaxing Li, Jingjing Wan, Siyuan Li, Shijia Tang, Li Wang, Liuyan Meng
Ceramics International.2026; 52(7): 9561. CrossRef - In-Vitro Comparative Adhesion Evaluation of Bioceramic and Dual-Cure Resin Endodontic Sealers Using SEM, AFM, Push-Out and FTIR
Radu Marcel Chisnoiu, Marioara Moldovan, Doina Prodan, Andrea Maria Chisnoiu, Dana Hrab, Ada Gabriela Delean, Alexandrina Muntean, Doina Iulia Rotaru, Ovidiu Pastrav, Mihaela Pastrav
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(10): 4454. CrossRef - Push-out Bond Strength of Fiber Posts Cemented Using New Universal Adhesives on Etched and Nonetched Intraradicular Dentin
Hani F Ounsi, Simone Grandini, Marco Ferrari, Valentina Spicciarelli, Giacomo Corsentino, Crystal Marruganti
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(1): 91. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of three different obturating systems to intraradicular dentin: An In vitro study
MohammedKhwaja Moinuddin, LKarthik Prasad, Nimeshika Ramachandruni, Shekar Kamishetty, RaviChandra Cherkupalli
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(4): 631. CrossRef - The influence of methodological variables on the push‐out resistance to dislodgement of root filling materials: a meta‐regression analysis
F. M. Collares, F. F. Portella, S. B. Rodrigues, R. K. Celeste, V. C. B. Leitune, S. M. W. Samuel
International Endodontic Journal.2016; 49(9): 836. CrossRef - Effect of photon induced photoacoustic streaming (PIPS) on bond strength to dentine of two root canal filling materials
Ivana Miletić, Nicoletta Chieffi, Carlo Rengo, Marco Ferrari, Dan Nathanson, Anja Baraba
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.2016; 48(10): 951. CrossRef
- In vitro comparative evaluation of physicochemical and mechanical properties, cytocompatibility, and antimicrobial efficacy of various bioceramic root canal sealers
- 1,685 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
- Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):95-103. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of three antioxidizing agents on pull-out bond strengths of dentin treated with sodium hypochlorite.
Materials and Methods Root canals of 75 single-rooted human teeth were prepared. Fifteen teeth were irrigated with normal saline for a negative control group, and the remaining 60 teeth (groups 2 - 5) with 2.5% NaOCl. The teeth in group 2 served as a positive control. Prior to post cementation, the root canals in groups 3 - 5 were irrigated with three antioxidizing agents including 10% rosmarinic acid (RA, Baridge essence), 10% hesperidin (HPN, Sigma), and 10% sodium ascorbate hydrogel (SA, AppliChem). Seventy-five spreaders (#55, taper .02, Produits Dentaires S.A) were coated with silica and silanized with the Rocatec system and ceramic bond. All the prepared spreaders were cemented with a self-adhesive resin cement (Bifix SE, Voco Gmbh) in the prepared canals. After storage in distilled water (24 h/37℃), the spreaders were pulled out in a universal testing machine at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. Pull-out strength values were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test (α = 0.05).
Results There were significant differences between study groups (
p = 0.016). The highest pull-out strength was related to the SA group. The lowest strength was obtained in the positive control group.Conclusions Irrigation with NaOCl during canal preparation decreased bond strength of resin cement to root dentin. Amongst the antioxidants tested, SA had superior results in reversing the diminishing effect of NaOCl irrigation on the bond strength to root dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of passive ultrasonic irrigation on the bond strength of two different self-etch adhesives to human pulp chamber dentine: a laboratory investigation
Mohammed Turky, Jukka Matinlinna, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul M. H. Dummer, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Nermin Alsayed Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of cavity design on the mechanical behavior of endo-crown restorations: an ex-vivo study
Mohamed Gomaa Altamimi, Omaima El Mahallawi, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Mohammed Turky
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Irrigants on Push-Out Bond Strength in Resin Cementation Protocols for Fiber Posts in Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Sandra García-Varela, João Carlos Ramos, María José Ginzo-Villamayor, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Ramón Méndez-Díaz, Marcos Aníbal Anache-D’Abate, Tania Gancedo-Gancedo, Manuel Ruíz-Piñón, Soledad Mareque-Bueno, Benjamín José Martín-Biedma
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1432. CrossRef - A facile method for rejuvenating the bonding efficacy of root canal sealer-smeared dentine
Wenqing Lin, Yuan Gao, Surong Chen, Yan Yang, Weihu Ye, Diana Tran, Brian E. Bergeron, Franklin R. Tay, Jingzhi Ma
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 136: 104591. CrossRef - The Effect of Antioxidants on Dentin Bond Strength after Application of Common Endodontic Irrigants: A Systematic Review
Regina Gascón, Leopoldo Forner, Carmen Llena
Materials.2023; 16(6): 2260. CrossRef - Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and thermal cycling on the bond strength of resin cements to the root dentin
Danielle Cristine Messias, Moisés Franco Barbosa da Silva, Natália Spadini de Faria, Tatiane Rocco Dias-Arnez, Fuad Jacob Rached-Júnior, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 854. CrossRef - Effect of Er
Horieh Moosavi, Farzaneh Ahrari, Maryam Zanjani
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 17. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite on adhesive charactersitics of dentin: A systematic review of laboratory-based testing
Ensanya A. Abou Neel, Jonathan C. Knowles, Laurent Bozec
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 95: 102419. CrossRef - Effect of irrigant neutralizing reducing agents on the compromised dislocation resistance of an epoxy resin and a methacrylate resin-based root canal sealer in vitro
Pallavi Reddy, Prasanna Neelakantan, Kavitha Sanjeev, Jukka Pekka Matinlinna
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2018; 82: 206. CrossRef - Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigation and Its Effect on Bond Strength to Dentin
Tariq S. Abuhaimed, Ensanya A. Abou Neel
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Impact of conditioning regimens and time on adhesion of a fiber post to root dentin using two resin cements
P. Neelakantan, R. Mohanraj, E. Chua, S. Belli
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2015; 29(4): 337. CrossRef - Effect of antioxidants on push-out bond strength of hydrogen peroxide treated glass fiber posts bonded with two types of resin cement
Maryam Khoroushi, Hamid Mazaheri, Pardis Tarighi, Pouran Samimi, Navid Khalighinejad
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 303. CrossRef
- Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,869 View
- 10 Download
- 15 Crossref

-
Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate on shear bond strength of composite resin to bleached enamel: an
in vitro study - Zahra Khamverdi, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Shahin Kasraei, Negin Ronasi, Shiva Rostami
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):241-247. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to determine the effect of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on the shear bond strength of composite resin to bleached enamel.
Materials and Methods Ninety enamel surfaces of maxillary incisors were randomly divided into 9 groups as follows: G1: control (no bleaching); G2: bleaching; G3: bleaching and storage for seven days; G4 - 6: bleaching and application of 600, 800 and 1,000 µmol of EGCG-containing solution for 10 minutes, respectively; G7 - 9: bleaching and application of 600, 800 and 1,000 µmol of EGCG-containing solution for 20 minutes, respectively. The specimens were bleached with 30% hydrogen peroxide gel and a composite resin cylinder was bonded on each specimen using a bonding agent. Shear bond strength of the samples were measured in MPa. Data was analyzed using the two-way ANOVA and Tukey HSD tests (α = 0.05).
Results The maximum and minimum mean shear bond strength values were observed in G1 and G2, respectively. Time and concentration of EGCG showed no significant effects on bond strength of the groups (
p > 0.05). Multiple comparison of groups did not reveal any significant differences between the groups except for G2 and all the other groups (p < 0.05).Conclusions There is a significant decrease in bond strength of composite resin to enamel immediately after bleaching. A delay of one week before bonding and the use of EGCG increased bond strength of composite resin to bleached enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the effect of two types of antioxidants, pomegranate peel and green tea, on the shear bond strength of composites on bleached enamel using universal bondings (lnvitro study)
Sara Khosravi, Salimeh Shobchari, Keivan Saati, Shahriar Jalalian
Journal of Research in Dental Sciences.2025; 22(3): 192. CrossRef - Investigating the effect of two types of antioxidants, pomegranate peel and green tea, on the shear bond strength of microhybrid composites on bleached enamel using sixth generation bondings (lnvitro study)
Parisa Hekmatnejad, Mansoureh Emami Arjomand2, Maryam Rahimikhoob, Bahareh Farar, Shahriar Jalalian
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(2): 116. CrossRef - Color stability of enamel treated with different antioxidant agents following at-home bleaching with 10% hydrogen peroxide
Rodrigo Chiles PEREIRA, Letícia Vasconcelos Silva de SOUZA, Matheus KURY, Iago César Ribeiro Teles MATOS, Reginna Vyctória da Trindade Souza de Melo CARNEIRO, Sandrine Bittencourt BERGER, Vanessa CAVALLI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Pomegranate Peel and Green Tea Extract as Antioxidants on Shear Bond Strength of a
Microhybrid Composite to Bleached Enamel
F Ghorbani, SH Pourhaghani, H Heshmat, SH Jalalian, MJ Kharazifard
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2022; 7(2): 62. CrossRef - Effect of nonthermal atmospheric plasma, grape seed extract, and bromelain on immediate bonding of composite to bleached and microabraded surfaces
MayanaAameena Banu, Nagesh Bolla, Sravanthi Tammineedi, Sayesh Vemuri, RamChowdary Basam, AnilKumar Ganapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(1): 42. CrossRef - Antioxidant Potential of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, Ascorbic Acid, and Sodium Ascorbate in Solution and Gel Forms by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
Virdah Dwi Dewaantari, Setyabudi Setyabudi, Kun Ismiyatin
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2021; 11(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of 6% cranberry, 10% green tea, 50% aloe vera and 10% sodium ascorbate on reversing the immediate bond strength of bleached enamel: In vitro study
Hena Rahman, Mohd Irfan Ansari, Monika Khangwal, Ravindra Solanki, Shahnaz Mansoori
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2021; 11(2): 107. CrossRef - Vital Bleaching Influences the Bond Strength of Adhesive Systems to Enamel and Dentin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis ofIn VitroStudies
TG Savian, J Oling, FZM Soares, RO Rocha
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(2): E80. CrossRef - Use of antioxidants to restore bond strength after tooth bleaching with peroxides
Dorcas E. R. P. Olmedo, Matheus Kury, Bruna A. Resende, Vanessa Cavalli
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Epigallocathecin-3-gallate as an Antioxidant After Dental Bleaching on Shear Bond Strength of Composite Resin Restoration
Syarifah Nadhira Assyafira Al-Habsyi, Kun Ismiyatin, Galih Sampoerno
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2021; 11(1): 42. CrossRef - Natural antioxidants to restore immediate bond strength to bleached enamel: Systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Juana Rodríguez‐Barragué, Joanna Vola‐Gelmini, Marcel Skuras‐Siedemburg, José Alejandro Rivera‐Gonzaga, Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suarez
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(5): 702. CrossRef - DİŞ BEYAZLATMA İŞLEMİNİN LİTYUM DİSİLİKAT SERAMİĞİN BAĞLANMA DAYANIMINA ETKİSİ
Merve YILDIRAK, Rıfat GÖZNELİ
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Influence of green tea extract in the color of composite resin restorations
R.G. Lopes, B. Oliveira-Reis, A.T. Maluly-Proni, M.H.T. Silva, A.L.F. Briso, P.H. dos Santos
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 100: 103408. CrossRef - Influence of protease inhibitors on the degradation of sound, sclerotic and caries-affected demineralized dentin
B. Oliveira-Reis, A.T. Maluly-Proni, T.C. Fagundes, G. Vasconcelos, E. Bresciani, A. Prakki, P.H. dos Santos
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 97: 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Immediate Bond Strength to Bleached Enamel Following Application of Various Antioxidant Solutions
Anshu Minocha, Ashu K. Gupta, Alisha Dhingra, Nayantara Sen
Dental Journal of Advance Studies.2017; 5(2): 84. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Abraded and Non-Abraded Bleached Enamel to Resin After Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation
Pedro H.C. Oliveira, Alessandra Cassoni, Aldo Brugnera, Ilana P. Tenório, José A. Rodrigues
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2017; 35(10): 530. CrossRef - Effect of dentin biomodifiers on the immediate and long-term bond strengths of a simplified etch and rinse adhesive to dentin
Payal Singh, Rajni Nagpal, Udai Pratap Singh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 188. CrossRef - The effect of green tea on the shear strength of brackets after home whitening treatment
Renata C. A. Schwertner, Joyce S. Y. Leoncio, Alessandro Schwertner, Ricardo D. Guiraldo, Murilo B. Lopes, Hellen C. De Carvalho, Alcides Gonini-Júnior, Sandrine B. Berger
Applied Adhesion Science.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Green Tea Application Time on Bond Strength after Enamel Bleaching
Andrezza Astafief Ozelin, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Rodrigo Varella de Carvalho, Murilo Baena Lopes, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
Brazilian Dental Journal.2014; 25(5): 399. CrossRef
- Investigating the effect of two types of antioxidants, pomegranate peel and green tea, on the shear bond strength of composites on bleached enamel using universal bondings (lnvitro study)
- 1,688 View
- 4 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Effect of chlorhexidine application on the bond strength of resin core to axial dentin in endodontic cavity
- Yun-Hee Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):207-214. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the influence of chlorhexidine (CHX) on the microtensile bonds strength (µTBS) of resin core with two adhesive systems to dentin in endodontic cavities.
Materials and Methods Flat dentinal surfaces in 40 molar endodontic cavities were treated with self-etch adhesive system, Contax (DMG) and total-etch adhesive system, Adper Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE) after the following surface treatments: (1) Priming only (Contax), (2) CHX for 15 sec + rinsing + priming (Contax), (3) Etching with priming (Adper Single Bond 2), (4) Etching + CHX for 15 sec + rinsing + priming (Adper Single Bond 2). Resin composite build-ups were made with LuxaCore (DMG) using a bulk method and polymerized for 40 sec. For each condition, half of specimens were submitted to µTBS after 24 hr storage and half of them were submitted to thermocycling of 10,000 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃ before testing. The data were analyzed using ANOVA and independent
t -test at a significance level of 95%.Results CHX pre-treatment did not affect the bond strength of specimens tested at the immediate testing period, regardless of dentin surface treatments. However, after 10,000 thermocycling, all groups showed reduced bond strength. The amount of reduction was greater in groups without CHX treatments than groups with CHX treatment. These characteristics were the same in both self-etch adhesive system and total-etch adhesive system.
Conclusions 2% CHX application for 15 sec proved to alleviate the decrease of bond strength of dentin bonding systems. No significant difference was shown in µTBS between total-etching system and self-etching system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro Tensile bond strength and microleakage assessment of total-etch and self-etch adhesive bonded to carious affected dentin disinfected with Chlorhexidine, Curcumin, and Malachite green
Zeeshan Qamar, Nishath Sayed Abdul, R Naveen Reddy, Mahesh Shenoy, Saleh Alghufaili, Yousef Alqublan, Ali Barakat
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 43: 103636. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef - Influence of chlorhexidine 2% and sodium hypochlorite 5.25% on micro-tensile bond strength of universal adhesive system (G-Premio Bond)
Nafiseh Fazelian, Abbas Rahimi Dashtaki, MohammadAmin Eftekharian, Batool Amiri
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effects of different methods of post space preparation in primary anterior teeth on the fracture resistance of tooth restorations
Bahman Seraj, Sara Ghadimi, Ebrahim Najafpoor, Fatemeh Abdolalian, razieh khanmohammadi
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 141. CrossRef - Chemical, microbial, and host‐related factors: effects on the integrity of dentin and the dentin–biomaterial interface
Marcela T. Carrilho, Fabiana Piveta, Leo Tjäderhane
Endodontic Topics.2015; 33(1): 50. CrossRef - MMP Inhibitors on Dentin Stability
A.F. Montagner, R. Sarkis-Onofre, T. Pereira-Cenci, M.S. Cenci
Journal of Dental Research.2014; 93(8): 733. CrossRef - Thermal cycling for restorative materials: Does a standardized protocol exist in laboratory testing? A literature review
Anna Lucia Morresi, Maurizio D'Amario, Mario Capogreco, Roberto Gatto, Giuseppe Marzo, Camillo D'Arcangelo, Annalisa Monaco
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 29: 295. CrossRef
- Micro Tensile bond strength and microleakage assessment of total-etch and self-etch adhesive bonded to carious affected dentin disinfected with Chlorhexidine, Curcumin, and Malachite green
- 1,380 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of different chlorhexidine application times on microtensile bond strength to dentin in Class I cavities
- Hyun-Jung Kang, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):9-15. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) with different application times on microtensile bonds strength (MTBS) to dentin in class I cavities and intended to search for ideal application time for a simplified bonding protocol.
Materials and Methods Flat dentinal surfaces with class I cavities (4 mm × 4 mm × 2 mm) in 40 molar teeth were bonded with etch-and-rinse adhesive system, Adper Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE) after: (1) etching only as a control group; (2) etching + CHX 5 sec + rinsing; (3) etching + CHX 15 sec + rinsing; (4) etching + CHX 30 sec + rinsing; and (5) etching + CHX 60 sec + rinsing. Resin composite was built-up with Z-250 (3M ESPE) using a bulk method and polymerized for 40 sec. For each condition, half of the specimens were immediately submitted to MTBS test and the rest of them were assigned to thermocycling of 10,000 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃ before testing. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA, at a significance level of 95%.
Results There was no significant difference in bond strength between CHX pre-treated group and control group at the immediate testing period. After thermocycling, all groups showed reduced bond strength irrespective of the CHX use. However, groups treated with CHX maintained significantly higher MTBS than control group (
p < 0.05). In addition, CHX application time did not have any significant influence on the bond strength among groups treated with CHX.Conclusion Application of 2% CHX for a short time period (5 sec) after etching with 37% phosphoric acid may be sufficient to preserve dentin bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of nonthermal atmospheric plasma application at different time intervals on the dentinal shear bond strength pretreated with 2% chlorhexidine as cavity disinfectant: An in vitro study
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Gali Praveen Kumar, Mayana Aameena Banu, Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha Anila, Shaik Afreen Kamal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(7): 769. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation ofEmblica officinalisas an etchant and an MMP inhibitor with orthophosphoric acid and chlorhexidine on the microshear bond strength of composite resin: anex vivostudy
Divya Sangeetha Rajkumar, Annapoorna Ballagere Mariswamy
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Cavity Disinfectants on Adhesion to Primary Teeth—A Systematic Review
Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Ana Apolónio, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4398. CrossRef - Effect of Different Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors on Shear Bond Strength of Composite Attached to Primary Teeth Dentin
Najmeh Mohammadi, Zahra Parsaie, Dana Jafarpour, Fatemeh Bizolm
European Journal of General Dentistry.2020; 9(03): 147. CrossRef
- Effect of nonthermal atmospheric plasma application at different time intervals on the dentinal shear bond strength pretreated with 2% chlorhexidine as cavity disinfectant: An in vitro study
- 1,921 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
- Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):490-497. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.490
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effect of the uncured dentin adhesives on the bond interface between the resin inlay and dentin.
Materials and Methods Dentin surface was exposed in 24 extracted human molars and the teeth were assigned to indirect and direct resin restoration group. For indirect resin groups, exposed dentin surfaces were temporized with provisional resin. The provisional restoration was removed after 1 wk and the teeth were divided further into 4 groups which used dentin adhesives (OptiBond FL, Kerr; One-Step, Bisco) with or without light-curing, respectively (Group OB-C, OB-NC, OS-C and OS-NC). Pre-fabricated resin blocks were cemented on the entire surfaces with resin cement. For the direct resin restoration groups, the dentin surfaces were treated with dentin adhesives (Group OB-D and OS-D), followed by restoring composite resin. After 24 hr, the teeth were assigned to microtensile bond strength (µTBS) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), respectively.
Results The indirect resin restoration groups showed a lower µTBS than the direct resin restoration groups. The µTBS values of the light cured dentin adhesive groups were higher than those of the uncured dentin adhesive groups (
p < 0.05). CLSM analysis of the light cured dentin adhesive groups revealed definite and homogenous hybrid layers. However, the uncured dentin adhesive groups showed uncertain or even no hybrid layer.Conclusions Light-curing of the dentin adhesive prior to the application of the cementing material in luting a resin inlay to dentin resulted in definite, homogenous hybrid layer formation, which may improve the bond strength.
- 1,597 View
- 10 Download

- Microshear bond strength of a self-etching primer adhesive to enamel according to the type of bur
- Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):477-482. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the microshear bond strength (uSBS) to enamel prepared with different burs and to determine what type of bur were chosen when a self-etching primer adhesive was used.
Materials and Methods Enamel of forty-two human molars were used. They were divided into one of six groups (n = 7), Group 1, coarse (125 - 150 µm) diamond bur; Group 2, standard (106 - 125 µm) diamond bur; Group 3, fine (53 - 63 µm) diamond bur; Group 4, extrafine (20 - 30 µm) diamond bur; Group 5, plain-cut carbide bur (no. 245); Group 6, cross-cut carbide bur (no. 557). Clearfil SE Bond and Clearfil AP-X (Kuraray Medical Inc.) was bonded to enamel surface. The bonded specimens were subjected to uSBS testing.
Results The uSBS of Group 4 was the highest among groups and it was significantly higher than that of Groups 1, 2, 3, and 6 (
p < 0.05), but it was not significantly different from that of Group 5.Conclusions Different burs used on enamel surface affected the microshear bond strengths of a self-etching primer adhesive to the enamel surface. In the case of Clearfil SE Bond, extrafine diamond and plain-cut carbide bur are recommended for bonding to enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sixty-month follow up of three different universal adhesives used with a highly-filled flowable resin composite in the restoration of non-carious cervical lesion
Fatma Dilsad Oz, Canan Ozturk, Reza Soleimani, Sevil Gurgan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(8): 5377. CrossRef
- Sixty-month follow up of three different universal adhesives used with a highly-filled flowable resin composite in the restoration of non-carious cervical lesion
- 1,027 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
- Tae-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Young-Jung Choi, So-Young Yang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):419-424. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was aimed to determine the effects of temporary sealing materials on microtensile bond strength between resin-coated dentin and resin inlay and to compare the bonding effectiveness of delayed dentin sealing and that of immediate dentin sealing.
Materials and Methods The teeth were divided into 4 groups: group 1, specimens were prepared using delayed dentin sealing after temporary sealing with zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE); group 2, specimens were prepared using immediate dentin sealing and ZOE sealing; group 3, specimens were prepared using immediate dentin sealing and Dycal (Dentsply) sealing; group 4, specimens were prepared using immediately sealed, and then temporarily sealed with a resin-based temporary sealing material.
After removing the temporary sealing material, we applied resin adhesive and light-cured. Then the resin inlays were applied and bonded to the cavity with a resin-based cement. The microtensile bond strength of the sectioned specimens were measured with a micro-tensile tester (Bisco Inc.). Significance between the specimen groups were tested by means of one-way ANOVA and multiple Duncan's test.
Results Group 1 showed the lowest bond strength, and group 4 showed the highest bond strength (
p < 0.01). When temporary sealing was performed with ZOE, immediate dentin sealing showed a higher bonding strength than delayed dentin sealing (p < 0.01).Conclusions Based on these results, immediate dentin sealing is more recommended than delayed dentin sealing in bonding a resin inlay to dentin. Also, resin-based temporary sealing materials have shown the best result.
- 987 View
- 2 Download

- Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
- Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):409-418. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.409
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the microshear bond strength (µSBS) and bonding interfaces of two-step total-etching and self-etching adhesive systems to three etch types of dentin either the acid etched, laser etched or laser and acid etched.
Materials and Methods The occlusal dentinal surfaces of thirty human molars were used. They were divided into six groups: group 1, 37% H3PO4 + Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE); group 2, Er:YAG laser (KEY Laser 3, KaVo) + Single Bond 2; group 3, Er:YAG laser + 37% H3PO4 + Single Bond 2; group 4, Clearfil SE Primer + Bond (Kuraray); group 5, Er:YAG laser + Clearfil SE Bond; group 6, Er:YAG laser + Clearfil SE Primer + Bond. The samples were subjected to µSBS testing 24 hr after bonding. Also scanning microscopic evaluations were made on the resin-dentin interfaces of six specimens.
Results The µSBS of group 2 was significantly lower than that of groups 1 and 3 in Single Bond 2 (
p < 0.05). There were significant differences among the uSBS of groups 4, 5, and 6 in Clearfil SE Bond (p < 0.05). Very short and slender resin tags were observed in groups 2 and 5. Long and slender resin tags and lateral branches of tags were observed in groups 3 and 6.Conclusions Treatment of dentin surface using phosphoric acid or self-etching primer improved the adhesion of Er:YAG lased dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Acid or Laser Treatment on Degradation of Dentin Matrix
Aslihan Usumez, Tugrul Sari, Roda Seseogullari Dirihan, Mehmet Esad Guven, Serra Oguz Ahmet, Norbert Gutknecht, Arzu Tezvergil Mutluay
Lasers in Dental Science.2022; 6(2): 99. CrossRef - Ablation of carious dental tissue using an ultrashort pulsed laser (USPL) system
Christoph Engelbach, Claudia Dehn, Christoph Bourauel, Jörg Meister, Matthias Frentzen
Lasers in Medical Science.2015; 30(5): 1427. CrossRef
- Effect of Acid or Laser Treatment on Degradation of Dentin Matrix
- 960 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of adhesive hydrophobicity on microtensile bond strength of low-shrinkage silorane resin to dentin
- So-Yeun Cho, Hyun-Young Kang, Kyoung-A Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):280-289. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate µTBS (microtensile bond strength) of current dentin bonding adhesives which have different hydrophobicity with low-shrinkage silorane resin.
Materials and Methods Thirty-six human third molars were used. Middle dentin was exposed. The teeth were randomly assigned to nine experimental groups: Silorane self-etch adhesives (SS), SS + phosphoric acid etching (SS + pa), Adper easy bond (AE), AE + Silorane system bonding (AE + SSb), Clearfil SE bond (CSE), CSE + SSb, All-Bond 2 (AB2), AB2 + SSb, All-Bond 3 (AB3). After adhesive's were applied, the clinical crowns were restored with Filtek LS (3M ESPE). The 0.8 mm × 0.8 mm sticks were submitted to a tensile load using a Micro Tensile Tester (Bisco Inc.). Water sorption was measured to estimate hydrophobicity adhesives.
Results µTBS of silorane resin to 5 adhesives: SS, 23.2 MPa; CSE, 19.4 MPa; AB3, 30.3 MPa; AB2 and AE, no bond. Additional layering of SSb: CSE + SSb, 26.2 MPa; AB2 + SSb, 33.9 MPa; AE + SSb, no bond. High value of µTBS was related to cohesive failure. SS showed the lowest water sorption. AE showed the highest solubility.
Conclusions The hydrophobicity of adhesive increased, and silorane resin bond-strength was also increased. Additional hydrophobic adhesive layer did not increase the bond-strength to silorane resin except AB2 + SSb. All-Bond 3 showed similar µTBS & water sorption with SS. By these facts, we could reach a conclusion that All-Bond 3 is a competitive adhesive which can replace the Silorane adhesive system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 23. CrossRef
- Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
- 1,442 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):203-210. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of various application methods of one-step self-etch adhesives to microtensile resin-dentin bond strength.
Materials and Methods Thirty-six extracted human molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to twelve groups (
n = 15), according to the three different adhesive systems (Clearfil Tri-S Bond, Adper Prompt L-Pop, G-Bond) and application methods. The adhesive systems were applied on the dentin as follows: 1) The single coating, 2) The double coating, 3) Manual agitation, 4) Ultrasonic agitation. Following the adhesive application, light-cure composite resin was constructed. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and prepared 15 specimens per groups. Then microtensile bond strength was measured and the failure mode was examined.Results Manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating and double coating did. Double coating of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating did and there was no significant difference between the manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation group. There was significant difference in microtensile bonding strength among all adhesives and Clearfil Tri-S Bond showed the highest bond strength.
Conclusions In one-step self-etching adhesives, there was significant difference according to application methods and type of adhesives. No matter of the material, the manual or ultrasonic agitation of the adhesive showed significantly higher microtensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
Nuray Zulkadir Ergin, Aslı Seçilmiş
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 16(3): 356. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef
- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
- 2,029 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
- Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):139-148. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of adhesives on the bond strength to dentin. The experimental adhesives containing various ratios of hydrophobic, low-viscosity Bis-M-GMA, with Bis-GMA and TEGDMA, were made and evaluated on the mechanical properties and bond strength to dentin.
Materials and Methods Five experimental adhesives formulated with various Bis-GMA/Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA ratios were evaluated on their viscosity, degree of conversion (DC), flexural strength (FS), and microtensile bond strength (MTBS). The bonded interfaces were evaluated with SEM and the solubility parameter was calculated to understand the wetting characteristics of the adhesives.
Results Although there were no significant differences in the DC between the experimental adhesives at 48 hr after curing (
p > 0.05), the experimental adhesives that did not contain Bis-GMA exhibited a lower FS than did those containing Bis-GMA (p < 0.05). The experimental adhesives that had very little to no TEGDMA showed significantly lower MTBS than did those containing a higher content of TEGDMA (p < 0.05). The formers exhibited gaps at the interface between the adhesive layer and the hybrid layer. The solubility parameter of TEGDMA approximated those of the components of the primed dentin, rather than Bis-GMA and Bis-M-GMA.Conclusions To achieve a good dentin bond, a strong base monomer, such as Bis-GMA, cannot be completely replaced by Bis-M-GMA for maintaining mechanical strength. For compatible copolymerization between the adhesive and the primed dentin as well as dense cross-linking of the adhesive layer, at least 30% fraction of TEGDMA is also needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Equivalence study of the resin-dentine interface of internal tunnel restorations when using an enamel infiltrant resin with ethanol-wet dentine bonding
Andrej M. Kielbassa, Sabrina Summer, Wilhelm Frank, Edward Lynch, Julia-Susanne Batzer
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole
Yasaman Delaviz, Timothy W. Liu, Ashley R. Deonarain, Yoav Finer, Babak Shokati, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): 229. CrossRef
- Equivalence study of the resin-dentine interface of internal tunnel restorations when using an enamel infiltrant resin with ethanol-wet dentine bonding
- 2,163 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Microshear bond strength of a flowable resin to enamel according to the different adhesive systems
- Jeong-Ho Kim, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):50-58. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the microshear bond strength (uSBS) of two total-etch and four self-etch adhesive systems and a flowable resin to enamel.
Materials and Methods Enamels of sixty human molars were used. They were divided into one of six equal groups (
n = 10) by adhesives used; OS group (One-Step Plus), SB group (Single Bond), CE group (Clearfil SE Bond), TY group (Tyrian SPE/One-Step Plus), AP group (Adper Prompt L-Pop) and GB group (G-Bond).After enamel surfaces were treated with six adhesive systems, a flowable composite resin (Filek Z 350) was bonded to enamel surface using Tygon tubes. the bonded specimens were subjected to uSBS testing and the failure modes of each group were observed under FE-SEM.
Results 1. The
u SBS of SB group was statistically higher than that of all other groups, and theu SBS of OS, SE and AP group was statistically higher than that of TY and GB group (p < 0.05).2. The
u SBS for TY group was statistically higher than that for GB group (p < 0.05).3. Adhesive failures in TY and GB group and mixed failures in SB group and SE group were often analysed. One cohesive failure was observed in OS, SB, SE and AP group, respectively.
Conclusions Although adhesives using the same step were applied the enamel surface, the uSBS of a flowable resin to enamel was different.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 180. CrossRef
- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- 1,137 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of 2% chlorhexidine application on microtensile bond strength of resin composite to dentin using one-step self-etch adhesives
- Soon-Ham Jang, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):486-491. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.486
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effect of 2% chlorhexidine on the µTBS of a direct composite restoration using one-step self-etch adhesives on human dentin.
Materials and Methods Twenty-four extracted permanent molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to six groups (
n = 10), according to the adhesive system and application of chlorhexidine. With or without the application of chlorhexidine, each adhesive system was applied to the dentin surface. After the bonding procedure, light-cure composite resin buildups were produced. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and then cut and glued to the jig of the microtensile testing machine. A tensile load was applied until the specimen failed. The failure mode was examined using an operating microscope. The data was analyzed statistically using one-way ANOVA, Student'st -test (p < 0.05) and Scheffé's test.Results Regardless of the application of chlorhexidine, the Clearfil S3 Bond showed the highest µTBS, followed by G-Bond and Xeno V. Adhesive failure was the main failure mode of the dentin bonding agents tested with some samples showing cohesive failure.
Conclusions The application of 2% chlorhexidine did not affect the µTBS of the resin composite to the dentin using a one-step self-etch adhesive.
- 1,444 View
- 3 Download

- Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
- Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):479-485. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the push-out bond strengths of resin cement/fiber post systems to post space dentin using different application methods of resin cement.
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human premolars were selected and randomly divided into 3 groups according to the technique used to place the cement into root canal: using lentulo-spiral instrument (group Lentulo), applying the cement onto the post surface (group Direct), and injecting the material using a specific elongation tip (group Elongation tip). After shaping and filling of the root canal, post space was drilled using Rely-X post drill. Rely-X fiber post was seated using Rely-X Unicem and resin cement was light polymerized. The root specimens were embedded in an acrylic resin and the specimens were sectioned perpendicularly to the long axis using a low-speed saw. Three slices per each root containing cross-sections of coronal, middle and apical part of the bonded fiber posts were obtained by sectioning. The push-out bond strength was measured using Universal Testing Machine. Specimens after bond failure were examined using operating microscope to evaluate the failure modes.
Results Push-out bond strengths were statistically influenced by the root regions. Group using the elongation tip showed significantly higher bond strength than other ways. Most failures occurred at the cement/dentin interface or in a mixed mode.
Conclusions The use of an elongation tip seems to reduce the number of imperfections within the self-adhesive cement interface compared to the techniques such as direct applying with the post and lentulo-spiral technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
Abdulaziz A. Al-Kheraif, Badreldin A. Mohamed, Aref Othman Hasan Sufyan, Aftab Ahmed Khan, Darshan Devang Divakar
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 36: 102526. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography analysis of gap and void formation in different prefabricated fiber post cementation materials and techniques
Aws ArRejaie, Saleh A. Alsuliman, Mohammed O. Aljohani, Hesham A. Altamimi, Emad Alshwaimi, Ahmad M. Al-Thobity
The Saudi Dental Journal.2019; 31(2): 236. CrossRef - Micro-computerized tomography analysis of cement voids and pull-out strength of glass fiber posts luted with self-adhesive and glass-ionomer cements in the root canal
Serkan Sarıdağ, Dilek Helvacıoğlu-Yiğit, Mutlu Özcan, Egemen Avcu, Güllü Kızıltaş
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(14): 1585. CrossRef - Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 95. CrossRef - Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef
- Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
- 1,264 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- The study of fractural behavior of repaired composite
- Sang-Soon Park, Wook Nam, Ah-Hyang Eom, Duck-Su Kim, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):461-472. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.461
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated microtensile bond strength (µTBS) and short-rod fracture toughness to explain fractural behavior of repaired composite restorations according to different surface treatments.
Materials and Methods Thirty composite blocks for µTBS test and sixty short-rod specimens for fracture toughness test were fabricated and were allocated to 3 groups according to the combination of surface treatment (none-treated, sand blasting, bur roughening). Each group was repaired immediately and 2 weeks later. Twenty-four hours later from repair, µTBS and fracture toughness test were conducted. Mean values analyzed with two-way ANOVA / Tukey's B test (α = 0.05) and correlation analysis was done between µTBS and fracture toughness. FE-SEM was employed on fractured surface to examine the crack propagation.
Results The fresh composite resin showed higher µTBS than the aged composite resin (
p < 0.001). Mechanically treated groups showed higher bond strength than non-mechanically treated groups except none-treated fresh group in µTBS (p < 0.05). The fracture toughness value of mechanically treated surface was higher than that of non-mechanically treated surface (p < 0.05). There was no correlation between fracture toughness and microtensile bond strength values. Specimens having high KIC showed toughening mechanism including crack deviation, microcracks and crack bridging in FE-SEM.Conclusions Surface treatment by mechanical interlock is more important for effective composite repair, and the fracture toughness test could be used as an appropriate tool to examine the fractural behavior of the repaired composite with microtensile bond strength.
- 1,021 View
- 1 Download

- The effect of the removal of chondroitin sulfate on bond strength of dentin adhesives and collagen architecture
- Jong-Ryul Kim, Sang-Jin Park, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):211-221. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.211
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Proteoglycan is highly hydrophilic and negatively charged which enable them attract the water. The objective of study was to investigate the effects of Proteoglycan on microtensile bond strength of dentin adhesives and on architecture of dentin collagen matrix of acid etched dentin by removing the chondroitin sulphate attached on Proteoglycan. A flat dentin surface in mid-coronal portion of tooth was prepared. After acid etching, half of the specimens were immersed in 0.1 U/mL chondroitinase ABC (C-ABC) for 48 h at 37℃, while the other half were stored in distilled water. Specimens were bonded with the dentin adhesive using three different bonding techniques (wet, dry and re-wet) followed by microtensile bond strength test. SEM examination was done with debonded specimen, resin-dentin interface and acid-etched dentin surface with/without C-ABC treatment.
For the subgroups using wet-bonding or dry-bonding technique, microtensile bond strength showed no significant difference after C-ABC treatment (p > 0.05). Nevertheless, the subgroup using rewetting technique after air dry in the Single Bond 2 group demonstrated a significant decrease of microtensile bond strength after C-ABC treatment. Collagen architecture is loosely packed and some fibrils are aggregated together and relatively collapsed compared with normal acid-etched wet dentin after C-ABC treatment. Further studies are necessary for the contribution to the collagen architecture of noncollagenous protein under the various clinical situations and several dentin conditioners and are also needed about long-term effect on bond strength of dentin adhesive.
- 1,067 View
- 1 Download

- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
- Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):173-179. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of the present study was to compare the influence of post-surface treatment with silane, hydrogen peroxide, hydrofluoric acid or sandblasting and to investigate the effect of silane in combination of the other treatments on the microtensile bond strength between fiber posts and composite resins for core build-up. Thirty-two glass-fiber posts (FRC Postec Plus, Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein) were divided into eight groups according to the different surface pretreatments performed: silane application (S); immersion in 28% hydrogen peroxide (HP); immersion in hydrogen peroxide followed by application of silane (HP-S); immersion in 4% hydrofluoric acid gel (HF); immersion in hydrofluoric acid gel followed by application of silane (HF-S); sandblasting with aluminum oxide particles (SB); sandblasting followed by application of silane (SB-S). In control group, no surface treatment was performed. The composite resin (Tetric Flow, Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein) was applied onto the posts to produce the composite cylinder specimen. It was sectioned into sticks to measure the microtensile bond strength. The data was analyzed with one-way ANOVA and LSD test for post hoc comparison (p < 0.05). Post pretreatment with sandblasting enhanced the interfacial strength between the fiber posts and core materials. Moreover, sand-blasting followed by application of silane appears to be the most effective method that can improve the clinical performance of glass fiber posts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and properties of glass fiber-reinforced endodontic (root canal therapy) posts
Jae-Yong Son, Kyoung-Ja Kim, Kyoung-Hun Kim, Joo-Seok Park, Kwang-Bo Shim
Journal of the Korean Crystal Growth and Crystal Technology.2015; 25(3): 105. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of upper central incisors restored with different posts and cores
Maryam Rezaei Dastjerdi, Kamran Amirian Chaijan, Saeid Tavanafar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 229. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 125. CrossRef
- Preparation and properties of glass fiber-reinforced endodontic (root canal therapy) posts
- 1,388 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
- Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):134-142. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation with hypersensitivity mode on microtensile bond strength of composite resin. Twenty extracted permanent molars were randomly assigned to six groups, according to the irradiation of Er,Cr:YSGG laser, adhesive system (Optibond FL or Clearfil SE bond) and application time of etchant (15 sec or 20 sec). Then composite resin was build up on each conditioned surface. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 h and twelve specimens for each group were prepared. All specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength and the fracture modes were evaluated. Also, the prepared dentin surface and laser irradiated dentin surface were examined under SEM.
The results were as follows:
The microtensile bond strength of laser irradiated group was lower than that of no laser irradiated group.
Regardless of laser irradiation, the microtensile bond strength of Optibond FL was higher than that of Clearfil SE bond. And the microtensile bond strength of 20 sec etching group was higher than that of 15 sec etching group when using Optibond FL.
The SEM image of laser irradiated dentin surface showed prominent peritubular dentin, opened dentinal tubules and no smear layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 180. CrossRef
- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- 1,510 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
- So-Rae Seong, Duck-kyu Seo, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):125-133. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Rapid polymerization of overlying composite resin causes high polymerization shrinkage stress at the adhesive layer. In order to alleviate the shrinkage stress, increasing the light intensity over the first 5 seconds was suggested as an exponential curing mode by an LED light curing unit (Elipar FreeLight2, 3M ESPE). In this study, the effectiveness of the exponential curing mode on reducing stress was evaluated with measuring microtensile bond strength of three adhesives after the overlying composite resin was polymerized with either continuous or exponential curing mode.
Methods Scotchbond Multipurpose Plus (MP, 3M ESPE), Single Bond 2 (SB, 3M ESPE), and Adper Prompt (AP, 3M ESPE) were applied onto the flat occlusal dentin of extracted human molar. The overlying hybrid composite (Denfil, Vericom, Korea) was cured under one of two exposing modes of the curing unit. At 48h from bonding, microtensile bond strength was measured at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. The fractured surfaces were observed under FE-SEM.
Results There was no statistically significant difference in the microtensile bond strengths of each adhesive between curing methods (Two-way ANOVA, p > 0.05). The microtensile bond strengths of MP and SB were significantly higher than that of AP (p < 0.05). Mixed failures were observed in most of the fractured surfaces, and differences in the failure mode were not observed among groups.
Conclusion The exponential curing method had no beneficial effect on the microtensile dentin bond strengths of three adhesives compared to continuous curing method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 139. CrossRef
- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
- 1,182 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
- Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):106-115. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microtensile bond strength (µTBS), failure modes and bonding interfaces of self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin.
Cylindrical composite blocks (Tescera, Bisco Inc.) were luted with resin cements (PA: Panavia F 2.0, Kuraray Medical Inc., RE: RelyX Unicem Clicker, 3M ESPE., MA: Maxem, Kerr Co., BI: BisCem, Bisco Inc.) on the prepared occlusal dentin surfaces of 20 extracted molars. After storage in distilled water for 24 h, 1.0 mm × 1.0 mm composite-dentin beams were prepared. µTBS was tested at a cross-head speed of 0.5 mm/min. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test. Dentin sides of all fractured specimens and interfaces of resin cements-dentin or resin cements-composite were examined at FE-SEM (Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope).
In conclusion, PA and RE showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than MA and BI when indirect composite blocks were luted to dentin using a self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements.
- 1,033 View
- 2 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


