Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Evaluation of platelet concentrates in regenerative endodontics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Anna Tsiolaki, Dimitrios Theocharis, Nikolaos Tsitsipas, Anastasia Fardi, Konstantinos Kodonas
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e38. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
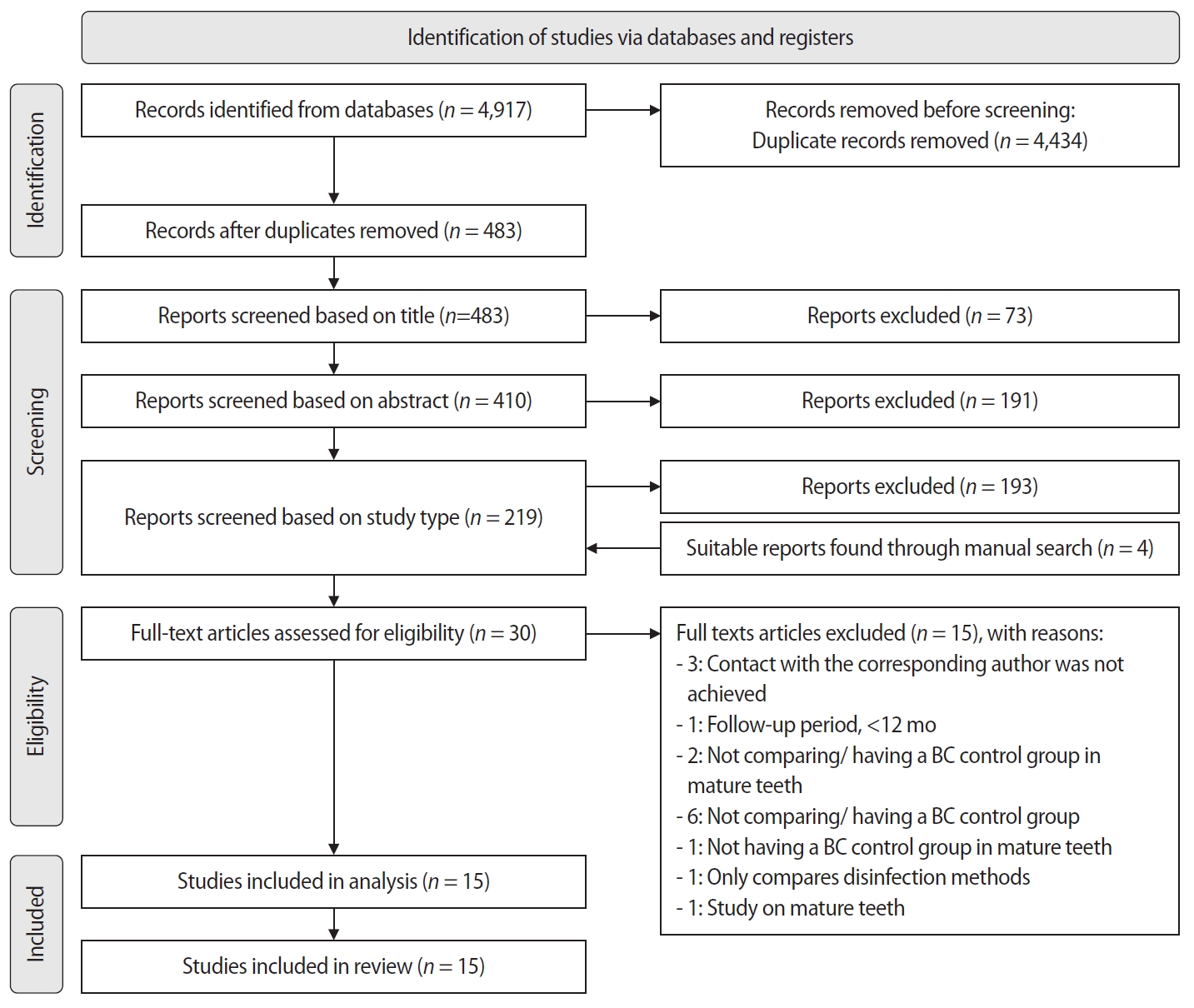
The aim of this systematic review is to compare the effectiveness of advanced platelet concentrates as regenerative endodontic therapeutic alternatives to blood clot (BC) revascularization in immature permanent necrotic teeth.
Methods
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing regenerative endodontic therapies using platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), or platelet pellet (PP) with the BC revascularization approach in immature permanent necrotic teeth were systematically searched in PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science until May 2025. Data was extracted and analyzed both qualitatively and quantitatively. Study quality was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. A meta-analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS software (version 29.0), with success rates expressed as risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
The initial search yielded 4,917 studies. After removing duplicates and applying eligibility criteria, 15 RCTs were included. Meta-analysis indicated no significant difference in the risk ratio (RR), as the BC method has similar success rates with PRP (10 studies; RR = 1.01; 95% CI, 0.94–1.09; p = 0.76) and PRF (8 studies; RR = 0.98; 95% CI, 0.89–1.08; p = 0.65) at 12 months. The primary outcomes evaluated were based on clinical and radiographic success.
Conclusions
Current evidence suggests PRP, PRF, and BC are all effective in treating immature permanent necrotic teeth with similar success rates. However, further research is needed to assess long-term outcomes.
- 1,443 View
- 85 Download

- Clinical and radiographic outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment performed by endodontic postgraduate students: a retrospective study
- Hadi Rajeh Alfahadi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Fawaz Hamad Alkazman, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Nada Al-Nazhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e24. Published online May 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Regenerative endodontic treatment is a clinical procedure aimed at biologically regenerating damaged root canal tissue of immature permanent teeth. This study aimed to report the outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment performed by endodontic postgraduate students.
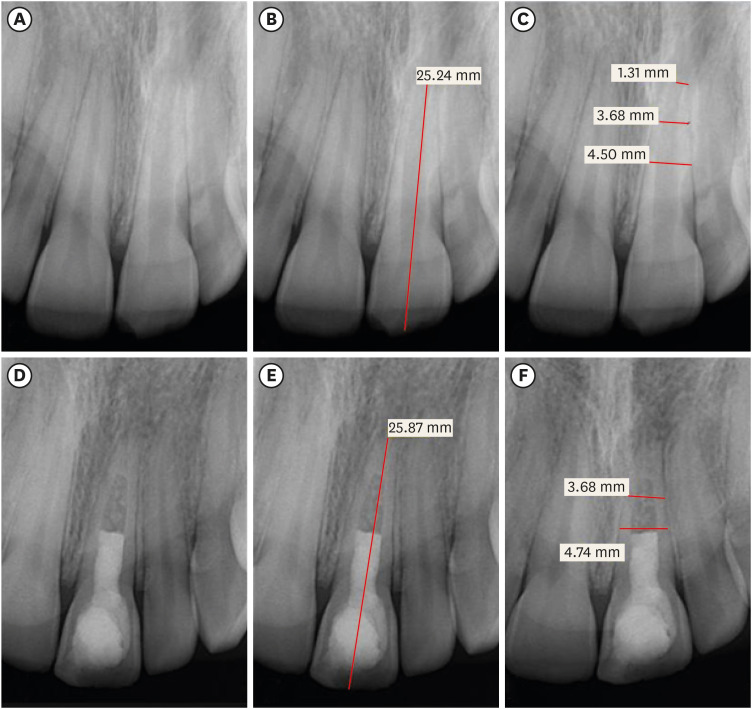
Materials and Methods Clinical and radiographic data of 27 patients, aged 10–22 years, who underwent regenerative treatment of immature permanent teeth from 2015 to 2019 were followed up, wherein clinical and radiographic examinations were performed for each patient. Postoperative success rate and tooth survival were analyzed, and the postoperative radiographic root area changes were quantified.
Results A total of 23 patients attended the dental appointments, showing that all teeth survived and were asymptomatic. Specifically, 7 periapical pathosis cases were completely healed, 12 were incompletely healed, and 4 cases failed. Moreover, significant differences were found between discolored and non-discolored teeth, and between the presence or absence of periapical radiolucency. Additionally, 3 anterior teeth showed complete closure of the apical foramen, while the apical foramen width was reduced in 17 teeth and failed in 3 teeth. Root length was also found to have been increased in 7 anterior and 4 posterior teeth, and the average length ranged from 4.00–0.63 mm in the anterior teeth, 2.85–1.48 mm of the mesial root, and 2.73–2.16 mm of the molar teeth distal root. Furthermore, calcified tissue deposition was observed in 7 teeth.
Conclusions A favorable outcome of regenerative endodontic treatment of immature permanent teeth with necrotic pulp was achieved with a high survival rate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regenerative Endodontics and Stem Cell-Based Therapies – A Systematic Review
Wjoud Ahmed Alshamrani, Sarah Sulaiman Alzarea, Joud Khalid Alabbas, Ayah Khalid Alabbas, Mawiyah Ibrahim Aljaddua, Osama Khattak, Rakhi Issrani
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2026; 18(Suppl 1): S29. CrossRef - Pre‐Operative Factors on Prognosis of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Filipe Colombo Vitali, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Pablo Silveira Santos, Ana Paula Portes Zeno, Patrícia de Andrade de Risso, Lucianne Cople Maia, Francine Benetti, Cleonice da Silveira da Teixeira
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(12): 1814. CrossRef - Clinical, radiographic, and biomarker perspectives of low-level laser therapy during regenerative endodontic procedures in necrotic immature young teeth: a randomized clinical study
Pragya Pandey, Neha Jasrasaria, Ramesh Bharti, Rakesh Kumar Yadav, Monika Kumari, Abinia Vaishnavi, Rahul Pandey
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Allogeneic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Transplantation Induces Dentin Pulp Complex-like Formation in Immature Teeth with Pulp Necrosis and Apical Periodontitis
Jose Francisco Gomez-Sosa, José E. Cardier, Olga Wittig, Dylana Díaz-Solano, Eloisa Lara, Kharelys Duque, Giselle Ramos-González
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(4): 483. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of dental post and core placement at different educational levels in an undergraduate student clinic: a 4-year retrospective study
Turki Alshehri, Nourhan M. Aly, Raand Altayyar, Deena Alghamdi, Shahad Alotaibi, Passent Ellakany
F1000Research.2024; 12: 976. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy of injectable platelet‐rich fibrin versus platelet‐rich plasma in the regeneration of traumatized necrotic immature maxillary anterior teeth: A randomized clinical trial
Maha Mohamed Abo‐Heikal, Jealan M. El‐Shafei, Samia A. Shouman, Nehal N. Roshdy
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(1): 61. CrossRef - Radiographical assessment of post and core placement errors encountered by Saudi dental students at different educational levels
Turki Alshehri, Nourhan M. Aly, Raand Altayyar, Deena Alghamdi, Shahad Alotaibi, Passent Ellakany
F1000Research.2023; 12: 976. CrossRef
- Regenerative Endodontics and Stem Cell-Based Therapies – A Systematic Review
- 4,291 View
- 78 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Push-out bond strength and marginal adaptation of apical plugs with bioactive endodontic cements in simulated immature teeth
- Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Eduardo Nunes, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Manoel Brito Júnior, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Stephen Cohen, Frank Ferreira Silveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e53. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
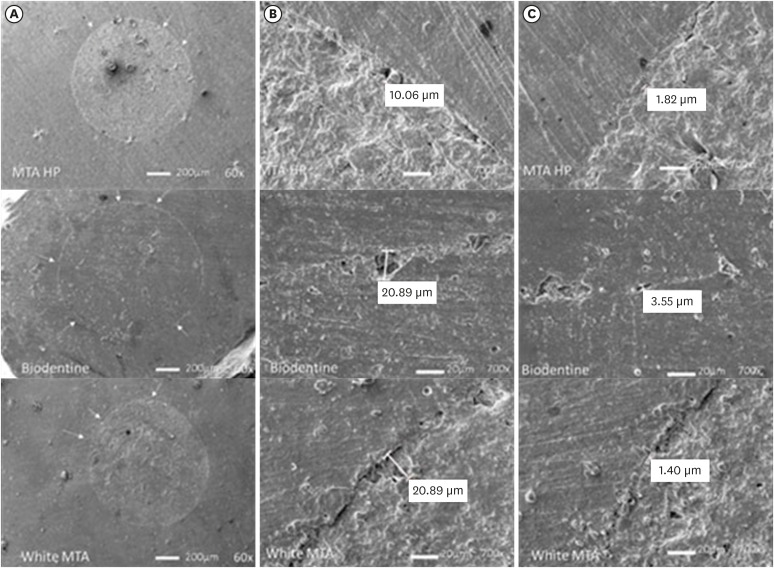
ePub Objectives This study evaluates the bond strength and marginal adaptation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) Repair HP and Biodentine used as apical plugs; MTA was used as reference material for comparison.
Materials and Methods A total of 30 single-rooted teeth with standardized, artificially created open apices were randomly divided into 3 groups (
n = 10 per group), according to the material used to form 6-mm-thick apical plugs: group 1 (MTA Repair HP); group 2 (Biodentine); and group 3 (white MTA). Subsequently, the specimens were transversely sectioned to obtain 2 (cervical and apical) 2.5-mm-thick slices per root. Epoxy resin replicas were observed under a scanning electron microscope to measure the gap size at the material/dentin interface (the largest and smaller gaps were recorded for each replica). The bond strength of the investigated materials to dentin was determined using the push-out test. The variable bond strengths and gap sizes were evaluated independently at the apical and cervical root dentin slices. Data were analyzed using descriptive and analytic statistics.Results The comparison between the groups regarding the variables' bond strengths and gap sizes showed no statistical difference (
p > 0.05) except for a single difference in the smallest gap at the cervical root dentin slice, which was higher in group 3 than in group 1 (p < 0.05).Conclusions The bond strength and marginal adaptation to root canal walls of MTA HP and Biodentine cement were comparable to white MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Biodentine for Apexification of Immature Teeth of Children: A Scoping Review
Liz M Gerard, Sumit Gaur
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(5): 573. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-Out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, a Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, and Two Novel Antibacterial-Enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Arokia Rajkumar Shancy Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Rajalakshmanan Eswaramoorthy, Abirami Arthanari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push out bond strength of hydraulic cements used at different thicknesses
C. Ruiz Durán, Dra L. Gancedo-Caravia, V. Vera González, C. González Losada
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,562 View
- 32 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
- Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e48. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
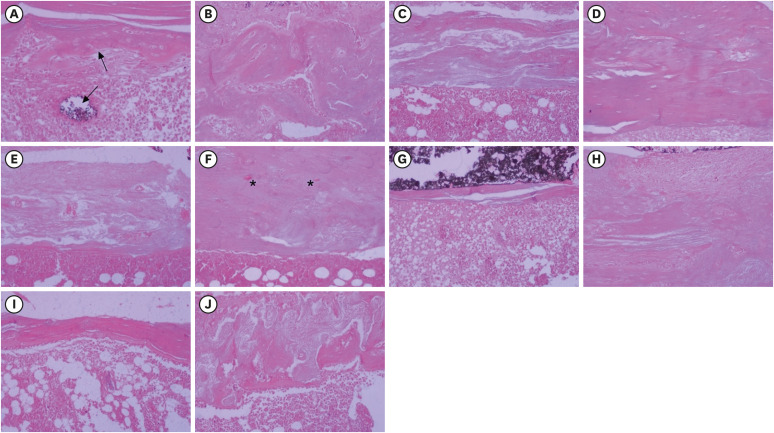
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effects on bone repair of different concentrations of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) added to AH Plus.
Materials and Methods Bone tissue reactions were evaluated in 30 rats (
Rattus norvegicus ) after 7 and 30 days. In the AH + MTA10, AH + MTA20, and AH + MTA30 groups, defects in the tibiae were filled with AH Plus with MTA in proportions of 10%, 20% and 30%, respectively; in the MTA-FILL group, MTA Fillapex was used; and in the control group, no sealer was used. The samples were histologically analyzed to assess bone union and maturation. The Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests were performed for multiple pairwise comparisons (p ≤ 0.05).Results At the 7-day time point, AH + MTA10 was superior to MTA-FILL with respect to bone union, and AH + MTA20 was superior to MTA-FILL with respect to bone maturity (
p < 0.05). At the 30-day time point, both the AH + MTA10 and AH + MTA20 experimental sealers were superior not only to MTA-FILL, but also to AH + MTA30 with respect to both parameters (p < 0.05). The results of the AH + MTA10 and AH + MTA20 groups were superior to those of the control group for both parameters and experimental time points (p < 0.05).Conclusions The results suggest the potential benefit of using a combination of these materials in situations requiring bone repair.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
Luciano Aparecido de Almeida-Junior, Giuliana de Campos Chaves Lamarque, Henry Herrera, Maya Fernanda Manfrin Arnez, Francine Lorencetti-Silva, Raquel Assed Bezerra Silva, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva, Francisco Wanderley Garcia Paula-Silva
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the research methods and progress of biocompatibility evaluation of root canal sealers
Xiliang Yang, Tianxia Zheng, Nuoya Yang, Zihan Yin, Wuliang Wang, Yuhong Bai
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 508. CrossRef - Effect of Vitapex Combined with AH-Plus Paste on Inflammation in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients with Periodontal-Endodontic Disease
Rong Hu, Fulan Zhang, Xiangyu Guo, Youren Jing, Xiaowan Lin, Liping Tian, Min Tang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
- 2,020 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Dentin moisture conditions strongly influence its interactions with bioactive root canal sealers
- Esin Ozlek, Hüseyin Gündüz, Elif Akkol, Prasanna Neelakantan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e24. Published online March 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
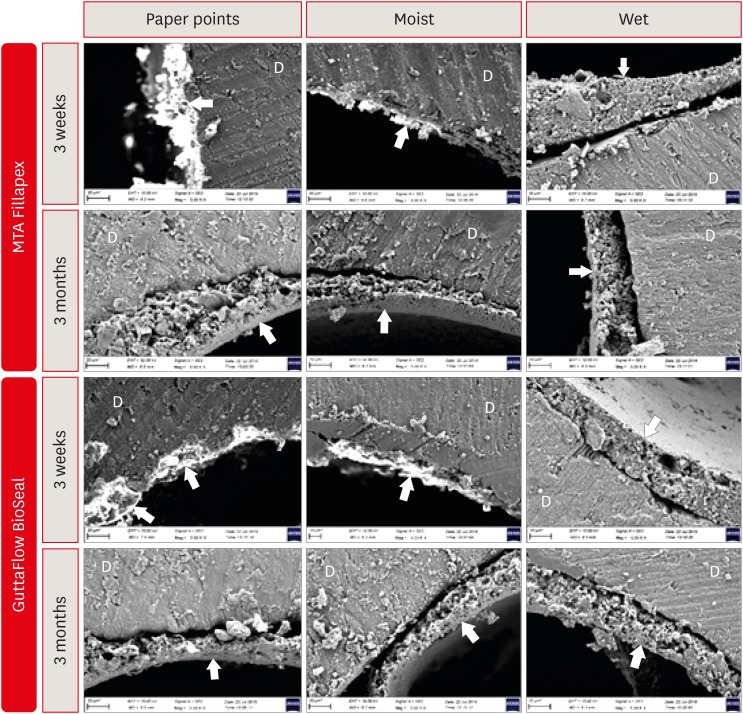
ePub Objectives It is known that bioactive materials interact with the dentin to undergo biomineralization. The exact role of moisture in this interaction is unknown. Here, we investigate the effects of dentin moisture conditions on the dislocation resistance of two bioactive root canal sealers (MTA Fillapex [Angelus Solucoes Odontologicas] and GuttaFlow BioSeal [Colténe/Whaledent AG]) at 3 weeks and 3 months after obturation.
Materials and Methods Mandibular premolars (
n = 120) were prepared and randomly divided into 3 groups based on the dentin condition: group 1, dry dentin; group 2, moist dentin; group 3, wet dentin. Each group was divided into 2 subgroups for root canal filling: MTA Fillapex and GuttaFlow BioSeal. Dislocation resistance was evaluated by measuring the push-out bond strength at 3 weeks and 3 months. Failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. Data were statistically analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test with a significance level of 5%.Results Moist dentin resulted in higher bond strength values for both materials at both time points. This was significantly higher than wet and dry dentin for both the sealers at the 3 months (
p < 0.05), while at 3 weeks it was significant only for GuttaFlow Bioseal. The different moisture conditions demonstrated similar trends in their effects on the dislocation resistance of the 2 root canal sealers.Conclusions The dentin moisture conditions had a significant impact on its interaction with the bioactive materials tested. Maintaining moist dentin, but not dry or wet dentin, may be advantageous before the filling root canals with bioactive sealers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of moisture conditions and canal morphologies on the filling quality of iRoot SP with single-cone technique in root canals: an ex-vivo study
Jing Yang, Xiran Xu, Jian Zhang, Kehua Que
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(7): 1989. CrossRef - Evaluation of apical seal and tubular penetration of a novel bioactive glass sealer, bioceramic sealer and resin–based sealer: an In-Vitro study
M. Bilal, S. Pasha, S. Kumar, S. Arif, S. Taj, A. Saleem
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 39. CrossRef - Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Post Space Conditioning Procedures and Different Endodontic Sealers on the Push-Out Bond Strengths of Fiber Posts
Leyla Ayranci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci, Fatih Sarı, Ahmet Çetinkaya
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 620. CrossRef - Evaluation of the retreatability of bioceramic root canal sealers with various formulations in simulated grooves
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Abdulaziz Bakhsh, Hakan Arslan
PeerJ.2025; 13: e20398. CrossRef - Preparation and characterization of novel nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based root canal sealer
Nawal Atiya Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 90. CrossRef - The flow behavior and sealing ability of calcium silicate root canal cement containing dimethyl sulfoxide: An in vitro study
Bokyung Shin, Ji-Hwan Seo, Wonjung Kim, Yu Jin Ahn, Ho-Young Kim, Won-Jun Shon
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106156. CrossRef - Nanoleakage of apical sealing using a calcium silicate-based sealer according to canal drying methods
Yoon-Joo Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of operators’ proficiency level and patients’ related factors on possible complications, using a high frequency polyamide sonic intracanal irrigation device: A prospective clinical cohort study
Tobias Hahn, David W. Christofzik, Karim Fawzy El-Sayed, Sandra Freitag-Wolf, Jonas Conrad, Christian Graetz, Birte Größner-Schreiber, Christof Dörfer, Artak Heboyan
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(5): e0285492. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Biocompatibility analysis in subcutaneous tissue and physico-chemical analysis of pre-mixed calcium silicate–based sealers
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Juliana Minto Boldieri, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Nilvan Alves da Silva, Ivo Milton Raimundo, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2221. CrossRef - Canal Drying Protocols to Use with Calcium Silicate–based Sealer: Effect on Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface
Lais Lima Pelozo, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Guilherme Nilson Alves dos Santos, Rafael Verardino Camargo, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(9): 1154. CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength of endodontic sealers after root canal drying with different techniques
Ahmadreza Sarrafan, Ali Soleymani, Tasnim Bagheri Chenari, Seyedali Seyedmajidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2023; 9(2): 314. CrossRef - Designing Calcium Silicate Cements with On-Demand Properties for Precision Endodontics
A. Cahyanto, P. Rath, T.X. Teo, S.S. Tong, R. Malhotra, B.N. Cavalcanti, L.Z. Lim, K.S. Min, D. Ho, W.F. Lu, V. Rosa
Journal of Dental Research.2023; 102(13): 1425. CrossRef - Outcome of root canal treatment using warm vertical compaction with bioceramic and resin‐based sealers: A randomised clinical trial
Jinghao Hu, Yunjie Zhu, Shuli Deng, Zeji Wang, Fuming He
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 170. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability and Bond Strength of Two Endodontic Root Canal Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Manuel Marques Ferreira, José Pedro Martinho, Inês Duarte, Diogo Mendonça, Ana Catarina Craveiro, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Ana Coelho, Anabela Paula, Siri Paulo, Nuno Chichorro, Ana Margarida Abrantes
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(11): 201. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of using calcium-silicate and silicone based root canal sealers in bulk or with main core material on bond strength
Gizem Kadı, Esin Özlek, Yousef Saed
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2022; 16(4): 229. CrossRef - Physico-chemical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers in powder/liquid and ready-to-use forms
Ana C P Janini, Lauter E Pelepenko, Brenda P F A Gomes, Marina A Marciano
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 18. CrossRef - Influence of dentin moisture conditions on the wetting action of different endodontic sealers using Rame-Hart goniometer: An in vitro study
Sivaji Kauravi, ShruthiH Attavar, GyanendraPratap Singh
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(6): 624. CrossRef - Heating stability, physical and chemical analysis of calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealers
T. B. M. Antunes, A. C. P. Janini, L. E. Pelepenko, G. F. Abuna, E. M. Paiva, M. A. C. Sinhoreti, I. M. Raimundo, B. P. F. A. Gomes, A. de‐Jesus‐Soares, M. A. Marciano
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1175. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
- The effect of moisture conditions and canal morphologies on the filling quality of iRoot SP with single-cone technique in root canals: an ex-vivo study
- 2,244 View
- 32 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Observation of an extracted premolar 2.5 years after mineral trioxide aggregate apexification using micro-computed tomography
- Gayeon Lee, Chooryung Chung, Sunil Kim, Su-Jung Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e4. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
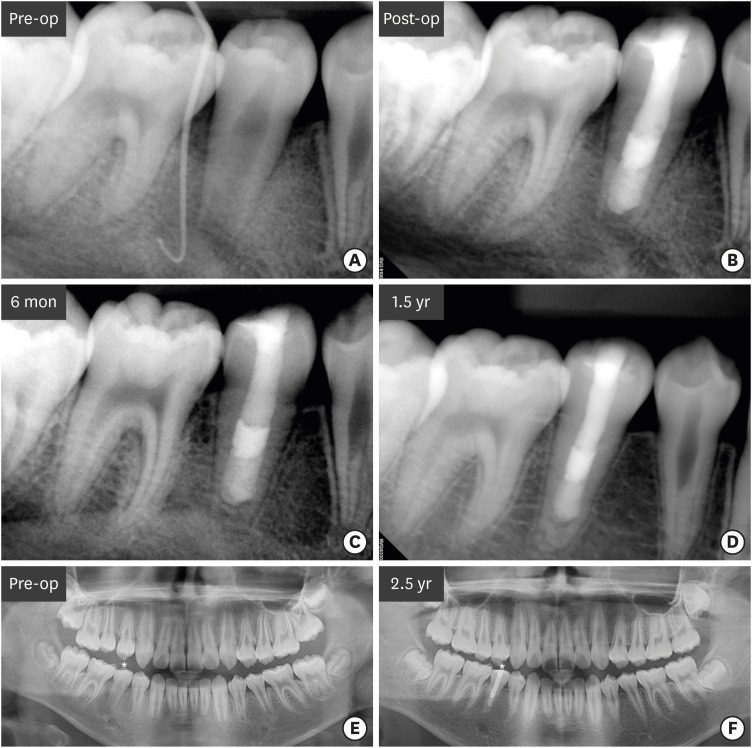
ePub Although numerous studies have been conducted on apexification using mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), direct observation of extracted human teeth after the procedure has been rarely reported. This case report describes a mandibular premolar treated 2.5 years ago and extracted recently for orthodontic treatment. The tubercle of the right mandibular premolar of a 12-year-old boy with dens evaginatus was fractured and the pulp was exposed. The tooth was diagnosed with pulp necrosis and asymptomatic periapical abscess. During the first visit, copious irrigation was performed with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. Calcium hydroxide paste was placed as an intracanal medicament. The sinus tract had disappeared at the second visit after 3 weeks. MTA was applied on to the bleeding point as a 4-mm-thick layer, followed by a 3-mm-thick gutta-percha filling and resin core build-up. After 2.5 years, the tooth and three other premolars were extracted for orthodontic treatment. The right and left mandibular premolars were scanned with micro-computed tomography to determine the root shape and canal anatomy. Irregular root growth was observed and the root outline of the right mandibular premolar differed from that of the contralateral tooth. Apexification with MTA leads to the formation of roots with irregular morphology, without any pulpal space.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
- 1,344 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
- Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e28. Published online June 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the latest findings and notions regarding ‘triple antibiotic paste’ (TAP) and its applications in dentistry, particularly endodontics. TAP is a combination of 3 antibiotics, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and minocycline. Despite the problems and pitfalls research pertaining to this paste has unveiled, it has been vastly used in endodontic treatments. The paste's applications vary, from vital pulp therapy to the recently introduced regeneration and revascularisation protocol. Studies have shown that the paste can eliminate the root canal microorganisms and prepare an appropriate matrix for further treatments. This combination is able to remove diverse groups of obligate and facultative gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, providing an environment for healing. In regeneration protocol cases, this allows the development, disinfection, and possible sterilization of the root canal system, so that new tissue can infiltrate and grow into the radicular area. Moreover, TAP is capable of creating a discipline in which other wanted and needed treatments can be successfully performed. In conclusion, TAP, as an antibacterial intracanal medication, has diverse uses. Nevertheless, despite its positive effects, the paste has shown drawbacks. Further research concerning the combined paste and other intracanal medications to control microbiota is a must.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Permanent Incisors: Two Case Reports with 6 Years of Follow-Up
María Biedma-Perea, Marcela Arenas-González, María José Barra-Soto, Carolina Caleza-Jiménez, David Ribas-Pérez
Children.2026; 13(2): 246. CrossRef - Evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of an herbal preparation vs triple antibiotic paste against E. faecalis: an in vitro study
Chandni Dhyani, Kalpna Chaudhry, Nitin Khanduri, Leina R. Pradhan, Yoshita Gupta
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics.2026; 13(3): 449. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Laser in Root Canal Disinfection in Pulp Regenerative Therapy: A Systematic Review
Kiran Kumar N, Abhishek M, Savitha B. Naik, Biji Brigit, Swetha Geervani V, M Manimozhi
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2025; 43(2): 53. CrossRef - Assessing Cell Viability: Comparative Analysis of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste, and Their Synergistic Impact on human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Dini Asrianti Bagio, Ibramanto Warganegara, Ike Dwi Maharti, Anggraini Margono, Citra Kusumasari, Sylva Dinie Alinda, Valeria Widita Wairooy
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(01): 073. CrossRef - Cytotoxic and Antibiofilm Properties of Antibiotic-Loaded Thermoresponsive Hydrogels for Root Canal Therapy
Cristiane Duque, Gabriela Pacheco de Almeida Braga, Juliana Machado de Carvalho, Karina Sampaio Caiaffa, Gabriel Pereira Nunes, Rafaela Laruzo Rabelo, Vanessa Rodrigues dos Santos, Geórgia Rondó Peres, Lucas da Silva Ribeiro, Emerson Rodrigues de Camargo
Processes.2025; 13(3): 661. CrossRef - Antibiofilm properties, cytotoxicity, and effect on protease activity of antibiotics and EGCG-based medications for endodontic purposes
Daniela Alvim Chrisostomo, Jesse Augusto Pereira, Polliana Mendes Candia Scaffa, Zach Gouveia, Gabriel Flores Abuna, Sergey V. Plotnikov, Anuradha Prakki, Cristiane Duque
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105660. CrossRef - The use of three-dimensional-printed guides, static navigation, and bioactive materials to treat bilateral and double dens invaginatus
Parth Patel, Nidhi Bharti, Ankit Arora, C. Nimisha Shah
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 207. CrossRef - To Assess the Cell Viability of Triple Antibiotic Paste under Confocal Microscope: An In Vitro Study
Elanthendral Saravanan, Mahesh Ramakrishnan
Journal of South Asian Association of Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 8(2): 81. CrossRef - Eficacia de la pasta triantibiótica en endodoncia: actividad antibacteriana frente a cepas resistentes de Enterococcus faecalis. Una revisión exhaustiva
Elena Patricia Cevallos Fernández, Katherine de los Ángeles Cuenca León
Anatomía Digital.2025; 8(3.1): 88. CrossRef - Efectividad de diferentes antimicóticos, junto con la pasta triantibiotica, para el tratamiento de Candida albicans en conductos radiculares
Carlos Andrés Rodríguez Tapia, Jessica María Sarmiento Ordoñez
Anatomía Digital.2025; 8(3.2): 45. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste, and Calcium Hydroxide with 2% Chlorhexidine as Intracanal Medicaments in Reducing Interappointment Pain during Endodontic Treatment: An In Vivo Study
Rachit Mathur, Shaista Gazal, Itika Jain, Shyam Agrawal, Akshada Mungee, Babra Khan
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(6): 628. CrossRef - In Vitro Effectiveness of Endodontic Triple Antibiotic Paste Associated With Daptomycin
Sabrina S Azevedo, Gabriela C Chianca, Bruna A Thurler, Raiane C Chamon, Helvécio C Corrêa Póvoa, Leonardo S Antunes, Natalia L Pontes Póvoa Iorio
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Chitosan and bioactive glass nanomaterials as intracanal medicaments on TGF-β1 release from intraradicular dentin
Sarah Salah Hashem, Mohammed M. Khalefa, Mahmoud Hassan Mohamed, Hemat M. ELSheikh, Fatma Abd El-Rahman Taher
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of lesion sterilization and tissue repair in primary teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Khlood Baghlaf, Rana A. Alamoudi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Cannabinoids on Bacteria Associated with Persistent Endodontic Infections
Cassandra Wieczerza, Haoyan Zhai, Mazin Askar, Zheng Zhou, Susan Paurazas
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11936. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Herbal Extracts and Triple Antibiotic Paste as Intracanal Medicament against Enterococcus faecalis: A Microbiological Study
Divya Singh, Rashi Singh, Nidhi Gupta, Natasha Gambhir, Saritha Golla
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(3): 285. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-Out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, a Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, and Two Novel Antibacterial-Enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Arokia Rajkumar Shancy Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Rajalakshmanan Eswaramoorthy, Abirami Arthanari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Oleanolic Acid as a Potential Root Canal Medicament on Viability and Proliferation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Khalifah A. Alhaila, Manal Farouk Badawi, Mohamed G. Elbeltagy, Amany E. Badr
European Journal of General Dentistry.2024; 13(01): 051. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Dentinogenesis Imperfecta‐Induced Apical Periodontitis
Ying Liao, Ting Pan, Xianghui Xing, Sivakumar Nuvvula
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efecto antimicrobiano como medicación intraconducto de la pasta triantibiótica.
Paúl Sebastián Ulloa Amores, Diana Álvarez Álvarez, María Elizabeth Moscoso Abad, Magda Zulay Bastidas Calva
Revista de la Asociación Dental Mexicana.2024; 81(4): 211. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Nanosilica-Coated Antibiotics, TAP: A Comprehensive Study Utilizing XRD, EDS, FTIR, SEM, and TEM – Invitro Study
Mahaboob S. Hameed, S. Delphine P. Antony, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Sandhya Raghu
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(5): 386. CrossRef - Association between host defence peptide IDR‐1002 and ciprofloxacin: Effects on human dental pulp cells
Danilo César Mota Martins, Maurício Gonçalves da Costa Sousa, Poliana Amanda Oliveira Silva, Lana Ribeiro Aguiar, Rosângela Vieira de Andrade, Amandda Évellin Silva‐Carvalho, Felipe Saldanha‐Araújo, Octávio Luiz Franco, Taia Maria Berto Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 547. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste and amoxicillin clavulanate paste as an intracanal medicament against Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro study
Dhandayuthapani Sasikala, Parisa Norouzi Baghkomeh, Jamaluddin Mohammed Farzan
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Game Changer in Endodontics
Kalagi G. Panchal, Karima Virani, Vraj Patel, Aquib Ali Khan, Anam Pettiwala, Srikala S. Puranik, Srushti Joshi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S1913. CrossRef - Non-surgical Management of a Large Periapical Lesion: A Case Study of the Successful Application of a Modified Triple Antibacterial Paste
Srushti Awghad, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Amit Reche, Ankita Burse, Aradhana Kibe
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing Antimicrobial Efficacy and Synergistic Effects of Nano-Silica-Based Combinations With Doxycycline, Metronidazole, and Ciprofloxacin Against Enterococcus faecalis Biofilms
Shahul Hameed, Delphine P Antony, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Sandhya Raghu, Hima Sandeep Adimulapu
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of periapical lesion by non-surgical endodontic therapy: A case series
Athira Ramesh, Rajesh Pillai, Afzal A, Anakha Santhosh, Arunima G.S, Sandeep K. V
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2024; 9(2): 99. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Versus Double Antibiotic Paste on Endodontic Treatment Outcomes in Teeth With Large Periapical Lesions: A Triple‐Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
Afsaneh Rahmati, Farshad Seyedein, Omid Dianat, Sara Saedi, Golriz Rostami, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Shima Sabertahan, Majid Kazem, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Can antimicrobial photodynamic therapy serve as an effective adjunct protocol for disinfecting the necrotic root canal system? A randomized controlled study
Remy Barazy, Hisham Alafif, Hassan Achour, Ahmad Al-Aloul, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Drain and Treat: A Rubber Dam Technique for Acute Periapical Abscess
S. Grover, K. Mala, J. D’Souza
Acta Medica Bulgarica.2024; 51(s2): 143. CrossRef - Microbial Dynamics in Endodontic Pathology—From Bacterial Infection to Therapeutic Interventions—A Narrative Review
Klara Wieczorkiewicz, Anna Jarząbek, Estera Bakinowska, Kajetan Kiełbowski, Andrzej Pawlik
Pathogens.2024; 14(1): 12. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of the effect of three intracanal medicaments – chlorhexidine gel, triple antibiotic paste, and calcium hydroxide paste on the push-out bond strength of MTA Plus, Biodentine, and calcium-enriched mixture
Gouthami Datta, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Gautham P Manjunath, Dishant Patel, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - The cytotoxic effect of cysteamine and its combinations with various endodontic intracanal medications on fibroblast cells: in vitro study
Esraa Adel Mohamed Abd Elhameed ElGammal, Abeer Hashem Mahran, Salma Hassan El Ashry, Sara Hossam Fahmy
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of large endodontic lesions using a new combination of triple antibiotics: A case report
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of herbal agents as intracanal medicaments individually or in combination with chitosan: An in vitro RTPCR study
Gaurav Patri, Kotni Sheetal, PrasantiKumar Pradhan, Pratik Agrawal, S Lata
Journal of International Oral Health.2023; 15(1): 89. CrossRef - Recent progress in carbon dots for anti-pathogen applications in oral cavity
Yuying Jiang, Chuqiang Yin, Jianning Mo, Xiaoyu Wang, Ting Wang, Guotai Li, Qihui Zhou
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair: An Alternative for Pulpectomy in Deciduous Teeth
Aparna Achanta, Amit Reche, Rishika Dakhale, Rudra R Bharate
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of Large Endodontic Lesions Using Long‐Term Application of a New Combination of Triple Antibiotics: A Series of Cases
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar, Maria Beatriz Duarte Gavião
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-cytotoxic Root Canal Dressing with Improved Antimicrobial Efficacy
Farzad Koosha, Jerome Cymerman, Thomas Manders, Marcia Simon, Stephen Walker, Miriam Rafailovich
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(2): 205. CrossRef - Triple antibiotics: A synergistic approach to combating infection
Hemant Sawhney, Anukriti Kumari, Ritik Kashwani, Geetanjali Gupta, SJ Das
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 8(4): 189. CrossRef - A 1-year Clinical and Radiographic Assessment of Regenerative Endodontic Therapy for Necrotic Primary Molars: A Randomized controlled Trial
Dina D Abdelmoneim, Amr M Abdelaziz, Gehan G Allam, Amira S Badran
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(2): 295. CrossRef - “BIODENTINE” THE DENTINE IN A CAPSULE AS AN APICAL BARRIER IN TRAUMATIZED MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISOR WITH TWO YEARS FOLLOW UP.
Savita Thakur, Udai Bhanu, Gurkirat Singh Grewal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 64. CrossRef - Long-term treatment of dentine with triple antibiotic paste promotes stem cell viability and attachment
Samiya Riaz, Ahmad Azlina, Zuliani Mahmood, Aung T. Htun
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2022; 17(4): 630. CrossRef - Non surgical management of trauma induced root resorption and large periapical
lesion using bioactive material- A case report
Tejasvini Prajapati, Sonali Kapoor, Purnil Shah, Ankit Arora, Hardik Rana
Clinical Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of antibiotic pastes versus calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies
Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Kamyar Khosravi, Nazanin Zargar, Armin Shirvani, MohammadHossein Nekoofar, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 463. CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Suitable Medicament for Intracanal Disinfection
Krutika Malu, Monika Khubchandani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Present status and future directions of intracanal medicaments
Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Alejandro Perez‐Ron, Zhou Ye, Jorge Vera
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 613. CrossRef - The effect of four different intracanal medicaments on the push-out bond strength of root canal sealers
Shalu Maan, Vijaya Dhar Bhatt, Rohit Singh, Sayak Gupta, Syed Alay Noorain, Aashna Gill, Pradeep Kumar, Sushil Yadav, Preeti Sharma
Journal of Medicine and Life.2022; 15(4): 448. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Microhardness and Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentin with Two Combinations of TAP and MTAP: An In Vitro Study
P Niharika, Saigeeta Kondamadugu, Nagireddy Venugopal Reddy, Muthumula Daneswari, Annie P Chris, Nikhila V Reddy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S2): S151. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Antibiotic Pastes for Root Canal Disinfection
Sadhna Sharma, Urvashi Bhushan, Mridula Goswami, CP Baveja
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S1): S12. CrossRef - Management of External Inflammatory Root Resorption following Tooth Autotransplantation Using a Modified Combination of Triple Antibiotics
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar, Paulo J. Palma
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic paste on the bond strength of epoxy and methacrylate resin-based sealers to root canal dentin
Fereshte Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl, Mahdi Sedigh-Shams, Hossein Mirkhaghani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 426. CrossRef - Progress of Research on the Application of Triple Antibiotic Paste and Hydrogel Scaffold Materials in Endodontic Revascularization: A Systematic Review
Jia Zhao, Tian Jiao Wang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The effect of different intracanal medicaments on the dislodgement resistance of mineral trioxide aggregate
Farzaneh Afkhami, Shahrzad Razavi, Sholeh Ghabraei
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole and Minocycline in Ordered Mesoporous Silica against Enterococcus faecalis for Dental Pulp Revascularization: An In-Vitro Study
Cintia Micaela Chamorro-Petronacci, Beatriz Santos Torres, Rocío Guerrero-Nieves, Mario Pérez-Sayáns, Marcia Carvalho-de Abreu Fantini, Luis Carlos Cides-da-Silva, Beatriz Magariños, Berta Rivas-Mundiña
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2266. CrossRef - Antibiotic Mixtures in Noninstrumental Endodontic Treatment of Primary Teeth with Necrotic Pulps: A Systematic Review
Farah Chouchene, Fatma Masmoudi, Ahlem Baaziz, Fethi Maatouk, Hichem Ghedira, Sivakumar Nuvvula
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Potential apply of hydrogel-carried chlorhexidine and metronidazole in root canal disinfection
Yanhong YAN, Peng ZHOU, Haibing LU, Yun GUAN, Ming MA, Juan WANG, Guangwei SHANG, Beizhan JIANG
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(4): 986. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Nitrofurantoin Paste as an Intracanal Medicament on the Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentine
Mewan Abdulrahman, Bestoon Faraj, Kawa Dizaye
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 8. CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Antibiofilm and cytotoxic effect of 3,3′-dihydroxycurcumin (DHC) as photosensitizer agent in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for endodontic purposes
Jesse Augusto Pereira, Carlos Roberto Polaquini, VanessaRodrigues dos Santos, Karina Sampaio Caiaffa, Rafaela Laruzo Rabelo, Reinaldo dos Santos Theodoro, Letícia Helena Theodoro, Luis Octavio Regasini, Cristiane Duque
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 36: 102534. CrossRef - An in-vitro Comparative Evaluation of Quantitative Release of Transforming Growth Factor β-1 from Dentin upon the Action of Endodontic Irrigants, Medicaments, Ultrasonic Activation, and Low-Level Laser Irradiation
Anilkumar Akhila, V. P. Prabath Singh, Kerala R. Varma, Senthil V. Vasudevan, V. Sukhithasri, Salu Sasikumar
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2021; 17(2): 34. CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide on the rate of healing of periapical lesions: A systematic review
NKiran Kumar, Biji Brigit, BS Annapoorna, SavithaB Naik, Seema Merwade, K Rashmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 307. CrossRef - Comparison of the efficacy of CanalBrush, EndoActivator, and Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation on the removal of triple antibiotic paste from root canal walls: An in vitro study
Santosh Kumar, Kavisha Desai, Aparna Palekar, Baswaraj Biradar, Ananjan Chatterjee, Khushboo Kumari
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2020; 10(4): 424. CrossRef - Apexification with Calcium Hydroxide vs. Revascularization
H. Boufdil, M. Mtalsi, S. El Arabi, B. Bousfiha, Jose López-López
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Intracanal Medicaments and Irrigants on the Release of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor from Cervical Root Dentin
Lívia Nazareth Ferreira, Regina Maria Puppin-Rontani, Fernanda Miori Pascon
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(11): 1616. CrossRef - Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Nitrofurantoin as an Experimental Intracanal Medicament in Endodontics
Mewan Salahalddin A. Alrahman, Bestoon Muhammed Faraj, Kawa F. Dizaye, Abdelwahab Omri
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - An in vitro assessment of effect on microhardness of dentin using vicker's hardness method
Manoj Chandak, Richa Modi, Rakesh Gogiya, Rakhi Chandak, Anuja Ikhar, Nikhil Mankar
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University.2020; 15(2): 251. CrossRef - Inspection of the Microbiota in Endodontic Lesions
Mario Dioguardi, Giovanni Di Gioia, Gaetano Illuzzi, Claudia Arena, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Giorgia Apollonia Caloro, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Iolanda Adipietro, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(2): 47. CrossRef - Materials for pulpotomy in immature permanent teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuan Chen, Xinlei Chen, Yali Zhang, Fangjie Zhou, Jiaxin Deng, Jing Zou, Yan Wang
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic therapy to conventional chemo-mechanical debridement of infected root canal systems: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Maryam Pourhajibagher, Abbas bahador
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2019; 26: 19. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Effects of Photodynamic Therapy, Modified Triple Antibiotic Paste and Calcium Hydroxide on Root Canals Infected With Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Mohammad Asnaashari, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Amirali Sahba Yaghmayi, Mehdi Shokri, Saranaz Azari-Marhabi
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2019; 10(5): S23. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 16,595 View
- 182 Download
- 74 Crossref

- Anatomical analysis of the resected roots of mandibular first molars after failed non-surgical retreatment
- Jiyoung Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Jihyun Bae, Yonghoon Choi
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e16. Published online March 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Understanding the reason for an unsuccessful non-surgical endodontic treatment outcome, as well as the complex anatomy of the root canal system, is very important. This study examined the cross-sectional root canal structure of mandibular first molars confirmed to have failed non-surgical root canal treatment using digital images obtained during intentional replantation surgery, as well as the causative factors of the failed conventional endodontic treatments.
Materials and Methods This study evaluated 115 mandibular first molars. Digital photographic images of the resected surface were taken at the apical 3 mm level and examined. The discolored dentin area around the root canal was investigated by measuring the total surface area, the treated areas as determined by the endodontic filling material, and the discolored dentin area.
Results Forty 2-rooted teeth showed discolored root dentin in both the mesial and distal roots. Compared to the original filled area, significant expansion of root dentin discoloration was observed. Moreover, the mesial roots were significantly more discolored than the distal roots. Of the 115 molars, 92 had 2 roots. Among the mesial roots of the 2-rooted teeth, 95.7% of the roots had 2 canals and 79.4% had partial/complete isthmuses and/or accessory canals.
Conclusions Dentin discoloration that was not visible on periapical radiographs and cone-beam computed tomography was frequently found in mandibular first molars that failed endodontic treatment. The complex anatomy of the mesial roots of the mandibular first molars is another reason for the failure of conventional endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro evaluation of the sealing ability of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling
Xu Dong, Qian Xie, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2969. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical diagnostic approach in the treatment of chronic periodontitis in mandibular molars: Clinical cases
M. A. Postnikov, A. M. Golovachev, S. E. Chigarina, D. N. Kudryashov, I. A. Zakharova, S. A. Burakshaev
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2023; 30(5): 100. CrossRef - Evaluation of interorifice distance in permanent mandibular first molar with middle mesial canal in Bengaluru city, Karnataka: A cone-beam computed tomography study
Shruthika Mahajan, N. Meena, Anithakumari Rangappa, Ali Mohammed Mashood, Chethana Murthy, M. Lokapriya
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 100. CrossRef - A comparative study of the effects of gutta‐percha solvents on human osteoblasts and murine fibroblasts
Gul Ipek Gundogan, Sare Durmus, Gulgun Cansu Ozturk, Nazmi Kucukyesil, Yasin Talat Acar, Rumeysa Balaban, Cenk Kig
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 569. CrossRef - Endodontic retreatment of curved root canals using the dual wavelength erbium, chromium:yttrium, scandium, gallium, garnet, and diode 940-nm lasers and the XP-Endoshaper/finisher technique
Riman Nasher, Ralf-Dieter Hilgers, Norbert Gutknecht
Lasers in Dental Science.2020; 4(4): 211. CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef
- In vitro evaluation of the sealing ability of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling
- 1,640 View
- 10 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
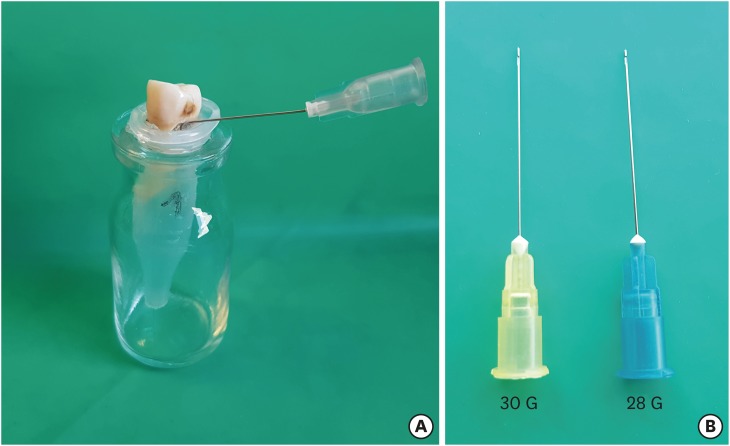
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed.Results Inserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (
p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both).Conclusions Following preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation needles used in endodontics: an in silico and an in vitro investigation
Maulee Sheth, Ankit Arora, Sonali Kapoor, Balraj Shukla
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 264. CrossRef - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,812 View
- 19 Download
- 10 Crossref

-
In vivo assessment of accuracy of Propex II, Root ZX II, and radiographic measurements for location of the major foramen - Fernanda Garcia Tampelini, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Marcos de Azevêdo Rios, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Daniel Guimarães Pedro Rocha, Sergio Luiz Pinheiro, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):200-205. Published online May 16, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vivo study was to assess the accuracy of 2 third-generation electronic apex locators (EALs), Propex II (Dentsply Maillefer) and Root ZX II (J. Morita), and radiographic technique for locating the major foramen (MF).Materials and Methods Thirty-two premolars with single canals that required extraction were included. Following anesthesia, access, and initial canal preparation with size 10 and 15 K-flex files and SX and S1 rotary ProTaper files, the canals were irrigated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. The length of the root canal was verified 3 times for each tooth using the 2 apex locators and once using the radiographic technique. Teeth were extracted and the actual WL was determined using size 15 K-files under a × 25 magnification. The Biostat 4.0 program (AnalystSoft Inc.) was used for comparing the direct measurements with those obtained using radiographic technique and the apex locators. Pearson's correlation analysis and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used for statistical analyses.
Results The measurements obtained using the visual method exhibited the strongest correlation with Root ZX II (
r = 0.94), followed by Propex II (r = 0.90) and Ingle's technique (r = 0.81;p < 0.001). Descriptive statistics using ANOVA (Tukey'spost hoc test) revealed significant differences between the radiographic measurements and both EALs measurements (p < 0.05).Conclusions Both EALs presented similar accuracy that was higher than that of the radiographic measurements obtained with Ingle's technique. Our results suggest that the use of these EALs for MF location is more accurate than the use of radiographic measurements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Do Different Image Modules Impact the Accuracy of Working Length Measurements in Digital Periapical Radiography? An In Vitro Study
Vahide Hazal Abat, Rabia Figen Kaptan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(3): 305. CrossRef - Influence of maintaining apical patency in post-endodontic pain
Snigdha Shubham, Manisha Nepal, Ravish Mishra, Kishor Dutta
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- How Do Different Image Modules Impact the Accuracy of Working Length Measurements in Digital Periapical Radiography? An In Vitro Study
- 1,764 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Retreatment of failed regenerative endodontic of orthodontically treated immature permanent maxillary central incisor: a case report
- Musaed Fahad Al-Tammami, Saad A. Al-Nazhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):65-71. Published online October 28, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.65

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub A revascularization procedure was shown to be the best alternative therapy for immature teeth with necrotic pulp and apical infection. A 12 year old female with a history of trauma to her upper central incisor and a sinus tract was referred for endodontic treatment. She was an active orthodontic patient and had undergone regenerative endodontic treatment for the past 2 years. Clinical examination revealed no response to sensibility, percussion, and palpation tests. The preoperative radiograph showed an open apex and apical rarefaction. The case was diagnosed as previously treated tooth with asymptomatic apical periodontitis. Regenerative endodontic retreatment was performed, and the case was followed for 3 years. Clinical, radiographic, and cone-beam computed tomography follow-up examination revealed an asymptomatic tooth, with evidence of periapical healing and root maturation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Revascularization of Non-Vital, Immature, Permanent Teeth with Two Bioceramic Cements: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Alaa Shaker, Mohamed Salem Rekab, Mohammad Alharissy, Naji Kharouf
Ceramics.2024; 7(1): 86. CrossRef - Orthodontically induced external apical root resorption considerations of root-filled teeth vs vital pulp teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Danning Zhao, Kun Xue, Jiayuan Meng, Meijing Hu, Fei Bi, Xuelian Tan
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Therapy for Management of an Immature Permanent Tooth with Recurrent Post-treatment Apical Periodontitis
Renato Lenzi, Sandra R Hernández, Flávio R F Alves, Isabela N Ro[Combining Circumflex Accent]c[COMBINING CEDILLA]as, Jose[Combining Acute Accent] F Siqueira
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2022; 12(4): 468. CrossRef - Rejeneratif Endodontik Tedavi: Bir Literatür Derlemesi
Enes Mustafa AŞAR, Murat Selim BOTSALI
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(1): 335. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment performed by endodontic postgraduate students: a retrospective study
Hadi Rajeh Alfahadi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Fawaz Hamad Alkazman, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Nada Al-Nazhan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Regenerative Procedures in Necrotic Adult Teeth
Sara Garrido-Parada, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Nancy Feijoo-Pato, José Gaviño-Orduña, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(9): 4212. CrossRef - Different Approaches to the Regeneration of Dental Tissues in Regenerative Endodontics
Anna M. Krupińska, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Tomasz Staniowski
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1699. CrossRef - Histologic, Radiographic, and Micro-Computed Tomography Evaluation of Experimentally Enlarged Root Apices in Dog Teeth with Apical Periodontitis after Regenerative Treatment
Mohammed S. Alenazy, Saad Al-Nazhan, Hezekiah A Mosadomi
Current Therapeutic Research.2021; 94: 100620. CrossRef - Revitalizing previously treated teeth with open apices: A case report and a literature review
Ali Nosrat, Behnam Bolhari, Shima Saber Tahan, Omid Dianat, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(10): 1782. CrossRef - PRICE 2020 guidelines for reporting case reports in Endodontics: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, B. S. Chong, P. McCabe, P. K. Shah, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 922. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Analysis of the Failed Cases
Waleed Almutairi, Ghaeth H. Yassen, Anita Aminoshariae, Kristin A. Williams, Andre Mickel
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(5): 567. CrossRef - Alternative to Avoid Tooth Discoloration after Regenerative Endodontic Procedure: A Systematic Review
Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Camila Guerner Springmann, Beatriz Dulcineia Mendes de Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Flávio Fernando Demarco, Mara Cristina Santos Felippe, Wilson Tadeu Felippe
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(5): 409. CrossRef
- Revascularization of Non-Vital, Immature, Permanent Teeth with Two Bioceramic Cements: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 2,006 View
- 15 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
- Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT.
Results The second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (
p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01).Conclusions For apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
- 2,253 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

-
An
in vitro evaluation of the accuracy of four electronic apex locators using stainless-steel and nickel-titanium hand files - Paras Mull Gehlot, Vinutha Manjunath, Mysore Krishnaswamy Manjunath
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):6-11. Published online January 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.6

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the accuracy of working length (WL) determination of four electronic apex locators (EALs), namely, Root ZX (RZX), Elements diagnostic unit and apex locator (ELE), SybronEndo Mini Apex locator (MINI) and Propex pixi (PIXI) using Stainless steel (SS) and nickel-titanium (NiTi) hand files. The null hypothesis was that there was no difference between canal length determination by SS and NiTi files of 4 EALs.Materials and Methods Sixty extracted, single rooted human teeth were decoronated and the canal orifice flared. The actual length (AL) was assessed visually, and the teeth were embedded in an alginate model. The electronic length (EL) measurements were recorded with all four EALs using SS and NiTi files at '0.5' reading on display. The differences between the AL and EL were compared.
Results The results obtained with each EAL with SS and NiTi files were compared with AL. A paired sample
t test showed that there was a statistical significant difference between EAL readings with SS and NiTi files for RZX and MINI (p < 0.05). The accuracy of RZX, ELE, MINI and PIXI within ± 0.5 mm of AL with SS/NiTi files were 93.3%/70%, 90%/91.7%, 95%/68.3%, and 83.3%/83.3%, respectively.Conclusions The results of this study indicate that Root ZX was statistically more accurate with NiTi files compared to SS files, while MINI was statistically more accurate with SS files compared to NiTi files. ELE and PIXI were not affected by the alloy type of the file used to determine WL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
Shayan Golkar, Abbasali Khademi, Amin Saatchi, Amir Ghorani, Pedram Iranmanesh
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy of two electronic apex locators in mandibular mesial canals and the influence of root canal anatomy: a micro-CT-based study
Zübeyde Gökçe Ürün, Berkan Çelikten, Ali Cemal Tınaz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locators using heat‐treatedNi‐Tifile
Kang‐Young Heo, Ho‐Keel Hwang, Hyoung‐Hoon Jo
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 111. CrossRef - Impact of nickel-titanium instrument heat treatment on the precision of an inbuilt electronic apex locator and endodontic motor
Syed Manzoor Ul Haq Bukhari, Rahil Bhat, Sheeeban Rashid
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 8(3): 155. CrossRef - Clinical Accuracy and Precision of 3 Multifrequency Electronic Apex Locators Assessed through Micro–Computed Tomographic Imaging
Gustavo De-Deus, Viviany Cozer, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões-Carvalho, Marco Aurélio Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(5): 487. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment of nickel–titanium instruments on the accuracy of an electronic apex locator integrated with endodontic motor
HermanoCamelo Paiva, Eduardo Akisue, GeorgeTáccio de Miranda Candeiro, Iandarade Lima Scardini, CelsoLuiz Caldeira, Giulio Gavini
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(6): 596. CrossRef - The accuracy of electronic apex locators for determining working length: An in vitro study with artificial teeth
Raquel C. F. D. Bernardo, Louise S. Alves, Adilia M. V. Bruno, Thais M. C. Coutinho, Heloisa Gusman
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(2): 217. CrossRef - LİTERATÜRDE IN VITRO ELEKTRONİK APEKS BULUCU ÇALIŞMALARINDA KULLANILAN ORTAM ÇEŞİTLERİ: BİR DERLEME
Hamza CUDAL, Tuğrul ASLAN, Yakup ÜSTÜN
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 454. CrossRef - Effect of solvent use on postoperative pain in root canal retreatment: a randomized, controlled clinical trial
Ozgur Genc Sen, Ali Erdemir, Burhan Can Canakci
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(1): 257. CrossRef - A clinical evaluation of two electronic apex locators and conventional radiography in working length determination in primary molar and its influence on children's behavioral responses
Krithi Nellamakkada, SandyaS Patil, Madhu Kakanur, RaviS Kumar, Rachna Thakur
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2020; 38(2): 158. CrossRef - Comparison of the accuracies of multi-frequency electronic apex locators in teeth with enlarged apical foramina: ex vivo
Mügem Aslı Ekici, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç, Adil Ekici
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Root ZX Electronic Foramen Locator: An Ex Vivo Study of Its Three Models’ Precision and Reproducibility
Bernardo Almeida Aguiar, Rafael Santos Reinaldo, Luciana Maria Arcanjo Frota, Mônica Sampaio do Vale, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos
International Journal of Dentistry.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Determination of the Accuracy of 5 Electronic Apex Locators in the Function of Different Employment Protocols
Tiago Nepomuceno Oliveira, Nilton Vivacqua-Gomes, Ricardo Affonso Bernardes, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Bruno Carvalho Vasconcelos
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1663. CrossRef
- Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
- 1,592 View
- 7 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Treatment of non-vital immature teeth with amoxicillin-containing triple antibiotic paste resulting in apexification
- Hyon-Beom Park, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):322-327. Published online August 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.322
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub A recent treatment option for non-vital immature teeth in young patients is revascularization with triple antibiotic paste (TAP). However, tooth discoloration was reported with the use of conventional minocycline-containing TAP. In this case report, amoxicillin-containing TAP was used for revascularization of non-vital immature teeth to prevent tooth discoloration. At the 1 yr follow up, the teeth were asymptomatic on clinical examination and showed slight discoloration of the crown due to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) filling rather than amoxicillin-containing TAP. Radiographic examination revealed complete resolution of the periapical radiolucency, and closed apex with obvious periodontal ligament space. However, the root growth was limited, and the treatment outcome was more like apexification rather than revascularization. These results may be due to unstable blood clot formation which could not resist the condensation force of MTA filling, whether or not a collagen matrix was in place. These cases showed that although revascularization was not successful, apexification could be expected, resulting in the resolution of the periapical radiolucency and the closure of the apex. Therefore, it is worthwhile attempting revascularization of non-vital immature teeth in young patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
Aparna Palekar, Piyush Mantri, Minal Awinashe, Basawaraj Biradar, Mukund Singh
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of Large Endodontic Lesions Using Long‐Term Application of a New Combination of Triple Antibiotics: A Series of Cases
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar, Maria Beatriz Duarte Gavião
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Antibiotic Pastes for Root Canal Disinfection
Sadhna Sharma, Urvashi Bhushan, Mridula Goswami, CP Baveja
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S1): S12. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics as the Future Treatment of Immature Permanent Teeth
Justyna Zbańska, Katarzyna Herman, Piotr Kuropka, Maciej Dobrzyński
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(13): 6211. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste in teeth with primary endodontic infection: A systematic review
Rhythm Bains, Aseem P. Tikku, Promila Verma, Pragya Pandey
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2021; 11: 2. CrossRef - Effectiveness of MTA apical plug in dens evaginatus with open apices
Khoa Van Pham, Thu Anh Tran
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair: A Literature Review
Ankit Rawat, Jyoti Nagpal, Shreeya Mehta, Divya Vyas, Abhishek Kumar, Fathima Amal
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 6. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric assessment of Tooth discoloration induced by various Antibiotic pastes
Ravi Gupta, Radhika Kewalramani, Dishant Patel
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2021; : 1979. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of calcium release of the apical plugs formed by mineral trioxide aggregate, Biodentine, and EndoSequence root repair material with and without 2% triple antibiotic powder: An in vitro study
PoojaNitin Mapara, ND Shashikiran, Sachin Gugawad, Namrata Gaonkar, Savita Hadakar, Swapnil Taur, Dhanshri Khade
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2020; 38(2): 132. CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic loaded apatitic nanocarriers on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm – An In vitro study
S. Nagarathinam, V. Sujatha, K. Madhumathi, S. Mahalaxmi, P.Pranav Vanajassun, T.S.Sampath Kumar
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2019; 51: 499. CrossRef - Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month ex vivo study
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Alternative to Avoid Tooth Discoloration after Regenerative Endodontic Procedure: A Systematic Review
Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Camila Guerner Springmann, Beatriz Dulcineia Mendes de Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Flávio Fernando Demarco, Mara Cristina Santos Felippe, Wilson Tadeu Felippe
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(5): 409. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment or Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apical Plug in Teeth with Necrotic Pulps and Open Apices: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mahmoud Torabinejad, Ali Nosrat, Prashant Verma, Oyoyo Udochukwu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1806. CrossRef - Revascularization in Immature Permanent Teeth with Necrotic Pulp and Apical Pathology: Case Series
López Carmen, Mendoza Asunción, Solano Beatriz, Yáñez-Vico Rosa, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
- 2,186 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- A review of the regenerative endodontic treatment procedure
- Bin-Na Lee, Jong-Wook Moon, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):179-187. Published online March 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Traditionally, apexification has been used to treat immature permanent teeth that have lost pulp vitality. This technique promotes the formation of an apical barrier to close the open apex so that the filling materials can be confined to the root canal. Because tissue regeneration cannot be achieved with apexification, a new technique called regenerative endodontic treatment was presented recently to treat immature permanent teeth. Regenerative endodontic treatment is a treatment procedure designed to replace damaged pulp tissue with viable tissue which restores the normal function of the pulp-dentin structure. After regenerative endodontic treatment, continued root development and hard tissue deposition on the dentinal wall can occur under ideal circumstances. However, it is difficult to predict the result of regenerative endodontic treatment. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to summarize multiple factors effects on the result of regenerative endodontic treatment in order to achieve more predictable results. In this study, we investigated the features of regenerative endodontic treatment in comparison with those of other pulp treatment procedures and analyzed the factors that have an effect on regenerative endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures Using Autologous Platelet Concentrate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elnaz Mousavi, Navid Nasrabadi, Samira Jamali, Arian Haddadi
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial 3D printed gelatin scaffolds for root canal disinfection in regenerative endodontics procedures
Mateo Dallos Ortega, Jenny Aveyard, Raghda Magdy Abdelgawad, Reem El-Gendy, Alexander Ciupa, David Whetnall, Julia Behnsen, Robert J. Poole, Raechelle A. D'Sa
Biomaterials Science.2025; 13(14): 3795. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Therapies: Harnessing Stem Cells, Scaffolds, and Growth Factors
Rosana Farjaminejad, Samira Farjaminejad, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
Polymers.2025; 17(11): 1475. CrossRef - Effects of combining hyaluronic acid hydrogel with injectable platelet rich fibrin on apical papilla stem cells proliferation and differentiation
Azal H. Al-Masoody, Nasrin Asadi, Hadiseh Mohammadpour, Mahshid Hodjat, Tahereh Sadat Jafarzadeh Kashi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Experts consensus on management of tooth luxation and avulsion
Ruijie Huang, Chenchen Zhou, Ling Zhan, Yuan Liu, Xian Liu, Qin Du, Jun Wang, Wei Zhao, Guangtai Song, Li-an Wu, Beizhan Jiang, Yanhong Li, Hongmei Zhang, Jing Zou
International Journal of Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A review of tissue engineering in regenerative endodontic treatment
Eric Priyo Prasetyo, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Galih Sampoerno, Wilson Sukandar, Shafy Shariz Bin Sharizal, Nurfahira Paidal, Menza Fadiyan Amriel, Nathania Elita Gunawan, Ketut Suardita, Evelyn Tjendronegoro
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2024; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Innovative Paradigms and Established Strategies in Tooth Revitalization: A Review
Ahmad Shah Khan, Zahid Mehmood Khan, Palwasha Ishaque, Muhammad Zubair, Syeda Fatima Tu Zahra, Sana Ashfaq
Dental Update.2024; 51(8): 570. CrossRef - Explore the most recent developments and upcoming outlooks in the field of dental nanomaterials
Ali Alsuraifi, Zainab M. Sulaiman, Noor Alhuda R. Mohammed, Jassim Mohammed, Sarah Kareem Ali, Yousef Husam Abdualihamaid, Fatimah Husam, Abdullah Ayad
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Regenerative Endodontics: A Review of Current Techniques and Future Directions
Firas A Alothman, Lamia S Hakami, Ali Alnasser, Faris M AlGhamdi, Abdullah A Alamri, Basel M Almutairii
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Response to a Bioceramic Dental Sealer and Photobiomodulation: An In Vitro Study
Hamed A Alshawkani, Mohamed Mansy, Mahmoud Al Ankily, Mohamed Shamel
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(4): 313. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - GelMA‐based hydrogel biomaterial scaffold: A versatile platform for regenerative endodontics
Lei Huang, Xuan Chen, XiaoXia Yang, Yinchun Zhang, Xiaoling Qiu
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Dentinogenesis Imperfecta‐Induced Apical Periodontitis
Ying Liao, Ting Pan, Xianghui Xing, Sivakumar Nuvvula
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro and in vivo evaluation of iRoot BP Plus as a coronal sealing material for regenerative endodontic procedures
Ning Yang, Wenxiao Yang, Rou Shen, Shengcai Zhang, Tianchi Ma, Yao Liu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of pH and Ca+ ion release from MTA on interaction with platelet-rich fibrin and blood clot: an in vitro study
Sonia Khatri, Sylvia Mathew, Shruthi Nagaraja, Swaroop Hegde, Soumyadeep Ghosh, Kavimalar Ravichandran
F1000Research.2023; 12: 364. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Therapy and Pulp-Regenerative Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Jiawen Yong, Sabine Gröger, Zuping Wu, Sabine Ruf, Yuer Ye, Xiaoyan Chen
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 371. CrossRef - Efficacy of disinfection procedures performed prior to regenerative endodontic therapy: An integrative review
Ketillyn da Silva Magalhães, Ana Clara Kuerten Gil, Taynara Santos Goulart, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Daniela de Rossi Figueiredo, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(2): 418. CrossRef - Newer Prospects of Regenerative Endodontics: A Comprehensive and Updated Review of Literature
Mohammad Kamran Khan, Mahendra Kumar Jindal
Journal of the Scientific Society.2023; 50(3): 299. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of pH and Ca+ ion release from MTA on interaction with platelet-rich fibrin and blood clot: an in vitro study
Sonia Khatri, Sylvia Mathew, Shruthi Nagaraja, Swaroop Hegde, Soumyadeep Ghosh, Kavimalar Ravichandran
F1000Research.2023; 12: 364. CrossRef - Effects of CEM cement and emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla: a comparative in vitro study
Elham Khoshbin, Leila Ghasemi, Rezvan Najafi, Hamed Karkehabadi
Biotechnology Letters.2023; 45(1): 69. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Regenerative Potential of Blood Clot and Platelet-rich Fibrin in Young Permanent Teeth Based on the Revised American Academy of Endodontics Clinical Considerations for Regenerative Procedure: 2016
Saraswathi V Naik, Prabhakar Attiguppe, Aarathi J Prakash
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S149. CrossRef - Biomechanical characterization of a fibrinogen–blood hydrogel for human dental pulp regeneration
Sofia Silvia Piglionico, Bela Varga, Orsolya Pall, Olivier Romieu, Csilla Gergely, Frédéric Cuisinier, Bernard Levallois, Ivan Vladislavov Panayotov
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(20): 6919. CrossRef - Intracellular bacterial eradication using a novel peptide in vitro
Wing Nok Isaac Ng, Shanthini Kalimuthu, Carmen Oi Kwan Law, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Terrence Chi Kong Lau, Yiu Yan Leung, Gary Shun Pan Cheung, Prasanna Neelakantan
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(11): 1360. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of Previously Treated Mature Permanent Tooth: A Case Report with 3-year Follow Up
Myung-Jin Lee
The Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2023; 47(6): 133. CrossRef - Clinical Outcome and Comparison of Regenerative and Apexification Intervention in Young Immature Necrotic Teeth—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Pratima Panda, Lora Mishra, Shashirekha Govind, Saurav Panda, Barbara Lapinska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3909. CrossRef - Evaluation of Attitude and Knowledge of Endodontic, Pedodontic and SBARD Residents in Saudi Arabia toward Regenerative Endodontics—A National Survey
Ali A. Assiry, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Roshan Noor Mohamed, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohammed Zameer
Medicina.2022; 58(4): 545. CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Antimicrobials on Viability and Differentiation of Stem Cells From the Apical Papilla: An In Vitro Study
Gavin Raddall, Isabel Mello, Brendan M. Leung
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(7): 880. CrossRef - Awareness and Acceptance of Vital Pulp Therapy and Regenerative Endodontic Procedures among Dental Professionals in India: A Web-based Survey
Saloni Rathi, Priya Chauhan, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Rolly Agarwal, Simar Kaur Manocha, Mrinali Chaddha
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 10. CrossRef - Exosomes as Biochemistry Tools for Stem Cell Differentiation: A Novel Cell-Based Treatment for Diseases
Saeed Azandeh, Darioush Bijan Nejad, Samaneh Karimi, Fereshtesadat Fakhredini
Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of biodentine coated with emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla
Hamed Karkehabadi, Erfan Ahmadyani, Rezvan Najafi, Elham Khoshbin
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 3685. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Laser‐Assisted Bleaching of the Teeth Discolored due to Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Suitable Medicament for Intracanal Disinfection
Krutika Malu, Monika Khubchandani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Microhardness and Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentin with Two Combinations of TAP and MTAP: An In Vitro Study
P Niharika, Saigeeta Kondamadugu, Nagireddy Venugopal Reddy, Muthumula Daneswari, Annie P Chris, Nikhila V Reddy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S2): S151. CrossRef - Comparing Antibiotic Pastes with Electrospun Nanofibers as Modern Drug Delivery Systems for Regenerative Endodontics
Nura Brimo, Dilek Çökeliler Serdaroğlu, Busra Uysal
Current Drug Delivery.2022; 19(9): 904. CrossRef - The Advances of Blood Clots Used as Biomaterials in Regenerative Medicine
Eliza VanZweden, Rachael Tolsma, Victor Hung, Peter Awad, Robert Sawyer, Yong Li
Regenerative Medicine.2022; 17(12): 957. CrossRef - Microstructure and color stability of calcium silicate-based dental materials exposed to blood or platelet-rich fibrin
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Ibrahim Abu Tahun, Shima Saber Tahan, Fatemeh Mohandes, Mohammad H. Nekoofar, Paul M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1193. CrossRef - Results of “proroot mta” application in treatment of chronic periodontitis in teeth with incomplete root formation
N.M. Korneeva, E.A. Novikova, D.S. Popova, K.S. Rabadanova, L.Ya Rzaeva
Stomatology for All / International Dental review.2022; (2(99)): 10. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Combined with Electrolyzed Superoxidized Solution at Neutral pH on Enterococcus faecalis Growth
Héctor Armando Jimenez-Gonzalez, María Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Sergio Eduardo Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Víctor Hugo Urrutia-Baca, Myriam Angélica De La Garza-Ramos, Juan Manuel Solis-Soto, Ricardo Gomez-Flores, Patricia Tamez-Guerra, Yeliz Guven
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Unpredictable Outcomes of a Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Zahra Mohammadi, Hadi Assadian, Behnam Bolhari, Mohammadreza Sharifian, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Nazanin Chitsaz, Andrea Scribante
Case Reports in Dentistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Revascularization of nonvital immature incisor with asymptomatic apical periodontitis
Ema Mulyawati, Pribadi Santosa, Tunjung Nugraheni
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(3): 134. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of calcium hydroxide apexification and regenerative endodontic procedure for root dentine growth stimulation in immature incisors with pulp necrosis
M.S. Rakhmanova, M.V. Korolenkova
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(6): 55. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of a Novel Antibiotic‐Eluting Injectable Platelet‐Rich Fibrin Scaffold against a Dual‐Species Biofilm in an Infected Immature Root Canal Model
Azade Rafiee, Mahtab Memarpour, Yasaman Najibi, Bahman Khalvati, Sedigheh Kianpour, Mohammad Hossein Morowvat, Sung-Hwan Choi
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exosomes Derived from Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla Promote Dentine-Pulp Complex Regeneration by Inducing Specific Dentinogenesis
Xueying Zhuang, Lingli Ji, Huan Jiang, Yao Liu, Xuemei Liu, Jing Bi, Weidong Zhao, Zhenjiang Ding, Xu Chen
Stem Cells International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Injectable Biomaterials for Dental Tissue Regeneration
Håvard Jostein Haugen, Poulami Basu, Mousumi Sukul, João F Mano, Janne Elin Reseland
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(10): 3442. CrossRef - Viability and Stimulation of Human Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla (hSCAPs) Induced by Silicate-Based Materials for Their Potential Use in Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review
José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, Alicia Almudéver, Julia Guerrero-Gironés, Carmen Llena
Materials.2020; 13(4): 974. CrossRef - An Innovative Drug Delivery System Loaded with a Modified Combination of Triple Antibiotics for Use in Endodontic Applications
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Fahimeh Tabatabaei, Saeed Asgary
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Defining Endodontic Residents' Clinical Experiences: A National Survey
Jonathan D. Blacher, Kamran E. Safavi, Robert H. Aseltine, Blythe M. Kaufman
Journal of Dental Education.2019; 83(5): 504. CrossRef - Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month ex vivo study
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Study between Revitalization of Necrotic Immature Permanent Anterior Teeth with and without Platelet Rich Fibrin: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Rasha Adel Ragab, Amr Ezzat Abd El Lattif, Norhan Abd El Wahab El Dokky
Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2019; 43(2): 78. CrossRef - Biomaterials and Scaffold Design Strategies for Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
Gavin Raddall, Isabel Mello, Brendan M. Leung
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Iloprost Induces Dental Pulp Angiogenesis in a Growth Factor–free 3-Dimensional Organ Culture System
Sonntana Seang, Prasit Pavasant, Chalida N. Limjeerajarus
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 759. CrossRef - Ratio and Rate of Induced Root Growth in Necrotic Immature Teeth
Eun Jung Sang, Ji-Soo Song, Teo Jeon Shin, Young-Jae Kim, Jung-Wook Kim, Ki-Taeg Jang, Sang-Hoon Lee, Hong-Keun Hyun
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(2): 225. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Traumatic avulsion and delayed replantation of maxillary incisors in an eleven-year-old child
Gokcen Deniz Bayrak
Edorium Journal of Dentistry.2018; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Diameter on the Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Teeth with Pulp Necrosis: A Review
Yanjun Fang, Xinhuan Wang, Jingjing Zhu, Chaonan Su, Ying Yang, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 414. CrossRef - Assessment of Regaining Pulp Sensibility in Mature Necrotic Teeth Using a Modified Revascularization Technique with Platelet-rich Fibrin: A Clinical Study
Mohamed Nageh, Geraldine M. Ahmed, Alaa A. El-Baz
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1526. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics
Kristina Feigin, Bonnie Shope
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2017; 34(3): 161. CrossRef - Intentional Replantation of an Avulsed Immature Permanent Incisor: A Case Report
Claudio Maniglia-Ferreira, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Marcelo de Morais Vitoriano
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1383. CrossRef - Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 12. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef - Effects of a Bioactive Scaffold Containing a Sustained Transforming Growth Factor-β1–releasing Nanoparticle System on the Migration and Differentiation of Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla
Craig Bellamy, Suja Shrestha, Calvin Torneck, Anil Kishen
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(9): 1385. CrossRef - Effects of Novel 3-dimensional Antibiotic-containing Electrospun Scaffolds on Dentin Discoloration
Margaret Louise A. Porter, Eliseu A. Münchow, Maria T.P. Albuquerque, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Anderson T. Hara, Marco C. Bottino
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(1): 106. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures Using Autologous Platelet Concentrate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 7,145 View
- 117 Download
- 63 Crossref

- Evaluation of electrical impedance ratio measurements in accuracy of electronic apex locators
- Pil-Jong Kim, Hong-Gee Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):113-122. Published online December 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this paper was evaluating the ratios of electrical impedance measurements reported in previous studies through a correlation analysis in order to explicit it as the contributing factor to the accuracy of electronic apex locator (EAL).
Materials and Methods The literature regarding electrical property measurements of EALs was screened using Medline and Embase. All data acquired were plotted to identify correlations between impedance and log-scaled frequency. The accuracy of the impedance ratio method used to detect the apical constriction (APC) in most EALs was evaluated using linear ramp function fitting. Changes of impedance ratios for various frequencies were evaluated for a variety of file positions.
Results Among the ten papers selected in the search process, the first-order equations between log-scaled frequency and impedance were in the negative direction. When the model for the ratios was assumed to be a linear ramp function, the ratio values decreased if the file went deeper and the average ratio values of the left and right horizontal zones were significantly different in 8 out of 9 studies. The APC was located within the interval of linear relation between the left and right horizontal zones of the linear ramp model.
Conclusions Using the ratio method, the APC was located within a linear interval. Therefore, using the impedance ratio between electrical impedance measurements at different frequencies was a robust method for detection of the APC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Anatomical Parameters on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in C-shaped Canals: A Novel Micro-CT Analysis Incorporating Feret Diameter
Kuan-Wei Tung, Hajime Sasaki, Bruno Cavalcanti, Richard Gardner, Neville McDonald
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(1): 134. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence techniques for ground fault line selection in power systems: State-of-the-art and research challenges
Fuhua Wang, Zongdong Zhang, Kai Wu, Dongxiang Jian, Qiang Chen, Chao Zhang, Yanling Dong, Xiaotong He, Lin Dong
Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering.2023; 20(8): 14518. CrossRef - Anin vitroevaluation of the accuracy of four electronic apex locators using stainless-steel and nickel-titanium hand files
Paras Mull Gehlot, Vinutha Manjunath, Mysore Krishnaswamy Manjunath
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 6. CrossRef
- Influence of Anatomical Parameters on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in C-shaped Canals: A Novel Micro-CT Analysis Incorporating Feret Diameter
- 1,865 View
- 17 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Calcium hydroxide dressing residues after different removal techniques affect the accuracy of Root-ZX apex locator
- Emel Uzunoglu, Ayhan Eymirli, Mehmet Özgür Uyanik, Semra Çalt, Emre Nagas
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):44-49. Published online November 5, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the ability of several techniques to remove calcium hydroxide (CH) from the root canal and determined the influence of CH residues on the accuracy of the electronic apex locator.
Materials and Methods Root canals of 90 human maxillary lateral incisors with confirmed true working length (TWL) were prepared and filled with CH. The teeth were randomly assigned to one of the experimental groups according to the CH removal technique (
n = 14): 0.9% saline; 0.9% saline + master apical file (MAF); 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA); 17% EDTA + MAF; 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); 5.25% NaOCl + MAF. Six teeth were used as negative control. After CH removal, the electronic working length was measured using Root-ZX (Morita Corp.) and compared with TWL to evaluate Root-ZX accuracy. All specimens were sectioned longitudinally, and the area of remaining CH (CH) and total canal area were measured using imaging software.Results The EDTA + MAF and NaOCl + MAF groups showed better CH removal than other groups (
p < 0.05). Root-ZX reliability to prevent overestimated working length to be > 85% within a tolerance of ± 1.0 mm (p < 0.05). There was strong negative correlation between amount of CH residues and EAL accuracy (r = -0.800 for ± 0.5 mm;r = -0.940 for ± 1.0 mm).Conclusions The mechanical instrumentation improves the CH removal of irrigation solutions although none of the techniques removed the dressing completely. Residues of CH medication in root canals affected the accuracy of Root-ZX adversely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Kürs¸at Er
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluation of heated sodium hypochlorite’s effect on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators: an in vitro study
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
Shayan Golkar, Abbasali Khademi, Amin Saatchi, Amir Ghorani, Pedram Iranmanesh
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a new irrigation solution -RISA- on removing calcium hydroxide from artificial standardized grooves in root canals - an in vitro study
İpek Eraslan Akyüz, Salih Düzgün, Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Apical Patency, Coronal Preflaring and Calcium Hydroxide on the Accuracy of Root ZX Apex Locator for Working Length Determination: An In Vitro Study
Mostafa Godiny, Reza Hatam, Roya Safari-Faramani, Atefeh Khavid, Mohammad Reza Rezaei
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(1): 38. CrossRef - Endodontic cement penetration after removal of calcium hydroxide dressing using XP-endo finisher
Alyssa Sales dos Santos, Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Eduardo Nunes
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of glycolic acid for the removal of calcium hydroxide from simulated internal Resorption cavities
Cangül Keskin, Ali Keleş, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4407. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Farklı Kanal İçi Ortamların Apeks Bulucuların Doğruluğu Üzerine Etkisi
Asena OKUR, Tuğrul ASLAN, Burak SAĞSEN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 859. CrossRef - Evaluation of the accuracy of different apex locators in determiningthe working length during root canal retreatment
Pelin Tufenkci, Aylin Kalaycı
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 125. CrossRef - Influence of calcium hydroxide residues after using different irrigants on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators: An in vitro study
NooshinSadat Shojaee, Zahra Zaeri, MohammadMehdi Shokouhi, Fereshteh Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl
Dental Research Journal.2020; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and File Sızes on the Accuracy of the Electronic Apex Locator in Simulated Immature Teeth
Leyla AYRANCİ, Ahmet ÇETİNKAYA, Serkan ÖZKAN
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2019; 5(3): 273. CrossRef - The Effect of File Size and Type and Irrigation Solutions on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators: AnIn VitroStudy on Canine Teeth
Maciej Janeczek, Piotr Kosior, Dagmara Piesiak-Pańczyszyn, Krzysztof Dudek, Aleksander Chrószcz, Agnieszka Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz, Małgorzata Kowalczyk-Zając, Aleksandra Gabren-Syller, Karol Kirstein, Aleksandra Skalec, Ewelina Bryła, Maciej Dobrzyński
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
- 1,702 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
- Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):120-125. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Use of an apical plug in management of cases with open apices has gained popularity in recent years. Biodentine, a new calcium silicate-based material has recently been introduced as a dentine substitute, whenever original dentine is damaged. This case report describes single visit apexification in a maxillary central incisor with necrotic pulp and open apex using Biodentine as an apical barrier, and a synthetic collagen material as an internal matrix. Following canal cleaning and shaping, calcium hydroxide was placed as an intracanal medicament for 1 mon. This was followed by placement of small piece of absorbable collagen membrane beyond the root apex to serve as matrix. An apical plug of Biodentine of 5 mm thickness was placed against the matrix using pre-fitted hand pluggers. The remainder of canal was back-filled with thermoplasticized gutta-percha and access cavity was restored with composite resin followed by all-ceramic crown. One year follow-up revealed restored aesthetics and function, absence of clinical signs and symptoms, resolution of periapical rarefaction, and a thin layer of calcific tissue formed apical to the Biodentine barrier. The positive clinical outcome in this case is encouraging for the use of Biodentine as an apical plug in single visit apexification procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)-Guided Non-surgical Management of Type II Dens Invaginatus in Maxillary Lateral Incisors Using Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Case Series
Prerna Priya
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal effects of restorative pretreatments on biodentine: an in-vitro study
Narendrakumar Akshaya, Hrudi Sundar Sahoo, Kurinji Amalavathy Ratnakaran, Adisree Ravichandran
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2026; 13: 109. CrossRef - A Prospective Randomised Clinical Trial Evaluating Pulpotomy in Primary Molars With Three Bioceramic Calcium Silicate Cements: 24 Month Follow‐Up
Abhinav L. Talekar, Prasad K. Musale, Gayatri S. Chaudhari, Tayaba M. H. Silotry, William F. Waggoner
International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry.2025; 35(4): 763. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sealing potential of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine, and bio-C repair in furcation perforations: A glucose penetration study
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira Anjum Sultana, A. Srirekha, C. Champa, Suditi Pal, V. Sahithi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 144. CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of interface gaps and internal voids in MTA-based biomaterials used for apexification with micro-CT
Huda Melike Bayram
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Immature Permanent Mandibular First Molar Using NeoPutty: A Case Report
Maryam Khorasanchi, Maryam Gharechahi, Zahra Azizi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Treating apical fenestration in a previously endodontically treated tooth
K. S Rajesh, Riza Farooq, F Abdul Rajak, Pradeep Kumar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1193. CrossRef - Influence of Bioceramic Cements on the Quality of Obturation of the Immature Tooth: An In Vitro Microscopic and Tomographic Study
Raya Al-Rayesse, Ossama Al-Jabban, Ammar Eid, Alaa Kabtoleh, Frédéric Addiego, Davide Mancino, Youssef Haikel, Naji Kharouf
Bioengineering.2024; 11(3): 213. CrossRef - Fracture Susceptibility in Non-Vital Apex Teeth Following Various Modified Apexification Procedure – An In Vitro Study
NJ Nagaraj, Peyush Pratap Singh Sikarwar, Debkant Jena, Rini Gangwal, Ipsita Mohanty, Adnan Haider Rizvi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 4): S3966. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Effects of Apical Barriers and Root Filling Materials on Stress Distribution in Immature Teeth: Finite Element Analysis Study
Minna Chun, Tory Silvestrin, Roberto Savignano, Gina Delia Roque-Torres
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(5): 575. CrossRef - Current Bio-based Cements and Radioactive Opacifiers in Endodontic Approaches: A Review of the Materials Used in Clinical Practice
A.Najah Saud, Erkan Koç , Olcay Özdemir
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 29(4): 930. CrossRef - Clinical Management of External Apical Root Resorption Using Amnion Membrane Matrix and Bio Dentine
Jeong-Kui Ku, In-Woong Um, Mi-Kyoung Jun, Il-hyung Kim
Journal of Current Research in Oral Surgery.2023; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Biodentine Apical Plug Thickness on Fracture Resistance of Immature Teeth
Pramod Mohite, Ankita Dadarao Ramteke, Ruchika Gupta, Suvarna Patil, Divya Gupta
Annals of African Medicine.2022; 21(3): 198. CrossRef - Comparison of sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine with and without bioactive glass as furcation repair materials
Shaik Afreen Kamal, Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Sayesh Vemuri, Bandaru Pydiahnaidu, Yandra Lakshmi Suvarna
Endodontology.2022; 34(1): 45. CrossRef - “BIODENTINE” THE DENTINE IN A CAPSULE AS AN APICAL BARRIER IN TRAUMATIZED MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISOR WITH TWO YEARS FOLLOW UP.
Savita Thakur, Udai Bhanu, Gurkirat Singh Grewal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 64. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Bioceramics Apexification in Periradicular Healing and Root-end Calcific Tissue Repair in Immature Traumatized Permanent Anterior Teeth
Shalini Garg, Sumit Singla, Satyavan Gangaram Damle, Abhishek Dhindsa, Ashish Loomba, Pragati Poddar
World Journal of Dentistry.2022; 13(S2): S194. CrossRef - Amnion Membrane Matrix And Bio Dentine In The Management Of An External Apical Root Resorption
Gyanendra Pratap Singh, Shruthi H Attavar, Sivaji Kavuri
Annals of Dental Specialty.2022; 10(2): 11. CrossRef - Morphological and Chemical Analysis of Different Types of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements
Okba Mahmoud, Nashwan Abdullah Al-Afifi, Mohideen Salihu Farook, Maysara Adnan Ibrahim, Saaid Al Shehadat, Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of a Novel Tool for Apical Plug Formation during Apexification of Immature Teeth
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Line Droubi, Saleh Alkurdi, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Nada Bshara, Thuraya Lazkani, Chaza Kouchaji, Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Ziad D. Baghdadi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5304. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of simulated immature roots using Biodentine and fiber post compared with different canal-filling materials under aging conditions
Amr Elnaghy, Shaymaa Elsaka
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1333. CrossRef - Modified Apexification Procedure for Immature Permanent Teeth with a Necrotic Pulp/Apical Periodontitis: A Case Series
Kamolthip Songtrakul, Talayeh Azarpajouh, Matthew Malek, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Bill Kahler, Louis M. Lin
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(1): 116. CrossRef - Efficacy of cavity liners with/without atmospheric cold helium plasma jet for dentin remineralization
Hamid Kermanshah, Reza Saeedi, Elham Ahmadi, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2020; 7(1): 120. CrossRef - APICAL MICROLEAKAGE OF VARIOUS BIOMATERIALS IN SIMULATED IMMATURE APICES
Fatih TULUMBACI, Volkan ARIKAN, Aylin AKBAY OBA, İşıl SÖNMEZ ŞAROĞLU
Selcuk Dental Journal.2019; 6(3): 247. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Recent Trends in Tricalcium Silicates for Vital Pulp Therapy
Imad About
Current Oral Health Reports.2018; 5(3): 178. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Will Bioceramics be the Future Root Canal Filling Materials?
Josette Camilleri
Current Oral Health Reports.2017; 4(3): 228. CrossRef - Clinical and Molecular Perspectives of Reparative Dentin Formation
Minju Song, Bo Yu, Sol Kim, Marc Hayashi, Colby Smith, Suhjin Sohn, Euiseong Kim, James Lim, Richard G. Stevenson, Reuben H. Kim
Dental Clinics of North America.2017; 61(1): 93. CrossRef - Management of Dens Invaginatus Type II Associated with Immature Apex and Large Periradicular Lesion Using Platelet-rich Fibrin and Biodentine
Shruti Goel, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1750. CrossRef - Biodentine: from biochemical and bioactive properties to clinical applications
Imad About
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2016; 30(2): 81. CrossRef - Apical Closure in Apexification: A Review and Case Report of Apexification Treatment of an Immature Permanent Tooth with Biodentine
Karla Vidal, Gabriela Martin, Oscar Lozano, Marco Salas, Jaime Trigueros, Gabriel Aguilar
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 730. CrossRef - Influence of Biodentine® - A Dentine Substitute - On Collagen Type I Synthesis in Pulp Fibroblasts In Vitro
Frangis Nikfarjam, Kim Beyer, Anke König, Matthias Hofmann, Manuel Butting, Eva Valesky, Stefan Kippenberger, Roland Kaufmann, Detlef Heidemann, August Bernd, Nadja Nicole Zöller, Dimitrios Karamichos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167633. CrossRef
- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)-Guided Non-surgical Management of Type II Dens Invaginatus in Maxillary Lateral Incisors Using Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Case Series
- 2,541 View
- 31 Download
- 34 Crossref

- Apexogenesis and revascularization treatment procedures for two traumatized immature permanent maxillary incisors: a case report
- Maryam Forghani, Iman Parisay, Amir Maghsoudlou
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):178-181. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Traumatic injuries to an immature permanent tooth may result in cessation of dentin deposition and root maturation. Endodontic treatment is often complicated in premature tooth with an uncertain prognosis. This article describes successful treatment of two traumatized maxillary central incisors with complicated crown fracture three months after trauma. The radiographic examination showed immature roots in maxillary central incisors of a 9-year-old boy with a radiolucent lesion adjacent to the right central incisor. Apexogenesis was performed for the left central incisor and revascularization treatment was considered for the right one. In 18-month clinical and radiographic follow-up both teeth were asymptomatic, roots continued to develop, and periapical radiolucency of the right central incisor healed. Considering the root development of these contralateral teeth it can be concluded that revascularization is an appropriate treatment method in immature necrotic teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Delayed endodontic management of traumatically exposed immature maxillary anterior teeth: a case series
Vignesh Ravi, Ruchi Singhal, Madhur Sharma, Ritu Namdev
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2026; 13: 81. CrossRef - The Efficacy of Photobiomodulation in Tooth Repair and Regeneration: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials in Animal Studies
Maryam Altuhafy, Anjan Kumar Thyagaraajen, Junad Khan
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 471. CrossRef - Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apexogenesis: A Systematic Review
Basmah M. Ageel, Omar A. El Meligy, Sarah M. A. Quqandi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2023; 15(Suppl 1): S11. CrossRef - Advances in Research on Stem Cell-Based Pulp Regeneration
Hua-Nien Lee, Cheng Liang, Li Liao, Wei-Dong Tian
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.2021; 18(6): 931. CrossRef - Different Approaches to the Regeneration of Dental Tissues in Regenerative Endodontics
Anna M. Krupińska, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Tomasz Staniowski
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1699. CrossRef - A comparison of MTA and Biodentine as medicaments for pulpotomy in traumatized anterior immature permanent teeth: A randomized clinical trial
Gihan Mohamed Abuelniel, Monty Singh Duggal, Nihal Kabel
Dental Traumatology.2020; 36(4): 400. CrossRef - Bone, Periodontal and Dental Pulp Regeneration in Dentistry: A Systematic Scoping Review
Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Marcus Cristian Muniz Conde, Guillermo Grazioli, Alissa Schmidt San Martin, Rodrigo Varella de Carvalho, Letícia Regina Morello Sartori, Flávio Fernando Demarco
Brazilian Dental Journal.2019; 30(2): 77. CrossRef - Regenerative in endodontics: how, when and where
AL Ahmar Rima, Bassam Sanaa, Salloum Sarah, El Husseini Hassan, AL Ahmar Rima
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018; 9(6): 531. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Diameter on the Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Teeth with Pulp Necrosis: A Review
Yanjun Fang, Xinhuan Wang, Jingjing Zhu, Chaonan Su, Ying Yang, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 414. CrossRef - Alternative to Avoid Tooth Discoloration after Regenerative Endodontic Procedure: A Systematic Review
Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Camila Guerner Springmann, Beatriz Dulcineia Mendes de Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Flávio Fernando Demarco, Mara Cristina Santos Felippe, Wilson Tadeu Felippe
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(5): 409. CrossRef - Retreatment of failed regenerative endodontic of orthodontically treated immature permanent maxillary central incisor: a case report
Musaed Fahad Al-Tammami, Saad A. Al-Nazhan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(1): 65. CrossRef - Pulp Revascularization: A Literature Review
Pollyana Rodrigues de Souza Araújo, Luciano Barreto Silva, Alexandrino Pereira dos Santos Neto, José Alcides Almeida de Arruda, Pâmella Recco Álvares, Ana Paula Veras Sobral, Severino Alves Júnior, Jair Carneiro Leão, Rodivan Braz da Silva, Gerhilde Callo
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 10(1): 48. CrossRef - Rejeneratif Pulpa Tedavilerine Genel Bir Bakış
Elif Sungurtekin Ekçi
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2017; 19(3): 238. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics
Kristina Feigin, Bonnie Shope
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2017; 34(3): 161. CrossRef - A scoping review of root canal revascularization: relevant aspects for clinical success and tissue formation
M. C. M. Conde, L. A. Chisini, R. Sarkis‐Onofre, H. S. Schuch, J. E. Nör, F. F. Demarco
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(9): 860. CrossRef - Histologic Findings of a Human Immature Revascularized/Regenerated Tooth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
Chufang Peng, Yuming Zhao, Wenjun Wang, Yuan Yang, Man Qin, Lihong Ge
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(6): 905. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment or Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apical Plug in Teeth with Necrotic Pulps and Open Apices: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mahmoud Torabinejad, Ali Nosrat, Prashant Verma, Oyoyo Udochukwu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1806. CrossRef - A Review of Tooth Discoloration after Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
Bill Kahler, Giampiero Rossi-Fedele
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 563. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Therapy: A Data Analysis of Clinical Protocols
Evangelos G. Kontakiotis, Christos G. Filippatos, Giorgos N. Tzanetakis, Anastasia Agrafioti
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(2): 146. CrossRef - Is revascularization of immature permanent teeth an effective and reproducible technique?
Yu‐Po Chen, Maria del Mar Jovani‐Sancho, Chirag C. Sheth
Dental Traumatology.2015; 31(6): 429. CrossRef - A review of the regenerative endodontic treatment procedure
Bin-Na Lee, Jong-Wook Moon, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 179. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate upregulates odonto/osteogenic capacity of bone marrow stromal cells from craniofacial bones via JNK and ERK MAPK signalling pathways
Y. Wang, J. Li, W. Song, J. Yu
Cell Proliferation.2014; 47(3): 241. CrossRef - The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 230. CrossRef - Levels of Evidence for the Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
Evangelos G. Kontakiotis, Christos G. Filippatos, Anastasia Agrafioti
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1045. CrossRef - Platelet rich fibrin - a novel acumen into regenerative endodontic therapy
Kavita Hotwani, Krishna Sharma
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Adult stem cell-based apexogenesis
Yao Li
World Journal of Methodology.2014; 4(2): 99. CrossRef
- Delayed endodontic management of traumatically exposed immature maxillary anterior teeth: a case series
- 2,775 View
- 25 Download
- 26 Crossref

- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
- Shin-Young Park, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):68-73. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.68
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the accuracy of Root ZX (J. Morita Corp.) according to the location of major foramen and open apex.
Materials and Methods 81 mandibular premolars with mature apices were selected. After access preparation, 27 teeth were instrumented to simulate open apices. 54 teeth were classified according to location of major foramen under surgical microscope (×16). The file was fixed at the location of apical constriction by Root ZX using glass ionomer cement. The apical 4 mm of the apex was exposed and photo was taken and the distance from file tip to the major foramen was measured by calibrating metal ruler on graph paper. The results were statistically analyzed using ANOVA and Scheffe test at
p < 0.05 level.Results Mean distance from file tip to major foramen was 0.308 mm in Tip foramen group (I), 0.519 mm in Lateral foramen group (II) and 0.932 mm in open apex group (III). Root ZX located apical constriction accurately within ± 0.5 mm in group I of 85.71%, in group II of 59.09%, and in group III of 33.33%. There was a statistically significant difference between group I and III (
p < 0.05).Conclusion Root ZX located apical constriction accurately regardless of location of major foramen. However, Root ZX couldn't find it in open apex. Clinicians have to use a combination of methods to determine an appropriate working length at open apex. It may be more successful than relying on just electronic apex locator.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of file size in measuring electronic working length of teeth with open apex
Ryeon Jin, Ju-Hee Jeong, A-Ra Cho, Hyoung-Hoon Jo
Oral Biology Research.2022; 46(1): 36. CrossRef
- Effect of file size in measuring electronic working length of teeth with open apex
- 1,348 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
- Chien-Yun Pi, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):453-460. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.453
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the accuracy and consistency of two different apex locators at both the Apex and 0.5 marks.
Materials and Methods Twenty-six root canals was scheduled for extraction for periodontal or prosthodontic reasons. Thirteen canals were measured using Root ZX and the rest by i-ROOT. The root canal length was measured both the at 0.5 mark and the Apex mark. The file was then fixed to the tooth, and the distance from the file tip to the major foramen of each canal was measured after removing the root dentin under the microscope so that the major foramen and the file tip were seen.
Results When the Apex mark was used, 100% of both the Root ZX and i-ROOT groups were within 0.5 mm of the major foramen.
When 0.5 mark was used, 100% of the Root ZX group and 77% of the i-ROOT group were within 0.5 mm of the major foramen.
In terms of standard deviation and quartile value, the Apex mark was more consistent than 0.5 mark in the Root ZX group, and 0.5 mark was more consistent in the i-ROOT group, but there was no statistically significant difference when compared with
t -test.The root canal length difference between the Apex mark and 0.5 mark was 0.22 mm and 0.46 mm in the Root ZX and i-ROOT groups, respectively.
Conclusions In this study, the Apex mark was the more consistent mark. Therefore, it is recommended to subtract 0.5 mm, which is the average length between the apex and apical constriction, from the root canal length at the Apex mark to obtain the working length clinically.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Apical Periodontitis on the Accuracy of 3 Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Devices: An In Vivo Study
Masoud Saatchi, Mohammad Ghasem Aminozarbian, Seyed Mohsen Hasheminia, Amin Mortaheb
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(3): 355. CrossRef
- Influence of Apical Periodontitis on the Accuracy of 3 Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Devices: An In Vivo Study
- 1,314 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
- Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):335-343. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.335
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To compared the effect of different levels of moisture of root canal on the sealing ability after filling with four different types of sealer.
Materials and Methods Single-rooted teeth (
n = 90) instrumented to and apical size of 0.06 / 45 were randomly assigned to 12 experimental groups (n = 7 per group), positive/negative control groups (n = 3 per group). The teeth of the experimental groups (a. DRY; b. PAPER POINT DRY; c. WET) were obturated with sealer (Group 1-3: Sealapex; Group 4-6: AH plus; Group 7-9: Tubuli-seal; Group 10-12: EndoRez) and warm vertical compaction method. After 7 days in 37℃, 100% humidity, the coronal-to-apical microleakage was evaluated quantitatively using a glucose leakage model. The leaked glucose concentration was measured with spectrophotometer at 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 30 days. Data were recorded ad mmol/L and statistically analysed with the two-way ANOVA and Duncan test (p = 0.05).Results Throughout the experimental period Tubuli-seal/WET (Group 9) showed the highest mean cumulative glucose penetration (178.75 mmol/L), whereas AH plus/DRY (Group 4) had the least (20.78 mmol/L).
Conclusions The results of this study demonstrated that the moisture condition of root canals at the time of obturation and the type of sealer that was used had a significant effect on leakage and sealing ability. Thus drying procedure according to sealer types is a critical step and should not be missed in endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - Effect of different root canal drying techniques on the push-out bond strength of ceraseal sealer – An in vitro study
R. Patil Pooja, D. N. Nirupama, Nainan Thomas Mohan, R. Vijay, Helen Thomas, P. K. Sneha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(7): 642. CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength of endodontic sealers after root canal drying with different techniques
Ahmadreza Sarrafan, Ali Soleymani, Tasnim Bagheri Chenari, Seyedali Seyedmajidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2023; 9(2): 314. CrossRef - Quantitative microleakage analysis of root canal filling materials in single‐rooted canals
Sin‐Young Kim, Kyung‐Jae Kim, Young‐Ah Yi, Deog‐Gyu Seo
Scanning.2015; 37(4): 237. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef
- Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
- 3,430 View
- 19 Download
- 5 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of the consistency of two electronic apex locators - Gyu-Young Hwang, Byoung-Duck Roh, Eui-Sung Kim, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):20-27. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.020
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the consistency of two electronic apex locators
in vitro model.Materials consisted of fifty two extracted premolars and two electronic apex locators; Root ZX (J. Morita, Osaka, Japan) and E-Magic Finder Deluxe (S-Denti, Cheonan, Korea). After access preparation, the teeth were embedded in a saline-mixed alginate model. Canal lengths of each tooth were measured at "0.5" and "Apex" mark of the apex locators, respectively so that each tooth had two measurements from 0.5 and Apex points. The file was fixed at final measurement using a glass ionomer cement. The apical 4 mm from the apex was exposed to measure the distance from the file tip to the major apical foramen of each tooth. Average distances and standard deviations were used to evaluate the consistency.
Results showed that all measurements of both Root ZX and E-Magic Finder located the major foramen the range of ± 0.5 mm level. Both apex locators showed better consistency at Apex mark than at 0.5 mark. The average distance of file tip-major foramen was - 0.18 mm at 0.5 mark and - 0.07 mm at Apex mark in Root ZX, - 0.25 mm at 0.5 mark and - 0.02 mm at Apex mark in E-Magic Finder. Standard deviation was 0.21 at 0.5 mark and 0.12 at Apex mark in Root ZX, 0.12 at 0.5 mark and 0.09 at Apex mark in E-Magic Finder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Variations in the morphology of apical constriction affecting electronic readings: An in vitro investigation using 3D‐printed tooth models
Juhee Nam, Lucila Piasecki, Doun Kwak, Jung Hwa Hong, Il‐Young Jung, Sung‐Ho Park, Sin‐Yeon Cho
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 245. CrossRef - In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
Chien-Yun Pi, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 453. CrossRef
- Variations in the morphology of apical constriction affecting electronic readings: An in vitro investigation using 3D‐printed tooth models
- 1,162 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of accuracy and consistency of four different electronic apex locators - Jae-Hyun Cho, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):390-397. Published online September 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and the consistency of four different electronic apex locators in an
in vitro model.Fourty extracted premolars were used for the study. Four electronic apex locators (EAL) were Root ZX, SmarPex, Elements Diagnostic Unit (EDU), and E-Magic Finder Deluxe (EMF). After access preparation, the teeth were embedded in an alginate model and the length measurements were carried out at "0.5"and "Apex"mark using four EALs. The file was cemented at the location of the manufacturers'instruction (Root ZX, EDU, EMF: 0.5 mark, SmarPex: Apex mark). The apical 4mm of the apex was exposed and the distance from the file tip to the major foramen was measured by Image ProPlus (× 100). The distance from the file tip to the major foramen was calculated at 0.5 and Apex mark and the consistency of 0.5 and Apex mark was compared by SD and Quartile of Box plots.
In this study, Root ZX and EMF located the apical constriction accurately within ± 0.5 mm in 100%, whereas SmarPex and EDU located in 90% and in 70% respectively. For Root ZX and EMF, there was no significant difference between the consistency of 0.5 and Apex mark. However, for the EDU and SmarPex, Apex mark was more consistent than 0.5 mark.
From the evaluation of the consistency in this study, for Root ZX and EMF, both 0.5 and Apex mark can be used as a standard mark. And for EDU and SmarPex, the Apex mark can be recommended to be used as a standard mark.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
Shin-Young Park, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 68. CrossRef
- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
- 1,399 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
In vitro comparison of measurement accuracy in pre-enlarged and enlarged canals with four apex locators - Sang-Yup Sung, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):371-377. Published online September 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.371
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purposes of this study were to assess the accuracy of measurements in pre-enlarged canals with small instruments and to compare the accuracies, in enlarged canal, with small size instruments and instruments that match the actual canal diameter using Root ZX, Bingo1020, SmarPex, and e-Magic Finder. Ten extracted teeth were embedded in an alginate model made for testing apex locators. A size 10 file was placed into the root canal until the tip of the file reached the plane of the major diameter of the foramen under a dental operating microscope at the 25 × magnification. The measurement was done with digital caliper and defined as actual length. Electronic length measurement with a size 10 file in pre-enlarged canal was done by reading the index indicating Apex of each device to gain a definite value. After completion of canal enlargement to a size 45 file, each difference between actual length and electric measurement value with a size 10 and 40 files in enlarged canal was recorded as L10 and L40. The one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's multiple range tests were computed for analyze the differences among the four apex locators in the same group. The Student's t-test between L10 and L40 of each locator was done. The accuracies of electronic measurements were significantly different among the 4 devices. The file size made no difference on the accuracy of electronic measurement in enlarged canal with same device. The e-Magic Finder was the most accurate device among the 4 apex locators used in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Working Length Determination Using Two Fifth-Generation Apex Locators With Radiovisiography: An In vivo Study
H. K. Shwetha, C. N. Vijay Kumar, Arun J. Kumar, Ashwini Bhaskar, M Kavyashree, S Amrita
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(2): 69. CrossRef
- Working Length Determination Using Two Fifth-Generation Apex Locators With Radiovisiography: An In vivo Study
- 1,302 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- An accuracy of the several electronic apex locators on the mesial root canal of the mandibular molar
- Young-Lin Cho, Wook-Hee Son, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):477-485. Published online November 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to compare the length between the mesio-buccal and mesio-lingual canal of the mandibular molars before and after early coronal flaring at the different measuring time using several electronic apex locators. Fifty mandibular molars with complete apical formation and patent foramens were selected. After establishing the initial working length of the buccal and lingual canal of the mesial root using a surgical microscope (Carl Zeiss Co. Germany) at 25X with #15 K-file tip just visible at the foramen, radiographs were taken for the working length. After measuring the length of mesio-buccal and mesio-lingual canal (control group), the electronic lengths were measured at different times using several electronic apex locators (experimental groups; I-Root ZX, II-Bingo, III-Propex, IV-Diagnostic). After early coronal flaring using the K3 file, the additional electronic lengths were measured using the same manner.
The results were as follows: One canal has a correct working length for the mesial root of the mandibular molar, it can be used effectively for measuring the electronic working length of another canal when the files are superimposed or encountered at the apex. In addition, the accuracy of the electronic apex locators was increased as the measurement was accomplished after the early coronal flaring of the root canal and the measuring time was repeated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
Shin-Young Park, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 68. CrossRef - Study of endodontic working length of Korean posterior teeth
Jeong-Yeob Kim, Sang-Hoon Lee, Gwang-Hee Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 429. CrossRef
- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
- 1,140 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The analysis of initial apical file size before and after coronal flaring
- Ho-Keel Hwang, Chan-Ho Park, Seong-Chul Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):64-71. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.064
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the initial apical file(IAF) first file that fits to the apex in each canal before and after early flaring to analyze if the size of file to fit to the apex would increase after flaring. Eighty anterior teeth with complete apical formation and patent foramens were selected. The samples were randomly divided into 4 groups(GG, OS, GT, PT Group) of 20 teeth each. A file was fit to the apex in each canal and that size recorded. Radicular flaring were completed using different types of instruments. After flaring a file was again fit to the apex in the same manner as before and its size recorded.
The results of this study were as follows:
1. The mean diameter of IAF before flaring(file diameters in mm×10-2) was 19.81±8.32 before and 25.94±9.21 after(p<0.05).
2. The increase in diameter of IAF was approximately one file size for all groups.
3. Ranking of increasing diameter of IAF were GG>GT>OS>PT group. There was a statistically significant difference between before and after flaring(p<0.05).
4. Ranking of the time for flaring were GG>GT>OS>PT group. There was a statistically significant difference between GG group and other groups(p<0.05).
5. In the case without change of IAF diameter, they showed decrease in force after flaring when IAF was pulled out from root canal(p<0.05).
This study suggested that early radicular flaring increases the file size that is snug at the apex, and awareness of that difference gives the clinician a better sense of canal size. Early flaring of the canal provides better apical size information and with this awareness, a better decision can be made concerning the appropriate final diameter needed for complete apical shaping.
- 2,211 View
- 11 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


