-
Difference in light transmittance and depth of cure of flowable composite depending on tooth thickness: an in vitro experimental study
-
Seong-Pyo Bae, Myung-Jin Lee, Kyung-San Min, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e39. Published online November 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e39
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
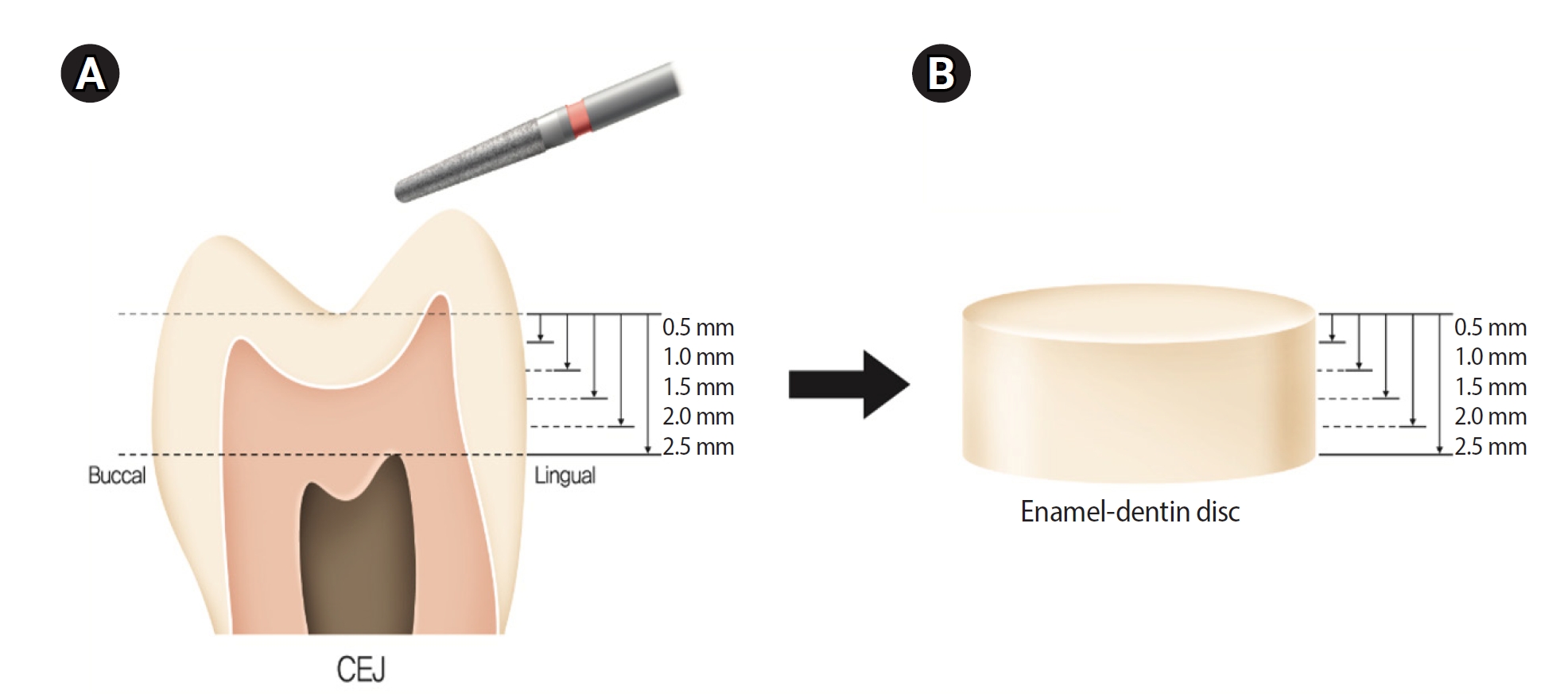
This study aimed to quantify light attenuation through varying tooth thicknesses and its impact on the depth of cure of composite resin.
Methods
Twenty extracted premolars were used to create enamel-dentin discs that were sanded progressively in 0.5 mm increments from 2.5 mm to 0.5 mm. Light irradiance was measured with and without tooth specimens to evaluate light transmittance. Resin was cured beneath different thicknesses, and the depth of cure was assessed using the Vickers hardness test.
Results
The results demonstrated that light transmittance significantly decreased as tooth thickness increased (p < 0.01), leading to reduced resin polymerization. In the 2.0-mm and 2.5-mm tooth thickness groups, the depth of cure was significantly lower than in the control group without tooth specimens (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Ultimately, for tooth structures exceeding 2 mm, self-cure or dual-cure resin polymerization is thought to be more efficient than light polymerization.
-
Surgical management of maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin after reestablishing maxillary sinus floor healing through a nonsurgical approach: a case report
-
Eun-Sook Kang, Min-Kyeong Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e12. Published online April 8, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e12
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
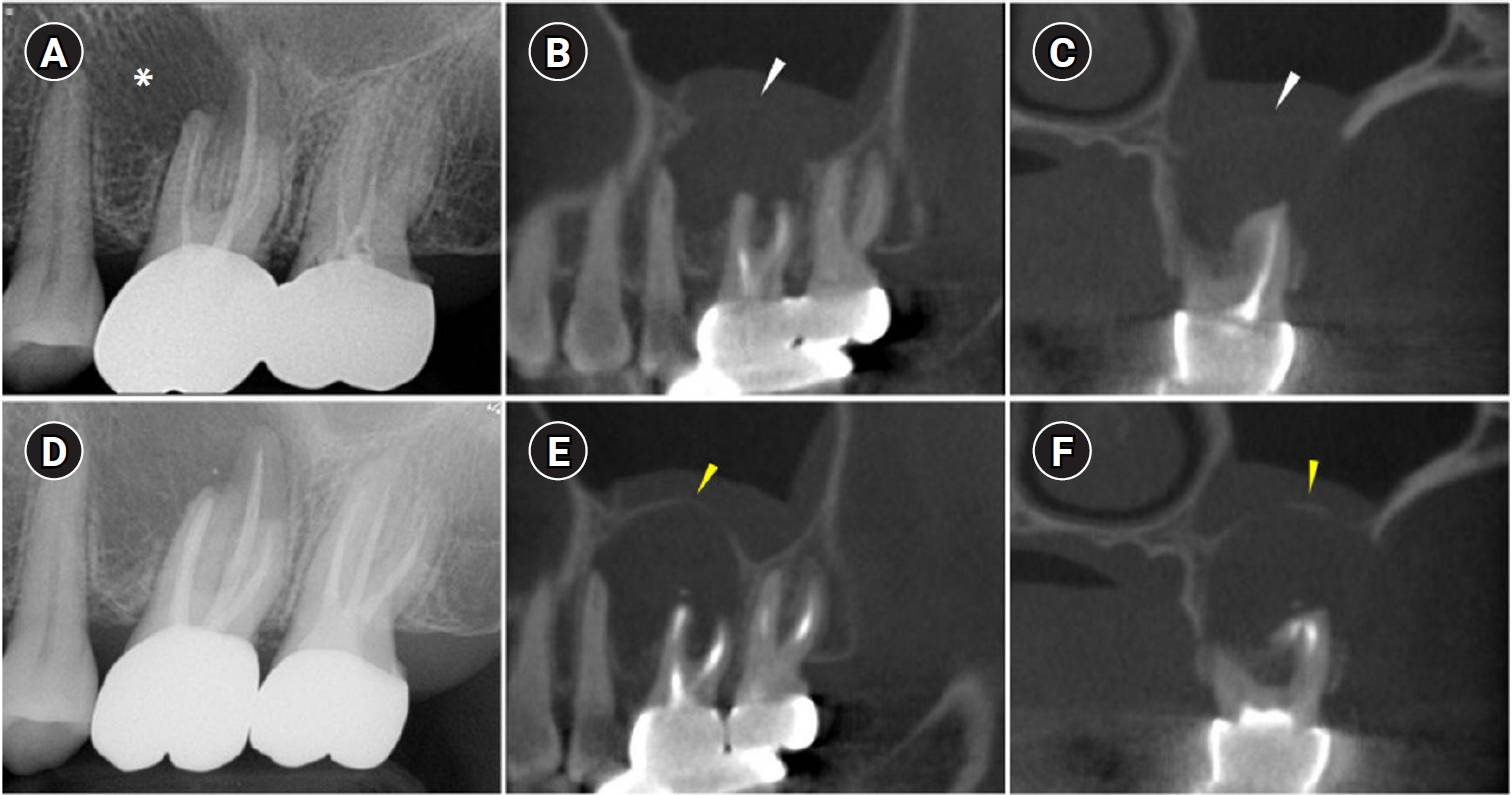
- When root canal infections breach the maxillary sinus floor (MSF), maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin (MSEO) can result. This case illustrates the surgical management of MSEO following the nonsurgical reestablishment of the MSF. A 55-year-old woman presented with left facial pain and was diagnosed with MSEO originating from the left upper first molar. Despite undergoing nonsurgical root canal treatment, there was no evidence of bony healing after 6 months. However, cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) scans revealed the reestablishment of MSF. Subsequently, surgical intervention was carried out using a dental operating microscope. Two years after surgery, CBCT images indicated that the mucosal edema had resolved, and the MSF was well reestablished. Preserving the MSF is crucial for the success of endodontic surgery. When MSEO is present, the integrity of the MSF must be assessed to determine appropriate treatment options.
-
Push-out bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a hydraulic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide as a vehicle
-
Ju-Ha Park, Hee-Jin Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e8. Published online January 20, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e8
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
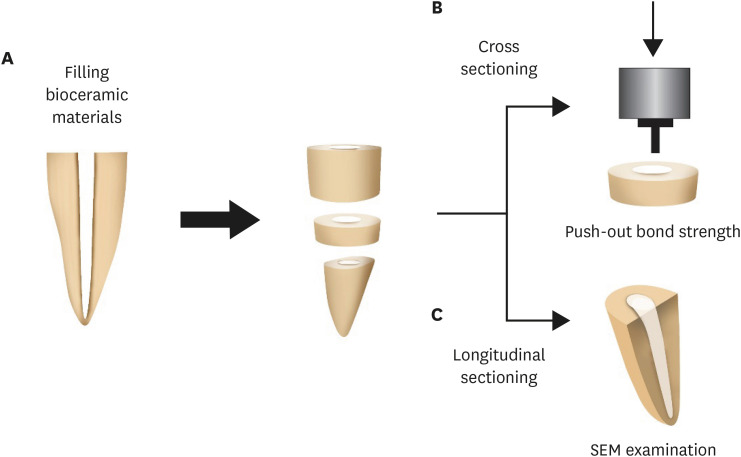
This study was designed to evaluate the parameters of bonding performance to root dentin, including push-out bond strength and dentinal tubular biomineralization, of a hydraulic bioceramic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide (Endocem MTA Premixed) in comparison to a conventional powder-liquid–type cement (ProRoot MTA). Materials and MethodsThe root canal of a single-rooted premolar was filled with either ProRoot MTA or Endocem MTA Premixed (n = 15). A slice of dentin was obtained from each root. Using the sliced specimen, the push-out bond strength was measured, and the failure pattern was observed under a stereomicroscope. The apical segment was divided into halves; the split surface was observed under a scanning electron microscope, and intratubular biomineralization was examined by observing the precipitates formed in the dentinal tubule. Then, the chemical characteristics of the precipitates were evaluated with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopic (EDS) analysis. The data were analyzed using the Student’s t-test followed by the Mann-Whitney U test (p < 0.05). ResultsNo significant difference was found between the 2 tested groups in push-out bond strength, and cohesive failure was the predominant failure type. In both groups, flake-shaped precipitates were observed along dentinal tubules. The EDS analysis indicated that the mass percentage of calcium and phosphorus in the precipitate was similar to that found in hydroxyapatite. ConclusionsRegarding bonding to root dentin, Endocem MTA Premixed may have potential for use as an acceptable root-end filling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of intratubular biomineralization between in vivo and in vitro conditions
Sieun Nam, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2026; 68(1): 30. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(7): 1989. CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical and radiographic outcome of premixed injectable mineral trioxide aggregate and conventional mineral trioxide aggregate as pulpotomy medicaments in primary molars – A split-mouth randomized control trial
U. S. Aiswarya, Sharan S. Sargod, Sundeep K. Hegde, H. T. Ajay Rao, Nanditha Hegde
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2025; 43(4): 559. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Removal efficiency of a fast setting pozzalan-based bioactive cement: a micro CT study
Feyza Çetinkaya, Ahter Şanal Çıkman, Ali Keleş, Banu Arıcıoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity and Sustained Effectiveness of Calcium Silicate-Based Cement as a Root-End Filling Material against Enterococcus faecalis
Seong-Hee Moon, Seong-Jin Shin, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Materials.2023; 16(18): 6124. CrossRef
-
3,400
View
-
94
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
-
Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e30. Published online July 29, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e30
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
We report the surgical endodontic treatment of a maxillary first premolar with a lateral lesion that originated from an accessory canal. Although lesions originating from accessory canals frequently heal with simple conventional endodontic therapy, some lesions may need additional and different treatment. In the present case, conventional root canal retreatment led to incomplete healing with the need for further treatment (i.e., surgery). Surgical endodontic management with a fast-setting calcium silicate cement was performed on the accessory canal using a dental operating microscope. At the patient's 9-month recall visit, the lesion was resolved upon radiography. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Predictive analysis of root canal morphology in relation to root canal treatment failures: a retrospective study
Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan, P. J. Nagarathna, Sudhir Rama Varma, Jayaraj Kodangattil Narayanan, Santosh R. Patil
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of internal replacement resorption of two maxillary central incisors with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography as the diagnostic tool: a case report and review of literature
Fatemeh Eskandari, Safoora Sahebi, Negar Ghorbani Jahandizi, Hossein Mofidi
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
-
1,700
View
-
17
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a calcium hydroxide paste using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone as a vehicle
-
Myung-Jin Lim, Hyun-Jin Jang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):290-300. Published online October 20, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.290
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study investigated the removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a newly developed calcium hydroxide paste (cleaniCal, Maruchi) using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone (NMP) as a vehicle in comparison with ApexCal (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Calcipex II (Nishika), which use different vehicles such as polyethylene glycol and propylene glycol, respectively. Materials and MethodsThirty maxillary premolars with oval-shaped canals were divided into 3 groups and the teeth were filled with one of the pastes. After removal of the paste, micro-computed tomographic (μ-CT) imaging was obtained to assess the volume of residual paste in the root canal of each tooth. The teeth were then split longitudinally and the area of the paste-coated surface was evaluated by stereomicroscopy. The cytotoxicity of each product was assessed using an agar overlay assay. The effect of each vehicle on cell viability was evaluated using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's tests to detect any significance (p < 0.05). ResultsIn the μ-CT and stereomicroscopic analysis, cleaniCal exhibited less remnants of medicament than ApexCal and Calcipex. cleaniCal showed a higher cytotoxicity than the other pastes in the agar overlay assay. Furthermore, NMP exhibited lower cell viability compared to the other vehicles. ConclusionscleaniCal showed better removal efficacy compared to the other products. However, clinicians should be aware of the higher cytotoxicity of the NMP-based material and consider its possible adverse effects on periradicular tissue when it is overfilled.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
Dohee Kim, Young Kim, Jeong Joon Han
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic effects of reduced graphene oxide on the antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments containing different vehicles
Mi-Ah Kim, Min-Kyeong Kim, Eun-Sook Kang, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - Lipoteichoic Acid from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG as a Novel Intracanal Medicament Targeting Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm Formation
Ji-Young Yoon, Somin Park, Dongwook Lee, Ok-Jin Park, WooCheol Lee, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2024; 62(10): 897. CrossRef - Rheological properties and handling characteristics of four injectable calcium hydroxide pastes
Min-Jung KIM, In-Bog LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 796. CrossRef - Role of vehicles on antimicrobial efficacy of calcium hydroxide
Dikshya Purohit, Shronika, Pradyumna Misra, Gaurav Jain, Preeti Shukla
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2023; 13: 9. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Using Biomimetic Material in a 9-Year-Old Boy
Sahili Mungekar-Markandey, Ashwin Jawdekar
Journal of Dental Research and Review.2022; 9(4): 320. CrossRef - Sonic irrigation for removal of calcium hydroxide in the apical root canal: A micro-CT and light-coupled tracking analysis
Wonjoon Moon, Shin Hye Chung, Juhea Chang, Zhaoqiang Zhang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0268791. CrossRef - Effect of N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Mi-Ah KIM, Prasanna NEELAKANTAN, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 774. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis, structure, and theoretical studies of a calcium complex of a unique dianion derived from 1-methylpyrrolidin-2-one
Ray J. Butcher, Andrew P. Purdy, Paul A. Brown, Daniel Gunlycke
Acta Crystallographica Section E Crystallographic Communications.2021; 77(1): 70. CrossRef - Effect of a calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicament containing N-2-methyl pyrrolidone as a vehicle against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm
Taegun KIM, Mi-Ah KIM, Yun-Chan HWANG, Vinicius ROSA, Massimo DEL FABBRO, Kyung-San MIN
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,224
View
-
11
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Recognition and management of palatogingival groove for tooth survival: a literature review
-
Hee-Jin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):77-86. Published online April 12, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.77
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Palatogingival groove (PGG) is an anomaly in the maxillary anterior teeth, often accompanied by the area of bony destruction adjacent to the teeth with no carious or traumatic history. The hidden trap in the tooth can harbor plaque and bacteria, resulting in periodontal destruction with or without pulpal pathologic change. Related diseases can involve periodontal destruction, combined endodontic-periodontal lesions, or separate endodontic and periodontal lesions. Disease severity and prognosis related to PGG depend on several factors, including location, range, depth, and type of the groove. Several materials have been used and recommended for cases of extensive periodontal destruction from PGG to remove and block the inflammatory source and recover the health of surrounding periodontal tissues. Even in cases of severe periodontal destruction, several studies have reported favorable treatment outcomes with proper management. With new options in diagnosis and treatment, clinicians need a detailed understanding of the characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of PGG to successfully manage the condition. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Prevalence of Palatal Grooves on Maxillary Anterior Teeth Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Oscar Lozano González, Marco Felipe Salas Orozco, Nuria Patiño Marín, Paul V. Abbott, Marc Garcia-Font, Francesc Abella Sans
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(1): 14. CrossRef - Endodontic bioceramics: current and futurity aspects
Roma M, Karthik Shetty, Laxmish Mallya, Krishna Prasad Shetty
Frontiers in Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Unified Deep Learning Framework for Visual Diagnosis of Palatal Radicular Grooves in CBCT Scans: A Multicenter Validation Study
Qikui Zhu, Weitao Fu, Yeyu Lin, Jiaxing Li, Wenhui Tang, Ying Zhang, Rui Zhang, Guanfan Lu, Yao Lin, Jing Shen, Zhuan Bian, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic and Periodontal Treatment of a Two‐Rooted Maxillary Lateral Incisor With a Type III Palatoradicular Groove: A Case Report With 2‐Year Follow‐Up
Katsuhiro Takeda, Tomoya Naruse, Yohei Takahashi, Reina Kawai, Kimiaki Yuhi, Hideki Shiba, Barbara Lapinska
Case Reports in Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-year follow-up case report: root canal treatment combined with intentional replantation for treating type III palatogingival groove in a maxillary lateral incisor
Jixu Jia, Miao Cheng, Sumeng Shi, Yanchun Qiao
Frontiers in Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove and its association with periapical lesions and periodontal bone loss: a cone beam computed tomography study
Dilan Pelin Yildirim, Selin Goker Kamali
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Morphology and Prevalence of Palatoradicular Grooves on Affected Maxillary Anterior Teeth Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: An Institutional Retrospective Study
Dilara Baştuğ, Leyla Benan Ayrancı
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 8031. CrossRef - Sulco palato-gengival e suas consequências: Revisão de literatura
Marielli de Paula Gonçalves, Maria Júlia Ribeiro Chalita Vieira, Mikaelly Kawany Martins da Silva, Fabiana Tavares Lunardi Palhari, Maria Isabel Gonçalves Fialho
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(8): e5014849388. CrossRef - Credibility of Intentional Reimplantation Techniques for Periodontally Compromised Teeth: A Report of Two Cases
Satarupa Suklabaidya, Ilakiya Mathi, Kennedy Babu, Gandhimadhi D, Manoj Margabandhu
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Palatal Radicular Groove in upper Lateral Incisors: A CBCT study at Isfahan Azad dental school
Amirreza Zefreh, Azadeh Torkzadeh, Hajar Shekarchizadeh, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Rojin Ardalani
Contemporary Orofacial Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A classification of radicular grooves from the perspective of periodontology
Huxiao Li, Zhaowei Tai, Jiachen Dong, Zhongchen Song
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Root Canal Therapy: Translational Innovations and the Role of Nanoparticles in Endodontic Treatment
Noha M. Badawi, Mohamed M. Kataia, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mozhgan Afshari
Journal of Nanotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation to estimate the prevalence of palatogingival groove in the maxillary anterior teeth and its radiographic characteristics: An institutional retrospective study
Mousumi Biswas, Dibyendu Mazumdar, Binayak Saha, Siddhi Agarwala, Kallol Kumar Saha, Kuntal Chowdhury
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 233. CrossRef - A Three-Dimensional Assessment of a Type I Shallow Palatogingival Groove by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ramachandra Reddy Gowda Venkatesha, Karthik Rajaram Mohan, Saramma Mathew Fenn, Sabitha Gokulraj, Kumar Appusamy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches of Palatogingival Groove: A Systematic Review
Greta Venskutė
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Palatal groove associated with periodontal lesions: a systematic review illustrated by a decisional tree for management
Yvan Gaudex, Vianney Gandillot, Isabelle Fontanille, Philippe Bouchard, Stephane Kerner, Maria Clotilde Carra
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Palatogingival Groove: The Known–unknown Devourer
Sandeep Tandon, Rinku Mathur, Ambika S Rathore, Tripti S Rai, Kanchan Kumari Dhaker, Sumedha Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(S1): S95. CrossRef - Nomogram to predict radicular grooves in maxillary lateral incisors in preoperative orthodontic population
Xiuneng Zhou, Jie Deng, Nianke Liu, Chunhui Yang, Shiyu Li, Yaling Song
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Palatogingival Groove in Maxillary Lateral Incisor: A Report of a Rare Case With a Brief Review of Literature
Irfan Ansari, Sanjay Miglani, Vijay Yadav, Shamimul Hasan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove affecting maxillary anterior teeth in Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomographic study with literature review
Ali Ibrahim Aljuailan, Roqayah Aljuailan, Rahul N. Gaikwad, Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi, Nasser Rufaydan Alamri
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(8): 1039. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Interdisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management of the tooth with type III palatogingival groove
Harakh Chand Baranwal, Jyoti Yadav
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 211. CrossRef - Progress in Diagnosis and Treatment of Palatogingival Groove
倩 郑
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 2723. CrossRef - Palatogingival grooves associated with periodontal bone Loss of maxillary incisors in a Chinese population
Rui Zhang, Jie Xiong, Markus Haapasalo, Ya Shen, Liuyan Meng
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 313. CrossRef - Surgical management of lateral lesions with intentional replantation in single-rooted mandibular first premolars with radicular groove
Ya-Hsin Yu, Minje Kim, Samuel Kratchman, Bekir Karabucak
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(4): 371. CrossRef - Management of the palato-radicular groove with a periodontal regenerative procedure and prosthodontic treatment: A case report
Dan-Hua Ling, Wei-Ping Shi, Yan-Hong Wang, Dan-Ping Lai, Yan-Zhen Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(17): 5732. CrossRef - Combined Periodontal and Endodontic Management of Palatal Radicular Groove with Platelet‐Rich Fibrin and Biodentine®
Arjun Hari Rijal, Bhageshwar Dhami, Pratistha Ghimire, Konstantinos Michalakis
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intentional replantation combined root resection therapy for the treatment of type III radicular groove with two roots: A case report
Dan Tan, Shi-Ting Li, Hao Feng, Zhong-Chao Wang, Cai Wen, Min-Hai Nie
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(20): 6991. CrossRef - DENTAL DEFECTS WITH SUBGINGIVAL EXTENSION: A RESTORATIVE CONUNDRUM
Seema Yadav
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 20. CrossRef - Misdiagnosis or Missed Diagnosis? Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Aided Multidisciplinary Management of Maxillary Central Incisor with Palatogingival Groove
R. Kurinji Amalavathy, K.M. Vidya, Sonali Nabil Sarooshi, Hrudi Sundar Sahoo
Indian Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 13(1): 46. CrossRef - Root and Root Canal Morphology: Study Methods and Classifications
Duaa M Shihab , Anas F Mahdee
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2021; 33(4): 11. CrossRef - Prevalence and radiological characteristics of palatogingival groove: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study in an Indian cohort
MS Lekshmi, Sheetal Sharma, ShaliniR Gupta, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 359. CrossRef - Successful Multidisciplinary Management of an Endodontic‐Periodontal Lesion Associated With a Palato‐Radicular Groove: A Case Report
Diksha Katwal, Jennifer K. Fiorica, Jane Bleuel, Stephen J. Clark
Clinical Advances in Periodontics.2020; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Anatomical, microbiological, and genetic considerations in treatment of Chinese periodontal patients
Edwin X. J. Goh, Marianne M. A. Ong
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A new system for classifying tooth, root and canal anomalies
H. M. A. Ahmed, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(4): 389. CrossRef
-
8,199
View
-
173
Download
-
35
Crossref
-
Effects of proanthocyanidin, a crosslinking agent, on physical and biological properties of collagen hydrogel scaffold
-
Yoorina Choi, Hee-Jin Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):296-303. Published online October 4, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.296
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effects of proanthocyanidin (PAC), a crosslinking agent, on the physical properties of a collagen hydrogel and the behavior of human periodontal ligament cells (hPDLCs) cultured in the scaffold. Materials and MethodsViability of hPDLCs treated with PAC was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The physical properties of PAC treated collagen hydrogel scaffold were evaluated by the measurement of setting time, surface roughness, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The behavior of the hPDLCs in the collagen scaffold was evaluated by cell morphology observation and cell numbers counting. ResultsThe setting time of the collagen scaffold was shortened in the presence of PAC (p < 0.05). The surface roughness of the PAC-treated collagen was higher compared to the untreated control group (p < 0.05). The thermogram of the crosslinked collagen exhibited a higher endothermic peak compared to the uncrosslinked one. Cells in the PAC-treated collagen were observed to attach in closer proximity to one another with more cytoplasmic extensions compared to cells in the untreated control group. The number of cells cultured in the PAC-treated collagen scaffolds was significantly increased compared to the untreated control (p < 0.05). ConclusionsOur results showed that PAC enhanced the physical properties of the collagen scaffold. Furthermore, the proliferation of hPDLCs cultured in the collagen scaffold crosslinked with PAC was facilitated. Conclusively, the application of PAC to the collagen scaffold may be beneficial for engineering-based periodontal ligament regeneration in delayed replantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Proliferative Effect of Proanthocyanidins on HGF-1 and HPDLF Cells: An In Vitro Study
Evelina Alkimavičienė, Nomeda Basevičienė, Arvydas Strazdauskas, Rasa Banienė, Nijolė Savickienė
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2098. CrossRef - A highly biocompatible CE-crosslinked collagen implant with exceptional anti-calcification and collagen regeneration capabilities for aging skin rejuvenation
Qi Wang, Huiyu Yan, Linyan Yao, Wenhua Li, Jianxi Xiao
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2024; 12(18): 4467. CrossRef - Dexamethasone release from hyaluronic acid microparticle and proanthocyanidin-gelatin hydrogel in sciatic tissue regeneration
Kazem Javanmardi, Hamideh Shahbazi, Ava Soltani Hekmat, Mehdi Khanmohammadi, Arash Goodarzi
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New Materials Based on Collagen and Taxifolin Derivatives: Production and Properties
Yu. V. Shatalin, M. I. Kobyakova, V. S. Shubina
Биологические мембраны Журнал мембранной и клеточной биологии.2024; 41(1): 82. CrossRef - Modulation of Adhesion and Migration of NIH/3T3 Cells in Collagen Materials by Taxifolin Derivatives
Yu. V. Shatalin, M. I. Kobyakova, V. S. Shubina
Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology.2023; 17(S1): S85. CrossRef - Development and characterization of crosslinked k-carrageenan/sericin blend with covalent agents or thermal crosslink for indomethacin extended release
Wedja Timóteo Vieira, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, Laura de Oliveira Nascimento, Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 246: 125558. CrossRef - New Challenges and Prospective Applications of Three-Dimensional Bioactive Polymeric Hydrogels in Oral and Craniofacial Tissue Engineering: A Narrative Review
Gamal Abdel Nasser Atia, Hany K. Shalaby, Naema Goda Ali, Shaimaa Mohammed Morsy, Mohamed Mohamady Ghobashy, Hager Abdel Nasser Attia, Paritosh Barai, Norhan Nady, Ahmad S. Kodous, Hasi Rani Barai
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(5): 702. CrossRef - Polyphenols: Bioavailability, Microbiome Interactions and Cellular Effects on Health in Humans and Animals
Michael B. Scott, Amy K. Styring, James S. O. McCullagh
Pathogens.2022; 11(7): 770. CrossRef - Advances of Hydrogel Therapy in Periodontal Regeneration—A Materials Perspective Review
Maoxue Li, Jiaxi Lv, Yi Yang, Guoping Cheng, Shujuan Guo, Chengcheng Liu, Yi Ding
Gels.2022; 8(10): 624. CrossRef - Collagen stabilization by natural cross-linkers: A qualitative and quantitative FTIR study on ultra-thin dentin collagen model
Rong WANG, Tyler STANLEY, Xiaomei YAO, Hang LIU, Yong WANG
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(3): 440. CrossRef - Cross-Linking Agents for Electrospinning-Based Bone Tissue Engineering
Dong-Jin Lim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5444. CrossRef - Dense lamellar scaffold, biomimetically inspired, for reverse cardiac remodeling: Effect of proanthocyanidins and glutaraldehyde
Thais Alves, Juliana Ferreira Souza, Venancio Alves Amaral, Alessandra Candida Rios, Tais Costa, Kessi Crescencio, Fernando Batain, Denise Grotto, Renata Lima, Lindemberg Silveira Filho, Jose Oliveira Junior, Patricia Severino, Norberto Aranha, Marco Chau
Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology.2021; 42(2): 248. CrossRef - The effect of the cross-linker ratio used in gellan gum biomaterial synthesis on biomineralization
Serbülent TÜRK, Burak ÜNLÜ, Mahmut ÖZACAR
Bulletin of Biotechnology.2021; 2(2): 27. CrossRef - The recent advances in scaffolds for integrated periodontal regeneration
Hyun Nyun Woo, Young Joon Cho, Solaiman Tarafder, Chang H. Lee
Bioactive Materials.2021; 6(10): 3328. CrossRef - Plant based cross-linkers for tissue engineering applications
Abhishek Indurkar, Ashish Pandit, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Journal of Biomaterials Applications.2021; 36(1): 76. CrossRef - Plant-based biomaterials in tissue engineering
Abhishek Indurkar, Ashish Pandit, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Bioprinting.2021; 21: e00127. CrossRef - Traditional Chinese Medicine and orthopedic biomaterials: Host of opportunities from herbal extracts
Huijuan Tang, Andrell Hosein, Monica Mattioli-Belmonte
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 120: 111760. CrossRef - Adsorption of Gold Ions onto Sericin and Alginate Particles Chemically Crosslinked by Proanthocyanidins: a Complete Fixed-Bed Column Study
Nilza Tatiane das Graças Santos, Richard Landers, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.2020; 59(1): 318. CrossRef - Proanthocyanidin as a crosslinking agent for fibrin, collagen hydrogels and their composites with decellularized Wharton’s-jelly-extract for tissue engineering applications
Elham Hasanzadeh, Narges Mahmoodi, Arefeh Basiri, Faezeh Esmaeili Ranjbar, Zahra Hassannejad, Somayeh Ebrahimi-Barough, Mahmoud Azami, Jafar Ai, Vafa Rahimi-Movaghar
Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers.2020; 35(6): 554. CrossRef - Hydrogels for the Delivery of Plant-Derived (Poly)Phenols
Nicola Micale, Andrea Citarella, Maria Sofia Molonia, Antonio Speciale, Francesco Cimino, Antonella Saija, Mariateresa Cristani
Molecules.2020; 25(14): 3254. CrossRef - Natural biopolymer‐based hydrogels for use in food and agriculture
Miri Klein, Elena Poverenov
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2020; 100(6): 2337. CrossRef - Grape Seed-Inspired Smart Hydrogel Scaffolds for Melanoma Therapy and Wound Healing
Hongshi Ma, Quan Zhou, Jiang Chang, Chengtie Wu
ACS Nano.2019; 13(4): 4302. CrossRef - Improvement of the Physical Properties of Guided Bone Regeneration Membrane from Porcine Pericardium by Polyphenols-Rich Pomace Extract
Nazario Russo, Clara Cassinelli, Elisa Torre, Marco Morra, Giorgio Iviglia
Materials.2019; 12(16): 2564. CrossRef - Novel Biomedical Applications of Crosslinked Collagen
Lisha Gu, Tiantian Shan, Yu-xuan Ma, Franklin R. Tay, Lina Niu
Trends in Biotechnology.2019; 37(5): 464. CrossRef - The prospects of collagen as a basis for curable and activated osteoplastic materials
N. L. Fatkhudinova, A. V. Vasilyev, T. B. Bukharova, E. O. Osidak, N. V. Starikova, S. P. Domogatsky, D. V. Goldshtein, A. A. Kulakov
Stomatologiya.2018; 97(6): 78. CrossRef
-
1,886
View
-
8
Download
-
26
Crossref
-
In vitro evaluation of a newly produced resin-based endodontic sealer
-
Yoo-Seok Song, Yoorina Choi, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Chan-Ui Hong, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):189-195. Published online July 26, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.189
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
A variety of root canal sealers were recently launched to the market. This study evaluated physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability of a newly launched resin-based sealer (Dia-Proseal, Diadent) compared to the existing root canal sealers (AHplus, Dentsply DeTrey and ADseal, Metabiomed). Materials and MethodsThe physicochemical properties of the tested sealers including pH, solubility, dimensional change, and radiopacity were evaluated. Biocompatibility was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For microleakage test, single-rooted teeth were instrumented, and obturated with gutta-percha and one of the sealers (n = 10). After immersion in 1% methylene blue solution for 2 weeks, the specimens were split longitudinally. Then, the maximum length of staining was measured. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey test (p = 0.05). ResultsDia-Proseal showed the highest pH value among the tested sealers (p < 0.05). ADseal showed higher dimensional change compared to AHplus and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The solubility values of AHplus and Dia-Proseal were similar, whereas ADseal had the lowest solubility value (p < 0.05). The flow values of sealer in increasing order were AHplus, DiaProseal, and ADseal (p < 0.05). The radiopacity of AHplus was higher than those of ADseal and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The cell viability of the tested materials was statistically similar throughout the experimental period. There were no significant differences in microleakage values among the tested samples. ConclusionsThe present study indicates that Dia-Proseal has acceptable physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Comparison of Apical Sealing Ability of Different Endodontic Sealers – An In Vitro Study
Supriya Patil, Rahul Singh, B Jyothi Lekshmi, Sameer Ahmed Khan, H Shalini, Prashanth Kumar Katta
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S513. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of ICON resin infiltration and bioactive glass adhesive for managing initial caries lesions using quantitative light-induced fluorescence: a randomized clinical trial
Zakereyya S.M. Albashaireh, Susan N. Al-Khateeb, Malak K. Altallaq
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 159: 105853. CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparison of Epoxy Resin Sealer Removal During Endodontic Retreatment
Prashant A Bondarde, Aditi S Patkar, Aishwarya R Pawar, Rukmini Pande, Akshata Deshpande, Rachana S Agrawal, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereomicroscopic evaluation of sealing ability of four different root canal sealers: an in-vitro study
Sonam Sah, Panna Mangat, Ajay Kumar, Neha Sah, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Marco Di Blasio, Gabriele Cervino, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological investigation of resinous endodontic sealers containing calcium hydroxide
Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Francine Benetti, Marina Tolomei Sandoval Cury, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Ana Cláudia Rodrigues da Silva, Rogério de Castilho Jacinto, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, E
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0287890. CrossRef - Comparison of the apical seal obtained by Adseal, Proseal, and AH26 sealers in root canal obturation with lateral compaction technique
Akam Saeidi, Romina Hajipour, Elham Mahmoudi, Farideh Feizi, Soraya Khafri
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Calcium Silicate-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Sealers: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Nezar Boreak, Mazen Ahmed Qadi, Faisal Hadi Khormi, Luay Mutaen Faqiri, Sadeem Omar Zaylai, Yaser Ali Jad, Bassam Ali Hamdi, Asayil Juraybi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(8): 610. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength of bioceramic and epoxy sealers after using various final irrigants: An in vitro study
Chandrasekhar Veeramachaneni, Swathi Aravelli, Sreeja Dundigalla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(2): 145. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Reinforcement Using MTA-based, Epoxy Resin-based, and Silicone-based Endodontic Sealers in Canals Instrumented with Single-file Rotary System: An In Vitro Study
Reshma Rajasekhar, Varsha Maria Sebastian, Farhat Nasreen, Pramod Junjanna, Azeem Hassan, Venkidesh Hari Maratt
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1098. CrossRef - The Short-Term Antibacterial Activity of Three Selected Endodontic Sealers against Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Culture
Matej Rosa, Yuliya Morozova, Roman Moštěk, Pavel Holík, Lucia Somolová, Barbora Novotná, Soňa Zábojníková, Kateřina Bogdanová, Kateřina Langová, Iva Voborná, Lenka Pospíšilová, Josef Paul Kovařík
Life.2022; 12(2): 158. CrossRef - Antimicrobial potential of AH Plus supplemented with bismuth lipophilic nanoparticles on E. faecalis isolated from clinical isolates
Jesús Alejandro Torres-Betancourt, Rene Hernandez-Delgadillo, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Juan Manuel Solís-Soto, Nayely Pineda-Aguilar, Maria Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Rosa Isela Sánchez-Nájera, Shankararaman Chellam, Claudio Cabral-Romero
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry Analysis and Radiopacity of Five Different Root Canal Sealers
Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Burcu Serefoglu, Pelin Güneri, Michael Hülsmann, Mehmet Kemal Caliskan
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(5): 1. CrossRef - Ultrasonic vibration and thermo‐hydrodynamic technique for filling root canals: Technical overview and a case series
Yong‐Sik Cho
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1668. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Two Generations of MTA-Based Root Canal Sealers
Sawsan Abu Zeid, Hadeel Yaseen Edrees, Abeer Abdulaziz Mokeem Saleh, Osama S. Alothmani
Materials.2021; 14(20): 5911. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiopacity of endodontic materials using two models for conversion to millimeters of aluminum
Victor Manuel OCHOA-RODRÍGUEZ, Jorge Homero WILCHES-VISBAL, Barbara ROMA, Hernán COAGUILA-LLERENA, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO, Andréa GONÇALVES, Rubens SPIN-NETO, Gisele FARIA
Brazilian Oral Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - SELECTED PROPERTIES OF CONTEMPORARY ENDODONTIC SEALERS: PART 1
M Rosa, Y Morozova, R Moštěk, A Jusku, V Kováčová, L Somolová, I Voborná, T Kovalský
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2020; 120(4): 107. CrossRef - Calcium phosphates as fillers for methacrylate-based sealer
Flávia Veronezi Rostirolla, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Fabio Rocha Bohns, Fernando Freitas Portella, Susana Maria Werner Samuel, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(12): 4417. CrossRef - Do in vitro solubility studies on endodontic sealers demonstrate a high level of evidence? A systematic review
Ankur Razdan, Ana Raquel Benetti, Lars Bjørndal
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(4): 253. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of two epoxy resin-based sealants: Topseal® and Adseal™. a comparative study
Julio César Cardona-Hidalgo, José Manuel González-Carreño, Julio César Avendaño-Rueda
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Materials.2019; 12(15): 2411. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Epoxy Resin-Based and Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
-
2,083
View
-
21
Download
-
27
Crossref
-
Evaluation of reparative dentin formation of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine and BioAggregate using micro-CT and immunohistochemistry
-
Jia Kim, Young-Sang Song, Kyung-San Min, Sun-Hun Kim, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):29-36. Published online January 4, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.29
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of two new calcium silicate-based pulp-capping materials (Biodentine and BioAggregate) to induce healing in a rat pulp injury model and to compare them with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). Materials and MethodsEighteen rats were anesthetized, cavities were prepared and the pulp was capped with either of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine, or BioAggregate. The specimens were scanned using a high-resolution micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) system and were prepared and evaluated histologically and immunohistochemically using dentin sialoprotein (DSP). ResultsOn micro-CT analysis, the ProRoot MTA and Biodentine groups showed significantly thicker hard tissue formation (p < 0.05). On H&E staining, ProRoot MTA showed complete dentin bridge formation with normal pulpal histology. In the Biodentine and BioAggregate groups, a thick, homogeneous hard tissue barrier was observed. The ProRoot MTA specimens showed strong immunopositive reaction for DSP. ConclusionsOur results suggest that calcium silicate-based pulp-capping materials induce favorable effects on reparative processes during vital pulp therapy and that both Biodentine and BioAggregate could be considered as alternatives to ProRoot MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of microhardness, monomer conversion, and antibacterial properties of an experimental pulp-capping material containing collagen–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and/or chlorhexidine
Hacer Balkaya, Sezer Demirbuğa, Fatih Duman, Ahmet Ceylan, Ömer Aydın
Odontology.2026; 114(1): 204. CrossRef - Clinical applications and classification of calcium silicate-based cements based on their history and evolution: a narrative review
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diode laser irradiation along with Biodentine on dental pulp stem cell proliferation and pluripotent gene expression
Ladan Alborzy, Sedighe Sadat Hashemikamangar, Mahshid Hodjat, Nasim Chiniforush, Behnaz Behniafar
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different treatment methods on apical closure and treatment success in immature permanent first molars with reversible pulpitis
Muhammed ALAGOZ, Sera SIMSEK DERELIOĞLU
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Novelties in pulp capping materials
Vani Grover, Namith Rai, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2025; 41(91): 3086. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of pulp response to alendronate and Biodentine as pulp capping agents: an animal study
Thangavel Boopathi, Sekar Manimaran, Joseline Charles Kerena, Mathew Sebeena, Kumaravadivel Karthick, Natesan Thangaraj Deepa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Clinical and Radiographic Success Rate of Bioceramic Premix vs Biosilicate-based Medicament as Indirect Pulp Treatment Materials in Primary Molars: A Double-blind Randomized Trial with a Follow-up of 12 Months
Aditi Mathur, Meenakshi Nankar, Sunnypriyatham Tirupathi, Payal Kothari, Rashmi Chauhan, Ashrita Suvarna
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(7): 748. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Evaluation of biocompatibility and bioactive potential of Well-Root PT by comparison with ProRoot MTA and Biodentine
Yong Kwon Chae, Ju Ri Ye, Ok Hyung Nam
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2218. CrossRef - Dentine Remineralisation Induced by “Bioactive” Materials through Mineral Deposition: An In Vitro Study
Marta Kunert, Ireneusz Piwonski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Francesco Inchingolo, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2024; 14(3): 274. CrossRef - Different pulp capping agents and their effect on pulp inflammatory response: A narrative review
Mustafa Tariq Mutar, Anas F Mahdee
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1295. CrossRef - Clinical application of calcium silicate-based bioceramics in endodontics
Xinyuan Wang, Yizhi Xiao, Wencheng Song, Lanxiang Ye, Chen Yang, Yuzhen Xing, Zhenglin Yuan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the pulp response following direct pulp capping with exogenous nitric oxide and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) a histologic study
Amirah Alnour, Ghassan Almohammad, Anas Abdo, Kinda Layous
Heliyon.2023; 9(7): e17458. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of dental pulp response to Biodentine, enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain), and mineral trioxide aggregate as direct pulp-capping agents – A randomized clinical trial
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ngairangbam Sanjeeta
Journal of Medical Society.2023; 37(3): 107. CrossRef - Effect of Intracoronal Sealing Biomaterials on the Histological Outcome of Endodontic Revitalisation in Immature Sheep Teeth—A Pilot Study
Elanagai Rathinam, Sivaprakash Rajasekharan, Heidi Declercq, Christian Vanhove, Peter De Coster, Luc Martens
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(4): 214. CrossRef - Restorative management of the posterior tooth that has undergone a pulpotomy
Nicholas N Longridge, James S Hyde, Fadi Jarad, Sondos Albadri
Dental Update.2023; 50(11): 932. CrossRef - Direct pulp capping procedures – Evidence and practice
Rafiqul Islam, Md Refat Readul Islam, Toru Tanaka, Mohammad Khursheed Alam, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Hidehiko Sano
Japanese Dental Science Review.2023; 59: 48. CrossRef - A novel analysis of the formation and resorption changes in dental hard tissue using longitudinal in vivo micro computed tomography
Yeon-Jee YOO, Joonil HWANG, So-Hyun PARK, Jaehong HWANG, Seungryong CHO, Sun-Young KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(5): 708. CrossRef - Evaluation of pH and Calcium Ion Diffusion from Intracanal MTA and Bioaggregate to Simulated External Resorption Cavities Through Dentinal Tubules
Umut AKSOY, Kaan POLATOĞLU, Feridun ŞAKLAR
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(3): 108. CrossRef - Pulpa Kuafajı ve Kuafaj Materyallerine Güncel Bir Bakış: Derleme
Dilek AKIN, Çiğdem ATALAYIN ÖZKAYA
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 617. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - Evaluation of shear bond strength of e-mineral trioxide aggregate and biodentine with glass ionomer cement
Hemalatha Hiremath, Aishwarya Singh Solanki, Shivangi Trivedi, Devansh Verma
Endodontology.2022; 34(2): 127. CrossRef - Multiple growth factors accommodated degradable submicron calcium sulfate hemihydrate/porous hydroxyapatite for dentin-pulp regeneration
Chih-Wen Chi, Bharathi Priya Lohanathan, Ching-Ching Wong, Che-Lun Chen, Hsun-Chang Lin, Yu-Chih Chiang
Biomaterials Advances.2022; 140: 213045. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF BLOOD CONTAMINATION ON SHEAR BOND STRENGTH OF CALCIUM SILICATE-BASED PULP CAPPING MATERIALS
Hasan Fatih YAVUZ, Güneş BULUT EYÜBOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 24(4): 371. CrossRef - Comparison of Four Dental Pulp-Capping Agents by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological Techniques—A Split-Mouth Design Ex Vivo Study
Jayanandan Muruganandhan, Govindarajan Sujatha, Saravanan Poorni, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Nezar Boreak, Ahmed Al-Kahtani, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hitesh Chohan, Shilpa Bhandi, A. Thirumal Raj, Alessio Zanza, Luca Testarelli, Shankargouda Patil
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3045. CrossRef - Effect of Naturally Occurring Biogenic Materials on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells (hDPSC): an In Vitro Study.
Prasanna T. Dahake, Vinod V. Panchal, Yogesh J. Kale, Mahesh V. Dadpe, Shrikant B. Kendre, Vijay M. Kumbar
Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine.2021; 7(4): 506. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Tailored 70S30C Bioactive glass induces severe inflammation as pulpotomy agent in primary teeth: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial
Yasmine Elhamouly, Rania M. El Backly, Dalia M. Talaat, Samia S. Omar, Maha El Tantawi, Karin M. L. Dowidar
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(6): 3775. CrossRef - Response of dental pulp capped with calcium-silicate based material, calcium hydroxide and adhesive resin in rabbit teeth
Cynthia Kassis, Pierre Khoury, Karim Corbani, Charbel Mansour, Louis Hardan, Ghassan Yared, Carole Chakar
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical expression of non-collagenous extracellular matrix molecules involved in tertiary dentinogenesis following direct pulp capping: a systematic review
C. Călin, M. Sajin, V.T. Moldovan, C. Coman, S.I. Stratul, A.C. Didilescu
Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger.2021; 235: 151674. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Indirect Pulp Treatment Materials for Primary Teeth: A Literature Review
Omar AES El Meligy, Afnan M Saber, Sumer M Alaki
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(6): 795. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of the regenerative potential of a novel treated dentin matrix hydrogel in direct pulp capping
Ahmed A. Holiel, Elsayed M. Mahmoud, Wegdan M. Abdel-Fattah, Khadiga Y. Kawana
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(4): 2101. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential of tailored amorphous multiporous calcium silicate glass for pulp capping regenerative endodontics—A preliminary assessment
Jie Liu, Chao-An Chen, Xiaofei Zhu, Brian R. Morrow, Ukrit Thamma, Tia J. Kowal, Hassan M. Moawad, Matthias M. Falk, Himanshu Jain, George T.-J. Huang
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 109: 103655. CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of direct pulp capping using a novel injectable treated dentin matrix hydrogel: a 2-year randomized controlled clinical trial
Ahmed A. Holiel, Elsayed M. Mahmoud, Wegdan M. Abdel-Fattah
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4621. CrossRef - Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA in vivo
Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydraulic cements for various intra-coronal applications: Part 1
Stephen J Bonsor, Josette Camilleri
Dental Update.2021; 48(8): 653. CrossRef - In vivo Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Calcium Silicate-Based Bioceramics in Endodontics
Wencheng Song, Wei Sun, Lili Chen, Zhenglin Yuan
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of dentinogenesis inducer biomaterials: an in vivo study
Anabela B. Paula, Mafalda Laranjo, Carlos-Miguel Marto, Siri Paulo, Ana M. Abrantes, Bruno Fernandes, João Casalta-Lopes, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Bio-Inductive Materials in Direct and Indirect Pulp Capping—A Review Article
Marta Kunert, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Materials.2020; 13(5): 1204. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Release of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 from Human Tooth Dentin after Application of Either ProRoot MTA or Biodentine as a Coronal Barrier
Kunlada Wattanapakkavong, Tanida Srisuwan
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(6): 701. CrossRef - Effect of Leptin on Odontoblastic Differentiation and Angiogenesis: An In Vivo Study
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Ji-Hyun Jang, Jeong-Tae Koh, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(11): 1332. CrossRef - Análise da composição química dos cimentos MTA Angelus® branco, cinza e HP Repair® através de Microscopia Eletrônica de Varredura (MEV) acoplada a Espectrômetro de Energia Dispersiva (EDS)
Gabriela Duarte Rocha SARZEDA, Marcelo Santos BAHIA, Paulo Victor Teixeira DORIGUÊTTO, Karina Lopes DEVITO, Anamaria Pessoa Pereira LEITE
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct Pulp Capping: Which is the Most Effective Biomaterial? A Retrospective Clinical Study
Anabela Paula, Eunice Carrilho, Mafalda Laranjo, Ana M. Abrantes, João Casalta-Lopes, Maria Filomena Botelho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel M. Ferreira
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3382. CrossRef - Characterization of Odontoblast-like Cell Phenotype and Reparative Dentin Formation In Vivo: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 241. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effects of calcium silicate cements on dental pulp cells: A systematic review
Ramy Emara, Karim Elhennawy, Falk Schwendicke
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 77: 18. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - The Relationship of Surface Characteristics and Antimicrobial Performance of Pulp Capping Materials
Cher Farrugia, Christie Y.K. Lung, Pierre Schembri Wismayer, Maria Teresa Arias-Moliz, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1115. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - Influence of Biodentine® - A Dentine Substitute - On Collagen Type I Synthesis in Pulp Fibroblasts In Vitro
Frangis Nikfarjam, Kim Beyer, Anke König, Matthias Hofmann, Manuel Butting, Eva Valesky, Stefan Kippenberger, Roland Kaufmann, Detlef Heidemann, August Bernd, Nadja Nicole Zöller, Dimitrios Karamichos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167633. CrossRef - Effect of an Experimental Direct Pulp-capping Material on the Properties and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Fan Yu, Yan Dong, Yan-wei Yang, Ping-ting Lin, Hao-han Yu, Xiang Sun, Xue-fei Sun, Huan Zhou, Li Huang, Ji-hua Chen
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,416
View
-
37
Download
-
57
Crossref
-
Reattachment of a fractured fragment with relined fiber post using indirect technique: a case report
-
Eun-Soo Kim, Kyung-San Min, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):324-328. Published online September 5, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.324
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Although fiber-reinforced posts have been widely used, they sometimes fail to obtain sufficient retention because of an extremely large canal space. To address this, several techniques have been introduced including relining of the fiber-reinforced posts. Here, we used a relined glass-fiber post to increase retention and fitness to the root canal in a crown reattachment case. The relining procedure was performed by using an indirect method on the working cast. This case also highlights the esthetic concerns regarding dehydration of the attached crown fragment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical Outcomes of Nonmetallic Customized Post-and-Core Systems: A Systematic Review
Jonathan Jun Xian Yuen, Yew Hin Beh, Zhi Kuan Saw, Hock Siang Chua
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,305
View
-
9
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Healing after horizontal root fractures: 3 cases with 2-year follow-up
-
Yoorina Choi, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee, Kyung-San Min, Su-Jung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):126-131. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.126
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Among dental traumas, horizontal root fractures are relatively uncommon injuries. Proper initial management and periodical evaluation is essential for the successful treatment of a root-fractured tooth. If pulpal necrosis develops, endodontic treatment is indicated, exclusively for the coronal fragment. Fragment diastases exert a great influence on healing at the fracture line and on pulpal necrosis. An adequately treated root-fractured tooth has a good prognosis. This case report describes the treatment and 2-yr follow up of 3 maxillary central incisors, first with horizontal root fracture, second with horizontal root fracture and avulsion, and third with horizontal root fracture and lateral luxation. All three cases were treated with mineral trioxide aggregate (ProRoot, Dentsply). During 2 yr of follow-up evaluation, the root-fractured teeth of the present patients were well retained in the arch, showing periodontal healing, even after endodontic treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Horizontal fracture of the tooth root: 3-year follow up study
Efka Zabokova-Bilbilova, Jasna Simonoska, Emilija Stefanovska, Mirjana Markovska-Arsovska
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2025; 41(91): 3061. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in maxillary central incisor with a horizontal mid root fracture after various management protocols
Kavitha Anantula, Bhavana Vankayala, SarjeevSingh Yadav
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 470. CrossRef - : The Use of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in The Treatment of Horizontal Root Fractures: A Case Presentation and Literature Update
Elif BALLIKAYA, Hamdi GÜNGÖR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 850. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef
-
2,515
View
-
22
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Washout resistance of fast-setting pozzolan cement under various root canal irrigants
-
Ga-Yeon Jang, Su-Jung Park, Seok-Mo Heo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):248-252. Published online November 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.248
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Fast-setting pozzolan cement (Endocem, Maruchi) was recently developed. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of various root canal irrigants on the washout of Endocem in comparison to the previously marketed mineral trioxide aggregate (ProRoot; Dentsply) in a furcal perforation model. Materials and MethodsProRoot and Endocem were placed into acrylic molds on moist Oasis. Each mold was then immediately exposed to either physiologic saline, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), or 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) under gentle shaking for five minutes. Washout testing was performed by scoring scanning electron microscope (SEM) images. ResultsEndocem exhibited higher washout resistance compared to ProRoot, especially in the NaOCl group. ConclusionsThese results suggest that Endocem can be considered a useful repair material for furcal perforation, especially in a single-visit scenario.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Harnessing and Optimizing α-TCP for Oral Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Dentistry
Wenbo Du, Yadong Guo, Janak Lal Pathak, Chen Xiaoshi, Hanfu Su, Liping Wang
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(1): 109288. CrossRef - The Washout Resistance of Bioactive Root-End Filling Materials—A Systematic Review
Joanna Falkowska-Ostrowska, Włodzimierz Dura
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(7): 2446. CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of L-ascorbic acid as an additive for improving the physical properties and setting behavior of fabricated calcium silicate cement
Yun-Jeong Park, Hyeon Seo, Yo-Han Song, Weon-Young Choi, Alphonse Umugire, Heejoo Ryu, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereomicroscopic Evaluation of Sealing Ability of Three Different Furcal Perforation Repair Materials: An In vitro Study
Sriparna De, N Sathyajith Naik, Shivangi Sharma, Pallavi Vashisth, Rasleen Dua, Priya Maheshwari
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 259. CrossRef - Chemical and physical properties of radiopaque Portland cement formulation with reduced particle size
Hoda Mohamed ELNAWAWY, Muralithran Govindan KUTTY, Noor Azlin YAHYA, Noor Hayaty ABU KASIM, Paul Roy COOPER, Josette CAMILLERI, Hany Mohamed Aly AHMED
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 672. CrossRef - The Washout Resistance of Bioactive Root-End Filling Materials
Joanna Falkowska, Tomasz Chady, Włodzimierz Dura, Agnieszka Droździk, Małgorzata Tomasik, Ewa Marek, Krzysztof Safranow, Mariusz Lipski
Materials.2023; 16(17): 5757. CrossRef - Effects of fast- and slow-setting calcium silicate–based root-end filling materials on the outcome of endodontic microsurgery: a retrospective study up to 6 years
Dohyun Kim, Hyunjung Lee, Minsun Chung, Sunil Kim, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(1): 247. CrossRef - Novel anti-biofouling bioactive calcium silicate-based cement containing 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine
Jae-Sung Kwon, Myung-Jin Lee, Ji-Young Kim, Dohyun Kim, Jeong-Hyun Ryu, Sungil Jang, Kwang-Mahn Kim, Chung-Ju Hwang, Sung-Hwan Choi, Jinkee Hong
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0211007. CrossRef - Surface and vertical dimensional changes of mineral trioxide aggregate and biodentine in different environmental conditions
Hacer Aksel, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevinc Askerbeyli Õrs, Eda Karaismailoğlu
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Push-out Bond Strength of Fast-setting Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Pozzolan-based Cements: ENDOCEM MTA and ENDOCEM Zr
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Nancy Kudsi Carvalho, Marta Reis da Costa Labanca Guberman, Marina Prado, Plinio Mendes Senna, Erick M. Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(5): 801. CrossRef - Dynamic intratubular biomineralization following root canal obturation with pozzolan‐based mineral trioxide aggregate sealer cement
Yeon‐Jee Yoo, Seung‐Ho Baek, Kee‐Yeon Kum, Won‐Jun Shon, Kyung‐Mi Woo, WooCheol Lee
Scanning.2016; 38(1): 50. CrossRef - Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
Jing-Ling Che, Jae-Hwan Kim, Seon-Mi Kim, Nam-ki Choi, Hyun-Joo Moon, Moon-Jin Hwang, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(1): 61. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of the Use of ProRoot Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Endocem as Direct Pulp Capping Materials: 3-month versus 1-year Outcomes
Youngjune Jang, Minju Song, Il-Sang Yoo, Yunjung Song, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(8): 1201. CrossRef - Odontogenic effects of a fast-setting calcium-silicate cement containing zirconium oxide
Kyoung-A KIM, Yeon-Mi YANG, Young-Sun KWON, Yun-Chan HWANG, Mi-Kyung YU, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2015; 34(4): 432. CrossRef - D90: The Strongest Contributor to Setting Time in Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Portland Cement
William N. Ha, Dale P. Bentz, Bill Kahler, Laurence J. Walsh
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1146. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of the Use of ProRoot Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Endocem as Direct Pulp Capping Materials
Minju Song, Minji Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(1): 11. CrossRef - Physical properties and biological/odontogenic effects of an experimentally developed fast-setting α-tricalcium phosphate-based pulp capping material
Jun-Bong Lee, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Ha Kim, Young-Sun Kwon, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
BMC Oral Health.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Surface Treatments on Morphology and Bond Strength to Composite Resin
Joo-Hee Shin, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1210. CrossRef
-
1,724
View
-
7
Download
-
19
Crossref
-
Comparison of the centering ability of Wave·One and Reciproc nickel-titanium instruments in simulated curved canals
-
Young-Jun Lim, Su-Jung Park, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):21-25. Published online February 26, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of newly marketed single-file instruments, Wave·One (Dentsply-Maillefer) and Reciproc (VDW GmbH), in terms of maintaining the original root canal configuration and curvature, with or without a glide-path. Materials and MethodsAccording to the instruments used, the blocks were divided into 4 groups (n = 10): Group 1, no glide-path / Wave·One; Group 2, no glide-path / Reciproc; Group 3, #15 K-file / Wave·One; Group 4, #15 K-file / Reciproc. Pre- and post-instrumented images were scanned and the canal deviation was assessed. The cyclic fatigue stress was loaded to examine the cross-sectional shape of the fractured surface. The broken fragments were evaluated under the scanning electron microscope (SEM) for topographic features of the cross-section. Statistically analysis of the data was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test (α = 0.05). ResultsThe ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1 and 2 mm levels was significantly lower in Group 1 (p < 0.05). The centering ratio at 3, 5, and 7 mm level were not significantly different. ConclusionsThe Wave·One file should be used following establishment of a glide-path larger than #15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of ProTaper, Mtwo, WaveOne, and Reciproc Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: In Vitro Study
M Remya, Asha Joseph, Prabath Singh, Anju Varughese, Pallavi Chandran, Deepthy Subramanian, S Vijay Kumar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(6): 589. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Canal transportation and centering ability of root canals prepared using rotary and reciprocating systems with and without PathFiles in cone-beam computed tomography-based three-dimensional molar prototypes
MSruthi Sunildath, Josey Mathew, Liza George, RV Vineet, Priya Thomas, Dhanya John
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 246. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciproc R25 File and Mtwo System Used in Continuous and Reciprocating Motion
Vincenzo Campanella, Leonardo Gianni, Antonio Libonati, Gianni Gallusi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(2): 171. CrossRef - Canal shaping with a reciprocating system is easy to learn
E. Muñoz, L. Forner, S. Garcet, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, C. Llena
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1244. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of HyFlex EDM and ProTaper Next Rotary Instruments in Curved Root Canals: A Micro-CT Study
Ahmed K Turkistani, Madiha M Gomaa, Lubna A Shafei, Loai Alsofi, Abdul Majeed, Emad AlShwaimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(6): 680. CrossRef - Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of ProTaper Next and 2Shape nickel–titanium files in simulated severe curved canals
Simone Staffoli, Taha Özyürek, Avi Hadad, Alex Lvovsky, Michael Solomonov, Hadas Azizi, Joe Ben Itzhak, Maurizo Bossù, Nicola M. Grande, Gianluca Plotino, Antonella Polimeni
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2018; 32(2): 52. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Rotary endodontics in primary teeth – A review
Sageena George, S. Anandaraj, Jyoti S. Issac, Sheen A. John, Anoop Harris
The Saudi Dental Journal.2016; 28(1): 12. CrossRef - Performance of Three Single Instrument Systems in the Preparation of Long Oval Canals
Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Fredson Marcio Acris de Carvalho, Flares Baratto-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2016; 27(2): 217. CrossRef - Quantitative transportation assessment in curved canals prepared with an off-centered rectangular design system
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal SILVA, Vania Cristina Gomes VIEIRA, Michele Dias Nunes TAMEIRÃO, Felipe Gonçalves BELLADONNA, Aline de Almeida NEVES, Erick Miranda SOUZA, Gustavo DE-DEUS
Brazilian Oral Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Cervical and Apical Enlargement Associated with the WaveOne System on the Transportation and Centralization of Endodontic Preparations
Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Kauhanna Vianna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 626. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Brushing Motion on the Cutting Behavior of 3 Reciprocating Files in Oval-shaped Canals
Shereen Alattar, Walid Nehme, Franck Diemer, Alfred Naaman
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 703. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue of instruments for endodontic glide path
Gianluca Gambarini, Gianluca Plotino, GianPaolo Sannino, Nicola Maria Grande, Alessio Giansiracusa, Lucila Piasecki, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Dina Al-Sudani, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2015; 103(1): 56. CrossRef - Influence of the glide path on various parameters of root canal prepared with WaveOne reciprocating file using cone beam computed tomography
Anil Dhingra, Nidhi Nagar, Vipul Sapra
Dental Research Journal.2015; 12(6): 534. CrossRef - Apical Transportation, Centering Ability, and Cleaning Effectiveness of Reciprocating Single-file System Associated with Different Glide Path Techniques
Guilherme Moreira de Carvalho, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Junior, Angela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido, Raphael Carlos Comelli Lia, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, André Augusto Franco Marques
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 2045. CrossRef - Influence of cervical preflaring on apical transportation in curved root canals instrumented by reciprocating file systems
Neisiana Barbieri, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marina Samara Baechtold, Gisele Maria Correr, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, João César Zielak, Flares Baratto-Filho
BMC Oral Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Assessment of Reciprocation in Endodontic Preparation: A Comprehensive Review—Part II: Properties and Effectiveness
Gianluca Plotino, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Nicola Maria Grande, Stephen Cohen, Frédéric Bukiet
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 1939. CrossRef - Influence of flexion angle of files on the decentralization of oval canals during instrumentation
Maria Antonieta Veloso Carvalho de OLIVEIRA, Letícia Duarte ALVES, Analice Giovani PEREIRA, Luís Henrique Araújo RAPOSO, João Carlos Gabrielli BIFFI
Brazilian Oral Research.2015; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Quantitative Transportation Assessment in Simulated Curved Canals Prepared with an Adaptive Movement System
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Michele Dias Nunes Tameirão, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1125. CrossRef - Efficacy of reciprocating and rotary systems for removing root filling material: A micro-computed tomography study
D. Helvacioglu-Yigit, A. Yilmaz, G. Kiziltas-Sendur, O. S. Aslan, P. V. Abbott
Scanning.2014; 36(6): 576. CrossRef - Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 104. CrossRef - Performance of RaCe Instrumentation System in Curved Root Canals: A Comprehensive Analysis by Three Study Methods
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Gilson Blitzkow Sydney, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Flares Baratto-Filho, Samantha Schaffer Pugsley Baratto, Paulo Sergio Cerri
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 230. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 167. CrossRef
-
1,661
View
-
8
Download
-
29
Crossref
-
Endodontic management of a C-shaped maxillary first molar with three independent buccal root canals by using cone-beam computed tomography
-
Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ok Hong, Wan Lee, Pyung-Sik Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):175-179. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.175
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to present a method for endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with unusual C-shaped morphology of the buccal root verified by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images. This rare anatomical variation was confirmed using CBCT, and nonsurgical endodontic treatment was performed by meticulous evaluation of the pulpal floor. Posttreatment image revealed 3 independent canals in the buccal root obturated efficiently to the accepted lengths in all 3 canals. Our study describes a unique C-shaped variation of the root canal system in a maxillary first molar, involving the 3 buccal canals. In addition, our study highlights the usefulness of CBCT imaging for accurate diagnosis and management of this unusual canal morphology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of C-shaped maxillary molars: case reports and review of literature
Ming Liu, Yanling Huang, Yixuan Wu, Yi Zhang, Zhisheng Zhang, Qianju Wu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Fused Rooted Maxillary First and Second Molars with Merged and C-shaped Canal Configurations: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Correlations in a Saudi Arabian Population
Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hemant Ramesh Chourasia, Ahmad Jabali, Abdulmajeed Almutairi, Gianluca Gambarini
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(10): 1209. CrossRef - C-shaped root canals of mandibular second molars in a Korean population: a CBCT analysis
Hee-Sun Kim, Daun Jung, Ho Lee, Yoon-Sic Han, Sohee Oh, Hye-Young Sim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of the Maxillary C-shaped Molar
Jorge N.R. Martins, António Mata, Duarte Marques, Craig Anderson, João Caramês
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(3): 383. CrossRef - Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 161. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 132. CrossRef
-
1,449
View
-
4
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
-
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):29-33. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.29
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microleakage of 4 temporary materials in teeth with Class II-type endodontic access preparations by using a glucose penetration model.
Materials and Methods
Glucose reaction test was performed to rule out the presence of any reaction between glucose and temporary material. Class II-type endodontic access preparations were made in extracted human premolars with a single root (n = 10). Each experimental group was restored with Caviton (GC), Spacer (Vericom), IRM (Dentsply-Caulk), or Fuji II(GC). Microleakage of four materials used as temporary restorative materials was evaluated by using a glucose penetration model. Data were analyzed by the one-way analysis of variance followed by a multiple-comparison Tukey test. The interface between materials and tooth were examined under a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results
There was no significant reaction between glucose and temporary materials used in this study. Microleakage was significantly lower for Caviton and Spacer than for Fuji II and IRM. SEM observation showed more intimate adaptation of tooth-restoration interfaces in Caviton and Spacer than in IRM and Fuji II.
Conclusions
Compared to IRM and Fuji II, Caviton and Spacer can be considered better temporary sealing materials in Class II-type endodontic access cavities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Sealing Ability, Water Absorption, and Solubility of Three Temporary Restorative Materials: An in vitro Study
AR Prabhakar, N Shantha Rani
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(2): 136. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef
-
2,113
View
-
11
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
-
Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):50-53. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.50
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is a useful diagnostic tool for identification of both internal and external root configurations. This case report describes the endodontic management of a lateral incisor with both dens invaginatus and external root irregularity by using CBCT. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment was performed on the lateral incisor with dens invaginatus. A perforation through the dens invaginatus and external concavity was repaired using mineral trioxide aggregate. After 18 mon of follow-up, there were no clinical symptoms. Recall radiographs appeared normal and showed healing of the periapical pathosis. The understanding of both internal root canal configuration and external root irregularity using CBCT can ensure predictable and successful results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cone-beam computed tomography for assessment of dens invaginatus in the Polish population
T. Katarzyna Różyło, Ingrid Różyło-Kalinowska, Magdalena Piskórz
Oral Radiology.2018; 34(2): 136. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of a Molar-Incisor Malformation-affected Mandibular First Molar: A Case Report
Wonyoung Yue, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 664. CrossRef - Three-year follow-up: Healing of a large periapical lesion related to a maxillary central incisor and two canalled lateral incisor after a single visit root canal treatment
Abu Mostafa Ammar
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Hygiene.2015; 7(4): 40. CrossRef - Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 172. CrossRef - Management of root canal perforation by using cone-beam computed tomography
Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 55. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
-
1,605
View
-
10
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Effect of infection control barrier thickness on light curing units
-
Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Ryun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Chang-Kyu Song, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):368-373. Published online September 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.368
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study investigated the effect of infection control barrier thickness on power density, wavelength, and light diffusion of light curing units.
Materials and Methods
Infection control barrier (Cleanwrap) in one-fold, two-fold, four-fold, and eight-fold, and a halogen light curing unit (Optilux 360) and a light emitting diode (LED) light curing unit (Elipar FreeLight 2) were used in this study. Power density of light curing units with infection control barriers covering the fiberoptic bundle was measured with a hand held dental radiometer (Cure Rite). Wavelength of light curing units fixed on a custom made optical breadboard was measured with a portable spectroradiometer (CS-1000). Light diffusion of light curing units was photographed with DSLR (Nikon D70s) as above.
Results
Power density decreased significantly as the layer thickness of the infection control barrier increased, except the one-fold and two-fold in halogen light curing unit. Especially, when the barrier was four-fold and more in the halogen light curing unit, the decrease of power density was more prominent. The wavelength of light curing units was not affected by the barriers and almost no change was detected in the peak wavelength. Light diffusion of LED light curing unit was not affected by barriers, however, halogen light curing unit showed decrease in light diffusion angle when the barrier was four-fold and statistically different decrease when the barrier was eight-fold (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
It could be assumed that the infection control barriers should be used as two-fold rather than one-fold to prevent tearing of the barriers and subsequent cross contamination between the patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Light curing infection control barriers: do some types jeopardize the concept of conventional bulk-fill composites?
Dalia I. Sherief, Mohamed M. Kandil, Dina Ahmed El-Refai
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Infection Control Barriers on Light Output from a Dental Light-Curing Unit Used in Various Positions
Jitte van der Zee, Andrew Tawse-Smith, Sunyoung Ma
Oral.2023; 3(2): 166. CrossRef - Evaluation of irradiance and spectral output of visible light curing units used in the laboratory
Yoorina Choi, Su-Beom Choi, Ji-Hye Jung, Hoon-Sang Chang
Oral Biology Research.2021; 45(4): 201. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Clinical Sterilization Methods in Dental Air/water Syringes
Seyoung Shin, Yeonmi Yang, Miah Kim, Jaegon Kim, Byeongju Baik
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2013; 40(4): 268. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef - Effect of a multi-layer infection control barrier on the micro-hardness of a composite resin
In-Nam Hwang, Sung-Ok Hong, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2012; 20(5): 576. CrossRef
-
1,147
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Clinical diagnosis of herpes zoster presenting as odontogenic pain
-
Seong-Hak Yang, Dong-Ho Jung, Hae-Doo Lee, Yoon Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):452-456. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.452
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Herpes zoster, an acute viral infection produced by the varicella zoster virus, may affect any of the trigeminal branches. This case report presents a patient with symptoms mimicking odontogenic pain. No obvious cause of the symptoms could be found based on clinical and radiographic examinations. After a dermatologist made a diagnosis of herpes zoster involving the third trigeminal branch, the patient was given antiviral therapy. Two months later, the facial lesions and pain had almost disappeared, and residual pigmented scars were present. During the diagnostic process, clinicians should keep in mind the possibility that orofacial pain might be related to herpes zoster. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Herpes Zoster Accompanying Odontogenic Inflammation: A Case Report with Literature Review
Soyeon Lee, Minsik Kim, Jong-Ki Huh, Jae-Young Kim
Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain.2021; 46(1): 9. CrossRef - Recurrent Herpetic Stomatitis Mimicking Post-Root Resection Complication
Sung-Ok Hong, Jae-Kwan Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2013; 29(4): 418. CrossRef - Diagnostic challenges of nonodontogenic toothache
Hyung-Ok Park, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 170. CrossRef
-
3,137
View
-
14
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Microleakage of endodontic temporary restorative materials under dynamic loading
-
Dong-Ho Jung, Young-Sin Noh, Hae-Doo Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):198-203. Published online May 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.198
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the sealing abilities of four endodontic temporary restorative materials using a methylene blue dye penetration test under dynamic loading. Standardized access cavities were prepared in forty-four intact human permanent molar teeth, and the cavities were restored with Caviton, MD-Temp, IRM, or ZOE. After thermocycling, an intermittent load of 98 N at 1 Hz was applied for 1,000 cycles to the long axis of the functional cusp of each of the teeth, which were immersed in a 1% methylene blue solution. The teeth were split in half, and the linear depth of dye penetration was evaluated according to the criteria. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (p = 0.05) and Duncan's multiple range test. The results demonstrated that Caviton and MD-Temp showed significantly lower microleakage than IRM and ZOE. It was concluded that Caviton and MD-Temp exhibited better sealing ability than IRM and ZOE under dynamic loading. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 29. CrossRef
-
2,087
View
-
18
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The palato-gingival groove - anatomical anomaly occurred in maxillary lateral incisors: case reports
-
Hyun-Il Kim, Young-Shin Noh, Hoon-Sang Chang, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):483-490. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.483
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This report describes clinical cases of a palato-gingival groove on a maxillary lateral incisor with associated localized periodontal disease and pulp necrosis. The tooth of the first case was extracted because of severe bone destruction. The palato-gingival groove of the second case was eliminated using a round bur, and the resulting defect was filled with synthetic graft and covered by an absorbable membrane. Both diagnosis and treatment of palato-gingival groove were very difficult and usually extraction of the involved tooth is the treatment of choice, but combined endodontic-periodontic treatment allowed the tooth to be saved. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Exploring anatomical uniqueness: A rare case report of the buccomesial groove variation in maxillary lateral incisor and its management
Shubhangi Kadoo, Pallav Mahesh Patni, Sanket Hans Pandey, Rahul Vaswani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 394. CrossRef - Radicular lingual groove: A contributory factor in periodontal pathology
Gaurav Didhra, Jagjit Singh, Rajan Gupta, Parveen Dahiya
Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences.2019; 7(2): 240. CrossRef - Management of a Palatal Gingival Groove in a Maxillary Lateral Incisor: A Case Report
Ashkan Salari, Maosumeh Faramarzi, Seyedeh Fereshteh Naser alavi
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry.2016; 7(2): 66. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
-
1,690
View
-
5
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Evaluation of the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of resinous root canal sealers
-
Chang-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Hoon-Sang Chang, Byung-Do Lee, Kyung-San Min, Chan-Ui Hong
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):419-425. Published online September 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.419
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of three resin-based (AH 26, EZ fill and AD Seal), a zinc oxide-eugenol-based (ZOB Seal), and a calcium hydroxide-based (Sealapex) root canal sealers. Specimens, 10 mm in diameter and 1 mm in thickness, were radiographed simultaneously with an aluminum step wedge using occlusal films, according to ISO 6876/2001 standards. Radiographs were digitized, and the radiopacity of sealers was compared to the different thicknesses of the aluminum step wedge, using the Scion image software. Using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, the cytotoxicity of each material was determined in immortalized human periodontal ligament (IPDL) cells.
The results demonstrated that EZ fill was the most radiopaque sealer, while Sealapex was the least radiopaque (p < 0.05). AH 26, AD Seal and ZOB Seal presented intermediate radiopacity values. All the materials evaluated, except for Sealapex, presented the minimum radiopacity required by ISO standards. The cell viabilities of resin-based root canal sealers were statistically higher than that of other type of root canal sealers through the all experimental time. Further, EZ fill showed statistically lower cell viability in 24 and 48 hours compared to AD Seal and in 72 hours compared to all other resin-based root canal sealers. However, there was no correlation between the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of three resin-based root canals sealers (p > 0.05).
These results indicate that resin-based root canal sealer is more biocompatible and has advantage in terms of radiopacity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Comparative Evaluation of Two Commonly Used GP Solvents on Different Epoxy Resin-based Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Sakshi Tyagi, Ekta Choudhary, Rajat Chauhan, Ashish Choudhary
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(1): 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of cytotoxicity of root canal sealers: anin vitrostudy
Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Manjusha Madhukar Warhadpande, Ganesh Kothiramji Meshram, Rakesh Namdeoraoji Bahadure, Shubha Gopal Tawani, Gopal Tawani, Shital Gautam Badole
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 204. CrossRef - Evaluation of radiopacity and discriminability of various fiber reinforced composite posts
Eun-Hye Lee, Hang-Moon Choi, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 188. CrossRef - A comparative study on radiopacity of root canal sealers
Tae-Min Kim, Seo-Kyoung Kim, In-Nam Hwang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Byung-Cheol Kang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Jae-Seo Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 61. CrossRef - A comparative study on radiopacity of canal filling and retrograde root-end filling materials
Yong-Sang Kim, Seo-Kyong Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(2): 107. CrossRef
-
1,957
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
The instrument-centering ability of four Nickel-Titanium instruments in simulated curved root canals
-
Jae-Hoon Ku, Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Woo Chang, Hwan-Hee Cho, Ji-Myung Bae, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):113-118. Published online March 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.113
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the ability of newly marketed NRT instruments to maintain the original root canal configuration and curvature during preparation in comparison with the three existing instruments in simulated root canals.
Simulated canals in resin blocks were prepared with ProFile, K3, ProTaper, and NRT instrument (n = 10 canals in each case). Pre- and post-operative images were recorded, and assessment of canal shape was completed with a computer image analysis program. The data were analyzed statistically using the One-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test.
The ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1-, 2-mm levels was significantly better in ProFile groups than in other groups (p < 0.05). The change of centering ratio in NRT groups at 5-mm level was significantly greater than ProFile group and at 6- and 7-mm level than all other groups (p < 0.05).
Although the NRT system was comparable to other systems in regards to its ability to maintain the canal configuration of apical portion, this system was more influenced by the mid-root curvature due to its stainless-steel files for coronal preflaring. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A comparison of the shaping ability of reciprocating NiTi instruments in simulated curved canals
Young-Sil Yoo, Yong-Bum Cho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 220. CrossRef - Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 424. CrossRef
-
1,262
View
-
0
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
A study on the hemolytic properties of Prevotella nigrescens
-
Ju-Seok Kwak, Hoon-Sang Jang, Seok-Woo Jang, Su-Jong Lee, Yong-Wook Yu, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):335-343. Published online July 30, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.335
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Hemolytic property is a specific feature of bacteria to obtain iron which is essential for its survival in host tissues. Therefore, it is thought to be one of several factors of virulence. The purpose of this study was to investigate the hemolytic properties of Prevotella nigrescens isolated from the teeth diagnosed as pulp necrosis and apical periodontitis under the presence of hemolysin inhibitors such as NaN3 and dithiothreitol, heat, various pH and cultural conditions.
The results were as follows;
1. Clinically isolated P. nigrescens strains and standard P. nigrscens ATCC 33563 showed hemolytic activity.
2. P. nigrescens showed higher hemolytic activity against human erythrocytes than sheep or horse erythrocytes.
3. NaN3 and dithiothreitol (DTT) reduced the hemolytic activity of P. nigrescens in a dose dependent manner (p < 0.05).
4. Optimal pH for the maximum hemolytic activity of P. nigrescens was 4.0 and the hemolysin was stable under the 50℃, but the hemolytic activity was significantly decreased at 95℃.
5. P. nigrescens cultured in 10% CO2 condition showed higher hemolytic activity than the bacteria cultured in the anaerobic condition.
-
The effect of additional enamel etching on microleakage of the adhesion of self-etching primer system
-
Jung-Jin Yoon, Kyung-San Min, Chan-Ui Hong
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):363-368. Published online September 30, 2003
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.363
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of additional enamel etching with phosphoric acid on the microleakage of the adhesion of self-etching primer system.
Class V cavity(4 mm×3 mm×1.5 mm) preparations with all margins in enamel were prepared on buccal surface of 42 extracted human upper central incisor teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into 3 groups.
Group 1 : no additional pretreatment with 37% phosphoric acid (NE).
Group 2 : additional pretreatment with 37% phosphoric acid for 10 seconds (E10s).
Group 3 : additional pretreatment with 37% phosphoric acid for 20 seconds (E20s).
The adhesives(Clearfil SE Bond®, Kuraray, Osaka, Japan) and composite resins(Clearfil AP-X®, Osaka, Kuraray, Japan) were applied following the manufacturer's instructions. All the specimens were finished with the polishing disc(3M dental product, St Paul, MN, USA), thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃ and resected apical 3-mm root. 0.028 stainless steel wire was inserted apically into the pulp chamber of each tooth and sealed into position with sticky wax. Surrounding tooth surface was covered with a nail varnish 2 times except areas 1 mm far from all the margins. After drying for one day, soaked the samples in the distilled water. Microleakage was assessed by electrochemical method(System 6514, Electrometer®, Keithley, USA) in the distilled water.
In this study, the microleakage was the lowest in group 1(NE) and the highest in group 3(E20s)(NE<E10s<E20s). But no statistically significant differences were found(p=0.5).
On the basis of findings from this experiment, it can be concluded that additional enamel etching has no influence on the microleakage of the adhesion of self-etching primer system.
-
A study of contraction shrinkage of composite resins and ormocers with various curing times
-
Yeon-Chung Chung, Kyung-San Min, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Yong-Bum Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(4):326-333. Published online July 31, 2003
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.4.326
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Ormocer has organic-inorganic compound polymers. One of advantages of ormocer is reduced polymerization shrinkage. The purpose of this study was to compare the amount of contraction shrinkage of composite resins and ormocers. Additionally, the time of each material when there is no further change of contraction shrinkage was analysed.
Four brands of composite resins (P-60, Surefil, Z-250 and Denfil) and two brands of ormocers (Definite and Admira) were used. 20 seconds, 40 seconds and 60 seconds of curing times were given. Contraction shrinkage of them were measured using a linometer for 80 seconds.
The effect of material and curing time to contraction shrinkage at the time of 80 seconds was analysed by two-way ANOVA. The effect of time to contraction shrinkage was analysed by one-way ANOVA, and the time when there was no further change of the contraction shrinkage was analysed. The results are as follows :
P-60, Definite, Z-250 and Denfil had no further change of contraction shrinkage from the time of 20 seconds, and Surefil and Admira had no further change of contraction shrinkage from the time of 10 seconds.
Statistical analysis revealed volumetric shrinkage varied among material (p<0.05). No significant difference of contraction shrinkage among different curing times was found, and there was no effect of interaction between materials and curing times to contraction shrinkage.
Definite and Admira showed the statistically same contraction shrinkage with those of Z-250 and P-60, which is higher than that of Surefil and lower than that of Denfil (p<0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Polymerization shrinkage and stress analysis during dental restoration observed by digital image correlation method
Jung-Hoon Park, Nak-Sam Choi
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2021; 35(12): 5435. CrossRef - Acoustic emission characteristics of methacrylate-based composite and silorane-based composite during dental restoration according to a variety of C-factor
Jung-Hoon Park, Ja-Uk Gu, Nak-Sam Choi
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2017; 31(9): 4067. CrossRef - Behavior of Polymerization Shrinkage Stress of Methacrylate-based Composite and Silorane-based Composite during Dental Restoration
Jung-Hoon Park, Nak-Sam Choi
Composites Research.2015; 28(1): 6. CrossRef
-
1,275
View
-
3
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Microleakage of various composite resin systems
-
In-Soo Kim, Kyung-San Min, Dong-Hoon Shin
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):127-133. Published online March 31, 2003
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.127
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The object of this study was to compare the microleakage between various composite resin systems of multistep, one-bottle, and self-etching systems using electrical conductivity.
After making class V cavities (4×3×1.5 mm around CEJ), they were bulk filled with three kinds of resins of A3. Teeth were storaged in a saline solution for one day, after then, they were finished and polished using Sof-Lex system. Another stress of thermocycling was made for 500 times from 5° to 55℃ with each dwelling time of 10 seconds. Electrical conductivity (microamphere, µA) was checked four times: before and after cavity preparation, after filling, after thermocycling.
One-way ANOVA and 95% Scheffe Post Hoc test was used for checking any statistical difference among groups. Another 95% Paired Samples T-test was also used for estimating any significant difference within group after cavity filling or thermocycling.
The results were as follows:
Every specimen showed various range of microleakage after filling.
There was, however, no difference between composite resin systems.
All composite resin systems showed marked increase in microleakage with a thermocycling (p<0.05), there was, however, no difference between composite resin systems.
Although there was no significant difference between groups (p=0.078), one-bottle and self-etching systems seemed to be unstable than multistep system.
Within the limits of this study, it was concluded that much more consideration should be needed when using thermally unstable one-bottle and self-etching systems that have multi-advantages from simplified step. More studies will be needed to solve these kinds of problems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of a new resin monomer on the microleakage of composite resin restorations
JH Bae, YK Kim, PY Yoon, MA Lee, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 469. CrossRef - Microhardness and microleakage of composite resin cured by visible light with various band of wavelength
Soo-Man Park, Jae-Yong Lee, Seung-Ryul Han, Sang-Yoon Ha, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2002; 27(4): 403. CrossRef
-
1,111
View
-
0
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Mechanical properties and microleakage of composite resin materials cured by variable light intensities
-
Seung-Ryul Han, Kyung-San Min, Dong-Hoon Shin
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):134-145. Published online March 31, 2003
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.134
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Mechanical properties and microleakage of two composites [conventional hybrid type DenFil (VERICOM Co., Anyang, Korea) / micro matrix hybrid type Esthet X (Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE, U.S.A.)] were evaluated to assess whether variable light intensity curing is better than conventional curing technique.
Curing was done for 40 seconds in two ways of 2 step soft-start technique and 5 step ramping technique. Three kinds of light intensities of 50, 100, 200 mW/cm2 were initially used for 10, 20, 30 seconds each and the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2 was used for the rest of curing time in a soft-start curing technique. In a ramping technique, curing was done with the same initial intensities and the light intensity was increased 5 times with the same rate to the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2.
After determining conditions that showed no different mechanical properties with conventional technique, Esthet X composite was filled in a class V cavity, which dimension was 4×3×1.5 mm and cured under those conditions.
Microleakage was evaluated in two ways of dye penetration and maximum gap estimation through SEM observation. ANOVA and Spearman's rho test were used to confirm any statistical significance among groups.
The results were as follows:
Several curing conditions of variable light intensities resulted in the similar mechanical properties with a conventional continuous curing technique, except conditions that start curing with an initial light intensity of 50 mW/cm2,
Conventional and ramping techniques were better than soft-start technique in mechanical properties of microhardness and compressive strength.
Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 100 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the least dye penetration. Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 200 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the smallest marginal gap, if there was no difference among groups.
Soft-start technique resulted in better dye-proof margin than conventional technique (p=0.014) and ramping technique(p=0.002).
There was a very low relationship(p=0.157) between the methods of dye penetration and marginal gap determination through SEM evaluation.
From the results of this study, it was revealed that ramping technique would be better than conventional technique in mechanical properties, however, soft-start technique might be better than conventional one in microleakage.
It was concluded that much endeavor should be made to find out the curing conditions, which have advantages of both aspects or to solve these kinds of problems through a novel idea of polymerization.
|