Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule occlusion by desensitizing agents after tooth bleaching: an in vitro study
- Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Spyros Papageorgiou, Kosmas Tolidis
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e8. Published online February 10, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
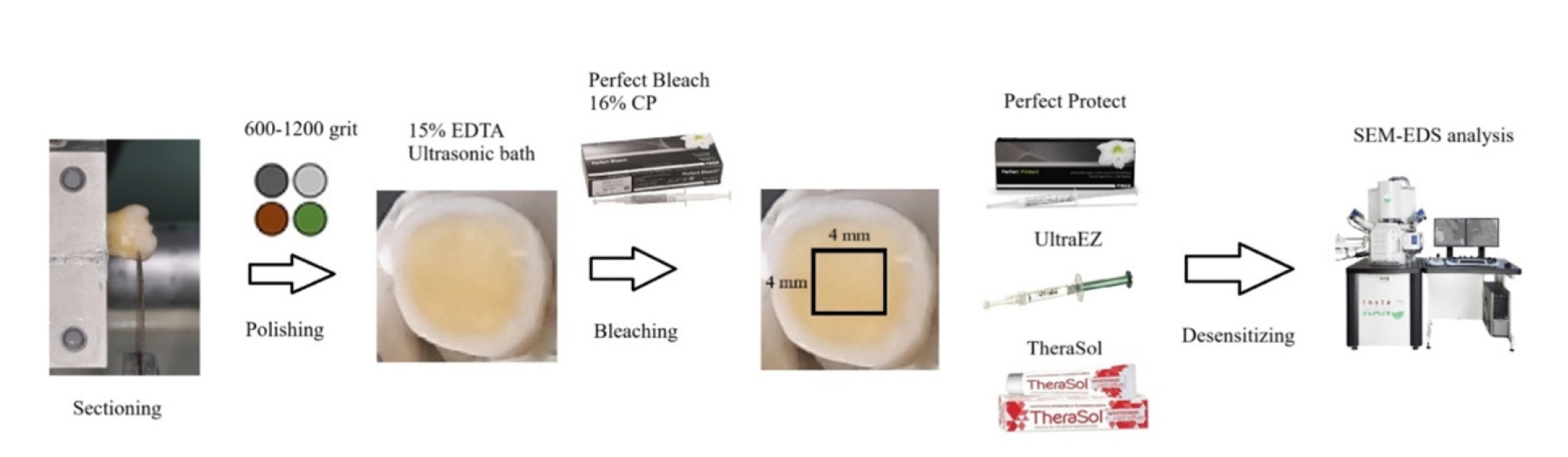
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of three commercially available desensitizing agents in occluding dentinal tubules, which may help reduce tooth sensitivity following a bleaching treatment.
Methods
Twenty healthy human third molars were utilized in this investigation. The samples were prepared by transversely sectioning 2.5 mm of the crowns to expose the dentin. They were initially treated with 15% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid gel for 4 minutes, followed by application of Perfect Bleach (VOCO GmbH) bleaching agent (16% carbamide peroxide) for 2 hours. The samples were randomly allocated into four groups (n = 5), each receiving one of the following treatments: group 1: No treatment (control), group 2: treated with UltraEZ (Ultradent Products Inc.,), containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride, group 3: treated with Perfect Protect (VOCO GmbH), also containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride and group 4: treated with TheraSol Whitening & Sensitive (ABC Kinitron IKE), containing strontium acetate and sodium monofluorophosphate. Subsequently, the specimens were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy to evaluate dentin tubule occlusion.
Results
SEM observations showed no occlusion of dentin tubules in the control group, whereas groups 2 to 4 exhibited significant occlusion. The most effective treatment was Perfect Protect (p < 0.05), while UltraEZ and TheraSol Whitening & Sensitive demonstrated similar effectiveness, with no statistically significant difference between them (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
The tested desensitizing agents effectively occluded dentin tubules to a considerable extent. Differences in their effectiveness were attributed to variations in their formulations.
- 441 View
- 32 Download

- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
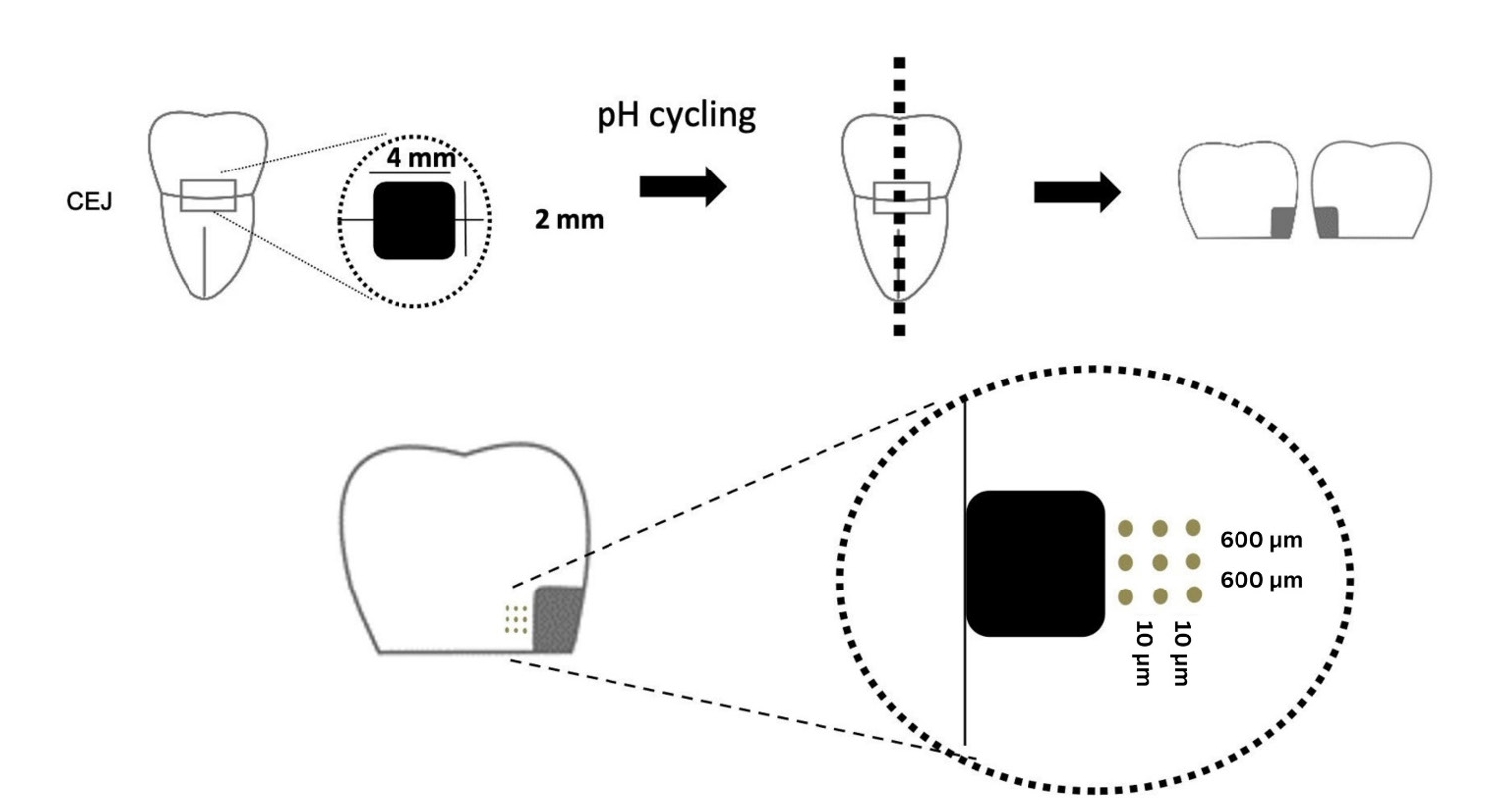
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,806 View
- 213 Download

- Effect of surface sealant on the color stability and whiteness index of single-shade resin composites after staining and bleaching
- Muhammet Fidan, Özhan Yağcı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e30. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
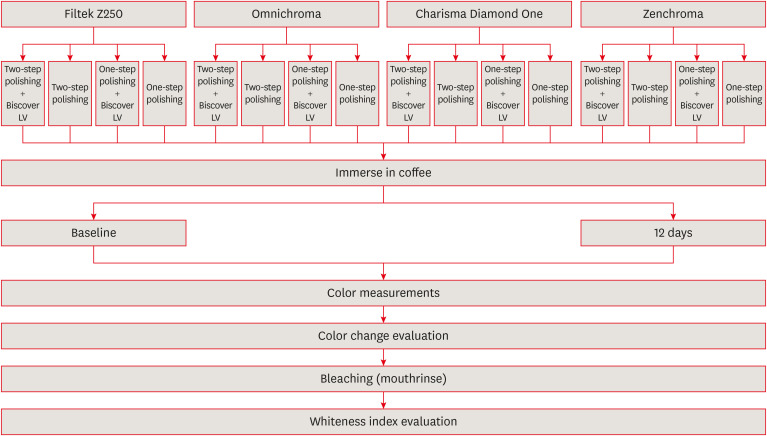
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study was to evaluate the effect of polishing systems and surface sealant on the color stability and whiteness index of single-shade resin composites after staining and bleaching.
Materials and Methods Three single-shade (Omnichroma, Charisma Diamond One, Zenchroma) and one multi-shade (Filtek Z250) materials were tested. From each resin composite, 40 specimens were prepared. The specimens were divided into 4 subgroups (
n = 10) according to the surface treatments: 1-step polishing, 1-step + Biscover LV, 2-step polishing, and 2-step polishing + Biscover LV. Color differences (ΔE00) were calculated after being immersed in the coffee solution for 12 days. After the staining, the specimens were immersed in a whitening mouthrinse (Crest-3D White) for 12 hours. Whiteness index differences (∆WID = WID after staining − WID after bleaching) values were recorded. The generalized linear model was used for analysis (p < 0.05).Results The lowest and highest ΔE00 values were found for Zenchroma and Charisma Diamond One respectively. Sealed groups indicated higher ΔE00 values than nonsealed groups with significant differences (
p = 0.008). The lowest and highest ΔWID values were found for Zenchroma and Charisma Diamond One respectively. Sealed groups indicated lower ΔWID values than nonsealed groups with significant differences (p = 0.022).Conclusions The use of surface sealant increased the discoloration and showed less whiteness change in resin materials. When the 1-step was compared with the 2-step polishing, the effects on the color stability and whiteness index values of the resin materials were similar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color and surface properties of conventional, injectable, and 3D-printed resin composites for anterior restorations: influence of a surface sealant
Soner Sismanoglu
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the effects of bleaching on color stability and surface roughness in single-shade and multi-shade resin composites
Hatice Tepe, Özge Çeliksöz, Zeynep Biçer, Batucan Yaman
Anatolian Current Medical Journal.2024; 6(6): 372. CrossRef
- Color and surface properties of conventional, injectable, and 3D-printed resin composites for anterior restorations: influence of a surface sealant
- 2,954 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- A global overview of enamel microabrasion for white spot lesions: a bibliometric review
- Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Karina Cardoso, Michely Cristina Goebel, Pablo Silveira Santos, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Juliana Silva Ribeiro, Carla Miranda Santana, Mariane Cardoso
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e29. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
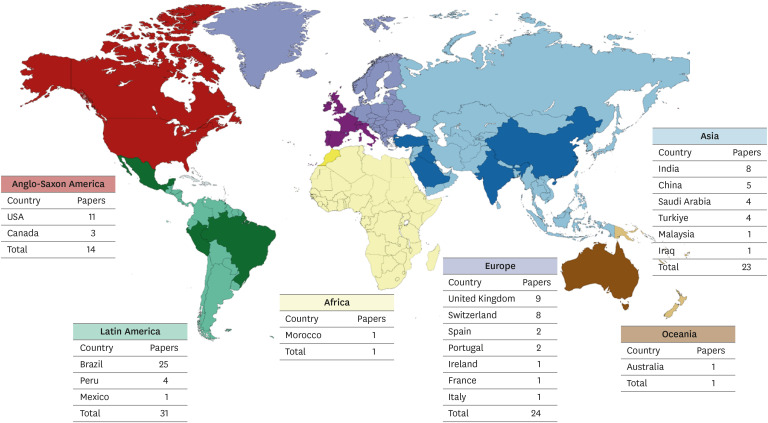
ePub This study aimed to identify and analyze articles on enamel microabrasion for the treatment of white spot lesions. A search was conducted on the Web of Science. The following parameters were recorded and analyzed: number of citations, year, journal, impact factor, study design, theme, country and continent, institution, authors, and keywords. Data was analyzed using VOSviewer software. The initial search resulted in 1,126 documents, of which 94 articles were included. The highest number of citations an article received was 65. The oldest article was published in 1975, and the most recent in 2023. The most frequent study design was case report (
n = 42). Regarding the themes, it was observed that the main objective of the studies was to evaluate the clinical performance of enamel microabrasion (n = 75), primarily using Opalustre (Ultradent Products Inc., South Jordan, UT, USA) (n = 37) for treating white stains caused by dental fluorosis (n = 41). Most articles originated from Latin America (n = 31), mainly from Brazil (n = 26). The most frequent author was Sundfeld RH (n = 10). This study reveals research trends in the field of enamel microabrasion. The publications were mainly case reports/series using Opalustre for the removal of fluorosis stains.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
Michael Willian Favoreto, Leticia Condolo, Camila Mendes Camargo, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Karol Carrillo, Abraham Lincoln Calixto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105655. CrossRef - Micro- and Macroabrasion in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review and Case Study
Jose Villalobos-Tinoco, Carlos A. Jurado, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Nechama S. Citrin, Staley Colvert, Jose Luis Gutierrez-Quintero, Salwa Mekled
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(5): 183. CrossRef - Evaluation of demineralization changes in molar tissues in vitro using electrical impedance spectroscopy
V. D. Goncharov, M. A. Gorelikova, K. V. Shadrina, L. Yu. Orekhova, V. D. Berezkin, E. S. Nemovskaya, A. A. Petrov
Parodontologiya.2025; 30(3): 254. CrossRef
- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
- 5,500 View
- 148 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Endodontic characteristics of mandibular premolar with dens evaginatus: a retrospective study
- Minjin Kim, Sujin Jeon, Min-Seock Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e28. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
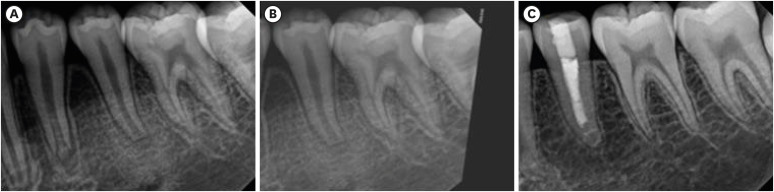
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the endodontic characteristics of mandibular premolars with dens evaginatus (DE) that require endodontic treatment.
Materials and Methods Patients who underwent endodontic treatment were enrolled. The inclusion criteria were patients who underwent root canal treatment in the lower permanent teeth with DE and were followed up for at least 1 year. Preoperative clinical and radiographic variables were obtained. The frequency distribution of the preoperative variables was compared using the χ2 or Fisher’s exact tests. The significance of the change in periapical health index (PAI) and root development stages before and after treatment was examined using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results A total of 150 teeth of 134 patients with an average age of 15.3 years were included. The percentage distribution comparison of the preoperative variables and obturation techniques revealed significant differences in pulpal and periapical diagnosis, and percussion, and especially regarding age, root development stage, and PAI. Age was the only statistically significant preoperative variable associated with root growth (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Approximately, 60% of DEs requiring endodontic treatment had immature roots. Age being the most significant predisposing factor, early treatment provides the greatest opportunity for full root development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A tooth with multiple supernumerary cusps and taurodontism concurrently accompanied with other taurodont teeth: a rare case report
Zihui Tang, Hongchen Zhang, Rongrong Dang, Qiushi Zhang, Yan Huang, Yanwei Yang
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A tooth with multiple supernumerary cusps and taurodontism concurrently accompanied with other taurodont teeth: a rare case report
- 3,406 View
- 106 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The prevalence of apical periodontitis in patients prior to hematopoietic cell transplantation: a systematic review
- Letícia Tainá de Oliveira Lemes, Carolina Horn Troian-Michel, Theodoro Weissheimer, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e22. Published online May 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
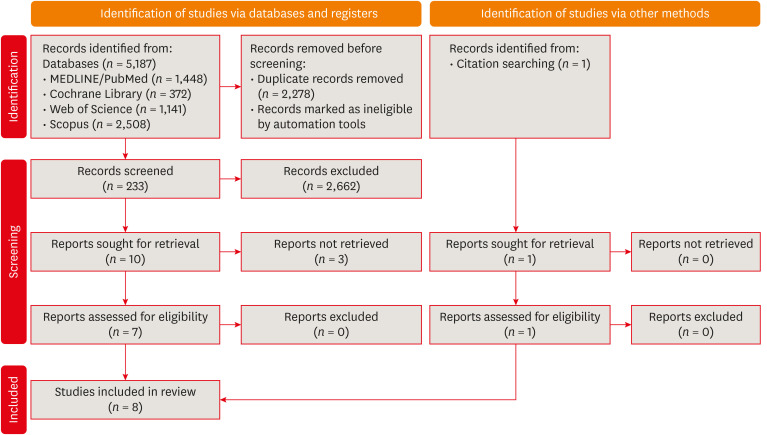
ePub Objectives This systematic review addressed the question: “What is the prevalence of apical periodontitis in patients prior to hematopoietic cell transplantation?”
Materials and Methods A systematic search was conducted in MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Grey Literature Report. Eligibility criteria were based on the condition, content, and population strategy: the condition was the radiographic prevalence of apical periodontitis, the content comprised patients scheduled for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and the population consisted of adult and pediatric patients. The revised Risk of Bias in Nonrandomized Studies of Exposure tool was used to assess the quality of studies. The Grading Recommendations Assessments, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) tool was used to assess the quality of evidence.
Results Eight studies were included in this review. The average number of patients with apical periodontitis was 15.65% (range, 2.1%–43.34%). One study was classified as having a very high risk of bias, 1 with a high risk of bias, and 6 with some concern for bias. GRADE analysis showed a very low certainty of evidence. Significant limitations concerning the absence of control over confounding variables were identified.
Conclusions With the caveat of the very low quality of evidence in the studies reviewed, there was a low to moderate prevalence of apical periodontitis in patients prior to undergoing hematopoietic cell transplantation.
- 2,100 View
- 51 Download

- Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
- Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e7. Published online January 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
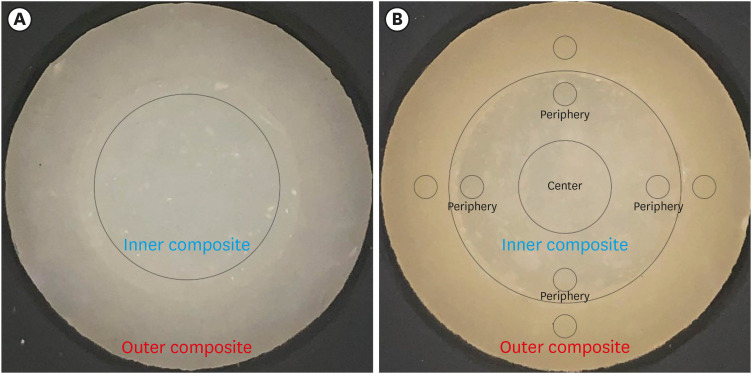
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the impact of substrate color and interface distance on the color adjustment of 2 single-shade composites, Vittra APS Unique and Charisma Diamond One.
Materials and Methods Dual disc-shaped specimens were created using Vittra APS Unique or Charisma Diamond One as the center composite, surrounded by shaded composites (A1 or A3). Color measurements were taken with a spectrophotometer against a gray background, recording the color coordinates in the CIELAB color space. Illumination with a light-correcting device and image acquisition using a polarizing filter-equipped cell phone were performed on specimens over the same background. Image processing software was used to measure the color coordinates in the center and periphery of the inner composite and in the outer composite. The color data were then converted to CIELAB coordinates and adjusted using data from the spectrophotometer. Color differences (ΔE00) between the center/periphery of single-shade and outer composites were calculated, along with color changes in single-shade composites caused by different outer composites. Color differences for the inner composites surrounded by A1 and A3 were also calculated. Data were analyzed using repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05).
Results The results showed that color discrepancies were lowest near the interface and when the outer composite was whiter (A1). Additionally, Charisma Diamond One exhibited better color adjustment ability than Vittra APS Unique.
Conclusions Color discrepancies between the investigated single-shade composites diminished towards the interface with the surrounding composite, particularly when the latter exhibited a lighter shade.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Staining Resistance of Two Single-Shade Composites in Coffee and Chlorhexidine: A Spectrophotometric Analysis
Unmesh Khanvilkar, Shrinath D Kulkarni, Siddhesh Bandekar, Ved M Talathi, Oshin Baghel, Priyanka Razdan, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Implications of Color Adjustment in Single-Shade Resins Post-Dental Bleaching: A Systematic Review
Samille Biasi Miranda, Caroline de Farias Charamba Leal, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Antonio Japiassu Resende Montes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(9): 3194. CrossRef - Accuracy and Reliability of Smartphone Versus Mirrorless Camera Images-Assisted Digital Shade Guides: An In Vitro Study
Soo Teng Chew, Suet Yeo Soo, Mohd Zulkifli Kassim, Khai Yin Lim, In Meei Tew
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 8070. CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,355 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
- Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e8. Published online February 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
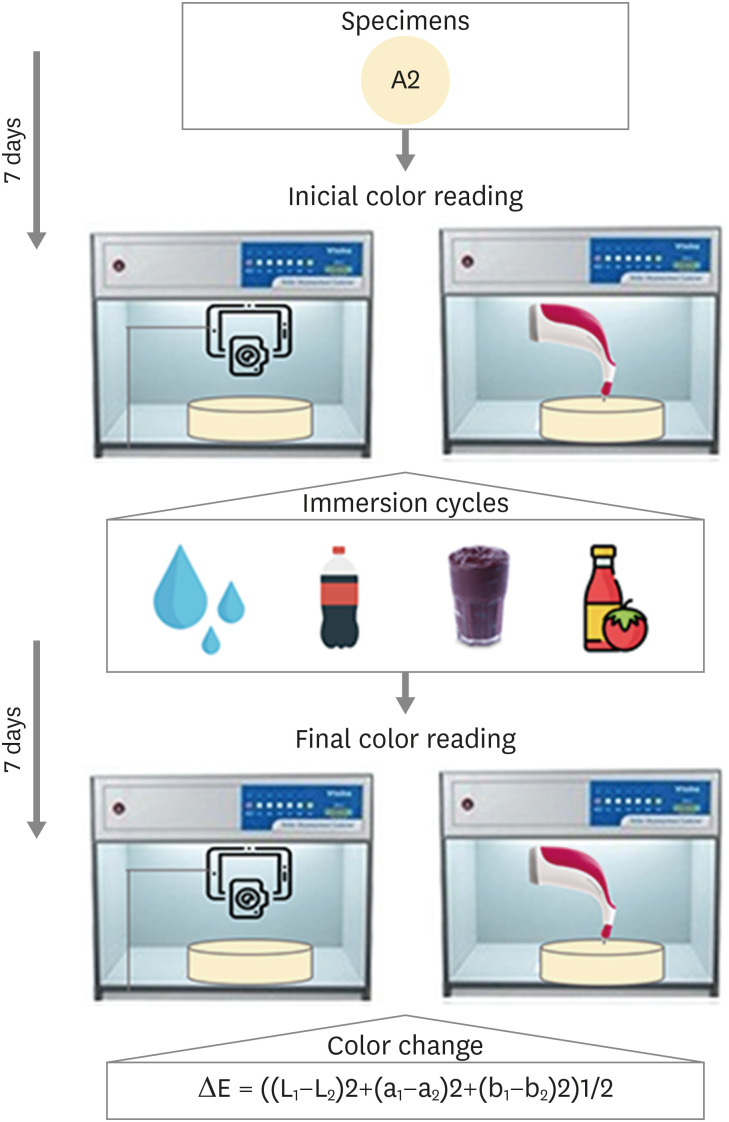
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the color change of the Giomer resin composite (Beautifil-Bulk) by using photographs obtained with a smartphone (iPhone 6S) associated with Adobe Photoshop software (digital method), with the spectrophotometric method (Vita Easyshade) after immersion in different pigment solutions.
Materials and Methods Twenty resin composite samples with a diameter of 15.0 mm and thickness of 1.0 mm were confectioned in A2 color (
n = 5). Photographs and initial color readings were performed with a smartphone and spectrophotometer, respectively. Then, samples were randomly divided and subjected to cycles of immersion in distilled water (control), açai, Coke, and tomato sauce, 3 times a day, 20 minutes for 7 days. Later, new photographs and color readings were taken.Results The analysis (2-way analysis of variance, Holm-Sidak,
p < 0.05) demonstrated no statistical difference (p < 0.005) between the methods in all groups. Similar color changes were observed for all pigment solutions when using the spectrophotometric method. For the digital method, all color changes were clinically unacceptable, with distilled water and tomato sauce similar to each other and with statistical differences (p < 0.005) for Coke and açai.Conclusions Only the tomato sauce produced a color change above the acceptability threshold using both methods of color assessment. The spectrophotometric and digital methods produce different patterns of color change. According to our results, the spectrophotometric method is more recommended in color change assessment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
Jamieson Wong, Constance Yeo, Michelle The, Filip Taneski, Uros Josic, Lorenzo Breschi, Vesna Miletic
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026; 38(1): 70. CrossRef - The effects of mechanical and chemical degradation on the surface roughness, gloss, and color stability of bulk-fill resin composites
Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Esra Özyurt, Naz Bayar, Mediha Büyükgöze Dindar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef
- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
- 2,756 View
- 39 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Color assessment of resin composite by using cellphone images compared with a spectrophotometer
- Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Ratto Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e23. Published online April 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
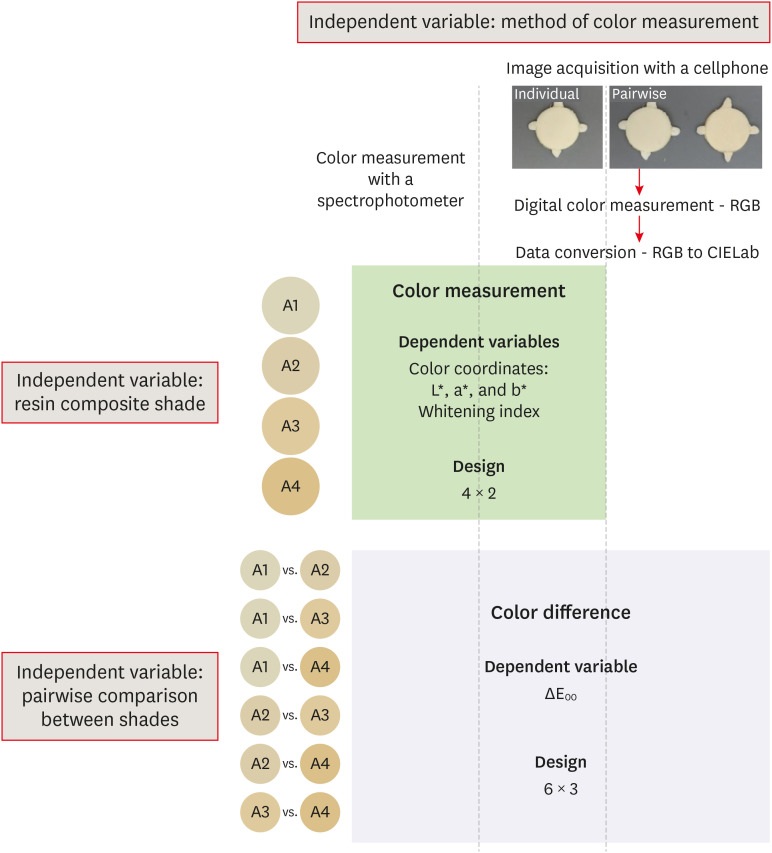
ePub Objectives This study assessed the reliability of digital color measurements using images of resin composite specimens captured with a cellphone.
Materials and Methods The reference color of cylindrical specimens built-up with the use of resin composite (shades A1, A2, A3, and A4) was measured with a portable spectrophotometer (CIELab). Images of the specimens were obtained individually or pairwise (compared shades in the same photograph) under standardized parameters. The color of the specimens was measured in the images using RGB system and converted to CIELab system using image processing software. Whiteness index (WID) and color differences (ΔE00) were calculated for each color measurement method. For the cellphone, the ΔE00 was calculated between the pairs of shades in separate images and in the same image. Data were analyzed using 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05). Linear regression models were used to predict the reference ΔE00 values of those calculated using color measured in the images.
Results Images captured with the cellphone resulted in different WID values from the spectrophotometer only for shades A3 and A4. No difference to the reference ΔE00 was observed when individual images were used. In general, a similar ranking of ΔE00 among resin composite shades was observed for all methods. Stronger correlation coefficients with the reference ΔE00 were observed using individual than pairwise images.
Conclusions This study showed that the use of cellphone images to measure the color difference seems to be a feasible alternative providing outcomes similar to those obtained with the spectrophotometer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How the Translucency and Color Stability of Single-Shade Universal Resin Composites Are Affected by Coffee?
Büşra Özdemir, Betül Kübra Kurucu Karadeniz, Seyit Bilal Özdemir, Ömer Akbulut
Current Research in Dental Sciences.2024; 34(4): 270. CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of VITA Shade Guide and Various Composite Shades Using Spectrophotometer, Digital Single-lens Reflex, and Cellphone: An In Vitro Study
Aman Verma, Sonali Taneja, Surabhi Ghosh
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 803. CrossRef - Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,625 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of post space preparation drills on the incidence of root dentin defects
- Thaíse Ayres Bezerra Zuli, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Gislaine Figueiredo Zarza Arguello Gonçalves, Aurélio Rosa da Silva Júnior, Álvaro Henrique Borges, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e53. Published online October 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
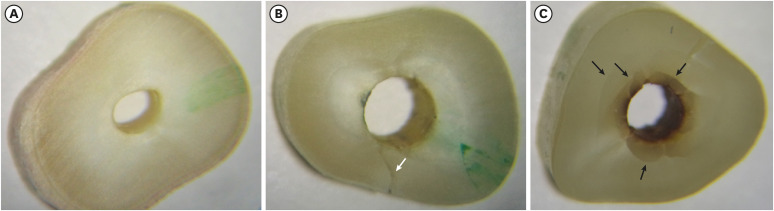
ePub Objectives This study investigated the incidence of root dentin defects after the use of different post space preparation (PSP) drills.
Materials and Methods Seventy-two bovine incisors were selected and obtained 14-mm-long root sections. Twelve roots served as controls with no intervention (G1). The 60 root canals remaining were instrumented using the crown-down technique with the ProTaper Next system and obturated using the lateral condensation technique. Specimens were randomly distributed into 5 groups (
n = 12) according to the operative steps performed: G2, root canal instrumentation and filling (I+F); G3, I+F and PSP with Gates-Glidden drills; G4, I+F and PSP with Largo-Peeso reamers; G5, I+F and PSP with Exacto drill; and G6, I+F and PSP with WhitePost drill. Roots were sectioned at 3, 6, 9, and 12 mm from the apex, and digital images were captured. The presence of root dentin defects was recorded. Data were analyzed by the χ2 test, withp < 0.05 considered to indicate statistical significance.Results Root dentin defects were observed in 39.6% of the root sections. No defects were observed in G1. G5 had significantly more cracks and craze lines than G1, G2, and G3 (
p < 0.05), and more fractures than G1, G2, G3, and G4 (p < 0.05). When all root sections were analyzed together, significantly more defects were observed at the 12-mm level than at the 3-mm level (p < 0.05).Conclusions PSP drills caused defects in the root dentin. Gates-Glidden drills caused fewer root defects than Largo-Peeso reamers and Exacto drills.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of dentinal crack formation during post space preparation using different fiber post systems with micro-computed tomography
Ayşe Nur Kuşuçar, Damla Kırıcı
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture and Crack Behavior of Weakened Incisors Restored With Fiber Posts, Polyethylene Reinforcement, or 3D-Printed Endocrowns
Diana Codas-Duarte, Laís L Pelozo, Jardel F Mazzi-Chaves, Fabiane C Lopes-Olhê, Manoel D Sousa-Neto, Aline E Souza-Gabriel
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Selecting drill size for post space preparation based on final endodontic radiographs: An in vitro study
Farzaneh Farid, Julfikar Haider, Marjan Sadeghpour Shahab, Nika Rezaeikalantari
Technology and Health Care.2024; 32(4): 2575. CrossRef - Cone Beam Computed Tomography Analysis of Post Space in Bifurcated Premolars Using ParaPost and Peeso Reamer Drills
Abdulaziz Saleh Alqahtani, Omar Nasser Almonabhi, Abdulmajeed Moh. Almutairi, Reem R. Alnatsha
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Real-Time Guided Dynamic Navigation and Conventional Techniques for Post Space Preparation During Post Endodontic Management: An In Vitro Study
Sherifa Shervani, Sihivahanan Dhanasekaran, Vijay Venkatesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
Giulliano C. Serpa, Orlando A. Guedes, Neurinelma S. S. Freitas, Julio A. Silva, Carlos Estrela, Daniel A. Decurcio
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 190. CrossRef
- Evaluation of dentinal crack formation during post space preparation using different fiber post systems with micro-computed tomography
- 2,752 View
- 34 Download
- 6 Crossref

-
Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an
in vitro study - Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e50. Published online October 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
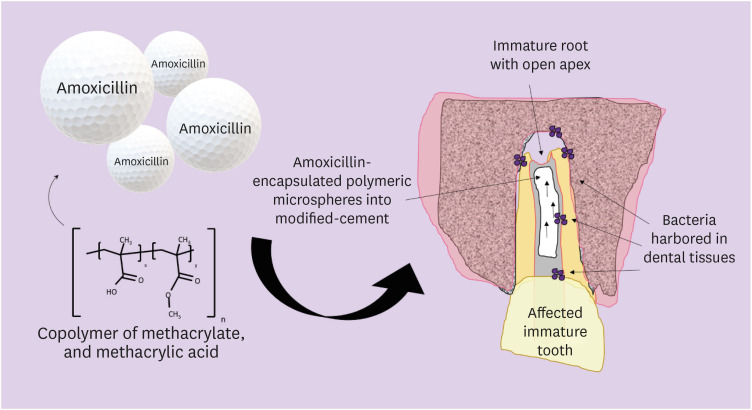
ePub Objectives In this study, we investigated the potential of amoxicillin-loaded polymeric microspheres to be delivered to tooth root infection sites via a bioactive reparative cement.
Materials and Methods Amoxicillin-loaded microspheres were synthesized by a spray-dray method and incorporated at 2.5% and 5% into a mineral trioxide aggregate cement clinically used to induce a mineralized barrier at the root tip of young permanent teeth with incomplete root development and necrotic pulp. The formulations were modified in liquid:powder ratios and in composition by the microspheres. The optimized formulations were evaluated
in vitro for physical and mechanical eligibility. The morphology of microspheres was observed under scanning electron microscopy.Results The optimized cement formulation containing microspheres at 5% exhibited a delayed-release response and maintained its fundamental functional properties. When mixed with amoxicillin-loaded microspheres, the setting times of both test materials significantly increased. The diametral tensile strength of cement containing microspheres at 5% was similar to control. However, phytic acid had no effect on this outcome (
p > 0.05). When mixed with modified liquid:powder ratio, the setting time was significantly longer than that original liquid:powder ratio (p < 0.05).Conclusions Lack of optimal concentrations of antibiotics at anatomical sites of the dental tissues is a hallmark of recurrent endodontic infections. Therefore, targeting the controlled release of broad-spectrum antibiotics may improve the therapeutic outcomes of current treatments. Overall, these results indicate that the carry of amoxicillin by microspheres could provide an alternative strategy for the local delivery of antibiotics for the management of tooth infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Local drug delivery for regeneration and disinfection in endodontics: A narrative review
Anu Elsa Swaroop, Sylvia Mathew, P. Harshini, Shruthi Nagaraja
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 119. CrossRef - Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate—A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements
C. Pushpalatha, Vismaya Dhareshwar, S. V. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Thilla Sekar Vinothkumar, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Amal Shaiban, Ateet Kakti, Shilpa H. Bhandi, Alok Dubey, Amulya V. Rai, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Local drug delivery for regeneration and disinfection in endodontics: A narrative review
- 1,876 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic assessment of the shaping ability of the One Curve, One Shape, and ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary systems
- Pelin Tufenkci, Kaan Orhan, Berkan Celikten, Burak Bilecenoglu, Gurkan Gur, Semra Sevimay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e30. Published online May 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
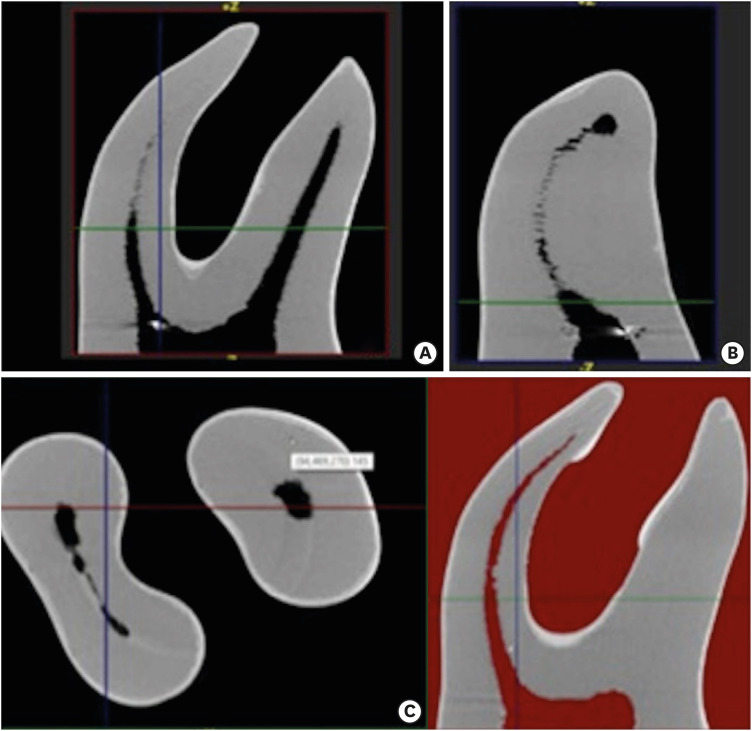
ePub Objectives This micro-computed tomographic (CT) study aimed to compare the shaping abilities of ProTaper Next (PTN), One Shape (OS), and One Curve (OC) files in 3-dimensionally (3D)-printed mandibular molars.
Materials and Methods In order to ensure standardization, 3D-printed mandibular molars with a consistent mesiobuccal canal curvature (45°) were used in the present study (
n = 18). Specimens were instrumented with the OC, OS, or PTN files. The teeth were scanned pre- and post-instrumentation using micro-CT to detect changes of the canal volume and surface area, as well as to quantify transportation of the canals after instrumentation. Two-way analysis of variance was used for statistical comparisons.Results No statistically significant differences were found between the OC and OS groups in the changes of the canal volume and surface area before and after instrumentation (
p > 0.05). The OC files showed significantly less transportation than the OS or PTN systems for the apical section (p < 0.05). In a comparison of the systems, similar values were found at the coronal and middle levels, without any significant differences (p > 0.05).Conclusions These 3 instrumentation systems showed similar shaping abilities, although the OC file achieved a lesser extent of transportation in the apical zone than the OS and PTN files. All 3 file systems were confirmed to be safe for use in mandibular mesial canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different kinematics and perforation diameter on integrated electronic apex locator accuracy in detecting root canal perforations
Ecenur Tuzcu, Safa Kurnaz
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro‐CT Evaluation of the Shaping Outcomes of Different Instruments in Oval‐Shaped Maxillary Premolar Canals
Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Seda Falakaloğlu, Ali Keleş, Özkan Adıgüzel, Sadullah Kaya
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bidirectional evaluation of canal transportation, centering ability and curvature changes of three NiTi rotary systems using cone beam computed tomography (invitro study)
Ahmed A. Soliman, Raef A. Sherif, Amr M. Abdallah, Ahmed M. Mobarak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Efficiencies of Different Rotary File Systems in Terms of Remaining Dentin Thickness Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An In Vitro Study
Vivek P Vadera , Sandhya K Punia, Saleem D Makandar, Rahul Bhargava, Pradeep Bapna
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Different Rotary Nickel–titanium Systems to Evaluate Coronal Leakage of Root Canals: An in Vitro Study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa
Dental Hypotheses.2023; 14(3): 81. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of canal transportation and canal centering ability in oval canals with newer nickel–titanium rotary single file systems – A cone-beam computed tomography study
SimarKaur Manocha, SuparnaGanguly Saha, RollyS Agarwal, Neelam Vijaywargiya, MainakKanti Saha, Anjali Surana
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 326. CrossRef - Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris and Root Canal Shaping Profiles Following Instrumentation with Gentlefile, One Curve, and Reciproc Blue
Chi Wai Chan, Virginia Rosy Romeo, Angeline Lee, Chengfei Zhang, Prasanna Neelakantan, Eugenio Pedullà
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(10): 1344. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of canal transportation and centering ability of rotary and reciprocating file systems using cone-beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Tanisha Singh, Manju Kumari, Rohit Kochhar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Retreatability of Bioceramic Sealer Using One Curve Rotary File Assessed by Microcomputed Tomography
Dina G Mufti, Saad A Al-Nazhan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1175. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef
- Effect of different kinematics and perforation diameter on integrated electronic apex locator accuracy in detecting root canal perforations
- 1,865 View
- 15 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Influence of pain-relieving therapies on inflammation and the expression of proinflammatory neuropeptides after dental bleaching treatment
- Livia Maria Alves Valentim da Silva, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Marjorie de Oliveira Gallinari, Francine Benetti, Vanessa Rahal, Edilson Ervolino, Sibele de Alcântara, André Luiz Fraga Briso
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e20. Published online February 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To minimize the tooth sensitivity caused by in-office bleaching, many dentists use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and topical desensitizing gels containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of these substances on inflammation and the expression of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in pulp nerve fibers.
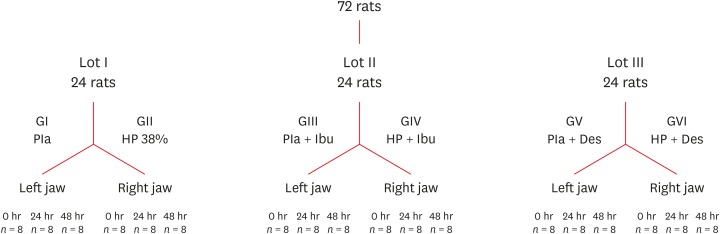
Materials and Methods Seventy-two rats were divided into 6 groups as follows: GI, control; GII, only dental bleaching; GIII, only ibuprofen; GIV, ibuprofen administered 30 minutes before and after the bleaching treatment and every 12 hours until the analysis; GV, only topical application of a desensitizing agent; and GVI, topical application of a desensitizing agent before dental bleaching. Placebo gel was applied to the upper left jaw and the bleaching agent was applied to the upper right jaw in all groups. Subsequently, the groups were divided into 3 subgroups based on the time of analysis: 0, 24, and 48 hours after bleaching (
n = 8). The rats were euthanized and the maxillae were processed and evaluated by histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses. The data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by the Dunn test (p < 0.05).Results In the bleaching groups, the inflammatory process and expression of neuropeptides decreased over time. The animals in which a desensitizing agent was applied showed better results within 24 hours.
Conclusions The use of a desensitizing agent had positive effects on inflammation and pain-related neuropeptide expression, minimizing the painful effects of dental bleaching treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Analgesics in Dental Whitening Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gabriella Alves Julião Costa, Caio Ferreira Freire Caetano, Ravy Jucá Farias, Diana Araújo Cunha, Dayrine Silveira de Paula, Edson Luiz Cetira Filho, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2025; 26(5): 639. CrossRef - The Use of Ozone Therapy in Combination with a Desensitizing Agent for Dentinal Tubules Occlusion: An In Vitro Study
Banna Alnufaiy
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of neurogenic inflammation in pulp repair and the techniques used for its assessment (narrative review)
Muna Sh. Ahmed, Anas F. Mahdee
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of dental bleaching on the pulp tissue: A systematic review of in vivo studies
Mariana Viana Donato, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Juliana Goto, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Francine Ben
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(6): 630. CrossRef - Role of induced nitric oxide synthases in orofacial nociception/discomfort after dental tooth bleaching with hydrogen peroxide
Marcílio Rodrigues Pinto, Kirlya Isabel da Silva Medeiros, Letícia Menezes Maia, Antonio Alexandre Coelho, Ana Paula Negreiros Nunes Alves, Caio Ferreira Freire Caetano, Karine Cestaro Mesquita, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva, Fabricio Bitu Sousa
Archives of Oral Biology.2024; 161: 105937. CrossRef - Can different agents reduce the damage caused by bleaching gel to pulp tissue? A systematic review of basic research
Letícia Aparecida Silva Batista, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Luís Fernando Santos Alves Morgan, Carolina Bosso André, Thaís Yumi Suzuki, Francine Benetti
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Different Drugs with Anti-Inflamatory Potential in Prevention of Pulp Damage During the Teeth Bleaching
Miona Glisic, Andjela Milojevic, Milica Milinkovic, Marina Rankovic
Experimental and Applied Biomedical Research (EABR).2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bleaching gel volume influences hydrogen peroxide diffusion, inflammation, and the presence of nitric oxide in the pulp tissue: in vitro and in vivo model
Sibele de ALCÂNTARA, Francine BENETTI, Lívia Maria Alves Valentim da SILVA, Nathália Evelyn da Silva MACHADO, Isabela Joane Prado SILVA, Lara Maria Bueno ESTEVES, Edilson ERVOLINO, Luciano Tavares Angelo CINTRA, André Luiz Fraga BRISO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of a thermosensitive ibuprofen-loaded nanogel as smart material applied as anti-inflammatory in tooth bleaching: An in vivo study
Samara K.S.C.F. Moura, Milena L.V. dos Santos, Lucas A. do Nascimento, Mariana F.A. da Silva, Glória M. de França, Lucas M. da Costa, Aldo C. Medeiros, Raimundo F. Araújo-Júnior, Aurigena A. de Araújo, Cláudia N. Oliveira, André L. Dorini, Rejane A. de Ca
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2022; 68: 103123. CrossRef - Topical application of Otosporin® before in-office bleaching: a split mouth, triple-blind, multicenter randomized clinical trial
Michael Willian Favoreto, Laína Vochikovski, Renata Maria Oleniki Terra, Veridiana Silva Campos, Mariana Evangelista Santos, Sônia Saeger Meireles, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(3): 2555. CrossRef - A novel tooth bleaching gel based on peroxymonosulfate/polyphosphates advanced oxidation process: Effective whitening avoiding pulp damage and sensitivity
Su Yang, Baiyan Sui, Xin Liu, Jiao Sun, Jun Wang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2022; 429: 132525. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Violet LED alone or in association with bleaching gel during dental photobleaching: A Systematic Review
Bianca Rossi, Susana Morimoto, Tamara Kerber Tedesco, Sandra Ribeiro Cunha, Anna Carolina Ratto Tempestini Horliana, Karen Müller Ramalho
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 38: 102813. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Analgesics in Dental Whitening Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,878 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Influence of 10-MDP concentration on the adhesion and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Kazuhiko Shibuya, Naoko Ohara, Serina Ono, Kumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Yoshiyama
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e45. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e45
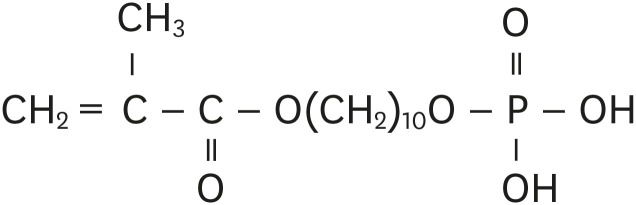
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Self-adhesive resin cements contain functional monomers that enable them to adhere to the tooth structure without a separate adhesive or etchant. One of the most stable functional monomers used for chemical bonding to calcium in hydroxyapatite is 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the10-MDP concentration on the bond strength and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods We used experimental resin cements containing 3 different concentrations of 10-MDP: 3.3 wt% (RC1), 6.6 wt% (RC2), or 9.9 wt% (RC3). The micro-tensile bond strength of each resin cement to dentin and a hybrid resin block (Estenia C&B, Kuraray Noritake Dental) was measured, and the fractured surface morphology was analyzed. Further, the flexural strength of the resin cements was measured using the three-point bending test. The water sorption and solubility of the cements following 30 days of immersion in water were measured.
Results The bond strength of RC2 was significantly higher than that of RC1. There was no significant difference between the bond strength of RC2 and that of RC3. The water sorption of RC3 was higher than that of any other cement. There were no significant differences in the three-point bending strength or water solubility among all three types of cements.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it is suggested that 6.6 wt% 10-MDP showed superior properties than 3.3 wt% or 9.9 wt% 10-MDP in self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Sofia Bignotto de Carvalho, Lívia Maiumi Uehara, João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104260. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Influence of temperature and curing modes on polymerization of self-adhesive resin cements
Hae-In Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(3): 143. CrossRef - Clinical Performance and Retention of Partial Implant Restorations Cemented with Fuji Plus® and DentoTemp™: A Retrospective Clinical Study with Mechanical Validation
Sergiu-Manuel Antonie, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Ioan-Achim Borsanu, Remus Christian Bratu, Emanuel-Adrian Bratu
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2183. CrossRef - A thorough assessment of 10-MDP primers in modern dental adhesive systems
Ahmed A Abduljawad, Harraa SM Salih, Omar F Tawfiq
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 79. CrossRef - Material properties and finite element analysis of adhesive cements used for zirconia crowns on dental implants
Megha Satpathy, Hai Pham, Shreya Shah
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Clinical reliability of self-adhesive luting resins compared to other adhesive procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammed Ahmed Alghauli, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 129: 104394. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization on bond strength between zirconia frameworks and Ti-base abutments using different resin cements
Reinhold Lang, Karl-Anton Hiller, Lena Kienböck, Katrin Friedl, Karl-Heinz Friedl
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(4): 617.e1. CrossRef - Varying 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP) level improves polymerisation kinetics and flexural strength in self-adhesive, remineralising composites
António H.S. Delgado, Nazanin Owji, Paul Ashley, Anne M. Young
Dental Materials.2021; 37(9): 1366. CrossRef - Investigating a Commercial Functional Adhesive with 12-MDPB and Reactive Filler to Strengthen the Adhesive Interface in Eroded Dentin
Madalena Belmar da Costa, António HS Delgado, Tomás Amorim Afonso, Luís Proença, Ana Sofia Ramos, Ana Mano Azul
Polymers.2021; 13(20): 3562. CrossRef
- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- 2,804 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Dental care for patients taking antiresorptive drugs: a literature review
- Minju Song
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Antiresorptive drugs (ARDs), such as bisphosphonates or denosumab, that prevent bone resorption are widely used in patients with osteoporosis or with cancer that has metastasized to the bones. Although osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is a well-documented complication of ARD use, the benefits ARDs outweigh the complication. Thus, research has focused on finding ways to prevent or reduce the risk of developing ONJ. Dentists, as part of a multi-professional team, have a critical role in preventing ONJ. However, many dentists tend to hesitate to provide dental care to patients with ONJ, or tend to think that it is a problem to be dealt with by oral surgeons. This review gives an overview of ARD-related ONJ and provides the guidelines for dental care in patients taking ARDs to lower the risk of developing ONJ.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Successful prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw after dental extractions by socket preservation with alloplast plus tetracycline in patients taking antiresorptive drugs
Liang-Ho Lin, Chun-Hsiang Wang, Shin-Yu Lu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 21(1): 468. CrossRef - Dynamic Navigation in Endodontics: Scope, Benefits, and Challenges - A Systematic Review
Ankita Kapoor, Ragavi Alagarsamy, Babu Lal, Amal Singh Rana, Amandeep Kaur, Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 879. CrossRef - Biosimilars in osteoporosis treatment: focus on denosumab
Matti Aapro, Peyman Hadji, Daniele Santini, Ralf Schmidmaier, Richard Eastell
Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy.2025; 25(8): 887. CrossRef - Assessment of the occurrence of apical periodontitis and endodontically treated/non-treated teeth in a Lower Austrian patient population treated for osteoporosis: a cohort study
Pascal Grün, Marius Meier, Johannes Dittrich, Arb Gjergjindreaj, Dragan Ströbele, Florian Pfaffeneder-Mantai, Sepideh Hatamikia, Margrit-Ann Geibel, Dritan Turhani
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(9): 5049. CrossRef - Endodontic and periapical status of patients with osteoporosis
Selin Goker Kamalı, Dilek Turkaydın
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2024; 155(12): 1022. CrossRef - Postoperative pain in oncological patients subjected to nonsurgical root canal treatment: a prospective case-control study
Kaline Romeiro, Luciana F. Gominho, Isabela N. Rôças, José F. Siqueira Jr
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Periodontal ligament‐associated protein‐1 promotes osteoclastogenesis in mice by modulating TGF‐β1/Smad1 pathway
Shuang Liu, Xijiao Yu, Qiushuang Guo, Shuaiqi Zhao, Kaixian Yan, Meng Hou, Fuxiang Bai, Shu Li
Journal of Periodontology.2024; 95(2): 146. CrossRef - What Is the Appropriate Antibiotic Administration During Tooth Extractions in Patients Receiving High-Dose Denosumab?
Eiji Iwata, Takumi Hasegawa, Hiroaki Ohori, Toshiya Oko, Tsutomu Minamikawa, Daisuke Miyai, Masaki Kobayashi, Naoki Takata, Shungo Furudoi, Junichiro Takeuchi, Kosuke Matsumoto, Akira Tachibana, Masaya Akashi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perfil Odontológico dos Pacientes em Uso de Bisfosfonatos em um Hospital Oncológico
Jade Fontenele Tagliabue, Lísia Daltro Borges Alves, Héliton Spíndola Antunes
Revista Brasileira de Cancerologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the Degree of Information of Dental Surgeons about Antiresorptive Drugs According to the Time Since Graduation in Dentistry
Flávia Godinho Costa Wanderley Rocha, Roberto Paulo Correia de Araújo
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteonecrosis of the Jaw and Antiresorptive Agents in Benign and Malignant Diseases: A Critical Review Organized by the ECTS
Athanasios D Anastasilakis, Jessica Pepe, Nicola Napoli, Andrea Palermo, Christos Magopoulos, Aliya A Khan, M Carola Zillikens, Jean-Jacques Body
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): 1441. CrossRef - Accuracy of Dynamic Navigation for Non-Surgical Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
Egle Marija Jonaityte, Goda Bilvinaite, Saulius Drukteinis, Andres Torres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(12): 3441. CrossRef - Periapical status in patients affected by osteoporosis: A retrospective clinical study
Erika Cadoni, Francesca Ideo, Giuseppe Marongiu, Silvia Mezzena, Luca Frigau, Quirico Mela, Antonio Capone, Henry F. Duncan, Elisabetta Cotti
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(5): 1068. CrossRef - LONG-TERM USE OF DENOSUMAB IN GIANT CELL TUMORS AND VERTEBRAL ANEURYSMAL BONE CYSTS
Pedro Luis Bazán, Micaela Cinalli, Felipe Lanari Zabiaur, Roberto Castelli, Claudio Silveri, José Luis Monayer, Enrique Gustavo Gobbi, Alejandro Maria Steverlynck
Coluna/Columna.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A 5-year retrospective cohort study of denosumab induced medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw in osteoporosis patients
Seoyeon Jung, Jaeyeon Kim, Jin Hoo Park, Ki-Yeol Kim, Hyung Jun Kim, Wonse Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Patients under Treatment with Monoclonal Antibodies and New Biological Therapies
Marta Amigo-Basilio, Covadonga Álvarez-González, Carlos Cobo-Vázquez, Isabel Leco-Berrocal, Luis Miguel Sáez-Alcaide, Cristina Méniz-García
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(11): 4865. CrossRef - Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw, a Hidden Enemy. An Integrative Review
Odel Chediak-Barbur
Universitas Odontologica.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Retrospective Observational Study of Risk Factors for Denosumab-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Patients with Bone Metastases from Solid Cancers
Satoe Okuma, Yuhei Matsuda, Yoshiki Nariai, Masaaki Karino, Ritsuro Suzuki, Takahiro Kanno
Cancers.2020; 12(5): 1209. CrossRef
- Successful prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw after dental extractions by socket preservation with alloplast plus tetracycline in patients taking antiresorptive drugs
- 4,438 View
- 52 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effect of the restorative technique on load-bearing capacity, cusp deflection, and stress distribution of endodontically-treated premolars with MOD restoration
- Daniel Maranha da Rocha, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Milena Cerqueira da Rocha, Rebeca Di Nicoló, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e33. Published online August 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the influence of the restorative technique on the mechanical response of endodontically-treated upper premolars with mesio-occluso-distal (MOD) cavity.
Materials and Methods Forty-eight premolars received MOD preparation (4 groups,
n = 12) with different restorative techniques: glass ionomer cement + composite resin (the GIC group), a metallic post + composite resin (the MP group), a fiberglass post + composite resin (the FGP group), or no endodontic treatment + restoration with composite resin (the CR group). Cusp strain and load-bearing capacity were evaluated. One-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test were used with α = 5%. Finite element analysis (FEA) was used to calculate displacement and tensile stress for the teeth and restorations.Results MP showed the highest cusp (
p = 0.027) deflection (24.28 ± 5.09 µm/µm), followed by FGP (20.61 ± 5.05 µm/µm), CR (17.72 ± 6.32 µm/µm), and GIC (17.62 ± 7.00 µm/µm). For load-bearing, CR (38.89 ± 3.24 N) showed the highest, followed by GIC (37.51 ± 6.69 N), FGP (29.80 ± 10.03 N), and MP (18.41 ± 4.15 N) (p = 0.001) value. FEA showed similar behavior in the restorations in all groups, while MP showed the highest stress concentration in the tooth and post.Conclusions There is no mechanical advantage in using intraradicular posts for endodontically-treated premolars requiring MOD restoration. Filling the pulp chamber with GIC and restoring the tooth with only CR showed the most promising results for cusp deflection, failure load, and stress distribution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to adaptively balance ‘classic’ or ‘conservative’ approaches in tooth defect management: a 3D-finite element analysis study
Jiani Xu, Xu Liang, Lili Hu, Chen Sun, Zhipeng Zhang, Jiawei Yang, Jie Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Inkjet-printed strain gauge sensors: Materials, manufacturing, and emerging applications
Lara Abdel Salam, Samir Mustapha, Alexandra Mikhael, Nisrine Bakri, Sahera Saleh, Massoud L. Khraiche
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.2025; 394: 116934. CrossRef - Influence of endodontic access cavity design on mechanical properties of a first mandibular premolar tooth: a finite element analysis study
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Burçin Arıcan, Mustafa Gündoğar, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Effect of Different Cavity Designs and Temporary Restoration Materials on the Fracture Resistance of Upper Premolars, Undergone Re-treatment: An In-Vitro Study
Parnian Alavinejad, Mohammad Yazdizadeh, Ali Mombeinipour, Ebrahim Karimzadeh
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences.2024; 94(3): 677. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and failure mode of endodontically treated premolars reconstructed by different preparation approaches: Cervical margin relocation and crown lengthening with complete and partial ferrule with three different post and core systems
Mehran Falahchai, Naghmeh Musapoor, Soroosh Mokhtari, Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Hamid Neshandar Asli
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(8): 774. CrossRef - Comparison of the stress distribution in base materials and thicknesses in composite resin restorations
Min-Kwan Jung, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e25040. CrossRef -
Fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated maxillary premolars restored with transfixed glass fiber post: an
in vitro
and finite element analysis
Saleem Abdulrab, Greta Geerts, Ganesh Thiagarajan
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 27(4): 419. CrossRef - Influence of size-anatomy of the maxillary central incisor on the biomechanical performance of post-and-core restoration with different ferrule heights
Domingo Santos Pantaleón, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Franklin García-Godoy
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Influence of internal angle and shape of the lining on residual stress of Class II molar restorations
Qianqian Zuo, Annan Li, Haidong Teng, Zhan Liu
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 27(5): 680. CrossRef - Evaluation of stress distribution in coronal base and restorative materials: A narrative review of finite element analysis studies
Yelda Polat, İzzet Yavuz
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2024; 14(2): 47. CrossRef - The influence of horizontal glass fiber posts on fracture strength and fracture pattern of endodontically treated teeth: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Saleem Abdulrab, Greta Geerts, Sadeq Ali Al‐Maweri, Mohammed Nasser Alhajj, Hatem Alhadainy, Raidan Ba‐Hattab
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(6): 469. CrossRef - Stress distribution of a novel bundle fiber post with curved roots and oval canals
Deniz Yanık, Nurullah Turker
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(3): 550. CrossRef - The Effect of Endodontic Treatment and Thermocycling on Cuspal Deflection of Teeth Restored with Different Direct Resin Composites
Cansu Atalay, Ayse Ruya Yazici, Aynur Sidika Horuztepe, Emre Nagas
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2022; 6(2): 38. CrossRef - The use of different adhesive filling material and mass combinations to restore class II cavities under loading and shrinkage effects: a 3D-FEA
P. Ausiello, S. Ciaramella, A. De Benedictis, A. Lanzotti, J. P. M. Tribst, D. C. Watts
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2021; 24(5): 485. CrossRef - Biomechanical Analysis of a Custom-Made Mouthguard Reinforced With Different Elastic Modulus Laminates During a Simulated Maxillofacial Trauma
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Pietro Ausiello, Arianna De Benedictis, Marco Antonio Bottino, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction.2021; 14(3): 254. CrossRef - Mechanical Assessment of Glass Ionomer Cements Incorporated with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Dental Applications
Manuela Spinola, Amanda Maria Oliveira Dal Piva, Patrícia Uchôas Barbosa, Carlos Rocha Gomes Torres, Eduardo Bresciani
Oral.2021; 1(3): 190. CrossRef - Stress Concentration of Endodontically Treated Molars Restored with Transfixed Glass Fiber Post: 3D-Finite Element Analysis
Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Manassés Tercio Vieira Grangeiro, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Renata Marques de Melo, Kusai Baroudi, Laís Regiane Silva-Concilio, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Materials.2021; 14(15): 4249. CrossRef - Computer Aided Design Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Premolar Proximal Cavities Restored with Resin Composites
Amanda Guedes Nogueira Matuda, Marcos Paulo Motta Silveira, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Luca Testarelli, Gabriella Mosca, Pietro Ausiello
Materials.2021; 14(9): 2366. CrossRef - Effect of Shrinking and No Shrinking Dentine and Enamel Replacing Materials in Posterior Restoration: A 3D-FEA Study
Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Antonio Lanzotti, Fausto Zamparini, Ettore Epifania, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(5): 2215. CrossRef - Effect of Fiber-Reinforced Composite and Elastic Post on the Fracture Resistance of Premolars with Root Canal Treatment—An In Vitro Pilot Study
Jesús Mena-Álvarez, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Alvaro Zubizarreta-Macho
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(21): 7616. CrossRef
- How to adaptively balance ‘classic’ or ‘conservative’ approaches in tooth defect management: a 3D-finite element analysis study
- 2,232 View
- 23 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Discoloration of teeth due to different intracanal medicaments
- Farzaneh Afkhami, Sadaf Elahy, Alireza Mahmoudi Nahavandi, Mohamad Javad Kharazifard, Aidin Sooratgar
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e10. Published online February 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e10

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The objective of this study was to assess coronal discoloration induced by the following intracanal medicaments: calcium hydroxide (CH), a mixture of CH paste and chlorhexidine gel (CH/CHX), and triple antibiotic paste (3Mix).
Materials and Methods Seventy extracted single-canal teeth were selected. Access cavities were prepared and each canal was instrumented with a rotary ProTaper system. The specimens were randomly assigned to CH, CH/CHX, and 3Mix paste experimental groups (
n = 20 each) or a control group (n = 10). Each experimental group was randomly divided into 2 subgroups (A and B). In subgroup A, medicaments were only applied to the root canals, while in subgroup B, the root canals were completely filled with medicaments and a cotton pellet dipped in medicament was also placed in the pulp chamber. Spectrophotometric readings were obtained from the mid-buccal surface of the tooth crowns immediately after placing the medicaments (T1) and at 1 week (T2), 1 month (T3), and 3 months (T4) after filling. The ∆E was then calculated. Data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), 3-way ANOVA, and the Scheffépost hoc test.Results The greatest color change (ΔE) was observed at 3 months (
p < 0.0001) and in 3Mix subgroup B (p = 0.0057). No significant color change occurred in the CH (p = 0.7865) or CH/CHX (p = 0.1367) groups over time, but the 3Mix group showed a significant ΔE (p = 0.0164).Conclusion Intracanal medicaments may induce tooth discoloration. Use of 3Mix must be short and it must be carefully applied only to the root canals; the access cavity should be thoroughly cleaned afterwards.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
Laila Mohamed Mohamed Kenawi, Mohamed Fattouh, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Abla Arafa
The Open Dentistry Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of tooth discoloration induced by different intracanal medicaments in regenerative endodontics: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Ashlesha Nageshwar Madankar, Sulabha Radke, Shanmuga Priya, Darshan Dakshindas
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of Intra-canal Medicaments on Infrared Light Energy Transmission Through Enamel and Dentin During Photobiomodulation: An In Vitro Study
Sachin Kulkarni, Laurence J. Walsh, Yash Bhurani, Roy George
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(5): 616. CrossRef - Tooth discoloration caused by nanographene oxide as an irrigant and intracanal medicament in the endodontic treatment of extracted single-rooted teeth: An ex-vivo study
Abbas Abbaszadegan, Zeinab Rafiee, Bahar Asheghi, Ahmad Gholami, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS One.2025; 20(6): e0325430. CrossRef - Investigation of Discoloration of Anterior Teeth With Three Types of Substances Used in Endodontic Treatment
Sahar Soltani, Eshagh Ali Saberi, Nazanin Shahradnia, Pedram Abdollahzade Sangrodi, Elham Majidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A New Disinfection Approach Using a Chitosan-Based Endodontic Irrigant
Alejandra Itzel Lopez-Flores, Ulises Velazquez-Enriquez, Rogelio Jose Scougall-Vilchis, Laura Susana Acosta-Torres, Laura Emma Rodriguez-Vilchis, Rosalía Contreras-Bulnes, Paloma Netzayeli Serrano-Diaz, Rene Garcia-Contreras
Materials.2025; 18(24): 5552. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric Analysis of Intracoronal Bleaching on Crown Discoloration Induced by Various Antibiotic Pastes: An In Vitro Study
Avneet Kaur, Harshit Srivastava, Deepak Raisingani, Ashwini B Prasad, Dileep Soni, Poorva R Sharma
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(12): 1443. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Versus Double Antibiotic Paste on Endodontic Treatment Outcomes in Teeth With Large Periapical Lesions: A Triple‐Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
Afsaneh Rahmati, Farshad Seyedein, Omid Dianat, Sara Saedi, Golriz Rostami, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Shima Sabertahan, Majid Kazem, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different intracanal irrigants on the push-out bond strength of dentin in damaged anterior primary teeth
Leila Bassir, Shirin Taravati, Farzad Nouri, Saeide Rahimi
Journal of Medicine and Life.2024; 17(5): 536. CrossRef - In Vıtro Evaluatıon of Dıscoloratıon Caused by Root Canal Sealers and Color Changes after Bleachıng
Emre Bodrumlu, Esma Dinger
Annals of Dental Specialty.2024; 12(1): 77. CrossRef - Assessment of Discoloration Induced by Root Canal Sealers and Color Alterations Post-Bleaching
T.P. Van der Burgt, T.P. Mullaney, A.J.M. Plasschaert
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2024; 4(1): 1. CrossRef - The effect of four different intracanal medicaments on the push-out bond strength of root canal sealers
Shalu Maan, Vijaya Dhar Bhatt, Rohit Singh, Sayak Gupta, Syed Alay Noorain, Aashna Gill, Pradeep Kumar, Sushil Yadav, Preeti Sharma
Journal of Medicine and Life.2022; 15(4): 448. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
- 3,117 View
- 58 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Mineral content analysis of root canal dentin using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
- Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu, Banu Sezer, Zeliha Yılmaz, İsmail Hakkı Boyacı
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e11. Published online February 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to introduce the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for evaluation of the mineral content of root canal dentin, and to assess whether a correlation exists between LIBS and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) methods by comparing the effects of irrigation solutions on the mineral content change of root canal dentin.
Materials and Methods Forty teeth with a single root canal were decoronated and longitudinally sectioned to expose the canals. The root halves were divided into 4 groups (
n = 10) according to the solution applied: group NaOCl, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 1 hour; group EDTA, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 2 minutes; group NaOCl+EDTA, 5.25% NaOCl for 1 hour and 17% EDTA for 2 minutes; a control group. Each root half belonging to the same root was evaluated for mineral content with either LIBS or SEM/EDS methods. The data were analyzed statistically.Results In groups NaOCl and NaOCl+EDTA, the calcium (Ca)/phosphorus (P) ratio decreased while the sodium (Na) level increased compared with the other groups (
p < 0.05). The magnesium (Mg) level changes were not significant among the groups. A significant positive correlation was found between the results of LIBS and SEM/EDS analyses (r = 0.84,p < 0.001).Conclusions Treatment with NaOCl for 1 hour altered the mineral content of dentin, while EDTA application for 2 minutes had no effect on the elemental composition. The LIBS method proved to be reliable while providing data for the elemental composition of root canal dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
Thalya Fernanda Horsth Maltarollo, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Henrique Augusto Banci, Mariana de Oliveira Bachega, Beatriz Melare de Oliveira, Marco Hungaro Antonio Duarte, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Luciano Angelo Tavares
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Using 5% Apple Vinegar Irrigation Solution Adjunct to Diode Laser on Smear Layer Removal and Calcium/Phosphorus Ion Ratio during Root Canal Treatment
Tarek AA Salam, Haythem SA Kader, Elsayed E Abdallah
CODS - Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 3. CrossRef - Evaluation of chemical composition of root canal dentin between two age groups using different irrigating solutions: An in vitro sem-eds study
Naresh Kumar K, Abhijith Kallu, Surender L.R, Sravani Nirmala, Narender Reddy
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 12(1): 18. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Novel Nanohydroxyapatite Gel and Er: YAG Laser Treatment on Dentin Hypersensitivity
Demet Sahin, Ceren Deger, Burcu Oglakci, Metehan Demirkol, Bedri Onur Kucukyildirim, Mehtikar Gursel, Evrim Eliguzeloglu Dalkilic
Materials.2023; 16(19): 6522. CrossRef - Chitosan Homogenizing Coffee Ring Effect for Soil Available Potassium Determination Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Xiaolong Li, Rongqin Chen, Zhengkai You, Tiantian Pan, Rui Yang, Jing Huang, Hui Fang, Wenwen Kong, Jiyu Peng, Fei Liu
Chemosensors.2022; 10(9): 374. CrossRef - Quantitative analysis of cadmium in rice roots based on LIBS and chemometrics methods
Wei Wang, Wenwen Kong, Tingting Shen, Zun Man, Wenjing Zhu, Yong He, Fei Liu
Environmental Sciences Europe.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
- 1,778 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
- Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare root canal volume change and canal transportation by Vortex Blue (VB; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties), ProTaper Next (PTN; Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Universal (PTU; Dentsply Maillefer) nickel-titanium rotary files in curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty canals with 20°–45° of curvature from extracted human molars were used. Root canal instrumentation was performed with VB, PTN, and PTU files up to #30.06, X3, and F3, respectively. Changes in root canal volume before and after the instrumentation, and the amount and direction of canal transportation at 1, 3, and 5 mm from the root apex were measured by using micro-computed tomography. Data of canal volume change were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test, while data of amount and direction of transportation were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney
U test.Results There were no significant differences among 3 groups in terms of canal volume change (
p > 0.05). For the amount of transportation, PTN showed significantly less transportation than PTU at 3 mm level (p = 0.005). VB files showed no significant difference in canal transportation at all 3 levels with either PTN or PTU files. Also, VB files showed unique inward transportation tendency in the apical area.Conclusions Other than PTN produced less amount of transportation than PTU at 3 mm level, all 3 file systems showed similar level of canal volume change and transportation, and VB file system could prepare the curved canals without significant shaping errors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
Yaprak Cesur, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Ahmet Serper, Mert Ocak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of Vortex Blue and TruNatomyTM Ni-Ti Rotary Systems
Batool Alghamdi, Mey Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman, Lina Bahanan, Ali Alrahlah, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Sarah Bukhari, Mohammed Howait, Loai Alsofi
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 980. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of nickel titanium rotary instruments on canal transportation and centering ability in curved canals by using cone beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Krishnaveni Krishnaveni, Nikitha Kalla, Nagalakshmi Reddy, Sharvanan Udayar
Journal of Dental Specialities.2023; 11(2): 105. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - A Comparison of Canal Width Changes in Simulated Curved Canals prepared with Profile and Protaper Rotary Systems
Aisha Faisal, Huma Farid, Robia Ghafoor
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 55. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Respect of the Root Canal Trajectory by Rotary Niti Instruments (Protaper®Universal): Retrospective Radiographic Study
Salma El Abbassi, Sanaa Chala, Majid Sakout, Faïza Abdallaoui
Integrative Journal of Medical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
- 1,787 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of two different methods of detecting residual caries
- Uzay Koç Vural, Zeynep Bilge Kütük, Esra Ergin, Filiz Yalçın Çakır, Sevil Gürgan
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):48-53. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.48

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the ability of the fluorescence-aided caries excavation (FACE) device to detect residual caries by comparing conventional methods
in vivo .Materials and Methods A total of 301 females and 202 males with carious teeth participated in this study. The cavity preparations were done by grade 4 (Group 1, 154 teeth), grade 5 (Group 2, 176 teeth), and postgraduate (Group 3, 173 teeth) students. After caries excavation using a handpiece and hand instruments, the presence of residual caries was evaluated by 2 investigators who were previously calibrated for visual-tactile assessment with and without magnifying glasses and trained in the use of a FACE device. The tooth number, cavity type, and presence or absence of residual caries were recorded. The data were analyzed using the Chi-square test, the Fisher's Exact test, or the McNemar test as appropriate. Kappa statistics was used for calibration. In all tests, the level of significance was set at
p = 0.05.Results Almost half of the cavities prepared were Class II (Class I, 20.9%; Class II, 48.9%; Class III, 20.1%; Class IV, 3.4%; Class V, 6.8%). Higher numbers of cavities left with caries were observed in Groups 1 and 2 than in Group 3 for all examination methods. Significant differences were found between visual inspection with or without magnifying glasses and inspection with a FACE device for all groups (
p < 0.001). More residual caries were detected through inspection with a FACE device (46.5%) than through either visual inspection (31.8%) or inspection with a magnifying glass (37.6%).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, the FACE device may be an effective method for the detection of residual caries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CariesXplainer: enhancing dental caries detection using Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping and transfer learning
Saira Asghar, Junaid Rashid, Anum Masood
Multimedia Tools and Applications.2025; 84(38): 46647. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of caries detector dyes and laser fluorescence systems for intraoperative diagnosis during selective caries removal: a scoping review
Ana Iglesias-Poveda, Javier Flores-Fraile, Diego González-Gil, Joaquín López-Marcos
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fluorescence as a Quantitative Indicator of Cariogenic Bacteria During Chemo-Mechanical Caries Excavation with BRIX 3000 in Primary Teeth
Zornitsa Lazarova, Raina Gergova, Nadezhda Mitova
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(12): 453. CrossRef - Examining the Efficacy of a 405 nm Wavelength Diode Laser as a Diagnostic Tool in Routine Dental Practice
Marwan El Mobader, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diş Çürüğünün Teşhisi ve Bu Amaçla Kullanılan Güncel Yöntemler
Oya BALA, Sümeyye KANLIDERE
Türk Diş Hekimliği Araştırma Dergisi.2023; 2(2): 219. CrossRef - Longitudinal study for dental caries calibration of dentists unexperienced in epidemiological surveys
Mariana NABARRETTE, Patrícia Rafaela dos SANTOS, Andréa Videira ASSAF, Glaucia Maria Bovi AMBROSANO, Marcelo de Castro MENEGHIM, Silvia Amélia Scudeler VEDOVELLO, Karine Laura CORTELLAZZI
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - CURRENT CONCEPTS AND TECHNIQUES IN CARIES EXCAVATION: A REVIEW
Priyanka Aggarwal, Shivani Mathur, Tanya Batra
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 26. CrossRef - Current Strategies to Control Recurrent and Residual Caries with Resin Composite Restorations: Operator- and Material-Related Factors
Moataz Elgezawi, Rasha Haridy, Moamen A. Abdalla, Katrin Heck, Miriam Draenert, Dalia Kaisarly
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6591. CrossRef - Rezidüel Çürük Tespitinde Kullanılan Geleneksel Yöntemin Farklı Yöntemlerle Klinik Olarak Doğrulanması
Fatma SAĞ GÜNGÖR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 402. CrossRef
- CariesXplainer: enhancing dental caries detection using Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping and transfer learning
- 2,020 View
- 14 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Dental management of patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia
- Bin-Na Lee, Hye-Yoon Jung, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):146-151. Published online January 6, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is a hereditary metabolic disease caused by the loss of phosphate through the renal tubules into the urine, and an associated decrease in serum calcium and potassium phosphate. Its dental features include spontaneous dental abscesses that occur in the absence of trauma or dental caries. The aim of this case report was to describe the dental problems of XLH patients and to evaluate limitations in their treatment. A 14 year old male and a 38 year old female with XLH were referred to the Department of Conservative Dentistry for endodontic treatment. The dental findings were periapical abscesses without obvious trauma or caries. Conservative endodontic treatment was performed in teeth with pulp necrosis and abscess. In case 1, the treated teeth showed improvements in bone healing, without clinical symptoms. However, in case 2, the implants and the treated tooth showed hypermobility, and the final restoration was therefore postponed. Early diagnosis, periodic examinations, and communication with the patient's pediatrician are important in the dental management of patients with XLH.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral Features in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets: An 8-Year Follow-Up Case Report
Soumaya Kachti, Manel Chalbi, Soumaya Boussaid, Faten Awled Brahim, Mohamed Ali Chemli
OBM Genetics.2025; 09(02): 1. CrossRef - Targeted Alkaline Phosphatase Therapy Enhances Alveolar Bone Healing in X‐Linked Hypophosphatemia in Mice
Aonjittra Phanrungsuwan, Bella Donnelly, José Luis Millán, Brian L. Foster
Journal of Periodontal Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental implant considerations in patients with systemic diseases: An updated comprehensive review
Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Sahar Talebi, Seied Omid Keyhan, Hamid Reza Fallahi, Mohammad Darvishi, Seyedeh Sara Aghili, Narges Tavahodi, Reza Abdollahi Namanloo, Artak Heboyan, Amirhossein Fathi
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 51(7): 1250. CrossRef - Inherited fibroblast growth factor 23 excess
Kripa Elizabeth Cherian, Thomas Vizhalil Paul
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 38(2): 101844. CrossRef - Dental abnormalities in rare genetic bone diseases: Literature review
Eiji Iwata, Shyam Kishor Sah, I‐Ping Chen, Ernst Reichenberger
Clinical Anatomy.2024; 37(3): 304. CrossRef - Implant Survival in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Case Report and Systematic Review of the Literature
Iris Alla, Felice Lorusso, Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, Francesco Inchingolo, Maristella Di Carmine, Antonio Scarano
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2401. CrossRef - X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: Orthodontic considerations and management. A case report
Clara Gibson, Suhaym Mubeen, Robert Evans
Journal of Orthodontics.2022; 49(2): 205. CrossRef - X-chromosomale Hypophosphatämie (XLH)/Phosphatdiabetes – Eine lebenslange Erkrankung
Adalbert Raimann, Roland Kocijan, Gabriel T. Mindler
Journal für Klinische Endokrinologie und Stoffwechsel.2022; 15(2): 63. CrossRef - Dental Manifestations and Oral Management of X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Rena Okawa, Kazuhiko Nakano
Endocrines.2022; 3(4): 654. CrossRef - Prospective Analysis of Muscle Adiposity in Children With X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets vs Control Children
Virginie Nguyen-Khac, Aurore Bonnet-Lebrun, Agnès Linglart, Marine de Tienda, Jugurtha Berkenou, Inès Mannes, Catherine Adamsbaum, Philippe Wicart, Wafa Skalli
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental and periodontal features and management in XLH children and adults
Martin Biosse Duplan, Elvire Le Norcy, Frédéric Courson, Catherine Chaussain
International Journal of Bone Fragility.2021; 1(2): 74. CrossRef - Hiding in plain sight: Gene panel and genetic markers reveal 26-year undiagnosed tumor-induced osteomalacia of the rib concurrently misdiagnosed as X-linked hypophosphatemia
Juan M. Colazo, Joseph A. DeCorte, Erin A. Gillaspie, Andrew L. Folpe, Kathryn M. Dahir
Bone Reports.2021; 14: 100744. CrossRef - X-linked hypophosphatemia and burosumab: Practical clinical points from the French experience
Justine Bacchetta, Anya Rothenbuhler, Iva Gueorguieva, Peter Kamenicky, Jean-Pierre Salles, Karine Briot, Agnès Linglart
Joint Bone Spine.2021; 88(5): 105208. CrossRef - Presentation and non‐surgical endodontic treatment of two patients with X‐linked hypophosphatemia: a case report
H. Bradley, A. Dutta, R. Philpott
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1403. CrossRef - Periodontal status evaluation in adolescents with hereditary rickets-like diseases
E.V. Vislobokova, L.P. Kiselnikova, D.A. Lezhnev, S.S. Murtazaev, N.A. Sholokhova
Stomatologiya.2021; 100(6): 63. CrossRef - Diagnosis, treatment-monitoring and follow-up of children and adolescents with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH)
Anya Rothenbuhler, Dirk Schnabel, Wolfgang Högler, Agnès Linglart
Metabolism.2020; 103: 153892. CrossRef - Long-term outcomes for Asian patients with X-linked hypophosphataemia: rationale and design of the SUNFLOWER longitudinal, observational cohort study
Takuo Kubota, Seiji Fukumoto, Hae Il Cheong, Toshimi Michigami, Noriyuki Namba, Nobuaki Ito, Shin Tokunaga, Yoshimi Gibbs, Keiichi Ozono
BMJ Open.2020; 10(6): e036367. CrossRef - X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets Manifesting as Sclerotic Bone Disease and Enthesopathy
Hiya Boro, Shailendra Singh Naik, Charandeep Singh, Saurav Khatiwada, Rajesh Khadgawat
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - X-linked hypophosphatemia diagnosed after identification of dental symptoms
Kaoruko Wato, Rena Okawa, Saaya Matayoshi, Yuko Ogaya, Ryota Nomura, Kazuhiko Nakano
Pediatric Dental Journal.2020; 30(2): 115. CrossRef - X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: A New Era in Management
Kathryn Dahir, Mary Scott Roberts, Stan Krolczyk, Jill H Simmons
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prosthetic rehabilitation of a patient with X-linked hypophosphatemia using dental implants: a case report and review of the literature
Martin James, Reza Vahid Roudsari
International Journal of Implant Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral symptoms and oral health-related quality of life of individuals with x-linked hypophosphatemia
Marcel Hanisch, Lauren Bohner, Martin M. I. Sabandal, Johannes Kleinheinz, Susanne Jung
Head & Face Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of adult patients with X‐linked hypophosphatemia caused by PHEX gene mutations
Douglas Chesher, Michael Oddy, Ulpee Darbar, Parag Sayal, Adrian Casey, Aidan Ryan, Annalisa Sechi, Charlotte Simister, Aoife Waters, Yehani Wedatilake, Robin H. Lachmann, Elaine Murphy
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease.2018; 41(5): 865. CrossRef
- Oral Features in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets: An 8-Year Follow-Up Case Report
- 2,896 View
- 15 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Effect of three nanobiomaterials on microhardness of bleached enamel
- Maryam Khoroushi, Farinaz Shirban, Sara Kaveh, Samaneh Doustfateme
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):196-201. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the effect of incorporating three different nanobiomaterials into bleaching material on microhardness of bleached enamel.Materials and Methods The crowns of 24 extracted sound human molars were sectioned. Sixty enamel specimens (2 × 3 × 4 mm) were selected and divided into five groups (
n = 12): Group 1 received no bleaching procedure (control); Group 2 underwent bleaching with a 40% hydrogen peroxide (HP) gel; Groups 3, 4, and 5 were bleached with a 40% HP gel modified by incorporation of bioactive glass (BAG), amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) and hydroxyapatite (HA), respectively. The enamel microhardness was evaluated. The differences in Knoop microhardness data of each group were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed bypost hoc Tukey tests.Results Significant differences were observed between the study groups. The enamel microhardness changes in Groups 1, 3, 4, and 5 were significantly lower than that of Group 2 (
p < 0.001).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that incorporation of each one of the three tested biomaterials as remineralizing agents might be effective in decreasing enamel microhardness changes subsequent to in-office bleaching.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of bleaching agents containing nano-hydroxyapatite on sound and demineralized enamel: an in vitro study
Merve Haberal, Çiğdem Çelik
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective role of calcium-based agents in dental bleaching gels: insights from a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical and laboratory evidence
Gabriel Pereira Nunes, Renata de Oliveira Alves, Geórgia Rondó Peres, Matheus Henrique Faccioli Ragghianti, Priscila Toninatto Alves de Toledo, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis Prado, Carla Ferreira-Baptista, Alberto Carlos Botazzo Delbem
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Enamel Surface and Shear Bond Strength with Orthodontic Bracket at Different Time Intervals After Bleaching Treatment
Yu-Jin Lee, Ji-Yeon Hong, Hye-Min Ku, Song-Yi Yang
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(2): 130. CrossRef - Effect of strontium fluorophosphate bioactive glass on color, microhardness and surface roughness of bleached enamel
Shiza Yezdani, Monisha Khatri, Sampath Vidhya, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Technology and Health Care.2024; 32(1): 285. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the effect of addition of biomaterials to carbamide peroxide on the bleaching efficacy and microhardness of enamel
Sowmya Kavoor, M. A. Ranjini, Naval Abdul Aziz, H. K. Ashok, Roopa R. Nadig
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 310. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogen peroxide and its combination with nano-hydroxyapatite or nano-bioactive glass on the enamel demineralization and tooth color: An in vitro study
Elham Kheradmand, Alirea Daneshkazemi, Abdolrahim Davari, Maede Kave, Solmaz Ghanbarnejad
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Over‐the‐counter bleaching agents can help with tooth whitening maintenance
Olívia Santana Jorge, Carolina Noronha Ferraz de Arruda, Rafaella Tonani Torrieri, Rocio Geng Vivanco, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires‐de‐Souza
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(2): 328. CrossRef - Effect of Indigenously Developed Nano-Hydroxyapatite Crystals from Chicken Egg Shell on the Surface Hardness of Bleached Human Enamel
Divya Kunam, Vidhya Sampath, Sujatha Manimaran, Mahalaxmi Sekar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 489. CrossRef - Influence of Time Intervals between Bleaching Procedures on Enamel Microhardness and Surface Roughness
Roberta Pimentel de Oliveira, Juliana Costa Pereira Baia, Mara Eliane Soares Ribeiro, Mario Honorato da Silva e Souza Junior, Sandro Cordeiro Loretto
The Open Dentistry Journal.2018; 12(1): 555. CrossRef
- Effects of bleaching agents containing nano-hydroxyapatite on sound and demineralized enamel: an in vitro study
- 1,659 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report
- Miguel Agostinho Beco Pinto Cardoso, Rita Brandão Noites, Miguel André Duarte Martins, Manuel Pedro da Fonseca Paulo
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):148-153. Published online February 22, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Tooth transposition is a disorder in which a permanent tooth develops and erupts in the normal position of another permanent tooth. Fusion and gemination are developmental disturbances presenting as the union of teeth. This article reports the nonsurgical retreatment of a very rare case of fused teeth with transposition. A patient was referred for endodontic treatment of her maxillary left first molar in the position of the first premolar, which was adjacent to it on the distobuccal side. Orthopantomography and periapical radiography showed two crowns sharing the same root, with a root canal treatment and an associated periapical lesion. Tooth fusion with transposition of a maxillary molar and a premolar was diagnosed. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment was performed. At four yr follow-up, the tooth was asymptomatic and the radiolucency around the apical region had decreased, showing the success of our intervention. The diagnosis and treatment of fused teeth require special attention. The canal system should be carefully explored to obtain a full understanding of the anatomy, allowing it to be fully cleaned and obturated. Thermoplastic techniques were useful in obtaining hermetic obturation. A correct anatomical evaluation improves the set of treatment options under consideration, leading to a higher likelihood of esthetically and functionally successful treatment.
- 1,482 View
- 12 Download

- Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):1-5. Published online February 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.1

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of ProTaper Gold (PTG, Dentsply Maillefer) in maintaining the original profile of root canal anatomy. For that, ProTaper Universal (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer) was used as reference techniques for comparison.
Materials and Methods Twenty simulated curved canals manufactured in clear resin blocks were randomly assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10) according to the system used for canal instrumentation: PTU and PTG groups, upto F2 files (25/0.08). Color stereomicroscopic images from each block were taken exactly at the same position before and after instrumentation. All image processing and data analysis were performed with an open source program (FIJI). Evaluation of canal transportation was obtained for two independent canal regions: straight and curved levels. Student'st test was used with a cut-off for significance set at α = 5%.Results Instrumentation systems significantly influenced canal transportation (
p < 0.0001). A significant interaction between instrumentation system and root canal level (p < 0.0001) was found. PTU and PTG systems produced similar canal transportation at the straight part, while PTG system resulted in lower canal transportation than PTU system at the curved part. Canal transportation was higher at the curved canal portion (p < 0.0001).Conclusions PTG system produced overall less canal transportation in the curved portion when compared to PTU system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
Wesley Viana de Sousa, Marina da Cunha Isaltino, Christianne Velozo, Silmara de Andrade Silva, Luiza de Almeida Souto Montenegro, Hugo Victor Dantas, Frederico Barbosa de Sousa, Diana Albuquerque, Cristiana Corsi
The Scientific World Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping, and disinfecting abilities of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Twisted Files: A correlative microcomputed tomographic and bacteriologic analysis
Malavika Sivakumar, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, CP Baveja, Rega Kumar, Sudha Yadav, S Santosh Kumar
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 54. CrossRef - Advancing Nitinol: From heat treatment to surface functionalization for nickel–titanium (NiTi) instruments in endodontics
Wai-Sze Chan, Karan Gulati, Ove A. Peters
Bioactive Materials.2023; 22: 91. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - An Appraisal on Newer Endodontic File Systems: A Narrative Review
Shalini Singh, Kailash Attur, Anjali Oak, Mohammed Mustafa, Kamal Kumar Bagda, Nishtha Kathiria
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 944. CrossRef - Shaping ability of modern Nickel–Titanium rotary systems on the preparation of printed mandibular molars
Seda Falakaloglu, Emmanuel Silva, Burcu Topal, Emre İriboz, Mustafa Gündoğar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 498. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna Dobrzańska
Processes.2022; 10(1): 101. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Kinematics on Stress Distribution During Root Canal Treatment: Analysis of Photoelastic Stress
Shelyn Akari Yamakami, Julia Adornes Gallas, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Manoel Sousa-Neto, Ana Paula Macedo, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 255. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Two Martensitic Alloy Systems in Endodontic Files Carried out by Unskilled Hands
Juan Algar, Alejandra Loring-Castillo, Ruth Pérez-Alfayate, Carmen Martín Carreras-Presas, Ana Suárez
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6289. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Canal Transportation, Separation Rate, and Preparation Time between One Shape and Neoniti (Neolix): An In Vitro CBCT Study
Maryam Kuzekanani, Faranak Sadeghi, Nima Hatami, Maryam Rad, Mansoureh Darijani, Laurence James Walsh, Sivakumar Nuvvula
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold, One Curve, and Self-Adjusting File systems in severely curved canals: A cone-beam computed tomography study
MeenuG Singla, Hemanshi Kumar, Ritika Satija
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 271. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of apical transportation and centering ratio of ProTaper and XP-endo Shaper NiTi rotary systems in curved canals: an in vitro study
Hamed Karkehabadi, Zeinab Siahvashi, Abbas Shokri, Nasrin Haji Hasani
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanical Tests, Metallurgical Characterization, and Shaping Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments: A Multimethod Research
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Jorge N.R. Martins, Carolina O. Lima, Victor T.L. Vieira, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Gustavo De-Deus, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(10): 1485. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of vibration characteristics of file systems for root canal shaping according to file length
Seong-Jun Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Hyo-Jin Ji, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys – a review
J. Zupanc, N. Vahdat‐Pajouh, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(10): 1088. CrossRef - Shaping ability of four root canal instrumentation systems in simulated 3D-printed root canal models
David Christofzik, Andreas Bartols, Mahmoud Khaled Faheem, Doreen Schroeter, Birte Groessner-Schreiber, Christof E. Doerfer, Cyril Charles
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0201129. CrossRef - OPEN-SOURCE SOFTWARE IN DENTISTRY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Małgorzata Chruściel-Nogalska, Tomasz Smektała, Marcin Tutak, Katarzyna Sporniak-Tutak, Raphael Olszewski
International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care.2017; 33(4): 487. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - A comparison of the shaping ability of three nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomography study via a contrast radiopaque technique in vitro
Zhao Wei, Zhi Cui, Ping Yan, Han Jiang
BMC Oral Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Transportation and Centering Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Mandibular Premolars Assessed Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Iussif Mamede-Neto, Alvaro Henrique Borges, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Durvalino de Oliveira, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Carlos Estrela
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 71. CrossRef - Blue Thermomechanical Treatment Optimizes Fatigue Resistance and Flexibility of the Reciproc Files
Gustavo De-Deus, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gianluca Plotino, Nicola Maria Grande
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 462. CrossRef
- Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
- 1,772 View
- 9 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Quality of root canal fillings using three gutta-percha obturation techniques
- Edith Siu Shan Ho, Jeffrey Wen Wei Chang, Gary Shun Pan Cheung
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):22-28. Published online January 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.22

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The goal of this study was to compare the density of gutta-percha root fillings obturated with the following techniques: cold lateral (CL) compaction, ultrasonic lateral (UL) compaction, and warm vertical (WV) compaction.
Materials and Methods Thirty-three extracted mandibular first molars, with two separate mesial canals in each, were selected. After instrumentation, the canals were stratified into three groups based on canal length and curvature, and underwent obturation with one of the techniques. No sealer was used in order to avoid masking any voids. The teeth were imaged pre- and post-obturation using micro-computed tomography. The reconstructed three-dimensional images were analyzed volumetrically to determine the amount of gutta-percha present in every 2 mm segment of the canal.
P values < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.Results The overall mean volume fraction of gutta-percha was 68.51 ± 6.75% for CL, 86.56 ± 5.00% for UL, and 88.91 ± 5.16% for WV. Significant differences were found between CL and UL and between CL and WV (
p < 0.05), but not between UL and WV (p = 0.526). The gutta-percha density of the roots treated with WV and UL increased towards the coronal aspect, but this trend was not noted in the CL group.Conclusions WV compaction and UL compaction produced a significantly denser gutta-percha root filling than CL compaction. The density of gutta-percha was observed to increase towards the coronal aspect when the former two techniques were used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
Jia Min Ng, Yan Yee Lee, Prashanti Chippagiri, Elaheh Ahanin, Abhishek Parolia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e3. CrossRef - Restorative and endodontic clinical strategies during COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: a revision of the literature
Manuele MANCINI, Flavio PALAZZI, Francesco IACONO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the tubular penetration of two different types of nanoparticle root canal sealers over apically separated files: a scanning electron microscopic study (in vitro study)
Alaa H. Nagdi, Nayera A. Mokhless, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Different strategies for treating intracanal fractured instruments in a single tooth: A case report
Rong Chai, Xinpei Jiang, Ruixia Ma, Qiang Zhang, E Yang, Ansheng Zhang
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An Experimental Anatomic CBCT Study on the Correlations Between MB1 and MB2 of the Mesio-Vestibular Root of the Upper First Molars
Luca Fiorillo, Cesare D’Amico, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Francesco Calanna, Alfio Pappalardo, Eugenio Pedullà
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(2): 672. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Different Obturation Techniques for Root Canal Filling of Permanent Teeth: An In-Vitro Study
Adhishree S Chib, Neeta S Padmawar, Sonali Waghmare, Durgesh A Tiwari, Shahinwaz Mulani, Megna Bhatt
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root canal treatment of a rhizomegaly tooth 36 mm long right permanent maxillary canine – A case report
Anita Kapri, Kiran Reddy, Varun Rana, Oliver Jacob, Pushpa Kumari
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 10(1): 59. CrossRef - Thermal and volumetric assessment of endodontic filling techniques using infrared thermography and micro-CT
Fernanda Clotilde M. Suassuna, Débora Ketley M. de Araújo, Ana Marly A. M. Amorim, Saulo Leonardo S. Melo, Richard J. Heck, Antonio Celso D. Antonino, Patrícia M. Bento, Diego Filipe B. Silva, Daniela P. de Melo
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(1): 34. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Various Obturating Techniques for the Presence of Voids
Rehan Ahmad Khan, Shailja Singh, Shazia Siddiqui, Mariyam Khan, Arfat Ahmad, Parul Shakarwal
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2023; 15(Suppl 2): S895. CrossRef - Influence of the root canal filling technique on the success rate of primary endodontic treatments: a systematic review
Daniel Feijolo Marconi, Giovana Siocheta da Silva, Theodoro Weissheimer, Isadora Ames Silva, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Leonardo Thomasi Jahnke, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Current trends in bio‐based elastomer materials
Shuai Tang, Jiao Li, Runguo Wang, Jichuan Zhang, Yonglai Lu, Guo‐Hua Hu, Zhao Wang, Liqun Zhang
SusMat.2022; 2(1): 2. CrossRef - Carrier-Based Obturation: Effect of Sonication Technique on Sealer Penetration in Dentinal Tubules: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Study
Riccardo Tonini, Matteo Salvadori, Marco Bartoli, Jacopo Francinelli, Paolo Bertoletti, Maria Luisa Garo, Stefano Salgarello
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(17): 8877. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - The effect of two endodontic sealers and interval before post-preparation and cementation on the bond strength of fiber posts
He Yuanli, Wu Juan, Ji Mengzhen, Chen Xuan, Xiong Kaixin, Yang Xueqin, Qiao Xin, Hu Hantao, Gao Yuan, Zou Ling
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(11): 6211. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - Root canal filling quality of mandibular molars with EndoSequence BC and AH Plus sealers: A micro‐CT study
Rafael Nigri Roizenblit, Fabiola Ormiga Soares, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Heloisa Gusman
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of four different root canal obturation techniques on marginal adaptation of bioceramic sealer: An in vitro scanning electron microscopic study
NawalA Al-Sabawi, MahaM Yahya, NjwanF Shehab
Journal of International Oral Health.2020; 12(5): 455. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantification of the tug-back by measuring the pulling force and micro computed tomographic evaluation
Su-Jin Jeon, Young-Mi Moon, Min-Seock Seo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 273. CrossRef
- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
- 2,791 View
- 30 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Changes in SIRT gene expression during odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp cells
- Young-Eun Jang, Su-Hee Go, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):223-228. Published online July 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.223
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of 7 different sirtuin genes (SIRT1-SIRT7) in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs), and to determine the role of SIRTs in the odontoblastic differentiation potential of HDPCs.
Materials and Methods HDPCs were isolated from freshly extracted third molar teeth of healthy patients and cultulred in odontoblastic differentiation inducing media. Osteocalcin (OCN) and dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) expression was analyzed to evaluate the odontoblastic differentiation of HDPCs by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), while alizarin red staining was used for the mineralization assay. To investigate the expression of SIRTs during odontoblastic differentiation of HDPCs, real time PCR was also performed with RT-PCR.
Results During the culture of HDPCs in the differentiation inducing media, OCN, and DSPP mRNA expressions were increased. Mineralized nodule formation was also increased in the 14 days culture. All seven SIRT genes were expressed during the odontogenic induction period. SIRT4 expression was increased in a time-dependent manner.
Conclusions Our study identified the expression of seven different SIRT genes in HDPCs, and revealed that SIRT4 could exert an influence on the odontoblast differentiation process. Further studies are needed to determine the effects of other SIRTs on the odontogenic potential of HDPCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biodegradable Zn‐5Dy Alloy with Enhanced Osteo/Angio‐Genic Activity and Osteointegration Effect via Regulation of SIRT4‐Dependent Mitochondrial Function
Yue Han, Xian Tong, Runqi Zhou, Yilin Wang, Yuge Chen, Liang Chen, Xinhua Hong, Linmei Wu, Zhiqiang Lin, Yichi Zhang, Xuejia Zhang, Chaoming Hu, Bin Li, Yifan Ping, Zelin Cao, Zhou Ye, Zhongchen Song, Yuncang Li, Cuie Wen, Yongsheng Zhou, Jixing Lin, Shen
Advanced Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Histone Acetylation Modification in Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Odontogenesis
Haoling Chen, Zijing Huang, Chuxiao Chen
Cellular Reprogramming.2023; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Metabolic Remodeling Impacts the Epigenetic Landscape of Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Haiyun Luo, Yachuan Zhou, Wenjing Liu, Jun Wang
Stem Cells International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - SIRT4 regulates rat dental papilla cell differentiation by promoting mitochondrial functions
Haoling Chen, Jun Kang, Fuping Zhang, Tong Yan, Wenguo Fan, Hongwen He, Fang Huang
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology.2021; 134: 105962. CrossRef - Sirtuins as Interesting Players in the Course of HIV Infection and Comorbidities
Karolina Jurkowska, Beata Szymańska, Brygida Knysz, Amadeusz Kuźniarski, Agnieszka Piwowar
Cells.2021; 10(10): 2739. CrossRef - Robust expression of SIRT6 inhibits pulpitis via activation of the TRPV1 channel
Jia Hu, Weiran Chen, Zailing Qiu, Hongbing Lv
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2020; 38(5): 676. CrossRef - Downregulation of microRNA‐143‐5p is required for the promotion of odontoblasts differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through the activation of the mitogen‐activated protein kinases 14‐dependent p38 mitogen‐activated protein kinases signaling pa
Bao‐Liang Wang, Zhi Wang, Xi Nan, Qing‐Cai Zhang, Wei Liu
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(4): 4840. CrossRef - A potential role for the silent information regulator 2 homologue 1 (SIRT1) in periapical periodontitis
H. Kudo, O. Takeichi, K. Hatori, K. Makino, K. Himi, B. Ogiso
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(7): 747. CrossRef - Overexpressed Sirt1 in MSCs Promotes Dentin Formation in Bmi1-Deficient Mice
H. Wang, C. Lv, Y. Gu, Q. Li, L. Xie, H. Zhang, D. Miao, W. Sun
Journal of Dental Research.2018; 97(12): 1365. CrossRef - Expression of silent information regulator 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1) in periapical granulomas
Hiroshi Kudo, Osamu Takeichi, Kosuke Makino, Keisuke Hatori, Bunnai Ogiso
Journal of Oral Science.2018; 60(3): 411. CrossRef - TET1 knockdown inhibits the odontogenic differentiation potential of human dental pulp cells
Li-Jia Rao, Bai-Cheng Yi, Qi-Meng Li, Qiong Xu
International Journal of Oral Science.2016; 8(2): 110. CrossRef
- Biodegradable Zn‐5Dy Alloy with Enhanced Osteo/Angio‐Genic Activity and Osteointegration Effect via Regulation of SIRT4‐Dependent Mitochondrial Function
- 1,735 View
- 6 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Autotransplantation combined with orthodontic treatment: a case involving the maxillary central incisors with root resorption after traumatic injury
- Manuel Marques Ferreira, Hugo M. Ferreira, Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):236-240. Published online May 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Traumatic dental injury can result in avulsion of anterior teeth. In young patients, it is a challenge to the dental professional because after replantation, late complications such as ankylosis require tooth extraction. Although prosthetic and orthodontic treatment, and implant placement have been described as the options for intervention, autogenous tooth transplantation could be an effective procedure in growing patients if there is a suitable donor tooth available. This case presents the treatment of a patient who suffered a traumatic injury at 9 years old with avulsion of tooth 21, which had been replanted, and intrusion of tooth 11. Both teeth ankylosed; thus they were removed and autotransplantation of premolars was carried out. After transplantation, the tooth underwent root canal treatment because of pulpal necrosis. Orthodontic treatment began 3 months after transplantation and during 7 years' follow-up the aesthetics and function were maintained without signs of resorption.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Traitement orthodontique des dents permanentes traumatisées
Chantal Naulin-Ifi, Hélène Desnoes, H. Desnoes
Revue d'Orthopédie Dento-Faciale.2023; 57(2): 143. CrossRef - Treatment of an Avulsed and Ankylosed Incisor through Single Tooth Alveolar Osteotomy and Conventional Orthodontic Mechanisms
Georgios Vasoglou, Chrysi Christina Markomanolaki, Michail Vasoglou, Andreas Markomanolakis
Children.2022; 9(5): 732. CrossRef - A conservative approach for an adult patient with a fractured tooth and crowding: Autotransplantation at the fracture site
Chang-Hyen Kim, Byungju Joh, Hee Jin Lim, Jae Hyun Park, Yoon-Ah Kook, Yoonji Kim
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2021; 159(2): 234. CrossRef - Influencing Factors in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Open Apex: A Review of the Literature
María P. Pecci Lloret, Elena Pina Martínez, Francisco J. Rodríguez Lozano, Miguel R. Pecci Lloret, Julia Guerrero Gironés, Francesco Riccitiello, Gianrico Spagnuolo
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(9): 4037. CrossRef - Central incisor ankylosis - A review article
Simona Dianišková, Ivana Moňoková
Stomatológ.2019; 29(1): 40. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef
- Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,544 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
- Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):123-127. Published online January 7, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Glide path preparation is recommended to reduce torsional failure of nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary instruments and to prevent root canal transportation. This study evaluated whether the repetitive insertions of G-files to the working length maintain the apical size as well as provide sufficient lumen as a glide path for subsequent instrumentation.
Materials and Methods The G-file system (Micro-Mega) composed of G1 and G2 files for glide path preparation was used with the J-shaped, simulated resin canals. After inserting a G1 file twice, a G2 file was inserted to the working length 1, 4, 7, or 10 times for four each experimental group, respectively (
n = 10). Then the canals were cleaned by copious irrigation, and lubricated with a separating gel medium. Canal replicas were made using silicone impression material, and the diameter of the replicas was measured at working length (D0) and 1 mm level (D1) under a scanning electron microscope. Data was analysed by one-way ANOVA andpost-hoc tests (p = 0.05).Results The diameter at D0 level did not show any significant difference between the 1, 2, 4, and 10 times of repetitive pecking insertions of G2 files at working length. However, 10 times of pecking motion with G2 file resulted in significantly larger canal diameter at D1 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Under the limitations of this study, the repetitive insertion of a G2 file up to 10 times at working length created an adequate lumen for subsequent apical shaping with other rotary files bigger than International Organization for Standardization (ISO) size 20, without apical transportation at D0 level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
Mahima Bharat Mehta, Anupam Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Ashwini A. Narayanan
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 101. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive up-and-down movements on torque/force generation, surface defects and shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: an ex vivo study
Moe Sandar Kyaw, Arata Ebihara, Yoshiko Iino, Myint Thu, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Pyae Hein Htun, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Number of Pecking Motions at Working Length on the Shaping Ability of Single-file Systems in Long Oval-shaped Curved Canals
Lixiao Wang, Ruitian Lin, Hui Chen, Zihan Li, Franklin R. Tay, Lisha Gu
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(4): 548. CrossRef - Influence of pecking frequency at working length on the volume of apically extruded debris: A micro-computed tomography analysis
Li-Xiao Wang, Hui Chen, Rui-Tian Lin, Li-Sha Gu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(3): 1274. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef
- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
- 1,507 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Detection of root perforations using conventional and digital intraoral radiography, multidetector computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography
- Abbas Shokri, Amir Eskandarloo, Maruf Noruzi-Gangachin, Samira Khajeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):58-67. Published online November 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.58
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the accuracy of conventional intraoral (CI) radiography, photostimulable phosphor (PSP) radiography, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) for detection of strip and root perforations in endodontically treated teeth.
Materials and Methods Mesial and distal roots of 72 recently extracted molar were endodontically prepared. Perforations were created in 0.2, 0.3, or 0.4 mm diameter around the furcation of 48 roots (strip perforation) and at the external surface of 48 roots (root perforation); 48 roots were not perforated (control group). After root obturation, intraoral radiography, CBCT and MDCT were taken. Discontinuity in the root structure was interpreted as perforation. Two observers examined the images. Data were analyzed using Stata software and Chi-square test.
Results The sensitivity and specificity of CI, PSP, CBCT and MDCT in detection of strip perforations were 81.25% and 93.75%, 85.42% and 91.67%, 97.92% and 85.42%, and 72.92% and 87.50%, respectively. For diagnosis of root perforation, the sensitivity and specificity were 87.50% and 93.75%, 89.58% and 91.67%, 97.92% and 85.42%, and 81.25% and 87.50%, respectively. For detection of strip perforation, the difference between CBCT and all other methods including CI, PSP and MDCT was significant (
p < 0.05). For detection of root perforation, only the difference between CBCT and MDCT was significant, and for all the other methods no statistically significant difference was observed.Conclusions If it is not possible to diagnose the root perforations by periapical radiographs, CBCT is the best radiographic technique while MDCT is not recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between radiographic measurements of alveolar bone in posterior single-tooth edentulous regions and non-alveolar jawbones using multidetector computed tomography
Imad Barngkgei, Leen Khattash, Samar Kakhia
Oral Radiology.2025; 41(1): 10. CrossRef - Prevention, Diagnostic Challenges, and Management of Endodontic Perforations: A Narrative Review
Taylor M. DeVine, Nora L. Paisner, Adeyinka F. Dayo
Complications.2025; 2(3): 17. CrossRef - Extrusion of debris during retreatment using various nickel-titanium files in teeth with simulated lateral root perforation
Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç, Alper Kuştarcı
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(3): 189. CrossRef - The importance of cone-beam computed tomography in endodontic therapy: A review
Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(7): 780. CrossRef - Assessment of the diagnostic accuracy of strip and furcal perforations in different sizes by cone beam computed tomography
Zahra Ghoncheh, Hanieh Kaviani, Sara Soleimani, Shifteh Nasri, Fatemeh Malekpour, Farzaneh Afkhami
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(4): 654. CrossRef - Konik Işınlı Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Endodontik Uygulamalarda Kullanımı
Gülsün AKAY, Kahraman GÜNGÖR
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 11(1): 8. CrossRef - CBCT Visualization of Furcation Perforation Repair Materials Using Different Voxel Sizes
Ayse Isıl ORHAN, Pelin TUFENKCİ, Aysenur ONCU, Sevinc SEVGI, Berkan CELİKTEN, Kaan ORHAN
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(4): 654. CrossRef - Accuracy of Conventional Periapical Radiography in Diagnosing Furcation Repair after Perforation Treatment
Stephanie Díaz Huamán, Maria Gerusa Brito Aragão, Ana Paula Dias Moreno, Alexandra Mussolino de Queiroz, Raquel Assed Bezerra da Silva, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula-Silva, Léa Assed Bezerra da Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 827. CrossRef - Association between marginal bone loss and bone quality at dental implant sites based on evidence from cone beam computed tomography and periapical radiographs
Amir Eskandarloo, Reza Arabi, Mohsen Bidgoli, Faezeh Yousefi, Jalal Poorolajal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(1): 36. CrossRef - Effect of exposure parameters of cone beam computed tomography on metal artifact reduction around the dental implants in various bone densities
Abbas Shokri, Mohammad Reza Jamalpour, Atefeh Khavid, Zeinab Mohseni, Masoud Sadeghi
BMC Medical Imaging.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing the three-dimensional visualization of a foreign object using Mimics software
Muhammad Khan Asif, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Iqra Muhammad Khan, Zeti Adura Binti Che Ab Aziz, Nora Sakina Binti Mohd Noor, Palasuntharam Shanmuhasuntharam, Norliza Ibrahim
Radiology Case Reports.2019; 14(12): 1545. CrossRef - Diagnostic Accuracy of Three Cone Beam Computed Tomography Systems and Periapical Radiography for Detection of Fenestration Around Dental Implants
Amir Eskandarloo, Samira Saati, Mahbubeh Purabdolahi Ardakani, Mohamadreza Jamalpour, Naser Mohammad Gholi Mezerji, Vahid Akheshteh
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2018; 9(3): 376. CrossRef - Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
Eyal Rosen, Igor Tsesis
Clinical Dentistry Reviewed.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence of pulp sensibility loss of anterior teeth after paramedian insertion of orthodontic mini-implants in the anterior maxilla
Jan Hourfar, Dirk Bister, Jörg A. Lisson, Björn Ludwig
Head & Face Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Image analysis for dental bone quality assessment using CBCT imaging
Suprijanto, L Epsilawati, M S Hajarini, E Juliastuti, H Susanti
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2016; 694: 012065. CrossRef - Identification of the Procedural Accidents During Root Canal Preparation Using Digital Intraoral Radiography and Cone Beam Computed Tomography
K.-Ivácson A.- Csinszka, Monea Adriana Maria, Monea Monica, Pop Mihai, Borda Angela
Acta Medica Marisiensis.2016; 62(3): 326. CrossRef
- The relationship between radiographic measurements of alveolar bone in posterior single-tooth edentulous regions and non-alveolar jawbones using multidetector computed tomography
- 2,248 View
- 11 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Clinical management of a fused upper premolar with supernumerary tooth: a case report
- Kyu-Min Cho, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang-Hyuk Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):319-323. Published online July 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.319
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In dentistry, the term 'fusion' is used to describe a developmental disorder of dental hard tissues. In the permanent dentition, fusion of a normal tooth and a supernumerary tooth usually involves the incisors or canines. However, a few cases of fusion involving premolars have also been reported to date. We present a rare case in which fusion of the maxillary left second premolar and a supernumerary tooth in a 13-year-old girl was diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT, Alphard-3030, Asahi Roentgen Ind. Co., Ltd.). The tooth was bicuspidized after routine nonsurgical root canal treatment, and the separated teeth underwent appropriate restoration procedures. The second premolar and supernumerary tooth remained asymptomatic without any signs of inflammation after a follow-up period of 9 years. Identification of anatomical anomalies is important for treatment in cases involving fusion with supernumerary tooth, and therefore the microscopic examinations and CBCT are essential for the diagnosis. Fused teeth can be effectively managed by the comprehensive treatment which includes both endodontic and periodontal procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
Tatsuya Akitomo, Satoru Kusaka, Momoko Usuda, Mariko Kametani, Ami Kaneki, Taku Nishimura, Masashi Ogawa, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Children.2023; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Malformed Teeth and Their Endodontic Implications
Annapoorna Annapoorna, Manjunatha M, Shubhashini N, Swetha H. B.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(04): 245. CrossRef - Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Ameya Parlikar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Common dental diseases in children and malocclusion
Jing Zou, Mingmei Meng, Clarice S Law, Yale Rao, Xuedong Zhou
International Journal of Oral Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary Central Incisor fused to a Supernumerary Tooth using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Unusual Clinical Presentation
Thilla S Vinothkumar, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Ganesh Arathi, Sathishkumar Ramkumar, Gnanasekaran Felsypremila
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(6): 522. CrossRef - Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report
Miguel Agostinho Beco Pinto Cardoso, Rita Brandão Noites, Miguel André Duarte Martins, Manuel Pedro da Fonseca Paulo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 148. CrossRef
- Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
- 2,035 View
- 22 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Influence of operator's experience level on lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in extracted teeth
- Abdulrahman Mohammed Saleh, Saeid Tavanafar, Pouyan Vakili-Gilani, Noor Jamal Al Sammerraie, Faahim Rashid
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):222-226. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to assess the influence of operator experience level on the lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) in extracted teeth.
Materials and Methods Moderately curved canals of extracted maxillary and mandibular molars were randomly distributed into 2 groups: experienced and inexperienced operators. Ten files were allocated to each group (
n = 10). Each canal was prepared until the working length was reached, and the same file was used to prepare additional canals until it separated. The number of canals prepared before file separation was recorded. The fragment length of each file was measured, and the location of the fragment in the canal was determined. Data were statistically analysed using the independent 2-samplet -test.Results The 2 operators prepared a total of 324 moderately curved canals of maxillary and mandibular molars. There was no significant intergroup difference in the mean number of canals prepared (
p = 0.27). The average lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file was 17.1 and 15.3 canals, and the longest lifespan was 25 and 20 canals, when used by experienced and inexperienced operators, respectively. There were no statistically significant intergroup differences in separated fragment length and location.Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, operator experience level appears to have no effect on the lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in preparation of moderately curved canals. Single teeth with multiple canals can be prepared safely even by a novice operator by using a single file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural, microchemical, and mechanical changes associated with the clinical reuse of two nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
Felipe Augusto Restrepo-Restrepo, Viviana Andrea Holguín-Vásquez, Syldana Julieth Cañas-Jiménez, Paula Andrea Villa-Machado, Sara Ochoa-Soto, Claudia Patricia Ossa-Orozco, Sergio Iván Tobón-Arroyave
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 48. CrossRef - Fracture incidence of WaveOne Gold files: a prospective clinical study
C. S. P. Bueno, D. P. Oliveira, R. A. Pelegrine, C. E. Fontana, D. G. P. Rocha, J. L. Gutmann, C. E. S. Bueno
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(9): 1192. CrossRef - Current Assessment of Reciprocation in Endodontic Preparation: A Comprehensive Review—Part II: Properties and Effectiveness
Gianluca Plotino, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Nicola Maria Grande, Stephen Cohen, Frédéric Bukiet
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 1939. CrossRef
- Microstructural, microchemical, and mechanical changes associated with the clinical reuse of two nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
- 1,504 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Misdiagnosis of florid cemento-osseous dysplasia leading to unnecessary root canal treatment: a case report
- Jong-Ki Huh, Su-Jung Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):160-166. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report demonstrates an unnecessary endodontic treatment of teeth with florid cemento-osseous dysplasia (FCOD) due to a misdiagnosis as periapical pathosis and emphasizes the importance of correct diagnosis to avoid unnecessary treatment. A 30-year-old woman was referred to our institution for apicoectomies of the mandibular left canine and both the lateral incisors. The periapical lesions associated with these teeth had failed to resolve after root canal treatment over a 3-year period. Radiographic examinations revealed multiple lesions on the right canine, the second premolar, and both first molars as well as the anterior region of the mandible. Based on clinical, radiographic and histological evaluations, the patient condition was diagnosed as FCOD. The patient has been monitored for 2 years. To avoid unnecessary invasive treatment, accurate diagnosis is essential before treatment is carried out in managing FCOD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Periapical cemento‐osseous dysplasia masquerading as asymptomatic chronic apical periodontitis in a Chinese woman: A case report
Yunjing Ma, Dong Fang, Mei Ji
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of The Jaw: A Retrospective Analysis
Saim Yanık, Mehmet Emrah Polat
European Journal of Therapeutics.2024; 30(5): 760. CrossRef - Radiological follow-up of cemento-osseous dysplasia on cone-beam computed tomography
Stefan F. Nemec, Steffen Schneider, Klaus M. Friedrich, Michael Weber, Ursula Schwarz-Nemec
Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 52(5): 644. CrossRef - Cemento osseous dysplasia(COD) of the mandibular teeth misdiagnosed as periapical lesion; cone beam CT-based case report
Won-Jeong Han
The Journal of The Korean Dental Association.2024; 62(7): 432. CrossRef - Surgical Management of Infection Secondary to Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
Farin Ebrahimi, Faraz Ebrahimi, Jingang An
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2023; 34(6): e614. CrossRef - Florid osseous dysplasia mimicking odontogenic infections: A report of two cases and literature review
A. Wajdi Bin Mohammed, Mohammed Mubarak Aldosari, Osama A. Alharbi, Ahmed Alzahrani, Abdullah M. Alsoghier
Saudi Journal of Oral Sciences.2023; 10(3): 195. CrossRef - Radiolucent lesions that may resemble inflammatory periapical lesions: A review article
Hamad Albagieh, Mohammed Aldosari, Abdulmajeed Alkhathlan, Nawaf Alfawaz, Mohammed Almutairi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(8): 916. CrossRef - Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia: A Detailed Comparison of the 2005 and 2017 WHO Classifications and Case Analysis
Jiankang Zhang, Yunbo Yu, Wei Tang, Jian Pan, Wei Jing
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The bony changes after mandibular incisors retraction on a severe skeletal Class II bimaxillary protrusion extraction patient with periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
Huijuan Wang, Yiwen Zhou, Baochao Li, Ling Huang, Huang Li
AJO-DO Clinical Companion.2022; 2(5): 496. CrossRef - Cemento-ossøs dysplasi – en diagnostisk utfordring
Stig Løvold, Sivakami Rethnam Haug
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2022; 132(11): 938. CrossRef - A retrospective cone beam computed tomography analysis of cemento-osseous dysplasia
Birsay Gumru, Melda Pelin Akkitap, Sevilay Deveci, Ender Idman
Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 16(4): 1154. CrossRef - Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
Prashanth Panta, Imran Shahid, Mukund Seshadri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 304. CrossRef - Natural history of florid osseous dysplasia of the jaws with important clinical implications
Camile S. Farah, Marie Anne T. Matias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 684. CrossRef - Clinical assessment of cemento‐osseous dysplasia based on three‐dimensional diagnostic imaging: A case report
Naoki Shibata, Kyoko Inamoto, Munetaka Naitoh, Eiichiro Ariji
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(1): 105. CrossRef - Odontogenic Cysts
Arvind Babu Rajendra Santosh
Dental Clinics of North America.2020; 64(1): 105. CrossRef - Difficulties in the diagnosis of periapical translucencies and in the classification of cemento-osseous dysplasia
Andrea Brody, Attila Zalatnai, Krisztian Csomo, Andrea Belik, Csaba Dobo-Nagy
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia of Osteolytic Stage Showing Cyst-Like Findings on CT and MRI: A Case Report
Kotaro Ito, Naohisa Hirahara, Norihito Iizuka, Eri Sawada, Shunya Okada, Masaaki Suemitsu, Kayo Kuyama, Takashi Kaneda
International Journal of Oral-Medical Sciences.2019; 17(3-4): 137. CrossRef - Oral management of a patient with cemento-osseous dysplasia: a case report
Camila de Nazaré Alves de Oliveira KATO, Juliana Diogo de Almeida SAMPAIO, Tânia Mara Pimenta do AMARAL, Lucas Guimarães ABREU, Cláudia Borges BRASILEIRO, Ricardo Alves MESQUITA
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cemento-osseous dysplasia: Re-visited
International Journal of Dental Research and Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective Study of 383 Cases of Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Jaws
Camila de Nazaré Alves de Oliveira Kato, Laiz Fernandes Mendes Nunes, Loliza Luiz Figueiredo Houri Chalub, Adriana Etges, Tarcília Aparecida Silva, Ricardo Alves Mesquita
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 76(11): 2348. CrossRef - Successful Implant Placement in a Case of Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia: A Case Report and Literature Review
Nasrin Esfahanizadeh, Hila Yousefi
Journal of Oral Implantology.2018; 44(4): 275. CrossRef - Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report
Chang-Ki Min, Kwang-Joon Koh, Kyoung-A Kim
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2018; 48(2): 131. CrossRef - Cemento-Osseous Dysplasias: Imaging Features Based on Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scans
Paulo Henrique Pereira Cavalcanti, Eduarda Helena Leandro Nascimento, Maria Luiza dos Anjos Pontual, Andréa dos Anjos Pontual, Priscylla Gonçalves Correia Leite de Marcelos, Danyel Elias da Cruz Perez, Flávia Maria de Moraes Ramos-Perez
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(1): 99. CrossRef - Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: a contraindication to orthodontic treatment in compromised areas
Alberto Consolaro, Sergio Rafael Baggio Paschoal, Jose Burgos Ponce, Dario A. Oliveira Miranda
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2018; 23(3): 26. CrossRef - Clinical, demographic, and radiographic analysis of 82 patients affected by florid osseous dysplasia: an international collaborative study
Débora Lima Pereira, Fábio Ramôa Pires, Márcio Ajudarte Lopes, Román Carlos, John Marshal Wright, Paras Patel, Willie van Heerden, Andre Uys, Pablo Agustin Vargas
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2016; 122(2): 250. CrossRef - Cone beam CT as an aid to diagnosing mixed radiopaque radiolucent lesions in the mandibular incisor region
Unni Krishnan, Manal Al Maslamani, Alex J Moule
BMJ Case Reports.2015; 2015: bcr2014207617. CrossRef - Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Craniofacial Area in Children and Adolescents: A Review
D.V. Rogozhin, F. Bertoni, D. Vanel, M. Gambarotti, A. Righi, I.V. Bulycheva, D.M. Konovalov, A.G. Talalaev, V.Yu. Roshin, A.P. Ektova, M.V. Bolotin, A.V. Lopatin
Arkhiv patologii.2015; 77(4): 63. CrossRef - Dysplasie osseuse floride mandibulaire : un cas de découverte fortuite et revue de la littérature
Eugénie Massereau, Ugo Ordioni, Maud Guivarc’h, Guillaume Royer, Jean-Hugues Catherine
Médecine Buccale Chirurgie Buccale.2015; 21(2): 101. CrossRef
- Periapical cemento‐osseous dysplasia masquerading as asymptomatic chronic apical periodontitis in a Chinese woman: A case report
- 2,473 View
- 19 Download
- 28 Crossref

- Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
- Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):128-133. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to evaluate the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength (CS) of Root MTA (RMTA) modified with Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) as setting accelerators over time.
Materials and Methods A total of 110 cylindrical specimens of RMTA were divided into 6 experimental groups as follows: Group1, RMTA; Group 2, RMTA modified with CaCl2 (RMTA-C); Group 3, RMTA modified with Na2HPO4 (RMTA-N); Group 4, RMTA contaminated with blood; Group 5, RMTA-C contaminated with blood; Group 6, RMTA-N contaminated with blood. The CS of specimens in all groups was evaluated after 3 hr, 24 hr, and 1 wk. In the modified groups (groups 2, 3, 5, and 6) the CS of five specimens per group was also evaluated after 1 hr.
Results Blood contamination significantly reduced the CS of all materials at all time intervals (
p < 0.05). After 3 hr, the CS of specimens in the RMTA groups (with and without blood contamination) was significantly lower than those in the RMTA-C and RMTA-N groups (p < 0.05). The CS values were not significantly different at the other time intervals. In all groups, the CS of specimens significantly increased over time (p < 0.05).Conclusions Blood contamination decreased the CS of both original and accelerated RMTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Behnam Bolhari, Faranak Noori, Hadi Assadian, Amir Raee, Sholeh Ghabraei, Ahmad-Reza Shamshiri, Artak Heboyan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push‐out bond strength of the calcium silicate‐based endodontic cements in the presence of blood: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Mahdieh Alipour, Leili Faraji Gavgani, Negin Ghasemi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(2): 571. CrossRef - Effect of bioactive glass addition on the physical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate
Jei Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Biomaterials Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the addition of nanoparticles of CaCO3 and different water‐to‐powder ratios on the physicochemical properties of white Portland cement
Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Jessica Coelho Wasielewsky, Giovanna Slongo dos Santos, Anarela Bernardi, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(4): 592. CrossRef - Assessment of the interaction of Portland cement-based materials with blood and tissue fluids using an animal model
P. Schembri Wismayer, C. Y. K. Lung, F. Rappa, F. Cappello, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the plant-based hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper® on the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate
Muzaffer Emir Dinçol, Hakan Ozbas, Bulent Yılmaz, Handan Ersev, Selcuk Gokyay, Vakur Olgac
BMC Oral Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface microhardness of three thicknesses of mineral trioxide aggregate in different setting conditions
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Leila Jafargholizadeh, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Maryam Raoof
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 253. CrossRef - Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 137. CrossRef
- The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- 1,889 View
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Autogenous tooth transplantation for replacing a lost tooth: case reports
- Ji-Youn Kang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Bin-Na Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):48-51. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The autogenous tooth transplantation is an alternative treatment replacing a missing tooth when a suitable donor tooth is available. It is also a successful treatment option to save significant amount of time and cost comparing implants or conventional prosthetics. These cases, which required single tooth extraction due to deep caries and severe periodontal disease, could have good results by transplanting non-functional but sound donor tooth to the extraction site.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autogenous tooth transplantation of canines: a prospective clinical study on the influence of extraoral storage time-guided adjunctive antibiotic therapy and patient-related risk factors affecting success, survival, and prognosis after two years of follow
Sebastian Meinzer, Dirk Nolte, Karin Christine Huth
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Autogenous Tooth Transplantation of Canines—A Prospective Clinical Study on the Influence of Adjunctive Antibiosis and Patient-Related Risk Factors During Initial Healing
Sebastian Meinzer, Dirk Nolte, Karin Christine Huth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(3): 821. CrossRef - 13-year follow-up of autotransplantation using an immature third molar: a case report
Hojin Moon
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 72. CrossRef - Template-Guided Autogenous Tooth Transplantation Using a CAD/CAM Dental Replica in a Complex Anatomical Scenario: A Case Report
Michael Alfertshofer, Florian Gebhart, Dirk Nolte
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 281. CrossRef - Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Dental autotransplantation: case report and follow-up
Kassandra García Covarrubias, Erika Etcheverry Doger, Jennifer Antón Sarabia, Mario Alberto Lagunes López
Revista Odontología Pediátrica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and evaluation of the effectiveness of autotransplantation of teeth
Filipp V. Dulov, Roman B. Gurkin, Ekaterina S. Derbentsova, Ulia V. Budanova
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2023; 27(3): 193. CrossRef - Pre- and peri-operative factors influence autogenous tooth transplantation healing in insufficient bone sites
Thanapon Suwanapong, Aurasa Waikakul, Kiatanant Boonsiriseth, Nisarat Ruangsawasdi
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Third molar autotransplantation: An alternative to dental implant - 9 years follow up of a case
Sanjay Kumar, Mansi Jain, Suma Sogi, Prinka Shahi, Saru Dhir, Swati Rana
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2020; 10(2): 529. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef - Post-Odontoma autotransplantation of an impacted tooth: A case report
Waikhom Robindro Singh, Kirankumar Aheibam, Anthopia Nameirakpam
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2015; 5(2): 120. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of a Mandibular Third Molar: A Case Report with 5 Years of Follow-up
Mauro Henrique Chagas e Silva, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Maria das Gracas Afonso Miranda Chaves, Celso Neiva Campos
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 289. CrossRef
- Autogenous tooth transplantation of canines: a prospective clinical study on the influence of extraoral storage time-guided adjunctive antibiotic therapy and patient-related risk factors affecting success, survival, and prognosis after two years of follow
- 2,026 View
- 6 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The effect of clinical performance on the survival estimates of direct restorations
- Kyou-Li Kim, Cheol Namgung, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):11-20. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In most retrospective studies, the clinical performance of restorations had not been considered in survival analysis. This study investigated the effect of including the clinically unacceptable cases according to modified United States Public Health Service (USPHS) criteria into the failed data on the survival analysis of direct restorations as to the longevity and prognostic variables.
Materials and Methods Nine hundred and sixty-seven direct restorations were evaluated. The data of 204 retreated restorations were collected from the records, and clinical performance of 763 restorations in function was evaluated according to modified USPHS criteria by two observers. The longevity and prognostic variables of the restorations were compared with a factor of involving clinically unacceptable cases into the failures using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard model.
Results The median survival times of amalgam, composite resin and glass ionomer were 11.8, 11.0 and 6.8 years, respectively. Glass ionomer showed significantly lower longevity than composite resin and amalgam. When clinically unacceptable restorations were included into the failure, the median survival times of them decreased to 8.9, 9.7 and 6.4 years, respectively.
Conclusions After considering the clinical performance, composite resin was the only material that showed a difference in the longevity (
p < 0.05) and the significantly higher relative risk of student group than professor group disappeared in operator groups. Even in the design of retrospective study, clinical evaluation needs to be included.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
Ömer Hatipoğlu, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Nessrin Taha, Thiyezen Abdullah Aldhelai, Daoud M. Ayyad, Ahmed A. Madfa, Benjamin Martin‐Biedma, Rafael Fernández‐Grisales, Bakhyt A. Omarova, Wen Yi Lim, Suha Alfirjani, Kacper Nijak
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 977. CrossRef - Clinical Performance of Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Veneers Cemented With Light-Cured Resin Cements: An Observational Study
Nguyen Thi Minh Hien, Tran Hung Lam, Do Thi Thao, Hoang Viet
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Failure Risk of Composite Resin and Amalgam Restorations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Woroud Al-Sulimmani, Asmaa Al-Rasheed, Hebah Al-Daraan, Muna Al-Mutairi, Yash Brahmbhatt, Hesham Al-Hazmi, Hend Al-Qaderi
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(4): 100871. CrossRef - The Effect of Polishing on the Clinical Performance of Amalgam Restorations Using the Mahler’s Scale and Modified United States Public Health Service Criteria: A Prospective Clinical Study
Soham Suraj Wadke, Dipali Y. Shah
Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry.2025; 23(3): 282. CrossRef - Navigating the practical-knowledge gap in deep margin elevation: A step towards a structured case selection – a review
Eman H. Ismail, Saba S. Ghazal, Rahaf D. Alshehri, Hajar N. Albisher, Rana S. Albishri, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(5): 674. CrossRef - A review of dental antibacterial agents and antibacterial modification of composite resins and dentin adhesives
Hojin Moon
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 189. CrossRef - Er:YAG laser in selective caries removal and dentin treatment with chitosan: a randomized clinical trial in primary molars
Rai Matheus Carvalho Santos, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Sérgio Luiz de Souza Salvador, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Longevity of composite restorations is definitely not only about materials
Flávio Fernando Demarco, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Anelise Fernandes Montagner, Verônica Pereira de Lima, Marcos Britto Correa, Rafael R. Moraes, Niek J.M. Opdam
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of different adhesive systems on dental defects and sensitivity to teeth in composite resin restoration: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Keda Fang, Kenan Chen, Mengqi Shi, Liang Wang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2495. CrossRef - Survival of direct resin composite onlays and indirect tooth-coloured adhesive onlays in posterior teeth: a systematic review
Colin E. McGrath, Stephen J. Bonsor
British Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A 2-year clinical evaluation of direct and semi-direct resin composite restorations in non-carious cervical lesions: a randomized clinical study
Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele, Laura Célia Fernandes Meirelles, Rafael Santos Rocha, Lucélia Lemes Gonçalves, Daniele Mara Silva Ávila, Sérgio Eduardo de Paiva Gonçalves, Eduardo Bresciani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1321. CrossRef - Treatment options for large posterior restorations: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Bruna M. Vetromilla, Niek J. Opdam, Ferdinan L. Leida, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, Flavio F. Demarco, Mark P.J. van der Loo, Maximiliano S. Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(8): 614. CrossRef - Effect of a novel prime‐and‐rinse approach on short‐ and long‐term dentin bond strength of self‐etch adhesives
Mingxing Li, Jingqiu Xu, Ling Zhang, Chaoyang Wang, Xiaoting Jin, Yan Hong, Baiping Fu, Matthias Hannig
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 127(6): 547. CrossRef - Longevity of resin-bonded fixed partial dental prostheses made with metal alloys
Naomi Tanoue
Clinical Oral Investigations.2016; 20(6): 1329. CrossRef - Amalgam vs Composite Restoration, Survival, and Secondary Caries
Muhanad Alhareky, Mary Tavares
Journal of Evidence Based Dental Practice.2016; 16(2): 107. CrossRef - Seal, replacement or monitoring amalgam restorations with occlusal marginal defects? Results of a 10-year clinical trial
G. Moncada, E. Fernández, K. Mena, J. Martin, P. Vildósola, O.B. De Oliveira, J. Estay, I.A. Mjör, V.V. Gordan
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(11): 1371. CrossRef - Longitudinal Results of a 10-year Clinical Trial of Repair of Amalgam Restorations
G Moncada, P Vildósola, E Fernández, J Estay, OB de Oliveira Júnior, MF de Andrade, J Martin, IA Mjör, VV Gordan
Operative Dentistry.2015; 40(1): 34. CrossRef - Amalgam and resin composite longevity of posterior restorations: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Vittorio Moraschini, Cheung Ka Fai, Raphael Monte Alto, Gustavo Oliveira dos Santos
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1043. CrossRef - Aumento de longevidad de restauraciones de resinas compuestas y de su unión adhesiva. Revisión de tema
Gustavo Moncada, Patricio Vildósola, Eduardo Fernandez, Juan Estay, Osmir B de Oliveira Junior, Javier Martin
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of resin-modified glass-ionomer and resin composite polymerisation shrinkage stress in a wet environment
Joshua J. Cheetham, Joseph E.A. Palamara, Martin J. Tyas, Michael F. Burrow
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 29: 33. CrossRef - Factors affecting the placement or replacement of direct restorations in a dental school
Samara Silvani, Roberta Ferreira Trivelato, Ruchele Dias Nogueira, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo-Martins
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2014; 5(1): 54. CrossRef
- Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
- 1,676 View
- 4 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry
- Hee-Jin Kim, Lorena Karanxha, Su-Jung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):236-239. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although several methods including composite resin restoration and microabrasion have been used for management of white spot lesion, tooth jewelry can be considered as another noninvasive option. This case report describes the management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry. This report also highlights the patients' preference for tooth jewelry as an esthetic concern.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Putting the mouth back in the body – the neglected area of dental and oral travel health
Irmgard L Bauer
Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth adornments, gems, and grills
Harpuneet Kaur
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2022; 12(2): 50. CrossRef - Gold Enamel Choumps – A Case report
Sargam D. Kotecha, Y. Deepa Hedge, Kalpna Chaudhry, Ramakrishna Yeluri, Updesh Masih, Chanchal Singh
Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences.2016; 6(3): 303. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef
- Putting the mouth back in the body – the neglected area of dental and oral travel health
- 1,470 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Management of horizontal root fractures by fabrication of canine protected occlusion using composite resin
- Joo-Hee Shin, Ryan Jin-Young Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):180-184. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Traumatic injuries of the face often involve root fractures especially in anterior teeth. The prognosis and the treatment of the root fracture depend on the extent of the fracture line, general health and patient compliance. This case report outlines a new conservative trial treatment modality to stabilize the maxillary central incisors with horizontal root fracture on the cervical to middle third by fabricating canine guidance to remove loading on the traumatized maxillary central incisors during eccentric movements and thus inducing spontaneous healing of the fractured line between the fragments. Radiographs after thirty months showed adequate healing with no signs of pathological changes including root resorption, ankylosis or displacement. Long term follow-up revealed that vitality, stability and aesthetics were maintained and the patient was satisfied with the outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Healing after horizontal root fractures: 3 cases with 2-year follow-up
Yoorina Choi, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee, Kyung-San Min, Su-Jung Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 126. CrossRef
- Healing after horizontal root fractures: 3 cases with 2-year follow-up
- 1,449 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Minimizing the extra-oral time in autogeneous tooth transplantation: use of computer-aided rapid prototyping (CARP) as a duplicate model tooth
- Seung-Jong Lee, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):136-141. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The maintenance of the healthy periodontal ligament cells of the root surface of donor tooth and intimate surface contact between the donor tooth and the recipient bone are the key factors for successful tooth transplantation. In order to achieve these purposes, a duplicated donor tooth model can be utilized to reduce the extra-oral time using the computer-aided rapid prototyping (CARP) technique.
Materials and Methods Briefly, a three-dimensional digital imaging and communication in medicine (DICOM) image with the real dimensions of the donor tooth was obtained from a computed tomography (CT), and a life-sized resin tooth model was fabricated. Dimensional errors between real tooth, 3D CT image model and CARP model were calculated. And extra-oral time was recorded during the autotransplantation of the teeth.
Results The average extra-oral time was 7 min 25 sec with the range of immediate to 25 min in cases which extra-oral root canal treatments were not performed while it was 9 min 15 sec when extra-oral root canal treatments were performed. The average radiographic distance between the root surface and the alveolar bone was 1.17 mm and 1.35 mm at mesial cervix and apex; they were 0.98 mm and 1.26 mm at the distal cervix and apex. When the dimensional errors between real tooth, 3D CT image model and CARP model were measured in cadavers, the average of absolute error was 0.291 mm between real teeth and CARP model.
Conclusions These data indicate that CARP may be of value in minimizing the extra-oral time and the gap between the donor tooth and the recipient alveolar bone in tooth transplantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- American Dental Association and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology patient selection for dental radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
Erika Benavides, Joseph R. Krecioch, Trishul Allareddy, Allison Buchanan, Martha Ann Keels, Ana Karina Mascarenhas, Mai-Ly Duong, Kelly K. O’Brien, Kathleen M. Ziegler, Ruth D. Lipman, Roger T. Connolly, Lucia Cevidanes, Kitrina Cordell, Satheesh Elangova
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2026; 157(1): 20. CrossRef - American Dental Association and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology patient selection for dental radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
Erika Benavides, Josep R. Krecioch, Trishul Allareddy, Allison Buchanan, Martha Ann Keels, Ana Karina Mascarenhas, Mai-Ly Duong, Kelly K. O'Brien, Kathleen M. Ziegler, Ruth D. Lipman, Roger T. Connolly, Lucia Cevidanes, Kitrina Cordell, Satheesh Elangovan
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2026; 141(3): 273. CrossRef - 13-year follow-up of autotransplantation using an immature third molar: a case report
Hojin Moon
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 72. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Printing in Dentistry: A Scoping Review of Clinical Applications, Advantages, and Current Limitations
Mi-Kyoung Jun, Jong-Woo Kim, Hye-Min Ku
Oral.2025; 5(2): 24. CrossRef - Template-Guided Autogenous Tooth Transplantation Using a CAD/CAM Dental Replica in a Complex Anatomical Scenario: A Case Report
Michael Alfertshofer, Florian Gebhart, Dirk Nolte
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 281. CrossRef - Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Effect of 3D printed replicas on the duration of third molar autotransplantation surgery: A controlled clinical trial
Miks Lejnieks, Ilze Akota, Gundega Jākobsone, Laura Neimane, Oskars Radzins, Sergio E. Uribe
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(2): 221. CrossRef - Use of 3D printing models for donor tooth extraction in autotransplantation cases
Rui Hou, Xiaoyong Hui, Guangjie Xu, Yongqing Li, Xia Yang, Jie Xu, Yanli Liu, Minghui Zhu, Qinglin Zhu, Yu Sun
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Autologous Transplantation Tooth Guide Design Based on Deep Learning
Lifen Wei, Shuyang Wu, Zelun Huang, Yaxin Chen, Haoran Zheng, Liping Wang
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 82(3): 314. CrossRef - Anterior tooth autotransplantation: a case series
DC‐V Ong, P Goh, G Dance
Australian Dental Journal.2023; 68(3): 202. CrossRef - Dental Auto Transplantation Success Rate Increases by Utilizing 3D Replicas
Peter Kizek, Marcel Riznic, Branislav Borza, Lubos Chromy, Karolina Kamila Glinska, Zuzana Kotulicova, Jozef Jendruch, Radovan Hudak, Marek Schnitzer
Bioengineering.2023; 10(9): 1058. CrossRef - Planificación digital y guía de fresado para autotrasplante de tercer molar
Silvio Llanos, Henry García, Carlos Manresa, Carolina Bonilla, Alessandra Baasch
Reporte Imagenológico Dentomaxilofacial.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Una alternativa a los implantes dentarios: manejo quirúrgico y endodóntico con planificación digital y guía de fresado de autotrasplantes de terceros molares. Reporte de un caso
Silvio Llanos, Henry García, Carlos Manresa, Carolina Bonilla, Julio Tebres, Stefanía Requejo, Alessandra Baasch
Latin American Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2023; 3(2): 80. CrossRef - Extraoral Root-End Resection May Promote Pulpal Revascularization in Autotransplanted Mature Teeth—A Retrospective Study
Petra Rugani, Barbara Kirnbauer, Irene Mischak, Kurt Ebeleseder, Norbert Jakse
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(23): 7199. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional (3D) Stereolithographic Tooth Replicas Accuracy Evaluation: In Vitro Pilot Study for Dental Auto-Transplant Surgical Procedures
Filiberto Mastrangelo, Rossella Battaglia, Dario Natale, Raimondo Quaresima
Materials.2022; 15(7): 2378. CrossRef - Surgical Management of Impacted Lower Second Molars: A Comprehensive Review
Diane Isabel Selvido, Nattharin Wongsirichat, Pratanporn Arirachakaran, Dinesh Rokaya, Natthamet Wongsirichat
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 465. CrossRef - Application effect of computer-aided design combined with three-dimensional printing technology in autologous tooth transplantation: a retrospective cohort study
Shuang Han, Hui Wang, Jue Chen, Jihong Zhao, Haoyan Zhong
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Application of Virtual Simulation Technology and 3-Dimensional-Printed Computer-Aided Rapid Prototyping in Autotransplantation of a Mature Third Molar
Hui Zhang, Min Cai, Zhiguo Liu, He Liu, Ya Shen, Xiangya Huang
Medicina.2022; 58(7): 953. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Surgical extrusion, intentional replantation and tooth autotransplantation
Gianluca Plotino, Francesc Abella Sans, Monty S. Duggal, Nicola M. Grande, Gabriel Krastl, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Gianluca Gambarini
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 827. CrossRef - Review on 3D printing in dentistry: conventional to personalized dental care
Shadaan Ahmad, Nazeer Hasan, Fauziya, Akash Gupta, Arif Nadaf, Lubna Ahmad, Mohd. Aqil, Prashant Kesharwani
Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition.2022; 33(17): 2292. CrossRef - Three-dimensional printing in endodontics: A review of literature
Jyoti Chauhan, Ida de Noronha de Ataide, Marina Fernandes
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2021; 6(4): 198. CrossRef - Pre- and peri-operative factors influence autogenous tooth transplantation healing in insufficient bone sites
Thanapon Suwanapong, Aurasa Waikakul, Kiatanant Boonsiriseth, Nisarat Ruangsawasdi
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - European Society of Endodontology position statement: Surgical extrusion, intentional replantation and tooth autotransplantation
G. Plotino, F. Abella Sans, M. S. Duggal, N. M. Grande, G. Krastl, V. Nagendrababu, G. Gambarini
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(5): 655. CrossRef - Successful pulp revascularization of an autotransplantated mature premolar with fragile fracture apicoectomy and plasma rich in growth factors: a 3‐year follow‐up
J. F. Gaviño Orduña, M. García García, P. Dominguez, J. Caviedes Bucheli, B. Martin Biedma, F. Abella Sans, M. C. Manzanares Céspedes
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(3): 421. CrossRef - Clinical procedures and outcome of surgical extrusion, intentional replantation and tooth autotransplantation – a narrative review
G. Plotino, F. Abella Sans, M. S. Duggal, N. M. Grande, G. Krastl, V. Nagendrababu, G. Gambarini
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(12): 1636. CrossRef - 3D printing in dentistry – Exploring the new horizons
Praveen Vasamsetty, Tejaswini Pss, Divya Kukkala, Madhavi Singamshetty, Shashivardhan Gajula
Materials Today: Proceedings.2020; 26: 838. CrossRef - The use of 3D additive manufacturing technology in autogenous dental transplantation
Pau Cahuana-Bartra, Abel Cahuana-Cárdenas, Lluís Brunet-Llobet, Marta Ayats-Soler, Jaume Miranda-Rius, Alejandro Rivera-Baró
3D Printing in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Autotransplantation of mature impacted tooth to a fresh molar socket using a 3D replica and guided bone regeneration: two years retrospective case series
Ye Wu, Jiaming Chen, Fuping Xie, Huanhuan Liu, Gang Niu, Lin Zhou
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Transplantations, réimplantations
M.-A. Fauroux, E. Malthiéry, C. Favre de Thierrens, M. Zanini, J.-H. Torres
EMC - Chirurgie orale et maxillo-faciale.2019; 32(2): 1. CrossRef - Endodontic applications of 3D printing
J. Anderson, J. Wealleans, J. Ray
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(9): 1005. CrossRef - Applications of additive manufacturing in dentistry: A review
Aishwarya Bhargav, Vijayavenkatraman Sanjairaj, Vinicius Rosa, Lu Wen Feng, Jerry Fuh YH
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2018; 106(5): 2058. CrossRef - Virtual Simulation of Autotransplantation Using 3-dimensional Printing Prototyping Model and Computer-assisted Design Program
Soram Oh, Sehoon Kim, Ha Seon Lo, Joo-Young Choi, Hyun-Jung Kim, Gil-Joo Ryu, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1883. CrossRef - Computer-aided autotransplantation of teeth with 3D printed surgical guides and arch bar: a preliminary experience
Wei He, Kaiyue Tian, Xiaoyan Xie, Enbo Wang, Nianhui Cui
PeerJ.2018; 6: e5939. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of teeth using computer-aided rapid prototyping of a three-dimensional replica of the donor tooth: a systematic literature review
J.P. Verweij, F.A. Jongkees, D. Anssari Moin, D. Wismeijer, J.P.R. van Merkesteyn
International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2017; 46(11): 1466. CrossRef - Contemporary Approach to Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Roots Using 3D-printing Technology
Jungha Park, Sangho Lee, Nanyoung Lee, Myoungkwan Jih, Hyeran Cheong
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2017; 44(4): 461. CrossRef - 3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: a systematic literature review
Philip Tack, Jan Victor, Paul Gemmel, Lieven Annemans
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of an Impacted Premolar Using Collagen Sponge after Cyst Enucleation
Jae-Hyung Lim, Jong-Ki Huh, Kwang-Ho Park, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(3): 417. CrossRef - Vertical Bone Growth after Autotransplantation of Mature Third Molars: 2 Case Reports with Long-term Follow-up
Sunil Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Yooseok Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(8): 1371. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of mesiodens for missing maxillary lateral incisor with cone‐beam CT‐fabricated model and orthodontics
Y. Lee, S. W. Chang, H. Perinpanayagam, Y. J. Yoo, S. M. Lim, S. R. Oh, Y. Gu, S. J. Ahn, K.‐Y. Kum
International Endodontic Journal.2014; 47(9): 896. CrossRef - Optimizing Third Molar Autotransplantation: Applications of Reverse-Engineered Surgical Templates and Rapid Prototyping of Three-Dimensional Teeth
Ji-Man Park, Jacquiline Czar I. Tatad, Maria Erika A. Landayan, Seong-Joo Heo, Sun-Jong Kim
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2014; 72(9): 1653. CrossRef - Immediate autotransplantation of third molars: an experience of 57 cases
Shakil Ahmed Nagori, Ongkila Bhutia, Ajoy Roychoudhury, Ravinder Mohan Pandey
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2014; 118(4): 400. CrossRef
- American Dental Association and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology patient selection for dental radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
- 1,903 View
- 10 Download
- 42 Crossref

- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
- Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):90-95. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of resin infiltration technique on color and surface hardness of white spot lesion (WSL) with various degrees of demineralization.
Materials and Methods Ten human upper premolars were cut and divided into quarters with a 3 × 4 mm window on the enamel surface. Each specimens were separated into four groups (
n = 10) and immersed in demineralization solution to create WSL: control, no treatment (baseline); 12 h, 12 hr demineralization; 24 h, 24 hr demineralization; 48 h, 48 hr demineralization. Resin infiltration was performed to the specimens using Icon (DMG). CIEL *a *b * color parameters of the enamel-dentin complex were determined using a spectroradiometer at baseline, after caries formation and after resin infiltration. Surface hardness was measured by Vickers Micro Hardness Tester (Shimadzu, HMV-2). The differences in color and hardness among the groups were analyzed with ANOVA followed by Tukey test.Results Resin infiltration induced color changes and increased the hardness of demineralized enamel. After resin infiltration, there was no difference in color change (Δ
E *) or microhardness among the groups (p < 0.05).Conclusion There was no difference in the effect of resin infiltration on color and hardness among groups with different extents of demineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Microabrasion and Resin Infiltration Materials on Enamel Microhardness and Penetration Depth
Elif Ercan Devrimci, İdil Gönüllü, Hande Kemaloğlu, Murat Türkün, Ayşegül Demirbaş
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 67. CrossRef - Resin infiltration revolution in minimal invasive treatment – A review
Akancha Kumari, Sonal Gupta, Ashima Varshney, Neha Lal
Journal of Global Oral Health.2025; 8: 124. CrossRef - Effect of CPP-ACPF, resin infiltration, and colloidal silica infiltration on surface microhardness of artificial white spot lesions in primary teeth: An in vitro study
ArantaAvinash Chindane, AnilT Patil, B Sandhyarani
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 52. CrossRef - IMMEDIATE RESULT OF ICON INFILTRATION IN WHITE SPOT LESIONS CAUSED BY FLUOROSIS: A CASE REPORT
Al-Sadi Abdulaziz Nasser Zain, P.M. Skrypnykov, V.I. Shynkevych, O.A. Pysarenko
Ukrainian Dental Almanac.2022; (2): 34. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of penetration depth and surface microhardness of Resin Infiltrant, CPP-ACPF and Novamin on enamel demineralization after banding: an in vitro study
Nishita Rana, Namita Singh, Shaila, Abi. M. Thomas, Rajan Jairath
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2021; 8(1): 64. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric Evaluation of Color Change in Tooth Enamel Defects Using Resin Infiltrate: An In Vivo Study
Anil Gupta, Shikha Dogra, Sakshi Joshi, Vimanyu Kataria, Jyotika Saini, Monika Nagpal, Payal Narula
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(2): 150. CrossRef - Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide–amorphous Calcium Phosphate and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate on Artificial Carious Lesions: Anin vitroStudy
Iqra Chaudhary, Abhay M Tripathi
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(3): 261. CrossRef - Effect of Resin Infiltration on Artificial Caries: Anin vitroEvaluation of Resin Penetration and Microhardness
Deepesh Prajapati, Rashmi Nayak, Deepika Pai, Nagraj Upadhya, Vipin K Bhaskar, Pujan Kamath
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef
- In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Microabrasion and Resin Infiltration Materials on Enamel Microhardness and Penetration Depth
- 1,537 View
- 12 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Colorimetric comparison of single layered dental composite with double layered dental composite
- Young-Sang Song, Ja-Hyun Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):84-89. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.84
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study analyzed the difference in color caused by different thickness in enamel layer of composite resins when applied with single and layering placement technique, and evaluated if the results agreed with the shade guide from the manufacturers to verify reliability of the color matching process of the manufacturers.
Materials and Methods For single composite resin samples, 6 mm diameter and 4 mm thickness cylindrical samples were fabricated using Ceram-X mono (DENTSPLY DeTrey) and CIE L*a*b* values were measured with spectrophotometer. Same process was done for layering composite resin samples, making 3 dentinal shade samples, 4 mm thickness, for each shade using Ceram-X duo (DENTSPLY DeTrey) and enamel shade resins were layered in 2 mm thickness and CIE L*a*b* values were measured. These samples were ground to 0.2 mm thickness each time, and CIE L*a*b* values were measured to 1 mm thickness of enamel shade resin.
Results Color difference (ΔE*) between single and layering composite resin was 1.37 minimum and 10.53 maximum when layering thicknesses were between 1 mm and 2 mm and 6 out of 10 same shade groups suggested by manufacturer showed remarkable color difference at any thickness (ΔE* > 3.3).
Conclusion When using Ceram-X mono and duo for composite resin restoration, following the manufacturer's instructions for choosing the shade is not appropriate, and more accurate information for Ceram-X duo is needed on the variation and expression of the shades depending on the thickness of the enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improvement of mechanical strength and water repellency of Hanji (traditional Korean paper) through acetylation in supercritical CO2
Seungmok Shin, Hwi-Sung Lee, Hee Suk Woo, Mulugeta G. Aregay, Tae Jun Yoon, Youn-Woo Lee
The Journal of Supercritical Fluids.2022; 190: 105735. CrossRef - Color Change in Tooth Induced by Various Calcium Silicate-Based Pulp-Capping Materials
Jiyoon Jeon, Namki Choi, Seonmi Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(3): 280. CrossRef
- Improvement of mechanical strength and water repellency of Hanji (traditional Korean paper) through acetylation in supercritical CO2
- 1,089 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Pre-prosthetic minor tooth movement with elastic separating ring & provisional restoration modification: case report
- Haneol Shin, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yoo-Seok Shin, Chan-Young Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):114-118. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Proximal caries or coronal defect in posterior teeth may result in the loss of proximal space and drifting of neighboring teeth, which makes restoration difficult. Inability to restore proper contours and to align tooth axis properly are commonly encountered problems when planning tooth restoration. Moreover, tilted teeth aggravate periodontal tissue breakdown, such as pseudo-pocket, and angular osseous defect. The purpose of this case presentation is to describe a simple technique for inducing minor tooth movement with orthodontic separating ring and provisional restoration modification. This method was used to create crown placement space on mesially tilted molar. This method is easy, simple and efficient technique which could be used in interproximal space gaining in selected situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three cases with long-term follow ups
Jae-Hyung Lim, Ji-Hyun Lee, Su-Jung Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 56. CrossRef
- Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three cases with long-term follow ups
- 1,271 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The autotransplantation of an anklyosed maxillary canine
- Chang-Kyu Song
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):336-339. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The clinical diagnosis of ankylosis can be made only when the affected tooth gives positive evidence of an inability to move. The inability to move is demonstrated either as a failure of the tooth to move with normal vertical dental alveolar growth or a failure of the tooth to move when the tooth is subjected to an orthodontic force system. This case report describes the autotransplantation of an ankylosed maxillary canine.
- 840 View
- 1 Download

- Evaluation of canal preparation for apical sealing with various Ni-Ti rotary instruments
- Yooseok Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):300-305. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the various NiTi rotary instruments regarding their ability to provide a circular apical preparation.
Materials and Methods 50 single canal roots were selected, cut at the cementodentinal junction and the coronal 1/3 of the canals was flared using Gates Glidden burs. Samples were randomly divided into 5 experimental groups of 10 each. In group I, GT files, Profile 04 and Quantec #9 and #10 files were used. In Group II Lightspeed was used instead of Quantec. In Group III, Orifice shaper, Profile .06 series and Lightspeed were used. In Group IV, Quantec #9 and #10 files were used instead of Lightspeed. In Group V, the GT file and the Profile .04 series were used to prepare the entire canal length. All tooth samples were cut at 1 mm, 3 mm and 5 mm from the apex and were examined under the microscope.
Results Groups II and III (Lightspeed) showed a more circular preparation in the apical 1mm samples than the groups that used Quantec (Group I & IV) or GT files and Profile .04 series.(Group V)(
p < 0.05) There was no significant difference statistically among the apical 3, 5 mm samples. In 5 mm samples, most of the samples showed complete circularity and none of them showed irregular shape.Conclusions Lightspeed showed circular preparation at apical 1 mm more frequently than other instruments used in this study. However only 35% of samples showed circularity even in the Lightspeed Group which were enlarged 3 ISO size from the initial apical binding file (IAF) size. So it must be considered that enlarging 3 ISO size isn't enough to make round preparation.
- 793 View
- 5 Download

- Understanding of the color in composite resin
- Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):271-279. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In clinic, esthetic restoration of a defective natural tooth with composite resin is challenging procedure and needs complete understanding of the color of tooth itself and materials used. The optical characteristics of the composites are different because the chemical compositions and microstructures are not same.
This review provided basic knowledge of the color and the color measurement devices, and analyze the color of the natural tooth. Further, the accuracy of the shade tab, color of the composite resins before and after curing, effect of the water, food and bleaching agent, and translucency, opalescence, and fluorescence effects were evaluated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Translucency and Masking Ability of Single-Shade Opaque Composite Resin Compared with Conventional Opaque Composite Resins According to Thickness
Junmo Jeong, Jongsoo Kim, Joonhaeng Lee, Jongbin Kim, Jisun Shin, Miran Han
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2025; 52(3): 312. CrossRef - Evaluation of Color Stability according to Shade of Temporary Crown Resin Using Digital Spectrophotometer: In Vitro Study
Hye-min Ku, Mi-Kyoung Jun
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2022; 22(3): 139. CrossRef - Effects of Children's Drinks on the Color Stability of Strip and Zirconia crown
Ilyong Jeong, Seoksoon Yi, Haney Lee, Daewoo Lee, Yeonmi Yang, Jaegon Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2017; 44(3): 306. CrossRef - Color and Translucency of Multi-Shade Layered Composites
Chang-Ha Lee, Bum-Soon Lim, In-Bog Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(4): 369. CrossRef - Color evaluation of composite resin using dental colorimeter according to the specimen size
Ji-Hye Jung, 심규리, 장훈상
Oral Biology Research.2016; 40(4): 198. CrossRef
- Translucency and Masking Ability of Single-Shade Opaque Composite Resin Compared with Conventional Opaque Composite Resins According to Thickness
- 2,146 View
- 55 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
- Woo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Ho Lee, Kyung-A Chun, Min-Seock Seo, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):231-237. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.231
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the optimal master apical file size with minimal transportation and optimal efficiency in removing infected dentin. We evaluated the transportation of the canal center and the change in untouched areas after sequential preparation with a #25 to #40 file using 3 different instruments: stainless steel K-type (SS K-file) hand file, ProFile and LightSpeed using microcomputed tomography (MCT).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human mandibular molars with separated orifices and apical foramens on mesial canals were used. Teeth were randomly divided into three groups: SS K-file, Profile, LightSpeed and the root canals were instrumented using corresponding instruments from #20 to #40. All teeth were scanned with MCT before and after instrumentation. Cross section images were used to evaluate canal transportation and untouched area at 1- , 2- , 3- , and 5- mm level from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed according to' repeated nested design'and Mann-Whitney test (
p = 0.05).Results In SS K-file group, canal transportation was significantly increased over #30 instrument. In the ProFile group, canal transportation was significantly increased after preparation with the #40 instrument at the 1- and 2- mm levels. LightSpeed group showed better centering ability than ProFile group after preparation with the #40 instrument at the 1 and 2 mm levels.
Conclusions SS K-file, Profile, and LightSpeed showed differences in the degree of apical transportation depending on the size of the master apical file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the shaping abilities of three nickel–titanium instrumentation systems using micro-computed tomography
Jin Yi Baek, Hyun Mi Yoo, Dong Sung Park, Tae Seok Oh, Kee Yeon Kum, Seung Yun Shin, Seok Woo Chang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2014; 9(2): 111. CrossRef
- Comparison of the shaping abilities of three nickel–titanium instrumentation systems using micro-computed tomography
- 1,076 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Matrix metalloproteinase-8 and substance P levels in root canal exudates of nonvital teeth
- Su-Jung Shin, Woocheol Lee, Jae-Il Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum, Won-Jun Shon, Kwang-Shik Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):196-202. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate levels of matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) and substance P (SP) in root canal exudates during root canal treatment (RCT) of nonvital, painful teeth.
Materials and Methods Patients scheduled for nonsurgical RCT were prospectively selected; the study was performed after obtaining informed consent from the patients and was approved by the Institutional Review Board for Clinical Research of Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University (3-2008-0118). Canal exudates samples were collected using sterilized paper points from teeth scheduled for RCT across three different time periods. MMP-8 and SP levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data were analyzed using a mixed model analysis and the Pearson correlation analysis (
p < 0.05).Results MMP-8 and SP levels in GCF were decreased during RCT (
p < 0.0001), and they showed a weak positive correlation to each other (p < 0.05). Patients'subjective pain levels and the response from percussion test were significantly related to SP level.Conclusions This study demonstrated that periradicular inflammation endodontic origin can elevate SP and MMP-8 levels in root canal exudates. Interestingly, SP level of canal exudates showed a possibility of being used as an indicator of pain due to periapical pathosis.
- 913 View
- 2 Download

- Effect of the difference in spectral outputs of the single and dual-peak LEDs on the microhardness and the color stability of resin composites
- Hye-Jung Park, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):108-113. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of the spectral output of single and dual-peak light emitting diode (LED) curing lights on the microhardness and color stability of commercial resin composites formulated with camphorquinone and alternative photoinitiators in combination.
Materials and Methods Three light-polymerized resin composites (Z100 (3M ESPE), Tetric Ceram (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Aelite LS Posterior (Bisco)) with different photoinitiator systems were used. The resin composites were packed into a Teflon mold (8 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness) on a cover glass. After packing the composites, they were light cured with single-peak and dual-peak LEDs. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and color difference (ΔE) for 30 days were measured. The data was analyzed statistically using a student's
t -test (p < 0.05).Results All resin composites showed improved microhardness when a third-generation dual-peak LED light was used. The color stability was also higher for all resin composites with dual-peak LEDs. However, there was a significant difference only for Aelite LS Posterior.
Conclusions The dual-peak LEDs have a beneficial effect on the microhardness and color stability of resin composites formulated with a combination of camphorquinone and alternative photoinitiators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of irradiance from curing units on the microhardness of composite - a systematic review
Neenu Francis, Rakesh R. Rajan, Vijay Kumar, Anju Varughese, Vineetha Karuveetil, C. M. Sapna
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography evaluation of volumetric polymerization shrinkage and degree of conversion of composites cured by various light power outputs
Pablo J. ATRIA, Camila S. SAMPAIO, Eduardo CÁCERES, Jessica FERNÁNDEZ, Andre F. REIS, Marcelo GIANNINI, Paulo G. COELHO, Ronaldo HIRATA
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(1): 33. CrossRef - Effect of the irradiance distribution from light curing units on the local micro-hardness of the surface of dental resins
Thomas Haenel, Berenika Hausnerová, Johannes Steinhaus, Richard B.T. Price, Braden Sullivan, Bernhard Moeginger
Dental Materials.2015; 31(2): 93. CrossRef - 1,3-Butadiene as an Adhesion Promoter Between Composite Resin and Dental Ceramic in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Jet
Geum-Jun Han, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Kyu Hwan Oh, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2013; 33(2): 539. CrossRef - Optimal combination of 3-component photoinitiation system to increase the degree of conversion of resin monomers
Chang-Gyu Kim, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 313. CrossRef
- Effect of irradiance from curing units on the microhardness of composite - a systematic review
- 1,326 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Management of white spots: resin infiltration technique and microabrasion
- Jeong-Hye Son, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):66-71. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report compared the effectiveness of resin infiltration technique (Icon, DMG) with microabrasion (Opalustre, Ultradent Products, Inc.) in management of white spot lesions. It demonstrates that although neither microabrasion nor resin infiltration technique can remove white spot lesions completely, resin infiltration technique seems to be more effective than microabrasion. Therefore resin infiltration technique can be chosen preferentially for management of white spot lesions and caution should be taken for case selection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Resin Infiltration for the Esthetic Improvement of Dental Fluorosis and White Spots: A Case Report
Sumayyah L Alkhudhayri, Shahad L Alhassani, Nada A AbdelAleem
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - White spot lesions in fixed orthodontic treatment: Etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and future research perspectives
Suma Shankarappa, Jerusha Titus Burk, Pradeep Subbaiah, Raghunath Nagasundara Rao, Vidya Gowdappa Doddawad
Journal of Orthodontic Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - White Spot Lesions in Fixed Orthodontics: A Literature Review on Etiology, Prevention, and Treatment
Deem Al-Blaihed, Omar El Meligy, Khlood Baghlaf, Rabab A Aljawi, Shahad Abudawood
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of low-viscosity resin infiltration (Icon) on color change of enamel white spot lesions: 1-year follow-up clinical study
Mohamed. H. Zaazou, Reham S. Saleh, Shahinaz N. Hassan, Ali Abdelnabi, Zeinab M. Zaki, Tamer M. Hamdy, Dalia Y. Zaki, Lamiaa M. Moharam
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual tooth segmentation in human teeth images using pseudo edge-region obtained by deep neural networks
Seongeun Kim, Chang-Ock Lee
Signal Processing: Image Communication.2024; 120: 117076. CrossRef - Surface topography and spectrophotometric assessment of white spot lesions restored with nano-hydroxyapatite-containing universal adhesive resin: an in-vitro study
Neven S. Aref, Rahaf M. Alsdrani
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Infiltrating Resins, Noninvasive Treatment of White Spot Lesions: A Case Report
Rubén Darío Miranda-Carreño, Jacqueline Adelina Rodríguez-Chávez, Abigailt Flores-Ledesma
Journal of Oral Health and Community Dentistry.2023; 17(2): 75. CrossRef - Management of Turner's Hypoplasia Using Resin Infiltration: A Case Report
Dhruvi Solanki, Punit Fulzele, Nilima Thosar, Unnati Shirbhate
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study)
Abdulaziz Alhotan, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Saleh Alhijji, Merry Angelyn Tan De Vera, Aref Sufyan, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Tamer M. Hamdy
Polymers.2023; 15(14): 3068. CrossRef - Effect of Resin Infiltration and Microabrasion on the Microhardness of the Artificial White Spot Lesions (An in Vitro Study)
Reem Majeed H.J. Al-Mamoori, Aseel Haidar M.J. Al Haidar
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2022; 34(1): 44. CrossRef - Effect of sodium fluoride plus tricalcium phosphate with and without CO2 laser on remineralization of white spot lesions
Nouran M. Eissa, Eman M. Elshourbagy, Nahla E. Gomaa
Heliyon.2022; 8(10): e10752. CrossRef - Efficacy of Resin Infiltration and Fluoride Casein Phosphopeptide Amorphous Calcium Phosphate Varnish on Non-cavitated Active White Spot Lesions in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Mohit Dhamija, Rish Tyagi, Namita Kalra, Amit Khatri
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual Tooth Segmentation in Human Teeth Images Using Pseudo Edge-Region Obtained by Deep Neural Networks
Seongeun Kim, Chang-Ock Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro, Influence Of In-Office Dental Whitening On The Color Of Teeth Treated With Resin Infiltration
Basil Almutairi, Mohammed Al-Refai, Bander AL-Meshary, Abdulrahman Al-Asim, Fahad Al-Sharidah, Abdullah Alshehri
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(4): 6. CrossRef - Evaluation of color changes of white spot lesions treated with three different treatment approaches: an in-vitro study
Shaza M. Hammad, Noha A. El-Wassefy, Mohamed A. Alsayed
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(1): 26. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric Evaluation of Color Change in Tooth Enamel Defects Using Resin Infiltrate: An In Vivo Study
Anil Gupta, Shikha Dogra, Sakshi Joshi, Vimanyu Kataria, Jyotika Saini, Monika Nagpal, Payal Narula
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(2): 150. CrossRef - Erosion Infiltration in the Management of Molar‐Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH) Defects
Rym Mabrouk, Souha Yahia, Afef Oueslati, Nadia Frih, Yuk Kwan Chen
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pediatric Dentists’ Educational Experiences, Attitudes, and Professional Behavior Concerning Resin Infiltration: Implications for Dental Education
Michael Jordan Halcomb, Marita R. Inglehart, Elisabeta Karl
Journal of Dental Education.2020; 84(3): 290. CrossRef - Esthetic improvements of postorthodontic white-spot lesions treated with resin infiltration and microabrasion: A split-mouth, randomized clinical trial
Xi Gu, Lin Yang, Deqin Yang, Yuan Gao, Xiaolei Duan, Xin Zhu, He Yuan, Jiyao Li
The Angle Orthodontist.2019; 89(3): 372. CrossRef - Effect of resin infiltration on the color and microhardness of bleached white‐spot lesions in bovine enamel (an in vitro study)
Sidika Aynur Horuztepe, Meserret Baseren
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2017; 29(5): 378. CrossRef - Effect of Resin Infiltration on Artificial Caries: Anin vitroEvaluation of Resin Penetration and Microhardness
Deepesh Prajapati, Rashmi Nayak, Deepika Pai, Nagraj Upadhya, Vipin K Bhaskar, Pujan Kamath
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef - Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry
Hee-Jin Kim, Lorena Karanxha, Su-Jung Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 236. CrossRef - Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 90. CrossRef
- Resin Infiltration for the Esthetic Improvement of Dental Fluorosis and White Spots: A Case Report
- 4,353 View
- 38 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Comparison of apical transportation and change of working length in K3, NRT AND PROFILE rotary instruments using transparent resin block
- Min-Jung Yoon, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):59-65. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study is to compare the apical transportation and working length change in curved root canals created in resin blocks, using 3 geometrically different types of Ni-Ti files, K3, NRT, and Profile.
Materials and Methods The curvature of 30 resin blocks was measured by Schneider technique and each groups of Ni-Ti files were allocated with 10 resin blocks at random. The canals were shaped with Ni-Ti files by Crown-down technique. It was analyzed by Double radiograph superimposition method (Backman CA 1992), and for the accuracy and consistency, specially designed jig, digital X-ray, and CAD/CAM software for measurement of apical transportation were used. The amount of apical transportation was measured at 0, 1, 3, 5 mm from 'apical foramen - 0.5 mm' area, and the alteration of the working length before and after canal shaping was also measured. For statistics, Kruskal-Wallis One Way Analysis was used.
Results There was no significant difference between the groups in the amount of working length change and apical transportation at 0, 1, and 3 mm area (
p = 0.027), however, the amount of apical transportation at 5 mm area showed significant difference between K3 and Profile system (p = 0.924).Conclusions As a result of this study, the 3 geometrically different Ni-Ti files showed no significant difference in apical transportation and working length change and maintained the original root canal shape.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 7. CrossRef
- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
- 1,110 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
- Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):1-11. Published online January 14, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract Introduction: The aim of this paper is to discuss the mechanical and geometric features of Nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files and its clinical effects. NiTi rotary files have been introduced to the markets with their own geometries and claims that they have better ability for the root canal shaping than their competitors. The contents of this paper include the (possible) interrelationship between the geometries of NiTi file (eg. tip, taper, helical angle, etc) and clinical performance of the files as follows;
- Fracture modes of NiTi rotary files
- Non-cutting guiding tip and glide path
- Taper and clinical effects
- Cross-sectional area and clinical effects
- Heat treatments and surface characteristics
- Screw-in effect and preservation of root dentin integrity
- Designs for reducing screw-in effect
Conclusions: Based on the reviewed contents, clinicians may have an advice to use various brands of NiTi rotary instruments regarding their advantages which would fit for clinical situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 31. CrossRef
- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
- 2,907 View
- 79 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


