Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Surface properties and susceptibility to staining of a resin composite after brushing with different whitening toothpastes
- Aline da Silva Barros, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Junior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e6. Published online February 26, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study investigated the effects of different whitening toothpaste (WT) on the surface properties and staining susceptibility of a resin composite.
Methods
Cylindrical samples were prepared with a micro-hybrid resin composite and were randomized into groups according to the toothpaste (n = 12): distilled water (DW), regular toothpaste (RT), WT with silica + pyrophosphate (WT-S/P), WT with pentaphosphate and pyrophosphate (WT-P/P), WT with hydrogen peroxide and pyrophosphate (WT-HP/P) and WT with charcoal and pyrophosphate (WT-Ch/P). The samples were brushed for 825 cycles in an automatic brushing machine, simulating 30 days of brushing. After that, an immersion in coffee (10 mL/sample) was performed for 30 minutes for 30 days. The analyses of color, surface microhardness (SMH), and surface roughness (Ra) were performed at the initial time, after brushing with toothpaste and after immersion in coffee. The ΔL*, Δa*, Δb*, ΔEab, Δand E00 values were calculated comparing after toothpaste with initial time and after coffee with after toothpaste. Data were analyzed using a mixed linear model for repeated measures (SMH), Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Friedman, and Nemenyi tests, with α = 0.05.
Results
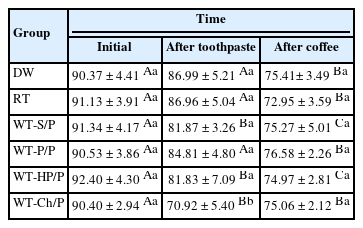
For ΔL*, the WT-Ch/P group had the lowest values and differed from the other groups comparing the after toothpaste with the initial time interval (p < 0.001). The WT-Ch/P group had the lowest SMH values in after-toothpaste time (p < 0.001). In after-toothpaste time and after coffee time, the WT-S/P group had the highest Ra values and differed from the groups except the WT-Ch/P group (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The toothpaste composition affects the surface characteristics and susceptibility to staining of the resin composite. The charcoal-based toothpaste had the worst performance for the color analyses and SMH.
- 4,999 View
- 166 Download

- Can discolored dental composites be bleached in depth?
- Luca Giachetti, Daniele Scaminaci Russo, Michele Nieri, Francesca Cinelli
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e23. Published online June 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Previous
in vitro studies determined the whitening effects of bleaching products on stained resin composite surfaces. Thisin vitro study aimed to verify the effectiveness of a whitening system on composite resin previously subjected to pigmentation, specifically examining the depth of whitening effectiveness within the material structure.Materials and Methods A commercially available nano-filled composite resin was used. Specimens were stained using a coffee-based solution and a 10% carbamide peroxide-based gel was employed as the whitening agent. The pigment’s penetration and the effect of the bleaching gel were evaluated by measuring color (CieLab values) from the outer edge to the inner part of the specimens. Color measurements were taken at 14 points, starting from 0.1 mm from the external perimeter up to 3.0 mm.
Results Analysis of variance tests showed a statistically significant difference between the Control Group (CG), Pigmentation Group, and Whitening Group. The whitening agent was effective up to 1.5 mm in depth, with Whiteness index (W) values not statistically different from those of CG up to 0.5 mm in depth.
Conclusions Whitening agents on nano-filled resin composite previously pigmented appear effective in restoring the W to values similar to the original, particularly in the superficial layers of the sample.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability of Tooth-Colored Restorative Materials After Exposure to Arabic Coffee and Black Tea: A Systematic Review
Abdulrhman Y Alenezi, Abdulwahab M AlEyada, Yousef H Aldhafiri, Mohammed S Alsubaie, Mohammed S Alshahrani, Mahesh Shenoy
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation to composite resin bleaching using ozone-enhanced low-concentration hydrogen peroxide
Mahmoud K. AL-Omiri, Dania Sa’ed Hussam Abuherra, Khaled M. AL-Omiri, Ali Y. Alsaeed, Mohammad Alamri, Ali M. Alqahtani, Saleh Ali Alqahtani, Ghadeer Saleh Alwadai, Naif Abogazalah, Edward Lynch
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of mechanical and chemical degradation on the surface roughness, gloss, and color stability of bulk-fill resin composites
Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Esra Özyurt, Naz Bayar, Mediha Büyükgöze Dindar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Color Stability of Tooth-Colored Restorative Materials After Exposure to Arabic Coffee and Black Tea: A Systematic Review
- 3,700 View
- 136 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Impact of combined at-home bleaching and whitening toothpaste use on the surface and color of a composite resin
- Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira-Junior, Marcia Hiromi Tanaka, Laura Nobre Ferraz
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e26. Published online July 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This
in vitro study aimed to evaluate the effects of different whitening toothpastes on a composite resin during at-home bleaching with 10% carbamide peroxide.Materials and Methods Sixty samples (7 mm × 2 mm) were used for color and roughness analyses, while another 60 samples (3 mm × 2 mm) were utilized to assess microhardness. The factors analyzed included toothpaste, for which 5 options with varying active agents were tested (distilled water; conventional toothpaste; whitening toothpaste with abrasive agents; whitening toothpaste with abrasive and chemical agents; and whitening toothpaste with abrasive, chemical, and bleaching agents). Brushing and application of whitening gel were performed for 14 days. Surface microhardness (SMH), surface roughness (Ra), and color (∆L*, ∆a*, ∆b, ∆E*ab, and ∆E00) were analyzed. The Ra and SMH data were analyzed using mixed generalized linear models for repeated measures, while the color results were assessed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests.
Results Between the initial and final time points, all groups demonstrated significant increases in Ra and reductions in SMH. No significant differences were found between groups for SMH at the final time point, at which all groups differed from the distilled water group. Conventional toothpaste exhibited the lowest Ra, while whitening toothpaste with abrasive agent had the highest value. No significant differences were observed in ∆L*, ∆a*, and ∆b.
Conclusions While toothpaste composition did not affect the color stability and microhardness of resin composite, combining toothbrushing with whitening toothpaste and at-home bleaching enhanced the change in Ra.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current evidence on the impact of whitening toothpastes on dental restorative materials: A comprehensive review
Soyeon Kim, Shin Hye Chung, Satoshi Yamaguchi, Taro Arima, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2026; 70(1): 4. CrossRef - Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
Mariana Ferreira da Silva, Giovana Contin Germinari, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Tatiane Cristina Dotta, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Júnior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2026; 25: e260366. CrossRef - At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
Luciana Vasconcelos Ramos, Dayana Fernandes Rocha Aparicio, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva, Maíra do Prado, Andréa Vaz Braga Pintor, Marcela Baraúna Magno
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1567. CrossRef - Surface properties and susceptibility to staining of a resin composite after brushing with different whitening toothpastes
Aline da Silva Barros, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Junior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e6. CrossRef - Dental Care Behaviors and Oral Health Challenges in School-Age Populations
Ahmad Mahmoud Saleh , Aishah Al Daragemeh , Asmaa Morgan Farahat Khatap , Prakash Palanivelu , Arul Vellaiyan , Elturabi Elsayed Ebrahim , Ahmad Rayan , Nermen Abdelftah Mohamed
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2025; 5: 1372. CrossRef - Effect of bleaching and repolishing on whiteness change and staining susceptibility of resin-based materials
Sultan Aktuğ Karademir, Samet Atasoy, Beyza Yılmaz
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of using different toothpaste during bleaching with violet LED light (405 nm) on the colour and roughness of dental enamel: an in vitro study
Franco Sousa Leticia, Mazzalli Redondo Victor, Ferraz Nobre Laura, Vitti Pino Rafael, Renata Siqueira Scatolin
Lasers in Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of coffee staining and simulated oral hygiene methods on the color and translucency of a nanoceramic resin
Luiz Felipe Schneider, Bruna Mueller, Rubens Nisie Tango, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 1020. CrossRef
- Current evidence on the impact of whitening toothpastes on dental restorative materials: A comprehensive review
- 5,278 View
- 62 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of surrounding and underlying shades on the color adjustment potential of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer
- Mariana Silva Barros, Paula Fernanda Damasceno Silva, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e7. Published online December 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
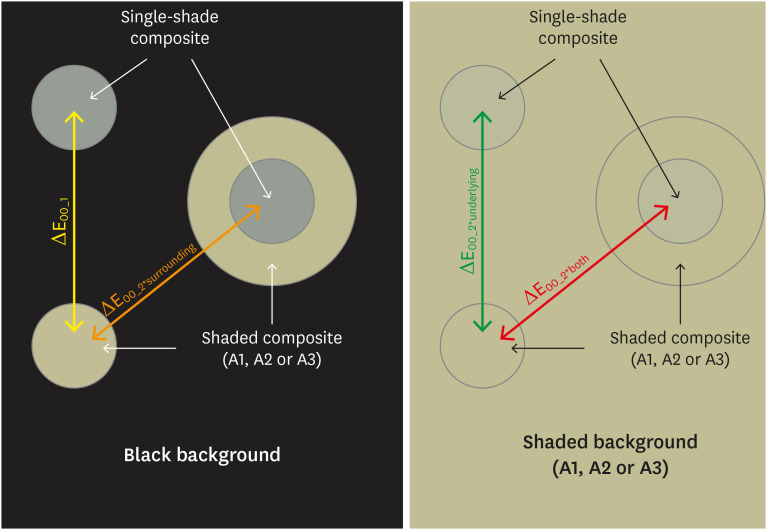
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the surrounding and underlying shades’ effect on the color adjustment potential (CAP) of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer.
Materials and Methods Cylinder specimens (1.0 mm thick) were built with the Vittra APS Unique composite, surrounded (dual specimens) or not (simple specimens) by a control composite (shade A1, A2, or A3). Simple specimens were also built only with the control composites. Each specimen’s color was measured against white and black backgrounds or the simple control specimens with a spectrophotometer (CIELAB system). The whiteness index for dentistry (WID) and translucency parameters (TP00) were calculated for simple specimens. Differences (ΔE00) in color between the simple/dual specimens and the controls were calculated. The CAP was calculated based on the ratios between data from simple and dual specimens.
Results The Vittra APS Unique composite showed higher WID and TP00 values than the controls. The highest values of ΔE00 were observed among simple specimens. The color measurements of Vittra APS Unique (simple or dual) against the control specimens presented the lowest color differences. Only surrounding the single-shade composite with a shaded composite barely impacted the ΔE00. The highest CAP values were obtained using a shaded composite under simple or dual specimens.
Conclusions The CAP of Vittra APS Unique was strongly affected by the underlying shade, while surrounding this composite with a shaded one barely affected its color adjustment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of water absorption on the translucency of single-shade and conventional resin composites: an in vitro comparative study
Ceyda Sari, Elifnur Aydemir Aydın
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
Luciana Vasconcelos Ramos, Dayana Fernandes Rocha Aparicio, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva, Maíra do Prado, Andréa Vaz Braga Pintor, Marcela Baraúna Magno
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1567. CrossRef - Evaluation of color matching of three single-shade composites employing simulated 3D printed cavities with different thicknesses using CIELAB and CIEDE2000 color difference formulae
Engin Kariper, Aylin Cilingir
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of kombucha, coffee, and turmeric beverages on the color stability of a single-shade versus a multi-shade resin-based composite
Hanin E. Yeslam, Abdulaziz F. Bakhsh
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19759. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Esthetic Outcome of Pedo Shades of Composite Resin—A Randomized Controlled Trial: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
Priyanka Raj, Shikha Choubey, Divya Doneria, Diksha Bhat, Shivani Mathur, Shailja Sinha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(S1): S22. CrossRef - Influence of cavity wall thickness on the color adjustment potential of single-shade resin composites
Fabrício Luscino Alves de Castro, Letícia Brandão Durand
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2024; 155(7): 605. CrossRef - Assessing color mismatch in single-shade composite resins for enamel replacement
Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Diana Leyva Del Rio, Luiz Alves Oliveira-Neto, William Michael Johnston
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 132(3): 613.e1. CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Is It Possible for Single-shade Composites to Mimic the Color, Lightness, Chroma, and Hue of Other Single-shade Composites? An In Vitro Study
M Buldur, G Ayan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 691. CrossRef - Color evaluation of a one-shade used for restoration of non-carious cervical lesions: an equivalence randomized clinical trial
Michael Willian Favoreto, Amanda de Oliveira de Miranda, Thalita P. Matos, Andrea dos Santos de Castro, Mylena de Abreu Cardoso, Julia Beatriz, Jenny Collantes-Acuña, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Thickness on the Translucency Parameter and Whiteness Index of Single-Shade Resin Composites
Ö Yağcı, M Fidan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(2): 189. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Ishihara Test With Various Displays
Thomas Klinke, Wolfgang Hannak, Klaus Böning, Holger Jakstat
International Dental Journal.2024; 74(4): 892. CrossRef - Color match evaluation using instrumental method for three single-shade resin composites before and after in-office bleaching
Aylin Cilingir, Engin Kariper
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of interface distance and underlying substrate on the color adjustment potential of single‐shade composites
Gabriella Jesus Santos de Livi, Tauan Rosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, Rosa Maria Viana de Bragança Garcez, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1279. CrossRef
- Impact of water absorption on the translucency of single-shade and conventional resin composites: an in vitro comparative study
- 4,738 View
- 101 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

- Relationship between battery level and irradiance of light-curing units and their effects on the hardness of a bulk-fill composite resin
- Fernanda Harumi Oku Prochnow, Patricia Valéria Manozzo Kunz, Gisele Maria Correr, Marina da Rosa Kaizer, Carla Castiglia Gonzaga
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e45. Published online November 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
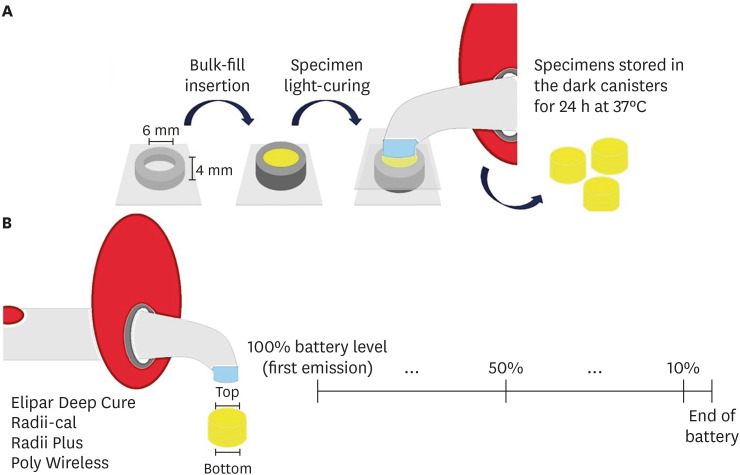
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the relationship between the battery charge level and irradiance of light-emitting diode (LED) light-curing units (LCUs) and how these variables influence the Vickers hardness number (VHN) of a bulk-fill resin.
Materials and Methods Four LCUs were evaluated: Radii Plus (SDI), Radii-cal (SDI), Elipar Deep Cure (Filtek Bulk Fill, 3M Oral Care), and Poly Wireless (Kavo Kerr). Irradiance was measured using a radiometer every ten 20-second activations until the battery was discharged. Disks (4 mm thick) of a bulk-fill resin (Filtek Bulk Fill, 3M Oral Care) were prepared, and the VHN was determined on the top and bottom surfaces when light-cured with the LCUs with battery levels at 100%, 50% and 10%. Data were analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance, the Tukey’s test, and Pearson correlations (α = 5%).
Results Elipar Deep Cure and Poly Wireless showed significant differences between the irradiance when the battery was fully charged versus discharged (10% battery level). Significant differences in irradiance were detected among all LCUs, within each battery condition tested. Hardness ratios below 80% were obtained for Radii-cal (10% battery level) and for Poly Wireless (50% and 10% battery levels). The battery level showed moderate and strong, but non-significant, positive correlations with the VHN and irradiance.
Conclusions Although the irradiance was different among LCUs, it decreased in half of the devices along with a reduction in battery level. In addition, the composite resin effectiveness of curing, measured by the hardness ratio, was reduced when the LCUs’ battery was discharged.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of erosive solutions and thermal cycling on the surface properties of universal injectable and regular consistency resin composites
Ahmed Abbas Rhaif, Hoda Saleh Ismail, Tawakol Ahmed Ahmed Enab, Nadia Mohamed Zaghloul
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Battery Level During Successive Charging Cycles on the Performance of Certified and Low-cost Uncertified Light-curing Units Available on E-commerce
TS Peres, G Oliveira, SP da Silva Sakamoto, M da Silva Faria, HL Carlo, CJ Soares
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 673. CrossRef - Influence of Exposure Distance on Light Irradiance of Dental Curing Lamps in Various Operating Modes
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Marta Mroczyk, Filip Podgórski, Beata Czarnecka, Anna Surdacka
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9999. CrossRef - ESTADO DA INTENSIDADE LUMINOSA DAS LÂMPADAS DE FOTOPOLIMERIZAÇÃO DAS CLÍNICAS ODONTOLÓGICAS DOS CENTROS DE SAÚDE DA CIDADE DE CUENCA
Milton Alexis Quinchiguano Caraguay, David Ismael Bravo Achundia , Esteban Eduardo Amoroso Calle, Manuel Estuardo Bravo Calderon
RECISATEC - REVISTA CIENTÍFICA SAÚDE E TECNOLOGIA - ISSN 2763-8405.2023; 3(6): e36296. CrossRef
- Effect of erosive solutions and thermal cycling on the surface properties of universal injectable and regular consistency resin composites
- 2,025 View
- 32 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

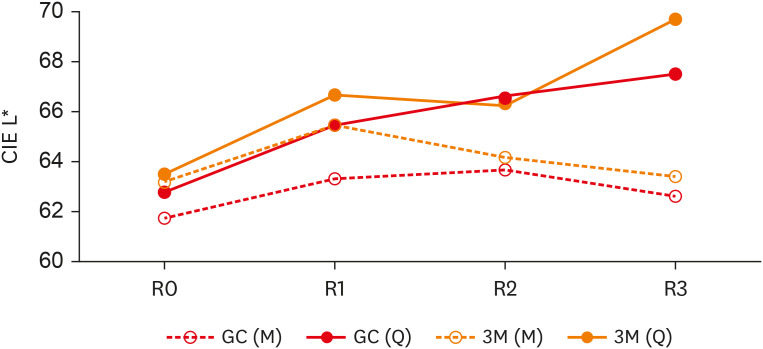
- Surface gloss, gloss retention, and color stability of 2 nano-filled universal resin composites
- Gustavo Fabián Molina, Ricardo Juan Cabral, Ignacio Mazzola, Michael Burrow
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e43. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the surface gloss (SG), gloss retention (GR), and color stability (CS) of 2 universal resin composites after chemical (CA) and mechanical (MA) aging.
Materials and Methods Twenty disc-shaped samples of G-ænial A´Chord (GC-Europe) and Filtek Universal (3M-ESPE) were polished with sequential abrasive papers. For CA, specimens were stored in 1 mL of 75% ethanol for 15 days at 37°C, and readings (SG, GR, and CS) were obtained at baseline and 5, 10, and 15 days. For MA, specimens were subjected to 10,750 simulated brushing cycles. SG and CS were evaluated after every 3,583 cycles. SG was measured with a glossmeter (geometrical configuration: 60°), and values were expressed in gloss units. Color was measured with a spectrophotometer using the CIE-L*a*b* color system. The Student’s
t -test, 1-way analysis of variance, and Scheffé test were used for statistical analysis (α = 0.05).Results G-ænial presented significantly higher SG values than Filtek (
p = 0.02), with GR reductions of 5.2% (CA) and 5.3% (MA) for G-ænial and 7.6% (CA) and 7.2% (MA) for Filtek. The aging protocol had no statistically significant effect on SG or GR (p = 0.25) from baseline to the final readings. G-ænial–MA presented the lowest color difference(∆E = 1.8), and G-ænial–CA and Filtek–CA had the largest changes (∆E = 8.6 and∆E = 11.8, respectively).Conclusion G-ænial presented higher SG values and better CS. Both restorative materials demonstrated acceptable GR and CS. Aging protocols impacted these properties negatively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color stability, surface roughness, and surface morphology of universal composites
Mohammad Meniawi, Nazlı Şirinsükan, Esra Can
Odontology.2026; 114(1): 149. CrossRef - Surface roughness of composite resins subjected to brushing with whitening toothpastes: an in vitro study
Nicolle Madruga Ramos FERREIRA, Vinicius Funghetto LIPPERT, Amanda Baptista da Silva HECK, Ana Maria SPOHR, Marcel Ferreira KUNRATH, Carlos Alberto FELDENS, Paulo Floriani KRAMER
Brazilian Oral Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Color Stability and Surface Abrasion of Nano-modified Glass Ionomer Cement with Dentifrices: An In Vitro Study
Jessy Paulraj, Subhabrata Maiti, Harini Palani
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 15(1): 10. CrossRef - Security inks with silanized zinc oxide quantum dots and cellulose ethers for the safeguarding of cultural heritage objects
Andrea Louise Matulac, Themis Krasoudaki, Francesca Battaglia, Carlo Spadoni, Martina Piletti, Daniela Iacopino, Rodorico Giorgi
Applied Materials Today.2025; 44: 102718. CrossRef - Gastric acid challenge: Mechanical proficiency and surface gloss of tooth-colored restorative materials
Ozge Gizem Yenidunya, Tugba Misilli, Ebru Yilmaz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of in-office bleaching agents on the optical properties of universal resin composites: an in vitro analysis
Esra Özyurt, Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Mediha Büyükgöze Dindar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface gloss and micro‐CT analysis of additively and subtractively manufactured resin composites and zirconia after simulated tooth brushing with different bristle types and toothpaste formulations: An in vitro study
Ahmet Faruk Ertürk, Rafat Sasany, Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Merve Yelken Kendirci
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Aging and Staining Effects on Optical Properties of Flowable Composites
M. M. Sly, Y. Korkmaz‐Ceyhan, F. Dini, R. L. Ocampo Escobedo, E. Abram, R. D. Paravina
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of The Effect of In-Office Bleaching Agent on Mechanical Properties of Different Single-Shade Resin Composites: An In-Vitro Study
Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Esra Özyurt
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2025; 14(3): 197. CrossRef - Surface gloss changes in 3D-printed resin materials following different polishing procedures and aging protocols
Ilayda Yumak, Hayal Boyacioglu, Lezize Sebnem Turkun
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Gloss Retention of Esthetic Restorations Following Simulated Brushing with Charcoal Oral Products: An In-Vitro Study
Fadia Awadalkreem, Nancy S Farghal, Nadin A Abouelhonoud, Raiyan I Khan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(5): 473. CrossRef - Effect of different finishing and polishing systems on surface properties of universal single shade resin-based composites
Ghada Alharbi, Hend NA Al Nahedh, Loulwa M. Al-Saud, Nourah Shono, Ahmed Maawadh
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Chemical Degradation and Polishing on the Gloss of Composite Dental Materials
Ružica Zovko, Stipo Cvitanović, Mirela Mabić, Zdenko Šarac, Anka Ćorić, Domagoj Glavina, Kristina Goršeta
Materials.2023; 16(10): 3727. CrossRef
- Color stability, surface roughness, and surface morphology of universal composites
- 3,208 View
- 47 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

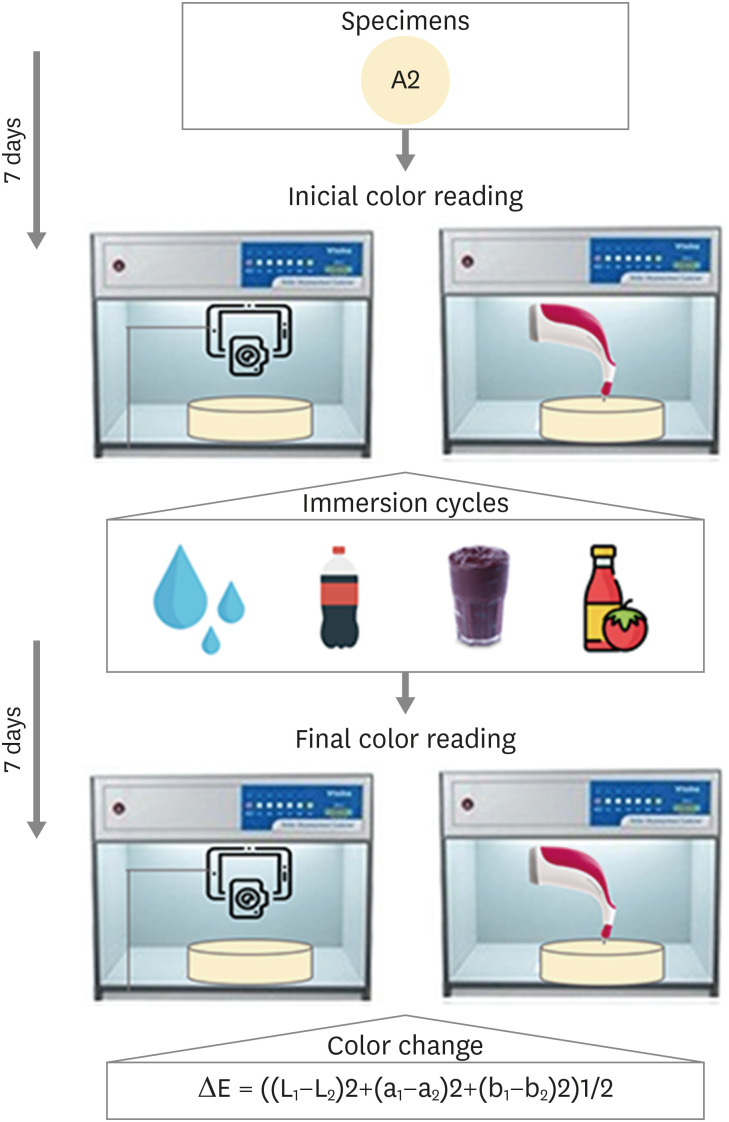
- Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
- Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e8. Published online February 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the color change of the Giomer resin composite (Beautifil-Bulk) by using photographs obtained with a smartphone (iPhone 6S) associated with Adobe Photoshop software (digital method), with the spectrophotometric method (Vita Easyshade) after immersion in different pigment solutions.
Materials and Methods Twenty resin composite samples with a diameter of 15.0 mm and thickness of 1.0 mm were confectioned in A2 color (
n = 5). Photographs and initial color readings were performed with a smartphone and spectrophotometer, respectively. Then, samples were randomly divided and subjected to cycles of immersion in distilled water (control), açai, Coke, and tomato sauce, 3 times a day, 20 minutes for 7 days. Later, new photographs and color readings were taken.Results The analysis (2-way analysis of variance, Holm-Sidak,
p < 0.05) demonstrated no statistical difference (p < 0.005) between the methods in all groups. Similar color changes were observed for all pigment solutions when using the spectrophotometric method. For the digital method, all color changes were clinically unacceptable, with distilled water and tomato sauce similar to each other and with statistical differences (p < 0.005) for Coke and açai.Conclusions Only the tomato sauce produced a color change above the acceptability threshold using both methods of color assessment. The spectrophotometric and digital methods produce different patterns of color change. According to our results, the spectrophotometric method is more recommended in color change assessment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
Jamieson Wong, Constance Yeo, Michelle The, Filip Taneski, Uros Josic, Lorenzo Breschi, Vesna Miletic
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026; 38(1): 70. CrossRef - The effects of mechanical and chemical degradation on the surface roughness, gloss, and color stability of bulk-fill resin composites
Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Esra Özyurt, Naz Bayar, Mediha Büyükgöze Dindar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef
- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
- 2,755 View
- 39 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- A 3-year retrospective study of clinical durability of bulk-filled resin composite restorations
- Muhittin Ugurlu, Fatmanur Sari
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e5. Published online December 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the clinical longevity of a bulk-fill resin composite in Class II restorations for 3-year.
Materials and Methods Patient record files acquired from the 40 patients who were treated due to needed 2 similar sizes Class II composite restorations were used for this retrospective study. In the experimental cavity, the flowable resin composite SDR was inserted in the dentinal part as a 4 mm intermediate layer. A 2 mm coverage layer with a nano-hybrid resin composite (CeramX) was placed on SDR. The control restoration was performed by an incremental technique of 2 mm using the nano-hybrid resin composite. The restorations were blindly assessed by 2 calibrated examiners using modified United States Public Health Service criteria at baseline and 1, 2, and 3 years. The data were analyzed using non-parametric tests (
p = 0.05).Results Eighty Class II restorations were evaluated. After 3-years, 4 restorations (5%) failed, 1 SDR + CeramX, and 3 CeramX restorations. The annual failure rate (AFR) of the restorations was 1.7%. The SDR + CeramX group revealed an AFR of 0.8%, and the CeramX group an AFR of 2.5% (
p > 0.05). Regarding anatomical form and marginal adaptation, significant alterations were observed in the CeramX group after 3-years (p < 0.05). The changes in the color match were observed in each group over time (p < 0.05).Conclusions The use of SDR demonstrated good clinical durability in deep Class II resin composite restorations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bond Strength of Bulk-Fill Resin Repairs: Impact of Surface and Adhesive Protocols
Samuel Eleutério Paiva Sousa, Fiorella Elizabeth Arévalo Tarrillo, Maria Paula Novaes Camargo Manna, Sandra Ribeiro de Barros da Cunha, Maria Ângela Pita Sobral
Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 1(1): 291. CrossRef - Evaluation of Surface Roughness and Microhardness of New Generation Bulk-Fill Composites
Zehra SÜSGÜN YILDIRIM, Ezgi SONKAYA, Zeliha Gonca BEK KÜRKLÜ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(2): 180. CrossRef - Damping Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Restorative Materials for Primary Teeth
Thomas Niem, Roland Frankenberger, Stefanie Amend, Bernd Wöstmann, Norbert Krämer
Materials.2022; 15(21): 7698. CrossRef
- Bond Strength of Bulk-Fill Resin Repairs: Impact of Surface and Adhesive Protocols
- 3,999 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Errors in light-emitting diodes positioning when curing bulk fill and incremental composites: impact on properties after aging
- Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora M. Garcia, Haifa Maktabi, Maria Salem Ibrahim, Qoot Alkhubaizi, Howard Strassler, Fabrício M. Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e51. Published online September 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e51

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of improper positioning single-peak and multi-peak lights on color change, microhardness of bottom and top, and surface topography of bulk fill and incremental composites after artificial aging for 1 year.
Materials and Methods Bulk fill and incremental composites were cured using multi-peak and single-peak light-emitting diode (LED) following 4 clinical conditions: (1) optimal condition (no angulation or tip displacement), (2) tip-displacement (2 mm), (3) slight tip angulation (α = 20°) and (4) moderate tip angulation (α = 35°). After 1-year of water aging, the specimens were analyzed for color changes (ΔE), Vickers hardness, surface topography (Ra, Rt, and Rv), and scanning electron microscopy.
Results For samples cured by single-peak LED, the improper positioning significantly increases the color change compared to the optimal position regardless of the type of composite (
p < 0.001). For multi-peak LED, the type of resin composite and the curing condition displayed a significant effect on ΔE (p < 0.001). For both LEDs, the Vickers hardness and bottom/top ratio of Vickers hardness were affected by the type of composite and the curing condition (p < 0.01).Conclusions The bulk fill composite presented greater resistance to wear, higher color stability, and better microhardness than the incremental composite when subjected to improper curing. The multi-peak LED improves curing under improper conditions compared to single-peak LED. Prevention of errors when curing composites requires the attention of all personnel involved in the patient's care once the clinical relevance of the appropriate polymerization reflects on reliable long-term outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
Elizbeth Christy Jose, Sakshi Jha, Prema Shantagouda Biradar, J Arun, TN Nandini, Thushara Mohanan
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2025; 15(1): 41. CrossRef - The demineralization resistance and mechanical assessments of different bioactive restorative materials for primary and permanent teeth: an in vitro study
Maria Salem Ibrahim, Fahad Rakad Aldhafeeri, Abdullah Sami Banaemah, Mana S. Alhaider, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef
- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
- 1,720 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

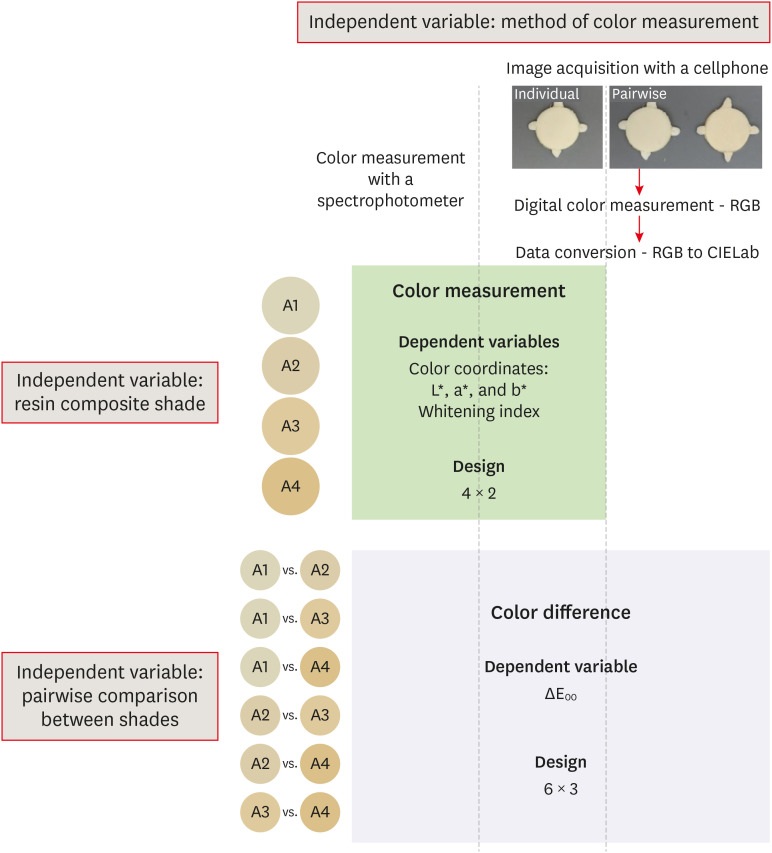
- Color assessment of resin composite by using cellphone images compared with a spectrophotometer
- Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Ratto Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e23. Published online April 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study assessed the reliability of digital color measurements using images of resin composite specimens captured with a cellphone.
Materials and Methods The reference color of cylindrical specimens built-up with the use of resin composite (shades A1, A2, A3, and A4) was measured with a portable spectrophotometer (CIELab). Images of the specimens were obtained individually or pairwise (compared shades in the same photograph) under standardized parameters. The color of the specimens was measured in the images using RGB system and converted to CIELab system using image processing software. Whiteness index (WID) and color differences (ΔE00) were calculated for each color measurement method. For the cellphone, the ΔE00 was calculated between the pairs of shades in separate images and in the same image. Data were analyzed using 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05). Linear regression models were used to predict the reference ΔE00 values of those calculated using color measured in the images.
Results Images captured with the cellphone resulted in different WID values from the spectrophotometer only for shades A3 and A4. No difference to the reference ΔE00 was observed when individual images were used. In general, a similar ranking of ΔE00 among resin composite shades was observed for all methods. Stronger correlation coefficients with the reference ΔE00 were observed using individual than pairwise images.
Conclusions This study showed that the use of cellphone images to measure the color difference seems to be a feasible alternative providing outcomes similar to those obtained with the spectrophotometer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How the Translucency and Color Stability of Single-Shade Universal Resin Composites Are Affected by Coffee?
Büşra Özdemir, Betül Kübra Kurucu Karadeniz, Seyit Bilal Özdemir, Ömer Akbulut
Current Research in Dental Sciences.2024; 34(4): 270. CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of VITA Shade Guide and Various Composite Shades Using Spectrophotometer, Digital Single-lens Reflex, and Cellphone: An In Vitro Study
Aman Verma, Sonali Taneja, Surabhi Ghosh
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 803. CrossRef - Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,623 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

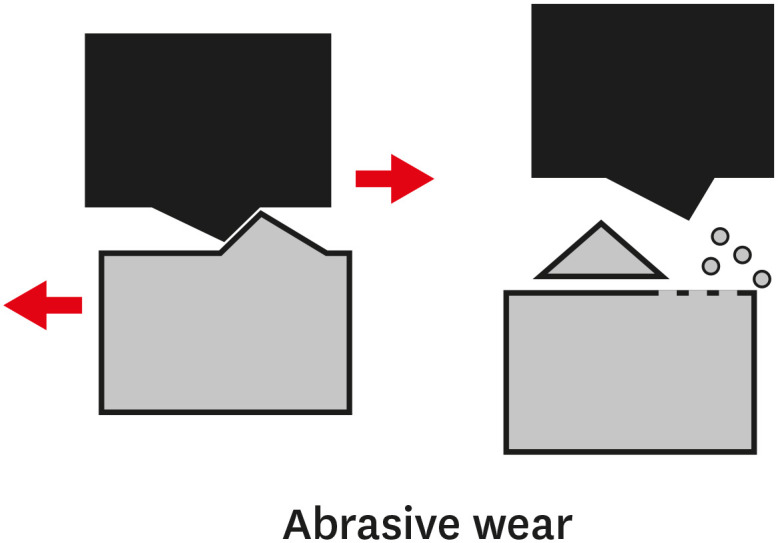
- Wear of contemporary dental composite resin restorations: a literature review
- Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Olga Gerasimidou
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e18. Published online February 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Composite resins are the most commonly used dental restorative materials after minimally invasive dental procedures, and they offer an aesthetically pleasing appearance. An ideal composite restorative material should have wear properties similar to those of tooth tissues. Wear refers to the damaging, gradual loss or deformation of a material at solid surfaces. Depending on the mechanism of action, wear can be categorized as abrasive, adhesive, fatigue, or corrosive. Currently used composite resins cover a wide range of materials with diverse properties, offering dental clinicians multiple choices for anterior and posterior teeth. In order to improve the mechanical properties and the resistance to wear of composite materials, many types of monomers, silane coupling agents, and reinforcing fillers have been developed. Since resistance to wear is an important factor in determining the clinical success of composite resins, the purpose of this literature review was to define what constitutes wear. The discussion focuses on factors that contribute to the extent of wear as well as to the prevention of wear. Finally, the behavior of various types of existing composite materials such as nanohybrid, flowable, and computer-assisted design/computer-assisted manufacturing materials, was investigated, along with the factors that may cause or contribute to their wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synergistic Effects of Simulated Energy Drink Exposure and Fatigue Loading on Bioactive and Conventional Resin Composites
Fatin A. Hasanain, Alaa Turkistani
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(1): 29. CrossRef - Direct and Semi-Direct Composite Techniques in Posterior Teeth: A Two-Year Follow-Up Comparative Study
Adriana Saceleanu, Anca Maria Fratila, Vasile Calin Arcas, Cristina Ana-Maria Arcas, Dragos Anton Dadarlat, Laura Stef
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2026; 15(2): 687. CrossRef - Micro-scratch and wear resistance of restorative dental materials: an in vitro study
Valeriya Aleksandrova, Neshka Manchorova, Veselina Todorova, Lyubomir Vangelov, Svetlin Alexandrov
Folia Medica.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanotechnology in contemporary dentistry: a comprehensive review of current clinical applications, bioactive materials, and future perspectives
Murtada A. Ahmed, Samar M. Albuhiri, Manal M. Alanazi, Ameerah A. Albogami, Jawaher N. Alharbi, Eman A. Alruwaili, Maryam A. Shabeen
International Journal Of Community Medicine And Public Health.2026; 13(2): 1044. CrossRef - Advances in Ecofriendly and High-Strength Dental Composites: Structural and Functional Perspectives
Sayem A. Mulla, Amit Patil, Himmat Jaiswal, Bhavani Sangala Nagendra, Ashima Jakhar, Waseem Z. Khan
European Journal of General Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter to the Editor regarding, “A digital workflow for tooth-supported complete overdentures with a composite resin injection technique to manage the treatment of a child with ectodermal dysplasia” by Liu et al
Meng Liu, Guoyan Quan
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - How surface electronegativity and calcium release in enamel mediate the adsorption and lubrication of salivary proteins: The role of interfacial water
Yue Tang, Lei Lei, Hujun Wang, Haonan Qiu, Jing Zheng, Zhongrong Zhou
Friction.2025; 13(3): 9440912. CrossRef - Effect of SiC particle size and content on the mechanical and tribological properties of porous Si3N4-SiC composites fabricated following a facile low-temperature processing route
Siddharth, Sakshi Tiwari, Pritam Biswas, Nilrudra Mandal, Siddhartha Roy
Ceramics International.2025; 51(14): 19508. CrossRef - Evaluation of Color Stability and Surface Abrasion of Nano-modified Glass Ionomer Cement with Dentifrices: An In Vitro Study
Jessy Paulraj, Subhabrata Maiti, Harini Palani
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 15(1): 10. CrossRef - Wear resistance of orthodontic attachments: a comparative analysis of different composite resins in clear aligner therapy
Irmak Ocak, Hande Gorucu-Coskuner, Muge Aksu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review: Resin‐Based Dental Materials and Their Characterization
Arda Bingül, Merve Nezir, Aykan Onur Atilla, Suat Özcan, Zafer Evis
Polymers for Advanced Technologies.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomechanical and Occlusal Factors Influencing the Longevity of Single-Unit Restorations: A Comprehensive Review
Wedad S Alaida, Safa A Gadi, Rokia E Al-Ghannam, Moayad F Alamri, Feras I Mirdad, Ruba M Argaibeh, Bushra A Alqahtani, Abdulrahman M Alqahtani, Abdulelah A Al Jaban, Turki M Alkuraydimi, Abdulrahman S Alamari
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Bleaching on Surface Roughness of Universal Composite Resins After Chlorhexidine-Induced Staining
Gözde Aksoy Vaizoğlu
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 277. CrossRef - Wear properties of hybrid antibacterial dental composite with micro-particles of S. persica and hydroxyapatite as fillers
Rihem Chaaben, Ayman Ayedi, Khaled Elleuch
Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration.2025; 10(4): 3055. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Direct and Indirect Composite Restorations in Class II Tooth Preparations - An In vivo Study
Akshun Gupta, Garima Arora, Aprajita Mehta, Satish Sane, Siddhi Nevrekar, Apurva Nagrale
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 550. CrossRef - Effect of Thermal Ageing on Flexural Strength and Microhardness of Novel High-Performance Polymer (Nanoksa G-Plus) in Comparison to a Widely Used Bio-HPP/PEEK
Ramy Abdallah Abdelrahim, Ahmed Ali Ezzeldine, Mahmoud Abdellah, SaadEldein Sadeq Elghazawi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(8): 370. CrossRef - A comparative 48 month randomized trial of clinical performance and wear of BISGMA based and BISGMA free nanoceramic resin composites
Samah Mohamed Bahig, Heba Helal El Sherbiney, Mohamed Moustafa Zayed, Shereen Hafez Ibrahim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bruxism Simulation in Aligner Therapy: Effects on Restored Posterior Teeth
Amelia Anita Boitor (Andreica), Adriana Objelean, Cristina Gasparik, Alexandru Victor Burde, Horațiu Alexandru Colosi, Diana Dudea
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(21): 7877. CrossRef - Comparison of wear behavior of occlusal device materials manufactured by different processes
Catherine Arreaza, Robert R. Seghi, Scott R. Schricker, William M. Johnston, Paola C. Saponaro
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Effects of Rapid High‐Intensity Light Curing on Bulk‐Fill Resin‐Based Composites: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Samille Biasi Miranda, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Giovana Lordsleem de Mendonça, Luiz Antonio Soares Falson, Matheus José Gusmão Simões Barza, Veronica Maria de Sá Rodrigues, Ana Karina Maciel de Andrade, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Antonio Japiassú
The Scientific World Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Various Toothpaste Tablets on Gloss and Surface Roughness of Resin-based Composite Materials
J Ko, A Tsao, R Kim, C Perry, U Oyoyo, SR Kwon
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(3): 282. CrossRef - Surface wear of attachments in patients during clear aligner therapy: a prospective clinical study
Qiuying Li, Kai Yang
Progress in Orthodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Awareness of possible complications associated with direct composite restorations: A multinational survey among dentists from 13 countries with meta-analysis
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Jakub Jankowski, David Donnermeyer, Paulo J. Palma, Milan Drobac, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Fatma Pertek Hatipoğlu, Indira Tulegenova, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Hamad Mohammad Alharkan, Olga Bekjanova, Sylvia Wyzga, Moataz
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 145: 105009. CrossRef - Evaluation of pre-heated composite resins with soft-start polymerization and conventional composite restorations in class-I carious lesions – A randomized clinical trial
Niral Kotecha, Nimisha C. Shah, Namita N. Gandhi, Priya Porwal, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Novaldy Wahjudianto, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Suraj Arora, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
Heliyon.2024; 10(10): e30794. CrossRef - Reabilitação estética de dente conóide: relato de caso
Anna Danielle Oliveira dos Santos, Diana Fernandes de Melo , Jorge Alberto Carrazana Moya , Kathleen Rebelo de Sousa , Lizete Karla Filgueiras de Souza, Marcela Lopes Linhares, Márcio Langbeck Castelo Branco , Márcio Lopes Linhares
Revista Clínica de Odontologia.2024; 5(1): 80. CrossRef - Non-collagenous protein analog-induced biomimetic mineralization strategy to restore the dentin interface
Ruhua Chen, Yimeng Xie, Liang Ma, Bing Li, Wei Yao
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2024; 10(6): 062004. CrossRef - Influence of Low pH on the Microhardness and Roughness Surface of Dental Composite—A Preliminary Study
Leszek Szalewski, Dorota Wójcik, Monika Sowa, Vladyslav Vivcharenko, Krzysztof Pałka
Materials.2024; 17(14): 3443. CrossRef - Fabrication of a novel aesthetic orthodontic bracket and evaluation of friction properties between PEEK and stainless steel wires
Jiaqi Wu, Xiujing Wang, Jiuhui Jiang, Yunyang Bai
Technology and Health Care.2024; 32(1): 269. CrossRef - Can wheel polishers improve surface properties and color stability of monochromatic resin composites?
Lezize Sebnem Turkun, Cankut Canevi, Alperen Degirmenci, Hayal Boyacioglu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of volumetric loss and surface roughness of composite dental restorations obtained by additive and subtractive manufacturing methods
Neslihan Güntekin, Ali Rıza Tunçdemir
Heliyon.2024; 10(4): e26269. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of microhardness of three restorative materials after immersion in chlorhexidine mouthwash: An in vitro study
Shilpa S. Shah, Nishtha K. Patel, Kruti P. Yagnik, Aarshati Vyas, Prerak Doshi, Pooja R. Keshrani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(5): 520. CrossRef - NON-INTERVENTION VERSUS REPAIR/REPLACEMENT DECISIONS IN POSTERIOR COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS AGED 3-5 YEARS: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
Galina Pancu, Andrei Georgescu , Antonia Moldovanu , Angela Ghiorghe , Simona Stoleriu , Irina Nica , Ionut Tărăboanţă , Alexandru Iovan , Sorin Andrian
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(2): 186. CrossRef - Effect of tooth brushing simulation on the surface properties of various resin‐matrix computer‐aided design/computer‐aided manufacturing ceramics
Evangelos Ximinis, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Constantinos Papadopoulos, Alexandros Tournavitis, Avraam Konstantinidis, Olga Naka
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(6): 937. CrossRef - Effect of toothpaste with different components on toothbrushing wear resistance of micro-hybrid/nano-filled resin composites
Seon-Mi Byeon, Jung-Eun Park, Kyeong-Seon Kim, Tae-Hwan Kim, Chung-Cha Oh, Seung-O Ko3, Min-Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2023; 50(4): 247. CrossRef - Release Kinetics of Monomers from Dental Composites Containing Fluoride-Doped Calcium Phosphates
Adrián M. Alambiaga-Caravaca, Alicia López-Castellano, Yu Fu Chou, Arlinda Luzi, Juan Manuel Núñez, Avijit Banerjee, María del Mar Jovani Sancho, Salvatore Sauro
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(7): 1948. CrossRef - Comparative study on the impact-sliding wear behaviour of CAD/CAM resin-ceramic materials and tooth enamel
Chunxiao Jin, Jiuhong Deng, Peiyue Pan, Yuhuan Xiong, Liqing Zhu, Shanshan Gao
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 25. CrossRef - The impact of dental varnishes on the immediate surface microhardness and roughness of restorative dental materials: An in vitro study
Jovana Lovric, Milisav Markovic, Marko Bulajic, Sasa Zeljkovic, Jana Ilic, Olivera Dolic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2023; 80(12): 1022. CrossRef - An In Vitro Study regarding the Wear of Composite Materials Following the Use of Dental Bleaching Protocols
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Ţuculină, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Andrei Osman, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Smaranda Adelina Bugălă, Mihaela Ionescu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Bogdan Dimitriu
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(10): 532. CrossRef - Investigation of aging resistance for dental resin composites with and without glass flakes
Dan Feng, Shujun Dong, Zuosen Shi, Zhanchen Cui, Song Zhu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6903. CrossRef - Tribological behavior and wear mechanisms of dental resin composites with different polymeric matrices
Vladja Torno, Paulo Soares
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2023; 144: 105962. CrossRef - Performance of two-flux and four-flux models for predicting the spectral reflectance and transmittance factors of flowable dental resin composites
Vincent Duveiller, Raphaël Clerc, Julien Eymard, Jean-Pierre Salomon, Mathieu Hébert
Dental Materials.2023; 39(8): 743. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of bulk-fill resins in vitro
Carla Junqueira, Paulo Mascarenhas, Mariana Avelar, Ana Clara Ribeiro, Isabel Barahona
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7851. CrossRef - Optimizing Dental Bond Strength: Insights from Comprehensive Literature Review and Future Implications for Clinical Practice
Yung-Shin Fan-Chiang, Peng-Chen Chou, Yu-Wen Hsiao, Yu-Hsuan Cheng, Yi Huang, Yu-Chieh Chiu, Yu-Ju Lin, Yuichi Mine, Sheng-Wei Feng, I-Ta Lee, Tzu-Yu Peng
Biomedicines.2023; 11(11): 2995. CrossRef - Polymères et résines composites en technique directe
T. Giraud, E. Casazza, B. Ballester, A. Raskin
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(6): 1. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Strength of Dentin Replacement in Complex Posterior Tooth Restoration
Nurhayaty Natsir, Farida Rahim, Juni Jekti Nugroho, Christine Anastasia Rovani, Syamsiah Syam, Muhammad Ruslin, Takashi Saito, Keng-Liang Ou
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(14): 6877. CrossRef - Calcium release-mediated adsorption and lubrication of salivary proteins on resin-based dental composites
Yue Tang, Lei Lei, Dan Yang, Jing Zheng, Qihang Zeng, Heng Xiao, Zhongrong Zhou
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 135: 105437. CrossRef - Modifications of Glass Ionomer Cements Using Nanotechnology: Recent Advances
Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Olga Gerasimidou, Constantinos Papadopoulos
Recent Progress in Materials.2022; 04(02): 1. CrossRef - Microleakage Evaluation in Class V Cavities Restored with Five Different Resin Composites: In vitro Dye Leakage Study
Sahar Bajabaa, Shaza Balbaid, Muruj Taleb, Lujain Islam, Salem Elharazeen, Ebaa Alagha
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2021; Volume 13: 405. CrossRef
- Synergistic Effects of Simulated Energy Drink Exposure and Fatigue Loading on Bioactive and Conventional Resin Composites
- 12,548 View
- 208 Download
- 39 Web of Science
- 48 Crossref

- Effect of dental bleaching on the microhardness and surface roughness of sealed composite resins
- Renan Aparecido Fernandes, Henrico Badaoui Strazzi-Sahyon, Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e12. Published online January 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the microhardness and surface roughness of composite resins before and after tooth bleaching procedures.Materials and Methods Sixty specimens were prepared of each composite resin (Filtek Supreme XT and Opallis), and BisCover LV surface sealant was applied to half of the specimens. Thirty enamel samples were obtained from the buccal and lingual surfaces of human molars for use as the control group. The surface roughness and microhardness were measured before and after bleaching procedures with 35% hydrogen peroxide or 16% carbamide (
n = 10). Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Fisher test (α = 0.05).Results Neither hydrogen peroxide nor carbamide peroxide treatment significantly altered the hardness of the composite resins, regardless of surface sealant application; however, both treatments significantly decreased the hardness of the tooth samples (
p < 0.05). The bleaching did not cause any change in surface roughness, with the exception of the unsealed Opallis composite resin and dental enamel, both of which displayed an increase in surface roughness after bleaching with carbamide peroxide (p < 0.05).Conclusions The microhardness and surface roughness of enamel and Opallis composite resin were influenced by bleaching procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
Mariana Ferreira da Silva, Giovana Contin Germinari, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Tatiane Cristina Dotta, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Júnior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2026; 25: e260366. CrossRef - Effect of Bleaching on Surface Roughness and Color Parameters of Coffee-Stained Nanohybrid Dental Composites with Different Viscosities
Hetaf S. Redwan, Mohamed A. Hussein, Mohamed M. Abdul-Monem
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(01): 027. CrossRef - Effect of Staining and External Bleaching on the Color Stability and Surface Roughness of Universal-Shade Resin-Based Composite
AlHanouf AlHabdan, Amal Alsuhaibani, Lama Alomran, Lulwah Almutib
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2025; Volume 17: 1. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Between Strip and Gels Indicated for at Home Bleaching: Analysis of Color Alteration, Roughness and Microhardness of Dental Enamel
K. M. S. Aidar, L. T. A. Cintra, M. C. B. Ferreira, T. C. Fagundes, L. M. B. Esteves, J. Goto, A. Catelan, A. L. F. Briso
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1504. CrossRef - Surface properties and susceptibility to staining of a resin composite after brushing with different whitening toothpastes
Aline da Silva Barros, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Junior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e6. CrossRef - Degradation Resistance of Next-Generation Dental Composites Under Bleaching and Immersion: A Multiscale Investigation
Syed Zubairuddin Ahmed, Shahad Al-Qahtani, Naif H. Al-Qahtani, Hussah Al-Mulhim, Maha Al-Qahtani, Ali Albalushi, Sultan Akhtar
Prosthesis.2025; 7(3): 57. CrossRef - Effect of Over-the-Counter Whitening Dentifrices on the Color Stability and Microhardness of Composite Resins
Xinnuo Yu, Maria Pilar Melo, Sofia Folguera, Carmen Llena
Journal of Composites Science.2025; 9(7): 324. CrossRef - From Microstructure to Shade Shift: Confocal and Spectrophotometric Evaluation of Peroxide-Induced Dental Bleaching
Berivan Laura Rebeca Buzatu, Magda Mihaela Luca, Atena Galuscan, Adrian Ovidiu Vaduva, Aurora Doris Fratila, Ramona Dumitrescu, Ruxandra Sava-Rosianu, Octavia Balean, Roxana Buzatu, Daniela Jumanca
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(13): 4642. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Chemical and Microhardness Alterations in Human Enamel Induced by Three Commercial In-Office Bleaching Agents
Berivan Laura Rebeca Buzatu, Atena Galuscan, Ramona Dumitrescu, Roxana Buzatu, Magda Mihaela Luca, Octavia Balean, Gabriela Vlase, Titus Vlase, Iasmina-Mădălina Anghel, Carmen Opris, Bianca Ioana Todor, Mihaela Adina Dumitrache, Daniela Jumanca
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(8): 357. CrossRef - Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Bleaching on Color Stability and Microhardness of Alkasite Restorative Materials: An In Vitro Study
Souad A Alfouzan, Rahaf A Alolayan, Asma Munir Khan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Color Stability and Surface Roughness of Nanohybrid Resin Composites with Different Photoinitiator Systems After Staining and Home/Office Bleaching: An In Vitro Study
Fatma Yılmaz, Buse Kesgin
Meandros Medical And Dental Journal.2025; 26(3): 240. CrossRef - The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide With Different Concentration on the Color and Surface Microhardness of the Resin Bracket
Song‐Yi Yang
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of different bleaching agents on the color stability, hardness and surface roughness of indirect esthetic restorative materials with different manufacturing methods
Ayse Atay, Defne Canpolat, Soner Sismanoglu, Aslihan Usumez
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Microhardness and Surface Roughness of New Nanofiber Filled Flowable Composite
Rumeysa Hatice ENGINLER OZLEN, Zumrut Ceren OZDUMAN, Burcu OGLAKCI OZKOC, Evrim ELIGUZELOGLU DALKILIC
Bezmialem Science.2024; 12(4): 406. CrossRef - Effect of Bleaching Agents on Composite Resins with and without Bis-GMA: An In Vitro Study
María Melo, Bianca Dumitrache, James Ghilotti, José Luis Sanz, Carmen Llena
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(6): 144. CrossRef - Changes in physical properties of universal composites and CAD/CAM materials after bleaching and antioxidant applications: Scanning electron microscope and atomic force microscope evaluation
Oguz Kaan Tuysuz, Merve Gurses
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(5): 977. CrossRef - The Effects of Home and Over-The-Counter Whitening Agents on Surface Roughness and Microhardness of High Aesthetic Composites
Elif İpek KILIÇ DÖNMEZ, İhsan HUBBEZOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2024; 27(1): 30. CrossRef - Effect of carbamide peroxide treatment on the ion release of different dental restorative materials
Merve Nur Yilmaz, Pinar Gul
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inorganic Phosphate Effect in a Hydrogen Peroxide-based Bleaching Agent: Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Morphological Properties of Dental Enamel
KG Garcia, GP Nunes, ACB Delbem, PH dos Santos, GLP Fernandes, HF Robles, PBB Lemos, M Danelon
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 465. CrossRef - Effect of bleaching and repolishing on whiteness change and staining susceptibility of resin-based materials
Sultan Aktuğ Karademir, Samet Atasoy, Beyza Yılmaz
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Low pH on the Microhardness and Roughness Surface of Dental Composite—A Preliminary Study
Leszek Szalewski, Dorota Wójcik, Monika Sowa, Vladyslav Vivcharenko, Krzysztof Pałka
Materials.2024; 17(14): 3443. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Effectiveness and pH Variation of Dental Bleaching Gels and Their Effect on Enamel Surface Roughness
Federica Veneri, Francesco Cavani, Giovanni Bolelli, Vittorio Checchi, Alessia Bizzi, Giacomo Setti, Luigi Generali
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(12): 415. CrossRef - Does the combination of whitening toothpaste and hydrogen peroxide bleaching increase the surface roughness and change the morphology of a nanofilled composite?
Cecília Pereira da Silva Braga Tenório, Matheus Kury, Geyse Maria dos Santos Muniz Mota, Cecília Pedroso Turssi, Flávia Lucisano Botelho do Amaral, Vanessa Cavalli
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e241938. CrossRef - Effect of peroxide‐free and peroxide‐based in‐office bleaching on the surface and mechanical properties of CAD/CAM esthetic restorative materials
Majed M. Alsarani, Aftab Ahmed Khan, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Hanan Alsunbul, Jukka P. Matinlinna
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Repolishing on Color Stability, Translucency, and Surface Roughness of Aged Monochromatic Dental Composites
Mohamed M. Abdul-Monem, Mohamed A. Hussein, Mona G. Abdelrehim
European Journal of General Dentistry.2024; 13(03): 240. CrossRef - Color changes of nanofiller composite resin after glycerin application immersed in turmeric extract
Sukaton, Galih Sampoerno, Widyajeng Ayu Laksmi, Daradhasih Bestari Santiaji
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2023; 13(1): 37. CrossRef - Effects of Dental Bleaching Agents on the Surface Roughness of Dental Restoration Materials
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Tuculina, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Cristiana Petcu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Ana Maria Rîcă, Ruxandra Voinea-Georgescu
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1067. CrossRef - Effect of Bleaching on the Microhardness and Modulus of Elasticity of ACTIVA BioACTIVE – RESTORATIVE: An In Vitro Study
Sushritha Sricharan, Swaroop Hegde, Narmada J., Indiresha H. Narayana, Chatura Mohan, Nithin K. Shetty
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2023; 14(2): 190. CrossRef - The effect of bleaching on surface roughness and gloss of different CAD/CAM ceramic and hybrid ceramic materials
Ruwaida Z Alshali, Mohammed A AlQahtani, Dalea M Bukhary, Mlak A Alzahrani, Shatha S Alsoraihi, Majed A Alqahtani
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of bleaching with 15% carbamide peroxide on color stability of microhybrid, nanohybrid, and nanofilled resin composites, each in 3 staining solutions (coffee, cola, red grape juice): A 3-phase study
Azadeh Ghaemi, Sanaz Sharifishoshtari, Mohsen Shahmoradi, Hossein Akbari, Parisa Boostanifard, Sepideh Bagheri, Mohammadreza Shokuhifar, Negin Ashoori, Vahid Rakhshan
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Hardness and Surface Roughness of Bulk-Fill Composite Resin: Effect of Surface Sealant Application and Two Bleaching Regimens
Reham Mohamad Attia, Eman Mohamed Sobhy, Mona El Said Abd El Hameed Essa
European Journal of General Dentistry.2023; 12(03): 169. CrossRef - Shear bond strength after using sealant before bonding: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Jennifer Hoppe, Thomas Lehmann, Christoph-Ludwig Hennig, Ulrike Schulze-Späte, Collin Jacobs
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of 16% Carbamide Peroxide and Activated-Charcoal-Based Whitening Toothpaste on Enamel Surface Roughness in Bovine Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Jorge Zamudio-Santiago, Marysela Ladera-Castañeda, Flor Santander-Rengifo, Carlos López-Gurreonero, Alberto Cornejo-Pinto, Ali Echavarría-Gálvez, Luis Cervantes-Ganoza, César Cayo-Rojas
Biomedicines.2022; 11(1): 22. CrossRef - Direct dentin bleaching: Would it be possible?
Camila Ferro Clemente, Sibele de Alcântara, Lívia Maria Alves Valentim da Silva, Lara Maria Bueno Esteves, Anderson Catelan, Karen Milaré Seiscento Aidar, Ticiane Cestari Fagundes, André Luiz Fraga Briso
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 40: 103121. CrossRef - EFFECT OF İN-OFFİCE BLEACHİNG ON THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF DİFFERENT COMPOSİTE RESİNS
Seher KAYA, Ozden OZEL BEKTAS
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(Supplement): 78. CrossRef - Effect of Polishing on the Surface Microhardness of Nanohybrid Composite Resins Subjected to 35% Hydrogen Peroxide
Giovanna Gisella Ramírez-Vargas, Julia Elbia Medina y Mendoza, Ana Sixtina Aliaga-Mariñas, Marysela Irene Ladera-Castañeda, Luis Adolfo Cervantes-Ganoza, César Félix Cayo-Rojas
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2021; 11(2): 216. CrossRef - Intrapulpal Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide of Teeth Restored With Bulk Fill and Conventional Bioactive Composites
DP Silva, BA Resende, M Kury, CB André, CPM Tabchoury, M Giannini, V Cavalli
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): E158. CrossRef - An Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy Evaluation on Comparison of Three Different Bleaching Agents using the Laser Activated in-Office Bleaching at Different Wavelengths
Shachi Goenka, Sushil Kumar Cirigiri, Kanika Poplai, Baig Mirza Aslam, Shalini Singh, Shweta Gangavane
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 2): S1478. CrossRef - Effects of Artificial Staining and Bleaching Protocols on the Surface Roughness, Color, and Whiteness Changes of an Aged Nanofilled Composite
Geyse Maria dos Santos Muniz Mota, Matheus Kury, Cecília Pereira da Silva Braga Tenório, Flávia Lucisano Botelho do Amaral, Cecília Pedroso Turssi, Vanessa Cavalli
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
- 2,874 View
- 43 Download
- 39 Crossref

- Functional and aesthetic rehabilitation in posterior tooth with bulk-fill resin composite and occlusal matrix
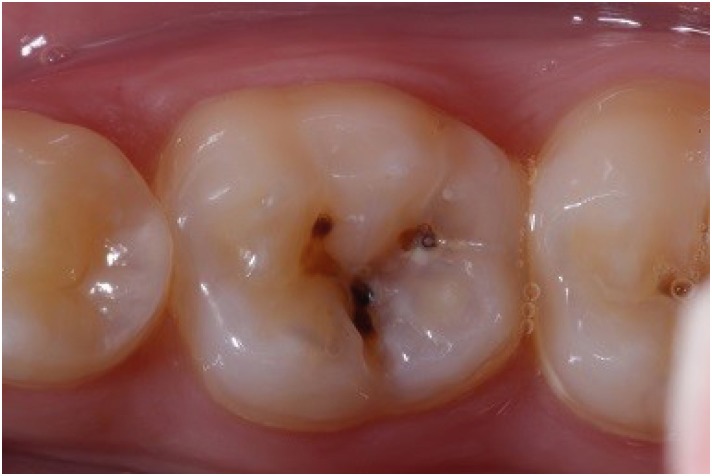
- Luciana Fávaro Francisconi-dos-Rios, Johnny Alexandre Oliveira Tavares, Luanderson Oliveira, Jefferson Chaves Moreira, Flavia Pardo Salata Nahsan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e9. Published online January 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative procedure in posterior teeth involves clinical steps related to professional skill, especially when using the incremental technique, which may fail in the long term. A recent alternative is bulk-fill resins, which can reduce polymerization shrinkage, decreasing clinical problems such as marginal leakage, secondary caries, and fracture. This scientific study aims to report a clinical case using bulk-fill resin with an occlusal matrix. As determined in the treatment plan, an acrylic resin matrix was produced to establish an improved oral and aesthetic rehabilitation of the right mandibular first molar, which presented a carious lesion with dentin involvement. The occlusal matrix is a simple technique that maintains the original dental anatomy, showing satisfactory results regarding function and aesthetic rehabilitation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
Yu. Kolenko
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2025; (2): 67. CrossRef - Color stability of bulk‐fill compared to conventional resin‐based composites: A scoping review
Gaetano Paolone, Mauro Mandurino, Nicola Scotti, Giuseppe Cantatore, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(4): 657. CrossRef - Evaluation of Abfraction Lesions Restored with Three Dental Materials: A Comparative Study
Bogdan Constantin Costăchel, Anamaria Bechir, Alexandru Burcea, Laurența Lelia Mihai, Tudor Ionescu, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Edwin Sever Bechir
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(5): 1043. CrossRef - Aesthetic restoration of posterior teeth using different occlusal matrix techniques
Elsa Reis Carneiro, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Eunice Carrilho
British Dental Journal.2021; 231(2): 88. CrossRef
- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
- 1,667 View
- 22 Download
- 4 Crossref

-
The effect of individualization of fiberglass posts using bulk-fill resin-based composites on cementation: an
in vitro study - Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Jairo Matozinho Cordeiro, Carolina Perez Rangel, Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e37. Published online October 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the bond strength of various fiberglass post cementation techniques using different resin-based composites.
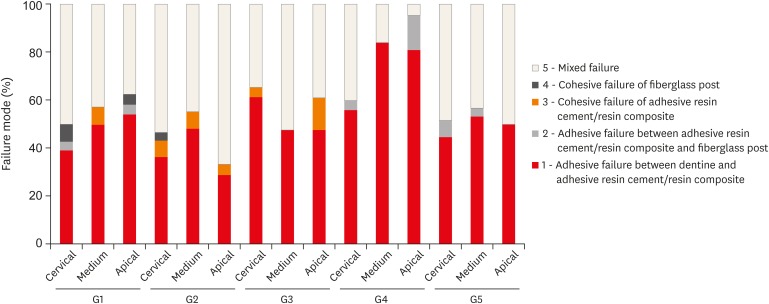
Materials and Methods The roots from a total of 100 bovine incisors were randomly assigned to 5 treatment groups: G1, post + Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (SBMP) + RelyX ARC luting agent; G2, relined post (Filtek Z250) + SBMP + RelyX ARC; G3, individualized post (Filtek Z250) + SBMP; G4, individualized post (Filtek Bulk-Fill) + SBMP; G5, individualized post (Filtek Bulk-Fill Flow) + SBMP. The samples were subjected to the push-out (
n = 10) and pull-out (n = 10) bond strength tests. Data from the push-out bond strength test were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Bonferronipost hoc test, and data from the pull-out bond strength test were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA.Results The data for push-out bond strength presented higher values for G2 and G5, mainly in the cervical and middle thirds, and the data from the apical third showed a lower mean push-out bond strength in all groups. No significant difference was noted for pull-out bond strength among all groups. The most frequent failure modes observed were adhesive failure between dentine and resin and mixed failure.
Conclusions Fiberglass post cementation using restorative and flowable bulk-fill composites with the individualization technique may be a promising alternative to existing methods of post cementation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- EVALUATION OF PUSH-OUT BOND STRENGTH OF GLASS FIBER POSTS USING DIFFERENT LUTING CEMENTS
Jannah Mohammed, Maha Agha
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 274. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance of weakened roots restored with relined or milled CAD-CAM glass fiber posts
Belizane das Graças Oliveira MAIA, Thais da Silva Alves SANTOS, Cláudio Antonio Talge CARVALHO, Francielle Silvestre VERNER, Rafael Binato JUNQUEIRA
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 92. CrossRef - Evaluation of pretreatments on intra‐radicular dentin bond strength of self‐adhesive resin cements
Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins, Jorge Rodrigo Soto‐Montero
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(7): 1051. CrossRef - Comparison of the Mechanical Properties and Push-out Bond Strength of Self-adhesive and Conventional Resin Cements on Fiber Post Cementation
MR Santi, RBE Lins, BO Sahadi, JR Soto-Montero, LRM Martins
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 346. CrossRef - Glass fiber posts
Renata Pereira, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Victória Castelan Rodrigues, Débora Alves Nunes Leite Lima, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins, Flávio Henrique Baggio Aguiar
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 19: e207508. CrossRef
- EVALUATION OF PUSH-OUT BOND STRENGTH OF GLASS FIBER POSTS USING DIFFERENT LUTING CEMENTS
- 1,461 View
- 11 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Finishing and polishing effects of multiblade burs on the surface texture of 5 resin composites: microhardness and roughness testing
- Elodie Ehrmann, Etienne Medioni, Nathalie Brulat-Bouchard
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e1. Published online November 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e1

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to test the effect of 2 finishing–polishing sequences (QB, combining a 12/15-fluted finishing bur and an EVO-Light polisher; QWB, adding a 30-fluted polishing bur after the 12/15-fluted finishing bur used in the QB sequence) on 5 nanotech-based resin composites (Filtek Z500, Ceram X Mono, Ceram X Duo, Tetric Evoceram, and Tetric Evoceram Bulk Fill) by comparing their final surface roughness and hardness values to those of a Mylar strip control group (MS).Materials and Methods Twelve specimens of each nanocomposite were prepared in Teflon moulds. The surface of each resin composite was finished with QB (5 samples), QWB (5 samples), or MS (2 samples), and then evaluated (60 samples). Roughness was analysed with an optical profilometer, microhardness was tested with a Vickers indenter, and the surfaces were examined by optical and scanning electron microscopy. Data were analysed using the Kruskal-Wallis test (
p < 0.05) followed by the Dunn test.Results For the hardness and roughness of nanocomposite resin, the QWB sequence was significantly more effective than QB (
p < 0.05). The Filtek Z500 showed significantly harder surfaces regardless of the finishing–polishing sequence (p < 0.05).Conclusions QWB yielded the best values of surface roughness and hardness. The hardness and roughness of the 5 nanocomposites presented less significant differences when QWB was used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
Melek Güven Bekdaş, Ihsan Hubbezoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different charcoal-containing whitening toothpastes on color and surface roughness of a supra-nanofilled composite resin
Meltem Nermin Polan, Sevil Gurgan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different polishing techniques on surface roughness, gloss, and microhardness of zirconium oxide reinforced flowable bulk-fill resin composite: an in vitro study
Amr Elsayed Elnahas, Mohamed Elshirbeny Elawsya, Abeer ElSayed ElEmbaby
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tek Renkli Monokromatik Kompozit Rezinlerle İlgili Bir Durum Değerlendirmesi
Kubra Nur Yeşilova, Sebnem Turkun
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(2): 331. CrossRef - Effect of different finishing and polishing systems on surface properties of universal single shade resin-based composites
Ghada Alharbi, Hend NA Al Nahedh, Loulwa M. Al-Saud, Nourah Shono, Ahmed Maawadh
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative study of polishing systems on optical properties and surface roughness of additively manufactured and conventional resin based composites
Ayse Tugba Erturk-Avunduk, Sevim Atılan-Yavuz, Hande Filiz, Esra Cengiz-Yanardag
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Instrument Lubricant on Mechanical Properties of Restorative Composite
G Pippin, D Tantbirojn, M Wolfgang, JS Nordin, A Versluis
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 475. CrossRef - An In Vitro Study regarding the Wear of Composite Materials Following the Use of Dental Bleaching Protocols
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Ţuculină, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Andrei Osman, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Smaranda Adelina Bugălă, Mihaela Ionescu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Bogdan Dimitriu
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(10): 532. CrossRef - Akıllı Kromatik Teknolojili Kompozit Rezinlerin Farklı pH Değerlerindeki Sıvılarda Bekletilmesi Sonrası Oluşan Yüzey Pürüzlülüğü ve Renk Değişimlerinin Değerlendirilmesi
Fatih ÖZNURHAN, Aylin ÖZEL
Farabi Tıp Dergisi.2023; 2(4): 17. CrossRef - Enamel surface roughness evaluation after debonding and residual resin removal using four different burs
Rapeti Madhu Vanya, Anil Chirla, Uday Kumar Digumarthi, Tarakesh Karri, Bommareddy Radhika, Sanapala Manojna
Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics.2023; 7(3): 173. CrossRef - Finishing and Polishing of Composite Restoration: Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Among Various Dental Professionals in India
Sankar Vishwanath, Sadasiva Kadandale, Senthil kumar Kumarappan, Anupama Ramachandran, Manu Unnikrishnan, Honap manjiri Nagesh
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of different composite resin finishing and polishing protocols by confocal laser scan microscopy
Kayo Matheus Rodrigues de Souza, Roberto Victor de Melo Silva, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Paulo Cardoso Lins-Filho, Claudio Heliomar Vicente da Silva, Renata Pedrosa Guimarães
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2022; 21: e225334. CrossRef - Laboratory methods to simulate the mechanical degradation of resin composite restorations
Veronica P. Lima, Jaqueline B. Machado, Yu Zhang, Bas A.C. Loomans, Rafael R. Moraes
Dental Materials.2022; 38(1): 214. CrossRef - FARKLI POLİSAJ SİSTEMLERİNİN POSTERİOR BÖLGEDE KULLANILAN KOMPOZİT REZİNLERİN YÜZEY PÜRÜZLÜLÜĞÜ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİ
Meltem Nermin DURSUN, Cansu ATALAY
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Additional Finishing and Polishing Sequences on Hardness and Roughness of Two Different Dental Composites: An In Vitro Study
Kıvanç Dülger
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 216. CrossRef - Effect of immediate and delayed finishing and polishing procedure on Streptococcal mutans adhesion and micro-hardness of composite resin surface: An in-vitro study
Tushar Kanti Majumdar, Moumita Khatua, Paromita Mazumdar, Sayantan Mukherjee
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2022; 10(1): 5. CrossRef - Comparison of Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Resin Based Composites Containing Different Monomers
Marina Gullo Augusto, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Ingrid Fernandes Mathias-Santamaria, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Journal of Composites Science.2022; 6(5): 146. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF PH-CYCLING AND TOOTHBRUSHING SIMULATIONS ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF BULK-FILL COMPOSITES
Tuğba MİSİLLİ, Nihan GONULOL, Özge Gizem CABADAĞ, Lena ALMASIFAR, Derya DİNÇ
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(3): 487. CrossRef - A three-year randomized clinical trial evaluating direct posterior composite restorations placed with three self-etch adhesives
Joseph Sabbagh, Layal El Masri, Jean Claude Fahd, Paul Nahas
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2021; 8(1): 92. CrossRef - Press-On Force Effect on the Efficiency of Composite Restorations Final Polishing—Preliminary In Vitro Study
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Natalia Potempa, Paweł Sieradzki, Mateusz Król, Olaf Czyż, Agnieszka Radziszewska, Anna Surdacka
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 705. CrossRef - Surface evaluations of a nanocomposite after different finishing and polishing systems for anterior and posterior restorations
Riccardo Monterubbianesi, Vincenzo Tosco, Giulia Orilisi, Simone Grandini, Giovanna Orsini, Angelo Putignano
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(12): 2922. CrossRef - Wear, roughness and microhardness analyses of single increment restorative materials submitted to different challenges in vitro
L. C. Oliveira, P. H. dos Santos, F. S. S. Ramos, M. D. Moda, A. L. F. Briso, T. C. Fagundes
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2021; 22(2): 247. CrossRef - Neurotic personality trait as a predictor in the prognosis of composite restorations: A 24-month clinical follow up study
Sulthan Ibrahim Raja Khan, Dinesh Rao, Anupama Ramachandran, Bhaskaran Veni Ashok, Jagan Kumar Baskaradoss
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces
Ksenia Babina, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Marianna Arakelyan, Nina Novozhilova
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1339. CrossRef - Surface Geometry of Four Conventional Nanohybrid Resin‐Based Composites and Four Regular Viscosity Bulk Fill Resin‐Based Composites after Two‐Step Polishing Procedure
Mateusz Granat, Janusz Cieloszyk, Urszula Kowalska, Jadwiga Buczkowska-Radlińska, Ryta Łagocka, Ali Nokhodchi
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
- 2,446 View
- 24 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Endocrown restorations for extensively damaged posterior teeth: clinical performance of three cases
- Konstantinos Tzimas, Maria Tsiafitsa, Paris Gerasimou, Effrosyni Tsitrou
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e38. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e38
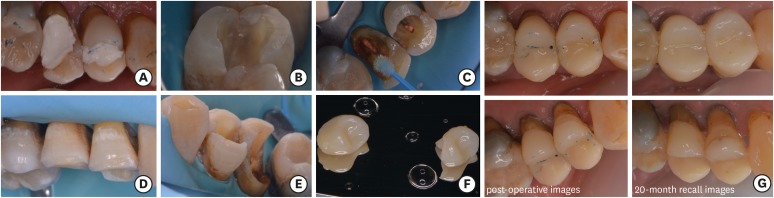
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restoration of endodontically treated teeth (ETT) with more than one cusp missing and thin remaining walls is challenging for the general practitioner. The use of posts combined with full coverage restorations is a well-established approach, yet not following the minimal invasive principles of adhesive dentistry. Endocrowns are indirect monoblock restorations that use the pulp chamber of the ETT for retention. In this study the fabrication of 4 endocrowns and their clinical performance will be discussed. Two clinical cases include computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing manufactured molar endocrowns (one feldspathic ceramic and one hybrid composite-ceramic restoration) and the other two are dental laboratory manufactured resin composite premolar endocrown restorations. The modified United States Public Health Service criteria were used to assess the clinical behavior of the restorations at different follow up periods. Endocrown restorations present a satisfactory clinical alternative, either by the use of resin composite or glass ceramic and hybrid materials. Specific guidelines with minimal alterations should be followed for an endocrown restoration to be successful. Due to limited evidence regarding the long term evaluation of this restorative technique, a careful selection of cases should be applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical performance of endocrown restorations in anterior teeth: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Julia Fehrenbach, Jéssica Lopes Soares de Soares, João Carlos Silva do Nascimento Foly, Leonardo Lamberti Miotti, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2025; 41(1): 28. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and mode of failure of modified Polyether-ether-ketone versus lithium disilicate endocrowns
Mohamed G. A. Kharboush, Hesham I. Othman, Mohamed F. Aldamaty, Ahmed M. L. Alameldin
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic assessment of composite CAD/CAM endocrowns and stainless steel crowns for endodontically treated first permanent molars in Egyptian children: randomized controlled pilot study
Basheer Ali Mabkhot, Sheriene Ezz Eldin Taha, Shaimaa Mohamed Sabry
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of cavity design on the mechanical behavior of endo-crown restorations: an ex-vivo study
Mohamed Gomaa Altamimi, Omaima El Mahallawi, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Mohammed Turky
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Microtensile Bonding Strength and Microleakage of Endocrowns Restorations Prepared With Two Different Materials
Emrah Ayna, Burcu Ayman, Cansel Belge
HRU International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Research.2025; 5(2): 66. CrossRef - Exploring the evolution of endocrowns: a bibliometric analysis (2010-2024)
Sanjana Jayakumar Nair, Jinesh Azhuvancheri, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Gopika Krishnan
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2025; 13(10): 4296. CrossRef - Beyond Traditional Restorations: Management With Endocrown in a Late Adolescent
Abdulaziz Binrayes, Abdullatif A AlGhazzi, Saud M Alotaibi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrown-retained fixed partial dentures: Revolutionizing tooth restoration or risky business? A finite element study
Nivedha Muthukumar, Parthasarathy Natarajan, Seenivasan Madhan Kumar, Shanmuganathan Natarajan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1234. CrossRef - Chinese dentists’ restorative preferences and choices for endodontically treated teeth: a representative survey
Wenhui Li, Ziting Zheng, Yuting Zeng, Zhiyan Zhou, Ping Xiao, Xincen Zhong, Wenjuan Yan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PHỤC HÌNH ENDOCROWN TRÊN RĂNG CỐI NHỎ ĐÃ NỘI NHA: BÁO CÁO MỘT CA LÂM SÀNG
Trịnh Minh Trí Trịnh Minh Trí, Lê Võ Thảo Phương Lê Võ Thảo Phương, Nguyễn Tấn Đạt Nguyễn Tấn Đạt, Phạm Nguyên Quân Phạm Nguyên Quân, Văn Hồng Phượng Văn Hồng Phượng
Tạp Chí Khoa Học Trường Đại Học Quốc Tế Hồng Bàng.2024; : 241. CrossRef - Application of one-piece endodontic crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM system to molars
Haruto Hiraba, Kensuke Nishio, Yoshimasa Takeuchi, Takashi Ito, Tetsuo Yamamori, Atsushi Kamimoto
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 81. CrossRef - Clinical performance and wear resistance of milled resin composite material versus direct nanohybrid bulk-fill resin composite in the restoration of endodontically treated posterior teeth over 1 year: Randomized clinical trial
Esraa Esmeail H. Elhaddad, Mohamed M. A. Mohsen, Dina Ezz Eldin Mohamed
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(4): 400. CrossRef - Roughness analysis on porcelain sectional surface of porcelain fused to Co-Cr alloy endocrowns
Xuesheng Li
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimal İnvaziv Protetik Tedavilerde CAD-CAM Kullanımı: İki Olgu Sunumu
Aynur Beyza Çavuşculu Güdül, Şükriye Ece Geduk, Gaye Sağlam
Journal of International Dental Sciences.2024; 10(3): 167. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Toughness and Marginal Adaptation of PEEK and Cast Metal Crowns for Restoring Posterior Teeth with Endocrown and Richmond Crown: An In Vitro Study
Lalit Kumar, Komalpreet Kaur, Shefali Singla, Charnpreet Singh, Sunint Singh
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 14(4): 234. CrossRef - Retrospective study on the evolution of teeth with endodontic treatment in a group of patients from Craiova – Romania
Mihaela-Roxana Boțilă, Mihaela Jana Țuculina , Oana Andreea Diaconu , Mihaela Ionescu , Petre Costin Mărășescu , Luana Corina Lascu , Veronica Mercut
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(2): 225. CrossRef - Criterios clínicos y radiológicos de los tratamientos endodónticos para rehabilitación Endocrown: meta análisis
Domenica Camila Astudillo Benavides, Rafael Bernardo Piedra Andrade, Amanda Isabel Pesantez Coronel, Jose Esteban Torrachi Carrasco
Anatomía Digital.2024; 7(4): 81. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Central Incisors Restored Using Different Post and Crown Materials
Nour Al-Deen Kharboutly, Mirza Allaf, Shaza Kanout
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of extended pulp chamber preparations on the clinical performance of endocrowns in Indian patients: A 1-year observational study
Preethi Duraisamy, Naveen Gopi Chander, Jetty Ramesh Reddy, Muthukumar Balasubramanium
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(5): 616. CrossRef - Endocrowns: Indications, Preparation Techniques, and Material Selection
Dalal S AlDabeeb, Nouf S Alakeel, Raneem M Al jfshar, Thakra K Alkhalid
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Awareness of Dental Practitioners About the Utilization of Endocrown in Post-endodontic Management
Ahmed A Madfa, Moazzy I Almansour, Asma F Alshammari, Nada M. Alenezi, Essa F. Alrashidi, Adel A. Aldhaban, Thoraya Aljohani, Faris A. Alshammari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Performance of Two CAD/CAM Fabricated Ceramic Restorations with Different Designs for MIH Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ayat G. Montaser, Sara N. Hashem, Menna-Allah S. Ali, Nour Alhoda Fathy, Hebatullah Ahmed Safwat, Alaa M. Eldehna
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrown as a restorative strategy in endodontically treated teeth: an integrative literature review
Robson de Lima GOMES, Andressa Cristina da Silva QUEIROZ, Viviane Maria Gonçalves de FIGUEIREDO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ENDOCROWN RESTORATION OF THE ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH BY USING CAD/CAM: CASE SERIES
Begüm ÜNLÜ KURŞUN, Ender AKAN
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(Suppl 1): 13. CrossRef - Clinical Evaluation of CAD/CAM Ceramic Endocrown Versus Prefabricated Zirconia Crown in the Restoration of Pulpotomized Primary Molars: A Two-Year Spilt-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial
Nagwa Mohmmad Ali Khattab, Yasmine Mohamed Farouk El Makawi, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 627. CrossRef - Hyperplastic Pulpitis Management with Endocrown: A Case Report
Pérez Jardón A, Otero Gayoso N, Otero. Rey E.M, Guerra Caamaño M, Chamorro-Petronacci C.M, Blanco Carrión A, Rivas Mundiña B
The Open Dentistry Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inner crown thickness on the bonding strength of porcelain fused to Co-Cr alloy endocrown
Xuesheng Li
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of pulp chamber depth on the accuracy of endocrown scans made with different intraoral scanners versus an industrial scanner: An in vitro study
Bahar Gurpinar, Onjen Tak
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(3): 430. CrossRef - Efectividad de las restauraciones en piezas con tratamiento de conducto: Una revisión clínica actual
Guiselle Andrea Verástegui Baldárrago
Revista Odontológica Basadrina.2022; 6(2): 41. CrossRef - “Conservative Bonded Restoration (An Alternative to Full Coverage Crown): A Case Report on Endocrown
Josey Mathew, Liza George, Sinju Paul, Aleesha Joy, Beulah M Bejoy, Sethuparvathi Anitha
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 42. CrossRef - Fractography of clinical failures of indirect resin composite endocrown and overlay restorations
Carlo M. Saratti, Giovanni T. Rocca, Stéphane Durual, Ulrich Lohbauer, Jack L. Ferracane, Susanne S. Scherrer
Dental Materials.2021; 37(6): e341. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - A Thorough Analysis of the Endocrown Restoration: A Literature Review
Dimokritos Papalexopoulos, Theodora-Kalliopi Samartzi, Aspasia Sarafianou
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(4): 422. CrossRef - Full‐Crown Versus Endocrown Approach: A 3D‐Analysis of Both Restorations and the Effect of Ferrule and Restoration Material
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Niek de Jager, Marco Antonio Bottino, Paul de Kok, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(4): 335. CrossRef - Monolithic Endocrown Vs. Hybrid Intraradicular Post/Core/Crown Restorations for Endodontically Treated Teeth; Cross-sectional Study
Mai Soliman, Lamar Alshamrani, Basma Yahya, Ghadah Alajlan, Alhanoof Aldegheishem, Elzahraa Eldwakhly
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(11): 6523. CrossRef - Which materials would account for a better mechanical behavior for direct endocrown restorations?
José Augusto Sedrez-Porto, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 103: 103592. CrossRef - Indications and Success Rate of Endo Crowns – A Systematic Review
Shahzeb Hasan Ansari, Abdullah Ahmed Alfaqeeh, Abdullah Al Buryk, Sara Ahmed Alfaqeeh, Abdullatif Yousif A. Almusharraf, Atheer Hussain N. Aljarullah
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(43): 3247. CrossRef
- Mechanical performance of endocrown restorations in anterior teeth: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- 5,727 View
- 115 Download
- 37 Crossref

- The effect of thermocycling on the degree of conversion and mechanical properties of a microhybrid dental resin composite
- Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Melika Firouzmanesh, Hossein Bagheri, Tahereh S. Jafarzadeh Kashi, Fateme Razazpour, Marjan Behroozibakhsh
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e26. Published online April 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The purpose of this study was to investigate the degree of conversion (DC) and mechanical properties of a microhybrid Filtek Z250 (3M ESPE) resin composite after aging.
Method The specimens were fabricated using circular molds to investigate Vickers microhardness (Vickers hardness number [VHN]) and DC, and were prepared according to ISO 4049 for flexural strength testing. The initial DC (%) of discs was recorded using attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transforming infrared spectroscopy. The initial VHN of the specimens was measured using a microhardness tester under a load of 300 g for 15 seconds and the flexural strength test was carried out with a universal testing machine (crosshead speed, 0.5 mm/min). The specimens were then subjected to thermocycling in 5°C and 55°C water baths. Properties were assessed after 1,000–10,000 cycles of thermocycling. The surfaces were evaluated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance followed by the Tukey honest significant difference
post hoc test.Results Statistical analysis showed that DC tended to increase up to 4,000 cycles, with no significant changes. VHN and flexural strength values significantly decreased upon thermal cycling when compared to baseline (
p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between initial and post-thermocycling VHN results at 1,000 cycles. SEM images after aging showed deteriorative changes in the resin composite surfaces.Conclusions The Z250 microhybrid resin composite showed reduced surface microhardness and flexural strength and increased DC after thermocycling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026; 32(1): 94. CrossRef - Evaluation of surface roughness of PEEK and Laser-Sintered cobalt–chromium subjected to different polishing protocols and thermocycling (an in vitro study)
Marzia Kareem Ahmed, Aras Maruf Rauf
Oxford Open Materials Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative influence of triton and cavity conditioners on the surface characteristics and bond strength of dentin, indicating triton as a cavity conditioner
Lena Bal, Cangül Keskin, Aybüke Karaca Sakallı, Bilge Özcan
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2026; 9(1): 98. CrossRef - The Influence of Thermal and Mechanical Aging on the Flexural Properties of Conventional and 3D-Printed Materials Used in Occlusal Splints Manufacturing
Joanna Smardz, Katarzyna Kresse-Walczak, Heike Meißner, Klaus Böning, Joanna Weżgowiec, Andrzej Małysa, Mieszko Więckiewicz
Materials.2026; 19(2): 421. CrossRef - Failure mechanism analysis and machine learning-based residual strength prediction of CFRP with different ply orientations and loading types under six typical accelerated aging environments
Guofeng Qin, Chenglong Su, Peiwen Mi, Peng Huang, Qiuhan Fan, Ming Li, Wei Tan
Construction and Building Materials.2026; 516: 145630. CrossRef - Discoloration, radiopacity, and push-out bond strength of bismuth-based radiopacifiers in endodontic sealers
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Mina Shekarian, Amir Abdolmaleki, Michael Conte, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
Ömer Hatipoğlu, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Nessrin Taha, Thiyezen Abdullah Aldhelai, Daoud M. Ayyad, Ahmed A. Madfa, Benjamin Martin‐Biedma, Rafael Fernández‐Grisales, Bakhyt A. Omarova, Wen Yi Lim, Suha Alfirjani, Kacper Nijak
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 977. CrossRef - An In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Bioactive Liner's Effect on Marginal Adaptation of Class II Composite Restorations: A Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
Girija S Sajjan, Naveena Ponnada, Praveen Dalavai, Madhu Varma Kanumuri, Venkata Karteek Varma Penmatsa, B V Sindhuja
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 15(9): 749. CrossRef - Different contemporary resin cements for intracanal luting of glass fiber posts - Bonding and polymerization assessments
Anna Caroliny Detogni, Vitaliano Gomes de Araújo Neto, Caio Felipe de Almeida Nobre, Victor Pinheiro Feitosa, Mário Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 138: 103951. CrossRef - Effect of food-simulating liquids and polishing times on the color stability of microhybrid and nanohybrid resin composites
Muhammet Fidan, Nevin Çankaya
Discover Nano.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols for post space preparation on the bond of the resin luting agent and post to a hydraulic calcium silicate filled root: An in vitro study
Nuttanun Poeaim, Sirawut Hiran-us, Yanee Tantilertanant
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(4): 1039.e1. CrossRef - Influence of Different Adhesives and Surface Treatments on Shear and Tensile Bond Strength and Microleakage with Micro-CT of Repaired Bulk-Fill Composites
Handan Yıldırım-Işık, Mediha Büyükgöze-Dindar
Polymers.2025; 17(12): 1680. CrossRef - Effect of thermal ageing on physico-mechanical properties and self-healing potential of experimental 3D-printed denture base resin composites
Mariam Raza Syed, Amr Fawzy
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2025; 170: 107123. CrossRef - Effects of aging on the physicomechanical, antimicrobial, and cytotoxicity properties of flowable composite resin with strontium-modified phosphate-based glass
Seo-Hyun Kim, Hye-Bin Go, Myung-Jin Lee, Jae-Sung Kwon
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Colour Stability and Optical Properties of Provisional Crowns Fabricated With Milling, 3D Printing, and Direct Technique
Tommaso Rinaldi, Carlos Serrano Granger, Andrea Santamaría Laorden, Jaime Orejas-Perez, Pablo Gómez Cogolludo
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(6): 103932. CrossRef - EVALUATE DEGREE OF CONVERSION OF NEW BIOACTIVE ORTHODONTIC ADHESIVE WITH COLOR CHANGE & FLUORESCENCE PROPERTY
Mohammed Younis, Neam Fakhri Neam Fakhri
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 39. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity and physicochemical properties of light-curable fluoride varnishes containing strontium phosphate-based glass
Na-Yeon Kim, Mi-Sol Ryu, Ji-Min Lee, Soo-Yeon Jeong, Hye-Been Choi, Myung-Jin Lee, Song-Yi Yang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Review of Studies Comparing Microleakage After Restoration With Cention and Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement in Human Extracted Teeth
Rashmi Misra, Mansi Vandekar, Gayatri Pendse, Omkar Bhosale, Pauravi Hegde, Aashaka Vaishnav
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the radiopacity of different universal composite resins aged by thermocycling
Dilber Çölkesen, Alican Kuran, Neslihan Tekçe
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the sources and routes of micro- and nanoplastics from dental products and materials: their impact on human health - a systematic review
Vidhya Selvaraj, R. Saravanan, N. Raj Vikram, Uma revathi Gopalakrishnan, Ramsamy M
Next Research.2025; 2(4): 100925. CrossRef - Investigation of the mechanical response of MWCNTs infused carbon/glass fiber-based hybrid composites using digital image correlation
Somaiah Chowdary Mallampati, Ujendra Kumar Komal, Paladugu Rakesh, Parthapratim Barman
Construction and Building Materials.2025; 492: 143068. CrossRef - Mechanical, Surface and Physicochemical Properties of Nanozeolite‐Modified 3D Printed Hybrid Ceramics at Varying Concentrations: An In Vitro Study
Ahmed A. Holiel, Yomna M. Ibrahim, Noha Morsy
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Graphitic Carbon Nitride on Dental Composite’s Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties
Zainab Rafaqat, Saad Liaqat, Ahmed Bari, Warda Khan Yousafzai, Umar Nishan, Sandleen Feroz, Nawshad Muhammad
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Biological and Chemical Properties of Emerging 3D-Printed Dental Resin Composites Compared to Conventional Light-Cured Materials
Nikola Živković, Stefan Vulović, Miloš Lazarević, Anja Baraba, Aleksandar Jakovljević, Mina Perić, Jelena Mitrić, Aleksandra Milić Lemić
Materials.2025; 18(22): 5170. CrossRef - Awareness of possible complications associated with direct composite restorations: A multinational survey among dentists from 13 countries with meta-analysis
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Jakub Jankowski, David Donnermeyer, Paulo J. Palma, Milan Drobac, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Fatma Pertek Hatipoğlu, Indira Tulegenova, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Hamad Mohammad Alharkan, Olga Bekjanova, Sylvia Wyzga, Moataz
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 145: 105009. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of bond strength and color stability of polyetheretherketone and zirconia layered with indirect composite before and after thermocycling: An in vitro study
Pooja Singh, Subhabrata Maiti, Amrutha Shenoy
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2024; 24(3): 252. CrossRef - Biaxial flexural strength of hydrothermally aged resin-based materials
Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Mariana Miranda de Toledo Piza, Bruna de Mello Silva, Thalya Fernanda Horsth Maltarollo, Gustavo Sivieri-Araujo, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Estevam Augusto Bonfante, Henrico Badaoui Strazzi-Sahyon
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 155: 106568. CrossRef - Comparative Strength Study of Indirect Permanent Restorations: 3D-Printed, Milled, and Conventional Dental Composites
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Adelheid Veerman, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva
Clinics and Practice.2024; 14(5): 1940. CrossRef - Influencia del termociclado sobre la estabilidad del color de dos resinas compuestas
//Influence of thermocycling on the color stability of two composite resins
Verónica Lucía Ventrera, María Eugenia Alejandra Barrionuevo
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Efeito do protocolo de polimento e do armazenamento em meio úmido na variação de cor, massa e rugosidade superficial de resinas compostas
Leonardo Cruz Morais, Mateus Victória Gontijo, Gabriela Rodrigues Pires, Victor de Morais Gomes, Milton Carlos Kuga, Francisco Fernando Massola Filho, Amanda Gonçalves Franco, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2024; 16(6): e4556. CrossRef - A comparison of the mechanical properties of 3D-printed, milled, and conventional denture base resin materials
Hyeong-Ju YU, You-Jung KANG, Yeseul PARK, Hoon KIM, Jee-Hwan KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 813. CrossRef - Effect of aging and fiber‐reinforcement on color stability, translucency, and microhardness of single‐shade resin composites versus multi‐shade resin composite
Muhammet Fidan, Özhan Yağci
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(4): 632. CrossRef - Impact of Artificial Aging on the Physical and Mechanical Characteristics of Denture Base Materials Fabricated via 3D Printing
Ahmed Altarazi, Julfikar Haider, Abdulaziz Alhotan, Nick Silikas, Hugh Devlin, Weihao Yuan
International Journal of Biomaterials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis, monomer conversion, and mechanical properties of polylysine based dental composites
Saadia Bano Lone, Rabia Zeeshan, Hina Khadim, Muhammad Adnan Khan, Abdul Samad Khan, Anila Asif
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106398. CrossRef - Bond strength and surface roughness assessment of novel antimicrobial polymeric coated dental cement
Ghada Naguib, Hisham Mously, Jumana Mazhar, Ibrahim Alkanfari, Abdulelah Binmahfooz, Mohammed Zahran, Mohamed T. Hamed
Discover Nano.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness, degree of conversion, and abrasion resistance of nanoglass and multiwalled carbon nanotubes reinforced three‐dimensionally printed denture base resins
Pansai Ashraf Mohamed, Yomna Mohamed Ibrahim, Kenda Ibrahim Hisham Hanno, Mohamed Mahmoud Abdul‐Monem
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of CAD-CAM block thickness and translucency on the polymerization of luting materials
Bengü Doğu Kaya, Selinsu Öztürk, Ayşe Aslı Şenol, Erkut Kahramanoğlu, Pınar Yılmaz Atalı, Bilge Tarçın
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Simulation of oral environmental conditions through artificial aging of teeth for the assessment of enamel discoloration in orthodontics
Celal Irgın
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Do universal adhesive systems affect color coordinates and color change of single-shade resin composites compared with a multi-shade composite?
Muhammet FİDAN, Özhan YAĞCI
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 886. CrossRef - Fabrication, Evaluation, and Performance Ranking of Tri-calcium Phosphate and Silica Reinforced Dental Resin Composite Materials
Sonu Saini, Anoj Meena, Ramkumar Yadav, Amar Patnaik
Silicon.2023; 15(18): 8045. CrossRef - Can Modification with Urethane Derivatives or the Addition of an Anti-Hydrolysis Agent Influence the Hydrolytic Stability of Resin Dental Composite?
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Izabela M. Barszczewska-Rybarek, Marta W. Chrószcz-Porębska, Karolina Kopacz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Kinga Bociong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4336. CrossRef - Effect of veneering material type and thickness ratio on flexural strength of bi-layered PEEK restorations before and after thermal cycling
Ahmed Gouda, Ashraf Sherif, Mennatallah Wahba, Tarek Morsi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2629. CrossRef - 3D printed denture base material: The effect of incorporating TiO2 nanoparticles and artificial ageing on the physical and mechanical properties
Ahmed Altarazi, Julfikar Haider, Abdulaziz Alhotan, Nick Silikas, Hugh Devlin
Dental Materials.2023; 39(12): 1122. CrossRef - Influence of silane coupling agent and aging on the repair bond strength of dental composites
Gustavo Jusué-Esparza, José Alejandro Rivera-Gonzaga, Guillermo Grazioli, Ana Josefina Monjarás-Ávila, J. Eliezer Zamarripa-Calderón, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(5): 913. CrossRef - Degree of conversion of light‐polymerized composite resin in implant prosthesis screw access opening
Se‐Hyun Park, Yoon‐Hyuk Huh, Chan‐Jin Park, Lee‐Ra Cho, Kyung‐Ho Ko
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(9): 829. CrossRef - Investigation of the effect of matrix-interface formed with silane-based coupling agents on physico-chemical behavior and flow distance of dental composites
Zerin Yeşil Acar, Merve Tunç Koçyiğit, Meltem Asiltürk
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2023; 378: 121600. CrossRef - Evaluation of Water Sorption and Solubility of 3D-Printed, CAD/CAM Milled, and PMMA Denture Base Materials Subjected to Artificial Aging
Mariya Dimitrova, Angelina Vlahova, Ilian Hristov, Rada Kazakova, Bozhana Chuchulska, Stoyan Kazakov, Marta Forte, Vanja Granberg, Giuseppe Barile, Saverio Capodiferro, Massimo Corsalini
Journal of Composites Science.2023; 7(8): 339. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on internal microhardness of high and low viscosity bulk fill composite resins in class I cavities
Sâmara Luciana de Andrade LIMA, Lais Lemos CABRAL, Natália Russo CARLOS, Saulo André de Andrade LIMA, Kamila Rosamilia KANTOVITZ, Flávia Lucisano Botelho do AMARAL
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of an Acidic Environment on the Strength and Chemical Changes of Resin-based Composites
S Kang, B-H Cho
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(4): E81. CrossRef - Influence of compressive forces and aging through thermocycling on the strength of mono incremental dental composite resins
Cristian Roberto Sigcho Romero, Henry Fabricio Mejía Mosquera, Sandra Marcela Quisiguiña Guevara, Yudy Jacqueline Alvarado Aguayo
Bionatura.2023; 8(4): 1. CrossRef - Push-out Bond Strength of Two Fiber Posts in Composite Resin Using Different Types of Silanization
RM Novis, BLT Leon, FMG França, CP Turssi, RT Basting, FLB Amaral
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(2): 173. CrossRef - Penetration and Adaptation of the Highly Viscous Zinc-Reinforced Glass Ionomer Cement on Contaminated Fissures: An In Vitro Study with SEM Analysis
Galiah AlJefri, Sunil Kotha, Muhannad Murad, Reham Aljudaibi, Fatmah Almotawah, Sreekanth Mallineni
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 6291. CrossRef - Surface Characteristics and Color Stability of Dental PEEK Related to Water Saturation and Thermal Cycling
Liliana Porojan, Flavia Roxana Toma, Mihaela Ionela Bîrdeanu, Roxana Diana Vasiliu, Ion-Dragoș Uțu, Anamaria Matichescu
Polymers.2022; 14(11): 2144. CrossRef - Effects of aging and light-curing unit type on the volume and internal porosity of bulk-fill resin composite restoration
Afnan O. Al-Zain, Elaf A. Alboloshi, Walaa A. Amir, Maryam A. Alghilan, Eliseu A. Münchow
The Saudi Dental Journal.2022; 34(3): 243. CrossRef - An Evaluation of the Hydrolytic Stability of Selected Experimental Dental Matrices and Composites
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Karolina Kopacz, Malgorzata Iwona Szynkowska-Jozwik, Jerzy Sokolowski, Kinga Bociong
Materials.2022; 15(14): 5055. CrossRef - Comparison of the Mechanical Properties and Push-out Bond Strength of Self-adhesive and Conventional Resin Cements on Fiber Post Cementation
MR Santi, RBE Lins, BO Sahadi, JR Soto-Montero, LRM Martins
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 346. CrossRef - Effect of Different Polymerization Times on Color Change, Translucency Parameter, and Surface Hardness of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites
HY Gonder, M Fidan
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(10): 1751. CrossRef - Surface degradation and biofilm formation on hybrid and nanohybrid composites after immersion in different liquids
Gabriela Escamilla-Gómez, Octavio Sánchez-Vargas, Diana M. Escobar-García, Amaury Pozos-Guillén, Norma V. Zavala-Alonso, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, José E. Pérez-López, Gregorio Sánchez-Balderas, Gabriel F. Romo-Ramírez, Marine Ortiz-Magdaleno
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(4): 263. CrossRef - Effects of Different Adhesive Systems and Orthodontic Bracket Material on Enamel Surface Discoloration: An In Vitro Study
Ali Alqerban, Doaa R. M. Ahmed, Ali S. Aljhani, Dalal Almadhi, Amjad AlShahrani, Hussah AlAdwene, Abdulaziz Samran
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(24): 12885. CrossRef - Effects of Immediate Coating on Unset Composite with Different Bonding Agents to Surface Hardness
Nantawan Krajangta, Supissara Ninbanjong, Sunisa Khosook, Kanjana Chaitontuak, Awiruth Klaisiri
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(04): 828. CrossRef - Rational durability of optical properties of chameleon effect of Omnichroma and Essentia composite thermocycled in black dark drinks (in vitro study)
Bassma Abdelhamed, Asmaa Abdel-Hakeem Metwally, Heba A. Shalaby
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Nanohybrid Composite Restoration After the Placement of Flowable Compomer and Composite Using the Snowplow Technique
Meghna Dugar, Anuja Ikhar, Pradnya Nikhade, Manoj Chandak, Nidhi Motwani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The First Step in Standardizing an Artificial Aging Protocol for Dental Composites—Evaluation of Basic Protocols
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Magdalena Fronczek, Katarzyna Ranoszek-Soliwoda, Jarosław Grobelny, Jerzy Sokolowski, Kinga Bociong
Molecules.2022; 27(11): 3511. CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Long‐Term Repair Bond Strength of Aged Methacrylate‐Based Resin Composite Restorations: A Systematic Review and Network Meta‐analysis
Mahdi Hadilou, Amirmohammad Dolatabadi, Morteza Ghojazadeh, Hossein Hosseinifard, Parnian Alizadeh Oskuee, Fatemeh Pournaghi Azar, Victor Feitosa
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Edge chipping resistance of veneering composite resins
Parissa Nassary Zadeh, Bogna Stawarczyk, Rüdiger Hampe, Anja Liebermann, Felicitas Mayinger
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2021; 116: 104349. CrossRef - The effect of radiation exposure and storage time on the degree of conversion and flexural strength of different resin composites
Ragia M. Taher, Lamiaa M. Moharam, Amin E. Amin, Mohamed H. Zaazou, Farid S. El-Askary, Mokhtar N. Ibrahim
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Load of CAD/CAM Fabricated Cantilever Implant-Supported Zirconia Framework: An In Vitro Study
Ibraheem F. Alshiddi, Syed Rashid Habib, Muhammad Sohail Zafar, Salwa Bajunaid, Nawaf Labban, Mohammed Alsarhan
Molecules.2021; 26(8): 2259. CrossRef - A numerical, theoretical and experimental study of the effect of thermocycling on the matrix-filler interface of dental restorative materials
Yoan Boussès, Nathalie Brulat-Bouchard, Pierre-Olivier Bouchard, Yannick Tillier
Dental Materials.2021; 37(5): 772. CrossRef - Impact of polymerization and storage on the degree of conversion and mechanical properties of veneering resin composites
Felicitas MAYINGER, Marcel REYMUS, Anja LIEBERMANN, Marc RICHTER, Patrick KUBRYK, Henning GROẞEKAPPENBERG, Bogna STAWARCZYK
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(2): 487. CrossRef - Intrapulpal Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide of Teeth Restored With Bulk Fill and Conventional Bioactive Composites
DP Silva, BA Resende, M Kury, CB André, CPM Tabchoury, M Giannini, V Cavalli
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): E158. CrossRef - Silane content influences physicochemical properties in nanostructured model composites
Larissa Maria Cavalcante, Lucielle Guimarães Ferraz, Karinne Bueno Antunes, Isadora Martini Garcia, Luis Felipe Jochims Schneider, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Dental Materials.2021; 37(2): e85. CrossRef - AĞIZ GARGARALARI VE ANTİSEPTİKLERİNİN FARKLI KOMPOZİT REZİNLERİN RENK STABİLİTESİNE ETKİSİ
Turan Emre KUZU, Özcan KARATAŞ
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Immediate and Delayed Microleakage of Class V Cavities Restored with Chitosan-incorporated Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study
Roopa R Nadig, Veena Pai, Arpita Deb
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(5): 621. CrossRef - Influence of Diode Laser for the Treatment of Dentin Hypersensitivity on Microleakage of Cervical Restorations
Doaa R. M. Ahmed, Diana G. Shaath, Jomana B. Alakeel, Abdulaziz A. Samran, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Ageing of Dental Composites Based on Methacrylate Resins—A Critical Review of the Causes and Method of Assessment
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Jerzy Sokolowski, Joanna Kleczewska, Kinga Bociong
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 882. CrossRef - Flexural strength and surface microhardness of materials used for temporary dental disocclusion submitted to thermal cycling: An in vitro study
Tamires Borges de Lima, José Guilherme Neves, Ana Paula Terossi de Godoi, Ana Rosa Costa, Viviane Veroni Degan, Américo Bortolazzo Correr, Heloisa Cristina Valdrighi
International Orthodontics.2020; 18(3): 519. CrossRef - Evaluation of the repair capacities and color stabilities of a resin nanoceramic and hybrid CAD/CAM blocks
Hasibe Sevilay Bahadır, Yusuf Bayraktar
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments of Resin Relined Fiber Posts Cemented With Self-adhesive Resin Cement on Push-out and Microtensile Bond Strength Tests
RV Machry, PE Fontana, TC Bohrer, LF Valandro, OB Kaizer
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(4): E185. CrossRef - Influences of Successive Exposure to Bleaching and Fluoride Preparations on the Surface Hardness and Roughness of the Aged Resin Composite Restoratives
Khalid M. Abdelaziz, Shugufta Mir, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Suheel M. Baba, Saud S. Alshahrani, Eman A. Alshahrani, Zahra A. Alsafi
Medicina.2020; 56(9): 476. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Lithıum Disilicate, Indirect Resin Composite and Zirconıa by Using Dual Cure Resin Cements
Mohammed BADWAN, Erkut KAHRAMANOĞLU
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2020; 10(4): 435. CrossRef - Effect of Stress-decreasing Resin Thickness as an Intermediate Layer on Fracture Resistance of Class II Composite Restoration: An In Vitro Study
Dennis Dennis, Arwin Leonardy, Trimurni Abidin
World Journal of Dentistry.2020; 11(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of Thermocycling on Biaxial Flexural Strength of CAD/CAM, Bulk Fill, and Conventional Resin Composite Materials
EB Benalcázar Jalkh, CM Machado, M Gianinni, I Beltramini, MMT Piza, PG Coelho, R Hirata, EA Bonfante
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(5): E254. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of hybrid computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials after aging treatments
Hae-Yong Jeong, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Yu-Sung Choi
Ceramics International.2018; 44(16): 19217. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 6,897 View
- 59 Download
- 83 Crossref

- Comparison of light-transmittance in dental tissues and dental composite restorations using incremental layering build-up with varying enamel resin layer thickness
- Rodrigo Rocha Maia, Dayane Oliveira, Tracy D'Antonio, Fang Qian, Frederick Skiff
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e22. Published online April 16, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e22

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate and compare light-transmittance in dental tissues and dental composite restorations using the incremental double-layer technique with varying layer thickness.
Materials and Methods B1-colored natural teeth slabs were compared to dental restoration build-ups with A2D and B1E-colored nanofilled, supra-nanofilled, microfilled, and microhybrid composites. The enamel layer varied from 0.3, 0.5, or 1.2 mm thick, and the dentin layer was varied to provide a standardized 3.7 mm overall sample thickness (
n = 10). All increments were light-cured to 16 J/cm2 with a multi-wave LED (Valo, Ultradent). Using a spectrophotometer, the samples were irradiated by an RGB laser beam. A voltmeter recorded the light output signal to calculate the light-transmittance through the specimens. The data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance followed by thepost hoc Tukey's test (p = 0.05).Results Mean light-transmittance observed at thicker final layers of enamel were significantly lower than those observed at thinner final layers. Within 1.2 mm final enamel resin layer (FERL) thickness, all composites were similar to the dental tissues, with exception of the nanofilled composite. However, within 0.5 mm FERL thickness, only the supra-nanofilled composite showed no difference from the dental tissues. Within 0.3 mm FERL thickness, none of the composites were similar to the dental tissues.
Conclusions The supra-nanofilled composite had the most similar light-transmittance pattern when compared to the natural teeth. However, for other composites, thicker FERL have a greater chance to match the light-transmittance of natural dental tissues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of water absorption on the translucency of single-shade and conventional resin composites: an in vitro comparative study
Ceyda Sari, Elifnur Aydemir Aydın
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - 3-year randomized clinical trial to evaluate the performance of posterior composite restorations lined with ion-releasing materials
Basma Ahmed, Ramy Ahmed Wafaie, Hamdi H. Hamama, Salah Hasab Mahmoud
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation on the Biaxial Flexural Strength of Universal Shade Resin-Based Composites
Keiko Sakuma, Taku Horie, Takafumi Kishimoto, Mayumi Maesako, Shigetaka Tomoda, Morioki Fujitani, Akimasa Tsujimoto
Polymers.2024; 16(13): 1853. CrossRef - Fabrication of color-graded feldspathic dental prosthetics for aesthetic and restorative dentistry
Imam Akbar Sutejo, Jeehwan Kim, Sinuo Zhang, Chang Woo Gal, Yeong-Jin Choi, Honghyun Park, Hui-suk Yun
Dental Materials.2023; 39(6): 568. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric evaluation of restorative composite shades and their match with a classical shade guide
Rafael Melara, Luciana Mendonça, Fábio Herrmann Coelho-de-Souza, Juliana Nunes Rolla, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro wear of dual‐cured bulkfill composites and flowable bulkfill composites
Jean‐François Roulet, Snigdha Gummadi, Hind S. Hussein, Nader Abdulhameed, Chiayi Shen
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2020; 32(5): 512. CrossRef
- Impact of water absorption on the translucency of single-shade and conventional resin composites: an in vitro comparative study
- 1,677 View
- 15 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Management of dental erosion induced by gastro-esophageal reflux disorder with direct composite veneering aided by a flexible splint matrix
- Sherin Jose Chockattu, Byathnal Suryakant Deepak, Anubhav Sood, Nandini T. Niranjan, Arun Jayasheel, Mallikarjun K. Goud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e13. Published online February 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e13
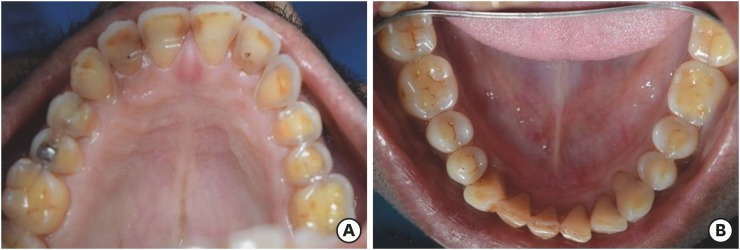
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental erosion is frequently overlooked in clinical practice. The management of erosion-induced damage to the dentition is often delayed, such that extensive occlusal rehabilitation is required. These cases can be diagnosed by a careful clinical examination and a thorough review of the patient's medical history and/or lifestyle habits. This case report presents the diagnosis, categorization, and management of a case of gastro-esophageal reflux disease-induced palatal erosion of the maxillary teeth. The early management of such cases is of utmost importance to delay or prevent the progression of damage both to the dentition and to occlusal stability. Non-invasive adhesively bonded restorations aid in achieving this goal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Acidic Media on Surface Topography and Color Stability of Two Different Glass Ceramics
Fatma Makkeyah, Nesrine A. Elsahn, Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mahmoud Al Ankily
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 173. CrossRef - Mechanical Performance and Surface Roughness of Lithium Disilicate and Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramics Before and After Exposure to Acidic Challenge
Ahmed Elsherbini, Salma M. Fathy, Walid Al-Zordk, Mutlu Özcan, Amal A. Sakrana
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 117. CrossRef - Biomechanical reinforcement by CAD-CAM materials affects stress distributions of posterior composite bridges: 3D finite element analysis.
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Islam M. Abdelraheem, David C. Watts, Sandipan Roy, Vamsi Krishna Dommeti, Abdulrahman Alshabib, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Rania R. Afifi
Dental Materials.2024; 40(5): 869. CrossRef - Surface Properties and Wear Resistance of Injectable and Computer-Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufacturing–Milled Resin Composite Thin Occlusal Veneers
Nesrine A. Elsahn, Hatem M. El-Damanhoury, Zainab Shirazi, Abdul Rahman M. Saleh
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(03): 663. CrossRef - Effect of acidic media on flexural strength and fatigue of CAD-CAM dental materials
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Rania. R Afifi, Rasha A. Alamoush, Islam Abdel Raheem, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 57. CrossRef - Three-year Follow-up of Conservative Direct Composite Veneers on Eroded Teeth
RQ Ramos, NF Coelho, GC Lopes
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(2): 131. CrossRef - The effects of intrinsic and extrinsic acids on nanofilled and bulk fill resin composites: Roughness, surface hardness, and scanning electron microscopy analysis
Milena F. Alencar, Mirella T. Pereira, Maria D. R. De‐Moraes, Sérgio L. Santiago, Vanara F. Passos
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(2): 202. CrossRef
- Effect of Acidic Media on Surface Topography and Color Stability of Two Different Glass Ceramics
- 2,287 View
- 20 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of water storage on flexural strength of silorane and methacrylate-based composite resins
- Narges Panahandeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Hani Naderi, Seyedeh Mahsa Sheikh-Al-Eslamian
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):309-315. Published online November 6, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study assessed the effect of water storage on the flexural strength (FS) of low shrinkage composites.
Materials and Methods A total of 165 bar-shaped specimens (2 × 2 × 25 mm) were fabricated of 2 low shrinkage composites (Filtek P90 [3M ESPE], GC Kalore [GC International]) and a conventional methacrylate-based composite (Filtek Z250 [3M ESPE]). The specimens were subjected to 3-point bending test at 6 time intervals, namely: immediately after curing, at 24 hours, 1 week, 1 month, 6 months, and 1 year following storage in wet and dry conditions. The FS of the specimens were measured by applying compressive load at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. Data was analyzed using 3-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test.
Results Three-way ANOVA revealed significant interactions between time, type of composite, and storage condition (
p = 0.001). Tukey's multiple comparison test revealed significant reductions in FS of all composites after 6 months and 1 year of storage in distilled water compared to dry condition.Conclusions Filtek P90 showed the highest and GC Kalore showed the lowest FS after 1 year storage in distilled water. The immediate high strength of Filtek Z250 significantly decreased at 1 year and its final value was lower than that of Filtek P90.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Graphene–Catechol Dental Sealant: Antibacterial and Mechanical Evaluation
Renata Pereira, Flávio H. B. Aguiar, Rodrigo B. E. Lins, Maria C. A. J. Mainairdi, Bruna G. Silva, Marcela A. Ferretti, Klaus Rischka
Advanced Engineering Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Bio-Aging on Mechanical Properties and Microbial Behavior of Different Resin Composites
Yuke Shou, Lanzhi Deng, Xiaoyu Huang, Xinyu Peng, Xinxuan Zhou, Zheng Wang, Yannan Huang, Bina Yang, Haohao Wang, Min Zhang, Lei Cheng
Biomolecules.2023; 13(7): 1125. CrossRef - Changes in color and contrast ratio of resin composites after curing and storage in water
Marlus da Silva Pedrosa, Fernando Neves Nogueira, Vitor de Oliveira Baldo, Igor Studart Medeiros
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(8): 1160. CrossRef - Ageing of Dental Composites Based on Methacrylate Resins—A Critical Review of the Causes and Method of Assessment
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Jerzy Sokolowski, Joanna Kleczewska, Kinga Bociong
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 882. CrossRef - Color stability of nanohybrid composite resins in drinks
Juliana Jendiroba Faraoni, Isabela Barbosa Quero, Lívia Semedo Schiavuzzo, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 18: e191601. CrossRef - Mechanical Degradation of Different Classes of Composite Resins Aged in Water, Air, and Oil
Weber Adad Ricci, Priscila Alfano, Saulo Pamato, Carlos Alberto dos Santos Cruz, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Effects of water and microbial-based aging on the performance of three dental restorative materials
Xinxuan Zhou, Suping Wang, Xian Peng, Yao Hu, Biao Ren, Mingyun Li, Liying Hao, Mingye Feng, Lei Cheng, Xuedong Zhou
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2018; 80: 42. CrossRef
- Graphene–Catechol Dental Sealant: Antibacterial and Mechanical Evaluation
- 1,651 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Survival rates against fracture of endodontically treated posterior teeth restored with full-coverage crowns or resin composite restorations: a systematic review
- Warattama Suksaphar, Danuchit Banomyong, Titalee Jirathanyanatt, Yaowaluk Ngoenwiwatkul
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):157-167. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This systematic review aims to summarize the current clinical studies that investigated survival rates against fracture of endodontically treated posterior teeth restored with crowns or resin composite restorations. Literature search were performed using keywords. Publications from 1980 to 2016 were searched in PubMed, ScienceDirect, Web of Science, MEDLINE, and SCOPUS. Included studies were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Three clinical studies were included: 1 randomized controlled trial and 1 prospective and 1 retrospective cohort studies. Pooled survival rates ranged from 94%–100% and 91.9%–100% for crowns and resin composite, respectively. The majority of teeth had no more than 3 surface loss of tooth structure. The studies included were heterogeneous, and were not appropriate for further meta-analysis. Current evidence suggested that the survival rates against the fracture of endodontically treated posterior teeth restored with crowns or resin composites were not significantly different in the teeth with minimum to moderate loss of tooth structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Outcomes and Complication Rates of Crown Restorations with Various Endodontic Posts: A Retrospective Analysis
Ali Alenezi, Hanin Alsalhi
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 84. CrossRef - Effect of using different materials and restorative techniques on cuspal deflection and microleakage in endodontically treated teeth
Ceyda Sari, Oya Bala, Sinem Akgul, Cemile Kedici Alp
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct restorations versus full crowns in endodontically treated molar teeth: A three-year randomized clinical trial
Motasum Abu-Awwad, Ruba Halasa, Laila Haikal, Ahmad El-Ma'aita, Mohammad Hammad, Haralampos Petridis
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105699. CrossRef - Is the use of an intraradicular post essential for reducing failures in restoring endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jacqueline Salomão Jardim, Vinicius de Menezes Félix Ferreira, Hiskell Francine Fernandes e Oliveira, Daniele Sorgatto Faé, Cleidiel Aparecido Araujo Lemos
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 159: 105739. CrossRef - Systematic Reviews Comparing Direct and Indirect Restorations: An Umbrella Review That Examines Restoration Type and Confidence in Results
Mona Kimmel, Clovis Mariano Faggion
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, Awareness, and Perceptions on Root Canal Treatment among Patients Reporting with Dental Pain to Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics Department: An Institution-based Survey
Abdu Semeer Palottil, Moopil Midhun Mohanan, N. T. Nishad, S. Jayasree
Journal of Primary Care Dentistry and Oral Health.2025; 6(2): 99. CrossRef - One-year clinical performance of restorations with and without a bulk-fill flowable base in endodontically treated premolars: a pilot randomized controlled trial
Brenda Leyton, Jullyana Dezanetti, Rodrigo Rached, Sérgio Ignácio, Evelise Souza
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - One-piece endodontic crown fixed partial denture: Is it possible?
João Paulo M. Tribst, Amanda Maria de O. Dal Piva, Joris Muris, Cornelis J. Kleverlaan, Albert J. Feilzer
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(6): 1118. CrossRef - Survival Rate Against Fracture of Endodontically Treated Premolars Restored with Crowns and Resin Composites: A Retrospective Study
Enas Khamakhim, Farida Alsayeh
AlQalam Journal of Medical and Applied Sciences.2024; : 398. CrossRef - Knowledge and Awareness of Root Canal Treatment among Patients in Tripoli: A Survey-Based Study
Sumaya Aghila
AlQalam Journal of Medical and Applied Sciences.2024; : 532. CrossRef - Clinical performance of polyethylenefiber reinforced resin composite restorations in endodontically treated teeth: (a randomized controlled clinical trial)
Ahmed Abdelsattar Metwaly, Amira Farid Elzoghby, Rawda Hesham Abd ElAziz
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct Versus Indirect Treatment Options of Endodontically Treated Posterior Teeth: A Narrative Review
Mai M Alhamdan, Rodina F Aljamaan, Munira M Abuthnain, Shahd A Alsumikhi, Ghada S Alqahtani, Reem A Alkharaiyef
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Single crown vs. composite for glass fiber post-retained restorations: An 8-year randomized clinical trial
Victório Poletto-Neto, Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Wietske Fokkinga, Cees Kreulen, Bas Loomans, Maximiliano Sérgio Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 142: 104837. CrossRef - Factors influencing the clinical performance of the restoration of endodontically treated teeth: An assessment of systematic reviews of clinical studies
Lara Dotto, Luiza Paloma S. Girotto, Yara Teresinha Correa Silva Sousa, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Ataís Bacchi, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(6): 1043. CrossRef - Influence of technical quality and coronal restoration on periapical health of root canal treatment performed by Malaysian undergraduate students
Norazlina Mohammad, Faizah Abdul Fatah, Azlan Jaafar, Siti Hajar Omar, Aimi Amalina Ahmad, Abdul Azim Asy Abdul Aziz, Aws Hashim Ali Al-Kadhim
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(1): 63. CrossRef - The success rate of indirect adhesive restorations in the distal dentition fabricated with chairside CAD/CAM system
Marek Šupler, Andrej Jenča, Michal Straka, Juraj Deglovič, Janka Jenčová
Stomatológ.2023; 33(2): 10. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Marginal Fit of Endocrowns Fabricated From Three Different Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) Ceramic Materials: An In Vitro Study
Esraa Attar, Shatha Alshali, Tariq Abuhaimed
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of titanium mesh and fibers in reinforcing endodontically treated molars: An in vitro study
Hemalatha Hiremath, Devansh Verma, Sheetal Khandelwal, AishwaryaSingh Solanki, Sonam Patidar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(2): 189. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment, ferrule height, and luting agent type on pull-out bond strength of monolithic zirconia endocrowns
Emine B. Buyukerkmen, Durmuş A. Bozkurt, Arslan Terlemez
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(4): 279. CrossRef - An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta‐Analyses Evaluating the Success Rate of Prosthetic Restorations on Endodontically Treated Teeth
Amirhossein Fathi, Behnaz Ebadian, Sara Nasrollahi Dezaki, Nahal Mardasi, Ramin Mosharraf, Sabire Isler, Shiva Sadat Tabatabaei, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - Fracture strength of non-invasively reinforced MOD cavities on endodontically treated teeth
René Daher, Stefano Ardu, Enrico Di Bella, Giovanni T. Rocca, Albert J. Feilzer, Ivo Krejci
Odontology.2021; 109(2): 368. CrossRef - Retrospective study of fracture survival in endodontically treated molars: the effect of single-unit crowns versus direct-resin composite restorations
Kanet Chotvorrarak, Warattama Suksaphar, Danuchit Banomyong
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An insight into patient's perceptions regarding root canal treatment: A questionnaire-based survey
Ramta Bansal, Aditya Jain
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(2): 1020. CrossRef - Endodontically treated posterior teeth restored with or without crown restorations: A 5‐year retrospective study of survival rates from fracture
Titalee Jirathanyanatt, Warattama Suksaphar, Danuchit Banomyong, Yaowaluk Ngoenwiwatkul
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance, gap and void formation in root‐filled mandibular molars restored with bulk‐fill resin composites and glass‐ionomer cement base
Nathamon Thongbai‐on, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Danuchit Banomyong, Michael F. Burrow, Sittichoke Osiri, Nattha Pattaravisitsate
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Current options concerning the endodontically-treated teeth restoration with the adhesive approach
Marco Aurélio de Carvalho, Priscilla Cardoso Lazari, Marco Gresnigt, Altair Antoninha Del Bel Cury, Pascal Magne
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Outcomes and Complication Rates of Crown Restorations with Various Endodontic Posts: A Retrospective Analysis
- 5,761 View
- 68 Download
- 27 Crossref

-
In vitro study ofStreptococcus mutans adhesion on composite resin coated with three surface sealants - Da Hye Kim, Tae-Yub Kwon
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):39-47. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.39

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Although the coating of surface sealants to dental composite resin may potentially reduce bacterial adhesion, there seems to be little information regarding this issue. This preliminary
in vitro study investigated the adhesion ofStreptococcus mutans (S. mutans ) on the dental composite resins coated with three commercial surface sealants.Materials and Methods Composite resin (Filtek Z250) discs (8 mm in diameter, 1 mm in thickness) were fabricated in a mold covered with a Mylar strip (control). In group PoGo, the surfaces were polished with PoGo. In groups PS, OG, and FP, the surfaces polished with PoGo were coated with the corresponding surface sealants (PermaSeal, PS; OptiGuard, OG; Fortify Plus, FP). The surfaces of the materials and
S. mutans cells were characterized by various methods.S. mutans adhesion to the surfaces was quantitatively evaluated using flow cytometry (n = 9).Results Group OG achieved the lowest water contact angle among all groups tested (
p < 0.001). The cell surface ofS. mutans tested showed hydrophobic characteristics. Group PoGo exhibited the greatest bacterial adhesion among all groups tested (p < 0.001). The sealant-coated groups showed statistically similar (groups PS and FP,p > 0.05) or significantly lower (group OG,p < 0.001) bacterial adhesion when compared with the control group.Conclusions The application of the surface sealants significantly reduced
S. mutans adhesion to the composite resin polished with the PoGo.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Magnesium oxide nanoparticles-modified 3D-printed denture tooth resin: Interfacial antibiofilm activity against Streptococcus mutans biofilms and material performance in vitro
Qi Xue, Wenshun Wang, Chongyi Wang, Ximei Xiao, Yongliang Wang, Meiwen Cao, Jing Fu
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects.2026; 732: 139162. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus spp. Colonization on Stainless Steel versus Zirconia Crowns in Root Canal-Treated Teeth
Bahni S Pathak, Alpana Talukdar, Indrani Barman, Shivansh Aggrohiya , Upasana Barman , Samar Khan, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative assessment of clinical performance and Streptococcus mutans adherence in primary molars restored with Bioflx and Zirconia crowns: A split-mouth pilot study
Apoorva Goswami, Hemalatha Ramkumar, Shankar Paulindraraj, Trophimus Gnanabagyan Jayakaran, Kalpana Hari Krishnan, Aroonika Bedre
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2025; 43(4): 575. CrossRef - Polychromatic Composite and Resin Infiltration Restorations in the Esthetic Zone: A Five-year Clinical Report
K Karimi, NG Fischer, CA Jurado, J Villalobos-Tinoco, A Tsujimoto
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(3): 245. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Zirconia Nanoparticles on Polyethyl Methacrylate Resin for Provisional Crowns
Hee-Seon Kim, Woohyung Jang, Yeong-Gwan Im, Hyun-Pil Lim
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2022; Volume 17: 6551. CrossRef - Do the differences in organic contents of composite resins affect surface roughness and Streptococcus mutans adhesion?
Duygu Hisarbeyli, Nazmiye Dönmez, Nursen Topçuoğlu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2022; 36(9): 921. CrossRef - The Effect of Liquid Rubber Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Ability to Inhibit Biofilm Formation of Dental Composites
Krzysztof Pałka, Małgorzata Miazga-Karska, Joanna Pawłat, Joanna Kleczewska, Agata Przekora
Materials.2021; 14(7): 1704. CrossRef - PLGA nanoparticles loaded with quaternary ammonium silane and riboflavin for potential applications in adhesive dentistry
Umer Daood, Meera Priyadarshini Balasankar, Marrwa A. Ibrahim, Mallikarjuna Rao Pichika, Kit-Kay Mak, Amr S. Fawzy
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2021; 105: 102797. CrossRef - Effect of Washing Condition on the Fracture Strength, and the Degree of Conversion of 3D Printing Resin
Woohyung Jang, Gyeong-Soo Kook, Jin-Ho Kang, Yeseul Kim, Yina Yun, Seon-Ki Lee, Sang-Won Park, Hyun-Pil Lim, Kwi-Dug Yun, Chan Park
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11676. CrossRef - Effect of surface sealant on surface roughness and bacterial adhesion of bulk-fill composites
Gunce Ozan, Meltem Mert Eren, Cansu Vatansever, Ugur Erdemir
Polymers and Polymer Composites.2021; 29(9_suppl): S475. CrossRef - Evaluation of adhesion of Streptococcus mutans, plaque accumulation on zirconia and stainless steel crowns, and surrounding gingival inflammation in primary molars: randomized controlled trial
Mebin George Mathew, S. R. Samuel, Ashu Jagdish Soni, Korishettar Basavaraj Roopa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(9): 3275. CrossRef - Influence of resin-coating agents on the roughness and color of composite resins
Fabio A.P. Rizzante, Juliana S.F. Bombonatti, Layla Vasconcelos, Thiago S. Porto, Sorin Teich, Rafael F.L. Mondelli
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 122(3): 332.e1. CrossRef - ANALYSIS OF THE CLINICAL EFFICIENCY OF RESTORATIVE FILLING MATERIALS
Valentina I. Kolodkina
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2019; 26(2): 64. CrossRef - Inhibitory effect of Bacillus velezensis on biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans
Yesol Yoo, Dong-Ho Seo, Hyunjin Lee, Eui-Sang Cho, Nho-Eul Song, Tea Gyu Nam, Young-Do Nam, Myung-Ji Seo
Journal of Biotechnology.2019; 298: 57. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the DHMAI monomer in the development of an antibacterial dental composite
Fatima Zohra Cherchali, Mohamed Mouzali, Jean Bernard Tommasino, Dominique Decoret, Nina Attik, Hazem Aboulleil, Dominique Seux, Brigitte Grosgogeat
Dental Materials.2017; 33(12): 1381. CrossRef
- Magnesium oxide nanoparticles-modified 3D-printed denture tooth resin: Interfacial antibiofilm activity against Streptococcus mutans biofilms and material performance in vitro
- 2,135 View
- 10 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effect of 38% carbamide peroxide on the microleakage of silorane-based versus methacrylate-based composite restorations
- Sedighe Sadat Hashemi Kamangar, Maryam Ghavam, Nazanin Mahinfar, Seyed Jalal Pourhashemi
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):172-179. Published online May 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the effect of 38% carbamide peroxide on the microleakage of class V cavities restored with either a silorane-based composite or two methacrylate-based composites.
Materials and Methods A total of 96 class V cavities were prepared on the buccal surface of extracted human teeth with both enamel and dentin margins and were randomly assigned into three groups of Filtek P90 (3M-ESPE) + P90 system adhesive (3M-ESPE)(group A), Filtek Z250 (3M-ESPE) + Adper Prompt L-Pop (3M-ESPE)(group B) and Filtek Z350XT (3M-ESPE) + Adper Prompt L-Pop (group C). Half of the teeth were randomly underwent bleaching (38% carbamide peroxide, Day White, Discus Dental, applying for 15 min, twice a day for 14 day) while the remaining half (control) were not bleached. Dye penetration was measured following immersion in basic fuchsine. Data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests at a level of 0.05.
Results No significant differences were found between composites in the control groups in enamel (
p = 0.171) or dentin (p = 0.094) margins. After bleaching, microleakage of Z250 (in enamel [p = 0.867] or dentin [p = 0.590] margins) and Z350 (in enamel [p = 0.445] or dentin [p = 0.591] margins) did not change significantly, but the microleakage of P90 significantly increased in both enamel (p = 0.042) and dentin (p = 0.002) margins.Conclusions No significant differences were noted between the bleached and control subgroups of two methacrylate-based composites in enamel or dentin margins. Microleakage of silorane-based composite significantly increased after bleaching.
- 1,141 View
- 3 Download

- Bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to composite submitted to different surface pretreatments
- Victor Hugo dos Santos, Sandro Griza, Rafael Ratto de Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):12-16. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Extensively destroyed teeth are commonly restored with composite resin before cavity preparation for indirect restorations. The longevity of the restoration can be related to the proper bonding of the resin cement to the composite. This study aimed to evaluate the microshear bond strength of two self-adhesive resin cements to composite resin.
Materials and Methods Composite discs were subject to one of six different surface pretreatments: none (control), 35% phosphoric acid etching for 30 seconds (PA), application of silane (silane), PA + silane, PA + adhesive, or PA + silane + adhesive (
n = 6). A silicone mold containing a cylindrical orifice (1 mm2 diameter) was placed over the composite resin. RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE) or BisCem (Bisco Inc.) self-adhesive resin cement was inserted into the orifices and light-cured. Self-adhesive cement cylinders were submitted to shear loading. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's test (p < 0.05).Results Independent of the cement used, the PA + Silane + Adhesive group showed higher microshear bond strength than those of the PA and PA + Silane groups. There was no difference among the other treatments. Unicem presented higher bond strength than BisCem for all experimental conditions.
Conclusions Pretreatments of the composite resin surface might have an effect on the bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to this substrate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
Yugandhar Garlapati, Sampath Krishna Veni, Jashva Vamsi Kogila, Polisetty Siva Krishna, K. N. Anand Kumar
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2025; 59(3): 279. CrossRef - Effect of Cement Type on Marginal Microleakage of Zirconia Crowns with or without Cervical Margin Relocation: An In Vitro Study
RI Farah
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(2): 194. CrossRef - Challenges faced when masking a single discoloured tooth - Part 2: indirect restoration procedures
May Aljanahi, Argwan Alhussin, Haitham Elbishari
British Dental Journal.2025; 239(1): 25. CrossRef - Influence of mechanochemical treatment and oxygen inhibited layer on the adhesion of self-adhesive resin cement to bulk-fill composite resin
Sreya Dutta, Samikhya Priyadarsani Sahu, Anushka Arora, Srikant Natarajan, Abhishek Parolia, Manuel Thomas
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2024; 27(2): 79. CrossRef - Substrate Rigidity Effect on CAD/CAM Restorations at Different Thicknesses
César Rogério Pucci, Ana Paula Valente Pinho Mafetano, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Cornelis J. Kleverlaan, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(04): 1020. CrossRef - Microgap Formation between a Dental Resin-Matrix Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing Ceramic Restorative and Dentin after Various Surface Treatments and Artificial Aging
Alexandros Galanopoulos, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Constantinos Papadopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Kosmas Tolidis
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(4): 2335. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef - Effect of full-step versus simplified resin cement luting strategies on the push-out bond strength of indirect resin composite restorations bonded to dentin
Bianca Cristina Dantas da Silva, Isabelle Helena Gurgel de Carvalho, Taciana Emília Leite Vila-Nova, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges, Marília Regalado Galvão Rabelo Caldas, Isauremi Vieira de Assunção, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(24): 3552. CrossRef - Effect of various polymerization protocols on the cytotoxicity of conventional and self-adhesive resin-based luting cements
Ece Irem Oguz, Ufuk Hasanreisoglu, Sadullah Uctasli, Mutlu Özcan, Mehmet Kiyan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1161. CrossRef - Repair bond strength of resin composite to three aged CAD/CAM blocks using different repair systems
Pinar Gul, Latife Altınok-Uygun
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 131. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Surface Characteristics of Dental CAD/CAM Materials after Different Surface Treatments
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Kimon Pahinis, Kyriaki Saltidou, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Effrosyni Tsitrou
Materials.2020; 13(4): 981. CrossRef - Adhesive Systems Used in Indirect Restorations Cementation: Review of the Literature
Cristian Abad-Coronel, Belén Naranjo, Pamela Valdiviezo
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(3): 71. CrossRef - Effects of different etching methods and bonding procedures on shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets applied to different CAD/CAM ceramic materials
S. Kutalmış Buyuk, Ahmet Serkan Kucukekenci
The Angle Orthodontist.2018; 88(2): 221. CrossRef - Ceramic repairs with resins: silanization protocols
Teresa Cristina Vasconcelos dos Santos
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different surface treatments on bond strength of novel CAD/CAM restorative materials to resin cement
Meltem Bektaş Kömürcüoğlu, Elçin Sağırkaya, Ayça Tulga
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(6): 439. CrossRef - Adhesive bonding to polymer infiltrated ceramic
Judith SCHWENTER, Fredy SCHMIDLI, Roland WEIGER, Jens FISCHER
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(5): 796. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of Silanization on Microtensile Bond Strength of Different Resin Cements to a Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramic
Cristina Parise Gré, Renan C de Ré Silveira, Shizuma Shibata, Carlo TR Lago, Luiz CC Vieira
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2016; 17(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of air abrasion with alumina or glass beads on surface characteristics of CAD/CAM composite materials and the bond strength of resin cements
ARAO Nobuaki, YOSHIDA Keiichi, SAWASE Takashi
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2015; 23(6): 629. CrossRef - Resin cement to indirect composite resin bonding: Effect of various surface treatments
Omer Kirmali, Cagatay Barutcugil, Osman Harorli, Alper Kapdan, Kursat Er
Scanning.2015; 37(2): 89. CrossRef - Impact of different adhesives on work of adhesion between CAD/CAM polymers and resin composite cements
Christine Keul, Manuel Müller-Hahl, Marlis Eichberger, Anja Liebermann, Malgorzata Roos, Daniel Edelhoff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Journal of Dentistry.2014; 42(9): 1105. CrossRef - Effect of Plasma Deposition Using Low-Power/Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Promoting Adhesion of Composite Resin to Enamel
Geum-Jun Han, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2014; 34(4): 933. CrossRef - Bonding efficacy of a self-adhesive resin cement to enamel and dentin
Linhu Wang, Haixing Xu, Songyang Li, Bin Shi, Rong Li, Mingfu Ye, Jing Yang
Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed..2014; 29(6): 1307. CrossRef
- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
- 1,787 View
- 8 Download
- 23 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


