Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bonding and fractographic characterization of universal adhesives applied to dentin in multimode strategies: an in vitro study
- Samaa M. Morsy, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Naji Kharouf, Ahmed A. Holiel
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e12. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
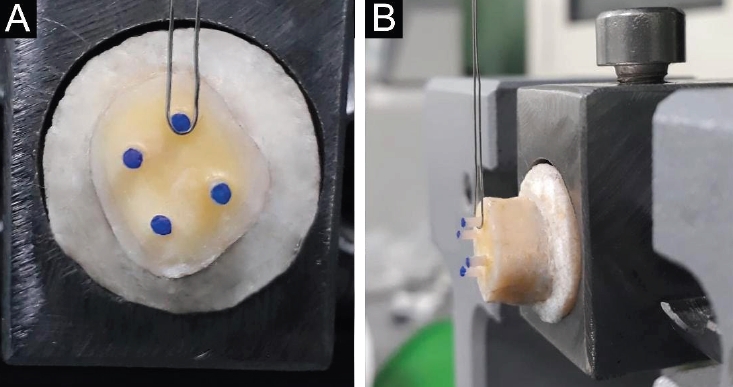
Universal adhesives (UAs) are marketed as versatile systems for both self-etch (SE) and total-etch (TE) modes. While their bond strength has been widely investigated, evidence linking fracture characteristics to bonding performance remains limited. This study evaluated the micro-shear bond strength (μSBS) and failure patterns of three UAs applied in SE and TE modes, complemented by fractographic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
Methods
Eighteen extracted human molars were sectioned to expose mid-coronal dentin and randomly allocated to SE or TE application. Three UAs were tested: Tetric N-Bond Universal, All-Bond Universal, and Single Bond Universal (SBU). Composite micro-rods (n = 72) were bonded, thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5°C and 55°C, and subjected to μSBS testing. Fracture surfaces were examined under SEM and classified as adhesive, cohesive, or mixed. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test, and Spearman correlation (α = 0.05).
Results
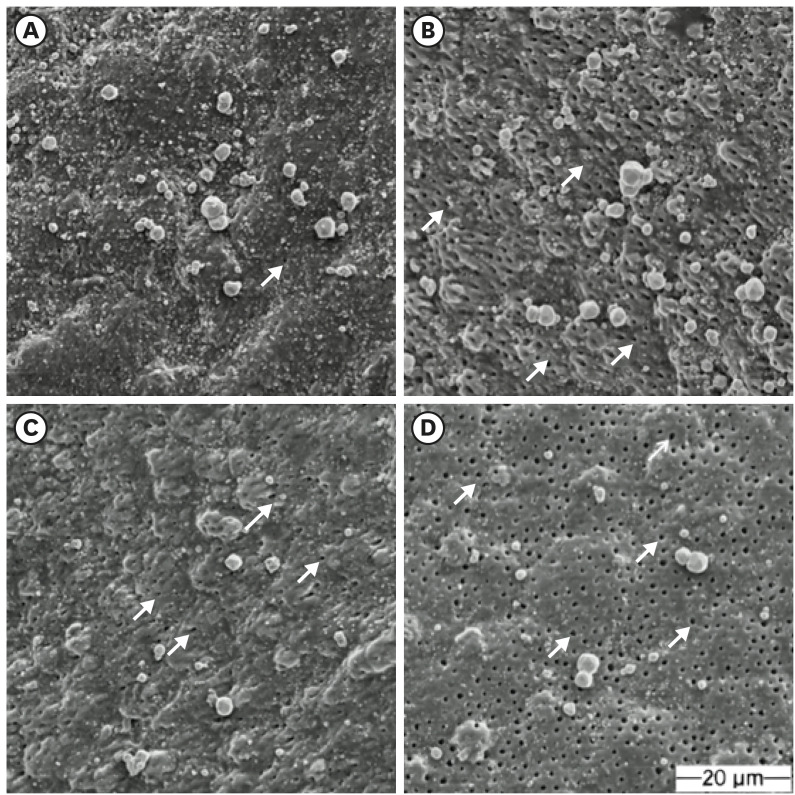
In TE mode, SBU demonstrated the highest μSBS (p < 0.001), whereas no significant differences were observed among adhesives in SE mode (p > 0.05). SEM analysis revealed adhesive failures as interfacial fractures, cohesive failures with beach marks, and mixed failures involving crack propagation through both dentin and composite. Adhesive failures correlated negatively with μSBS (rs = –0.77), while mixed failures correlated positively (rs = 0.81).
Conclusions
Both the etching strategy and adhesive formulation significantly affect bond strength and fracture behavior. Fractographic SEM analysis provides critical insights into the mechanical reliability of UAs and informs their clinical application.
- 189 View
- 17 Download

- Bonding effects of cleaning protocols and time-point of acid etching on dentin impregnated with endodontic sealer
- Tatiane Miranda Manzoli, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, João Felipe Besegato, Flávia Angélica Guiotti, Andréa Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e21. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the bonding effects of cleaning protocols on dentin impregnated with endodontic sealer residues using ethanol (E) or xylol (X). The effects of dentin acid etching immediately (I) or 7 days (P) after cleaning were also evaluated. For bonding to dentin, universal adhesive (Scotchbond Universal; 3M ESPE) was used. The persistence of sealer residues, hybrid layer formation and microshear bond strength were the performed analysis.
Materials and Methods One hundred and twenty bovine dentin specimens were allocated into 4 groups (
n = 10): G1 (E+I); G2 (X+I); G3 (E+P); and G4 (X+P). The persistence of sealer residues was evaluated by SEM. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were taken to measure the formed hybrid layer using the Image J program. For microshear bond strength, 4 resin composite cylinders were placed over the dentin after the cleaning protocols. ANOVA followed by Tukey test and Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn test were used for parametric and non-parametric data, respectively (α = 5%).Results G2 and G4 groups showed a lower persistence of residues (
p < 0.05) and thicker hybrid layer than the other groups (p < 0.05). No bond strength differences among all groups were observed (p > 0.05).Conclusions Dentin cleaning using xylol, regardless of the time-point of acid etching, provided lower persistence of residues over the surface and thicker hybrid layer. However, the bond strength of the universal adhesive system in etch-and-rinse strategy was not influenced by the cleaning protocols or time-point of acid etching.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of Post-Endodontic Access Cavity Cleaning Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Study
Ayse Karadayi, Elif Irem Altintas, Ezgi Tüter Bayraktar, Bora Korkut
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 166. CrossRef - Does cleaning of post space before cementation of fiber reinforced post affect the push-out bond strength to resin cement?
Maher S. Hajjaj, Khalid A. Alghamdi, Abdulrahman A. Alshehri, Hassan A. Almusallam, Nabeel M. Munshi, Osamah A. Alsulimani, Naseeba H. Khouja, Yousef A. Alnowailaty, Saeed J. Alzahrani
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Use of a Mixed Solution of Equal Amounts of Amyl Acetate, Acetone, and Ethanol on the Cleaning of Endodontic Sealer Residues on the Bond Strength of the Fiber Post Cementation System: A Laboratory Investigation
Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Ana Paula Aparecida Raimundo Alves Freitas, Frederico Guilherme Otto Kokol, Elizangela Maria Pereira de Souza, Adirson Jorge Junior, Cristiane de Melo Alencar, Marcelo Ferrarezi de Andrade, Milton Carlos Kuga
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the application protocol and bonding strategy of the universal adhesive on dentin previously impregnated with bioceramic sealer
Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Jardel Camilo do Carmo Monteiro, Lucas David Galvani, Marcelo Ferrarezi de Andrade, José Roberto Cury Saad, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2024; 134: 103765. CrossRef - Influência do protocolo de remoção de resíduos de cimentos à base de resina epóxi sobre a interface de adesão com o adesivo universal, utilizado na estratégia condiciona-e-lava
Paulo Firmino Da Costa Neto, Mariana Bena Gelio, Elisângela Maria Pereira De Souza, Jardel Camilo do Carmo Monteiro, Adirson Jorge Júnior, Thais Piragine Leandrin, José Roberto Cury Saad, Milton Carlos Kuga
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2023; 15(5): 4802. CrossRef
- Efficacy of Post-Endodontic Access Cavity Cleaning Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Study
- 2,300 View
- 40 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of dentin surface preparations on bonding of self-etching adhesives under simulated pulpal pressure
- Chantima Siriporananon, Pisol Senawongse, Vanthana Sattabanasuk, Natchalee Srimaneekarn, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e4. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of different smear layer preparations on the dentin permeability and microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of 2 self-etching adhesives (Clearfil SE Bond [CSE] and Clearfil Tri-S Bond Universal [CTS]) under dynamic pulpal pressure.
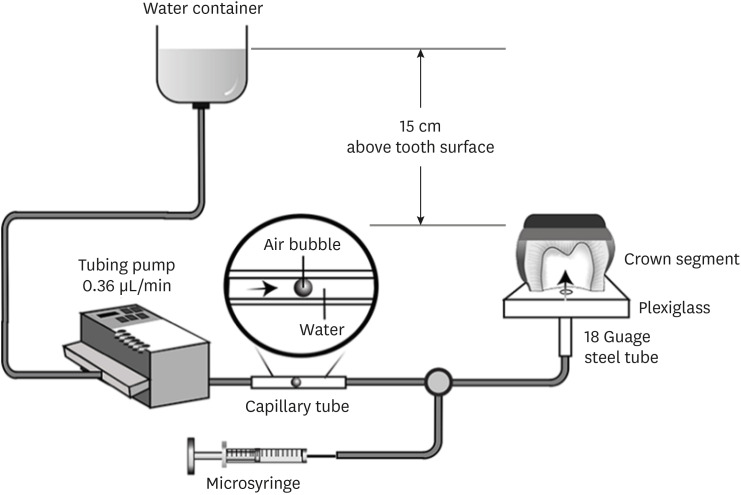
Materials and Methods Human third molars were cut into crown segments. The dentin surfaces were prepared using 4 armamentaria: 600-grit SiC paper, coarse diamond burs, superfine diamond burs, and carbide burs. The pulp chamber of each crown segment was connected to a dynamic intra-pulpal pressure simulation apparatus, and the permeability test was done under a pressure of 15 cmH2O. The relative permeability (%P) was evaluated on the smear layer-covered and bonded dentin surfaces. The teeth were bonded to either of the adhesives under pulpal pressure simulation, and cut into sticks after 24 hours water storage for the µTBS test. The resin-dentin interface and nanoleakage observations were performed using a scanning electron microscope. Statistical comparisons were done using analysis of variance and
post hoc tests.Results Only the method of surface preparation had a significant effect on permeability (
p < 0.05). The smear layers created by the carbide and superfine diamond burs yielded the lowest permeability. CSE demonstrated a higher µTBS, with these values in the superfine diamond and carbide bur groups being the highest. Microscopic evaluation of the resin-dentin interface revealed nanoleakage in the coarse diamond bur and SiC paper groups for both adhesives.Conclusions Superfine diamond and carbide burs can be recommended for dentin preparation with the use of 2-step CSE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
Chavakorn Atsavathavornset, Pipop Saikaew, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Hidehiko Sano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Universal adhesive systems in dentistry: A narrative review
Svetlana N. Razumova, Anzhela S. Brago, Oxana R. Ruda, Zoya A. Guryeva, Elvira V. Adzhieva
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2024; 28(5): 512. CrossRef - Delayed light activation of resin composite affects the bond strength of adhesives under dynamic simulated pulpal pressure
Nattaporn Sukprasert, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Pisol Senawongse, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(11): 6743. CrossRef
- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
- 3,106 View
- 48 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Adhesive systems applied to dentin substrate under electric current: systematic review
- Carolina Menezes Maciel, Tatiane Cristina Vieira Souto, Bárbara de Almeida Pinto, Laís Regiane Silva-Concilio, Kusai Baroudi, Rafael Pino Vitti
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e55. Published online November 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
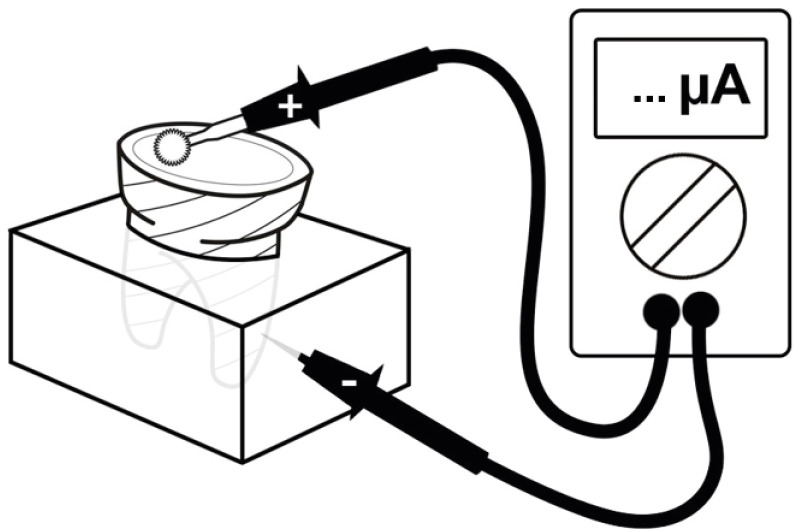
ePub Objectives The purpose of this systematic review was to collect and discuss the technique of adhesive systems application on dentin substrate under electric current.
Materials and Methods The first search strategy was based on data available at PubMed, LILACS, Scielo, Scopus, and Cochrane Library, using a combination of descriptors such as “dentin bond agents OR adhesive system AND electric current OR electrobond” or “dentin bonding agents OR dentin bonding agent application OR adhesive system AND electric current OR electrobond”, with no limit regarding the publication year. The second search strategy was based on the articles' references found previously. An additional search strategy was applied that concerned the proposed theme in the SBU-UNICAMP (Unicamp's Library System Institutional Repository).
Results Twelve studies published between 2006 and 2020 were found. The analyses of the selected studies showed that the use of electric current during adhesive systems application on dentin, whether conventional or self-conditioning, increases resinous monomer infiltration in the dentin substrate, which improves the hybridization processes and the bond strength of the restorative material to dentin.
Conclusions Despite the favorable results related to the use of this technique, there is still no specific protocol for the application of adhesive systems under electric current.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
Rim Bourgi
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Iontophoresis effects of two-step self-etch and total-etch systems on dentin permeability and sealing of composite restoration under simulated pulpal pressure
Orapin Ajcharanukul, Peeraya Santikulluk, Palat Sasingha, Sirithorn Sabpawat, Kanokporn Sukyanan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
- 2,033 View
- 14 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Interface between calcium silicate cement and adhesive systems according to adhesive families and cement maturation
- Nelly Pradelle-Plasse, Caroline Mocquot, Katherine Semennikova, Pierre Colon, Brigitte Grosgogeat
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e3. Published online December 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
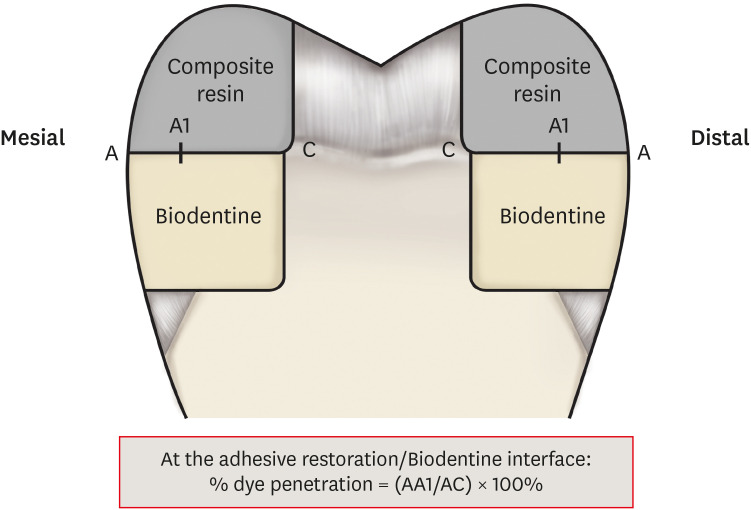
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the interface between a calcium silicate cement (CSC), Biodentine and dental adhesives in terms of sealing ability.
Materials and Methods Microleakage test: 160 standardized class II cavities were prepared on 80 extracted human molars. The cavities were filled with Biodentine and then divided into 2 experimental groups according to the time of restoration: composite resin obturation 15 minutes after Biodentine handling (D0); restoration after 7 days (D7). Each group was then divided into 8 subgroups (
n = 5) according to the adhesive system used: etch-and-rinse adhesive (Prime & Bond); self-etch adhesive 2 steps (Optibond XTR and Clearfil SE Bond); self-etch adhesive 1 step (Xeno III, G-aenial Bond, and Clearfil Tri-S Bond); and universal used as etch-and-rinse or self-etch (ScotchBond Universal ER or SE). After thermocycling, the teeth were immersed in a silver nitrate solution, stained, longitudinally sectioned, and the Biodentine/adhesive percolation was quantified. Scanning electron microscopic observations: Biodentine/adhesive interfaces were observed.Results A tendency towards less microleakage was observed when Biodentine was etched (2.47%) and when restorations were done without delay (D0: 4.31%, D7: 6.78%), but this was not significant. The adhesives containing 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate monomer showed the most stable results at both times studied. All Biodentine/adhesive interfaces were homogeneous and regular.
Conclusions The good sealing of the CSC/adhesive interface is not a function of the system adhesive family used or the cement maturation before restoration. Biodentine can be used as a dentine substitute.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of compressive strength, surface microhardness, and surface microstructure of different types of bioceramics following varying surface treatments
Zeynep Hale Keleş, Vasfiye Işık, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er Cr YSGG laser etching procedure on the bond strength of different calcium silicate cements
Yesim Sesen Uslu, Hakan Yasin Gönder, Pinar Sesen, Gizem Gunduz Bektaş
Lasers in Dental Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Resistance of Natural Molars vs. Additive-Manufactured Simulators Treated with Pulpotomy and Endocrown
Marie-Laure Munoz-Sanchez, Alexis Gravier, Olivier Francois, Emmanuel Nicolas, Martine Hennequin, Nicolas Decerle
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(9): 444. CrossRef - Characterisation of the calcium silicate‐based cement–composite interface and the bonding strength with total‐etch or single/two‐stage self‐etch adhesive systems
Abidin Talha Mutluay, Merve Mutluay
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 501. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Adhesive Systems to Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
Louis Hardan, Davide Mancino, Rim Bourgi, Alejandra Alvarado-Orozco, Laura Emma Rodríguez-Vilchis, Abigailt Flores-Ledesma, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Ammar Eid, Maya-Line Danhache, Maryline Minoux, Youssef Haïkel, Naji Kharo
Gels.2022; 8(5): 311. CrossRef
- Comparison of compressive strength, surface microhardness, and surface microstructure of different types of bioceramics following varying surface treatments
- 2,889 View
- 52 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- The influence of nanofillers on the properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives
- Leonardo Bairrada Tavares da Cruz, Marcelo Tavares Oliveira, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Adriano Fonseca Lima
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
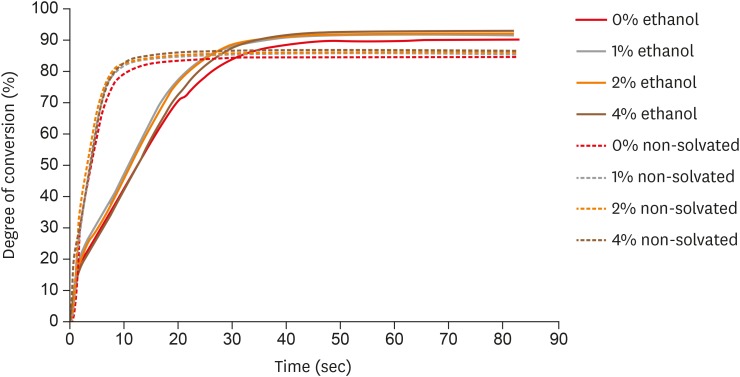
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of different concentrations of nanofillers on the chemical and physical properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives.
Materials and Methods Eight experimental adhesives were prepared with different nanofiller concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 4 wt%) and 2 solvent concentrations (0% and 10% ethanol). Several properties of the experimental adhesives were evaluated, such as water sorption and solubility (
n = 5, 20 seconds light activation), real-time degree of conversion (DC;n = 3, 20 and 40 seconds light activation), and stability of cohesive strength at 6 months (CS;n = 20, 20 seconds light activation) using the microtensile test. A light-emitting diode (Bluephase 20i, Ivoclar Vivadent) with an average light emittance of 1,200 mW/cm2 was used.Results The presence of solvent reduced the DC after 20 seconds of curing, but increased the final DC, water sorption, and solubility of the adhesives. Storage in water reduced the strength of the adhesives. The addition of 1 wt% and 2 wt% nanofillers increased the polymerization rate of the adhesives.
Conclusions The presence of nanofillers and ethanol improved the final DC, although the DC of the solvated adhesives at 20 seconds was lower than that of the non-solvated adhesives. The presence of ethanol reduced the strength of the adhesives and increased their water sorption and solubility. However, nanofillers did not affect the water sorption and strength of the tested adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
Ellen Pick, Andrea Gubler, Thomas Attin, Patrick R. Schmidlin
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(3): 142. CrossRef - Effect of boric acid on the color stability and mechanical properties of 3D-printed permanent resins
Dalndushe Abdulai, Rafat Sasany, Raghib Suradi, Mehran Moghbel, Seyed Ali Mosaddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Boron Nitride-Filled Dental Adhesive System
Senthilguru Kulanthaivel, Jeremiah Poppen, Sandra Ribeiro Cunha, Benjamin Furman, Kyumin Whang, Erica C. Teixeira
Polymers.2023; 15(17): 3512. CrossRef - Analyses of Experimental Dental Adhesives Based on Zirconia/Silver Phosphate Nanoparticles
Abdul Khan, Yasmin Alhamdan, Hala Alibrahim, Khalid Almulhim, Muhammad Nawaz, Syed Ahmed, Khalid Aljuaid, Ijlal Ateeq, Sultan Akhtar, Mohammad Ansari, Intisar Siddiqui
Polymers.2023; 15(12): 2614. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef
- In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
- 1,505 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Influence of different universal adhesives on the repair performance of hybrid CAD-CAM materials
- Gülbike Demirel, İsmail Hakkı Baltacıoğlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e23. Published online May 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
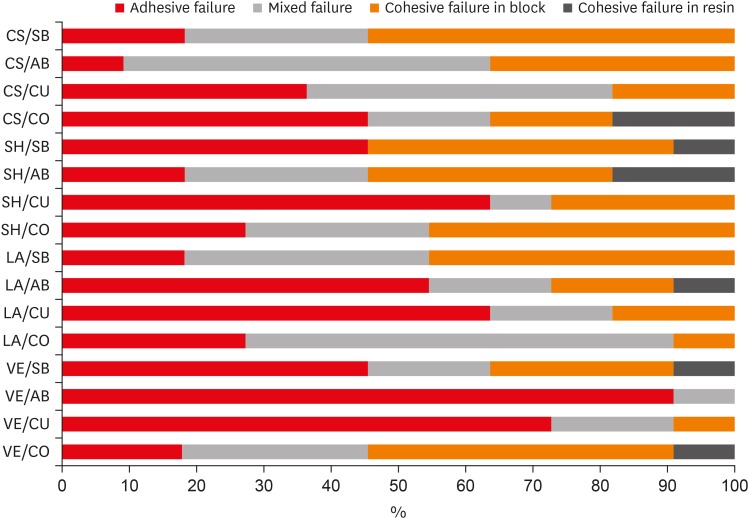
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the microshear bond strength (μSBS) of different universal adhesive systems applied to hybrid computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) restorative materials repaired with a composite resin.
Materials and Methods Four types of CAD-CAM hybrid block materials—Lava Ultimate (LA), Vita Enamic (VE), CeraSmart (CS), and Shofu Block HC (SH)—were used in this study, in combination with the following four adhesive protocols: 1) control: porcelain primer + total etch adhesive (CO), 2) Single Bond Universal (SB), 3) All Bond Universal (AB), and 4) Clearfil Universal Bond (CU). The μSBS of the composite resin (Clearfil Majesty Esthetic) was measured and the data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test, with the level of significance set at
p < 0.05.Results The CAD-CAM block type and block-adhesive combination had significant effects on the bond strength values (
p < 0.05). Significant differences were found between the following pairs of groups: VE/CO and VE/AB, CS/CO and CS/AB, VE/CU and CS/CU, and VE/AB and CS/AB (p < 0.05).Conclusions The μSBS values were affected by hybrid block type. All tested universal adhesive treatments can be used as an alternative to the control treatment for repair, except the AB system on VE blocks (the VE/AB group). The μSBS values showed variation across different adhesive treatments on different hybrid CAD-CAM block types.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength of resin-repaired resin matrix CAD-CAM ceramic: A scoping review
Ana Beatriz de Souza Albergardi, João Pedro Justino de Oliveira Limírio, Jéssica Marcela de Luna Gomes, Aldiéris Alves Pesqueira, Eduardo Piza Pellizzer
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 154: 105594. CrossRef - Bond strength to aged CAD/CAM composites and polymer-infiltrated ceramic network using a universal adhesive with or without previous application of a universal primer
Clemens Lechte, Lisa Sophia Faesser, Jana Biermann, Alexandra Schmidt, Philipp Kanzow, Annette Wiegand
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 140: 104017. CrossRef - The Influence of Thermocycling and Ultraviolet Aging on Surface Characteristics and the Repair Bond Strength of CAD/CAM Resin Nanoceramics
Beyza Unalan Degirmenci, Alperen Degirmenci, Zelal Seyfioglu Polat
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 156. CrossRef - Impact of in vitro findings on clinical protocols for the adhesion of CAD-CAM blocks: A systematic integrative review and meta-analysis
Maria João Calheiros-Lobo, Ricardo Carbas, Lucas F.M. da Silva, Teresa Pinho
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(6): 1051. CrossRef - Repair protocols for indirect monolithic restorations: a literature review
Lucas Saldanha da Rosa, Rafaela Oliveira Pilecco, Pablo Machado Soares, Marília Pivetta Rippe, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Luiz Felipe Valandro, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Albert J. Feilzer, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
PeerJ.2024; 12: e16942. CrossRef - Bonding performance of universal adhesives with concomitant use of silanes to CAD/CAM blocks
Marina AMARAL, Jaqueline Maria Brandão RIZZATO, Victoria Caroline Souza de ALMEIDA, Priscila Christiane Suzy LIPORONI, Rayssa Ferreira ZANATTA
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistencia a la fractura de una nanocerámica CAD/CAM reparada con dos tratamientos de superficie: estudio in vitro
Marcelo Geovanny Cascante-Calderón, Kevin Alejandro Reascos Flores, Inés María Villacís-Altamirano, Anggely Maite Bayas Salinas, Jessica Elizabeth Taraguay Galindo
Universitas Odontologica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and adhesive protocols on repair bond strength of glass‐matrix and resin‐matrix CAD/CAM ceramics
Rana Turunç‐Oğuzman, Soner Şişmanoğlu
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1322. CrossRef - Effect of Anti-COVID-19 Mouthwashes on Shear Bond Strength of Resin-Matrix Ceramics Repaired with Resin Composite Using Universal Adhesive: An In Vitro Study
Wichuda Limsiriwong, Awiruth Klaisiri, Nantawan Krajangta
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(3): 158. CrossRef - Effect of ceramic primers with different chemical contents on the shear bond strength of CAD/CAM ceramics with resin cement after thermal ageing
Mehmet Uğur, İdris Kavut, Özgür Ozan Tanrıkut, Önder Cengiz
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of microstructure of reinforced CAD/CAM hybrid composite resin block on shear bond strength of composite resin
Sung-Ho Um, Minjeong Shin, Shin-hye Chung, Young-Seok Park, Bum-Soon Lim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2023; 50(1): 29. CrossRef - Dentin contamination during repair procedures: A threat to universal adhesives?
Anne‐Katrin Lührs, Cosima Brachmann, Silke Jacker‐Guhr
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(3): 771. CrossRef - Influence of mechanical and chemical pre-treatments on the repair of a hybrid ceramic
Sascha Niklas Jung, Stefan Rüttermann
Dental Materials.2022; 38(7): 1140. CrossRef - Influence of different repair protocols and artificial aging on bond strength of composite to a CAD/CAM polymer-infiltrated ceramic
Ece İrem OĞUZ, Gökhan ÇİÇEKCİ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2021; 24(1): 37. CrossRef - REZİN MATRİKS SERAMİKLER-DERLEME
Elif Melike AKARCA, Dilara ŞAHİN, Ragibe Şenay CANAY
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - REZİN MATRİKS SERAMİKLER-DERLEME
Elif Melike AKARCA, Dilara ŞAHİN, Ragibe Şenay CANAY
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Microshear bond strength of contemporary self-adhesive resin cements to CAD/CAM restorative materials: effect of surface treatment and aging
Soner Şişmanoğlu, Rana Turunç-Oğuzman
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(22): 2484. CrossRef - Influence of different surface treatments and universal adhesives on the repair of CAD-CAM composite resins: An in vitro study
Soner Sismanoglu, Zuhal Yildirim-Bilmez, Aysegul Erten-Taysi, Pınar Ercal
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2020; 124(2): 238.e1. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength of resin-repaired resin matrix CAD-CAM ceramic: A scoping review
- 2,337 View
- 18 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Do universal adhesives promote bonding to dentin? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ali A. Elkaffas, Hamdi H. H. Hamama, Salah H. Mahmoud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e29. Published online June 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
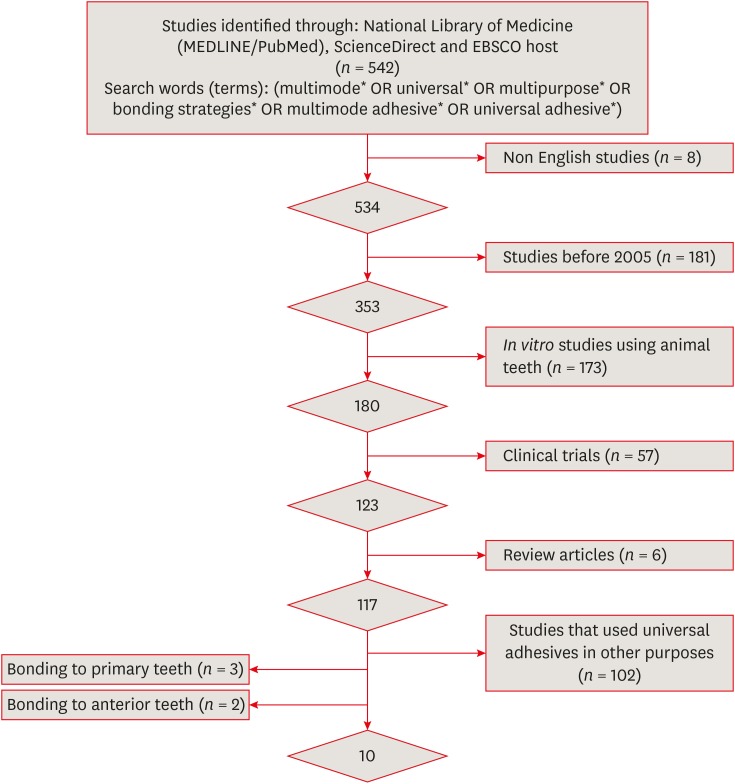
ePub Objectives The aims of this study were to conduct a systematic review of the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of multi-mode adhesives to dentin and to perform a meta-analysis to assess the significance of differences in the µTBS of one of the most commonly used universal adhesives (Scotchbond Universal, 3M ESPE) depending on whether the etch-and-rinse or self-etch mode was used.
Materials and Methods An electronic search was performed of MEDLINE/PubMed, ScienceDirect, and EBSCOhost. Laboratory studies that evaluated the µTBS of multi-mode adhesives to dentin using either the etch-and-rinse or self-etch mode were selected. A meta-analysis was conducted of the reviewed studies to quantify the differences in the µTBS of Scotchbond Universal adhesive.
Results Only 10 studies fulfilled the inclusion criteria for the systematic review. Extensive variation was found in the restorative materials, testing methodologies, and failure mode in the reviewed articles. Furthermore, variation was also observed in the dimensions of the microtensile testing beams. The meta-analysis showed no statistically significant difference between the etch-and-rinse and self-etch modes for Scotchbond Universal adhesive (
p > 0.05).Conclusions Multi-mode ‘universal’ adhesives can achieve substantial bonding to dentin, regardless of the used modes (either etch-and-rinse or self-etch).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The potential cytotoxic effect of recent universal adhesives with modified monomeric compositions on human gingival epithelial cells
Omar Abd El-Maksoud, Nessma Sultan, Hoda Saleh Ismail, Ramy Ahmed Wafaie, Hamdi H. Hamama, Salah Hasab Mahmoud
Scientific Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Proximal-Cervical Undermined Enamel Areas on Marginal Quality and Enamel Integrity of Laboratory and CAD/CAM Ceramic Inlays and Partial Crowns
Roland Frankenberger, Katharina Friedrich, Marie-Christine Dudek, Julia Winter, Norbert Krämer, Matthias J. Roggendorf
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(3): 82. CrossRef - Improving Bonding Protocols: The Effect of Selective Dentin Etching with Two Different Universal Adhesives—An In Vitro Study
Sandro Ferreira, Tiago Rodrigues, Mariana Nunes, Ana Mano Azul, José João Mendes, Ana Filipa Chasqueira, Joana Costa
Polymers.2025; 17(9): 1215. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on glass ionomers in sandwich restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory studies
Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e13. CrossRef - Wet vs. Dry Dentin Bonding: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Adhesive Performance and Hybrid Layer Integrity
Mircea Popescu, Mădălina Malița, Andrei Vorovenci, Andreea Angela Ștețiu, Viorel Ștefan Perieanu, Radu Cătălin Costea, Mihai David, Raluca Mariana Costea, Maria Antonia Ștețiu, Andi Ciprian Drăguș, Cristina Maria Șerbănescu, Andrei Burlibașa, Oana Eftene,
Oral.2025; 5(3): 63. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Multimode Adhesives On Microleakage of Class V Composite Restorations in Three Etching Modes
Fatma Yılmaz, Sevgi Kurşun, Zeliha Öztürk
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2025; 14(3): 177. CrossRef - Controversies about refrigeration of dental adhesives: a review
Omar Abd El-Maksoud, Hamdi Hosni Hamdan Hamama, Ramy Ahmed Wafaie, Salah Hasab Mahmoud
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth-composite bond failure with a universal and an etch-and-rinse adhesive depending on mode and frequency of application
Ellen Schulz-Kornas, Mathilde Tittel, Hartmut Schneider, Maximilian Bemmann, Marco Pellino, Tobias Meissner, Florian Fuchs, Christian Hannig, Florian Tetschke, Kyung-Jin Park, Michaela Strumpski, Rainer Haak
Dental Materials.2024; 40(2): 359. CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative hypersensitivity between Total-etch and Universal adhesive system: a randomized clinical trial
Kiran Javed, Nouman Noor, Muhammad Zubair Nasir, Manzoor Ahmed Manzoor
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesion and sealing of different universal adhesive systems associated with bulk‐fill resins after using endodontic irrigation solutions: An in vitro study
Érika Mayumi Omoto, Anderson Catelan, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Fernanda de Souza e Silva Ramos, Caio César Pavani, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Ticiane Cestari Fagundes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 309. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effects of combined application of dimethylaminohexadecyl methacrylate and MDP on dentin bonding and antimicrobial properties
Jiadi Shen, Ming Ma, Yun Huang, Haochen Miao, Xin Wei
Journal of Materials Science.2023; 58(31): 12685. CrossRef - Efficacy of adhesive strategies for restorative dentistry: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled trials over 12 months of follow-up
Kevin Sheng-Kai Ma, Li-Tzu Wang, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2023; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - Impact of Preceded Tumor Therapeutic Irradiation on the Microtensile Bond Strength of Universal Adhesives Applied in Self-Etch Mode to Human Dentin In Vitro
Sina Broscheit, Dirk Vordermark, Reinhard Gerlach, Christian Ralf Gernhardt
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(13): 7873. CrossRef - Effect of the Adhesive Strategy on Clinical Performance and Marginal Integrity of a Universal Adhesive in Non-Carious Cervical Lesions in a Randomized 36-Month Study
Rainer Haak, Gesa Stache, Hartmut Schneider, Matthias Häfer, Gerhard Schmalz, Ellen Schulz-Kornas
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(18): 5776. CrossRef - Universal Adhesives in Clinical Dentistry
Fusun Ozer, Shilpa Patnaikuni
Science, Art and Religion.2023; 2(1--2): 6. CrossRef - Deep proximal margin rebuilding with direct esthetic restorations: a systematic review of marginal adaptation and bond strength
Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf I. Ali, Rabab El. Mehesen, Jelena Juloski, Franklin Garcia-Godoy, Salah H. Mahmoud
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving Properties of an Experimental Universal Adhesive by Adding a Multifunctional Dendrimer (G-IEMA): Bond Strength and Nanoleakage Evaluation
Joana Vasconcelos e Cruz, António H. S. Delgado, Samuel Félix, José Brito, Luísa Gonçalves, Mário Polido
Polymers.2022; 14(7): 1462. CrossRef - Scoping review of trials evaluating adhesive strategies in pediatric dentistry: where do simplified strategies lie?
António H. S. Delgado, Hasan Jamal, Anne Young, Paul Ashley
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Does acid etching prior to applying universal adhesives affect the bond strength of glass fiber post to root dentin?
Helder Callegaro Velho, Eduardo Trindade Dalence, Pablo Soares Machado, Marília Pivetta Rippe, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Vinícius Felipe Wandscher
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2021; 105: 102795. CrossRef - Does Adhesive Layer Thickness and Tag Length Influence Short/Long-Term Bond Strength of Universal Adhesive Systems? An In-Vitro Study
Naji Kharouf, Tarek Ashi, Ammar Eid, Levi Maguina, Jihed Zghal, Nairy Sekayan, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Salvatore Sauro, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(6): 2635. CrossRef - Chronological history and current advancements of dental adhesive systems development: a narrative review
Maicon Sebold, Carolina Bosso André, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Lorenzo Breschi, Marcelo Giannini
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(18): 1941. CrossRef - Laboratory methods for measuring adhesive bond strength between restoration materials and hard tooth tissues
I.Ya. Poyurovskaya, A.P. Polikarpova, F.S. Rusanov
Stomatologiya.2021; 100(5): 88. CrossRef - Effect of Curcumin Suspension and Vitamin C on Dentin Shear Bond Strength and Durability. A Pilot Study
Dalia A. Abuelenain, Ensanya A. Abou Neel, Tariq S. Abuhaimed, Amal M. Alamri, Hanan S. Ammar, Sahar M. N. Bukhary
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 540. CrossRef - Effect of 9.3 μm CO2 and 2.94 μm Er:YAG Laser vs. Bur Preparations on Marginal Adaptation in Enamel and Dentin of Mixed Class V Cavities Restored With Different Restorative Systems
Clara Isabel Anton y Otero, Enrico Di Bella, Ivo Krejci, Tissiana Bortolotto
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesion strategy and curing mode of a universal adhesive influence the bonding of dual-cured core build-up resin composite to dentin
Ahmed Eid Elsayed, Mohamed Amr Kamel, Farid Sabry El-Askary
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(1): 52. CrossRef - Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
Stefan Dačić, Milan Miljković, Aleksandar Mitić, Goran Radenković, Marija Anđelković‐Apostolović, Milica Jovanović
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(6): 1212. CrossRef - Universal adhesives - a new direction in the development of adhesive systems
A. Tichý, K. Hosaka, J. Tagami
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2020; 120(1): 4. CrossRef - Effect of Over-Etching and Prolonged Application Time of a Universal Adhesive on Dentin Bond Strength
Phoebe Burrer, Hoang Dang, Matej Par, Thomas Attin, Tobias T. Tauböck
Polymers.2020; 12(12): 2902. CrossRef - Profile of a 10-MDP-based universal adhesive system associated with chlorhexidine: Dentin bond strength and in situ zymography performance
Marina Ciccone Giacomini, Polliana Mendes Candia Scaffa, Rafael Simões Gonçalves, Giovanna Speranza Zabeu, Cristina de Mattos Pimenta Vidal, Marcela Rocha de Oliveira Carrilho, Heitor Marques Honório, Linda Wang
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 110: 103925. CrossRef - Universal dental adhesives: Current status, laboratory testing, and clinical performance
Sanket Nagarkar, Nicole Theis‐Mahon, Jorge Perdigão
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2019; 107(6): 2121. CrossRef - Modifying Adhesive Materials to Improve the Longevity of Resinous Restorations
Wen Zhou, Shiyu Liu, Xuedong Zhou, Matthias Hannig, Stefan Rupf, Jin Feng, Xian Peng, Lei Cheng
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(3): 723. CrossRef
- The potential cytotoxic effect of recent universal adhesives with modified monomeric compositions on human gingival epithelial cells
- 5,482 View
- 51 Download
- 31 Crossref

- Effect of various bleaching treatments on shear bond strength of different universal adhesives and application modes
- Fatma Dilsad Oz, Zeynep Bilge Kutuk
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e20. Published online April 16, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
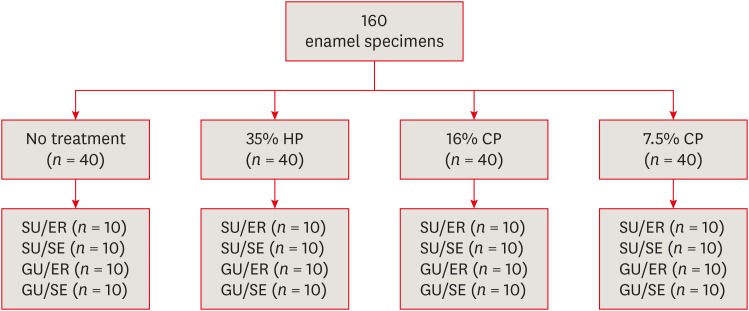
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the bond strength of 2 universal adhesives used in different application modes to bleached enamel.Materials and Methods Extracted 160 sound human incisors were used for the study. Teeth were divided into 4 treatment groups: No treatment, 35% hydrogen peroxide, 16% carbamid peroxide, 7.5% carbamid peroxide. After bleaching treatments, groups were divided into subgroups according to the adhesive systems used and application modes (
n = 10): 1) Single Bond Universal, etch and rinse mode; 2) Single Bond Universal, self-etch mode; 3) Gluma Universal, etch and rinse mode; 4) Gluma Universal, self-etch mode. After adhesive procedures nanohybrid composite resin cylinders were bonded to the enamel surfaces. All specimens were subjected to shear bond strength (SBS) test after thermocycling. Data were analyzed using a 3-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukeypost hoc test.Results No significant difference were found among bleaching groups (35% hydrogen peroxide, 16% carbamid peroxide, 7.5% carbamid peroxide, and no treatment groups) in the mean SBS values. There was also no difference in SBS values between Single Bond Universal and Gluma Universal at same application modes, whereas self-etch mode showed significantly lower SBS values than etch and rinse mode (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The bonding performance of the universal adhesives was enhanced with the etch and rinse mode application to bleached enamel and non-bleached enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antioxidant effect on shear bond strength of resin composite to in-office versus home bleached enamel surface
Maha Mosaad Mohamed, Magda E. -A. Shalaby, Eman A. E. -G. Shebl
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(3): 409. CrossRef - Effects of Time-Elapsed Bleaching on the Surface and Mechanical Properties of Dentin Substrate Using Hydrogen Peroxide-Free Nanohydroxyapatite Gel
Aftab Khan, Abdulaziz AlKhureif, Manal Almutairi, Abrar Nooh, Saeed Hassan, Yasser Alqahtani
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2024; Volume 19: 10307. CrossRef - Effect of sodium ascorbate on the shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets to bleached enamel using universal dental adhesive
Saeid Sadeghian, Kamyar Fathpour, Mahshid Biglari
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative Measurements of the Depth of Enamel Demineralization before and after Bleach: An In Vitro Study
Sara Naim, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Essam Osman, Syed Sarosh Mahdi, Gopi Battineni, Syed Saad B. Qasim, Mariangela Cernera, Hasna Rifai, Nada Jaafar, Elie Maalouf, Carina Mehanna Zogheib, Konstantinos Michalakis
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - DİŞ BEYAZLATMA İŞLEMİNİN LİTYUM DİSİLİKAT SERAMİĞİN BAĞLANMA DAYANIMINA ETKİSİ
Merve YILDIRAK, Rıfat GÖZNELİ
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Bleaching Protocols, Used with and without Sodium Ascorbate, on Bond Strength between Composite and Enamel
Maroun Ghaleb, Giovanna Orsini, Angelo Putignano, Sarah Dabbagh, Georges Haber, Louis Hardan
Materials.2020; 13(12): 2710. CrossRef - Influence of phototherapy on adhesive strength and microleakage of bleached enamel bonded to orthodontic brackets: An in-vitro study
Erum Khan, Ibrahim Alshahrani, Muhammad Abdullah Kamran, Abdulaziz Samran, Ali Alqerban, Saad Abdul Rehman
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2019; 25: 344. CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG Laser on Microtensile Bond Strength of Bleached Dentin to Composite
Mohsen Rezaei, Elham Aliasghar, Mohammad Bagher Rezvani, Nasim Chiniforush, Zohreh Moradi
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2019; 10(2): 117. CrossRef
- Antioxidant effect on shear bond strength of resin composite to in-office versus home bleached enamel surface
- 2,336 View
- 21 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of smear layer deproteinization on bonding of self-etch adhesives to dentin: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Khaldoan H. Alshaikh, Hamdi H. H. Hamama, Salah H. Mahmoud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e14. Published online March 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
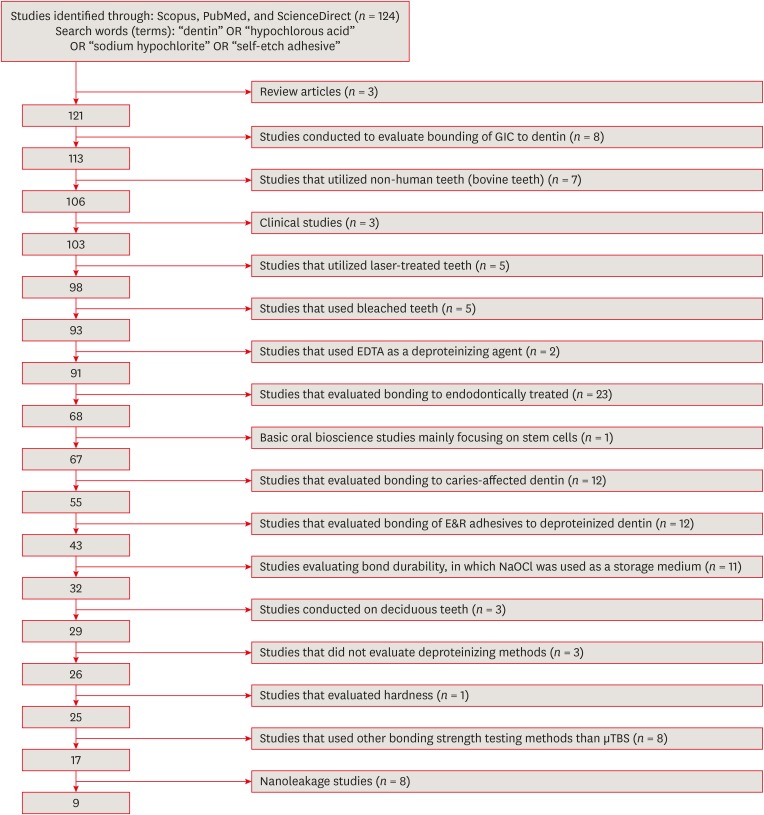
ePub Objectives The aim of this systematic review was to critically analyze previously published studies of the effects of dentin surface pretreatment with deproteinizing agents on the bonding of self-etch (SE) adhesives to dentin. Additionally, a meta-analysis was conducted to quantify the effects of the above-mentioned surface pretreatment methods on the bonding of SE adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods An electronic search was performed using the following databases: Scopus, PubMed and ScienceDirect. The online search was performed using the following keywords: ‘dentin’ or ‘hypochlorous acid’ or ‘sodium hypochlorite’ and ‘self-etch adhesive.’ The following categories were excluded during the assessment process: non-English articles, randomized clinical trials, case reports, animal studies, and review articles. The reviewed studies were subjected to meta-analysis to quantify the effect of the application time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl) deproteinizing agents on bonding to dentin.
Results Only 9 laboratory studies fit the inclusion criteria of this systematic review. The results of the meta-analysis revealed that the pooled average microtensile bond strength values to dentin pre-treated with deproteinizing agents (15.71 MPa) was significantly lower than those of the non-treated control group (20.94 MPa).
Conclusions In light of the currently available scientific evidence, dentin surface pretreatment with deproteinizing agents does not enhance the bonding of SE adhesives to dentin. The HOCl deproteinizing agent exhibited minimal adverse effects on bonding to dentin in comparison with NaOCl solutions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of finishing protocols on dentin surface characteristics and bond strength after tooth preparation for indirect restorations
Paola Bernardes, Amanda das Graças Soares, Bárbara Inácio de Melo, Leandro Maruki Pereira, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Rafael Rocha Pacheco, Marcel Santana Prudente, Luís Henrique Araújo Raposo
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2026; 135(2): 371.e1. CrossRef - Is the Percentage of Collagen in Coronal Dentin Related to Microtensile Strength? An In Vitro Study
Taíssa Cássia de Souza Furtado, Gilberto Antonio Borges, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo-Martins, Bruno Henrique dos Reis Souza Oliveira, Renata Margarida Etchebehere, Sanívia Aparecida de Lima Pereira
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Biomodification on the Survival of Resin Composite Restorations: An Umbrella Review
El Alaoui Nihal, Chala Sanaa, Ghoul Sonia
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(2): 109446. CrossRef - Coronal cavity pretreatment agents and restoration protocols effect on microleakage of endodontically treated teeth
Lena Bal, Cangül Keskin, Aybüke Karaca Sakallı, Osman Fatih Aydın
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2026; 7(1): 40. CrossRef -
Evaluating the remnants of Al
2
O
3
particles on different dentine substrate after sandblasting and various cleaning protocols
Faeze Hamze, Khotan Aflatoonian, Mahshid Mohammadibassir, Mohammad-Bagher Rezvani
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2025; 39(6): 869. CrossRef - Preservation Strategies for Interfacial Integrity in Restorative Dentistry: A Non-Comprehensive Literature Review
Carmem S. Pfeifer, Fernanda S. Lucena, Fernanda M. Tsuzuki
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(2): 42. CrossRef - Outcome of Er, Cr:YSGG laser and antioxidant pretreatments on bonding quality to caries-induced dentin
Lamiaa M. Moharam, Haidy N. Salem, Ahmed Abdou, Rasha H. Afifi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - A comparison of different cleaning approaches for blood contamination after curing universal adhesives on the dentine surface
Ting Liu, Haifeng Xie, Chen Chen
Dental Materials.2024; 40(11): 1786. CrossRef - Effect of fiber-reinforced direct restorative materials on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated mandibular molars restored with a conservative endodontic cavity design
Merve Nezir, Beyza Arslandaş Dinçtürk, Ceyda Sarı, Cemile Kedici Alp, Hanife Altınışık
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the use of bromelain associated with bioactive glass-ceramic on dentin/adhesive interface
Rocio Geng Vivanco, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Viviane de de Cássia Oliveira, Mário Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experimental and Chitosan-Infused Adhesive with Dentin Pretreated with Femtosecond Laser, Methylene Blue-Activated Low-Level Laser, and Phosphoric Acid
Fahad Alkhudhairy
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(10): 634. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effective Bond Strength of Composite Resin to Etched Dentin after Dentin Pretreatment: An In-vitro Study
Muhammed Bilal, Shiraz Pasha, Arathi S. Nair
Journal of the Scientific Society.2024; 51(4): 545. CrossRef - Comparison of Different Dentin Deproteinizing Agents on Bond Strength and Microleakage of Universal Adhesive to Dentin
Fatih Bedir, Gül Yıldız Telatar
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2023; 14(1): 44. CrossRef - Addition of metal chlorides to a HOCl conditioner can enhance bond strength to smear layer deproteinized dentin
Kittisak Sanon, Antonin Tichy, Takashi Hatayama, Ornnicha Thanatvarakorn, Taweesak Prasansuttiporn, Takahiro Wada, Yasushi Shimada, Keiichi Hosaka, Masatoshi Nakajima
Dental Materials.2022; 38(8): 1235. CrossRef - Internal and Marginal Adaptation of Adhesive Resin Cements Used for Luting Inlay Restorations: An In Vitro Micro-CT Study
Linah M. Ashy, Hanadi Marghalani
Materials.2022; 15(17): 6161. CrossRef - Collagen-depletion strategies in dentin as alternatives to the hybrid layer concept and their effect on bond strength: a systematic review
António H. S. Delgado, Madalena Belmar Da Costa, Mário Cruz Polido, Ana Mano Azul, Salvatore Sauro
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - NaOCl Application after Acid Etching and Retention of Cervical Restorations: A 3-Year Randomized Clinical Trial
M Favetti, T Schroeder, AF Montagner, RR Moraes, T Pereira-Cenci, MS Cenci
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 268. CrossRef - Resin infiltrant protects deproteinized dentin against erosive and abrasive wear
Ana Theresa Queiroz de Albuquerque, Bruna Oliveira Bezerra, Isabelly de Carvalho Leal, Maria Denise Rodrigues de Moraes, Mary Anne S. Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bis[2-(Methacryloyloxy) Ethyl] Phosphate as a Primer for Enamel and Dentine
R. Alkattan, G. Koller, S. Banerji, S. Deb
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(10): 1081. CrossRef - Influence of Dentine Pre-Treatment by Sandblasting with Aluminum Oxide in Adhesive Restorations. An In Vitro Study
Bruna Sinjari, Manlio Santilli, Gianmaria D’Addazio, Imena Rexhepi, Alessia Gigante, Sergio Caputi, Tonino Traini
Materials.2020; 13(13): 3026. CrossRef - A novel prime-&-rinse mode using MDP and MMPs inhibitors improves the dentin bond durability of self-etch adhesive
Jingqiu Xu, Mingxing Li, Wenting Wang, Zhifang Wu, Chaoyang Wang, Xiaoting Jin, Ling Zhang, Wenxiang Jiang, Baiping Fu
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 104: 103698. CrossRef - The effects of deproteinization and primer treatment on microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to dentin
In-Hye Bae, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(2): 99. CrossRef - Effect of Papain and Bromelain Enzymes on Shear Bond Strength of Composite to Superficial Dentin in Different Adhesive Systems
Farahnaz Sharafeddin, Mina Safari
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(9): 1077. CrossRef
- Effect of finishing protocols on dentin surface characteristics and bond strength after tooth preparation for indirect restorations
- 2,748 View
- 26 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Effect of additional etching and ethanol-wet bonding on the dentin bond strength of one-step self-etch adhesives
- Joonghee Ahn, Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):68-74. Published online November 18, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.68
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effects of additional acid etching on the dentin bond strength of one-step self-etch adhesives with different compositions and pH. The effect of ethanol wetting on etched dentin bond strength of self-etch adhesives was also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Forty-two human permanent molars were classified into 21 groups according to the adhesive types (Clearfil SE Bond [SE, control]; G-aenial Bond [GB]; Xeno V [XV]; Beauti Bond [BB]; Adper Easy Bond [AE]; Single Bond Universal [SU]; All Bond Universal [AU]), and the dentin conditioning methods. Composite resins were placed on the dentin surfaces, and the teeth were sectioned. The microtensile bond strength was measured, and the failure mode of the fractured specimens was examined. The data were analyzed statistically using two-way ANOVA and Duncan's
post hoc test.Results In GB, XV and SE (pH ≤ 2), the bond strength was decreased significantly when the dentin was etched (
p < 0.05). In BB, AE and SU (pH 2.4 - 2.7), additional etching did not affect the bond strength (p > 0.05). In AU (pH = 3.2), additional etching increased the bond strength significantly (p < 0.05). When adhesives were applied to the acid etched dentin with ethanol-wet bonding, the bond strength was significantly higher than that of the no ethanol-wet bonding groups, and the incidence of cohesive failure was increased.Conclusions The effect of additional acid etching on the dentin bond strength was influenced by the pH of one-step self-etch adhesives. Ethanol wetting on etched dentin could create a stronger bonding performance of one-step self-etch adhesives for acid etched dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Different Application Modes of a Universal Adhesive System on the Bond Strength of Bulk‐Fill Composite Resin to Enamel and Dentin in Primary Teeth
Ali Nozari, Maryam Pakniyat Jahromi, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Zahra Jowkar, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a novel pretreatment on the microtensile bond strength of universal adhesives with dentin
Yixiang Pan, Jiajia Xu, Xue Cai, Xiaodong Li, Xiaoyan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1148. CrossRef - Microfluidic Organ-on-A-chip: A Guide to Biomaterial Choice and Fabrication
Uyen M. N. Cao, Yuli Zhang, Julie Chen, Darren Sayson, Sangeeth Pillai, Simon D. Tran
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3232. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on bond strength and interfacial integrity of universal adhesive to deep dentin
Ahmed Mostafa Attia, Ahmed Fawzy Abo-Elezz, Rehab Khalil Safy
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 116. CrossRef - Microtensile Bond Strength of Total-Etch and Self-Etch Universal Adhesives Containing 10-MDP: A Systematic Review
I. Hisham Ismail, N.A. Abdul Razak, N.D. Mohd Ramzi, M.Y.P. Mohd Yusof
The Journal of Dentists.2022; 10: 12. CrossRef - Biomodification of dentin collagen by primers with crosslinking reagents using ethanol wet bonding technique
Talita Arrais Daniel Mendes, Samuel Chillavert Dias Pascoal, Marcelo Victor Sidou Lemos, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Juliano Sartori Mendonça
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2022; 119: 103254. CrossRef - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef - The effect of additional chlorhexidine and/or ethanol on the bond strength of universal adhesives
Zeynep Buket Kaynar, Magrur Kazak, Nazmiye Donmez, Evrim Eliguzeloglu Dalkilic
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(4): 375. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on the Microshear Bond Strength of Composite Resin Restorations to Dentin using Different Adhesive Systems and the Effect of Thermocycling
Sara Valizadeh, Elham Farhadi, Aida Moradi, Sedighe S. Hashemikamangar
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 734. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Universal Adhesives to Dentin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Naji Kharouf, Davide Mancino, Maciej Zarow, Natalia Jakubowicz, Youssef Haikel, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez
Polymers.2021; 13(5): 814. CrossRef - Effects of simplified ethanol–wet bonding and hydrophobic coating on resin–dentin bonding properties
Xia Wang, He Li, Liang Chen, Yue Wang, Jianfei Bai, Defei Wang, Hong Liu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(9): 913. CrossRef - Effect of dentin biomodification techniques on the stability of the bonded interface
Nida Mehmood, Rajni Nagpal, UdaiPratap Singh, Meenal Agarwal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 265. CrossRef - Assessment of nanohardness, elastic modulus, and nanoleakage of the adhesive interface using the ethanol-wet-bonding technique
Mauricio Yugo Souza, Jéssica Lopes Andrade, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele, Eduardo Bresciani
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2020; 99: 102572. CrossRef - The improvement of biocompatibility of adhesives
Cigdem Atalayin, Huseyin Tezel, Zeynep Ergucu, Nimet Unlu, Guliz Armagan, Taner Dagci, Timur Kose
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(8): 3213. CrossRef - Comparison of the micro-tensile bond strengths of four different universal adhesives to caries-affected dentin after ER:YAG laser irradiation
Nazmiye DÖNMEZ, Ayça Sarıalioğlu GÜNGÖR, Barış KARABULUT, Şeyda Hergüner SİSO
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(2): 218. CrossRef - Six-month performance of restorations produced with the ethanol-wet-bonding technique: a randomized trial
Maurício Yugo de SOUZA, Ana Luiza Barbosa JUREMA, Taciana Marco Ferraz CANEPPELE, Eduardo BRESCIANI
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of ethanol-wet dentin, adhesive mode of application, and aging on bond strength of universal adhesive
Mauricio Yugo de SOUZA, Rebeca DI NICOLÓ, Eduardo BRESCIANI
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of light curing modes and ethanol-wet bonding on dentin bonding properties
Mu-zi Li, Jin-rui Wang, Hong Liu, Xia Wang, Kang Gan, Xiu-ju Liu, De-li Niu, Xiao-qing Song
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2016; 17(9): 703. CrossRef - Effect of an Er,Cr:YSGG laser preparation on dentin bond strength of a universal adhesive
A. Rüya Yazici, Emel Karaman, Duygu Tuncer, Gizem Berk, Atilla Ertan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(22): 2477. CrossRef - The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
Jayang Kim, Sungok Hong, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 299. CrossRef
- Influence of Different Application Modes of a Universal Adhesive System on the Bond Strength of Bulk‐Fill Composite Resin to Enamel and Dentin in Primary Teeth
- 1,990 View
- 6 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):180-186. Published online May 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the microleakage and penetration of fissure sealant in permanent molar teeth with fluorosis after pretreatment of the occlusal surface.Materials and Methods A total of 120 third molars with mild dental fluorosis were randomly divided into 6 groups (
n = 20). The tooth surfaces were sealed with an unfilled resin fissure sealant (FS) material. The experimental groups included: 1) phosphoric acid etching (AE) + FS (control); 2) AE + One-Step Plus (OS, Bisco) + FS; 3) bur + AE + FS; 4) bur + AE + OS + FS; 5) Er:YAG laser + AE + FS; and 6) Er:YAG laser + AE + OS + FS. After thermocycling, the teeth were immersed in 0.5% fuchsin and sectioned. Proportions of mircoleakage (PM) and unfilled area (PUA) were measured by digital microscope.Results Overall, there were significant differences among all groups in the PM (
p = 0.00). Group 3 showed the greatest PM, and was significantly different from groups 2 to 6 (p < 0.05). Group 6 showed the lowest PM. Pretreatment with Er:YAG with or without adhesive led to less PM than bur pretreatment. There were no significant differences among groups in PUA.Conclusions Conventional acid etching provided a similar degree of occlusal seal in teeth with fluorosis compared to those pretreated with a bur or Er:YAG laser. Pretreatment of pits and fissures with Er:YAG in teeth with fluorosis may be an alternative method before fissure sealant application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Retention Rates of Composite Resin Pit and Fissure Sealants Placed on Permanent Molars Treated with Air Abrasion and Acid Etching: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Vishal Raut, Deepak Sharma, Ashish K Jain, Rahul Rao, Laresh N Mistry, Supriya Solanke
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2026; 19(2): 271. CrossRef - Effects of Er: YAG laser and acid etching on bond strength of clear aligner attachments to fluorotic enamel
Rui Xia, Jie Lei, Maoxuan Luo, Yao Xiao, Rawaa A. Faris
PLOS One.2025; 20(8): e0328937. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetrative and Adaptive Properties of Unfilled and Filled Resin-Based Sealants When Placed using Conventional acid Etching, Lasing, and Fissurotomy Bur Technique of Enamel Preparation
Poonam Ramrao Shingare, Vishwas Chaugule, Neha Pankey, Pallavi Kakade
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 349. CrossRef - Laser Tooth Preparation for Pit and Fissure Sealing
Yair Schwimmer, Nurit Beyth, Diana Ram, Eitan Mijiritsky, Esti Davidovich
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 7813. CrossRef - The clinical effects of laser preparation of tooth surfaces for fissure sealants placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yunhan Zhang, Yan Wang, Yandi Chen, Yang Chen, Qiong Zhang, Jing Zou
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of laser preparation on adhesion of a self‐adhesive flowable composite resin to primary teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Faranak Razmjoei, Nasrin Kianimanesh
Microscopy Research and Technique.2016; 79(4): 334. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Retention Rates of Composite Resin Pit and Fissure Sealants Placed on Permanent Molars Treated with Air Abrasion and Acid Etching: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- 1,660 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
- Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):409-418. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.409
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the microshear bond strength (µSBS) and bonding interfaces of two-step total-etching and self-etching adhesive systems to three etch types of dentin either the acid etched, laser etched or laser and acid etched.
Materials and Methods The occlusal dentinal surfaces of thirty human molars were used. They were divided into six groups: group 1, 37% H3PO4 + Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE); group 2, Er:YAG laser (KEY Laser 3, KaVo) + Single Bond 2; group 3, Er:YAG laser + 37% H3PO4 + Single Bond 2; group 4, Clearfil SE Primer + Bond (Kuraray); group 5, Er:YAG laser + Clearfil SE Bond; group 6, Er:YAG laser + Clearfil SE Primer + Bond. The samples were subjected to µSBS testing 24 hr after bonding. Also scanning microscopic evaluations were made on the resin-dentin interfaces of six specimens.
Results The µSBS of group 2 was significantly lower than that of groups 1 and 3 in Single Bond 2 (
p < 0.05). There were significant differences among the uSBS of groups 4, 5, and 6 in Clearfil SE Bond (p < 0.05). Very short and slender resin tags were observed in groups 2 and 5. Long and slender resin tags and lateral branches of tags were observed in groups 3 and 6.Conclusions Treatment of dentin surface using phosphoric acid or self-etching primer improved the adhesion of Er:YAG lased dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Acid or Laser Treatment on Degradation of Dentin Matrix
Aslihan Usumez, Tugrul Sari, Roda Seseogullari Dirihan, Mehmet Esad Guven, Serra Oguz Ahmet, Norbert Gutknecht, Arzu Tezvergil Mutluay
Lasers in Dental Science.2022; 6(2): 99. CrossRef - Ablation of carious dental tissue using an ultrashort pulsed laser (USPL) system
Christoph Engelbach, Claudia Dehn, Christoph Bourauel, Jörg Meister, Matthias Frentzen
Lasers in Medical Science.2015; 30(5): 1427. CrossRef
- Effect of Acid or Laser Treatment on Degradation of Dentin Matrix
- 967 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
- Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test,
p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test,p < 0.05).Conclusions When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
- 1,282 View
- 1 Download

- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):203-210. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of various application methods of one-step self-etch adhesives to microtensile resin-dentin bond strength.
Materials and Methods Thirty-six extracted human molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to twelve groups (
n = 15), according to the three different adhesive systems (Clearfil Tri-S Bond, Adper Prompt L-Pop, G-Bond) and application methods. The adhesive systems were applied on the dentin as follows: 1) The single coating, 2) The double coating, 3) Manual agitation, 4) Ultrasonic agitation. Following the adhesive application, light-cure composite resin was constructed. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and prepared 15 specimens per groups. Then microtensile bond strength was measured and the failure mode was examined.Results Manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating and double coating did. Double coating of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating did and there was no significant difference between the manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation group. There was significant difference in microtensile bonding strength among all adhesives and Clearfil Tri-S Bond showed the highest bond strength.
Conclusions In one-step self-etching adhesives, there was significant difference according to application methods and type of adhesives. No matter of the material, the manual or ultrasonic agitation of the adhesive showed significantly higher microtensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
Nuray Zulkadir Ergin, Aslı Seçilmiş
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 16(3): 356. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef
- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
- 2,039 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparison of marginal microleakage between low and high flowable resins in class V cavity
- Sang-Bae Bae, Young-Gon Cho, Myeong-Seon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):477-483. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the microleakage of low and high viscosity flowable resins in class V cavities applied with 1-step adhesives.
Forty class V cavities were prepared on the cervices of buccal and lingual surfaces of extracted molar teeth and divided into four groups (n=8). Cavities were restored with AQ Bond Plus/Metafil Flo α, G-Bond/UniFil LoFlo Plus (Low flow groups), AQ Bond Plus/Metafil Flo and G-Bond/UniFil Flow (High flow group), respectively.
Specimens were immersed in a 2% methylene blue solution for 24 hours, and bisected longitudinally. They were observed microleakages at the enamel and dentinal margins.
In conclusion, the low viscosity flowable resins showed lower marginal microleakage than do the high viscosity flowable resins in class V cavities.
- 891 View
- 6 Download

- The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
- Jin-hee Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):526-536. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.526
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of various dentin bonding systems on microtensile bond strength of immediate dentin sealing (IDS) and delayed dentin sealing (DDS). Eighteen extracted permanent molars were used in this study. The teeth for DDS group were restored with a provisional restorations, and immersed in saline solution for 1 week, and divided into 3 subgroups according to various dentin bonding adhesives; SB subgroup (3 step total-etch adhesive), SE subgroup (2 step self-etch adhesive), XE subgroup (1 step self-etch adhesive). In IDS group, the teeth were divided into 3 subgroups, and applied with bonding adhesives as in DDS group. The teeth were restored with provisional restorations, and immersed in saline solution for 1 week. Indirect composite disc was cemented with resin cement, and all specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength. The data were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Student t-test.
The results were as follows:
The IDS group showed significantly higher µTBS than DDS group in 3 step total-etch and 2 step self-etch adhesive (p < 0.05).
In IDS and DDS group, 3 step total-etch adhesive showed the highest µTBS value, followed by 2 step self-etch, and 1 step self-etch adhesive. In IDS group, the µTBS value for 1 step self-etch adhesive was significantly different from those of the other subgroups (p < 0.05), and in DDS group, there were statistical differences in all subgroup (p < 0.05).
Failure modes of tested dentin bonding adhesives were mostly mixed failure and only 1 step self-etch adhesive showed adhesive failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 134. CrossRef
- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
- 1,679 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of the additional application of a resin layer on dentin bonding using single-step adhesives
- Seung-Mo Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):313-326. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.313
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to prove that an intermediate resin layer (IRL) can increase the bond strength to dentin by reducing the permeability of single-step adhesives.
Flat dentin surfaces were created on buccal and lingual side of freshly extracted third molar using a low-speed diamond saw under copious water flow. Approximately 2.0 mm thick axially sectioned dentin slice was abraded with wet #600 SiC paper. Three single-step self-etch adhesives; Adper Prompt L-Pop (3M ESPE, St Paul, MN, USA), One-Up Bond F (Tokuyama Corp, Tokyo, Japan) and Xeno III (Dentsply, Konstanz, Germany) were used in this study. Each adhesive groups were again subdivided into ten groups by; whether IRL was used or not; whether adhesives were cured with light before application of IRL or not; the mode of composite application.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. Bond strength of single-step adhesives increased by an additional coating of intermediate resin layer, and this increasement was statistically signigicant when self-cured composite was used (p < 0.001).
2. When using IRL, there were no difference on bond strengths regardless the curing procedure of single-step adhesives.
3. There were no significant difference on bond strengths between usage of AB2 or SM as an IRL.
4. The thickness of hybrid layer was correlated with the acidity of adhesive used, and the nanoleakage represented by silver deposits and grains was examined within hybrid and adhesive layer in most of single-step adhesives.
5. Neither thickness of hybrid layer nor nanoleakage were related to bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative comparison of permeability in the adhesive interface of four adhesive systems
Juhea Chang, Keewook Yi, Hae-Young Kim, In Bog Lee, Byeong Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 51. CrossRef
- Quantitative comparison of permeability in the adhesive interface of four adhesive systems
- 1,597 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
- Sae-Hee Han, Eun-Soung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):169-179. Published online May 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was to compare the microshear bond strength (µSBS) of light- and chemically cured composites to enamel coupled with four 2-step self-etch adhesives and also to evaluate the incompatibility between 2-step self-etch adhesives and chemically cured composite resin.
Crown segments of extracted human molars were cut mesiodistally, and a 1 mm thickness of specimen was made. They were assigned to four groups by adhesives used: SE group (Clearfil SE Bond), AdheSE group (AdheSE), Tyrian group (Tyrian SPE/One-Step Plus), and Contax group (Contax). Each adhesive was applied to a cut enamel surface as per the manufacturer's instruction. Light-cured (Filtek Z250) or chemically cured composite (Luxacore Smartmix Dual) was bonded to the enamel of each specimen using a Tygon tube. After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, the bonded specimens were subjected to µSBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. The mean µSBS (n=20 for each group) was statistically compared using two-way ANOVA, Tukey HSD, and t test at 95% level. Also the interface of enamel and composite was evaluated under FE-SEM.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The µSBS of the SE Bond group to the enamel was significantly higher than that of the AdheSE group, the Tyrian group, and the Contax group in both the light-cured and the chemically cured composite resin (p < 0.05).
2. There was not a significant difference among the AdheSE group, the Tyrian group, and the Contax group in both the light-cured and the chemically cured composite resin.
3. The µSBS of the light-cured composite resin was significantly higher than that of the chemically cured composite resin when same adhesive was applied to the enamel (p < 0.05).
4. The interface of enamel and all 2-step self-etch adhesives showed close adaptation, and so the incompatibility of the chemically cured composite resin did not show.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 30. CrossRef
- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
- 1,156 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Compatibility of self-etching dentin adhesives with resin luting cements
- Do-Wan Kim, Sang-Jin Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):493-504. Published online November 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.493
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was performed to investigate the compatibility between 4 dentin adhesives and 4 resin luting cements.
Dentin adhesives used in this study were All-Bond 2 (Bisco Inc., Schaumbrug, IL, USA), Clearfil SE-Bond (Kuraray Medical Inc, Osaka, Japan), Prompt L-Pop (3M Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, USA), One-Up Bond F (Tokuyama corp., Tokyo, Japan). Resin luting cements used in this study were Choice (Bisco Inc., Schaumbrug, IL, USA), Panavia F (Kuraray Medical Inc, Osaka, Japan), RelyX ARC (3M Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, USA), Bistite II DC (Tokuyama corp., Tokyo, Japan). Combination of each dentin adhesive and corresponding resin cement was made to 16 experimental groups.
Flat dentin surfaces was created on mid-coronal dentin of extracted mandibular third molars, then dentin surface was polished with 320-grit silicon carbide abrasive papers.
Indirect resin composite block (Tescera, Bisco) was fabricated. Its surface for bonding to tooth was polished with silicon carbide abrasive papers. Each dentin adhesive was treated on tooth surface and resin composite overlay were luted with each resin cement. Each bonded specimen was poured in epoxy resin and sectioned occluso-gingivally into 1.0 mm thick slab, then further sectioned into 1.0 × 1.0 mm2 composite-dentin beams. Microtensile bond strength was tested at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. The data were analysed by one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple comparison tests.
The results of this study were as follows;
2-step self-etching dentin adhesive which has additional bonding resin is more compatible than 1-step self-etching dentin adhesive.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
Tae-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Young-Jung Choi, So-Young Yang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 419. CrossRef - Effect of the additional etching procedure on push-out bond strength of one-step resin cement
Soon-Il Kang, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(5): 443. CrossRef - The study of shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin luting cement to dentin
Hee-Sun In, Jong-Il Park, Jong-In Choi, Hye-Won Cho, Jin-Keun Dong
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2008; 46(5): 535. CrossRef - Comparison of bond strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements
Hyun-A Lee, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 499. CrossRef - The Effect of Temporary Filling Materials on The Adhesion between Dentin Adhesive-coated Surface and Resin Inlay
Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 553. CrossRef - The bonding durability of resin cements
Min-Woo Cho, Sang-Hyuk Park, Jong-Ryul Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 343. CrossRef
- Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
- 1,448 View
- 4 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Microshear bond strength of adhesives according to the direction of enamel rods
- Young-Gon Cho, Jong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):344-351. Published online July 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study compared the microshear bond strength (µSBS) to end and side of enamel rod bonded by four adhesives including two total etch adhesives and two self-etch adhesives.
Crown segments of extracted human molars were cut mesiodistally. The outer buccal or lingual surface was used as specimens cutting the ends of enamel rods, and inner slabs used as specimens cutting the sides of enamel rods.
They were assigned to four groups by used adhesives: Group 1 (All-Bond 2), Group 2 (Single Bond), Group 3 (Tyrian SPE/One-Step Plus), Group 4 (Adper Prompt L-Pop). After each adhesive was applied to enamel surface, three composite cylinders were adhered to it of each specimen using Tygon tube. After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, the bonded specimens were subjected to µSBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. The results of this study were as follows;
1. The µSBS of Group 2 (16.50 ± 2.31 MPa) and Group 4 (15.83 ± 2.33 MPa) to the end of enamel prism was significantly higher than that of Group 1 (11.93 ± 2.25 MPa) and Group 3 (11.97 ± 2.05 MPa) (p < 0.05).
2. The µSBS of Group 2 (13.43 ± 2.93 MPa) to the side of enamel prism was significantly higher than that of Group 1 (8.64 ± 1.53 MPa), Group 3 (9.69 ± 1.80 MPa), and Group 4 (10.56 ± 1.75 MPa) (p < 0.05).
3. The mean µSBS to the end of enamel rod was significantly higher than that to the side of enamel rod in all group (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
Sae-Hee Han, Eun-Soung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 169. CrossRef
- Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
- 1,207 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of single step adhesives to dentin
- Young-Gon Cho, Young-Jae Kee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):312-318. Published online July 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.312
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study compared the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of three single step adhesives to dentin.
Occlusal superficial dentin was exposed in fifteen human molars. They were assigned to three groups by used adhesives: Xeno group (Xeno III), Prompt group (Adper Prompt L-Pop), AQ group (AQ Bond).
Each adhesive was applied to dentin surface, and composite of same manufacturer was constructed. The bonded specimens were sectioned into sticks with an interface area approximately 1 mm2, and subjected to µTBS testing with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/minute. The results of this study were as follows;
The µTBS to dentin was 48.78 ± 9.83 MPa for Xeno III, 30.22 ± 4.52 MPa for Adper Prompt L-Pop, and 26.31 ± 7.07 MPa for AQ Bond.
The mean µTBS of Xeno group was significantly higher than that of Prompt group and AQ group (p < 0.05).
There was no significant difference between the µTBS of Prompt group and AQ group.
- 1,002 View
- 5 Download

- Marginal microleakage of single step adhesives
- Young-Gon Cho, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Jae Ki, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):162-169. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the marginal microleakage of five single step adhesives. Class V cavity preparations with occlusal margins in enamel and gingival margins in dentin were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of extracted human molar teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into five groups and restored using one of the single step adhesives and composite resins: Prompt L-Pop/Filtek Z-250 (Group 1), AQ Bond/Metafil CX (Group 2), One-Up Bond F/Palfique Toughwell (Group 3), Futurabond/Admira (Group 4), Xeno III/Spectrum TPH (Group 5).
The restored teeth were thermocycled. Microleakage was assessed by dye penetration using 2% methylene blue dye solution. The teeth were bisected buccolingually and evaluated for microleakage under steromicroscope. The data were statistically analysed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney tests.
The results of this study were as follows;
Microleakage of enamel margins in group 3 was statistically higher than that in groups 1, 2, 4, 5 (p < 0.05).
Microleakage of dentin margins in group 1 was statistically higher than that in groups 2, 5, and that in group 3 was statistically higher than that in groups 2, 4, 5 (p < 0.05).
Dentin marginal microleakage was higher than enamel marginal microleakage in all experimental groups.
In conclusion, Prompt L-Pop showed the least leakage at enamel margin, and AQ Bond showed at dentin margin in this study. Marginal miroleakage in dentin was higher than that in enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microtensile bond strength of single step adhesives to dentin
Young-Gon Cho, Young-Jae Kee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 312. CrossRef - Comparative bond strength of single step adhesives to different dentinal depths
Young-Gon Cho, Cheol-Hee Jin, Jung-Bum Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 319. CrossRef
- Microtensile bond strength of single step adhesives to dentin
- 1,059 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of microhardness and fluoride content of tooth structure by fluoride-containing restorative materials
- Su-Jong Lee, Young-Gon Cho, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):36-43. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the microhardness and the fluoride content of enamel and dentin around fluoride- or non fluoride-containing restorations. Forty extracted human teeth were used and prepared cervical cavities on proximal surface. Experimental teeth were divided into five groups. Group 1 : Prime & Bond NT and Z100, Group 2 : Prime & Bond NT and F2000, Group 3 : Scotchbond Multi-Purpose and Z100, Group 4 : Scothcbond Multi-purpose and F2000, Group 5 : Fuji II LC. The cavities were filled with dentin adhesives and restorative materials. After each tooth was bisected, one half was tested microhardness and the other half was analyzed the fluoride at the enamel and dentin by an EPMA-WDX device. The results were as follows:
1. There was no statistical difference among the microhardness of enamel surface in all group.
2. The microhardness at dentin of 100 µm point in Group 2 and 20 µm point in Group 4 was lower than that of normal dentin (p>0.05).
3. There was no statistical difference among the fluoride content of enamel surface in all group.
4. The fluoride content at the dentin of 30 µm point in Group 2 and 5 were higher than those at 100 µm and 200 µm point in Group 2 and normal dentin (p<0.05).
5. At the dentin of 30 µm point, Group 2 showed higher fluoride content than Group 1 and 3, and Group 5 showed higher fluoride content than other groups.
- 870 View
- 1 Download

- Micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer and resin-based adhesives to dentin
- Hyun-Kyung Hong, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(4):314-325. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.4.314
- 1,103 View
- 1 Download

- The influence of IRM temporary restorations on marginal microleakage of dentin adhesives
- Young-Gon Cho, Hyun-Kyung Kim, Young-Gon Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):1-10. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the influence of IRM on marginal microleakage of 5th generation adhesives. Class V cavities with gingival margins in dentin were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of 60 extracted human molar teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into six groups. Group 1 and 4 received no temporary restoration with IRM. Group 2 and 5 were covered with IRM mixed at P/L ratio(10g/1g). Group 3 and 6 were covered with IRM mixed at P/L ratio(10g/2g). The temporary restorations were removed mechanically with an ultrasonic scaler after one-week storage in distilled water. The cavities were restored using one of two adhesives and composites; Single Bond/Filtek Z 250(Group 1, 2 and 3), UniFil Bond/UniFil F(Group 4, 5 and 6).
Following one day storage in distilled water, the restored teeth were thermocycled for 500 cycles(between 5℃ and 55℃) and immersed in 2% methylene blue for dye penetration testing. The results were analysed using Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked test at a significance level of 0.05.
The results of this study were as follows:
1. Ranking of mean microleakage scores at the enamel margins was Group 1<Group 3<Group 2<Group 4<Group 5<Group 6. The microleakage of Group 6 was significantly higher than that of Groups 1, 2 and 3(p<0.05).
2. At the enamel margins, without regard to pretreatment with IRM, the microleakage of Single Bond was lower than that of UniFil Bond.
3. Ranking of mean microleakage scores at the dentin margins was Group 4<Group 1<Group 5<Group 6<Group 3<Group 2. But there were no significant difference among microleakages of each group(p>0.05).
4. At the dentin margins, the microleakage of the group not pretreated with IRM was lower than that of the group pretreated with IRM. And the microleakage of UniFil Bond was lower than that of Single Bond.
5. Compared with microleakages between the enamel and dentin margins of each groups, Group 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 at dentin margin were higher microleakage than those at enamel margin. There were significant difference between enamel and dentin microleakage of Group 2 and 3(p<0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 327. CrossRef
- Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
- 1,141 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Marginal microleakage of self-etching primer adhesives and a self-etching adhesive
- Young-Gon Cho, Kong-Chul Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(5):493-501. Published online September 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.5.493
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the microleakage performance of four self-etcing primer adhesives(Clearfil SE Bond, Clearfil Liner Bond 2, UniFil Bond, and FL Bond) and one self-etching adhesive(Prompt L-Pop). Class V cavity preparations with occlusal margins in enamel and gingival margins in dentin were prepared on both buccal and lingual surfaces of 50 extracted human molar teeth. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into five groups and restored using one of five adhesives and composite resins: Prompt L-Pop/Filtek Z 250(Group 1), Clearfil SE Bond/Clearfil AP-X(Group 2), Clearfil Liner Bond 2/Clearfil AP-X(Group 3), UniFil Bond/UniFil F(Group 4), and FL Bond/Filtek Z 250(Group 5).
Following one day storage in room temperature water, the restored teeth were thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃. Marginal microleakage was assessed by dye penetration using 2% methylene blue dye. After 24 hours, the teeth were sectioned longitudinally and evaluated for microleakage under steromicroscope. The data were statistically analysed by Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranked tests.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microleakges at both enamel and dentinal margins were the lowest in group 4, increasing among groups in the following order: group 2, follwed by group 5, follwed by group 1, and the highest in group 3.
2. At the enamel margins, the microleakage of group 3 was significantly higher than those of groups 2, 4 and 5(p<0.05), and also the microleakage of group 1 was statistically higher than those of groups 2 and 5(p<0.05).
3. At the dentinal margins, microleakage of group 3 was significantly higher than microleakages of groups 1, 2, 4 and 5(p<0.05).
4. Compared with microleakages between the enamel and dentinal margins of each group, groups 1, 4 and 5 at enamel margin and group 2 and group 3 at dentinal margin were higher microleakage. But there was no significant difference between enamel and dentinal microleakages of each group(p>0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Young-Gon Lee, So-Ra Moon, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 13. CrossRef - Comparison of bond strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements
Hyun-A Lee, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 499. CrossRef - Enamel adhesion of light- and chemical-cured composites coupled by two step self-etch adhesives
Sae-Hee Han, Eun-Soung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 169. CrossRef - Effect of microleakage of a self-etching primer adhesive according to types of cutting instruments
Yong-Hee Kim, Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 327. CrossRef - Influence of appication time of self-etching primers on dentinal microtensile bond strength
Young-Gon Cho, Young-Gon Lee, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park, Jong-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2004; 29(5): 430. CrossRef - Morphological patterns of self-etching primers and self-etching adhesive bonded to tooth structure
Young-Gon Cho, Seok-Jong Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Lee, Soo-Mee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(1): 23. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of self-etching adhesives to dentin and sem analysis
Young-Gon Cho, Kee-Sun Roh, Soo-Mee Kim, Young-Gon Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Jae Ki
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(3): 222. CrossRef - The effect of additional enamel etching on microleakage of the adhesion of self-etching primer system
Jung-Jin Yoon, Kyung-San Min, Chan-Ui Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(5): 363. CrossRef
- Effect of cutting instruments on the dentin bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
- 1,046 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


