-
The influence of bioactive glass (BGS-7) on enamel remineralization: an in vitro study
-
Chaeyoung Lee, Eunseon Jeong, Kun-Hwa Sung, Su-Jung Park, Yoorina Choi
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e33. Published online October 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e33
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
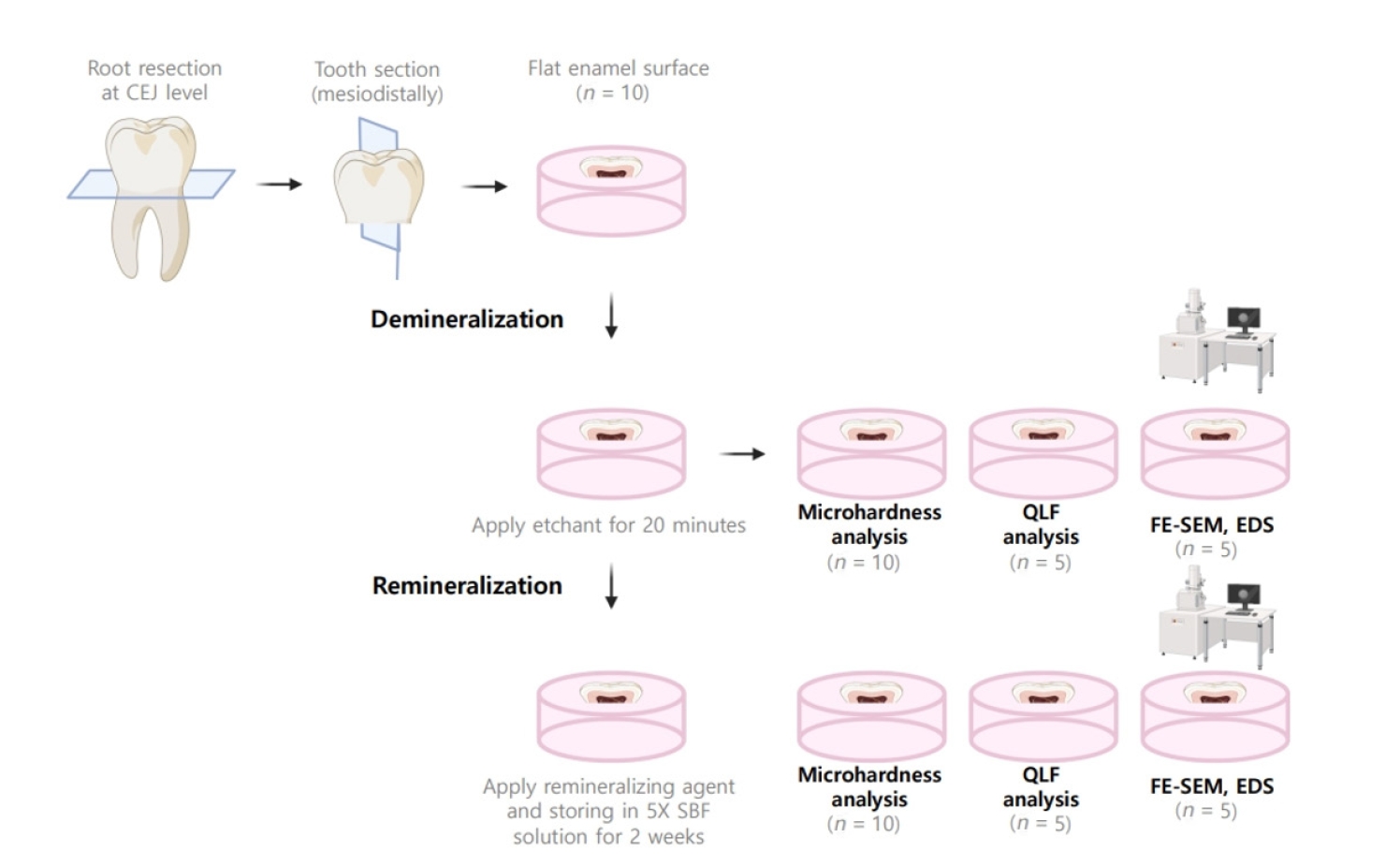
The aim of this study was to compare the remineralizing capacity of bioactive glass (BGS-7, CGBIO) with other agents.
Methods
Twenty caries-free third molars were sectioned and demineralized. Specimens were divided into four groups: (1) control, (2) Clinpro XT varnish (Solventum), (3) 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel, and (4) a new type of CaO-SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 system of bioactive glass ceramics (BGS-7). Agents were applied and stored in simulated body fluid at 37℃ for 2 weeks. Microhardness was measured using the Vickers hardness testing method. Five specimens per group were analyzed using quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF) to assess mineral loss. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) were used to examine the surface morphology and elemental composition. Data were analyzed using paired t-test and one-way analysis of variance (p < 0.05).
Results
BGS-7 showed the highest microhardness values and the greatest recovery in QLF analysis (p < 0.05). FE-SEM revealed granular precipitates on demineralized enamel in the BGS-7 group. EDS confirmed the presence of newly formed silicon and fluoride layers.
Conclusions
BGS-7 demonstrated superior remineralization capacity compared to other agents, suggesting its potential as an effective remineralizing material.
-
Healing after horizontal root fractures: 3 cases with 2-year follow-up
-
Yoorina Choi, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee, Kyung-San Min, Su-Jung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):126-131. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.126
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Among dental traumas, horizontal root fractures are relatively uncommon injuries. Proper initial management and periodical evaluation is essential for the successful treatment of a root-fractured tooth. If pulpal necrosis develops, endodontic treatment is indicated, exclusively for the coronal fragment. Fragment diastases exert a great influence on healing at the fracture line and on pulpal necrosis. An adequately treated root-fractured tooth has a good prognosis. This case report describes the treatment and 2-yr follow up of 3 maxillary central incisors, first with horizontal root fracture, second with horizontal root fracture and avulsion, and third with horizontal root fracture and lateral luxation. All three cases were treated with mineral trioxide aggregate (ProRoot, Dentsply). During 2 yr of follow-up evaluation, the root-fractured teeth of the present patients were well retained in the arch, showing periodontal healing, even after endodontic treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in maxillary central incisor with a horizontal mid root fracture after various management protocols
Kavitha Anantula, Bhavana Vankayala, SarjeevSingh Yadav
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 470. CrossRef - : The Use of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in The Treatment of Horizontal Root Fractures: A Case Presentation and Literature Update
Elif BALLIKAYA, Hamdi GÜNGÖR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 850. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef
-
2,121
View
-
18
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Washout resistance of fast-setting pozzolan cement under various root canal irrigants
-
Ga-Yeon Jang, Su-Jung Park, Seok-Mo Heo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):248-252. Published online November 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.248
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Fast-setting pozzolan cement (Endocem, Maruchi) was recently developed. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of various root canal irrigants on the washout of Endocem in comparison to the previously marketed mineral trioxide aggregate (ProRoot; Dentsply) in a furcal perforation model. Materials and MethodsProRoot and Endocem were placed into acrylic molds on moist Oasis. Each mold was then immediately exposed to either physiologic saline, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), or 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) under gentle shaking for five minutes. Washout testing was performed by scoring scanning electron microscope (SEM) images. ResultsEndocem exhibited higher washout resistance compared to ProRoot, especially in the NaOCl group. ConclusionsThese results suggest that Endocem can be considered a useful repair material for furcal perforation, especially in a single-visit scenario.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Harnessing and Optimizing α-TCP for Oral Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Dentistry
Wenbo Du, Yadong Guo, Janak Lal Pathak, Chen Xiaoshi, Hanfu Su, Liping Wang
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(1): 109288. CrossRef - The Washout Resistance of Bioactive Root-End Filling Materials—A Systematic Review
Joanna Falkowska-Ostrowska, Włodzimierz Dura
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(7): 2446. CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of L-ascorbic acid as an additive for improving the physical properties and setting behavior of fabricated calcium silicate cement
Yun-Jeong Park, Hyeon Seo, Yo-Han Song, Weon-Young Choi, Alphonse Umugire, Heejoo Ryu, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereomicroscopic Evaluation of Sealing Ability of Three Different Furcal Perforation Repair Materials: An In vitro Study
Sriparna De, N Sathyajith Naik, Shivangi Sharma, Pallavi Vashisth, Rasleen Dua, Priya Maheshwari
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 259. CrossRef - Chemical and physical properties of radiopaque Portland cement formulation with reduced particle size
Hoda Mohamed ELNAWAWY, Muralithran Govindan KUTTY, Noor Azlin YAHYA, Noor Hayaty ABU KASIM, Paul Roy COOPER, Josette CAMILLERI, Hany Mohamed Aly AHMED
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 672. CrossRef - The Washout Resistance of Bioactive Root-End Filling Materials
Joanna Falkowska, Tomasz Chady, Włodzimierz Dura, Agnieszka Droździk, Małgorzata Tomasik, Ewa Marek, Krzysztof Safranow, Mariusz Lipski
Materials.2023; 16(17): 5757. CrossRef - Effects of fast- and slow-setting calcium silicate–based root-end filling materials on the outcome of endodontic microsurgery: a retrospective study up to 6 years
Dohyun Kim, Hyunjung Lee, Minsun Chung, Sunil Kim, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(1): 247. CrossRef - Novel anti-biofouling bioactive calcium silicate-based cement containing 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine
Jae-Sung Kwon, Myung-Jin Lee, Ji-Young Kim, Dohyun Kim, Jeong-Hyun Ryu, Sungil Jang, Kwang-Mahn Kim, Chung-Ju Hwang, Sung-Hwan Choi, Jinkee Hong
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0211007. CrossRef - Surface and vertical dimensional changes of mineral trioxide aggregate and biodentine in different environmental conditions
Hacer Aksel, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevinc Askerbeyli Õrs, Eda Karaismailoğlu
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Push-out Bond Strength of Fast-setting Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Pozzolan-based Cements: ENDOCEM MTA and ENDOCEM Zr
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Nancy Kudsi Carvalho, Marta Reis da Costa Labanca Guberman, Marina Prado, Plinio Mendes Senna, Erick M. Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(5): 801. CrossRef - Dynamic intratubular biomineralization following root canal obturation with pozzolan‐based mineral trioxide aggregate sealer cement
Yeon‐Jee Yoo, Seung‐Ho Baek, Kee‐Yeon Kum, Won‐Jun Shon, Kyung‐Mi Woo, WooCheol Lee
Scanning.2016; 38(1): 50. CrossRef - Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
Jing-Ling Che, Jae-Hwan Kim, Seon-Mi Kim, Nam-ki Choi, Hyun-Joo Moon, Moon-Jin Hwang, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(1): 61. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of the Use of ProRoot Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Endocem as Direct Pulp Capping Materials: 3-month versus 1-year Outcomes
Youngjune Jang, Minju Song, Il-Sang Yoo, Yunjung Song, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(8): 1201. CrossRef - Odontogenic effects of a fast-setting calcium-silicate cement containing zirconium oxide
Kyoung-A KIM, Yeon-Mi YANG, Young-Sun KWON, Yun-Chan HWANG, Mi-Kyung YU, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2015; 34(4): 432. CrossRef - D90: The Strongest Contributor to Setting Time in Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Portland Cement
William N. Ha, Dale P. Bentz, Bill Kahler, Laurence J. Walsh
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1146. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of the Use of ProRoot Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Endocem as Direct Pulp Capping Materials
Minju Song, Minji Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(1): 11. CrossRef - Physical properties and biological/odontogenic effects of an experimentally developed fast-setting α-tricalcium phosphate-based pulp capping material
Jun-Bong Lee, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Ha Kim, Young-Sun Kwon, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
BMC Oral Health.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Surface Treatments on Morphology and Bond Strength to Composite Resin
Joo-Hee Shin, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1210. CrossRef
-
1,494
View
-
6
Download
-
19
Crossref
-
Comparison of the centering ability of Wave·One and Reciproc nickel-titanium instruments in simulated curved canals
-
Young-Jun Lim, Su-Jung Park, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):21-25. Published online February 26, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of newly marketed single-file instruments, Wave·One (Dentsply-Maillefer) and Reciproc (VDW GmbH), in terms of maintaining the original root canal configuration and curvature, with or without a glide-path. Materials and MethodsAccording to the instruments used, the blocks were divided into 4 groups (n = 10): Group 1, no glide-path / Wave·One; Group 2, no glide-path / Reciproc; Group 3, #15 K-file / Wave·One; Group 4, #15 K-file / Reciproc. Pre- and post-instrumented images were scanned and the canal deviation was assessed. The cyclic fatigue stress was loaded to examine the cross-sectional shape of the fractured surface. The broken fragments were evaluated under the scanning electron microscope (SEM) for topographic features of the cross-section. Statistically analysis of the data was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test (α = 0.05). ResultsThe ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1 and 2 mm levels was significantly lower in Group 1 (p < 0.05). The centering ratio at 3, 5, and 7 mm level were not significantly different. ConclusionsThe Wave·One file should be used following establishment of a glide-path larger than #15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of ProTaper, Mtwo, WaveOne, and Reciproc Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: In Vitro Study
M Remya, Asha Joseph, Prabath Singh, Anju Varughese, Pallavi Chandran, Deepthy Subramanian, S Vijay Kumar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(6): 589. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Canal transportation and centering ability of root canals prepared using rotary and reciprocating systems with and without PathFiles in cone-beam computed tomography-based three-dimensional molar prototypes
MSruthi Sunildath, Josey Mathew, Liza George, RV Vineet, Priya Thomas, Dhanya John
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 246. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciproc R25 File and Mtwo System Used in Continuous and Reciprocating Motion
Vincenzo Campanella, Leonardo Gianni, Antonio Libonati, Gianni Gallusi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(2): 171. CrossRef - Canal shaping with a reciprocating system is easy to learn
E. Muñoz, L. Forner, S. Garcet, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, C. Llena
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1244. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of HyFlex EDM and ProTaper Next Rotary Instruments in Curved Root Canals: A Micro-CT Study
Ahmed K Turkistani, Madiha M Gomaa, Lubna A Shafei, Loai Alsofi, Abdul Majeed, Emad AlShwaimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(6): 680. CrossRef - Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of ProTaper Next and 2Shape nickel–titanium files in simulated severe curved canals
Simone Staffoli, Taha Özyürek, Avi Hadad, Alex Lvovsky, Michael Solomonov, Hadas Azizi, Joe Ben Itzhak, Maurizo Bossù, Nicola M. Grande, Gianluca Plotino, Antonella Polimeni
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2018; 32(2): 52. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Rotary endodontics in primary teeth – A review
Sageena George, S. Anandaraj, Jyoti S. Issac, Sheen A. John, Anoop Harris
The Saudi Dental Journal.2016; 28(1): 12. CrossRef - Performance of Three Single Instrument Systems in the Preparation of Long Oval Canals
Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Fredson Marcio Acris de Carvalho, Flares Baratto-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2016; 27(2): 217. CrossRef - Quantitative transportation assessment in curved canals prepared with an off-centered rectangular design system
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal SILVA, Vania Cristina Gomes VIEIRA, Michele Dias Nunes TAMEIRÃO, Felipe Gonçalves BELLADONNA, Aline de Almeida NEVES, Erick Miranda SOUZA, Gustavo DE-DEUS
Brazilian Oral Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Cervical and Apical Enlargement Associated with the WaveOne System on the Transportation and Centralization of Endodontic Preparations
Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Kauhanna Vianna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 626. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Brushing Motion on the Cutting Behavior of 3 Reciprocating Files in Oval-shaped Canals
Shereen Alattar, Walid Nehme, Franck Diemer, Alfred Naaman
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 703. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue of instruments for endodontic glide path
Gianluca Gambarini, Gianluca Plotino, GianPaolo Sannino, Nicola Maria Grande, Alessio Giansiracusa, Lucila Piasecki, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Dina Al-Sudani, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2015; 103(1): 56. CrossRef - Influence of the glide path on various parameters of root canal prepared with WaveOne reciprocating file using cone beam computed tomography
Anil Dhingra, Nidhi Nagar, Vipul Sapra
Dental Research Journal.2015; 12(6): 534. CrossRef - Apical Transportation, Centering Ability, and Cleaning Effectiveness of Reciprocating Single-file System Associated with Different Glide Path Techniques
Guilherme Moreira de Carvalho, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Junior, Angela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido, Raphael Carlos Comelli Lia, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, André Augusto Franco Marques
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 2045. CrossRef - Influence of cervical preflaring on apical transportation in curved root canals instrumented by reciprocating file systems
Neisiana Barbieri, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marina Samara Baechtold, Gisele Maria Correr, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, João César Zielak, Flares Baratto-Filho
BMC Oral Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Assessment of Reciprocation in Endodontic Preparation: A Comprehensive Review—Part II: Properties and Effectiveness
Gianluca Plotino, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Nicola Maria Grande, Stephen Cohen, Frédéric Bukiet
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 1939. CrossRef - Influence of flexion angle of files on the decentralization of oval canals during instrumentation
Maria Antonieta Veloso Carvalho de OLIVEIRA, Letícia Duarte ALVES, Analice Giovani PEREIRA, Luís Henrique Araújo RAPOSO, João Carlos Gabrielli BIFFI
Brazilian Oral Research.2015; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Quantitative Transportation Assessment in Simulated Curved Canals Prepared with an Adaptive Movement System
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Michele Dias Nunes Tameirão, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1125. CrossRef - Efficacy of reciprocating and rotary systems for removing root filling material: A micro-computed tomography study
D. Helvacioglu-Yigit, A. Yilmaz, G. Kiziltas-Sendur, O. S. Aslan, P. V. Abbott
Scanning.2014; 36(6): 576. CrossRef - Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 104. CrossRef - Performance of RaCe Instrumentation System in Curved Root Canals: A Comprehensive Analysis by Three Study Methods
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Gilson Blitzkow Sydney, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Flares Baratto-Filho, Samantha Schaffer Pugsley Baratto, Paulo Sergio Cerri
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 230. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 167. CrossRef
-
1,433
View
-
7
Download
-
29
Crossref
-
Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry
-
Hee-Jin Kim, Lorena Karanxha, Su-Jung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):236-239. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.236
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Although several methods including composite resin restoration and microabrasion have been used for management of white spot lesion, tooth jewelry can be considered as another noninvasive option. This case report describes the management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry. This report also highlights the patients' preference for tooth jewelry as an esthetic concern. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Putting the mouth back in the body – the neglected area of dental and oral travel health
Irmgard L Bauer
Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth adornments, gems, and grills
Harpuneet Kaur
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2022; 12(2): 50. CrossRef - Gold Enamel Choumps – A Case report
Sargam D. Kotecha, Y. Deepa Hedge, Kalpna Chaudhry, Ramakrishna Yeluri, Updesh Masih, Chanchal Singh
Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences.2016; 6(3): 303. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef
-
1,310
View
-
4
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
-
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):29-33. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.29
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microleakage of 4 temporary materials in teeth with Class II-type endodontic access preparations by using a glucose penetration model.
Materials and Methods
Glucose reaction test was performed to rule out the presence of any reaction between glucose and temporary material. Class II-type endodontic access preparations were made in extracted human premolars with a single root (n = 10). Each experimental group was restored with Caviton (GC), Spacer (Vericom), IRM (Dentsply-Caulk), or Fuji II(GC). Microleakage of four materials used as temporary restorative materials was evaluated by using a glucose penetration model. Data were analyzed by the one-way analysis of variance followed by a multiple-comparison Tukey test. The interface between materials and tooth were examined under a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results
There was no significant reaction between glucose and temporary materials used in this study. Microleakage was significantly lower for Caviton and Spacer than for Fuji II and IRM. SEM observation showed more intimate adaptation of tooth-restoration interfaces in Caviton and Spacer than in IRM and Fuji II.
Conclusions
Compared to IRM and Fuji II, Caviton and Spacer can be considered better temporary sealing materials in Class II-type endodontic access cavities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Sealing Ability, Water Absorption, and Solubility of Three Temporary Restorative Materials: An in vitro Study
AR Prabhakar, N Shantha Rani
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(2): 136. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef
-
1,916
View
-
10
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
The evaluation of color and color difference according to the layering placement of Incisal shade composites on the body composites of the indirect resin restoration
-
Su-Jung Park, Han-Young Lee, Myong-Yun Nah, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):37-49. Published online January 14, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
Objectives:
The aim of this study was to evaluate the surface color of indirect resin restoration according to the layering placement of different shade of incisal composite.
Materials and Methods:
In this study, CIE L*a*b* value of 16 Body composite of Tescera ATL (Bisco, Schaumburg IL, USA) was measured by spectrophotometer (NF999, Nippon Denshuku, Japan), and compared to CIE L*a*b* value of Vitapan shade guide. Nine shade Incisal composite of Tescera ATL were buildup to 1 mm thickness on Body composites inlay block, and CIE L*a*b* value was measured. Incisal composite was ground to 0.5 mm thickness and CIE L*a*b* value was re-measured. Color difference between Body composite and Incisal composites layered on Body composite was calculated as a function of thickness.
Results:
Color difference between corresponding shade of Tescera Body composite and Vitapan shade guide was from 6.88 to 12.80.
L* and b*value was decreased as layering thickness of Incisal composite on Body composite was increased. But, a* value did not show specific change tendency.
Conclusions:
Surface color difference between Body composites and Incisal composites layered on Body composite was increased as the layering thickness of Incisal composite increased (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Color stability of esthetic restorative materials after application of fluoride varnishes
Chul-Hoon Jang, Dong-Gil Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2021; 48(3): 147. CrossRef - Color Change in Tooth Induced by Various Calcium Silicate-Based Pulp-Capping Materials
Jiyoon Jeon, Namki Choi, Seonmi Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(3): 280. CrossRef - Discrimination between FRC-post and core according to the color difference
Jou-Hwe Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2015; 31(2): 75. CrossRef - Optical characteristics of resin composite before and after polymerization
Ah-Hyang Eom, Duck-Su Kim, Soo-Hee Lee, Chang-Won Byun, Noh-Hoon Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 219. CrossRef
-
1,049
View
-
2
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Influence of the color of composite resins applied to lingual surface on the labial tooth color
-
Seung-Hui Mun, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):309-323. Published online July 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.309
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
In this study we evaluated the influence of both the thickness of residual enamel and the color of the composite resins applied to lingual surface on the labial surface color.
Background plates were made by randomly (A1, A2, A6D, B1, B2, B3, C1, C2, C6D) selected colors of Filtek Supreme (3M ESPE, St. Paul, U.S.A.) composite resin.
Crown portion of 9 maxillary central incisors were cut off and embedded with acrylic resin except labial surface. Samples of average thickness of 2.2 mm were obtained after cutting it in a thickness of 2.5 mm from the labial surface and sandpaper polish.
The shade of composite resin background was measured using Spectrophotometer (Spectrolino® GretagMacbeth, Regensdorf, Switzerland). And CIE L*a*b* value of 2.2 mm thickness tooth samples were measured on the 9 composite resin backgrounds. And then, the cutting side of tooth samples was ground to the extent of 1.9 mm, 1.6 mm, 1.3 mm, 1.0 mm and placed on composite resin backgrounds and measured L*a*b* values with the same method.
In all samples, L* value and b* value seemed to have a tendency of decreasing as thickness of tooth sample becomes thinner regardless of background colors (p < 0.05). But, a* value didn't show the significant differences depending on the thickness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of Use of Opaque Single-Shade Composite Resin and Residual Dentin Thickness on the Esthetic Performance of Single-Shade Composite Resin
Suyeon Lee, Juhyun Lee, Minho Hong, Haeni Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2025; 52(3): 253. CrossRef - Evaluation of the color stability of light cured composite resins according to the resin matrices
Da-Hye Yu, Hyun-Jin Jung, Sung-Hyeon Choi, In-Nam Hwang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(2): 109. CrossRef
-
912
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Color difference of the dental composites measured by different color measuring instruments
-
Su-Jung Park, Eun-Young Noh, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):199-207. Published online May 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.199
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of color measuring instrument by measuring the color of dental composite resins.
Nine shade light cured composite resin disks were prepared (diameter : 15 mm, thickness : 4 mm). CIE L*a*b* color scale of each disk was measured with 3 different types of spectrophotometer [MiniScan XE plus (Model 4000S, Hunter Lab, USA), CM-3500d (Minolta, Japan) and Specbos 2100 Miniature VIS Reflection spectrometer (Serial No: 319416, JETI Technishe VIS Instrumentic GmbH, Germany)]. Miniscan XE Plus and CM-3500d using identical measuring geometry with different size of viewing aperture. But Specbos 2100 using different measuring geometry.
Within the limitation of this study, there were color difference (ΔE*) from 2.4 to 7.8 between Miniscan XE Plus and CM-3500d, but L*, a*, b* values showed the high correlation. However, there were great color difference (ΔE*) in the extent of about 20 between instruments with the different measuring geometry.
Therefore, color scale measured by color measuring instrument should be used as a relative value rather than an absolute value in the field of dentistry. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Color Change in Tooth Induced by Various Calcium Silicate-Based Pulp-Capping Materials
Jiyoon Jeon, Namki Choi, Seonmi Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(3): 280. CrossRef - Effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion and flexural strength
Ji-A Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 324. CrossRef
-
878
View
-
5
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Influence of adhesive application on shear bond strength of the resin cement to indirect resin composite
-
Mi-Hae Song, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):419-427. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.419
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study analyzed the influence of dental adhesive/primer on the bond strength between indirect resin composite and the resin cement.
Seventy disc specimens of indirect resin composite (Tescera Dentin, Bisco) were fabricated. And bonding area of all specimens were sandblasted and silane treated for one minute. The resin cements were used with or without application of adhesive/primer to bonding area of indirect resin restoration: Variolink-II (Ivoclar-Vivadent): Exite DSC, Panavia-F (Kuraray): ED-Primer, RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE): Single-Bond, Duolink (Bisco): One-step, Mulitlink (Ivoclar-Vivadent): Multilinh Primer.
Shear bond strength was measured by Instron universal testing machine.
Adhesive application improved shear bond strength (p < 0.05). But Variolink II and Panavia-F showed no statistically significant difference according to the adhesive application.
With the above results, when resin inlay is luted by resin cement it seems that application of dental adhesive/primer is necessary in order to improve the bond strength. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 223. CrossRef - Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 103. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
-
1,058
View
-
3
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Evaluating the reliability and repeatability of the digital color analysis system for dentistry
-
Joong-Jae Jeong, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):352-368. Published online July 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.352
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study was done to evaluate the reliability of the digital color analysis system (ShadeScan, CYNOVAD, Montreal, Canada) for dentistry.
Sixteen tooth models were made by injecting the A2 shade chemical cured resin for temporary crown into the impression acquired from 16 adults. Surfaces of the model teeth were polished with resin polishing cloth. The window of the ShadeScan handpiece was placed on the labial surface of tooth and tooth images were captured, and each tooth shade was analyzed with the ShadeScan software. Captured images were selected in groups, and compared one another.
Two models were selected to evaluate repeatability of ShadeScan, and shade analysis was performed 10 times for each tooth.
And, to ascertain the color difference of same shade code analyzed by ShadeScan, CIE L*a*b*values of shade guide of Gradia Direct (GC, Tokyo, Japan) were measured on the white and black background using the Spectrolino (GretagMacbeth, USA), and Shade map of each shade guide was captured using the ShadeScan.
There were no teeth that were analyzed as A2 shade and unique shade. And shade mapping analyses of the same tooth revealed similar shade and distribution except incisal third.
Color difference (ΔE*) among the Shade map which analyzed as same shade by ShadeScan were above 3.
Within the limits of this study, digital color analysis instrument for dentistry has relatively high repeatability, but has controversial in accuracy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development of polarization dental imaging modality and evaluation of its clinical feasibility
Eunji Kim, Taeyoon Son, Yoon Lee, Byungjo Jung
Journal of Dentistry.2012; 40: e18. CrossRef
-
1,210
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Color stability of the resin cements with accelerated aging
-
Ha-Jeung Song, Su-Jung Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):389-396. Published online July 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.389
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the color stability of resin cements with accelerated test. Four dual curing resin cements: Panavia-F (KURARAY), Duolink (BISCO), Variolink-II (Ivoclar Vivadent), and RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE) and 1 self curing resin cement: Resiment CE (j. l. Blosser) were used in this study. In control group, Gradia Anterior (GC) composite resin and Tescera Dentin (Bisco) indirect composite were used. Ten disk shape specimens were made from each resin cement. The specimens were subjected to an accelerated aging process in a refrigerated bath circulator at 60℃ for 15 and 30 days. Spectrophotometric analyses were made before and after 15 days and 30 days of accelerated aging time.
The color characteristics (L*, a*, b*) and the color difference (ΔE*) of the specimens before and after immersion were measured and computed.
Regardless of type of the resin cements, L* value was decreased and a* value was increased, but there were no significant difference. But b* value was increased significantly (p < 0.05). Tescera inlay showed least color change (p < 0.05), but Gradia showed notable color change after 15 days.
After 30 days on accelerated aging, ΔE* value was increased (Panavia-F < Variolink-II < Resiment CE < Duolink < Unicem) (p < 0.05), but there were no significant difference among Panavia-F, Variolink-II, and Resiment CE groups. After 30 days of accelerated aging, ΔE* value of all resin cements were greater than 3.0 and could be perceived by the human eye. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of light-curing on the translucence change and color stability of amine-free dual-cured resin cements
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Bo-Ram Lee, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(3): 165. CrossRef - Effect of Accelerated Aging on the Color Stability of Dual-Cured Self-Adhesive Resin Cements
Ah-Rang Kim, Yong-Chan Jeon, Chang-Mo Jeong, Mi-Jung Yun, Jung-Bo Huh
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2015; 8(2): 49. CrossRef
-
1,198
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Influence of the labial surface irregularity on the measurement of the tooth color by spectrometer
-
Yong-Jin Choi, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Byung-Ju Park, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):411-418. Published online September 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.411
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The most scientific and reliable method for deciding the tooth color is the instrumental measurement. However, such color measuring instrument shows the difference of the measuring value according to the diversified measuring condition.
This study was conducted to evaluate what effect of the labial surface irregularity of the tooth to the result of the color measured by spectrometer.
11 models of the teeth were made by injecting the A2 shade Luxatemp Automix Plus (DMG, Germany) into the impression acquired from 11 adults. Standard disk samples (15 mm diameter, 7 mm thickness) were made with same material. CIE L*a*b* value was measured at the incisal, central, and gingival area of the central incisor, lateral incisor, canine and first premolar using Specbos 2100 (JETI, Germany) spectrometer. Color difference was calculated between labial surface and standard samples.
Among all models of the teeth, L* and b* value showed the reducing tendency as they go toward the gingival area, but a* value showed the increasing tendency.
Color difference between model teeth and standard samples showed the most difference at the incisal area, but the gingival area showed the least difference. And the canine showed the least color difference from the comparison of standard sample, and the central incisor showed the highest difference (p < 0.01).
Although the visually detectable difference of the measuring value showed notably depending on the type and measured area (p < 0.05), L* and a* value showed notable differences depending more on the measured areas than on the type of the teeth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Study on Digital Color Reproduction for Recording Color Appearance of Cultural Heritage
Hyeong Rok Song, Young Hoon Jo
Journal of Conservation Science.2022; 38(2): 154. CrossRef
-
1,015
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Proposal of new dental color-space for aesthetic dental materials
-
Yun-Jeong Oh, Su-Jung Park, Dong-Jun Kim, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):19-27. Published online January 31, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.019
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to develope new dental color-space system. Twelve kinds of dental composites and one kind of dental porcelain were used in this study. Disk samples (15 mm in diameter, 4 mm in thickness) of used materials were made and sample's CIE L*a*b* value was measured by Spectrocolorimeter (MiniScan XE plus, Model 4000S, diffuse/8° viewing mode, 14.3 mm Port diameters, Hunter Lab. USA). The range of measured color distribution was analyzed. All the data were applied in the form of T### which is expression unit in CNU Cons Dental Color Chart.
The value of L* lies between 80.40 and 52.70. The value of a* are between 10.60 and 3.60 and b* are between 28.40 and 2.21. The average value of L* is 67.40, and median value is 67.30. The value of a* are 2.89 and 2.91 respectively. And for the b*, 14.30 and 13.90 were obtained. The data were converted to T### that is the unit count system in CNU-Cons Dental Color Chart. The value of L* is converted in the first digit of the numbering system. Each unit is 2.0 measured values. The second digit is the value of a* and is converted new number by 1.0 measured value. For the third digit b* is replaced and it is 2.0 measured unit apart. T555 was set to the value of L* ranging from 66.0 to 68.0, value of a* ranging from 3 to 4 and b* value ranging from 14 to 16. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Difference in color and translucency according to dental zirconia A3 colorant
Joo-Hee Lee, Jin-Young Park
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2022; 44(4): 118. CrossRef
-
978
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Influence of the Surface roughness on translucency and surface color of the dental composite resins
-
Kyu-Jeong Cho, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):312-322. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.312
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effect of surface roughness on the surface color and translucency of the composite resins.
Two composite resins (Esthet-X, Dentsply, Milford, USA and Charisma, Kulzer, Domagen, Germany) were used to investigate the surface color. Charisma was used to investigate the translucency. 40 disc samples (diameter: 8 mm, thickness: 5 mm) were made by each product to measure the surface color. Polymerized each sample's one side was treated by Sof-Lex finishing and polishing system (Group C, M, F, SF). 40 disc samples (diameter: 6 mm, thickness: 1 mm) were prepared to measure the opacity. 1 mm samples were ground one side with #600, #1000, #1500 and #2000 sandpapers. CIE L*a*b* values of each 5 mm thickness samples, and XYZ values of 1 mm thickness samples on the white and black background were measured with spectrophotometer (Spectrolino, GretagMacbeth, Regensdorf, Switzerland).
Mean surface roughness (Ra) of all samples before and after surface treatment was measured using the Surface Roughness Tester SJ-301 (Mytutoyo, Tokyo, Japan).
Regardless of type and shade of the composite resin, L* values measured in group C were higher than others (p < 0.05), and L* value decreased as the Ra value decreased except B3 shade of Esthet-X. But there were no significant difference in a* values among groups. In control group and SF, highest b* values were measured (p < 0.05), except B1 shade of Esthet-X.
Contrast ratio decreased as the Ra value decreased (p < 0.05).
With the above results, difference of surface roughness has influence on surface color and translucency of dental composite resins. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of Smokeless Tobacco on Color Stability and Surface Roughness of 3D-Printed, CAD/CAM-Milled, and Conventional Denture Base Materials: An In Vitro Study
Maryam H. Mugri, Saurabh Jain, Mohammed E. Sayed, Amjad Hussain Asiri Halawi, Safa Ahmed Ibrahim Hamzi, Raniya Abdulaziz Saad Aljohani, Zainab Mousa Ali Madkhali, Asaad Khalid, Hossam F. Jokhadar, Mai Almarzouki, Ghaida A. Alhumaidan, Ahid Amer Alshahrani
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 491. CrossRef - Optical characteristics of resin composite before and after polymerization
Ah-Hyang Eom, Duck-Su Kim, Soo-Hee Lee, Chang-Won Byun, Noh-Hoon Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 219. CrossRef - Surface roughness and color stability of various composite resins
Sung-Yi Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 542. CrossRef
-
1,365
View
-
0
Download
-
3
Crossref
|