Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- In vitro experimental study comparing continuous and intermittent irrigation protocols: influence of sodium hypochlorite volume and contact time on tissue dissolution
- Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Gwenael Rolin, Camille Coussens, Aurelian Louvrier, Felipe G Belladonna, Edouard Euvrard, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e36. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
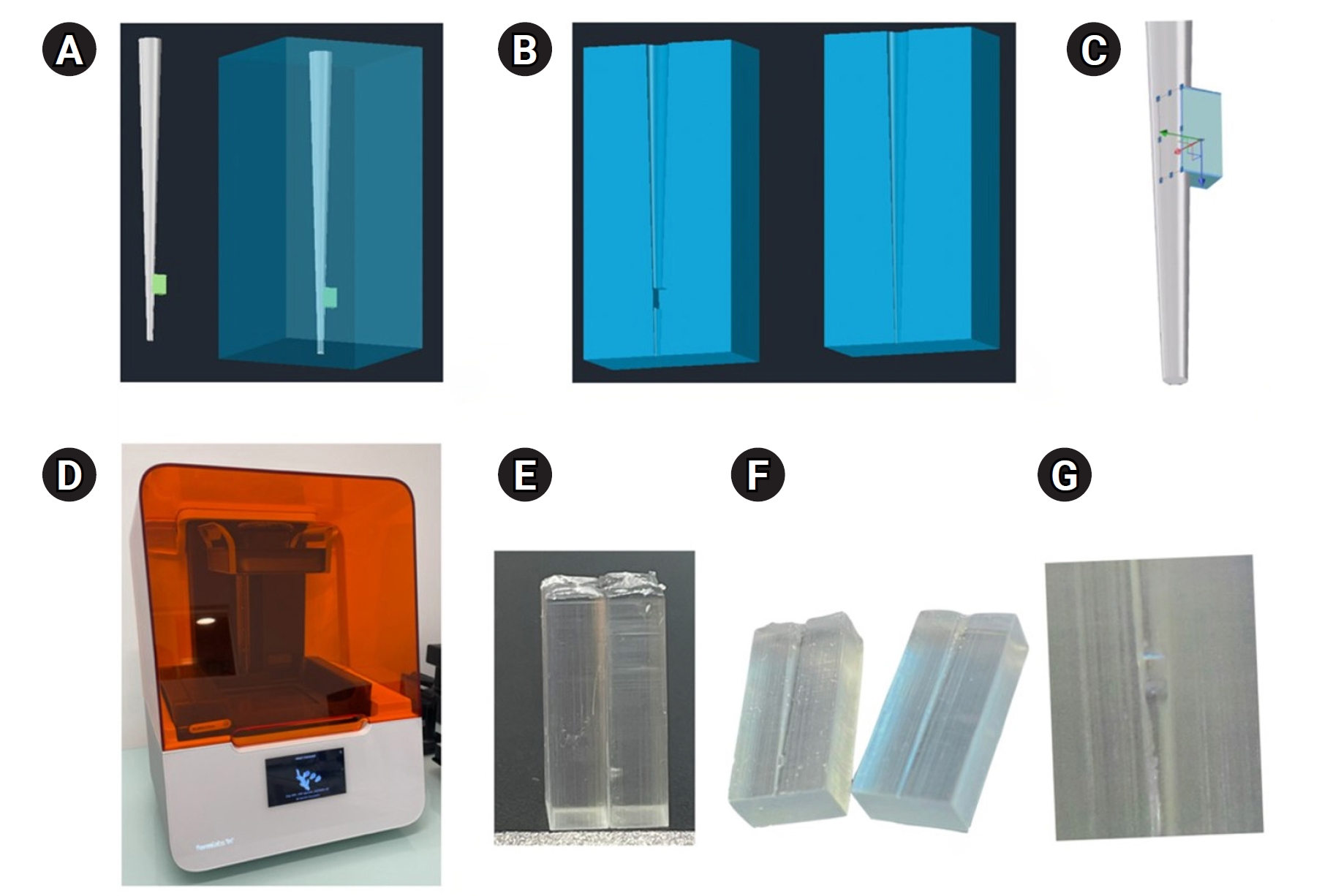
This study aimed to evaluate whether continuous irrigation with larger volumes or allowing sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) resting time is more critical for pulp tissue dissolution using a controlled artificial root canal system.
Methods
A three-dimensional printed artificial root canal with a lateral canal in the apical third was fabricated. Standardized bovine pulp tissue specimens were inserted, and three irrigation protocols were tested: group A (continuous NaOCl irrigation at 1 mL/min via syringe pump), group B (intermittent NaOCl irrigation with 0.1 mL and a 3-minute resting period), and group C (control, saline irrigation). The time for complete dissolution and the total NaOCl volume were recorded.
Results
Complete dissolution occurred in groups A and B, with significant differences in NaOCl volume and time (p < 0.05). In group A, complete dissolution was consistently observed after the 6th irrigation cycle, corresponding to a total NaOCl volume of 6.0 ± 0.66 mL per test. The average time required for complete dissolution in this group was 6 ± 0.66 minutes. In group B, complete dissolution occurred after the 4th cycle, with a total NaOCl volume of 0.4 ± 0.06 mL per test and a mean dissolution time of 12.6 ± 1.8 minutes.
Conclusions
NaOCl volume and exposure time significantly influence pulp tissue dissolution.
- 1,549 View
- 159 Download

- The effect of limonene extract on the adhesion of different endodontic cements to root dentin: an in vitro experimental study
- Nayara Lima Ferraz Aguiar, Eduardo José Soares, Guilherme Nilson Alves dos Santos, Anna Luísa Araújo Pimenta, Laryssa Karla Romano, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e16. Published online May 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
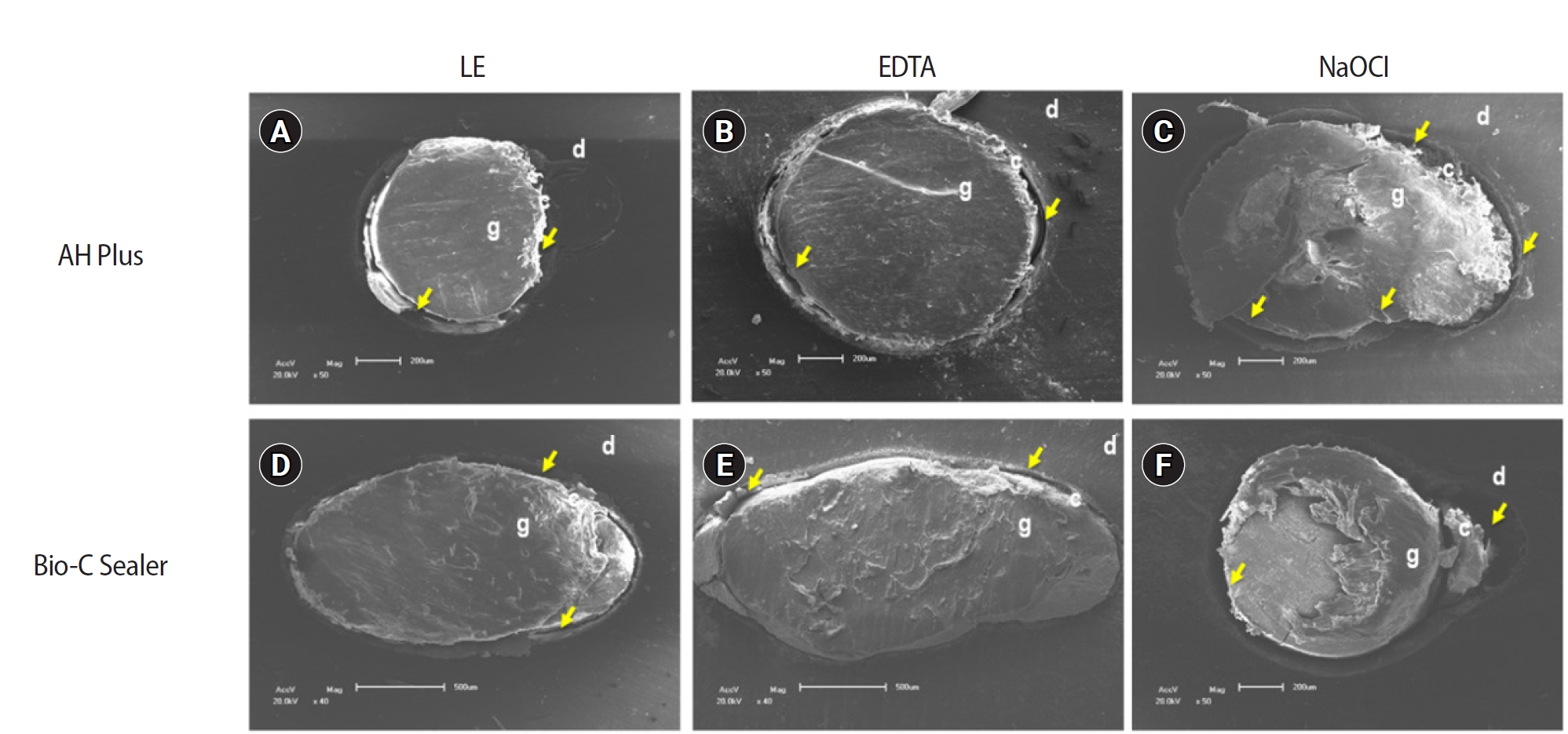
The study aimed to evaluate the effect of limonene extract (LE) on push-out bond strength (BS) to root dentin in endodontically treated teeth.
Methods
Single-rooted teeth were selected and instrumented using the reciprocating technique, then divided into three groups based on the final irrigating solution: 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and 5% LE. The roots were further divided (n = 12) and obturated using the single-cone technique with epoxy resin-based (ERB) or bioceramic sealer (Bio-C). After 3 days, the roots were sectioned into 2-mm slices, obtaining two slices from each root third. Push-out BS testing was conducted at 0.5 mm/min, followed by failure pattern and adhesive interface analysis using scanning electron microscopy. Push-out BS data were analyzed by three-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
Results
ERB showed higher BS when irrigated with EDTA (5.0 ± 2.3 MPa) compared to NaOCl (1.8 ± 1.1 MPa) (p = 0.0005), particularly in the cervical third. LE yielded intermediate values without significant differences from the other irrigants (3.5 ± 1.9 MPa) (p > 0.05). For Bio-C, the highest BS was observed in the apical third, especially with LE (9.4 ± 5.0 MPa), differing from other thirds and final irrigating solutions (p < 0.05). Mixed failure patterns were most prevalent, regardless of the irrigant solutions.
Conclusions
The combination of LE with Bio-C demonstrated superior BS in the apical third, suggesting its potential as a final irrigating solution in endodontic treatments.
- 2,499 View
- 220 Download

- Impact of different agitation methods on smear layer cleaning of mesial canals with accentuated curvature
- Abel Teves Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Michel Espinosa Klymus, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e12. Published online March 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the impact of different methods of irrigant agitation on smear layer removal in the apical third of curved mesial canals of 3 dimensionally (D) printed mandibular molars.
Materials and Methods Sixty 3D-printed mandibular second molars were used, presenting a 70° curvature and a Vertucci type II configuration in the mesial root. A round cavity was cut 2 mm from the apex using a trephine of 2 mm in diameter, 60 bovine dentin disks were made, and a smear layer was formed. The dentin disks had the adaptation checked in the apical third of the teeth with wax. The dentin disks were evaluated in environmental scanning electron microscope before and after the following irrigant agitation methods: G1(PIK Ultrasonic Tip), G2 (Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation with Irrisonic– PUI), G3 (Easy Clean), G4 (HBW Ultrasonic Tip), G5 (Ultramint X Ultrasonic tip), and G6 (conventional irrigation-CI) (
n = 10). All groups were irrigated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid.Results All dentin disks were 100% covered by the smear layer before treatment, and all groups significantly reduced the percentage of the smear layer after treatment. After the irrigation protocols, the Ultra-X group showed the lowest coverage percentage, statistically differing from the conventional, PIK, and HBW groups (
p < 0.05). There was no significant difference among Ultramint X, PUI-Irrisonic, and Easy Clean (p > 0.05). None of the agitation methods could remove the smear layer altogether.Conclusions Ultramint X resulted in the most significant number of completely clean specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A new cleaning protocol in minimally invasive endodontic surgery: RUA (“retro irrigant activation”)
Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Massimo Pisano, Sara De Fontaine, Alfredo Iandolo
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(3): 297. CrossRef - Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e15. CrossRef - Smear layer removal comparing conventional irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoActivator System, and a new sonic device (Perfect Clean System) by scanning electron microscopy: An ex vivo study
Bruna Fernanda Alionço Gonçalves, Divya Reddy, Ricardo Machado, Paulo César Soares Júunior, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Douglas Augusto Fernandes Couto, Karine Santos Frasquetti, Vânia Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Everdan Carneiro, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Net
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314940. CrossRef
- A new cleaning protocol in minimally invasive endodontic surgery: RUA (“retro irrigant activation”)
- 2,508 View
- 131 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
- Seda Falakaloğlu, Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Betül Güneş, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mustafa Gündoğar, Burcu Güçyetmez Topal
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e25. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
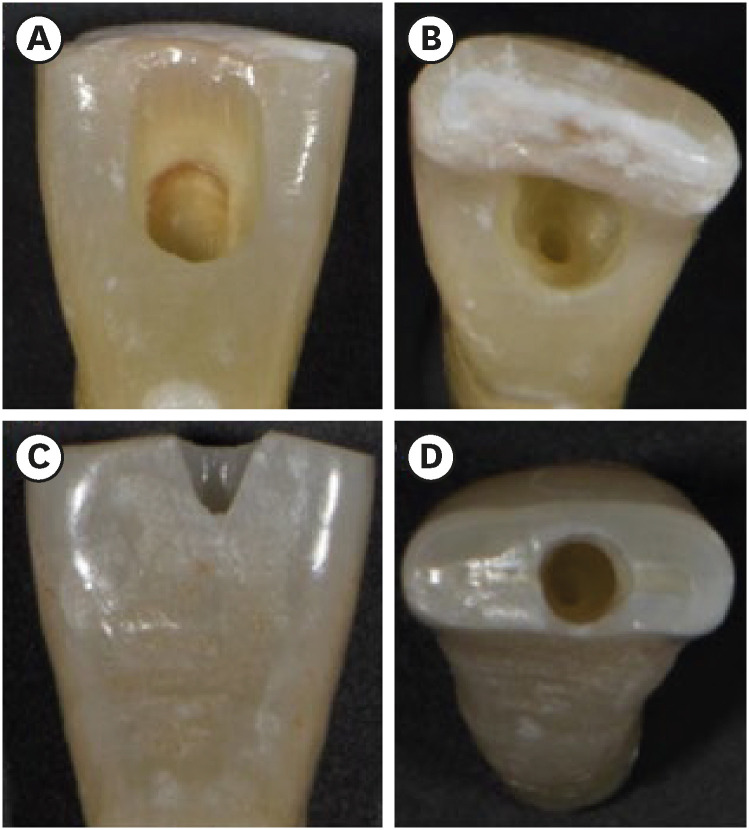
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of endodontic access cavities design on the removal of calcium hydroxide medication of the apical third of mandibular incisor root canal walls and dentinal tubules with different cleaning protocols: EDDY sonic activation, Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation, or conventional irrigation with IrriFlex.
Materials and Methods Seventy-eight extracted human mandibular incisors were assigned to 6 experimental groups (
n = 13) according to the endodontic access cavity and cleaning protocol for calcium hydroxide removal: traditional access cavity (TradAC)/EDDY; ultraconservative access cavity performed in the incisal edge (UltraAC.Inc)/EDDY; TradAC/Er,Cr:YSGG; UltraAC.Inc/Er,Cr:YSGG; TradAC/IrriFlex; or UltraAC.Inc/IrriFlex. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were used to measure the non-penetration percentage, maximum residual calcium hydroxide penetration depth, and penetration area at 2 and 4 mm from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed using Shapiro-Wilk and WRS2 package for 2-way comparison of non-normally distributed parameters (depth of penetration, area of penetration, and percentage of non-penetration) according to cavity and cleaning protocol with the significance level set at 5%.Results The effect of cavity and cleaning protocol interactions on penetration depth, penetration area and non-penetration percentage was not found statistically significant at 2 and 4 mm levels (
p > 0.05).Conclusions The present study demonstrated that TradAC or UltraAC.Inc preparations with different cleaning protocols in extracted mandibular incisors did not influence the remaining calcium hydroxide at 2 and 4 mm from the apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
Rania Lebbos, Naji Kharouf, Deepak Mehta, Jamal Jabr, Cynthia Kamel, Roula El Hachem, Youssef Haikel, Marc Krikor Kaloustian
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 678. CrossRef - Combination of Chitosan Nanoparticles, EDTA, and Irrigation Activation Enhances TGF-β1 Release from Dentin: A Laboratory Study
Sıla Nur Usta, Emre Avcı, Ayşe Nur Oktay, Cangül Keskin
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(8): 1081. CrossRef
- Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
- 3,022 View
- 73 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of irrigants on the color stability, solubility, and surface characteristics of calcium-silicate based cements
- Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Hacer Aksel, Şenay Canay, Duygu Karasan
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e10. Published online February 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e10

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the color stability, solubility, and surface characteristics of 3 calcium silicate-based cements (CSCs) after immersion in different solutions.
Materials and Methods ProRoot white mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and Endosequence Root Repair Material (ERRM) were placed in cylindrical molds and stored at 37°C for 24 hours. Each specimen was immersed in distilled water, 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine, or 0.1% octenidine hydrochloride (OCT) for 24 hours. Color changes were measured with a spectrophotometer. Solubility was determined using an analytical balance with 10−5 g accuracy. The surface characteristics were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectroscopy. Data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance, the Tukey test, and the paired
t -test.Results MTA exhibited significant discoloration in contact with NaOCl (
p < 0.05). White precipitation occurred on the surfaces of Biodentine and ERRM after contact with the solutions, and none of the materials presented dark brown discoloration. All materials showed significant solubility after immersion in the solutions (p < 0.05), irrespective of the solution type (p > 0.05). The surface topography and elemental composition of the samples showed different patterns of crystal formation and precipitation depending on the solution type.Conclusions All materials presented some amount of solubility and showed crystal precipitation after contact with the solutions. Biodentine and ERRM are suitable alternatives to ProRoot MTA as they do not exhibit discoloration. The use of OCT can be considered safe for CSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
Laila Mohamed Mohamed Kenawi, Mohamed Fattouh, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Abla Arafa
The Open Dentistry Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical and in vivo analyses of calcium silicate‐based materials in bone and connective tissues
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Matheus Barros‐Costa, Isabela Alvarenga Maciel dos Santos, Fábio Roberto de Souza Batista, Juliana de Aguiar Silveira Meira, Mariza Akemi Ma
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(3): 484. CrossRef - Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi, Eva Habazaj, Kleves Elezi, Rialda Xhizdari, Nevila Alliu
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bismuth release from endodontic materials: Proposed mechanisms for systemic circulation and organ accumulation
Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Benjamin Hewitt, Rodrigo Bueno de Oliveira, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Débora C. Coraça-Huber, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Marina Angélica Marciano
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2025; 494: 138580. CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Data about application of chlorhexidine as a periodontal irrigant –
Systematic Review.
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi , Eva Habazaj , Kristi Sulanjaku , Nevila Alliu
Acta Stomatologica Marisiensis Journal.2025; 8(1): 6. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Cement MTA FlowTM on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells In Vitro
Paulius Tušas, Josette Camilleri, Milda Alksnė, Egidijus Šimoliūnas, Saulius Drukteinis, Eglė Marija Urbonė, Virginija Bukelskienė, Vygandas Rutkūnas, Vytautė Pečiulienė
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(7): 252. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effects of Different Irrigation Solutions on MTA and Dentin Microhardness
Gokay Buyukcolpan, İdil Özden, Hesna Sazak Öveçoğlu
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 524. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Intratubular Penetration Ability of Two Retrograde Obturation Techniques in Micro-Endodontic Surgical Procedure: An In Vitro Study with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Alberto Casino Alegre, Michell Ramírez López, Manuel Monterde Hernández, Susana Aranda Verdú, Jorge Rubio Climent, Antonio Pallarés Sabater
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(11): 509. CrossRef - The outcome of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling in endodontic microsurgery: a randomized controlled trial
Xu Dong, Qin Su, Wen Li, Jinbo Yang, Dongzhe Song, Jing Yang, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions
Sıla Nur Usta, Cangül Keskin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of various irrigation solutions on the color stabilities of five calcium silicate cement: an in-vitro study
Aslı Soğukpınar Onsuren, Onur Kesici, Elif Uğurbekler Hündü
Selcuk Dental Journal.2024; 11(3): 313. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers on tooth color: A 3-year in vitro experimental study
Carmen Llena, Ana Herrero, Sandra Lloret, Martha Barraza, Jose Luis Sanz
Heliyon.2023; 9(2): e13237. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Four Bioceramic Materials with Different Restorative Materials and Timings
Abeer S. Alqahtani, Ayman M. Sulimany, Abdullah S. Alayad, Abdulaziz S. Alqahtani, Omar A. Bawazir
Materials.2022; 15(13): 4668. CrossRef
- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
- 2,163 View
- 37 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref

-
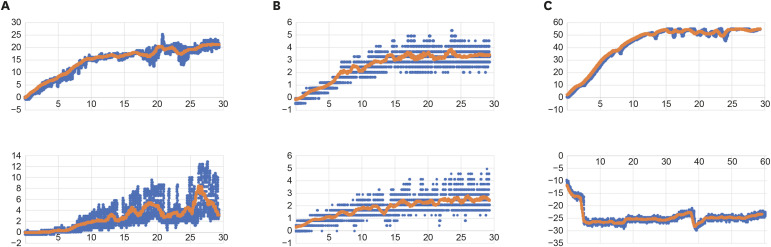
In vitro apical pressure created by 2 irrigation needles and a multisonic system in mandibular molars - Ronald Ordinola-Zapata, Joseph T. Crepps, Ana Arias, Fei Lin
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e14. Published online February 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the apical pressure generated by 2 endodontic irrigation needles and the GentleWave system in mandibular molars.
Materials and Methods The mesial and distal root canals of 12 mandibular molars were irrigated with a 30-gauge close-end needle or with a 30-gauge open-end needle. Procedures were performed in the mesial and distal canals. The GentleWave procedure and irrigation at 1 mm from the apex in the distal roots using an open-end needle were used, respectively, as negative and positive controls. The apical pressure was measured using a data acquisition pressure setup. Apical pressure exerted by the different needles in the 2 different canal types was statistically compared using 2-way analysis of variance.
Results Significant differences were found in the apical pressure for both needles and the canal type. The lowest values were obtained with close-end needles and in mesial canals. Negative apical pressure values were obtained using GentleWave.
Conclusions The needle and the canal type influenced the apical pressure. The GentleWave procedure produced negative apical pressure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- GentleWave versus Established Irrigation Techniques: Current Evidence from a Scoping Review
Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Abdul Habeeb Adil, Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of the gentlewave system in endodonticsUse of the gentlewave system in endodontics
Daiana Jacobi Lazzarotto, Mayara Colpo Prado, Lara Dotto, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2025; 24: e254250. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e17. CrossRef - The effect of ultrasonic and multisonic irrigation on root canal microbial communities: An ex vivo study
Ki Hong Park, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Bruno P. Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(7): 895. CrossRef - Efficacy of the GentleWave System in the removal of biofilm from the mesial roots of mandibular molars before and after minimal instrumentation: An ex vivo study
Kwang Ho Kim, Céline Lévesque, Gevik Malkhassian, Bettina Basrani
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(7): 922. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study irrigants and irrigation systems
Christos Boutsioukis, Maria Teresa Arias‐Moliz, Luis E. Chávez de Paz
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 295. CrossRef - Outcomes of the GentleWave system on root canal treatment: a narrative review
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Eduarda Gaeta, Gisele Faria
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- GentleWave versus Established Irrigation Techniques: Current Evidence from a Scoping Review
- 2,411 View
- 25 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

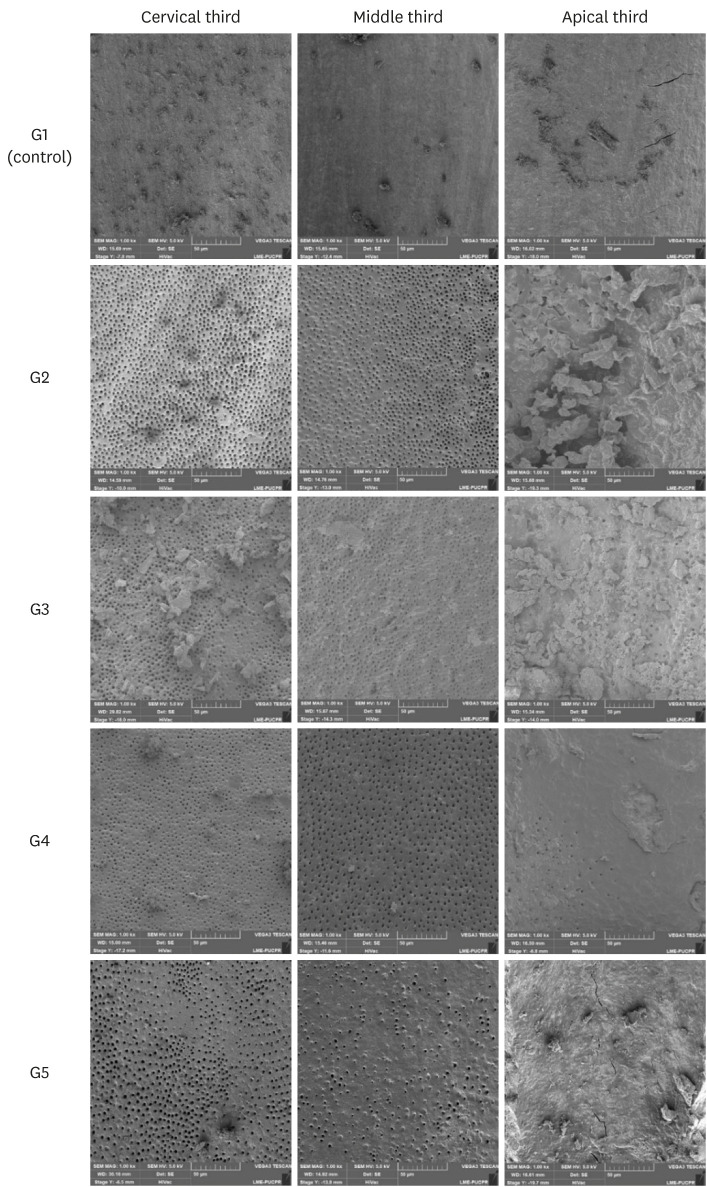
- Smear layer removal by passive ultrasonic irrigation and 2 new mechanical methods for activation of the chelating solution
- Ricardo Machado, Isadora da Silva, Daniel Comparin, Bianca Araujo Marques de Mattos, Luiz Rômulo Alberton, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e11. Published online January 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare smear layer removal by conventional application (CA), passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), EasyClean (EC), and XP-Endo Finisher (XPF), using 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) after chemomechanical preparation, as evaluated with scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Materials and Methods Forty-five single-rooted human mandibular premolars were selected for this study. After chemomechanical preparation, the teeth were randomly divided into 5 groups according to the protocol for smear layer removal, as follows: G1 (control): CA of distilled water; G2 (CA): CA of 17% EDTA; G3 (PUI): 17% EDTA activated by PUI; G4 (EC): 17% EDTA activated by EC; and G5 (XPF): 17% EDTA activated by XPF. SEM images (×1,000) were obtained from each root third and scored by 3 examiners. Data were evaluated using the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests (
p < 0.05).Results In the apical third, there were no statistically significant differences among the groups (
p > 0.05). In the cervical and middle thirds, the experimental groups performed better than the control group (p < 0.05); however, G2 presented better results than G3, G4, and G5 (p < 0.05), which showed no differences among one another (p > 0.05).Conclusions No irrigation method was able to completely remove the smear layer, especially in the apical third. Using CA for the chelating solution performed better than any form of activation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanoscale Approaches to Oro-Dental Tissue Engineering: A Review of Strategies, Composites, and Translational Challenges
Pei Wang, Yingtong Ye, Keyi Mei, Biaoqi Chen, Ranjith Kankala, Fei Tong
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2026; Volume 21: 1. CrossRef - Smear layer removal comparing conventional irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoActivator System, and a new sonic device (Perfect Clean System) by scanning electron microscopy: An ex vivo study
Bruna Fernanda Alionço Gonçalves, Divya Reddy, Ricardo Machado, Paulo César Soares Júunior, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Douglas Augusto Fernandes Couto, Karine Santos Frasquetti, Vânia Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Everdan Carneiro, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Net
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314940. CrossRef - Impact of different agitation methods on smear layer cleaning of mesial canals with accentuated curvature
Abel Teves Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Michel Espinosa Klymus, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in hybridized nanoarchitectures for improved oro-dental health
Jun Guo, Pei Wang, Yuyao Li, Yifan Liu, Yingtong Ye, Yi Chen, Ranjith Kumar Kankala, Fei Tong
Journal of Nanobiotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cleaning and disinfection of the root canal system provided by four active supplementary irrigation methods
Alessandra Timponi Goes Cruz, Adriane Antoniw Klemz, Edvaldo Antônio Ribeiro Rosa, Fabiana Soares Grecca, Bianca Mattos, Lucila Piasecki, Ricardo Machado, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Scanning electron microscopic study of smear layer changes following ultrasonic endoactivator irrigation system during root canal treatment of primary teeth
Mohamed Ghaly, Aya Alsherif, Arafa Khatab
Tanta Dental Journal.2023; 20(2): 137. CrossRef - Influence of agitation methods of irrigants after methylene blue-mediated PDT on the bonding interface of a fiber post cementation system
Lucas David Galvani, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, João Felipe Besegato, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante-Otárola, Milton Carlos Kuga
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 37: 102708. CrossRef
- Nanoscale Approaches to Oro-Dental Tissue Engineering: A Review of Strategies, Composites, and Translational Challenges
- 2,850 View
- 29 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Improved dentin disinfection by combining different-geometry rotary nickel-titanium files in preparing root canals
- Marwa M. Bedier, Ahmed Abdel Rahman Hashem, Yosra M. Hassan
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e46. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e46

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was to evaluate the antibacterial effect of different instrumentation and irrigation techniques using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) after root canal inoculation with
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ).Materials and Methods Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of extracted mandibular molars were apically enlarged up to a size 25 hand K-file, then autoclaved and inoculated with
E. faecalis . The samples were randomly divided into 4 main groups according to the system of instrumentation and irrigation: an XP-endo Shaper (XPS) combined with conventional irrigation (XPS/C) or an XP-endo Finisher (XPF) (XPS/XPF), and iRaCe combined with conventional irrigation (iRaCe/C) or combined with an XPF (iRaCe/XPF). A middle-third samplewas taken from each group, and then the bacterial reduction was evaluated using CLSM at a depth of 50 µm inside the dentinal tubules. The ratio of red fluorescence (dead cells) to green-and-red fluorescence (live and dead cells) represented the percentage of bacterial reduction. The data were then statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for comparisons across the groups and the Dunn test was used for pairwise comparisons.Results The instrumentation and irrigation techniques had a significant effect on bacterial reduction (
p < 0.05). The iRaCe/XPF group showed the strongest effect, followed by the XPS/XPF and XPS/C group, while the iRaCe/C group had the weakest effect.Conclusions Combining iRaCe with XPF improved its bacterial reduction effect, while combining XPS with XPF did not yield a significant improvement in its ability to reduce bacteria at a depth of 50 µm in the dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
Oksana A. Shuliatnikova, Mikhail V. Yakovlev, Anatoliy P. Godovalov
HERALD of North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.2025; 17(2): 89. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Shaping ability of non‐adaptive and adaptive core nickel–titanium single‐file systems with supplementary file in ribbon‐shaped canals analysed by micro‐computed tomography
Parichat Chinchiyanont, Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Nathamon Thongbai‐On
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - In vitro reduction in Enterococcus faecalis count following root canal preparation with Neolix and XP shaper rotary files
Mina Mehrjouei, Somayeh Teimoori, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Seyed Majed Mortazavi, Maryam Khorasanchi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 236. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite versus apple cider vinegar against Enterococcus faecalis in contracted endodontic cavity
Kaur Supreet, Karkala Venkappa Kishan, Nimisha Chinmay Shah
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 254. CrossRef - Ex vivo evaluation of the effectiveness of XP-endo Finisher on the removal of smear layer from the root canal
Sângela Maria PEREIRA, Ceci Nunes CARVALHO, Rudys Rodolfo TAVAREZ, Paulo NELSON-FILHO, Léa Assed Bezerra DA SILVA, Etevaldo Matos MAIA FILHO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biofilm elimination from infected root canals using four different single files
Sarah A. Hamed, Sarah Shabayek, Hayam Y. Hassan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adaptive, Rotary, and Manual Root Canal Instrumentation in Primary Molars: A Triple-Armed, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Bhaggyashri A. Pawar, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Anuj Bhardwaj, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Amelia Kristanti Rahardjo, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Zvi Metzger, Anda Kfir
Biology.2021; 10(1): 42. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Endodontic Access Cavity Design and Using XP-endo Finisher on the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal System
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Koray Yılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 419. CrossRef - Irrigation in Endodontics: a Review
Sarah Bukhari, Alaa Babaeer
Current Oral Health Reports.2019; 6(4): 367. CrossRef
- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
- 1,629 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
- Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):149-154. Published online March 4, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) into root dentinal tubules and the influence of passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty freshly extracted anterior teeth were decoronated and instrumented using Mtwo rotary files up to size 40, 4% taper. The samples were randomly divided into two groups (
n = 10), that is, conventional syringe irrigation (CSI) and PUI. CHX was mixed with Rhodamine B dye and was used as the final irrigant. The teeth were sectioned at coronal, middle and apical levels and viewed under CLSM to record the penetration depth of CHX. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results The mean penetration depths of 2% CHX in coronal, middle and apical thirds were 138 µm, 80 µm and 44 µm in CSI group, respectively, whereas the mean penetration depths were 209 µm, 138 µm and 72 µm respectively in PUI group. Statistically significant difference was present between CSI group and PUI group at all three levels (
p < 0.01 for coronal third andp < 0.001 for middle and apical thirds). On intragroup analysis, both groups showed statistically significant difference among three levels (p < 0.001).Conclusions Penetration depth of 2% CHX into root dentinal tubules is deeper in coronal third when compared to middle and apical third. PUI aided in deeper penetration of 2% CHX into dentinal tubules when compared to conventional syringe irrigation at all three levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Penetration Depth and Bactericidal Efficacy of 2% Chlorhexidine Iontophoresis in Human Coronal Dentin In Vitro
Kanittha Kijsamanmith, Napat Satitthummanit, Chinnawat Thotsaphonphaisan, Chanisara Kurucharoenporn, Thidaporn Ratarsa, Varit Lerdmaneepha, Nanthasak Kanchanathipkhachorn, Arthit Klaophimai, Ratchapin Srisatjaluk
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(2): 109439. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Khadirarishta and Chlorhexidine as Intracanal Medicament on Enterococcus faecalis using a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope – An in vitro Study
Harika Paluru, Lavanya Anumula, Chinni Suneel Kumar, Kiranmayi Govula, Sannapureddy Swapna, Paleti Pranaviteja
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2025; 15(3): 237. CrossRef - The ability of different diffusing enhancers to deliver chlorhexidine into dentinal tubules: An in vitro evaluation
Yi Luo, Mengting Duan, Runze Liu, Pei Liu, Wei Fan, Bing Fan
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2226. CrossRef - The effect of 2% chlorhexidine iontophoresis on dentin sealing ability of etch-and-rinse adhesive: An in vitro study
Kanittha Kijsamanmith, Panisara Srisatayasatien, Nichapa Thanindratarn, Chanisa Vichainarong, Jirapat Panyasukum
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 846. CrossRef - Influence of different presentation forms of chlorhexidine on contaminated root canals during agitation
Ana B. S. Lopes, Augusto R. Lima, Juliana D. Bronzato, Daniel R. Herrera, Priscila A. Francisco, Maria C. C. Carvalho, Gabriel Abuna, Mario Sinhoreti, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 513. CrossRef - Evaluation of the transdentinal capability of the intrinsic antibacterial cetylpyridinium chloride/cholesterol sterosomes in vitro and in vivo
Xiaojun Yang, Chaoning Zhan, Tianjiao Cheng, Minchun Huang, Weiwen Ge, Yiqing Zhang, Ting Chen, Yanli Lu, Zhong‐Kai Cui, Jin Hou
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(2): 245. CrossRef - Dentinal tubule penetration of sodium hypochlorite in root canals with and without mechanical preparation and different irrigant activation methods
Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Matheus Albino Souza, Rodrigo Gonçalves Ribeiro, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Lipidic Nanoplatform for Intra-Oral Delivery of Chlorhexidine: Characterization, Biocompatibility, and Assessment of Depth of Penetration in Extracted Human Teeth
Krishnaraj Somyaji Shirur, Bharath Singh Padya, Abhijeet Pandey, Manasa Manjunath Hegde, Aparna I. Narayan, Bola Sadashiva Satish Rao, Varadaraj G. Bhat, Srinivas Mutalik
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(19): 3372. CrossRef - Value addition property of a cationic surfactant on endodontic irrigant: A confocal laser scanning microscope study
Sembagalakshmi Thirunarayanan, MithraN Hegde
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 380. CrossRef - The effect of different irrigants on sealer penetration into dentinal tubules with and without activation, using confocal scanning microscope
HelaylA Alshaibani, ShibuThomas Mathew
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2022; 14(1): 37. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide/iodoform nanoparticles as an intracanal filling medication: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro study using a bovine primary tooth model
Arturo Garrocho-Rangel, Diana María Escobar-García, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Denisse Herrera-Badillo, Fernanda Carranco-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Flores-Arriaga, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 687. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation methods on dentinal tubule penetration of Chlorhexidine, QMix and Irritrol: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Meltem Küçük, Fatma Kermeoğlu
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 202. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of different root canal sealers used with coated core materials
Derya Deniz Sungur, Nuhan Purali, Erdal Coşgun, Semra Calt
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 114. CrossRef
- The Penetration Depth and Bactericidal Efficacy of 2% Chlorhexidine Iontophoresis in Human Coronal Dentin In Vitro
- 2,207 View
- 25 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
- Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):143-148. Published online February 11, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the maximum depth and percentage of irrigant penetration into dentinal tubules by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human teeth were instrumented and divided into three groups. According to final irrigation regimen, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (Group A, NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine (Group B, CHX) and saline solution (Group C, control group) were applied with Irrisafe 20 tips (Acteon) and PUI. Irrigant was mixed with 0.1% rhodamine B. Sections at 2 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm from the apex were examined with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The percentage and maximum depth of irrigant penetration were measured. Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test were performed for overall comparison between groups at each level and for pairwise comparison, respectively. Within a group, Wilcoxon test was performed among different levels.
p values less than 0.05 were considered significant.Results In all groups, highest penetration depth and percentage of penetration were observed at the 8 mm level. At 2 mm level, Groups A and B had significantly greater depths and percentages in penetration than Group C (
p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences between Groups A and B. At 5 mm level, penetration depths and percentage of penetration was not significantly different among the groups.Conclusions NaOCl and CHX applied by PUI showed similar depth and percentage of penetration at all evaluated levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
Anjali Meena, Nidhi Sharma, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Sarita Singh, Anu Dhawan, Neha Verma
Endodontology.2025; 37(1): 80. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Sonic versus ultrasonic activation for the cleaning of the root canal after post space preparation: an in vitro study.
René Carrasco, Ricardo Román, Makarena Ojeda, Carolina Vergara
Journal Oral Of Research.2015; 4(4): 255. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
- 1,613 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Review of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Su-Jeong Shin, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):180-187. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Introduction Eliminating the residual debris and bacteria in the root canal system is one of the main purposes of the endodontic treatment. However, the complexity on the anatomy of the root canal system makes it difficult to eliminate the bacterial biofilm existing along the root canal surface and necrotic pulp tissue by mechanical instrumentation and chemical irrigation. Recently, more effective irrigant delivery systems for root canal irrigation have been developed. The purpose of this review was to present an overview of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices available in endodontics.
Review The contents of this paper include as follows;
- syringe-needle irrigation, manual dynamic irrigation, brushes
- sonic and ultrasonic irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, rotary brush, RinsEndo, EndoVac, Laser
Conclusion Though technological advances during the last decade have brought to fruition new agitation devices that rely on various mechanisms, there are few evidence based study to correlate the clinical efficacy of these devices with improved outcomes except syringe irrigation with needle and ultrasonic irrigation.
The clinicians should try their best efforts to deliver antimicrobial and tissue solvent solutions in predictable volumes safely to working length.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
Gilhwan Sung, Jaeyong Sung, Myeong Ho Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Visualization.2016; 14(1): 40. CrossRef
- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
- 1,714 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
- Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):80-87. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.080
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the different canal irrigation methods to prevent the formation of precipitate between sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and chlorhexidine (CHX).
Extracted 50 human single-rooted teeth were used. The root canals were instrumented using NiTi rotary file (Profile .04/#40) with 2.5% NaOCl and 17% EDTA as irrigants. Teeth were randomly divided into four experimental groups and one control group as follows; Control group: 2.5% NaOCl only, Group 1: 2.5% NaOCl + 2% CHX, Group 2: 2.5% NaOCl + paper points + 2% CHX, Group 3: 2.5% NaOCl + preparation with one large sized-file + 2% CHX, Group 4: 2.5% NaOCl +95% alcohol+ 2% CHX.
The teeth were split in bucco-lingual aspect and the specimens were observed using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope. The percentages of remaining debris and patent dentinal tubules were determined. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Energy Dispersive x-ray Spectroscopy was used for analyzing the occluded materials in dentinal tubule for elementary analysis.
There were no significant differences in percentage of remaining debris and patent tubules between all experimental groups at all levels (p > .05).
In elementary analysis, the most occluded materials in dentinal tubule were dentin debris. NaOCl/CHX precipitate was detected in one tooth specimen of Group 1.
In conclusion, there were no significant precipitate on root canal, but suspected material was detected on Group 1. The irrigation system used in this study could be prevent the precipitate formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 295. CrossRef
- Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
- 1,726 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A COMPARISON OF THE IRRIGATION SYSTEMS IN CALCIUM HYDROXIDE REMOVAL
- Jae-Seung Eun, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):508-514. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.508
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purposes of this study were to compare the efficacy of irrigation systems by removing a calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) paste from the apical third of the root canal and the effect of the patency file. Sixty single rooted human teeth were used in this study. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down manner with .04 taper ProFile to ISO #35. Ca(OH)2 and distilled water were mixed and placed inside the root canals. The teeth were divided into 6 groups according to the root canal irrigation system and the use of patency file as follows: group 1 - conventional method; group 2 - EndoActivator®; group 3 - EndoVac®; group 4 - conventional method, patency; group 4 - EndoActivator®, patency; group 6 - EndoVac®, patency. All teeth were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. After the root canal irrigation, the teeth were split in bucco-lingual aspect. Percentage of the root canal surface coverage with residual Ca(OH)2 until 3 mm from working length was analyzed using Image Pro Plus ver. 4.0. Statistical analysis was performed using the One-way ANOVA, t-test and Scheffe's post-hoc test. Conventional groups had significantly more Ca(OH)2 debris than EndoActivator®, EndoVac® groups. There was no significant difference between EndoActivator® and EndoVac® groups. Groups with patency file showed more effective in removing Ca(OH)2 paste than no patency groups, but, it was no significant difference. This study showed that EndoActivator® and EndoVac® systems were more effective in removing Ca(OH)2 paste from the apical third of the root canal than conventional method.
- 949 View
- 3 Download

-
EVALUATION OF
ENTEROCOCCUS FAECALIS REMOVAL EFFICACY OF THE ENDOVAC® AND ENDOACTIVATOR® INTRACANAL IRRIGATION METHODS - Seung-Gon Song, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(5):390-396. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The aim of this study was to evaluate endodontic irrigation methods with EndoVac® and EndoActivator® in the elimination of
Enterococcus faecalis from the root canals. Extracted 70 human single-rooted teeth were used. The canals were instrumented by a crown-down technique with .04 taper ProFile to ISO size 40. After the teeth were autoclaved, the canals were inoculated withE. faecalis and incubated for 48 h. The teeth were randomly divided into three experimental groups of 20 teeth each according to canal irrigation methods and two control groups as follows: group 1 - EndoVac®; group 2 - EndoActivator®; group 3 - Conventional needle irrigation method. After canal irrigation using 2.5% NaOCl, first samples (S1) were taken using sterile paper point. And the canals were filled with sterile brain heart infusion (BHI) broth and incubated for 24 h, then second samples (S2) were taken. The samples were cultured on BHI agar plate to determine the numbers of colony forming units (CFU). In first sampling (S1), only one canal of conventional method among the all experimental groups was positive cultured. In second sampling (S2), EndoVac® group showed the least positive culture numbers ofE. faecalis . There was statistically significant difference between the EndoVac® and conventional needle irrigation methods in the mean value of Log CFU. According to the results of this study, EndoVac® showed better efficacy than conventional needle irrigation method in the elimination ofE. faecalis from the root canal.
- 838 View
- 8 Download

- IN VITRO EVALUATION OF CLEANING EFFICACY OF VARIOUS IRRIGATION METHODS IN MANDIBULAR MOLARS
- So-Young Lee, Won-Jun Son, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Kwang-Shik Bae, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):215-222. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the cleaning efficacy of various irrigation methods in the mandibular mesial roots. The forty five mesial root canals were shaped by Profile .06 instruments to apical size #30 and irrigated with 5 ml of 3.5% NaOCl. The teeth were divided into 3 groups and irrigated finally for 1 minute; Group 1: syringe irrigation, Group 2: ultrasonic irrigation, Group 3: RinsEndo irrigation.
After histological processing, the cross sections of apical 1, 3, and 5 mm level were examined with an optical microscope. The cleanliness values of canals and isthmuses were calculated and analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test.
There were no significant differences in both canal and isthmus cleanliness between syringe irrigation and ultrasonic irrigation except 5 mm level of isthmus.
RinsEndo irrigation had significantly higher canal cleanliness values than syringe irrigation at 1 mm and 3 mm levels (p < 0.05). Also, RinsEndo irrigation had significantly higher isthmus cleanliness values than syringe irrigation at all levels evaluated (p < 0.05).
There were no statistical differences in both canal and isthmus cleanliness between ultrasonic irrigation and RinsEndo irrigation except 3 mm level of canal. From this study, RinsEndo irrigation can be useful as an additional irrigation procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multivariate analysis of the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation techniques in the canal and isthmus of mandibular posterior teeth
Yeon-Jee Yoo, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 154. CrossRef - Review of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Su-Jeong Shin, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 180. CrossRef
- Multivariate analysis of the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation techniques in the canal and isthmus of mandibular posterior teeth
- 953 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
- Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):397-404. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.397
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of MTAD, EDTA and sodium hypochlorite(NaOCl) as final irrigants on coronal leakage resistance to
Enterococcus faecalis . Forty extracted human maxillary molars were used in this experiment. The teeth were randomly divided into positive control group (Group 1; n = 5), negative control group (Group 2; n = 5) and three experimental groups (n = 30). In Group 3 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. In Group 4 (n = 10) and 5 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite and rinsed with EDTA and MTAD, respectively. The teeth in each group were cleaned and shaped to #40 profile with .04 taper, and obturated with gutta-percha and AH-26 root canal sealer. The coronal portion of each tooth was placed in contact with inoculum ofEnterococcus faecalis in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) culture media. Each root tip was placed in a vial containing sterile culture media. The vials were placed in anaerobic chamber and observed everyday for turbidity for 180 days. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher's Exact Test. After 180 days, Group 3, 4, and 5 showed 7, 4 and 5 leaking samples respectively. The differences in leakage resistance were not statistically significant among Group 3, 4 and 5.
- 2,033 View
- 6 Download

- Effect of irrigation methods on the adhesion of Resilon/Epiphany sealer and gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer to intracanal dentin
- Seo-Kyong Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):98-106. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether intracanal irrigation method could affect the adhesion between intracanal dentin and root canal filling materials (Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer and Resilon/Epiphany sealer).
Thirty extracted human incisor teeth were prepared. Canals were irrigated with three different irrigation methods as a final rinse and obturated with two different canal filling materials (G groups : Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer, R groups : Resilon/Epiphany sealer) respectively.
Group G1, R1 - irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl
Group G2, R2 - irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl, sterile saline
Group G3, R3 - irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl, 17% EDTA, sterile saline
Thirty obturated roots were horizontally sliced and push-out bond strength test was performed in the universal testing machine. After test, the failure patterns of the specimens were observed using Image-analyzing microscope.
The results were as follows.
Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer groups had significantly higher push-out bond strength compared with the Resilon/Epiphany sealer groups (p < 0.05).
Push-out bond strength was higher when using 17% EDTA followed by sterile saline than using NaOCl as a final irrigation solution in the Resilon/Epiphany sealer groups (p < 0.05).
In the failure pattern analysis, there was no cohesive failure in Group G1, G2, and R1. Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer groups appeared to exhibit predominantly adhesive and mixed failure patterns, whereas Resilon/Epiphany sealer groups exhibited mixed failures with the cohesive failure occurred within the Resilon substrate.
- 866 View
- 4 Download

- Time-dependent effects of EDTA application on removal of smear layer in the root canal system
- Ja-Kyong Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):169-178. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was to verify that the combined application of NaOCl and EDTA was more effective in removal of smear layer than the application of NaOCl alone. Furthermore it was aimed to find out the optimal time for the application of EDTA.
Thirty five single rooted teeth were cleaned and shaped. NaOCl solution was used as an irrigant during instrumentation. After instrumentation, root canals of the control group were irrigated with 5 ml of NaOCl for 2 minutes. 30 sec, 1 min, and 2 min group were irrigated with 5 ml of 17% EDTA for 30 sec, 1 min, and 2 min respectively. Then the roots were examined with scanning electron microscopy for evaluating removal of smear layer and erosion of dentinal tubule.
The results were as follows;
The control group:
The smear layer was not removed at all.
The other groups:
1) Middle⅓: All groups showed almost no smear layer. And the erosion occurred more frequently as increasing irrigation time.
2) Apical⅓: The cleaning effect of 2 min group was better than the others.
The results suggest that 2 min application of 17% EDTA should be adequate to remove smear layer on both apical⅓ and middle⅓.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing the Antibacterial Effect of Erythrosine-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy with Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
MinKi Choi, Haeni Kim, Siyoung Lee, Juhyun Lee
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2024; 51(1): 32. CrossRef - Apical foramen morphology according to the length of merged canal at the apex
Hee-Ho Kim, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 26. CrossRef - Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 335. CrossRef
- Enhancing the Antibacterial Effect of Erythrosine-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy with Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
- 1,730 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The irrigating effect before and after coronal flaring
- Ho-Keel Hwang, Seong-Chul Bae, Young-Lin Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):72-79. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this in vitro study was to evaluate the efficacy of a Ca(OH)2 removal before and after early coronal flaring using different types of instruments. 100 plastic blocks with 30° artificial curved canals were used in this study and randomly divided into a control group and 4 experimental groups(GG, OS, GT, PT Group) 20 teeth each. The canals were instrumented, and Ca(OH)2 was temporary filled into the each canal. Irrigation was performed with Max-i-Probe 25-, 30-gauge probes before and after recapitulation.
The results of this study were as follows:
1. There were no significant difference among the groups in size of irrigating needle(p<0.05).
2. There was a significant difference between before and after recapitulation regardless size of irrigating needle(p<0.05).
3. Before recapitulation, there was a significant difference between 25- and 30-gauge needle in all groups(p<0.05).
4. After recapitulation, there was a significant difference between 25- and 30-gauge needle in the control group(p<0.05). But there were no significant difference among the experimental groups.
It is concluded that the effectiveness of canal irrigation was decided to the depth of irrigating needle into the canal. The effect of canal irrigation tend to facilitate by the early coronal flaring. The recapitulation was the most effective during canal irrigation regardless the size of irrigating needle. Therefore, the recapitulation is a mandatory way to facilitate the effectiveness of canal irrigation during canal enlargement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro evaluation of cleaning efficacy of various irrigation methods in mandibular molars
So-Young Lee, Won-Jun Son, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Kwang-Shik Bae, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 215. CrossRef - Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
Seung-Gon Song, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 390. CrossRef
- In vitro evaluation of cleaning efficacy of various irrigation methods in mandibular molars
- 1,142 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


