Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 28(1); 2003 > Article
- Original Article The irrigating effect before and after coronal flaring
- Ho-Keel Hwang, Seong-Chul Bae, Young-Lin Cho
-
2003;28(1):-79.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.072
Published online: January 31, 2003
Department of Conservative Dentistry, Oral Biology Research Institute, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Korea.
- Corresponding author (rootcanal@hanmail.net)
Copyright © 2003 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,173 Views
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
-
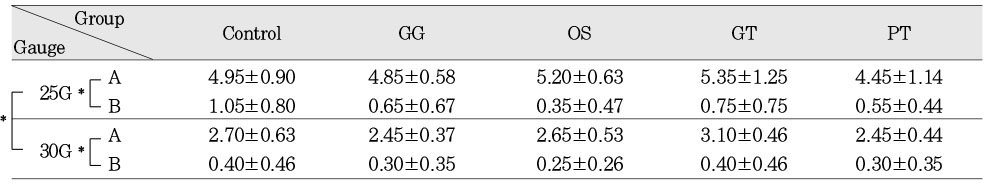
The objective of this in vitro study was to evaluate the efficacy of a Ca(OH)2 removal before and after early coronal flaring using different types of instruments. 100 plastic blocks with 30° artificial curved canals were used in this study and randomly divided into a control group and 4 experimental groups(GG, OS, GT, PT Group) 20 teeth each. The canals were instrumented, and Ca(OH)2 was temporary filled into the each canal. Irrigation was performed with Max-i-Probe 25-, 30-gauge probes before and after recapitulation.The results of this study were as follows:1. There were no significant difference among the groups in size of irrigating needle(p<0.05).2. There was a significant difference between before and after recapitulation regardless size of irrigating needle(p<0.05).3. Before recapitulation, there was a significant difference between 25- and 30-gauge needle in all groups(p<0.05).4. After recapitulation, there was a significant difference between 25- and 30-gauge needle in the control group(p<0.05). But there were no significant difference among the experimental groups.It is concluded that the effectiveness of canal irrigation was decided to the depth of irrigating needle into the canal. The effect of canal irrigation tend to facilitate by the early coronal flaring. The recapitulation was the most effective during canal irrigation regardless the size of irrigating needle. Therefore, the recapitulation is a mandatory way to facilitate the effectiveness of canal irrigation during canal enlargement.
- 1. Cohen S, Burns R. Pathways of the pulp. 1994;6th ed. St. Louis: CV Mosby; 179-218.
- 2. Gambarini G. Shaping and cleaning the root canal system: A scanning electron microscopic evaluation of a new instrumentation and irrigation technique. J Endod. 1999;25(12):800-803.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Siqueira JF Jr, Rocas IN, Snatos SR, Lima KC, Magalhaes FA, Uzeda M. Efficacy of instrumentation techniques and irrigation regimens in reducing the bacterial population within root canals. J Endod. 2002;28(3):181-184.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Hoen MM, LaBounty GL, Struttmatter EJ. Conservative treatment of persistent periradicular lesions using aspiration and irrigation. J Endod. 1990;16(4):182-186.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Jeansonne MJ, White RR. A comparison of 2.0% chlorhexidine gluconate and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite as antimicrobial endodontic irrigants. J Endod. 1994;20(6):276-278.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Valera MC, Rego JM, Jorge AOC. Effect of sodium hypochlorite and five intracanal medicants on candida albicans in root canals. J Endod. 2001;27(6):401-403.PubMed
- 7. Doğan H, Calt S. Effects of chelating agents and sodium hypochlorite on mineral content of root dentin. J Endod. 2001;27(9):578-580.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kuruvilla JR, Kamath MP. Antimicrobial activity of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite and 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate separately and combined, as endodontic irrignats. J Endod. 1998;24(7):472-476.PubMed
- 9. Scelza MF, Antoniazzi JH, Scelza P. Efficacy of final irrigation-a scanning electron microscopic Evaluation. J Endod. 2000;26(6):355-358.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Siqueira JF Jr, Machado AG, Silveira RM, Lopes HP, Uzeda MD. Evaluation of the effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite used with three irrigation methods in the elimination of enterococcus faecalis from the root canal, in vitro. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 279-282.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Siqueira JF Jr, Rocas IN, Favieri A, Lima KC. Chemomechanical reduction of the bacterial population in the root canal after instrumentation and irrigation with 1%, 2.5%, and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 2000;26(6):331-334.PubMed
- 12. Tanomaru Filho M, Leonardo MR, Silva LAB. Effect of irrigating solution and calcium hydroxide root canal dressing on the repair of apical and periapical tissues of teeth with periapical lesion. J Endod. 2002;28(4):295-299.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Hülsmann M, Hahn W. Complications during root canal irrigation-literature review and case reports. Int Endod J. 2000;33: 186-193.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Sukawat C, Srisuwan T. A comparison of the antimicrobial efficacy of three calcium hydroxide formulations on human dentin infected with Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod. 2002;28(2):102-104.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Siqueira JF Jr, Rocas IN, Magalhaes FA, de Uzeda M. Antifungal effects of endodontic medicaments. Aust Endod J. 2001;27(3):112-114.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Peters LB, Winkelhoff AJ, Buijs JF, Wesselink PR. Effects of instrumentation, irrigation and dressing with calcium hydroxide on infection in pulpless teeth with periapical bone lesions. Int Endod J. 2002;35: 13-21.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Ferguson JW, Hatton JF, Gillespie MJ. Effectiveness of intracanal irrigants and medications against the yeast Candida albicans. J Endod. 2002;28(2):68-71.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Goldberg F, Artaza LP, De S. Influence of calcium hydroxide dressing on the obturation of simulated lateral canals. J Endod. 2002;28(2):99-101.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Miletić I, Ribaric SP, Karlovic Z, Jukic S, Bosnjak A, Anic I. Apical leakage of five root canal sealers after one year of storage. J Endod. 2002;28(6):431-432.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Murray PE, Hafez AA, Smith AJ, Cox CF. Bacterial microleakage and pulp inflammation associated with various restorative materials. Dent Mater. 2002;18(6):470-478.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Lee KW, Willams MC, Camps JJ, Pashley DH. Adhesion of endodontic sealers to dentin and gutta-percha. J Endod. 2002;28(10):684-688.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Siqueira JF Jr, Lima KC, Magalhaes FA, Lopes HP, Uzeda M. Mechanical reduction of the bacterial population in the root canal by three instrumentation techniques. J Endod. 1999;25(5):332-335.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Pataky L, Ivanyi I, Grigar A, Fazekas A. antimicrobial efficacy of various root canal preparation techniques: an in vitro comparative study. J Endod. 2002;28(8):603-605.PubMed
- 24. Coldero LG, McHugh S, MacKenzie D, Saunders WP. Peduction in intracanal bacteria during root canal preparation with and without apical enlargement. Int Endod J. 2002;35: 437-446.PubMed
- 25. Lim SS. Clinical Endodontology. 1999;2nd ed. Seoul: Uichihaksa; 137-141.
- 26. Baumgartner JC, Cuenin PR. Efficacy of several concentrations of sodium hypochlorite for root canal irrigation. J Endod. 1992;18(12):605-612.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Haikel Y, Gorce F, Allemann C, Voegel JC. In vitro efficiency of endodontic irrigation solutions on protein desorption. Int Endod J. 1994;27: 16-20.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Shuping GB, Orstavik MD, Sigurdsson A, Trope M. Reduction of intracanal bacteria using nickel titanium rotary instrumentation and various medications. J Endod. 2000;26(12):751-755.PubMed
- 29. Almyroudi A, Mackenzie D, McHugh S, Saunders WP. The effectiveness of various disinfectants used as endodontic intracanal medications: an in vitro study. J Endod. 2002;28(3):163-167.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Andreasen JO, Farik B, Munksgaard EC. Long-term calcium hydroxide as a root canal dressing may increase risk of root fracture. Dent Traumatol. 2002;18(3):134-137.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Dalton BC, Phillips C, Pettiette M, Trope M. Bacterial reduction with nickel-titanium rotary instrumentation. J Endod. 1998;24(11):763-767.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Evans GE, Speight PM, Gulabivala K. The influence of preparation technique and sodium hypochlorite on removal of pulp and predentine from root canals of posterior teeth. Int Endod J. 2001;34: 322-330.PubMed
- 33. Heard F, Walton RE. Scanning electron microscope study comparing four root canal preparation techniques in small curved canals. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 323-331.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Hinrichs RE, Walker WA, Schindler WG. A comparison of amounts of extruded debris using handpiece-driven nickel-titanium instrument systems. J Endod. 1998;24: 102-106.PubMed
- 35. Peters OA, Barbakow F. Effects of irrigation on debris and smear layer on canal walls prepared by two rotary techniques: a scanning electron microscopic study. J Endod. 2000;26(1):6-10.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Lambrianidis T, Tosounidou DE, Tzoanopoulou M. The effect of maintaining apical patency on periapical extrusion. J Endod. 2001;27: 696-698.PubMed
- 37. Williams CE, Reid JS, Sharkey SW, Saunders WP. In-vitro measurement of apically extruded irrigant in primary molars. Int Endod J. 1995;28: 221-225.PubMed
- 38. Bradford CE, Eleazer PD, Downs KE, Scheetz JP. Apical pressures developed by needles for canal irrigation. J Endod. 2002;28: 333-335.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Brown DC, Moore BK, Brown CE, Newton CW. An in vitro study of apical extrusion of sodium hypochlorite during endodontic canal preparation. J Endod. 1995;21(12):587-591.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Kahn FH, Rosenberg PA, Gliksberg J. An in vitro evaluation of the irrigating characteristics of ultrasonic and subsonic handpieces and irrigating needles and probes. J Endod. 1995;21(5):277-280.PubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- In vitro evaluation of cleaning efficacy of various irrigation methods in mandibular molars
So-Young Lee, Won-Jun Son, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Kwang-Shik Bae, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 215. CrossRef - Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
Seung-Gon Song, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 390. CrossRef
The irrigating effect before and after coronal flaring
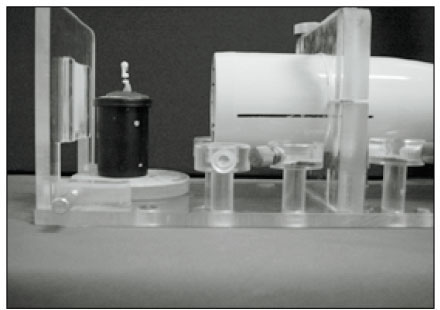
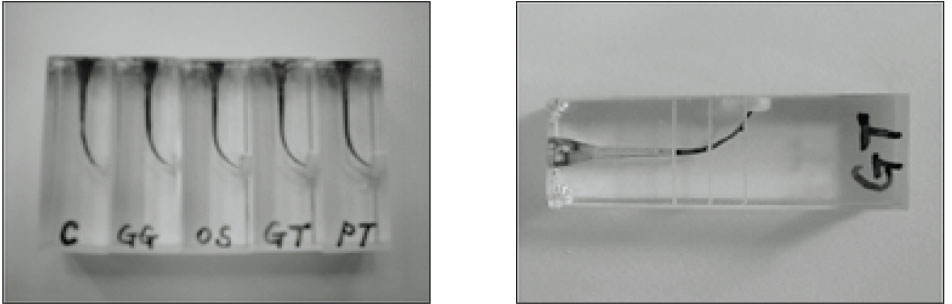
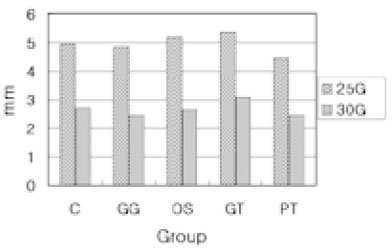
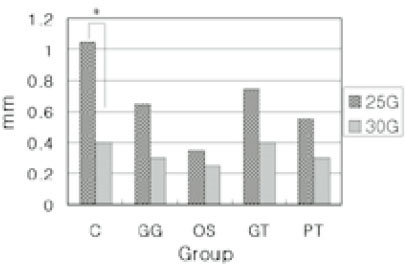
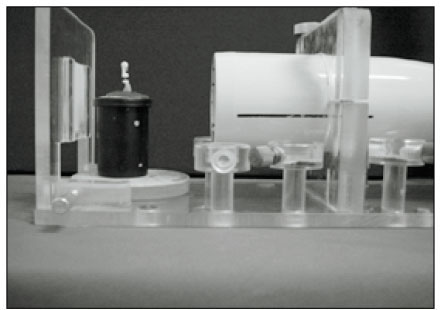
Fig. 1
The device for taking a standard radiograph at same position
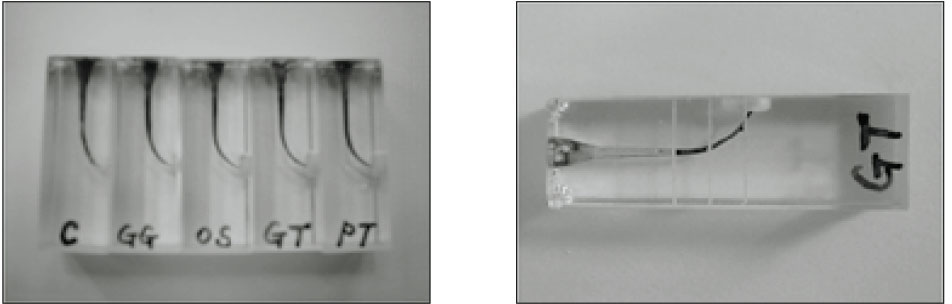
Fig. 2
Evaluation of remaining Ca(OH)2 by steroscope
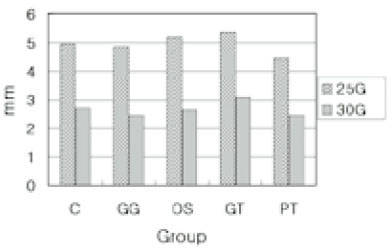
Fig. 3
Average extent of remaining Ca(OH)2 before recapitulation
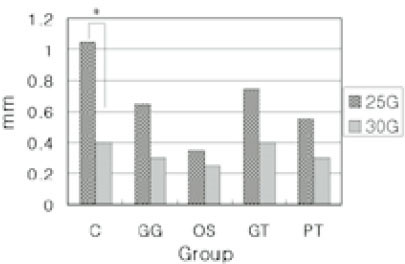
Fig. 4
Average extent of remaining Ca(OH)2 after recapitulation
*: Significantly different at p<0.05(paired t-test)
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
The irrigating effect before and after coronal flaring
Group classification according to instruments
Average extent of remaining Ca(OH)2 after canal irrigation (unit: mm)
A: before recapitulation B: after recapitulation
*: Significantly different at p<0.05(paired t-test)
Table 1
Group classification according to instruments
Table 2
Average extent of remaining Ca(OH)2 after canal irrigation (unit: mm)
A: before recapitulation B: after recapitulation *: Significantly different at p<0.05(paired t-test)

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

