Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
-
Fracture resistance after root canal filling removal using ProTaper Next, ProTaper Universal Retreatment or hybrid instrumentation: an
ex vivo study - Hadeel Hassan Hanafy, Marwa Mahmoud Bedier, Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e38. Published online October 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
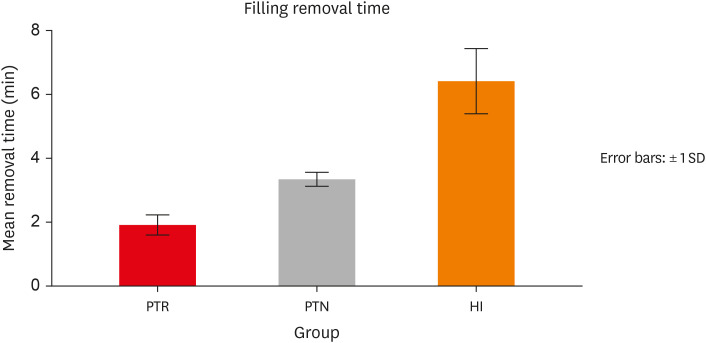
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of ProTaper Next (PTN), ProTaper Universal Retreatment (PTR) and hybrid instrumentation (HI) for canal filling removal on the fracture resistance (FR), mode of failure (MoF), and filling removal time.
Materials and Methods Ninety-six, mandibular premolars were decoronated and randomly divided into 6 groups (
n = 16), as follows: sound (S), untreated canals; prepared teeth (P), canals only prepared to ProTaper Universal finishing instrument (F4); endodontically-treated (ET), prepared and obturated canals using the single-cone technique; and groups PTN, PTR, and HI where filling was removed using PTN, PTR, or HI respectively. FR under vertical loading; MoF and time were assessed. Data were analyzed (Significance level [α] = 0.05).Results There was a significant difference in FR among all groups (
p < 0.001) (HI < P < PTN < S < ET < PTR). HI showed lower FR than S, ET and PTR, and P showed lower FR than PTR (p < 0.05). For experimental groups, there was a significant difference between every group pair (p < 0.05) No significant difference was found regarding MoF distribution (p > 0.05). HI required the highest filling removal time, while PTR required the least (p < 0.05 between every group pair).Conclusions The effect of filling removal on FR may depend on the filling removal technique/system used. PTR could be faster and protect against fracture followed by PTN; HI could adversely affect FR. FR may be associated with filling removal time.
- 3,050 View
- 125 Download

- Comparison of shaping ability of the Reciproc Blue and One Curve with or without glide path in simulated S-shaped root canals
- Vincenzo Biasillo, Raffaella Castagnola, Mauro Colangeli, Claudia Panzetta, Irene Minciacchi, Gianluca Plotino, Simone Staffoli, Luca Marigo, Nicola Maria Grande
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e3. Published online December 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e3

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the impact of a glide-path on the shaping ability of 2 single-file instruments and to compare the centering ability, maintenance of original canal curvatures and area of instrumentation in simulated S-shaped root canals.
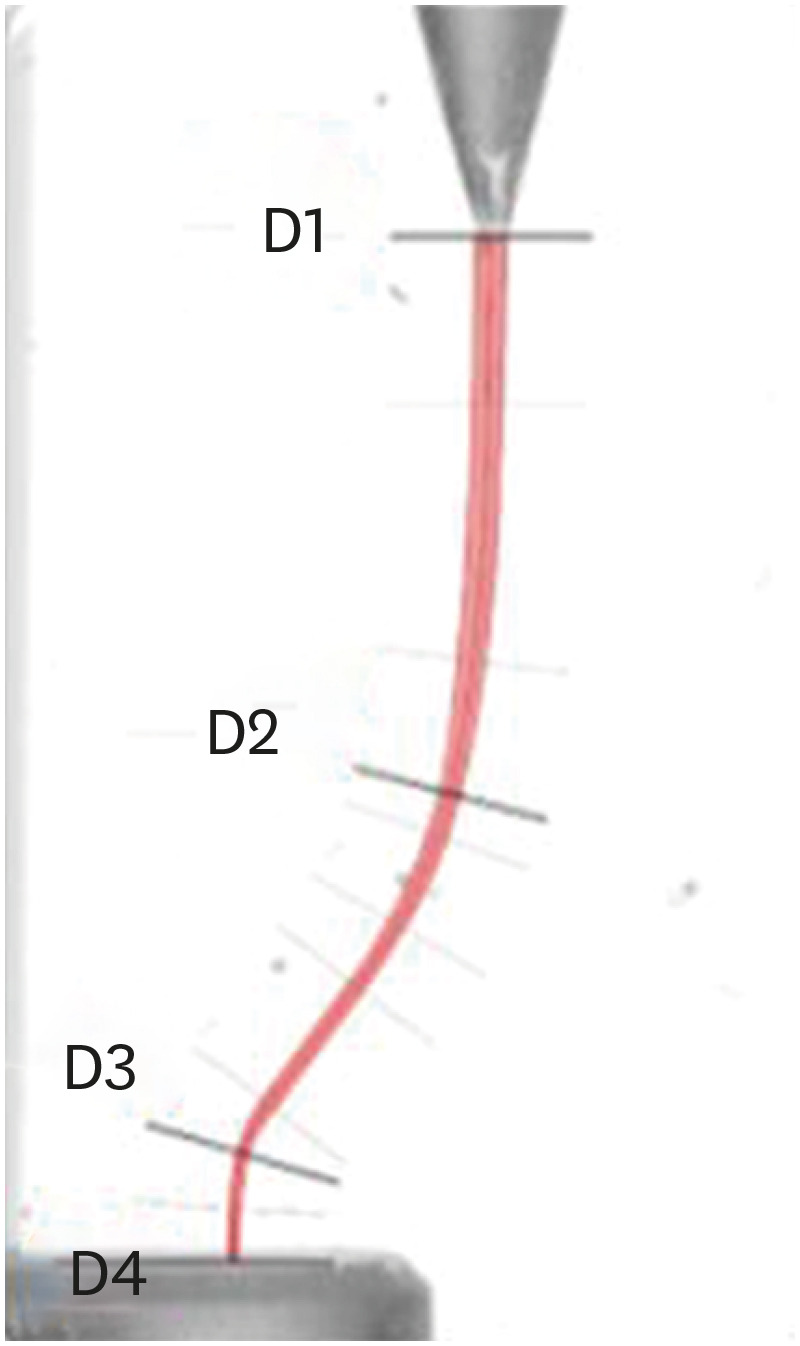
Materials and Methods Forty simulated S-shaped root canals were used and were prepared with One Curve (group OC), One G and OC (group GOC), Reciproc Blue (group RB) and R-Pilot and RB (group PRB) and scanned before and after instrumentation. The images were analyzed using AutoCAD. After superimposing the samples, 4 levels (D1, D2, D3, and D4) and 2 angles (Δ1 and Δ2) were established to evaluate the centering ability and modification of the canal curvatures. Then, the area of instrumentation (ΔA) was measured. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and Tukey's test for multiple comparisons (
p < 0.05).Results Regarding the centering ability in the apical part (D3, D4), the use of the glide-path yielded better results than the single-file groups. Among the groups at D4, OC showed the worst results (
p < 0.05). The OC system removed less material (ΔA) than the RB system, and for Δ1, OC yielded a worse result than RB (p < 0.05).Conclusions The glide-path improved the centering ability in the apical part of the simulated S-shaped canals. The RB system showed a better centering ability in the apical part and major respect of the canal curvatures compared with OC system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Apical Debris Extrusion and the Remaining Canal Material during Retreatment of a Bioceramic Sealer by the XP-endo Finisher File System, Followed by Various Supplementary Methods: An in Vitro Study
Paras Mull Gehlot, Parvathi Sudeep, Annapoorna B Mariswamy
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 15(10): 837. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Rotary NiTi Systems in S‐Shaped Root Canals of Mandibular Molars
Renata M. S. Leal, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Maria C. B. P. Campos, Clarissa T. Rodrigues, Marco A. H. Duarte, Bruno C. Cavenago
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(1): 133. CrossRef - Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
Taher Al Omari, Layla Hassouneh, Khawlah Albashaireh, Alaa Dkmak, Rami Albanna, Ali Al-Mohammed, Ahmed Jamleh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
Mahima Bharat Mehta, Anupam Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Ashwini A. Narayanan
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 101. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - In Vitro Research Methods Used to Evaluate Shaping Ability of Rotary Endodontic Files—A Literature Review
Ranya F. Elemam, Ana Mano Azul, João Dias, Khaled El Sahli, Renato de Toledo Leonardo
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 334. CrossRef - Endodontic glide path - importance and performance techniques
Milica Jovanovic-Medojevic, Мiljan Stosic, Vanja Opacic-Galic, Violeta Petrovic
Srpski arhiv za celokupno lekarstvo.2023; 151(5-6): 380. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Apical Debris Extrusion and the Remaining Canal Material during Retreatment of a Bioceramic Sealer by the XP-endo Finisher File System, Followed by Various Supplementary Methods: An in Vitro Study
- 3,068 View
- 46 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
- Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e28. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
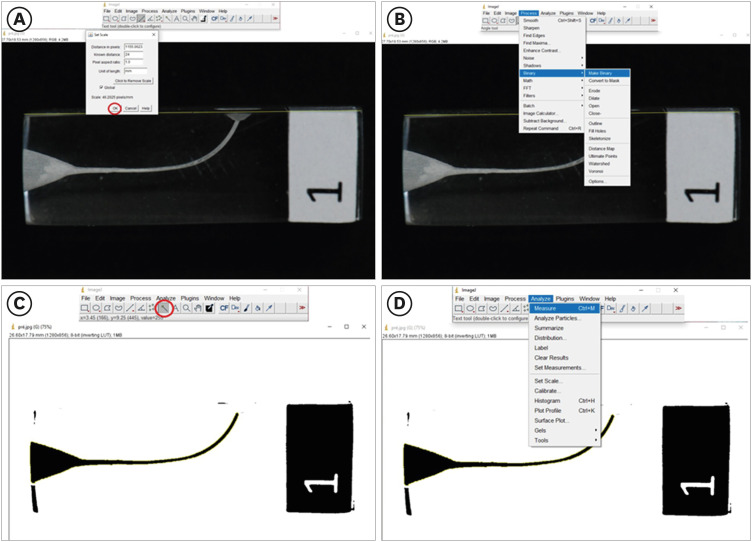
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of repeated uses and autoclaving in the instrumented area, fracture resistance, and time of instrumentation of thermally treated nickel-titanium reciprocating systems.
Materials and Methods Two hundred simulated canals were instrumented using Reciproc Blue and WaveOne Gold. Each file was used up to 10 times or until fracture. The instrumented area was measured in pre- and post-operative images, using ImageJ software. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis evaluated the number of uses of instruments before fracture. Instrumented area and time of instrumentation were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis. Correlations among the number of uses and instrumented area were measured. The level of statistical significance was set at
p < 0.05.Results Reciproc Blue presented a higher estimated number of uses in comparison with WaveOne Gold (
p = 0.026), but autoclaving did not affect the resistance to fracture of instruments (p > 0.05). The instrumented area was different among the evaluated groups (p = 0.039), and the instrumented area along the uses of both tested instruments was reduced. With the time of instrumentation, there was also a significant difference among the evaluated groups; the groups without sterilization cycles were faster, in comparison to those submitted to autoclaving (p = 0.010).Conclusions Reciproc Blue was more resistant than WaveOne Gold, suffering later fracture. Additionally, the sterilization cycles did not influence the estimated number of uses of thermally treated reciprocating instruments, but the instrumented area of root canals was reduced along with the repeated uses of both instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of sterilization on the cutting efficiency of two different rotary NiTi instruments (An In- vitro Study)
Merna Mamdouh Botros, Kariem Mostafa ElBatouty, Tariq Yehia Abdelrahman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Risk of Endodontic Files: Clinical Analysis of Reciproc and X1 Blue After Multiple Uses
Elisa Korte Fortes Gollo, Fábio de Almeida Gomes, Katerine Jahnecke Pilownic, Daiana Elisabeth Böttcher, Carolina Clasen Vieira, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 699. CrossRef - The influence of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue of M-wire rotary endodontic instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Antonije Stankovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Marija Nikolic, Kosta Todorovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2024; 81(10): 642. CrossRef
- Effect of sterilization on the cutting efficiency of two different rotary NiTi instruments (An In- vitro Study)
- 1,590 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Age-dependent root canal instrumentation techniques: a comprehensive narrative review
- Michael Solomonov, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Avi Hadad, Dan Henry Levy, Joe Ben Itzhak, Oleg Levinson, Hadas Azizi
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e21. Published online March 4, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this article was to review age-dependent clinical recommendations for appropriate root canal instrumentation techniques. A comprehensive narrative review of canal morphology, the structural characteristics of dentin, and endodontic outcomes at different ages was undertaken instead of a systematic review. An electronic literature search was carried out, including the Medline (Ovid), PubMed, and Web of Science databases. The searches used controlled vocabulary and free-text terms, as follows: ‘age-related root canal treatment,’ ‘age-related instrumentation,’ ‘age-related chemo-mechanical preparation,’ ‘age-related endodontic clinical recommendations,’ ‘root canal instrumentation at different ages,’ ‘geriatric root canal treatment,’ and ‘pediatric root canal treatment.’ Due to the lack of literature with practical age-based clinical recommendations for an appropriate root canal instrumentation technique, a narrative review was conducted to suggest a clinical algorithm for choosing the most appropriate instrumentation technique during root canal treatment. Based on the evidence found through the narrative review, an age-related clinical algorithm for choosing appropriate instrumentation during root canal treatment was proposed. Age affects the morphology of the root canal system and the structural characteristics of dentin. The clinician’s awareness of root canal morphology and dentin characteristics can influence the choice of instruments for root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Challenges Faced by Undergraduate Dental Students During Root Canal Treatment (RCT) and the Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients After RCT
Mubashir Baig Mirza, Abdullah Bajran Almuteb, Abdulaziz Tariq Alsheddi, Qamar Hashem, Mohammed Ali Abuelqomsan, Ahmed AlMokhatieb, Shahad AlBader, Abdullah AlShehri
Medicina.2025; 61(2): 215. CrossRef - OUTCOMES OF COMBINED ENDODONTIC TREATMENT AND APICAL SURGERY IN MANAGING LARGE PERIAPICAL CYSTS: A CLINICAL STUDY
Sapna Pandey, P Nihar, Amit Kumar, Nitin Bhagat, Vikram Karande, Zameer Pasha, Anukriti Kumari
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 329. CrossRef - El Uso del hipoclorito de sodio en endodoncia: concentración, temperatura y activación
Ábilson Josue Fabiani Ticona, Fernanda Camargo Espejo
Revista de investigación e información en salud.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Anatomical Dentin Thickness in Mandibular First Molar: An In Vivo Cone‐Beam Computed Tomographic Study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Jerry Jose, Mariangela Cernera, Parisa Soltani, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral Health Concerns of the ‘Sunset Age’
Pradnya V. Kakodkar, Amandeep Kaur, Shivasakthy Manivasakan, Sounyala Rayannavar, Revati Deshmukh, Smita Athavale
Journal of Medical Evidence.2023; 4(2): 141. CrossRef - Root canal treatment of a six-canal first mandibular molar with extensive periapical lesion: A case report
Xin Li, Shuyu Sun, Tengyi Zheng
Medicine.2023; 102(30): e34336. CrossRef - Endodontic Dentistry: Analysis of Dentinal Stress and Strain Development during Shaping of Curved Root Canals
Laura Iosif, Bogdan Dimitriu, Dan Florin Niţoi, Oana Amza
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2918. CrossRef - Mechanisms of age-related changes in the morphology of the pulp system of the first lower molars
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, V.A. Venediktova
Stomatologiya.2022; 101(2): 19. CrossRef
- Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Challenges Faced by Undergraduate Dental Students During Root Canal Treatment (RCT) and the Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients After RCT
- 3,271 View
- 36 Download
- 8 Crossref

-
Dentinal defects induced by 6 different endodontic files when used for oval root canals: an
in vitro comparative study - Ajinkya M Pawar, Bhagyashree Thakur, Anda Kfir, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e31. Published online July 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
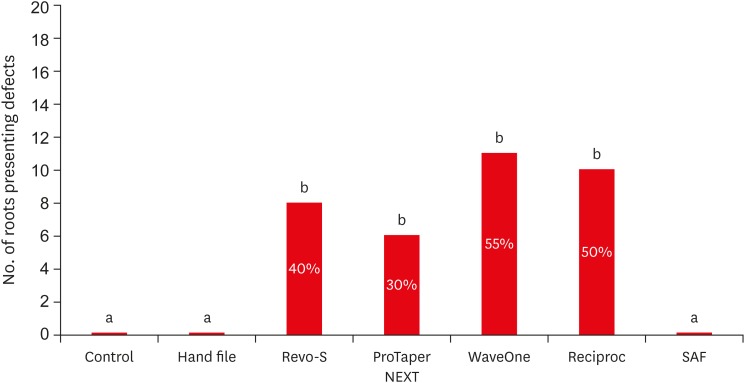
ePub Objectives To compare the formation of dentinal defects using stainless-steel hand K-files (HFs), rotary files, reciprocating files, and Self-Adjusting File (SAF), when used for oval root canals.
Materials and Methods One hundred and forty extracted human mandibular premolar with single root and oval canal were selected for this study. Oval canals were confirmed by exposing to mesio-distal and bucco-lingual radiographs. Teeth with open apices or anatomic irregularities were excluded. All selected teeth were de-coronated perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth, leaving roots segments approximately of 16 mm in length. Twenty teeth were left unprepared (control), and the remaining 120 teeth were divided into 6 groups (
n = 20) and instrumented using HF (size 40/0.02), Revo-S (RS; size 40/0.06), ProTaper NEXT (PTN; size 40/0.06), WaveOne (WO; size 40/0.09), RECIPROC (RC; size 40/0.06), and the SAF (2 mm). Roots were then sectioned 3, 6, and 9 mm from the apex, and observed under stereomicroscope, for presence of dentinal defects. “No defect” was defined as root dentin that presented with no visible microcracks or fractures. “Defect” was defined by microcracks or fractures in the root dentin.Results The control, HF, and SAF did not exhibit any dentinal defects. In roots instrumented by RS, PTN, WO, and RC files exhibited microcracks (incomplete or complete) in 40%, 30%, 55%, and 50%, respectively.
Conclusions The motor-driven root canal instrumentation with rotary and reciprocating files may create microcracks in radicular dentine, whereas the stainless-steel hand file instrumentation, and the SAF produce minimal or less cracks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of dentinal crack formation during post space preparation using different fiber post systems with micro-computed tomography
Ayşe Nur Kuşuçar, Damla Kırıcı
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Computational Insights into Root Canal Treatment: A Survey of Selected Methods in Imaging, Segmentation, Morphological Analysis, and Clinical Management
Jianning Li, Kerstin Bitter, Anh Duc Nguyen, Hagay Shemesh, Paul Zaslansky, Stefan Zachow
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(12): 579. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using three different endodontic retreatment systems – An in vitro study
S. Aarthi, J. S. Sivakumar, A. Andamuthu Sivakumar, J. Saravanapriyan Soundappan, M. Chittrarasu, G. Jayanthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 262. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dentin Cracks by Stereomicroscope after Preparation of Mesiobuccal Canal of Maxillary First Molars Using Edge Taper Platinum and ProTaper Gold Rotary Files: A Laboratory Study
Narjes Hoshyari, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Eghlima Malakan, Abolfazl Hosseinnataj, Azam Haddadi Kohsar
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2023; 15(4): 167. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of dentinal defects after root canal preparation with different rotary and reciprocal systems
Ece Yakın, Berna Aslan, Emine Odabaşı Tezer
Northwestern Medical Journal.2023; 3(3): 147. CrossRef - Comparison of Dentinal Defects Induced by Rotary, Reciprocating, and Hand Files in Oval Shaped Root Canal - An In-Vitro Study
Harakh Chand Branawal, Neelam Mittal, Prachi Rani, Aiyman Ayubi, Silviya Samad
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2023; 34(4): 433. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using hand, rotary, and reciprocating files: An ex vivo study
Debanjan Das, Sudipto Barai, Rohit Kumar, Sourav Bhattacharyya, AsimB Maity, Pushpa Shankarappa
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(1): 78. CrossRef - Effect of XP‐endo Shaper versus conventional rotary files on postoperative pain and bacterial reduction in oval canals with necrotic pulps: a randomized clinical study
R. S. Emara, S. I. Gawdat, H. M. M. El‐Far
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1026. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Formation by Single Reciprocating File Systems: An In Vitro Study
Baby James, A Devadathan, Manuja Nair, Ashitha T Kulangara, Jose Jacob
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2020; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - The potential effect of instrumentation with different nickel titanium rotary systems on dentinal crack formation—An in vitro study
Márk Fráter, András Jakab, Gábor Braunitzer, Zsolt Tóth, Katalin Nagy, Andrej M. Kielbassa
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238790. CrossRef
- Evaluation of dentinal crack formation during post space preparation using different fiber post systems with micro-computed tomography
- 1,990 View
- 24 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured instruments: a bibliometric analysis
- Lora Mishra, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Priti Pragati Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e2. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this research was to identify the top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured or broken instruments and to perform a bibliometric analysis thereof.
Materials and Methods Published articles related to fractured instruments were screened from online databases, such as Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect, and highly cited papers, with at least 50 citations since publication, were identified. The most-cited articles were selected and analysed with regard to publication title, authorship, the journal of publication, year, institution, country of origin, article type, and number of citations.
Results The top 10 most-cited articles were from various journals. Most were published in the
Journal of Endodontics , followed by theInternational Endodontic Journal , andDental Traumatology . The leading countries were Australia, Israel, Switzerland, the USA, and Germany, and the leading institution was the University of Melbourne. The majority of articles among the top 10 articles were clinical research studies (n = 8), followed by a basic research article and a non-systematic review article.Conclusions This bibliometric analysis revealed interesting information about scientific progress in endodontics regarding fractured instruments. Overall, clinical research studies and basic research articles published in high-impact endodontic journals had the highest citation rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Endodontide Mikro-Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Kullanımı Konusunda Yayımlanan Makalelerin Bibliyometrik Analizi: Nicel Araştırma
Özge Kurt, Emine Şimşek
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 18(3): 309. CrossRef - A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Top-Cited Articles on Vertical Root Fractures
Pillai Arun Gopinathan , Ikram UI Haq, Nawaf Alfahad, Saleh Alwatban, Abdullah Alghamdi, Amal Alamri, Kiran Iyer
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most‐cited case reports and case series in Endodontic journals
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Jelena Jacimovic, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(3): 185. CrossRef - The Most Highly Cited Publications on Basketball Originate From English-Speaking Countries, Are Published After 2000, Are Focused on Medicine-Related Topics, and Are Level III Evidence
Zachary D. Griffin, Jordan R. Pollock, M. Lane Moore, Kade S. McQuivey, Jaymeson R. Arthur, Anikar Chhabra
Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation.2022; 4(3): e891. CrossRef - Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Publication trends in micro‐CT endodontic research: a bibliometric analysis over a 25‐year period
U. Aksoy, M. Küçük, M. A. Versiani, K. Orhan
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(3): 343. CrossRef
- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
- 1,600 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Improved dentin disinfection by combining different-geometry rotary nickel-titanium files in preparing root canals
- Marwa M. Bedier, Ahmed Abdel Rahman Hashem, Yosra M. Hassan
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e46. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e46

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was to evaluate the antibacterial effect of different instrumentation and irrigation techniques using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) after root canal inoculation with
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ).Materials and Methods Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of extracted mandibular molars were apically enlarged up to a size 25 hand K-file, then autoclaved and inoculated with
E. faecalis . The samples were randomly divided into 4 main groups according to the system of instrumentation and irrigation: an XP-endo Shaper (XPS) combined with conventional irrigation (XPS/C) or an XP-endo Finisher (XPF) (XPS/XPF), and iRaCe combined with conventional irrigation (iRaCe/C) or combined with an XPF (iRaCe/XPF). A middle-third samplewas taken from each group, and then the bacterial reduction was evaluated using CLSM at a depth of 50 µm inside the dentinal tubules. The ratio of red fluorescence (dead cells) to green-and-red fluorescence (live and dead cells) represented the percentage of bacterial reduction. The data were then statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for comparisons across the groups and the Dunn test was used for pairwise comparisons.Results The instrumentation and irrigation techniques had a significant effect on bacterial reduction (
p < 0.05). The iRaCe/XPF group showed the strongest effect, followed by the XPS/XPF and XPS/C group, while the iRaCe/C group had the weakest effect.Conclusions Combining iRaCe with XPF improved its bacterial reduction effect, while combining XPS with XPF did not yield a significant improvement in its ability to reduce bacteria at a depth of 50 µm in the dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
Oksana A. Shuliatnikova, Mikhail V. Yakovlev, Anatoliy P. Godovalov
HERALD of North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.2025; 17(2): 89. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Shaping ability of non‐adaptive and adaptive core nickel–titanium single‐file systems with supplementary file in ribbon‐shaped canals analysed by micro‐computed tomography
Parichat Chinchiyanont, Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Nathamon Thongbai‐On
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - In vitro reduction in Enterococcus faecalis count following root canal preparation with Neolix and XP shaper rotary files
Mina Mehrjouei, Somayeh Teimoori, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Seyed Majed Mortazavi, Maryam Khorasanchi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 236. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite versus apple cider vinegar against Enterococcus faecalis in contracted endodontic cavity
Kaur Supreet, Karkala Venkappa Kishan, Nimisha Chinmay Shah
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 254. CrossRef - Ex vivo evaluation of the effectiveness of XP-endo Finisher on the removal of smear layer from the root canal
Sângela Maria PEREIRA, Ceci Nunes CARVALHO, Rudys Rodolfo TAVAREZ, Paulo NELSON-FILHO, Léa Assed Bezerra DA SILVA, Etevaldo Matos MAIA FILHO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biofilm elimination from infected root canals using four different single files
Sarah A. Hamed, Sarah Shabayek, Hayam Y. Hassan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adaptive, Rotary, and Manual Root Canal Instrumentation in Primary Molars: A Triple-Armed, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Bhaggyashri A. Pawar, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Anuj Bhardwaj, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Amelia Kristanti Rahardjo, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Zvi Metzger, Anda Kfir
Biology.2021; 10(1): 42. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Endodontic Access Cavity Design and Using XP-endo Finisher on the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal System
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Koray Yılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 419. CrossRef - Irrigation in Endodontics: a Review
Sarah Bukhari, Alaa Babaeer
Current Oral Health Reports.2019; 6(4): 367. CrossRef
- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
- 1,630 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref

-
Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an
in vitro study - Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):316-323. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the amount of apically extruded bacteria during the glide-path preparation by using multi-file and single-file glide-path establishing nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary systems.
Materials and Methods Sixty mandibular first molar teeth were used to prepare the test apparatus. They were decoronated, blocked into glass vials, sterilized in ethylene oxide gas, infected with a pure culture of
Enterococcus faecalis, randomly assigned to 5 experimental groups, and then prepared using manual stainless-steel files (group KF) and glide-path establishing NiTi rotary files (group PF with PathFiles, group GF with G-Files, group PG with ProGlider, and group OG with One G). At the end of canal preparation, 0.01 mL NaCl solution was taken from the experimental vials. The suspension was plated on brain heart infusion agar and colonies of bacteria were counted, and the results were given as number of colony-forming units (CFU).Results The manual instrumentation technique tested in group KF extruded the highest number of bacteria compared to the other 4 groups (
p < 0.05). The 4 groups using rotary glide-path establishing instruments extruded similar amounts of bacteria.Conclusions All glide-path establishment instrument systems tested caused a measurable apical extrusion of bacteria. The manual glide-path preparation showed the highest number of bacteria extruded compared to the other NiTi glide-path establishing instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Warley O. Silva, Jeferson O. Marques, Ana Carolina S.P. Guerra, Flávio R.F. Alves
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 866. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Multiple Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Severely Curved Mesial Roots of Mandibular Molars: An In Vitro Study
Niranjan Desai, Ashish S Bhadane, Nishant K Vyavahare, Dipali Y Shah, Akash S Kale, Simran K Chaudhari
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Impact of Different Glidepath Techniques on the Overall Performance of WaveOne Gold in an Artificial S-Shape Canal
Vlad Mircea Lup, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Carlo Gaeta, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 182. CrossRef - Influence of different irrigant activation methods on apical debris extrusion and bacterial elimination from infected root canals
KSadia Ada, Shibani Shetty, KB Jayalakshmi, PrasannaLatha Nadig, PG Manje Gowda, ArulK Selvan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of glide path files with different metallurgy on intracanal bacterial extrusion by HyFlex electrical discharge machining file
Priyanka Soni, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja, Anshi Jain
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 168. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris using Three Rotary and One Reciprocating Instrumentation Ni-Ti Systems
Maha Adnan Habeeb
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2022; 14(2): 93. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of a glide path creation necessity at the initial stages of endodontic treatment
Z. S. Khabadze, Yu. A. Generalova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Apically extruded debris produced during glide path preparation using R‐Pilot, WaveOne Gold Glider and ProGlider in curved root canals
Cangül Keskin, Özlem Sivas Yilmaz, Uğur Inan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(3): 439. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Glide Path Preparation Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Joo-Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(2): 199. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Postoperative pain after glide path preparation using manual, reciprocating and continuous rotary instruments: a randomized clinical trial
C. Keskin, Ö. Sivas Yilmaz, U. Inan, Ö. Özdemir
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(5): 579. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef - Effects of Different Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Curved Root Canals
Betul Gunes, Kubra Yesildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1191. CrossRef
- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
- 1,664 View
- 13 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Intraoperative discomfort associated with the use of a rotary or reciprocating system: a prospective randomized clinical trial
- Aline Cristine Gomes, Adriana Jesus Soares, Erick M Souza, Alexandre Augusto Zaia, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):140-145. Published online April 20, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.140
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this randomized, controlled, prospective clinical study was to evaluate patients' intraoperative discomfort during root canal preparations in which either multi-file rotary (Mtwo) or single-file reciprocating (Reciproc) systems were used.
Materials and Methods Fifty-five adult patients, aged between 25 and 69 years old, with irreversible pulpitis or pulp necrosis participated in this study. Either the mesiobuccal or the distobuccal canals for maxillary molars and either the mesiobuccal or the mesiolingual canals for mandibular molars were randomly chosen to be instrumented with Mtwo multi-file rotary or Reciproc single-file reciprocating systems. Immediately after each canal instrumentation under anesthesia, patient discomfort was assessed using a 1 - 10 visual analog scale (VAS), ranging from ‘least possible discomfort’ (1) to ‘greatest possible discomfort’ (10). The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to determine significant differences at
p < 0.05.Results Little intraoperative discomfort was found in all cases. No statistically significant differences in intraoperative discomfort between the 2 systems were found (
p = 0.660).Conclusions Root canal preparation with multi-file rotary or single-file reciprocating systems had similar and minimal effects on patients' intraoperative discomfort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Post-Operative Pain in Reciprocating Versus Rotary Kinematics Post-Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
Youssef Algarni
Archives of Pharmacy Practice.2024; 15(2): 53. CrossRef - Postoperative pain perception and associated risk factors in children after continuous rotation versus reciprocating kinematics: A randomised prospective clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Dania Ibrahem Sermani, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 345. CrossRef - Patient discomfort levels during instrumentation procedure using nickel‐titanium files with different kinetic movements
So‐Ra Park, Se‐Hee Park, Kyung‐Mo Cho, Jin‐Woo Kim, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 372. CrossRef - Effect of XP‐endo Shaper versus conventional rotary files on postoperative pain and bacterial reduction in oval canals with necrotic pulps: a randomized clinical study
R. S. Emara, S. I. Gawdat, H. M. M. El‐Far
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1026. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a reciprocating single file, single cone endodontic treatment approach: a randomized controlled pragmatic clinical trial
Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Laila F. Lima, Ludmila S. Oliveira, Maria A. Ribeiro, Marcos B. Correa, Manoel Brito-Junior, André L. Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(7): 2247. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain intensity following the use of three different instrumentation techniques: A randomized clinical trial
Mehmet Adiguzel, Pelin Tufenkci, ismail Ilker Pamukcu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 133. CrossRef - Reciprocating kinematics leads to lower incidences of postoperative pain than rotary kinematics after endodontic treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
ChristineMen Martins, VictorEduardo De Souza Batista, AmandaCaselato Andolfatto Souza, AnaCristina Andrada, GrazielaGarrido Mori, JoaoEduardo Gomes Filho
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2019; 22(4): 320. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef
- Post-Operative Pain in Reciprocating Versus Rotary Kinematics Post-Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
- 2,089 View
- 18 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):1-5. Published online February 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.1

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of ProTaper Gold (PTG, Dentsply Maillefer) in maintaining the original profile of root canal anatomy. For that, ProTaper Universal (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer) was used as reference techniques for comparison.
Materials and Methods Twenty simulated curved canals manufactured in clear resin blocks were randomly assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10) according to the system used for canal instrumentation: PTU and PTG groups, upto F2 files (25/0.08). Color stereomicroscopic images from each block were taken exactly at the same position before and after instrumentation. All image processing and data analysis were performed with an open source program (FIJI). Evaluation of canal transportation was obtained for two independent canal regions: straight and curved levels. Student'st test was used with a cut-off for significance set at α = 5%.Results Instrumentation systems significantly influenced canal transportation (
p < 0.0001). A significant interaction between instrumentation system and root canal level (p < 0.0001) was found. PTU and PTG systems produced similar canal transportation at the straight part, while PTG system resulted in lower canal transportation than PTU system at the curved part. Canal transportation was higher at the curved canal portion (p < 0.0001).Conclusions PTG system produced overall less canal transportation in the curved portion when compared to PTU system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
Wesley Viana de Sousa, Marina da Cunha Isaltino, Christianne Velozo, Silmara de Andrade Silva, Luiza de Almeida Souto Montenegro, Hugo Victor Dantas, Frederico Barbosa de Sousa, Diana Albuquerque, Cristiana Corsi
The Scientific World Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping, and disinfecting abilities of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Twisted Files: A correlative microcomputed tomographic and bacteriologic analysis
Malavika Sivakumar, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, CP Baveja, Rega Kumar, Sudha Yadav, S Santosh Kumar
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 54. CrossRef - Advancing Nitinol: From heat treatment to surface functionalization for nickel–titanium (NiTi) instruments in endodontics
Wai-Sze Chan, Karan Gulati, Ove A. Peters
Bioactive Materials.2023; 22: 91. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - An Appraisal on Newer Endodontic File Systems: A Narrative Review
Shalini Singh, Kailash Attur, Anjali Oak, Mohammed Mustafa, Kamal Kumar Bagda, Nishtha Kathiria
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 944. CrossRef - Shaping ability of modern Nickel–Titanium rotary systems on the preparation of printed mandibular molars
Seda Falakaloglu, Emmanuel Silva, Burcu Topal, Emre İriboz, Mustafa Gündoğar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 498. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna Dobrzańska
Processes.2022; 10(1): 101. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Kinematics on Stress Distribution During Root Canal Treatment: Analysis of Photoelastic Stress
Shelyn Akari Yamakami, Julia Adornes Gallas, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Manoel Sousa-Neto, Ana Paula Macedo, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 255. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Two Martensitic Alloy Systems in Endodontic Files Carried out by Unskilled Hands
Juan Algar, Alejandra Loring-Castillo, Ruth Pérez-Alfayate, Carmen Martín Carreras-Presas, Ana Suárez
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6289. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Canal Transportation, Separation Rate, and Preparation Time between One Shape and Neoniti (Neolix): An In Vitro CBCT Study
Maryam Kuzekanani, Faranak Sadeghi, Nima Hatami, Maryam Rad, Mansoureh Darijani, Laurence James Walsh, Sivakumar Nuvvula
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold, One Curve, and Self-Adjusting File systems in severely curved canals: A cone-beam computed tomography study
MeenuG Singla, Hemanshi Kumar, Ritika Satija
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 271. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of apical transportation and centering ratio of ProTaper and XP-endo Shaper NiTi rotary systems in curved canals: an in vitro study
Hamed Karkehabadi, Zeinab Siahvashi, Abbas Shokri, Nasrin Haji Hasani
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanical Tests, Metallurgical Characterization, and Shaping Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments: A Multimethod Research
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Jorge N.R. Martins, Carolina O. Lima, Victor T.L. Vieira, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Gustavo De-Deus, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(10): 1485. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of vibration characteristics of file systems for root canal shaping according to file length
Seong-Jun Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Hyo-Jin Ji, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys – a review
J. Zupanc, N. Vahdat‐Pajouh, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(10): 1088. CrossRef - Shaping ability of four root canal instrumentation systems in simulated 3D-printed root canal models
David Christofzik, Andreas Bartols, Mahmoud Khaled Faheem, Doreen Schroeter, Birte Groessner-Schreiber, Christof E. Doerfer, Cyril Charles
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0201129. CrossRef - OPEN-SOURCE SOFTWARE IN DENTISTRY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Małgorzata Chruściel-Nogalska, Tomasz Smektała, Marcin Tutak, Katarzyna Sporniak-Tutak, Raphael Olszewski
International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care.2017; 33(4): 487. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - A comparison of the shaping ability of three nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomography study via a contrast radiopaque technique in vitro
Zhao Wei, Zhi Cui, Ping Yan, Han Jiang
BMC Oral Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Transportation and Centering Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Mandibular Premolars Assessed Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Iussif Mamede-Neto, Alvaro Henrique Borges, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Durvalino de Oliveira, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Carlos Estrela
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 71. CrossRef - Blue Thermomechanical Treatment Optimizes Fatigue Resistance and Flexibility of the Reciproc Files
Gustavo De-Deus, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gianluca Plotino, Nicola Maria Grande
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 462. CrossRef
- Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
- 1,770 View
- 9 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of a C-shaped mandibular second premolar with four root canals and three apical foramina: a case report
- Thikamphaa Bertrand, Sahng Gyoon Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):68-73. Published online January 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.68

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report describes a unique C-shaped mandibular second premolar with four canals and three apical foramina and its endodontic management with the aid of cone-beam computer tomography (CBCT). C-shaped root canal morphology with four canals was identified under a dental operating microscope. A CBCT scan was taken to evaluate the aberrant root canal anatomy and devise a better instrumentation strategy based on the anatomy. All canals were instrumented to have a 0.05 taper using 1.0 mm step-back filing with appropriate apical sizes determined from the CBCT scan images and filled using a warm vertical compaction technique. A C-shaped mandibular second premolar with multiple canals is an anatomically rare case for clinicians, yet its endodontic treatment may require a careful instrumentation strategy due to the difficulty in disinfecting the canals in the thin root area without compromising the root structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unique root anatomy of mandibular second premolars: clinical strategies for effective disinfection and preservation of dentine structure in root canal treatment—a case report
Ji Wook Jeong, Erika Silguero Gonzalez, Scott R. Makins, Timothy Kirkpatrick
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PRICE 2020 guidelines for reporting case reports in Endodontics: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, B. S. Chong, P. McCabe, P. K. Shah, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 922. CrossRef - A cone-beam computed tomography study of C-shaped root canal systems in mandibular second premolars in a Taiwan Chinese subpopulation
Yi-Chin Chen, Chia-Lun Tsai, Yi-Chen Chen, Gin Chen, Shue-Fen Yang
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2018; 117(12): 1086. CrossRef - Anatomic Comparison of Contralateral Premolars
Gaute Floer Johnsen, Sazan Dara, Sameenah Asjad, Pia Titterud Sunde, Håvard Jostein Haugen
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(6): 956. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary Central Incisor fused to a Supernumerary Tooth using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Unusual Clinical Presentation
Thilla S Vinothkumar, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Ganesh Arathi, Sathishkumar Ramkumar, Gnanasekaran Felsypremila
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(6): 522. CrossRef
- Unique root anatomy of mandibular second premolars: clinical strategies for effective disinfection and preservation of dentine structure in root canal treatment—a case report
- 2,752 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
- Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):167-171. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Biomechanical preparation of root canals with accentuated curvature is challenging. New rotatory systems, such as Reciproc, require a shorter period of time to prepare curved canals, and became a viable alternative for endodontic treatment of teeth with root dilaceration. Thus, this study aimed to report a clinical case of endodontic therapy of root with accentuated dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system. Mandibular right second molar was diagnosed as asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis. Pulp chamber access was performed, and glide path was created with #10 K-file (Dentsply Maillefer) and PathFile #13, #16 and #19 (Dentsply Maillefer) up to the temporary working length. The working length measured corresponded to 20 mm in the mesio-buccal and mesio-lingual canals, and 22 mm in the distal canal. The R25 file (VDW GmbH) was used in all the canals for instrumentation and final preparation, followed by filling with Reciproc gutta-percha cones (VDW GmbH) and AH Plus sealer (Dentsply Maillefer), using thermal compaction technique. The case has been receiving follow-up for 6 mon and no painful symptomatology or periapical lesions have been found. Despite the difficulties, the treatment could be performed in a shorter period of time than the conventional methods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Characteristics of Reciprocating Instruments Before and After Use - A SEM Analysis
Aida Rene Assayag Hanan, Daniely Amorin de Meireles, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Simone Hanan, Milton Carlos Kuga, Idomeo Bonetti Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2015; 26(2): 121. CrossRef - Endodontic Treatment of an Anomalous Anterior Tooth with the Aid of a 3-dimensional Printed Physical Tooth Model
Chanhee Byun, Changhwan Kim, Seungryong Cho, Seung Hoon Baek, Gyutae Kim, Sahng G. Kim, Sun-Young Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 961. CrossRef
- Surface Characteristics of Reciprocating Instruments Before and After Use - A SEM Analysis
- 1,570 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of canal enlargement and irrigation needle depth on the cleaning of the root canal system at 3 mm from the apex
- Ho-Jin Moon, Chan-Ui Hong
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):24-28. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis, that the effectiveness of irrigation in removing smear layer in the apical third of root canal system is dependent on the depth of placement of the irrigation needle into the root canal and the enlargement size of the canal.
Materials and Methods Eighty sound human lower incisors were divided into eight groups according to the enlargement size (#25, #30, #35 and #40) and the needle penetration depth (3 mm from working length, WL-3 mm and 9 mm from working length, WL-9 mm). Each canal was enlarged to working length with Profile.06 Rotary Ni-Ti files and irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl. Then, each canal received a final irrigation with 3 mL of 3% EDTA for 4 min, followed by 5 mL of 5.25% NaOCl at different level (WL-3 mm and WL-9 mm) from working length. Each specimen was prepared for the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Photographs of the 3mm area from the apical constriction of each canal with a magnification of ×250, ×500, ×1,000, ×2,500 were taken for the final evaluation.
Results Removal of smear layer in WL-3 mm group showed a significantly different effect when the canal was enlarged to larger than #30. There was a significant difference in removing apical smear layer between the needle penetration depth of WL-3 mm and WL-9 mm.
Conclusions Removal of smear layer from the apical portion of root canals was effectively accomplished with apical instrumentation to #35/40 06 taper file and 3 mm needle penetration from the working length.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numerical Evaluation of Flow Pattern for Root Canal Irrigation Including icrobubbles
Joon Hyun Kim, Chan U Lee, Inwhan Lee, Jaeyong Sung
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2023; 32(5): 251. CrossRef
- Numerical Evaluation of Flow Pattern for Root Canal Irrigation Including icrobubbles
- 1,199 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
- Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub To evaluate the change of working length with various instrumentation techniques in curved canals, working length and canal curvature were determined before and after canal instrumentation in buccal or mesial canals of extracted human molars. Stainless steel K-files (MANI®, Matsutani Seisakusho Co. Takanezawa, Japan), nickel-titanium K-files (Naviflex NT™, Brassler, Savannah, USA), ProFile®, and ProTaper™ (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) were used to prepare the canals with crown-down technique. In two hand instrumentation groups, coronal flaring was made with Gates Glidden burs. Apical canals were instrumented until apical diameter had attained a size of 30. Positional relation between the tooth apex and the #10 K-file tip was examined by using AutoCAD 2000 (Autodesk Corp., San Rafael. CA, USA) under a stereomicroscope before and after coronal flaring, and after apical instrumentation. Degree of canal curvature was also measured with Schneider's method in radiographs. Data of working length and canal curvature changes were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's studentized range test.
Working length and canal curvature were decreased significantly in each step in all instrumentation groups. Coronal flaring using Gates Glidden burs in hand instrument groups and whole canal instrumentation using stainless steel hand K-files caused significantly more working length change than in ProFile instrumentation group (p < 0.05).
The result of this study demonstrates that all of the above kinds of instrumentation in curved canals cause reduction of working length and canal curvature at each instrumentation steps, and hand instrumentation causes more working length change than ProFile.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Accuracy of an Endomotor-Integrated Apex Locator Versus a Standalone Electronic Apex Locator in Teeth with Simulated Apical Root Resorption: An In Vitro Study
Yunus Emre Çakmak, Damla Erkal, Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç
European Journal of Therapeutics.2025; 31(3): 173. CrossRef - Does Root Canal Shaping Effect the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in Curved and Straight Root Canals?
Dide Tekinarslan, Damla Erkal, Esen Ercan, Simay Koc, Kürşat Er
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2024; 14(3): 727. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Four Endodontic File Systems to Assess Changes in Working Length during Root Canal Instrumentation and the Effect of Canal Curvature on Working Length Change
Michelle Tien, Hermawan Tjoa, Maggie Zhou, Paul V. Abbott
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(1): 110. CrossRef - Study of endodontic working length of Korean posterior teeth
Jeong-Yeob Kim, Sang-Hoon Lee, Gwang-Hee Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 429. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Accuracy of an Endomotor-Integrated Apex Locator Versus a Standalone Electronic Apex Locator in Teeth with Simulated Apical Root Resorption: An In Vitro Study
- 2,061 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The effect of early coronal flaring about apical extrusion of debris
- Min-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Beom Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):147-152. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate the quantity of debris which was extruded apically after canal instrumentation using different types of enlarging instrument in endodontic resin models.
Five groups of 9 endodontic resin models were instrumented using each different technique: hand instrumentation without early coronal flaring, hand instrumentation after early coronal flaring, and three nickel-titanium engine-driven instrumentations (Hero 642, Protaper, K3). Debris extruded from apical foramen during instrumentation was collected on preweighed CBC bottle, desiccated and weighted using electronic balance. The results were analyzed using Kruskal-wallis test and Mann-Whitney
U rank sum test at a significance level of 0.05.The results were as follows:
All of instrumentation techniques produced apically extruded debris.
Group without early coronal flaring extruded significant more debris than groups with early coronal flaring.
There was no significant difference among early coronal flaring groups.
The early coronal flaring is very important to reduce the amount of debris extruded apically.
- 903 View
- 0 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


