Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 37(1); 2012 > Article
- Research Article Effects of canal enlargement and irrigation needle depth on the cleaning of the root canal system at 3 mm from the apex
- Ho-Jin Moon, DDS, MSD1, Chan-Ui Hong, DDS, MSD, PhD2
-
2012;37(1):-28.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.24
Published online: March 2, 2012
1Biomaterials & Tissue Engineering Lab., Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
2Department of Conservative Dentistry, Plant Dental Hospital, Daejon, Korea.
- Correspondence to Ho-Jin Moon, DDS, MSD. Researcher, Biomaterials & Tissue Engineering Lab., Dankook University, Sinbu-dong, Dongnam-gu, Cheonan, Korea 330-716. TEL, +82-10-2062-5288; FAX, +82-41-553-5288; alkydes@dankook.ac.kr
©Copyights 2012. The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.
- 1,218 Views
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis, that the effectiveness of irrigation in removing smear layer in the apical third of root canal system is dependent on the depth of placement of the irrigation needle into the root canal and the enlargement size of the canal.
-
Materials and Methods Eighty sound human lower incisors were divided into eight groups according to the enlargement size (#25, #30, #35 and #40) and the needle penetration depth (3 mm from working length, WL-3 mm and 9 mm from working length, WL-9 mm). Each canal was enlarged to working length with Profile.06 Rotary Ni-Ti files and irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl. Then, each canal received a final irrigation with 3 mL of 3% EDTA for 4 min, followed by 5 mL of 5.25% NaOCl at different level (WL-3 mm and WL-9 mm) from working length. Each specimen was prepared for the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Photographs of the 3mm area from the apical constriction of each canal with a magnification of ×250, ×500, ×1,000, ×2,500 were taken for the final evaluation.
-
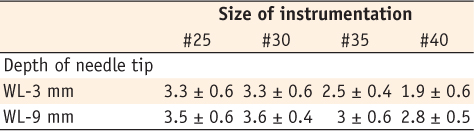
Results Removal of smear layer in WL-3 mm group showed a significantly different effect when the canal was enlarged to larger than #30. There was a significant difference in removing apical smear layer between the needle penetration depth of WL-3 mm and WL-9 mm.
-
Conclusions Removal of smear layer from the apical portion of root canals was effectively accomplished with apical instrumentation to #35/40 06 taper file and 3 mm needle penetration from the working length.
- 1. Baugh D, Wallace J. The role of apical instrumentation in root canal treatment: a review of the literature. J Endod. 2005;31: 333-340.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am. 1974;18: 269-296.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;58: 589-599.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Verma P, Love RM. A Micro CT study of the mesiobuccal root canal morphology of the maxillary first molar tooth. Int Endod J. 2011;44: 210-217.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Zehnder M. Root canal irrigants. J Endod. 2006;32: 389-398.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Rutala WA, Weber DJ. Uses of inorganic hypochlorite (bleach) in health-care facilities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997;10: 597-610.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Bystrom A, Sundqvist G. The antibacterial action of sodium hypochlorite and EDTA in 60 cases of endodontic therapy. Int Endod J. 1985;18: 35-40.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Yang SE, Bae KS. SEM study on the anaerobic bacterial adhesion to the dentin of root canal. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2001;26: 350-359.
- 9. Chow TW. Mechanical effectiveness of root canal irrigation. J Endod. 1983;9: 475-479.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Abou-Rass M, Piccinino MV. The effectiveness of four clinical irrigation methods on the removal of root canal debris. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982;54: 323-328.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kahn FH, Rosenberg PA, Gliksberg J. An in vitro evaluation of the irrigating characteristics of ultrasonic and subsonic handpieces and irrigating needles and probes. J Endod. 1995;21: 277-280.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Sedgley CM, Nagel AC, Hall D, Applegate B. Influence of irrigant needle depth in removing bioluminescent bacteria inoculated into instrumented root canals using real-time imaging in vitro. Int Endod J. 2005;38: 97-104.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Boutsioukis C, Lambrianidis T, Vasiliadis L. Clinical relevance of standardization of endodontic irrigation needle dimensions according to the ISO 9,626:1991 and 9,626:1991/Amd 1:2001 specification. Int Endod J. 2007;40: 700-706.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Boutsioukis C, Lambrianidis T, Kastrinakis E. Irrigant flow within a prepared root canal using various flow rates: a computational fluid dynamics study. Int Endod J. 2009;42: 144-155.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Boutsioukis C, Lambrianidis T, Kastrinakis E, Bekiaroglou P. Measurement of pressure and flow rates during irrigation of a root canal ex vivo with three endodontic needles. Int Endod J. 2007;40: 504-513.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Boutsioukis C, Gogos C, Verhaagen B, Versluis M, Kastrinakis E, Van der Sluis LW. The effect of apical preparation size on irrigant flow in root canals evaluated using an unsteady computational fluid dynamics model. Int Endod J. 2010;43: 874-881.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lendini M, Alemanno E, Migliaretti G, Berutti E. The effect of highXMLLink_XYZfrequency electrical pulses on organic tissue in root canals. Int Endod J. 2005;38: 531-538.PubMed
- 18. Calvo Pérez V, Medina Cárdenas ME, Sánchez Planells U. The possible role of pH changes during EDTA demineralization of teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989;68: 220-222.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Gulabivala K, Ng YL, Gilbertson M, Eames I. The fluid mechanics of root canal irrigation. Physiol Meas. 2010;31: R49-R84.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Aktener BO, Bilkay U. Smear layer removal with different concentrations of EDTA-ethylenediamine mixtures. J Endod. 1993;19: 228-231.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Perez F, Rouqueyrol-Pourcel N. Effect of a low-concentration EDTA solution on root canal walls: a scanning electron microscopic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99: 383-387.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Torabinejad M, Khademi AA, Babagoli J, Cho Y, Johnson WB, Bozhilov K, Kim J, Shabahang S. A new solution for the removal of the smear layer. J Endod. 2003;29: 170-175.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Nakashima K, Terata R. Effect of pH modified EDTA solution to the properties of dentin. J Endod. 2005;31: 47-49.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Ram Z. Effectiveness of root canal irrigation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1977;44: 306-312.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Orstavik D, Kerekes K, Molven O. Effects of extensive apical reaming and calcium hydroxide dressing on bacterial infection during treatment of apical periodontitis: a pilot study. Int Endod J. 1991;24: 1-7.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Hoskinson SE, Ng YL, Hoskinson AE, Moles DR, Gulabivala K. A retrospective comparison of outcome of root canal treatment using two different protocols. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93: 705-715.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Kerekes K, Tronstad L. Long-term results of endodontic treatment performed with a standardized technique. J Endod. 1979;5: 83-90.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
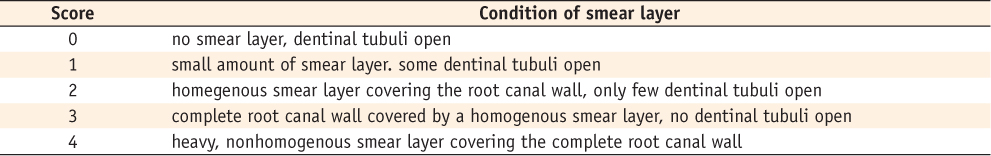
This table was adopted from Lendini, M. (2005) The effect of high-frequency electrical pulses on organic tissue in root canals. Int Endod J, 38, 534.
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Numerical Evaluation of Flow Pattern for Root Canal Irrigation Including icrobubbles
Joon Hyun Kim, Chan U Lee, Inwhan Lee, Jaeyong Sung
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2023; 32(5): 251. CrossRef
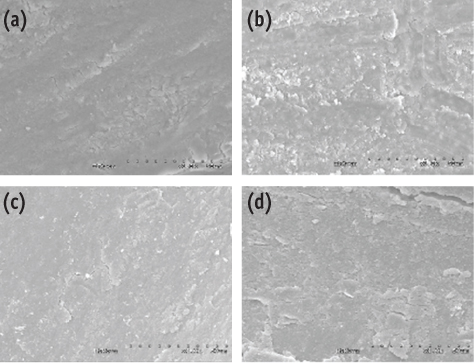
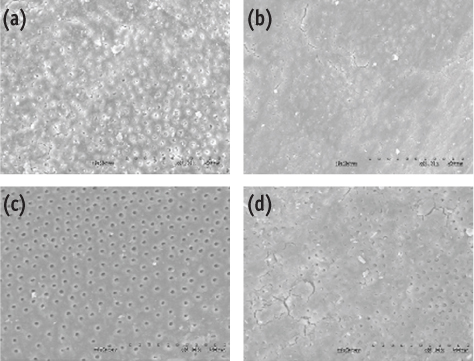
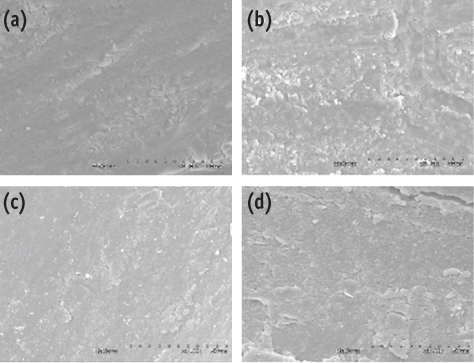
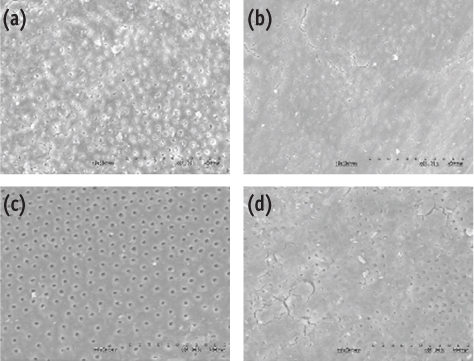
Figure 1
Figure 2
Smear layer score
This table was adopted from Lendini, M. (2005) The effect of high-frequency electrical pulses on organic tissue in root canals. Int Endod J, 38, 534.
Score of remaining smear layer according to instrumentation size and needle position from the apex in mm scale (mean ± SD, n = 10)
WL-3 mm, Needle position is 3 mm from the apex; WL-9 mm, Needle position is 9 mm from the apex.
The statistic analysis among instrument size
WL-3 mm, Needle position is 3 mm from the apex; WL-9 mm, Needle position is 9 mm from the apex.
This table was adopted from Lendini, M. (2005) The effect of high-frequency electrical pulses on organic tissue in root canals.
WL-3 mm, Needle position is 3 mm from the apex; WL-9 mm, Needle position is 9 mm from the apex.
WL-3 mm, Needle position is 3 mm from the apex; WL-9 mm, Needle position is 9 mm from the apex.

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

