Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Ex vivo comparative analysis of retrievability among four calcium silicate-based sealers for regaining apical patency
- Darian Shomali, Timothy Kirkpatrick, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Ji Wook Jeong
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e3. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Efficient retrievability is a key requirement for endodontic sealers. This study evaluated the retrievability of four different calcium silicate-based sealers (CSS).
Methods
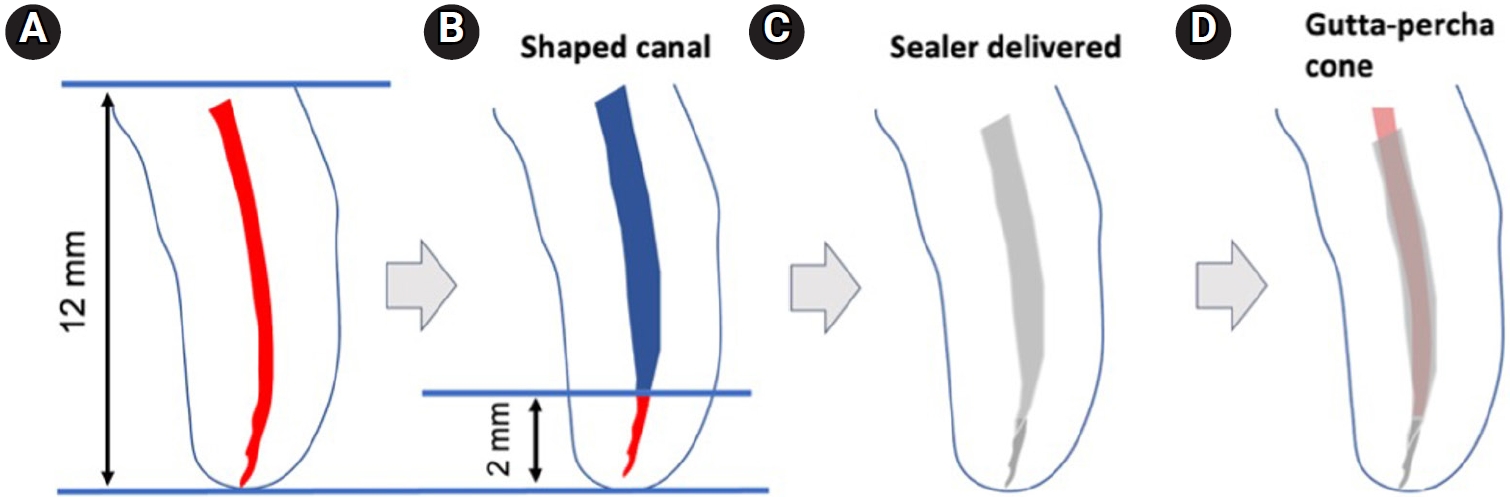
A total of 153 single-rooted human teeth with straight canals were decoronated to a standardized working length of 12 mm. The canals were negotiated to working length using K files up to size 15/.02, followed by rotary instrumentation up to 35/.04, 2 mm short of working length. The teeth were randomly assigned to five groups: NeoSEALER Flo (NEO; Avalon Biomed), Ceraseal (CS; Meta Biomed), Endosequence BC Sealer (BC; Brasseler USA), AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer (AHB; Dentsply Sirona), and a negative control group. Sealer application and obturation with a 35/.04 gutta-percha cone were performed. After incubation at 37°C in 100% humidity for 7 days, retreatment was performed until apical patency was obtained, with retrievability assessed by regaining apical patency. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey contrast test were used to determine whether there was a significant difference among the four different CSS (p < 0.05).
Results
Success rates in regaining apical patency were NEO (79.4%), CS (37.0%), BC (50.0%), and AHB (69.7%). NEO demonstrated the highest retrievability, while CS had the lowest (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
The type of CSS used has a considerable impact on retreatment difficulty. Among the tested sealers, Neo- SEALER Flo showed the highest retrievability, making it the most retrievable CSS in terms of retreatment efficacy.
- 511 View
- 35 Download

- Effect of moisture and pH on setting time and microhardness of three premixed calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: an in vitro experimental study
- Sooyoun Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e41. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to investigate how environmental conditions impact the setting time and microhardness of premixed calcium silicate-based sealers.
Methods
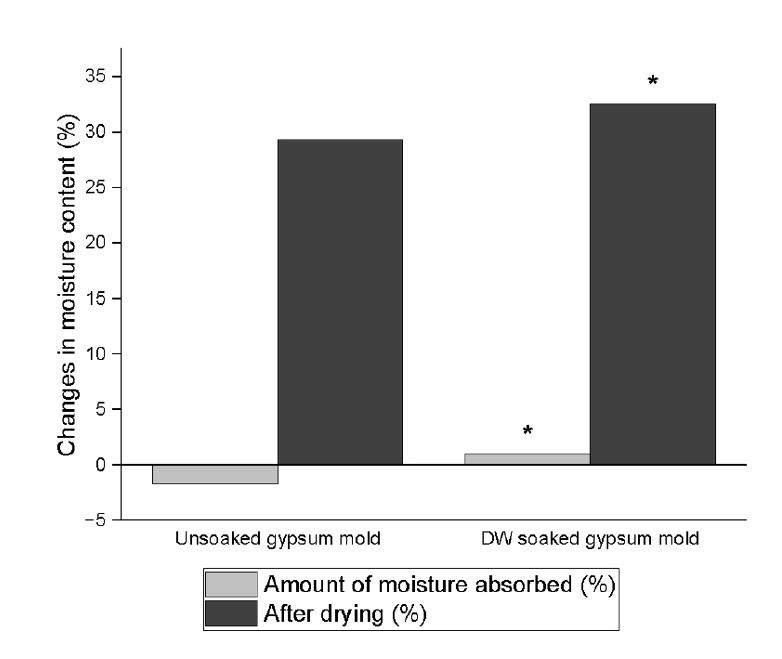
The setting time and microhardness of three sealers (Endoseal MTA [MARUCHI], One-Fil [MEDICLUS], and Well-Root ST [VERICOM]) were evaluated under four environmental conditions: unsoaked, distilled water-soaked, phosphate-buffered saline-soaked, and pH 5-soaked gypsum molds (n = 12/group/condition). The setting time was measured with Gilmore needles, and microhardness was assessed using a Vickers tester after 3 days. Welch’s analysis of variance and Games-Howell post hoc tests were used for statistical analysis.
Results
The sealer type and environmental conditions significantly influenced setting time and microhardness (p < 0.001). The initial and final setting times were the shortest in the unsoaked samples. For Endoseal MTA and One-Fil, the unsoaked condition exhibited significantly shorter setting times than the soaked conditions. Well-Root ST exhibited significantly longer setting times in acidic conditions. Surface microhardness was highest in the unsoaked group (p < 0.001). Among the soaked groups, the phosphate-buffered saline-soaked group had the lowest hardness for Endoseal MTA, whereas the pH 5-soaked group exhibited the lowest hardness for One-Fil and Well-Root ST. Endoseal MTA consistently demonstrated a lower microhardness than the other sealers (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Moisture, pH, and solution chemistry influenced the setting time and microhardness of premixed calcium silicate sealers. Although acidic conditions generally prolong the setting time and reduce hardness, the effects vary based on the sealers used and the setting environment.
- 981 View
- 69 Download

- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,805 View
- 213 Download

- Does the use of different root canal sealers and adhesive resin cements impact the bond strength of glass fiber posts?
- Ália Regina Neves de Paula Porto, Rudá França Moreira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e29. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
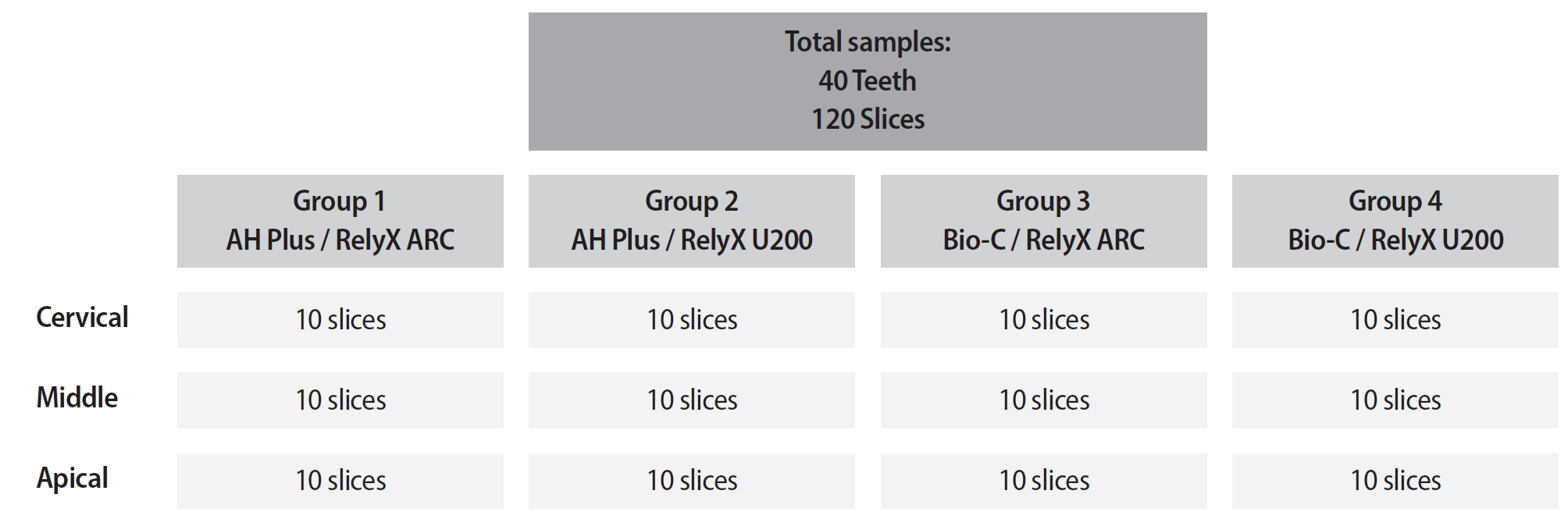
This study aimed to assess the influence of two endodontic sealers on the bond strength of glass fiber posts using conventional and self-adhesive resin cement through a push-out test. Methods: Forty central human incisors were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) based on sealer (epoxy resin- based or calcium silicate-based) and cement (conventional and self-adhesive resin) types: AH Plus (Dentsply De- Trey)/RelyX ARC (3M ESPE), AH Plus/RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), Bio-C Sealer (Angelus)/RelyX ARC, and Bio-C Sealer/RelyX U200. After canal filling and post cementation, roots were sectioned to obtain one specimen per root third. A pushout test and failure pattern assessment were conducted, with bond strength analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test. Results: AH Plus/RelyX ARC showed the highest bond strength values, with a significant difference in the middle third. The most common failure was mixed (55%), while adhesive failures made up 45%, with 23.5% at the cement/post interface and 21.5% at the cement/dentin interface. Conclusions: AH Plus/RelyX ARC provided the highest bond strength values for glass fiber posts to dentin.
- 1,815 View
- 146 Download

- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
- Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e20. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
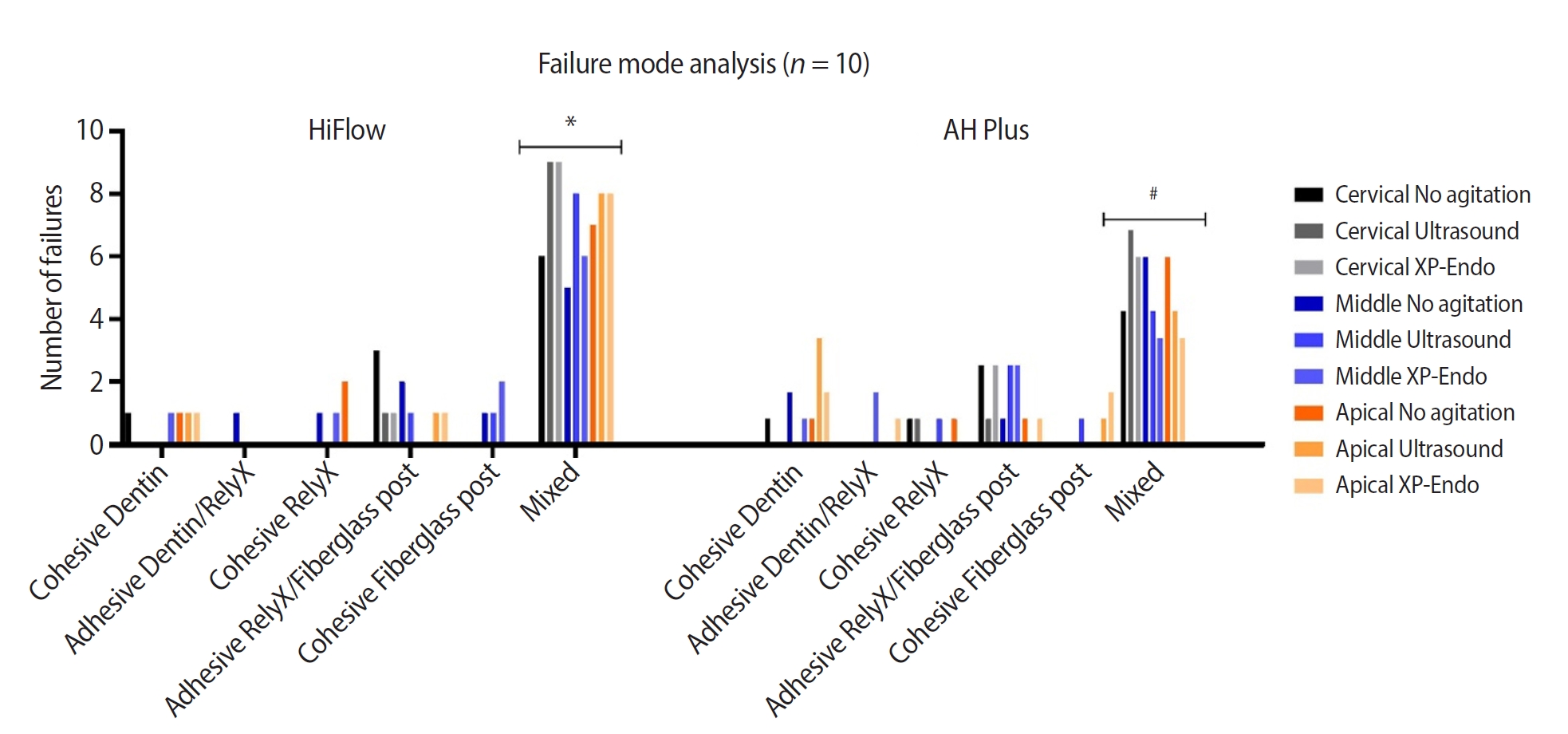
This study aimed to evaluate whether the agitation protocols using ultrasonic inserts or the XP-endo Finisher R file improved the removal of two different endodontic sealer remnants and the bond strength of fiberglass posts to dentin.
Methods
Seventy-two human teeth were selected. The canals were prepared with Reciproc 50 and Easy ProDesign 30/.10 and root filled according to the endodontic sealer groups: AH Plus or EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow. The samples were kept at 37ºC and 95% humidity for 28 days. During the post space preparation, the obturation was removed with Largo burs, and the groups were divided according to the irrigant agitation protocols (n = 12): no agitation, agitation with R1-Clearsonic associated with E1-Irrisonic ultrasonic inserts, or agitation with XP-endo Finisher R file. The fiberglass posts were cemented with RelyX ARC. The roots were sectioned into slices and submitted to the push-out test. Micro-computed tomography analysis was used to check the effectiveness of irrigating solution agitation in the elimination of remnants.
Results
The cleaning protocols with agitation were more effective in increasing the bond strength of posts to dentin for both sealer groups compared to non-agitation (p < 0.05). There was no difference between the same cleaning protocols for the different sealers. Among the different thirds, there was no statistical difference for the same sealer in the different cleaning protocols (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Both agitation protocols effectively clean root-filled canals sealed with resin-based and calcium silicate-based sealers during fiberglass post space preparation. These protocols result in improved bond strength compared to non-agitation methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cleaning efficacy and bond interaction of glycine-based air polishing and glass microparticles abrasion on dentin impregnated with premixed bioceramic sealer
Ândresson Aurélio Fernandes Martins, Maria Carolina Sidonio Alves, Bruno Martins Maciel, José Rodolfo Estruc Verbicário, João Felipe Besegato, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante-Otárola, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 147: 104277. CrossRef
- Cleaning efficacy and bond interaction of glycine-based air polishing and glass microparticles abrasion on dentin impregnated with premixed bioceramic sealer
- 3,962 View
- 209 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Nanoleakage of apical sealing using a calcium silicate-based sealer according to canal drying methods
- Yoon-Joo Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e20. Published online April 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e20

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the nanoleakage of root canal obturations using calcium silicate-based sealer according to different drying methods.
Materials and Methods Fifty-two extracted mandibular premolars with a single root canal and straight root were selected for this study. After canal preparation with a nickel-titanium rotary file system, the specimens were randomly divided into 4 groups according to canal drying methods (1: complete drying, 2: blot drying/distilled water, 3: blot drying/NaOCl, 4: aspiration only). The root canals were obturated using a single-cone filling technique with a calcium silicate–based sealer. Nanoleakage was evaluated using a nanoflow device after 24 hours, 1 week, and 1 month. Data were collected twice per second at the nanoscale and measured in nanoliters per second. Data were statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann–Whitney
U -tests (p < 0.05).Results The mean flow rate measured after 24 hours showed the highest value among the time periods in all groups. However, the difference in the flow rate between 1 week and 1 month was not significant. The mean flow rate of the complete drying group was the highest at all time points. After 1 month, the mean flow rate in the blot drying group and the aspiration group was not significantly different.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, the canal drying method had a significant effect on leakage and sealing ability in root canal obturations using a calcium silicate-based sealer. Thus, a proper drying procedure is critical in endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
- 2,510 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- A scientometric, bibliometric, and thematic map analysis of hydraulic calcium silicate root canal sealers
- Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi, Christos Gogos
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e41. Published online November 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This scientometric and bibliometric analysis explored scientific publications related to hydraulic calcium silicate-based (HCSB) sealers used in endodontology, aiming to describe basic bibliometric indicators and analyze current research trends.
Materials and Methods A comprehensive search was conducted in Web of Science and Scopus using specific HCSB sealer and general endodontic-related terms. Basic research parameters were collected, including publication year, authorship, countries, institutions, journals, level of evidence, study design and topic of interest, title terms, author keywords, citation counts, and density.
Results In total, 498 articles published in 136 journals were retrieved for the period 2008–2023. Brazil was the leading country, and the universities of Bologna in Italy and Sao Paolo in Brazil were represented equally as leading institutions. The most frequently occurring keywords were “calcium silicate,” “root canal sealer MTA-Fillapex,” and “biocompatibility,” while title terms such as “calcium,” “sealers,” “root,” “canal,” “silicate based,” and “endodontic” occurred most often. According to the thematic map analysis, “solubility” appeared as a basic theme of concentrated research interest, and “single-cone technique” was identified as an emerging, inadequately developed theme. The co-occurrence analysis revealed 4 major clusters centered on sealers’ biological and physicochemical properties, obturation techniques, retreatability, and adhesion.
Conclusions This analysis presents bibliographic features and outlines changing trends in HCSB sealer research. The research output is dominated by basic science articles scrutinizing the biological and specific physicochemical properties of commonly used HCSB sealers. Future research needs to be guided by studies with a high level of evidence that utilize innovative, sophisticated technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-cited articles on vital pulp therapy for irreversible pulpitis in permanent teeth: a bibliometric analysis
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Ferda Karabay
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Agri-Food Sector: Contemporary Trends, Possible Gaps, and Prospective Directions
José Roberto Herrera Cantorani, Meire Ramalho de Oliveira, Luiz Alberto Pilatti, Thales Botelho de Sousa
Metrics.2025; 2(1): 3. CrossRef - Scientific mapping of experimental research on solar cookers: Global trends, evolution, and future directions
Flavio Odoi-Yorke, Bismark Baah, Richard Opoku
Solar Energy Advances.2025; 5: 100093. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e17. CrossRef - Top 100 Most Cited Articles on Antibiotics in Endodontics: A Bibliometric Analysis
Hajar Albanyan, Mohammed Asseery, Haitham Alahmari, Ikram Ul Haq, Ali Alaqla
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Scientometric Review of Practical Applications in Quantum Natural Language Processing (QNLP): Trends, Gaps, and Research Opportunities
Victor R. Silva, Fábio R. Barbosa, Jasson C. Silva, Francisco J. Santos, Ricardo A. L. Rabelo, Joel J. P. C. Rodrigues
IEEE Access.2025; 13: 210169. CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of global research trend and progress on Dy doped materials
Sangeeta Kadyan, Manju Nain, Ashima Makhija, Poonam Punia, Anil Ohlan, Sajjan Dahiya, R. Punia, A.S. Maan
Journal of Alloys and Compounds Communications.2024; 3: 100006. CrossRef - Comparative bioactivity and immunomodulatory potential of the new Bioroot Flow and AH Plus Bioceramic sealer: An in vitro study on hPDLSCs
José Luis Sanz, Sergio López-García, David García-Bernal, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Leopoldo Forner, Adrián Lozano, Laura Murcia
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analyzing collaboration and impact: A bibliometric review of four highly published authors’ research profiles on collaborative maps
Willy Chou, Julie Chi Chow
Medicine.2024; 103(28): e38686. CrossRef
- Top-cited articles on vital pulp therapy for irreversible pulpitis in permanent teeth: a bibliometric analysis
- 2,918 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
- Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e18. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
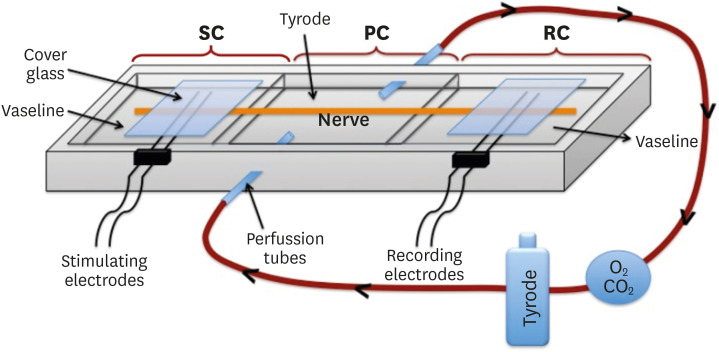
ePub Objectives This study evaluated alterations in neuronal conductivity related to calcium silicate cements (CSCs) by investigating compound action potentials (cAPs) in rat sciatic nerves.
Materials and Methods Sciatic nerves were placed in a Tyrode bath and cAPs were recorded before, during, and after the application of test materials for 60-minute control, application, and recovery measurements, respectively. Freshly prepared ProRoot MTA, MTA Angelus, Biodentine, Endosequence RRM-Putty, BioAggregate, and RetroMTA were directly applied onto the nerves. Biopac LabPro version 3.7 was used to record and analyze cAPs. The data were statistically analyzed.
Results None of the CSCs totally blocked cAPs. RetroMTA, Biodentine, and MTA Angelus caused no significant alteration in cAPs (
p > 0.05). Significantly lower cAPs were observed in recovery measurements for BioAggregate than in the control condition (p < 0.05). ProRoot MTA significantly but transiently reduced cAPs in the application period compared to the control period (p < 0.05). Endosequence RRM-Putty significantly reduced cAPs.Conclusions Various CSCs may alter cAPs to some extent, but none of the CSCs irreversibly blocked them. The usage of fast-setting CSCs during apexification or regeneration of immature teeth seems safer than slow-setting CSCs due to their more favorable neuronal effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
Anna Błaszczyk-Pośpiech, Natalia Struzik, Maria Szymonowicz, Przemysław Sareło, Maria Wiśniewska-Wrona, Kamila Wiśniewska, Maciej Dobrzyński, Magdalena Wawrzyńska
Materials.2025; 18(18): 4259. CrossRef
- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
- 1,593 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Comparative analysis of bond strength to root dentin and compression of bioceramic cements used in regenerative endodontic procedures
- Maykely Naara Morais Rodrigues, Kely Firmino Bruno, Ana Helena Gonçalves de Alencar, Julyana Dumas Santos Silva, Patrícia Correia de Siqueira, Daniel de Almeida Decurcio, Carlos Estrela
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e59. Published online November 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
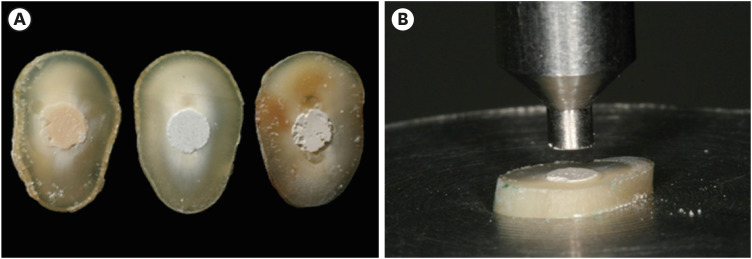
ePub Objectives This study compared the Biodentine, MTA Repair HP, and Bio-C Repair bioceramics in terms of bond strength to dentin, failure mode, and compression.
Materials and Methods Fifty-four slices obtained from the cervical third of 18 single-rooted human mandibular premolars were randomly distributed (
n = 18). After insertion of the bioceramic materials, the push-out test was performed. The failure mode was analyzed using stereomicroscopy. Another set of cylindrically-shaped bioceramic samples (n = 10) was prepared for compressive strength testing. The normality of data distribution was analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Kruskal-Wallis and Friedman tests were used for the push-out test data, while compressive strength was analyzed with analysis of variance and the Tukey test, considering a significance level of 0.05.Results Biodentine presented a higher median bond strength value (14.79 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (8.84 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (3.48 MPa), with a significant difference only between Biodentine and Bio-C Repair. In the Biodentine group, the most frequent failure mode was mixed (61%), while in the MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair groups, it was adhesive (94% and 72%, respectively). Biodentine showed greater resistance to compression (29.59 ± 8.47 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (18.68 ± 7.40 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (19.96 ± 3.96 MPa) (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Biodentine showed greater compressive strength than MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair, and greater bond strength than Bio-C Repair. The most frequent failure mode of Biodentine was mixed, while that of MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair was adhesive.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Obturation quality analysis of furcation perforations repaired with different magnifications and biomaterials
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Merve Işık Aydın, Ali Keleş
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparación de la resistencia compresiva entre el Agregado Trióxido Mineral y BiodentineTM en perforaciones de furca de molares inferiores permanentes
Jheymy Gerardo Huatuco-Granda, John Paul Torres-Navarro, Rosa Josefina Roncal-Espinoza
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Dentin Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Natalia Radulica, José Luis Sanz, Adrián Lozano
Applied Sciences.2023; 14(1): 104. CrossRef - Evaluation Of The Push-out Bond Strength Of The Bio-C Repair And Compare It With The Mineral Trioxide Aggregate And Amalgam When Used As Root-end Filling Material
Fatimah R. Hammadi, Zainab M Abdul-Ameer
Dental Hypotheses.2023; 14(2): 62. CrossRef - Effect of different root canal irrigants on push-out bond strength of two novel root-end filling materials
Nada Omar, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Tamer M. Hamdy
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of irrigation systems on the bond strength of calcium-silicate-based cement used as pulp barrier in regenerative endodontic treatment
Cihan Hascizmeci, Burak Buldur
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(23): 3393. CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 3,296 View
- 73 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Push-out bond strength and marginal adaptation of apical plugs with bioactive endodontic cements in simulated immature teeth
- Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Eduardo Nunes, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Manoel Brito Júnior, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Stephen Cohen, Frank Ferreira Silveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e53. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
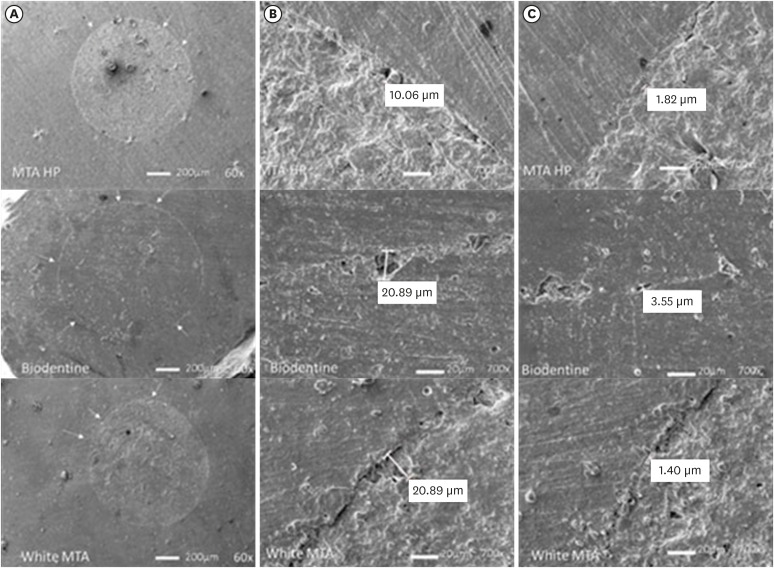
ePub Objectives This study evaluates the bond strength and marginal adaptation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) Repair HP and Biodentine used as apical plugs; MTA was used as reference material for comparison.
Materials and Methods A total of 30 single-rooted teeth with standardized, artificially created open apices were randomly divided into 3 groups (
n = 10 per group), according to the material used to form 6-mm-thick apical plugs: group 1 (MTA Repair HP); group 2 (Biodentine); and group 3 (white MTA). Subsequently, the specimens were transversely sectioned to obtain 2 (cervical and apical) 2.5-mm-thick slices per root. Epoxy resin replicas were observed under a scanning electron microscope to measure the gap size at the material/dentin interface (the largest and smaller gaps were recorded for each replica). The bond strength of the investigated materials to dentin was determined using the push-out test. The variable bond strengths and gap sizes were evaluated independently at the apical and cervical root dentin slices. Data were analyzed using descriptive and analytic statistics.Results The comparison between the groups regarding the variables' bond strengths and gap sizes showed no statistical difference (
p > 0.05) except for a single difference in the smallest gap at the cervical root dentin slice, which was higher in group 3 than in group 1 (p < 0.05).Conclusions The bond strength and marginal adaptation to root canal walls of MTA HP and Biodentine cement were comparable to white MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Biodentine for Apexification of Immature Teeth of Children: A Scoping Review
Liz M Gerard, Sumit Gaur
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(5): 573. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-Out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, a Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, and Two Novel Antibacterial-Enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Arokia Rajkumar Shancy Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Rajalakshmanan Eswaramoorthy, Abirami Arthanari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push out bond strength of hydraulic cements used at different thicknesses
C. Ruiz Durán, Dra L. Gancedo-Caravia, V. Vera González, C. González Losada
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,520 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of single-cone obturation with three sealers
- Sahar Zare, Ivy Shen, Qiang Zhu, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e25. Published online April 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
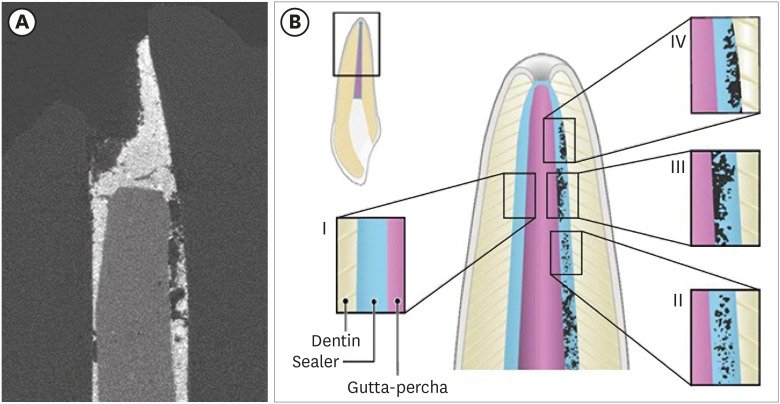
ePub Objectives This study used micro-computed tomography (µCT) to compare voids and interfaces in single-cone obturation among AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype surface pre-reacted glass ionomer (S-PRG) sealers and to determine the percentage of sealer contact at the dentin and gutta-percha (GP) interfaces.
Materials and Methods Fifteen single-rooted human teeth were shaped using ProTaper NEXT size X5 rotary files using 2.5% NaOCl irrigation. Roots were obturated with a single-cone ProTaper NEXT GP point X5 with AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, or prototype S-PRG sealer (
n = 5/group).Results The volumes of GP, sealer, and voids were measured in the region of 0–2, 2–4, 4–6, and 6–8 mm from the apex, using image analysis of sagittal µCT scans. GP volume percentages were: AH Plus (75.5%), EndoSequence BC (87.3%), and prototype S-PRG (94.4%). Sealer volume percentages were less: AH Plus (14.3%), EndoSequence BC (6.8%), and prototype S-PRG (4.6%). Void percentages were AH Plus (10.1%), EndoSequence BC (5.9%), and prototype S-PRG (1.0%). Dentin-sealer contact ratios of AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype S-PRG groups were 82.4% ± 6.8%, 71.6% ± 25.3%, and 70.2% ± 9.4%, respectively. GP-sealer contact ratios of AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype S-PRG groups were 65.6% ± 29.1%, 80.7% ± 25.8%, and 87.0% ± 8.6%, respectively.
Conclusions Prototype S-PRG sealer created a low-void obturation, similar to EndoSequence BC sealer with similar dentin-sealer contact (> 70%) and GP-sealer contact (> 80%). Prototype S-PRG sealer presented comparable filling quality to EndoSequence BC sealer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of gap areas of root filling techniques in teeth with 3D-printed different configurations of C-shaped root canals: a micro-computed tomography study
Tuba Gok, Adem Gok, Haydar Onur Aciksoz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the quality of root canal filling using three different sealers: Micro-computed tomography and scanning electron microscope study
Loai Alsofi, Mohammed Yagmoor, Tariq AbuHaimed, Hassan Abed, Ehab Alshouibi, Rafif Mandura, Turki Bakhsh, Hanaa Ashkar, Mey Al-Habib
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 152. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of bioactive calcium silicate coating on functionalized gutta-percha and its effect on bioceramic sealer wettability – An in vitro study
Bollineni Swetha, B. Devi Priya, K. Hanisha Reddy, G. Prasanthi, T. Murali Mohan, Dumpa Tejaswi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(7): 613. CrossRef - Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
Yang Yu, Chong-Yang Yuan, Xing-Zhe Yin, Xiao-Yan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 169. CrossRef - Micro-CT determination of the porosity of two tricalcium silicate sealers applied using three obturation techniques
Jinah Kim, Kali Vo, Gurmukh S. Dhaliwal, Aya Takase, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(3): 163. CrossRef - Ex-vivo evaluation of clinically-set hydraulic sealers used with different canal dryness protocols and obturation techniques: a randomized clinical trial
Nawar Naguib Nawar, Mohamed Mohamed Elashiry, Ahmed El Banna, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Edgar Schäfer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydraulic (Single Cone) Versus Thermogenic (Warm Vertical Compaction) Obturation Techniques: A Systematic Review
Haytham S Jaha
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sealing ability of various endodontic sealers with or without ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment on bovine root canal
Yusuke AIGAMI, Tomofumi SAWADA, Shunsuke SHIMIZU, Akiko ASANO, Mamoru NODA, Shinji TAKEMOTO
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(3): 420. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Effect of Heat on the Physical-Chemical Properties of Calcium Silicate–Based Sealers
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, James Ghilotti, María Melo
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(8): 1044. CrossRef - Assessment of the Prevalence of Head Lice Infestation and Parents’ Attitudes Towards Its Management: A School-based Epidemiological Study in İstanbul, Türkiye
Özben Özden, İnci Timur, Hale Ezgi Açma, Duygu Şimşekli, Barış Gülerman, Özgür Kurt
Turkish Journal of Parasitology.2023; 47(2): 112. CrossRef - Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Use of micro-CT to examine effects of heat on coronal obturation
Ivy Shen, Joan Daniel, Kali Vo, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(3): 224. CrossRef - Obturation of Root Canals By Vertical Condensation of Gutta-Percha – Benefits and Pitfalls
Calkovsky Bruno, Slobodnikova Ladislava, Bacinsky Martin, Janickova Maria
Acta Medica Martiniana.2021; 21(3): 103. CrossRef
- Assessment of gap areas of root filling techniques in teeth with 3D-printed different configurations of C-shaped root canals: a micro-computed tomography study
- 2,253 View
- 32 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Interface between calcium silicate cement and adhesive systems according to adhesive families and cement maturation
- Nelly Pradelle-Plasse, Caroline Mocquot, Katherine Semennikova, Pierre Colon, Brigitte Grosgogeat
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e3. Published online December 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
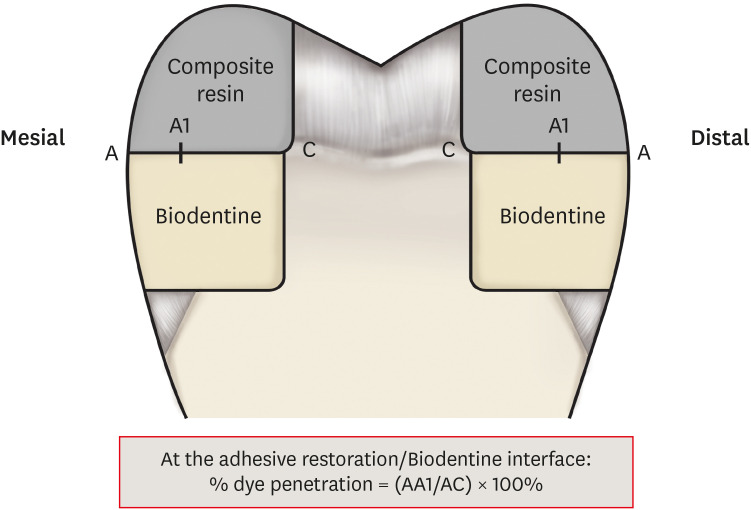
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the interface between a calcium silicate cement (CSC), Biodentine and dental adhesives in terms of sealing ability.
Materials and Methods Microleakage test: 160 standardized class II cavities were prepared on 80 extracted human molars. The cavities were filled with Biodentine and then divided into 2 experimental groups according to the time of restoration: composite resin obturation 15 minutes after Biodentine handling (D0); restoration after 7 days (D7). Each group was then divided into 8 subgroups (
n = 5) according to the adhesive system used: etch-and-rinse adhesive (Prime & Bond); self-etch adhesive 2 steps (Optibond XTR and Clearfil SE Bond); self-etch adhesive 1 step (Xeno III, G-aenial Bond, and Clearfil Tri-S Bond); and universal used as etch-and-rinse or self-etch (ScotchBond Universal ER or SE). After thermocycling, the teeth were immersed in a silver nitrate solution, stained, longitudinally sectioned, and the Biodentine/adhesive percolation was quantified. Scanning electron microscopic observations: Biodentine/adhesive interfaces were observed.Results A tendency towards less microleakage was observed when Biodentine was etched (2.47%) and when restorations were done without delay (D0: 4.31%, D7: 6.78%), but this was not significant. The adhesives containing 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate monomer showed the most stable results at both times studied. All Biodentine/adhesive interfaces were homogeneous and regular.
Conclusions The good sealing of the CSC/adhesive interface is not a function of the system adhesive family used or the cement maturation before restoration. Biodentine can be used as a dentine substitute.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of compressive strength, surface microhardness, and surface microstructure of different types of bioceramics following varying surface treatments
Zeynep Hale Keleş, Vasfiye Işık, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er Cr YSGG laser etching procedure on the bond strength of different calcium silicate cements
Yesim Sesen Uslu, Hakan Yasin Gönder, Pinar Sesen, Gizem Gunduz Bektaş
Lasers in Dental Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Resistance of Natural Molars vs. Additive-Manufactured Simulators Treated with Pulpotomy and Endocrown
Marie-Laure Munoz-Sanchez, Alexis Gravier, Olivier Francois, Emmanuel Nicolas, Martine Hennequin, Nicolas Decerle
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(9): 444. CrossRef - Characterisation of the calcium silicate‐based cement–composite interface and the bonding strength with total‐etch or single/two‐stage self‐etch adhesive systems
Abidin Talha Mutluay, Merve Mutluay
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 501. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Adhesive Systems to Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
Louis Hardan, Davide Mancino, Rim Bourgi, Alejandra Alvarado-Orozco, Laura Emma Rodríguez-Vilchis, Abigailt Flores-Ledesma, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Ammar Eid, Maya-Line Danhache, Maryline Minoux, Youssef Haïkel, Naji Kharo
Gels.2022; 8(5): 311. CrossRef
- Comparison of compressive strength, surface microhardness, and surface microstructure of different types of bioceramics following varying surface treatments
- 2,876 View
- 50 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
- Miyoung Lim, Chanyong Jung, Dong-Hoon Shin, Yong-bum Cho, Minju Song
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e35. Published online June 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Epoxy resin-based sealers are currently widely used, and several studies have considered AH Plus to be the gold-standard sealer. However, it still has limitations, including possible mutagenicity, cytotoxicity, inflammatory response, and hydrophobicity. Drawing upon the advantages of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium silicate-based sealers were introduced with high levels of biocompatibility and hydrophilicity. Because of the hydrophilic environment in root canals, water resorption and solubility of root canal sealers are important factors contributing to their stability. Sealers displaying lower microleakage and stronger push-out bond strength are also needed to endure the dynamic tooth environment. Although the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers meet International Organization for Standardization recommendations, and they have consistently reported to be biocompatible, they have not overcome conventional resin-based sealers in actual practice. Therefore, further studies aiming to improve the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
Lokhasudhan Govindaraju, Rajeswari Kalaiselvam, Mathan Rajan Rajendran, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Jelena Jacimovic, Henry F. Duncan, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2026; 59(3): 341. CrossRef - Evidence synthesis of postoperative pain with bioceramic vs. epoxy resin sealers: umbrella review of randomized trials within existing systematic reviews
Mrunali Dahikar, Ashish Mandwe, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Suraj Arora, Unmesh Khanvilkar, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical and mechanical properties of a strontium silicate-based sealer
Shannon Wong, Xiaofei Zhu, Tun-Yi Hsu, Sami Chogle, Russell A. Giordano, Yuwei Fan
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of bioceramic-based sealers following different irrigation activation techniques
Fatma Begüm Peker, Hümeyra Çapkın, Ahsen Narbay
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Tapered Gutta-Percha Points on Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Root Canal Sealers
Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanothum
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 285. CrossRef - Effect of Electrical Heat Carrier Temperature on Bacterial Leakage of Endodontically Treated Teeth Using a Bioceramic Sealer
Mir Ahmad Nabavi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Pedram Fattahi, Saber Khazaei
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Assessing the antimicrobial properties of bioceramic sealers enhanced with herbal extracts against E. faecalis
KS Sachin, K Shibani Shetty, KB Jeyalakshmi, S Harishma, S Harshini
Folia Medica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio comparativo de la solubilidad de dos selladores endodónticos biocerámicos y un sellador a base de resinas
//Comparative study of the solubility of two bioceramic endodontic sealers and one epoxi-resin based sealer
Alejandro Leonhardt, Nicolás Paduli, Osvaldo Zmener, Miguel Chantiri
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Bioceramic Endodontic Sealers in HepG2 and V79 Cell Lines: An In Vitro Study Using the Comet and Micronucleus Assays
Antonija Tadin, Marija Badrov, Danijela Juric Kacunic, Nada Galic, Matea Macan, Ivan Kovacic, Davor Zeljezic
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 169. CrossRef - In Vitro Apatite-Forming Ability of Different Root Canal Sealers (A Comparative Study)
Raghad A Al-Askary, Wiaam M. O. Al-Ashou, Sawsan H. Al-Jubori
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(2): 173. CrossRef - Microstructural and elemental characterization of novel bioactive glass bioceramic sealer using Fourier transform infrared and X-ray diffraction analysis
Poulomi Guha, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Antony, Nishitha Arun, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Surendar Ramamoorthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(5): 412. CrossRef - Microstructural and Elemental Characterization of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Ireneusz Piwonski, Tomasz Szmechtyk, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(10): 756. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure-enhanced sealer infiltration for obturating long oval-shaped root canals with the single-cone technique
Yaxu Feng, Brian E. Bergeron, Shijin Zhang, Danyang Sun, Kole Fisher, Franklin R. Tay, Bing Fan
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105909. CrossRef - Effects of different apical preparation sizes and root canal sealers on the fracture resistance of roots aged for 12 months in endodontically retreated mandibular premolars
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Sevda Durust Baris, Ali Turkyilmaz, Ali Erdemir
British Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different endodontic treatment protocols on tooth survival: A retrospective cohort study with multistate analysis and group balancing
Ahmed Elmaasarawi, Mohamed Mekhemar, Andreas Bartols
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(10): 1529. CrossRef - Evaluation of 2,6-xylidine precipitate on sealer penetration of calcium silicate-based sealer and resin-based sealer: An in vitro study
M. B. Kalpana, Divya Shetty, Rajaram Naik
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 183. CrossRef - Translational Advances in Regenerative Dentistry: Functional Biomaterials and Emerging Technologies
Seher Yaylacı, Hacer Eberliköse, Hakan Ceylan
Current Oral Health Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of heat and non-heat compatible bioceramic sealers in warm obturation: an in vitro SEM study
Thanomsuk Jearanaiphaisarn, Thanida Leelayuttakarn, Panisara Amatamahuthana, Pinmanus Chenpairojsakul, Keskanya Subbalekha, Pavena Chivatxaranukul
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
Steven K. Uttech, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Maria Martell, Bruno Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1764. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of adhesion abilities between AH Plus® Bioceramic, Ceraseal® and AH Plus® on root canal dentine surfaces
Ike Dwi Maharti, Indira Larasputri, Nendar Herdianto, Anggraini Margono, Riesma Tasomara, Romilda Rosseti
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(9): 881. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of single-cone bioceramic obturation versus traditional techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Firas Elmsmari, Yousef Elsayed, Abdelrahman Aboubakr, Mahdi Kaafarani, Osama Nour, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(6): 1422. CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation Solutions on the Setting Time, Solubility, and pH of Three Types of Premixed Bioceramic‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Kitichai Singharat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Zhengrui Li
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteogenic Potential of Various Premixed Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers on Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Na-Hyun You, Donghee Lee, Yemi Kim, Sieun Nam, Sin-Young Kim
Materials.2025; 18(23): 5326. CrossRef - Polydopamine‐Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Root Canal Sealer: Characterization, Biological, and Physicochemical Properties
Arul Nayagi Raj, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Giuseppe Ciccarella
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of rarely seen internal tunnelling root resorption associated with a maxillary permanent incisor
Kirsty A. Carney, Thibault N. E. Colloc, Julie K. Kilgariff
British Dental Journal.2024; 236(12): 955. CrossRef - Top tips for treatment planning: tooth-by-tooth prognosis - Part 3: endodontic prognosis
Prashanti Eachempati, Andrew Harris, Guy Lambourn, Tony Francis, Ewen McColl
British Dental Journal.2024; 237(9): 686. CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate-based sealers based on micro-computed tomographic evaluation − A systematic review
Sundus Mohammed Bukhary
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1278. CrossRef - Evaluation of Setting Time, Flowability, Film Thickness, and Radiopacity of Experimental Monocalcium Silicate‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Sukanya Juntha, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Carlos M. Ardila
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment and Demand for Continuing Education among Thai Dental Practitioners
Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Pakit Tungsawat, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanotham
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic sealers after exposure to chlorhexidine digluconate: An assessment of physicochemical properties
Vasileios Kapralos, Josette Camilleri, Andreas Koutroulis, Håkon Valen, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Dental Materials.2024; 40(3): 420. CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Interfacial adaptation of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2024; 18(2): 115. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Solubility of Endoseal and AH26 Root Canal Sealers
Nooshin Fakhari, Ali Reza Mirjani, Abbas Bagheri, Jalil Modaresi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2024; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Novel bioactive nanospheres show effective antibacterial effect against multiple endodontic pathogens
Jin Liu, Haoze Wu, Jun Qiu, Sirui Yang, Doudou Xiang, Xinhua Zhang, Jinxin Kuang, Min Xiao, Qing Yu, Xiaogang Cheng
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28266. CrossRef - Evaluation of canal patency and cleanliness following retreatment of bioceramic sealer‐obturated root canals using three different irrigant activation protocols
Daiasharailang Lyngdoh, Sharique Alam, Huma Iftekhar, Surendra Kumar Mishra
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 475. CrossRef - Antibiofilm Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Based Endodontic Sealers
Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Vsevolod Fedoseev, Carmen Solana, Cecilia Muñoz-Sandoval, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3937. CrossRef - Enhancing the Biological Properties of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Calcium Silicate Cements: An In Vitro Study
Minji Choi, Jiyoung Kwon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Duck-Su Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 337. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and cell migration evaluation of a strontium silicate-based root canal sealer on stem cells from rat apical papilla: an in vitro study
Guanglei Zhou, Yu Zhao, Liangjing Cai, Liwei Liu, Xu Li, Lu Sun, Jiayin Deng
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Analysis of Physico–Mechanical Properties of Commercial and Experimental Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Abdulmajeed Kashaf, Faisal Alonaizan, Khalid S. Almulhim, Dana Almohazey, Deemah Abdullah Alotaibi, Sultan Akhtar, Ashwin C. Shetty, Abdul Samad Khan
Bioengineering.2024; 11(11): 1079. CrossRef - Chemical, Antibacterial, and Cytotoxic Properties of Four Different Endodontic Sealer Leachates Over Time
Jo-Hsun Chen, Veksina Raman, Sarah A. Kuehne, Josette Camilleri, Josefine Hirschfeld
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(11): 1612. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Fracture Resistance of Endodontic Sealer Types and Filling Methods
Yun Song, Kee-Deog Kim, Bock-Young Jung, Wonse Park, Nan-Sim Pang
Materials.2024; 18(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Removal of Bioceramic Sealers Using Rotary Retreatment Files Supplemented with Passive Ultrasonic Activation: An In Vitro Study
Anuradha B Patil, Amrut Bambawale, Pooja R Barghare, Sumanthini V Margasahayam, Divya Naik, Jayeeta S Verma
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 292. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of Nonperforating Internal Root Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor: A Case Report with a 4-Year Follow-Up
Paras M. Gehlot, Divya S. Rajkumar, Annapoorna B. Mariswamy, Upendra Natha N. Reddy, Chaitanya Chappidi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S3005. CrossRef - Evaluating the Sealing Performance of Endodontic Sealers: Insights Into Achieving Complete Sealing
Ajay Chhabra, Ramya K P., Saravana Prathap, Priyanka Yadav, Himani Mehra, Sona J Parvathy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vehicles on the physical properties and biocompatibility of premixed calcium silicate cements
Gitae SON, Gyeung Mi SEON, Sang Hoon CHOI, Hyeong-Cheol YANG
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(2): 276. CrossRef - Comparative cytotoxicity study of putty- and powder-type calcium silicate cements
Sora Park, Dohyun Cho, Ji Hyeon Yoon, Yeonjoo Kang, Quang Canh Vo, Gitae Son, Hongjoo Park, Hyeong-Cheol Yang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 259. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Dentinal Tubule Penetrability and Bond Strength of Two Novel Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karissa Shieh, Jack Yang, Elsa Heng Zhu, Ove Andreas Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour
Materials.2023; 16(9): 3309. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Activity of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers Compared to Conventional Resin-Based Sealer in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells
Mohammad Shokrzadeh, Farzaneh Sadat Motafeghi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Mohammad Ghorbani, Azam Haddadi Kohsar, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of three different photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy on bond strength of a calcium silicate‐based sealer to radicular dentin
Cihan Küden, Seda Nur Karakaş
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 265. CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealer on postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis
Cynthia Maria Chaves Monteiro, Ana Cristina Rodrigues Martins, Alessandra Reis, Juliana Larocca de Geus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Activity of Five Calcium Silicate Based Root Canal Sealers against a Multispecies Engineered Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Carla Zogheib, Issam Khalil, Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, Germain Sfeir, May Mallah, Roula El Hachem
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 707. CrossRef - Calcium silicate sealers in endodontics
Archana Chavan, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2023; 39(87): 2624. CrossRef - Assessing the Sealing Performance and Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Treatment in Patients with Chronic Apical Periodontitis Using Epoxy Resin and Calcium Salicylate Seals
Razvan Mihai Horhat, Bogdan Andrei Bumbu, Laura Orel, Oana Velea-Barta, Laura Cirligeriu, Gratiana Nicoleta Chicin, Marius Pricop, Mircea Rivis, Stefania Dinu, Delia Ioana Horhat, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Rodica Anamaria Negrean, Luminita
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1137. CrossRef -
In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Potential of an Endodontic Bioceramic Material
Soumya Sheela, Mohannad Nassar, Fatma M. AlGhalban, Mehmet O. Gorduysus
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(02): 548. CrossRef - Dislodgment Resistance, Adhesive Pattern, and Dentinal Tubule Penetration of a Novel Experimental Algin Biopolymer-Incorporated Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealer
Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Norhayati Luddin, Huwaina Abd Ghani, Josephine Chang Hui Lai, Tahir Yusuf Noorani
Polymers.2023; 15(5): 1317. CrossRef - Impact of Final Irrigation Protocol on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Types of Endodontic Sealers
Germain Sfeir, Frédéric Bukiet, Wajih Hage, Roula El Hachem, Carla Zogheib
Materials.2023; 16(5): 1761. CrossRef - Clinical Approaches to the Three-Dimensional Endodontic Obturation Protocol for Teeth with Periapical Bone Lesions
Angela Gusiyska, Elena Dyulgerova
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9755. CrossRef - Evaluating the bioactivity of endodontic sealers with respect to their thermo-nanomechanical properties
Andreea Marica, Luminita Fritea, Florin Banica, Iosif Hulka, Gerlinde Rusu, Cosmin Sinescu, Traian Octavian Costea, Simona Cavalu
Materials Science-Poland.2023; 41(3): 126. CrossRef - Advances and challenges in regenerative dentistry: A systematic review of calcium phosphate and silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells
B. Christie, N. Musri, N. Djustiana, V. Takarini, N. Tuygunov, M.N. Zakaria, A. Cahyanto
Materials Today Bio.2023; 23: 100815. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - Biodentine Inhibits the Initial Microbial Adhesion of Oral Microbiota In Vivo
Ali Al-Ahmad, Michael Haendel, Markus Altenburger, Lamprini Karygianni, Elmar Hellwig, Karl Wrbas, Kirstin Vach, Christian Tennert
Antibiotics.2022; 12(1): 4. CrossRef - Pilot Evaluation of Sealer-Based Root Canal Obturation Using Epoxy-Resin-Based and Calcium-Silicate-Based Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Minju Song, Min-Gyu Park, Sang-Won Kwak, Ruben H. Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2022; 15(15): 5146. CrossRef - The antibacterial activity of mineral trioxide aggregate containing calcium fluoride
Miyoung Lim, Seunghoon Yoo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(2): 836. CrossRef - Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Premixed Calcium Silicate and Resin Sealers
Naji Kharouf, Salvatore Sauro, Ammar Eid, Jihed Zghal, Hamdi Jmal, Anta Seck, Valentina Macaluso, Frédéric Addiego, Francesco Inchingolo, Christine Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, Florent Meyer, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 14(1): 9. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Resistance between Single-cone and Warm Vertical Compaction Technique Using Bio-C Sealer® in Mandibular Incisors: An In Vitro Study
Raphael Lichaa, George Deeb, Rami Mhanna, Carla Zogheib
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - In vitro physicochemical characterization of five root canal sealers and their influence on an ex vivo oral multi‐species biofilm community
Flavia M. Saavedra, Lauter E. Pelepenko, William S. Boyle, Anqi Zhang, Christopher Staley, Mark C. Herzberg, Marina A. Marciano, Bruno P. Lima
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 772. CrossRef - Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealer Reinforced with Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles to Improve Biological Properties
Min-Kyung Jung, So-Chung Park, Yu-Jin Kim, Jong-Tae Park, Jonathan C. Knowles, Jeong-Hui Park, Khandmaa Dashnyam, Soo-Kyung Jun, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jung-Hwan Lee
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1903. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - The influence of humidity on bond strength of AH Plus, BioRoot RCS, and Nanoseal-S sealers
Sunanda Laxman Gaddalay, Damini Vilas Patil, Ramchandra Kabir
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 202. CrossRef - The Effect of Bioceramic HiFlow and EndoSequence Bioceramic Sealers on Increasing the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Mohamad Khir Abdulsamad Alskaf, Hassan Achour, Hasan Alzoubi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unravelling the effects of ibuprofen-acetaminophen infused copper-bioglass towards the creation of root canal sealant
Chitra S, Riju Chandran, Ramya R, Durgalakshmi D, Balakumar S
Biomedical Materials.2022; 17(3): 035001. CrossRef - A Micro-CT Analysis of Initial and Long-Term Pores Volume and Porosity of Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Michal Leski, Adam K. Puszkarz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2403. CrossRef - A comprehensive in vitro comparison of the biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive root canal sealers
Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Christian Diegritz, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth, Maximilian Kollmuss
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(10): 6209. CrossRef - Stability and solubility test of endodontic materials
Ivan Matovic, Jelena Vucetic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(4): 169. CrossRef - Antimicrobial effectiveness of root canal sealers againstEnterococcus faecalis
Paola Castillo-Villagomez, Elizabeth Madla-Cruz, Fanny Lopez-Martinez, Idalia Rodriguez-Delgado, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Guadalupe Ismael Malagon-Santiago, Myriam Angelica de La Garza-Ramos
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2022; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Influence of variations in the environmental pH on the solubility and water sorption of a calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer
E. J. N. L. Silva, C. M. Ferreira, K. P. Pinto, A. F. A. Barbosa, M. V. Colaço, L. M. Sassone
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1394. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Calcium-Silicate Nanobioceramics with Magnesium: Effect of Heat Treatment on Biological, Physical and Chemical Properties
Konstantina Kazeli, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Anna Theocharidou, Lamprini Malletzidou, Jonathan Rhoades, Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Eleni Likotrafiti, Konstantinos Chrissafis, Theodoros Lialiaris, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Eleana Kontonasaki, Evgenia Lymperaki
Ceramics.2021; 4(4): 628. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - In Vitro Microleakage Evaluation of Bioceramic and Zinc-Eugenol Sealers with Two Obturation Techniques
Francesco De Angelis, Camillo D’Arcangelo, Matteo Buonvivere, Rachele Argentino, Mirco Vadini
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 727. CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef - Apical Sealing Ability of Two Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers Using a Radioactive Isotope Method: An In Vitro Apexification Model
Inês Raquel Pereira, Catarina Carvalho, Siri Paulo, José Pedro Martinho, Ana Sofia Coelho, Anabela Baptista Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho, Maria Filomena Botelho, Ana Margarida Abrantes, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6456. CrossRef
- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
- 13,685 View
- 249 Download
- 100 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer
- Jong Cheon Kim, Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e18. Published online February 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
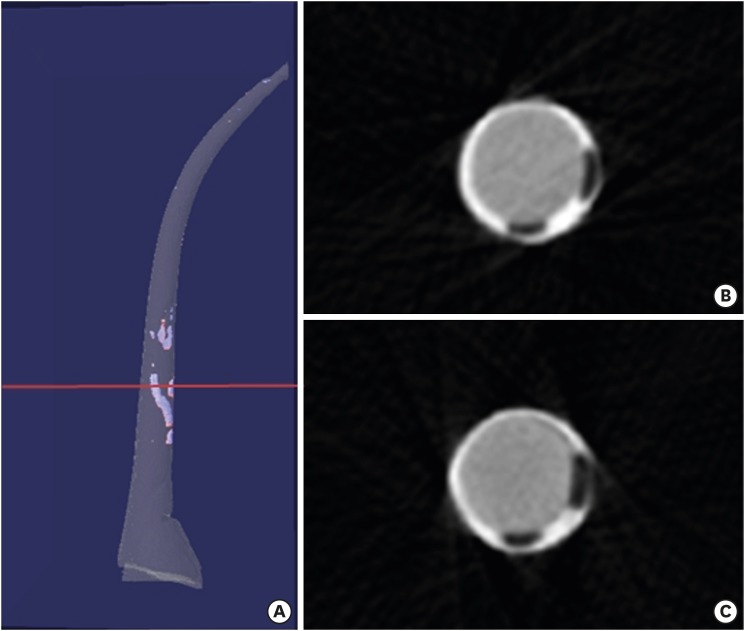
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the void of root canal filling over time when a calcium silicate sealer was used in the single gutta-percha cone technique.
Materials and Methods Twenty-four J-shaped simulated root canals and twenty-four palatal root canals from extracted human maxillary molars were instrumented with ProFile Ni-Ti rotary instruments up to size 35/0.06 or size 40/0.06, respectively. Half of the canals were filled with Endoseal MTA and the other half were with AH Plus Jet using the single gutta-percha cone technique. Immediately after and 4 weeks after the root canal filling, the samples were scanned using micro-computed tomography at a resolution of 12.8 μm. The scanned images were reconstructed using the NRecon software and the void percentages were calculated using the CTan software, and statistically analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance, paired
t- test and Tukeypost hoc test.Results After 4 weeks, there were no significant changes in the void percentages at all levels in both material groups (
p > 0.05), except at the apical level of the AH Plus Jet group (p < 0.05) in the simulated root canal showing more void percentage compared to other groups. Immediately after filling the extracted human root canals, the Endoseal MTA group showed significantly less void percentage compared to the AH Plus Jet group (p < 0.05).Conclusions Under the limitations of this study, the Endoseal MTA does not seem to reduce the voids over time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Evaluation of various obturation techniques with bioceramic sealers in 3D-printed C-shaped canals
Maryam Gharechahi, Melika Hoseinzadeh, Saeed Moradi, Mina Mehrjouei
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of obturation quality in natural and replica teeth root-filled using different sealers and techniques
Chuta Kooanantkul, Richard M Shelton, Josette Camilleri
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2407. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Sealer Application Methods on Voids Volume after Aging of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
Amre R. Atmeh, Rakan Alharbi, Ibrahim Aljamaan, Abdulrahman Alahmari, Ashwin C. Shetty, Ahmed Jamleh, Imran Farooq
Tomography.2022; 8(2): 778. CrossRef - Clinical Efficacy of Sealer-based Obturation Using Calcium Silicate Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Ji-hyung Kim, Sin-Yeon Cho, Yoonwoo Choi, Do-hyun Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Il-Young Jung
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 144. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - Physico-Chemical Properties of Calcium-Silicate vs. Resin Based Sealers—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory-Based Studies
Viresh Chopra, Graham Davis, Aylin Baysan
Materials.2021; 15(1): 229. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
- 2,284 View
- 18 Download
- 11 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomography evaluation of voids using calcium silicate-based materials in teeth with simulated internal root resorption
- Vildan Tek, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e5. Published online November 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e5
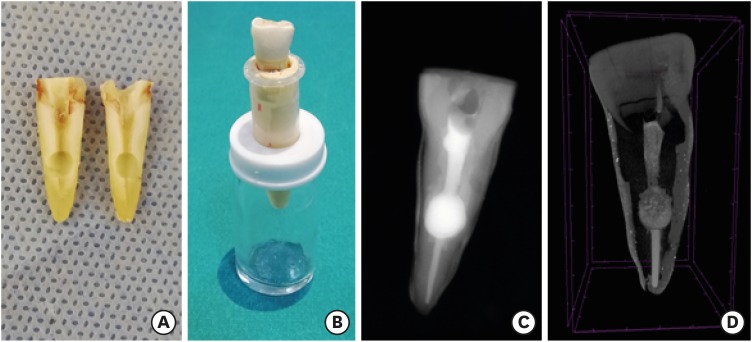
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The obturation quality of MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC root canal sealer (RCS), and warm gutta-percha (WGP) in teeth with simulated internal root resorption (IRR) was evaluated by using micro-computed tomography.
Materials and Methods Standardized IRR cavities were created using 40 extracted maxillary central incisor teeth and randomly assigned into 4 groups (
n = 10). IRR cavities were filled with MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC RCS (bulk-fill form) and WGP + Total Fill BC RCS. Percentage of voids between resorptive cavity walls and obturation material (external void), and inside the filling materials (internal voids) were measured.Results Total Fill BC sealer in the bulk-fill form presented significantly highest values of external and internal void percentages (
p < 0.05). Biodentine showed a significantly lowest external void percentage (p < 0.05). WGP + Total Fill BC RCS presented significantly lower values of internal void percentages than all groups (p < 0.05), except Biodentine (p > 0.05).Conclusion None of the filling materials were created void-free obturation in resorption cavities. Biodentine may favor its application in teeth with IRR over Angelus MTA and bulk-fill form of Total Fill BC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Measurement of Obturation Quality of Bioceramic Materials in Filling Artificial Internal Root Resorption Cavities Using Different Obturation Techniques: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Ammar M. Sharki, Ahmed H. Ali
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 997. CrossRef - Evaluation of calcium hydroxide root canal filling materials by cone beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling
Asel Usdat Ozturk, Ekin Dogan, Venus Seyedoskuyi, Berk Senguler, Asli Topaloglu-Ak
Folia Medica.2024; 66(2): 250. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef
- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
- 2,496 View
- 34 Download
- 10 Crossref

-
Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month
ex vivo study - Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e25. Published online July 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate discoloration of teeth undergoing regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) using blood clot or platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) as the scaffolds and different calcium silicate-based materials as the intracanal coronal barriers in an
ex vivo model.Materials and Methods Forty-eight bovine incisors were prepared and disinfected using 1 mg/mL double antibiotic paste (DAP). The specimens were then randomly divided into 2 groups (
n = 24) according to the scaffolds (blood or PRF). After placement of scaffolds each group was divided into 2 subgroups (n = 12) according to the intracanal coronal barriers (ProRoot MTA or Biodentine). The pulp chamber walls were sealed with dentin bonding agent before placement of DAP and before placement of scaffolds. The color changes (∆E) were measured at different steps. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance.Results Coronal discoloration induced by DAP was not clinically perceptible (ΔE ≤ 3.3). Regarding the type of the scaffold, coronal discoloration was significantly higher in blood groups compared with PRF groups at the end of REP and after 1 month (
p < 0.05). However, no significant difference was found between PRF and blood clot after 6 months (p > 0.05). Considering the type of intracanal coronal barrier, no significant difference existed between ProRoot MTA and Biodentine (p > 0.05).Conclusions With sealing the dentinal tubules of pulp chamber with a dentin bonding agent and application of DAP as an intracanal medicament, coronal color change of the teeth following the use of PRF and blood sealed with either ProRoot MTA or Biodentine was not different at 6-month follow-up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Biodentine Placement on Fracture Resistance and its Influence on Discoloration with Different Scaffolds
Evren Sarıyılmaz, Öznur Sarıyılmaz, Burak Çarıkçıoğlu, Gülşah Uslu, Raif Alan
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(9): 1199. CrossRef - Effect of pH on the solubility and volumetric change of ready-to-use Bio-C Repair bioceramic material
Luana Raphael da SILVA, Jader Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Potassium Iodide and Glutathione for Correlation of Dentin Discoloration Caused by Silver Diamine Fluoride
Mahsa Samani, Hamid Majzoub, Faramarz Zakavi, Ayyub Mojaddami
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Intracanal medicaments and coronal sealing materials influence on root fracture resistance and coronal discoloration: An in vitro study
Rasoul Sahebalam, Marzie Boskabady, Maryam Naghavi, Samira Dehghanitafti
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 199. CrossRef - Potential Crown Discoloration Induced by the Combination of Various Intracanal Medicaments and Scaffolds Applied in Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
NB Altun, A Turkyilmaz
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(7): 897. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different treatment approaches in preventing coronal discoloration caused by regenerative endodontic treatment
Melis Oya Ateş, Zeliha Uğur Aydın
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(8): 4595. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Laser‐Assisted Bleaching of the Teeth Discolored due to Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Teeth Whitening after Regenerative Endodontics Procedures: An In Vitro Study
Irini Fagogeni, Joanna Metlerska, Tomasz Falgowski, Maciej Górski, Mariusz Lipski, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(23): 7016. CrossRef - Microstructure and color stability of calcium silicate-based dental materials exposed to blood or platelet-rich fibrin
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Ibrahim Abu Tahun, Shima Saber Tahan, Fatemeh Mohandes, Mohammad H. Nekoofar, Paul M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1193. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric analysis of internal bleaching of traumatized teeth with coronal discoloration following regenerative endodontic procedures
Jaqueline Lazzari, Walbert Vieira, Vanessa Pecorari, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Adriana De-Jesus-Soares
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological parameters, discolouration and radiopacity of calcium silicate‐based materials in a simulated model of partial pulpotomy
Lilian Vieira Oliveira, Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gisele Rodrigues da Silva, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Ana Paula Turrioni, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(11): 2133. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different calcium silicate-based pulp capping materials on tooth discoloration: an in vitro study
Ahmad S. Al-Hiyasat, Dana M. Ahmad, Yousef S. Khader
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of undergraduate students concerning Regenerative Endodontics
Ligia B. da Silva, Mariana Gabriel, Márcia M. Marques, Fernanda C. Carrer, Flávia Gonçalves, Giovanna Sarra, Giovanna L. Carvalho, Ana Armas-Vega, Maria S. Moreira
Minerva Stomatologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronal Discoloration Related to Bioceramic and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Coronal Barrier in Non-vital Mature Teeth Undergoing Regenerative Endodontic Procedures
Mazen Doumani, Mohammad Yaman Seirawan, Kinda Layous, Mohammad Kinan Seirawan
World Journal of Dentistry.2020; 11(1): 52. CrossRef
- Impact of Biodentine Placement on Fracture Resistance and its Influence on Discoloration with Different Scaffolds
- 2,160 View
- 26 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effects of the exposure site on histological pulpal responses after direct capping with 2 calcium-silicate based cements in a rat model
- Panruethai Trongkij, Supachai Sutimuntanakul, Puangwan Lapthanasupkul, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Rebecca Wong, Danuchit Banomyong
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e36. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e36

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Direct pulp capping is a treatment for mechanically exposed pulp in which a biocompatible capping material is used to preserve pulpal vitality. Biocompatibility tests in animal studies have used a variety of experimental protocols, particularly with regard to the exposure site. In this study, pulp exposure on the occlusal and mesial surfaces of molar teeth was investigated in a rat model.
Materials and Methods A total of 58 maxillary first molars of Wistar rats were used. Forty molars were mechanically exposed and randomly assigned according to 3 factors: 1) the exposure site (occlusal or mesial), 2) the pulp-capping material (ProRoot White MTA or Bio-MA), and 3) 2 follow-up periods (1 day or 7 days) (
n = 5 each). The pulp of 6 intact molars served as negative controls. The pulp of 12 molars was exposed without a capping material (n = 3 per exposure site for each period) and served as positive controls. Inflammatory cell infiltration and reparative dentin formation were histologically evaluated at 1 and 7 days using grading scores.Results At 1 day, localized mild inflammation was detected in most teeth in all experimental groups. At 7 days, continuous/discontinuous calcified bridges were formed at exposure sites with no or few inflammatory cells. No significant differences in pulpal response according to the exposure site or calcium-silicate cement were observed.
Conclusions The location of the exposure site had no effect on rat pulpal healing. However, mesial exposures could be performed easily, with more consistent results. The pulpal responses were not significantly different between the 2 capping materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioactivity and biocompatibility of bioceramic-based pulp capping materials in laboratory and animal models
Rafiqul Islam, Md. Refat Readul Islam, Kenta Tsuchiya, Yu Toida, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The road map to proper dental pulp experiments in animal models
Nuha A Elmubarak
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 11(4): 163. CrossRef - Treatment outcomes of root perforations repaired by calcium silicate-based cements with or without an accelerator: A randomized controlled trial
Kanyarat Tungputsa, Danuchit Banomyong, Sittichoke Osiri, Supachai Sutimuntanakul
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 315. CrossRef - Biological evaluation of novel phosphorylated pullulan‐based calcium hydroxide formulations as direct pulp capping materials: An in vivo study on a rat model
Md Refat Readul Islam, Rafiqul Islam, Yunqing Liu, Yu Toida, Yasuhiro Yoshida, Hidehiko Sano, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Atsushi Tomokiyo
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(9): 1247. CrossRef - 3D-printed microgels supplemented with dentin matrix molecules as a novel biomaterial for direct pulp capping
Diana Cunha, Nayara Souza, Manuela Moreira, Nara Rodrigues, Paulo Silva, Cristiane Franca, Sivaporn Horsophonphong, Ashley Sercia, Ramesh Subbiah, Anthony Tahayeri, Jack Ferracane, Pamela Yelick, Vicente Saboia, Luiz Bertassoni
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1215. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Pulpal response to mineral trioxide aggregate containing phosphorylated pullulan-based capping material
Yu TOIDA, Shimpei KAWANO, Rafiqul ISLAM, Fu JIALE, AFM A CHOWDHURY, Shuhei HOSHIKA, Yasushi SHIMADA, Junji TAGAMI, Masahiro YOSHIYAMA, Satoshi INOUE, Ricardo M. CARVALHO, Yasuhiro YOSHIDA, Hidehiko SANO
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(1): 126. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium-Silicate Cements on Reparative Dentinogenesis Following Direct Pulp Capping on Animal Models
Mihai Andrei, Raluca Paula Vacaru, Anca Coricovac, Radu Ilinca, Andreea Cristiana Didilescu, Ioana Demetrescu
Molecules.2021; 26(9): 2725. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of a novel phosphorylated pullulan‐based pulp capping material: An in vivo study on rat molars
Rafiqul Islam, Yu Toida, Fei Chen, Toru Tanaka, Satoshi Inoue, Tetsuya Kitamura, Yasuhiro Yoshida, Abu Faem Mohammad Almas Chowdhury, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Hidehiko Sano
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(10): 1902. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - A strontium and amorphous calcium phosphate dipped premixed injectable calcium silicate-based ceramic for dental root canal sealing
Huimin Jin, Yuzhu Li, Qingqing Wang, Menglu Dong, Mengmeng Yang, Wendy Chen, Shengrui Wang, Heng Zhang, Shunli Zheng, Chris Ying Cao, Zheng Zhou, Quan-Li Li
Ceramics International.2021; 47(23): 33738. CrossRef - Bioactive tri/dicalcium silicate cements for treatment of pulpal and periapical tissues
Carolyn M. Primus, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2019; 96: 35. CrossRef
- Bioactivity and biocompatibility of bioceramic-based pulp capping materials in laboratory and animal models
- 2,120 View
- 20 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
- Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):258-262. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative management of deep carious lesions and the preservation of pulp vitality of immature teeth present real challenges for dental practitioners. New tricalcium silicate cements are of interest in the treatment of such cases. This case describes the immediate management and the follow-up of an extensive carious lesion on an immature second right mandibular premolar. Following anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, the carious lesion was removed and a partial pulpotomy was performed. After obtaining hemostasis, the exposed pulp was covered with a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine, Septodont) and a glass ionomer cement (Fuji IX extra, GC Corp.) restoration was placed over the tricalcium silicate cement. A review appointment was arranged after seven days, where the tooth was asymptomatic with the patient reporting no pain during the intervening period. At both 3 and 6 mon follow up, it was noted that the tooth was vital, with normal responses to thermal tests. Radiographic examination of the tooth indicated dentin-bridge formation in the pulp chamber and the continuous root formation. This case report demonstrates a fast tissue response both at the pulpal and root dentin level. The use of tricalcium silicate cement should be considered as a conservative intervention in the treatment of symptomatic immature teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
A. Lavanya
The Traumaxilla.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of pulpotomy materials in permanent teeth: a systematic review of calcium hydroxide, MTA, biodentine, and iRoot BP plus
Anggi Putri Riandani, Arief Cahyanto, Rana Abdelbaset Lotfy Diab, Ratih Widyasari, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Evaluation of Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement after Chlorhexidine Irrigation
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(19): 8702. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Protección pulpar directa y posterior apexogénesis. Informe de un caso clínico / Direct pulp capping followed by apexogenesis. A clinical case report
Osvaldo Zmener, Ana C. Boetto
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation with Citric Acid on Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement: SEM-EDS In Vitro Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2022; 15(10): 3467. CrossRef - The Immunomodulatory and Regenerative Effect of Biodentine™ on Human THP‐1 Cells and Dental Pulp Stem Cells: In Vitro Study
Duaa Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Rand Zaza, Hanan Jafar, Suzan Zalloum, Renata Atoom, Walhan Alshaer, Mairvat Al-Mrahleh, Abdalla Awidi, Bruna Sinjari
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine: Material of choice for apexification
Himanshu Aeran, Mahema Sharma, Avantika Tuli
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry.2021; 7(1): 54. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine Pulpotomies on Permanent Traumatized Teeth with Complicated Crown Fractures
Léa Haikal, Beatriz Ferraz dos Santos, Duy-Dat Vu, Marina Braniste, Basma Dabbagh
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1204. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite and ultrasounds on surface features and chemical composition of Biodentine tricalcium silicate-based material
Aleksandra PALATYŃSKA-ULATOWSKA, Katarzyna BUŁA, Leszek KLIMEK
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(4): 587. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting pulp-capping materials on cell viability and osteogenic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Yan Sun, Jun Liu, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Ling Zou
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 100: 100. CrossRef - Healing Capacity of Autologous Bone Marrow–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Partially Pulpotomized Dogs' Teeth
Mona H. El-Zekrid, Salah H. Mahmoud, Fawzy A. Ali, Mohamed E. Helal, Mohammed E. Grawish
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 287. CrossRef - Large Periapical or Cystic Lesions in Association with Roots Having Open Apices Managed Nonsurgically Using 1-step Apexification Based on Platelet-rich Fibrin Matrix and Biodentine Apical Barrier: A Case Series
Sarang Sharma, Vivek Sharma, Deepak Passi, Dhirendra Srivastava, Shibani Grover, Shubha Ranjan Dutta
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(1): 179. CrossRef - Microleakage and Shear Bond Strength of Biodentine at Different Setting Time
Yong Ho Song, Nanyoung Lee, Sangho Lee, Myeongkwan Jih
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(3): 344. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Case Report: Immediate pain relief after partial pulpotomy of cariously exposed young permanent molar using mineral trioxide aggregate and root maturation, with two years follow-up
Passant Nagi, Nevine Waly, Adel Elbardissy, Mohammed Khalifa
F1000Research.2018; 7: 1616. CrossRef - Factors affecting the outcomes of direct pulp capping using Biodentine
Mariusz Lipski, Alicja Nowicka, Katarzyna Kot, Lidia Postek-Stefańska, Iwona Wysoczańska-Jankowicz, Lech Borkowski, Paweł Andersz, Anna Jarząbek, Katarzyna Grocholewicz, Ewa Sobolewska, Krzysztof Woźniak, Agnieszka Droździk
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(5): 2021. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Dislodgement resistance of calcium silicate‐based materials from root canals with varying thickness of dentine
Ö. İ. Ulusoy, Y. N. Paltun, N. Güven, B. Çelik
International Endodontic Journal.2016; 49(12): 1188. CrossRef - Expression of Mineralization Markers during Pulp Response to Biodentine and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Mariana O. Daltoé, Francisco Wanderley G. Paula-Silva, Lúcia H. Faccioli, Patrícia M. Gatón-Hernández, Andiara De Rossi, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 596. CrossRef - Biodentine Reduces Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha–induced TRPA1 Expression in Odontoblastlike Cells
Ikhlas A. El Karim, Maelíosa T.C. McCrudden, Mary K. McGahon, Tim M. Curtis, Charlotte Jeanneau, Thomas Giraud, Chris R. Irwin, Gerard J. Linden, Fionnuala T. Lundy, Imad About
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 589. CrossRef - Coronal Pulpotomy Technique Analysis as an Alternative to Pulpectomy for Preserving the Tooth Vitality, in the Context of Tissue Regeneration: A Correlated Clinical Study across 4 Adult Permanent Molars
Raji Viola Solomon, Umrana Faizuddin, Parupalli Karunakar, Grandhala Deepthi Sarvani, Sevvana Sree Soumya, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review on Biodentine, a Contemporary Dentine Replacement and Repair Material
Özlem Malkondu, Meriç Karapinar Kazandağ, Ender Kazazoğlu
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 230. CrossRef - Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 120. CrossRef
- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
- 2,101 View
- 5 Download
- 28 Crossref

- Chemical characteristics of mineral trioxide aggregate and its hydration reaction
- Seok-Woo Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):188-193. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) was developed in early 1990s and has been successfully used for root perforation repair, root end filling, and one-visit apexification. MTA is composed mainly of tricalcium silicate and dicalcium silicate. When MTA is hydrated, calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) and calcium hydroxide is formed. Formed calcium hydroxide interacts with the phosphate ion in body fluid and form amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) which finally transforms into calcium deficient hydroxyapatite (CDHA). These mineral precipitate were reported to form the MTA-dentin interfacial layer which enhances the sealing ability of MTA. Clinically, the use of zinc oxide euginol (ZOE) based materials may retard the setting of MTA. Also, the use of acids or contact with excessive blood should be avoided before complete set of MTA, because these conditions could adversely affect the hydration reaction of MTA. Further studies on the chemical nature of MTA hydration reaction are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discoloration, radiopacity, and push-out bond strength of bismuth-based radiopacifiers in endodontic sealers
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Mina Shekarian, Amir Abdolmaleki, Michael Conte, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrieval of AH Plus Bioceramic and Ceraseal Versus AH Plus in Endodontic Retreatment
Eurok Shim, Jee Woo Son, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(6): 1826. CrossRef - Inducing Osteogenesis in Human Pulp Stem Cells Cultured on Nano-Hydroxyapatite and Naringin-Coated 3D-Printed Poly Lactic Acid Scaffolds
Reem Mones Dawood, Anas Falah Mahdee
Polymers.2025; 17(5): 596. CrossRef - Enhancing the Physical Properties of Calcium Silicate Cement Modified with Elastin-like Polypeptides and Bioactive Glass
Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 188. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and apatite precipitation behavior of experimental calcium silicate-based cements doped with phosphate compounds
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Dental Materials.2025; 41(9): 1058. CrossRef - Microstructural Evaluation of the Mineralized Apical Barrier Induced by a Calcium Hydroxide Paste Containing Iodoform: A Case Report
Motoki Okamoto, Katsuaki Naito, Henry Fergus Duncan, Yoshifumi Kinomoto, Nanako Kuriki, Jiro Miura, Manabu Mizuhira, Maiko Suzuki, Mikako Hayashi
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 243. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement with ProRoot MTA and MTA Angelus
Siddharth Anand, Ravi Prakash, Nimish Tyagi, Chandrakar Chaman, Anjali Dhull, Himanshu Tomar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(1): 35. CrossRef - Analysis of the bond strength between conventional, putty or resin‐modified calcium silicate cement and bulk fill composites
İ Ipek, B Karaağaç Eskibağlar, Ş Yildiz, O Ataş, M Ünal
Australian Dental Journal.2023; 68(4): 265. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Effect of different chelating agents on the shear bond strength of calcium silicate‐based cements to coronal dentin
Mohamed Ahmed Elsayed, Md Sofiqul Islam, Karim Elbeltagy, Mohannad Nassar
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 426. CrossRef - Phosphoric acid treatment enhances adaptation of glass-ionomer cement to bioceramic sealer-conditioned dentin
Nandini Suresh, Sooriaprakas Chandrasekaran, M. C. V. Ashritha, Mohammed Abdul Raoufe, Aishwarya Vasudevan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface Morphological Analysis and Evaluation of the Sealing Ability of a Nanoparticle-Incorporated Hydraulic Root-End Cement
Teena Sheethal Dsouza, Aditya Shetty
International Journal of Nanoscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Four Bioceramic Materials with Different Restorative Materials and Timings
Abeer S. Alqahtani, Ayman M. Sulimany, Abdullah S. Alayad, Abdulaziz S. Alqahtani, Omar A. Bawazir
Materials.2022; 15(13): 4668. CrossRef - Alkalizing Properties of Six Calcium-Silicate Endodontic Biomaterials
Katarzyna Kot, Łukasz Kucharski, Ewa Marek, Krzysztof Safranow, Mariusz Lipski
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6482. CrossRef - Physicochemical and biological properties of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements
Seok Woo Chang, Alexis Gaudin, Mirek Tolar, Soram Oh, Su-Young Moon, Ove A. Peters
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1586. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of bioactive glass addition on the physical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate
Jei Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Biomaterials Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Different Pulp-Capping Materials against Enterococcus faecalis: An In vitro Study
Jenny Atom, Ningthoukhongjam Rati Devi, Ronel Lairenlakpam, Mohammed Hussain Dafer Al Wadei, Abdulrahim R. Hakami, Abdulkarim S. BinShaya
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S608. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Bioactivity of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Bioactive Endodontic Type Cements: A Systematic Review
Uma Dixit, Rucha Shivajirao Bhise Patil, Rupanshi Parekh
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - A Silk Fibroin Based Hydration Accelerator for Root Canal Filling Materials
Ching-Shuan Huang, Sung-Chih Hsieh, Nai-Chia Teng, Wei-Fang Lee, Poonam Negi, Wendimi Fatimata Belem, Hsuan-Chen Wu, Jen-Chang Yang
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 994. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of novel calcium phosphate glass-derived cements for vital pulp therapy
Jerry Howard, Levi Gardner, Zahra Saifee, Aladdin Geleil, Isaac Nelson, John S. Colombo, Steven E. Naleway, Krista Carlson
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on osteo/odontogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive and systematic literature review
Danial Babaki, Sanam Yaghoubi, Maryam M. Matin
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2020; 7(1): 175. CrossRef - APICAL MICROLEAKAGE OF VARIOUS BIOMATERIALS IN SIMULATED IMMATURE APICES
Fatih TULUMBACI, Volkan ARIKAN, Aylin AKBAY OBA, İşıl SÖNMEZ ŞAROĞLU
Selcuk Dental Journal.2019; 6(3): 247. CrossRef - Effects of the exposure site on histological pulpal responses after direct capping with 2 calcium-silicate based cements in a rat model
Panruethai Trongkij, Supachai Sutimuntanakul, Puangwan Lapthanasupkul, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Rebecca Wong, Danuchit Banomyong
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Histopathological evaluation of periodontium after repairing furcation perforation with MTA and biodentine
Nehal Youssef Youssef Abdelati, Ibrahim Hassan Elkalla, Salwa Mohamed Awad, Hanaa Mahmoud Shalan
Pediatric Dental Journal.2018; 28(1): 33. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial activity of two Biocompatible materials i.e. Biodentine and MTA when used as a direct pulp capping agent against streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis- An in vitro study
Aditi Subodh Jain, Asmita Singh Gupta, Rupika Agarwal
Endodontology.2018; 30(1): 66. CrossRef - Superfast Set, Strong and Less Degradable Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Cement
Abdullah Alqedairi, Carlos A. Muñoz-Viveros, Eugene A. Pantera, Marc Campillo-Funollet, Hussam Alfawaz, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Tariq S. Abuhaimed
International Journal of Dentistry.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of physicochemical properties of root-end filling materials using conventional and Micro-CT tests
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves TORRES, Roberta BOSSO-MARTELO, Camila Galletti ESPIR, Joni Augusto CIRELLI, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(4): 374. CrossRef - Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 12. CrossRef - In vivo evaluation of the effects of hydraulic calcium silicate dental cements on plasma and liver aluminium levels in rats
Kadriye Demirkaya, Birsen Can Demirdöğen, Zeynep Öncel Torun, Onur Erdem, Serdar Çetinkaya, Cemal Akay
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2016; 124(1): 75. CrossRef - Healing of Large Periapical with Tricalcium Silicate-based Root End Filling Material
Snehal S Sonarkar, Rucheet Purba, Rajesh Podar
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2016; 1(2): 41. CrossRef - The Effect of Blood Contamination on the Chemical Characterization of Hydrated Mineral Trioxide Aggregates and Their Dentin-Interface: A Comparative Study
Sawsan T. Abu Zeid, Lubna A. Shafie, Abeer A. Mokeem Saleh, Monazah G. Khafagi
Spectroscopy Letters.2015; 48(9): 631. CrossRef - A review of the physical, chemical properties of MTA
Yong-Bum Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(1): 51. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 89. CrossRef - Study on Biocompatibility and Mineralization Potential of Capseal
Kwang Shik Bae, Seok Woo Chang, Kee Yeon Kum, Woo Cheol Lee
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2014; 7(1): 1. CrossRef - Surface microhardness of three thicknesses of mineral trioxide aggregate in different setting conditions
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Leila Jafargholizadeh, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Maryam Raoof
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 253. CrossRef - Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 120. CrossRef - Tooth Discoloration after the Use of New Pozzolan Cement (Endocem) and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and the Effects of Internal Bleaching
Ji-Hyun Jang, Minji Kang, Soyeon Ahn, Soyeon Kim, Wooksung Kim, Yaelim Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1598. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 128. CrossRef - Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 113. CrossRef - Washout resistance of fast-setting pozzolan cement under various root canal irrigants
Ga-Yeon Jang, Su-Jung Park, Seok-Mo Heo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 248. CrossRef - A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 227. CrossRef - Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 258. CrossRef
- Discoloration, radiopacity, and push-out bond strength of bismuth-based radiopacifiers in endodontic sealers
- 2,713 View
- 24 Download
- 44 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


