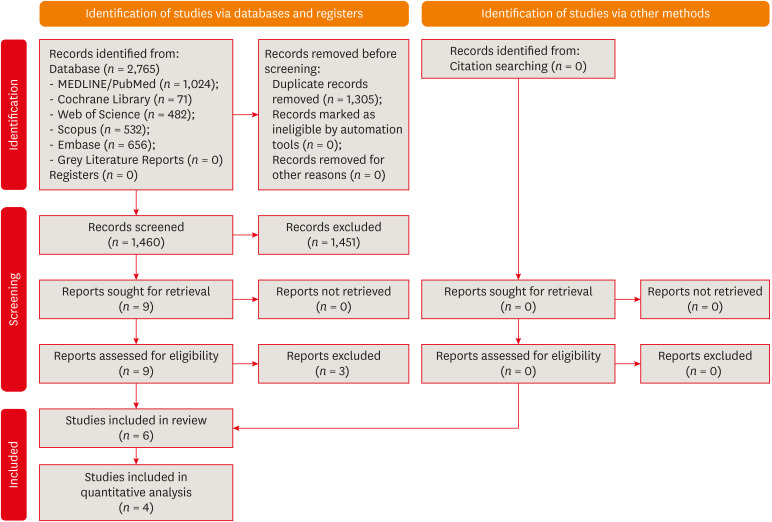
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Disinfectant effectiveness of chlorhexidine gel compared to sodium hypochlorite: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- Theodoro Weissheimer, Karem Paula Pinto, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e37. Published online October 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to compare the disinfectant ability of chlorhexidine (CHX) gel and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Systematic searches were conducted from inception until December 8th, 2022 (MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and Grey Literature databases). Only randomized clinical trials were included. The revised Cochrane risk of bias tools for randomized trials were used to assess the quality of studies. Meta-analyses were performed. The overall quality of evidence was assessed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation tool. Six studies were included. Five had a low risk of bias and 1 had some concerns. Three studies assessed bacterial reduction. Two were included in the meta-analysis for bacterial reduction (mean difference, 75.03 [confidence interval, CI, −271.15, 421.22],
p = 0.67;I 2 = 74%); and 3 in the meta-analysis for cultivable bacteria after chemomechanical preparation (odds ratio, 1.03 [CI, 0.20, 5.31],P = 0.98;I 2 = 49%). Five studies assessed endotoxin reduction. Three were included in a meta-analysis (mean difference, 20.59 [CI, −36.41, 77.59],p = 0.48;I 2 = 74%). There seems to be no difference in the disinfectant ability of CHX gel and NaOCl, but further research is necessary.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- REGENERATIVE ENDODONTIC PROCEDURES: MAPPING AND CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF CLINICAL TRIAL EVIDENCE
Felipe Oliveira Nunes, Eduardo Borges Sollim, Carolynne Ferreira dos Santos, Maria Karolina Martins Ferreira, João Daniel Mendonça Moura, Juliana Melo Brandão, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Paulo Jorge Palma, Rafael Rodrigues Lima
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Bactericidal Effects of Ultraviolet-C Light-Emitting Diode Prototype Device Through Thin Optical Fiber
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Deog-Gyu Seo
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4504. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Irrigation Protocols in Endodontic Therapy: An Umbrella Review
Manuel J. Orozco-Gallego, Eliana L. Pineda-Vélez, Wilder J. Rojas-Gutiérrez, Martha L. Rincón-Rodríguez, Andrés A. Agudelo-Suárez
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 273. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Disinfectants on Gutta-Percha Cones: Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans
Tringa Kelmendi, Donika Bajrami Shabani, Aida Meto, Hani Ounsi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 6846. CrossRef - Preparing porcine lens to mimic human lens capsule
Yajing Pei, Shaofeng Han, Mingfeng Lu, Yang Yang, Ke Ma
Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery.2024; 50(9): 963. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Disinfection Protocols for Dental Impressions in Prosthodontics
Subhash Sonkesriya, Ghanshyam Gaur, Akanksha Maheshwari, Arun Kumar Ashahiya, Simran Kaur Aulakh, Amit Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- REGENERATIVE ENDODONTIC PROCEDURES: MAPPING AND CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF CLINICAL TRIAL EVIDENCE
- 6,429 View
- 124 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Comparison of the sealing ability of various bioceramic materials for endodontic surgery
- Benjamin Rencher, Ana M. Chang, Hanson Fong, James D. Johnson, Avina Paranjpe
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e35. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
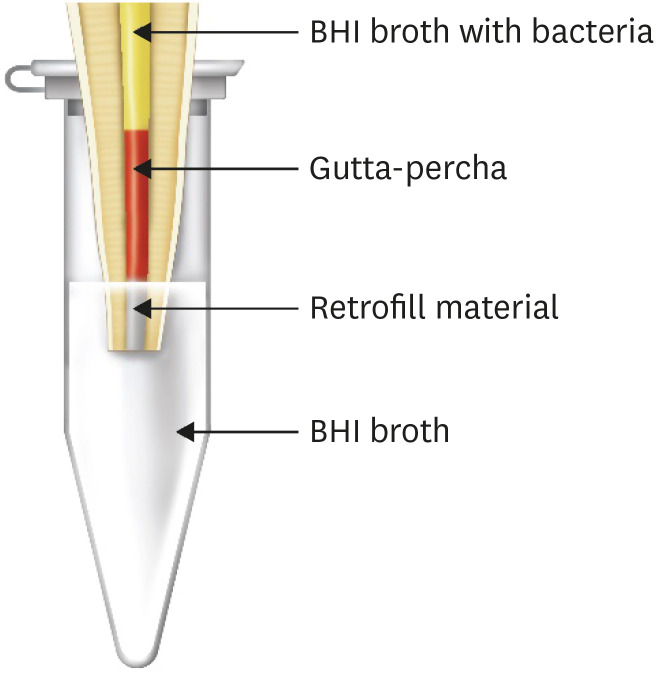
ePub Objectives Endosequence Bioceramic Root Repair Material (BC-RRM) is used in endodontic microsurgery. It is available as a paste and a putty. However, no studies to date have examined the sealing ability of these forms alone or in combination as root-end filling materials. Hence, this study aimed to compare the sealing properties of these 2 forms of BC-RRM.
Materials and Methods Forty-two extracted upper anterior teeth were divided into 3 experimental groups, a positive and negative control. After the root canal treatment, the root ends were resected, retroprepared and retrofilled with either putty, paste + putty or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). The teeth were mounted in tubes so the apical 3 mm was submerged in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth. The coronal portions of the canals were inoculated with
Enterococcus faecalis and BHI broth and incubated for 30 days. The broth in the tubes was analyzed for colony forming units to check for leakage of bacteria from the canal. The teeth from the groups were sectioned and analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Kruskal-Wallis test and analysis of variance were used to analyze the data with a significance levelp < 0.05.Results The BC-RRM and MTA groups showed similar sealing ability. The positive control showed leakage in all samples. The SEM imaging showed the presence of bacteria in all experimental groups at the material-tooth interface.
Conclusions No significant differences were noted in the experimental groups, providing sufficient evidence that any combination could be effectively used during endodontic microsurgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sealing ability and marginal adaptation of premixed versus manually mixed bioceramic root-end filling materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ayham Hattab, Mouhammad Al-Tayyan, Osama Hajeer
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - An Ex-vivo Evaluation of Sealability of Three Bioceramic Physical Variants in Coronal and Apical Thirds of Root Canals
Murali H Rao, Rajkumar Krishnan, Pavithra Gopal, Elizabeth Thomas
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(11): 1022. CrossRef - Clinical applications and classification of calcium silicate-based cements based on their history and evolution: a narrative review
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Strontium- and bioactive glass-enriched dentin repair cement: Mechanical performance and physicochemical characteristics
Nathalia Cristina Tavella-Silva, Larissa Moreira Spinola Castro Raucci, Victor Miguel Polizeli, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Ivone Regina de Oliveira, Walter Raucci Neto
Ceramics International.2025; 51(22): 35947. CrossRef - Conventional vs. Ready‐To‐Use Bioceramic Cements: In Vitro Bond Strength Performance in Blood‐Contaminated Dentine
Gabriela Kato Bego, Graziela Bianchi Leoni, Elias Daniel Covas Rodrigues, Larissa Moreira Spinola de Castro Raucci, Walter Raucci Neto
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 466. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based repair sealers on bone healing in rat skull defects: histological and histomorphometric study
J. M. Sauer, C. E. S. Bueno, R. A. Pelegrine, C. E. Fontana, E. F. Martinez, P. G. Montagner, W. M. Nascimento, A. G. S. Limoeiro, D. G. P. Rocha, M. F. V. Marceliano-Alves, M. P. W. Galhardi, M. Klymus, A. S. Martin
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(3): 433. CrossRef - Randomized Trial of Bioceramic Apical Barrier Methods in Necrotic Immature Incisors: Effects on Pain, Extrusion, and Procedure Duration
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Nada Bshara, Osama Aljabban, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Marwan Alhaji, Imad-Addin Almasri, Ziad D. Baghdadi
Children.2025; 12(10): 1423. CrossRef - Sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate: A scoping review of laboratory assessment methods
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Deepak Mehta, Kyung‐San Min, Atsushi Tomokiyo
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Development Following Bioceramic Material Application in Immature Permanent Teeth: A Case Series With 24‐Month Follow‐Up
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Nada Bshara, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Marwan Alhaji, Osama Aljabban, Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Ziad D. Baghdadi, Hannah Wesley
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Laboratory study of the sealing ability of materials used in retrograde root filling
L.A. Nadzharyan, A.V. Vasilyev, V.A. Badalyan, A.S. Galkin, A.V. Mironov, F.F. Losev
Stomatology.2025; 104(6): 5. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Marginal Adaptation of Two Hydraulic Calcium Silicate Cements Used in Apical Plugs: An In Vitro Study
Sara Filipe, José Pedro Martinho, Siri Paulo, Catarina Carvalho, Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Eunice Carrilho, Anabela Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Henrique Girão, Mónica Zuzarte, Ana S. Pires, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(2): 480. CrossRef - A Study on Nanoleakage of Apical Retrograde Filling of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Cement Using a Lid Technique
Nyamsuren Enkhbileg, Jin Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung Mo Cho, Yoon Lee
Materials.2024; 17(10): 2366. CrossRef - The outcome of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling in endodontic microsurgery: a randomized controlled trial
Xu Dong, Qin Su, Wen Li, Jinbo Yang, Dongzhe Song, Jing Yang, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial sealing ability of calcium silicate-based sealer for endodontic surgery: an in-vitro study
Mai M. Mansour, Sybel M. Moussa, Marwa A. Meheissen, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Marginal Adaptation of Three Biomaterials as Apical Barrier in Experimental Apexification Model
Nagehan Aktaş, Didem Sakaryalı Uyar, Didem Atabek
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 13(3): 409. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the sealing ability of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling
Xu Dong, Qian Xie, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2969. CrossRef - Outcomes of endodontic microsurgery using different calcium silicate–based retrograde filling materials: a cohort retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Rawan F. Eskandar, Mey A. Al-Habib, Mohammed A. Barayan, Hadeel Y. Edrees
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Biological properties of Ceraputty as a retrograde filling material: an in vitro study on hPDLSCs
Sergio López-García, Francisco J. Rodríguez-Lozano, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, María Pilar Pecci-Lloret, Adrián Lozano, Laura Murcia, Sonia Sánchez-Bautista, Ricardo E. Oñate-Sánchez
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(8): 4233. CrossRef - Bone Window Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery – Report of Two Cases
Spyros Floratos, Vasileios Molonis, Apostolos Tsolakis, Stylianos Kykalos, Konstantinos Kontzoglou
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022; 2: 24. CrossRef
- Sealing ability and marginal adaptation of premixed versus manually mixed bioceramic root-end filling materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 5,886 View
- 100 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref

-
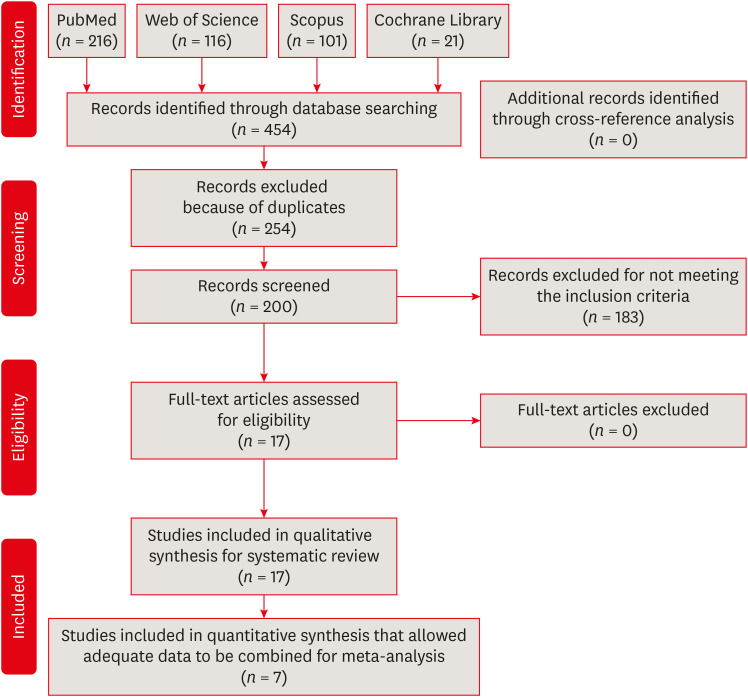
Influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
in vitro studies - Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu-Özyürek, Sevilay Karahan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e19. Published online March 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of
in vitro studies regarding the effectiveness of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction in root canals.Materials and Methods PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, and the gray literature were searched through December 2019. Studies comparing the influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on the removal of microorganisms from root canals that quantified the antimicrobial effect were included. Data extraction was completed using a systematic form for data collection. The risk of bias of the studies was evaluated. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random effects meta-analysis.
Results Seventeen
in vitro studies were included in this systematic review, of which 7 provided adequate data for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Both reciprocating and rotary systems were similarly effective in reducing the microbial load in infected root canals (SMD [95% CI], 0.0481 [−0.271, 0.367]). Three studies showed a low risk of bias, whereas most of the studies (82%) presented a medium risk.Conclusions Although both techniques decrease the microbial content (with reductions of 23.32%–88.47% and 23.33%–89.86% for reciprocating and rotary instrumentation, respectively)
, they are not able to provide complete disinfection of root canals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Evandro Piva, Leandro Perello Duro, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(4): 179. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Does minimally invasive canal preparation provide higher fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review ofin vitrostudies
Sıla Nur Usta, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Seda Falakaloğlu, Mustafa Gündoğar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Different Access Cavity Designs and Ni–Ti Files on the Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal System: An In Vitro Study
Gizem Andac, Atakan Kalender, Buket Baddal, Fatma Basmaci
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(4): 2049. CrossRef - Shaping Properties and Outcomes of Nickel-Titanium Reciprocation Systems in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
SelvaKumar Haridoss, Bhavyaa R, Kavitha Swaminathan, Aruna P
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Root Canal Sealers and Obturation Techniques on Vertical Root Fracture Resistance. An In Vitro Experiment
Mazen F. Alkahtany, Khalid H. Almadi, Fahad A. Alahmad, Abdullah M. Alshehri, Abdulrahman A. AlSwayyed, Omar M. AlZahran, Ali AlHadan, Abdulaziz S. Almustafa, Fahim Vohra, Tariq Abduljabbar
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(17): 8022. CrossRef
- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
- 2,429 View
- 34 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of octenidine as an antimicrobial agent againstStaphylococcus epidermidis in disinfecting the root canal system - Jia Da Chum, Darryl Jun Zhi Lim, Sultan Omer Sheriff, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Anand Suresh, Fabian Davamani
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e8. Published online February 8, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
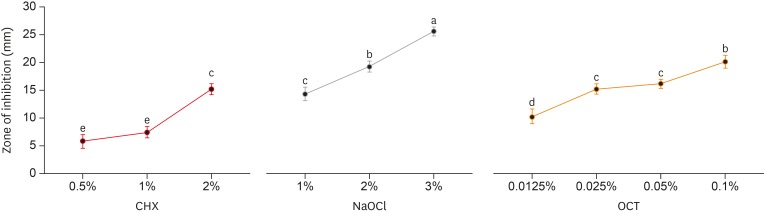
ePub Objectives Irrigants are imperative in endodontic therapy for the elimination of pathogens from the infected root canal. The present study compared the antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride (OCT) with chlorhexidine (CHX) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) against
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis ) for root canal disinfection.Materials and Methods The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was obtained using serial dilution method. The agar diffusion method was then used to determine the zones of inhibition for each irrigant. Lastly, forty 6-mm dentin blocks were prepared from human mandibular premolars and inoculated with
S. epidermidis . Samples were randomly divided into 4 groups of 10 blocks and irrigated for 3 minutes with saline (control), 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, or 0.1% OCT. Dentin samples were then collected immediately for microbial analysis, including an analysis of colony-forming units (CFUs).Results The MICs of each tested irrigant were 0.05% for CHX, 0.25% for NaOCl, and 0.0125% for OCT. All tested irrigants showed concentration-dependent increase in zones of inhibition, and 3% NaOCl showed the largest zone of inhibition amongst all tested irrigants (
p < 0.05). There were no significant differences among the CFU measurements of 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, and 0.1% OCT showing complete elimination ofS. epidermidis in all samples.Conclusions This study showed that OCT was comparable to or even more effective than CHX and NaOCl, demonstrating antimicrobial activity at low concentrations against
S. epidermidis .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Gülgün Atay Yılmaz, Nihan Şengül, Ahmet Keleş, Selen Küçükkaya Eren
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Substantivity of different antiseptic oral gels. An In vitro study
Nirit Tagger Green, Roni Kolerman, Carlos Nemcovsky, Shlomo Matalon, Dan Gaukhman, Liat Chaushu
Heliyon.2025; : e42654. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of crustacean-derived chitosan against Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes
Sivainesh Devi Remesh, Pratheep Sandrasaigaran, Santhaniswarman Remesh, Veeradasan Perumal, Joshua Yap Lip Vun, Sivasangkary Gandhi, Hanan Hasan
Food Bioscience.2025; : 106697. CrossRef - Glycerol-Enhanced Gum Karaya Hydrogel Films with a Sandwich-like Structure Enriched with Octenidine for Antibacterial Action against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Eva Černá, Vilém Neděla, Eva Tihlařiková, Jana Brtníková, Zdenka Fohlerová, Břetislav Lipový, Lukáš Vacek, Filip Růžička, Jana Matulová, Lucy Vojtová
ACS Omega.2025; 10(27): 29530. CrossRef - Effect of Mouth Rinsing and Antiseptic Solutions on Periodontitis Bacteria in an In Vitro Oral Human Biofilm Model
Jan Tinson Strenge, Ralf Smeets, Maria Geffken, Thomas Beikler, Ewa Klara Stuermer
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 324. CrossRef - In Vitro Investigation of the Effects of Octenidine Dihydrochloride on Nasal Septum Squamous Carcinoma Cells
Ihsan Hakki Ciftci, Asuman Deveci Ozkan, Gulay Erman, Elmas Pinar Kahraman Kilbas, Mehmet Koroglu
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2668. CrossRef - Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein-S as a Dual-Action Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Agent Against Staphylococcus aureus
Priya Verma, Priyanka Swaroop, Surabhi Pandit, Ved Prakash, Surender Kumar Sharawat, T. P. Singh, Sujata Sharma, Pradeep Sharma
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Effects of Endodontic Irrigants Containing Disodium Edetate and Chlorhexidine Gluconate, Octenidine Dihydrochloride, and Benzalkonium Bromide Against Intracanal Enterococcus faecalis
Anna Siemińska, Katarzyna Kot, Ewa Marek, Agnieszka Chamarczuk, Magdalena Kaczała, Joanna Rasławska-Socha, Laurentia Schuster, Till Dammaschke, Liliana Szyszka-Sommerfeld, Mariusz Lipski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 7100. CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain in endodontic retreatment with apical periodontitis using ozonated 2% chlorhexidine and 0.1% octenidine application: A randomized clinical trial
Nidhi Sinha, Geeta Asthana, Girish Parmar, Akshayraj Langaliya, Jinali Shah, Bijay Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 654. CrossRef - Research on NiTi instruments combined with ultrasonic irrigation and multiantibiotic paste in root canal therapy of periapical inflammation in deciduous teeth
Zongxia Zhu, Guangli Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride, superoxidized solution, ozonated water, 0.1% silver nanoparticle solution, and Q mix™ 2 in 1 in root canals infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Mahenaz Salam Inamdar, Dayanand G. Chole, Shrinivas S. Bakle, Preeti B. Vaprani, Neha P. Gandhi, Nikhil R. Hatte
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(10): 1059. CrossRef - Causal relationship, shared genes between rheumatoid arthritis and pulp and periapical disease: evidence from GWAS and transcriptome data
Huili Wu, Lijuan Wang, Chenjie Qiu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of octenidine dihydrochloride on the antibacterial activity of a formulated resin composite: an in vitro study
Mahitab Mansour, Tarek Salah, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between pulp and periapical disease with type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Yuqiang Wang, Jiakang Zhu, Ying Tang, Cui Huang
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 566. CrossRef - New Insights Regarding the Use of Relevant Synthetic Compounds in Dentistry
Stefania-Irina Dumitrel, Anamaria Matichescu, Stefania Dinu, Roxana Buzatu, Ramona Popovici, Dorin Dinu, Dana Bratu
Molecules.2024; 29(16): 3802. CrossRef - Formulation and Characterization of a Novel Palm-Oil-Based α-Mangostin Nano-Emulsion (PO-AMNE) as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant: An In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Haresh Kumar A/L Kantilal, Khoo Suan Phaik, Hira Choudhury, Fabian Davamani
Processes.2023; 11(3): 798. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Formulations of Septilin and Triphala with Conventional 2% Chlorhexidine on Root Canal and Oral Commensal Bacteria using Kirby Bauer Method
Shadab Ahmed, Kamil Shahnawaz, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Mamnoon Ghafir, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Gaurav Vishal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 383. CrossRef - A comparative assessment of pomegranate extract, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, Myrrh (Commiphora molmol), tulsi extract against Enterococcus faecalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Staphylococci epidermidis
Mallwika Sisodiya, Shadab Ahmed, Ranjan Sengupta, Priyanka, Ankit Kumar Saha, Gourav Verma
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2021; 25(2): 369. CrossRef - Effects of Octenidine on the Formation and Disruption of Dental Biofilms: An Exploratory In Situ Study in Healthy Subjects
B. Reda, J. Dudek, M. Martínez-Hernández, M. Hannig
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(9): 950. CrossRef - Does Cavity Disinfectant Affect Sealing Ability of Universal Self-etch Adhesive?
S Lata, Prasanti Kumari Pradhan, Gaurav Patri, Subhasmita Bhol, Kanhu C Sahoo, Khushboo Ghosh
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 273. CrossRef - Effect of duration and dilution on antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine hydrochloride as an intracanal medicament with chitosan carrier against Enterococcus faecalis – A modified direct contact test
VinayaSusan Varghese, Nirmal Kurian
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2020; 23(5): 463. CrossRef
- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
- 2,572 View
- 20 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Bacterial leakage and micro-computed tomography evaluation in round-shaped canals obturated with bioceramic cone and sealer using matched single cone technique
- Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Ratchapin Laovanitch Srisatjaluk
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e30. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e30
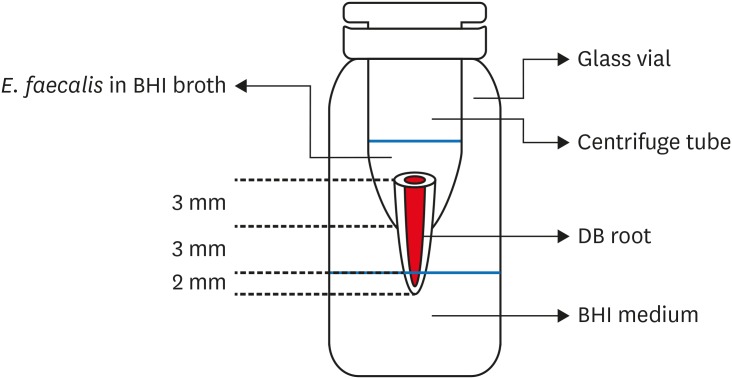
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate sealing ability of root canals obturated with bioceramic-impregnated gutta percha cone (BCC) or gutta percha (GP), with bioceramic sealer (BCS) or AH Plus (AH; Dentsply-Maillefer), in roundly-prepared canals using matched single-cone technique, based on bacterial leakage test, and to analyze obturation quality using micro-computed tomography (CT) analysis.
Materials and Methods Ninety-two distobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared using nickel-titanium files to apical size 40/0.06. The roots were divided into 4 groups (
n = 20) that were obturated with a master cone and sealer: GP/AH, BCC/AH, GP/BCS, and BCC/BCS. Bacterial leakage model usingEnterococcus faecalis was used to evaluate sealing ability for 60-day period. Obturated samples from each group (n = 4) were analyzed using micro-CT.Results All groups showed bacterial leakage at 20%–45% of samples with mean leakage times of 42–52 days. There were no significant differences in bacterial leakage among the groups. Micro-CT showed minimal gaps and voids in all groups at less than 1%.
Conclusions In roundly-prepared canals, the single cone obturation with BCC/BCS was comparable to GP/AH for bacterial leakage at 60 days.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-Dependent Volumetric and Porosity Changes of Bioceramic, Silicone Bioactive Glass-Based, and Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Micro-CT Analysis
Thanh Quang Nguyen, Chantida Pawaputanon Na Mahasarakham, Pinpana Thaweesit, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Angsana Jainaen
European Journal of Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - Synthesis, physical properties, and root canal sealing of experimental MTA- and salicylate-based root canal sealers
Rafael Pino Vitti, Kusai Baroudi, Tarun Walia, Raghavandra M. Shetty, Flávia Goulart da Rosa Cardoso, Flávia de Moura Pereira, Evandro Piva, Cesar Henrique Zanchi, Gabriel Flores Abuna, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Flávio
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0329476. CrossRef - Impact of cone system compatibility on single cone bioceramic obturation in canals prepared with variable taper NiTi rotary files
Reem M. Barakat, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Njoom Aleid, Hoor Almowais, Aljawhara Alharbi, Meshal Al-Sharafa, Ali Alrahlah
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio de la obturación con selladores biocerámicos de conductos radiculares de premolares inferiores
Alicia Beatriz Bonafé, Cecilia Inés Rourera, Carla Pedraza, Yamila Victoria Zanoni, Soledad Salduna, Cecilia Noemi De Caso, Gabriela Martín
Methodo Investigación Aplicada a las Ciencias Biológicas.2025; 10(3): 31. CrossRef - Sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate: A scoping review of laboratory assessment methods
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Deepak Mehta, Kyung‐San Min, Atsushi Tomokiyo
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial Leakage Testing in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Review on Methods, Models, and Clinical Relevance
Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Sukhamoy Gorai
Scientifica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro comparative evaluation of apical leakage using a bioceramic sealer with three different obturating techniques: A glucose leakage model
Tanvi S Agrawal, Shishir Singh, Rajesh S Podar, Gaurav Kulkarni, Anuprita Gadkari, Navin Agarwal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 76. CrossRef - In Vitro Microscopical and Microbiological Assessment of the Sealing Ability of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karin Christine Huth, Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Leander Benz, Stefan Kist, Maximilian Kollmuss
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 341. CrossRef - Comparison between AH plus sealer and total fill bioceramic sealer performance in previously untreated and retreatment cases of maxillary incisors with large-sized periapical lesion: a randomized controlled trial
Eisa Wahbi, Hassan Achour, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial sealing ability of calcium silicate-based sealer for endodontic surgery: an in-vitro study
Mai M. Mansour, Sybel M. Moussa, Marwa A. Meheissen, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Assessment of Bacterial Sealing Ability of Two Different Bio-Ceramic Sealers in Single-Rooted Teeth Using Single Cone Obturation Technique: An In Vitro Study
Doaa M. AlEraky, Ahmed M. Rahoma, Hatem M. Abuohashish, Abdullh AlQasser, Abbas AlHamali, Hussain M. AlHussain, Hussain M. AlShoalah, Zakrya AlSaghah, Abdulrahman Khattar, Shimaa Rifaat
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(5): 2906. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Morse taper implant design on microleakage at implant-healing abutment interface
Soyeon KIM, Joo Won LEE, Jae-Heon KIM, Van Mai TRUONG, Young-Seok PARK
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 767. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - Comparison of Sealing Ability of Bioceramic Sealer, AH Plus, and GuttaFlow in Conservatively Prepared Curved Root Canals Obturated with Single-Cone Technique: An In vitro Study
Shalan Kaul, Ajay Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani, Laxmi Sukhtankar, M. Madhumitha, Amit Kumar
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S857. CrossRef - Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Root Canal Obturation Techniques
Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Amin Mortaheb, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Brett E. Gilbert, Marilena Vivona
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Both Fiber Post/Core Resin Construction System and Root Canal Sealer on the Material Interface in Deep Areas of Root Canal
Hiroki Miura, Shinji Yoshii, Masataka Fujimoto, Ayako Washio, Takahiko Morotomi, Hiroshi Ikeda, Chiaki Kitamura
Materials.2021; 14(4): 982. CrossRef - Sealing ability and microbial leakage of root-end filling materials: MTA versus epoxy resin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Giancarlo Malagnino, Michele Di Cosola, Angela Pia Cazzolla, Luigi Laino, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Heliyon.2021; 7(7): e07494. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - BIOCERAMIC-BASED ROOT CANAL SEALERS
L Somolová, Z Zapletalová, M Rosa, B Novotná, I Voborná, Y Morozova
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2021; 121(4): 116. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Physico-Chemical Properties of Calcium-Silicate vs. Resin Based Sealers—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory-Based Studies
Viresh Chopra, Graham Davis, Aylin Baysan
Materials.2021; 15(1): 229. CrossRef - Comparison of apical sealing ability of bioceramic sealer and epoxy resin-based sealer using the fluid filtration technique and scanning electron microscopy
Widcha Asawaworarit, Thitapa Pinyosopon, Kanittha Kijsamanmith
Journal of Dental Sciences.2020; 15(2): 186. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer
Jong Cheon Kim, Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sealing ability of gutta percha and resilon as root canal filling materials- a systematic review
Pragya Pandey, Himanshi Aggarwal, A.P. Tikku, Arpit Singh, Rhythm Bains, Shambhavi Mishra
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 220. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Root fillings with a matched-taper single cone and two calcium silicate–based sealers: an analysis of voids using micro-computed tomography
Eugenio Pedullà, Roula S. Abiad, Gianluca Conte, Giusy R. M. La Rosa, Ernesto Rapisarda, Prasanna Neelakantan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(12): 4487. CrossRef - Influence of different disinfection protocols on gutta-percha cones surface roughness assessed by two different methods
A.M. Nunes, J.P. Gouvea, L. da Silva
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2019; 8(6): 5464. CrossRef - Endodontic sealers based on calcium silicates: a systematic review
David Donnermeyer, Sebastian Bürklein, Till Dammaschke, Edgar Schäfer
Odontology.2019; 107(4): 421. CrossRef
- Time-Dependent Volumetric and Porosity Changes of Bioceramic, Silicone Bioactive Glass-Based, and Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Micro-CT Analysis
- 2,815 View
- 36 Download
- 33 Crossref

-
Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an
in vitro study - Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):316-323. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the amount of apically extruded bacteria during the glide-path preparation by using multi-file and single-file glide-path establishing nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary systems.
Materials and Methods Sixty mandibular first molar teeth were used to prepare the test apparatus. They were decoronated, blocked into glass vials, sterilized in ethylene oxide gas, infected with a pure culture of
Enterococcus faecalis, randomly assigned to 5 experimental groups, and then prepared using manual stainless-steel files (group KF) and glide-path establishing NiTi rotary files (group PF with PathFiles, group GF with G-Files, group PG with ProGlider, and group OG with One G). At the end of canal preparation, 0.01 mL NaCl solution was taken from the experimental vials. The suspension was plated on brain heart infusion agar and colonies of bacteria were counted, and the results were given as number of colony-forming units (CFU).Results The manual instrumentation technique tested in group KF extruded the highest number of bacteria compared to the other 4 groups (
p < 0.05). The 4 groups using rotary glide-path establishing instruments extruded similar amounts of bacteria.Conclusions All glide-path establishment instrument systems tested caused a measurable apical extrusion of bacteria. The manual glide-path preparation showed the highest number of bacteria extruded compared to the other NiTi glide-path establishing instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Warley O. Silva, Jeferson O. Marques, Ana Carolina S.P. Guerra, Flávio R.F. Alves
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 866. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Multiple Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Severely Curved Mesial Roots of Mandibular Molars: An In Vitro Study
Niranjan Desai, Ashish S Bhadane, Nishant K Vyavahare, Dipali Y Shah, Akash S Kale, Simran K Chaudhari
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Impact of Different Glidepath Techniques on the Overall Performance of WaveOne Gold in an Artificial S-Shape Canal
Vlad Mircea Lup, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Carlo Gaeta, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 182. CrossRef - Influence of different irrigant activation methods on apical debris extrusion and bacterial elimination from infected root canals
KSadia Ada, Shibani Shetty, KB Jayalakshmi, PrasannaLatha Nadig, PG Manje Gowda, ArulK Selvan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of glide path files with different metallurgy on intracanal bacterial extrusion by HyFlex electrical discharge machining file
Priyanka Soni, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja, Anshi Jain
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 168. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris using Three Rotary and One Reciprocating Instrumentation Ni-Ti Systems
Maha Adnan Habeeb
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2022; 14(2): 93. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of a glide path creation necessity at the initial stages of endodontic treatment
Z. S. Khabadze, Yu. A. Generalova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Apically extruded debris produced during glide path preparation using R‐Pilot, WaveOne Gold Glider and ProGlider in curved root canals
Cangül Keskin, Özlem Sivas Yilmaz, Uğur Inan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(3): 439. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Glide Path Preparation Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Joo-Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(2): 199. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Postoperative pain after glide path preparation using manual, reciprocating and continuous rotary instruments: a randomized clinical trial
C. Keskin, Ö. Sivas Yilmaz, U. Inan, Ö. Özdemir
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(5): 579. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef - Effects of Different Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Curved Root Canals
Betul Gunes, Kubra Yesildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1191. CrossRef
- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
- 1,669 View
- 13 Download
- 23 Crossref

-
Antibacterial effect of urushiol on
E. faecalis as a root canal irrigant - Sang-Wan Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):54-59. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.54

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the antibacterial activity of urushiol against
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) to that of NaOCl.Materials and Methods The canals of thirty two single rooted human teeth were instrumented with Ni-Ti files (ProTaper Next X1, X2, X3, Dentsply). A pure culture of
E. faecalis ATCC 19433 was prepared in sterile brain heart infusion (BHI) broth. The teeth were submerged in the suspension ofE. faecalis and were incubated at 37℃ for 7 days to allow biofilm formation. The teeth were randomly divided into three experimental groups according to the irrigant used, and a negative control group where no irrigant was used (n = 8). Group 1 used physiologic normal saline, group 2 used 6% NaOCl, and group 3 used 10 wt% urushiol solution. After canal irrigation, each sample was collected by the sequential placement of 2 sterile paper points (ProTaper NEXT paper points, size X3, Dentsply). Ten-fold serial dilutions on each vials, and 100 µL were cultured on a BHI agar plate for 8 hours, and colony forming unit (CFU) analysis was done. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-whitney U tests.Results Saline group exhibited no difference in the CFU counts with control group, while NaOCl and urushiol groups showed significantly less CFU counts than saline and control groups (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The result of this study suggests 10% urushiol and 6% NaOCl solution had powerful antibacterial activity against
E. faecalis when they were used as root canal irrigants.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A critical review on innovative targets for signal disruption in Enterococcus faecalis infection management
Kayeen Vadakkan, Gajanan Sampatrao Ghodake, Chin Wei Lai, Selvaraj Vijayanand, Janarthanam Hemapriya
Microbial Pathogenesis.2025; 207: 107876. CrossRef - Effect of proanthocyanidins application on push-out bond strength of root canal filling after different final irrigation procedures
Funda Fundaoğlu Küçükekenci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Silver-Ion-Coated Rotary Nickel Titanium Files - An In Vitro Study
Jhanvi H. Sadaria, Kondas V. Venkatesh, Dhanasekaran Sihivahanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(3): 344. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of natural-based endodontic solutions: a systematic review with a network meta-analysis
Danilo Cassiano FERRAZ, Anahi de Paula MELO, Felipe de Souza MATOS, Luiz Renato PARANHOS, Camilla Christian Gomes MOURA, Cauane BLUMENBERG, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Irrigants and irrigation activation systems in Endodontics
Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Emelly Aveiro, Anil Kishen
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(4): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite gel and solutions in endodontics: A systematic review
Sourabh Barbhi, SR Srinidhi, Rajesh Shetty, Poonam Joshi, Vini Mehta, Sanket Aras
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 290. CrossRef - Antibiofilm activity of phytochemicals against Enterococcus faecalis: A literature review
Islam A. A. Ali, Prasanna Neelakantan
Phytotherapy Research.2022; 36(7): 2824. CrossRef - Chemical compounds Anti-bacterial of Citrus aurantifolia Ethanol Extract to Inhibit the Early Biofilm Formation and Growth of Enterococcus faecalis Root Canal Isolate
Nur Asmah, Dewi Fatma Suniarti, Endang Winiati Bachtiar, Dewi Angraini Margono, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2667. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of silver diamine fluoride as a root canal irrigant
Ebtissam M. Al‐Madi, Manar A. Al‐Jamie, Noura M. Al‐Owaid, Amal A. Almohaimede, Albandary M. Al‐Owid
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2019; 5(5): 551. CrossRef
- A critical review on innovative targets for signal disruption in Enterococcus faecalis infection management
- 2,073 View
- 19 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Comparative assessment of antibacterial activity of different glass ionomer cements on cariogenic bacteria
- Rahul Gaybarao Naik, Arun Suresh Dodamani, Mahesh Ravindra Khairnar, Harish Chaitram Jadhav, Manjiri Abhay Deshmukh
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):278-282. Published online September 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.278
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Glass ionomer cements (GICs), which are biocompatible and adhesive to the tooth surface, are widely used nowadays for tooth restoration. They inhibit the demineralization and promote the remineralization of the tooth structure adjacent to the restoration, as well as interfere with bacterial growth. Hence, the present study was conducted to assess and compare the antimicrobial activity of three commercially available GICs against two cariogenic bacteria.
Materials and Methods An agar plate diffusion test was used for evaluating the antimicrobial effect of three different GICs (Fuji IX, Ketac Molar, and d-tech) on
Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans ) andLactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus ). Thirty plates were prepared and divided into two groups. The first group was inoculated withS. mutans , and the second group was inoculated withL. acidophilus . These plates were then incubated at 37℃ for 24 hours. Zones of bacterial growth inhibition that formed around each well were recorded in millimeters (mm).Results The zones of inhibition for Fuji IX, Ketac Molar, and d-tech on
S. mutans were found to be 10.84 ± 0.22 mm, 10.23 ± 0.15 mm, and 15.65 ± 0.31 mm, respectively, whereas those forL. acidophilus were found to be 10.43 ± 0.12 mm, 10.16 ± 0.11 mm, and 15.57 ± 0.13 mm, respectively.Conclusions D-tech cement performed better in terms of the zone of bacterial inhibition against the two test bacteria, than the other two tested glass ionomers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of conditioning and 3-year aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin
Ahmed Zubaer, Rime Shamme Akter, Al Azad Salahuddin, Rahman Mir Ayubur, Sano Hidehiko, Hoshika Shuhei
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(2): 1229. CrossRef - Surface energetics of antibiofilm property of dental material added with green synthesized copper nanoparticles
Haris Saddique, Muhammad Aasim, Tariq Khan, Ajab Khan, Haroon Muhammad Ali, Umar Aziz
AMB Express.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of titanium dioxide nanotubes incorporated into conventional glass ionomer cement on L. acidophilus
Layse de Góis SENA, Maria Davoli MEYER, Mariana Gallante RICARDO, Isaac Jordão de Souza ARAÚJO, Julia Puppin RONTANI, Vanessa Arias PECORARI, Elizabeth Ferreira MARTINEZ, Lucas Novaes TEIXEIRA, Francisco Humberto NOCITI-JUNIOR, Paulo Noronha LISBOA-FILHO,
Brazilian Oral Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Modifications of polyalkenoic acid and its effect on glass ionomer cement
Sreejith Sasidharan Lathikumari, Manju Saraswathy
Materials Advances.2024; 5(7): 2719. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Clinical Impact and In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Two Bioactive Restoratives against S. mutans ATCC 25175 in Class II Carious Restorations
YA Maher, MT Rajeh, FA Hamooda, GO Zerain, RM Habis, RH Sulaimani, ST Albar, FMH Ali, NA Abdelaleem
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 26(4): 404. CrossRef - Comparison and Advanced Antimicrobial Strategies of Silver and Copper Nanodrug-Loaded Glass Ionomer Cement against Dental Caries Microbes
Amal Adnan Ashour, Mohammed Fareed Felemban, Nayef H. Felemban, Enas T. Enan, Sakeenabi Basha, Mohamed M. Hassan, Sanaa M. F. Gad El-Rab
Antibiotics.2022; 11(6): 756. CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity and Biofilm Inhibition of New-Generation Hybrid/Fluoride-Releasing Restorative Materials
Sevil Gurgan, Uzay Koc Vural, Cansu Atalay, Herve Tassery, Ivana Miletic, Suna Sibel Gurpinar
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(5): 2434. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of long-term fluoride release and antibacterial activity of an alkasite, nanoionomer, and glass ionomer restorative material – An in vitro study
RV Aparajitha, PSenthamil Selvan, AShafie Ahamed, S Bhavani, V Nagarajan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 485. CrossRef - Dental Restorative Materials for Elderly Populations
Yuyao Huang, Bingqing Song, Xuedong Zhou, Hui Chen, Haohao Wang, Lei Cheng
Polymers.2021; 13(5): 828. CrossRef - The Comparison of Biofilm Formation, Mechanical and Chemical Properties between Glass Ionomer Cement and Giomer
Sylva Dinie Alinda, Anggraini Margono, Aditya Wisnu Putranto, Ike Dwi Maharti, Retno Amalina, Sherly Firsta Rahmi
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 274. CrossRef - Effect of conditioning and 1 year aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin
Shuhei Hoshika, Shihchun Ting, Zubaer Ahmed, Fei Chen, Yu Toida, Norihito Sakaguchi, Bart Van Meerbeek, Hidehiko Sano, Sharanbir K. Sidhu
Dental Materials.2021; 37(1): 106. CrossRef - The synergistic effects of SrF2 nanoparticles, YSZ nanoparticles, and poly-ε-l-lysin on physicomechanical, ion release, and antibacterial-cellular behavior of the flowable dental composites
Saeed Hesaraki, Mohammad Karimi, Nader Nezafati
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2020; 109: 110592. CrossRef
- Effect of conditioning and 3-year aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin
- 1,696 View
- 8 Download
- 12 Crossref

-
Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles on
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus - Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):109-114. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Recurrent caries was partly ascribed to lack of antibacterial properties in composite resin. Silver and zinc nanoparticles are considered to be broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the antibacterial properties of composite resins containing 1% silver and zinc-oxide nanoparticles on
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus .Materials and Methods Ninety discoid tablets containing 0%, 1% nano-silver and 1% nano zinc-oxide particles were prepared from flowable composite resin (
n = 30). The antibacterial properties of composite resin discs were evaluated by direct contact test. Diluted solutions ofStreptococcus mutans (PTCC 1683) andLactobacillus (PTCC 1643) were prepared. 0.01 mL of each bacterial species was separately placed on the discs. The discs were transferred to liquid culture media and were incubated at 37℃ for 8 hr. 0.01 mL of each solution was cultured on blood agar and the colonies were counted. Data was analyzed with Kruskall-Wallis and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results Composites containing nano zinc-oxide particles or silver nanoparticles exhibited higher antibacterial activity against
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The effect of zinc-oxide onStreptococcus mutans was significantly higher than that of silver (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the antibacterial activity againstLactobacillus between composites containing silver nanoparticles and those containing zinc-oxide nanoparticles.Conclusions Composite resins containing silver or zinc-oxide nanoparticles exhibited antibacterial activity against
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabricated modified compomer bearing CF/SBA-15 nanomaterials: Physicochemical and antibacterial properties
Fatma Nur Kızılay, Mustafa Aydınbelge, Sezer Demirbuğa, Kevser Kolçakoğlu, Nilay Ildız, Serkan Dayan
Dental Materials.2026; 42(3): 451. CrossRef - Physicochemical and antibacterial evaluation of novel nano α-TCP–AgNPs biocomposites for direct pulp-capping applications
Selviana Wulansari, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Nasrul Wathoni, Rosalina Tjandrawinata, Arief Cahyanto, Moehamad Orliando Roeslan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental plaque biofilm-targeting composite nanomaterials: advances and outlook
Jiaxuan Zhao, Shengyuan Huang, Yongjia Yang, Jilei Wang, Qianqian Guo, Yueming Xu, Bingyin Jiang, Jiang Lin
Biomaterials Science.2026; 14(4): 952. CrossRef - Next-Gen Restorative Materials to Revolutionise Smiles
John Yun Niu, Kelsey Xingyun Ge, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Olivia Lili Zhang, Irene Shuping Zhao, Chun Hung Chu
Bioengineering.2026; 13(2): 143. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of tricalcium silicate-based cements with different antibacterial additives
Reda Banon, Luc Martens, Peter De Coster, Jakob van Acker, Jerina Boelens, Elanagai Rathinam, Sivaprakash Rajasekharan
Scientific Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Roles of Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Bonding Materials
Maria Arampatzi, Ellas Spyratou, Iosif Sifakakis, Efstathios P. Efstathopoulos
Applied Sciences.2026; 16(4): 1996. CrossRef - The effect of photoinitiator systems on resin-based composite containing ZnO-nanoparticles
Abdulaziz Alayed, Nikolaos Silikas, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2025; 41(2): 220. CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant effects of propolis nanoparticles and cinnamon nanostructures in preventive dentistry: Experimental and theoretical approaches
Faeze Hamze, Mahnaz Amiri, Zeinab Sadat Islami, Tayebeh Shamspur, Razieh Razavi, Payam Khazaeli
Phytochemical Analysis.2025; 36(8): 2236. CrossRef - Synthesis of boron nitride@copper oxide‐based light‐curing resin composites: Investigating mechanical and antibacterial properties
Shuya Li, Dawei Liu, Zegang Shi, Wenyi Yu, Tingting Yang, Yufeng Bai, Tianlu He, Tai Peng
Polymer Composites.2025; 46(3): 2073. CrossRef - Long-lasting antimicrobial effect of multipurpose ZnO nanoparticle-loaded dental resins enhanced by blue light photodynamic therapy
Maria Luisa Leite, Patricia Comeau, Ala Zaghwan, Ya Shen, Adriana Pigozzo Manso
Dental Materials.2025; 41(3): 347. CrossRef - Use of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles for the Management of Dental Diseases
Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Anjaneyulu Udduttulla, Veena Wenqing Xu, Kitty Jieyi Chen, Monica Yuqing Zhang, Chun Hung Chu
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(3): 209. CrossRef - Assessment of cytotoxicity of clear aligners coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles
Indu Ravi, Vignesh Kailasam
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(2): 262. CrossRef - Emerging developments in plant-based metal nanomaterials for diverse versatile applications - A review
Garima Rana, Vivek Kumar Dhiman, Syed Kashif Ali, Ankush Chauhan, Majid S. Jabir, Suresh Ghotekar
Results in Chemistry.2025; 15: 102231. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Assessment of the Antimicrobial Properties of Mesoporous Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Against Streptococcus mutans: An In Vitro Investigation
Zahra Jowkar, Shima Askarzadeh, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi, Zahra Fattah, Ali Moaddeli, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of theranostic nanoparticles in dental infectious diseases: A review
Mitra Rostami, Pouria Farahani, Moslem Karimzadeh, Samar Esmaelian, Abbas Fadel Hussein, Kamyar Nasiri, Hareth A. Alrikabi, Naghmeh Shenasa
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2025; 112: 107223. CrossRef - Effect on hygroscopic characteristics of n‐ZnO additions to resin composite
Abdulaziz Alayed, Nikolaos Silikas, David C. Watts
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Applications of Nanoparticles in Endodontics as an Antibacterial Agent: A Mini-review
Mina Saliminasab
Advances in Applied NanoBio-Technologies.2025; 6(2): 46. CrossRef - Effect of Nanohydroxyapatite and Silver Nanoparticle Incorporation on the Flexural Strength of Resin Composites
Marzie Moradaian, Maryam Saadat, Shahab Agharezaei, Zahra Khorshidi Asl, Baisakhi Banerjee
BioMed Research International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage and Microhardness of Omnichroma and Silver Nanoparticles- incorporated Omnichroma
Mrithyunjay Satish Mendon, Mansi Jain, Suma Sogi, Gulbar Shah, Gagandeep Bhagat, Simran Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(10): 1181. CrossRef - EVOLUTION OF DENTAL IMPLANT AND IMPLANT SURFACE TREATMENTS- A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Wamiq Fareed, Hossam Mossa, Medhat Mohamed, Malik Almutairi, Rashed Alfehaid, Yousef Ahmad
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 303. CrossRef - Comprehensive review on zinc oxide nanoparticle production and the associated antibacterial mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Aeshah M. Mohammed, Mohammed Mohammed, Jawad K. Oleiwi, Falah H. Ihmedee, Tijjani Adam, Bashir O. Betar, Subash C.B. Gopinath
Nano Trends.2025; 11: 100145. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy and surface roughness of orthodontic brackets coated with silver–copper hybrid or zinc oxide nanoparticles: An in-vitro study
Aseem Sharma, Tanushree Sharma, Nambi. Rammohan. Shrinivaasan, Geetika Tomer, Nisha Gupta, Pramada Kishore, Prashant Babaji, Azhar Mohammed, Ananya Neralla
Journal of Orthodontic Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy, antibiofilm effect, and resistance to biodegradation of a novel composite against Streptococcus mutans
S. Pallavi, A. Devadathan, Lizymol Philipose Pampadykandathil, Vibha Chandrababu, N J Nagaraj, Arvind Kumar Alexander
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1001. CrossRef - Cymbopogon citratus essential oil infused zinc oxide nanoparticles for eco-friendly anticariogenic action
Preeti Pallavi, Saswat Aryan, Pragnya Paramita Sahoo, Adyasha Anapurba Sahoo, Sangeeta Raut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Computational Insights Into Antimicrobial Peptide‐Enhanced Dental Resin Composites: Targeting Porphyromonas gingivalis Heme‐Binding Proteins and Biofilms
Ravinder S. Saini, Doni Dermawan, Abdulkhaliq Ali F. Alshadidi, Rayan Ibrahim H. Binduhayyim, Rajesh Vyas, Fahad Hussain Alhamoudi, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Mohamed Saheer Kuruniyan, Lujain Ibrahim N. Aldosari, Artak Heboyan
MicrobiologyOpen.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The formation of cariogenic plaque to contemporary adhesive restorative materials: an in vitro study
Anna Lehrkinder, Olivia Rydholm, Anna Wänström, Keisuke Nakamura, Ulf Örtengren
Odontology.2024; 112(4): 1090. CrossRef - The Impact of Incorporating Five Different Boron Materials into a Dental Composite on Its Mechanical Properties
Mehmet Kutluhan Ucuk, Musa Kazim Ucuncu
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(3): 1054. CrossRef - Albumin nanoparticles are a promising drug delivery system in dentistry
Mohammad Kiarashi, Saman Yasamineh
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Three Antibacterial Nanoparticle Coatings on the Surface Characteristics of Stainless Steel
Ahmed Al-Mayali, Ammar Kadhum, Thair Alzubaydi
Metals.2024; 14(8): 853. CrossRef - Bioresponsive nanotechnology in pediatric dental drug delivery
Seyed Ebrahim Alavi, Lieba Malik, Raghad Matti, Farah Al-Najafi, Hasan Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, Lavanya A. Sharma
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2024; 93: 105436. CrossRef - Visible light-activated curcumin-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles integrated into orthodontic adhesive on Micro-tensile bond strength, degree of conversion, and antibacterial effectiveness against Staphylococcus Aureus. An investigation using scanning elect
Abdullah A. Alnazeh, Muhammad Abdullah Kamran, Salem Almoammar, Mohammed Mohsen Al Jearah, Muhammad Qasim, Ibrahim Alshahrani
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology.2024; 253: 112888. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of PMMA enriched with nano-clay loaded with metronidazole and chlorhexidine
Eduardo Buozi Moffa, Samuel Santana Malheiros, Larissa Tavares Sampaio Silva, Delcio Ildefonso Branco, Regis Cléo Fernandes Grassia Junior, William Cunha Brandt, Flavia Goncalves, Valentim Adelino Ricardo Barao, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating Antibacterial Frontiers: A Panoramic Exploration of Antibacterial Landscapes, Resistance Mechanisms, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Krittika Ralhan, Kavita A. Iyer, Leilani Lotti Diaz, Robert Bird, Ankush Maind, Qiongqiong Angela Zhou
ACS Infectious Diseases.2024; 10(5): 1483. CrossRef - Use of nanotechnology-based nanomaterial as a substitute for antibiotics in monogastric animals
Abdul Qadeer, Aamir Khan, Noor Muhammad Khan, Abdul Wajid, Kaleem Ullah, Sylvie Skalickova, Pompido Chilala, Petr Slama, Pavel Horky, Mohammed S. Alqahtani, Maha Awjan Alreshidi
Heliyon.2024; 10(11): e31728. CrossRef - Local and systemic adverse effects of nanoparticles incorporated in dental materials- a critical review
Harini Karunakaran, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta, Mukesh Doble
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(1): 158. CrossRef - Determining the cytotoxicity of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles in ESBL and carbapenemase producing Proteus mirabilis isolated from clinical samples in Shiraz, Southwest Iran
Farshad Kakian, Esmaeil Mirzaei, Afagh Moattari, Sara Takallu, Abdollah Bazargani
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New insights into nanotherapeutics for periodontitis: a triple concerto of antimicrobial activity, immunomodulation and periodontium regeneration
Jiaxin Li, Yuxiao Wang, Maomao Tang, Chengdong Zhang, Yachen Fei, Meng Li, Mengjie Li, Shuangying Gui, Jian Guo
Journal of Nanobiotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of silver and calcium fluoride nanoparticles on antibacterial activity of composite resin against Streptococcus mutans: An in vitro study
Mehdi Fathi, Zahra Hosseinali, Tina Molaei, Somayeh Hekmatfar
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Flowable resin-based composites modified with chlorhexidine-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles induce superior antibiofilm properties
Barsha Shrestha, Sultan Aati, Sheetal Maria Rajan, Amr Fawzy
Journal of Nanoparticle Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Temporary Acrylic Soft Denture Lining Material Enriched with Silver-Releasing Filler-Cytotoxicity, Mechanical and Antifungal Properties
Grzegorz Chladek, Igor Kalamarz, Wojciech Pakieła, Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Zenon Czuba, Anna Mertas
Materials.2024; 17(4): 902. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Properties of a Reinforced Zinc Oxide Eugenol Combined with Cloisite 5A Nanoclay: An In-Vitro Study
Bahareh Nazemisalman, Shaghayegh Niaz, Shayan Darvish, Ayda Notash, Ali Ramazani, Ionut Luchian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(7): 198. CrossRef - Assessing the physico-mechanical, anti-bacterial, and anti-demineralization properties of orthodontic resin composite containing different concentrations of photoactivated zinc oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans biofilm around ceramic and metal o
Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Rashin Bahrami, Maryam Pourhajibagher
International Orthodontics.2024; 22(4): 100901. CrossRef - Biosynthesis of a Novel Composite Resin Incorporating Gamma Radiation Synthesized Pomegranate Extract–Coated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and In Vitro Assessment Against Streptococcus mutans Causing Dental Caries
Amany Badr El-Deen Abd El-Aziz, Mehreshan El-Mokadem, Hoda Hassan Abo-Ghalia, Zakaria Ahmed Mattar, Abdelrazq Ibrahim Sallam
BioNanoScience.2024; 14(5): 5017. CrossRef - Global trend and hotspot of resin materials for dental caries repair: a bibliometric analysis
Baodi Han, Lian Wang
Frontiers in Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Studying the Application of Nanoparticles in Orthodontics: A Review Study
Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafal J. Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Adam Lubojanski, Karolina Kurek, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Zakrzewski
Annals of Dental Specialty.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs): Photocatalysis, antibacterial, toxicity and genotoxicity
Olcay Gençyılmaz, Fahriye Zemheri Navruz, Sinan İnce, Abdulsattar Ali Abbas, Abdullah Hüssein Salim Salim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2024; 456: 115847. CrossRef - Advancements in Nanoparticle-Based Strategies for Enhanced Antibacterial Interventions
Madineh Moradialvand, Nastaran Asri, Mahtab Jahdkaran, Maryam Beladi, Hamidreza Houri
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics.2024; 82(4): 3071. CrossRef - Performance evaluation of carbon quantum dots impregnated glass ionomer cement to avoid peri-implant disease
Febina Josephraj, Ashwin Kumar N, Vidyashree Nandini V, Sujatha S, Varshini Karthik
Biomedical Materials.2024; 19(3): 035040. CrossRef - Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensor for periodontitis detection
Mohammad Hosseini Hooshiar, Masoud Amiri Moghaddam, Mohammad Kiarashi, Athraa Y. Al-Hijazi, Abbas Fadel Hussein, Hareth A.Alrikabi, Sara Salari, Samar Esmaelian, Hassan Mesgari, Saman Yasamineh
Journal of Biological Engineering.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the antibacterial properties of Resin cements with and without the addition of nanoparticles: a systematic review
Ravinder Saini, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Masroor Ahmed Kanji, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Saeed Awod Bin Hassan, Sukumaran Anil, Deepti Shrivastava, Kumar Chandan Srivastava
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanotecnologia aplicada a Biomateriais em técnicas preventivas e restauradoras
Lucas Mateus Do Nascimento, Ricardo Felipe Ferreira Da Silva
Revista Sociedade Científica.2024; 7(1): 2326. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetration of Various Nano-sized Intra-canal Medicaments: An In Vitro Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Mounika Veeraiyan, Chikine Yashas Chandhar, Deepa Mastammanavar, Kantheti Kavya, Deepa Jarupula, Gangishetti Sairam
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1690. CrossRef - Preparation and characterization of nano silver antibacterial gel for gynecolog
Qiuqun Xiao, Jingnan Zhu, Tao Fang, Ruyi Peng, Jiayi Chen, Kailan Liu, Yanshi Ceng, Meng Yuan, Yunrui Hu
Ferroelectrics.2024; 618(13-14): 2249. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their biocompatibility in L929 fibroblasts
Zahra Jowkar, Ali Moaddeli, Fereshteh Shafiei, Tara Tadayon, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Nanoparticles on Dental Composites: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dhruv Ahuja, M. R. Akhila, Ashish Kumar Singh, Puneet Batra
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 439. CrossRef - Nanotechnology in Orthodontics: Current Applications and Future Perspectives
Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafal J. Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Adam Lubojanski, Karolina Kurek, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Zakrzewski
Asian Journal of Periodontics and Orthodontics.2024; 4(1): 24. CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Nanoparticles on Addition to Orthodontic
Materials- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Crystal Runa Soans, Deesha Kumari, Shalin Shersha, Rahila Mansoor, M.S. Ravi
Nanoscience & Nanotechnology-Asia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inorganic nanoparticles on dental materials’ mechanical properties. A narrative review
Ghada Naguib, Abdulrahman A. Maghrabi, Abdulghani I. Mira, Hisham A. Mously, Maher Hajjaj, Mohamed T. Hamed
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Restorative Dentistry
Rutvik Mandhalkar, Priyanka Paul, Amit Reche
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The germicidal effect, biosafety and mechanical properties of antibacterial resin composite in cavity filling
Jiamu Ren, Xinwei Guo
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19078. CrossRef - Influence of the Loading with Newly Green Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Equisetum sylvaticum on the Antibacterial Activity and Surface Hardness of a Composite Resin
Ionuț Tărăboanță, Ana Flavia Burlec, Simona Stoleriu, Andreia Corciovă, Adrian Fifere, Denisa Batir-Marin, Monica Hăncianu, Cornelia Mircea, Irina Nica, Andra Claudia Tărăboanță-Gamen, Sorin Andrian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(8): 402. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Ocimum tenuiflorum and Stevia rebaudiana-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles – An In vitro Study
Indumathy Pandiyan, Meignana Indiran Arumugham, Sri Sakthi Doraikannan, Pradeep Kumar Rathinavelu, Jayashri Prabakar, S. Rajeshkumar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2023; 14(2): 109. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Properties of an Orthodontic Composite Containing Silver and Amor-phous Tricalcium Phosphate Nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans: An In Vitro Study
Zahra Tavakolinejad, Mahmood Sheikh Fathollahi, farzaneh Mirzaei, Farzaneh Mirzaei, Elham Mirzaei
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 257. CrossRef - Effect of incorporating silica-hydroxyapatite-silver hybrid nanoparticles into the resin-modified glass ionomer on the adhesive remnant index score and shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets: An in vitro study
Nazila Biglar, Elahe Chaychi Raghimi, Somayeh Sadighian, Farzaneh Karamitanha, Elham Zajkani, Azin Nourian
International Orthodontics.2023; 21(3): 100761. CrossRef - Method development for the intraoral release of nanoparticles from dental restorative materials
Laura Kleinvogel, Gregor Wemken, Cosima Reidelbach, Manuel Garcia-Käufer, Kirstin Vach, Elmar Hellwig, Benedikt C. Spies, Olga Polydorou
Dental Materials.2023; 39(8): 693. CrossRef - Recent advancements in blended and reinforced polymeric systems as bioscaffolds
Jasmin Joseph, Ramesh Parameswaran, Unnikrishnan Gopalakrishna Panicker
International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials.2023; 72(11): 834. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Copper-Doped Phosphate Glass on Pathogenic Bacteria
Sunaina Shetty, Priyadharshini Sekar, Raghavendra M. Shetty, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel
Molecules.2023; 28(7): 3179. CrossRef - Effect of Zinc Oxide Incorporation on the Antibacterial, Physicochemical, and Mechanical Properties of Pit and Fissure Sealants
Ji-Won Choi, Song-Yi Yang
Polymers.2023; 15(3): 529. CrossRef - Novel bioactive dental restorations to inhibit secondary caries in enamel and dentin under oral biofilms
Wen Zhou, Hong Chen, Michael D. Weir, Thomas W. Oates, Xuedong Zhou, Suping Wang, Lei Cheng, Hockin H.K. Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 133: 104497. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of glass-ionomer cement incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles against mutans streptococci and lactobacilli under orthodontic bands: An in vivo split-mouth study
Maryam Shirazi, Fatemeh Fotoohi Qazvini, Saeed Mohamadrezaie
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the cell viability and antimicrobial effects of orthodontic bands coated with silver or zinc oxide nanoparticles: An in vitro study
Rashin Bahrami, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Alireza Badiei, Reza Masaeli, Behrad Tanbakuchi
Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2023; 53(1): 16. CrossRef - Evaluation and comparison of the effect of incorporating zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the bond strength and microleakage of two orthodontic fixed retainer adhesives
Leila Jazi, Ahmad Sodagar, Sepehr Sobhani Kazemi, Amirhossein Mirhashemi
Journal of the World Federation of Orthodontists.2023; 12(1): 22. CrossRef - Bioactive Materials for Caries Management: A Literature Review
Olivia Lili Zhang, John Yun Niu, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Ollie Yiru Yu, May Lei Mei, Chun Hung Chu
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(3): 59. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of zinc oxide nanoparticle-coated aligners on Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans
Prathima Anita, Haritha Pottipalli Sathyanarayana, Kennedy Kumar, Krishnapriya Ramanathan, Vignesh Kailasam
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2023; 163(3): 338. CrossRef - The Impact of Adhesive-Containing Nanoparticles of ZrO2and TiO2 on Antimicrobial Effectiveness, the Strength of Bonding, and the Extent of Microleakage in Dentin Affected by Caries
Fayez Hussain Niazi, Shadi El Bahra, Nisren Ansary, Zeeshan Qamar, Hajar Albahkaly, Badr Bamousa, Ahlam Smran, Ahmed Al Ahmari, Saleh Wael S. Al-Akki, Abdulaziz Samran
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2023; 13(9): 946. CrossRef - Comparitive evaluation of antimicrobial effectiveness of silver oxide coatings on different types of ceramic brackets against Streptococcus mutans
S. V. Ramesh Goud, K. Raja Sigamani, Bhaskar, Kurinchi Kumaran, Mohammed Arafat, S.N Reddy Duvvuri
The Journal of Dental Panacea.2022; 4(2): 75. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial and mechanical features of dental adhesives containing colloidal gold nanoparticles
Sara Dadkan, Mehrdad Khakbiz, Lida Ghazanfari, Meizi Chen, Ki-Bum Lee
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2022; 365: 119824. CrossRef - Preparation of electrospun silver/poly(vinyl alcohol) fibrous membranes and characterization of the effect of sterilization processes on the antibacterial activity
Wen-Cheng Chen, Chia-Ying Ko, Kai-Chi Chang, Chih-Hua Chen, Dan-Jae Lin
Journal of Industrial Textiles.2022; 51(4_suppl): 7205S. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-Based Zinc Ion Interference Therapy to Combat Bacterial Infections
Yongbin Wei, Jiaming Wang, Sixuan Wu, Ruixue Zhou, Kaixiang Zhang, Zhenzhong Zhang, Junjie Liu, Shangshang Qin, Jinjin Shi
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative Investigation of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Used in Dentistry
Ajay Kumar Tiwari, Saket Jha, Abhimanyu Kumar Singh, Sheo Kumar Mishra, Ashok Kumar Pathak, Rudra Prakash Ojha, Raghvendra Singh Yadav, Anupam Dikshit
Crystals.2022; 12(8): 1063. CrossRef - Efficient Route for the Preparation of Composite Resin Incorporating Silver Nanoparticles with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties
Drake Beery, Mohammad Abdul Mottaleb, Mohammed J. Meziani, James Campbell, Isabella Pires Miranda, Michael Bellamy
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(3): 471. CrossRef - Antibacterial performance of composite containing quaternary ammonium silica (QASi) filler – A preliminary study
Michal Dekel-Steinkeller, Ervin I. Weiss, Trudi Lev-Dor Samovici, Itzhak Abramovitz
Journal of Dentistry.2022; 123: 104209. CrossRef - Therapeutic Applications of Antimicrobial Silver-Based Biomaterials in Dentistry
Qiyu Wang, Yu Zhang, Qiang Li, Li Chen, Hui Liu, Meng Ding, Heng Dong, Yongbin Mou
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2022; Volume 17: 443. CrossRef - In-vitro Comparative Assessment of Antibacterial and Anti-adherent Effect of Two Types of Surface Modificants on Stainless Steel Orthodontic Brackets Against Streptococcus mutans
Mrunmaye Math, Alok G. Shah, Parag Gangurde, Anita G. Karandikar, Anjali Gheware, Bhagyashree S. Jadhav
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2022; 56(3): 282. CrossRef - Dental Composites with Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Prevent Secondary Caries in the Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Model
Tahreem Tanweer, Nosheen Fatima Rana, Iqra Saleem, Iqra Shafique, Sultan M. Alshahrani, Hanadi A. Almukhlifi, Amenah S. Alotaibi, Sohad Abdulkaleg Alshareef, Farid Menaa
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15926. CrossRef - Effect of Different Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles on the Quality of the Chemical Bond of Glass Ionomer Cement Dentine in Primary Teeth
Faisal Mohammed Abed, Sunil Babu Kotha, Haneen AlShukairi, Fatmah Nasser Almotawah, Rwan Abdulali Alabdulaly, Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity of Dental Composite with Ciprofloxacin Loaded Silver Nanoparticles
Wafa Arif, Nosheen Rana, Iqra Saleem, Tahreem Tanweer, Muhammad Khan, Sohad Alshareef, Huda Sheikh, Fatima Alaryani, Manal AL-Kattan, Hanan Alatawi, Farid Menaa, Aroosa Nadeem
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7182. CrossRef - Experimental composite containing silicon dioxide-coated silver nanoparticles for orthodontic bonding: Antimicrobial activity and shear bond strength
Rogéria Christina de Oliveira AGUIAR, Larissa Pereira NUNES, Eduardo Silva BATISTA, Marina Mariante VIANA, Marcela Charantola RODRIGUES, Bruno BUENO-SILVA, Marina Guimarães ROSCOE
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - DEAE-Dextran Coated AgNPs: A Highly Blendable Nanofiller Enhances Compressive Strength of Dental Resin Composites
Shabia Azhar, Nosheen Fatima Rana, Amer Sohail Kashif, Tahreem Tanweer, Iqra Shafique, Farid Menaa
Polymers.2022; 14(15): 3143. CrossRef - Synthesis of a Novel, Biocompatible and Bacteriostatic Borosiloxane Composition with Silver Oxide Nanoparticles
Denis N. Chausov, Veronika V. Smirnova, Dmitriy E. Burmistrov, Ruslan M. Sarimov, Alexander D. Kurilov, Maxim E. Astashev, Oleg V. Uvarov, Mikhail V. Dubinin, Valery A. Kozlov, Maria V. Vedunova, Maksim B. Rebezov, Anastasia A. Semenova, Andrey B. Lisitsy
Materials.2022; 15(2): 527. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties, Biocompatibility and Anti-Bacterial Adhesion Property Evaluation of Silicone-Containing Resin Composite with Different Formulae
Muzi Liao, Hui Tong, Xiangya Huang, Fang Liu, Jingwei He, Sui Mai
Journal of Renewable Materials.2022; 10(12): 3201. CrossRef - Current trends and future perspectives on dental nanomaterials – An overview of nanotechnology strategies in dentistry
Vidhya Rekha Umapathy, Prabhu Manickam Natarajan, C. SumathiJones, Bhuminathan Swamikannu, W.M.S. Johnson, V. Alagarsamy, Ashequr Rahman Milon
Journal of King Saud University - Science.2022; 34(7): 102231. CrossRef - Boron nitride nanosheets modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles as novel fillers of dental resin composite
Ameenah Saad Alansy, Thekra Ali Saeed, Reem Al-Attab, Yuqing Guo, Yanwei Yang, Bin Liu, Zengjie Fan
Dental Materials.2022; 38(10): e266. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review on Its Applications in Dentistry
C Pushpalatha, Jithya Suresh, VS Gayathri, SV Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Antibacterial Activity of Nano Titania-Enriched Alkasite Restorative Material: An In Vitro Study
Neven S. Aref, Reham M. Abdallah
The Open Dentistry Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Properties of a Methacrylate-Based Dental Material Loaded with ZnO Nanoparticles
Patricia Comeau, Julia Burgess, Niknaz Malekafzali, Maria Luisa Leite, Aidan Lee, Adriana Manso
Materials.2022; 15(14): 5075. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef - Development of Direct Immobilization Technique of Ag Nanoparticles on Resin Substrates Imparting High Antibacterial and Antiviral Activities
Satoshi Seino, Yuji Ohkubo, Tomonari Magara, Hiroki Enomoto, Eri Nakajima, Tomoki Nishida, Yasuo Imoto, Takashi Nakagawa
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(17): 3046. CrossRef - Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
Pooja Jain, Uzma Farooq, Nazia Hassan, Mohammed Albratty, Md. Shamsher Alam, Hafiz A. Makeen, Mohd. Aamir Mirza, Zeenat Iqbal
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 1935. CrossRef - Impact of Different Antibacterial Substances in Dental Composite Materials: A Comprehensive Review
Badr Soliman AlHussain, Abdulrahman Abdulaziz AlFayez, Abdullah Abdulrahman AlDuhaymi, Essam Abdulaziz AlMulhim, Mohammad Yahya Assiri, Shahzeb Hasan Ansari
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2022; 2(1): 1. CrossRef - Chlorhexidine in operative dentistry - A review
TanviSanjay Satpute, SanjyotA Mulay
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 80. CrossRef - Nanotechnology-based materials as emerging trends for dental applications
Tejas Barot, Deepak Rawtani, Pratik Kulkarni
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2021; 60(1): 173. CrossRef - A Brief Review on the Evolution of Metallic Dental Implants: History, Design, and Application
Sumanth Ratna Kandavalli, Qingge Wang, Mahmoud Ebrahimi, Ceren Gode, Faramarz Djavanroodi, Shokouh Attarilar, Shifeng Liu
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans, antioxidant property and cytotoxicity of novel nano-zinc oxide varnish
Manali Deb Barma, Indumathy Muthupandiyan, Srinivasan Raj Samuel, Bennett T. Amaechi
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 126: 105132. CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Orthodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Adam Lubojanski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 337. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of new denture base material modified with gold nanoparticles
Adamović Tijana, Veselinović Valentina, Trtić Nataša, Hadži-Mihailović Miloš, Gotovac Atlagić Suzana, Balaban Milica, Hattori Yoshiyuki, Sugiyama Hironori, Andrej Ivanič, Rudolf Rebeka
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2021; 65(2): 155. CrossRef - Dynamics of different ion release from denture-base acrylic resins and their mechanical properties after the addition of bioactive materials
Zbigniew Raszewski
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(8): 1071. CrossRef - Genotoxic assay of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by leaf extract of Garcinia livingstonei T. Anderson: A comparative study
AzharuddinB Daphedar, SiddappaB Kakkalameli, Govindappa Melappa, TarikereChandrashekharappa Taranath, Chandrashekar Srinivasa, Chandan Shivamallu, Asad Syed, Najat Marraiki, AbdallahM Elgorban, Ravindra Veerapur, SharangoudaS Patil, ShivaPrasad Kollur
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2021; 17(5): 114. CrossRef - Nanostructures as Targeted Therapeutics for Combating Oral Bacterial Diseases
Shima Afrasiabi, Nasim Chiniforush, Hamid Reza Barikani, Alireza Partoazar, Ramin Goudarzi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(10): 1435. CrossRef - Well-Orientation Strategy Biosynthesis of Cefuroxime-Silver Nanoantibiotic for Reinforced Biodentine™ and Its Dental Application against Streptococcus mutans
Sanaa M. F. Gad El-Rab, Amal A. Ashour, Sakeenabi Basha, Amal Ahmed Alyamani, Nayef H. Felemban, Enas Tawfik Enan
Molecules.2021; 26(22): 6832. CrossRef - Application of Selected Nanomaterials and Ozone in Modern Clinical Dentistry
Adam Lubojanski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Nicole Nowak, Justyna Rewak-Soroczynska, Klaudia Sztyler, Wojciech Zakrzewski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Katarzyna Wiglusz, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 259. CrossRef - Nanomaterials as drug delivery systems with antibacterial properties: current trends and future priorities
Khatereh Khorsandi, Reza Hosseinzadeh, Homa Sadat Esfahani, Saeedeh Keyvani-Ghamsari, Saeed Ur Rahman
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy.2021; 19(10): 1299. CrossRef - Synthesis and antibacterial activity of polymer–antibiotic conjugates incorporated into a resin-based dental adhesive
Ziwen Zhang, Megan M. Jones, Camila Sabatini, Stephen T. Vanyo, Ming Yang, Abhishek Kumar, Yancheng Jiang, Mark T. Swihart, Michelle B. Visser, Chong Cheng
Biomaterials Science.2021; 9(6): 2043. CrossRef - Effect Of Various Antibacterial Materials In Dental Composites: A Systematic Review
Abdulrahman Abdulaziz Alfayez, Abdullah Abdulrahman Alduhaymi, Essam Abdulaziz Almulhim, Mohammad Yahya Assiri, Shahzeb Hasan Ansari
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(3): 39. CrossRef - Low-temperature flow-synthesis-assisted urethane-grafted zinc oxide-based dental composites: physical, mechanical, and antibacterial responses
Jaffar Hussain Bukhari, Abdul Samad Khan, Kashif Ijaz, Shahreen Zahid, Aqif Anwar Chaudhry, Muhammad Kaleem
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of nano‐technology applications in resin‐based restorative materials
Natalia Almeida Bastos, Sandro Basso Bitencourt, Emerson Alves Martins, Grace Mendonca De Souza
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(4): 567. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Therapies for the Management of Dental Caries—A Literature Review
Hetal Desai, Cameron Stewart, Yoav Finer
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 147. CrossRef - In-vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles and Its Indigenous Mouthwash
Lichi. A. Solanki, KK Shantha Sundari, S Rajeshkumar
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2021; 15(2): 735. CrossRef - Antibacterial response of oral microcosm biofilm to nano-zinc oxide in adhesive resin
Isadora Martini Garcia, AbdulRahman A. Balhaddad, Maria S. Ibrahim, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dental Materials.2021; 37(3): e182. CrossRef - Toxic mechanisms of Roth801, Canals, microparticles and nanoparticles of ZnO on MG-63 osteoblasts
Mei-Chi Chang, Chia-Mei Tang, Yu-Heng Lin, Hsin-Cheng Liu, Tong-Mei Wang, Wen-Chien Lan, Ru-Hsiu Cheng, Yan-Ru Lin, Hsiao-Hua Chang, Jiiang-Huei Jeng
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 119: 111635. CrossRef - Initial Mechanical Stabilization of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cements with Different Active Principles
Caroline Santos Ribeiro, Mayra Manoella Perez, Pablo Lenin Benitez-Sellan, Renata de Oliveira Guaré, Eduardo Bresciani, Michele Baffi Diniz
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinc oxide nanoparticles inhibit bacterial biofilm formation via altering cell membrane permeability
Tanvir Kaur, Chayanika Putatunda, Ashish Vyas, Gaurav Kumar
Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology.2021; 51(4): 309. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, mechanical, and bonding properties of a dental adhesive modified with antibacterial monomer and cross-linker
Hoda Moussa, Megan M. Jones, Ningbo Huo, Runsheng Zhang, Mayuresh Keskar, Michelle B. Visser, Mark T. Swihart, Chong Cheng, Camila Sabatini
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2877. CrossRef - The Benefits of Smart Nanoparticles in Dental Applications
Silvia Vasiliu, Stefania Racovita, Ionela Aurica Gugoasa, Maria-Andreea Lungan, Marcel Popa, Jacques Desbrieres
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(5): 2585. CrossRef - Microshear Bond Strength of Nanoparticle-Incorporated Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer to Caries-Affected Dentin
Zahra Fattah, Zahra Jowkar, Safoora Rezaeian, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - An Insight in to Various Metallic Oxide Nanoparticles as Antimicrobials and Their Applications in Dentistry
Hema Kanathila, Ashwin M. Pangi, Suvidha Patil, Shilpa Shirlal, Rahul Jaiswal
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(33): 2803. CrossRef - Innovative Strategies in Minimally Invasive Dentistry for Caries Management: A Literature Synthesis
Mariana Vega, Hugo Fuentes, Valeria Cordero, Luis Silva, Regina Cabrera
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2021; 1(2): 66. CrossRef - Nanoparticle technology and its implications in endodontics: a review
Natasha Raura, Anirudh Garg, Arpit Arora, M. Roma
Biomaterials Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Use of Silver Nanomaterials for Caries Prevention: A Concise Review
Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Irene Shuping Zhao, May Lei Mei, Quanli Li, Ollie Yiru Yu, Chun Hung Chu
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 3181. CrossRef- Study on a novel antibacterial light-cured resin composite containing nano-MgO
Zhongyuan Wu, Haiping Xu, Wei Xie, Meimei Wang, Cunjin Wang, Cheng Gao, Fang Gu, Jie Liu, Jing Fu
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces.2020; 188: 110774. CrossRef - Effect of Addition of Nano-TiO2, Nano-SiO2, and a Combination of Both, on Antimicrobial Activity of an Orthodontic Composite
Abbas Bahador, Mohammad J Kharazifard, Nazanin Kiomarsi, Paniz Zamani, Sedighe S Hashemikamangar, Maryam Pourhajibagher
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(8): 857. CrossRef - Biomimetic Aspects of Oral and Dentofacial Regeneration
Akshaya Upadhyay, Sangeeth Pillai, Parisa Khayambashi, Hisham Sabri, Kyungjun T. Lee, Maryam Tarar, Stephanie Zhou, Ingrid Harb, Simon D. Tran
Biomimetics.2020; 5(4): 51. CrossRef Dental Materials Incorporated with Nanometals and Their Effect on the Bacterial Growth of Staphylococcus aureus
Rabeah Yousef Rawashdeh, Reyad Sawafta, Hanan I Malkawi
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 4325. CrossRef- Does the Addition of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Improve the Antibacterial Properties of Direct Dental Composite Resins? A Systematic Review
Divya Arun, Dulanja Adikari Mudiyanselage, Rumana Gulam Mohamed, Michael Liddell, Nur Mohammad Monsur Hassan, Dileep Sharma
Materials.2020; 14(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on broilers’ performance and health status
Usama T. Mahmoud, Hosnia S. Abdel-Mohsein, Manal A. M. Mahmoud, Omar A. Amen, Rasha I. M. Hassan, Ashraf M. Abd-El-Malek, Sohair M. M. Rageb, Hanan S. A. Waly, Aly A. Othman, Mohamed A. Osman
Tropical Animal Health and Production.2020; 52(4): 2043. CrossRef - The potential anti‐infective applications of metal oxide nanoparticles: A systematic review
Yasmin Abo‐zeid, Gareth R. Williams
WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - ZnO Modulates Swine Gut Microbiota and Improves Growth Performance of Nursery Pigs When Combined with Peptide Cocktail
Xiaoyuan Wei, Tsungcheng Tsai, Joshua Knapp, Kristopher Bottoms, Feilong Deng, Robert Story, Charles Maxwell, Jiangchao Zhao
Microorganisms.2020; 8(2): 146. CrossRef - Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial activity of silica-coated silver nanoparticles for esthetic dental applications
Marcela Charantola Rodrigues, Wallace Rosado Rolim, Marina Mariante Viana, Thaís Rodrigues Souza, Flavia Gonçalves, Caio Junji Tanaka, Bruno Bueno-Silva, Amedea Barozzi Seabra
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 96: 103327. CrossRef - Advances of Anti-Caries Nanomaterials
Hui Chen, Lisha Gu, Binyou Liao, Xuedong Zhou, Lei Cheng, Biao Ren
Molecules.2020; 25(21): 5047. CrossRef - Antibacterial Properties of Nanoparticles in Dental Restorative Materials. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elena Ferrando-Magraner, Carlos Bellot-Arcís, Vanessa Paredes-Gallardo, José Manuel Almerich-Silla, Verónica García-Sanz, Mercedes Fernández-Alonso, José María Montiel-Company
Medicina.2020; 56(2): 55. CrossRef - Polymeric and inorganic nanoscopical antimicrobial fillers in dentistry
Pooyan Makvandi, Jun Ting Gu, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Behnaz Ashtari, Arash Moeini, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2020; 101: 69. CrossRef - The effect of incorporation Nano Cinnamon powder on the shear bond of the orthodontic composite (an in vitro study)
Saba N. Yaseen, Amer A. Taqa, Ali R. Al-Khatib
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 128. CrossRef - Synthesis of an anti-cariogenic experimental dental composite containing novel drug-decorated copper particles
Mehwish Pasha, Nawshad Muhammad, Maleeha Nayyer, Jaffar Hussain Bokhari, Hina Ashraf, Sher Zaman Safi, Muhammad Kaleem
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2020; 114: 111040. CrossRef The Effects of Silver, Zinc Oxide, and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Used as Dentin Pretreatments on the Microshear Bond Strength of a Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement to Dentin
Zahra Jowkar, Zahra Fattah, Saeedreza Ghanbarian, Fereshteh Shafiei
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 4755. CrossRef- Metal‐Based Nanomaterials in Biomedical Applications: Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity Aspects
Pooyan Makvandi, Chen‐yu Wang, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Assunta Borzacchiello, Li‐na Niu, Franklin R. Tay
Advanced Functional Materials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Biomedical Materials
Maria P. Nikolova, Murthy S. Chavali
Biomimetics.2020; 5(2): 27. CrossRef - Comparison of antibacterial effects of orthodontic composites containing different nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans at different times
Soghra Yassaei, Ali Nasr, Hengameh Zandi, Mohammad Nima Motallaei
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(2): 52. CrossRef - Nanoparticles as Anti-Microbial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Remineralizing Agents in Oral Care Cosmetics: A Review of the Current Situation
Florence Carrouel, Stephane Viennot, Livia Ottolenghi, Cedric Gaillard, Denis Bourgeois
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(1): 140. CrossRef - Nanometals in Dentistry: Applications and Toxicological Implications—a Systematic Review
Rupali Agnihotri, Sumit Gaur, Sacharia Albin
Biological Trace Element Research.2020; 197(1): 70. CrossRef - Ex vivo investigation on internal tunnel approach/internal resin infiltration and external nanosilver-modified resin infiltration of proximal caries exceeding into dentin
Andrej M. Kielbassa, Marlene R. Leimer, Jens Hartmann, Stephan Harm, Markus Pasztorek, Ina B. Ulrich, Yogendra Kumar Mishra
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(1): e0228249. CrossRef - Nanocomposites based on low density polyethylene filled with carbon nanotubes prepared by high energy ball milling and their potential antibacterial activity
Erika Benigno, Miguel A Lorente, Dania Olmos, Gustavo González‐Gaitano, Javier González‐Benito
Polymer International.2019; 68(6): 1155. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide and modified titanium dioxide by silver nanoparticles as an anti biofilm filler content for composite resins
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Taís Maria Bauab, Antônio Carlos Hernandes, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): e36. CrossRef - Synthesis, characterization and application of Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles in a composite resin
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Valéria Spolon Marangoni, Adilson César de Abreu Bernardi, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli, Antônio Carlos Hernandes
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 96: 391. CrossRef - The effect of silver nanoparticles incorporation in the self-etch adhesive system on its antibacterial activity and degree of conversion: an in-vitro study
Heba F. Mohammed, Mona I. Riad
F1000Research.2019; 8: 244. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on resin-dentin bond strength durability in a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive system
Zahra Jowkar, Fereshteh Shafiei, Elham Asadmanesh, Fatemeh Koohpeima
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and status of resin composite as dental restorative materials
Xinxuan Zhou, Xiaoyu Huang, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Lei Cheng
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticle solution on the mechanical properties of resin cements and intrarradicular dentin
Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, Juno Gallego, Wirley Gonçalves Assunção, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Chun-Pin Lin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(6): e0217750. CrossRef - Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole
Yasaman Delaviz, Timothy W. Liu, Ashley R. Deonarain, Yoav Finer, Babak Shokati, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): 229. CrossRef - Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry
Wenjing Song, Shaohua Ge
Molecules.2019; 24(6): 1033. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of a tissue conditioner used in complete dentures after incorporation of ZnO‒Ag nanoparticles
Seyed Amin Mousavi, Reza Ghotaslou, Abolfazl Akbarzadeh, Niloufar Azima, Ali Aeinfar, Azin Khorramdel
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(1): 11. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Mechanical Properties of Pit and Fissure Sealants Containing Zinc Oxide and Calcium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Dara Lakshmi Swetha, C. Vinay, K. S. Uloopi, Kakarla Sri RojaRamya, Rayala Chandrasekhar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 477. CrossRef - Addition of antibacterial agent effect on color stability of composites after immersion of different beverages
Makbule T. Tuncdemir, Nilgun Gulbahce
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 31(5): 508. CrossRef - Toward dental caries: Exploring nanoparticle-based platforms and calcium phosphate compounds for dental restorative materials
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Anmar A. Kansara, Denise Hidan, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Bioactive Materials.2019; 4: 43. CrossRef - Antibacterial effects of polymeric PolymP-n Active nanoparticles. An in vitro biofilm study
M.C. Sánchez, M. Toledano-Osorio, J. Bueno, E. Figuero, M. Toledano, A.L. Medina-Castillo, R. Osorio, D. Herrera, M. Sanz
Dental Materials.2019; 35(1): 156. CrossRef - Potencial antimicrobiano de diferentes retentores intrarradiculares frente a Enterococcus faecalis: uma avaliação in vitro
Nicole Hoffmann FINGER, Marília PAULUS, Alexandra Flávia GAZZONI
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomedicine for anticancer and antimicrobial treatment: an overview
Shatavari Kulshrestha, Asad U. Khan
IET Nanobiotechnology.2018; 12(8): 1009. CrossRef - Effect of Silver Nanoparticles, Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Microshear Bond Strength to Enamel and Dentin
Fatemeh Koohpeima, Zahra Jowkar, Nazbanoo Farpour, Mohammad J Mokhtari, Fereshteh Shafiei
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(11): 1405. CrossRef - Studies on the Curing Efficiency and Mechanical Properties of Bis-GMA and TEGDMA Nanocomposites Containing Silver Nanoparticles
Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Grzegorz Chladek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(12): 3937. CrossRef - Properties of Experimental Dental Composites Containing Antibacterial Silver-Releasing Filler
Robert Stencel, Jacek Kasperski, Wojciech Pakieła, Anna Mertas, Elżbieta Bobela, Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Grzegorz Chladek
Materials.2018; 11(6): 1031. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial properties on polysulfone composite membranes using synthesized biogenic silver nanoparticles with Ulva compressa (L.) Kütz. and Cladophora glomerata (L.) Kütz. extracts
Fozia T. Minhas, Gulsin Arslan, I. Hilal Gubbuk, Cengiz Akkoz, Betul Yılmaz Ozturk, Baran Asıkkutlu, Ugur Arslan, Mustafa Ersoz
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2018; 107: 157. CrossRef - Human In Situ Study of the effect of Bis(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl) Dimethylammonium Bromide Immobilized in Dental Composite on Controlling Mature Cariogenic Biofilm
Mary Anne S. Melo, Michael D. Weir, Vanara F. Passos, Juliana P. M. Rolim, Christopher D. Lynch, Lidiany K. A. Rodrigues, Hockin H. K. Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(11): 3443. CrossRef - A systematic review on antibacterial activity of zinc against Streptococcus mutans
Manal Mohamed Almoudi, Alaa Sabah Hussein, Mohamed Ibrahim Abu Hassan, Nurhayati Mohamad Zain
The Saudi Dental Journal.2018; 30(4): 283. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and diametrical tensile strength of an interim cement modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles and terpenes: An in vitro study
Verónica Andrade, Alejandra Martínez, Ninón Rojas, Helia Bello-Toledo, Paulo Flores, Gabriela Sánchez-Sanhueza, Alfonso Catalán
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2018; 119(5): 862.e1. CrossRef - Developing a New Generation of Therapeutic Dental Polymers to Inhibit Oral Biofilms and Protect Teeth
Ke Zhang, Bashayer Baras, Christopher Lynch, Michael Weir, Mary Melo, Yuncong Li, Mark Reynolds, Yuxing Bai, Lin Wang, Suping Wang, Hockin Xu
Materials.2018; 11(9): 1747. CrossRef - Do quaternary ammonium monomers induce drug resistance in cariogenic, endodontic and periodontal bacterial species?
Suping Wang, Haohao Wang, Biao Ren, Hao Li, Michael D. Weir, Xuedong Zhou, Thomas W. Oates, Lei Cheng, Hockin H.K. Xu
Dental Materials.2017; 33(10): 1127. CrossRef - Antimicrobial nanomaterials against biofilms: an alternative strategy
Chunhua Liu, Jing Guo, Xiaoqing Yan, Yongbing Tang, Asit Mazumder, Shikai Wu, Yan Liang
Environmental Reviews.2017; 25(2): 225. CrossRef - Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future
Azhwar Raghunath, Ekambaram Perumal
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.2017; 49(2): 137. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Polymers in the Nano-World
Marta Álvarez-Paino, Alexandra Muñoz-Bonilla, Marta Fernández-García
Nanomaterials.2017; 7(2): 48. CrossRef - Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles on Orthodontic Elastomeric Modules: Evaluation of Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties
Alma Hernández-Gómora, Edith Lara-Carrillo, Julio Robles-Navarro, Rogelio Scougall-Vilchis, Susana Hernández-López, Carlo Medina-Solís, Raúl Morales-Luckie
Molecules.2017; 22(9): 1407. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Influence Microflora in Ileal Digesta and Correlate Well with Blood Metabolites
Yanni Feng, Lingjiang Min, Weidong Zhang, Jing Liu, Zhumei Hou, Meiqiang Chu, Lan Li, Wei Shen, Yong Zhao, Hongfu Zhang
Frontiers in Microbiology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial activity of glass ionomer cement modified by zinc oxide nanoparticles
Patrícia Petromilli Nordi Sasso Garcia, Mariana Florian Bell Cardia, Renata Serignoli Francisconi, Lívia Nordi Dovigo, Denise Madalena Palomari Spolidório, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli, Ana Carolina Botta
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(5): 456. CrossRef - Effects on cytotoxicity and antibacterial properties of the incorporations of silver nanoparticles into the surface coating of dental alloys
Xiao-ting Shen, Yan-zhen Zhang, Fang Xiao, Jing Zhu, Xiao-dong Zheng
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2017; 18(7): 615. CrossRef - Nanosilver coated orthodontic brackets:in vivoantibacterial properties and ion release
Gamze Metin-Gürsoy, Lale Taner, Gülçin Akca
The European Journal of Orthodontics.2017; 39(1): 9. CrossRef - Prenatal Exposure to Nanosized Zinc Oxide in Rats: Neurotoxicity and Postnatal Impaired Learning and Memory Ability
Feng Xiaoli, Wu Junrong, Lai Xuan, Zhang Yanli, Wei Limin, Liu Jia, Shao Longquan
Nanomedicine.2017; 12(7): 777. CrossRef - Heat-Polymerized Resin Containing Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate Inhibits Candida albicans Biofilm
Hui Chen, Qi Han, Xuedong Zhou, Keke Zhang, Suping Wang, Hockin Xu, Michael Weir, Mingye Feng, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Lei Cheng
Materials.2017; 10(4): 431. CrossRef - Zinc oxide 3D microstructures as an antimicrobial filler content for composite resins
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Matheus Aparecido dos Santos Ramos, Tamara Carolina Trevisan, Taís Maria Bauab, Antônio Carlos Hernandes, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(6): 634. CrossRef - Polymer-Ceramic Bionanocomposites for Dental Application
Jung-Hwan Lee, Hae-Won Kim, Seog-Jin Seo
Journal of Nanomaterials.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of nanosilver-coated orthodontic brackets: an in vivo study
Gamze Metin-Gürsoy, Lale Taner, Emre Barış
Progress in Orthodontics.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Restorative materials containing antimicrobial agents: is there evidence for their antimicrobial and anticaries effects? A systematic review
GS do Amaral, T Negrini, M Maltz, RA Arthur
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(1): 6. CrossRef - Evaluation of Bond Strength and Microleakage of a Novel Metal-titanate Antibacterial Agent
S Deng, KH Chung, DCN Chan, C Spiekerman
Operative Dentistry.2016; 41(3): E48. CrossRef - Investigation of optical, structural, morphological and antimicrobial properties of carboxymethyl cellulose capped Ag-ZnO nanocomposites prepared by chemical and mechanical methods
Magdalena-Valentina Lungu, Eugeniu Vasile, Mariana Lucaci, Delia Pătroi, Natalia Mihăilescu, Florentina Grigore, Virgil Marinescu, Alexandra Brătulescu, Sorina Mitrea, Arcadie Sobetkii, Arcadii A. Sobetkii, Marcela Popa, Mariana-Carmen Chifiriuc
Materials Characterization.2016; 120: 69. CrossRef - Substantivity of Ag–Ca–Si mesoporous nanoparticles on dentin and its ability to inhibit Enterococcus faecalis
Wei Fan, Yujie Wu, Tengjiao Ma, Yanyun Li, Bing Fan
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomaterials for Tissue Engineering In Dentistry
Manila Chieruzzi, Stefano Pagano, Silvia Moretti, Roberto Pinna, Egle Milia, Luigi Torre, Stefano Eramo
Nanomaterials.2016; 6(7): 134. CrossRef - Alternative Antimicrobial Approach: Nano-Antimicrobial Materials
Nurit Beyth, Yael Houri-Haddad, Avi Domb, Wahid Khan, Ronen Hazan
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Advances in Dental Materials through Nanotechnology: Facts, Perspectives and Toxicological Aspects
Gislaine C. Padovani, Victor P. Feitosa, Salvatore Sauro, Franklin R. Tay, Gabriela Durán, Amauri J. Paula, Nelson Durán
Trends in Biotechnology.2015; 33(11): 621. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of conventional restorative filling materials and advances in antimicrobial properties of composite resins and glass ionomer cements—A literature review
Cher Farrugia, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2015; 31(4): e89. CrossRef - Biofilm and Dental Biomaterials
Marit Øilo, Vidar Bakken
Materials.2015; 8(6): 2887. CrossRef - Antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles as a vehicle for calcium hydroxide medicament against Enterococcus faecalis
Farzaneh Afkhami, Seyyed Jalal Pourhashemi, Mona Sadegh, Yasaman Salehi, Mohammad Javad Kharrazi Fard
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(12): 1573. CrossRef - Physical Properties of an Ag-Doped Bioactive Flowable Composite Resin
Hiba Kattan, Xanthippi Chatzistavrou, James Boynton, Joseph Dennison, Peter Yaman, Petros Papagerakis
Materials.2015; 8(8): 4668. CrossRef - Effect of sterilization techniques prior to antimicrobial testing on physical properties of dental restorative materials
Cher Farrugia, Glenn Cassar, Vasilis Valdramidis, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(6): 703. CrossRef - The effects of gold coated and uncoated zinc oxide nanohexagons on the photophysicochemical properties of the low symmetry zinc phthalocyanine
Sarah D'Souza, Racheal Ogbodu, Tebello Nyokong
Journal of Molecular Structure.2015; 1099: 551. CrossRef - In Vitro Activity of Curcumin and Silver Nanoparticles Against Blastocystis hominis
Mona Abdel-Fattah Ahmed, Khadiga Ahmed Ismail, Sabah Abd-El-Ghany Ahmed, Ayman Nabil Ibrahim, Yousry Mahmoud Gohar
Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice.2015; 23(3): 135. CrossRef - Development and characterization of novel ZnO-loaded electrospun membranes for periodontal regeneration
Eliseu A. Münchow, Maria Tereza P. Albuquerque, Bianca Zero, Krzysztof Kamocki, Evandro Piva, Richard L. Gregory, Marco C. Bottino
Dental Materials.2015; 31(9): 1038. CrossRef - Review of Nanomaterials in Dentistry: Interactions with the Oral Microenvironment, Clinical Applications, Hazards, and Benefits
Alexandros Besinis, Tracy De Peralta, Christopher J. Tredwin, Richard D. Handy
ACS Nano.2015; 9(3): 2255. CrossRef - Study on the Bactriostasis of Nano-Silver against Penicillium
Lu Qiu, Mei Hua Xie, Jia Yan Lv, Shu Guo Fan, Jian Hui Gao
Advanced Materials Research.2014; 1051: 62. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Satureja hortensis Extract on Isolated Bacillus cereus from Soil of Sistan Plain
Ebrahim Shirmohammadi, Saeide Saeidi, Taher Mohasseli, Ali Rahimian Boogar
International Journal of Infection.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Strategies to Improve Biocompatibility of Dental Materials
Gottfried Schmalz
Current Oral Health Reports.2014; 1(4): 222. CrossRef
- Fabricated modified compomer bearing CF/SBA-15 nanomaterials: Physicochemical and antibacterial properties
- 5,902 View
- 58 Download
- 209 Crossref

-
Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems on
Streptococcus mutans - Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):32-38. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we evaluated the antibacterial activity of self-etching adhesive systems against
Streptococcus mutans using the agar diffusion method.Materials and Methods Three 2-step systems, Clearfil SE Bond (SE, Kuraray), Contax (CT, DMG), and Unifil Bond (UnB, GC), and three 1-step systems, Easy Bond (EB, 3M ESPE), U-Bond (UB, Vericom), and All Bond SE (AB, BISCO) were used. 0.12% chlorhexidine (CHX, Bukwang) and 37% phosphoric acid gel (PA, Vericom) were used as positive controls.
Results The antibacterial activity of CHX and PA was stronger than that of the other groups, except SE. After light activation, the inhibition zone was reduced in the case of all 2-step systems except CT. However, all 1-step systems did not exhibit any inhibition zone upon the light activation.
Conclusions SE may be better than CT or UnB among the 2-step systems with respect to antibacterial activity, however, 1-step systems do not exhibit any antibacterial activity after light curing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Three Universal Bonding Agents Against Streptococcus mutans on Demineralized Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Kirti Rathee, Charu Dayal, Reena Rani, A Anukriti, Anjum Zia, Ankita Sundan, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Incorporation of chlorhexidine in self-adhesive resin cements
Idris M. MEHDAWI, Ranna KITAGAWA, Haruaki KITAGAWA, Satoshi YAMAGUCHI, Nanako HIROSE, Tomoki KOHNO, Satoshi IMAZATO
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 675. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Bonding Properties of Universal Adhesive Dental Polymers Doped with Pyrogallol
Naji Kharouf, Ammar Eid, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Youri Arntz, Hamdi Jmal, Federico Foschi, Salvatore Sauro, Vincent Ball, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1538. CrossRef - Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and Epigallocatechin-3-O-(3-O-methyl)-gallate Enhance the Bonding Stability of an Etch-and-Rinse Adhesive to Dentin
Hao-Han Yu, Ling Zhang, Fan Yu, Fang Li, Zheng-Ya Liu, Ji-Hua Chen
Materials.2017; 10(2): 183. CrossRef - An In vitro Assessment of Antibacterial Activity of Three Self-etching Primers Against Oral Microflora
Sneha Dipak Shinde, Vikram Pai, R. Vijay Naik
APOS Trends in Orthodontics.2017; 7: 181. CrossRef - Functional Dental Restorative Materials That Hinder Oral Biofilm
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Victor Trassi Fernandes da Silva Souza, Rafael Amorim Martins, Ana Carolina Bosco Mendes, Monica Irma Aparecida Valdeci de Souza, Ângela Cristina Cilense Zuanon, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Current Oral Health Reports.2017; 4(1): 22. CrossRef - In vitroantibacterial activity of various adhesive materials against oral streptococci
Emre Ozel, Fetiye Kolayli, Elif Bahar Tuna, Doganhan Er
Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment.2016; 30(1): 121. CrossRef - A systematic review about antibacterial monomers used in dental adhesive systems: Current status and further prospects
Alexandra Rubin Cocco, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Rafael Guerra Lund, Evandro Piva
Dental Materials.2015; 31(11): 1345. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Three Universal Bonding Agents Against Streptococcus mutans on Demineralized Dentin: An In Vitro Study
- 1,504 View
- 5 Download
- 8 Crossref

-
Inhibition of
Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation on composite resins containing ursolic acid - Soohyeon Kim, Minju Song, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):65-72. Published online May 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the inhibitory effect of ursolic acid (UA)-containing composites on
Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans ) biofilm.Materials and Methods Composite resins with five different concentrations (0.04, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 wt%) of UA (U6753, Sigma Aldrich) were prepared, and their flexural strengths were measured according to ISO 4049. To evaluate the effect of carbohydrate source on biofilm formation, either glucose or sucrose was used as a nutrient source, and to investigate the effect of saliva treatment, the specimen were treated with either unstimulated whole saliva or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). For biofilm assay, composite disks were transferred to
S. mutans suspension and incubated for 24 hr. Afterwards, the specimens were rinsed with PBS and sonicated. The colony forming units (CFU) of the disrupted biofilm cultures were enumerated. For growth inhibition test, the composites were placed on a polystyrene well cluster, andS. mutans suspension was inoculated. The optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was recorded by Infinite F200 pro apparatus (TECAN). One-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction were used for the data analyses.Results The flexural strength values did not show significant difference at any concentration (
p > 0.01). In biofilm assay, the CFU score decreased as the concentration of UA increased. The influence of saliva pretreatment was conflicting. The sucrose groups exhibited higher CFU score than glucose group (p < 0.05). In bacterial growth inhibition test, all experimental groups containing UA resulted in complete inhibition.Conclusions Within the limitations of the experiments, UA included in the composite showed inhibitory effect on
S. mutans biofilm formation and growth.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Environmental Stress Induces Altered Composition of Streptococcus mutans Membrane Vesicles: pH‐Driven Changes in Membrane Vesicle Production and Composition
Taylor C. Boone, Swetha K. Shankar, Melodie L. Weller
Molecular Oral Microbiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-cariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid using dental microcosm biofilm
Jonghyun Jo, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Sun Kyu Park, Su-Jung Shin, Baek-il Kim, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105447. CrossRef - Rapid specific detection of oral bacteria using Cas13-based SHERLOCK
Jett Liu, Camden Carmichael, Hatice Hasturk, Wenyuan Shi, Batbileg Bor
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Bioactive Nanocomposites Containing Calcium Fluoride and Calcium Phosphate with Antibacterial and Low-Shrinkage-Stress Capabilities to Inhibit Dental Caries
Abdullah Alhussein, Rashed Alsahafi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Lamia Mokeem, Abraham Schneider, Mary-Ann Jabra-Rizk, Radi Masri, Gary D. Hack, Thomas W. Oates, Jirun Sun, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H. K. Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(9): 991. CrossRef - Quorum sensing inhibition and antibiofilm action of triterpenoids: An updated insight
Sudipta Paul Bhattacharya, Snigdha Karmakar, Kusumita Acharya, Arijit Bhattacharya
Fitoterapia.2023; 167: 105508. CrossRef - The Application of Small Molecules to the Control of Typical Species Associated With Oral Infectious Diseases
Sirui Yang, Xiaoying Lyu, Jin Zhang, Yusen Shui, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Planktonic and Anti-Biofilm Properties of Pentacyclic Triterpenes—Asiatic Acid and Ursolic Acid as Promising Antibacterial Future Pharmaceuticals
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska, Dorota Wojnicz
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 98. CrossRef - Development and Physicochemical Characterization of Eugenia brejoensis Essential Oil-Doped Dental Adhesives with Antimicrobial Action towards Streptococcus mutans
Maury Luz Pereira, Danyelle Cristina Pereira Santos, Carlos Alberto Mendes Soares Júnior, Tamyris Alicely Xavier Nogueira Bazan, Clovis Macêdo Bezerra Filho, Márcia Vanusa da Silva, Maria Tereza dos Santos Correia, Andres Felipe Millan Cardenas, Fabiana S
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(3): 149. CrossRef - Does Secondary Plant Metabolite Ursolic Acid Exhibit Antibacterial Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Living in Single- and Multispecies Biofilms?
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Wojnicz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(8): 1691. CrossRef - Prolonged Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Growth and Biofilm Formation by Sustained Release of Chlorhexidine from Varnish Coated Dental Abutments: An in Vitro Study
Mark Feldman, Walid Shaaban Moustafa Elsayed, Michael Friedman, Irith Gati, Doron Steinberg, Hesham Marei, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interkingdom Signaling Interference: The Effect of Plant-Derived Small Molecules on Quorum Sensing in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria
Janak Raj Joshi, Netaly Khazanov, Amy Charkowski, Adi Faigenboim, Hanoch Senderowitz, Iris Yedidia
Annual Review of Phytopathology.2021; 59(1): 153. CrossRef - Small Molecule Compounds, A Novel Strategy against Streptococcus mutans
Sirui Yang, Jin Zhang, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Pathogens.2021; 10(12): 1540. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide nanotubes added to glass ionomer cements affect S. mutans viability and mechanisms of virulence
Isaac Jordão de Souza ARAÚJO, Mariana Gallante RICARDO, Orisson Ponce GOMES, Priscila Alves GIOVANI, Júlia PUPPIN-RONTANI, Vanessa Arias PECORARI, Elizabeth Ferreira MARTINEZ, Marcelo Henrique NAPIMOGA, Francisco Humberto NOCITI JUNIOR, Regina Maria PUPPI
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ursolic and Oleanolic Acids on Lipid Membranes: Studies on MRSA and Models of Membranes
Sandrine Verstraeten, Lucy Catteau, Laila Boukricha, Joelle Quetin-Leclercq, Marie-Paule Mingeot-Leclercq
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1381. CrossRef - Ursolic acid inhibits multi-species biofilms developed by Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguinis, and Streptococcus gordonii
Xiaoying Lyu, Liang Wang, Yusen Shui, Qingsong Jiang, Lan Chen, Wen Yang, Xiaoya He, Jumei Zeng, Yuqing Li
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 125: 105107. CrossRef - The physical properties and anticariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid
Hyunkyung Yoo, So Youn Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 641. CrossRef - Ursolic acid: A systematic review of its pharmacology, toxicity and rethink on its pharmacokinetics based on PK-PD model
Qiang Sun, Man He, Meng Zhang, Sha Zeng, Li Chen, Lijuan Zhou, Haibo Xu
Fitoterapia.2020; 147: 104735. CrossRef - Effects of UVB and UVC irradiation on cariogenic bacteria in vitro
Shigeki Uchinuma, Yasushi Shimada, Khairul Matin, Keiichi Hosaka, Masahiro Yoshiyama, Yasunori Sumi, Junji Tagami
Lasers in Medical Science.2019; 34(5): 981. CrossRef - Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential
Dharambir Kashyap, Hardeep Singh Tuli, Anil K. Sharma
Life Sciences.2016; 146: 201. CrossRef - Protective Effects on Gastric Lesion of Ursolic acid
Sun Whoe Kim, In Young Hwang, Sun Yi Lee, Choon Sik Jeong
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2016; 31(4): 286. CrossRef - Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities
Łukasz Woźniak, Sylwia Skąpska, Krystian Marszałek
Molecules.2015; 20(11): 20614. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Dental materials with antibiofilm properties
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Dental Materials.2014; 30(2): e1. CrossRef - Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles onStreptococcus mutansandLactobacillus
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 109. CrossRef - Synergistic effect of xylitol and ursolic acid combination on oral biofilms
Yunyun Zou, Yoon Lee, Jinyoung Huh, Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 288. CrossRef - The virulence of Streptococcus mutans and the ability to form biofilms
W. Krzyściak, A. Jurczak, D. Kościelniak, B. Bystrowska, A. Skalniak
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.2014; 33(4): 499. CrossRef
- Environmental Stress Induces Altered Composition of Streptococcus mutans Membrane Vesicles: pH‐Driven Changes in Membrane Vesicle Production and Composition
- 1,919 View
- 5 Download
- 26 Crossref

-
Inhibitory effect on
Streptococcus mutans and mechanical properties of the chitosan containing composite resin - Ji-Sun Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):36-42. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the antibacterial effect and mechanical properties of composite resins (LCR, MCR, HCR) incorporating chitosan with three different molecular weights (L, Low; M, Medium; H, High).
Materials and Methods Streptococcus (S). mutans 100 mL and each chitosan powder were inoculated in sterilized 10 mL Brain-Heart Infusion (BHI) solution, and was centrifuged for 12 hr. Absorbance of the supernatent was measured at OD660 to estimate the antibacterial activities of chitosan. AfterS. mutans was inoculated in the disc shaped chitosan-containing composite resins, the disc was cleansed with BHI and diluted with serial dilution method.S. mutans was spread onMitis-salivarius bacitracin agar. After then, colony forming unit (CFU) was measured to verify the inhibitory effect onS. mutans biofilm. To ascertain the effect on the mechanical properties of composite resin, 3-point bending and Vickers hardness tests were done after 1 and 3 wk water storage, respectively. Using 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Scheffe test, statistical analysis was done with 95% significance level.Results All chitosan powder showed inhibition effect against
S. mutans . CFU number in chitosan-containing composite resins was smaller than that of control resin without chitosan. The chitosan containing composite resins did not show any significant difference in flexural strength and Vickers hardness in comparison with the control resin. However, the composite resin, MCR showed a slightly decreased flexural strength and the maximum load than those of control and the other composite resins HCR and LCR.Conclusions LCR and HCR would be recommended as a feasible antibacterial restorative due to its antibacterial nature and mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dental Resin Composites Modified with Chitosan: A Systematic Review
Wojciech Dobrzyński, Paweł J. Piszko, Jan Kiryk, Sylwia Kiryk, Mateusz Michalak, Agnieszka Kotela, Julia Kensy, Witold Świenc, Natalia Grychowska, Jacek Matys, Maciej Dobrzyński
Marine Drugs.2025; 23(5): 199. CrossRef - Bactericidal Effects of Ultraviolet-C Light-Emitting Diode Prototype Device Through Thin Optical Fiber
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Deog-Gyu Seo
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4504. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity, and microshear bond strength of an experimental adhesive system containing chitosan-based silver oxide particles
Hamideh Sadat Mohammadipour, Alireza Boruziniat, Seyedeh Azam Hoseini, Hosein Bagheri, Navid Ramezanian, Abbas Tanhaieian, Solmaz Pourgonabadi, Arsalan Shahri
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of a novel antibacterial nanocomposite resin restorative material
Rasha Abd El Rahman El Naggar, Manal A. ElEbiary, ElRefaie Kenawy, Gehan A. Elolimy
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(3): 439. CrossRef - The impact of chitosan in experimental resin with different photoinitiator systems
Isaías Donizeti Silva, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Bruno Vilela Muniz, Karina Cogo-Muller, Flávia Gonçalves, William Cunha Brandt
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106323. CrossRef - The effect of adding chitosan nanoparticles on different properties of the adhesive and high-filled composite resin
Mahan Masoumi, Sara Valizadeh, Ricardo M. Carvalho, Alireza Akbari Moghaddam, Safoura Ghodsi
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2024; 134: 103766. CrossRef - Prospective and applications of bacterial nanocellulose in dentistry
Yasmin Alimardani, Esmaeel Mirzakhani, Fereshteh Ansari, Hadi Pourjafar, Nadia Sadeghi
Cellulose.2024; 31(13): 7819. CrossRef - BNN/TiO2 nanocomposite system–modified dental flow resins and the mechanism of the enhancement of mechanical and antibacterial properties
Xinzi Kong, Qize Han, Axue Jiang, Yurui Wang, Ruizhi Li, Yuting Wang, Shengjie Xiao, Rong Wei, Yu Ma
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(8): 2775. CrossRef - Influence of the Loading with Newly Green Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Equisetum sylvaticum on the Antibacterial Activity and Surface Hardness of a Composite Resin
Ionuț Tărăboanță, Ana Flavia Burlec, Simona Stoleriu, Andreia Corciovă, Adrian Fifere, Denisa Batir-Marin, Monica Hăncianu, Cornelia Mircea, Irina Nica, Andra Claudia Tărăboanță-Gamen, Sorin Andrian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(8): 402. CrossRef - The Impact of Adding Chitosan Nanoparticles on Biofilm Formation, Cytotoxicity, and Certain Physical and Mechanical Aspects of Directly Printed Orthodontic Clear Aligners
Botan Barzan Taher, Tara Ali Rasheed
Nanomaterials.2023; 13(19): 2649. CrossRef - Synthesis of Submicrometric Chitosan Particles Loaded with Calcium Phosphate for Biomedical Applications
Diana Pereira Lopes, Selma Regina Muniz Freitas, Carina Baptiston Tanaka, Giovanne Delechiave, Lucia Nobuco Takamori Kikuchi, Roberto R. Braga, Jamie J. Kruzic, Maria Stella Moreira, Leticia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Luiz Henrique Catalani, Flávia Gonçalve
AAPS PharmSciTech.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodegradable Nonwoven Materials with Antipathogenic Layer
Longina Madej-Kiełbik, Karolina Gzyra-Jagieła, Jagoda Jóźwik-Pruska, Maria Wiśniewskia-Wrona, Marzena Dymel
Environments.2022; 9(7): 79. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of eighth-generation bonding agent modified with 7% arginine and 0.12% chitosan for antibacterial property and microtensile bond strength
HimaliRajan Desai, SanjyotA Mulay, RonitR Shinde, PradeepK Shetty, SoumyaS Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 440. CrossRef - Effects of the crosslinking of chitosan/DCPA particles in the antimicrobial and mechanical properties of dental restorative composites
Lucia Nobuco Takamori Kikuchi, Selma Regina Muniz Freitas, Aldo Ferreira Amorim, Giovanne Delechiave, Luiz Henrique Catalani, Roberto Ruggiero Braga, Maria Stella Moreira, Leticia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Flávia Gonçalves
Dental Materials.2022; 38(9): 1482. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of lactoferrin-chitosan-gellan nanoparticles and their influence on strawberry preservation
Larissa G.R. Duarte, Carolina S.F. Picone
Food Research International.2022; 159: 111586. CrossRef - Polyphenol-Enriched Extract of Lacquer Sap Used as a Dentine Primer with Benefits of Improving Collagen Cross-Linking and Antibacterial Functions
Ying Zhao, Xi He, Han Wang, Huimin Wang, Zuosen Shi, Song Zhu, Zhanchen Cui
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2022; 8(9): 3741. CrossRef - Evaluation of the changes in physical properties and mineral content of enamel exposed to radiation after treating with remineralization agent
Merve Pelin Dur, Neslihan Celik, Nilgun Seven
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(9): 5673. CrossRef - Evaluation of Immediate and Delayed Microleakage of Class V Cavities Restored with Chitosan-incorporated Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study
Roopa R Nadig, Veena Pai, Arpita Deb
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(5): 621. CrossRef - Evaluation of Microleakage of Micro Hybrid Composite Resins versus Chitosan-Incorporated Composite Resins When Restored in Class V Cavities Using Total Etch and Self-Etch Adhesives
Arpita Deb, Veena Pai, Aesha Akhtar, Roopa R. Nadig
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(4): 346. CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Orthodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Adam Lubojanski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 337. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect on Enterococcus Faecalis and Physical Properties of Chitosan Added Calcium Hydroxide Canal Filling Material
Sol Song, Yu-Jin Kim, Jung-Hwan Lee, Joonhaeng Lee, Jisun Shin, Jongbin Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(2): 198. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Bonding Properties of Universal Adhesive Dental Polymers Doped with Pyrogallol
Naji Kharouf, Ammar Eid, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Youri Arntz, Hamdi Jmal, Federico Foschi, Salvatore Sauro, Vincent Ball, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1538. CrossRef - Efficacy of chitosan-based chewing gum on reducing salivary S. mutans counts and salivary pH: a randomised clinical trial
Zahra Khamverdi, Fatemeh Farhadian, Salman Khazaei, Maryam Adabi
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2021; 79(4): 268. CrossRef - Effect of antiseptic gels in the microbiologic colonization of the suture threads after oral surgery
Samuel Rodríguez Zorrilla, Andrés Blanco Carrión, Abel García García, Pablo Galindo Moreno, Xabier Marichalar Mendía, Rafael Seoane Prado, Antonio J. Pérez Estévez, Mario Pérez-Sayáns
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating antibacterial and surface mechanical properties of chitosan modified dental resin composites
Shahid Ali, Laila Sangi, Naresh Kumar, Bharat Kumar, Zohaib Khurshid, Muhammad S. Zafar
Technology and Health Care.2020; 28(2): 165. CrossRef - Comparison of antibacterial effects of orthodontic composites containing different nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans at different times
Soghra Yassaei, Ali Nasr, Hengameh Zandi, Mohammad Nima Motallaei
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(2): 52. CrossRef - Development of novel dental restorative composites with dibasic calcium phosphate loaded chitosan fillers
Carina B. Tanaka, Diana P. Lopes, Lucia N.T. Kikuchi, Maria Stella Moreira, Luiz H. Catalani, Roberto R. Braga, Jamie J. Kruzic, Flávia Gonçalves
Dental Materials.2020; 36(4): 551. CrossRef - Effect of iodonium salt and chitosan on the physical and antibacterial properties of experimental infiltrants
Mariana Dias FLOR-RIBEIRO, Talita Signoreti GRAZIANO, Flávio Henrique Baggio AGUIAR, Rafael Nóbrega STIPP, Giselle Maria MARCHI
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan/Fluoride Nanoparticles for Preventing Dental Caries
Niousha Ebrahimi, Ali Asghar Soleimani, Jamal Rashidiani, Beheshteh Malekafzali, Fatemeh Abedini, Hossein Hosseinkhani
Current Dentistry.2019; 1(1): 61. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of model composites containing quaternary ammonium methacrylates
Marina Lermenn Vidal, Guilherme Ferreira Rego, Gil Mendes Viana, Lucio Mendes Cabral, Juliana Primo Basílio Souza, Nick Silikas, Luis Felipe Schneider, Larissa Maria Cavalcante
Dental Materials.2018; 34(1): 143. CrossRef - Chitosan—PRP nanosphere as a growth factors slow releasing device with superior antibacterial capability
Radyum Ikono, Etik Mardliyati, Iis Tentia Agustin, Muhammad Mufarrij Fuad Ulfi, Dimas Andrianto, Uswatun Hasanah, Boy Muchlis Bachtiar, Nofa Mardianingsih, Endang Winiati Bachtiar, Nurwenda Novan Maulana, Nurul Taufiqu Rochman, Li Xianqi, Hideaki Kagami,
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2018; 4(4): 045026. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Effect of Two Cavity Disinfectants against One of Cariogenic Pathogen: An In vitro Comparative Study
Hanaa M. Elgamily, Hoda S. El-Sayed, Ali Abdelnabi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2018; 9(3): 457. CrossRef - Chitosan-Properties and Applications in Dentistry
Kmiec M
Advances in Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine: Open Access.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the shelf life of chitosan stored in different types of packaging, using colorimetry and dentin microhardness
Antonio Miranda da Cruz-Filho, Angelo Rafael de Vito Bordin, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Débora Fernandes da Costa Guedes, Paulo César Saquy, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Jesus Djalma Pécora
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 87. CrossRef - Restorative materials containing antimicrobial agents: is there evidence for their antimicrobial and anticaries effects? A systematic review
GS do Amaral, T Negrini, M Maltz, RA Arthur
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(1): 6. CrossRef - Antibacterial capacity of cavity disinfectants against Streptococcus mutans and their effects on shear bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Han-Sol CHA, Dong-Hoon SHIN
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(1): 147. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect and Physical-Mechanical Properties of Temporary Restorative Material Containing Antibacterial Agents
Amanda Mahammad Mushashe, Carla Castiglia Gonzaga, Paulo Henrique Tomazinho, Leonardo Fernandes da Cunha, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Janes Francio Pissaia, Gisele Maria Correr
International Scholarly Research Notices.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of conventional restorative filling materials and advances in antimicrobial properties of composite resins and glass ionomer cements—A literature review
Cher Farrugia, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2015; 31(4): e89. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Dental materials with antibiofilm properties
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Dental Materials.2014; 30(2): e1. CrossRef - Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles onStreptococcus mutansandLactobacillus
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 109. CrossRef - Antibakterielle fyllinger - hvor står vi i dag?
Nils Jacobsen
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2014; 124(8): 616. CrossRef
- Dental Resin Composites Modified with Chitosan: A Systematic Review
- 1,913 View
- 14 Download
- 42 Crossref

- Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
- Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):500-507. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.500
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to compare the antibacterial effect of Listerine® on two microorganisms (
P. gingivalis andE. faecalis ) with various root canal irrigants (NaOCl, CHX, EDTA) and to identify possibility of using Listerine® as a root canal irrigant.Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 3327 andEnterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 were used in this experiment. For the test irrigants, 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%, 5.25% NaOCl, 0.1%, 0.2%, 1%, 2% CHX, 0.5M EDTA (18.6% EDTA) and Listerine® were prepared. Distiled water was used as control. Two methods-1) Comparison of turbidity in broth and 2) Agar diffusion test-were used to determine the extent of antibacterial effect of Listerine® and to compare it with that of NaOCl, CHX, and EDTA. All solutions tested were effective against two bacterial strains compared with control (p<0.001). Any concentration of NaOCl, CHX, and EDTA showed similarly high effectiveness against all bacterial strains. In all experiment, Listerine® showed significantly low antibacterial effect compared with the other root canal irrigants (p<0.05).In conclusion, the results reflect remarkably low antibacterial effect of Listerine® as compared with root canal irrigants in general so it is not suitable for the root canal irrigant.
- 967 View
- 2 Download

- The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
- Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):397-404. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.397
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of MTAD, EDTA and sodium hypochlorite(NaOCl) as final irrigants on coronal leakage resistance to
Enterococcus faecalis . Forty extracted human maxillary molars were used in this experiment. The teeth were randomly divided into positive control group (Group 1; n = 5), negative control group (Group 2; n = 5) and three experimental groups (n = 30). In Group 3 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. In Group 4 (n = 10) and 5 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite and rinsed with EDTA and MTAD, respectively. The teeth in each group were cleaned and shaped to #40 profile with .04 taper, and obturated with gutta-percha and AH-26 root canal sealer. The coronal portion of each tooth was placed in contact with inoculum ofEnterococcus faecalis in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) culture media. Each root tip was placed in a vial containing sterile culture media. The vials were placed in anaerobic chamber and observed everyday for turbidity for 180 days. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher's Exact Test. After 180 days, Group 3, 4, and 5 showed 7, 4 and 5 leaking samples respectively. The differences in leakage resistance were not statistically significant among Group 3, 4 and 5.
- 2,051 View
- 6 Download

- Isolation and identification of bacteria from the root canal of the teeth diagnosed as the acute pulpitis and acute periapical abscess
- Yeon-Jae Lee, Mi-Kwang Kim, Ho-Keel Hwang, Joong-Ki Kook
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):409-422. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.409
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to identify the bacteria isolated from acute endodontic lesions by cell culture and 16S rDNA sequencing. The necrotic pulpal tissue was collected from 17 infected root canals, which were diagnosed as being either an acute pulpitis or acute periapical abscess. Samples were collected aseptically from the infected pulpal tissue of the infected root canals using a barbed broach and a paper point. The cut barbed broaches and paper points were transferred to an eppendorf tube containing 500 ul of 1 X PBS. The sample solution was briefly mixed and plated onto a BHI-agar plate containing 5% sheep blood. The agar plates were incubated in a 37℃ anaerobic chamber for 7 days. The bacteria growing on the agar plate were identified by 16S rRNA coding gene (rDNA) cloning and sequencing at the species level. Among the 71 colonies grown on the agar plates, 56 strains survived and were identified. In dental caries involving the root canals,
Streptococcus spp. were mainly isolated.Actinomyces ,Clostridia ,Bacteroides andFusobacteria were isolated in the periapical lesion without dental caries. Interestingly, two newActinomyces spp. (ChDC B639 and ChDC B631) were isolated in this study. These results showed that there was diversity among the species in endodontic lesions. This suggests that an endodontic infection is a mixed infection with a polymicrobial etiology. These results may offer the bacterial strains for pathogenesis studies related to an endodontic infection.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 258. CrossRef - Microbial profile of asymptomatic and symptomatic teeth with primary endodontic infections by pyrosequencing
Sang-Min Lim, Tae-Kwon Lee, Eun-Jeong Kim, Jun-Hong Park, Yoon Lee, Kwang-Shik Bae, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 498. CrossRef
- Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
- 1,423 View
- 11 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
Bacteriologic
in vitro coronal leakage study of before and after post space preparation - Hyo-An Lee, Eui-Seong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):16-21. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of present study was to compare the speed of coronal leakage before and after post space preparation using
Streptococcus mutans .Forty straight extracted human teeth were selected. The crowns were removed to a uniform remaining root length 14 mm. Canals were enlarged by 06 taper Profiles® to a size #40 as a master apical file. And these were filled with gutta percha point and Tubuliseal® sealer, using continuous wave technique. Groupings are as follows.
Group 1 - These teeth were obturated without sealer.
Group 2 - These teeth were obturated and covered the surface of the root completely with sticky wax.
Group 3 - These teeth were obturated.
Group 4 - These teeth were obturated and prepared for post space remaining 5 mm of gutta percha.
The teeth were suspended in plastic tubes. The upper chamber received the bacterial suspension everyday to simulate clinical situation. The lower chamber consisted of BHI added Andrade's indicator.
All roots in the positive control group (Group 1) turned yellow within 24 h and those of negative control group (Group 2) remained red throughout the experimental period (70 days). The samples of group 3 were contaminated within an average of 27.2 days. The samples of group 4 were contaminated within an average of 15.7 days, ranging from 9 to 22 days.
There was significant difference between group 3 and group 4 statistically (p < 0.05).
- 836 View
- 1 Download

- Antibacterial effect of polyphosphate on endodontopathic bacteria
- Jeong-Hee Shin, Sang-Jin Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):435-448. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.435
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was performed to observe the antibacterial effect of polyphosphate (polyP) with various chain lengths (P3~P75) on virulent, invasive strains of
P. gingivalis A7A1-28 and W50, and multidrug resistantE. faecalis ATCC29212.P. gingivalis strains were grown in brain-heart infusion broth (BHI) containing hemin and vitamin K with or without polyP. PolyP was added at the very beginning of the culture or during the exponential growth phase of the culture. Inhibition of the growth ofP. gingivalis was determined by measuring the absorbancy at 540nm of the grown cells. Viable cell counts of the culture and release of intracellular nucleotide fromP. gingivalis were measured.E. faecalis was grown in plain BHI with antibiotics alone or in combination with polyP(calgon; 0.1~1.0%) and the bacterial absorbancy was measured.The overall results suggest that polyP has a strong antibacterial effect on the growth of the virulent strains of
P. gingivalis and the antibacterial activity of polyP seems largely bactericidal, accompanying bacteriolysis in which chelation phenomenon is not involved. Although polyP does not exert antibacterial activity againstE. faecalis , it appears to increase antibacterial effect of erythromycin and tetracycline on the bacterium. Therefore, polyP alone or in combination with antibiotics may be developed as a candidate for the agent controlling oral infections including endodontic infection.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Minocycline-loaded calcium polyphosphate glass microspheres as a potential drug-delivery agent for the treatment of periodontitis
Iain Gibson, Arash Momeni, Mark Filiaggi
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 500. CrossRef
- Minocycline-loaded calcium polyphosphate glass microspheres as a potential drug-delivery agent for the treatment of periodontitis
- 1,047 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A study of ionic dissociation on various calcium hydroxide pastes using molecular sieving model
- Kyoung-Sun Lee, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(6):632-643. Published online November 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.6.632
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was two-fold. First was to evaluate whether the molecular sieving model was appropriate for ionic dissociation experiment. Second was to compare the dissociation of calcium and hydroxyl ions from five types of calcium hydroxide pastes (Pure calcium hydroxide paste, DT temporary dressing®, Metapaste®, Chidopex®, Metapex®) in three vehicles (aqueous, viscous and oily) and the antibacterial effect.
Each calcium hydroxide pastes was placed into 0.65ml tube with cap and then 15% polyacrylamide gel was placed onto calcium hydroxide pastes. After the gel was hardened, the tubes were filled with tridistilled water (pH 7.14) and closed with cap. The tubes were stored in 37℃, 100% incubator. The pH reading and the concentration of calcium ions were taken at 1, 4, 7, 10, and 14 days. The brain heart infusion agar plates with
S. mutans andA. actinomycetemcomitans were used for antibacterial activity test. Middle of agar plate was filled with the calcium hydroxide pastes. The plates were incubated at 37℃ and observations were made to detect the zones of inhibition. These data were evaluated statistically by use of the analysis of variance and duncan test.The results were as follows.
1. In fresh mixing state, the pH of five types of calcium hydroxide pastes were measured between 12.5 and 12.8.
2. The pH was increased in all five types of calcium hydroxide pastes compared with control group. In 14 days, Pure calcium hydroxide paste (11.45) and DT temporary dressing® (11.33) showed highest pH, followed by Metapaste® (9.49), Chidopex® (8.37) and Metapex® (7.59).
3. Calcium was higher in all five types of calcium hydroxide pastes compared with control group. In 14 days, Pure calcium hydroxide paste (137.29 mg%) and DT temporary dressing® (124.6 mg%) showed highest value, followed by Metapaste® (116.74 mg%), Chidopex® (111.84 mg%) and Metapex® (60.22 mg%).
4. The zones of bacterial inhibition were seen around all five types of calcium hydroxide pastes. Chidopex® and Metapex® groups which include iodoform were observed significantly larger zone of inhibition in A. actinomycetemcomitans compared with the other calcium hydroxide groups (p<0.05). However, Metapex® showed the least antibacterial effect on S. mutans compared with other groups (p<0.05).
The molecular sieving model was found to be acceptable in dissociation experiment of hydroxyl and calcium ions when compared with the previous tooth model study. But this model was not appropriate for the antibacterial test.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of the irrigation systems in calcium hydroxide removal
Jae-Seung Eun, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 508. CrossRef
- A Comparison of the irrigation systems in calcium hydroxide removal
- 1,181 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of ultrasonic and sonic root end preparations using anaerobic bacterial leakage model
- Nak-Yeon Cho, Dong-Sung Park, Hyeon-Mee Yoo, Tae-Seok Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(5):530-534. Published online September 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.5.530
- 1,048 View
- 5 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


