Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 28(6); 2003 > Article
- Original Article Antibacterial effect of polyphosphate on endodontopathic bacteria
- Jeong-Hee Shin, Sang-Jin Park, Gi-Woon Choi
-
2003;28(6):-448.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.435
Published online: November 30, 2003
Department of Conservative Dentistry, Division of Dentistry, Graduate School of Kyung Hee University, Korea.
- Corresponding author (gwchoi@khu.ac.kr)
Copyright © 2003 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,042 Views
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
-
This study was performed to observe the antibacterial effect of polyphosphate (polyP) with various chain lengths (P3~P75) on virulent, invasive strains of P. gingivalis A7A1-28 and W50, and multidrug resistant E. faecalis ATCC29212. P. gingivalis strains were grown in brain-heart infusion broth (BHI) containing hemin and vitamin K with or without polyP. PolyP was added at the very beginning of the culture or during the exponential growth phase of the culture. Inhibition of the growth of P. gingivalis was determined by measuring the absorbancy at 540nm of the grown cells. Viable cell counts of the culture and release of intracellular nucleotide from P. gingivalis were measured. E. faecalis was grown in plain BHI with antibiotics alone or in combination with polyP(calgon; 0.1~1.0%) and the bacterial absorbancy was measured.The overall results suggest that polyP has a strong antibacterial effect on the growth of the virulent strains of P. gingivalis and the antibacterial activity of polyP seems largely bactericidal, accompanying bacteriolysis in which chelation phenomenon is not involved. Although polyP does not exert antibacterial activity against E. faecalis, it appears to increase antibacterial effect of erythromycin and tetracycline on the bacterium. Therefore, polyP alone or in combination with antibiotics may be developed as a candidate for the agent controlling oral infections including endodontic infection.
- 1. Dahlen G, Moller AJR. In: Slots J, Taubman MA, editors. Microbiology of endodontic infections. Contemporary oral microbiology and immunology. 1992;St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book Inc; 444-475.
- 2. Miller WD. Microorganisms of the human mouth. 1890;Philadelphia: S.S. White Dental Co.
- 3. Henrici AT, Hartzell TB. The bacteriology of vital pulp. J Dent Res. 1919;1: 419-422.ArticlePDF
- 4. Haapasalo M. Black-pigmented Gram-negative anaerobes in endodontic infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993;6: 213-218.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Kobayashi T, Hayashi A, Yoshikawa R, Okuda K, Hara K. The microbial flora from root canals and periodontal pockets of non-vital teeth associated with advanced periodontitis. Int Endod J. 1990;23: 100-106.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Van Winkelhoff AJ, Carlee AW, de Graaff J. Bacteroides endodontalis and other black-pigmented Bacteroides species in odontogenic abscesses. Infect Immun. 1985;49: 494-497.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Haapasalo M. Bacteroides spp. in dental root canal infections. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1989;5: 1-10.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Sundqvist G, Johansson E, Sjögren U. Prevalence of black-pigmented Bacteroides species in root canal infections. J Endod. 1989;15: 13-19.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Rupf S, Kannengiesser S, Merte K, Pfister W, Sigusch B, Eschrich K. Comparison of profiles of key periodontal pathogens in periodontium and endodontium. Endod Dent Traumatol. 2000;16: 269-275.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Rocas IN, Siqueira JF Jr, Santos KR, Coelho AM. "Red complex"(Bacteroides forsythus, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Treponema denticola) in endodontic infections: a molecular approach. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;91: 468-471.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Sundqvist G. Bacteriological studies of necrotic dental pulps. 1976;Umea University, Odontology; Thesis. Dissertation No. 7, (cited from the reference No. 4).
- 12. Griffee MB, Patterson SS, Miller CH, Kafrawy AH, Newton CW. The relationship of Bacteroides melaninogenicus to symptoms associated with pulpal necrosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1980;50: 457-461.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Yoshida M, Fukushima H, Yamamoto K, Ogawa K, Toda T, Sagawa H. Correlation between clinical symptoms and microorganisms isolated from root canals with periapical lesions. J Endod. 1987;13: 24-28.PubMed
- 14. Haapasalo M, Ranta H, Ranta K, Shah H. Black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. in human apical periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1986;53: 149-153.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Mayrand D, Holt SC. Biology of asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides species. Microbiol Rev. 1988;52: 134-152.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Socransky SS, Haffajee AD. Microbial mechanisms in the pathogenesis of destructive periodontal diseases: a critical assessment. J Periodont Res. 1991;26: 195-212.Article
- 17. Van Winkelhoff AJ, van Steenbergen TJM, Kippuw N, de Graaff J. Enzymatic characterization of oral and nonoral black-pigmented Bacteroides species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1986;52: 163-171.PubMed
- 18. Nakamura R, Hinode D, Terai H, Morioka M. In: Hamada S, Holt SC, McGhee JR, editors. Extracellualr enzymes of Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis in relation to periodontal destruction. Periodontal diseases: pathogens and host immune responses. 1991;Tokyo: Quintessence Publishing Co., Ltd.; 129-141.
- 19. Wingrove JA, DiScipio RG, Chen Z, Potempa J, Travis J, Hugli TE. Activation of complements C3 and C5 by a cysteine proteinase (Gingipain-1) from Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. J Biol Chem. 1992;267: 18902-18907.PubMed
- 20. Frandsen EVG. In: Shah HN, Mayrand D, Genco RJ, editors. Hydrolysis of immunoglobulins. Biology of the species Porphyromonas gingivalis. 1993;Boca Raton: CRC Press; 219-226.
- 21. Jagels MA, Travis J, Potempa J, Pike R, Hugli TE. Proteolytic inactivation of the leukocyte C5a receptor by proteinases derived from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1996;64: 1984-1991.PubMedPMC
- 22. Tai H, Kobayashi T, Hara K. Changes in complement and immunoglobulin G receptor expresssion on neutrophils associated with Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced inhibition of phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1993;61: 3533-3535.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Ding Y, Haapasalo M, Kerosuo E, Lounatmaa K, Kotiranta A, Sorsa T. Release and activation of human neutrophil matrix metallo- and serine proteinases during phagocytosis of Fusobacterium nucleatum, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola. J Clin Periodontol. 1997;24: 237-248.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Hamada N, Watanabe K, Arai M, Hiramine H, Umemoto T. Cytokine production induced by a 67-kDa fimbrial protein from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002;17: 197-200.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Lee JY, Sojar HT, Bedi GS, Genco RJ. Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbrillin: size, amino-terminal sequence, and antigenic heterogeneity. Infect Immun. 1991;59: 383-389.PubMedPMC
- 26. Amano A, Nakagawa I, Kataoka K, Morisaki I, Hamada S. Distribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis strains with fimA genotypes in periodontitis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37: 1426-1430.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Genco CA, Cutler CW, Kapczynski D, Maloney K, Arnold RR. A novel mouse model to study the virulence of and host response to Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1991;59: 1255-1263.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Evans RT, Klausen B, Ramamurthy NS, Golub LM, Sfintescu C, Genco RJ. Periodontopathic potential of two strains of Porphyromonas gingivalis in gnotobiotic rat. Arch Oral Biol. 1992;37: 813-819.PubMed
- 29. Katz J, Ward DC, Michalek SM. Effect of host responses on the pathogenicity of strains of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1996;11: 309-318.PubMed
- 30. Ebersole JL, Kesavalu L, Schneider SL, Machen RL, Holt SC. Comparative virulence of periodontopathogens in a mouse abscess model. Oral Dis. 1995;1: 115-128.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Baker PJ, Dixon M, Evans RT, Roopenian DC. Heterogeneity of Porphyromonas gingivalis strains in the induction of alveolar bone loss in mice. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2000;15: 27-32.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Sundqvist G, Figdor D, Persson S, Sjogren U. Microbiologic analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;85: 86-93.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Hancock HH 3rd, Sigurdsson A, Trope M, Moiseiwitsch J. Bacteria isolated after unsuccessful endodontic treatment in a North American population. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;91: 579-586.PubMed
- 34. Morrison D, Woodford N, Cookson B. Enterococci as emerging pathogens of humans. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1997;26: S89-S99.ArticlePDF
- 35. Jett BD, Huycke MM, Gilmore MS. Virulence of enterococci. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1994;7: 462-478.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 36. Wahlin YB, Holm AK. Changes in the oral microflora in patients with acute leukemia and related disorders during the period of induction therapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988;65: 411-417.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Rams TE, Feik D, Lisgarten MA, Slots J. Enterococci in human periodontitis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1992;7: 249-252.PubMed
- 38. Dahlen G, Samuelsson W, Molander A, Reit C. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococci isolated from the root canal. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2000;15: 309-312.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Linden PK. Treatment options for vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infections. Drugs. 2002;62: 425-441.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Lima KC, Fava LR, Siqueira JF Jr. Susceptibilities of Enterococcus faecalis biofilms to some antimicrobial medications. J Endod. 2001;27: 616-619.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Gomes BP, Ferraz CC, Vianna ME, Berber VB, Teixeira FB, Souza-Filho FJ. In vitro antimicrobial activity of several concentrations of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate in the elimination of Enterococcus faecalis. Int Endod J. 2001;34: 424-428.PubMed
- 42. Almyroudi A, Mackenzie D, McHugh S, Saunders WP. The effectiveness of various disinfectants used as endodontic intracanal medications: an in vitro study. J Endod. 2002;28: 163-167.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Love RM. Enterococcus faecalis--a mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int Endod J. 2001;34: 399-405.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 44. Ørstavik D, Haapasalo M. Disinfection by endodontic irrigants and dressings of experimentally infected dentinal tubules. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990;6: 142-149.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Haapasalo HK, Sirén EK, Waltimo TM, Ørstavik D, Haapasalo MP. Inactivation of local root canal medicaments by dentine: an in vitro study. Int Endod J. 2000;33: 126-131.PubMed
- 46. Molander A, Reit C, Dahlen G. The antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide in root canals pretreated with 5% iodine potassium iodide. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1999;15: 205-209.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Sirén EK, Haapasalo MP, Ranta K, Salmi P, Kerosuo EN. Microbiological findings and clinical treatment procedures in endodontic cases selected for microbiological investigation. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 91-95.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Fuss Z, Charniaque O, Pilo R, Weiss E. Effect of various mixing ratios on antibacterial properties and hardness of endodontic sealers. J Endod. 2000;26: 519-522.ArticlePubMed
- 49. Fuss Z, Weiss EI, Shalhav M. Antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-containing endodontic sealers on Enterococcus faecalis in vitro. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 397-402.PubMed
- 50. Shalhav M, Fuss Z, Weiss EI. In vitro antibacterial activity of a glass ionomer endodontic sealer. J Endod. 1997;23: 616-619.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Park SB, Choi GU, Choi HY. Effect of polyphosphate in root canal sealers on the growth of oral bacteria. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2001;26: 141-152.
- 52. Economides N, Kotsaki-Kovatsi VP, Poulopoulos A, Kolokuris I, Rozos G, Shore R. Experimental study of the biocompatibility of four root canal sealers and their influence on the zinc and calcium content of several tissues. J Endod. 1995;21: 122-127.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Andrés MT, Chung WO, Roberts MC, Fierro JF. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, and Prevotella nigrescens spp. isolated in Spain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42: 3022-3023.PubMedPMC
- 54. Chung WO, Gabany J, Persson GR, Roberts MC. Distribution of erm(F) and tet(Q) genes in 4 oral bacterial species and genotypic variation between resistant and susceptible isolates. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29: 152-158.PubMed
- 55. Kulaev IS. Biochemistry of inorganic polyphosphates. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;73: 131-158.ArticlePubMed
- 56. Kornberg A, Narayama NR, Ault-Riche D. Inorganic polyphosphate: a molecule of many functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68: 89-125.ArticlePubMed
- 57. U. S. Department of Agriculture. Meat and poultry products: phosphates and sodium hydroxide. Federal Regist Rule Regul. 1982;47: 10779.
- 58. Zaika LL, Kim AH. Effect of sodium polyphosphate on growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Food Prot. 1993;56: 577-580.PubMed
- 59. Lee RM, Hartman PA, Stahr HM, Olson DG, Williams FD. Antibacterial mechanism of long-chain polyphosphates in Staphylococcus aureus. J Food Prot. 1994;57: 289-294.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 60. Tanzer JM, Hageage GJ Jr. Polyphosphate inhibition of growth of plaque formed by streptococci and diphtheroids implicated in oral disease. Infect Immun. 1970;1: 604-606.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 61. Shibata H, Morioka T. Antibacterial action of condensed phosphates on the bacterium Streptococcus mutans and experimental caries in the hamster. Arch Oral Biol. 1982;27: 809-816.PubMed
- 62. Gong HJ, Choi HY, Min BS, Park SJ, Lee JY, Choi GU. Eeffect of polyphosphate on the growth of oral bacterium, Prevotella intermedia. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1998;23: 550-560.
- 63. Choi EG, Kim HY, Lee JY, Choi IS, Park BL, Shin JW, Choi YC. Antibacterial Effect of Polyphosphates on Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1999;34: 285-301.
- 64. Ayres HM, Furr JR, Russell AD. Effect of permeabilizers on antibiotic sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1999;28: 13-16.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 65. Socransky SS, Haffajee AD, Cugini MA, Smith C, Kent RL Jr. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25: 134-144.PubMed
- 66. Yao ES, Lamont RJ, Leu SP, Weinberg A. Interbacterial binding among strains of pathogenic and commensal oral bacterial species. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1996;11: 35-41.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Nilius AM, Spencer SC, Simonson LG. Stimulation of in vitro growth of Treponema denticola by extracellular growth factors produced by Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1993;72: 1027-1031.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 68. Torabinejad M, Hong CU, Pitt Ford TR, Kettering JD. Antibacterial effets of some root end filling materials. J Endod. 1995;21: 403-406.PubMed
- 69. Jones ME, Gesu G, Ortisi G, Sahm DF, Critchley IA, Goglio A. Proficiency of Italian clinical laboratories in detecting reduced glycopeptide susceptibility in Enterococcus and Staphylococcus spp. using routine laboratory methodologies. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2002;8: 101-111.PubMed
- 70. Chow JW, Davidson A, Sanford E 3rd, Zervos MJ. Superinfection with Enterococcus faecalis during quinupristin/dalfopristin therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24: 91-92.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Choi SB, Park SJ, Choi GW, Choi HY. Mechanism in antibacterial activity of polyphosphates against Porphyromonas endodontalis. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2000;25: 561-574.
- 72. Kang KS. Antibacterial effect of polyphosphates on mutans streptococci. 2001;Kyung Hee University; Doctoral dissertation.
- 73. Kim TJ. Antibacterial effect of polyphosphate on Candida albicans. 2002;Kyung Hee University; Master's thesis.
- 74. Knabel SJ, Walker HW, Hartman PA. Inhibition of Aspergillus flavus and selected Gram-positive bacteria by chelation of essential metal contains by polyphosphate. J Food Prot. 1991;54: 360-365.PubMed
- 75. Ellwood DC, Tempest DW. Effects of environment on bacterial wall content and composition. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;7: 83-117.
- 76. Post FJ, Krishnamurty GB, Flanagan MD. Influence of sodium hexametaphosphate on selected bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1963;11: 430-435.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 77. Van Steenbergen TJM, Kastelein P, Touw JJA, de Graaff J. Virulence of black-pigmented Bacteroides strains from periodontal pockets and other sites in experimentally induced skin lesions in mice. J Periodontal Res. 1982;17: 41-49.ArticlePubMed
- 78. Neiders ME, Chen PB, Suido H, Reynolds HS, Zambon JJ, Shlossman M, Genco RJ. Heterogeneity of virulence among strains of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Periodontal Res. 1989;24: 192-198.ArticlePubMed
- 79. Chen PB, Neiders ME, Millar SJ, Reynolds HS, Zambon JJ. Effect of immunization on experimental Bacteroides gingivalis infection in a murine model. Infect Immun. 1987;55: 2534-2537.PubMedPMC
- 80. Engström B. The significance of enterococci in root canal treatment. Odont Revy. 1964;15: 87-106.
- 81. Ayres H, Furr JR, Russell AD. A rapid method of evaluating permeabilizing activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1993;17: 149-151.Article
- 82. Seymour RA, Heasman PA. Tetracyclines in the management of periodontal diseases. A review. J Clin Periodontol. 1995;22: 22-35.PubMed
- 83. Vernillo AT, Rifkin BR. Effects of tetracyclines on bone metabolism. Adv Dent Res. 1998;12: 56-62.PubMed
- 84. Lee JY, Ryu DM, Shin JW. Inorganic polyphosphate promotes bone regeneration. Korean J Oral Anat. 1999;23: 219-235.
REFERENCES
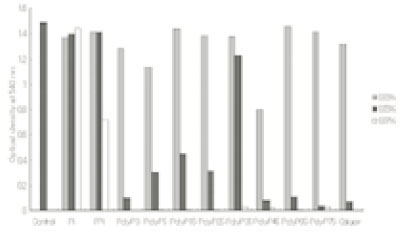
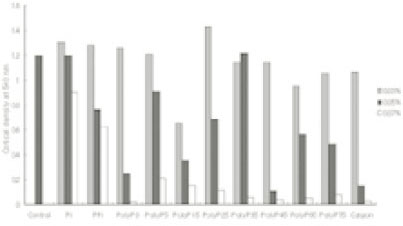
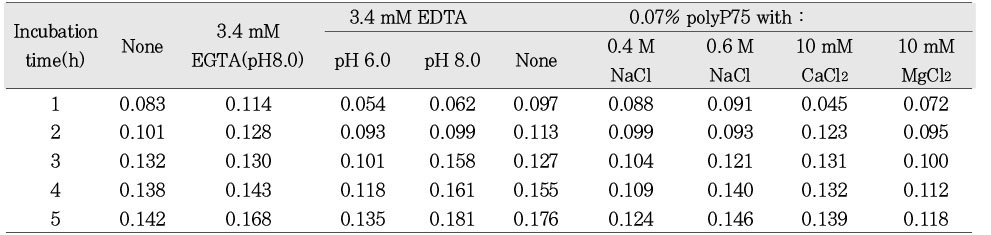
a; Cells grown up to their optical density of 0.6 at 540 nm were further incubated with various reagents alone or in combination and then intracellular nucleotide release from the cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm.
a; Cells grown up to their optical density of 0.6 at 540 nm were further incubated with various reagents alone or in combination and then intracellular nucleotide release from the cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm.
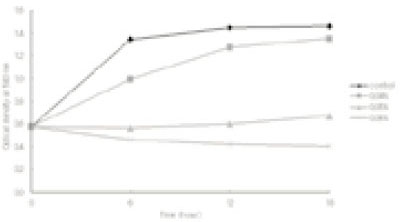
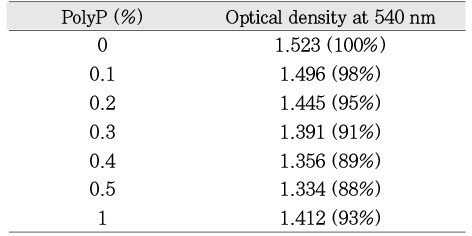
a; Calgon at the concentrations of 0.1~1.0% was added to an inoculum of E. faecalis in BHI at the very beginning of the culture and incubated for 12 h anaerobically. Change in the growth of the bacterial cells was determined by measuring the optical density at 540 nm.
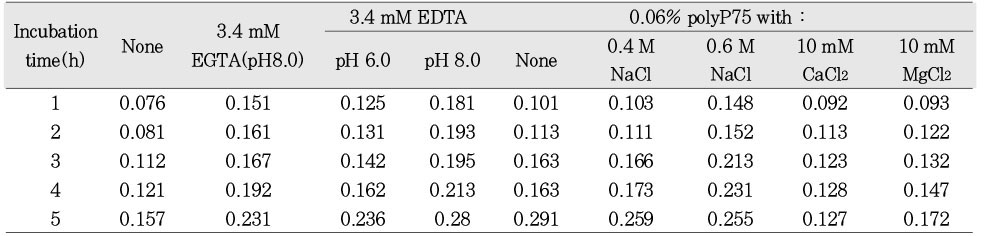
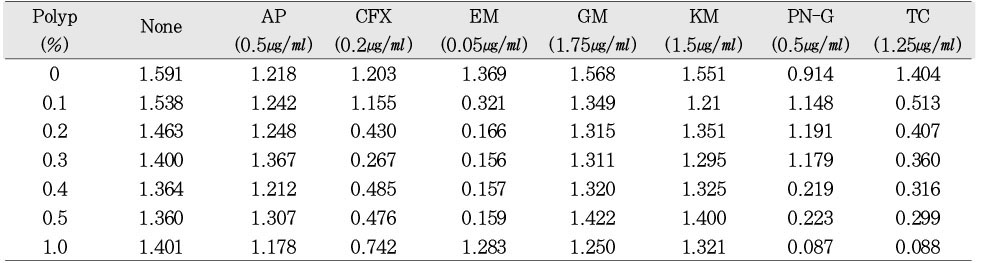
a; Antibiotics at lower concentrations with or without Calgon (0.1~1.0%) were added to the culture and incubated as described in Table 3. The optical density of growing E. faecalis cells was determined at 540 nm.
Abbreviation; AP, ampicillin; CFX, cefotaxime; EM, erythromycin; GM, gentamicin; KM, kanamycin; PN-G, pencillin-G; TC, tetracycline.
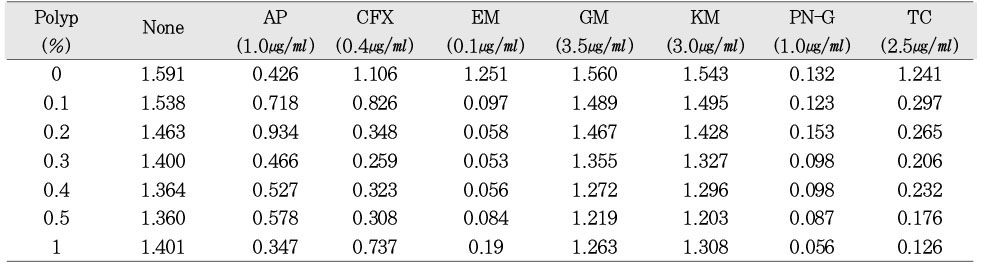
a; The experiment was performed as described in Table 4 except that the amount of antibiotics added was doubled.
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Minocycline-loaded calcium polyphosphate glass microspheres as a potential drug-delivery agent for the treatment of periodontitis
Iain Gibson, Arash Momeni, Mark Filiaggi
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 500. CrossRef
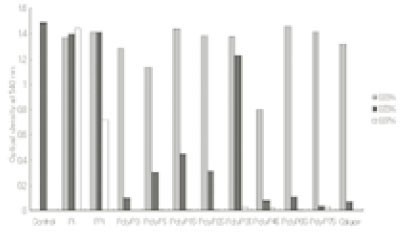
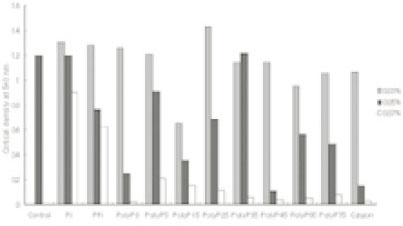
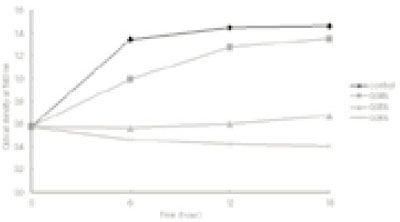
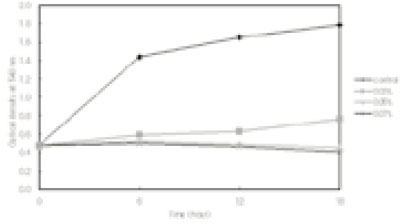
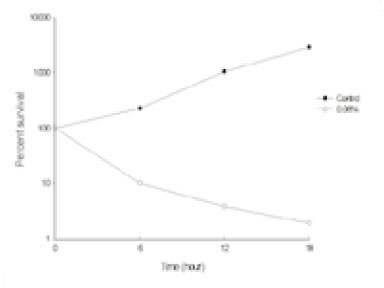
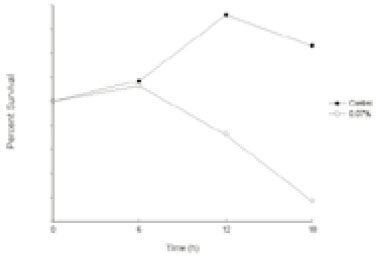
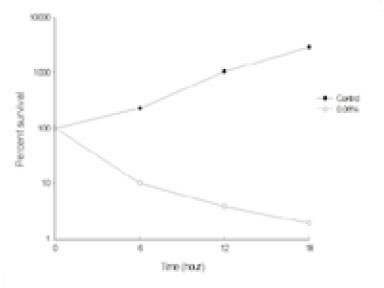
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
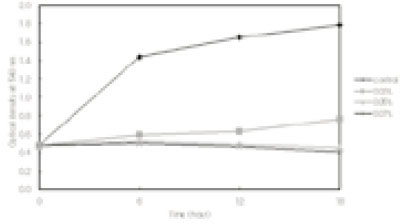
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Leakage of intracellular nucleotide from P. gingivalis A7A1-28 in the presence of polyP75a
a; Cells grown up to their optical density of 0.6 at 540 nm were further incubated with various reagents alone or in combination and then intracellular nucleotide release from the cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm.
Leakage of intracellular nucleotide from P. gingivalis W50 in the presence of polyP75a
a; Cells grown up to their optical density of 0.6 at 540 nm were further incubated with various reagents alone or in combination and then intracellular nucleotide release from the cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm.
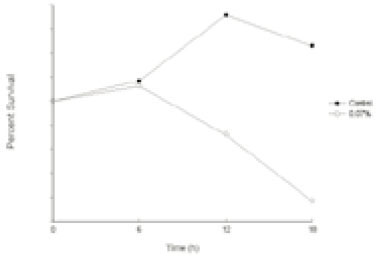
Effect of polyP (Calgon) on the growth of E. faecalis ATCC 29212a
a; Calgon at the concentrations of 0.1~1.0% was added to an inoculum of E. faecalis in BHI at the very beginning of the culture and incubated for 12 h anaerobically. Change in the growth of the bacterial cells was determined by measuring the optical density at 540 nm.
Permeabilizing effect of polyP on sensitivity of E. faecalis to various antibiotics at lower concentrations as measured the bacterial optical density at 540 nma
a; Antibiotics at lower concentrations with or without Calgon (0.1~1.0%) were added to the culture and incubated as described in
Abbreviation; AP, ampicillin; CFX, cefotaxime; EM, erythromycin; GM, gentamicin; KM, kanamycin; PN-G, pencillin-G; TC, tetracycline.
Permeabilizing effect of polyP on sensitivity of E. faecalis to various antibiotics at higher concentrations as measured the bacterial optical density at 540 nma
a; The experiment was performed as described in
a; Cells grown up to their optical density of 0.6 at 540 nm were further incubated with various reagents alone or in combination and then intracellular nucleotide release from the cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm.
a; Cells grown up to their optical density of 0.6 at 540 nm were further incubated with various reagents alone or in combination and then intracellular nucleotide release from the cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm.
a; Calgon at the concentrations of 0.1~1.0% was added to an inoculum of E. faecalis in BHI at the very beginning of the culture and incubated for 12 h anaerobically. Change in the growth of the bacterial cells was determined by measuring the optical density at 540 nm.
a; Antibiotics at lower concentrations with or without Calgon (0.1~1.0%) were added to the culture and incubated as described in Abbreviation; AP, ampicillin; CFX, cefotaxime; EM, erythromycin; GM, gentamicin; KM, kanamycin; PN-G, pencillin-G; TC, tetracycline.
a; The experiment was performed as described in

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

