Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of 3 different light-curing units on the physico-mechanical properties of bleach-shade resin composites
- Azin Farzad, Shahin Kasraei, Sahebeh Haghi, Mahboubeh Masoumbeigi, Hassan Torabzadeh, Narges Panahandeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e9. Published online February 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
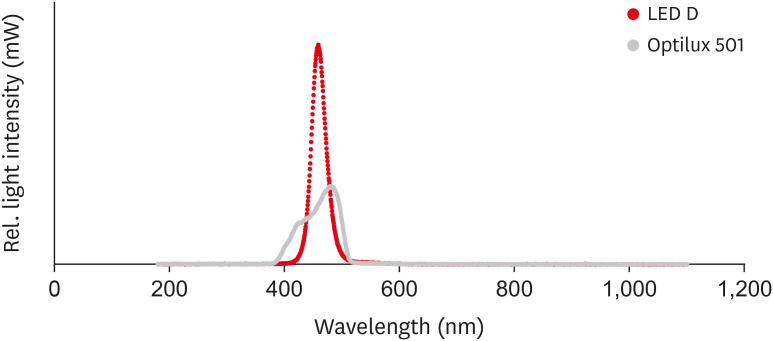
ePub Objectives This study investigated the microhardness, flexural strength, and color stability of bleach-shade resin composites cured with 3 different light-curing units.
Materials and Methods In this
in vitro experimental study, 270 samples were fabricated of bleach and A2 shades of 3 commercial resin composites (Point 4, G-aenial Anterior, and Estelite Sigma Quick). Samples (n = 5 for each trial) were cured with Bluephase N, Woodpecker LED.D, and Optilux 501 units and underwent Vickers microhardness and flexural strength tests. The samples were tested after 24 hours of storage in distilled water. Color was assessed using a spectrophotometer immediately after preparation and 24 hours after curing. Data were analyzed using 3-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test (p ≤ 0.001).Results Samples cured with Optilux exhibited the highest and those cured with LED.D exhibited the lowest microhardness (
p = 0.023). The bleach shade of Point 4 composite cured with Optilux displayed the highest flexural strength, while the same composite and shade cured with Sigma Quick exhibited the lowest (p ≤ 0.001). The color change after 24 hours was greatest for the bleach shade of G-aenial cured with Bluephase N and least for the A2 shade of Sigma Quick cured with Optilux (p ≤ 0.001).Conclusions Light curing with polywave light-emitting diode (LED) yielded results between or statistically similar to those of quartz-tungsten-halogen and monowave LED in the microhardness and flexural strength of both A2 and bleach shades of resin composites. However, the brands of light-curing devices showed significant differences in color stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
Ghada H. Naguib, Jumana Mazhar, Abeer Alnowaiser, Abdulghani Mira, Hisham Mously, Rabab Aljawi, Samar H. Abuzinadah, Mohamed T. Hamed
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1136. CrossRef - Repair Bond Strength of Aged Composite: Effect of Thermocycling and Surface Treatment
Sina Yarmoradian, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani, Elham Ahmadi, Niyousha Rafeie, Mahdi Abbasi, Nastaran Dabiri Shahabi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(3): 228. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Depth of Cure by Microhardness of Bulk-Fill Composites with Monowave and Polywave LED Light-Curing Units
Socratis Thomaidis, Dimitris Kampouropoulos, Maria Antoniadou, Afrodite Kakaboura
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11532. CrossRef - Effect of hard segment chemistry and structure on the self‐healing properties of UV‐curable coatings based on the urethane acrylates with built‐in Diels–Alder adduct
Paulina Bednarczyk, Karolina Mozelewska, Małgorzata Nowak, Joanna Klebeko, Joanna Rokicka, Paula Ossowicz‐Rupniewska
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dental Bleaching Agents on the Surface Roughness of Dental Restoration Materials
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Tuculina, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Cristiana Petcu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Ana Maria Rîcă, Ruxandra Voinea-Georgescu
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1067. CrossRef - Effect of Polywave and Monowave Light Curing Units on Color Change of Composites Containing Trime-thylbenzoyl-Diphenyl-Phosphine Before and After Aging
Negar Madihi, Maryam Hoorizad ganjkar, Negin Nasoohi, Ali Kaboudanian Ardestani
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 249. CrossRef
- Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
- 2,212 View
- 35 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Errors in light-emitting diodes positioning when curing bulk fill and incremental composites: impact on properties after aging
- Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora M. Garcia, Haifa Maktabi, Maria Salem Ibrahim, Qoot Alkhubaizi, Howard Strassler, Fabrício M. Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e51. Published online September 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e51

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of improper positioning single-peak and multi-peak lights on color change, microhardness of bottom and top, and surface topography of bulk fill and incremental composites after artificial aging for 1 year.
Materials and Methods Bulk fill and incremental composites were cured using multi-peak and single-peak light-emitting diode (LED) following 4 clinical conditions: (1) optimal condition (no angulation or tip displacement), (2) tip-displacement (2 mm), (3) slight tip angulation (α = 20°) and (4) moderate tip angulation (α = 35°). After 1-year of water aging, the specimens were analyzed for color changes (ΔE), Vickers hardness, surface topography (Ra, Rt, and Rv), and scanning electron microscopy.
Results For samples cured by single-peak LED, the improper positioning significantly increases the color change compared to the optimal position regardless of the type of composite (
p < 0.001). For multi-peak LED, the type of resin composite and the curing condition displayed a significant effect on ΔE (p < 0.001). For both LEDs, the Vickers hardness and bottom/top ratio of Vickers hardness were affected by the type of composite and the curing condition (p < 0.01).Conclusions The bulk fill composite presented greater resistance to wear, higher color stability, and better microhardness than the incremental composite when subjected to improper curing. The multi-peak LED improves curing under improper conditions compared to single-peak LED. Prevention of errors when curing composites requires the attention of all personnel involved in the patient's care once the clinical relevance of the appropriate polymerization reflects on reliable long-term outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
Elizbeth Christy Jose, Sakshi Jha, Prema Shantagouda Biradar, J Arun, TN Nandini, Thushara Mohanan
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2025; 15(1): 41. CrossRef - The demineralization resistance and mechanical assessments of different bioactive restorative materials for primary and permanent teeth: an in vitro study
Maria Salem Ibrahim, Fahad Rakad Aldhafeeri, Abdullah Sami Banaemah, Mana S. Alhaider, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef
- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
- 1,719 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of adhesive application method on repair bond strength of composite
- Hee Kyeong Oh, Dong Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e32. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
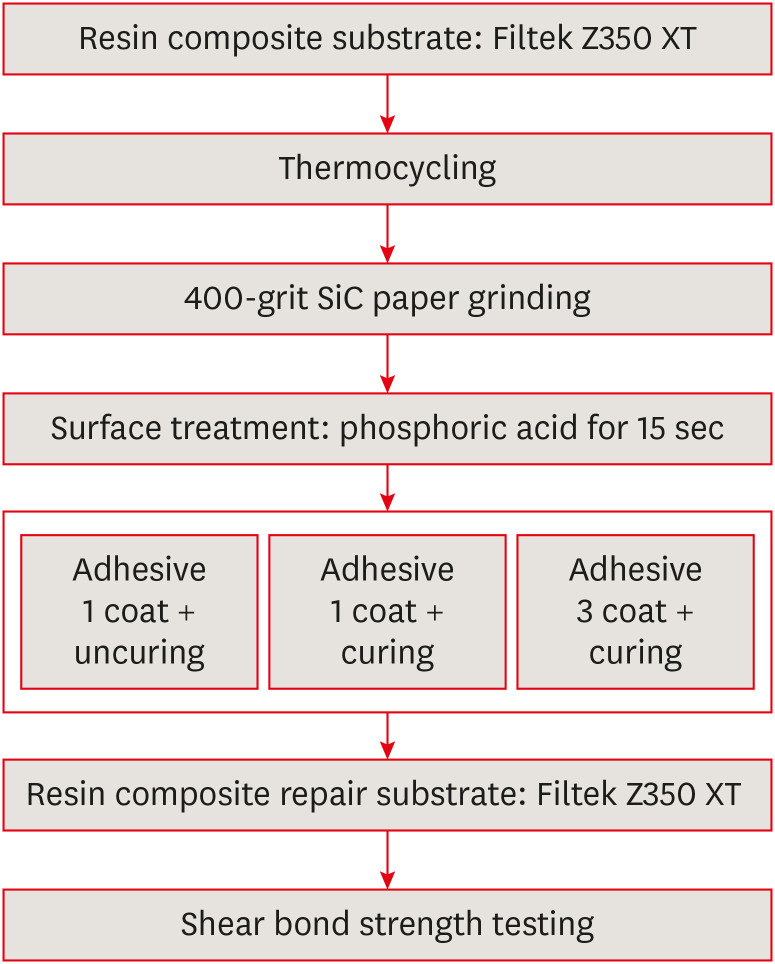
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of the application method of universal adhesives on the shear bond strength (SBS) of repaired composites, applied with different thicknesses.
Materials and Methods The 84 specimens (Filtek Z350 XT) were prepared, stored in distilled water for a week and thermocycled (5,000 cycles, 5°C to 55°C). They were roughened using 400-grit sandpapers and etched with phosphoric acid. Then, specimens were equally divided into 2 groups; Single Bond Universal (SU) and Prime&Bond Universal (PB). Each group was subdivided into 3 subgroups according to application methods (
n = 14); UC: 1 coat + uncuring, 1C: 1 coat + curing, 3C: 3 coats + curing. After storage of the repaired composite for 24 hours, specimens were subjected to the SBS test and the data were statistically analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance and independentt -tests. Specimens were examined with a stereomicroscope to analyze fracture mode and a scanning electron microscope to observe the interface.Results Adhesive material was a significant factor (
p = 0.001). Bond strengths with SU were higher than PB. The highest strength was obtained from the 1C group with SU. Bonding in multiple layers increased adhesive thicknesses, but there was no significant difference in SBS values (p = 0.255). Failure mode was predominantly cohesive in old composites.Conclusions The application of an adequate bonding system plays an important role in repairing composite resin. SU showed higher SBS than PB and the additional layers increased the adhesive thickness without affecting SBS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different surface treatments and adhesive systems on shear bond strength in universal nanohybrid composite resin repair
Merve Kütük Ömeroğlu, Melek Çam, Işıl Doğruer, Zeynep Buket Kaynar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Universal Adhesive Etching Mode on Shear Bond Strength of Pulp Capping Materials to Deep Dentin
Shahram Amirifar, Saba Tohidkhah, Seyedeh Mahsa Sheikh-Al-Eslamian, Mahdi Abbasi, Fatemeh Farshad, Elham Ahmadi, Carlos M. Ardila
BioMed Research International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength and Finite Element Stress Analysis of Composite Repair Using Various Adhesive Strategies With and Without Silane Application
Elif Ercan Devrimci, Hande Kemaloglu, Cem Peskersoy, Tijen Pamir, Murat Turkun
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(15): 8159. CrossRef
- The effect of different surface treatments and adhesive systems on shear bond strength in universal nanohybrid composite resin repair
- 3,798 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Assessment of the radiant emittance of damaged/contaminated dental light-curing tips by spectrophotometric methods
- Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora Garcia, Fabrício Collares, Cristopher M. Felix, Nisha Ganesh, Qoot Alkabashi, Ward Massei, Howard Strassler, Mary Anne Melo
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e55. Published online November 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
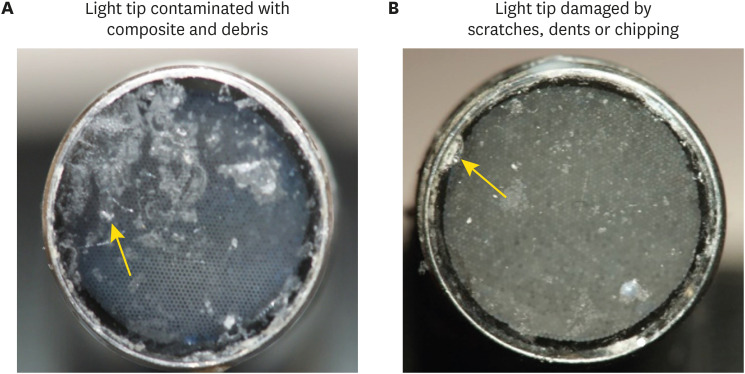
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effects of physically damaged and resin-contaminated tips on radiant emittance, comparing them with new undamaged, non-contaminated tips using 3 pieces of spectrophotometric laboratory equipment.
Materials and Methods Nine tips with damage and/or resin contaminants from actual clinical situations were compared with a new tip without damage or contamination (control group). The radiant emittance was recorded using 3 spectrophotometric methods: a laboratory-grade thermopile, a laboratory-grade integrating sphere, and a portable light collector (checkMARC).
Results A significant difference between the laboratory-grade thermopile and the laboratory-grade integrating sphere was found when the radiant emittance values of the control or damaged/contaminated tips were investigated (
p < 0.05), but both methods were comparable to checkMARC (p > 0.05). Regardless of the method used to quantify the light output, the mean radiant emittance values of the damaged/contaminated tips were significantly lower than those of the control (p < 0.05). The beam profile of the damaged/contaminated tips was less homogeneous than that of the control.Conclusions Damaged/contaminated tips can reduce the radiant emittance output and the homogeneity of the beam, which may affect the energy delivered to composite restorations. The checkMARC spectrophotometer device can be used in dental offices, as it provided values close to those produced by a laboratory-grade integrated sphere spectrophotometer. Dentists should assess the radiant emittance of their light-curing units to ensure optimal curing in photoactivated, resin-based materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of damage or contamination to the tips of 200 light-curing units
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Hassan A. Alyami, Husain A. Almakrami, Osama A. Alsulaiman, Eman H. Ismail, Richard B. Price, Ahmed A. Alsulaiman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Performance of Light-curing Units Used in Different Clinics at Aseer Region, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-sectional Study
Mohammed M Al Moaleem, Ghadeer S Alwadai, Nada A Alamoudi, Naif N Abogazalah, Saleh A Alqahtani, Faisal H Alshehri, Wafa H Alaajam, Mohammad A Alamri, Amjad Y Alhaydan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 784. CrossRef - Evaluation of Radiant Power of the Light Curing Units Used in Clinics at Governmental and Privates Dental Faculties
Sami Ali Hasan, Ibrahim Al-Shami, Mohsen Al-Hamzi, Ghadeer Alwadai, Nada Alamoudi, Saleh Alqahtani, Arwa Daghrery, Wafa Alaajam, Mansoor Shariff, Hussain Kinani, Mohammed Al Moaleem
Medical Devices: Evidence and Research.2024; Volume 17: 301. CrossRef - Evaluation of the information provided in the instruction manuals of dental light‐curing units
Afnan O. Al‐Zain, Eman H. Ismail, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Osamah Toras, Yousif Alharthy, Rafa Alsultan, Abeer Alrossais, Richard B. Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(10): 1466. CrossRef - Utilizing Light Cure Units: A Concise Narrative Review
Fatin A. Hasanain, Hani M. Nassar
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1596. CrossRef - Improper Light Curing of Bulkfill Composite Drives Surface Changes and Increases S. mutans Biofilm Growth as a Pathway for Higher Risk of Recurrent Caries around Restorations
Haifa Maktabi, Maria Salem Ibrahim, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Qoot Alkhubaizi, Isadora Martini Garcia, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares, Howard Strassler, Ana Paula P. Fugolin, Carmem S. Pfeifer, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(8): 83. CrossRef
- Effect of damage or contamination to the tips of 200 light-curing units
- 1,742 View
- 8 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Light transmittance of CAD/CAM ceramics with different shades and thicknesses and microhardness of the underlying light-cured resin cement
- Zahra Jafari, Homayoon Alaghehmand, Yasaman Samani, Mina Mahdian, Soraya Khafri
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e27. Published online June 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the effects of the thickness and shade of 3 types of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials.Materials and Methods A total of 120 specimens of 2 shades (A1 and A3) and 2 thicknesses (1 and 2 mm) were fabricated using VITA Mark II (VM; VITA Zahnfabrik), IPS e.max CAD (IE; IvoclarVivadent), and VITA Suprinity (VS; VITA Zahnfabrik) (
n = 10 per subgroup). The amount of light transmission through the ceramic specimens was measured by a radiometer (Optilux, Kerr). Light-cured resin cement samples (Choice 2, Bisco) were fabricated in a Teflon mold and activated through the various ceramics with different shades and thicknesses using an LED unit (Bluephase, IvoclarVivadent). In the control group, the resin cement sample was directly light-cured without any ceramic. Vickers microhardness indentations were made on the resin surfaces (KoopaPazhoohesh) after 24 hours of dark storage in a 37°C incubator. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance followed by the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05).Results Ceramic thickness and shade had significant effects on light transmission and the microhardness of all specimens (
p < 0.05). The mean values of light transmittance and microhardness of the resin cement in the VM group were significantly higher than those observed in the IE and VS groups. The lowest microhardness was observed in the VS group, due to the lowest level of light transmission (p < 0.05).Conclusion Greater thickness and darker shades of the 3 types of CAD/CAM ceramics significantly decreased the microhardness of the underlying resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
Shervin Reybod, Fariba Ezoji, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenouz, Behnaz Esmaeili
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Ultrasonic Scaling on Microleakage in Lithium Disilicate Crowns Luted With Different Resin Cements
Waleed AL-Mutairi, Marwa Eltayeb I. Elagra, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Polymerization through Glass-ceramics: Influence of Light-polymerizing Unit’s Emitted Power and Restoration Parameters (Shade, Translucency, and Thickness) on Transmitted Radiant Power
Ra’fat I. Farah, Ibrahim A. Alblihed, Alhareth A. Aljuoie, Bandar Alresheedi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 35. CrossRef - Effect of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing bleach shade ceramic thickness on its light transmittance and microhardness of light-cured resin cement
Pardis Sheibani, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenous, Behnaz Esmaeili, Ali Bijani
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of shade and thickness on the translucency parameter of anatomic-contour zirconia, transmitted light intensity, and degree of conversion of the resin cement
Noppamath Supornpun, Molly Oster, Kamolphob Phasuk, Tien-Min G. Chu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 129(1): 213. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Color Stabilities of Lithium Disilicate Material
Onur Doğan DAĞ, Göknil ALKAN DEMETOĞLU, Ayşegül KURT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(2): 395. CrossRef - Effect of thickness of CAD/CAM materials on light transmission and resin cement polymerization using a blue light‐emitting diode light‐curing unit
Eduardo Fernandes de Castro, Bruna Marin Fronza, Jorge Soto‐Montero, Marcelo Giannini, Carlos Tadeu dos‐Santos‐Dias, Richard Bengt Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(2): 368. CrossRef - Effect of Optical Properties of Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramics and Light-Curing Protocols on the Curing Performance of Resin Cement
Kejing Meng, Lu Wang, Jintao Wang, Zhuoqun Yan, Bin Zhao, Bing Li
Coatings.2022; 12(6): 715. CrossRef - Effect of the thickness of CAD‐CAM materials on the shear bond strength of light‐polymerized resin cement
Yener Okutan, Banucicek Kandemir, Mustafa Borga Donmez, Munir Tolga Yucel
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inhomogeneity of the polymerization light beam on the microhardness of resin cement under a CAD-CAM block
Yu-Ra Go, Kwang-Man Kim, Sung-Ho Park
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(5): 802.e1. CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness and water sorption/solubility of dual-cure resin cement through monolithic zirconia in different shades
Elham Ansarifard, Zahra Panbehzan, Rashin Giti
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(1): 50. CrossRef - Comparison between Different Shades of Monolithic Zirconia over Microhardness and Water Solubility and Sorption of Dual-cure Resin Cement
Sarika Sharma, Soni Kumari, Nikita Raman, Ashish K Srivastava, Gunja LNU, Arunendra S Chauhan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1019. CrossRef - Effect of light intensity, light-curing unit exposure time, and porcelain thickness of ips e.max press and vintage LD press on the hardness of resin cement
Silvia Naliani, Suzan Elias, Rosalina Tjandrawinata
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(1): 21. CrossRef
- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
- 2,046 View
- 8 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of radiant exposure and wavelength spectrum of light-curing units on chemical and physical properties of resin cements
- Adriano Fonseca Lima, Stephanie Ellen Ferreira Formaggio, Lígia França Aires Zambelli, Alan Rodrigo Muniz Palialol, Giselle Maria Marchi, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Marcelo Tavares de Oliveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):271-277. Published online September 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we evaluated the influence of different radiant exposures provided by single-peak and polywave light-curing units (LCUs) on the degree of conversion (DC) and the mechanical properties of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Six experimental groups were established for each cement (RelyX ARC, 3M ESPE; LuxaCore Dual, Ivoclar Vivadent; Variolink, DMG), according to the different radiant exposures (5, 10, and 20 J/cm2) and two LCUs (single-peak and polywave). The specimens were made (7 mm in length × 2 mm in width × 1 mm in height) using silicone molds. After 24 hours of preparation, DC measurement was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. The same specimens were used for the evaluation of mechanical properties (flexural strength, FS; elastic modulus,
E ) by a three-point bending test. Data were assessed for normality, after which two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey's test were performed.Results No properties of the Variolink cement were influenced by any of the considered experimental conditions. In the case of the RelyX ARC cement, DC was higher when polywave LCU was used; FS and E were not influenced by the conditions evaluated. The LuxaCore cement showed greater sensitivity to the different protocols.
Conclusions On the basis of these results, both the spectrum of light emitted and the radiant exposure used could affect the properties of resin cements. However, the influence was material-dependent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
Eduardo Fernández Godoy, Alain Chaple Gil, Rodrigo Caviedes Thomas, Cristian Bersezio Miranda, Javier Martín Casielles, Gonzalo Rodríguez Martínez, Pablo Angel Aguirre
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Transmittance and Depth of Cure of a Bulk Fill Composite Based on the Exposure Reciprocity Law
Mateus Garcia Rocha, Jean-François Roulet, Mario Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Américo Bortolazzo Correr, Dayane Oliveira
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(1): 78. CrossRef
- Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
- 1,833 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Translucency changes of direct esthetic restorative materials after curing, aging and treatment
- Yong-Keun Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):239-245. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.239
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this article was to review the changes in translucency of direct esthetic restorative materials after curing, aging and treatment. As a criterion for the evaluation of clinical translucency changes, visual perceptibility threshold in translucency parameter difference (ΔTP) of 2 was used. Translucency changes after curing were perceivable depending on experimental methods and products (largest ΔTP in resin composites = 15.9). Translucency changes after aging were reported as either relatively stable or showed perceivable changes by aging protocols (largest ΔTP in resin composites = -3.8). Translucency changes after curing, aging and treatment were perceivable in several products and experimental methods. Therefore, shade matching of direct esthetic materials should be performed considering these instabilities of translucency in direct esthetic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Bleaching on Surface Roughness and Color Parameters of Coffee-Stained Nanohybrid Dental Composites with Different Viscosities
Hetaf S. Redwan, Mohamed A. Hussein, Mohamed M. Abdul-Monem
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(01): 027. CrossRef - Effect of Mouthwashes on Optical Properties of Novel Zirconia Ceramics
Merve Buse Kultas Kaleli, Necla Demir
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(3): 403. CrossRef - Color variation of composite resins in relation to the Vita Classical shade guide
João Vitor Andrade Denadai, Roberto Zimmer, Eduardo Galia Reston, Guilherme Anziliero Arossi
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e240869. CrossRef - Effect of whitening concepts on surface roughness and optical characteristics of resin‐based composites: An AFM study
Ayse Tugba Erturk‐Avunduk, Ebru Delikan, Esra Cengiz‐Yanardag, Izgen Karakaya
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(2): 214. CrossRef - Color Appearance of Various Provisional Restorative Materials for Rehabilitation Upon Aging
Niwut Juntavee, Apa Juntavee, Supichaya Srisontisuk
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(04): 1263. CrossRef - Comparison of mechanical and optical properties of a newly marketed universal composite resin with contemporary universal composite resins: An in vitro study
Sevil Gurgan, Uzay Koc Vural, Ivana Miletic
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(3): 1171. CrossRef - Comparison between translucencies of anterior resin composites and natural dental tissues
Melin Balci, Zeynep Ergucu, Esra Uzer Çelik, Lezize Sebnem Turkun
Color Research & Application.2021; 46(3): 635. CrossRef - Translucency of Zirconia Ceramics before and after Artificial Aging
Katarzyna Walczak, Heike Meißner, Ursula Range, Andreas Sakkas, Klaus Boening, Mieszko Wieckiewicz, Ioannis Konstantinidis
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Use of Composite Layering Technique to Mask a Discolored Background: Color Analysis of Masking Ability After Aging—Part II
BG Perez, LL Miotti, AH Susin, LB Durand
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(5): 488. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 1,595 View
- 6 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
- Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Maryam Khoroushi, Mohammadreza Moharreri, Mohammad Atai
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):155-163. Published online May 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Light-curing of resin-based materials (RBMs) increases the pulp chamber temperature, with detrimental effects on the vital pulp. This
in vitro study compared the temperature rise under demineralized human tooth dentin during light-curing and the degrees of conversion (DCs) of three different RBMs using quartz tungsten halogen (QTH) and light-emitting diode (LED) units (LCUs).Materials and Methods Demineralized and non-demineralized dentin disks were prepared from 120 extracted human mandibular molars. The temperature rise under the dentin disks (
n = 12) during the light-curing of three RBMs, i.e. an Ormocer-based composite resin (Ceram. X, Dentsply DeTrey), a low-shrinkage silorane-based composite (Filtek P90, 3M ESPE), and a giomer (Beautifil II, Shofu GmbH), was measured with a K-type thermocouple wire. The DCs of the materials were investigated using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.Results The temperature rise under the demineralized dentin disks was higher than that under the non-demineralized dentin disks during the polymerization of all restorative materials (
p < 0.05). Filtek P90 induced higher temperature rise during polymerization than Ceram.X and Beautifil II under demineralized dentin (p < 0.05). The temperature rise under demineralized dentin during Filtek P90 polymerization exceeded the threshold value (5.5℃), with no significant differences between the DCs of the test materials (p > 0.05).Conclusions Although there were no significant differences in the DCs, the temperature rise under demineralized dentin disks for the silorane-based composite was higher than that for dimethacrylate-based restorative materials, particularly with QTH LCU.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Shade and Light Curing Mode on the Degree of Conversion of Silorane-Based and Methacrylate-Based Resin Composites
Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Mohammad Atai, Negar Salehi, Arman Salehi
SSRN Electronic Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature rise in light-cure bonding of brackets with and without primer, in intact versus restored teeth
Gabriela Cenci SCHMITZ, Fernanda de Souza HENKIN, Mauricio MEZOMO, Mariana MARQUEZAN, Gabriela BONACINA, Maximiliano Schünke GOMES, Eduardo Martinelli Santayana de LIMA
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef -
In Vivo Pulp Temperature Changes During Class V Cavity Preparation and Resin Composite Restoration in Premolars
DC Zarpellon, P Runnacles, C Maucoski, DJ Gross, U Coelho, FA Rueggeberg, CAG Arrais
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(4): 374. CrossRef
- Effect of Shade and Light Curing Mode on the Degree of Conversion of Silorane-Based and Methacrylate-Based Resin Composites
- 1,600 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Thermal irritation of teeth during dental treatment procedures
- Su-Jung Kwon, Yoon-Jung Park, Sang-Ho Jun, Jin-Soo Ahn, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Deog-Gyu Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):105-112. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub While it is reasonably well known that certain dental procedures increase the temperature of the tooth's surface, of greater interest is their potential damaging effect on the pulp and tooth-supporting tissues. Previous studies have investigated the responses of the pulp, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone to thermal irritation and the temperature at which thermal damage is initiated. There are also many
in vitro studies that have measured the temperature increase of the pulp and tooth-supporting tissues during restorative and endodontic procedures. This review article provides an overview of studies measuring temperature increases in tooth structures during several restorative and endodontic procedures, and proposes clinical guidelines for reducing potential thermal hazards to the pulp and supporting tissues.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Various Sleeve Materials on Temperature Variations During Guided Endodontic Access Cavity Preparation Utilizing Finite‐Element Analysis
Anna Muryani, Wandi Prasetia, Dudi Aripin, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Zainul Ahmad Rajion, Satrio Wicaksono
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of microcrack formation and fracture resistance of root dentin with the use of three different rotary files: An in vitro study
Paridhi Maheshwari, Sayantan Mukherjee, Ipsita Maity, Paromita Mazumdar
Journal of Oral Research and Review.2026; 18(1): 59. CrossRef - External Root Temperature and Its Relationship With Dentin Thickness During Gutta-Percha Removal Procedures With Ultrasound. An Ex Vivo Study
Juan Ramon Salazar-Silva, Carlos Emilio Paschoal, Daniela de Fatima Teixeira da Silva, Denise Maria Zezell, Fábio Luiz Cunha D'Assuncao, Celso Luiz Caldeira
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(3): 340. CrossRef - Temperature Changes of NaOCl after Irrigation Using Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation, Easy Clean, and XP-Endo Finisher: A Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial
Geraldo Edson Freitas Athayde de Moraes, Daniel Guimarães Pedro Rocha, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Índia Olinta De Azevedo Queiroz, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 660. CrossRef - Real‐Time Analysis of Changes in Internal and External Root Temperatures Using Different Systems for Activating the Irrigation Solution
Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Julia Menezes Savaris, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Tamer Ferreira Schmidt, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Behaviour of Teeth With Internal Root Resorption During Obturation and Enhancing Thermal Simulations: A Finite-Element Analysis
Alper Kabakci, Ayca Yilmaz, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(6): 103903. CrossRef - Determination of a safe protocol for using laser ablation with indocyanine green dye in endodontic treatment. In vitro, in vivo and human study
Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Mirtha Perdomo, Marcelo Costa Perdomo, María Betania Acevedo Giménez, Celso Kenji Nishiyama, Fernando Accorsi Orosco, Arturo Javier Aranda Garcia, Carolina Sayuri Wajima, Cristiane Cantiga-Silva, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Flávio
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial PEEK-Ag Surfaces: Development and In Vitro Evaluation Against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Flávio Rodrigues, Mariana Fernandes, Filipe Samuel Silva, Óscar Carvalho, Sara Madeira
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(10): 388. CrossRef - The effect of di̇fferent preheati̇ng methods on the intrapulpal temperature of bulk-fi̇ll composi̇te resi̇ns
Hilal Ateş, Merve İşcan Yapar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of increase in temperature on the external root surface of teeth during retrieval of broken NiTi instrument using two ultrasonic tips and two power settings: An in vitro study
Ashish K. Jain, Rishabhkumar Jain, Rahul Rao, Prajakta Rao, Pooja Yadav, Vinayak Thorat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 634. CrossRef - Dental health concerns for patients suffering from facial, peri-oral burns, and inhalation injury: A persistent yet underappreciated challenge
Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, Isabelle Rennekampff, Mayer Tenenhaus
Burns.2024; 50(9): 107224. CrossRef - Recent advances in the pathogenesis and prevention strategies of dental calculus
Yu Wei, Gao-peng Dang, Zhao-yang Ren, Mei-chen Wan, Chen-yu Wang, Hong-bo Li, Tong Zhang, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Root Surface Temperature Using Different Endodontic Filling Techniques
Lea Külzer, Theresia Saban, Andreas Braun, Johannes-S. Wenzler
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9830. CrossRef - Accuracy comparison of single- and double-sleeve endodontic guides for fiber post removal
Omid Dianat, Mandana Naseri, Yaser Safi, Ali Modaberi, Nazanin Zargar, Ove A. Peters, Mehran Farajollahi
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Water Coolant and Bur Type on Pulp Temperature When Removing Tooth Structure and Restorative Dental Materials
C Mafrici, M Kingston, R Grice, PV Abbott
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(1): 91. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Temperature Variations in Incisor Root Surfaces During Root Canal Preparation Using Various Rotary Systems and Irrigation Protocols
Mihai Paven, Adrian-George Marinescu, Osama Abuabboud, Laura-Elena Cirligeriu, Luminita Maria Nica, Vlad Tiberiu Alexa, Ruxandra Sava Rosianu, Atena Galuscan, Roxana Oancea
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(23): 7484. CrossRef - The Effect of Restoration Polymerization and Residual Dentine Thickness on Thermal Changes of Pulp Chamber of Immature Permanent Teeth
Kevser Kolçakoğlu, Merve Aksoy, Cenkhan Bal, Akif Demirel, Firdevs Tulga Öz
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of pulpotomy in managing irreversible pulpitis in mature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuanyuan Li, Wenying Wang, Qian Zeng, Michelle Tang, Joshua Massey, Brian E. Bergeron, Lisha Gu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 144: 104923. CrossRef - Evaluation of diamond rotary instruments marketed for removing zirconia restorations
Severin Hunziker, Lea Thorpe, Nicola U. Zitzmann, Nadja Rohr
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(5): 895. CrossRef - Influence of different cutting instruments and rotational speeds on heat generation and cutting efficiency when sectioning different types of zirconia
Lisa Türp, Frank Lehmann, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 160: 106715. CrossRef - Loss of pulp vitality correlated with the duration of the interim restoration and the experience of the dentist: A retrospective study
Göran Nilsson, Stefan Ellner, Liselott Arnebrant, Lars Brudin, Christel Larsson
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(6): 833. CrossRef - Thermal Sensing of Photo-Activated Dental Resin Composites Using Infrared Thermography
Turki A. Bakhsh, Abdulaziz Alfaifi, Yousef Alghamdi, Mohannad Nassar, Roaa A. Abuljadyel
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4117. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation acid solutions on cleaning and bond strength to post‐space dentin
C. de Melo Alencar, J. Ferrari Zaniboni, J. Felipe Besegato, A. Patricia Oliveira Barros, M. Bena Gélio, L Garcia Belizário, E. Maximiliano Fernandez Godoy, M. Carlos Kuga
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Intermediate Irrigation on Temperature Rise during Broken NiTi File Removal Using Ultrasonic Device
László Pintér, Károly Krajczár, Fanni Őry, József Szalma, Edina Lempel
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9761. CrossRef - Top tips for improving crown preparations
James Baker, Ewen McColl, Christopher Tredwin
British Dental Journal.2023; 234(1): 16. CrossRef - Evaluation of knowledge and awareness of pediatric oral health among school teachers of Hazaribag before and after oral health education.
Vipin Ahuja, Annapurna Ahuja, Nilima Thosar
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1292. CrossRef - Applications of single laser pulse from Nd:doped lasers for cleaning of small diameter carious lesions. Modelling and analytical study
T Uzunov, M Deneva, P Uzunova, M Nenchev
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2023; 2487(1): 012022. CrossRef - Accuracy of a 3D printed sleeveless guide system used for fiber post removal: An in vitro study
Siyi Mo, Yongwei Xu, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104367. CrossRef - Heat generated during dental treatments affecting intrapulpal temperature: a review
Xin Er Lau, Xiaoyun Liu, Helene Chua, Wendy Jingwen Wang, Maykon Dias, Joanne Jung Eun Choi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2277. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature rise in light-cure bonding of brackets with and without primer, in intact versus restored teeth
Gabriela Cenci SCHMITZ, Fernanda de Souza HENKIN, Mauricio MEZOMO, Mariana MARQUEZAN, Gabriela BONACINA, Maximiliano Schünke GOMES, Eduardo Martinelli Santayana de LIMA
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature Rise in Curing Modes of Two Different Dental Light-Curing Units: The Importance of Heating Rate
Ahmad Soori, Faezeh Soori, Farshad Kowsary, Shahin Kasraei
International Journal of Thermophysics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effective application of suitable single pulse of Nd:doped lasers for cleaning of initial carious lesions of human teeth. Experimental study
T Uzunov, M Deneva, V Kazakov, P Uzunova, N Kaimakanova, M Nenchev
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2023; 2487(1): 012021. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Intrapulpal Thermal Changes during the Polymerization of Different Adhesive Resin Materials: An In Vitro Study
Pavithra K Ramanna, Suneel V Vadavadagi, Konsam Bidya Devi, Pawankumar Kamalapurkar, Shreeshail Indi, Vineetha Chakravarthy Srinivas
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(5): 539. CrossRef - Anesthetic-, irrigation- and pain-free dentistry? The case for a femtosecond laser enabled intraoral robotic device
Ludovic Rapp, Steve Madden, Andrei V. Rode, Laurence J. Walsh, Heiko Spallek, Quan Nguyen, Van Dau, Peter Woodfield, Dzung Dao, Omar Zuaiter, Alaa Habeb, Timothy R. Hirst
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - 4D Printing of Shape‐Memory Semi‐Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Based On Aromatic Heterochain Polymers
Kseniia N. Bardakova, Bato Ch. Kholkhoev, Ivan A. Farion, Evgenii O. Epifanov, Olga S. Korkunova, Yuri M. Efremov, Nikita V. Minaev, Anna B. Solovieva, Peter S. Timashev, Vitaliy F. Burdukovskii
Advanced Materials Technologies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How does indirect air-cooling influence pulp chamber temperature in different volume teeth and absence/presence of resin-based composite during light curing?
Mathieu Mouhat, Lina Stangvaltaite-Mouhat, Emil Finnäs, Amani Andersen, Anneli Lirhus Evertsen, Bo W. Nilsen
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intrapulpal temperature changes during the cementation of ceramic veneers
Edina Lempel, Dóra Kincses, Donát Szebeni, Dóra Jordáki, Bálint Viktor Lovász, József Szalma
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Femtosecond laser dentistry for precise and efficient cavity preparation in teeth
Ludovic Rapp, Steve Madden, Julia Brand, Laurence J. Walsh, Heiko Spallek, Omar Zuaiter, Alaa Habeb, Timothy R. Hirst, Andrei V. Rode
Biomedical Optics Express.2022; 13(9): 4559. CrossRef - Three Dimensional mapping of the root apex: distances between apexes and anatomical structures and external cortical plates
Carlos Henrique FERRARI, Amjad ABU HASNA, Frederico Canato MARTINHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of 9,300 nm Carbon Dioxide Laser on Dental Hard Tissue: A Concise Review
Vicky Wenqing Xue, Irene Shuping Zhao, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, John Yun Niu, Edward Chin Man Lo, Chun Hung Chu
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2021; Volume 13: 155. CrossRef - PHOTOPOLYMERIZED COMPOSITIONS AND LIGHT SOURCES FOR DENTAL PRACTICE (REVIEW)
A. M. Lalatovich, M. A. Vaniev, N. V. Sidorenko, Y. A. Makedonova, D. Yu. Dyachenko, S. V. Dyachenko
IZVESTIA VOLGOGRAD STATE TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY.2021; (12(259)): 7. CrossRef - Spray mist reduction by means of a high-volume evacuation system—Results of an experimental study
Martin Koch, Christian Graetz, Essam Al-Moraissi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(9): e0257137. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature changes during orthodontic bonding – an in vitro study
Aysegul Ayhan Bani, Burcu Balos Tuncer, Cumhur Tuncer
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(2): 157. CrossRef - Thermal Behavior of Teeth During Restoration Procedure With Composite: Experimental Tests and Numerical Simulation
M. Potenza, P. Coppa, L. Cerroni, G. Bovesecchi
Journal of Heat Transfer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Thermal Alterations on External Root Surface during Mechanical Instrumentation and Thermoplasticized Gutta-percha Obturation: An Ex Vivo Study
Rohit Sharma, Atul Jain, Madhurima Sharma, Shivani Chauhan, Abhinay Agarwal
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(5): 367. CrossRef - Degree of conversion and in vitro temperature rise of pulp chamber during polymerization of flowable and sculptable conventional, bulk-fill and short-fibre reinforced resin composites
Edina Lempel, Zsuzsanna Őri, Dóra Kincses, Bálint Viktor Lovász, Sándor Kunsági-Máté, József Szalma
Dental Materials.2021; 37(6): 983. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature changes during orthodontic bonding – an in vitro study
Aysegul Ayhan Bani, Burcu Balos Tuncer, Cumhur Tuncer
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(2): 157. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature Dependence of Specific Heat of Human Enamel and Dentin: An Experimental Study
Ahmad Soori, Farshad Kowsary, Shahin Kasraei
International Journal of Thermophysics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prosthodontic Applications of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): An Update
Muhammad Sohail Zafar
Polymers.2020; 12(10): 2299. CrossRef - The effect of halogen bulb and light-emitting diode light curing units on temperature increase and fibroblast viability
Georgia Memari Trava, Juliane Almeida Santos, Lucas Paula Ramos, Pamela Beatriz Rosário Estevam dos Santos, Amjad Abu Hasna, Karen Cristina Yui, Adriano Bressane, Luciane Dias de Oliveira, Marianne Spalding
F1000Research.2020; 9: 1369. CrossRef - A Study on Temperature Changes during Bone Scaling and Cutting of Dental Ultrasonic Scaling/Surgery System
Min-Woo Sa, Tae-Jo Ko, Jong Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2020; 19(2): 1. CrossRef - Controlling In Vivo, Human Pulp Temperature Rise Caused by LED Curing Light Exposure
DC Zarpellon, P Runnacles, C Maucoski, U Coelho, FA Rueggeberg, CAG Arrais
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(3): 235. CrossRef - Pulp Temperature Rise Induced by Light-Emitting Diode Light-Curing Units Using an Ex Vivo Model
Alexandra Vinagre, João Ramos, Clara Rebelo, José Basto, Ana Messias, Nélia Alberto, Rogério Nogueira
Materials.2019; 12(3): 411. CrossRef - The cooling efficiency of different dental high-speed handpiece coolant port designs
Helene Chua, Joanne Jung Eun Choi, Rishi Sanjay Ramani, Ritu Ganjigatti, John Neil Waddell
Heliyon.2019; 5(8): e02185. CrossRef - Polymerisation Shrinkage Profiling of Dental Composites using Optical Fibre Sensing and their Correlation with Degree of Conversion and Curing Rate
Ginu Rajan, Raju Raju, Sagar Jinachandran, Paul Farrar, Jiangtao Xi, B. Gangadhara Prusty
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth sectioning for coronectomy: how to perform?
József Szalma, László Vajta, Lajos Olasz, Edina Lempel
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(2): 519. CrossRef - Dentistry Applications of Fiber Bragg Gratings: Irradiation Protocols for Bulk Fill Flow Dental Composites
Ana Paula Gebert de Oliveira Franco, Manoella Maria Machado Costa, Leandro Zen Karam, Osnara Maria Mongruel Gomes, Hypolito Jose Kalinowski
Journal of Lightwave Technology.2019; 37(18): 4881. CrossRef - In Vitro Analysis of Techniques that Alter the Surface Hardness of a Glass Ionomer Restorative Material
Riaan Mulder, Naeemah Noordien, Shaun Rossouw, Luzaan van Zyl
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(12): 1362. CrossRef - Changes in the radicular pulp-dentine complex in healthy intact teeth and in response to deep caries or restorations: A histological and histobacteriological study
Domenico Ricucci, Simona Loghin, Li-na Niu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 73: 76. CrossRef - Effect of Irradiance and Exposure Duration on Temperature and Degree of Conversion of Dual-Cure Resin Cement for Ceramic Restorations
JS Shim, SH Han, N Jha, ST Hwang, W Ahn, JY Lee, JJ Ryu
Operative Dentistry.2018; 43(6): E280. CrossRef - Protective Effects of Base Cements against Intrapulpal Temperature Rise during Curing of Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study by Pulpal Blood Microcirculation Model
Ihsan F Ertugrul, Basak Yazkan, Ceylan Ç Ertugrul
International Journal of Experimental Dental Science.2018; 7(2): 85. CrossRef - Thermal imaging of the pulp during residual adhesive removal
Gökmen Kurt, Nisa Gül, Özgür Er, Gülşen Çakmak, Emre Bendeş, Veysel Aslantaş
Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopädie.2017; 78(4): 330. CrossRef - Influence of the material for preformed moulds on the polymerization temperature of resin materials for temporary FPDs
Philipp-Cornelius Pott, Hans Schmitz-Wätjen, Meike Stiesch, Michael Eisenburger
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(4): 294. CrossRef - Light curing in dentistry and clinical implications: a literature review
Frederick Allen RUEGGEBERG, Marcelo GIANNINI, Cesar Augusto Galvão ARRAIS, Richard Bengt Thomas PRICE
Brazilian Oral Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Intrapulpal temperature changes during curing of different bulk-fill restorative materials
Elif YASA, Cigdem ATALAYIN, Gamze KARACOLAK, Tugrul SARI, L. Sebnem TURKUN
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(5): 566. CrossRef - Can Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Nanoparticulate EndoSequence Root Repair Material Produce Injurious Effects to Rat Subcutaneous Tissues?
Wafaa A. Khalil, Siham K. Abunasef
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1151. CrossRef - Comparison of photopolymerization temperature increases in internal and external positions of composite and tooth cavities in real time: Incremental fillings of microhybrid composite vs. bulk filling of bulk fill composite
Ryan Jin-Young Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Ji-Yun Hwang, In-Bog Lee, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1093. CrossRef - Real-Time Analysis of Temperature Changes in Composite Increments and Pulp Chamber during Photopolymerization
Ryan Jin-Young Kim, In-Bog Lee, Jin-Young Yoo, Su-Jung Park, Sin-Young Kim, Young-Ah Yi, Ji-Yun Hwang, Deog-Gyu Seo
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Maryam Khoroushi, Mohammadreza Moharreri, Mohammad Atai
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 155. CrossRef - Comparison of Exothermic Release during the Polymerization of Four Materials used to fabricate Provisional Restorations
Minu Raju
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2014; 4(1): 1. CrossRef
- Impact of Various Sleeve Materials on Temperature Variations During Guided Endodontic Access Cavity Preparation Utilizing Finite‐Element Analysis
- 5,243 View
- 37 Download
- 71 Crossref

- The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
- Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test,
p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test,p < 0.05).Conclusions When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
- 1,272 View
- 1 Download

- Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
- Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):132-138. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate curing degree of three dual-cure resin cements with the elapsed time in self-cure and dual-cure mode by means of the repeated measure of micro-hardness.
Materials and Methods Two dual-cure self-adhesive resin cements studied were Maxcem Elite (Kerr), Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE) and one conventional dual-cure resin cement was Rely-X ARC resin cement (3M ESPE). Twenty specimens for each cements were made in Teflon mould and divided equally by self-cure and dual-cure mode and left in dark, 36℃, 100% relative humidity conditional-micro-hardness was measured at 10 min, 30 min, 1 hr, 3 hr, 6 hr, 12 hr and 24 hr after baseline. The results of micro-hardness value were statistically analyzed using independent samples
t -test and one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons using Scheffe's test.Results The micro-hardness values were increased with time in every test groups. Dual-cure mode obtained higher micro-hardness value than self-cure mode except after one hour of Maxcem. Self-cured Rely-X Unicem showed lowest value and dual-cured Rely-X Unicem showed highest value in every measuring time.
Conclusions Sufficient light curing to dual-cure resin cements should provided for achieve maximum curing.
- 1,035 View
- 9 Download

- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):353-358. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to measure the power density of light curing units transmitted through resin inlays fabricated with direct composite (Filtek Z350, Filtek Supreme XT) and indirect composite (Sinfony).
Materials and Methods A3 shade of Z350, A3B and A3E shades of Supreme XT, and A3, E3, and T1 shades of Sinfony were used to fabricate the resin inlays in 1.5 mm thickness. The power density of a halogen light curing unit (Optilux 360) and an LED light curing unit (Elipar S10) through the fabricated resin inlays was measured with a hand held dental radiometer (Cure Rite). To investigate the effect of each composite layer consisting the resin inlays on light transmission, resin specimens of each shade were fabricated in 0.5 mm thickness and power density was measured through the resin specimens.
Results The power density through the resin inlays was lowest with the Z350 A3, followed by Supreme XT A3B and A3E. The power density was highest with Sinfony A3, E3, and T1 (
p < 0.05). The power density through 0.5 mm thick resin specimens was lowest with dentin shades, Sinfony A3, Z350 A3, Supreme XT A3B, followed by enamel shades, Supreme XT A3E and Sinfony E3. The power density was highest with translucent shade, Sinfony T1 (p < 0.05).Conclusions Using indirect lab composites with dentin, enamel, and translucent shades rather than direct composites with one or two shades could be advantageous in transmitting curing lights through resin inlays.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of polymerization shrinkage of dual-cure core build-up resin according to shade and curing mode
Yoorina Choi, Karl Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(4): 243. CrossRef - Early Hardness and Shear Bond Strength of Dual-cure Resin Cement Light Cured Through Resin Overlays With Different Dentin-layer Thicknesses
H-S Chang, J-W Kim
Operative Dentistry.2014; 39(4): 398. CrossRef - Effects of layering technique on the shade of resin overlays and the microhardness of dual cure resin cement
Hoon-Sang Chang, Sung-Ok Hong
Brazilian Oral Research.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Light curing of dual cure resin cement
Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 266. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef
- Comparison of polymerization shrinkage of dual-cure core build-up resin according to shade and curing mode
- 1,198 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
- So-Rae Seong, Duck-kyu Seo, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):125-133. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Rapid polymerization of overlying composite resin causes high polymerization shrinkage stress at the adhesive layer. In order to alleviate the shrinkage stress, increasing the light intensity over the first 5 seconds was suggested as an exponential curing mode by an LED light curing unit (Elipar FreeLight2, 3M ESPE). In this study, the effectiveness of the exponential curing mode on reducing stress was evaluated with measuring microtensile bond strength of three adhesives after the overlying composite resin was polymerized with either continuous or exponential curing mode.
Methods Scotchbond Multipurpose Plus (MP, 3M ESPE), Single Bond 2 (SB, 3M ESPE), and Adper Prompt (AP, 3M ESPE) were applied onto the flat occlusal dentin of extracted human molar. The overlying hybrid composite (Denfil, Vericom, Korea) was cured under one of two exposing modes of the curing unit. At 48h from bonding, microtensile bond strength was measured at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. The fractured surfaces were observed under FE-SEM.
Results There was no statistically significant difference in the microtensile bond strengths of each adhesive between curing methods (Two-way ANOVA, p > 0.05). The microtensile bond strengths of MP and SB were significantly higher than that of AP (p < 0.05). Mixed failures were observed in most of the fractured surfaces, and differences in the failure mode were not observed among groups.
Conclusion The exponential curing method had no beneficial effect on the microtensile dentin bond strengths of three adhesives compared to continuous curing method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 139. CrossRef
- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
- 1,183 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
- Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):103-112. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of curing methods of adhesive resins and resin cements in the root canal. Crown portions of 32 single-rooted mandibular premolars were removed. Routine endodontic treatment was done, and 9 mm deep post spaces were prepared within root canals. No. 3 FRC Postec posts (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Liechtenstein) were cemented in the post spaces by self-(SC) or light-curing (LC) using two dual-cured adhesives (Adper Scotchbond multi-purpose plus and Exite DSC )and resin cements (RelyX ARC and Variolink II). They were assigned to 4 groups (n=8); R-SC, R-LC, V-SC, V-LC group.
After stored in distilled water for 24 hours, each root was transversally sectioned with 1.5 mm thick and made three slices. The specimens were subjected to push-out test in a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu Co., Japan) with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. The data were analyzed with repeated ANOVA and one-way.
ANOVA. Also the interface of post-resin cement and resin cement-canal wall of each group was observed under FE-SEM.
When fiber posts were cemented into the root canal using total-etch adhesives, the bond strength and adaptation between post and root canal dentin was affected by curing method. Self-cure of adhesives and resin cements showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than light-cure of them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 125. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 479. CrossRef
- Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
- 1,126 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The effect of different curing modes on composite resin/dentin bond strength in class icavities
- Shin-young Baek, Young-Gon Cho, Byeong-Choon Song
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):428-434. Published online September 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.428
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the microtensile bond strength in Class I cavities associated with different light curing modes of same light energy density.
Occlusal enamel was removed to expose a flat dentin surface and twenty box-shaped Class I cavities were prepared in dentin. Single Bond (3M Dental product) was applied and Z 250 was inserted using bulk technique. The composite was light-cured using one of four techniques; pulse delay (PD group), soft-start (SS group), pulse cure (PC group) and standard continuous cure (CC group). The light-curing unit capable of adjusting time and intensity (VIP, Bisco Dental product) was selected and the light energy density for all curing modes was fixed at 16 J/cm2. After storage for 24 hours, specimens were sectioned into beams with a rectangular cross-sectional area of approximately 1 mm2. Microtensile bond strength (µTBS) test was performed using a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu Co.). The results were analyzed using oneway ANOVA and Tukey's test at significance level 0.05. The µTBS of PD group and SS group was higher than that of PC group and CC group.
Within the limitations of this in vitro study, modification of curing modes such as pulse delay and soft start polymerization can improve resin/dentin bond strength in Class I cavities by controlling polymerization velocity of composite resin.
- 954 View
- 4 Download

- Polymerization of dual cured composites by different thickness
- Yun Ju Kim, Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):169-176. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of thickness, filling methods and curing methods on the polymerization of dual cured core materials by means of microhardness test.
Two dual cured core materials, MultiCore Flow (Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) and Bis-Core (Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA) were used in this study. 2 mm (bulky filled), 4 mm (bulky filled), 6 mm (bulky and incrementally filled) and 8 mm (bulky and incrementally filled)-thickness specimens were prepared with light cure or self cure mode. After storage at 37℃ for 24 hours, the Knoop hardness values (KHN) of top and bottom surfaces were measured and the microhardness ratio of top and bottom surfaces was calculated. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe multiple comparison test, with α = 0.05.
The effect of thickness on the polymerization of dual cured composites showed material specific results. In 2, 4 and 6 mm groups, the KHN of two materials were not affected by thickness. However, in 8 mm group of MultiCore Flow, the KHN of the bottom surface was lower than those of other groups (
p < 0.05). The effect of filling methods on the polymerization of dual cured composites was different by their thickness or materials. In 6 mm thickness, there was no significant difference between bulk and incremental filling groups. In 8 mm thickness, Bis-Core showed no significant difference between groups. However, in MultiCore Flow, the microhardness ratio of bulk filling group was lower than that of incremental filling group (p < 0.05). The effect of curing methods on the polymerization of dual cured composites showed material specific results. In Bis-Core, the KHN of dual cured group were higher than those of self cured group at both surfaces (p < 0.05). However, in MultiCore Flow, the results were not similar at both surfaces. At the top surface, dual cured group showed higher KHN than that of self cured group (p < 0.05). However, in the bottom surface, dual cured group showed lower value than that of self cured group (p < 0.05).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of polymerization behaviors, microhardness and compressive strength between bulk-fill resin and dual-cured core resin
Hye Jeong Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Reuben H. Kim, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef
- Comparison of polymerization behaviors, microhardness and compressive strength between bulk-fill resin and dual-cured core resin
- 2,069 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of intermittent composite curing on marginal adaptation
- Yong-Hwan Yun, Sung-Ho Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):248-259. Published online May 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.248
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this research was to study the effect of intermittent polymerization on marginal adaptation by comparing the marginal adaptation of intermittently polymerized composite to that of continuously polymerized composite.
The materials used for this study were Pyramid (Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, U.S.A.) and Heliomolar (Ivoclar Vivadent, Liechtenstein). The experiment was carried out in class II MOD cavities prepared in 48 extracted human maxillary premolars. The samples were divided into 4 groups by light curing method; group 1- continuous curing (60s light on with no light off); group 2- intermittent curing (cycles of 3s with 2s light on & 1s light off for 90s); group 3- intermittent curing (cycles of 2s with 1s light on & 1s light off for 120s); group 4- intermittent curing (cycles of 3s with 1s light on & 2s light off for 180s). Consequently the total amount of light energy radiated was same in all the groups. Each specimen went through thermo-mechanical loading (TML) which consisted of mechanical loading (720,000 cycles, 5.0 kg) with a speed of 120 rpm for 100 hours and thermocycling (6000 thermocycles of alternating water of 50℃ and 55℃). The continuous margin (CM) (%) of the total margin and regional margins, occlusal enamel (OE), vertical enamel (VE), and cervical enamel (CE)) was measured before and after TML under a × 200 digital light microscope.
Three-way ANOVA and Duncan's Multiple Range Test was performed at 95% level of confidence to test the effect of 3 variables on CM (%) of the total margin: light curing conditions, composite materials and effect of TML. In each group, One-way ANOVA and Duncan's Multiple Range Test was additionally performed to compare CM (%) of regions (OE, VE, CE).
The results indicated that all the three variables were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Before TML, in groups using Pyramid, groups 3 and 4 showed higher CM (%) than groups 1 and 2, and in groups using Heliomolar, groups 3 and 4 showed higher CM (%) than group 1 (p < 0.05). After TML, in both Pyramid and Heliomolar groups, group 3 showed higher CM (%) than group 1 (p < 0.05). CM (%) of the regions are significantly different in each group (p < 0.05). Before TML, no statistical difference was found between groups within the VE and CE region. In the OE region, group 4 of Pyramid showed higher CM (%) than group 2, and groups 2 and 4 of Heliomolar showed higher CM (%) than group 1 (p < 0.05). After TML, no statistical difference was found among groups within the VE and CE region. In the OE region, group 3 of Pyramid showed higher CM (%) than groups 1 and 2, and groups 2,3 and 4 of Heliomolar showed higher CM (%) than group 1 (p < 0.05).
It was concluded that intermittent polymerization may be effective in reducing marginal gap formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
So-Rae Seong, Duck-kyu Seo, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 125. CrossRef
- Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
- 1,024 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Polymerization shrinkage of composite resins cured by variable light intensities
- Mi-Young Lim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Chan-Ui Hong
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):28-36. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.028
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of exponential curing method with conventional curing and soft start curing method on polymerization shrinkage of composite resins.
Three brands of composite resins (Synergy Duo Shade, Z250, Filtek Supreme) and three brands of light curing units (Spectrum 800, Elipar Highlight, Elipar Trilight) were used. 40 seconds curing time was given. The shrinkage was measured using linometer for 90 seconds.
The effect of time on polymerization shrinkage was analysed by one-way ANOVA and the effect of curing modes and materials on polymerization shrinkage at the time of 90s were analysed by two-way ANOVA. The shrinkage ratios at the time of 20s to 90s were taken and analysed the same way. The results were as follows:
1. All the groups except Supreme shrank almost within 20s. Supreme cured by soft start and exponential curing had no further shrinkage after 30s (p < 0.05).
2. Statistical analysis revealed that polymerization shrinkage varied among materials (p = 0.000) and curing modes (p = 0.003). There was no significant interaction between material and curing mode.
3. The groups cured by exponential curing showed the statistically lower polymerization shrinkage at 90s than the groups cured by conventional curing and soft start curing (p < 0.05).
4. The initial shrinkage ratios of soft start and exponential curing were statistically lower than conventional curing (p < 0.05).
From this study, the use of low initial light intensities may reduce the polymerization rate and, as a result, reduce the stress of polymerization shrinkage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Degree of Conversion and Polymerization Shrinkage of Low and High Viscosity Bulk-Fill Giomer-based and Resin-based composites
Heera Kim, Jaesik Lee, Hyunjung Kim, Taeyub Kwon, Soonhyeun Nam
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2019; 46(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of the exponential curing of composite resin on the microtensile dentin bond strength of adhesives
So-Rae Seong, Duck-kyu Seo, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 125. CrossRef
- Degree of Conversion and Polymerization Shrinkage of Low and High Viscosity Bulk-Fill Giomer-based and Resin-based composites
- 1,523 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The polymerization rate and the degree of conversion of composite resins by different light sources
- Joo-Hee Ryoo, In-Bog Lee, Hyun-Mee Yoo, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Hyuk-Choon Kwon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):386-398. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to observe the reaction kinetics and the degree of polymerization of composite resins when cured by different light sources and to evaluate the effectiveness of the blue Light Emitting Diode Light Curing Units (LED LCUs) compared with conventional halogen LCUs.
Materials and Methods First, thermal analysis was performed by a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). The LED LCU (Elipar Freelight, 320 mW/cm2) and the conventional halogen LCU (XL3000, 400 mW/cm2) were used in this study for curing three composite resins (SureFil, Z-250 and AEliteFLO). Second, the degree of conversion was obtained in the composite resins cured according to the above curing mode with a FTIR. Third, the measurements of depth of cure were carried out in accordance with ISO 4049 standards. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA test at 95% levels of confidence and Duncan's procedure for multiple comparisons.
Results The heat of cure was not statistically different among the LCUs (p > 0.05). The composites cured by the LED (Exp) LCUs were statistically more slowly polymerized than by the halogen LCU and the LED (Std) LCU (p < 0.05). The composite resin groups cured by the LED (Exp) LCUs had significantly greater degree of conversion value than by the halogen LCU and the LED (Std) LCU (p = 0.0002). The composite resin groups cured by the LED (Std) LCUs showed significantly greater depth of cure value than by the halogen LCU and the LED (Exp) LCU (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Features of polymerization kinetics and heat realize of epoxy resin modified with silicone, silane and siloxane additives
Sergey Savotchenko, Ekaterina Kovaleva
Polymer Bulletin.2024; 81(15): 13419. CrossRef - Kinetic features of polymerization of epoxy resin modified by silicon‐containing additives and mineral fillers
Ekaterina G. Kovaleva, Sergey E. Savotchenko
Polymer Engineering & Science.2022; 62(1): 75. CrossRef - Characterization of curing behavior of UV-curable LSR for LED embedded injection mold
Joon-Sung Tae, Kyung-Gyu Yim, Byung-Ohk Rhee, Jae B. Kwak
Korea-Australia Rheology Journal.2016; 28(4): 247. CrossRef
- Features of polymerization kinetics and heat realize of epoxy resin modified with silicone, silane and siloxane additives
- 1,612 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Influence of the curing time for the adhesive on the oxygen-inhibited layer thickness and the shear bond strength to dentin
- Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae, Ho-Hyun Son, In-Bog Lee, Chung-Moon Um, Seung-Ho Baek, Oh-Young Kim, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):177-184. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT Objectives: This study investigated the hypothesis that increasing light-curing time would leave the oxygen-inhibited layer (OIL) of the adhesive thinner, and in turn, result in lower shear bond strength (SBS) than those obtained by the routine curing procedures.
Methods: 120 human extracted posterior teeth were randomly divided into three groups for bonding with three adhesives: All Bond 2®, One Step®, and Adper Prompt®. They were subsequently divided into four subgourps with different light-curing time (10, 20, 30 and 60 s). The assigned adhesives were applied on superficial occlusal dentin according to the manufacturer’s instructions and cured with one of the four curing times. Composite resin cylinder, 2.35 mm in diameter, were built on the cured adhesive and light-cured for 40 s. SBS were measured after 24 h from the bonding using a universal testing machine (crosshead speed 1.0 mm/min). The relative thickness of the OIL and the degree of conversion (DC) were determined from the adhesive on a slide glass using FT-NIR in an absorbance mode. Data were analysed with One-way ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple test (p < 0.05).
Results: With increasing cure time, although there were no significant difference in th SBS of One-step and Adper Prompt (p > 0.05), those of All Bond 2 decreased significantly (p < 0.05). The relative thicknesses of the OIL on each adhesive were not affected by the cure time (p > 0.05). Although the DC of All-Bond 2 were statistically not different with increasing cure time (p > 0.05), those of One-Step and Adper Prompt showed an increasing trends with increasing cure time (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Increasing light-curing time did not affect on the relative thickness of the OIL of the adhesives, and in turn, on the SBS to dentin.
- 922 View
- 0 Download

- Polymerization ability of several light curing sources on composite resin
- Hye-Jin Shin, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):156-161. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the polymerization ability of three different light sources by microhardness test. Stainless steel molds of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm in thickness of 7 mm in diameter were prepared. The hybrid composite Z100 was packed into the hole of the mold and curing light was activated for designated time. Three different light sources, conventional halogen, light emitting diode, and plasma arc, were used for curing of composite. Two different curing times applied; one is to follow the manufacturer's recommendation and the other is to extend the curing time of LED and plasma arc for balancing the light energy with halogen. Immediately after curing, the Vickers hardness was measured at the bottom of specimen.
The results were as follows.
The composite cured with LED showed equal to higher microhardnesss than halogen.
The composite was cured with plasma arc by manufacturer's recommendation showed lowest microhardness at all thickness. However, when curing time was extended, microhardness was higher than the others.
In conclusion, this study suggested that plasma arc needs properly extended curing time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- 1,166 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Mechanical properties and microleakage of composite resin materials cured by variable light intensities
- Seung-Ryul Han, Kyung-San Min, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):134-145. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mechanical properties and microleakage of two composites [conventional hybrid type DenFil (VERICOM Co., Anyang, Korea) / micro matrix hybrid type Esthet X (Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE, U.S.A.)] were evaluated to assess whether variable light intensity curing is better than conventional curing technique.
Curing was done for 40 seconds in two ways of 2 step soft-start technique and 5 step ramping technique. Three kinds of light intensities of 50, 100, 200 mW/cm2 were initially used for 10, 20, 30 seconds each and the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2 was used for the rest of curing time in a soft-start curing technique. In a ramping technique, curing was done with the same initial intensities and the light intensity was increased 5 times with the same rate to the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2.
After determining conditions that showed no different mechanical properties with conventional technique, Esthet X composite was filled in a class V cavity, which dimension was 4×3×1.5 mm and cured under those conditions.
Microleakage was evaluated in two ways of dye penetration and maximum gap estimation through SEM observation. ANOVA and Spearman's rho test were used to confirm any statistical significance among groups.
The results were as follows:
Several curing conditions of variable light intensities resulted in the similar mechanical properties with a conventional continuous curing technique, except conditions that start curing with an initial light intensity of 50 mW/cm2,
Conventional and ramping techniques were better than soft-start technique in mechanical properties of microhardness and compressive strength.
Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 100 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the least dye penetration. Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 200 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the smallest marginal gap, if there was no difference among groups.
Soft-start technique resulted in better dye-proof margin than conventional technique (p=0.014) and ramping technique(p=0.002).
There was a very low relationship(p=0.157) between the methods of dye penetration and marginal gap determination through SEM evaluation.
From the results of this study, it was revealed that ramping technique would be better than conventional technique in mechanical properties, however, soft-start technique might be better than conventional one in microleakage.
It was concluded that much endeavor should be made to find out the curing conditions, which have advantages of both aspects or to solve these kinds of problems through a novel idea of polymerization.
- 888 View
- 2 Download

- Color changes in composites according to various light curing sources
- Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Cho Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(1):87-94. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.1.087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the color changes of composite resin polymerized with three type of light curing units. Composite resin (Z100, shade A2) were applied in a cylindrical metal mold(2 mm thick, 7 mm diameter).
Twenty specimens according to light curing units were made.
Group1: the specimens were polymerized with Apollo 95E for 3seconds(1370 mW/cm2).
Group2: the specimens were polymerized with XL 3000 for 40seconds(480 mW/cm2).
Group3: the specimens were polymerized with Spectrum 800 for 10 seconds(250 mW/cm2) and 30 seconds(700 mW/cm2).
The microhardness values(VHN) of upper and lower surfaces specimens after light polymerization were measured for the degree of polymerization. All specimens were stored in distilled water at 60℃ for 30 days.
The color characteristics(L*, a*, b*) of the specimens before and after immersion were measured by spectrophotometer and the total color difference (ΔE*) was computed.
The results obtained were as follows:
1. The microhardness values of Group I showed significantly lower than those of Group II and III(p<0.05).
2. In all groups the ΔE* values presented below 2.0.
3. Group I showed the highest ΔE* values followed order from highest to lowest by Group II and III (p<0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion and flexural strength
Ji-A Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 324. CrossRef - Effect of the difference in spectral outputs of the single and dual-peak LEDs on the microhardness and the color stability of resin composites
Hye-Jung Park, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 108. CrossRef - Color changes in composite resins exposed to xenon lamp
Young-Gon Cho, Jeong-Il Seo, Soo-Mee Kim, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2003; 28(3): 195. CrossRef
- Effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion and flexural strength
- 1,103 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- EFFECT OF LIGHT SOURCE AND SHADE ON DEPTH OF CURE OF COMPOSITES
- Joon-Sok Na, Sun-Wa Jeong, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Ho Kim, Chang Yun, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(6):561-568. Published online January 14, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.6.561
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT Purpose of this research is estimating polymerization depth of different source of light. XL 3000 for halogen light, Apollo 95E for plasma arc light and Easy cure for LED light source were used in this study. Different shade (B1 & A3) resin composites (Esthet-X, Dentsply, U.S.A.) were used to measure depth of cure. 1, 2, and 3 mm thick samples were light cured for three seconds, six seconds or 10 seconds with Apollo 95E and they were light cured with XL-3000 and Easy cure for 10 seconds, 20 seconds, or 40 seconds. Vicker's hardness test carried out after store samples for 24 hours in distilled water.
Results were as following.
Curing time increases from all source of lights, curing depth increased(p<0.05).
Depth (that except 1mm group and 2mm group which lighten to halogen source of light) deepens in all groups, Vickers hardness decreased(p<0.05).
Vicker's hardness of A3 shade composite was lower in all depths more than B1 shade composites in group that do polymerization for 10 seconds and 20 seconds using halogen source of light(p<0.05), but group that do polymerization for 40 seconds did not show difference(p>0.05).
Groups that do polymerization using Plasma arc and LED source of light did not show Vicker's hardness difference according to color at surface and 1mm depth(p>0.05), but showed difference according to color at 2mm and 3mm depth(p<0.05). The results showed that Apollo 95E need more polymerization times than manufacturer's recommendation (3 seconds), and Easy cure need polymerization time of XL-3000 at least.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- 1,146 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- MICROHARDNESS AND MICROLEAKAGE OF COMPOSITE RESIN CURED BY VISIBLE LIGHT WITH VARIOUS BAND OF WAVELENGTH
- Soo-Man Park, Jae-Yong Lee, Seung-Ryul Han, Sang-Yoon Ha, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(4):403-410. Published online January 14, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.4.403
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT Several ways of curing are being tried to improve material’s properties and reduce marginal gap. However, all are considering about the pattern of light intensity. It was noted from the preliminary study the change of light wavelength from filter changing may give an impact on material’s property and microleakage.
The object of this study was to verify the effect of filters with various wavelength width on the microhardness and microleakage of composite resin; hybrid type of DenFil and submicron hybrid type of Esthet X. Composite resins were cured using 3 kinds of filter; narrow-banded(465-475 nm), mid-banded(430-470 nm), wide-banded(400-500 nm). After the estimation of microhardness, degree of dye penetration and the maximum gap from SEM evaluation were done between 4 groups that showed no difference in microhardness value of the lower surface.
The results were as follows:
Adequate microhardness could not be gained with a narrow-banded filter irrespective of curing time. At the upper surface, DenFil should be polymerized with middle or wide-banded filter for 20 seconds at least, while Esthet X be cured with middle or wide-banded filter for 30 seconds at least to get similar hardness value to control group.
There was little dye penetration in enamel margin, but all dentin margins showed much more dye penetration irrespective of curing conditions. Although there was no statistical difference, groups cured with mid-banded filter for 40 seconds and with wide-width filter for 20 seconds showed relatively less dye penetration.
It was revealed from the SEM examination that group cured with wide-banded filter had the smallest gap without statistical significance. Spearman’s rho test showed that the correlation between the results of dye penetration and SEM examination was very low.
From these results, it could be concluded that curing with wide-width filter would be better than the other techniques, even though the curing technique using mid-width filter seems to have its own unique advantage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Two Different Light-Curing Units and Curing Times on Bulk-Fill Restorative Materials
Gokcen Deniz Bayrak, Elif Yaman-Dosdogru, Senem Selvi-Kuvvetli
Polymers.2022; 14(9): 1885. CrossRef
- The Effect of Two Different Light-Curing Units and Curing Times on Bulk-Fill Restorative Materials
- 1,117 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


