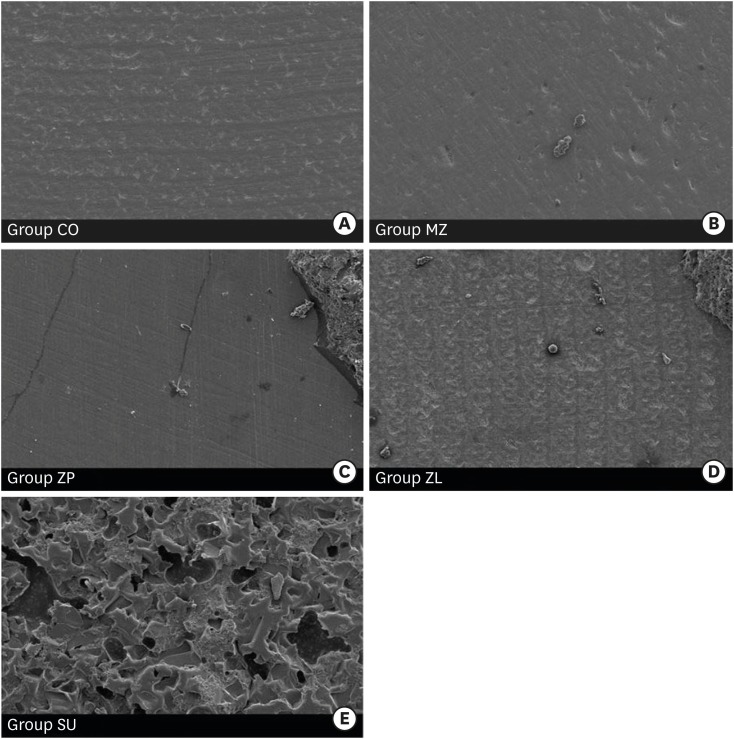
-
Comparison of bond strengths of ceramic brackets bonded to zirconia surfaces using different zirconia primers and a universal adhesive
-
Ji-Yeon Lee, Jaechan Ahn, Sang In An, Jeong-won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e7. Published online January 22, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study is to compare the shear bond strengths of ceramic brackets bonded to zirconia surfaces using different zirconia primers and universal adhesive. Materials and MethodsFifty zirconia blocks (15 × 15 × 10 mm, Zpex, Tosoh Corporation) were polished with 1,000 grit sand paper and air-abraded with 50 µm Al2O3 for 10 seconds (40 psi). They were divided into 5 groups: control (CO), Metal/Zirconia primer (MZ, Ivoclar Vivadent), Z-PRIME Plus (ZP, Bisco), Zirconia Liner (ZL, Sun Medical), and Scotchbond Universal adhesive (SU, 3M ESPE). Transbond XT Primer (used for CO, MZ, ZP, and ZL) and Transbond XT Paste was used for bracket bonding (Gemini clear ceramic brackets, 3M Unitek). After 24 hours at 37°C storage, specimens underwent 2,000 thermocycles, and then, shear bond strengths were measured (1 mm/min). An adhesive remnant index (ARI) score was calculated. The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni test (p = 0.05). ResultsSurface treatment with primers resulted in increased shear bond strength. The SU group showed the highest shear bond strength followed by the ZP, ZL, MZ, and CO groups, in that order. The median ARI scores were as follows: CO = 0, MZ = 0, ZP = 0, ZL = 0, and SU = 3 (p < 0.05). ConclusionsWithin this experiment, zirconia primer can increase the shear bond strength of bracket bonding. The highest shear bond strength is observed in SU group, even when no primer is used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness of universal adhesives for orthodontic bonding to enamel and restorative materials: A systematic review
Claire-Adeline Dantagnan, Maureen Boudrot, Julia Bosco, Gauthier Dot, Ali Nassif, Philippe François, Jean-Pierre Attal
International Orthodontics.2026; 24(2): 101089. CrossRef - State-of-the-Art Zirconia and Glass–Ceramic Materials in Restorative Dentistry: Properties, Clinical Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Sorin Gheorghe Mihali, Adela Hiller
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12841. CrossRef - Shear bond strength and ARI scores of metal brackets to glazed glass ceramics and zirconia: an in vitro study investigating surface treatment protocols
Claire Pédemay, Philippe François, Vincent Fouquet, Sarah Abdel-Gawad, Jean-Pierre Attal, Claire-Adeline Dantagnan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different pretreatments and attachment materials on shear bond strength of indirectly bonded brackets using CAD/CAM transfer trays to monolithic zirconia
Rebecca Jungbauer, Christian M. Hammer, Daniel Edelhoff, Peter Proff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Dental Materials.2023; 39(2): 170. CrossRef - Mechanical and chemical surface treatment enhances bond strength between zirconia and orthodontic brackets: an in vitro study
Nareudee Limpuangthip, Atikom Surintanasarn, Ploylada Vitavaspan
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments and Orthodontic Bracket Type on Shear Bond Strength of High‐Translucent Zirconia: An In Vitro Study
Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Hamid Neshandar Asli, Mehran Falahchai, Sina Safary, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Does Surface Treatment With Different Primers Increase The Shear Bond Strength Between Metallic Bracket and Monolithic Zirconia?
Emine Begüm BÜYÜKERKMEN, Ayşe Selenge AKBULUT, Murat KEÇECİ
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 451. CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Surface Roughness and Orthodontic Bond Strength of Partially-stabilized Zirconia
Mustafa Borga Dönmez, Betül Ballı Demirel, Münir Demirel, Yasemin Gündoğdu, Hamdi Şükür Kılıç
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2022; 23(3): 335. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of Polypropylene Fiber in Orthodontic Adhesive on Glazed Monolithic Zirconia
Dhanabhol Riowruangsanggoon, Apiwat Riddhabhaya, Nattisa Niyomtham, Irin Sirisoontorn
Polymers.2022; 14(21): 4627. CrossRef - Effects of Three Novel Bracket Luting Agents Containing Zirconia Primer on Shear Bond Strength of Metal Orthodontic Brackets Attached to Monolithic Zirconia Crowns: A Preliminary In Vitro Study
Milad Shamohammadi Heidari, Mehrnaz Moradinejad, Hamed Tabatabaei, Vahid Rakhshan, Dinesh Rokaya
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different pretreatments and attachment materials on shear bond strength between monolithic zirconia restorations and metal brackets
Rebecca Jungbauer, Peter Proff, Daniel Edelhoff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bracket Bonding to All-Ceramic Materials with Universal Adhesives
Cecilia Goracci, Giuseppe Di Bello, Lorenzo Franchi, Chris Louca, Jelena Juloski, Jovana Juloski, Alessandro Vichi
Materials.2022; 15(3): 1245. CrossRef - Effect of enamel-surface modifications on shear bond strength using different adhesive materials
Bo-wen Zheng, Shan Cao, Majedh Abdo Ali Al-Somairi, Jia He, Yi Liu
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of various mechanical and chemical surface conditioning on the bonding of orthodontic brackets to all ceramic materials
Dalia A. Abuelenain, Amal I. Linjawi, Ahmed S. Alghamdi, Fahad M. Alsadi
Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 16(1): 370. CrossRef - The Performance of Universal Adhesives on Orthodontic Bracket Bonding
Muhittin Ugurlu, Muhammed Hilmi Buyukcavus
European Journal of General Dentistry.2021; 10(01): 019. CrossRef - A comparison of shear bond strength of brackets bonded to zirconia
Hannah Knott, Xiaoming Xu, Edwin Kee, Qingzhao Yu, Paul Armbruster, Richard Ballard
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(1): 62. CrossRef - Influence of Surface Treatment and Resin Cements on the Bond Strength between the Y-TZP Zirconia and Composite Resin Interface
Lucas Campagnaro Maciel, Amanda Pádua Proeza, Hélyda Coelho Guimarães Balbino, Marcela Moráo Corteletti, Ricardo Huver De Jesus, Laís Regiane da Silva Concílio
Journal of Health Sciences.2019; 21(5): 477. CrossRef - Effect of Simplified Bonding on Shear Bond Strength between Ceramic Brackets and Dental Zirconia
Ga-Youn Ju, Soram Oh, Bum-Soon Lim, Hyun-Seung Lee, Shin Hye Chung
Materials.2019; 12(10): 1640. CrossRef
-
2,274
View
-
16
Download
-
18
Crossref
-
A study on the compatibility between one-bottle dentin adhesives and composite resins using micro-shear bond strength
-
Minju Song, Yooseok Shin, Jeong-Won Park, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):30-36. Published online September 26, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.30
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study was performed to determine whether the combined use of one-bottle self-etch adhesives and composite resins from same manufacturers have better bond strengths than combinations of adhesive and resins from different manufacturers. Materials and Methods25 experimental micro-shear bond test groups were made from combinations of five dentin adhesives and five composite resins with extracted human molars stored in saline for 24 hr. Testing was performed using the wire-loop method and a universal testing machine. Bond strength data was statistically analyzed using two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's post hoc test. ResultsTwo way ANOVA revealed significant differences for the factors of dentin adhesives and composite resins, and significant interaction effect (p < 0.001). All combinations with Xeno V (Dentsply De Trey) and Clearfil S3 Bond (Kuraray Dental) adhesives showed no significant differences in micro-shear bond strength, but other adhesives showed significant differences depending on the composite resin (p < 0.05). Contrary to the other adhesives, Xeno V and BondForce (Tokuyama Dental) had higher bond strengths with the same manufacturer's composite resin than other manufacturer's composite resin. ConclusionsNot all combinations of adhesive and composite resin by same manufacturers failed to show significantly higher bond strengths than mixed manufacturer combinations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
Stefan Dačić, Milan Miljković, Aleksandar Mitić, Goran Radenković, Marija Anđelković‐Apostolović, Milica Jovanović
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(6): 1212. CrossRef - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef - Dentin bond strengths of all-in-one adhesives combined with different manufacturers’ flowable resin composites
Koichi SHINKAI, Daiki YOSHII, Akira KOIDE, Masaya SUZUKI, Shiro SUZUKI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(5): 1094. CrossRef - DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE ADEZİV SİSTEMLER
Elmas TÜRKER, Buket AYNA
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of EDC on Dentin-Resin Shear Bond Strength and Demineralized Dentin Thermal Properties
Lin Tang, Yi Zhang, Yuhua Liu, Yongsheng Zhou
Materials.2016; 9(11): 920. CrossRef
-
1,309
View
-
7
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Synergistic effect of xylitol and ursolic acid combination on oral biofilms
-
Yunyun Zou, Yoon Lee, Jinyoung Huh, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):288-295. Published online August 27, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.288
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study was designed to evaluate the synergistic antibacterial effect of xylitol and ursolic acid (UA) against oral biofilms in vitro. Materials and MethodsS. mutans UA 159 (wild type), S. mutans KCOM 1207, KCOM 1128 and S. sobrinus ATCC 33478 were used. The susceptibility of S. mutans to UA and xylitol was evaluated using a broth microdilution method. Based on the results, combined susceptibility was evaluated using optimal inhibitory combinations (OIC), optimal bactericidal combinations (OBC), and fractional inhibitory concentrations (FIC). The anti-biofilm activity of xylitol and UA on Streptococcus spp. was evaluated by growing cells in 24-well polystyrene microtiter plates for the biofilm assay. Significant mean differences among experimental groups were determined by Fisher's Least Significant Difference (p < 0.05). ResultsThe synergistic interactions between xylitol and UA were observed against all tested strains, showing the FICs < 1. The combined treatment of xylitol and UA inhibited the biofilm formation significantly and also prevented pH decline to critical value of 5.5 effectively. The biofilm disassembly was substantially influenced by different age of biofilm when exposed to the combined treatment of xylitol and UA. Comparing to the single strain, relatively higher concentration of xylitol and UA was needed for inhibiting and disassembling biofilm formed by a mixed culture of S. mutans 159 and S. sobrinus 33478. ConclusionsThis study demonstrated that xylitol and UA, synergistic inhibitors, can be a potential agent for enhancing the antimicrobial and anti-biofilm efficacy against S. mutans and S. sobrinus in the oral environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Therapeutic potential of ursolic acid (UA) and their derivatives with nanoformulations to combat nosocomial pathogens
Umesh Chand, Pramod Kumar Kushawaha
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-cariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid using dental microcosm biofilm
Jonghyun Jo, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Sun Kyu Park, Su-Jung Shin, Baek-il Kim, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105447. CrossRef - Alteration of oral microbial biofilms by sweeteners
Geum-Jae Jeong, Fazlurrahman Khan, Nazia Tabassum, Young-Mog Kim
Biofilm.2024; 7: 100171. CrossRef - Synergistic inhibitory activity of Glycyrrhizae Radix and Rubi Fructus extracts on biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans
Youngseok Ham, Tae-Jong Kim
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Planktonic and Anti-Biofilm Properties of Pentacyclic Triterpenes—Asiatic Acid and Ursolic Acid as Promising Antibacterial Future Pharmaceuticals
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska, Dorota Wojnicz
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 98. CrossRef - Does Secondary Plant Metabolite Ursolic Acid Exhibit Antibacterial Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Living in Single- and Multispecies Biofilms?
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Wojnicz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(8): 1691. CrossRef - The physical properties and anticariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid
Hyunkyung Yoo, So Youn Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 641. CrossRef - Exploration of singular and synergistic effect of xylitol and erythritol on causative agents of dental caries
Siiri Kõljalg, Imbi Smidt, Anirikh Chakrabarti, Douwina Bosscher, Reet Mändar
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The investigation of synergistic activity of protamine with conventional antimicrobial agents against oral bacteria
Masashi Fujiki, Michiyo Honda
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2020; 523(3): 561. CrossRef - Concentration in Saliva and Antibacterial Effect of Xylitol Chewing Gum: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
Fabio Cocco, Maria Grazia Cagetti, Osama Majdub, Guglielmo Campus
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(8): 2900. CrossRef - Enhanced synergistic effects of xylitol and isothiazolones for inhibition of initial biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538
Gang Zhou, Hong Peng, Ying-si Wang, Xiao-mo Huang, Xiao-bao Xie, Qing-shan Shi
Journal of Oral Science.2019; 61(2): 255. CrossRef - Alkyl rhamnosides, a series of amphiphilic materials exerting broad-spectrum anti-biofilm activity against pathogenic bacteria via multiple mechanisms
Guanghua Peng, Xucheng Hou, Wenxi Zhang, Maoyuan Song, Mengya Yin, Jiaxing Wang, Jiajia Li, Yajie Liu, Yuanyuan Zhang, Wenkai Zhou, Xinru Li, Guiling Li
Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology.2018; 46(sup3): 217. CrossRef - Ursolic acid from apple pomace and traditional plants: A valuable triterpenoid with functional properties
Simone Tasca Cargnin, Simone Baggio Gnoatto
Food Chemistry.2017; 220: 477. CrossRef - Phytochemicals for human disease: An update on plant-derived compounds antibacterial activity
Ramona Barbieri, Erika Coppo, Anna Marchese, Maria Daglia, Eduardo Sobarzo-Sánchez, Seyed Fazel Nabavi, Seyed Mohammad Nabavi
Microbiological Research.2017; 196: 44. CrossRef - Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential
Dharambir Kashyap, Hardeep Singh Tuli, Anil K. Sharma
Life Sciences.2016; 146: 201. CrossRef - Experimental Models of Oral Biofilms Developed on Inert Substrates: A Review of the Literature
Lopez-Nguyen Darrene, Badet Cecile
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Multi-functional Liposomes Enhancing Target and Antibacterial Immunity for Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Yansha Meng, Xucheng Hou, Jiongxi Lei, Mengmeng Chen, Shuangchen Cong, Yuanyuan Zhang, Weiming Ding, Guiling Li, Xinru Li
Pharmaceutical Research.2016; 33(3): 763. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity of constituents from Salvia buchananii Hedge (Lamiaceae)
Angela Bisio, Anna Maria Schito, Anita Parricchi, Giacomo Mele, Giovanni Romussi, Nicola Malafronte, Patrizia Oliva, Nunziatina De Tommasi
Phytochemistry Letters.2015; 14: 170. CrossRef
-
2,020
View
-
6
Download
-
18
Crossref
-
Esthetic rehabilitation of single anterior edentulous space using fiber-reinforced composite
-
Hyeon Kim, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):220-225. Published online May 19, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.220
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
A fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) fixed prosthesis is an innovative alternative to a traditional metal restoration, as it is a conservative treatment method. This case report demonstrates a detailed procedure for restoring a missing anterior tooth with an FRC. A 44-year-old woman visited our department with an avulsed tooth that had fallen out on the previous day and was completely dry. This tooth was replanted, but it failed after one year. A semi-direct technique was used to fabricate a FRC fixed partial prosthesis for its replacement. The FRC framework and the pontic were fabricated using a duplicated cast model and nanofilled composite resin. Later on, interproximal contact, tooth shape, and shade were adjusted at chairside. This technique not only enables the clinician to replace a missing tooth immediately after extraction for minimizing esthetic problems, but it also decreases both tooth reduction and cost. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Anterior provisional fixed partial dentures: A finite element analysis
Nouf Almeganni, Rotana Abulaban, Ghada Naguib, Mohamed Tharwat, Hani M. Nassar
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(4): 367. CrossRef - FİBERLE GÜÇLENDİRİLMİŞ ADEZİV KÖPRÜLER VE UYGULAMA YÖNTEMLERİ
Gözde YALÇIN, Asude Dilek NALBANT
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Fiber-reinforced composite resin bridges: an alternative method to treat root-fractured teeth
Gun Heo, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A New Technique for Direct Fabrication of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Bridge: A Long-Term Clinical Observation
Matías Ferrán Escobedo Martínez, Samuel Rodríguez López, Jairo Valdés Fontela, Sonsoles Olay García, Mario Mauvezín Quevedo
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(2): 48. CrossRef - Customized Treatment Option for Malpositioned Dental Implant Placed in Aesthetic Zone
Priyanka N. Khungar, Trupti M. Dahane, Ramnath P. Revankar, Rupali Patel
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(39): 2930. CrossRef - Fiber reinforced composite bridge as a replacement for missing upper permanent lateral incisor – a case report
Ana Todorović, Danica Popović, Igor Djordjević, Vojkan Lazić
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2016; 63(3): 133. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Viability of Rat Periodontal Ligament Cells after Storing at 0℃/2 MPa Condition up to One Week: In Vivo MTT Method
Sun Mi Jang, Sin-Yeon Cho, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2016; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Semidirect Restorations in Multidisciplinary Treatment: Viable Option for Children and Teenagers
Mateus Rodrigues Tonetto, Milton Carlos Kuga, Fausto Frizzera, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Shilpa H Bhandi, Célia Regina Maio Pinzan-Vercelino, Monica Barros da Silva, Kamila Figueiredo Pereira
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2015; 16(4): 280. CrossRef
-
1,737
View
-
5
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation on composite resins containing ursolic acid
-
Soohyeon Kim, Minju Song, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):65-72. Published online May 28, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.65
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the inhibitory effect of ursolic acid (UA)-containing composites on Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) biofilm. Materials and MethodsComposite resins with five different concentrations (0.04, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 wt%) of UA (U6753, Sigma Aldrich) were prepared, and their flexural strengths were measured according to ISO 4049. To evaluate the effect of carbohydrate source on biofilm formation, either glucose or sucrose was used as a nutrient source, and to investigate the effect of saliva treatment, the specimen were treated with either unstimulated whole saliva or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). For biofilm assay, composite disks were transferred to S. mutans suspension and incubated for 24 hr. Afterwards, the specimens were rinsed with PBS and sonicated. The colony forming units (CFU) of the disrupted biofilm cultures were enumerated. For growth inhibition test, the composites were placed on a polystyrene well cluster, and S. mutans suspension was inoculated. The optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was recorded by Infinite F200 pro apparatus (TECAN). One-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction were used for the data analyses. ResultsThe flexural strength values did not show significant difference at any concentration (p > 0.01). In biofilm assay, the CFU score decreased as the concentration of UA increased. The influence of saliva pretreatment was conflicting. The sucrose groups exhibited higher CFU score than glucose group (p < 0.05). In bacterial growth inhibition test, all experimental groups containing UA resulted in complete inhibition. ConclusionsWithin the limitations of the experiments, UA included in the composite showed inhibitory effect on S. mutans biofilm formation and growth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Anti-cariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid using dental microcosm biofilm
Jonghyun Jo, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Sun Kyu Park, Su-Jung Shin, Baek-il Kim, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105447. CrossRef - Rapid specific detection of oral bacteria using Cas13-based SHERLOCK
Jett Liu, Camden Carmichael, Hatice Hasturk, Wenyuan Shi, Batbileg Bor
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Bioactive Nanocomposites Containing Calcium Fluoride and Calcium Phosphate with Antibacterial and Low-Shrinkage-Stress Capabilities to Inhibit Dental Caries
Abdullah Alhussein, Rashed Alsahafi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Lamia Mokeem, Abraham Schneider, Mary-Ann Jabra-Rizk, Radi Masri, Gary D. Hack, Thomas W. Oates, Jirun Sun, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H. K. Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(9): 991. CrossRef - Quorum sensing inhibition and antibiofilm action of triterpenoids: An updated insight
Sudipta Paul Bhattacharya, Snigdha Karmakar, Kusumita Acharya, Arijit Bhattacharya
Fitoterapia.2023; 167: 105508. CrossRef - The Application of Small Molecules to the Control of Typical Species Associated With Oral Infectious Diseases
Sirui Yang, Xiaoying Lyu, Jin Zhang, Yusen Shui, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Planktonic and Anti-Biofilm Properties of Pentacyclic Triterpenes—Asiatic Acid and Ursolic Acid as Promising Antibacterial Future Pharmaceuticals
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska, Dorota Wojnicz
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 98. CrossRef - Development and Physicochemical Characterization of Eugenia brejoensis Essential Oil-Doped Dental Adhesives with Antimicrobial Action towards Streptococcus mutans
Maury Luz Pereira, Danyelle Cristina Pereira Santos, Carlos Alberto Mendes Soares Júnior, Tamyris Alicely Xavier Nogueira Bazan, Clovis Macêdo Bezerra Filho, Márcia Vanusa da Silva, Maria Tereza dos Santos Correia, Andres Felipe Millan Cardenas, Fabiana S
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(3): 149. CrossRef - Does Secondary Plant Metabolite Ursolic Acid Exhibit Antibacterial Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Living in Single- and Multispecies Biofilms?
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Wojnicz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(8): 1691. CrossRef - Prolonged Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Growth and Biofilm Formation by Sustained Release of Chlorhexidine from Varnish Coated Dental Abutments: An in Vitro Study
Mark Feldman, Walid Shaaban Moustafa Elsayed, Michael Friedman, Irith Gati, Doron Steinberg, Hesham Marei, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interkingdom Signaling Interference: The Effect of Plant-Derived Small Molecules on Quorum Sensing in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria
Janak Raj Joshi, Netaly Khazanov, Amy Charkowski, Adi Faigenboim, Hanoch Senderowitz, Iris Yedidia
Annual Review of Phytopathology.2021; 59(1): 153. CrossRef - Small Molecule Compounds, A Novel Strategy against Streptococcus mutans
Sirui Yang, Jin Zhang, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Pathogens.2021; 10(12): 1540. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide nanotubes added to glass ionomer cements affect S. mutans viability and mechanisms of virulence
Isaac Jordão de Souza ARAÚJO, Mariana Gallante RICARDO, Orisson Ponce GOMES, Priscila Alves GIOVANI, Júlia PUPPIN-RONTANI, Vanessa Arias PECORARI, Elizabeth Ferreira MARTINEZ, Marcelo Henrique NAPIMOGA, Francisco Humberto NOCITI JUNIOR, Regina Maria PUPPI
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ursolic and Oleanolic Acids on Lipid Membranes: Studies on MRSA and Models of Membranes
Sandrine Verstraeten, Lucy Catteau, Laila Boukricha, Joelle Quetin-Leclercq, Marie-Paule Mingeot-Leclercq
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1381. CrossRef - Ursolic acid inhibits multi-species biofilms developed by Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguinis, and Streptococcus gordonii
Xiaoying Lyu, Liang Wang, Yusen Shui, Qingsong Jiang, Lan Chen, Wen Yang, Xiaoya He, Jumei Zeng, Yuqing Li
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 125: 105107. CrossRef - The physical properties and anticariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid
Hyunkyung Yoo, So Youn Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 641. CrossRef - Ursolic acid: A systematic review of its pharmacology, toxicity and rethink on its pharmacokinetics based on PK-PD model
Qiang Sun, Man He, Meng Zhang, Sha Zeng, Li Chen, Lijuan Zhou, Haibo Xu
Fitoterapia.2020; 147: 104735. CrossRef - Effects of UVB and UVC irradiation on cariogenic bacteria in vitro
Shigeki Uchinuma, Yasushi Shimada, Khairul Matin, Keiichi Hosaka, Masahiro Yoshiyama, Yasunori Sumi, Junji Tagami
Lasers in Medical Science.2019; 34(5): 981. CrossRef - Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential
Dharambir Kashyap, Hardeep Singh Tuli, Anil K. Sharma
Life Sciences.2016; 146: 201. CrossRef - Protective Effects on Gastric Lesion of Ursolic acid
Sun Whoe Kim, In Young Hwang, Sun Yi Lee, Choon Sik Jeong
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2016; 31(4): 286. CrossRef - Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities
Łukasz Woźniak, Sylwia Skąpska, Krystian Marszałek
Molecules.2015; 20(11): 20614. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Dental materials with antibiofilm properties
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Dental Materials.2014; 30(2): e1. CrossRef - Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles onStreptococcus mutansandLactobacillus
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 109. CrossRef - Synergistic effect of xylitol and ursolic acid combination on oral biofilms
Yunyun Zou, Yoon Lee, Jinyoung Huh, Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 288. CrossRef - The virulence of Streptococcus mutans and the ability to form biofilms
W. Krzyściak, A. Jurczak, D. Kościelniak, B. Bystrowska, A. Skalniak
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.2014; 33(4): 499. CrossRef
-
1,678
View
-
5
Download
-
25
Crossref
-
Considerations during crown reattachment procedure over the pulpal exposure: case report
-
Bona Kim, Yoon Lee, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):240-244. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.240
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Crown reattachment is the most conservative treatment which can be used to restore fractured tooth, presumably with sufficient strength, while maintaining original contour, incisal translucency, and reducing chair time and cost. However, in case of crown fracture with pin-point pulp exposure, we should cautiously minimize the irritation to the pulp and consider pre-treatment pulpal status, choice of pulp capping materials, choice of bonding system and treatment sequence during crown reattachment procedures. This case reports the considerations while crown reattachment with direct pulp capping using calcium hydroxide (Dycal, Dentsply Caulk). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Conservative Approach to the Management of a Dental Trauma for Immediate Natural Esthetics
Pallav Mahesh Patni, Pradeep Jain, Mona Jain Patni
Archives of Trauma Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,254
View
-
7
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
'Wet or Dry tooth surface?' - for self-adhesive resin cement
-
Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):249-250. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.249
-
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Polymerization of resin cements by self-curing with or without adhesive treatment
Su Young LEE, Yasushi SHIMADA, Alireza SADR, Tomoko TABATA, Takaaki SATO, Ji-Eun BYUN, Seung-Hoon HAN
Dental Materials Journal.2025; 44(2): 129. CrossRef - Degree of conversion and interfacial adaptation of touch-cure resin cement polymerized by self-curing or dual-curing with reduced light
Su Young Lee, Yasushi Shimada, Alireza Sadr, Tomoko Tabata, Takaaki Sato, Ji-Eun Byun, Seung-Hoon Han
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Survival Rate of Self-Adhesive Resin Cement on Various Crown Materials: A Scoping Review
Annisa Fildzah Larasati, Veni Takarini, Vita Mulya Passa Novianti
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(4): 267. CrossRef - Effect of dentin moisture on the adhesive properties of luting fiber posts using adhesive strategies
Renata Terumi JITUMORI, Rafaela Caroline RODRIGUES, Alessandra REIS, João Carlos GOMES, Giovana Mongruel GOMES
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Pretreatment and Activation Mode on the Interfacial Adaptation of Nanoceramic Resin Inlay and Self-adhesive Resin Cement
Seung-Hoon Han, Yasushi Shimada, Alireza Sadr, Junji Tagami, Kee-Yeon Kum, Sung-Ho Park
Dental Materials.2020; 36(9): 1170. CrossRef - Interfacial Evaluation of CAD/CAM Resin Inlays on the Cavity Floor Using Swept-source Optical Coherence Tomography
S-H Han, Y Shimada, A Sadr, J Tagami, S-E Yang
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(6): 664. CrossRef - Development and characterization of biological bovine dentin posts
Alice Gonçalves Penelas, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Laiza Tatiana Poskus, Amanda Cypriano Alves, Isis Ingrid Nogueira Simões, Viviane Hass, José Guilherme Antunes Guimarães
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 92: 197. CrossRef - Influence of different drying methods on microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to dentin
Young Kyung Kim, Bong Ki Min, Jun Sik Son, Kyo-Han Kim, Tae-Yub Kwon
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2014; 72(8): 954. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef
-
1,117
View
-
3
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Effect of moisture and drying time on the bond strength of the one-step self-etching adhesive system
-
Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):155-159. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.155
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To investigate the effect of dentin moisture degree and air-drying time on dentin-bond strength of two different one-step self-etching adhesive systems. Materials and MethodsTwenty-four human third molars were used for microtensile bond strength testing of G-Bond and Clearfil S3 Bond. The dentin surface was either blot-dried or air-dried before applying these adhesive agents. After application of the adhesive agent, three different air drying times were evaluated: 1, 5, and 10 sec. Composite resin was build up to 4 mm thickness and light cured for 40 sec with 2 separate layers. Then the tooth was sectioned and trimmed to measure the microtensile bond strength using a universal testing machine. The measured bond strengths were analyzed with three-way ANOVA and regression analysis was done (p = 0.05). ResultsAll three factors, materials, dentin wetness and air drying time, showed significant effect on the microtensile bond strength. Clearfil S3 Bond, dry dentin surface and 10 sec air drying time showed higher bond strength. ConclusionsWithin the limitation of this experiment, air drying time after the application of the one-step self-etching adhesive agent was the most significant factor affecting the bond strength, followed by the material difference and dentin moisture before applying the adhesive agent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - An in vitro study on comparative evaluation of shear bond strength of bioactive composite to tooth structure with various dentin conditioning agents
Priyanka Pokkula, Shaik Mohammed Asif, Abdullah Alqarni, Shahabe Saquib Abullais, Shaik Mohamed Shamsudeen, Syed M Yassin, Abosofyan S. Atta, Wahaj Ahmad Khan
AIP Advances.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Drying Time, Application Mode, and Agitation on the Dentin Bond Strength of a Novel Mesoporous Bioactive Glass-Containing Universal Dentin Adhesive
Jiyoung Kwon, Jungwon Kim, Dongseok Choi, Duck-Su Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(7): 247. CrossRef - The occluding effects of layered calcium phosphate and cyanoacrylate on dentinal tubules: a SEM study
Özge Uzuner Bilgiç, Sühan Gürbüz, Altan Dogan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of two newly marketed self‐adhesive resin cements to different substrates: A light and scanning electron microscopy evaluation
Cansu Atalay, Uzay Koc Vural, Ivana Miletic, Sevil Gurgan
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(5): 1694. CrossRef - The effect of curing mode of dual-cure resin cements on bonding performance of universal adhesives to enamel, dentin and various restorative materials
Erick LUZ MADRIGAL, Antonin TICHY, Keiichi HOSAKA, Masaomi IKEDA, Masatoshi NAKAJIMA, Junji TAGAMI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(2): 446. CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef - Effect of pre-curing of two universal adhesives on the shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia
Ga-Eun Son, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2019; 46(1): 21. CrossRef - Bonding effectiveness of different dentin conditions on etch-and-rinse mode of two universal adhesives: the confocal laser scanning and shear bond strength
Jounghyun Lee, Ka-Young Cho, Jin-Young Kim, Sungho Park, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yooseok shin
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2017; 31(9): 933. CrossRef - Effect of dentin dehydration and composite resin polymerization mode on bond strength of two self-etch adhesives
Pooran Samimi, Mehdi Alizadeh, Farinaz Shirban, Amin Davoodi, Maryam Khoroushi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2016; 7(1): 16. CrossRef - Effect of different air-drying time on the microleakage of single-step self-etch adhesives
Horieh Moosavi, Maryam Forghani, Esmatsadat Managhebi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(2): 73. CrossRef
-
1,390
View
-
7
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Prevention of tooth discoloration associated with triple antibiotics
-
Bona Kim, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):119-122. Published online May 18, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Regenerative endodontics has a potential to heal a partially necrotic pulp, which can be beneficial for the continued root development and strengthening of immature teeth. For this purpose, triple antibiotic mixture of ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and minocycline was recommended as intracanal medicament in an attempt to disinfect the root canal system for revascularization of a tooth with a necrotic pulp. However, discoloration of the tooth was reported after applying this. This case shows the idea for preventing the tooth discoloration using a delivery syringe (SW-O-01, Shinwoo dental) to avoid the contact between the clinical crown and the antibiotics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Non-surgical Management of a Large Periapical Lesion: A Case Study of the Successful Application of a Modified Triple Antibacterial Paste
Srushti Awghad, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Amit Reche, Ankita Burse, Aradhana Kibe
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of two combinations of drugs on bacteria taken from infected primary teeth (in vitro)
R. Rafatjou, R. Yousefimashouf, M. Farhadian, S. Afzalsoltani
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2019; 20(6): 609. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Effectiveness of Different Polishing Systems and Self-Etch Adhesives in Class V Composite Resin Restorations: Two-Year Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
J-H Jang, H-Y Kim, S-M Shin, C-O Lee, DS Kim, K-K Choi, S-Y Kim
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Revascularization of Necrotic Immature Permanent Teeth: An Update
N Velmurugan
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 1(1): 18. CrossRef - Treatment of non-vital immature teeth with amoxicillin-containing triple antibiotic paste resulting in apexification
Hyon-Beom Park, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 322. CrossRef
-
1,117
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
-
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):16-23. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.16
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
Present study was undertaken to investigate the crystal growth onto synthetic hydroxyapatite (HA) seeds in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions with different fluoride concentrations.
Materials and Methods
8 groups of pH 4.3 and 7.0 calcium phosphate supersaturated solutions were prepared with different fluoride concentrations (0, 1, 2 and 4 ppm). Calcium phosphate precipitates yield crystal growth onto the HA seed surface while solutions flow. For evaluation of crystallizing process, the changes of Ca2+, PO43-, F- concentrations of the inlet and outlet solutions were determined. The recovered solid samples were weighed to assess the amount of minerals precipitated, and finally determined their composition to deduce characteristics of crystals.
Results
During the seeded crystal growth, there were significantly more consumption of Ca2+, PO43-, F- in pH 4.3 solutions than pH 7.0 (p < 0.05). As fluoride concentration increased in pH 4.3 solution, Ca2+, PO43-, F- consumption in experimental solutions, weight increment of HA seed, and fluoride ratio in crystallized samples were increased. There were significant differences among the groups (p < 0.05). But in pH 7.0 solution, these phenomena were not significant. In pH 7.0 solutions, analyses of crystallized samples showed higher Ca/P ratio in higher fluoride concentration. There were significant differences among the groups (p < 0.05). But in pH 4.3 solution, there were not significant differences in Ca/P
ratio.
Conclusions
Crystal growth in pH 4.3 solutions was superior to that in pH 7.0 solutions. In pH 4.3 solutions, crystal growth increased with showed in higher fluoride concentration up to 4 ppm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Qualitative analysis on crystal growth of synthetic hydroxyapatite influenced by fluoride concentration
Sumi Kang, Jeong Taeg Seo, Sung-Ho Park, Il Young Jung, Chan Young Lee, Jeong-Won Park
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 104: 52. CrossRef
-
1,111
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Understanding of the color in composite resin
-
Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):271-279. Published online July 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.271
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
In clinic, esthetic restoration of a defective natural tooth with composite resin is challenging procedure and needs complete understanding of the color of tooth itself and materials used. The optical characteristics of the composites are different because the chemical compositions and microstructures are not same.
This review provided basic knowledge of the color and the color measurement devices, and analyze the color of the natural tooth. Further, the accuracy of the shade tab, color of the composite resins before and after curing, effect of the water, food and bleaching agent, and translucency, opalescence, and fluorescence effects were evaluated. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Translucency and Masking Ability of Single-Shade Opaque Composite Resin Compared with Conventional Opaque Composite Resins According to Thickness
Junmo Jeong, Jongsoo Kim, Joonhaeng Lee, Jongbin Kim, Jisun Shin, Miran Han
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2025; 52(3): 312. CrossRef - Evaluation of Color Stability according to Shade of Temporary Crown Resin Using Digital Spectrophotometer: In Vitro Study
Hye-min Ku, Mi-Kyoung Jun
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2022; 22(3): 139. CrossRef - Effects of Children's Drinks on the Color Stability of Strip and Zirconia crown
Ilyong Jeong, Seoksoon Yi, Haney Lee, Daewoo Lee, Yeonmi Yang, Jaegon Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2017; 44(3): 306. CrossRef - Color and Translucency of Multi-Shade Layered Composites
Chang-Ha Lee, Bum-Soon Lim, In-Bog Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(4): 369. CrossRef - Color evaluation of composite resin using dental colorimeter according to the specimen size
Ji-Hye Jung, 심규리, 장훈상
Oral Biology Research.2016; 40(4): 198. CrossRef
-
1,951
View
-
47
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Patients' perception and satisfaction with apicoectomy
-
Euiseong Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):114-118. Published online March 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.114
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study was aimed to examine the patients' perception and satisfaction with the results of endodontic microsurgery which was apicoectomy with retrofilling.
Materials and Methods
A questionnaire was given to 109 patients, who were recalled after a minimum of 3 months upon endodontic microsurgery in the Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University. A contingency table and correlation analysis were used to determine if there were any correlations between age/gender and the patients' responses (p = 0.05).
Results
Approximately 60% of respondents answered they had never heard of surgical endodontic procedures. 63.3% of respondents chose the surgical option because they wanted to keep their natural teeth. If the patient required the same procedure on another tooth later, 100 out of 109 respondents answered they would choose microsurgery instead of extraction. Most patients (82.57%) appeared to be satisfied with the surgical procedure.
Conclusions
Endodontic microsurgery consisting of apicoectomy and retrofilling seems to appeal to majority of patients as a satisfactory and valuable treatment choice.
-
The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
-
Ye-Mi Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Min-Ju Song, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):119-124. Published online March 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate four different polishing systems of their polishability and polishing time.
Materials and Methods
4 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness Teflon mold was made. Z-250 (3M ESPE) hybrid composite resin was slightly overfilled and pressed with slide glass and cured with Optilux 501 for 40 sec each side. Then the surface roughness (glass pressed: control group) was measured with profilometer. One surface of the specimen was roughened by #320 grit sand paper and polished with one of the following polishing systems; Sof-Lex (3M ESPE), Jiffy (Ultradent), Enhance (Dentsply/Caulk), or Pogo (Dentsply/Caulk). The surface roughness and the total polishing time were measured. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
Results
The surface roughness was lowest in Pogo, and highest in Sof-Lex. Polishing times were shortest with Pogo, and followed by the Sof-Lex, Enhance and Jiffy.
Conclusions
One-step polishing system (Pogo) is very effective to get the smooth surface in a short time, therefore it can be recommended for final polishing system of the restoration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Observation of surface roughness on three types of resin based on grinding time of dental automatic barrel finishing
An-Na Jung, Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(2): 56. CrossRef - Observations of surface roughness of Co-Cr alloys according to grinding time of dental barrel finishing
Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(3): 93. CrossRef - Component and surface residue observation of barrel finishing media for grinding dental resins
An-Na Jung, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(4): 145. CrossRef - Performance of a novel polishing rubber wheel in improving surface roughness of feldspathic porcelain
Geum-Jun HAN, Jae-Hoon KIM, Mi-Ae LEE, So-Yeon CHAE, Yun-Hee LEE, Byeong-Hoon CHO
Dental Materials Journal.2014; 33(6): 739. CrossRef
-
1,473
View
-
9
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Influence of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in the immature tooth model
-
Jong-Hyun Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Il-Young Jung
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):257-266. Published online July 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.257
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in immature tooth model with various restorative techniques. Bovine incisors were sectioned 8 mm above and 12 mm below the cementoenamel junction to simulate immature tooth model. To compare various post-and-core restorations, canals were restored with gutta-percha and resin core, or reinforced dentin wall with dual-cured resin composite, followed by placement of D.T. LIGHT-POST, ParaPost XT, and various sizes of EverStick Post individually. All of specimens were stored in the distilled water for 72 hours and underwent 6,000 thermal cycles. After simulation of periodontal ligament structure with polyether impression material, compressive load was applied at 45 degrees to the long axis of the specimen until fracture was occurred.
Experimental groups reinforced with post and composite resin were shown significantly higher fracture strength than gutta-percha group without post placement (p < 0.05). Most specimens fractured limited to cervical third of roots. Post types did not influence on fracture resistance and fracture level significantly when cement space was filled with dual-cured resin composite. In addition, no statistically significant differences were seen between customized and standardized glass fiber posts, which cement spaces were filled with resin cement or composite resin individually. Therefore, root reinforcement procedures as above in immature teeth improved fracture resistance regardless of post types and sizes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Dental Posts used in Restoring Badly Broken Primary teeth
Tebra Alkayakh, Abdulrahim Aldarewesh
Libyan Journal of Medical Research.2024; 18(1): 65. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of fracture resistance of immature teeth subjected to apexification using three different bioactive materials
Aarshati Vyas, Shilpa Shah, Nishtha K Patel, Krushnangi Yagnik, Vyoma Hirpara, Rajvi Shah
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 7(4): 172. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Fracture Resistance of Simulated Immature Teeth Reinforced with a Novel Anatomic Post and MTA or Biodentine as an Apical Barrier: An In Vitro Study
Shivani H Dholakia, Mrunalini J Vaidya
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020; 4(2): 62. CrossRef - Rehabilitation of compromised permanent incisors with anatomically adjustable fiber post
Talat M. Beltagy
Tanta Dental Journal.2018; 15(1): 52. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of upper central incisors restored with different posts and cores
Maryam Rezaei Dastjerdi, Kamran Amirian Chaijan, Saeid Tavanafar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 229. CrossRef - Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef
-
1,347
View
-
4
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
The remineralization aspect of enamel according to change of the degree of saturation of the organic acid buffering solution in pH 5.5
-
Jin-Sung Park, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):96-105. Published online March 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.096
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to observe and compare the remineralization tendencies of artificial enamel caries lesion by remineralization solutions of different degree of saturations at pH 5.5, using a polarizing microscope and computer programs (Photoshop, Image pro plus, Scion Image, Excel).
For this study, 48 sound permanent teeth with no signs of demineralization, cracks, or dental restorations were used. The specimens were immersed in lactic acid demineralization solution for 2 days in order to produce artificial dental caries that consist of surface and subsurface lesions. Each of 9 or 10 specimens was immersed in pH 5.5 lactic acid buffering remineralization solution of four different degrees of saturation (0.507, 0.394, 0.301, and 0.251) for 12 days. After the demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by a polarizing microscope (×100). The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens, and using computer programs, the density of caries lesions were estimated.
While the group with the lowest degree of saturation (0.251) showed total remineralization feature from the surface to the subsurface of the lesion, the group with the highest degree of saturation (0.507) showed demineralization mainly on the surface of the lesion at the constant organic acid concentration 0.01 M and pH 5.5. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of a Mouthwash Containing Glycyrrhiza uralensis Extract for Preventing Dental Caries
Yu-Rin Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 242. CrossRef - Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
-
990
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Comparison of the residual stress of the nanofilled composites
-
Jeong-won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):457-462. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.457
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
"Residual stress" can be developed during polymerization of the dental composite and it can be remained after this process was completed. The total amount of the force which applied to the composite restoration can be calculated by the sum of external and internal force. For the complete understanding of the restoration failure behavior, these two factors should be considered. In this experiment, I compared the residual stress of the recently developed nanofilled dental composite by ring slitting methods.
The composites used in this study can be categorized in two groups, one is microhybrid type-Z250, as control group, and nanofilled type-Grandio, Filtek Supreme, Ceram-X, as experimental ones. Composite ring was made and marked two reference points on the surface. Then measure the change of the distance between these two points before and after ring slitting. From the distance change, average circumferential residual stress (σθ) was calculated. In 10 minutes and 1 hour measurement groups, Filtek Supreme showed higher residual stress than Z250 and Ceram-X. In 24 hour group, Filtek showed higher stress than the other groups.
Following the result of this experiment, nanofilled composite showed similar or higher residual stress than Z250, and when comparing the Z250 and Filtek Supreme, which have quite similar matrix components, Filtek Supreme groups showed higher residual stress. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems
Ji-Hoon Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 333. CrossRef
-
1,152
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The effectiveness of sealing technique on in-office bleaching
-
Yoon Lee, So-Ran Kwon, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):463-471. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.463
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study investigated the clinical effectiveness and safety of sealed bleaching compared to conventional in-office bleaching using a randomized clinical trial of split arch design. Ten participants received a chairside bleaching treatment on the upper anterior teeth, and each side was randomly designated as sealed or control side. A mixture of Brite powder (PacDent, Walnut, USA), 3% hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide (KoolWhite, PacDent, Walnut, USA) were used as bleaching agent. The control side was unwrapped and the experimental side was covered with a linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) wrap for sealed bleaching. The bleaching gel was light activated for 1 hour. The tooth shades were evaluated before treatment, after treatment, and at one week check up by means of a visual shade (VS) assessment using a value oriented shade guide and a computer assisted shade assessment using a spectrophotometer (SP). The data were analyzed by paired t-test.
In the control and sealed groups, the visual shade scores after bleaching treatment and at check up showed statistically significant difference from the preoperative shade scores (p < .05). The shade scores of the sealed group were significantly lighter than the control immediately after bleaching and at the check-up appointment (p < 0.05). Compared to prebleaching status, the ΔE values at post-bleaching condition were 4.35 ± 1.38 and 5.08 ± 1.34 for the control and sealed groups, respectively. The ΔE values at check up were 3.73 ± 1.95 and 4.38 ± 2.08 for the control and sealed groups. ΔE values were greater for the sealed group both after bleaching (p < .05) and at check up (p < .05).
In conclusion, both ΔE and shade score changes were greater for the sealed bleaching group than the conventional bleaching group, effectively demonstrating the improvement of effectiveness through sealing.
-
The influence of cavity configuration on the microtensile bond strength between composite resin and dentin
-
Yemi Kim, Jeong-won Park, Chan young Lee, Yoon jung Song, Deok Kyu Seo, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):472-480. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.472
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study was conducted to evaluate the influence of the C-factor on the bond strength of a 6th generation self-etching system by measuring the microtensile bond strength of four types of restorations classified by different C-factors with an identical depth of dentin.
Eighty human molars were divided into four experimental groups, each of which had a C-factor of 0.25, 2, 3 or 4. Each group was then further divided into four subgroups based on the adhesive and composite resin used. The adhesives used for this study were AQ Bond Plus (Sun Medical, Japan) and Xeno III (DENTSPLY, Germany). And composite resins used were Fantasista (Sun Medical, Japan) and Ceram-X mono (DENTSPLY, Germany).
The results were then analyzed using one-way ANOVA, a Tukey's test, and a Pearson's correlation test and were as follows.
There was no significant difference among C-factor groups with the exception of groups of Xeno III and Ceram-X mono (p < 0.05).
There was no significant difference between any of the adhesives and composite resins in groups with C-factor 0.25, 2 and 4.
There was no correlation between the change in C-factor and microtensile bond strength in the Fantasista groups.
It was concluded that the C-factor of cavities does not have a significant effect on the microtensile bond strength of the restorations when cavities of the same depth of dentin are restored using composite resin in conjunction with the 6th generation self-etching system. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of different chlorhexidine application times on microtensile bond strength to dentin in Class I cavities
Hyun-Jung Kang, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 9. CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Effect of Chlorhexidine Application Methods on Microtensile Bond Strength to Dentin in Class I Cavities
Y-E. Chang, D-H. Shin
Operative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 618. CrossRef - Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef
-
972
View
-
1
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Influence of thickness on the degree of cure of composite resin core material
-
Pyoung-Cheol Kwon, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):352-358. Published online September 30, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.352
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of thickness on the degree of cure of dual-cured composite core.
2, 4, 6, 8 mm thickness Luxacore Dual and Luxacore Self (DMG Inc, Hamburg, Germany) core composites were cured by bulk or incremental filling with halogen curing unit or self-cure mode. The specimens were stored at 37℃ for 24 hours and the Knoop's hardness of top and bottom surfaces were measured.
The statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Tukey's test at p = 0.05 significance level.
In self cure mode, polymerization is not affected by the thickness. In Luxacore dual, polymerization of the bottom surface was effective in 2, 4 and 6 (incremental) mm specimens. However the 6 (bulk) and 8 (bulk, incremental) mm filling groups showed lower bottom/top hardness ratio (p < 0.05). Within the limitation of this experiment, incremental filling is better than bulk filling in case of over 4 mm depth, and bulk filling should be avoided. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Strategies for enhancing the shear bond strength using highly acidic universal adhesive and dual-cured composite resin
Sumin Choi, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 11. CrossRef - A Study of Composite Surface Hardness When Cured Using Special Accessories with a Curing Light
Samir Koheil
Dental Research and Management.2020; : 11. CrossRef - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef
-
1,200
View
-
3
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Influence of additional etching on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive system to enamel
-
Sun-Jin Yoo, Young-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Won Park, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):263-268. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.263
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Recently, self-etching adhesive system has been introduced to simplify the clinical bonding procedures. It is less acidic compared to the phosphoric acid, thus there is doubt whether this system has enough bond strength to enamel. The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of additional etching on the adhesion of resin composite to enamel.
Ninety extracted bovine permanent anterior teeth were used. The labial surfaces of the crown were ground with 600-grit abrasive paper under wet condition. The teeth were randomly divided into six groups of 15 teeth each. Clearfil SE Bond®, Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE™ were used as self-etching primers. Each self-etching primers were applied in both enamel specimens with and without additional etching. For additional etching groups, enamel surface was pretreated with 32% phosphoric acid (UNI-ETCH, Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA). Hybrid resin composite Clearfil AP-X, (Kuraray Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) was packed into the mold and light-cured for 40 seconds. Twenty-four hours after storage, the specimens were tested in shear bond strength. The data for each group were subjected to independent t - test at p < 0.01 to make comparisons among the groups.
In Clearfil SE Bond®, shear bond strength of additional etching group was higher than no additional etching group (p < 0.01). In Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE, there were no significant difference between additional etching and non-etching groups (p > 0.01).
In conclusion, self-etching adhesive system with weak acid seems to have higher bond strength to enamel with additional etching, while self-etching adhesive system with strong acid seems not. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 23. CrossRef
-
1,254
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Evaluation of retrievability using a new soft resin based root canal filling material
-
Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):323-329. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.323
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the retrievability of Resilon as a root canal filling material. Twenty-seven human single-rooted extracted teeth were instrumented utilizing a crown down technique with Gates-Glidden burs and ProFile system. In group1 (n = 12) canals were obturated with gutta percha and AH-26 plus sealer using a continuous wave technique and backfilled. In group 2 (n = 15) Resilon was used as a filling material. Then teeth were sealed and kept in 37℃ and 100% humidity for 7 days. For retreatment, the samples were re-accessed and filling material was removed using Gates-Glidden burs and ProFiles. Teeth were sectioned longitudinally to compare the general cleanliness and amount of debris (× 75) using SEM. Chi-square test was used (α = 0.05) to analyze the data. The total time required for removal of filling materials was expressed as mean ± SD (min) and analyzed by the Student t-test (α = 0.05). Required time for retreatment was 3.25 ± 0.32 minutes for gutta percha/AH 26 plus sealer and 3.05 ± 0.34 minutes for Resilon. There was no statistically significant difference between the two experimental groups. There was no significant difference between the groups in the cleanliness of the root canal wall. This study showed that Resilon was effectively removed by Gates-Glidden burs and ProFiles. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - An in vitro evaluation of effectiveness of Xylene, Thyme oil and Orange oil in dissolving three different endodontic sealers
N Aiswarya, TN Girish, KC Ponnappa
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 305. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Two Commonly Used GP Solvents on Different Epoxy Resin-based Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Sakshi Tyagi, Ekta Choudhary, Rajat Chauhan, Ashish Choudhary
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(1): 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef - Microleakage of resilon by methacrylate-based sealer and self-adhesive resin cement
Sun-Young Ham, Jin-Woo Kim, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(3): 204. CrossRef - Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(2): 133. CrossRef
-
1,333
View
-
2
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Comparison of shear bond strength of different bonding systems on bleached enamel
-
Kwang-Keun Kim, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.030
-
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
Jeong-Lyong Son, Gye-Young Lee, Yu-Mi Kang, Young-Taek Oh, Kwang-Won Lee, Tae-Gun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 406. CrossRef - Effect of vital tooth bleaching agent on dentin bonding
Na-Young Jeong, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 79. CrossRef
-
1,132
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The effect of irradiation modes on polymerization and microleakage of composite resin
-
Jong-Jin Park, Jeong-Won Park, Sung-Ho Park, Ju-Myong Park, Tae-Kyung Kwon, Sung-Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):158-174. Published online March 31, 2002
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.158
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of light irradiation modes on polymerization shrinkage, degree of cure and microleakage of a composite resin.
VIP™ (Bisco Dental Products, Schaumburg, IL, USA) and Optilux 501™ (Demetron/Kerr, Danbury, CT, USA) were used for curing Filtek™ Z-250 (3M Dental Products, St. Paul., MN, USA) composite resin using following irradiation modes: VIP™ (Bisco) 200mW/cm2 (V2), 400mW/cm2 (V4), 600mW/cm2 (V6), Pulse-delay (200 mW/cm2 3 seconds, 5 minutes wait, 600mW/cm2 30seconds, VPD) and Optilux 501™ (Demetron/Kerr) C-mode (OC), R-mode (OR).
Linear polymerization shrinkage of the composite specimens were measured using Linometer (R&B, Daejeon, Korea) for 90 seconds for V2, V4, V6, OC, OR groups and for up to 363 seconds for VPD group (n=10, each).
Degree of conversion was measured using FTIR spectrometer (IFS 120 HR, Bruker Karlsruhe, Germany) at the bottom surface of 2 mm thick composite specimens. V2, V4, V6, OC groups were measured separately at five irradiation times (5, 10, 20, 40, 60 seconds) and OR, VPD groups were measured in the above mentioned irradiation modes (n=5, each).
Microhardness was measured using Digital microhardness tester (FM7, Future-Tech Co., Tokyo, Japan) at the top and bottom surfaces of 2mm thick composite specimens after exposure to the same irradiation modes as the test of degree of conversion(n=3, each).
For the microleakage test, class V cavities were prepared on the distal surface of the ninety extracted human third molars. The cavities were restored with one of the following irradiation modes: V2/60 seconds, V4/40 seconds, V6/30 seconds, VPD, OC and OR. Microleakage was assessed by dye penetration along enamel and dentin margins of cavities.
Mean polymerization shrinkage, mean degree of conversion and mean microhardness values for all groups at each time were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test, and using chi-square test for microleakage values.
The results were as follows:
·Polymerization shrinkage was increased with higher light intensity in groups using VIP™ (Bisco): the highest with 600mW/cm2, followed by Pulse-delay, 400mW/cm2 and 200mW/cm2 groups. The degree of polymerization shrinkage was higher with Continuous mode than with Ramp mode in groups using Optilux 501™ (Demetron/Kerr).
·Degree of conversion and microhardness values were higher with higher light intensity. The final degree of conversion was in the range of 44.7 to 54.98% and the final microhardness value in the range of 34.10 to 56.30.
·Microleakage was greater in dentin margin than in enamel margin. Higher light intensity showed more microleakage in dentin margin in groups using VIP™ (Bisco). The micoleakage was the lowest with Continuous mode in enamel margin and with Ramp mode in dentin margin when Optilux 501™(Demetron/Kerr) was used. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Study on the Effect of Soft-Start Light on Microleakage in Pit and Fissure Closure
Yong Chen, Ling Guo
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2023; 32(2): 105. CrossRef - Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
-
1,007
View
-
0
Download
-
2
Crossref
|