Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 36(2); 2011 > Article
- Basic Research The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
- Ye-Mi Kim, DDS, MS1, Su-Jung Shin, DDS, MS2, Min-Ju Song, DDS, MS2, Jeong-Won Park, DDS, PhD2
-
2011;36(2):-124.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.119
Published online: March 31, 2011
1Department of Dentistry, Ewha Woman's University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Conservative Dentistry, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- Correspondence to Jeong-Won Park, DDS, PhD. Associate Professor, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, 146-92 Dogok-dong Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea 135-720. TEL, +82-2-2019-1350; FAX, +82-2-3463-4052; pjw@yuhs.ac
• Received: January 19, 2011 • Revised: February 22, 2011 • Accepted: February 23, 2011
Copyright © 2011 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,602 Views
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref
Abstract
-
Objectives The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate four different polishing systems of their polishability and polishing time.
-
Materials and Methods 4 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness Teflon mold was made. Z-250 (3M ESPE) hybrid composite resin was slightly overfilled and pressed with slide glass and cured with Optilux 501 for 40 sec each side. Then the surface roughness (glass pressed: control group) was measured with profilometer. One surface of the specimen was roughened by #320 grit sand paper and polished with one of the following polishing systems; Sof-Lex (3M ESPE), Jiffy (Ultradent), Enhance (Dentsply/Caulk), or Pogo (Dentsply/Caulk). The surface roughness and the total polishing time were measured. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
-
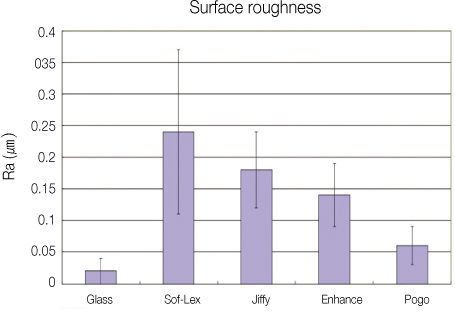
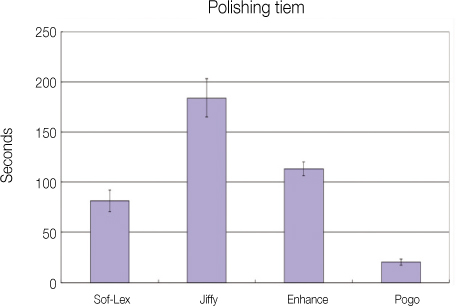
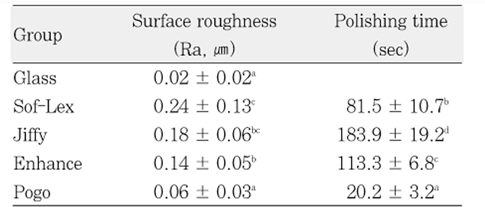
Results The surface roughness was lowest in Pogo, and highest in Sof-Lex. Polishing times were shortest with Pogo, and followed by the Sof-Lex, Enhance and Jiffy.
-
Conclusions One-step polishing system (Pogo) is very effective to get the smooth surface in a short time, therefore it can be recommended for final polishing system of the restoration.
- 1. Yap AU, Yap SH, Teo CK, Ng JJ. Finishing/polishing of composite and compomer restoratives: effectiveness of one-step systems. Oper Dent. 2004;29: 275-279.PubMed
- 2. Aykent F, Yondem I, Ozyesil AG, Gunal SK, Avunduk MC, Ozkan S. Effect of different finishing techniques for restorative materials on surface roughness and bacterial adhesion. J Prosthet Dent. 2010;103: 221-227.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bollen CM, Lambrechts P, Quirynen M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: a review of the literature. Dent Mater. 1997;13: 258-269.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Choi MS, Lee YK, Lim BS, Rhee SH, Yang HC. Changes in surface characteristics of dental resin composites after polishing. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2005;16: 347-353.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Neme AL, Frazier KB, Roeder LB, Debner TL. Effect of prophylactic polishing protocols on the surface roughness of esthetic restorative materials. Oper Dent. 2002;27: 50-58.PubMed
- 6. Stoddard JW, Johnson GH. An evaluation of polishing agents for composite resins. J Prosthet Dent. 1991;65: 491-495.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Chung KH. Effects of finishing and polishing procedures on the surface texture of resin composites. Dent Mater. 1994;10: 325-330.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Korkmaz Y, Ozel E, Attar N, Aksoy G. The influence of one-step polishing systems on the surface roughness and microhardness of nanocomposites. Oper Dent. 2008;33: 44-50.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Chen MH. Update on dental nanocomposites. J Dent Res. 2010;89: 549-560.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Türkün LS, Türkün M. The effect of one-step polishing system on the surface roughness of three esthetic resin composite materials. Oper Dent. 2004;29: 203-211.PubMed
- 11. Lee JY, Shin DH. Surface roughness of universal composites after polishing procedures. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2003;28: 369-377.Article
- 12. van Noort R, Davis LG. The surface finish of composite resin restorative materials. Br Dent J. 1984;157: 360-364.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Da Costa J, Ferracane J, Paravina RD, Mazur RF, Roeder L. The effect of different polishing systems on surface roughness and gloss of various resin composites. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2007;19: 214-224 discussion 225-216.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Quirynen M, Bollen CM, Papaioannou W, Van Eldere J, van Steenberghe D. The influence of titanium abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: short-term observations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996;11: 169-178.PubMed
- 15. Jones CS, Billington RW, Pearson GJ. The in vivo perception of roughness of restorations. Br Dent J. 2004;196: 42-45 discussion 31.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Fruits TJ, Miranda FJ, Coury TL. Effects of equivalent abrasive grit sizes utilizing differing polishing motions on selected restorative materials. Quintessence Int. 1996;27: 279-285.PubMed
- 17. St-Georges AJ, Bolla M, Fortin D, Muller-Bolla M, Thompson JY, Stamatiades PJ. Surface finish produced on three resin composites by new polishing systems. Oper Dent. 2005;30: 593-597.PubMed
- 18. Almeida GS, Poskus LT, Guimaräes JG, da Silva EM. The effect of mouthrinses on salivary sorption, solubility and surface degradation of a nanofilled and a hybrid resin composite. Oper Dent. 2010;35: 105-111.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Heintze SD, Forjanic M, Ohmiti K, Rousson V. Surface deterioration of dental materials after simulated tooth-brushing in relation to brushing time and load. Dent Mater. 2010;26: 306-319.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Khalichi P, Singh J, Cvitkovitch DG, Santerre JP. The influence of triethylene glycol derived from dental composite resins on the regulation of Streptococcus mutans gene expression. Biomaterials. 2009;30: 452-459.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Senawongse P, Pongprueksa P. Surface roughness of nanofill and nanohybrid resin composites after polishing and brushing. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2007;19: 265-273 discussion 274-275.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Evaluation of surface characteristic changes in a dental Co-Cr alloy with the automatic polishing time
Yeong-cheol Jeong, Byung-Wook Jeon, Sungmin Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2025; 47(4): 232. CrossRef - Observation of surface roughness on three types of resin based on grinding time of dental automatic barrel finishing
An-Na Jung, Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(2): 56. CrossRef - Observations of surface roughness of Co-Cr alloys according to grinding time of dental barrel finishing
Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(3): 93. CrossRef - Component and surface residue observation of barrel finishing media for grinding dental resins
An-Na Jung, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(4): 145. CrossRef - Performance of a novel polishing rubber wheel in improving surface roughness of feldspathic porcelain
Geum-Jun HAN, Jae-Hoon KIM, Mi-Ae LEE, So-Yeon CHAE, Yun-Hee LEE, Byeong-Hoon CHO
Dental Materials Journal.2014; 33(6): 739. CrossRef
The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
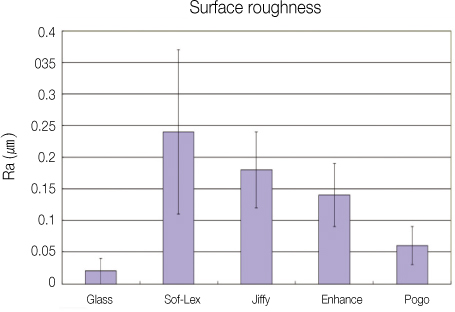
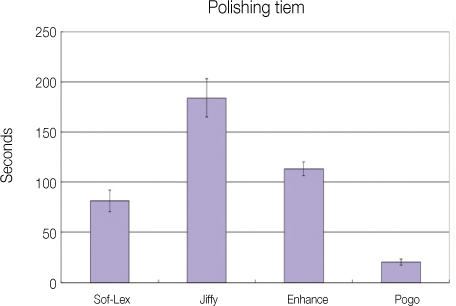
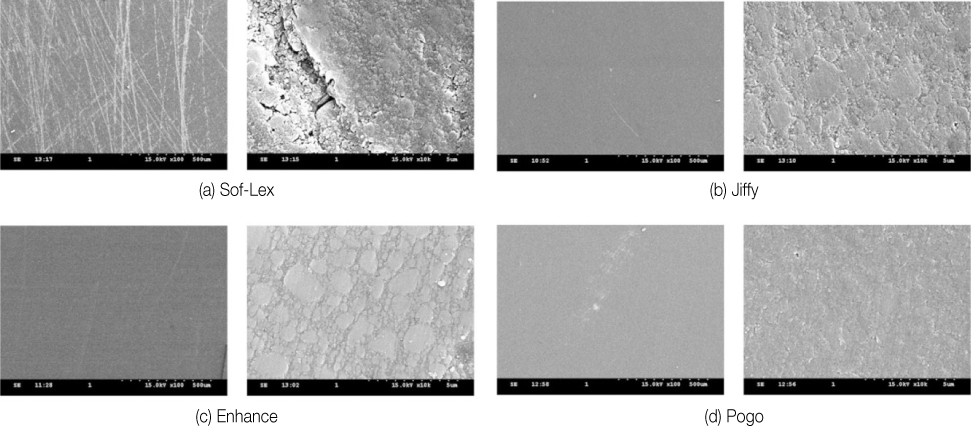
Figure 1
Surface roughness (Ra, µm) of composite resins with 4 different polishing systems.
Figure 2
Polishing time (seconds) of 4 different polishing systems.
Figure 3
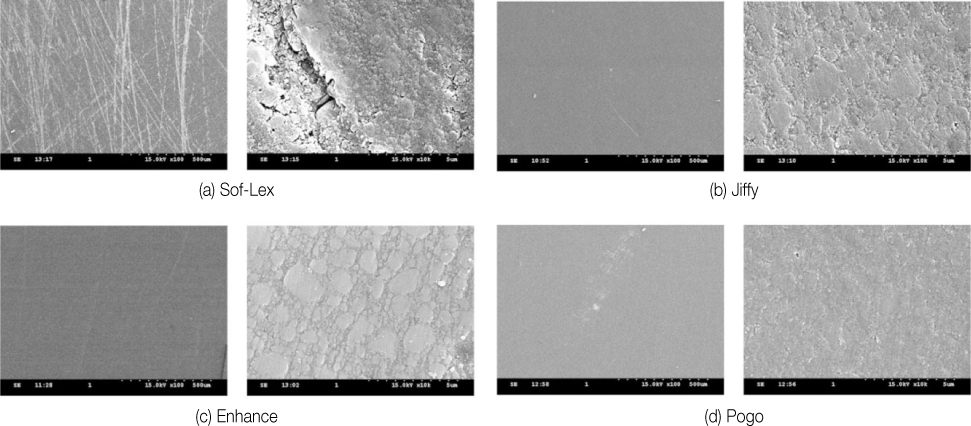
SEM image of the polished composite surface with each polishing system (left ×100, right ×10,000). SEM, scanning electron microscopr.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
Polishing systems used in this experiment
Surface roughness and polishing time for each polishing system (n = 13)
Different superscript in the same column means statistically significant difference (p < 0.05).
Table 1
Polishing systems used in this experiment
Table 2
Surface roughness and polishing time for each polishing system (n = 13)
Different superscript in the same column means statistically significant difference (

 KACD
KACD

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

