Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Resolvin E1 incorporated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold accelerates repair of dental pulp stem cells under inflammatory conditions: a laboratory investigation
- Hemalatha P Balasubramanian, Nandini Suresh, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e40. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
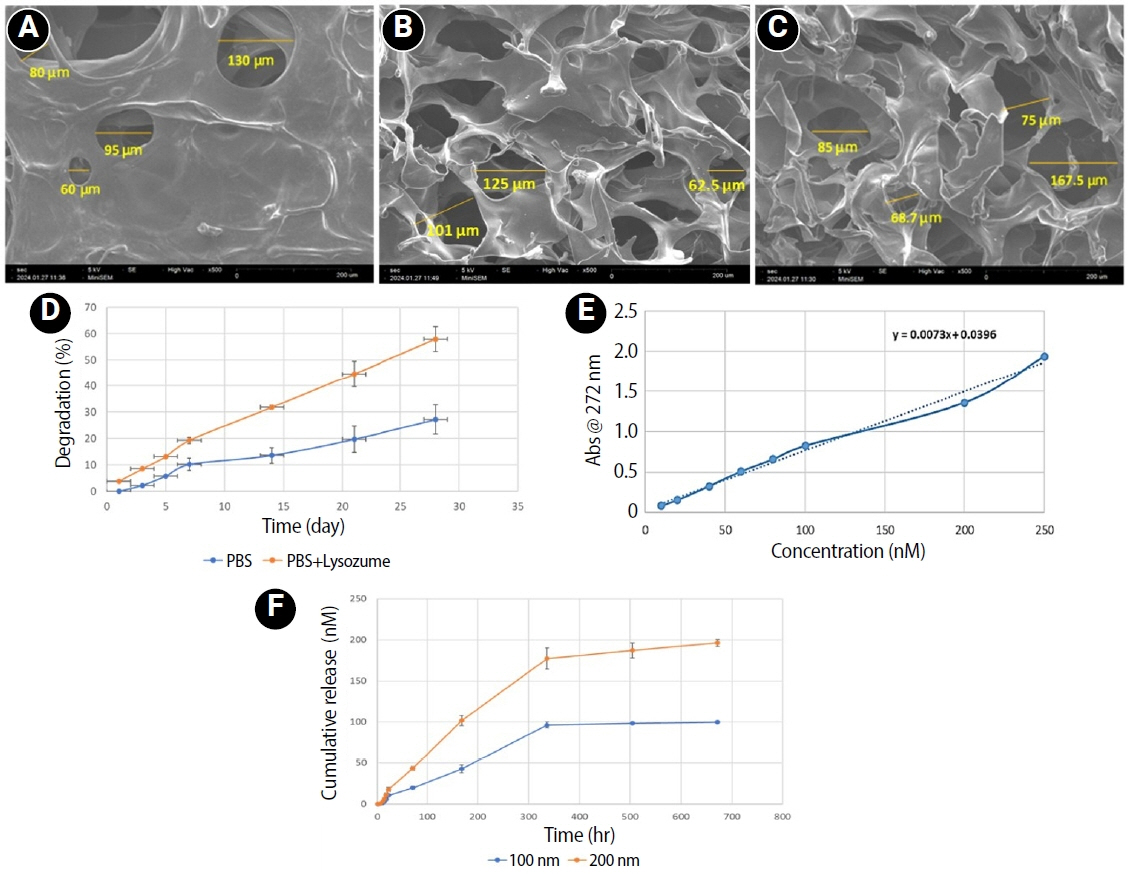
This study fabricated and characterized a resolvin E1 (RvE1)-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) scaffold and determined its cytotoxicity and mineralization potential on inflamed human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Methods
CMC scaffold incorporated with two concentrations of RvE1 (100 and 200 nM) was fabricated and characterized. The scaffolds’ porosity, drug release kinetics, and degradation were assessed. The impact of RvE1 on inflamed hDPSCs proliferation, proinflammatory gene expression (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), alkaline phosphatase activity, and alizarin red S staining was evaluated.
Results
Scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated a highly porous interconnected microstructure. Release kinetics showed gradual RvE1 release peaking at day 14. Cumulative degradation of the CMC scaffold at 28 days was 57.35%. Inflamed hDPSCs exposed to 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold exhibited significantly improved viability compared to 100 nM. Both RvE1-CMC scaffolds significantly suppressed the expression of TNF-α at 7 days. Alkaline phosphatase activity was enhanced by both RvE1 concentrations on days 7 and 14. Alizarin red staining revealed superior mineralization potential of 200 nM RvE1 on days 14 and 21.
Conclusions
This study concludes 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold is a promising therapy for inflamed pulp conditions, enhancing cell proliferation and biomineralization potential in inflamed hDPSCs.
- 754 View
- 36 Download

- Endodontic micro-resurgery and guided tissue regeneration of a periapical cyst associated to recurrent root perforation: a case report
- Fernando Córdova-Malca, Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Lucía Garré-Arnillas, Jorge Rayo-Iparraguirre, Gisele Faria
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e35. Published online September 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
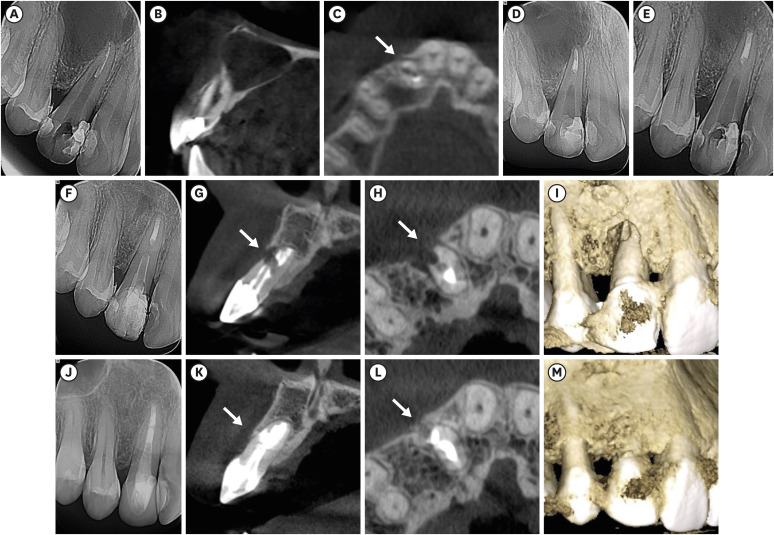
ePub Although the success rates of microsurgery and micro-resurgery are very high, the influence of a recurrent perforation combined with radicular cyst remains unclear. A 21-year-old white female patient had a history of root perforation in a previously treated right maxillary lateral incisor. Analysis using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) revealed an extensive and well-defined periapical radiolucency, involving the buccal and palatal bone plate. The perforation was sealed with bioceramic material (Biodentine) in the pre-surgical phase. In the surgical phase, guided tissue regeneration (GTR) was performed by combining xenograft (lyophilized bovine bone) and autologous platelet-rich fibrin applied to the bone defect. The root-end preparation was done using an ultrasonic tip. The retrograde filling was performed using a bioceramic material (Biodentine). Histopathological analysis confirmed a radicular cyst. The patient returned to her referring practitioner to continue the restorative procedures. CBCT analysis after 1-year recall revealed another perforation in the same place as the first intervention, ultimately treated by micro-resurgery using the same protocol with GTR, and a bioceramic material (MTA Angelus). The 2-year recall showed healing and bone neoformation. In conclusion, endodontic micro-resurgery with GTR showed long-term favorable results when a radicular cyst and a recurrent perforation compromised the success.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcome of endodontic micro-resurgery: A systematic review
Faisal Alnassar, Riyadh Alroomy, Qamar Hashem, Abdullah Alqedairi, Nabeel Almotairy
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 112. CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Endodontics: A Scoping Review
Simão Rebimbas Guerreiro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Anabela Paula, Joana Rita de Azevedo Pereira, Eunice Carrilho, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Siri Vicente Paulo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5479. CrossRef - Non-surgical Approach to a Maxillary Cyst-Like Lesion: Orthograde Endodontic Treatment With Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) Decontamination of the Canal System
Beatrice Spaggiari, Paolo Vescovi, Silvia Pizzi, Roberta Iaria, Ilaria Giovannacci
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Persistent Periradicular Lesion Associated With Concurrent Root Fracture and Odontogenic Keratocyst: A Case Report
Mehdi Vatanpour, Fatemeh Rezaei
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Apico-marginal Defects With Endodontic Microsurgery and Guided Tissue Regeneration: A Report of Thirteen Cases
Abayomi O. Baruwa, Jorge N.R. Martins, Mariana D. Pires, Beatriz Pereira, Pedro May Cruz, António Ginjeira
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(9): 1207. CrossRef
- Outcome of endodontic micro-resurgery: A systematic review
- 3,078 View
- 56 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin in endodontic microsurgery: a report of 2 cases
- Mariana Domingos Pires, Jorge N. R. Martins, Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Beatriz Pereira, António Ginjeira
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e17. Published online March 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
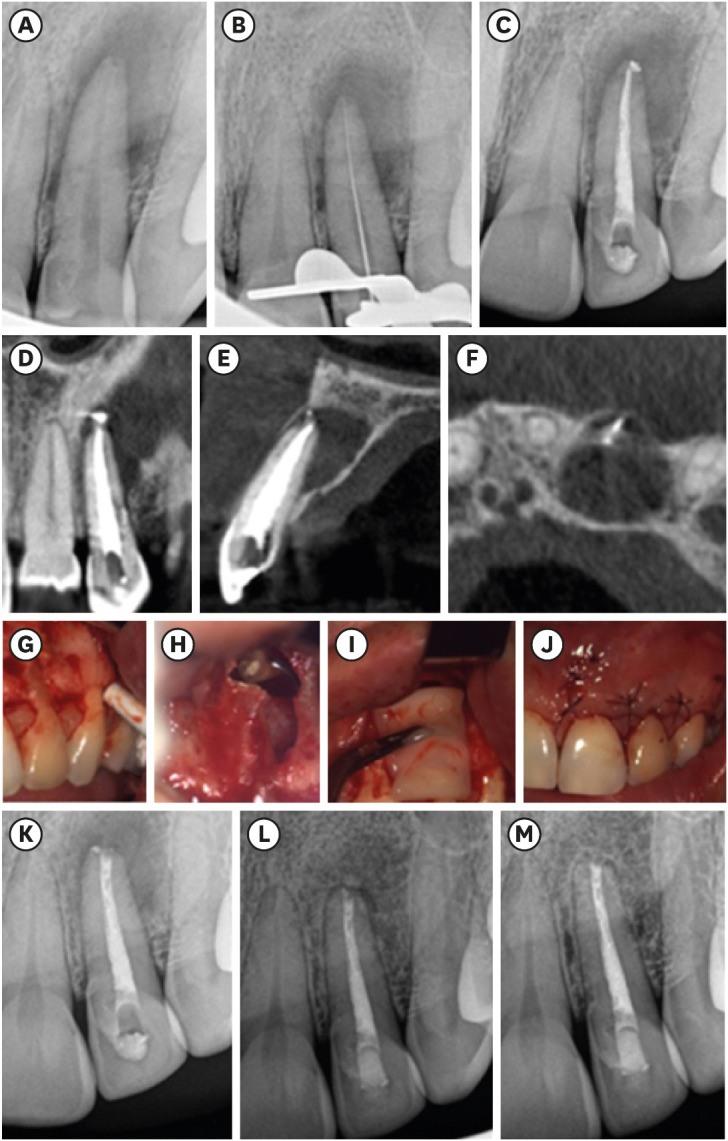
ePub Endodontic microsurgery is a predictable treatment option when orthograde treatment or retreatment is unsuccessful or unfeasible. However, when there is a gross compromise of periapical bone, achievement of bone regeneration after the surgical procedure may be hampered. In such cases, the application of guided tissue regeneration principles, with adjunctive use of leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin to fill the bone defect as a bone substitute and as a membrane to cover the site, provides a cost-effective solution with the benefits of accelerated physiological healing and reduced post-surgical pain and discomfort. This case report presents 2 cases of endodontic microsurgery of the upper lateral incisors with loss of buccal cortical plate, where platelet-rich fibrin was successfully applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Focuses and Trends of Research on Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
Ying Zhao, Chen Dong, Liumeizi Fan, Ting Lei, Xin Ge, Zhou Yu, Sheng Hu
Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery.2024; 57(05): 356. CrossRef
- Focuses and Trends of Research on Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
- 1,724 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
- Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e48. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
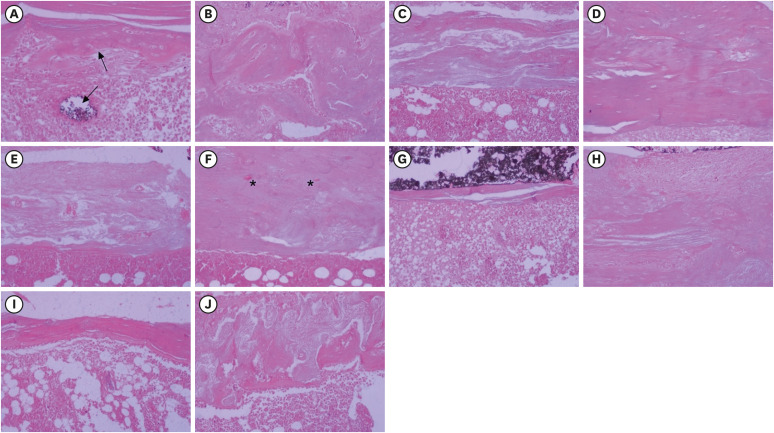
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effects on bone repair of different concentrations of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) added to AH Plus.
Materials and Methods Bone tissue reactions were evaluated in 30 rats (
Rattus norvegicus ) after 7 and 30 days. In the AH + MTA10, AH + MTA20, and AH + MTA30 groups, defects in the tibiae were filled with AH Plus with MTA in proportions of 10%, 20% and 30%, respectively; in the MTA-FILL group, MTA Fillapex was used; and in the control group, no sealer was used. The samples were histologically analyzed to assess bone union and maturation. The Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests were performed for multiple pairwise comparisons (p ≤ 0.05).Results At the 7-day time point, AH + MTA10 was superior to MTA-FILL with respect to bone union, and AH + MTA20 was superior to MTA-FILL with respect to bone maturity (
p < 0.05). At the 30-day time point, both the AH + MTA10 and AH + MTA20 experimental sealers were superior not only to MTA-FILL, but also to AH + MTA30 with respect to both parameters (p < 0.05). The results of the AH + MTA10 and AH + MTA20 groups were superior to those of the control group for both parameters and experimental time points (p < 0.05).Conclusions The results suggest the potential benefit of using a combination of these materials in situations requiring bone repair.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
Luciano Aparecido de Almeida-Junior, Giuliana de Campos Chaves Lamarque, Henry Herrera, Maya Fernanda Manfrin Arnez, Francine Lorencetti-Silva, Raquel Assed Bezerra Silva, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva, Francisco Wanderley Garcia Paula-Silva
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the research methods and progress of biocompatibility evaluation of root canal sealers
Xiliang Yang, Tianxia Zheng, Nuoya Yang, Zihan Yin, Wuliang Wang, Yuhong Bai
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 508. CrossRef - Effect of Vitapex Combined with AH-Plus Paste on Inflammation in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients with Periodontal-Endodontic Disease
Rong Hu, Fulan Zhang, Xiangyu Guo, Youren Jing, Xiaowan Lin, Liping Tian, Min Tang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
- 1,997 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development of a mouse model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research: a preliminary study
- Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Han-Sung Jung, Sun-Young Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e20. Published online May 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
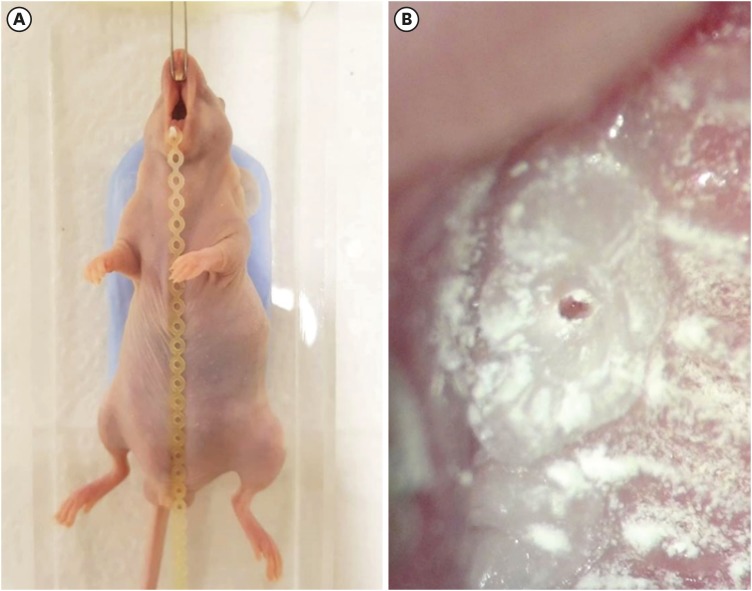
ePub Objectives To achieve pulp-dentin complex regeneration with tissue engineering, treatment efficacies and safeties should be evaluated using
in vivo orthotopic transplantation in a sufficient number of animals. Mice have been a species of choice in which to study stem cell biology in mammals. However, most pulp-dentin complex regeneration studies have used large animals because the mouse tooth is too small. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the utility of the mouse tooth as a transplantation model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research.Materials and Methods Experiments were performed using 7-week-old male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice; a total of 35 mice had their pulp exposed, and 5 mice each were sacrificed at 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, 12 and 14 days after pulp exposure. After decalcification in 5% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, the samples were embedded and cut with a microtome and then stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were observed under a high-magnification light microscope.
Results Until 1 week postoperatively, the tissue below the pulp chamber orifice appeared normal. The remaining coronal portion of the pulp tissue was inflammatory and necrotic. After 1 week postoperatively, inflammation and necrosis were apparent in the root canals inferior to the orifices. The specimens obtained after experimental day 14 showed necrosis of all tissue in the root canals.
Conclusions This study could provide opportunities for researchers performing
in vivo orthotopic transplantation experiments with mice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
Iago Ramirez, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula-Silva, Aline Aparecida Ferraresi Tiballi, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Christie Ramos Andrade Leite-Panissi, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 177: 106320. CrossRef - PRIASE 2021 guidelines for reporting animal studies in Endodontology: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, A. Kishen, P. E. Murray, M. H. Nekoofar, J. A. P. de Figueiredo, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, A. Jakovljevic, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(6): 858. CrossRef
- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
- 1,772 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Revitalization of necrotic mature permanent incisors with apical periodontitis: a case report
- Emre Nagas, M. Ozgur Uyanik, Zafer C. Cehreli
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e31. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
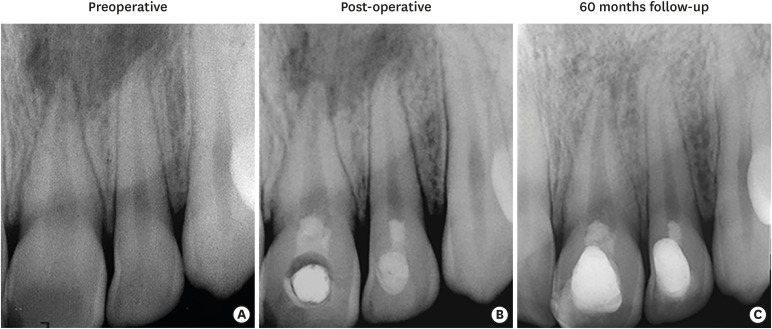
ePub Despite considerable focus on the regenerative endodontic treatment of immature teeth with necrotic infected pulps and apical periodontitis, little data exist with regard to its possible implementation in necrotic permanent teeth with complete apical and radicular development. The present report describes the procedures and outcome of a regenerative endodontic treatment approach in 2 previously-traumatized incisors with closed apex with apical periodontitis. A 2-visit treatment procedure was employed. At initial visit, the root canals were copiously irrigated, followed by placement of a triple antibiotic paste containing ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and clindamycin into the root canals. After 4 weeks, the antibiotic paste was removed, and apical bleeding was initiated with size 10 hand files beyond the apices. The root canals were coronally sealed with mineral trioxide aggregate, and the access cavities were restored with bonded resin composite. At post-operative 60 months, both teeth were remained asymptomatic, with the recall radiographs showing complete resolution of apical radiolucency and reestablishment of periradicular tissues. In both teeth, the dimensions of root space remained unchanged as verified by image analysis. The revitalization protocol utilizing root canal disinfection and induced apical bleeding in necrotic, closed-apex incisors may offer a clinically acceptable alternative to conventional root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role and Efficacy of Scaffolds in Regenerative Endodontics: A Survey of Current Practices and Perspective among Clinicians: A Questionnaire-based Study
Minusha Mohanan, Shabna Moyin, Shamsheer Thayyil, Anju Balachandran, Mary Elizabeth Nellickapalley Jacob, Koroth Valappil Harsha
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2026; 8(1): 10. CrossRef - Regenerative potential of concentrated growth factor compared to platelet-rich fibrin in treatment of necrotic mature teeth: a randomized clinical trial
Taghreed Salah, Wael Hussein, Heba Abdelkafy
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Pulp Revascularization in the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis in Mature Necrotic Teeth: An Umbrella Review
Wanderson Limeira de Sousa Barbosa, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Márcia Valente de Brito Dantas, Rômulo Dias Jesuino, João Marcos da Costa Ribeiro, Walbert A. Vieira, Felipe de Souza Matos
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 495. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of non-surgical retreatment of mature maxillary incisors using two regenerative endodontic techniques in adolescents: a 24-month randomized clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Sherif Shafik EL Bahnasy, Yassmin Mohamed ElMakawi, Mohammed Turky, Eman Farouk Ahmed, Norhan Khaled Omar Wahba
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of chitosan medicaments loaded with green-synthesized silver nanoparticles on basic fibroblast growth factor release from infected dentin
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Zehra Gun Gok, Nebahat Aytuna Cerci, Eray Ceylanoglu, Bengisu Ozturk, Ozum Hekim Harput, Sevda Durust Baris, Filiz Kiper, Ali Erdemir
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revolutionizing Endodontics: Innovative Approaches for Treating Mature Teeth With Closed Apices and Apical Lesions: A Report of Two Cases
Claudia Brizuela, Gastón Meza, Maroun Khoury
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 596. CrossRef - Current Aspects of Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review
A. V. Mitronin, K. A. Archakov, D. A. Ostanina, Yu. A. Mitronin, T. V. Khizrieva
Endodontics Today.2024; 21(4): 287. CrossRef - Correlation between pulp sensibility and magnetic resonance signal intensity following regenerative endodontic procedures in mature necrotic teeth- a retrospective cohort study
Noha Mohamed El-Kateb, Amr Mohamed Abdallah, Rania Noaman ElBackly
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of periapical lesion size on healing outcome following regenerative endodontic procedures: a clinical investigation
Noha Mohamed El Kateb, Mahmoud Mostafa Fata
Oral Radiology.2022; 38(4): 480. CrossRef - Do alternative scaffolds used in regenerative endodontics promote better root development than that achieved with blood clots?
Letícia de Araújo, Taynara Santos Goulart, Ana Clara Kuerten Gil, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Daniela de Rossi Figueiredo, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 22. CrossRef - Endodontic Regenerative Procedures in Necrotic Adult Teeth
Sara Garrido-Parada, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Nancy Feijoo-Pato, José Gaviño-Orduña, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(9): 4212. CrossRef - Combined conventional and regenerative treatment in molars with coexistent closed and open apices: A case series
Zafer C. Cehreli, Gizem Erbas Unverdi, Pinar Eymirli, Irem Mergen, Ezgihan Arslan, Gulce Esenturk
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 197. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Procedures for the Treatment of Necrotic Mature Teeth with Apical Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Antonios Glynis, Federico Foschi, Ismini Kefalou, Despina Koletsi, Giorgos N. Tzanetakis
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 873. CrossRef - Different Approaches to the Regeneration of Dental Tissues in Regenerative Endodontics
Anna M. Krupińska, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Tomasz Staniowski
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1699. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Intracanal Regenerated Tissues after Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Mature Teeth Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Noha Mohamed El-Kateb, Rania Noaman El-Backly, Wessam Mohamed Amin, Amr Mohamed Abdalla
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(5): 563. CrossRef
- The Role and Efficacy of Scaffolds in Regenerative Endodontics: A Survey of Current Practices and Perspective among Clinicians: A Questionnaire-based Study
- 2,499 View
- 30 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
- Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e28. Published online June 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the latest findings and notions regarding ‘triple antibiotic paste’ (TAP) and its applications in dentistry, particularly endodontics. TAP is a combination of 3 antibiotics, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and minocycline. Despite the problems and pitfalls research pertaining to this paste has unveiled, it has been vastly used in endodontic treatments. The paste's applications vary, from vital pulp therapy to the recently introduced regeneration and revascularisation protocol. Studies have shown that the paste can eliminate the root canal microorganisms and prepare an appropriate matrix for further treatments. This combination is able to remove diverse groups of obligate and facultative gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, providing an environment for healing. In regeneration protocol cases, this allows the development, disinfection, and possible sterilization of the root canal system, so that new tissue can infiltrate and grow into the radicular area. Moreover, TAP is capable of creating a discipline in which other wanted and needed treatments can be successfully performed. In conclusion, TAP, as an antibacterial intracanal medication, has diverse uses. Nevertheless, despite its positive effects, the paste has shown drawbacks. Further research concerning the combined paste and other intracanal medications to control microbiota is a must.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Permanent Incisors: Two Case Reports with 6 Years of Follow-Up
María Biedma-Perea, Marcela Arenas-González, María José Barra-Soto, Carolina Caleza-Jiménez, David Ribas-Pérez
Children.2026; 13(2): 246. CrossRef - Evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of an herbal preparation vs triple antibiotic paste against E. faecalis: an in vitro study
Chandni Dhyani, Kalpna Chaudhry, Nitin Khanduri, Leina R. Pradhan, Yoshita Gupta
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics.2026; 13(3): 449. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Laser in Root Canal Disinfection in Pulp Regenerative Therapy: A Systematic Review
Kiran Kumar N, Abhishek M, Savitha B. Naik, Biji Brigit, Swetha Geervani V, M Manimozhi
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2025; 43(2): 53. CrossRef - Assessing Cell Viability: Comparative Analysis of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste, and Their Synergistic Impact on human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Dini Asrianti Bagio, Ibramanto Warganegara, Ike Dwi Maharti, Anggraini Margono, Citra Kusumasari, Sylva Dinie Alinda, Valeria Widita Wairooy
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(01): 073. CrossRef - Cytotoxic and Antibiofilm Properties of Antibiotic-Loaded Thermoresponsive Hydrogels for Root Canal Therapy
Cristiane Duque, Gabriela Pacheco de Almeida Braga, Juliana Machado de Carvalho, Karina Sampaio Caiaffa, Gabriel Pereira Nunes, Rafaela Laruzo Rabelo, Vanessa Rodrigues dos Santos, Geórgia Rondó Peres, Lucas da Silva Ribeiro, Emerson Rodrigues de Camargo
Processes.2025; 13(3): 661. CrossRef - Antibiofilm properties, cytotoxicity, and effect on protease activity of antibiotics and EGCG-based medications for endodontic purposes
Daniela Alvim Chrisostomo, Jesse Augusto Pereira, Polliana Mendes Candia Scaffa, Zach Gouveia, Gabriel Flores Abuna, Sergey V. Plotnikov, Anuradha Prakki, Cristiane Duque
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105660. CrossRef - The use of three-dimensional-printed guides, static navigation, and bioactive materials to treat bilateral and double dens invaginatus
Parth Patel, Nidhi Bharti, Ankit Arora, C. Nimisha Shah
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 207. CrossRef - To Assess the Cell Viability of Triple Antibiotic Paste under Confocal Microscope: An In Vitro Study
Elanthendral Saravanan, Mahesh Ramakrishnan
Journal of South Asian Association of Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 8(2): 81. CrossRef - Eficacia de la pasta triantibiótica en endodoncia: actividad antibacteriana frente a cepas resistentes de Enterococcus faecalis. Una revisión exhaustiva
Elena Patricia Cevallos Fernández, Katherine de los Ángeles Cuenca León
Anatomía Digital.2025; 8(3.1): 88. CrossRef - Efectividad de diferentes antimicóticos, junto con la pasta triantibiotica, para el tratamiento de Candida albicans en conductos radiculares
Carlos Andrés Rodríguez Tapia, Jessica María Sarmiento Ordoñez
Anatomía Digital.2025; 8(3.2): 45. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste, and Calcium Hydroxide with 2% Chlorhexidine as Intracanal Medicaments in Reducing Interappointment Pain during Endodontic Treatment: An In Vivo Study
Rachit Mathur, Shaista Gazal, Itika Jain, Shyam Agrawal, Akshada Mungee, Babra Khan
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(6): 628. CrossRef - In Vitro Effectiveness of Endodontic Triple Antibiotic Paste Associated With Daptomycin
Sabrina S Azevedo, Gabriela C Chianca, Bruna A Thurler, Raiane C Chamon, Helvécio C Corrêa Póvoa, Leonardo S Antunes, Natalia L Pontes Póvoa Iorio
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Chitosan and bioactive glass nanomaterials as intracanal medicaments on TGF-β1 release from intraradicular dentin
Sarah Salah Hashem, Mohammed M. Khalefa, Mahmoud Hassan Mohamed, Hemat M. ELSheikh, Fatma Abd El-Rahman Taher
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of lesion sterilization and tissue repair in primary teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Khlood Baghlaf, Rana A. Alamoudi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Cannabinoids on Bacteria Associated with Persistent Endodontic Infections
Cassandra Wieczerza, Haoyan Zhai, Mazin Askar, Zheng Zhou, Susan Paurazas
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11936. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Herbal Extracts and Triple Antibiotic Paste as Intracanal Medicament against Enterococcus faecalis: A Microbiological Study
Divya Singh, Rashi Singh, Nidhi Gupta, Natasha Gambhir, Saritha Golla
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(3): 285. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-Out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, a Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, and Two Novel Antibacterial-Enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Arokia Rajkumar Shancy Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Rajalakshmanan Eswaramoorthy, Abirami Arthanari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Oleanolic Acid as a Potential Root Canal Medicament on Viability and Proliferation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Khalifah A. Alhaila, Manal Farouk Badawi, Mohamed G. Elbeltagy, Amany E. Badr
European Journal of General Dentistry.2024; 13(01): 051. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Dentinogenesis Imperfecta‐Induced Apical Periodontitis
Ying Liao, Ting Pan, Xianghui Xing, Sivakumar Nuvvula
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efecto antimicrobiano como medicación intraconducto de la pasta triantibiótica.
Paúl Sebastián Ulloa Amores, Diana Álvarez Álvarez, María Elizabeth Moscoso Abad, Magda Zulay Bastidas Calva
Revista de la Asociación Dental Mexicana.2024; 81(4): 211. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Nanosilica-Coated Antibiotics, TAP: A Comprehensive Study Utilizing XRD, EDS, FTIR, SEM, and TEM – Invitro Study
Mahaboob S. Hameed, S. Delphine P. Antony, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Sandhya Raghu
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(5): 386. CrossRef - Association between host defence peptide IDR‐1002 and ciprofloxacin: Effects on human dental pulp cells
Danilo César Mota Martins, Maurício Gonçalves da Costa Sousa, Poliana Amanda Oliveira Silva, Lana Ribeiro Aguiar, Rosângela Vieira de Andrade, Amandda Évellin Silva‐Carvalho, Felipe Saldanha‐Araújo, Octávio Luiz Franco, Taia Maria Berto Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 547. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste and amoxicillin clavulanate paste as an intracanal medicament against Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro study
Dhandayuthapani Sasikala, Parisa Norouzi Baghkomeh, Jamaluddin Mohammed Farzan
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Game Changer in Endodontics
Kalagi G. Panchal, Karima Virani, Vraj Patel, Aquib Ali Khan, Anam Pettiwala, Srikala S. Puranik, Srushti Joshi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S1913. CrossRef - Non-surgical Management of a Large Periapical Lesion: A Case Study of the Successful Application of a Modified Triple Antibacterial Paste
Srushti Awghad, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Amit Reche, Ankita Burse, Aradhana Kibe
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing Antimicrobial Efficacy and Synergistic Effects of Nano-Silica-Based Combinations With Doxycycline, Metronidazole, and Ciprofloxacin Against Enterococcus faecalis Biofilms
Shahul Hameed, Delphine P Antony, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Sandhya Raghu, Hima Sandeep Adimulapu
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of periapical lesion by non-surgical endodontic therapy: A case series
Athira Ramesh, Rajesh Pillai, Afzal A, Anakha Santhosh, Arunima G.S, Sandeep K. V
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2024; 9(2): 99. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Versus Double Antibiotic Paste on Endodontic Treatment Outcomes in Teeth With Large Periapical Lesions: A Triple‐Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
Afsaneh Rahmati, Farshad Seyedein, Omid Dianat, Sara Saedi, Golriz Rostami, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Shima Sabertahan, Majid Kazem, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Can antimicrobial photodynamic therapy serve as an effective adjunct protocol for disinfecting the necrotic root canal system? A randomized controlled study
Remy Barazy, Hisham Alafif, Hassan Achour, Ahmad Al-Aloul, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Drain and Treat: A Rubber Dam Technique for Acute Periapical Abscess
S. Grover, K. Mala, J. D’Souza
Acta Medica Bulgarica.2024; 51(s2): 143. CrossRef - Microbial Dynamics in Endodontic Pathology—From Bacterial Infection to Therapeutic Interventions—A Narrative Review
Klara Wieczorkiewicz, Anna Jarząbek, Estera Bakinowska, Kajetan Kiełbowski, Andrzej Pawlik
Pathogens.2024; 14(1): 12. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of the effect of three intracanal medicaments – chlorhexidine gel, triple antibiotic paste, and calcium hydroxide paste on the push-out bond strength of MTA Plus, Biodentine, and calcium-enriched mixture
Gouthami Datta, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Gautham P Manjunath, Dishant Patel, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - The cytotoxic effect of cysteamine and its combinations with various endodontic intracanal medications on fibroblast cells: in vitro study
Esraa Adel Mohamed Abd Elhameed ElGammal, Abeer Hashem Mahran, Salma Hassan El Ashry, Sara Hossam Fahmy
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of large endodontic lesions using a new combination of triple antibiotics: A case report
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of herbal agents as intracanal medicaments individually or in combination with chitosan: An in vitro RTPCR study
Gaurav Patri, Kotni Sheetal, PrasantiKumar Pradhan, Pratik Agrawal, S Lata
Journal of International Oral Health.2023; 15(1): 89. CrossRef - Recent progress in carbon dots for anti-pathogen applications in oral cavity
Yuying Jiang, Chuqiang Yin, Jianning Mo, Xiaoyu Wang, Ting Wang, Guotai Li, Qihui Zhou
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair: An Alternative for Pulpectomy in Deciduous Teeth
Aparna Achanta, Amit Reche, Rishika Dakhale, Rudra R Bharate
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of Large Endodontic Lesions Using Long‐Term Application of a New Combination of Triple Antibiotics: A Series of Cases
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar, Maria Beatriz Duarte Gavião
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-cytotoxic Root Canal Dressing with Improved Antimicrobial Efficacy
Farzad Koosha, Jerome Cymerman, Thomas Manders, Marcia Simon, Stephen Walker, Miriam Rafailovich
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(2): 205. CrossRef - Triple antibiotics: A synergistic approach to combating infection
Hemant Sawhney, Anukriti Kumari, Ritik Kashwani, Geetanjali Gupta, SJ Das
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 8(4): 189. CrossRef - A 1-year Clinical and Radiographic Assessment of Regenerative Endodontic Therapy for Necrotic Primary Molars: A Randomized controlled Trial
Dina D Abdelmoneim, Amr M Abdelaziz, Gehan G Allam, Amira S Badran
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(2): 295. CrossRef - “BIODENTINE” THE DENTINE IN A CAPSULE AS AN APICAL BARRIER IN TRAUMATIZED MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISOR WITH TWO YEARS FOLLOW UP.
Savita Thakur, Udai Bhanu, Gurkirat Singh Grewal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 64. CrossRef - Long-term treatment of dentine with triple antibiotic paste promotes stem cell viability and attachment
Samiya Riaz, Ahmad Azlina, Zuliani Mahmood, Aung T. Htun
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2022; 17(4): 630. CrossRef - Non surgical management of trauma induced root resorption and large periapical
lesion using bioactive material- A case report
Tejasvini Prajapati, Sonali Kapoor, Purnil Shah, Ankit Arora, Hardik Rana
Clinical Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of antibiotic pastes versus calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies
Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Kamyar Khosravi, Nazanin Zargar, Armin Shirvani, MohammadHossein Nekoofar, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 463. CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Suitable Medicament for Intracanal Disinfection
Krutika Malu, Monika Khubchandani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Present status and future directions of intracanal medicaments
Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Alejandro Perez‐Ron, Zhou Ye, Jorge Vera
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 613. CrossRef - The effect of four different intracanal medicaments on the push-out bond strength of root canal sealers
Shalu Maan, Vijaya Dhar Bhatt, Rohit Singh, Sayak Gupta, Syed Alay Noorain, Aashna Gill, Pradeep Kumar, Sushil Yadav, Preeti Sharma
Journal of Medicine and Life.2022; 15(4): 448. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Microhardness and Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentin with Two Combinations of TAP and MTAP: An In Vitro Study
P Niharika, Saigeeta Kondamadugu, Nagireddy Venugopal Reddy, Muthumula Daneswari, Annie P Chris, Nikhila V Reddy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S2): S151. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Antibiotic Pastes for Root Canal Disinfection
Sadhna Sharma, Urvashi Bhushan, Mridula Goswami, CP Baveja
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S1): S12. CrossRef - Management of External Inflammatory Root Resorption following Tooth Autotransplantation Using a Modified Combination of Triple Antibiotics
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar, Paulo J. Palma
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic paste on the bond strength of epoxy and methacrylate resin-based sealers to root canal dentin
Fereshte Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl, Mahdi Sedigh-Shams, Hossein Mirkhaghani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 426. CrossRef - Progress of Research on the Application of Triple Antibiotic Paste and Hydrogel Scaffold Materials in Endodontic Revascularization: A Systematic Review
Jia Zhao, Tian Jiao Wang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The effect of different intracanal medicaments on the dislodgement resistance of mineral trioxide aggregate
Farzaneh Afkhami, Shahrzad Razavi, Sholeh Ghabraei
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole and Minocycline in Ordered Mesoporous Silica against Enterococcus faecalis for Dental Pulp Revascularization: An In-Vitro Study
Cintia Micaela Chamorro-Petronacci, Beatriz Santos Torres, Rocío Guerrero-Nieves, Mario Pérez-Sayáns, Marcia Carvalho-de Abreu Fantini, Luis Carlos Cides-da-Silva, Beatriz Magariños, Berta Rivas-Mundiña
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2266. CrossRef - Antibiotic Mixtures in Noninstrumental Endodontic Treatment of Primary Teeth with Necrotic Pulps: A Systematic Review
Farah Chouchene, Fatma Masmoudi, Ahlem Baaziz, Fethi Maatouk, Hichem Ghedira, Sivakumar Nuvvula
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Potential apply of hydrogel-carried chlorhexidine and metronidazole in root canal disinfection
Yanhong YAN, Peng ZHOU, Haibing LU, Yun GUAN, Ming MA, Juan WANG, Guangwei SHANG, Beizhan JIANG
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(4): 986. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Nitrofurantoin Paste as an Intracanal Medicament on the Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentine
Mewan Abdulrahman, Bestoon Faraj, Kawa Dizaye
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 8. CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Antibiofilm and cytotoxic effect of 3,3′-dihydroxycurcumin (DHC) as photosensitizer agent in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for endodontic purposes
Jesse Augusto Pereira, Carlos Roberto Polaquini, VanessaRodrigues dos Santos, Karina Sampaio Caiaffa, Rafaela Laruzo Rabelo, Reinaldo dos Santos Theodoro, Letícia Helena Theodoro, Luis Octavio Regasini, Cristiane Duque
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 36: 102534. CrossRef - An in-vitro Comparative Evaluation of Quantitative Release of Transforming Growth Factor β-1 from Dentin upon the Action of Endodontic Irrigants, Medicaments, Ultrasonic Activation, and Low-Level Laser Irradiation
Anilkumar Akhila, V. P. Prabath Singh, Kerala R. Varma, Senthil V. Vasudevan, V. Sukhithasri, Salu Sasikumar
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2021; 17(2): 34. CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide on the rate of healing of periapical lesions: A systematic review
NKiran Kumar, Biji Brigit, BS Annapoorna, SavithaB Naik, Seema Merwade, K Rashmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 307. CrossRef - Comparison of the efficacy of CanalBrush, EndoActivator, and Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation on the removal of triple antibiotic paste from root canal walls: An in vitro study
Santosh Kumar, Kavisha Desai, Aparna Palekar, Baswaraj Biradar, Ananjan Chatterjee, Khushboo Kumari
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2020; 10(4): 424. CrossRef - Apexification with Calcium Hydroxide vs. Revascularization
H. Boufdil, M. Mtalsi, S. El Arabi, B. Bousfiha, Jose López-López
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Intracanal Medicaments and Irrigants on the Release of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor from Cervical Root Dentin
Lívia Nazareth Ferreira, Regina Maria Puppin-Rontani, Fernanda Miori Pascon
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(11): 1616. CrossRef - Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Nitrofurantoin as an Experimental Intracanal Medicament in Endodontics
Mewan Salahalddin A. Alrahman, Bestoon Muhammed Faraj, Kawa F. Dizaye, Abdelwahab Omri
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - An in vitro assessment of effect on microhardness of dentin using vicker's hardness method
Manoj Chandak, Richa Modi, Rakesh Gogiya, Rakhi Chandak, Anuja Ikhar, Nikhil Mankar
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University.2020; 15(2): 251. CrossRef - Inspection of the Microbiota in Endodontic Lesions
Mario Dioguardi, Giovanni Di Gioia, Gaetano Illuzzi, Claudia Arena, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Giorgia Apollonia Caloro, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Iolanda Adipietro, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(2): 47. CrossRef - Materials for pulpotomy in immature permanent teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuan Chen, Xinlei Chen, Yali Zhang, Fangjie Zhou, Jiaxin Deng, Jing Zou, Yan Wang
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic therapy to conventional chemo-mechanical debridement of infected root canal systems: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Maryam Pourhajibagher, Abbas bahador
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2019; 26: 19. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Effects of Photodynamic Therapy, Modified Triple Antibiotic Paste and Calcium Hydroxide on Root Canals Infected With Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Mohammad Asnaashari, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Amirali Sahba Yaghmayi, Mehdi Shokri, Saranaz Azari-Marhabi
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2019; 10(5): S23. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 16,429 View
- 181 Download
- 74 Crossref

- Management of apicomarginal defect in esthetic region associated with a tooth with anomalies
- Vinayak Venkoosa Meharwade, Dipali Yogesh Shah, Pradyna Prabhakar Mali, Vidya Vinayak Meharwade
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):314-321. Published online June 24, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.314
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Tooth related factors such as palatoradicular groove can be one of the causes for localized periodontal destruction. Such pathological process may result in apicomarginal defect along with inflammation of pulp. This creates challenging situation which clinician must be capable of performing advanced periodontal regenerative procedures for the successful management. This case report discusses clinical management of apicomarginal defect associated with extensive periradicular destruction in a maxillary lateral incisor, along with histopathologic aspect of the lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical treatment of apico-marginal defect associated with maxillary incisor teeth with a large periapical lesion using sticky bone & platelet rich fibrin membrane – A case report
Snigdho Das, Parthasarathi Mondal, Dipanjan Das, Kurchi Mandal, Kallol Kumar Saha
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sticky bone with guided tissue regeneration and platelet-rich fibrin membranes in healing of apicomarginal defects with periapical pathology: An in-vivo study
D. Das, P. Mondal, K. K. Saha, S. Das, D. Karmakar, A. Bhagawati
Endodontics Today.2024; 22(4): 335. CrossRef
- Surgical treatment of apico-marginal defect associated with maxillary incisor teeth with a large periapical lesion using sticky bone & platelet rich fibrin membrane – A case report
- 1,459 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration procedures on microhardness and chemical structure of dentin
- Ghaeth Hamdon Yassen, George Joseph Eckert, Jeffrey Allen Platt
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):104-112. Published online December 24, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to investigate the effects of different intracanal medicaments on chemical structure and microhardness of dentin.
Materials and Methods Fifty human dentin discs were obtained from intact third molars and randomly assigned into two control groups and three treatment groups. The first control group received no treatment. The second control group (no medicament group) was irrigated with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), stored in humid environment for four weeks and then irrigated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The three treatment groups were irrigated with NaOCl, treated for four weeks with either 1 g/mL triple antibiotic paste (TAP), 1 mg/mL methylcellulose-based triple antibiotic paste (DTAP), or calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] and finally irrigated with EDTA. After treatment, one half of each dentin disc was subjected to Vickers microhardness (
n = 10 per group) and the other half was used to evaluate the chemical structure (phosphate/amide I ratio) of treated dentin utilizing attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (n = 5 per group). One-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's least significant difference were used for statistical analyses.Results Dentin discs treated with different intracanal medicaments and those treated with NaOCl + EDTA showed significant reduction in microhardness (
p < 0.0001) and phosphate/amide I ratio (p < 0.05) compared to no treatment control dentin. Furthermore, dentin discs treated with TAP had significantly lower microhardness (p < 0.0001) and phosphate/amide I ratio (p < 0.0001) compared to all other groups.Conclusions The use of DTAP or Ca(OH)2 medicaments during endodontic regeneration may cause significantly less microhardness reduction and superficial demineralization of dentin compared to the use of TAP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments on Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Fereshte Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl, Negin Firouzi, Saeed Moravej, Samina Gavahianjahromi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of allicin-incorporated graphene oxide hydrogel on dentin microhardness
Rathna Piriyanga, Manish Ranjan, Anand Sherwood, Mohammad Fareed, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Injectable Hydrogel Biotherapeutics for Regenerative Dental Medicine
Renan Dal‐Fabbro, Arwa Daghrery, Caroline Anselmi, Igor Paulino M. Soares, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Pedro Henrique Chaves de Oliveira, Marco C. Bottino
Macromolecular Bioscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ex vivo analysis of clindamycin’s impact on dentin microhardness and surface chemistry
Mandana Naseri, Farshid Gholami, Kamyar Khosravi, Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Mohammad Atai, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 982. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
Aparna Palekar, Piyush Mantri, Minal Awinashe, Basawaraj Biradar, Mukund Singh
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Use of Nanofibers in Regenerative Endodontic Therapy—A Systematic Review
Sebastian Candrea, Alexandrina Muntean, Anida-Maria Băbțan, Antonia Boca, Claudia Nicoleta Feurdean, Ioana Roxana Bordea, Adina Bianca Boșca, Aranka Ilea
Fibers.2024; 12(5): 42. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid activated by laser and ultrasonic energy on surface morphology and chemical composition of intracanal dentin
Adriana Katunarić, Sandra Flinčec Grgac, Dragana Gabrić, Božidar Pavelić, Ivona Bago
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(4): 818. CrossRef - Development of a Thermoresponsive Core–Shell Hydrogel for Sequential Delivery of Antibiotics and Growth Factors in Regenerative Endodontics
Sayna Shamszadeh, Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Akrami, Fatemeh Mashhadiabbas, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Forough Shams
Frontiers in Bioscience-Elite.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Intracanal medicaments and coronal sealing materials influence on root fracture resistance and coronal discoloration: An in vitro study
Rasoul Sahebalam, Marzie Boskabady, Maryam Naghavi, Samira Dehghanitafti
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 199. CrossRef - Final irrigation with bioglass solution in regenerative endodontic procedure induces tissue formation inside the root canals, collagen maturation, proliferation cell and presence of osteocalcin
Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Witalo Pereira de Jesus, Juliana Goto, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Marina Verçosa, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Edilson Ervolino, Raphael Escorsim Szawka, Murilo Camuri Crovace, Ricardo Alves d
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 586. CrossRef - In vitro analysis of compressive strength of root dentin on application of intracanal medicaments for different time periods
Kushal Kumar Ghosh, Sayantan Mukherjee, Paromita Mazumdar, Sahil Ali, Lovely Das
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1289. CrossRef - Effects of endodontic root canal irrigants on tooth dentin revealed by infrared spectroscopy: a systematic literature review
Hamza Elfarraj, Franco Lizzi, Kerstin Bitter, Paul Zaslansky
Dental Materials.2024; 40(8): 1138. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste and propolis extract using three different vehicles as intracanal medicament: An in vitro study
Gunde Veronica, B. V Thimma Reddy, Uday K. Chowdary Birapu, Raghavendra K. Jadadoddi, R Hemanth Kumar, Kanamarlapudi V. Saikiran
Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences.2024; 13(4): 323. CrossRef - Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Nonvital Immature Permanent Teeth Using 2 Intracanal Medications: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Study
Aladdin Al-Qudah, Mohammad Almomani, Layla Hassoneh, Lama Awawdeh
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(7): 776. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste and Chlorhexidine on Pain in Teeth with Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Asma Munir Khan, Irfana Khursheed Ahmed Gangoo, Naila Amir Ali, Mansoor Khan, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Mustafa Hussein AlAttas, Ayman M. Abulhamael, Hammam Ahmed Bahammam, Loai Alsofi, Rayan Suliman Al Yahya
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3091. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the depth of penetration and postoperative pain associated with the use of continuous chelation using HEBP and standard irrigation protocol in the endodontic treatment of adult permanent nonvital teeth: A randomized controlled tr
Janhvi Samir Parekh, Mrunalini J. Vaidya, Vibha R. Hegde
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 344. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics and Minimally Invasive Dentistry: Intertwining Paths Crossing Over Into Clinical Translation
Hisham Elnawam, Menatallah Abdelmougod, Ahmed Mobarak, Mai Hussein, Hamdy Aboualmakarem, Michael Girgis, Rania El Backly
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effects of Various Irrigating Solutions on Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin Using FTIR, SEM, and EDS: An In Vitro Study
Indu Padmakumar, Dharam Hinduja, Abdul Mujeeb, Raghu Kachenahalli Narasimhaiah, Ashwini Kumar Saraswathi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ali Robaian, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Giuseppe Alessandro Scardina
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 197. CrossRef - The Effects of Double Antibiotic Paste and Amoxicillin-clavulanate Paste Used in Endodontic Regeneration on Microhardness of Radicular Dentine: An In vitro Study
Meenu Madhukumar, Praveena Geetha, K. Radhakrishnan Nair, Manu Unnikrishnan
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S510. CrossRef - The effect of intracanal medication variations on microhardness of simulated immature root dentin
Pınar Serdar Eymirli, Ayhan Eymirli, Emel Uzunoğlu Özyürek
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 616. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect and Bioactivity of Innovative and Currently Used Intracanal Medicaments in Regenerative Endodontics
Sarah Alfadda, Theeb Alquria, Eda Karaismailoglu, Hacer Aksel, Adham A. Azim
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(8): 1294. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Nitrofurantoin Paste as an Intracanal Medicament on the Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentine
Mewan Abdulrahman, Bestoon Faraj, Kawa Dizaye
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 8. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Radicular Dentin Treated with Different Concentrations of Calcium Hydroxide in Endodontic Regeneration Procedures
Sara N. Hashem, Maha Adel Elhousiny
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 324. CrossRef - Effect of medicaments used in endodontic regeneration on the morphological characteristics of bovine radicular dentin: Experimental immature tooth model
Maira C. Conte, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo A. Bortoluzzi, Wilson T. Felippe, Luciane G. P. dos Santos, Mariana T. Pandolfo, Patrícia da Agostim Cancelier, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(4): 354. CrossRef - Effect of intracanal medicaments on radicular dentine: An attenuated total reflection-Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis
Promila Verma, Afsana Ansari, Aseem Prakash Tikku, Anil Chandra, Rakesh Kumar Yadav, Ramesh Bharti, Rhythm Bains
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2020; 10: 3. CrossRef - Effect of Hydrogel-Based Antibiotic Intracanal Medicaments on Push-Out Bond Strength
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(04): 575. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Enterococcus faecalis Isolated From Root Canal: An In Vitro Study
Nazanin Zargar, Mohammad J Nasiri, Hengameh Ashraf, Bahareh Hajikhani, Shirin Etminani Esfahani, Maryam Etminani Esfahani
Avicenna Journal of Pharmaceutical Research.2020; 1(2): 60. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and Nano–calcium Hydroxide on Microhardness and Superficial Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin: An Ex Vivo Study
Mandana Naseri, Leila Eftekhar, Farshid Gholami, Mohammad Atai, Omid Dianat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1148. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticle solution on the mechanical properties of resin cements and intrarradicular dentin
Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, Juno Gallego, Wirley Gonçalves Assunção, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Chun-Pin Lin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(6): e0217750. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Retention of BioAggregate and MTA as coronal plugs after intracanal medication for regenerative endodontic procedures: an ex vivo study
Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin, Shaimaa Ismail Gawdat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) application chemical characterization of enamel, dentin and bone
Camila de Carvalho Almança Lopes, Pedro Henrique Justino Oliveira Limirio, Veridiana Resende Novais, Paula Dechichi
Applied Spectroscopy Reviews.2018; 53(9): 747. CrossRef - Chlorhexidine Prevents Root Dentine Mineral Loss and Fracture Caused by Calcium Hydroxide over Time
Michael Ranniery Garcia Ribeiro, Érika Bárbara Abreu Fonseca Thomaz, Darlon Martins Lima, Tarcísio Jorge Leitão, José Bauer, Soraia De Fátima Carvalho Souza
International Journal of Dentistry.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Attachment and proliferation of dental pulp stem cells on dentine treated with different regenerative endodontic protocols
M. A. Alghilan, L. J. Windsor, J. Palasuk, G. H. Yassen
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(7): 667. CrossRef - Second-generation Platelet Concentrate (Platelet-rich Fibrin) as a Scaffold in Regenerative Endodontics: A Case Series
Hengameh Bakhtiar, Shahram Esmaeili, Setareh Fakhr Tabatabayi, Mohammad Reza Ellini, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul M.H. Dummer
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 401. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effects of Antimicrobials Used in Regenerative Endodontics against Biofilm Bacteria Obtained from Mature and Immature Teeth with Necrotic Pulps
Jordon C. Jacobs, Alex Troxel, Ygal Ehrlich, Kenneth Spolnik, Josef S. Bringas, Richard L. Gregory, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(4): 575. CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Polymer Nanofibers for Intracanal Drug Delivery: Effects on Dual Species Biofilm and Cell Function
Divya Pankajakshan, Maria T.P. Albuquerque, Joshua D. Evans, Malgorzata M. Kamocka, Richard L. Gregory, Marco C. Bottino
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1490. CrossRef - Inhibitory effect of gels loaded with a low concentration of antibiotics against biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis and Porphyromonas gingivalis
Amnah A. Algarni, Ghaeth H. Yassen, Richard L. Gregory
Journal of Oral Science.2015; 57(3): 213. CrossRef
- The Effects of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments on Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Dentin: An In Vitro Study
- 2,469 View
- 26 Download
- 41 Crossref

- Clinical effectiveness of combining platelet rich fibrin with alloplastic bone substitute for the management of combined endodontic periodontal lesion
- Lata Goyal
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):51-55. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The term "endo-perio" lesion has been proposed to describe the destructive lesion resulting from inflammatory products found in varying degrees in both the periodontium and the pulpal tissues. In most of the cases, clinical symptoms disappear following successful endodontic therapy. However failure after conventional root canal treatment calls for surgical intervention. A 35 year old male patient with endo-perio lesion in right maxillary lateral incisor was treated with platelet rich fibrin (PRF) and alloplastic bone substitute after conventional endodontic therapy. At the end of 6 months there was gain in clinical attachment, increased radiographic bone fill and reduction in probing depth which was maintained till 18 month follow-up. Present case report aims to evaluate the efficacy of PRF and alloplastic bone substitute in the management of intrabony defect associated with endo-perio lesion in maxillary lateral incisor because the healing potential of PRF and bone graft has not been widely studied in endodontics. The use of PRF allows the clinician to optimize tissue remodelling, wound healing and angiogenesis by the local delivery of growth factors and proteins. The novel technique described here enables the clinician to be benefited from the full regenerative capacity of this autologous biologic material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- To Analyze the Efficacy of Platelet-rich Plasma in Contrast to Platelet-rich Fibrin along with Synthetic Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite and β-tricalcium Phosphate Bone Graft in Regeneration of Bony Defects in Children
Anshul Sharma, Sonali Saha, Amit Rai, Kavita Dhinsa, Nonie Marianne Koksi Sangma Shadap, Gunjan Yadav
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 16(6): 842. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Management of an Immature Necrotic Premolar Using Advanced Platelet‐Rich Fibrin
Sepideh Hosseini, Nazanin Chitsaz, Mohammad Hassan Hamrah, Donya Maleki, Emad Taghizadeh, Hamdi Cem Gungor
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of biodentine coated with emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla
Hamed Karkehabadi, Erfan Ahmadyani, Rezvan Najafi, Elham Khoshbin
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 3685. CrossRef - Healing Assessment of Osseous Defects after Surgical Removal of Periapical Lesions in the Presence of Hydroxyapatite, Nanohydroxyapatite, and a Combination of Nanohydroxyapatite and Platelet-rich Fibrin: A Clinical Study
Amira Elkholly, Maged Negm, Reham Hassan, Nada Omar
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(D): 406. CrossRef - Case report on combining PRF with alloplastic bone substitute in Endo-Perio lesion
Mansi Bansal, Manish Khatri, Komal Puri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef Treatment of an Endo-Perio Lesion with Ozone Gas in a Patient with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Clinical Case Report and Literature Review
Maria K Makeeva, Fatima Yu Daurova, Svetlana F Byakova, Anna Yu Turkina
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2020; Volume 12: 447. CrossRef- Revisit to endo-perio lesion a review
Roopali Sharma, Akshita Gupta, K K. Gupta, Sarah Jameel, Rashmika Kapoor
IP International Journal of Periodontology and Implantology.2020; 5(2): 48. CrossRef - Autologous platelet-rich derivatives along with alloplastic bone substitute in the management of complex perio-endo cases
Lata Goyal, Namita Gupta, NarinderDev Gupta
Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology.2020; 24(2): 182. CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Fibrin as a Bone Graft Material in Oral and Maxillofacial Bone Regeneration: Classification and Summary for Better Application
Yiping Liu, Xiaolin Sun, Jize Yu, Jia Wang, Peisong Zhai, Siyu Chen, Manxuan Liu, Yanmin Zhou
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Acute periodontal lesions (periodontal abscesses and necrotizing periodontal diseases) and endo‐periodontal lesions
David Herrera, Belén Retamal‐Valdes, Bettina Alonso, Magda Feres
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Acute periodontal lesions (periodontal abscesses and necrotizing periodontal diseases) and endo‐periodontal lesions
David Herrera, Belén Retamal‐Valdes, Bettina Alonso, Magda Feres
Journal of Periodontology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative in endodontics: how, when and where
AL Ahmar Rima, Bassam Sanaa, Salloum Sarah, El Husseini Hassan, AL Ahmar Rima
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018; 9(6): 531. CrossRef - Effect of Choukroun Platelet-Rich Fibrin Combined With Autologous Micro-Morselized Bone on the Repair of Mandibular Defects in Rabbits
Tian Zhou, Hua-Wei Yang, Zhuo-Wei Tian, Yang Wang, Xiao-Shan Tang, Jing-Zhou Hu
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 76(1): 221. CrossRef - Preliminary Results of Bone Regeneration in Oromaxillomandibular Surgery Using Synthetic Granular Graft
Noemi Mazzone, E. Mici, A. Calvo, M. Runci, S. Crimi, F. Lauritano, E. Belli
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Treatment of endo-periodontal lesion using leukocyte- platelet- rich fibrin. A case report
Pablo Betancourt, Ricardo Elgueta, Ramon Fuentes
Colombia Medica.2017; 48(4): 204. CrossRef - The impact of autologous platelet concentrates on endodontic healing: a systematic review
Nastaran Meschi, Ana B. Castro, Katleen Vandamme, Marc Quirynen, Paul Lambrechts
Platelets.2016; 27(7): 613. CrossRef - A review of the regenerative endodontic treatment procedure
Bin-Na Lee, Jong-Wook Moon, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 179. CrossRef - Platelet preparations in dentistry: How? Why? Where? When?
Luigi Fabrizio Rodella
World Journal of Stomatology.2015; 4(2): 39. CrossRef
- To Analyze the Efficacy of Platelet-rich Plasma in Contrast to Platelet-rich Fibrin along with Synthetic Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite and β-tricalcium Phosphate Bone Graft in Regeneration of Bony Defects in Children
- 1,734 View
- 4 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Pulp tissue regeneration and root formation of permanent teeth with pulpal/periapical deseases
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek, Ho-Hyun Son
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):238-245. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Numerous cases about additional growth of roots or pulp tissue regeneration by using various intracanal medicaments in immature permanent teeth with periapical or pulpal disease have been reported. The underlying mechanism has not been clearly delineated, but it has been widely accepted that undifferentiated mesenchymal cells and stem cells are involved. Moreover, the growth and deposition of osteoid or cementoid tissues have been observed in regenerated pulp and roots. This new and non-invasive treatment has brightened the future of endodontics, and enlarged the vision of regenerative root canal treatment with multi-potent stem cells and various tissue engineering techniques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Platelet rich fibrin - a novel acumen into regenerative endodontic therapy
Kavita Hotwani, Krishna Sharma
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 1. CrossRef
- Platelet rich fibrin - a novel acumen into regenerative endodontic therapy
- 1,294 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Tissue engineering of dental pulp on type I collagen
- Gwang-Hee Lee, Sung-Yoon Huh, Sang-Hyuk Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):370-377. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.370
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to regenerate human dental pulp tissues similar to native pulp tissues. Using the mixture of type I collagen solution, primary cells collected from the different tissues (pulp, gingiva, and skin) and NIH 3T3 (1 × 105 cells/ml/well) were cultured at 12-well plate at 37℃ for 14 days. Standardized photographs were taken with digital camera during 14 days and the diameter of the contracted collagen gel matrix was measured and statistically analyzed with student t-test. As one of the pulp tissue engineering, normal human dental pulp tissue and collagen gel matrix cultured with dental pulp cells for 14 days were fixed and stained with Hematoxyline & Eosin.
According to this study, the results were as follows:
1. The contraction of collagen gel matrix cultured with pulp cells for 14 days was significantly higher than other fibroblasts (gingiva, skin) (p < 0.05).
2. The diameter of collagen gel matrix cultured with pulp cells was reduced to 70.4% after 7 days, and 57.1% after 14 days.
3. The collagen gel without any cells did not contract, whereas the collagen gel cultured with gingiva and skin showed mild contraction after 14 days (88.1% and 87.6% respectively).
4. The contraction of the collagen gel cultured with NIH 3T3 cells after 14 days was higher than those cultured with gingival and skin fibroblasts, but it was not statistically significant (72.1%, p > 0.05).
5. The collagen gel matrix cultured with pulp cells for 14 days showed similar shape with native pulp tissue without blood vessels.
This approach may provide a means of engineering a variety of other oral tissue as well and these cell behaviors may provide information needed to establish pulp tissue engineering protocols.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Human amniotic membrane extracellular matrix scaffold for dental pulp regeneration in vitro and in vivo
Hengameh Bakhtiar, Azin Ashoori, Sarah Rajabi, Mohamad Pezeshki‐Modaress, Alireza Ayati, Mohammad Reza Mousavi, Mohammad Reza Ellini, Amir Kamali, Amir Azarpazhooh, Anil Kishen
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(4): 374. CrossRef
- Human amniotic membrane extracellular matrix scaffold for dental pulp regeneration in vitro and in vivo
- 1,594 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


