Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Does the use of different root canal sealers and adhesive resin cements impact the bond strength of glass fiber posts?
- Ália Regina Neves de Paula Porto, Rudá França Moreira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e29. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
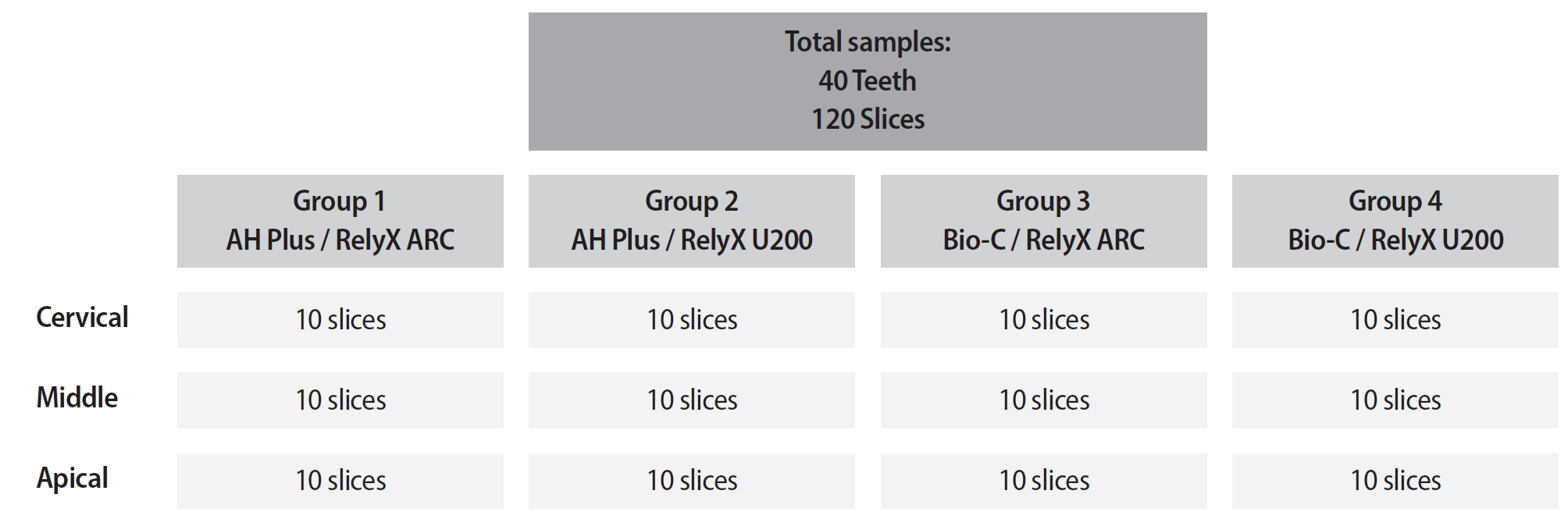
This study aimed to assess the influence of two endodontic sealers on the bond strength of glass fiber posts using conventional and self-adhesive resin cement through a push-out test. Methods: Forty central human incisors were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) based on sealer (epoxy resin- based or calcium silicate-based) and cement (conventional and self-adhesive resin) types: AH Plus (Dentsply De- Trey)/RelyX ARC (3M ESPE), AH Plus/RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), Bio-C Sealer (Angelus)/RelyX ARC, and Bio-C Sealer/RelyX U200. After canal filling and post cementation, roots were sectioned to obtain one specimen per root third. A pushout test and failure pattern assessment were conducted, with bond strength analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test. Results: AH Plus/RelyX ARC showed the highest bond strength values, with a significant difference in the middle third. The most common failure was mixed (55%), while adhesive failures made up 45%, with 23.5% at the cement/post interface and 21.5% at the cement/dentin interface. Conclusions: AH Plus/RelyX ARC provided the highest bond strength values for glass fiber posts to dentin.
- 1,819 View
- 146 Download

- Push-out bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a hydraulic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide as a vehicle
- Ju-Ha Park, Hee-Jin Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e8. Published online January 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
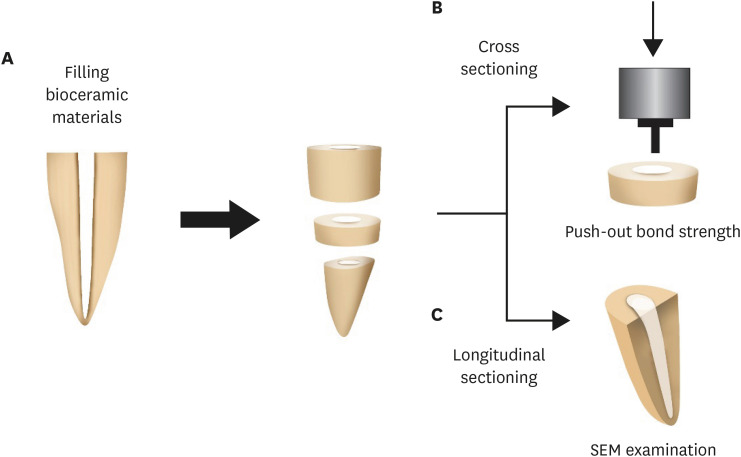
ePub Objectives This study was designed to evaluate the parameters of bonding performance to root dentin, including push-out bond strength and dentinal tubular biomineralization, of a hydraulic bioceramic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide (Endocem MTA Premixed) in comparison to a conventional powder-liquid–type cement (ProRoot MTA).
Materials and Methods The root canal of a single-rooted premolar was filled with either ProRoot MTA or Endocem MTA Premixed (
n = 15). A slice of dentin was obtained from each root. Using the sliced specimen, the push-out bond strength was measured, and the failure pattern was observed under a stereomicroscope. The apical segment was divided into halves; the split surface was observed under a scanning electron microscope, and intratubular biomineralization was examined by observing the precipitates formed in the dentinal tubule. Then, the chemical characteristics of the precipitates were evaluated with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopic (EDS) analysis. The data were analyzed using the Student’st -test followed by the Mann-WhitneyU test (p < 0.05).Results No significant difference was found between the 2 tested groups in push-out bond strength, and cohesive failure was the predominant failure type. In both groups, flake-shaped precipitates were observed along dentinal tubules. The EDS analysis indicated that the mass percentage of calcium and phosphorus in the precipitate was similar to that found in hydroxyapatite.
Conclusions Regarding bonding to root dentin, Endocem MTA Premixed may have potential for use as an acceptable root-end filling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of intratubular biomineralization between in vivo and in vitro conditions
Sieun Nam, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2026; 68(1): 30. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(7): 1989. CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical and radiographic outcome of premixed injectable mineral trioxide aggregate and conventional mineral trioxide aggregate as pulpotomy medicaments in primary molars – A split-mouth randomized control trial
U. S. Aiswarya, Sharan S. Sargod, Sundeep K. Hegde, H. T. Ajay Rao, Nanditha Hegde
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2025; 43(4): 559. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Removal efficiency of a fast setting pozzalan-based bioactive cement: a micro CT study
Feyza Çetinkaya, Ahter Şanal Çıkman, Ali Keleş, Banu Arıcıoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity and Sustained Effectiveness of Calcium Silicate-Based Cement as a Root-End Filling Material against Enterococcus faecalis
Seong-Hee Moon, Seong-Jin Shin, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Materials.2023; 16(18): 6124. CrossRef
- Comparison of intratubular biomineralization between in vivo and in vitro conditions
- 3,370 View
- 94 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Push-out bond strength and marginal adaptation of apical plugs with bioactive endodontic cements in simulated immature teeth
- Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Eduardo Nunes, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Manoel Brito Júnior, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Stephen Cohen, Frank Ferreira Silveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e53. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
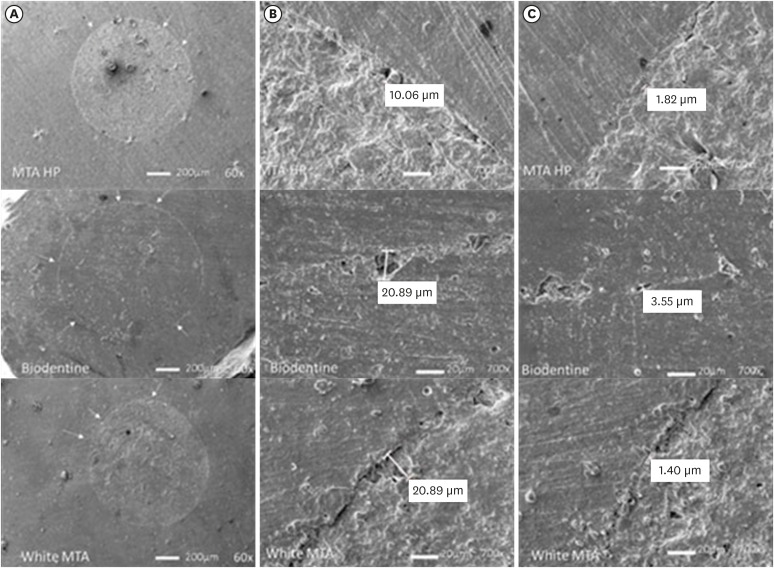
ePub Objectives This study evaluates the bond strength and marginal adaptation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) Repair HP and Biodentine used as apical plugs; MTA was used as reference material for comparison.
Materials and Methods A total of 30 single-rooted teeth with standardized, artificially created open apices were randomly divided into 3 groups (
n = 10 per group), according to the material used to form 6-mm-thick apical plugs: group 1 (MTA Repair HP); group 2 (Biodentine); and group 3 (white MTA). Subsequently, the specimens were transversely sectioned to obtain 2 (cervical and apical) 2.5-mm-thick slices per root. Epoxy resin replicas were observed under a scanning electron microscope to measure the gap size at the material/dentin interface (the largest and smaller gaps were recorded for each replica). The bond strength of the investigated materials to dentin was determined using the push-out test. The variable bond strengths and gap sizes were evaluated independently at the apical and cervical root dentin slices. Data were analyzed using descriptive and analytic statistics.Results The comparison between the groups regarding the variables' bond strengths and gap sizes showed no statistical difference (
p > 0.05) except for a single difference in the smallest gap at the cervical root dentin slice, which was higher in group 3 than in group 1 (p < 0.05).Conclusions The bond strength and marginal adaptation to root canal walls of MTA HP and Biodentine cement were comparable to white MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Biodentine for Apexification of Immature Teeth of Children: A Scoping Review
Liz M Gerard, Sumit Gaur
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(5): 573. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Managing Cracked Teeth with Root Extension: A Prospective Preliminary Study Using Biodentine™ Material
Kênia Maria Soares de Toubes, Isabella Sousa Corrêa, Regina Célia Lopes Valadares, Stephanie Quadros Tonelli, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Dr Karthikeyan Ramalingam
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-Out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, a Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, and Two Novel Antibacterial-Enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Arokia Rajkumar Shancy Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Rajalakshmanan Eswaramoorthy, Abirami Arthanari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push out bond strength of hydraulic cements used at different thicknesses
C. Ruiz Durán, Dra L. Gancedo-Caravia, V. Vera González, C. González Losada
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,526 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
- Miyoung Lim, Chanyong Jung, Dong-Hoon Shin, Yong-bum Cho, Minju Song
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e35. Published online June 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Epoxy resin-based sealers are currently widely used, and several studies have considered AH Plus to be the gold-standard sealer. However, it still has limitations, including possible mutagenicity, cytotoxicity, inflammatory response, and hydrophobicity. Drawing upon the advantages of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium silicate-based sealers were introduced with high levels of biocompatibility and hydrophilicity. Because of the hydrophilic environment in root canals, water resorption and solubility of root canal sealers are important factors contributing to their stability. Sealers displaying lower microleakage and stronger push-out bond strength are also needed to endure the dynamic tooth environment. Although the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers meet International Organization for Standardization recommendations, and they have consistently reported to be biocompatible, they have not overcome conventional resin-based sealers in actual practice. Therefore, further studies aiming to improve the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
Lokhasudhan Govindaraju, Rajeswari Kalaiselvam, Mathan Rajan Rajendran, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Jelena Jacimovic, Henry F. Duncan, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2026; 59(3): 341. CrossRef - Evidence synthesis of postoperative pain with bioceramic vs. epoxy resin sealers: umbrella review of randomized trials within existing systematic reviews
Mrunali Dahikar, Ashish Mandwe, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Suraj Arora, Unmesh Khanvilkar, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical and mechanical properties of a strontium silicate-based sealer
Shannon Wong, Xiaofei Zhu, Tun-Yi Hsu, Sami Chogle, Russell A. Giordano, Yuwei Fan
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of bioceramic-based sealers following different irrigation activation techniques
Fatma Begüm Peker, Hümeyra Çapkın, Ahsen Narbay
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Tapered Gutta-Percha Points on Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Root Canal Sealers
Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanothum
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 285. CrossRef - Effect of Electrical Heat Carrier Temperature on Bacterial Leakage of Endodontically Treated Teeth Using a Bioceramic Sealer
Mir Ahmad Nabavi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Pedram Fattahi, Saber Khazaei
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Assessing the antimicrobial properties of bioceramic sealers enhanced with herbal extracts against E. faecalis
KS Sachin, K Shibani Shetty, KB Jeyalakshmi, S Harishma, S Harshini
Folia Medica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio comparativo de la solubilidad de dos selladores endodónticos biocerámicos y un sellador a base de resinas
//Comparative study of the solubility of two bioceramic endodontic sealers and one epoxi-resin based sealer
Alejandro Leonhardt, Nicolás Paduli, Osvaldo Zmener, Miguel Chantiri
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Bioceramic Endodontic Sealers in HepG2 and V79 Cell Lines: An In Vitro Study Using the Comet and Micronucleus Assays
Antonija Tadin, Marija Badrov, Danijela Juric Kacunic, Nada Galic, Matea Macan, Ivan Kovacic, Davor Zeljezic
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 169. CrossRef - In Vitro Apatite-Forming Ability of Different Root Canal Sealers (A Comparative Study)
Raghad A Al-Askary, Wiaam M. O. Al-Ashou, Sawsan H. Al-Jubori
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(2): 173. CrossRef - Microstructural and elemental characterization of novel bioactive glass bioceramic sealer using Fourier transform infrared and X-ray diffraction analysis
Poulomi Guha, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Antony, Nishitha Arun, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Surendar Ramamoorthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(5): 412. CrossRef - Microstructural and Elemental Characterization of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Ireneusz Piwonski, Tomasz Szmechtyk, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(10): 756. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure-enhanced sealer infiltration for obturating long oval-shaped root canals with the single-cone technique
Yaxu Feng, Brian E. Bergeron, Shijin Zhang, Danyang Sun, Kole Fisher, Franklin R. Tay, Bing Fan
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105909. CrossRef - Effects of different apical preparation sizes and root canal sealers on the fracture resistance of roots aged for 12 months in endodontically retreated mandibular premolars
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Sevda Durust Baris, Ali Turkyilmaz, Ali Erdemir
British Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different endodontic treatment protocols on tooth survival: A retrospective cohort study with multistate analysis and group balancing
Ahmed Elmaasarawi, Mohamed Mekhemar, Andreas Bartols
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(10): 1529. CrossRef - Evaluation of 2,6-xylidine precipitate on sealer penetration of calcium silicate-based sealer and resin-based sealer: An in vitro study
M. B. Kalpana, Divya Shetty, Rajaram Naik
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 183. CrossRef - Translational Advances in Regenerative Dentistry: Functional Biomaterials and Emerging Technologies
Seher Yaylacı, Hacer Eberliköse, Hakan Ceylan
Current Oral Health Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of heat and non-heat compatible bioceramic sealers in warm obturation: an in vitro SEM study
Thanomsuk Jearanaiphaisarn, Thanida Leelayuttakarn, Panisara Amatamahuthana, Pinmanus Chenpairojsakul, Keskanya Subbalekha, Pavena Chivatxaranukul
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
Steven K. Uttech, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Maria Martell, Bruno Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1764. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of adhesion abilities between AH Plus® Bioceramic, Ceraseal® and AH Plus® on root canal dentine surfaces
Ike Dwi Maharti, Indira Larasputri, Nendar Herdianto, Anggraini Margono, Riesma Tasomara, Romilda Rosseti
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(9): 881. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of single-cone bioceramic obturation versus traditional techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Firas Elmsmari, Yousef Elsayed, Abdelrahman Aboubakr, Mahdi Kaafarani, Osama Nour, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(6): 1422. CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation Solutions on the Setting Time, Solubility, and pH of Three Types of Premixed Bioceramic‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Kitichai Singharat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Zhengrui Li
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteogenic Potential of Various Premixed Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers on Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Na-Hyun You, Donghee Lee, Yemi Kim, Sieun Nam, Sin-Young Kim
Materials.2025; 18(23): 5326. CrossRef - Polydopamine‐Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Root Canal Sealer: Characterization, Biological, and Physicochemical Properties
Arul Nayagi Raj, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Giuseppe Ciccarella
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of rarely seen internal tunnelling root resorption associated with a maxillary permanent incisor
Kirsty A. Carney, Thibault N. E. Colloc, Julie K. Kilgariff
British Dental Journal.2024; 236(12): 955. CrossRef - Top tips for treatment planning: tooth-by-tooth prognosis - Part 3: endodontic prognosis
Prashanti Eachempati, Andrew Harris, Guy Lambourn, Tony Francis, Ewen McColl
British Dental Journal.2024; 237(9): 686. CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate-based sealers based on micro-computed tomographic evaluation − A systematic review
Sundus Mohammed Bukhary
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1278. CrossRef - Evaluation of Setting Time, Flowability, Film Thickness, and Radiopacity of Experimental Monocalcium Silicate‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Sukanya Juntha, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Carlos M. Ardila
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment and Demand for Continuing Education among Thai Dental Practitioners
Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Pakit Tungsawat, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanotham
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic sealers after exposure to chlorhexidine digluconate: An assessment of physicochemical properties
Vasileios Kapralos, Josette Camilleri, Andreas Koutroulis, Håkon Valen, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Dental Materials.2024; 40(3): 420. CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Interfacial adaptation of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2024; 18(2): 115. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Solubility of Endoseal and AH26 Root Canal Sealers
Nooshin Fakhari, Ali Reza Mirjani, Abbas Bagheri, Jalil Modaresi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2024; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Novel bioactive nanospheres show effective antibacterial effect against multiple endodontic pathogens
Jin Liu, Haoze Wu, Jun Qiu, Sirui Yang, Doudou Xiang, Xinhua Zhang, Jinxin Kuang, Min Xiao, Qing Yu, Xiaogang Cheng
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28266. CrossRef - Evaluation of canal patency and cleanliness following retreatment of bioceramic sealer‐obturated root canals using three different irrigant activation protocols
Daiasharailang Lyngdoh, Sharique Alam, Huma Iftekhar, Surendra Kumar Mishra
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 475. CrossRef - Antibiofilm Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Based Endodontic Sealers
Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Vsevolod Fedoseev, Carmen Solana, Cecilia Muñoz-Sandoval, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3937. CrossRef - Enhancing the Biological Properties of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Calcium Silicate Cements: An In Vitro Study
Minji Choi, Jiyoung Kwon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Duck-Su Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 337. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and cell migration evaluation of a strontium silicate-based root canal sealer on stem cells from rat apical papilla: an in vitro study
Guanglei Zhou, Yu Zhao, Liangjing Cai, Liwei Liu, Xu Li, Lu Sun, Jiayin Deng
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Analysis of Physico–Mechanical Properties of Commercial and Experimental Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Abdulmajeed Kashaf, Faisal Alonaizan, Khalid S. Almulhim, Dana Almohazey, Deemah Abdullah Alotaibi, Sultan Akhtar, Ashwin C. Shetty, Abdul Samad Khan
Bioengineering.2024; 11(11): 1079. CrossRef - Chemical, Antibacterial, and Cytotoxic Properties of Four Different Endodontic Sealer Leachates Over Time
Jo-Hsun Chen, Veksina Raman, Sarah A. Kuehne, Josette Camilleri, Josefine Hirschfeld
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(11): 1612. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Fracture Resistance of Endodontic Sealer Types and Filling Methods
Yun Song, Kee-Deog Kim, Bock-Young Jung, Wonse Park, Nan-Sim Pang
Materials.2024; 18(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Removal of Bioceramic Sealers Using Rotary Retreatment Files Supplemented with Passive Ultrasonic Activation: An In Vitro Study
Anuradha B Patil, Amrut Bambawale, Pooja R Barghare, Sumanthini V Margasahayam, Divya Naik, Jayeeta S Verma
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 292. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of Nonperforating Internal Root Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor: A Case Report with a 4-Year Follow-Up
Paras M. Gehlot, Divya S. Rajkumar, Annapoorna B. Mariswamy, Upendra Natha N. Reddy, Chaitanya Chappidi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S3005. CrossRef - Evaluating the Sealing Performance of Endodontic Sealers: Insights Into Achieving Complete Sealing
Ajay Chhabra, Ramya K P., Saravana Prathap, Priyanka Yadav, Himani Mehra, Sona J Parvathy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vehicles on the physical properties and biocompatibility of premixed calcium silicate cements
Gitae SON, Gyeung Mi SEON, Sang Hoon CHOI, Hyeong-Cheol YANG
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(2): 276. CrossRef - Comparative cytotoxicity study of putty- and powder-type calcium silicate cements
Sora Park, Dohyun Cho, Ji Hyeon Yoon, Yeonjoo Kang, Quang Canh Vo, Gitae Son, Hongjoo Park, Hyeong-Cheol Yang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 259. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Dentinal Tubule Penetrability and Bond Strength of Two Novel Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karissa Shieh, Jack Yang, Elsa Heng Zhu, Ove Andreas Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour
Materials.2023; 16(9): 3309. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Activity of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers Compared to Conventional Resin-Based Sealer in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells
Mohammad Shokrzadeh, Farzaneh Sadat Motafeghi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Mohammad Ghorbani, Azam Haddadi Kohsar, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of three different photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy on bond strength of a calcium silicate‐based sealer to radicular dentin
Cihan Küden, Seda Nur Karakaş
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 265. CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealer on postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis
Cynthia Maria Chaves Monteiro, Ana Cristina Rodrigues Martins, Alessandra Reis, Juliana Larocca de Geus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Activity of Five Calcium Silicate Based Root Canal Sealers against a Multispecies Engineered Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Carla Zogheib, Issam Khalil, Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, Germain Sfeir, May Mallah, Roula El Hachem
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 707. CrossRef - Calcium silicate sealers in endodontics
Archana Chavan, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2023; 39(87): 2624. CrossRef - Assessing the Sealing Performance and Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Treatment in Patients with Chronic Apical Periodontitis Using Epoxy Resin and Calcium Salicylate Seals
Razvan Mihai Horhat, Bogdan Andrei Bumbu, Laura Orel, Oana Velea-Barta, Laura Cirligeriu, Gratiana Nicoleta Chicin, Marius Pricop, Mircea Rivis, Stefania Dinu, Delia Ioana Horhat, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Rodica Anamaria Negrean, Luminita
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1137. CrossRef -
In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Potential of an Endodontic Bioceramic Material
Soumya Sheela, Mohannad Nassar, Fatma M. AlGhalban, Mehmet O. Gorduysus
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(02): 548. CrossRef - Dislodgment Resistance, Adhesive Pattern, and Dentinal Tubule Penetration of a Novel Experimental Algin Biopolymer-Incorporated Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealer
Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Norhayati Luddin, Huwaina Abd Ghani, Josephine Chang Hui Lai, Tahir Yusuf Noorani
Polymers.2023; 15(5): 1317. CrossRef - Impact of Final Irrigation Protocol on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Types of Endodontic Sealers
Germain Sfeir, Frédéric Bukiet, Wajih Hage, Roula El Hachem, Carla Zogheib
Materials.2023; 16(5): 1761. CrossRef - Clinical Approaches to the Three-Dimensional Endodontic Obturation Protocol for Teeth with Periapical Bone Lesions
Angela Gusiyska, Elena Dyulgerova
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9755. CrossRef - Evaluating the bioactivity of endodontic sealers with respect to their thermo-nanomechanical properties
Andreea Marica, Luminita Fritea, Florin Banica, Iosif Hulka, Gerlinde Rusu, Cosmin Sinescu, Traian Octavian Costea, Simona Cavalu
Materials Science-Poland.2023; 41(3): 126. CrossRef - Advances and challenges in regenerative dentistry: A systematic review of calcium phosphate and silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells
B. Christie, N. Musri, N. Djustiana, V. Takarini, N. Tuygunov, M.N. Zakaria, A. Cahyanto
Materials Today Bio.2023; 23: 100815. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - Biodentine Inhibits the Initial Microbial Adhesion of Oral Microbiota In Vivo
Ali Al-Ahmad, Michael Haendel, Markus Altenburger, Lamprini Karygianni, Elmar Hellwig, Karl Wrbas, Kirstin Vach, Christian Tennert
Antibiotics.2022; 12(1): 4. CrossRef - Pilot Evaluation of Sealer-Based Root Canal Obturation Using Epoxy-Resin-Based and Calcium-Silicate-Based Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Minju Song, Min-Gyu Park, Sang-Won Kwak, Ruben H. Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2022; 15(15): 5146. CrossRef - The antibacterial activity of mineral trioxide aggregate containing calcium fluoride
Miyoung Lim, Seunghoon Yoo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(2): 836. CrossRef - Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Premixed Calcium Silicate and Resin Sealers
Naji Kharouf, Salvatore Sauro, Ammar Eid, Jihed Zghal, Hamdi Jmal, Anta Seck, Valentina Macaluso, Frédéric Addiego, Francesco Inchingolo, Christine Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, Florent Meyer, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 14(1): 9. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Resistance between Single-cone and Warm Vertical Compaction Technique Using Bio-C Sealer® in Mandibular Incisors: An In Vitro Study
Raphael Lichaa, George Deeb, Rami Mhanna, Carla Zogheib
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - In vitro physicochemical characterization of five root canal sealers and their influence on an ex vivo oral multi‐species biofilm community
Flavia M. Saavedra, Lauter E. Pelepenko, William S. Boyle, Anqi Zhang, Christopher Staley, Mark C. Herzberg, Marina A. Marciano, Bruno P. Lima
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 772. CrossRef - Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealer Reinforced with Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles to Improve Biological Properties
Min-Kyung Jung, So-Chung Park, Yu-Jin Kim, Jong-Tae Park, Jonathan C. Knowles, Jeong-Hui Park, Khandmaa Dashnyam, Soo-Kyung Jun, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jung-Hwan Lee
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1903. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - The influence of humidity on bond strength of AH Plus, BioRoot RCS, and Nanoseal-S sealers
Sunanda Laxman Gaddalay, Damini Vilas Patil, Ramchandra Kabir
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 202. CrossRef - The Effect of Bioceramic HiFlow and EndoSequence Bioceramic Sealers on Increasing the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Mohamad Khir Abdulsamad Alskaf, Hassan Achour, Hasan Alzoubi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unravelling the effects of ibuprofen-acetaminophen infused copper-bioglass towards the creation of root canal sealant
Chitra S, Riju Chandran, Ramya R, Durgalakshmi D, Balakumar S
Biomedical Materials.2022; 17(3): 035001. CrossRef - A Micro-CT Analysis of Initial and Long-Term Pores Volume and Porosity of Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Michal Leski, Adam K. Puszkarz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2403. CrossRef - A comprehensive in vitro comparison of the biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive root canal sealers
Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Christian Diegritz, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth, Maximilian Kollmuss
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(10): 6209. CrossRef - Stability and solubility test of endodontic materials
Ivan Matovic, Jelena Vucetic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(4): 169. CrossRef - Antimicrobial effectiveness of root canal sealers againstEnterococcus faecalis
Paola Castillo-Villagomez, Elizabeth Madla-Cruz, Fanny Lopez-Martinez, Idalia Rodriguez-Delgado, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Guadalupe Ismael Malagon-Santiago, Myriam Angelica de La Garza-Ramos
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2022; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Influence of variations in the environmental pH on the solubility and water sorption of a calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer
E. J. N. L. Silva, C. M. Ferreira, K. P. Pinto, A. F. A. Barbosa, M. V. Colaço, L. M. Sassone
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1394. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Calcium-Silicate Nanobioceramics with Magnesium: Effect of Heat Treatment on Biological, Physical and Chemical Properties
Konstantina Kazeli, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Anna Theocharidou, Lamprini Malletzidou, Jonathan Rhoades, Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Eleni Likotrafiti, Konstantinos Chrissafis, Theodoros Lialiaris, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Eleana Kontonasaki, Evgenia Lymperaki
Ceramics.2021; 4(4): 628. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - In Vitro Microleakage Evaluation of Bioceramic and Zinc-Eugenol Sealers with Two Obturation Techniques
Francesco De Angelis, Camillo D’Arcangelo, Matteo Buonvivere, Rachele Argentino, Mirco Vadini
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 727. CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef - Apical Sealing Ability of Two Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers Using a Radioactive Isotope Method: An In Vitro Apexification Model
Inês Raquel Pereira, Catarina Carvalho, Siri Paulo, José Pedro Martinho, Ana Sofia Coelho, Anabela Baptista Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho, Maria Filomena Botelho, Ana Margarida Abrantes, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6456. CrossRef
- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
- 13,692 View
- 249 Download
- 100 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic cleaning on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic root canal sealer
- Fernando Peña Bengoa, Maria Consuelo Magasich Arze, Cristobal Macchiavello Noguera, Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo Da Silveira Bueno
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e19. Published online February 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
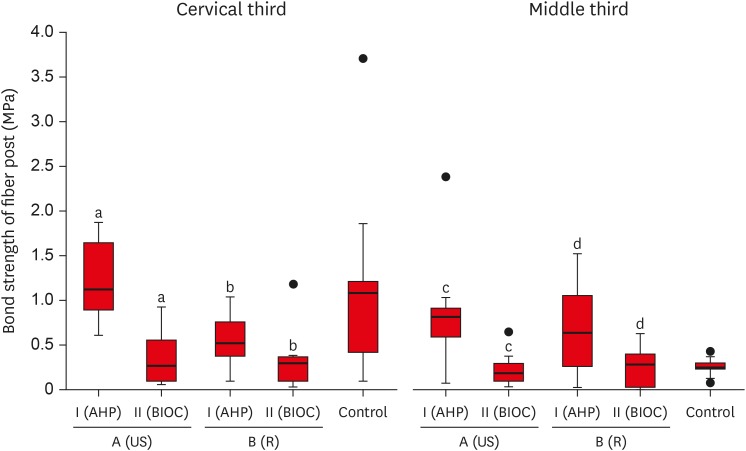
ePub Objective This study aimed to evaluate the effect of ultrasonic cleaning of the intracanal post space on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic (Bio-C Sealer [BIOC]) root canal sealer.
Materials and Methods Fifty premolars were endodontically prepared and divided into 5 groups (
n = 10), based on the type of root canal filling material used and the post space cleaning protocol. A1: gutta-percha + AH Plus (AHP) and post space preparation with ultrasonic cleaning, A2: gutta-percha + BIOC and post space preparation with ultrasonic cleaning, B1: gutta-percha + AHP and post space preparation, B2: gutta-percha + BIOC and post space preparation, C: control group. Fiber posts were cemented with a self-adhesive luting material, and 1 mm thick slices were sectioned from the middle and cervical third to evaluate the remaining filling material microscopically. The samples were subjected to a push-out test to analyze the bond strength of the fiber post, and the results were analyzed with the Shapiro-Wilk, Bonferroni, Kruskal-Wallis, and Mann-Whitney tests (p < 0.05). Failure modes were evaluated using optical microscopy.Results The results showed that the fiber posts cemented in canals sealed with BIOC had lower bond strength than those sealed with AHP. The ultrasonic cleaning of the post space improved the bond strength of fiber posts in canals sealed with AHP, but not with BIOC.
Conclusions BIOC decreased the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals, regardless of ultrasonic cleaning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e20. CrossRef - In Vitro Effect of Using Endo‐Activator on Pushout Bond Strength of Radicular Dentin to Prefabricated Fiber Post in Using Natural Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors
Nadia Elyassi Gorji, Homayoun Alaghemand, Faraneh Mokhtarpour, Elham Mahmodnia
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of different mechanical cleaning protocols associated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in the removal of residues from the post space
Matheus Sousa Vitória, Eran Nair Mesquita de Almeida, Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Eliane Cristina Gulin de Oliveira, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Andrea Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 274. CrossRef - Fiber post cemented using different adhesive strategies to root canal dentin obturated with calcium silicate-based sealer
Lalita Patthanawijit, Kallaya Yanpiset, Pipop Saikaew, Jeeraphat Jantarat
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealers on push-out bond strength of CAD-CAM or prefabricated fiber glass posts
Andréa Pereira de Souza PINTO, Fabiana Mantovani Gomes FRANÇA, Roberta Tarkany BASTING, Cecilia Pedroso TURSSI, José Joatan RODRIGUES JÚNIOR, Flávia Lucisano Botelho AMARAL
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of mechanical cleaning protocols in the fiber post space on the adhesive interface between universal adhesive and root dentin
Gabriela Mariana Castro‐Núnez, José Rodolfo Estruc Verbicário dos Santos, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante‐Otárola, Thiago Soares Porto, Milton Carlos Kuga
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(6): 2131. CrossRef - Effect of bioceramic root canal sealers on the bond strength of fiber posts cemented with resin cements
Rafael Nesello, Isadora Ames Silva, Igor Abreu De Bem, Karolina Bischoff, Matheus Albino Souza, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu Da Rosa
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols on root canal wall after post preparation: a micro-CT and microhardness study
Camila Maria Peres de Rosatto, Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Lilian Vieira Oliveira, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira Soares, Carlos José Soares, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
- 2,215 View
- 27 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The push-out bond strength of BIOfactor mineral trioxide aggregate, a novel root repair material
- Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Durmus Alperen Bozkurt, Arslan Terlemez, Melek Akman
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e5. Published online January 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the push-out bond strength of a novel calcium silicate-based root repair material-BIOfactor MTA to root canal dentin in comparison with white MTA-Angelus (Angelus) and Biodentine (Septodont).Materials and Methods The coronal parts of 12 central incisors were removed and the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. Midroot dentin of each sample was horizontally sectioned into 1.1 mm slices and 3 slices were obtained from each root. Three canal-like standardized holes having 1 mm in diameter were created parallel to the root canal on each dentin slice with a diamond bur. The holes were filled with MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, or BIOfactor MTA. Wet gauze was placed over the specimens and samples were stored in an incubator at 37°C for 7 days to allow complete setting. Then samples were subjected to the push-out test method using a universal test machine with the loading speed of 1 mm/min. Data was statistically analyzed using Friedman test and
post hoc Wilcoxon signed rank test with Bonferroni correction.Results There were no significant differences among the push-out bond strength values of MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA (
p > 0.017). Most of the specimens exhibited cohesive failure in all groups, with the highest rate found in Biodentine group.Conclusions Based on the results of this study, MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA showed similar resistances to the push-out testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Examination of the Bond Strength of Retrograde Filling in Teeth with Failed Apical Resection After Retreatment
Sevda Tok, Leyla Benan Ayranci
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(7): 3441. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Physicocomechanical Properties of MTA and Biodentine with Addition of Graphene Oxide to MTA and Biodentine: An In-vitro Study
Tanvi Arvind Jagtap, Budhabhushan A. Sonvane, Guruprasad Handal, Jayashri Nimba Bhangare, Kedar Vilas Saraf, Abhishek Mulay
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S608. CrossRef - Influence of Incubation Duration on Bond Strength and Microhardness of Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials
Emine Şimşek, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 438. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength after root perforation repair using recently introduced bioceramic and calcium silicate-based materials – An in vitro study
Gurinder Kaur, Deepak Kurup, Deepyanti Dubey, Ajit Hindlekar, Ganesh Ranganath Jadhav, Priya Mittal, Siddharth Shinde
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 194. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, and Two Novel Antibacterial-enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Sanjeev Khanagar, Suman Panda, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Satish Vishwanathaiah, Ather A Syed, Sara Kalagi, Arokia RS Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Aram AlShehri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(2): 168. CrossRef - Influence of Phase Composition and Morphology on the Calcium Ion Release of Several Classical and Hybrid Endodontic Cements
Ivanka Dimitrova, Galia Gentscheva, Ivanka Spassova, Daniela Kovacheva
Materials.2024; 17(22): 5568. CrossRef - The Effect of Two Different MTA (Mineral Trioxide Aggregate) On Thermal Insulation
Gizem Akkus, Ecem Salmaz, Didem Oner Ozdas
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength and apical microleakage of different calcium silicate‐based cements after using EDTA, chitosan and phytic acid irrigations
Tutku Koçak Şahin, Murat Ünal
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(9): 2072. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the physical characteristics and push-out bond strength of new experimental nano-MTA
Nada Omar, Yousra Aly, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interfacial characteristics of BIOfactor MTA and Biodentine with dentin
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Şeref Nur Mutlu, Mehmet Ali Soylu, Emine Şimşek
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(2): 258. CrossRef - Systemic effect of calcium silicate-based cements with different radiopacifiers-histopathological analysis in rats
Osman Ataş, Kubra Bılge, Semsettin Yıldız, Serkan Dundar, Ilknur Calik, Asime Gezer Ataş, Alihan Bozoglan
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15376. CrossRef - The push-out bond strength of three root canal materials used in primary teeth: in vitro study
Hazal Özer, Merve Abaklı İnci, Sevcihan Açar Tuzluca
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different irrigation protocols on push-out bond strength of pre-mixed calcium silicate-based cements
Sabiha Ceren İlisulu, Aliye Tugce Gürcan, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2023; 59(5): 1381. CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Sealing Quality and Bond Strength of Different MTA Apical Plugs
Taibe Tokgöz Kaplan, Murat Selim Botsalı
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Kan kontaminasyonunun farklı kök ucu dolgu materyallerinin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Şeyma Nur GERÇEKCİOĞLU, Melike BAYRAM, Emre BAYRAM
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2023; 40(1): 9. CrossRef - Tooth Discoloration Effect of BIOfactor Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A 6-Month In Vitro Study
Şeref Nur Mutlu, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(15): 8914. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Push-Out Bond Strength of Root-End Filling Materials by Using Different Condensation Methods
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Sevinç Sevgi, Ayşenur Öncü, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Berkan Çelikten
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Different Adhesive Strategies on the Microshear Bond Strength of Calcium-Silicate-Based Materials
Aliye Tuğçe Gürcan, Soner Şişmanoğlu, Görkem Sengez
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 191. CrossRef - BIOfactor MTA’nın Radyoopasitesinin Dijital Radyografi ile Değerlendirilmesi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Bilge AKBULUT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 520. CrossRef - Morphological and Chemical Analysis of Different Types of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements
Okba Mahmoud, Nashwan Abdullah Al-Afifi, Mohideen Salihu Farook, Maysara Adnan Ibrahim, Saaid Al Shehadat, Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Blood Contamination on Push-Out Bond Strength of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Cristina Rodrigues Paulo, Joana A. Marques, Diana B. Sequeira, Patrícia Diogo, Rui Paiva, Paulo J. Palma, João Miguel Santos
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6849. CrossRef - An In vitro comparative evaluation of effect of novel irrigant Qmix and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the push-out bond strength of biodentine and endosequence bioceramic root repair material
VandanaJ Gade, Aparajita Gangrade, JaykumarR Gade, Neelam Rahul
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 124. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,064 View
- 12 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):234-240. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of intraradicular moisture on the pushout bond strength of a fibre post luted with several self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods Endodontically treated root canals were treated with one of three luting cements: (1) RelyX U100, (2) Clearfil SA, and (3) G-Cem. Roots were then divided into four subgroups according to the moisture condition tested: (I) dry: excess water removed with paper points followed by dehydration with 95% ethanol, (II) normal moisture: canals blot-dried with paper points until appearing dry, (III) moist: canals dried by low vacuum using a Luer adapter, and (IV) wet: canals remained totally flooded. Two 1-mm-thick slices were obtained from each root sample and bond strength was measured using a push-out test setup. The data were analysed using a two-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni
post hoc test withp = 0.05.Results Statistical analysis demonstrated that moisture levels had a significant effect on the bond strength of luting cements (
p < 0.05), with the exception of G-Cem. RelyX U100 displayed the highest bond strength under moist conditions (III). Clearfil SA had the highest bond strength under normal moisture conditions (II). Statistical ranking of bond strength values was as follows: RelyX U100 > Clearfil SA > G-Cem.Conclusions The degree of residual moisture significantly affected the adhesion of luting cements to radicular dentine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Dentin bond strength of resin luting agents under a simulated intra-oral environment
Takashi Washino, Hanemi Tsuruta, Masaomi Ikeda, Michael F. Burrow, Toru Nikaido
Asian Pacific Journal of Dentistry.2024; 24(2): 13. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of dentin moisture on the adhesive properties of luting fiber posts using adhesive strategies
Renata Terumi JITUMORI, Rafaela Caroline RODRIGUES, Alessandra REIS, João Carlos GOMES, Giovana Mongruel GOMES
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different intraradicular chemical pretreatments on the bond strength of adhesive interface between dentine and fiber post cements: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Ana Luiza Barbosa Jurema, Ayla Macyelle de Oliveira Correia, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SELF ADEZİV REZİN SİMANLAR / SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
Kübra AMAÇ, Engin ESENTÜRK, Bilge TURHAN BAL
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Development and characterization of biological bovine dentin posts
Alice Gonçalves Penelas, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Laiza Tatiana Poskus, Amanda Cypriano Alves, Isis Ingrid Nogueira Simões, Viviane Hass, José Guilherme Antunes Guimarães
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 92: 197. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite on the bond strength of glass fibre post
Beau Knight, Robert M. Love, Roy George
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(3): 267. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Is the bonding of self-adhesive cement sensitive to root region and curing mode?
Thaynara Faelly BOING, Giovana Mongruel GOMES, João Carlos GOMES, Alessandra REIS, Osnara Maria Mongruel GOMES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(1): 2. CrossRef - A Twofold Comparison between Dual Cure Resin Modified Cement and Glass Ionomer Cement for Orthodontic Band Cementation
Hanaa El Attar, Omnia Elhiny, Ghada Salem, Ahmed Abdelrahman, Mazen Attia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2016; 4(4): 695. CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of various self-adhesive resin cements between bovine dentin and 4 types of adherends
Ah-Jin Kim, Da-Ryeong Park, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(4): 365. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 1,775 View
- 4 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
- Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):479-485. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the push-out bond strengths of resin cement/fiber post systems to post space dentin using different application methods of resin cement.
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human premolars were selected and randomly divided into 3 groups according to the technique used to place the cement into root canal: using lentulo-spiral instrument (group Lentulo), applying the cement onto the post surface (group Direct), and injecting the material using a specific elongation tip (group Elongation tip). After shaping and filling of the root canal, post space was drilled using Rely-X post drill. Rely-X fiber post was seated using Rely-X Unicem and resin cement was light polymerized. The root specimens were embedded in an acrylic resin and the specimens were sectioned perpendicularly to the long axis using a low-speed saw. Three slices per each root containing cross-sections of coronal, middle and apical part of the bonded fiber posts were obtained by sectioning. The push-out bond strength was measured using Universal Testing Machine. Specimens after bond failure were examined using operating microscope to evaluate the failure modes.
Results Push-out bond strengths were statistically influenced by the root regions. Group using the elongation tip showed significantly higher bond strength than other ways. Most failures occurred at the cement/dentin interface or in a mixed mode.
Conclusions The use of an elongation tip seems to reduce the number of imperfections within the self-adhesive cement interface compared to the techniques such as direct applying with the post and lentulo-spiral technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
Abdulaziz A. Al-Kheraif, Badreldin A. Mohamed, Aref Othman Hasan Sufyan, Aftab Ahmed Khan, Darshan Devang Divakar
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 36: 102526. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography analysis of gap and void formation in different prefabricated fiber post cementation materials and techniques
Aws ArRejaie, Saleh A. Alsuliman, Mohammed O. Aljohani, Hesham A. Altamimi, Emad Alshwaimi, Ahmad M. Al-Thobity
The Saudi Dental Journal.2019; 31(2): 236. CrossRef - Micro-computerized tomography analysis of cement voids and pull-out strength of glass fiber posts luted with self-adhesive and glass-ionomer cements in the root canal
Serkan Sarıdağ, Dilek Helvacıoğlu-Yiğit, Mutlu Özcan, Egemen Avcu, Güllü Kızıltaş
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(14): 1585. CrossRef - Pull-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to NaOCl-treated root dentin: effect of antioxidizing agents
Maryam Khoroushi, Marzieh Kachuei
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 95. CrossRef - Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef
- Photodynamic therapy and other pretreatment methods on epoxy-based glass fiber post on the push-out bond strength to radicular dentin
- 1,264 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
- Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):103-112. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of curing methods of adhesive resins and resin cements in the root canal. Crown portions of 32 single-rooted mandibular premolars were removed. Routine endodontic treatment was done, and 9 mm deep post spaces were prepared within root canals. No. 3 FRC Postec posts (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Liechtenstein) were cemented in the post spaces by self-(SC) or light-curing (LC) using two dual-cured adhesives (Adper Scotchbond multi-purpose plus and Exite DSC )and resin cements (RelyX ARC and Variolink II). They were assigned to 4 groups (n=8); R-SC, R-LC, V-SC, V-LC group.
After stored in distilled water for 24 hours, each root was transversally sectioned with 1.5 mm thick and made three slices. The specimens were subjected to push-out test in a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu Co., Japan) with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. The data were analyzed with repeated ANOVA and one-way.
ANOVA. Also the interface of post-resin cement and resin cement-canal wall of each group was observed under FE-SEM.
When fiber posts were cemented into the root canal using total-etch adhesives, the bond strength and adaptation between post and root canal dentin was affected by curing method. Self-cure of adhesives and resin cements showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than light-cure of them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment of FRC-Post on bonding strength to resin cements
Chan-Hyun Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 125. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 479. CrossRef
- Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
- 1,126 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Comparison of bond strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements
- Hyun-A Lee, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):499-506. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.499
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the push-out strength of a fiber post cemented with various resin cements. Newly extracted 36 human mandibular premolars which had single root canal were selected and their crown portions were removed. The root canal was instrumented using PROTAPER™ system and obturated using continuous wave technique. In each root, a 9-mm deep post space was prepared. #2 translucent fiber post (DT Light post, Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A.) was cemented using injection technique with Uni-dose needle tip (Bisco) and six different resin cements. The tested resin cements were Duo-Link (Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A.), Variolink II (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Schann, Liechtenstein), Panavia F (Kuraray Medical Inc., Okayama, Japan), Multilink Automix (Ivoclar-Vivadent AG, Schann, Liechtenstein), RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.), and Maxcem (Kerr Co., CA, U.S.A.). After storage in distilled water for 24 hours, each root was transversally sectioned into approximately 1-mm thick sections. This procedure resulted in 6 serial sections per root. Push-out test was performed using a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu Co.) with a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. The data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey HSD (p=0.05).
The push-out strength of the groups which cemented fiber post with Panavia F and Multilink Automix were lower than those of the other groups. But, there were no statistically significant difference among groups at a probability level of 0.05.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of post according to cement application methods
Seo-Ryeong Kim, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 479. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
- 1,171 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of irrigation methods on the adhesion of Resilon/Epiphany sealer and gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer to intracanal dentin
- Seo-Kyong Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(2):98-106. Published online March 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether intracanal irrigation method could affect the adhesion between intracanal dentin and root canal filling materials (Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer and Resilon/Epiphany sealer).
Thirty extracted human incisor teeth were prepared. Canals were irrigated with three different irrigation methods as a final rinse and obturated with two different canal filling materials (G groups : Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer, R groups : Resilon/Epiphany sealer) respectively.
Group G1, R1 - irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl
Group G2, R2 - irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl, sterile saline
Group G3, R3 - irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl, 17% EDTA, sterile saline
Thirty obturated roots were horizontally sliced and push-out bond strength test was performed in the universal testing machine. After test, the failure patterns of the specimens were observed using Image-analyzing microscope.
The results were as follows.
Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer groups had significantly higher push-out bond strength compared with the Resilon/Epiphany sealer groups (p < 0.05).
Push-out bond strength was higher when using 17% EDTA followed by sterile saline than using NaOCl as a final irrigation solution in the Resilon/Epiphany sealer groups (p < 0.05).
In the failure pattern analysis, there was no cohesive failure in Group G1, G2, and R1. Gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer groups appeared to exhibit predominantly adhesive and mixed failure patterns, whereas Resilon/Epiphany sealer groups exhibited mixed failures with the cohesive failure occurred within the Resilon substrate.
- 867 View
- 4 Download

- EFFECT OF THE ADDITIONAL ETCHING PROCEDURE ON PUSH-OUT BOND STRENGTH OF ONE-STEP RESIN CEMENT
- Soon-Il Kang, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):443-451. Published online January 14, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of additional etching procedure prior to Maxcem resin cement application in indirect restoration cementation using push-out bonding strength.
One hundred and two extracted human molars were used to make indirect resin restorations of gold inlay and Synfony. These restorations were cemented using Maxcem and Variolink II. Additional etching procedures were done for one group with Maxcem. Three groups have 17 specimens in both restoration types. Push-out bond strength was measured using multi-purpose tester and calculated for bonding strength per sqaure-millimeter area. The mean bonding strength values were compared using SPSS 12.0K program for one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's Test with 95% significance.
Under the condition of this study, the additional etching procedure prior to usage of Maxcem resulted in reduced bond strength for both of restoration types.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
- 1,055 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


