Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparison of vibration characteristics of file systems for root canal shaping according to file length
- Seong-Jun Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Hyo-Jin Ji, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e51. Published online October 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
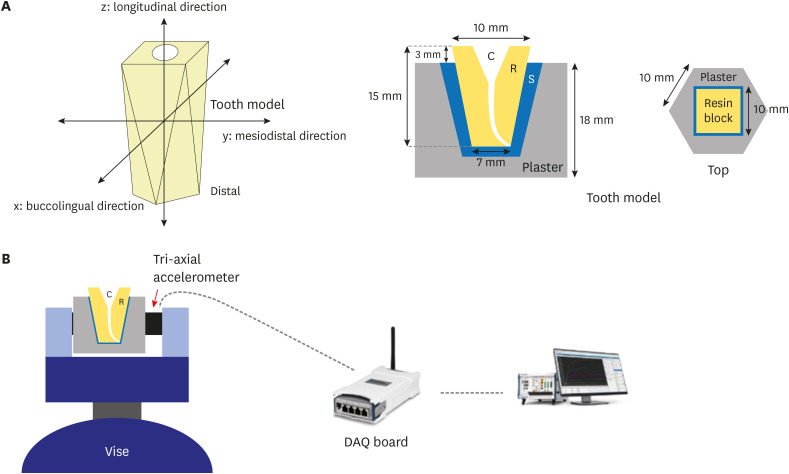
ePub Objectives No studies have yet assessed vibration characteristics according to endodontic file length. Accordingly, the objective of the present study was to examine the vibration characteristics according to nickel-titanium file length and to compare these characteristics between different file systems.
Materials and Methods A total of 45 root canal models were divided into 3 experimental groups (
n = 15 each) based on the file system used (ProTaper Gold [PTG], ProTaper Next, or WaveOne Gold [WOG]). Each experimental group was further divided into 3 subgroups according to file length (21, 25, or 31 mm). An electric motor (X-SMART PLUS) was used in the experiment. For each file system, vibrations generated when using a size 25 file were measured and used to calculate the average vibration acceleration. The differences in vibrations were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Scheffépost hoc test with a confidence interval of 95%.Results In the PTG file system, significantly lower vibration acceleration was observed when using a 21-mm file than when using a 31-mm file. In the WOG file system, significantly stronger vibration acceleration was observed when using a 31-mm file than when using 21- or 25-mm files. Regardless of the file length, the WOG group exhibited significantly stronger vibration acceleration than the other 2 experimental groups.
Conclusions In clinical practice, choosing a file with the shortest length possible could help reduce vibrations. Additionally, consideration should be given to vibrations that could be generated when using WOG files with reciprocating motion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison vibration characteristics of several wireless endodontic handpieces
Bo-Kyung Lee, Yoon Lee, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2022; 38(2): 81. CrossRef
- Comparison vibration characteristics of several wireless endodontic handpieces
- 1,494 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of ProTaper Gold and EdgeEvolve files in canals with single- and double-curvature
- Wafaa A. Khalil, Zuhair S. Natto
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e19. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
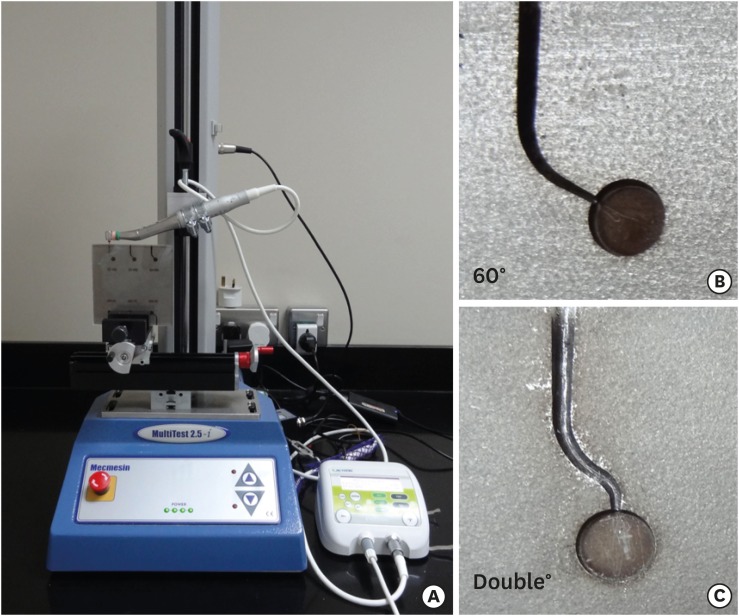
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of EdgeEvolve (EdgeEndo) and ProTaper Gold (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties) nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files.
Materials and Methods The instruments (
n = 15/each) were tested for cyclic fatigue in single- (60° curvature, 5-mm radius) and double-curved (coronal curvature 60°, 5-mm radius, and apical curvature of 30° and 2-mm radius) artificial canals. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated. The bending resistance of both files were tested using a universal testing machine where the files were bent until reach 45°. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray energy-dispersive spectrometric analysis were used for imaging the fractured segments, while the atomic force microscope was used to quantify the surface roughness average (Ra).Results EdgeEvolve files exhibited higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in single- and double-curved canals (
p < 0.05) and both files were more resistant to cyclic fatigue in single-curved canals than double-curved canals (p < 0.05). EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly more flexibility than did ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05). Both files had approximately similar Ni and Ti contents (p > 0.05). EdgeEvolve files showed significantly lower Ra values than ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitation of this study, EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in both single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
Mert Unal, Elif Bahar Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2026; 89(1): 87. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of alterations in surface topographies of three different rotary files after root canal preparation with different irrigating solutions: Atomic force microscopic study
PremSai Parepalli, TB. V G. Raju, PKrishna Prasad, GowtamDev Dondapati, VenkataSrija Kintada, Alekhya Mediboyina
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 299. CrossRef - Assessment of surface topographic changes of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic file at repeated usage: An in vitro study
E. Viswas, VSS Krishna, E. Sridevi, A. J. Sai Sankar, K. Siva Sankar, B. Nagesh
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 149. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Influence of nickel-titanium rotary systems with varying cross-sectional, pitch, and rotational speed on deflection and cyclic fatigue: a finite element analysis study
Wignyo Hadriyanto, Lukita Wardani, Christina Nugrohowati, Ananto Alhasyimi, Rachmat Sriwijaya, Margareta Rinastiti, Widowati Siswomihardjo, Gunadi, T. Yamada, A.A.C. Pramana, Y. Ophinni, A. Gusnanto, W.A. Kusuma, J. Yunus, Afiahayati, R. Dharmastiti, T.
BIO Web of Conferences.2021; 41: 05005. CrossRef - Can the Separated Instrument be Removed From the Root Canal System out by Magnetism? A Hypothesis
Mohammad Daryaeian, Sanjay Miglani, AbdolMahmood Davarpanah, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Mohsen Ramazani
Dental Hypotheses.2019; 10(4): 108. CrossRef - Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis
Raymond Scott, Ana Arias, José C. Macorra, Sanjay Govindjee, Ove A. Peters
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(3): 400. CrossRef
- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,547 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
- Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
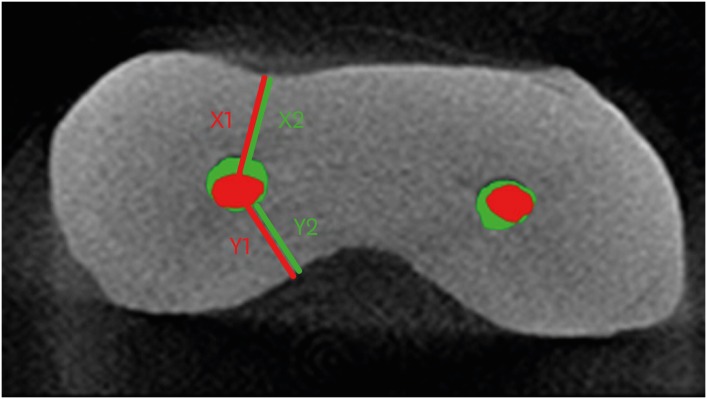
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare root canal volume change and canal transportation by Vortex Blue (VB; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties), ProTaper Next (PTN; Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Universal (PTU; Dentsply Maillefer) nickel-titanium rotary files in curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty canals with 20°–45° of curvature from extracted human molars were used. Root canal instrumentation was performed with VB, PTN, and PTU files up to #30.06, X3, and F3, respectively. Changes in root canal volume before and after the instrumentation, and the amount and direction of canal transportation at 1, 3, and 5 mm from the root apex were measured by using micro-computed tomography. Data of canal volume change were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test, while data of amount and direction of transportation were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney
U test.Results There were no significant differences among 3 groups in terms of canal volume change (
p > 0.05). For the amount of transportation, PTN showed significantly less transportation than PTU at 3 mm level (p = 0.005). VB files showed no significant difference in canal transportation at all 3 levels with either PTN or PTU files. Also, VB files showed unique inward transportation tendency in the apical area.Conclusions Other than PTN produced less amount of transportation than PTU at 3 mm level, all 3 file systems showed similar level of canal volume change and transportation, and VB file system could prepare the curved canals without significant shaping errors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
Yaprak Cesur, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Ahmet Serper, Mert Ocak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of Vortex Blue and TruNatomyTM Ni-Ti Rotary Systems
Batool Alghamdi, Mey Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman, Lina Bahanan, Ali Alrahlah, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Sarah Bukhari, Mohammed Howait, Loai Alsofi
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 980. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of nickel titanium rotary instruments on canal transportation and centering ability in curved canals by using cone beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Krishnaveni Krishnaveni, Nikitha Kalla, Nagalakshmi Reddy, Sharvanan Udayar
Journal of Dental Specialities.2023; 11(2): 105. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - A Comparison of Canal Width Changes in Simulated Curved Canals prepared with Profile and Protaper Rotary Systems
Aisha Faisal, Huma Farid, Robia Ghafoor
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 55. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Respect of the Root Canal Trajectory by Rotary Niti Instruments (Protaper®Universal): Retrospective Radiographic Study
Salma El Abbassi, Sanaa Chala, Majid Sakout, Faïza Abdallaoui
Integrative Journal of Medical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
- 1,786 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of adaptive motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of a nickel titanium instrument designed for retreatment
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):34-38. Published online December 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.34

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file (Dentsply Maillefer) under continuous and adaptive motion.
Materials and Methods Forty ProTaper Universal D1 files were included in this study. The cyclic fatigue tests were performed using a dynamic cyclic fatigue testing device, which had an artificial stainless steel canal with a 60° angle of curvature and a 5 mm radius of curvature. The files were randomly divided into two groups (Group 1, Rotary motion; Group 2, Adaptive motion). The time to failure of the files were recorded in seconds. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated for each group. The data were statistically analyzed using Student's
t -test. The statistical significant level was set atp < 0.05.Results The cyclic fatigue resistance of the adaptive motion group was significantly higher than the rotary motion group (
p < 0.05).Conclusion Within the limitations of the present study, the ‘Adaptive motion’ significantly increased the resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file to cyclic facture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
Anas Sira, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 64. CrossRef - Surface Alterations of Ni‐Ti Files After Retreatment of Root Canals Filled With Different Sealers: AFM and SEM Study
Duygu Aksoy, Sibel Koçak, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(10): 2704. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Assessment the impact of operator experience on cyclic fatigue resistance in reciprocating and rotary NiTi files: a comparative study between dental students and pediatric dentistry specialists
Hande Özyürek, Mesut Elbay, Taha Özyürek
Frontiers in Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef - Influences of Continuous Rotation and TF adaptive Motion on the Resistance of Different Retreatment File Systems to Deformation and Fracture: An In Vitro study
Divya Meena, Ramyadharshini LNU, V Nivedha, Anand Sherwood
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018; 3(2): 71. CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium files: an examination using high-speed camera
Taha Özyürek, Neslihan Büşra Keskin, Fatma Furuncuoğlu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 224. CrossRef
- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
- 1,586 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):1-5. Published online February 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.1

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of ProTaper Gold (PTG, Dentsply Maillefer) in maintaining the original profile of root canal anatomy. For that, ProTaper Universal (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer) was used as reference techniques for comparison.
Materials and Methods Twenty simulated curved canals manufactured in clear resin blocks were randomly assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10) according to the system used for canal instrumentation: PTU and PTG groups, upto F2 files (25/0.08). Color stereomicroscopic images from each block were taken exactly at the same position before and after instrumentation. All image processing and data analysis were performed with an open source program (FIJI). Evaluation of canal transportation was obtained for two independent canal regions: straight and curved levels. Student'st test was used with a cut-off for significance set at α = 5%.Results Instrumentation systems significantly influenced canal transportation (
p < 0.0001). A significant interaction between instrumentation system and root canal level (p < 0.0001) was found. PTU and PTG systems produced similar canal transportation at the straight part, while PTG system resulted in lower canal transportation than PTU system at the curved part. Canal transportation was higher at the curved canal portion (p < 0.0001).Conclusions PTG system produced overall less canal transportation in the curved portion when compared to PTU system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
Wesley Viana de Sousa, Marina da Cunha Isaltino, Christianne Velozo, Silmara de Andrade Silva, Luiza de Almeida Souto Montenegro, Hugo Victor Dantas, Frederico Barbosa de Sousa, Diana Albuquerque, Cristiana Corsi
The Scientific World Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping, and disinfecting abilities of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Twisted Files: A correlative microcomputed tomographic and bacteriologic analysis
Malavika Sivakumar, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, CP Baveja, Rega Kumar, Sudha Yadav, S Santosh Kumar
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 54. CrossRef - Advancing Nitinol: From heat treatment to surface functionalization for nickel–titanium (NiTi) instruments in endodontics
Wai-Sze Chan, Karan Gulati, Ove A. Peters
Bioactive Materials.2023; 22: 91. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - An Appraisal on Newer Endodontic File Systems: A Narrative Review
Shalini Singh, Kailash Attur, Anjali Oak, Mohammed Mustafa, Kamal Kumar Bagda, Nishtha Kathiria
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 944. CrossRef - Shaping ability of modern Nickel–Titanium rotary systems on the preparation of printed mandibular molars
Seda Falakaloglu, Emmanuel Silva, Burcu Topal, Emre İriboz, Mustafa Gündoğar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 498. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna Dobrzańska
Processes.2022; 10(1): 101. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Kinematics on Stress Distribution During Root Canal Treatment: Analysis of Photoelastic Stress
Shelyn Akari Yamakami, Julia Adornes Gallas, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Manoel Sousa-Neto, Ana Paula Macedo, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 255. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Two Martensitic Alloy Systems in Endodontic Files Carried out by Unskilled Hands
Juan Algar, Alejandra Loring-Castillo, Ruth Pérez-Alfayate, Carmen Martín Carreras-Presas, Ana Suárez
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6289. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Canal Transportation, Separation Rate, and Preparation Time between One Shape and Neoniti (Neolix): An In Vitro CBCT Study
Maryam Kuzekanani, Faranak Sadeghi, Nima Hatami, Maryam Rad, Mansoureh Darijani, Laurence James Walsh, Sivakumar Nuvvula
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold, One Curve, and Self-Adjusting File systems in severely curved canals: A cone-beam computed tomography study
MeenuG Singla, Hemanshi Kumar, Ritika Satija
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 271. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of apical transportation and centering ratio of ProTaper and XP-endo Shaper NiTi rotary systems in curved canals: an in vitro study
Hamed Karkehabadi, Zeinab Siahvashi, Abbas Shokri, Nasrin Haji Hasani
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanical Tests, Metallurgical Characterization, and Shaping Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments: A Multimethod Research
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Jorge N.R. Martins, Carolina O. Lima, Victor T.L. Vieira, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Gustavo De-Deus, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(10): 1485. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of vibration characteristics of file systems for root canal shaping according to file length
Seong-Jun Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Hyo-Jin Ji, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys – a review
J. Zupanc, N. Vahdat‐Pajouh, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(10): 1088. CrossRef - Shaping ability of four root canal instrumentation systems in simulated 3D-printed root canal models
David Christofzik, Andreas Bartols, Mahmoud Khaled Faheem, Doreen Schroeter, Birte Groessner-Schreiber, Christof E. Doerfer, Cyril Charles
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0201129. CrossRef - OPEN-SOURCE SOFTWARE IN DENTISTRY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Małgorzata Chruściel-Nogalska, Tomasz Smektała, Marcin Tutak, Katarzyna Sporniak-Tutak, Raphael Olszewski
International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care.2017; 33(4): 487. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - A comparison of the shaping ability of three nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomography study via a contrast radiopaque technique in vitro
Zhao Wei, Zhi Cui, Ping Yan, Han Jiang
BMC Oral Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Transportation and Centering Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Mandibular Premolars Assessed Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Iussif Mamede-Neto, Alvaro Henrique Borges, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Durvalino de Oliveira, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Carlos Estrela
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 71. CrossRef - Blue Thermomechanical Treatment Optimizes Fatigue Resistance and Flexibility of the Reciproc Files
Gustavo De-Deus, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gianluca Plotino, Nicola Maria Grande
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 462. CrossRef
- Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
- 1,769 View
- 9 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):286-289. Published online September 2, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim was to evaluate dentinal crack formation after root canal preparation with ProTaper Next system (PTN) with and without a glide path.
Materials and Methods Forty-five mesial roots of mandibular first molars were selected. Fifteen teeth were left unprepared and served as controls. The experimental groups consist of mesiobuccal and mesiolingual root canals of remaining 30 teeth, which were divided into 2 groups (
n = 15): Group PG/PTN, glide path was created with ProGlider (PG) and then canals were shaped with PTN system; Group PTN, glide path was not prepared and canals were shaped with PTN system only. All roots were sectioned perpendicular to the long axis at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 mm from the apex, and the sections were observed under a stereomicroscope. The presence/absence of cracks was recorded. Data were analyzed with chi-square tests with Yates correction.Results There were no significant differences in crack formation between the PTN with and without glide path preparation. The incidence of cracks observed in PG/PTN and PTN groups was 17.8% and 28.9%, respectively.
Conclusions The creation of a glide path with ProGlider before ProTaper Next rotary system did not influence dentinal crack formation in root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
Prajna Pattanaik, Akilan Balasubramanian, P. Veeralakshmi, Gautam Singh, Vandana Sadananda, Hina Ahmed, J. Suresh Babu, C. Swarnalatha, Abhishek Singh Nayyar
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2025; 13(4): 177. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Microscopic Assessment of Dentinal Defects Induced by ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Hyflex Electric Discharge Machining Rotary File Systems – An in vitro Study
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ng Sanjeeta
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 230. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
- 1,559 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
- Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):104-108. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effect of passive ultrasonic agitation on the cleaning capacity of a hybrid instrumentation technique.
Materials and Methods Twenty mandibular incisors with mesiodistal-flattened root shape had their crowns sectioned at 1 mm from the cementoenamel junction. Instrumentation was initiated by catheterization with K-type files (Denstply Maillefer) #10, #15, and #20 at 3 mm from the working length. Cervical preparation was performed with Largo bur #1 (Dentsply Maillefer) followed by apical instrumentation with K-type files #15, #20 and #25, and finishing with ProTaper F2 file (Denstply Maillefer). All files were used up to the working length under irrigation with 1 mL of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (Biodynâmica) at each instrument change. At the end of instrumentation, the roots were randomly separated into 2 groups (
n = 10). All specimens received final irrigation with 1 mL of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. The solution remained in the root canals in Group 1 for one minute; and ultrasonic agitation was performed in Group 2 for one minute using a straight tip inserted at 1 mm from working length. The specimens were processed histologically and the sections were analyzed under optic microscope (×64) to quantify debris present in the root canal.Results The samples submitted to ultrasonic agitation (Group 2) presented significant decrease in the amount of debris in comparison with those of Group 1 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The hybrid instrumentation technique associated with passive ultrasonic agitation promoted greater debris removal in the apical third of the root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro-CT Evaluation of Different Root Canal Irrigation Protocols on the Removal of Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ailin Liang, Luo Huang, Baoyu Li, Yihua Huang, Xiaoyan Zhou, Xufang Zhang, Qimei Gong
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6053. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation during Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Petruţa E. Căpută, Anastasios Retsas, Lydwien Kuijk, Luis E. Chávez de Paz, Christos Boutsioukis
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on Crown Fracture Resistance
Marina Baechtold, Leonardo da Cunha, Erick Souza, Marilisa Gabardo, Kauhanna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto-Filho, Denise Leonardi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(7): 768. CrossRef - Influence of Prior Cervical Enlargement on Apical Cleaning Using Single File
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Celso Alfredo Schramm, Allan Fernando Giovanini, Cibelli Mariane Silveira, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho, Flares Baratto-Filho
The Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College.2015; 56(2): 85. CrossRef - Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 143. CrossRef - Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 149. CrossRef
- Micro-CT Evaluation of Different Root Canal Irrigation Protocols on the Removal of Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,578 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
- Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):215-219. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the screw-in effect and torque generation depending on the size of glide path during root canal preparation.
Materials and Methods Forty Endo-Training Blocks (REF A 0177, Dentsply Maillefer) were used. They were divided into 4 groups. For groups 1, 2, 3, and 4, the glide path was established with ISO #13 Path File (Dentsply Maillefer), #15 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX (Dentsply Maillefer), modified #16 Path File (equivalent to #18), and #20 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX, respectively. The screw-in force and resultant torque were measured using a custom-made experimental apparatus while canals were instrumented with ProTaper S1 (Dentsply Maillefer) at a constant speed of 300 rpm with an automated pecking motion. A statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance and the Duncan
post hoc comparison test.Results Group 4 showed lowest screw-in effect (2.796 ± 0.134) among the groups (
p < 0.05). Torque was inversely proportional to the glide path of each group. In #20 glide path group, the screw-in effect and torque decreased at the last 1 mm from the apical terminus. However, in the other groups, the decrease of the screw-in effect and torque did not occur in the last 1 mm from the apical terminus.Conclusions The establishment of a larger glide path before NiTi rotary instrumentation appears to be appropriate for safely shaping the canal. It is recommended to establish #20 glide path with NiTi file when using ProTaper NiTi rotary instruments system safely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
Taher Al Omari, Layla Hassouneh, Khawlah Albashaireh, Alaa Dkmak, Rami Albanna, Ali Al-Mohammed, Ahmed Jamleh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Printed Teeth in Endodontics: A New Protocol for Microcomputed Tomography Studies
Tiago Reis, Cláudia Barbosa, Margarida Franco, Ruben Silva, Nuno Alves, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Jose Martín-Cruces, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Materials.2024; 17(8): 1899. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation and fracture resistance of endodontically retreated teeth using hyflex remover, Mtwo, and ProTaper retreatment file systems: An in vitro study
Isha Singh, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Pallavi Sharma, Kunal Bedi, Priyanka Rani, Swapnil Vats
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Morphological and structural variations of Nickel-Titanium endodontic instruments subjected to instrumentation loads: in vitro study
Yenny Marcela Orozco-Ocampo, César Augusto Álvarez-Vargas, Francy Nelly Jiménez-García, Daniel Escobar-Rincón, Paola Ximena Jaramillo-Gil
Revista UIS Ingenierías.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Efficiency to Remove the Infected Dentin via Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Count and to Adequately Shape the Canal Using Hand Kedo-SH Files, Rotary Kedo-SG (Blue) and Pro AF Baby Gold Files in Primary Molars: An In Vitro Study
Shruthi B Patil, Kaavya Shanker
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S142. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, torque, and force generation during retreatment with D-RaCe, HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo retreatment files
Yoojin Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic and torsional fatigue resistance of a new rotary file on a rotary and reciprocating motion
Gabriel Barcelos Só, Giovana Siocheta, Pedro Calefi, Murilo Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antônio H. Duarte, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(12): 1635. CrossRef - Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Hayate Unno, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1170. CrossRef - Dynamic torque and screw-in force of four different glide path instruments assessed in simulated single- and double-curved canals: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Moe-Sandar Kyaw, Yuka Kasuga, Miki Nishijo, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(4): 1598. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - Evolution and development: engine-driven endodontic rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Yuhong Liang, Lin Yue
International Journal of Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Endodontic Rotary Files, What Should an Endodontist Know?
Ana-Belén Dablanca-Blanco, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Ramón Miguéns-Vila, Pablo Álvarez-Novoa, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 719. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Canal shaping
Ana Arias, Ove A. Peters
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 637. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimum glide path motion is safer than continuous rotation of files in glide path preparation
Giulio Gavini, Eduardo Akisue, Dirce Akemi Sacaguti Kawakami, Celso Luiz Caldeira, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Húngaro Duarte
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 544. CrossRef - Root canals shaped by nickel-titanium instrumentation with automated computerized numerical control systems
Liming Wang, Wenxiang Li, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Kee-Yeon Kum, Yu Gu
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Update on Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Endodontics: Mechanical Characteristics, Testing and Future Perspective—An Overview
Alessio Zanza, Maurilio D’Angelo, Rodolfo Reda, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2021; 8(12): 218. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Cleaning Efficiency and Apical Extrusion of Debris Using Two Pediatric Rotary Endodontic Files: An In Vitro Study
Nilima Thosar, Sudhindra Baliga, Faraz Ahmed, Nilesh Rathi, Shreyans A Jain, Jayati Mehta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(2): 196. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 188. CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TORQUE SETTINGS ON THE AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS DURING ROTARY INSTRUMENTATION
Demet ALTUNBAŞ, Mustafa TOYOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2020; 23(3): 160. CrossRef - Glide Path: “Path to the successful root canal instrumentation”- Review
Anjali Mairal Oak
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional fatigue strength of reciprocating and rotary pathfinding instruments manufactured from different NiTi alloys
Rodrigo Ricci VIVAN, Murilo Priori ALCALDE, George CANDEIRO, Giulio GAVINI, Celso Luis CALDEIRA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne nickel-titanium files
Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Real‐time dynamic torque values and axial forces during preparation of straight root canals using three different endodontic motors and hand preparation
S. Bürklein, J. P. Stüber, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(1): 94. CrossRef - Comparison of glide paths created with K-files, PathFiles, and the ProGlider file, and their effects on subsequent WaveOne preparation in curved canals
Linxia Zheng, Xiongfei Ji, Chengxi Li, Lulu Zuo, Xin Wei
BMC Oral Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance and bending properties of two reciprocating nickel‐titanium glide path files
T. Özyürek, G. Uslu, M. Gündoğar, K. Yılmaz, N. M. Grande, G. Plotino
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(9): 1047. CrossRef - Root Canal Shaping Effect of Instruments with Offset Mass of Rotation in the Mandibular First Molar: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Jung Hong Ha, Myoung Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 822. CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Effect of the Glide Path Establishment on the Torque Generation to the Files during Instrumentation: An In Vitro Measurement
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 496. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel Glide Path Instruments with Different Alloy Properties and Kinematics
Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Micoogullari Kurt, Mehmet Kemal Çalişkan
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(9): 1422. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of R‐Pilot, HyFlex EDM and PathFile nickel‐titanium glide path files in artificial canals with double (S‐shaped) curvature
G. Uslu, T. Özyürek, K. Yılmaz, M. Gündoğar
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(5): 584. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Used and New Glide Path Files
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 477. CrossRef - Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an in vitro study
Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 316. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Torsional Performance of ProTaper Gold Rotary Instruments during Shaping of Small Root Canals after 2 Different Glide Path Preparations
Ana Arias, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Alexis Hernández, Ove A. Peters
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 447. CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef -
In vitro comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, One G, and ProGlider nickel titanium glide path instruments in single and double curvature canals
Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 282. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef - Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 304. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Differences in torsional performance of single- and multiple-instrument rotary systems for glide path preparation
Ana Arias, Rupinderpal Singh, Ove A. Peters
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 192. CrossRef - Effect of glide path and apical preparation size on the incidence of apical crack during the canal preparation using Reciproc, WaveOne, and ProTaper Next systems in curved root canals: A stereomicroscope study
Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu, Salih Düzgün, Firdevs Akpek, Gamze Topçuoğlu
Scanning.2016; 38(6): 585. CrossRef - Geometric Optimization for Development of Glide Path Preparation Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Sang-Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Dongseok Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 916. CrossRef - Glide Path Management with Single- and Multiple-instrument Rotary Systems in Curved Canals: A Micro–Computed Tomographic Study
Alison Luís Kirchhoff, Rene Chu, Isabel Mello, Andres Dario Plazas Garzon, Marcelo dos Santos, Rodrigo Sanches Cunha
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1880. CrossRef - Safe root canal preparation using reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments
Jung-Hong Ha
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 253. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 123. CrossRef - Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 286. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of 5 Different Rotary Pathfinding Instruments Made of Conventional Nickel-Titanium Wire, M-wire, and Controlled Memory Wire
Ismail Davut Capar, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Hüseyin Ertas, Bilge Hakan Sen
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(4): 535. CrossRef - Comparision of two different preparation protocol of Ni-Ti Rotary PathFile-ProTaper instruments in simulated s-shaped canals
Elıf Delve Başer Can, Müzeyyen Gerek, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Kambız Mohsenı, Hakki Sunay, Gündüz Bayirli
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2014; 72(1): 76. CrossRef - Torsional and cyclic fatigue resistances of glide path preparation instruments: G‐file and PathFile
Sang Yup Sung, Jung‐Hong Ha, Sang‐Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Kyeongmin Byeon, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2014; 36(5): 500. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Different Nickel-Titanium Systems in Simulated S-shaped Canals with and without Glide Path
Sebastian Bürklein, Thomas Poschmann, Edgar Schäfer
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1231. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Self-Adjusting File Movement: Minimally Invasive Instrumentation
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Yup Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Michael Solomonov, Jung-Min Lee, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1572. CrossRef
- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
- 2,455 View
- 13 Download
- 76 Crossref

- Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
- Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):530-541. Published online November 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.530
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Currently, various Nickel-Titanium rotary files are used in endodontic treatment, but there is no one perfect system that can be applied to any clinical situation. Therefore, the combined uses of various file systems which can emphasize the advantages of each system are introduced as hybrid instrumentation.
The ProTaper system is efficient in body shaping and apical pre-enlargement but is reported to have more possibility of transportation and produce more aberrations and deformation in more or less severe curved canals. Recently, new ProTaper system (ProTaper Universal) with different configuration and cross-sectional design to overcome the week points of ProTaper have been marketed.
The purpose of this study was to compare and evaluate the shaping abilities of ProTaper, ProTaper Universal system, and two hybrid methods using S-series of ProTaper Universal and Hero Shaper or ProFile.
The time lapses for instrumentation were measured and the used files were inspected for distortion. The pre- and post-instrumented root canals were scanned and superimposed to evaluate the aberrations and reduction of root canal curvature and change of radius of canal curvature. The increased canal width and apical centering ratio were calculated at 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm levels from apical foramen.
Under the conditions of this study, the ProTaper Universal seems to have better shaping ability than ProTaper in terms of instrumented width and instrumentation time. It may be suggested that the ProTaper Universal system is efficient as much as hybrid instrumentation using ProTaper and other constant-tapered NiTi file systems in highly experienced operators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 201. CrossRef - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
- 1,404 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A study on transportation of apical foramen after overinstrumentation by ProFile®, ProTaper™ and K3TM in simulated canals with different curvatures
- Hyun Yang, In-Seok Yang, Yun-Chann Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Won-Jae Kim, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):87-94. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was done to evaluate transportation of the apical foramen after 0.5 mm overinstrumentation by ProFile, ProTaper and K3 in simulated resin root canal.
Sixty simulated resin root canal with a curvature of J and S-shape were divided into two groups. Each group consisted of three subgroups with 10 blocks according to the instruments used: ProFile®, ProTaper™, and K3TM. Simulated resin root canal was prepared by ProFile, ProTaper and K3 with 300 rpm by the crown-down preparation technique. Pre- and post-instrumentation apical foramen images were overlapped and recorded with Image-analyzing microscope 100X (Camcope, Sometech Inc, Korea). The amounts of difference in width and dimension on overlapped images were measured after reference points were determined by Image Analysis program (Image-Pro® Express, Media Cybernetic, USA). Data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U-test.
The results suggest that ProFile showed significantly less canal transportation and maintained original apical foramen shape better than K3 and ProTaper.
- 813 View
- 4 Download

- A comparison of canal centering abilities of four root canal instrument systems using X-ray micro-computed tomography
- Hye-Suk Ko, Heyon-Mee You, Dong-Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):61-68. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.061
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the centering abilities of four root canal instrument systems and the amounts of dentin removed after root canal shaping using them.
The mesial canals of twenty extracted mandibular first molars having 10 - 20° curvature were scanned using X-ray micro-computed tomography (XMCT)-scanner before root canals were instrumented. They were divided into four groups (n = 10 per group). In Group 1, root canals were instrumented by the step-back technique with stainless steel K-Flexofile after coronal flaring. The remainders were instrumented by the crown-down technique with Profile (Group 2), ProTaper (Group 3) or K3 system (Group 4). All canals were prepared up to size 25 at the end-point of preparation and scanned again. Scanned images were processed to reconstruct three-dimensional images using three-dimensional image software and the changes of total canal volume were measured. Pre- and post-operative cross-sectional images of 1, 3, 5, and 7 mm from the apical foramen were compared. For each level, centering ratio were calculated using Adobe Photoshop 6.0 and image software program.
ProTaper and K3 systems have a tendency to remove more dentin than the other file systems. In all groups, the lowest value of centering ratio at 3 mm level was observed. And except at 3 mm level, ProTaper system made canals less centered than the other systems (p < 0.05).
- 1,349 View
- 5 Download

- A study of insertion depth of buchanan plugger after shaping using NI-TI rotary files in simulated resin root canals
- Youn-Sik Park, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):125-132. Published online March 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was conducted to evaluate the insertion depth of Buchanan plugger after shaping by various Ni-Ti rotary files. It was conducted to determine which size of plugger are appropriate, when root canals are shaped with Ni-Ti rotary files and obturated by Continuous wave of condensation technique.
Two type of eighty simulated resin blocks were used : J-shaped and straight shaped canal. The simulated canals were instrumented by ProTaper and ProFile. Buchanan pluggers were inserted into the canal, and then the image was recorded to scanner. The distance from the apex of the canal to the plugger tip was measured by image analysis program. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe's test.
The results were as follows
1. In straight canal finished up to ProTaper F2 and F3 file, F and FM pluggers were inserted more than 5 mm short of working length.
2. In J-shaped canal finished up to ProTaper F2 file, F pluggers were inserted more than 5 mm short of working length. Finished up to ProTaper F3 file, F and FM pluggers were inserted more than 5 mm short of working length.
3. In straight and J-shaped canal finished up to ProFile .06/#20 and .06/#25, any of Buchanan plugger could not be inserted more than 5 mm short of working length.
These results suggest that canals shaped by ProTaper could be obturated by Continuous wave of condensation technique with F and FM size Buchanan plugger.
- 876 View
- 0 Download

- Step by step analysis of root canal instrumentation with ProTaper®
- Mi-Hee Kim, Bock Huh, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):50-57. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.050
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate influence of each file step of ProTaper® system on canal transportation.
Twenty simulated canals were prepared with either engine-driven ProTaper® or manual ProTaper®. Group R-resin blocks were instrumented with rotary ProTaper® and group M-resin blocks were instrumented with manual ProTaper®. Pre-operative resin blocks and post-operative resin blocks after each file step preparation were scanned. Original canal image and the image after using each file step were superimposed for calculation of centering ratio. The image after using each file step and image after using previous file step were superimposed for calculation of the amount of deviation. Measurements were taken horizontally at five different levels (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm) from the level of apical foramen.
In rotary ProTaper® instrumentation group, centering ratio and the amount of deviation of each step at all levels were not significantly different (p > 0.05). In manual ProTaper® instrumentation group, centering ratio and the amount of deviation of each step at all levels except of 1 mm were not significantly different (p > 0.05). At the level of 1 mm, F2 file step had significantly large centering ratio and the amount of deviation (p < 0.05).
Under the condition of this study, F2 file step of manual ProTaper® tended to transport the apical part of the canals than that of rotary ProTaper®.
- 2,252 View
- 11 Download

- Comparison of shaping ability between various hybrid instrumentation methods with ProTaper
- Eun-Sook Hong, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):11-19. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare and evaluate the shaping abilities of various hybrid instrumentation method using constant tapered file systems with ProTaper® S1 and the difference between experts and inexperienced clinicians in use of NiTi file.
Three hybrid methods used in this study were composed of ProTaper® S1 and K-Flexofile® (group S), ProTaper® S1 and HeroShaper® (group H), and ProTaper® S1 and ProFile® (group P), respectively. The ProTaper®-alone method (group C) was introduced as a control group.
After canal preparation, the lapse of time was recorded. The images of pre- and post-operative canal were scanned and superimposed. Amounts of instrumented canal widths and centering ratio were measured at apical 1, 2 and 3 mm levels and statistical analysis was performed.
In this study, both of the group C and S took more time to prepare canals than other groups. Inexperienced operators required more time for the entire preparation with the groups C and H than the experienced (
p < 0.05). And the centering ratio of group P were preferable to ProTaper®-alone method or the hybrid technique using stainless steel files. As such, within experienced operators, group H also showed better results in addition to the group P.Under these condition, the hybrid methods of each the ProFile® system and HeroShaper® with ProTaper® are recommendable comparative to ProTaper®-alone method. According to the results, the hybrid instrumentation method is a more appropriate method of canal preparation than single file system for narrow or curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of Forces Generated During Root Canal Shaping and Residual Stresses of Three Nickel–Titanium Rotary Files by Using a Three-Dimensional Finite-element Analysis
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Soon-Il Kang
Journal of Endodontics.2008; 34(6): 743. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between single length technique and crown-down technique using Mtwo rotary file
Yoo-Kyoung Lim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(4): 385. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef
- Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
- 1,564 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A comparative study of the canal configuration after shaping by protaper rotary and hand files in resin simulated canals
- In-Seok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):393-401. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.393
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the canal configuration after shaping by ProTaper rotary files and ProTaper hand files in resin simulated canals.
Forty resin simulated canals with a curvature of J-shape and S-shape were divided into four groups by 10 blocks each. Simulated root canals in resin block were prepared by ProTaper rotary files and ProTaper hand files using a crown-down pressureless technique. All simulated canals were prepared up to size #25 file at end-point of preparation. Pre- and post-instrumentation images were recorded with color scanner. Assessment of canal shape was completed with an image analysis program. Measurements were made at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 mm from the apex. At each level, outer canal width, inner canal width, total canal width, and amount of transportation from original axis were recorded. Instrumentation time was recorded. The data were analyzed statistically using independent
t -test.The result was that ProTaper hand files cause significantly less canal transportation from original axis of canal body and maintain original canal configuration better than ProTaper rotary files, however ProTaper hand files take more shaping time.
- 851 View
- 3 Download

- The change of canal configuration after instrumentation by several nickel-titanium files in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature
- Jung-Jang Lim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):303-311. Published online July 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate which type of Ni-Ti files are able to maintain canal configuration better in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature near it's apex.
Ninety six simulated root canals were made in epoxy resin and #15 finger spreader was used as root canal templates. The simulated root canals were made with radius of curvature of 1.5 mm, 3.0 mm, 4.0 mm, 6.0 mm respectively and the angle of curvature of all simulated canals were adjusted to 90 degree. The simulated canals were instrumented by ProFile, ProTaper, Hero 642, and K3 at a 300 rpm using crown-down pressureless technique. Pre-instrumented and post-instrumented images were taken by digital camera and were superimposed with Adobe Photoshop 6.0 program. Images were compared by image analysis program.
The changes of canal width at the inner and outer side of the canal curvature, canal transportation were measured at 9 measuring point with 1 mm interval. Statistical analysis among the types of Ni-Ti files was performed using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U-test.
The result was that ProFile maintain original canal configuration better than other engine driven Ni-Ti files in the canals above 3.0 mm radius of curvature, and in the 1.5 mm radius of curvature, most of Ni-Ti flies were deformed or separated during instrumentation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on transportation of apical foramen after overinstrumentation by ProFile®, ProTaper™ and K3TMin simulated canals with different curvatures
Hyun Yang, In-Seok Yang, Yun-Chann Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Won-Jae Kim, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 87. CrossRef
- A study on transportation of apical foramen after overinstrumentation by ProFile®, ProTaper™ and K3TMin simulated canals with different curvatures
- 1,088 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A comparative study on the canal configuration after shaping by ProFile, ProTaper™ and K-Flexofile in simulated canals with different angles of curvature
- Bo-Kum Lee, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(4):294-302. Published online July 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.294
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the canal configuration after shaping by ProFile, ProTaper and K-Flexofile in simulated resin canals with different angles of curvature.
Three types of instruments were used : ProFile, ProTaper, K-Flexofile. Simulated root canals, which were made of epoxy resin, were prepared by ProFile, ProTaper with rotary instrument using a crown-down pressureless technique, and hand instrumentation was performed by K-Flexofile using a step-back technique. All simulated canals were prepared up to size 25 file at end-point of preparation. Pre and post instrumentation images were recorded with Scanner. Assessment of canal shape was completed with Image Analysis program. Measurements were made at 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 mm from the apex. At each level, outer canal width, inner canal width, total canal width, and amount of transportation from original axis were recorded. Instrument deformation and fracture were recorded. Data were analyzed by means of one-way ANOVA analysis of variance and the Sheffe's test.
The result was that ProFile and ProTaper maintain original canal shape regardless of the increase of angle of curvature than K-Flexofile. ProFile show significantly less canal transportation and maintained original canal shape better than ProTaper.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on transportation of apical foramen after overinstrumentation by ProFile®, ProTaper™ and K3TMin simulated canals with different curvatures
Hyun Yang, In-Seok Yang, Yun-Chann Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Won-Jae Kim, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 87. CrossRef
- A study on transportation of apical foramen after overinstrumentation by ProFile®, ProTaper™ and K3TMin simulated canals with different curvatures
- 1,633 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A comparison of shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals
- So-Youn Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):58-65. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals.
Thirty resin blocks were divided into 3 groups with 10 canals each. Each group was instrumented with manual ProTaper® (Group M), rotary ProTaper® (Group R), and hybrid technique (Group H). Canal preparation time was recorded. The images of pre- and post-instrumented root canals were scanned and superimposed. The amounts of canal deviation, total canal width, inner canal width, outer canal width and centering ratio were measured at apical 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 mm levels.
1. Canal preparation time was the shortest in R group (p < 0.05).
2. The amounts of total canal width in R group was generally larger than the other groups, but no significant differences were observed except at the 1, 3 mm levels (p > 0.05).
3. The amounts of inner canal width in R group was larger than M group at the 1 mm level and H group was larger than R group at the 6 mm level (p < 0.05). The amounts of outer canal width in R group was larger than H group only at the 1 mm level (p < 0.05).
4. The direction of canal deviation in H, R group at the 1, 2, 3 mm levels was outward and that in M group at the 1, 2 mm levels was inward. The amounts of canal deviation in H group was larger than R group at the 6 mm level (p < 0.05).
5. The amounts of centering ratio in H group was larger than R group at the 6 mm level (p < 0.05).
- 796 View
- 0 Download

- Shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium instruments to prepare root canal at danger zone
- Seok-Dong Choi, Myoung-Uk Jin, Ki-Ok Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):446-453. Published online September 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.446
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping abilities of four different rotary nickel-titanium instruments with anticurvature motion to prepare root canal at danger zone by measuring the change of dentin thickness in order to have techniques of safe preparation of canals with nickel-titanium files.
Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of forty mesial roots of extracted human lower molars were instrumented using the crown-down technique with ProFile, GT™ Rotary file, Quantec file and ProTaper™. In each root, one canal was prepared with a straight up-and-down motion and the other canal was with an anticurvature motion. Canals were instrumented until apical foramens were up to size of 30 by one operator. The muffle system was used to evaluate the root canal preparation. After superimposing the pre- and post-instrumentation canal, change in root dentin thickness was measured at the inner and outer sides of the canal at 1, 3, and 5 mm levels from the furcation. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA.
Root dentin thickness at danger zone was significantly thinner than that at safe zone at all levels (
p < 0.05).There was no significant difference in the change of root dentin thickness between the straight up-and-down and the anticurvature motions at both danger and safe zones in all groups (
p > 0.05).ProTaper removed significantly more dentin than other files especially at furcal 3 mm level of danger and safe zones (
p < 0.05)Therefore, it was concluded that anticurvature motion with nickel-titanium rotary instruments does not seem to be effective in danger zone of lower molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Conservation of dentin thickness in the root canals orifice following two preparation techniques
Ranjdar Talabani, Shawbo Ahmad, Arass Noori
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2014; 1(2): 6. CrossRef - Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 30. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef
- Conservation of dentin thickness in the root canals orifice following two preparation techniques
- 1,467 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The effect of early coronal flaring about apical extrusion of debris
- Min-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Beom Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):147-152. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate the quantity of debris which was extruded apically after canal instrumentation using different types of enlarging instrument in endodontic resin models.
Five groups of 9 endodontic resin models were instrumented using each different technique: hand instrumentation without early coronal flaring, hand instrumentation after early coronal flaring, and three nickel-titanium engine-driven instrumentations (Hero 642, Protaper, K3). Debris extruded from apical foramen during instrumentation was collected on preweighed CBC bottle, desiccated and weighted using electronic balance. The results were analyzed using Kruskal-wallis test and Mann-Whitney
U rank sum test at a significance level of 0.05.The results were as follows:
All of instrumentation techniques produced apically extruded debris.
Group without early coronal flaring extruded significant more debris than groups with early coronal flaring.
There was no significant difference among early coronal flaring groups.
The early coronal flaring is very important to reduce the amount of debris extruded apically.
- 901 View
- 0 Download

- THE EFFECT OF GUTTA-PERCHA REMOVAL USING NICKEL-TITANIUM ROTARY INSTRUMENTS
- Jeong-Hun Jeon, Jeong-Beom Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):212-218. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.212
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to quantify the amount of remaining gutta-percha/sealer on the walls of root canals when three types of nickel-titanium rotary instruments(Profile, ProTaper and K3) and a hand instrument(Hedstrom file) used to remove these materials.
The results of this study were as follows:
In the total time for gutta-percha removal, Profile group was the fastest and followed by K3, Protaper, Hedstrom file group.
In case of the evaluation of the volume of remained gutta-percha from radiograph, K3 group got the highest score and followed by Protaper, Hedstrom file, Profile group in the apical 1/3.
In case of the evaluation of the volume of gutta-percha remained from stereomicroscope, K3 group got the highest score and followed by Protaper, Hedstrom file, Profile group in the apical 1/3.
These results showed that instrumentation using nickel-titanium rotary instrument groups was faster than that using hand instrument group. The effect of gutta-percha removal using Profile group was better than that using Protaper and K3 group in the nickel-titanium rotary instrument groups.
- 943 View
- 0 Download

- Effect of various canal preparation techniques using rotary nickel-titanium files on the maintenance of canal curvature
- Cheol-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Chan-Ui Hong
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):41-49. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are increasing usage of Nickel-Titanium rotary files in modern clinical endodontic treatment because it is effective and faster than hand filing due to reduced step.
This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of canal preparations using 3 different rotary Nickel-Titanium files that has different cross sectional shape and taper on the maintenance of canal curvature. Simulated resin block were instrumented with Profile(Dentsply, USA), GT rotary files(Dentsply, USA), Hero 642(Micro-Mega, France), and Pro-Taper(Dentsply, USA).
The image of Pre-instrumentation and Post-instrumentation were acquired using digital camera and overspreaded in the computer. Then the total differences of canal diameter, deviation at the outer portion of curvature, deviation at the inner portion of curvature, movement of center of the canal and the centering ratio at the pre-determined level from the apex were measured.
Results were statistically analyzed by means of ANOVA, followed by Scheffe test at a significance level of 0.05.
The results were as follows;
1. Deviation at the outer portion of curvature, deviation at the inner portion of curvature were showed largest in Pro-Taper, so also did in the total differences of canal diameter(p<0.05).
2. All the groups showed movements of center. Profile combined with GT rotary files and Hero 642 has no difference but Pro-Taper showed the most deviation(p<0.05).
3. At the 1, 2, 3mm level from the apex movements of center directed toward the outer portion of curvature, but in 4, 5 mm level directed toward the inner portion of curvature(p<0.05).
As a results of this study, it could be concluded that combined use of other Nickel-Titanium rotary files is strongly recommended when use Pro-Taper file because it could be remove too much canal structure and also made more deviation of canal curvature than others.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
T. O. Kim, G. S. P. Cheung, J. M. Lee, B. M. Kim, B. Hur, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2009; 42(1): 14. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - A study of insertion depth of buchanan plugger after shaping using NI-TI rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Youn-Sik Park, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 125. CrossRef - Step by step analysis of root canal instrumentation with ProTaper®
Mi-Hee Kim, Bock Huh, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 50. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef - A comparison of shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals
So-Youn Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(1): 58. CrossRef
- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
- 1,098 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


