Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 30(4); 2005 > Article
- Original Article The change of canal configuration after instrumentation by several nickel-titanium files in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature
- Jung-Jang Lim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
-
2005;30(4):-311.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.4.303
Published online: July 30, 2005
Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, DSRI, Chonnam National University, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Won-Mann Oh. Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National Universtiy, 8 Hak-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju, Korea, 501-757. Tel: 82-62-220-4431, Fax: 82-62-225-8387, wmoh@chonnam.ac.kr
• Received: November 11, 2004 • Revised: December 29, 2004 • Accepted: February 15, 2005
Copyright © 2005 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,120 Views
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
The purpose of this study was to evaluate which type of Ni-Ti files are able to maintain canal configuration better in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature near it's apex.Ninety six simulated root canals were made in epoxy resin and #15 finger spreader was used as root canal templates. The simulated root canals were made with radius of curvature of 1.5 mm, 3.0 mm, 4.0 mm, 6.0 mm respectively and the angle of curvature of all simulated canals were adjusted to 90 degree. The simulated canals were instrumented by ProFile, ProTaper, Hero 642, and K3 at a 300 rpm using crown-down pressureless technique. Pre-instrumented and post-instrumented images were taken by digital camera and were superimposed with Adobe Photoshop 6.0 program. Images were compared by image analysis program.The changes of canal width at the inner and outer side of the canal curvature, canal transportation were measured at 9 measuring point with 1 mm interval. Statistical analysis among the types of Ni-Ti files was performed using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U-test.The result was that ProFile maintain original canal configuration better than other engine driven Ni-Ti files in the canals above 3.0 mm radius of curvature, and in the 1.5 mm radius of curvature, most of Ni-Ti flies were deformed or separated during instrumentation.
- 1. Mandel E, Yazdi MA, Benhamou LM, Lachkar T, Mesgouez C, Sobel M. Rotary Ni-Ti profile systems for preparing curved canals in resin blocks : influence of operator on instrument breakage. Int Endod J. 1999;32: 436-443.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Bramante CM, Berbert A, Borges RP. A methodology for evaluation of root canal instrument. J Endod. 1987;13: 243-245.PubMed
- 3. Royal JR, Donnelly JC. A comparison of maintenance of canal curvature using balanced-forced instrumentation with three difference file type. J Endod. 1995;21: 300-304.PubMed
- 4. Esposito PT, Cunningham CJ. A comparison of canal preparation with nickel-titanium and stainless steel instruments. J Endod. 1995;21: 173-176.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Walia H, Brantley WA, Gerstein H. An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of nitinol root canal files. J Endod. 1988;14: 346-351.PubMed
- 6. Thompson SA, Dummer PMH. Shaping ability of Hero 642 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals: Part 1. Int Endod J. 2000;33: 248-254.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Park HS, Lee MG, Kim JJ, Im YJ, Jang MS, Lee JY. A study on the shape of a canal prepared with 'three-file' technique in a curved canal. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2000;25: 494-498.
- 8. Coleman CL, Svec TA. Analysis of Ni-Ti versus stainless steel instrumentation in resin simulated canals. J Endod. 1997;23: 232-235.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Hata GI, Uemura M, Kato AS, Imura N, Novo NF, Toda T. A comparison of shaping ability using ProFile, GT file, and Flex-R endodontic instruments in simulated canals. J Endod. 2002;28: 316-321.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Bishop K, Dummer PMH. A comparison of stainless steel Flexofiles and nickel-titanium NiTiFlex files during the shaping of simulated canals. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 25-34.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Park H. A comparison of Greater Taper files, ProFiles, and stainless steel files to shape curved root canals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;91: 715-718.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Gambill JM, Alder M, del Rio CE. Comparison of nickel-titanium and stainless steel hand-file instrumentation using computed tomography. J Endod. 1996;22: 369-375.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kim YT, Beak SH, Bae KS, Lim SS, Yoon SH. A Comparison of Three Stainless Steel Instruments in the Preparation of Curved Root Canals in vitro. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2001;26: 9-15.
- 14. Dummer PMH, Alodeh MHA. A method for the construction of simulated root canals in clear resin blocks. Int Endod J. 1991;24: 63-66.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kum KY, Spängberg L, Cha BY, Jung IY, Lee SJ, Lee CY. Shaping ability of three ProFile rotary instrumentation techniques in simulated resin root canals. J Endod. 2000;26: 719-723.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Schäfer E. Shaping ability of Hero 642 rotary nickel-titanium instruments and stainless steel hand K-Flexofiles in simulated curved root canals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;92: 215-220.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Bonetti Filho I, Miranda Esberard R, de Toledo Leonardo R, del Rio CE. Microscopic evaluation of three endodontic files pre- and postinstrumentation. J Endod. 1998;24: 461-464.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Thompson SA, Dummer PMH. Shaping ability of ProFile .04 taper series 29 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 1. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 1-7.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Pruett JP, Clement DJ, Carnes DL. Cyclic fatigue testing of Nickel-Titanium endodontic instruments. J Endod. 1997;23: 77-85.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Schäfer E, Schlingemann R. Efficiency of rotary nickel-titanium K3 instruments compared with stainless steel hand K-Flexofile. Part2. Cleaning effectiveness and shaping ability in severely curved root canals of extracted teeth. Int Endod J. 2003;36: 208-217.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Versumer J, Hülsmann M, Schäfers F. A comparative study of root canal preparation using ProFile .04 and Lightspeed rotary Ni-Ti instruments. Int Endod J. 2002;35: 37-46.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Park HS, Lee MG, Kim JJ, Lee JY. A study on the shape of a canal prepared with profiles in a curved canal. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1999;24: 633-638.
- 23. Im GA, Yoon SH. A Comparison of Stainless Steel K-file, Profile .04, and Quantec LX Instruments to Shape Curved Root Canals in vitro. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2000;25: 133-143.
- 24. Thompson SA, Dummer PMH. Shaping ability of ProFile .04 taper series 29 rotary nickel-titanium instruments in simulated root canals. Part 2. Int Endod J. 1997;30: 8-15.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Lee SJ, Shin YG, Hwang HG. Transportation of curved canal after canal enlargement according to filing instruments. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1999;24: 503-510.
REFERENCES
Figure 2
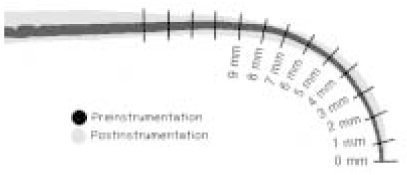
Pre- and Post-image of root canal and Measuring points were measured with 1 mm interval from 1 mm to 9 mm.

Figure 3
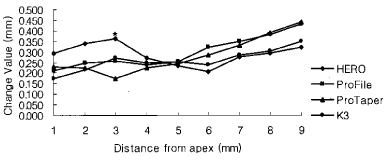
Change of total canal width of the curvature in 3.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).

Figure 4
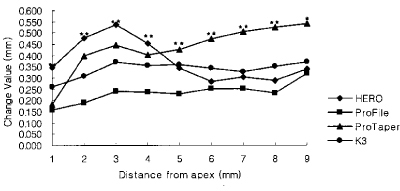
Change of total canal width of the curvature in 4.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).

Figure 5
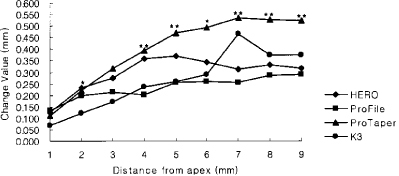
Change of total canal width of the curvature in 6.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).

Figure 6
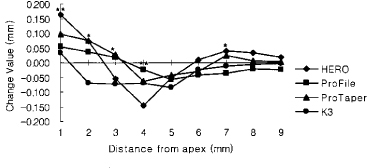
Canal transportation of 3.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Negative value means inside transportation from
central axis of original root canal.

Figure 7
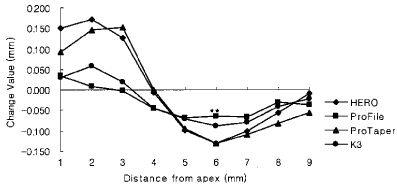
Canal transportation of 4.0 mm radius group (Unit : mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Negative value means inside transportation from central axis of original root canal.

Figure 8
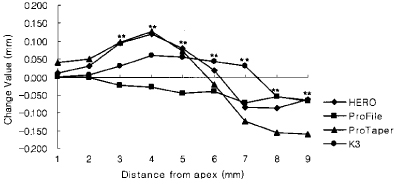
Canal transportation of 6.0 mm radius group (Unit : mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Negative value means inside transportation from central axis of original root canal.

Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- A study on transportation of apical foramen after overinstrumentation by ProFile®, ProTaper™ and K3TMin simulated canals with different curvatures
Hyun Yang, In-Seok Yang, Yun-Chann Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Won-Jae Kim, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 87. CrossRef
The change of canal configuration after instrumentation by several nickel-titanium files in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature
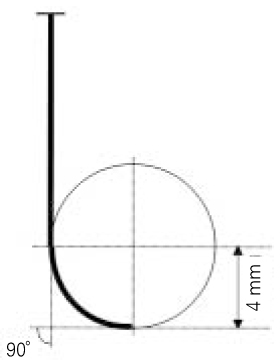
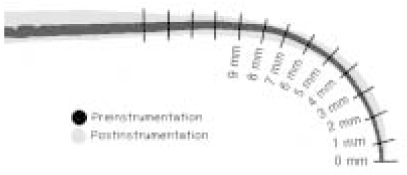
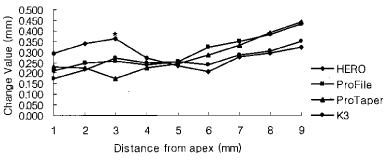
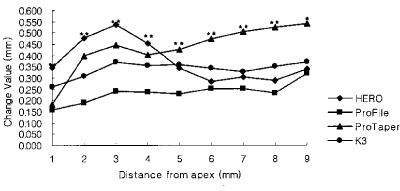
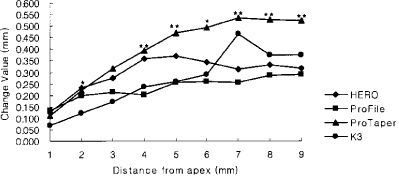
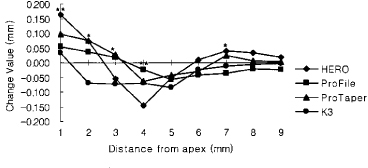
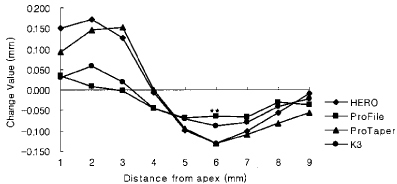
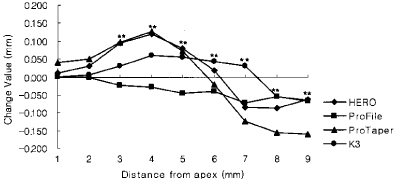
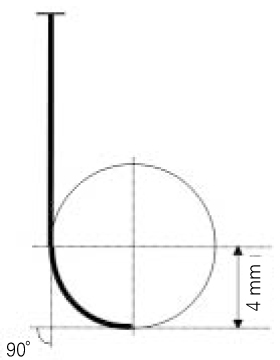
Figure 1
4.0 mm radius of curvature of finger spreader
Figure 2
Pre- and Post-image of root canal and Measuring points were measured with 1 mm interval from 1 mm to 9 mm.
Figure 3
Change of total canal width of the curvature in 3.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
Figure 4
Change of total canal width of the curvature in 4.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Figure 5
Change of total canal width of the curvature in 6.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Figure 6
Canal transportation of 3.0 mm radius group (Unit: mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Negative value means inside transportation from
central axis of original root canal.
Figure 7
Canal transportation of 4.0 mm radius group (Unit : mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Negative value means inside transportation from central axis of original root canal.
Figure 8
Canal transportation of 6.0 mm radius group (Unit : mm).
*significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.05).
**significant difference among Ni-Ti files at each measuring point (p < 0.01).
Negative value means inside transportation from central axis of original root canal.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 8
The change of canal configuration after instrumentation by several nickel-titanium files in the simulated canal with abrupt curvature
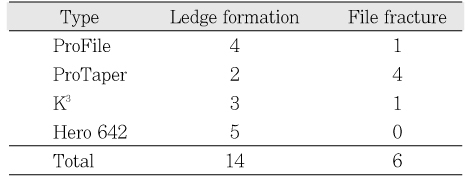
The number of ledge formation and File fracture
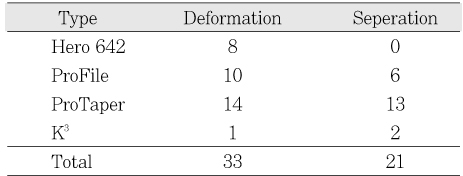
Deformation and separation of Ni-Ti files
Table 1
The number of ledge formation and File fracture
Table 2
Deformation and separation of Ni-Ti files

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

