Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
- Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e48. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
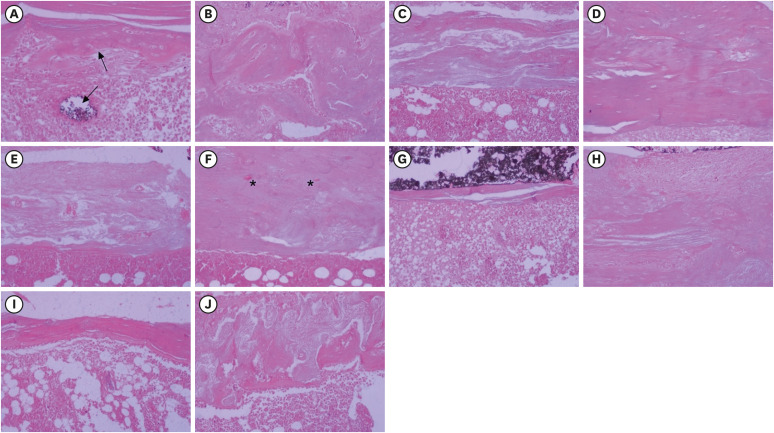
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effects on bone repair of different concentrations of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) added to AH Plus.
Materials and Methods Bone tissue reactions were evaluated in 30 rats (
Rattus norvegicus ) after 7 and 30 days. In the AH + MTA10, AH + MTA20, and AH + MTA30 groups, defects in the tibiae were filled with AH Plus with MTA in proportions of 10%, 20% and 30%, respectively; in the MTA-FILL group, MTA Fillapex was used; and in the control group, no sealer was used. The samples were histologically analyzed to assess bone union and maturation. The Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests were performed for multiple pairwise comparisons (p ≤ 0.05).Results At the 7-day time point, AH + MTA10 was superior to MTA-FILL with respect to bone union, and AH + MTA20 was superior to MTA-FILL with respect to bone maturity (
p < 0.05). At the 30-day time point, both the AH + MTA10 and AH + MTA20 experimental sealers were superior not only to MTA-FILL, but also to AH + MTA30 with respect to both parameters (p < 0.05). The results of the AH + MTA10 and AH + MTA20 groups were superior to those of the control group for both parameters and experimental time points (p < 0.05).Conclusions The results suggest the potential benefit of using a combination of these materials in situations requiring bone repair.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
Luciano Aparecido de Almeida-Junior, Giuliana de Campos Chaves Lamarque, Henry Herrera, Maya Fernanda Manfrin Arnez, Francine Lorencetti-Silva, Raquel Assed Bezerra Silva, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva, Francisco Wanderley Garcia Paula-Silva
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the research methods and progress of biocompatibility evaluation of root canal sealers
Xiliang Yang, Tianxia Zheng, Nuoya Yang, Zihan Yin, Wuliang Wang, Yuhong Bai
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 508. CrossRef - Effect of Vitapex Combined with AH-Plus Paste on Inflammation in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients with Periodontal-Endodontic Disease
Rong Hu, Fulan Zhang, Xiangyu Guo, Youren Jing, Xiaowan Lin, Liping Tian, Min Tang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
- 1,993 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

-
Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA
in vivo - Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e17. Published online February 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
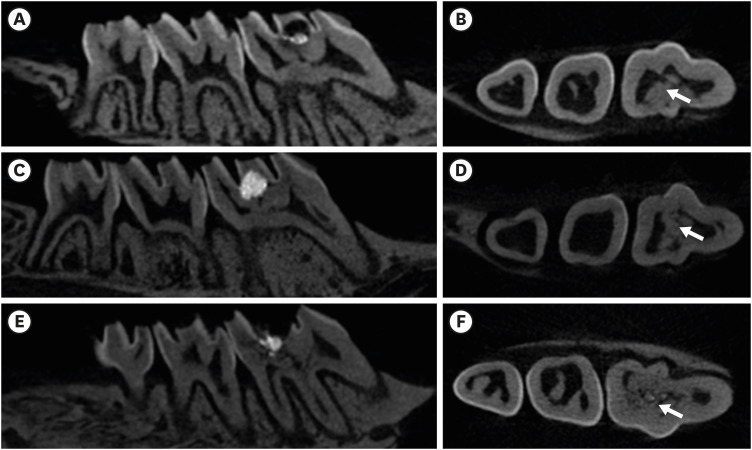
ePub Objectives In recent
in vitro study, it was reported that osteostatin (OST) has an odontogenic effect and synergistic effect with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) in human dental pulp cells. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate whether OST has a synergistic effect with MTA on hard tissue formationin vivo .Materials and Methods Thirty-two maxillary molars of Spraque-Dawley rats were used in this study. An occlusal cavity was prepared and the exposed pulps were randomly divided into 3 groups: group 1 (control; ProRoot MTA), group 2 (OST 100 μM + ProRoot MTA), group 3 (OST 10 mM + ProRoot MTA). Exposed pulps were capped with each material and cavities were restored with resin modified glass ionomer. The animals were sacrificed after 4 weeks. All harvested teeth were scanned with micro-computed tomography (CT). The samples were prepared and hard tissue formation was evaluated histologically. For immunohistochemical analysis, the specimens were sectioned and incubated with primary antibodies against dentin sialoprotein (DSP).
Results In the micro-CT analysis, it is revealed that OST with ProRoot MTA groups showed more mineralized bridge than the control (
p < 0.05). In the H&E staining, it is showed that more quantity of the mineralized dentin bridge was formed in the OST with ProRoot MTA group compared to the control (p < 0.05). In all groups, DSP was expressed in newly formed reparative dentin area.Conclusions OST can be a supplementary pulp capping material when used with MTA to make synergistic effect in hard tissue formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulpal responses to mineral trioxide aggregate with and without zinc oxide addition in mature canine teeth after full pulpotomy
Behnam Bolhari, Neda Kardouni Khouzestani, Hadi Assadian, Saeed Farzad-Mohajeri, Mohammad Mehdi Dehghan, Soheil Niavarzi, Behnam Dorost, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Henry F. Duncan, Artak Heboyan, Antonio Signore, Stefano Benedicenti
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Advancements in Peptides for Promoting Reparative Dentin Regeneration in Direct Pulp Capping: A Narrative Review
Jiawen Wang, Shuwei Qiao, Tianjia Huang, Junjie Lian, Song Zhu
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and pro-mineralization effects of premixed calcium silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro and in vivo study
Nyein Chan KO, Sonoko NODA, Yamato OKADA, Kento TAZAWA, Nobuyuki KAWASHIMA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 729. CrossRef - Osteostatin, a peptide for the future treatment of musculoskeletal diseases
Daniel Lozano, Arancha R. Gortazar, Sergio Portal-Núñez
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 223: 116177. CrossRef - Comparison of bioactive material failure rates in vital pulp treatment of permanent matured teeth – a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Péter Komora, Orsolya Vámos, Noémi Gede, Péter Hegyi, Kata Kelemen, Adél Galvács, Gábor Varga, Beáta Kerémi, János Vág
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hard tissue formation in pulpotomized primary teeth in dogs with nanomaterials MCM-48 and MCM-48/hydroxyapatite: an in vivo animal study
Sahar Talebi, Nosrat Nourbakhsh, Ardeshir Talebi, Amir Abbas Nourbakhsh, Abbas Haghighat, Maziar Manshayi, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi, Razieh Karimi, Rahman Nazeri, Kenneth J.D. Mackenzie
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reparative Mineralized Tissue Characterization by Different Bioactive Direct Pulp-capping Agents
Mrunal Shinde, Varsha Pandit, Sarita Singh, Aniket Jadhav, Sarah Marium, Smita Patil
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Effects of barium titanate on the dielectric constant, radiopacity, and biological properties of tricalcium silicate-based bioceramics
Yoorina CHOI, Yun-Chan HWANG, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 55. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - A Breakthrough in the Era of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements: A Critical Review
Payal S Chaudhari, Manoj G Chandak, Akshay A Jaiswal, Nikhil P Mankar, Priyanka Paul
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef
- Pulpal responses to mineral trioxide aggregate with and without zinc oxide addition in mature canine teeth after full pulpotomy
- 2,942 View
- 38 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Dentin moisture conditions strongly influence its interactions with bioactive root canal sealers
- Esin Ozlek, Hüseyin Gündüz, Elif Akkol, Prasanna Neelakantan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e24. Published online March 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
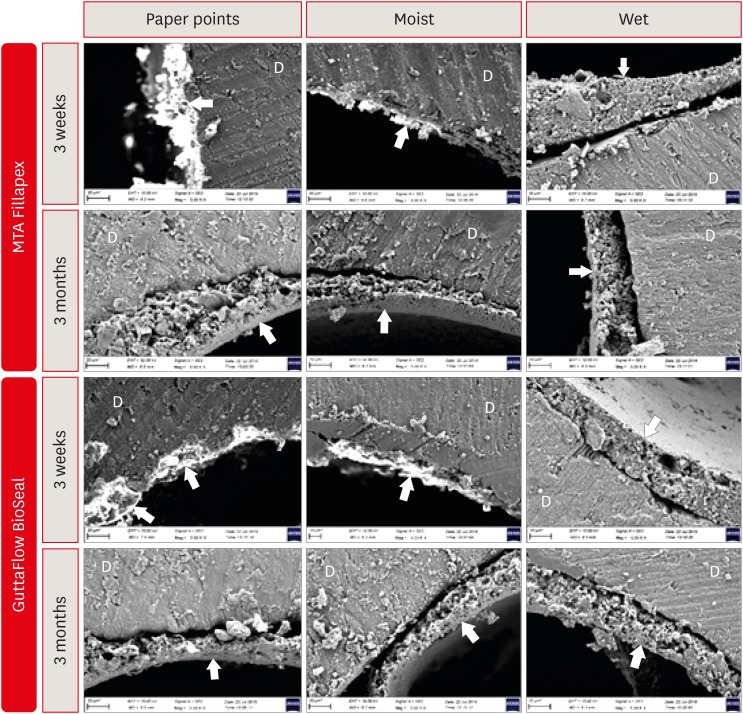
ePub Objectives It is known that bioactive materials interact with the dentin to undergo biomineralization. The exact role of moisture in this interaction is unknown. Here, we investigate the effects of dentin moisture conditions on the dislocation resistance of two bioactive root canal sealers (MTA Fillapex [Angelus Solucoes Odontologicas] and GuttaFlow BioSeal [Colténe/Whaledent AG]) at 3 weeks and 3 months after obturation.
Materials and Methods Mandibular premolars (
n = 120) were prepared and randomly divided into 3 groups based on the dentin condition: group 1, dry dentin; group 2, moist dentin; group 3, wet dentin. Each group was divided into 2 subgroups for root canal filling: MTA Fillapex and GuttaFlow BioSeal. Dislocation resistance was evaluated by measuring the push-out bond strength at 3 weeks and 3 months. Failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. Data were statistically analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test with a significance level of 5%.Results Moist dentin resulted in higher bond strength values for both materials at both time points. This was significantly higher than wet and dry dentin for both the sealers at the 3 months (
p < 0.05), while at 3 weeks it was significant only for GuttaFlow Bioseal. The different moisture conditions demonstrated similar trends in their effects on the dislocation resistance of the 2 root canal sealers.Conclusions The dentin moisture conditions had a significant impact on its interaction with the bioactive materials tested. Maintaining moist dentin, but not dry or wet dentin, may be advantageous before the filling root canals with bioactive sealers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of moisture conditions and canal morphologies on the filling quality of iRoot SP with single-cone technique in root canals: an ex-vivo study
Jing Yang, Xiran Xu, Jian Zhang, Kehua Que
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(7): 1989. CrossRef - Evaluation of apical seal and tubular penetration of a novel bioactive glass sealer, bioceramic sealer and resin–based sealer: an In-Vitro study
M. Bilal, S. Pasha, S. Kumar, S. Arif, S. Taj, A. Saleem
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 39. CrossRef - Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Post Space Conditioning Procedures and Different Endodontic Sealers on the Push-Out Bond Strengths of Fiber Posts
Leyla Ayranci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci, Fatih Sarı, Ahmet Çetinkaya
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 620. CrossRef - Evaluation of the retreatability of bioceramic root canal sealers with various formulations in simulated grooves
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Abdulaziz Bakhsh, Hakan Arslan
PeerJ.2025; 13: e20398. CrossRef - Preparation and characterization of novel nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based root canal sealer
Nawal Atiya Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 90. CrossRef - The flow behavior and sealing ability of calcium silicate root canal cement containing dimethyl sulfoxide: An in vitro study
Bokyung Shin, Ji-Hwan Seo, Wonjung Kim, Yu Jin Ahn, Ho-Young Kim, Won-Jun Shon
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106156. CrossRef - Nanoleakage of apical sealing using a calcium silicate-based sealer according to canal drying methods
Yoon-Joo Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of operators’ proficiency level and patients’ related factors on possible complications, using a high frequency polyamide sonic intracanal irrigation device: A prospective clinical cohort study
Tobias Hahn, David W. Christofzik, Karim Fawzy El-Sayed, Sandra Freitag-Wolf, Jonas Conrad, Christian Graetz, Birte Größner-Schreiber, Christof Dörfer, Artak Heboyan
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(5): e0285492. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Biocompatibility analysis in subcutaneous tissue and physico-chemical analysis of pre-mixed calcium silicate–based sealers
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Juliana Minto Boldieri, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Nilvan Alves da Silva, Ivo Milton Raimundo, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2221. CrossRef - Canal Drying Protocols to Use with Calcium Silicate–based Sealer: Effect on Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface
Lais Lima Pelozo, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Guilherme Nilson Alves dos Santos, Rafael Verardino Camargo, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(9): 1154. CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength of endodontic sealers after root canal drying with different techniques
Ahmadreza Sarrafan, Ali Soleymani, Tasnim Bagheri Chenari, Seyedali Seyedmajidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2023; 9(2): 314. CrossRef - Designing Calcium Silicate Cements with On-Demand Properties for Precision Endodontics
A. Cahyanto, P. Rath, T.X. Teo, S.S. Tong, R. Malhotra, B.N. Cavalcanti, L.Z. Lim, K.S. Min, D. Ho, W.F. Lu, V. Rosa
Journal of Dental Research.2023; 102(13): 1425. CrossRef - Outcome of root canal treatment using warm vertical compaction with bioceramic and resin‐based sealers: A randomised clinical trial
Jinghao Hu, Yunjie Zhu, Shuli Deng, Zeji Wang, Fuming He
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 170. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability and Bond Strength of Two Endodontic Root Canal Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Manuel Marques Ferreira, José Pedro Martinho, Inês Duarte, Diogo Mendonça, Ana Catarina Craveiro, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Ana Coelho, Anabela Paula, Siri Paulo, Nuno Chichorro, Ana Margarida Abrantes
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(11): 201. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of using calcium-silicate and silicone based root canal sealers in bulk or with main core material on bond strength
Gizem Kadı, Esin Özlek, Yousef Saed
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2022; 16(4): 229. CrossRef - Physico-chemical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers in powder/liquid and ready-to-use forms
Ana C P Janini, Lauter E Pelepenko, Brenda P F A Gomes, Marina A Marciano
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 18. CrossRef - Influence of dentin moisture conditions on the wetting action of different endodontic sealers using Rame-Hart goniometer: An in vitro study
Sivaji Kauravi, ShruthiH Attavar, GyanendraPratap Singh
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(6): 624. CrossRef - Heating stability, physical and chemical analysis of calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealers
T. B. M. Antunes, A. C. P. Janini, L. E. Pelepenko, G. F. Abuna, E. M. Paiva, M. A. C. Sinhoreti, I. M. Raimundo, B. P. F. A. Gomes, A. de‐Jesus‐Soares, M. A. Marciano
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1175. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
- The effect of moisture conditions and canal morphologies on the filling quality of iRoot SP with single-cone technique in root canals: an ex-vivo study
- 2,204 View
- 32 Download
- 24 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomography evaluation of voids using calcium silicate-based materials in teeth with simulated internal root resorption
- Vildan Tek, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e5. Published online November 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
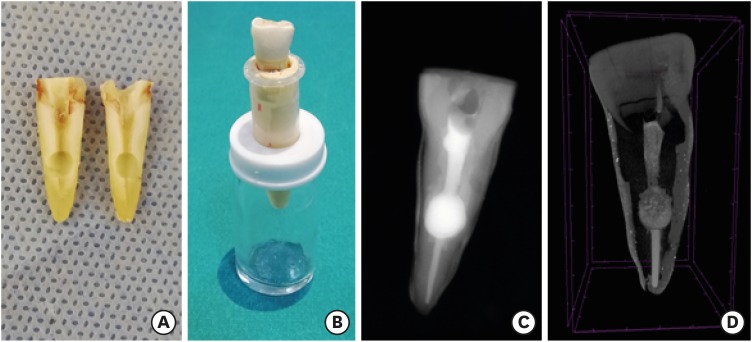
ePub Objectives The obturation quality of MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC root canal sealer (RCS), and warm gutta-percha (WGP) in teeth with simulated internal root resorption (IRR) was evaluated by using micro-computed tomography.
Materials and Methods Standardized IRR cavities were created using 40 extracted maxillary central incisor teeth and randomly assigned into 4 groups (
n = 10). IRR cavities were filled with MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC RCS (bulk-fill form) and WGP + Total Fill BC RCS. Percentage of voids between resorptive cavity walls and obturation material (external void), and inside the filling materials (internal voids) were measured.Results Total Fill BC sealer in the bulk-fill form presented significantly highest values of external and internal void percentages (
p < 0.05). Biodentine showed a significantly lowest external void percentage (p < 0.05). WGP + Total Fill BC RCS presented significantly lower values of internal void percentages than all groups (p < 0.05), except Biodentine (p > 0.05).Conclusion None of the filling materials were created void-free obturation in resorption cavities. Biodentine may favor its application in teeth with IRR over Angelus MTA and bulk-fill form of Total Fill BC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Measurement of Obturation Quality of Bioceramic Materials in Filling Artificial Internal Root Resorption Cavities Using Different Obturation Techniques: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Ammar M. Sharki, Ahmed H. Ali
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 997. CrossRef - Evaluation of calcium hydroxide root canal filling materials by cone beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling
Asel Usdat Ozturk, Ekin Dogan, Venus Seyedoskuyi, Berk Senguler, Asli Topaloglu-Ak
Folia Medica.2024; 66(2): 250. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef
- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
- 2,497 View
- 34 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Evaluation of reparative dentin formation of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine and BioAggregate using micro-CT and immunohistochemistry
- Jia Kim, Young-Sang Song, Kyung-San Min, Sun-Hun Kim, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):29-36. Published online January 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.29

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of two new calcium silicate-based pulp-capping materials (Biodentine and BioAggregate) to induce healing in a rat pulp injury model and to compare them with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA).
Materials and Methods Eighteen rats were anesthetized, cavities were prepared and the pulp was capped with either of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine, or BioAggregate. The specimens were scanned using a high-resolution micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) system and were prepared and evaluated histologically and immunohistochemically using dentin sialoprotein (DSP).
Results On micro-CT analysis, the ProRoot MTA and Biodentine groups showed significantly thicker hard tissue formation (
p < 0.05). On H&E staining, ProRoot MTA showed complete dentin bridge formation with normal pulpal histology. In the Biodentine and BioAggregate groups, a thick, homogeneous hard tissue barrier was observed. The ProRoot MTA specimens showed strong immunopositive reaction for DSP.Conclusions Our results suggest that calcium silicate-based pulp-capping materials induce favorable effects on reparative processes during vital pulp therapy and that both Biodentine and BioAggregate could be considered as alternatives to ProRoot MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of microhardness, monomer conversion, and antibacterial properties of an experimental pulp-capping material containing collagen–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and/or chlorhexidine
Hacer Balkaya, Sezer Demirbuğa, Fatih Duman, Ahmet Ceylan, Ömer Aydın
Odontology.2026; 114(1): 204. CrossRef - Clinical applications and classification of calcium silicate-based cements based on their history and evolution: a narrative review
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diode laser irradiation along with Biodentine on dental pulp stem cell proliferation and pluripotent gene expression
Ladan Alborzy, Sedighe Sadat Hashemikamangar, Mahshid Hodjat, Nasim Chiniforush, Behnaz Behniafar
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different treatment methods on apical closure and treatment success in immature permanent first molars with reversible pulpitis
Muhammed ALAGOZ, Sera SIMSEK DERELIOĞLU
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Novelties in pulp capping materials
Vani Grover, Namith Rai, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2025; 41(91): 3086. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of pulp response to alendronate and Biodentine as pulp capping agents: an animal study
Thangavel Boopathi, Sekar Manimaran, Joseline Charles Kerena, Mathew Sebeena, Kumaravadivel Karthick, Natesan Thangaraj Deepa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Clinical and Radiographic Success Rate of Bioceramic Premix vs Biosilicate-based Medicament as Indirect Pulp Treatment Materials in Primary Molars: A Double-blind Randomized Trial with a Follow-up of 12 Months
Aditi Mathur, Meenakshi Nankar, Sunnypriyatham Tirupathi, Payal Kothari, Rashmi Chauhan, Ashrita Suvarna
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(7): 748. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Evaluation of biocompatibility and bioactive potential of Well-Root PT by comparison with ProRoot MTA and Biodentine
Yong Kwon Chae, Ju Ri Ye, Ok Hyung Nam
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2218. CrossRef - Dentine Remineralisation Induced by “Bioactive” Materials through Mineral Deposition: An In Vitro Study
Marta Kunert, Ireneusz Piwonski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Francesco Inchingolo, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2024; 14(3): 274. CrossRef - Different pulp capping agents and their effect on pulp inflammatory response: A narrative review
Mustafa Tariq Mutar, Anas F Mahdee
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1295. CrossRef - Clinical application of calcium silicate-based bioceramics in endodontics
Xinyuan Wang, Yizhi Xiao, Wencheng Song, Lanxiang Ye, Chen Yang, Yuzhen Xing, Zhenglin Yuan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the pulp response following direct pulp capping with exogenous nitric oxide and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) a histologic study
Amirah Alnour, Ghassan Almohammad, Anas Abdo, Kinda Layous
Heliyon.2023; 9(7): e17458. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of dental pulp response to Biodentine, enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain), and mineral trioxide aggregate as direct pulp-capping agents – A randomized clinical trial
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ngairangbam Sanjeeta
Journal of Medical Society.2023; 37(3): 107. CrossRef - Effect of Intracoronal Sealing Biomaterials on the Histological Outcome of Endodontic Revitalisation in Immature Sheep Teeth—A Pilot Study
Elanagai Rathinam, Sivaprakash Rajasekharan, Heidi Declercq, Christian Vanhove, Peter De Coster, Luc Martens
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(4): 214. CrossRef - Restorative management of the posterior tooth that has undergone a pulpotomy
Nicholas N Longridge, James S Hyde, Fadi Jarad, Sondos Albadri
Dental Update.2023; 50(11): 932. CrossRef - Direct pulp capping procedures – Evidence and practice
Rafiqul Islam, Md Refat Readul Islam, Toru Tanaka, Mohammad Khursheed Alam, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Hidehiko Sano
Japanese Dental Science Review.2023; 59: 48. CrossRef - A novel analysis of the formation and resorption changes in dental hard tissue using longitudinal in vivo micro computed tomography
Yeon-Jee YOO, Joonil HWANG, So-Hyun PARK, Jaehong HWANG, Seungryong CHO, Sun-Young KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(5): 708. CrossRef - Evaluation of pH and Calcium Ion Diffusion from Intracanal MTA and Bioaggregate to Simulated External Resorption Cavities Through Dentinal Tubules
Umut AKSOY, Kaan POLATOĞLU, Feridun ŞAKLAR
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(3): 108. CrossRef - Pulpa Kuafajı ve Kuafaj Materyallerine Güncel Bir Bakış: Derleme
Dilek AKIN, Çiğdem ATALAYIN ÖZKAYA
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 617. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - Evaluation of shear bond strength of e-mineral trioxide aggregate and biodentine with glass ionomer cement
Hemalatha Hiremath, Aishwarya Singh Solanki, Shivangi Trivedi, Devansh Verma
Endodontology.2022; 34(2): 127. CrossRef - Multiple growth factors accommodated degradable submicron calcium sulfate hemihydrate/porous hydroxyapatite for dentin-pulp regeneration
Chih-Wen Chi, Bharathi Priya Lohanathan, Ching-Ching Wong, Che-Lun Chen, Hsun-Chang Lin, Yu-Chih Chiang
Biomaterials Advances.2022; 140: 213045. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF BLOOD CONTAMINATION ON SHEAR BOND STRENGTH OF CALCIUM SILICATE-BASED PULP CAPPING MATERIALS
Hasan Fatih YAVUZ, Güneş BULUT EYÜBOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 24(4): 371. CrossRef - Comparison of Four Dental Pulp-Capping Agents by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological Techniques—A Split-Mouth Design Ex Vivo Study
Jayanandan Muruganandhan, Govindarajan Sujatha, Saravanan Poorni, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Nezar Boreak, Ahmed Al-Kahtani, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hitesh Chohan, Shilpa Bhandi, A. Thirumal Raj, Alessio Zanza, Luca Testarelli, Shankargouda Patil
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3045. CrossRef - Effect of Naturally Occurring Biogenic Materials on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells (hDPSC): an In Vitro Study.
Prasanna T. Dahake, Vinod V. Panchal, Yogesh J. Kale, Mahesh V. Dadpe, Shrikant B. Kendre, Vijay M. Kumbar
Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine.2021; 7(4): 506. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Tailored 70S30C Bioactive glass induces severe inflammation as pulpotomy agent in primary teeth: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial
Yasmine Elhamouly, Rania M. El Backly, Dalia M. Talaat, Samia S. Omar, Maha El Tantawi, Karin M. L. Dowidar
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(6): 3775. CrossRef - Response of dental pulp capped with calcium-silicate based material, calcium hydroxide and adhesive resin in rabbit teeth
Cynthia Kassis, Pierre Khoury, Karim Corbani, Charbel Mansour, Louis Hardan, Ghassan Yared, Carole Chakar
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical expression of non-collagenous extracellular matrix molecules involved in tertiary dentinogenesis following direct pulp capping: a systematic review
C. Călin, M. Sajin, V.T. Moldovan, C. Coman, S.I. Stratul, A.C. Didilescu
Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger.2021; 235: 151674. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Indirect Pulp Treatment Materials for Primary Teeth: A Literature Review
Omar AES El Meligy, Afnan M Saber, Sumer M Alaki
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(6): 795. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of the regenerative potential of a novel treated dentin matrix hydrogel in direct pulp capping
Ahmed A. Holiel, Elsayed M. Mahmoud, Wegdan M. Abdel-Fattah, Khadiga Y. Kawana
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(4): 2101. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential of tailored amorphous multiporous calcium silicate glass for pulp capping regenerative endodontics—A preliminary assessment
Jie Liu, Chao-An Chen, Xiaofei Zhu, Brian R. Morrow, Ukrit Thamma, Tia J. Kowal, Hassan M. Moawad, Matthias M. Falk, Himanshu Jain, George T.-J. Huang
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 109: 103655. CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of direct pulp capping using a novel injectable treated dentin matrix hydrogel: a 2-year randomized controlled clinical trial
Ahmed A. Holiel, Elsayed M. Mahmoud, Wegdan M. Abdel-Fattah
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4621. CrossRef - Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA in vivo
Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydraulic cements for various intra-coronal applications: Part 1
Stephen J Bonsor, Josette Camilleri
Dental Update.2021; 48(8): 653. CrossRef - In vivo Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Calcium Silicate-Based Bioceramics in Endodontics
Wencheng Song, Wei Sun, Lili Chen, Zhenglin Yuan
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of dentinogenesis inducer biomaterials: an in vivo study
Anabela B. Paula, Mafalda Laranjo, Carlos-Miguel Marto, Siri Paulo, Ana M. Abrantes, Bruno Fernandes, João Casalta-Lopes, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Bio-Inductive Materials in Direct and Indirect Pulp Capping—A Review Article
Marta Kunert, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Materials.2020; 13(5): 1204. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Release of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 from Human Tooth Dentin after Application of Either ProRoot MTA or Biodentine as a Coronal Barrier
Kunlada Wattanapakkavong, Tanida Srisuwan
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(6): 701. CrossRef - Effect of Leptin on Odontoblastic Differentiation and Angiogenesis: An In Vivo Study
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Ji-Hyun Jang, Jeong-Tae Koh, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(11): 1332. CrossRef - Análise da composição química dos cimentos MTA Angelus® branco, cinza e HP Repair® através de Microscopia Eletrônica de Varredura (MEV) acoplada a Espectrômetro de Energia Dispersiva (EDS)
Gabriela Duarte Rocha SARZEDA, Marcelo Santos BAHIA, Paulo Victor Teixeira DORIGUÊTTO, Karina Lopes DEVITO, Anamaria Pessoa Pereira LEITE
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct Pulp Capping: Which is the Most Effective Biomaterial? A Retrospective Clinical Study
Anabela Paula, Eunice Carrilho, Mafalda Laranjo, Ana M. Abrantes, João Casalta-Lopes, Maria Filomena Botelho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel M. Ferreira
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3382. CrossRef - Characterization of Odontoblast-like Cell Phenotype and Reparative Dentin Formation In Vivo: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 241. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effects of calcium silicate cements on dental pulp cells: A systematic review
Ramy Emara, Karim Elhennawy, Falk Schwendicke
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 77: 18. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - The Relationship of Surface Characteristics and Antimicrobial Performance of Pulp Capping Materials
Cher Farrugia, Christie Y.K. Lung, Pierre Schembri Wismayer, Maria Teresa Arias-Moliz, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1115. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - Influence of Biodentine® - A Dentine Substitute - On Collagen Type I Synthesis in Pulp Fibroblasts In Vitro
Frangis Nikfarjam, Kim Beyer, Anke König, Matthias Hofmann, Manuel Butting, Eva Valesky, Stefan Kippenberger, Roland Kaufmann, Detlef Heidemann, August Bernd, Nadja Nicole Zöller, Dimitrios Karamichos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167633. CrossRef - Effect of an Experimental Direct Pulp-capping Material on the Properties and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Fan Yu, Yan Dong, Yan-wei Yang, Ping-ting Lin, Hao-han Yu, Xiang Sun, Xue-fei Sun, Huan Zhou, Li Huang, Ji-hua Chen
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of microhardness, monomer conversion, and antibacterial properties of an experimental pulp-capping material containing collagen–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and/or chlorhexidine
- 3,292 View
- 37 Download
- 57 Crossref

- Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
- Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):12-21. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.12

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effects of three acids on the microhardness of set mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and root dentin, and cytotoxicity on murine macrophage.
Materials and Methods OrthoMTA (BioMTA) was mixed and packed into the human root dentin blocks of 1.5 mm diameter and 5 mm height. Four groups, each of ten roots, were exposed to 10% citric acid (CA), 5% glycolic acid (GA), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and saline for five minutes after setting of the OrthoMTA. Vickers surface microhardness of set MTA and dentin was measured before and after exposure to solutions, and compared between groups using one-way ANOVA with Tukey test. The microhardness value of each group was analyzed using student
t test. Acid-treated OrthoMTA and dentin was examined by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Cell viability of tested solutions was assessed using WST-8 assay and murine macrophage.Results Three test solutions reduced microhardness of dentin. 17% EDTA demonstrated severe dentinal erosion, significantly reduced the dentinal microhardness compared to 10% CA (
p = 0.034) or 5% GA (p = 0.006). 10% CA or 5% GA significantly reduced the surface microhardness of set MTA compared to 17% EDTA and saline (p < 0.001). Acid-treated OrthoMTA demonstrated microporous structure with destruction of globular crystal. EDTA exhibited significantly more cellular toxicity than the other acidic solutions at diluted concentrations (0.2, 0.5, 1.0%).Conclusions Tested acidic solutions reduced microhardness of root dentin. Five minute's application of 10% CA and 5% GA significantly reduced the microhardness of set OrthoMTA with lower cellular cytotoxicity compared to 17% EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
Mohammed A. Hussein, Rasha H. Jehad
Journal of Medical and Oral Biosciences.2025; : 36. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - Effect of Various Acid Solutions as an Aid in Removing the OrthoMTA-Based Root Canal Filling
Naveen Chhabra, Abhishek Parolia
Materials.2023; 16(13): 4535. CrossRef - Effect of Glycolic Acid, Maleic Acid, and EDTA in the Removal of Smear Layer from Root Canal Dentin
Tarini Mullick, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the effect of various chelating agents on the microhardness of root canal dentin: An in vitro study
Mineet Kaul, Zinnie Nanda, Kranthikumar Reddy, Rahul Deore, Divya Mandlecha, Esha Jaiswal
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Influence of Acidic Environmental Conditions on Push‐Out Bonding Strength of Four Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials to Root Dentin
Beliz Özel, Raif Erişen, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the microhardness of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and TotalFill Bioceramic Putty
Jacklyn H.R. Chu, Kalie Y. Chia, Alexander L. Qui, Alex Moule, William N. Ha
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 33. CrossRef - Pre-application of dentin bonding agent prevents discoloration caused by mineral trioxide aggregate
Yoo-Lim Choi, Young-Eun Jang, Bom Sahn Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Yemi Kim
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolic acid as the final irrigant in endodontics: Mechanical and cytotoxic effects
Yuri Dal Bello, Hisadora Fracaro Porsch, Ana Paula Farina, Matheus Albino Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Ana Karina Bedran-Russo, Doglas Cecchin
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 100: 323. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 246. CrossRef
- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
- 2,647 View
- 17 Download
- 13 Crossref

- A review of the regenerative endodontic treatment procedure
- Bin-Na Lee, Jong-Wook Moon, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):179-187. Published online March 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Traditionally, apexification has been used to treat immature permanent teeth that have lost pulp vitality. This technique promotes the formation of an apical barrier to close the open apex so that the filling materials can be confined to the root canal. Because tissue regeneration cannot be achieved with apexification, a new technique called regenerative endodontic treatment was presented recently to treat immature permanent teeth. Regenerative endodontic treatment is a treatment procedure designed to replace damaged pulp tissue with viable tissue which restores the normal function of the pulp-dentin structure. After regenerative endodontic treatment, continued root development and hard tissue deposition on the dentinal wall can occur under ideal circumstances. However, it is difficult to predict the result of regenerative endodontic treatment. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to summarize multiple factors effects on the result of regenerative endodontic treatment in order to achieve more predictable results. In this study, we investigated the features of regenerative endodontic treatment in comparison with those of other pulp treatment procedures and analyzed the factors that have an effect on regenerative endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures Using Autologous Platelet Concentrate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elnaz Mousavi, Navid Nasrabadi, Samira Jamali, Arian Haddadi
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial 3D printed gelatin scaffolds for root canal disinfection in regenerative endodontics procedures
Mateo Dallos Ortega, Jenny Aveyard, Raghda Magdy Abdelgawad, Reem El-Gendy, Alexander Ciupa, David Whetnall, Julia Behnsen, Robert J. Poole, Raechelle A. D'Sa
Biomaterials Science.2025; 13(14): 3795. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Therapies: Harnessing Stem Cells, Scaffolds, and Growth Factors
Rosana Farjaminejad, Samira Farjaminejad, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
Polymers.2025; 17(11): 1475. CrossRef - Effects of combining hyaluronic acid hydrogel with injectable platelet rich fibrin on apical papilla stem cells proliferation and differentiation
Azal H. Al-Masoody, Nasrin Asadi, Hadiseh Mohammadpour, Mahshid Hodjat, Tahereh Sadat Jafarzadeh Kashi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Experts consensus on management of tooth luxation and avulsion
Ruijie Huang, Chenchen Zhou, Ling Zhan, Yuan Liu, Xian Liu, Qin Du, Jun Wang, Wei Zhao, Guangtai Song, Li-an Wu, Beizhan Jiang, Yanhong Li, Hongmei Zhang, Jing Zou
International Journal of Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A review of tissue engineering in regenerative endodontic treatment
Eric Priyo Prasetyo, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Galih Sampoerno, Wilson Sukandar, Shafy Shariz Bin Sharizal, Nurfahira Paidal, Menza Fadiyan Amriel, Nathania Elita Gunawan, Ketut Suardita, Evelyn Tjendronegoro
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2024; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Innovative Paradigms and Established Strategies in Tooth Revitalization: A Review
Ahmad Shah Khan, Zahid Mehmood Khan, Palwasha Ishaque, Muhammad Zubair, Syeda Fatima Tu Zahra, Sana Ashfaq
Dental Update.2024; 51(8): 570. CrossRef - Explore the most recent developments and upcoming outlooks in the field of dental nanomaterials
Ali Alsuraifi, Zainab M. Sulaiman, Noor Alhuda R. Mohammed, Jassim Mohammed, Sarah Kareem Ali, Yousef Husam Abdualihamaid, Fatimah Husam, Abdullah Ayad
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Regenerative Endodontics: A Review of Current Techniques and Future Directions
Firas A Alothman, Lamia S Hakami, Ali Alnasser, Faris M AlGhamdi, Abdullah A Alamri, Basel M Almutairii
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Response to a Bioceramic Dental Sealer and Photobiomodulation: An In Vitro Study
Hamed A Alshawkani, Mohamed Mansy, Mahmoud Al Ankily, Mohamed Shamel
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(4): 313. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - GelMA‐based hydrogel biomaterial scaffold: A versatile platform for regenerative endodontics
Lei Huang, Xuan Chen, XiaoXia Yang, Yinchun Zhang, Xiaoling Qiu
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Dentinogenesis Imperfecta‐Induced Apical Periodontitis
Ying Liao, Ting Pan, Xianghui Xing, Sivakumar Nuvvula
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro and in vivo evaluation of iRoot BP Plus as a coronal sealing material for regenerative endodontic procedures
Ning Yang, Wenxiao Yang, Rou Shen, Shengcai Zhang, Tianchi Ma, Yao Liu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of pH and Ca+ ion release from MTA on interaction with platelet-rich fibrin and blood clot: an in vitro study
Sonia Khatri, Sylvia Mathew, Shruthi Nagaraja, Swaroop Hegde, Soumyadeep Ghosh, Kavimalar Ravichandran
F1000Research.2023; 12: 364. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Therapy and Pulp-Regenerative Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Jiawen Yong, Sabine Gröger, Zuping Wu, Sabine Ruf, Yuer Ye, Xiaoyan Chen
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 371. CrossRef - Efficacy of disinfection procedures performed prior to regenerative endodontic therapy: An integrative review
Ketillyn da Silva Magalhães, Ana Clara Kuerten Gil, Taynara Santos Goulart, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Daniela de Rossi Figueiredo, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(2): 418. CrossRef - Newer Prospects of Regenerative Endodontics: A Comprehensive and Updated Review of Literature
Mohammad Kamran Khan, Mahendra Kumar Jindal
Journal of the Scientific Society.2023; 50(3): 299. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of pH and Ca+ ion release from MTA on interaction with platelet-rich fibrin and blood clot: an in vitro study
Sonia Khatri, Sylvia Mathew, Shruthi Nagaraja, Swaroop Hegde, Soumyadeep Ghosh, Kavimalar Ravichandran
F1000Research.2023; 12: 364. CrossRef - Effects of CEM cement and emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla: a comparative in vitro study
Elham Khoshbin, Leila Ghasemi, Rezvan Najafi, Hamed Karkehabadi
Biotechnology Letters.2023; 45(1): 69. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Regenerative Potential of Blood Clot and Platelet-rich Fibrin in Young Permanent Teeth Based on the Revised American Academy of Endodontics Clinical Considerations for Regenerative Procedure: 2016
Saraswathi V Naik, Prabhakar Attiguppe, Aarathi J Prakash
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S149. CrossRef - Biomechanical characterization of a fibrinogen–blood hydrogel for human dental pulp regeneration
Sofia Silvia Piglionico, Bela Varga, Orsolya Pall, Olivier Romieu, Csilla Gergely, Frédéric Cuisinier, Bernard Levallois, Ivan Vladislavov Panayotov
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(20): 6919. CrossRef - Intracellular bacterial eradication using a novel peptide in vitro
Wing Nok Isaac Ng, Shanthini Kalimuthu, Carmen Oi Kwan Law, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Terrence Chi Kong Lau, Yiu Yan Leung, Gary Shun Pan Cheung, Prasanna Neelakantan
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(11): 1360. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of Previously Treated Mature Permanent Tooth: A Case Report with 3-year Follow Up
Myung-Jin Lee
The Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2023; 47(6): 133. CrossRef - Clinical Outcome and Comparison of Regenerative and Apexification Intervention in Young Immature Necrotic Teeth—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Pratima Panda, Lora Mishra, Shashirekha Govind, Saurav Panda, Barbara Lapinska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3909. CrossRef - Evaluation of Attitude and Knowledge of Endodontic, Pedodontic and SBARD Residents in Saudi Arabia toward Regenerative Endodontics—A National Survey
Ali A. Assiry, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Roshan Noor Mohamed, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohammed Zameer
Medicina.2022; 58(4): 545. CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Antimicrobials on Viability and Differentiation of Stem Cells From the Apical Papilla: An In Vitro Study
Gavin Raddall, Isabel Mello, Brendan M. Leung
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(7): 880. CrossRef - Awareness and Acceptance of Vital Pulp Therapy and Regenerative Endodontic Procedures among Dental Professionals in India: A Web-based Survey
Saloni Rathi, Priya Chauhan, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Rolly Agarwal, Simar Kaur Manocha, Mrinali Chaddha
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 10. CrossRef - Exosomes as Biochemistry Tools for Stem Cell Differentiation: A Novel Cell-Based Treatment for Diseases
Saeed Azandeh, Darioush Bijan Nejad, Samaneh Karimi, Fereshtesadat Fakhredini
Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of biodentine coated with emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla
Hamed Karkehabadi, Erfan Ahmadyani, Rezvan Najafi, Elham Khoshbin
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 3685. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Laser‐Assisted Bleaching of the Teeth Discolored due to Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Suitable Medicament for Intracanal Disinfection
Krutika Malu, Monika Khubchandani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Microhardness and Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentin with Two Combinations of TAP and MTAP: An In Vitro Study
P Niharika, Saigeeta Kondamadugu, Nagireddy Venugopal Reddy, Muthumula Daneswari, Annie P Chris, Nikhila V Reddy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S2): S151. CrossRef - Comparing Antibiotic Pastes with Electrospun Nanofibers as Modern Drug Delivery Systems for Regenerative Endodontics
Nura Brimo, Dilek Çökeliler Serdaroğlu, Busra Uysal
Current Drug Delivery.2022; 19(9): 904. CrossRef - The Advances of Blood Clots Used as Biomaterials in Regenerative Medicine
Eliza VanZweden, Rachael Tolsma, Victor Hung, Peter Awad, Robert Sawyer, Yong Li
Regenerative Medicine.2022; 17(12): 957. CrossRef - Microstructure and color stability of calcium silicate-based dental materials exposed to blood or platelet-rich fibrin
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Ibrahim Abu Tahun, Shima Saber Tahan, Fatemeh Mohandes, Mohammad H. Nekoofar, Paul M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1193. CrossRef - Results of “proroot mta” application in treatment of chronic periodontitis in teeth with incomplete root formation
N.M. Korneeva, E.A. Novikova, D.S. Popova, K.S. Rabadanova, L.Ya Rzaeva
Stomatology for All / International Dental review.2022; (2(99)): 10. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Combined with Electrolyzed Superoxidized Solution at Neutral pH on Enterococcus faecalis Growth
Héctor Armando Jimenez-Gonzalez, María Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Sergio Eduardo Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Víctor Hugo Urrutia-Baca, Myriam Angélica De La Garza-Ramos, Juan Manuel Solis-Soto, Ricardo Gomez-Flores, Patricia Tamez-Guerra, Yeliz Guven
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Unpredictable Outcomes of a Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Zahra Mohammadi, Hadi Assadian, Behnam Bolhari, Mohammadreza Sharifian, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Nazanin Chitsaz, Andrea Scribante
Case Reports in Dentistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Revascularization of nonvital immature incisor with asymptomatic apical periodontitis
Ema Mulyawati, Pribadi Santosa, Tunjung Nugraheni
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(3): 134. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of calcium hydroxide apexification and regenerative endodontic procedure for root dentine growth stimulation in immature incisors with pulp necrosis
M.S. Rakhmanova, M.V. Korolenkova
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(6): 55. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of a Novel Antibiotic‐Eluting Injectable Platelet‐Rich Fibrin Scaffold against a Dual‐Species Biofilm in an Infected Immature Root Canal Model
Azade Rafiee, Mahtab Memarpour, Yasaman Najibi, Bahman Khalvati, Sedigheh Kianpour, Mohammad Hossein Morowvat, Sung-Hwan Choi
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exosomes Derived from Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla Promote Dentine-Pulp Complex Regeneration by Inducing Specific Dentinogenesis
Xueying Zhuang, Lingli Ji, Huan Jiang, Yao Liu, Xuemei Liu, Jing Bi, Weidong Zhao, Zhenjiang Ding, Xu Chen
Stem Cells International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Injectable Biomaterials for Dental Tissue Regeneration
Håvard Jostein Haugen, Poulami Basu, Mousumi Sukul, João F Mano, Janne Elin Reseland
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(10): 3442. CrossRef - Viability and Stimulation of Human Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla (hSCAPs) Induced by Silicate-Based Materials for Their Potential Use in Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review
José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, Alicia Almudéver, Julia Guerrero-Gironés, Carmen Llena
Materials.2020; 13(4): 974. CrossRef - An Innovative Drug Delivery System Loaded with a Modified Combination of Triple Antibiotics for Use in Endodontic Applications
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Fahimeh Tabatabaei, Saeed Asgary
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Defining Endodontic Residents' Clinical Experiences: A National Survey
Jonathan D. Blacher, Kamran E. Safavi, Robert H. Aseltine, Blythe M. Kaufman
Journal of Dental Education.2019; 83(5): 504. CrossRef - Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month ex vivo study
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Study between Revitalization of Necrotic Immature Permanent Anterior Teeth with and without Platelet Rich Fibrin: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Rasha Adel Ragab, Amr Ezzat Abd El Lattif, Norhan Abd El Wahab El Dokky
Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2019; 43(2): 78. CrossRef - Biomaterials and Scaffold Design Strategies for Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
Gavin Raddall, Isabel Mello, Brendan M. Leung
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Iloprost Induces Dental Pulp Angiogenesis in a Growth Factor–free 3-Dimensional Organ Culture System
Sonntana Seang, Prasit Pavasant, Chalida N. Limjeerajarus
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 759. CrossRef - Ratio and Rate of Induced Root Growth in Necrotic Immature Teeth
Eun Jung Sang, Ji-Soo Song, Teo Jeon Shin, Young-Jae Kim, Jung-Wook Kim, Ki-Taeg Jang, Sang-Hoon Lee, Hong-Keun Hyun
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(2): 225. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Traumatic avulsion and delayed replantation of maxillary incisors in an eleven-year-old child
Gokcen Deniz Bayrak
Edorium Journal of Dentistry.2018; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Diameter on the Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Teeth with Pulp Necrosis: A Review
Yanjun Fang, Xinhuan Wang, Jingjing Zhu, Chaonan Su, Ying Yang, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 414. CrossRef - Assessment of Regaining Pulp Sensibility in Mature Necrotic Teeth Using a Modified Revascularization Technique with Platelet-rich Fibrin: A Clinical Study
Mohamed Nageh, Geraldine M. Ahmed, Alaa A. El-Baz
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1526. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics
Kristina Feigin, Bonnie Shope
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2017; 34(3): 161. CrossRef - Intentional Replantation of an Avulsed Immature Permanent Incisor: A Case Report
Claudio Maniglia-Ferreira, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Marcelo de Morais Vitoriano
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1383. CrossRef - Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 12. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef - Effects of a Bioactive Scaffold Containing a Sustained Transforming Growth Factor-β1–releasing Nanoparticle System on the Migration and Differentiation of Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla
Craig Bellamy, Suja Shrestha, Calvin Torneck, Anil Kishen
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(9): 1385. CrossRef - Effects of Novel 3-dimensional Antibiotic-containing Electrospun Scaffolds on Dentin Discoloration
Margaret Louise A. Porter, Eliseu A. Münchow, Maria T.P. Albuquerque, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Anderson T. Hara, Marco C. Bottino
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(1): 106. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures Using Autologous Platelet Concentrate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 7,085 View
- 116 Download
- 63 Crossref

- The effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and enamel matrix derivative on the bioactivity of mineral trioxide aggregate in MC3T3-E1cells
- Youngdan Jeong, Wonkyung Yang, Hyunjung Ko, Miri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):187-194. Published online June 19, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and enamel matrix derivative (EMD) respectively with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on hard tissue regeneration have been investigated in previous studies. This study aimed to compare the osteogenic effects of MTA/BMP-2 and MTA/EMD treatment in MC3T3-E1 cells.
Materials and Methods MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with MTA (ProRoot, Dentsply), BMP-2 (R&D Systems), EMD (Emdogain, Straumann) separately and MTA/BMP-2 or MTA/EMD combination. Mineralization was evaluated by staining the calcium deposits with alkaline phosphatase (ALP, Sigma-Aldrich) and Alizarin red (Sigma-Aldrich). The effects on the osteoblast differentiation were evaluated by the expressions of osteogenic markers, including ALP, bone sialoprotein (BSP), osteocalcin (OCN), osteopontin (OPN) and osteonectin (OSN), as determined by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis (RT-PCR, AccuPower PCR, Bioneer).
Results Mineralization increased in the BMP-2 and MTA/BMP-2 groups and increased to a lesser extent in the MTA/EMD group but appeared to decrease in the MTA-only group based on Alizarin red staining. ALP expression largely decreased in the EMD and MTA/EMD groups based on ALP staining. In the MTA/BMP-2 group, mRNA expression of OPN on day 3 and BSP and OCN on day 7 significantly increased. In the MTA/EMD group, OSN and OCN gene expression significantly increased on day 7, whereas ALP expression decreased on days 3 and 7 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions These results suggest the MTA/BMP-2 combination promoted more rapid differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells than did MTA/EMD during the early mineralization period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Elucidating epigenetic mechanisms governing odontogenic differentiation in dental pulp stem cells: an in-depth exploration
Lei Huang, Xuan Chen, Xiaoxia Yang, Yinchun Zhang, Yiyun Liang, Xiaoling Qiu
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and bioactivity of calcium silicate-based cements
Merve Esen, Yeliz Guven, Mehmet Fatih Seyhan, Handan Ersev, Elif Bahar Tuna-Ince
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - GelMA‐based hydrogel biomaterial scaffold: A versatile platform for regenerative endodontics
Lei Huang, Xuan Chen, XiaoXia Yang, Yinchun Zhang, Xiaoling Qiu
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experimental Validation of Antiobesogenic and Osteoprotective Efficacy of Ginsenoside CK via Targeting Lipid and Atherosclerosis Pathways
Md. Niaj Morshed, Reshmi Akter, Imran Mahmud, Ah-Yeong Gwon, Jin Woo Jeang, Yeong-Geun Lee, Dae Won Park, Deok Chun Yang, Yeon Ju Kim, Se-Chan Kang
Life.2024; 15(1): 41. CrossRef - Anti-osteoporosis effects of triterpenoids from the fruit of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) through the promotion of osteoblast differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells, C3H10T1/2
Da Eun Lee, Kun Hee Park, Joo-Hyun Hong, Seon Hee Kim, Ki-Moon Park, Ki Hyun Kim
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2023; 46(9-10): 771. CrossRef - In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation of Antiobesogenic and Osteoprotective Effect of Pomegranate Juice Fermented by Tannin Acyl Hydrolase and Lactobacillus vespulae DCY75 via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
Reshmi Akter, Vinothini Boopathi, Muhammad Awais, Juha Park, Byoung Man Kong, Se-Woung Oh, Ji-Hyung Oh, Jong Chan Ahn, Deok Chun Yang
ACS Food Science & Technology.2023; 3(11): 1975. CrossRef - Early induction of Hes1 by bone morphogenetic protein 9 plays a regulatory role in osteoblastic differentiation of a mesenchymal stem cell line
Chang‐Hwan Seong, Norika Chiba, Mardiyantoro Fredy, Joji Kusuyama, Kiyohide Ishihata, Toshiro Kibe, Muhammad Subhan Amir, Ryohei Tada, Tomokazu Ohnishi, Norifumi Nakamura, Tetsuya Matsuguchi
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2023; 124(9): 1366. CrossRef - Effects of Fucoidan Powder Combined with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as a Direct Pulp-Capping Material
Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Bo Yu, Thomas K. Lee, Reuben H. Kim, Deuk-Won Jo
Polymers.2022; 14(12): 2315. CrossRef - Nerve growth factor promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via BMP-2/Smads pathway
Xuming Yang, Donggang Mou, Qunying Yu, Jimei Zhang, Ying Xiong, Zhimin Zhang, Shan Xing
Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger.2022; 239: 151819. CrossRef - Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of the Fruit of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) through Promotion of Osteogenic Differentiation in Ovariectomized Mice
Kun Hee Park, Joo-Hyun Hong, Seon-Hee Kim, Jin-Chul Kim, Ki Hyun Kim, Ki-Moon Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3604. CrossRef - Oroactive dental biomaterials and their use in endodontic therapy
Ebrahim Patel, Priyamvada Pradeep, Pradeep Kumar, Yahya E. Choonara, Viness Pillay
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2020; 108(1): 201. CrossRef - BMP-2 and type I collagen preservation in human deciduous teeth after demineralization
Nina Bono, Paolo Tarsini, Gabriele Candiani
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - An assessment of the overexpression of BMP‐2 in transfected human osteoblast cells stimulated by mineral trioxide aggregate and Biodentine
E. M. Rodrigues, A. L. Gomes‐Cornélio, A. Soares‐Costa, L. P. Salles, M. Velayutham, C. Rossa‐Junior, J. M. Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, M. Tanomaru‐Filho
International Endodontic Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Sandblasting and fibronectin-derived peptide immobilization on titanium surface increase adhesion and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells (MC3T3-E1)
Samdharu Pramono, Kamolparn Pugdee, Jintamai Suwanprateep, Sittichai Koontongkaew
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(4): 427. CrossRef - Combined Effects of Growth Hormone and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate on Growth, Differentiation, and Angiogenesis in Human Dental Pulp Cells
Hyung-Mun Yun, Seok-Woo Chang, Kyung-Ran Park, Lan Herr, Eun-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 269. CrossRef - Combined effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and human placental extract on rat pulp tissue and growth, differentiation and angiogenesis in human dental pulp cells
Seok-Woo Chang, Ji-Youn Kim, Mi-Joo Kim, Ga-Hyun Kim, Jin-Kyu Yi, Deok-Won Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eun-Cheol Kim
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2016; 74(4): 298. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate induces osteoblastogenesis via Atf6
Toyonobu Maeda, Atsuko Suzuki, Satoshi Yuzawa, Yuh Baba, Yuichi Kimura, Yasumasa Kato
Bone Reports.2015; 2: 36. CrossRef - Locally controlled delivery of TNFα antibody from a novel glucose-sensitive scaffold enhances alveolar bone healing in diabetic conditions
Qi Wang, Hao Li, Yu Xiao, Shuan Li, Bo Li, Xiaowen Zhao, Lin Ye, Bin Guo, Xinmin Chen, Yi Ding, Chongyun Bao
Journal of Controlled Release.2015; 206: 232. CrossRef
- Elucidating epigenetic mechanisms governing odontogenic differentiation in dental pulp stem cells: an in-depth exploration
- 1,510 View
- 3 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
- Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):89-94. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.89
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the cytotoxicity, setting time and compressive strength of MTA and two novel tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials, Bioaggregate (BA) and Biodentine (BD).
Materials and Methods Cytotoxicity was evaluated by using a 2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-5-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-2H-tetrazolium hydroxide (XTT) assay. Measurements of 9 heavy metals (arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, manganese, nickel, and zinc) were performed by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) of leachates obtained by soaking the materials in distilled water. Setting time and compressive strength tests were performed following ISO requirements.
Results BA had comparable cell viability to MTA, whereas the cell viability of BD was significantly lower than that of MTA. The ICP-MS analysis revealed that BD released significantly higher amount of 5 heavy metals (arsenic, copper, iron, manganese, and zinc) than MTA and BA. The setting time of BD was significantly shorter than that of MTA and BA, and the compressive strength of BA was significantly lower than that of MTA and BD.
Conclusions BA and BD were biocompatible, and they did not show any cytotoxic effects on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. BA showed comparable cytotoxicity to MTA but inferior physical properties. BD had somewhat higher cytotoxicity but superior physical properties than MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the physical properties of bromelain-modified biodentine for direct pulp capping
Paridhi Agrawal, Manoj Chandak, Aditya Patel, Jay Bhopatkar
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
H.K. Abd El-Hamid, A.M. Fayad, R.L. Elwan
Ceramics International.2024; 50(14): 25322. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Strength of a cement-based dental material: Early age testing and first micromechanical modeling at mature age
Petr Dohnalík, Christian Hellmich, Gilles Richard, Bernhard L. A. Pichler
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Biomimetic Approaches in Clinical Endodontics
Naresh Kumar, Nazrah Maher, Faiza Amin, Hani Ghabbani, Muhammad Sohail Zafar, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Ricardo E. Oñate-Sánchez
Biomimetics.2022; 7(4): 229. CrossRef - Effect of different manipulations on the physical, chemical and microstructural characteristics of Biodentine
Mariana Domingos Pires, Joana Cordeiro, Isabel Vasconcelos, Mariana Alves, Sérgio André Quaresma, António Ginjeira, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2021; 37(7): e399. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Material Pulp Cells and Tissue Interactions
Nastaran Meschi, Biraj Patel, Nikita B. Ruparel
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): S150. CrossRef - Biological Effects of Tricalcium Silicate Nanoparticle-Containing Cement on Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth
Yoonsun Jung, Ji-Young Yoon, Kapil Dev Patel, Lan Ma, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jongbin Kim, Jung-Hwan Lee, Jisun Shin
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1373. CrossRef - Physicochemical, mechanical and cytotoxicity evaluation of chitosan-based accelerated portland cement
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2020; 9(5): 11574. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cements: osteogenic and angiogenic responses of human bone marrow stem cells
Mohamed R. W. Ali, Manal Mustafa, Asgeir Bårdsen, Athanasia Bletsa
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 127(3): 261. CrossRef - Bioactive tri/dicalcium silicate cements for treatment of pulpal and periapical tissues
Carolyn M. Primus, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2019; 96: 35. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on the setting times and tensile strengths of calcium silicate‐based cements
Ozgur Uyanik, Emre Nagas, Selen Kucukkaya Eren, Zafer C. Cehreli, Pekka K. Vallittu, Lippo V.J. Lassila
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 241. CrossRef - Effects of four novel root-end filling materials on the viability of periodontal ligament fibroblasts
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Pembegul Uyar Arpaci, Ayce Unverdi Eldeniz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Root perforations: a review of diagnosis, prognosis and materials
Carlos Estrela, Daniel de Almeida Decurcio, Giampiero Rossi-Fedele, Julio Almeida Silva, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Álvaro Henrique Borges
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of chelating agent and acids on Biodentine
V Ballal, JN Marques, CN Campos, CO Lima, RA Simão, M Prado
Australian Dental Journal.2018; 63(2): 170. CrossRef - Biological interactions of a calcium silicate based cement (Biodentine™) with Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous teeth
Eirini Athanasiadou, Maria Paschalidou, Anna Theocharidou, Nikolaos Kontoudakis, Konstantinos Arapostathis, Athina Bakopoulou
Dental Materials.2018; 34(12): 1797. CrossRef - Retention of BioAggregate and MTA as coronal plugs after intracanal medication for regenerative endodontic procedures: an ex vivo study
Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin, Shaimaa Ismail Gawdat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Dens Invaginatus Type II Associated with Immature Apex and Large Periradicular Lesion Using Platelet-rich Fibrin and Biodentine
Shruti Goel, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1750. CrossRef - Brain aluminium accumulation and oxidative stress in the presence of calcium silicate dental cements
K Demirkaya, B Can Demirdöğen, Z Öncel Torun, O Erdem, E Çırak, YM Tunca
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2017; 36(10): 1071. CrossRef - Calcium silicate‐based cements: composition, properties, and clinical applications
Alaa E. Dawood, Peter Parashos, Rebecca H.K. Wong, Eric C. Reynolds, David J. Manton
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological response of commercially available different tricalcium silicate‐based cements and pozzolan cement
Serhat Köseoğlu, Tuğba Pekbağr?yan?k, Ebru Kucukyilmaz, Mehmet Sağlam, Sukru Enhos, Ayşe Akgün
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(9): 994. CrossRef - Modified tricalcium silicate cement formulations with added zirconium oxide
Xin Li, Kumiko Yoshihara, Jan De Munck, Stevan Cokic, Pong Pongprueksa, Eveline Putzeys, Mariano Pedano, Zhi Chen, Kirsten Van Landuyt, Bart Van Meerbeek
Clinical Oral Investigations.2017; 21(3): 895. CrossRef - Cytotoxic effects of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium enrichedmixture cement, Biodentine and octacalcium pohosphate onhuman gingival fibroblasts
Eshagh A. Saberi, Narges Farhadmollashahi, Faroogh Ghotbi, Hamed Karkeabadi, Roholla Havaei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2016; 10(2): 75. CrossRef - The effect of working time on the displacement of Biodentine™ beneath prefabricated stainless steel crown: a laboratory study
Alaa E. Dawood, David J. Manton, Peter Parashos, Rebecca H. K. Wong
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2016; 7(4): 391. CrossRef - Evaluation of reparative dentin formation of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine and BioAggregate using micro-CT and immunohistochemistry
Jia Kim, Young-Sang Song, Kyung-San Min, Sun-Hun Kim, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 29. CrossRef
- Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
- 1,877 View
- 6 Download
- 30 Crossref

- A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
- Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):227-233. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of the study was to evaluate human dental pulp response to pulpotomy with calcium hydroxide (CH), mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), and calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement.
Materials and Methods A total of nine erupted third molars were randomly assigned to each pulpotomy group. The same clinician performed full pulpotomies and coronal restorations. The patients were followed clinically for six months; the teeth were then extracted and prepared for histological assessments. The samples were blindly assessed by an independent observer for pulp vitality, pulp inflammation, and calcified bridge formation.
Results All patients were free of clinical signs/symptoms of pulpal/periradicular diseases during the follow up period. In CH group, one tooth had necrotic radicular pulp; other two teeth in this group had vital uninflamed pulps with complete dentinal bridge formation. In CEM cement and MTA groups all teeth had vital uninflamed radicular pulps. A complete dentinal bridge was formed beneath CEM cement and MTA in all roots. Odontoblast-like cells were present beneath CEM cement and MTA in all samples.
Conclusions This study revealed that CEM cement and MTA were reliable endodontic biomaterials in full pulpotomy treatment. In contrast, the human dental pulp response to CH might be unpredictable.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A meta‐analysis of calcium silicate‐based cements and calcium hydroxide as promoters of hard tissue bridge formation
Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Karem P. Pinto, Fernanda N. S. J. Riche, Maristela G. H. Carestiato, Jorge N. R. Martins, Henry F. Duncan, Marco A. Versiani, Gustavo De‐Deus
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(5): 685. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of pulpotomy materials in permanent teeth: a systematic review of calcium hydroxide, MTA, biodentine, and iRoot BP plus
Anggi Putri Riandani, Arief Cahyanto, Rana Abdelbaset Lotfy Diab, Ratih Widyasari, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hard tissue formation in pulpotomized primary teeth in dogs with nanomaterials MCM-48 and MCM-48/hydroxyapatite: an in vivo animal study
Sahar Talebi, Nosrat Nourbakhsh, Ardeshir Talebi, Amir Abbas Nourbakhsh, Abbas Haghighat, Maziar Manshayi, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi, Razieh Karimi, Rahman Nazeri, Kenneth J.D. Mackenzie
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Growth Factor Delivery Systems on Cellular Activities of Dental
Stem Cells: A Systematic Review (Part II)
Sayna Shamszadeh, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Asgary
Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2024; 19(4): 587. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Cements in Restorative Dentistry: Vital Pulp Therapy Clinical, Radiographic, and Histological Outcomes on Deciduous and Permanent Dentition—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Maria Teresa Xavier, Ana Luísa Costa, João Carlos Ramos, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jorge N. R. Martins
Materials.2024; 17(17): 4264. CrossRef - Pulpotomy: An alternative treatment modality to conventional root canal treatment
Günther Streit, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2023; 78(06): 309. CrossRef - A Comparative Histological Analysis of Human Pulp Following Direct Pulp Capping with Propolis or Biodentine
Nehad A Ahmad, Nevin A. Gad, Marwa H. Abdulmonaem
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2022; 5(3): 281. CrossRef - Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases-8 and Myeloperoxidase in Pulp Tissue after Pulpotomy with Calcium Silicate Cements
Nayara Nery de Oliveira Cunha, Marina Azevedo Junqueira, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Laís da Silveira Terra Santos, George Augusto Veloso de Oliveira, Rafael Tobias Moretti Neto, Denismar Alves Nogueira, Maísa Ribeiro Pereira Lima Brigagão, Ana Beatriz da Silve
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Outcomes of Full Pulpotomy in Permanent Molars for Patients Treated in a Single, Short Session under Special Conditions
Natacha Linas, Nicolas Decerle, Marie-Laure Munoz-Sanchez, Denise Faulks, Valérie Collado, Emmanuel Nicolas, Martine Hennequin, Pierre-Yves Cousson
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(11): 1597. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Root Development after Regenerative Endodontic Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Teng Kai Ong, Ghee Seong Lim, Maharaj Singh, Alissa V. Fial
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(12): 1856. CrossRef - Dexamethasone- loaded polymeric porous sponge as a direct pulp capping agent
Amjad Alagha, Abdulwahab Nourallah, Sahar Alhariri
Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition.2020; 31(13): 1689. CrossRef - Postendodontic Pain after Pulpotomy or Root Canal Treatment in Mature Teeth with Carious Pulp Exposure: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Ali Haeri, Arash Shahravan, Ali Kazemi, Fariborz Moazami, Mohammad Ali Mozayeni, Eshaghali Saberi, Mohammad Samiei, Mehdi Vatanpour, Alireza Akbarzade Baghban, Mahta Fazlyab, Ardavan Parhizkar, Mahboobe Ahmadi, Nazila Akbarian Rad,
Pain Research and Management.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Vital Pulp Therapy as a Conservative Approach for Management of Invasive Cervical Root Resorption: A Case Series
Saeed Asgary, Mahdieh Nourzadeh, Prashant Verma, M. Lamar Hicks, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1161. CrossRef - Which procedures and materials could be applied for full pulpotomy in permanent mature teeth? A systematic review
M. Zanini, M. Hennequin, PY. Cousson
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(7): 541. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Treatment Outcomes of 4 Vital Pulp Therapies in Mature Molars
Saeed Asgary, Raheleh Hassanizadeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - A Review of Criteria for the Evaluation of Pulpotomy Outcomes in Mature Permanent Teeth
Marjorie Zanini, Martine Hennequin, Pierre-Yves Cousson
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1167. CrossRef - Calcium-Enriched Mixture Pulpotomy of Primary Molar Teeth with Irreversible Pulpitis. A Clinical Study
Mahtab Memarpour, Soleiman Fijan, Saeed Asgary, Marzieh Keikhaee
The Open Dentistry Journal.2016; 10(1): 43. CrossRef - Endodontie in der unreifen bleibenden Dentition — Maßnahmen zur Vitalerhaltung, Apexifikation und Regeneration der Pulpa
Martin Jung
Oralprophylaxe & Kinderzahnheilkunde.2016; 38(1): 29. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Class 4 Invasive Cervical Root Resorption Using Calcium-enriched Mixture Cement
Saeed Asgary, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1291. CrossRef - Permanent teeth pulpotomy survival analysis: retrospective follow-up
Gustavo Golgo Kunert, Itaborai Revoredo Kunert, Luiz Cesar da Costa Filho, José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1125. CrossRef - Cytocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties of Capping Materials
Claudio Poggio, Carla Renata Arciola, Riccardo Beltrami, Annachiara Monaco, Alberto Dagna, Marco Lombardini, Livia Visai
The Scientific World Journal.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 137. CrossRef - Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Surface Treatments on Morphology and Bond Strength to Composite Resin
Joo-Hee Shin, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1210. CrossRef
- A meta‐analysis of calcium silicate‐based cements and calcium hydroxide as promoters of hard tissue bridge formation
- 2,103 View
- 13 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Evaluation of the rat tissue reaction to experimental new resin cement and mineral trioxide aggregate cement
- Won-Kyung Yang, Hyun-Jung Ko, Mi-Ri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):194-200. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives New resin cement (NRC) has been developed as a root repairing material and the material is composed of organic resin matrix and inorganic powders. The aim of this study was to compare the rat subcutaneous tissue response to NRC and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) cement and to investigate the tissue toxicity of both materials.
Materials and Methods Sixty rats received two polyethylene tube-implants in dorsal subcutaneous regions, MTA and NRC specimens. Twenty rats were sacrificed respectively at 1, 4 and 8 wk after implantation and sectioned to 5 µm thickness and stained with Hematoxylin-Eosin (H-E) or von-Kossa staining. The condition of tissue adjacent to the implanted materials and the extent of inflammation to each implant were evaluated by two examiners who were unaware of the type of implanted materials in the tissues. Data were statistically analyzed with paired
t -test (p < 0.05).Results In specimens implanted with both NRC and MTA, severe inflammatory reactions were present at one wk, which decreased with time. At eighth wk, MTA implanted tissue showed mild inflammatory reaction, while there were moderate inflammatory reactions in NRC implanted tissue, respectively. In NRC group, von-Kossa staining showed more calcification materials than MTA group at eighth wk.
Conclusions It was concluded that the calcium reservoir capability of NRC may contribute to mineralization of the tissues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
Ranjdar Mahmood Talabani, Balkees Taha Garib, Reza Masaeli, Kavosh Zandsalimi, Farinaz Ketabat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotoxicity of root canal sealers: a literature review
Fábio Miguel dos Santos Costa, Maria Helena Fernandes, Silvia Regina Batistuzzo de Medeiros
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(10): 3347. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation, solubility and biocompatibility of TheraCal LC compared with MTA-angelus and biodentine as a furcation perforation repair material
M. A. Alazrag, A. M. Abu-Seida, K. M. El-Batouty, S. H. El Ashry
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation in vivo of biocompatibility of differents resin-modified cements for bonding orthodontic bands
JANAINA A. MESQUITA, ROGÉRIO LACERDA-SANTOS, GÊISA A.M. SAMPAIO, GUSTAVO P. GODOY, CASSIANO F.W. NONAKA, POLLIANNA M. ALVES
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências.2017; 89(3 suppl): 2433. CrossRef - A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 227. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef
- Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
- 1,367 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Failure of orthograde MTA filling: MTA wash-out?
- Yuran Kim, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseoung Kim, Il-Young Jung
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):510-514. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.510
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), which was originally developed for repair of root perforations, is a biocompatible material with numerous clinical applications in endodontics. MTA must be allowed to set in the presence of moisture to optimize the material's physical and chemical properties. In the clinic, occasionally unset MTA has been detected after application of MTA on the tooth, and the reason has been unclear.
This case report presents MTA washed-out for several years after placement at the root apex as an apical plug, and discusses the reason and things to consider in clinics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate—A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements
C. Pushpalatha, Vismaya Dhareshwar, S. V. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Thilla Sekar Vinothkumar, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Amal Shaiban, Ateet Kakti, Shilpa H. Bhandi, Alok Dubey, Amulya V. Rai, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of volumetric changes of three different retrograde calcium silicate materials placed under different pH condititions
So Yeon Kwon, Min-Seock Seo
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of RetroMTA on osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells
Hyo-Il Lee, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2018; 45(2): 97. CrossRef - The effect of human blood on the setting and surface micro-hardness of calcium silicate cements
Minju Song, Wonyoung Yue, Soyeon Kim, Wooksung Kim, Yaelim Kim, Jeong-Woong Kim, Euiseong Kim
Clinical Oral Investigations.2016; 20(8): 1997. CrossRef - Biological Effects and Washout Resistance of a Newly Developed Fast-setting Pozzolan Cement
Yoorina Choi, Su-Jung Park, Seoung-Hoon Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(4): 467. CrossRef
- Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate—A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements
- 1,164 View
- 14 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
- Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):473-478. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.473
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to investigate the biocompatibility of newly introduced Bioaggregate on human pulp and PDL cells.
Materials and Methods Cells were collected from human pulp and PDL tissue of extracted premolars. Cell culture plate was coated either with Bioaggregate or white MTA, then the same number of cells were poured to cell culture dishes. Cell attachment and growth was examined under a phase microscope after 1,3 and 7 days of seeding. Cell viability was measured and the data was analyzed using Student
t -test and one way ANOVA.Results Both types of cells used in this study were well attached and grew healthy on Bioaggregate and MTA coated culture dishes. No cell inhibition zone was observed in Bioaggregate group. There was no statistical difference of viable cells between bioaggreagte and MTA groups.
Conclusions Bioaggregate appeared to be biocompatible compared with white MTA on human pulp and PDL cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
H.K. Abd El-Hamid, A.M. Fayad, R.L. Elwan
Ceramics International.2024; 50(14): 25322. CrossRef - Influence of insulin on the healing of exposed dental pulp after pulp capping: An experimental study in a dog model
Mokhtar A. Al‐Anesi, Ashraf M. Abu‐Seida, Salma H. El Ashry, Abeer H. Mahran, Ehab S. Abd‐Elhamid
Special Care in Dentistry.2021; 41(1): 49. CrossRef - ROOT END FILLING MATERIALS – A REVIEW
Bynagari Chandra Shekar, Veerendra Uppin, Madhu Pujar
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 5. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 89. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef
- Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
- 1,483 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
- Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):445-452. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.445
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare apical sealing ability and physical properties of MTA, MTA - AH-plus mixture (AMTA) and experimental Portland cement - Epoxy resin mixture (EPPC) for a development of a novel retro-filling material.
Materials and Methods Forty-nine extracted roots were instrumented and filled with gutta-percha. Apical root was resected at 3 mm and the retro-filling cavity was prepared for 3 mm depth. Roots were randomly divided into 3 groups of 15 roots each. The retro-filling was done using MTA, AMTA, and EPPC as the groups divided. Four roots were used as control groups. After setting in humid condition for 24 hours, the roots were immersed in 1% methylene blue dye solution for 72 hours to test the apical leakage. After immersion, the roots were vertically sectioned and photos were taken to evaluate microleakage. Setting times were measured with Vicat apparatus and digital radiographs were taken to evaluate aluminum equivalent thickness using aluminum step wedge. The results of microleakage and setting time were compared between groups using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's post-hoc comparison at the significance level of 95%.
Results AMTA and EPPC showed less microleakage than MTA group (
p < 0.05). AMTA showed the highest radio-opacity than other groups and the novel EPPC showed 5 mm aluminum thickness radio-opacity. EPPC showed the shortest initial and final setting times than other groups while the MTA showed the longest (p < 0.05).Conclusions Under the condition of this study, the novel composite using Portland cement-Epoxy resin mixture may useful for retro-filling with the properties of favorable leakage resistance, radio-opacity and short setting time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
Jing-Ling Che, Jae-Hwan Kim, Seon-Mi Kim, Nam-ki Choi, Hyun-Joo Moon, Moon-Jin Hwang, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(1): 61. CrossRef - Biological Effects and Washout Resistance of a Newly Developed Fast-setting Pozzolan Cement
Yoorina Choi, Su-Jung Park, Seoung-Hoon Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(4): 467. CrossRef
- Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
- 1,221 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
- Jeong-Ho Lee, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):222-228. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA; Dentsply, Tulsa Dental, Tulsa, OK, USA), which is widely used as root-end filling material, with DiaRoot BioAggregate (DB; Innovative BioCaramix Inc, Vancouver, BC, Canada), newly developed product, by using MG63 osteoblast-like cells. MTA, DB, and Intermediate Restorative Material (IRM; Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE, USA) were used for root-end filling material while tissue culture plastic was used for control group. Each material was mixed and, the mixtures were left to set for 24 hours. MG63 cells were seeded to each group and then they were cultured for attachment for 4 hours. Following the attachment of cells to the root-end filling material, early cellular response was observed. After another 12 hours'culture, the level of attachment between cells and material was observed and in order to identify the effect of each material to bone formation, transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFβ1) and osteocalin (OC) were estimated by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the amount of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was also measured. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. As a result, only at OC and the number of cells which were attached to materials, there was no statistical difference between MTA and DB. At other items, there was statistically significant difference in all groups. Although DB has not shown exactly the same cellular response like that of MTA, the number of attached cells shows that biocompatibility of the material and OC indicates bone formation rate. Therefore, if DB is used for root end filling material, it is expected to lead to similar results to MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef - Bone regeneration in a periodontally challenged hopeless tooth
Jammula Surya Prasanna, Parupalli Karunakar, Dasari Rajashree, Raji V. Solomon
Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences.2013; 2(4): 296. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
- 1,361 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Mineral trioxied aggregate and its substitutes
- Yong-Bum Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):149-151. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Since its introduction in 1993, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) has been shown to be superior to others in sealing, biocompatibility, and many other aspects of clinical endodontics. MTA is primarily Portland cement with bismuth oxide as a radiopacitifier.
Although some studies suggested that the reasonable-priced Portland cement could be used instead of MTA, but MTAs are different from Portland cement in its composition, especially in heavy metal contents. Therefore, clinicians should be meticulous adapting the Portland cement as a MTA substitute.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 50. CrossRef
- Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
- 1,465 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Apical microleakage of MTA with 4-META/MMA & TBB resin as a root-end filling material
- Jin-Cheol Kim, Mi-Ri Kim, Hyun-Jung Ko, Won-Kyung Yang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):371-376. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.371
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub We evaluated
in vitro microleakage of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) powder with 4-methacryloxyethyl trimellitate anhydride (4-META) / methyl methacrylate (MMA) & tri-n-butylborane (TBB) resin as a retrograde filling material by using methylene blue dye method.Fifty-two single rooted, extracted teeth were instrumented and obturated with gutta percha and AH plus sealer. The apical 3mm of each root was resected and 3mm deep ultrasonic root end preparation was done. External surface of roots was coated with nail varnish. Prepared teeth were randomly divided into five groups; Negative control: completely covered with nail varnish; Positive control: coated with nail varnish except for apical foramen; Group 1 (retrofilled with Portland cement); Group 2 (retrofilled with MTA); Group 3 (retrofilled with MTA powder mixed with 4-META/MMA & TBB resin). Immediately after completion of root-end filling, all specimens were submerged in methylene blue dye for 72 hours in 37℃ incubator. The roots were longitudinally sectioned and measured for extent of dye penetration by three different examiners under microscope (×10). The results were statistically analyzed using one way ANOVA and Turkey's HSD test. No leakage was evident in negative control and complete leakage in positive control group. Group 3 showed significantly less leakage than group 1 and 2 (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference between group 1 and 2 (p > 0.01).
It was concluded that MTA powder with 4-META/MMA & TBB resin was excellent in reducing initial apical microleakage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of novel root-end filling material using epoxy resin and Portland cement
Sang-Jin Lee, Jin Chung, Hee-Sam Na, Eun-Joo Park, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Clinical Oral Investigations.2013; 17(3): 1009. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef - Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 445. CrossRef
- Characteristics of novel root-end filling material using epoxy resin and Portland cement
- 1,229 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
- Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):208-214. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.208
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the dye leakage of MTA (mineral trioxide aggregate) apical plug produced by two orthograde placement techniques (hand condensation technique and ultrasonically assisted hand condensation technique).
To simulate straight canal, 60 transparent acrylic blocks with straight canal were fabricated. These transparent acrylic blocks were divided into 2 groups (Group C; hand condensation technique (HC) and Group U; ultrasonically assisted hand condensation technique (UAHC)) of 30 blocks with each MTA application method. Each group was divided into 2 subgroups (n = 15) with different canal size of #70 (subgroup C70 and subgroup U70) and #120 (subgroup C120 and subgroup U120). After apical plug was created, a wet paper point was placed over the MTA plug and specimen was kept in a humid condition at room temperature to allow MTA to set. After 24 hours, remaining canal space was backfilled using Obtura II. All specimens were transferred to floral form socked by 0.2% rhodamine B solution and stored in 100% humidity at room temperature. After 48 hours, resin block specimens were washed and scanned using a scanner. The maximum length of microleakage was measured from the scanned images of four surfaces of each resin block using Photoshop 6.0.
Statistical analysis was performed with Mann-Whitney U test. Group U of UAHC had significantly lower leakage than Group C of HC in #70-size canal (subgroup U70) (p < 0.05).
- 991 View
- 2 Download

- Comparison of biocompatibility of four root perforation repair materials
- Min-Kyung Kang, In-Ho Bae, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):192-198. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was carried out in order to determine in vitro biocompatibility of white mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), and to compare it with that of the commonly used materials, i. e. calcium hydroxide liner (Dycal), glass ionomer cement (GIC), and Portland cement which has a similar composition of MTA. To assess the biocompatibility of each material, cytotoxicity was examined using MG-63 cells. The degree of cytotoxicity was evaluated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and a colorimetric method, based on reduction of the tetrazolium salt 2,3 bis {2methoxy 4nitro 5[(sulfenylamino) carbonyl] 2H tetrazolium hydroxide} (XTT) assay.
The results of SEM revealed the cells in contact with GIC, MTA, and Portland cement at 1 and 3 days were apparently healthy. In contrast, cells in the presence of Dycal appeared rounded and detached. In XTT assay, the cellular activities of the cells incubated with all the test materials except Dycal were similar, which corresponded with the SEM observation. The present study supports the view that MTA is a very biocompatible root perforation repair material. It also suggests that cellular response of Portland cement and GIC are very similar to that of MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
Jeong-Ho Lee, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 222. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Min-Jae Oh, Yu-Na Jeong, In-Ho Bae, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 359. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 344. CrossRef
- The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
- 1,468 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
- Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):397-404. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.397
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of MTAD, EDTA and sodium hypochlorite(NaOCl) as final irrigants on coronal leakage resistance to
Enterococcus faecalis . Forty extracted human maxillary molars were used in this experiment. The teeth were randomly divided into positive control group (Group 1; n = 5), negative control group (Group 2; n = 5) and three experimental groups (n = 30). In Group 3 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. In Group 4 (n = 10) and 5 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite and rinsed with EDTA and MTAD, respectively. The teeth in each group were cleaned and shaped to #40 profile with .04 taper, and obturated with gutta-percha and AH-26 root canal sealer. The coronal portion of each tooth was placed in contact with inoculum ofEnterococcus faecalis in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) culture media. Each root tip was placed in a vial containing sterile culture media. The vials were placed in anaerobic chamber and observed everyday for turbidity for 180 days. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher's Exact Test. After 180 days, Group 3, 4, and 5 showed 7, 4 and 5 leaking samples respectively. The differences in leakage resistance were not statistically significant among Group 3, 4 and 5.
- 2,033 View
- 6 Download

- Ingredients and cytotoxicity of MTA and 3 kinds of Portland cements
- Seok-Woo Chang, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Dong Sung Park, Tae-Seok Oh, Kwang-Shik Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):369-376. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.369
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to compare the compositions and cytotoxicity of white ProRoot MTA (white mineral trioxide aggregate) and 3 kinds of Portland cements. The elements, simple oxides and phase compositions of white MTA (WMTA), gray Portland cement (GPC), white Portland cement (WPC) and fast setting cement (FSC) were measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD). Agar diffusion test was carried out to evaluate the cytotoxicity of WMTA and 3 kinds of Portland cements.
The results showed that WMTA and WPC contained far less magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) than GPC and FSC. FSC contained far more aluminum oxide (Al2O3) than WMTA, GPC, and WPC. WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC were composed of main phases, such as tricalcicium silicate (3CaO·SiO2), dicalcium silicate (2CaO·SiO2), tricalcium aluminate (3CaO·Al2O3), and tetracalcium aluminoferrite (4CaO·Al2O3·Fe2O3). The significance of the differences in cellular response between WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC was statistically analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis Exact test with Bonferroni's correction. The result showed no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05).
WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC showed similar compositions. However there were notable differences in the content of minor elements, such as aluminum (Al), magnesium, iron, manganese, and zinc. These differences might influence the physical properties of cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Multi-functional Composite Cement with Strength Improvement Using Disposable Waste Masks
Jong-Won Chung, Hyun-Kyoung Yang
Journal of Power System Engineering.2022; 26(3): 31. CrossRef - The effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on osteo/odontogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive and systematic literature review
Danial Babaki, Sanam Yaghoubi, Maryam M. Matin
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2020; 7(1): 175. CrossRef - Remineralization of demineralized dentin using a dual analog system
Neha Saxena, Stefan Habelitz, Grayson W. Marshall, Laurie B. Gower
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2019; 22(S1): 76. CrossRef - Chemical analysis and biological properties of two different formulations of white portland cements
Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Norhayati Luddin, Thirumulu Ponnuraj Kannan, Khairani Idah Mokhtar, Azlina Ahmad
Scanning.2016; 38(4): 303. CrossRef - In vitrocytotoxicity of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements on human monocytes, a colorimetric MTT assay
Sedigheh Khedmat, Somayyeh Dehghan, Jamshid Hadjati, Farimah Masoumi, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 149. CrossRef - Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 258. CrossRef - Chemical characteristics of mineral trioxide aggregate and its hydration reaction
Seok-Woo Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 188. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 344. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 473. CrossRef - Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 445. CrossRef - A bioactivity study of Portland cement mixed with β-glycerophosphosphate on human pulp cell
Young-Hwan Oh, Young-Joo Jang, Yong-Bum Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of biocompatibility of four root perforation repair materials
Min-Kyung Kang, In-Ho Bae, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 208. CrossRef
- Development of Multi-functional Composite Cement with Strength Improvement Using Disposable Waste Masks
- 1,418 View
- 3 Download
- 13 Crossref

-
Tissue response of Pro-Root® MTA with
rh BMP-2 in pulpotomized rat teeth - Kyungtae Park, Wonkyung Yang, Hyunjung Ko, Miri Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):403-410. Published online September 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.403
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate whether
rh BMP-2 (BMP2) could induce synergistic effect with Pro-Root® MTA (MTA) in pulpotomized teeth in the rats. Healthy upper first molars from thirty-two, 10 weeks old, Sprague-Dawley rats were used for this investigation. The molars were exposed with round bur, and light pressure was applied with sterilized cotton to control hemorrhage. 1.2 grams of MTA cement was placed in right first molars as a control group. In left first molars, 1 µg of BMP2 was additionally placed on exposed pulps with MTA. All cavities were back-filled with light-cured glass-ionomer cements. The rats were sacrificed after 2 weeks and 7 weeks, respectively. Then histologic sections were made and assessed by light microscopy. Data were statistically analyzed via student t-test with SPSSWIN 12.0 program (p < 0.05).Inflammation observed in 2 weeks groups were severe compared to the 7 weeks groups. But the differences were not statistically significant. BMP2-addition groups had less inflammation than MTA groups in both periods, though these differences were also not statistically significant. In conclusion, the combination of BMP2 and MTA showed no differences with MTA only for pulpotomy of rat teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A bioactivity study of Portland cement mixed with β-glycerophosphosphate on human pulp cell
Young-Hwan Oh, Young-Joo Jang, Yong-Bum Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 415. CrossRef
- A bioactivity study of Portland cement mixed with β-glycerophosphosphate on human pulp cell
- 1,310 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of mineral trioxide aggregate on the production of growth factors and cytokine by human periodontal ligament fibroblasts
- Ji-Yoon Kwon, Sung-Sam Lim, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae, Myung-Hoe Kang, Woocheol Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):191-197. Published online May 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) would influence healing of periapical tissues by modulating the production of growth factors and cytokines from PDL fibroblasts, however, the studies are insufficient. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to monitor the expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1), fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) from PDL fibroblasts in the presence of MTA. The human PDL fibroblasts were seeded onto the set MTA or IRM at a level of 1 × 105 cells per unit well, and further incubated for 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours. The levels of TGF-β1, FGF-2, and IL-6 from the supernatant were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. The level of TGF-β1 was down-regulated when the cells were grown in the presence of MTA except at 6 hours. The levels of FGF-2 release were significantly suppressed when PDL fibroblasts were grown in the presence of MTA or IRM at all time intervals (p < 0.05). The expressions of IL-6 from MTA treated cells were comparable to those of untreated control cells throughout the observation periods. We presume that this material inhibits the stimulatory function of growth factors on granulation tissue formation and in turn, it promotes the healing process modulated by other bone-remodeling cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Osteo/odontogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Platelet-rich Plasma and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Shanthi Vanka, Amit Vanka, Sandeep Kumar Vishwakarma, Manohar K Bhat, Othman Wali, Aleem A Khan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(10): 1171. CrossRef - The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
Jeong-Ho Lee, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 222. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Min-Jae Oh, Yu-Na Jeong, In-Ho Bae, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 359. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 473. CrossRef - Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 208. CrossRef
- Osteo/odontogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Platelet-rich Plasma and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
- 1,514 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Pulp response of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium sulfate or calcium hydroxide
- Young-Ran Yun, In-Seok Yang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Hong-Ran Choi, Suk-Ja Yoon, Sun-Hun Kim, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):95-101. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was performed to verify the possibility of MTA and calcium sulfate as a pulp capping agent through comparing the dental pulp response in dogs after capping with MTA, calcium sulfate, and calcium hydroxide.
24 teeth of 2 dogs, 8 month old, were used in this study.
Under general anesthesia, cervical cavities were prepared and pulp was exposed with sterilized #2 round bur in a high speed handpiece.
MTA, calcium hydroxide, and calcium sulfate were applied on the exposed pulp. Then the coronal openings were sealed with IRM and light-cured composite.
Two months after treatment, the animals were sacrificed. The extracted teeth were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin solution and were decalcified in formic acid-sodium citrate. They were prepared for histological examination in the usual manner. The sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin.
In MTA group, a hard tissue bridges formation and newly formed odontoblasts layer was observed. There was no sign of pulp inflammatory reaction in pulp tissue.
In calcium hydroxide group, there was no odontoblast layer below the dentin bridge. In pulpal tissue, chronic inflammatory reaction with variable intensity and extension occurred in all samples.
In calcium sulfate group, newly formed odontoblast layer was observed below the bridge. Mild chronic inflammation with a few neutrophil infiltrations was observed on pulp tissue.
These results suggest that MTA is more biocompatible on pulp tissue than calcium hydroxide or calcium sulfate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the exposure site on histological pulpal responses after direct capping with 2 calcium-silicate based cements in a rat model
Panruethai Trongkij, Supachai Sutimuntanakul, Puangwan Lapthanasupkul, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Rebecca Wong, Danuchit Banomyong
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 258. CrossRef - Comparison of gene expression profiles of human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 397. CrossRef - Pulp response of beagle dog to direct pulp capping materials: Histological study
Ji-Hyun Bae, Young-Gyun Kim, Pil-Young Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Yong-Hoon Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 5. CrossRef - Gene expression profiling in human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 152. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Min-Jae Oh, Yu-Na Jeong, In-Ho Bae, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 359. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 473. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 344. CrossRef - The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
Jeong-Ho Lee, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 222. CrossRef - Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 208. CrossRef - Comparison of biocompatibility of four root perforation repair materials
Min-Kyung Kang, In-Ho Bae, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 192. CrossRef - A bioactivity study of Portland cement mixed with β-glycerophosphosphate on human pulp cell
Young-Hwan Oh, Young-Joo Jang, Yong-Bum Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 415. CrossRef
- Effects of the exposure site on histological pulpal responses after direct capping with 2 calcium-silicate based cements in a rat model
- 1,547 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- An electrochemical study of the sealing ability of three retrofilling materials
- Dong-Sung Park, Suh-Jin Sohn, Tae-Seok Oh, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Chan-Je Park, Soon-Ho Yim, Young-Kyoo Lee, Seung-Bum Kye
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):365-369. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.365
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the apical sealing ability of Super-EBA, MTA and Dyract-flow as retrofilling materials. Forty-eight extracted human teeth with straight and single root canal were used in this study. The root canals were prepared to a #40 apical canal size and obturated with gutter-percha. Apicoectomies were performed and root end cavities were prepared to a depth of 3mm using an ultrasonic device. The root end cavities were filled with Super-EBA, MTA or Dyract-flow. Leakage was measured using an electrochemical technique for 4 weeks.
According to this study, the results were as follows.
1. Increasing leakage with time was observed in all groups.
2. No significant difference was noted among the 3 groups with time (p = 0.216).
3. No significant difference was noted among the 3 groups when measured within the same time interval (p = 0.814).
The results of this study suggest that the sealing ability of Dyract-flow is equal to that of Super-EBA and MTA, and Dyract-flow may be an alternative to other materials for root-end filling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Sealing Effect and Working Time of Root Canal Filling MTA Materials
Hyojin Kim, Youngjin Kim, Soonhyeun Nam, Kwon Taeyub, Hyunjung Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2016; 43(2): 129. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Sealing Effect and Working Time of Root Canal Filling MTA Materials
- 1,551 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Spectrophotometric evaluation of sealing effects of several root-end filling materials
- Jin-Gyu Yi, Sang-Jin Park, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):449-456. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.449
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the sealing effect of several root-end filling materials using spectrophotometric analysis. 180 single root teeth with one canal were instrumented and canal filled. Root resected and root end preparation was made. Teeth were randomly classified to 5 experimental group(MTA, EBA, IRM, TCP, ZOE) and 1 control group according to root-end filling material MTA group used PRO ROOT MTA, EBA group used Super EBA, TCP group used NEW APATITE LINER TYPE II main component of which is α-tricalcium phosphate(TCP). According to manufacture's instruction experimental material was mixed and retrfilled. After 2% methylene blue solution penetration absorbance for each test sample was measured with spectrophotometer (JASCO UV-530, Japan).
The mean absorbance of control and experimental group was as follows;
MTA : 0.092, IRM : 0.226, Super EBA : 0.255, ZOE : 0.374, Control : 0.425, TCP : 0.501 and the result analyzed by Turkey test at P=0.05 level.
Conclusions of this study are as follows;
The absorbance increase in follwing sequence MTA, IRM, Super EBA, ZOE, Control, TCP.
MTA showed the least leakage but was not significant with IRM or Super EBA and was significant with control or TCP(p<0.05).
TCP had the most leakage and was not significant with control group.
- 857 View
- 4 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


