Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
- Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e37. Published online October 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
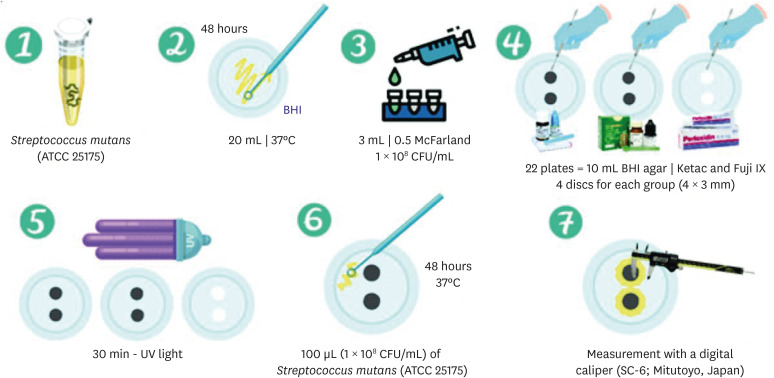
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the physical-mechanical, chemical, and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements (GICs).
Materials and Methods Different proportions of graphene powder were incorporated into 2 high-viscosity self-curing GIC, Ketac Molar (GKetac) and Fuji IX (GFuji), in 4 different concentrations: 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 5%. The control groups included the GICs without graphene. Experiments were performed to analyze linear (Ra) and volumetric roughness (Sa), antimicrobial activity, radiopacity, fluoride release, microhardness, solubility, and water sorption. Data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis, Mann-Whitney, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance, and Tukey’s test (
p ≤ 0.05).Results The GKetac 0% and GFuji0% groups presented higher Ra (4.05 and 2.72) and Sa (4.76 and 5.16), respectively. No inhibition zone was observed, and the incorporation of graphene reduced radiopacity. Moreover, there was no influence on the solubility and water sorption after 21 days. A greater fluoride release was observed in the period of 7 days for most of the groups. After 21 days, GKetac 5%, 2%, and 1% presented higher releasing than 0% and 0.5% (
p ≤ 0.05).Conclusions The graphene incorporation improved the microhardness of GICs in lower concentrations. Graphene incorporation to GICs modified some physical-mechanical, and chemical, but not affected biological properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laboratory-Based Additive Modifications in Glass Ionomer Cements: A Scoping Review Using a Systematic Data Mining and Trend Analysis Framework (2015-2024)
Kenta Tsuchiya, Sharanbir K Sidhu, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, James Kit Hon Tsoi, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Journal of Dentistry.2026; : 106349. CrossRef
- Laboratory-Based Additive Modifications in Glass Ionomer Cements: A Scoping Review Using a Systematic Data Mining and Trend Analysis Framework (2015-2024)
- 2,621 View
- 169 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of different curing methods on the color stability of composite resins
- Massimo Pisano, Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Andrea Chiacchio, Marzio Galdi, Stefano Martina
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e33. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the effects of different polymerization strategies and the effectiveness of finishing and polishing procedures of composite resins on color stability.
Materials and Methods The samples were divided into 4 main groups according to the polymerization strategy, and all groups except the control group received surface treatment. Each group was subsequently divided into 3 subgroups respectively: Kuraray Clearfil Majesty ES-2 Classic, Premium and Universal. Approximately 24 hours after preparation of the samples, they were immersed for 7 days in a coffee solution. A first color measurement was performed after the preparation of the samples, the second measurement was performed after 7 days in the coffee solution. All measurements were carried out using a dental spectrophotometer to assess the CIE
L *a *b * color parameters.Results There was a statistically significant difference between ΔE values for different procedures (
p = 0.003); in particular, the differences were found only between the groups that received surface treatment and the control group. In addition, a statistically significant difference was observed between the values of ΔE for different composites in the different procedure groups.Conclusions Spectrophotometric analysis showed that the additional photopolymerization and oxygen inhibition procedures did not yield better results in relation to color stability. In addition, finishing and polishing provided better color stability compared to not performing these procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Abrasiveness and Bleaching Level of Toothpastes on Composite Resins: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Novel Brushing Simulator
Simge Meseli, Elif Alkan, Bora Korkut, Ozlem Kanar, Dilek Tagtekin
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(5): 2314. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Direct and Indirect Composite Restorations in Class II Tooth Preparations - An In vivo Study
Akshun Gupta, Garima Arora, Aprajita Mehta, Satish Sane, Siddhi Nevrekar, Apurva Nagrale
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 550. CrossRef - Micro- and Nanoplastics and the Oral Cavity: Implications for Oral and Systemic Health, Dental Practice, and the Environment—A Narrative Review
Federica Di Spirito, Veronica Folliero, Maria Pia Di Palo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Leonardo Aulisio, Stefano Martina, Luca Rinaldi, Gianluigi Franci
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 332. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 5,954 View
- 323 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of surrounding and underlying shades on the color adjustment potential of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer
- Mariana Silva Barros, Paula Fernanda Damasceno Silva, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e7. Published online December 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
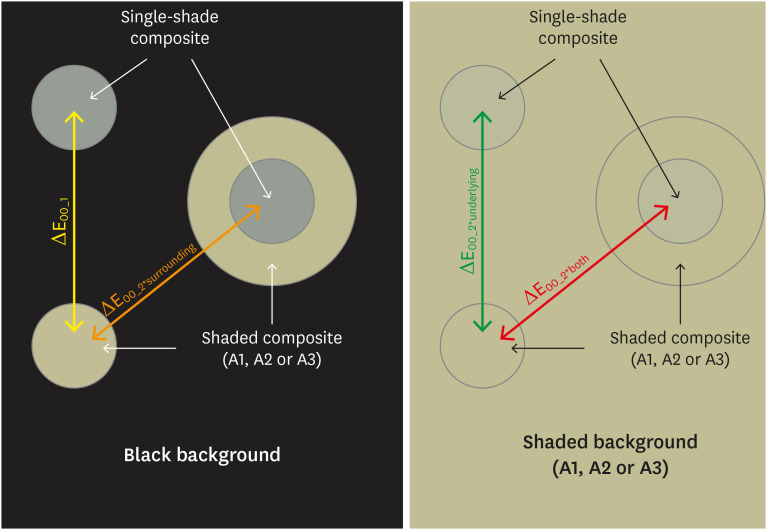
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the surrounding and underlying shades’ effect on the color adjustment potential (CAP) of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer.
Materials and Methods Cylinder specimens (1.0 mm thick) were built with the Vittra APS Unique composite, surrounded (dual specimens) or not (simple specimens) by a control composite (shade A1, A2, or A3). Simple specimens were also built only with the control composites. Each specimen’s color was measured against white and black backgrounds or the simple control specimens with a spectrophotometer (CIELAB system). The whiteness index for dentistry (WID) and translucency parameters (TP00) were calculated for simple specimens. Differences (ΔE00) in color between the simple/dual specimens and the controls were calculated. The CAP was calculated based on the ratios between data from simple and dual specimens.
Results The Vittra APS Unique composite showed higher WID and TP00 values than the controls. The highest values of ΔE00 were observed among simple specimens. The color measurements of Vittra APS Unique (simple or dual) against the control specimens presented the lowest color differences. Only surrounding the single-shade composite with a shaded composite barely impacted the ΔE00. The highest CAP values were obtained using a shaded composite under simple or dual specimens.
Conclusions The CAP of Vittra APS Unique was strongly affected by the underlying shade, while surrounding this composite with a shaded one barely affected its color adjustment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
Luciana Vasconcelos Ramos, Dayana Fernandes Rocha Aparicio, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva, Maíra do Prado, Andréa Vaz Braga Pintor, Marcela Baraúna Magno
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1567. CrossRef - Evaluation of color matching of three single-shade composites employing simulated 3D printed cavities with different thicknesses using CIELAB and CIEDE2000 color difference formulae
Engin Kariper, Aylin Cilingir
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of kombucha, coffee, and turmeric beverages on the color stability of a single-shade versus a multi-shade resin-based composite
Hanin E. Yeslam, Abdulaziz F. Bakhsh
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19759. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Esthetic Outcome of Pedo Shades of Composite Resin—A Randomized Controlled Trial: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
Priyanka Raj, Shikha Choubey, Divya Doneria, Diksha Bhat, Shivani Mathur, Shailja Sinha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(S1): S22. CrossRef - Influence of cavity wall thickness on the color adjustment potential of single-shade resin composites
Fabrício Luscino Alves de Castro, Letícia Brandão Durand
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2024; 155(7): 605. CrossRef - Assessing color mismatch in single-shade composite resins for enamel replacement
Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Diana Leyva Del Rio, Luiz Alves Oliveira-Neto, William Michael Johnston
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 132(3): 613.e1. CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Is It Possible for Single-shade Composites to Mimic the Color, Lightness, Chroma, and Hue of Other Single-shade Composites? An In Vitro Study
M Buldur, G Ayan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 691. CrossRef - Color evaluation of a one-shade used for restoration of non-carious cervical lesions: an equivalence randomized clinical trial
Michael Willian Favoreto, Amanda de Oliveira de Miranda, Thalita P. Matos, Andrea dos Santos de Castro, Mylena de Abreu Cardoso, Julia Beatriz, Jenny Collantes-Acuña, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Thickness on the Translucency Parameter and Whiteness Index of Single-Shade Resin Composites
Ö Yağcı, M Fidan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(2): 189. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Ishihara Test With Various Displays
Thomas Klinke, Wolfgang Hannak, Klaus Böning, Holger Jakstat
International Dental Journal.2024; 74(4): 892. CrossRef - Color match evaluation using instrumental method for three single-shade resin composites before and after in-office bleaching
Aylin Cilingir, Engin Kariper
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of interface distance and underlying substrate on the color adjustment potential of single‐shade composites
Gabriella Jesus Santos de Livi, Tauan Rosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, Rosa Maria Viana de Bragança Garcez, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1279. CrossRef
- At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
- 4,466 View
- 95 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e2. Published online December 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
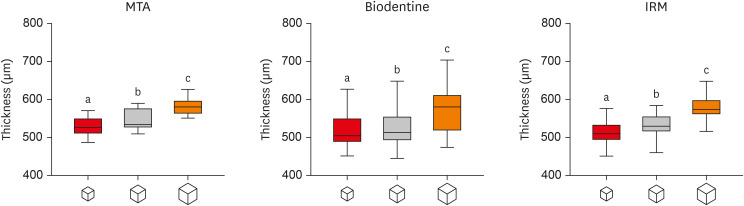
ePub Objectives This study investigated the impact of micro-computed tomography (micro-CT)-based voxel size on the analysis of material/dentin interface voids and thickness of different endodontic cements.
Materials and Methods Following root-end resection and apical preparation, maxillary premolars were filled with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and intermediate restorative material (IRM) (
n = 24). The samples were scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272; Bruker) and the cement/dentin interface and thickness of materials were evaluated at voxel sizes of 5, 10, and 20 µm. Analysis of variance and the Tukey test were conducted, and the degree of agreement between different voxel sizes was evaluated using the Bland and Altman method (p < 0.05).Results All materials showed an increase in thickness from 5 to 10 and 20 µm (
p < 0.05). When evaluating the interface voids, materials were similar at 5 µm (p > 0.05), while at 10 and 20 µm Biodentine showed the lowest percentage of voids (p < 0.05). A decrease in the interface voids was observed for MTA and IRM at 20 µm, while Biodentine showed differences among all voxel sizes (p < 0.05). The Bland-Altman plots for comparisons among voxel sizes showed the largest deviations when comparing images between 5 and 20 µm.Conclusions Voxel size had an impact on the micro-CT evaluation of thickness and interface voids of endodontic materials. All cements exhibited an increase in thickness and a decrease in the void percentage as the voxel size increased, especially when evaluating images at 20 µm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
Shuting Feng, Weiqing Zhou, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1380. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef
- Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
- 1,949 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Spectrophotometric evaluation of restorative composite shades and their match with a classical shade guide
- Rafael Melara, Luciana Mendonça, Fábio Herrmann Coelho-de-Souza, Juliana Nunes Rolla, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e60. Published online November 12, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to verify the match between 5 shades of composites from different manufacturers with a shade guide and among the systems using a portable spectrophotometer.
Materials and Methods Shade measurements were performed on specimens of Z350 XT (3M ESPE), Charisma Diamond (Heraeus Kulzer GmbH), Esthet X-HD (Dentsply Caulk), and Empress Direct (Ivoclar-Vivadent) for shades A1, A2, A3, B1, and C3 using a Vita Easyshade spectrophotometer (Vita Zahnfabrik) against a white background. Corresponding shades of Vitapan Classical (Vita Zahnfabrik) guide were measured likewise and shade variation (ΔE) was calculated based on International Commission on Illumination L*a*b* parameters. The ΔE of the composites in each shade was compared by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's
post hoc test (α = 0.05).Results All composites presented ΔE > 3.7 compared with the shade guide. Variation in shades A3, B1, and C3 was significantly different for all composites. ΔE of Z350 XT was significantly lower for A1 than for the other shades, whereas ΔE of Z350 XT and Charisma Diamond were significantly lower for A2 than for the other shades.
Conclusions No composite shade matched with the shade guide. Equivalent shades of the restorative composite from different manufacturers may show clinically noticeable ΔE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Instrumental and visual evaluation of the color adjustment potential of a recently introduced single‑shade composite resin versus multishade composite resins
Jiakang Zhu, Yue Xu, Mengxun Li, Cui Huang
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(3): 832. CrossRef - Evaluation of the roughness, color match, and color stability of two monochromatic composite resins: a randomized controlled laboratory study
Iara Campos Santana, Sabrina Sobral de Oliveira, Karolina Pena Botelho, Renan Leonardi de Oliveira Rigotti, José Cristiano Ramos Glória, Adriana Maria Botelho, Dhelfeson Willya Douglas-de-Oliveira, Karine Taís Aguiar Tavano
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different finishing and polishing protocols of composite CAD CAM blocks on surface roughness and biological response of gingival mesenchymal stem cells
Mohamed F. Haridy, Mohamed Shamel, Raghda A. Khalil, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Hoda Fouda, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Instrumental and Visual Evaluation of the Chameleon Effect of Single-shaded Composite Resins
RM Adiguzel, LK Kose, N Arhun
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 432. CrossRef - Color Stability of Bioactive Restorative Material vs Nanohybrid Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
Esraa H Saber, Mohsen H Abielhassan, Yasser A Abed, Shereen E Fahim
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(3): 221. CrossRef - A system for reliable composite shade matching: Custom shade tabs and an intra‐oral mockup
Adamo Notarantonio, Amanda Seay
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(5): 787. CrossRef - Color Stability of Bioactive Restorative Materials After Immersion in Various Media
Shara I Sajini, Ali B Mushayt, Talal A Almutairi, Roaa Abuljadayel
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2022; 12(4): 418. CrossRef
- Instrumental and visual evaluation of the color adjustment potential of a recently introduced single‑shade composite resin versus multishade composite resins
- 1,893 View
- 29 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

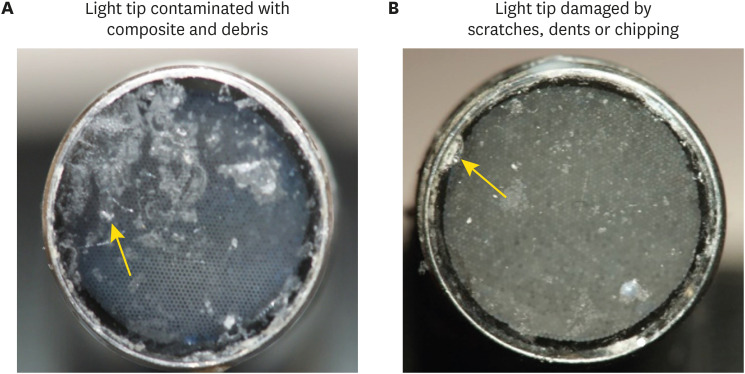
- Assessment of the radiant emittance of damaged/contaminated dental light-curing tips by spectrophotometric methods
- Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora Garcia, Fabrício Collares, Cristopher M. Felix, Nisha Ganesh, Qoot Alkabashi, Ward Massei, Howard Strassler, Mary Anne Melo
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e55. Published online November 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effects of physically damaged and resin-contaminated tips on radiant emittance, comparing them with new undamaged, non-contaminated tips using 3 pieces of spectrophotometric laboratory equipment.
Materials and Methods Nine tips with damage and/or resin contaminants from actual clinical situations were compared with a new tip without damage or contamination (control group). The radiant emittance was recorded using 3 spectrophotometric methods: a laboratory-grade thermopile, a laboratory-grade integrating sphere, and a portable light collector (checkMARC).
Results A significant difference between the laboratory-grade thermopile and the laboratory-grade integrating sphere was found when the radiant emittance values of the control or damaged/contaminated tips were investigated (
p < 0.05), but both methods were comparable to checkMARC (p > 0.05). Regardless of the method used to quantify the light output, the mean radiant emittance values of the damaged/contaminated tips were significantly lower than those of the control (p < 0.05). The beam profile of the damaged/contaminated tips was less homogeneous than that of the control.Conclusions Damaged/contaminated tips can reduce the radiant emittance output and the homogeneity of the beam, which may affect the energy delivered to composite restorations. The checkMARC spectrophotometer device can be used in dental offices, as it provided values close to those produced by a laboratory-grade integrated sphere spectrophotometer. Dentists should assess the radiant emittance of their light-curing units to ensure optimal curing in photoactivated, resin-based materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of damage or contamination to the tips of 200 light-curing units
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Hassan A. Alyami, Husain A. Almakrami, Osama A. Alsulaiman, Eman H. Ismail, Richard B. Price, Ahmed A. Alsulaiman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Performance of Light-curing Units Used in Different Clinics at Aseer Region, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-sectional Study
Mohammed M Al Moaleem, Ghadeer S Alwadai, Nada A Alamoudi, Naif N Abogazalah, Saleh A Alqahtani, Faisal H Alshehri, Wafa H Alaajam, Mohammad A Alamri, Amjad Y Alhaydan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 784. CrossRef - Evaluation of Radiant Power of the Light Curing Units Used in Clinics at Governmental and Privates Dental Faculties
Sami Ali Hasan, Ibrahim Al-Shami, Mohsen Al-Hamzi, Ghadeer Alwadai, Nada Alamoudi, Saleh Alqahtani, Arwa Daghrery, Wafa Alaajam, Mansoor Shariff, Hussain Kinani, Mohammed Al Moaleem
Medical Devices: Evidence and Research.2024; Volume 17: 301. CrossRef - Evaluation of the information provided in the instruction manuals of dental light‐curing units
Afnan O. Al‐Zain, Eman H. Ismail, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Osamah Toras, Yousif Alharthy, Rafa Alsultan, Abeer Alrossais, Richard B. Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(10): 1466. CrossRef - Utilizing Light Cure Units: A Concise Narrative Review
Fatin A. Hasanain, Hani M. Nassar
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1596. CrossRef - Improper Light Curing of Bulkfill Composite Drives Surface Changes and Increases S. mutans Biofilm Growth as a Pathway for Higher Risk of Recurrent Caries around Restorations
Haifa Maktabi, Maria Salem Ibrahim, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Qoot Alkhubaizi, Isadora Martini Garcia, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares, Howard Strassler, Ana Paula P. Fugolin, Carmem S. Pfeifer, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(8): 83. CrossRef
- Effect of damage or contamination to the tips of 200 light-curing units
- 1,576 View
- 8 Download
- 6 Crossref

-
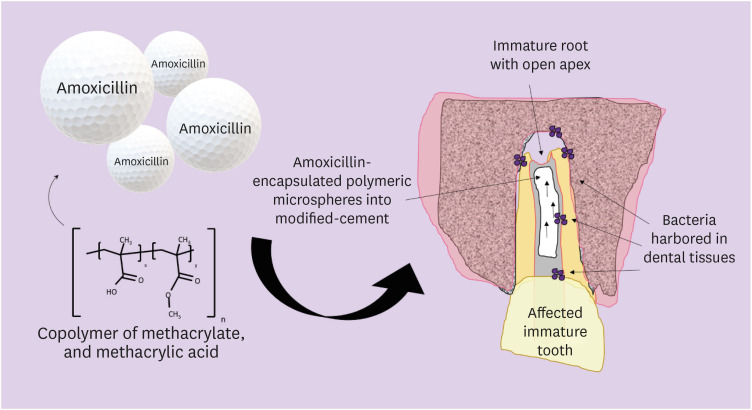
Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an
in vitro study - Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e50. Published online October 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we investigated the potential of amoxicillin-loaded polymeric microspheres to be delivered to tooth root infection sites via a bioactive reparative cement.
Materials and Methods Amoxicillin-loaded microspheres were synthesized by a spray-dray method and incorporated at 2.5% and 5% into a mineral trioxide aggregate cement clinically used to induce a mineralized barrier at the root tip of young permanent teeth with incomplete root development and necrotic pulp. The formulations were modified in liquid:powder ratios and in composition by the microspheres. The optimized formulations were evaluated
in vitro for physical and mechanical eligibility. The morphology of microspheres was observed under scanning electron microscopy.Results The optimized cement formulation containing microspheres at 5% exhibited a delayed-release response and maintained its fundamental functional properties. When mixed with amoxicillin-loaded microspheres, the setting times of both test materials significantly increased. The diametral tensile strength of cement containing microspheres at 5% was similar to control. However, phytic acid had no effect on this outcome (
p > 0.05). When mixed with modified liquid:powder ratio, the setting time was significantly longer than that original liquid:powder ratio (p < 0.05).Conclusions Lack of optimal concentrations of antibiotics at anatomical sites of the dental tissues is a hallmark of recurrent endodontic infections. Therefore, targeting the controlled release of broad-spectrum antibiotics may improve the therapeutic outcomes of current treatments. Overall, these results indicate that the carry of amoxicillin by microspheres could provide an alternative strategy for the local delivery of antibiotics for the management of tooth infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Local drug delivery for regeneration and disinfection in endodontics: A narrative review
Anu Elsa Swaroop, Sylvia Mathew, P. Harshini, Shruthi Nagaraja
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 119. CrossRef - Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate—A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements
C. Pushpalatha, Vismaya Dhareshwar, S. V. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Thilla Sekar Vinothkumar, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Amal Shaiban, Ateet Kakti, Shilpa H. Bhandi, Alok Dubey, Amulya V. Rai, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Local drug delivery for regeneration and disinfection in endodontics: A narrative review
- 1,662 View
- 11 Download
- 3 Crossref

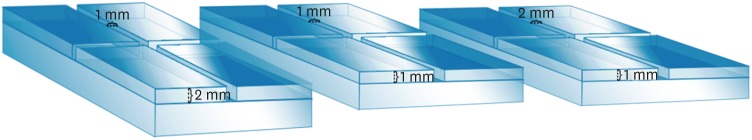
- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e11. Published online January 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the flow and filling of several retrograde filling materials using new different test models.
Materials and Methods Glass plates were manufactured with a central cavity and 4 grooves in the horizontal and vertical directions. Grooves with the dimensions used in the previous study (1 × 1 × 2 mm; length, width, and height respectively) were compared with grooves measuring 1 × 1 × 1 and 1 × 2 × 1 mm. Biodentine, intermediate restorative material (IRM), and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) were evaluated. Each material was placed in the central cavity, and then another glass plate and a metal weight were placed over the cement. The glass plate/material set was scanned using micro-computed tomography. Flow was calculated by linear measurements in the grooves. Central filling was calculated in the central cavity (mm3) and lateral filling was measured up to 2 mm from the central cavity.
Results Biodentine presented the least flow and better filling than IRM when evaluated in the 1 × 1 × 2 model. In a comparison of the test models, MTA had the most flow in the 1 × 1 × 2 model. All materials had lower lateral filling when the 1 × 1 × 2 model was used.
Conclusions Flow and filling were affected by the size of the test models. Higher grooves and materials with greater flow resulted in lower filling capacity. The test model measuring 1 × 1 × 2 mm showed a better ability to differentiate among the materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical, chemical and biological properties of MTA Angelus and novel AGM MTA: an in vitro analysis
Sara Nashibi, Parisa Amdjadi, SeyedehSana Ahmadi, Sara Hekmatian, Maryam Torshabi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Evaluation of the physical properties of bromelain-modified biodentine for direct pulp capping
Paridhi Agrawal, Manoj Chandak, Aditya Patel, Jay Bhopatkar
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef
- Physical, chemical and biological properties of MTA Angelus and novel AGM MTA: an in vitro analysis
- 1,533 View
- 14 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Unwanted effects due to interactions between dental materials and magnetic resonance imaging: a review of the literature
- Sherin Jose Chockattu, Deepak Byathnal Suryakant, Sophia Thakur
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e39. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
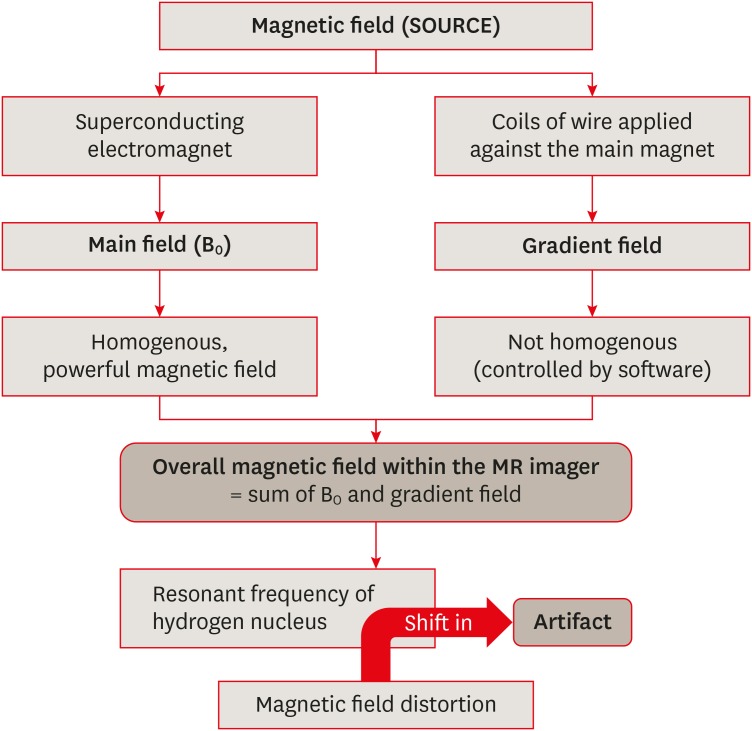
ePub Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an advanced diagnostic tool used in both medicine and dentistry. Since it functions based on a strong uniform static magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses, it is advantageous over imaging techniques that rely on ionizing radiation. Unfortunately, the magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses generated within the magnetic resonance imager interact unfavorably with dental materials that have magnetic properties. This leads to unwanted effects such as artifact formation, heat generation, and mechanical displacement. These are a potential source of damage to the oral tissue surrounding the affected dental materials. This review aims to compile, based on the current available evidence, recommendations for dentists and radiologists regarding the safety and appropriate management of dental materials during MRI in patients with orthodontic appliances, maxillofacial prostheses, dental implants, direct and indirect restorative materials, and endodontic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck: Unwanted effects caused by implant-supported restorations fabricated with different alloys
Lauren Bohner, Dieter Dirksen, Marcel Hanisch, Newton Sesma, Johannes Kleinheinz, Norbert Meier
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(6): 1574. CrossRef - The influence of preformed metal crowns versus zirconia crowns on the diagnostic quality of magnetic resonance images
O. Dalzell, P. Haghighi, J. Ho, T. Rayner, L. Vidarsson, G. A. Garisto
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2025; 26(1): 109. CrossRef - Interference of titanium and zirconia implants on dental-dedicated MR image quality: ex vivo and in vivo assessment
Katrine M Johannsen, Jennifer Christensen, Louise Hauge Matzen, Brian Hansen, Rubens Spin-Neto
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2025; 54(2): 132. CrossRef - Accuracy of Ionizing‐Radiation‐Based and Non‐Ionizing Imaging Assessments for the Diagnosis of Periodontitis: Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Nicola Discepoli, Isabella De Rubertis, Cecile Wasielewski, Giuseppe Troiano, Maria Clotilde Carra
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2025; 52(S29): 74. CrossRef - The Effect of MRI Exposure on the Shear Bond Strength and Adhesive Remnant Index of Different Bracket Types
Luka Šimunović, Jakov Stojanović, Katarina Tečić, Dijana Zadravec, Senka Meštrović
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 108. CrossRef - Impact of Artifacts Caused by Intraoral Dental Materials in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Divya Josephraj, Ravindranath Vineetha, Priya Pattath Sankaran, Prakashini Koteshwara, Mathangi Kumar, Kalyana Chakravarthy Pentapati
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Orthodontic appliances and their diagnostic impact to brain MRI
Lisa Latzko, Anna Schmit, Bernhard Glodny, Astrid E. Grams, Christoph Birkl, Adriano G. Crismani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Intra-Oral Dental Materials on Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Perspective Survey from Dental Professionals
Sejal Gupta, Mathangi Kumar, Kalyana C Pentapati, Ravindranath Vineetha, Vinu Thomas George, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal, Priya Pattath Sankaran
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S551. CrossRef - Beyond radiation: Emerging applications of MRI in dental diagnostics and clinical practice
Gerta Halilaj, Nebi Cemeta
Journal of Dentistry and Multidisciplinary Sciences.2025; 1(1): 31. CrossRef - Nonionizing diagnostic imaging modalities for visualizing health and pathology of periodontal and peri‐implant tissues
Andy Wai Kan Yeung, Abeer AlHadidi, Rutvi Vyas, Michael M. Bornstein, Hiroshi Watanabe, Ray Tanaka
Periodontology 2000.2024; 95(1): 87. CrossRef - Cortical thickness and grey-matter volume anomaly detection in individual MRI scans: Comparison of two methods
David Romascano, Michael Rebsamen, Piotr Radojewski, Timo Blattner, Richard McKinley, Roland Wiest, Christian Rummel
NeuroImage: Clinical.2024; 43: 103624. CrossRef - Association between dental restorations and artefacts on head magnetic resonance images in paediatric patients
Pitchaya Tunlayadechanont, Padcha Tunlayadechanont, Nantana Sriudomporn, Ploy Wisetsathon, Duangporn Duangthip, Varangkanar Jirarattanasopha
International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry.2024; 34(5): 546. CrossRef - Commercially Pure Titanium Implants With Selenium and Hyaluronic Acid Coating for Dental Applications
Soorya Ganesh, Gheena S, Kalaiyarasan Madhu
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multibraided Fixed Retainers with Different Diameters after Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): In Vitro Study Investigating Temperature Changes and Bonding Efficacy
Maria Francesca Sfondrini, Maurizio Pascadopoli, Paola Gandini, Lorenzo Preda, Domenico Sfondrini, Karin Bertino, Cinzia Rizzi, Andrea Scribante
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 255. CrossRef - Chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis of the mandible – orthodontic considerations and management: A case report
Saskia Andrea Schwabe, Sean Booth, Susi Caldwell
Journal of Orthodontics.2024; 51(4): 415. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of periodontal and periapical disease
Katrine Mølgaard Johannsen, João Marcus de Carvalho E Silva Fuglsig, Louise Hauge Matzen, Jennifer Christensen, Rubens Spin-Neto
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Surveillance of head neck cancer: Case for personalized and standardized surveillance
Shrikant B. Mali
Oral Oncology.2023; 139: 106354. CrossRef - Effect of Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 1.5 T and 3 T on Temperature and Bond Strength of Orthodontic Bands with Welded Tubes: An In Vitro Study
Maria Francesca Sfondrini, Simone Gallo, Maurizio Pascadopoli, Cinzia Rizzi, Andrea Boldrini, Simone Santagostini, Luca Anemoni, Maria Sole Prevedoni Gorone, Lorenzo Preda, Paola Gandini, Andrea Scribante
Materials.2023; 16(2): 651. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging artefacts caused by orthodontic appliances and/or implant-supported prosthesis: a systematic review
Katrine Mølgaard Johannsen, João Marcus de Carvalho E Silva Fuglsig, Brian Hansen, Ann Wenzel, Rubens Spin-Neto
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(2): 394. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging investigations in patients with metallic dental prosthesis: “The associated dilemma for medical fraternity and the dentist's role”
Ritika Bhambhani, SantanuSen Roy, Shubha Joshi
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2023; 23(2): 203. CrossRef - Recent advances in the application and biological mechanism of silicon nitride osteogenic properties: a review
Ziyi Liu, Ruijie Wang, Wenjing Liu, Yushan Liu, Xiaoli Feng, Fujian Zhao, Pei Chen, Longquan Shao, Mingdeng Rong
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(21): 7003. CrossRef - Techniques, Tricks, and Stratagems of Oral Cavity Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Davide Maraghelli, Michele Pietragalla, Linda Calistri, Luigi Barbato, Luca Giovanni Locatello, Martina Orlandi, Nicholas Landini, Antonio Lo Casto, Cosimo Nardi
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(3): 1473. CrossRef - GEÇICI VE DAIMI SIMANLARIN DENTINE OLAN BAĞLANMA DAYANIMI ÜZERINE MANYETIK REZONANS GÖRÜNTÜLEME İŞLEMININ ETKISININ ARAŞTIRILMASI
Melih ÜLGEY, Oğuzhan GÖRLER, İsmail ŞALK, Derya ÖZDEMİR DOĞAN
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Performance of PROPELLER FSE T2WI in reducing metal artifacts of material porcelain fused to metal crown: a clinical preliminary study
Wenjin Li, Jing Shi, Wenjin Bian, Jianting Li, Xiaoqing Chen, Juan Feng, Jiali Yu, Jun Wang, Jinliang Niu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tracking the Molecular Fingerprint of Head and Neck Cancer for Recurrence Detection in Liquid Biopsies
Araceli Diez-Fraile, Joke De Ceulaer, Charlotte Derpoorter, Christophe Spaas, Tom De Backer, Philippe Lamoral, Johan Abeloos, Tim Lammens
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(5): 2403. CrossRef - Review on Biocompatibility and Prospect Biomedical Applications of Novel Functional Metallic Glasses
Michał Biały, Mariusz Hasiak, Amadeusz Łaszcz
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 245. CrossRef - MRI compatibility of orthodontic brackets and wires: systematic review article
Adrienn Dobai, Fanni Dembrovszky, Tamás Vízkelety, Péter Barsi, Fanni Juhász, Csaba Dobó-Nagy
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The interaction and interference of preformed metal crowns on magnetic resonance imaging: a scoping review with a systematic methodology
O. Sumner, R. Goldsmith, N. Heath, G. D. Taylor
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2021; 22(6): 1023. CrossRef - An Evidence-based Protocol for the Management of Orthodontic Patients Undergoing MRI Scans
Rachael Shivam, Sheelagh Rogers, Nicholas Drage
Orthodontic Update.2021; 14(1): 32. CrossRef - Reversal of Osseointegration as a Novel Perspective for the Removal of Failed Dental Implants: A Review of Five Patented Methods
Rolf G. Winnen, Kristian Kniha, Ali Modabber, Faruk Al-Sibai, Andreas Braun, Reinhold Kneer, Frank Hölzle
Materials.2021; 14(24): 7829. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging as a diagnostic tool for periodontal disease: A prospective study with correlation to standard clinical findings—Is there added value?
Monika Probst, Egon Burian, Teresa Robl, Dominik Weidlich, Dimitrios Karampinos, Teresa Brunner, Claus Zimmer, Florian Andreas Probst, Matthias Folwaczny
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2021; 48(7): 929. CrossRef - An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review
Rodolfo Reda, Alessio Zanza, Alessandro Mazzoni, Andrea Cicconetti, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Journal of Imaging.2021; 7(5): 75. CrossRef - Implant-supported overdentures: part 1
David Gray, Jaymit Patel
British Dental Journal.2021; 231(2): 94. CrossRef - Oral and dental considerations in pediatric cancers
Priyanshi Ritwik, Tammuella E. Chrisentery-Singleton
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2020; 39(1): 43. CrossRef - Recent advances in bioelectronics chemistry
Yin Fang, Lingyuan Meng, Aleksander Prominski, Erik N. Schaumann, Matthew Seebald, Bozhi Tian
Chemical Society Reviews.2020; 49(22): 7978. CrossRef - Imaging of root canal treatment using ultra high field 9.4T UTE-MRI – a preliminary study
Maximilian Timme, Max Masthoff, Nina Nagelmann, Malte Masthoff, Cornelius Faber, Sebastian Bürklein
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2020; 49(1): 20190183. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging based computer‐guided dental implant surgery—A clinical pilot study
Florian Andreas Probst, Josef Schweiger, Maria Juliane Stumbaum, Dimitrios Karampinos, Egon Burian, Monika Probst
Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research.2020; 22(5): 612. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging artifacts produced by dental implants with different geometries
Lauren Bohner, Norbert Meier, Felix Gremse, Pedro Tortamano, Johannes Kleinheinz, Marcel Hanisch
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2020; 49(8): 20200121. CrossRef - Implications and Considerations of Dental Materials in MRI: A Case Report and Literature Review
Brenton J. Wilson, Phoebe E. O’hare, John Zacariah, Wen Lin Chai
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck: Unwanted effects caused by implant-supported restorations fabricated with different alloys
- 6,266 View
- 55 Download
- 39 Crossref

- Effects of a bleaching agent on properties of commercial glass-ionomer cements
- Fernanda Lúcia Lago de Camargo, Ailla Carla Lancellotti, Adriano Fonseca de Lima, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo Martins, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e32. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
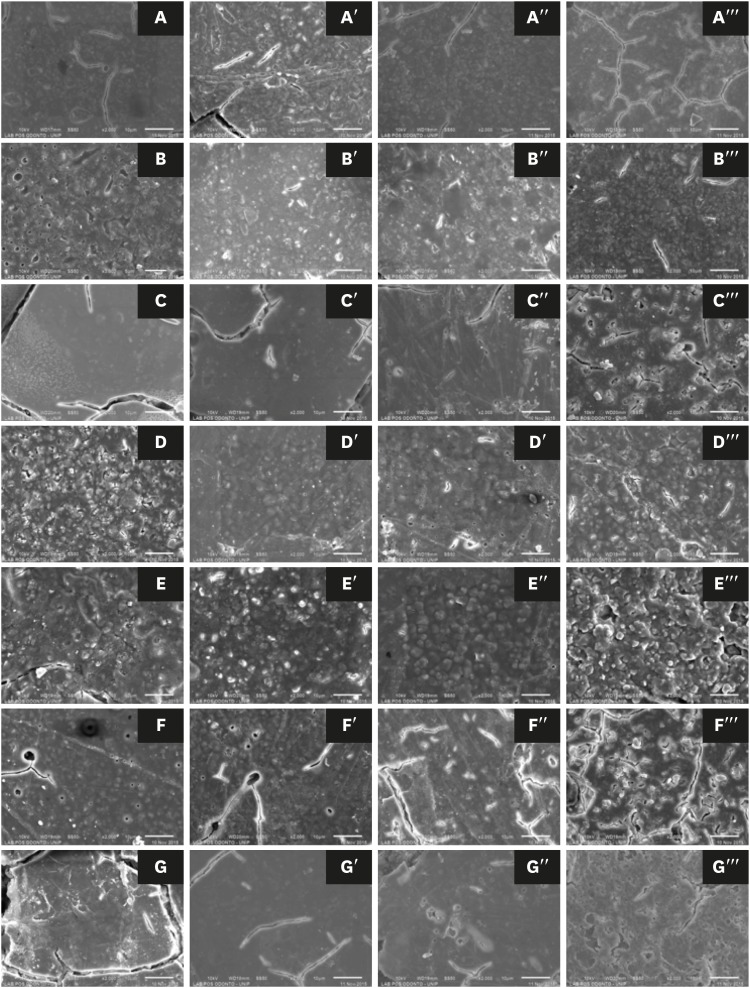
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of a bleaching agent on the composition, mechanical properties, and surface topography of 6 conventional glass-ionomer cements (GICs) and one resin-modified GIC.
Materials and Methods For 3 days, the specimens were subjected to three 20-minute applications of a 37% H2O2-based bleaching agent and evaluated for water uptake (WTK), weight loss (WL), compressive strength (CS), and Knoop hardness number (KHN). Changes in surface topography and chemical element distribution were also analyzed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. For statistical evaluation, the Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon paired tests (
α = 0.05) were used to evaluate WTK and WL. CS specimens were subjected to 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05), and KH was evaluated by one-way ANOVA, the Holm-Sidakpost hoc test (α = 0.05), and thet -test for independent samples (α = 0.05).Results The bleaching agent increased the WTK of Maxxion R, but did not affect the WL of any GICs. It had various effects on the CS, KHN, surface topography, and the chemical element distribution of the GICs.
Conclusions The bleaching agent with 37% H2O2 affected the mechanical and surface properties of GICs. The extent of the changes seemed to be dependent on exposure time and cement composition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multidisciplinary conservative management of a severely discolored nonvital tooth
Álvaro Ferrando Cascales, Francesc Abella Sans, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, José Amengual Lorenzo
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(4): 941. CrossRef - The effects of bleaching products on the color stability of ion-releasing restoratives
Jian Sheng Lee, Noor Azlin Yahya, Azwatee Abdul Aziz, Adrian U-Jin Yap
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Exploration of Interaction Mechanisms of Intracoronal Bleaching on the Compressive Strength of Conventional and Calcium Silicate–Based Self‐Adhesive Resins and Their Bonding to Composite Resin Restorative Material
Fereshteh Shafiei, Paria Dehghanian, Shadi Tivay, Yasamin Ghahramani, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharama, E. Terrer
EMC - Odontologie.2023; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Home and In-Office Bleaching on Microhardness and Color of Different CAD/CAM Ceramic Materials
Ruwaida Z. Alshali, Mohammed A. Alqahtani
Materials.2022; 15(17): 5948. CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharama, E. Terrer
EMC - Médecine buccale.2022; 15(4): 1. CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharam, E. Terrer
EMC - Orthopédie dentofaciale.2022; 34(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Glass Polyalkenoate Cements: An In Vivo Pilot Study Using a Sheep Model
Leyla Hasandoost, Daniella Marx, Paul Zalzal, Oleg Safir, Mark Hurtig, Cina Mehrvar, Stephen D. Waldman, Marcello Papini, Mark R. Towler
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2021; 12(3): 44. CrossRef - The Effect of Simulated Field Storage Conditions on Dental Restorative Materials for Military Field Use
David J Lemon, Wen Chen, Trevor Smith, April A Ford, Steven X Moffett, Jeffrey T Hoyle, Nicholas J Hamlin, Yoon Y Hwang
Military Medicine.2020; 185(5-6): e831. CrossRef
- Multidisciplinary conservative management of a severely discolored nonvital tooth
- 1,434 View
- 5 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Do conventional glass ionomer cements release more fluoride than resin-modified glass ionomer cements?
- Maria Fernanda Costa Cabral, Roberto Luiz de Menezes Martinho, Manoel Valcácio Guedes-Neto, Maria Augusta Bessa Rebelo, Danielson Guedes Pontes, Flávia Cohen-Carneiro
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):209-215. Published online May 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.209
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the fluoride release of conventional glass ionomer cements (GICs) and resin-modified GICs.
Materials and Methods The cements were grouped as follows: G1 (Vidrion R, SS White), G2 (Vitro Fil, DFL), G3 (Vitro Molar, DFL), G4 (Bioglass R, Biodinâmica), and G5 (Ketac Fil, 3M ESPE), as conventional GICs, and G6 (Vitremer, 3M ESPE), G7 (Vitro Fil LC, DFL), and G8 (Resiglass, Biodinâmica) as resin-modified GICs. Six specimens (8.60 mm in diameter; 1.65 mm in thickness) of each material were prepared using a stainless steel mold. The specimens were immersed in a demineralizing solution (pH 4.3) for 6 hr and a remineralizing solution (pH 7.0) for 18 hr a day. The fluoride ions were measured for 15 days. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test with 5% significance were applied.
Results The highest amounts of fluoride release were found during the first 24 hr for all cements, decreasing abruptly on day 2, and reaching gradually decreasing levels on day 7. Based on these results, the decreasing scale of fluoride release was as follows: G2 > G3 > G8 = G4 = G7 > G6 = G1 > G5 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions There were wide variations among the materials in terms of the cumulative amount of fluoride ion released, and the amount of fluoride release could not be attributed to the category of cement, that is, conventional GICs or resin-modified GICs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fluoride Uptake and Surface Characteristics of Ion-Releasing Restoratives After Brushing with Fluoride Toothpastes
Llubitza Slaviza Banic Vidal, Ivan Šalinović, Nikolina Nika Veček, Anja Ivica, Ivana Miletić, Silvana Jukić Krmek
Materials.2025; 18(9): 2152. CrossRef - Strategic approaches for enhancing the bioactivity of glass ionomer cement: A mechanistic and clinical perspective in terms of structural and surface modifications
Ali Saatchifard, Nader Nezafati, Saeed Hesaraki
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 163: 106126. CrossRef - Antibacterial effects of bioactive restorative dental materials on Streptococcus mutans: An in vitro study using the direct contact test
Sirirat Boondireke, Onsasi Kitrueangphatchara, Charnsak Sukajintanakarn, Sirichan Chiaraputt
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef -
Impact of biofilm model of
Streptococcus mutans
on the pH, ions release, and sorption/solubility of glass ionomer cements enriched with 45S5 bioglass
Fábia Regina Vieira de Oliveira Roma, Mayron Guedes Silva, Tarcisio Jorge Leitão de Oliveira, José Bauer, Leily Macedo Firoozmand
Biofouling.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Ion release of the glass ionomer restoration with silver diamine fluoride dentin pretreatment
Kelsey Xingyun Ge, Ryan Quock, Feng Yan, Walter Yu-Hang Lam, Chun-Hung Chu, Ollie Yiru Yu
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 148: 105247. CrossRef - Dual function of anti-biofilm and modulating biofilm equilibrium of orthodontic cement containing quaternary ammonium salt
Wenqi YU, Chaochao REN, Ning ZHANG, Li CAO, Michael D. WEIR, Kai YANG, Hockin H. K. XU, Yuxing BAI
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(2): 149. CrossRef - Fluoride exchange by glass-ionomer dental cements and its clinical effects: a review
John W. Nicholson, Sharanbir K. Sidhu, Beata Czarnecka
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Protective Surface Coating on Fluoride Release and Recharge of Recent Uncoated High-Viscosity Glass Ionomer Cement
Nantawan Krajangta, Chayanee Dulsamphan, Tongjai Chotitanmapong
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(12): 233. CrossRef - Reinforcing an immature tooth model using three different restorative materials
Pooja Misar, Hemalatha Hiremath, Chhaya Harinkhere, ShailendraS Sonawane, Vinay Sharma, KuldeepSingh Rana
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 28. CrossRef - Fluoride release from two types of fluoride-containing orthodontic adhesives: Conventional versus resin-modified glass ionomer cements—An in vitro study
Yasemin Dziuk, Sachin Chhatwani, Stephan C. Möhlhenrich, Sabrina Tulka, Ella A. Naumova, Gholamreza Danesh, Richard Johannes Wierichs
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0247716. CrossRef - Phosphate Ion Release and Alkalizing Potential of Three Bioactive Dental Materials in Comparison with Composite Resin
Shahin Kasraei, Sahebeh Haghi, Sara Valizadeh, Narges Panahandeh, Sogol Nejadkarimi, Shinn Jyh Ding
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - The effect of the polishing procedure and surface sealant application on the fluoride release of different restorative materials
Muhittin Ugurlu, Hikmet Orhan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(2): 135. CrossRef - Mechanical and antimicrobial property of different surface treated glass ionomer cements under desiccated condition
Hemalatha Hiremath, Chhaya Harinkhere, Pooja Misar, Kshitij Sabley, Trupti Bajpai
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 64. CrossRef - Dental Restorative Materials for Elderly Populations
Yuyao Huang, Bingqing Song, Xuedong Zhou, Hui Chen, Haohao Wang, Lei Cheng
Polymers.2021; 13(5): 828. CrossRef - Monomer conversion, dimensional stability, biaxial flexural strength, and fluoride release of resin-based restorative material containing alkaline fillers
Piyaphong PANPISUT, Arnit TONELUCK
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(4): 608. CrossRef - Factors influencing fluoride release in atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) materials: A review
P.Divya Kumari, Shahnawaz Khijmatgar, Avidyuti Chowdhury, Edward Lynch, Chitta R. Chowdhury
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2019; 9(4): 315. CrossRef - Incorporation of chlorhexidine and nano-sized sodium trimetaphosphate into a glass-ionomer cement: Effect on mechanical and microbiological properties and inhibition of enamel demineralization
Márjully Eduardo Rodrigues da Silva, Marcelle Danelon, José Antonio Santos Souza, Dinah Fressato Silva, Jesse Augusto Pereira, Denise Pedrini, Emerson Rodrigues de Camargo, Alberto Carlos Botazzo Delbem, Cristiane Duque
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 84: 81. CrossRef
- Fluoride Uptake and Surface Characteristics of Ion-Releasing Restoratives After Brushing with Fluoride Toothpastes
- 2,665 View
- 8 Download
- 17 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


