Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Marginal adaptation of three root-end filling materials in cavities prepared with laser and ultrasonic tips: an in vitro comparative study
- Busra Zengin, Seda Aydemir, Nicholas Paul Chandler
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e32. Published online September 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e32

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
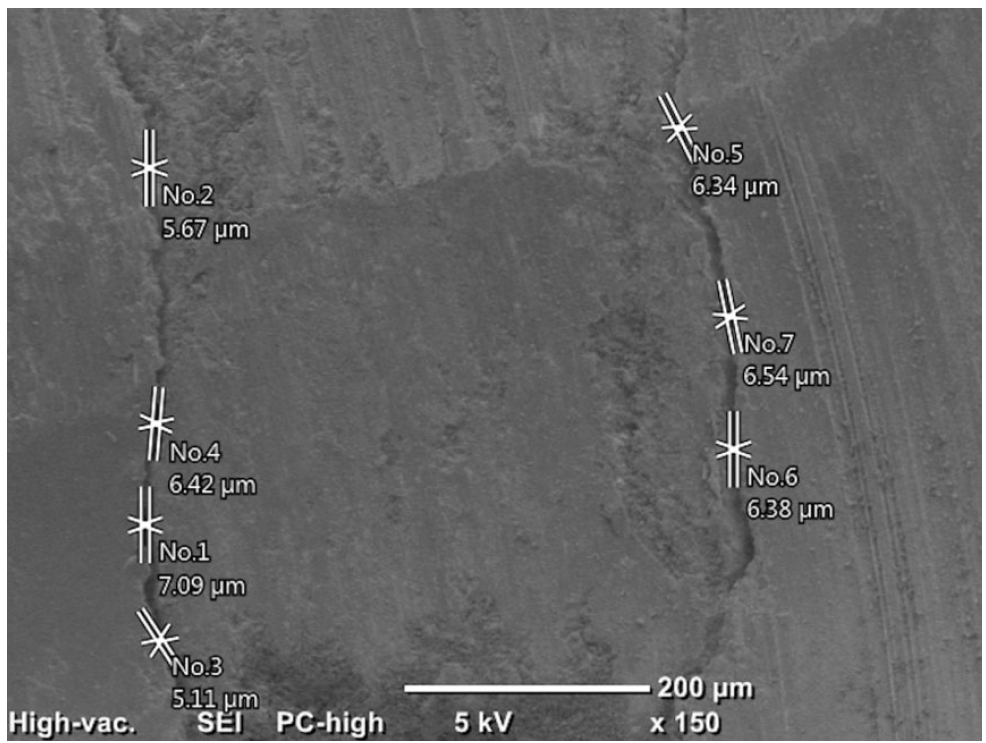
This study evaluated the marginal adaptation of ProRoot MTA (Dentsply Tulsa Dental), Biodentine (Septodont), and TotalFill BC RRM (FKG) placed in root-end cavities prepared with ultrasonic or Er,Cr:YSGG laser tips, using scanning electron microscopy.
Methods
The canals of 90 extracted maxillary central incisors were prepared and obturated and their roots resected. Six groups of 15 specimens were allocated as follows: ultrasonic + ProRoot MTA, ultrasonic + Biodentine, ultrasonic + TotalFill, laser + ProRoot MTA, laser + Biodentine, and laser + TotalFill. Roots were sectioned longitudinally to expose the filling material. Apical and coronal micrographs were taken, and the greatest distance between dentin and filling material was measured. The total gap area was also calculated using further micrographs.
Results
Cavities prepared with the ultrasonic tips and filled with Biodentine showed significantly greater gap dimensions compared with TotalFill (p < 0.001) and ProRoot MTA (p = 0.007) in the apical region. The ultrasonic group showed significantly higher void values compared to the laser group for ProRoot MTA (p = 0.026), when comparing the total values of void. The Biodentine group was significantly higher than the TotalFill group in root-end cavities prepared with ultrasonic tips (p < 0.001). The Biodentine group was significantly higher than the ProRoot MTA group in root-end cavities prepared with the laser tip (p = 0.002).
Conclusions
Under the conditions of this study, it was determined that the root-end cavity preparation technique had an effect on the amount of gaps formed between the dentin and the three filling materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Marginal Adaptability of Harvard MTA and Biodentine Used as Root-End Filling Material: A Comparative SEM Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Materials.2025; 18(19): 4598. CrossRef
- Marginal Adaptability of Harvard MTA and Biodentine Used as Root-End Filling Material: A Comparative SEM Study
- 1,886 View
- 181 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

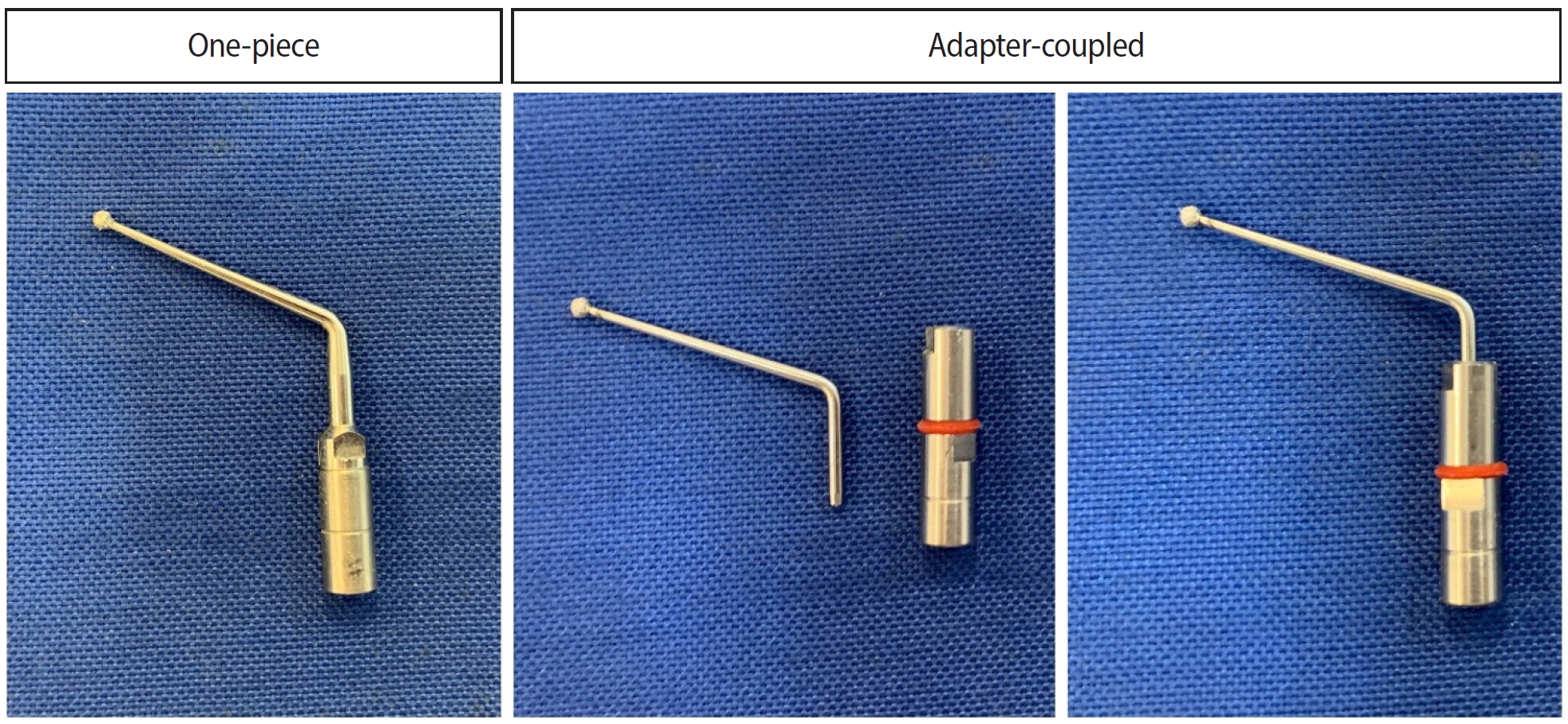
- Analysis of thermal profiles on tooth structure and insert during one-piece or adapter-coupled ultrasonic insert use: an in vitro experimental study
- Gabriela Loewen Brotto, Bruno Monguilhott Crozeta, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Alysson Nunes Diógenes, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e24. Published online July 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate temperature variation on the external surface of mandibular molars and within ultrasonic inserts when using adapter-coupled versus one-piece inserts.
Methods
Twenty-four extracted human mandibular molars were divided into two groups based on the type of ultrasonic insert used: adapter-coupled and one-piece inserts. Temperature on the external surface of each tooth was measured with a thermocouple probe positioned in the furcation area, capturing data continuously. The temperature of the ultrasonic inserts was monitored in real-time using a thermal imaging camera. Measurements were taken in a controlled environment without cooling for over 120 seconds. Statistical analysis was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-way ANOVA with repeated measures to evaluate temperature variations between groups and over time, with significance set at 5%.
Results
In the external tooth surface temperature measurements, no significant differences were observed between the groups during the initial 15 seconds (p = 0.185) and 30 seconds (p = 0.067). However, significant differences emerged at 60 seconds (p = 0.025), 90 seconds (p = 0.024), and 120 seconds (p = 0.020), with the one-piece insert group demonstrating higher temperatures in the furcation region. Thermal imaging of the inserts revealed a significant difference at all time points (p < 0.001), with adapter-coupled inserts showing greater heating.
Conclusions
The use of ultrasonic inserts leads to a gradual rise in temperature on the external tooth surface. One-piece inserts generated higher temperatures on the tooth, while adapter-coupled inserts exhibited greater heating within the insert.
- 1,626 View
- 80 Download

- Pattern of endodontic instrument separation and factors affecting its retrieval: a 10-year retrospective observational study in a postgraduate institute
- Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Aswathi Varghese, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Srinivasan Narasimhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e7. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the pattern of endodontic instrument separation, their retrievability, and factors affecting its retrieval, in a postgraduate institute.
Methods
Cases referred for the management of separated endodontic instruments (SEI) from 2013 to 2023 were considered for this study. Data related to demographics, tooth type, file type, and retrieval were documented in an Excel sheet. Eight prognostic factors assumed to influence the retrieval were analyzed in this study. The secondary aim was to compare the pattern of SEI and retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. Retrieval was attempted by a senior endodontist under the dental operating microscope. Various ultrasonic tips and a Broken Tool Removal loop system were used during retrieval. Simple descriptive statistics were performed. Binomial logistic regression was done to identify the effect of the eight prognostic factors on the retrieval outcome.
Results
A total of 190 SEI was reported. SEI occurred more often in posterior teeth than anterior teeth, mandibular arch than maxillary arch, and in larger files than smaller files. Separation occurred more often in the apical third compared to the other levels. Retrieval was attempted in 88 cases and successful in 70 cases (79.5%). The larger taper and apical position of the SEI negatively influenced the retrieval by 1.4 and 8.7 times, respectively.
Conclusions
Retrieval of SEI was successful in the majority of the cases. An increase in taper and apically placed SEI negatively impacted the retrieval. There was no difference in the pattern of separation nor retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Le Zhao, WangYu Luo, Yue Shen, WanNing Yu, Liu Yang, Xiaolei Zhang
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of microscope-assisted root canal treatment in permanent posterior teeth: A retrospective cohort study
Ya-Ching Chang, Ting-Ya Wang
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 157: 105771. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Nildem İnönü, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, Kaan Orhan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(14): 1744. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF INTRACANAL SEPARATED INSTRUMENTS: FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO ENDODONTIC FILE SEPARATION — A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Tareq Hajaj, Paul Freiman , Serban Talpos Niculescu , Mihai Rominu , Tiberiu Hosszu , Ioana Veja
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(2): 993. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
- 7,254 View
- 343 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
- Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e56. Published online October 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated 2 nickel-titanium rotary systems and a complementary protocol with an ultrasonic tip and a small-diameter instrument in flattened root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty-two human maxillary second premolars with flattened canals (buccolingual diameter ≥4 times larger than the mesiodistal diameter) at 9 mm from the radiographic apex were selected. The root canals were prepared by ProDesign Logic (PDL) 30/0.01 and 30/0.05 or Hyflex EDM (HEDM) 10/0.05 and 25/0.08 (
n = 16), followed by application of the Flatsonic ultrasonic tip in the cervical and middle thirds and a PDL 25/0.03 file in the apical third (FPDL). The teeth were scanned using micro-computed tomography before and after the procedures. The percentage of volume increase, debris, and uninstrumented surface area were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance/Tukey, and paired and unpairedt -tests (α = 0.05).Results No significant difference was found in the volume increase and uninstrumented surface area between PDL and HEDM (
p > 0.05). PDL had a higher percentage of debris than HEDM in the middle and apical thirds (p < 0.05). The FPDL protocol resulted in less debris and uninstrumented surface area for PDL and HEDM (p < 0.05). This protocol, with HEDM, reduced debris in the middle and apical thirds and uninstrumented surface area in the apical third (p < 0.05).Conclusions High percentages of debris and uninstrumented surface area were observed after preparation of flattened root canals. The HEDM, Flatsonic tip, and 25/0.03 instrument protocol enhanced cleaning in flattened root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
Ayşenur Kızıltaş Gül, Turan Mert Hisar, Seniha Miçooğulları
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(1): 157. CrossRef - Flatsonic Ultrasonic Tip Optimizes the Removal of Remaining Filling Material in Flattened Root Canals: A Micro–computed Tomographic Analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 612. CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heat-treated NiTi instruments and final irrigation protocols for biomechanical preparation of flattened canals
Kleber Kildare Teodoro CARVALHO, Igor Bassi Ferreira PETEAN, Alice Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Rafael Verardino CAMARGO, Jardel Francisco MAZZI-CHAVES, Yara Terezinha Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Manoel Damião SOUSA-NETO
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
- 1,679 View
- 26 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Clinical efficacy of activated irrigation in endodontics: a focused review
- Amelia Wan Tin Cheung, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Gary Shun Pan Cheung
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e10. Published online January 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Root canal debridement, which includes the removal of infected tissues and microbial biofilms, is considered the corner stone of root canal treatment. Chemical adjuncts play a multitude of functions in this regard, as tissue solvents, antimicrobial agents and for removing the smear layer. These adjuncts (irrigants) are usually delivered using a syringe and needle. With increasing knowledge of the complexity of root canal anatomy and tenacity of microbial biofilms, the need for strategies that potentiate the action of these irrigants within the root canal system cannot be overemphasized. Several such activated irrigation strategies exist. The aim of this review is to comprehensively discuss the different irrigant activation methods from the context of clinical studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of Er: YAG, continuous-wave, and pulsed diode laser-activated irrigation on smear layer removal: a comparative microscopic study
Muhammad Mahmoud Abaza, Tarek Abdel Hamid Harhash, Ahmed Abbas Zaky
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite accident approach with photobiomodulation during an endodontic procedure: a case report
Johanna Hernandez La Rotta, Marggie Grajales
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium dichloroisocyanurate and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid intracanal medicaments on Enterococcus faecalis: A comparative in-vitro study
Rasmina K. Nizar, Anju Varughese, M. Remya, V.P. Prabath Singh, Gayathri Usha, Gayathri Presannakumar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(5): 1149. CrossRef - ВПЛИВ ХІМІЧНИХ ІРИГАНТІВ НА СТАН БІОПЛІВКИ КОРЕНЕВОГО КАНАЛУ ПРИ ЛІКУВАННІ ПЕРІОДОНТИТІВ
Р. І. Новосядлий, М. М. Рожко
Art of Medicine.2025; : 33. CrossRef - REVOLUCIONANDO LA ENDODONCIA: LA IMPORTANCIA DE IRRIGANTES MÚLTIPLES PARA UNA DESINFECCIÓN EFECTIVA DEL SISTEMA DE CONDUCTOS RADICULARES UNA REVISIÓN NARRATIVA
Irving Pablo Fernandez Calle, Edwin Macias Limachi , Abigail Marisol Vargas Ticona , Jenny Paula Aguilar Avalos , Marivel Irene Condori Escobar, Alcides Ramber Maldonado Huaycho , Jenny Claudia Apaza Cayo , Miguel Angel Espinoza Vega , Jesús Alejan
RECIMA21 - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar - ISSN 2675-6218.2024; 5(11): e5115929. CrossRef - Cleaning and disinfection of the root canal system provided by four active supplementary irrigation methods
Alessandra Timponi Goes Cruz, Adriane Antoniw Klemz, Edvaldo Antônio Ribeiro Rosa, Fabiana Soares Grecca, Bianca Mattos, Lucila Piasecki, Ricardo Machado, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Postendodontic Pain Using Single File System with Different Irrigation Protocols in Single-visit Root Canal Treatment: A Randomized Control Trial
Kiran Patel, Kailash Attur, Nishtha Patel, Kamal M Bagda, Karthik P Venkataraghavan, Mohammed B Mustafa, Shylaja K Attur
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(2): 180. CrossRef - Bacteria debridement efficacy of two sonic root canal irrigant activation systems
Chang Zeng, Pei Hu, Colin P. Egan, Brian E. Bergeron, Franklin Tay, Jingzhi Ma
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 140: 104770. CrossRef - Evaluation of different activated irrigation protocols on debridement quality in various access cavity designs
Urvashi M. Ujariya, Mitul Lallubhai Gangani, Rajendra P. Bharatiya, Anjali K. Kothari
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 400. CrossRef - Synergistic antimicrobial potential of EGCG and fosfomycin against biofilms associated with endodontic infections
Cristiane DUQUE, Amanda Caselato Andolfatto SOUZA, Kelly Limi AIDA, Jesse Augusto PEREIRA, Karina Sampaio CAIAFFA, Vanessa Rodrigues dos SANTOS, Leopoldo COSME-SILVA, Anuradha PRAKKI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insights of fluid dynamics in an optimally shaped root canal system
Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Krishnamachari Janani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 216. CrossRef - Diamond–coated ultrasonic tip decreases debris and uninstrumented surface after preparation of curved canals with isthmus
Maria Luiza GIOSTER–RAMOS, Mariana Mena Barreto PIVOTO–JOÃO, Jáder Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO–TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU–FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation Protocols in Simulated Complex Root Canal Cavities
Flávia A. Plazza, Renan Dal-Fabbro, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Paulo C. T. Duarte, Caroline Loureiro, Vitória Z. Custódio, Luciano T. A. Cintra, Marco A. H. Duarte, João Eduardo Gomes-Filho
Oral.2022; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of sealer penetration of sonic activation versus conventional needle irrigation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Li Tan, Qiong Liu, Yun Chen, Ya-Qiong Zhao, Jie Zhao, Marie Aimee Dusenge, Yao Feng, Qin Ye, Jing Hu, Ze-Yue Ou-Yang, Ying-Hui Zhou, Yue Guo, Yun-Zhi Feng
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Photoinduced Photoacoustic Streaming and Diode Laser Irrigation Techniques on Smear Layer Removal, Sealer Penetration and Push-out Bond Strength
Latifa Mohamed Abdelgawad, Nancy Attia Ahmed ElShafei, Somaia Abdlatif Eissa, Dalia Yahia Ibrahim
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2022; 13(1): e12. CrossRef - Microbiological Aspects of Root Canal Infections and Disinfection Strategies: An Update Review on the Current Knowledge and Challenges
Jasmine Wong, Daniel Manoil, Peggy Näsman, Georgios N. Belibasakis, Prasanna Neelakantan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of efficacy of two endodontic sonic-powered irrigant agitation systems in killing single-species intracanal biofilms
Chang Zeng, Joseph Everett, Stephanie Sidow, Brian E. Bergeron, Fucong Tian, Jingzhi Ma, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 115: 103859. CrossRef - A novel three‐dimensionally printed model to assess biofilm removal by ultrasonically activated irrigation
Min‐Ji Choi, Mi‐Ah Kim, Yoorina Choi, Prasanna Neelakantan, Mi‐Kyung Yu, Kyung‐San Min
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(10): 1871. CrossRef
- Efficacy of Er: YAG, continuous-wave, and pulsed diode laser-activated irrigation on smear layer removal: a comparative microscopic study
- 6,964 View
- 111 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

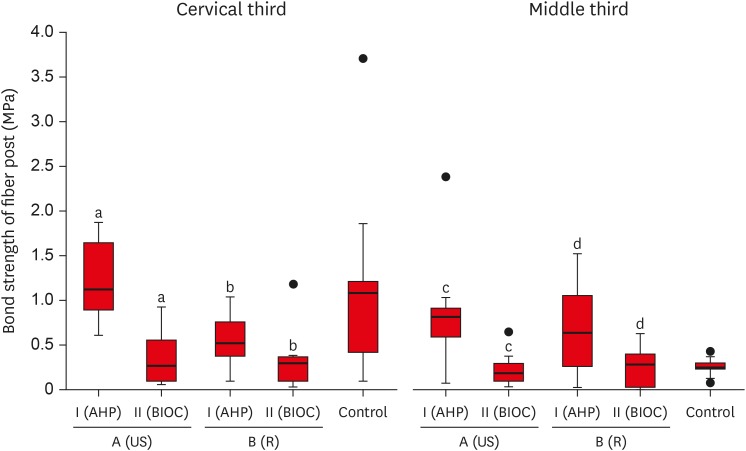
- Effect of ultrasonic cleaning on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic root canal sealer
- Fernando Peña Bengoa, Maria Consuelo Magasich Arze, Cristobal Macchiavello Noguera, Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo Da Silveira Bueno
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e19. Published online February 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This study aimed to evaluate the effect of ultrasonic cleaning of the intracanal post space on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic (Bio-C Sealer [BIOC]) root canal sealer.
Materials and Methods Fifty premolars were endodontically prepared and divided into 5 groups (
n = 10), based on the type of root canal filling material used and the post space cleaning protocol. A1: gutta-percha + AH Plus (AHP) and post space preparation with ultrasonic cleaning, A2: gutta-percha + BIOC and post space preparation with ultrasonic cleaning, B1: gutta-percha + AHP and post space preparation, B2: gutta-percha + BIOC and post space preparation, C: control group. Fiber posts were cemented with a self-adhesive luting material, and 1 mm thick slices were sectioned from the middle and cervical third to evaluate the remaining filling material microscopically. The samples were subjected to a push-out test to analyze the bond strength of the fiber post, and the results were analyzed with the Shapiro-Wilk, Bonferroni, Kruskal-Wallis, and Mann-Whitney tests (p < 0.05). Failure modes were evaluated using optical microscopy.Results The results showed that the fiber posts cemented in canals sealed with BIOC had lower bond strength than those sealed with AHP. The ultrasonic cleaning of the post space improved the bond strength of fiber posts in canals sealed with AHP, but not with BIOC.
Conclusions BIOC decreased the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals, regardless of ultrasonic cleaning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e20. CrossRef - In Vitro Effect of Using Endo‐Activator on Pushout Bond Strength of Radicular Dentin to Prefabricated Fiber Post in Using Natural Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors
Nadia Elyassi Gorji, Homayoun Alaghemand, Faraneh Mokhtarpour, Elham Mahmodnia
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of different mechanical cleaning protocols associated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in the removal of residues from the post space
Matheus Sousa Vitória, Eran Nair Mesquita de Almeida, Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Eliane Cristina Gulin de Oliveira, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Andrea Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 274. CrossRef - Fiber post cemented using different adhesive strategies to root canal dentin obturated with calcium silicate-based sealer
Lalita Patthanawijit, Kallaya Yanpiset, Pipop Saikaew, Jeeraphat Jantarat
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealers on push-out bond strength of CAD-CAM or prefabricated fiber glass posts
Andréa Pereira de Souza PINTO, Fabiana Mantovani Gomes FRANÇA, Roberta Tarkany BASTING, Cecilia Pedroso TURSSI, José Joatan RODRIGUES JÚNIOR, Flávia Lucisano Botelho AMARAL
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of mechanical cleaning protocols in the fiber post space on the adhesive interface between universal adhesive and root dentin
Gabriela Mariana Castro‐Núnez, José Rodolfo Estruc Verbicário dos Santos, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante‐Otárola, Thiago Soares Porto, Milton Carlos Kuga
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(6): 2131. CrossRef - Effect of bioceramic root canal sealers on the bond strength of fiber posts cemented with resin cements
Rafael Nesello, Isadora Ames Silva, Igor Abreu De Bem, Karolina Bischoff, Matheus Albino Souza, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu Da Rosa
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols on root canal wall after post preparation: a micro-CT and microhardness study
Camila Maria Peres de Rosatto, Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Lilian Vieira Oliveira, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira Soares, Carlos José Soares, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
- 1,998 View
- 24 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit for the removal of separated endodontic instruments
- Preeti Jain Pruthi, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, Mahesh Verma
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e14. Published online February 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to perform a comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit (TFRK) for the removal of broken endodontic instruments.
Materials and Methods A total of 80 extracted human first mandibular molars with moderate root canal curvature were selected. Following access cavity preparation canal patency was established with a size 10/15 K-file in the mesiobuccal canals of all teeth. The teeth were divided into 2 groups of 40 teeth each: the P group (ProUltra tips) and the T group (TFRK). Each group was further subdivided into 2 smaller groups of 20 teeth each according to whether ProTaper F1 rotary instruments were fractured in either the coronal third (C constituting the PC and TC groups) or the middle third (M constituting the PM and TM groups). Instrument retrieval was performed using either ProUltra tips or the TFRK.
Results The overall success rate at removing the separated instrument was 90% in group P and 95% in group T (
p > 0.05) The mean time for instrument removal was higher with the ultrasonic tips than with the TFRK (p > 0.05).Conclusion Both systems are acceptable clinical tools for instrument retrieval but the loop device in the TFRK requires slightly more dexterity than is needed for the ProUltra tips.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of success rate and operator variability in loop.based versus ultrasonic retrieval of fractured endodontic instruments: An ex vivo study
Tanushree Saxena, Vivek Devidas Mahale, Manish Ranjan, Sanyuta Singh, E. Aparna Mohan, M. Hema
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 73. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of time efficiency and dentin preservation in ultrasonic versus loop retrieval of separated endodontic files: An ex vivo study with pilot nano-computed tomography analysis
Tanushree Saxena, Vivek Devidas Mahale, Manish Ranjan, M. Hema, Sanyukta Singh, E. Aparna Mohan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 90. CrossRef - Comparison of the pull-out force of different microtube-based methods in fractured endodontic instrument removal: An in-vitro study
Nasim Hashemi, Mohsen Aminsobhani, Mohammad Javad Kharazifard, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Pegah Sarraf
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance and volumetric dentin change after management of broken instrument using static navigation – An in vitro study
Shady Atef Adeeb Yassa, Mohamed Nabeel, Ahmed M. Ghobashy, Moataz B. Alkhawas
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Remoção de instrumento fraturado com a técnica do laço: relato de caso
Larissa Sousa Rangel, Ryhan Menezes Cardoso, Thayane Kelly Trajano da Silva, Robeci Alves Macêdo Filho, Andressa Cartaxo de Almeida, Mariana Camilly Tavares Ferreira, Thalles Gabriel Germano Lima, Diana Santana de Albuquerque
Caderno Pedagógico.2025; 22(7): e16332. CrossRef - Would It Necessarily Require Retrieving Endodontic Files on Every Instance? Implementing Separated Files with the Bypass Technique: Report of Three Cases
Mohit S. Zarekar, Apurva S. Satpute, Mohini S. Zarekar
Journal of Primary Care Dentistry and Oral Health.2025; 6(2): 118. CrossRef - Novel electromagnetic device to retrieve fractured stainless steel endodontic files: an in-vitro investigation
Ashraf Mohammed Alhumaidi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ahmed A. Alelyani, Raid A. Almnea, Amal S. Shaiban, Ahmed Altuwalah, Riyadh Alroomy, Ahmed Abdullah Al Malwi, Ahmad Jabali, Mohammed M. Al Moaleem
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of Root Canal Treatment Using Loops While Endodontic Treatment: A Clinical Study
Chitharanjan Shetty, Kodithala Sravya, Abhilasha Bhawalkar, Alok Dubey, Tejaswi Kala, Prachi Sethy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of fractured file retrieval according to different nickel-titanium alloys and fragment lengths
Joon Hyuk Yoon, Yoshitsugu Terauchi, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Broken Instrument Removal Methods with a Minireview of the Literature
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Nasim Hashemi, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Pegah Sarraf, Giovanni Mergoni
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Marco A. Versiani
Materials.2024; 17(10): 2345. CrossRef - Management of an Intracanal Separated Instrument in the Lower Right First Molar: A Case Report
Pratik Rathod, Aditya Patel, Anuja Ikhar, Manoj Chandak, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Tejas Suryawanshi, Jay Patil, Priti Mahale
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of two instrument retrieval techniques in removing separated rotary and reciprocating nickel-titanium files in mandibular molars – An in vitro study
S. Jitesh, Smita Surendran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1240. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Eunmi Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Samuel O. Dorn, Ya Shen, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Won Kwak
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 213. CrossRef - Efficacy of instrument removal techniques in root canal treatment: a literature review
Rómulo Guillermo López Torres, Jairo Romario Moreno Ochoa, Verónica Alejandra Salame Ortiz
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of the HBW Ultrasonic Ring for retrieval of fragmented manual or rotatory instruments
Jennifer Galván-Pacheco, Verónica Méndez-González, Ana González-Amaro, Heriberto Bujanda-Wong, Amaury Pozos-Guillén, Arturo Garrocho-Rangel
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 278. CrossRef - Retrieving Fragments
Swayangprabha Sarangi, Manoj Ghanshyamdasji Chandak, Kajol Naresh Relan, Payal Sandeep Chaudhari, Pooja Chandak, Anuja Ikhar
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University.2022; 17(2): 429. CrossRef - A novel approach for retrieval of separated endodontic instrument: Two case reports
Tanvi Kohli, Syed Shahid Hilal
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2022; 7(3): 143. CrossRef - A novel endodontic extractor needle for separated instrument retrieval
Saaid Al Shehadat, Colin Alexander Murray, Sunaina Shetty Yadadi
Advances in Biomedical and Health Sciences.2022; 1(2): 116. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Removal of fractured instruments
Yoshi Terauchi, Wagih Tarek Ali, Mohamed Mohsen Abielhassan
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 685. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Use in Endodontic Management Approach, Review Article
Bakheet Mohammed Al-Ghannam, Khalid Abdulmohsen Almuhrij, Rund Talal Basfar, Raghad Omar Alamoudi, Aseel Mohammed Alqahtani, Ahmed Atef Sait, Ahmed Loay Ghannam, Sultan Khalid Abdoun
World Journal of Environmental Biosciences.2021; 10(1): 61. CrossRef - The Time Taken for Retrieval of Separated Instrument and the Change in Root Canal Volume after Two Different Techniques Using Cbct
Balu Santhosh Kumar, Sridevi Krishnamoorthy, Sandhya Shanmugam, Angambakkam Rajasekharan PradeepKumar
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2021; 32(4): 489. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of success rate and operator variability in loop.based versus ultrasonic retrieval of fractured endodontic instruments: An ex vivo study
- 3,605 View
- 100 Download
- 23 Crossref

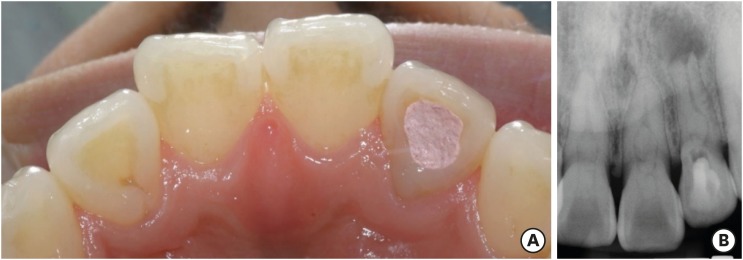
- A case report of multiple bilateral dens invaginatus in maxillary anteriors
- Shin Hye Chung, You-Jeong Hwang, Sung-Yeop You, Young-Hye Hwang, Soram Oh
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e39. Published online October 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The present report presents a case of dens invaginatus (DI) in a patient with 4 maxillary incisors. A 24-year-old female complained of swelling of the maxillary left anterior region and discoloration of the maxillary left anterior tooth. The maxillary left lateral incisor (tooth #22) showed pulp necrosis and a chronic apical abscess, and a periapical X-ray demonstrated DI on bilateral maxillary central and lateral incisors. All teeth responded to a vitality test, except tooth #22. The anatomic form of tooth #22 was similar to that of tooth #12, and both teeth had lingual pits. In addition, panoramic and periapical X-rays demonstrated root canal calcification, such as pulp stones, in the maxillary canines, first and second premolars, and the mandibular incisors, canines, and first premolars bilaterally. The patient underwent root canal treatment of tooth #22 and non-vital tooth bleaching. After a temporary filling material was removed, the invaginated mass was removed using ultrasonic tips under an operating microscope. The working length was established, and the root canal was enlarged up to #50 apical size and obturated with gutta-percha and AH 26 sealer using the continuous wave of condensation technique. Finally, non-vital bleaching was performed, and the access cavity was filled with composite resin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The use of three-dimensional-printed guides, static navigation, and bioactive materials to treat bilateral and double dens invaginatus
Parth Patel, Nidhi Bharti, Ankit Arora, C. Nimisha Shah
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 207. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dens in Dente – A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series
Sanket Dilip Aras, Anamika Chetan Borkar, Sonal Kale, Sayali Maral, Prakriti Jaggi, Shailendra Sonawane
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(1): 17. CrossRef - Dens invaginatus of fourteen teeth in a pediatric patient
Momoko Usuda, Tatsuya Akitomo, Mariko Kametani, Satoru Kusaka, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Pediatric Dental Journal.2023; 33(3): 240. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Maturation of an Immature Dens Invaginatus Despite Unsuccessful Revitalization Procedure: A Case Report and Recommendations for Educational Purposes
Julia Ludwig, Marcel Reymus, Alexander Winkler, Sebastian Soliman, Ralf Krug, Gabriel Krastl
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(2): 47. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Infraorbital Space Infection Secondary to Type III B Dens Invaginatus: A Case Report
Ashima Goyal, Aditi Kapur, Manoj A Jaiswal, Gauba Krishan, Raja Raghu, Sanjeev K Singh
Journal of Postgraduate Medicine, Education and Research.2022; 56(4): 192. CrossRef
- The use of three-dimensional-printed guides, static navigation, and bioactive materials to treat bilateral and double dens invaginatus
- 2,447 View
- 28 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic agitation on push-out bond strength and adaptation of root-end filling materials
- Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marina Angélica Marciano, Jussaro Alves Duque, Samuel Lucas Fernandes, Mariana Bailo Rosseto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e23. Published online April 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of ultrasonic agitation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), calcium silicate-based cement (CSC), and Sealer 26 (S26) on adaptation at the cement/dentin interface and push-out bond strength.
Materials and Methods Sixty maxillary canines were divided into 6 groups (
n = 10): MTA, S26, and CSC, with or without ultrasonic activation (US). After obturation, the apical portions of the teeth were sectioned, and retrograde cavities were prepared and filled with cement by hand condensation. In the US groups, the cement was activated for 60 seconds: 30 seconds in the mesio-distal direction and 30 seconds in the buccal-lingual direction, using a mini Irrisonic insert coupled with the ultrasound transducer. After the materials set, 1.5-mm thick sections were obtained from the apexes. The presence of gaps and the bond between cement and dentin were analyzed using low-vacuum scanning electron microscopy. Push-out bond strength was measured using a universal testing machine.Results Ultrasonic agitation increased the interfacial adaptation of the cements. The S26 US group showed a higher adaptation value than MTA (
p < 0.05). US improved the push-out bond strength for all the cements (p < 0.05).Conclusions The US of retrograde filling cements enhanced the bond to the dentin wall of the root-end filling materials tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
Simone Argenta Scalabrin, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Milton Carlos Kuga, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different disinfection protocols on the bond strength of NeoMTA 2 bioceramic sealer used as a root canal apical plug (in vitro study)
Nada Omar, Nihal Refaat Kabel, Muhammad Abbass Masoud, Tamer M. Hamdy
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Endo-Z bur or Bladesonic ultrasonic tip on the adaptation of filling material. A micro-CT study
Pedro Henrique Fiorin de Souza, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(5): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Different Mixing Methods on Physicochemical Properties of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Systematic Review
Amin Salem Milani, Faraz Radmand, Behrad Rahbani, Mahdi Hadilou, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Fatemeh Salehnia, Milad Baseri, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Micro-CT comparative evaluation of porosity and dentin adaptation of root end filling materials applied with incremental, bulk, and ultrasonic activation techniques
Berkan Celikten, Aysenur Oncu, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Mert Ocak, Kaan Orhan
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2022; 236(8): 1209. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of the adhesive system on dentin tubule penetration and the pushout bond strength of fiber posts
Isabel Verdum, Igor Abreu de Bem, Pedro Henrique Marks Duarte, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(2): 295. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental discoloration caused by Grey-MTAFlow cement: analysis of its physicochemical, biological and antimicrobial properties
Lauter Eston PELEPENKO, Flávia SAAVEDRA, Gabriela Fernanda BOMBARDA, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida GOMES, Adriana DE-JESUS-SOARES, Alexandre Augusto ZAIA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Marina Angélica MARCIANO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers on Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength to Root Dentin
Igor Abreu De Bem, Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1302. CrossRef
- Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
- 1,540 View
- 9 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Smear layer removal by different chemical solutions used with or without ultrasonic activation after post preparation
- Daniel Poletto, Ana Claudia Poletto, Andressa Cavalaro, Ricardo Machado, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Cássia Cilene Dezan Garbelini, Márcio Grama Hoeppner
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):324-331. Published online November 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.324
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated smear layer removal by different chemical solutions used with or without ultrasonic activation after post preparation.
Materials and Methods Forty-five extracted uniradicular human mandibular premolars with single canals were treated endodontically. The cervical and middle thirds of the fillings were then removed, and the specimens were divided into 9 groups: G1, saline solution (NaCl); G2, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); G3, 2% chlorhexidine (CHX); G4, 11.5% polyacrylic acid (PAA); G5, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). For the groups 6, 7, 8, and 9, the same solutions used in the groups 2, 3, 4, and 5 were used, respectively, but activated with ultrasonic activation. Afterwards, the roots were analyzed by a score considering the images obtained from a scanning electron microscope.
Results EDTA achieved the best performance compared with the other solutions evaluated regardless of the irrigation method (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Ultrasonic activation did not significantly influence smear layer removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- O papel do ultrassom no tratamento e retratamento de canais radiculares: Revisão de literatura
Carlos Roberto Souza Hipp, Joaquim Carlos Fest da Silveira, Luiz Felipe Gilson de Oliveira Rangel, Tatiana Federici de Souza Fest da Silveira, Carla Minozzo Mello, Rodrigo Simões de Oliveira
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(8): e1314849323. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and dual-rinse irrigation on dentin adhesion using an etch-and-rinse or self-etch approach
Matej Par, Tobias Steffen, Selinay Dogan, Noah Walser, Tobias T. Tauböck
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Poloxamer on Smear Layer Removal Using Apical Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
Chandra Prabha, Chitharanjan Shetty, Aditya Shetty
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 498. CrossRef - Laboratory Assessment of Antibacterial Efficacy of Five Different Herbal-based Potential Endodontic Irrigants
Anjali A Oak, Kailash Attur, Kamal Bagda, Nitish Mathur, Lubna Mohammad, Nikhat M Attar
Advances in Human Biology.2023; 13(4): 350. CrossRef - Dental Surface Conditioning Techniques to Increase the Micromechanical Retention to Fiberglass Posts: A Literature Review
Paulina Leticia Moreno-Sánchez, Maricela Ramírez-Álvarez, Alfredo del Rosario Ayala-Ham, Erika de Lourdes Silva-Benítez, Miguel Ángel Casillas-Santana, Diana Leyva del Rio, León Francisco Espinosa-Cristóbal, Erik Lizárraga-Verdugo, Mariana Melisa Avendaño
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(14): 8083. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols on smear layer removal, bond strength and nanoleakage of fiber posts using a self-adhesive resin cement
Rodrigo Stadler Alessi, Renata Terumi Jitumori, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, Giovana Mongruel Gomes, João Carlos Gomes
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of using different root canal sealers and protocols for cleaning intraradicular dentin on the bond strength of a composite resin used to reinforce weakened roots
Luiz Pascoal Vansan, Ricardo Machado, Celso Bernardes de Souza, Ricardo Gariba, Antônio Miranda da Cruz, Cinara Muniz, Jardel FranciscoX Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Oral Research.2022; 11(6): 1. CrossRef - Influence of the use of chelating agents as final irrigant on the push‐out bond strength of epoxy resin‐based root canal sealers: A systematic review
Carla M. Augusto, Miguel A. Cunha Neto, Karem P. Pinto, Ana Flavia A. Barbosa, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Ana Paula P. dos Santos, Luciana M. Sassone
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 347. CrossRef - Adhesion and whitening efficacy of P11-4 self-assembling peptide and HAP suspension after using NaOCl as a pre-treatment agent
Niloofar Hojabri, Karl-Heinz Kunzelmann
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of resin cements and root canal disinfection techniques on the adhesive bond strength of fibre reinforced composite post to radicular dentin
Zaid A. Al Jeaidi
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 33: 102108. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Efficacy and In Vivo Toxicity of Sodium Hypochlorite and Electrolyzed Oxidizing (EO) Water-Based Endodontic Irrigating Solutions
Sung-Chih Hsieh, Nai-Chia Teng, Chia Chun Chu, You-Tai Chu, Chung-He Chen, Liang-Yu Chang, Chieh-Yun Hsu, Ching-Shuan Huang, Grace Ying-Wen Hsiao, Jen-Chang Yang
Materials.2020; 13(2): 260. CrossRef
- O papel do ultrassom no tratamento e retratamento de canais radiculares: Revisão de literatura
- 2,460 View
- 17 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The use of auxiliary devices during irrigation to increase the cleaning ability of a chelating agent
- Marina Carvalho Prado, Fernanda Leal, Renata Antoun Simão, Heloisa Gusman, Maíra do Prado
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):105-110. Published online February 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the cleaning ability of ultrasonically activated irrigation (UAI) and a novel activation system with reciprocating motion (EC, EasyClean, Easy Equipamentos Odontológicos) when used with a relatively new chelating agent (QMix, Dentsply). In addition, the effect of QMix solution when used for a shorter (1 minute) and a longer application time (3 minutes) was investigated.
Materials and Methods Fifty permanent human teeth were prepared with K3 rotary system and 6% sodium hypochlorite. Samples were randomly assigned to five groups (
n = 10) according to the final irrigation protocol: G1, negative control (distilled water); G2, positive control (QMix 1 minute); G3, QMix 1 minute/UAI; G4, QMix 1 minute/EC; G5, QMix 3 minutes. Subsequently the teeth were prepared and three photomicrographs were obtained in each root third of root walls, by scanning electron microscopy. Two blinded and pre-calibrated examiners evaluated the images using a four-category scoring system. Data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests (p < 0.05).Results There were differences among groups (
p < 0.05). UAI showed better cleaning ability than EC (p < 0.05). There were improvements when QMix was used with auxiliary devices in comparison with conventional irrigation (p < 0.05). Conventional irrigation for 3 minutes presented significantly better results than its use for 1 minute (p < 0.05).Conclusions QMix should be used for 1 minute when it is used with UAI, since this final irrigation protocol showed the best performance and also allowed clinical optimization of this procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Different Methods of Activation of Chelating Solution for Smear Layer Removal in the Apical Portion of the Root Canal Using a Scanning Electron Microscopy: An In Vitro Study
Mrunal B Alhat, Sudha B Mattigatti, Rushikesh R Mahaparale, Kapil D Wahane, Apoorva Jadhav
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Laser-Activated and Conventional Irrigation Techniques on Sealer Penetration into Dentinal Tubules
Dilara Koruk, Fatma Basmacı, Dilan Kırmızı, Umut Aksoy
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2022; 40(8): 565. CrossRef - Utilização dos atuais métodos de agitação de soluções endodônticas no canal radicular
Lívia Rodrigues Schneider, Larissa Giovanella
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2022; : 135. CrossRef - Smear layer removal by passive ultrasonic irrigation and 2 new mechanical methods for activation of the chelating solution
Ricardo Machado, Isadora da Silva, Daniel Comparin, Bianca Araujo Marques de Mattos, Luiz Rômulo Alberton, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Proteomic analysis of human dental pulp in different clinical diagnosis
Poliana Amanda Oliveira Silva, Stella Maris de Freitas Lima, Mirna de Souza Freire, André Melro Murad, Octávio Luiz Franco, Taia Maria Berto Rezende
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 3285. CrossRef - Effect of QMix irrigant in removal of smear layer in root canal system: a systematic review of in vitro studies
Margaret Soo Yee Chia, Abhishek Parolia, Benjamin Syek Hur Lim, Jayakumar Jayaraman, Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of 17% EDTA and QMiX ultrasonic activation on smear layer removal and sealer penetration: ex vivo study
Felipe de Souza Matos, Fabrício Rutz da Silva, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura, Eduardo Bresciani, Marcia Carneiro Valera
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of different final irrigation protocols on the removal of hard-tissue debris from isthmus-containing mesial root of mandibular molars
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carla Rodrigues Carvalho, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marina Carvalho Prado, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Gustavo De-Deus, Edson Jorge Lima Moreira
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(2): 681. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Different Methods of Activation of Chelating Solution for Smear Layer Removal in the Apical Portion of the Root Canal Using a Scanning Electron Microscopy: An In Vitro Study
- 1,259 View
- 6 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Quality of root canal fillings using three gutta-percha obturation techniques
- Edith Siu Shan Ho, Jeffrey Wen Wei Chang, Gary Shun Pan Cheung
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):22-28. Published online January 4, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.22

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The goal of this study was to compare the density of gutta-percha root fillings obturated with the following techniques: cold lateral (CL) compaction, ultrasonic lateral (UL) compaction, and warm vertical (WV) compaction.
Materials and Methods Thirty-three extracted mandibular first molars, with two separate mesial canals in each, were selected. After instrumentation, the canals were stratified into three groups based on canal length and curvature, and underwent obturation with one of the techniques. No sealer was used in order to avoid masking any voids. The teeth were imaged pre- and post-obturation using micro-computed tomography. The reconstructed three-dimensional images were analyzed volumetrically to determine the amount of gutta-percha present in every 2 mm segment of the canal.
P values < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.Results The overall mean volume fraction of gutta-percha was 68.51 ± 6.75% for CL, 86.56 ± 5.00% for UL, and 88.91 ± 5.16% for WV. Significant differences were found between CL and UL and between CL and WV (
p < 0.05), but not between UL and WV (p = 0.526). The gutta-percha density of the roots treated with WV and UL increased towards the coronal aspect, but this trend was not noted in the CL group.Conclusions WV compaction and UL compaction produced a significantly denser gutta-percha root filling than CL compaction. The density of gutta-percha was observed to increase towards the coronal aspect when the former two techniques were used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
Jia Min Ng, Yan Yee Lee, Prashanti Chippagiri, Elaheh Ahanin, Abhishek Parolia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e3. CrossRef - Restorative and endodontic clinical strategies during COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: a revision of the literature
Manuele MANCINI, Flavio PALAZZI, Francesco IACONO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the tubular penetration of two different types of nanoparticle root canal sealers over apically separated files: a scanning electron microscopic study (in vitro study)
Alaa H. Nagdi, Nayera A. Mokhless, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Different strategies for treating intracanal fractured instruments in a single tooth: A case report
Rong Chai, Xinpei Jiang, Ruixia Ma, Qiang Zhang, E Yang, Ansheng Zhang
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An Experimental Anatomic CBCT Study on the Correlations Between MB1 and MB2 of the Mesio-Vestibular Root of the Upper First Molars
Luca Fiorillo, Cesare D’Amico, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Francesco Calanna, Alfio Pappalardo, Eugenio Pedullà
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(2): 672. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Different Obturation Techniques for Root Canal Filling of Permanent Teeth: An In-Vitro Study
Adhishree S Chib, Neeta S Padmawar, Sonali Waghmare, Durgesh A Tiwari, Shahinwaz Mulani, Megna Bhatt
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root canal treatment of a rhizomegaly tooth 36 mm long right permanent maxillary canine – A case report
Anita Kapri, Kiran Reddy, Varun Rana, Oliver Jacob, Pushpa Kumari
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 10(1): 59. CrossRef - Thermal and volumetric assessment of endodontic filling techniques using infrared thermography and micro-CT
Fernanda Clotilde M. Suassuna, Débora Ketley M. de Araújo, Ana Marly A. M. Amorim, Saulo Leonardo S. Melo, Richard J. Heck, Antonio Celso D. Antonino, Patrícia M. Bento, Diego Filipe B. Silva, Daniela P. de Melo
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(1): 34. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Various Obturating Techniques for the Presence of Voids
Rehan Ahmad Khan, Shailja Singh, Shazia Siddiqui, Mariyam Khan, Arfat Ahmad, Parul Shakarwal
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2023; 15(Suppl 2): S895. CrossRef - Influence of the root canal filling technique on the success rate of primary endodontic treatments: a systematic review
Daniel Feijolo Marconi, Giovana Siocheta da Silva, Theodoro Weissheimer, Isadora Ames Silva, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Leonardo Thomasi Jahnke, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Current trends in bio‐based elastomer materials
Shuai Tang, Jiao Li, Runguo Wang, Jichuan Zhang, Yonglai Lu, Guo‐Hua Hu, Zhao Wang, Liqun Zhang
SusMat.2022; 2(1): 2. CrossRef - Carrier-Based Obturation: Effect of Sonication Technique on Sealer Penetration in Dentinal Tubules: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Study
Riccardo Tonini, Matteo Salvadori, Marco Bartoli, Jacopo Francinelli, Paolo Bertoletti, Maria Luisa Garo, Stefano Salgarello
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(17): 8877. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - The effect of two endodontic sealers and interval before post-preparation and cementation on the bond strength of fiber posts
He Yuanli, Wu Juan, Ji Mengzhen, Chen Xuan, Xiong Kaixin, Yang Xueqin, Qiao Xin, Hu Hantao, Gao Yuan, Zou Ling
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(11): 6211. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - Root canal filling quality of mandibular molars with EndoSequence BC and AH Plus sealers: A micro‐CT study
Rafael Nigri Roizenblit, Fabiola Ormiga Soares, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Heloisa Gusman
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of four different root canal obturation techniques on marginal adaptation of bioceramic sealer: An in vitro scanning electron microscopic study
NawalA Al-Sabawi, MahaM Yahya, NjwanF Shehab
Journal of International Oral Health.2020; 12(5): 455. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantification of the tug-back by measuring the pulling force and micro computed tomographic evaluation
Su-Jin Jeon, Young-Mi Moon, Min-Seock Seo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 273. CrossRef
- Effect of quality of radiographs taken during root canal treatment on technical quality of root canal fillings and endodontic outcome
- 2,512 View
- 26 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
- Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):149-154. Published online March 4, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) into root dentinal tubules and the influence of passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty freshly extracted anterior teeth were decoronated and instrumented using Mtwo rotary files up to size 40, 4% taper. The samples were randomly divided into two groups (
n = 10), that is, conventional syringe irrigation (CSI) and PUI. CHX was mixed with Rhodamine B dye and was used as the final irrigant. The teeth were sectioned at coronal, middle and apical levels and viewed under CLSM to record the penetration depth of CHX. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results The mean penetration depths of 2% CHX in coronal, middle and apical thirds were 138 µm, 80 µm and 44 µm in CSI group, respectively, whereas the mean penetration depths were 209 µm, 138 µm and 72 µm respectively in PUI group. Statistically significant difference was present between CSI group and PUI group at all three levels (
p < 0.01 for coronal third andp < 0.001 for middle and apical thirds). On intragroup analysis, both groups showed statistically significant difference among three levels (p < 0.001).Conclusions Penetration depth of 2% CHX into root dentinal tubules is deeper in coronal third when compared to middle and apical third. PUI aided in deeper penetration of 2% CHX into dentinal tubules when compared to conventional syringe irrigation at all three levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparative Evaluation of Khadirarishta and Chlorhexidine as Intracanal Medicament on Enterococcus faecalis using a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope – An in vitro Study
Harika Paluru, Lavanya Anumula, Chinni Suneel Kumar, Kiranmayi Govula, Sannapureddy Swapna, Paleti Pranaviteja
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2025; 15(3): 237. CrossRef - The ability of different diffusing enhancers to deliver chlorhexidine into dentinal tubules: An in vitro evaluation
Yi Luo, Mengting Duan, Runze Liu, Pei Liu, Wei Fan, Bing Fan
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2226. CrossRef - The effect of 2% chlorhexidine iontophoresis on dentin sealing ability of etch-and-rinse adhesive: An in vitro study
Kanittha Kijsamanmith, Panisara Srisatayasatien, Nichapa Thanindratarn, Chanisa Vichainarong, Jirapat Panyasukum
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 846. CrossRef - Influence of different presentation forms of chlorhexidine on contaminated root canals during agitation
Ana B. S. Lopes, Augusto R. Lima, Juliana D. Bronzato, Daniel R. Herrera, Priscila A. Francisco, Maria C. C. Carvalho, Gabriel Abuna, Mario Sinhoreti, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 513. CrossRef - Evaluation of the transdentinal capability of the intrinsic antibacterial cetylpyridinium chloride/cholesterol sterosomes in vitro and in vivo
Xiaojun Yang, Chaoning Zhan, Tianjiao Cheng, Minchun Huang, Weiwen Ge, Yiqing Zhang, Ting Chen, Yanli Lu, Zhong‐Kai Cui, Jin Hou
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(2): 245. CrossRef - Dentinal tubule penetration of sodium hypochlorite in root canals with and without mechanical preparation and different irrigant activation methods
Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Matheus Albino Souza, Rodrigo Gonçalves Ribeiro, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Lipidic Nanoplatform for Intra-Oral Delivery of Chlorhexidine: Characterization, Biocompatibility, and Assessment of Depth of Penetration in Extracted Human Teeth
Krishnaraj Somyaji Shirur, Bharath Singh Padya, Abhijeet Pandey, Manasa Manjunath Hegde, Aparna I. Narayan, Bola Sadashiva Satish Rao, Varadaraj G. Bhat, Srinivas Mutalik
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(19): 3372. CrossRef - Value addition property of a cationic surfactant on endodontic irrigant: A confocal laser scanning microscope study
Sembagalakshmi Thirunarayanan, MithraN Hegde
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 380. CrossRef - The effect of different irrigants on sealer penetration into dentinal tubules with and without activation, using confocal scanning microscope
HelaylA Alshaibani, ShibuThomas Mathew
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2022; 14(1): 37. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide/iodoform nanoparticles as an intracanal filling medication: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro study using a bovine primary tooth model
Arturo Garrocho-Rangel, Diana María Escobar-García, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Denisse Herrera-Badillo, Fernanda Carranco-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Flores-Arriaga, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 687. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation methods on dentinal tubule penetration of Chlorhexidine, QMix and Irritrol: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Meltem Küçük, Fatma Kermeoğlu
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 202. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of different root canal sealers used with coated core materials
Derya Deniz Sungur, Nuhan Purali, Erdal Coşgun, Semra Calt
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 114. CrossRef
- A Comparative Evaluation of Khadirarishta and Chlorhexidine as Intracanal Medicament on Enterococcus faecalis using a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope – An in vitro Study
- 2,012 View
- 21 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
- Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):143-148. Published online February 11, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the maximum depth and percentage of irrigant penetration into dentinal tubules by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human teeth were instrumented and divided into three groups. According to final irrigation regimen, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (Group A, NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine (Group B, CHX) and saline solution (Group C, control group) were applied with Irrisafe 20 tips (Acteon) and PUI. Irrigant was mixed with 0.1% rhodamine B. Sections at 2 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm from the apex were examined with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The percentage and maximum depth of irrigant penetration were measured. Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test were performed for overall comparison between groups at each level and for pairwise comparison, respectively. Within a group, Wilcoxon test was performed among different levels.
p values less than 0.05 were considered significant.Results In all groups, highest penetration depth and percentage of penetration were observed at the 8 mm level. At 2 mm level, Groups A and B had significantly greater depths and percentages in penetration than Group C (
p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences between Groups A and B. At 5 mm level, penetration depths and percentage of penetration was not significantly different among the groups.Conclusions NaOCl and CHX applied by PUI showed similar depth and percentage of penetration at all evaluated levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
Anjali Meena, Nidhi Sharma, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Sarita Singh, Anu Dhawan, Neha Verma
Endodontology.2025; 37(1): 80. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Sonic versus ultrasonic activation for the cleaning of the root canal after post space preparation: an in vitro study.
René Carrasco, Ricardo Román, Makarena Ojeda, Carolina Vergara
Journal Oral Of Research.2015; 4(4): 255. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
- 1,457 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Cutting efficiency of apical preparation using ultrasonic tips with microprojections: confocal laser scanning microscopy study
- Sang-Won Kwak, Young-Mi Moon, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):276-281. Published online July 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the cutting efficiency of a newly developed microprojection tip and a diamond-coated tip under two different engine powers.
Materials and Methods The apical 3-mm of each root was resected, and root-end preparation was performed with upward and downward pressure using one of the ultrasonic tips, KIS-1D (Obtura Spartan) or JT-5B (B&L Biotech Ltd.). The ultrasonic engine was set to power-1 or -4. Forty teeth were randomly divided into four groups: K1 (KIS-1D / Power-1), J1 (JT-5B / Power-1), K4 (KIS-1D / Power-4), and J4 (JT-5B / Power-4). The total time required for root-end preparation was recorded. All teeth were resected and the apical parts were evaluated for the number and length of cracks using a confocal scanning micrscope. The size of the root-end cavity and the width of the remaining dentin were recorded. The data were statistically analyzed using two-way analysis of variance and a Mann-Whitney test.
Results There was no significant difference in the time required between the instrument groups, but the power-4 groups showed reduced preparation time for both instrument groups (
p < 0.05). The K4 and J4 groups with a power-4 showed a significantly higher crack formation and a longer crack irrespective of the instruments. There was no significant difference in the remaining dentin thickness or any of the parameters after preparation.Conclusions Ultrasonic tips with microprojections would be an option to substitute for the conventional ultrasonic tips with a diamond coating with the same clinical efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
- 1,389 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal
- Anny Carine Barros Aguiar, Daniely Amorim de Meireles, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Angela Delfina Bitencourt Garrido, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):265-269. Published online July 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effect of different ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal.
Materials and Methods The crowns of forty human canine teeth were removed, and after biomechanical preparation and filling, the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. The post spaces were made, and root canal molding was performed with self-cured acrylic resin. After casting (Cu-Al), the posts were cemented with zinc phosphate cement. The specimens were randomly separated into 4 groups (
n = 10), as follows: G1 - no ultrasonic vibration (control); G2 - ultrasonic vibration using an elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip; G3 - ultrasonic vibration with a flattened convex and linear active tip; G4 - ultrasonic vibration with active semicircular tapered tip. Ultrasonic vibration was applied for 15 seconds on each post surface and tensile test was performed in a Universal Testing Machine (Instron 4444 - 1 mm/min).Results G4 presented the highest mean values, however, with no statistically significant difference in comparison to G3 (
P > 0.05). G2 presented the lowest mean values with statistically significant difference to G3 and G4 (P < 0.05).Conclusions Ultrasonic vibration with elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip was most effective in reducing force required for intraradicular post removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
Giulliano C. Serpa, Orlando A. Guedes, Neurinelma S. S. Freitas, Julio A. Silva, Carlos Estrela, Daniel A. Decurcio
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 190. CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Endodontic Retreatment Using Dynamic Navigation: A Case Report
Jonathan Bardales-Alcocer, Marco Ramírez-Salomón, Elma Vega-Lizama, María López-Villanueva, Gabriel Alvarado-Cárdenas, Kenneth S. Serota, Jorgeraul Ramírez-Wong
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 1007. CrossRef - Assessment of a Cavity to Optimize Ultrasonic Efficiency to Remove Intraradicular Posts
Izabela Araujo Aguiar Graça, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, André Augusto Franco Marques, Leandro de Moura Martins, Ângela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1350. CrossRef - REMOVAL ALLOY CAST ROOT INLAY BY LOWPOWER ULTRASONIC AND STANDARD TIP
L. D. Vejsgejm, T. N. Gomenjuk
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2017; 14(4): 37. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
- The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
- 1,484 View
- 14 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
- Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):104-108. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effect of passive ultrasonic agitation on the cleaning capacity of a hybrid instrumentation technique.
Materials and Methods Twenty mandibular incisors with mesiodistal-flattened root shape had their crowns sectioned at 1 mm from the cementoenamel junction. Instrumentation was initiated by catheterization with K-type files (Denstply Maillefer) #10, #15, and #20 at 3 mm from the working length. Cervical preparation was performed with Largo bur #1 (Dentsply Maillefer) followed by apical instrumentation with K-type files #15, #20 and #25, and finishing with ProTaper F2 file (Denstply Maillefer). All files were used up to the working length under irrigation with 1 mL of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (Biodynâmica) at each instrument change. At the end of instrumentation, the roots were randomly separated into 2 groups (
n = 10). All specimens received final irrigation with 1 mL of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. The solution remained in the root canals in Group 1 for one minute; and ultrasonic agitation was performed in Group 2 for one minute using a straight tip inserted at 1 mm from working length. The specimens were processed histologically and the sections were analyzed under optic microscope (×64) to quantify debris present in the root canal.Results The samples submitted to ultrasonic agitation (Group 2) presented significant decrease in the amount of debris in comparison with those of Group 1 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The hybrid instrumentation technique associated with passive ultrasonic agitation promoted greater debris removal in the apical third of the root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro-CT Evaluation of Different Root Canal Irrigation Protocols on the Removal of Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ailin Liang, Luo Huang, Baoyu Li, Yihua Huang, Xiaoyan Zhou, Xufang Zhang, Qimei Gong
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6053. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation during Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Petruţa E. Căpută, Anastasios Retsas, Lydwien Kuijk, Luis E. Chávez de Paz, Christos Boutsioukis
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on Crown Fracture Resistance
Marina Baechtold, Leonardo da Cunha, Erick Souza, Marilisa Gabardo, Kauhanna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto-Filho, Denise Leonardi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(7): 768. CrossRef - Influence of Prior Cervical Enlargement on Apical Cleaning Using Single File
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Celso Alfredo Schramm, Allan Fernando Giovanini, Cibelli Mariane Silveira, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho, Flares Baratto-Filho
The Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College.2015; 56(2): 85. CrossRef - Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 143. CrossRef - Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 149. CrossRef
- Micro-CT Evaluation of Different Root Canal Irrigation Protocols on the Removal of Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,435 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Multivariate analysis of the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation techniques in the canal and isthmus of mandibular posterior teeth
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):154-159. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation regimens in canal and isthmus of mandibular molars, and to evaluate the influence of related variables on cleaning efficacy of the irrigation systems.
Materials and Methods Mesial root canals from 60 mandibular molars were prepared and divided into 4 experimental groups according to the final irrigation technique: Group C, syringe irrigation; Group U, ultrasonics activation; Group SC, VPro StreamClean irrigation; Group EV, EndoVac irrigation. Cross-sections at 1, 3 and 5 mm levels from the apex were examined to calculate remaining debris area in the canal and isthmus spaces. Statistical analysis was completed by using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test for comparison among groups, and multivariate linear analysis to identify the significant variables (regular replenishment of irrigant, vapor lock management, and ultrasonic activation of irrigant) affecting the cleaning efficacy of the experimental groups.
Results Group SC and EV showed significantly higher canal cleanliness values than group C and U at 1 mm level (
p < 0.05), and higher isthmus cleanliness values than group U at 3 mm and all levels of group C (p < 0.05). Multivariate linear regression analysis demonstrated that all variables had independent positive correlation at 1 mm level of canal and at all levels of isthmus with statistical significances.Conclusions Both VPro StreamClean and EndoVac system showed favorable result as final irrigation regimens for cleaning debris in the complicated root canal system having curved canal and/or isthmus. The debridement of the isthmi significantly depends on the variables rather than the canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of different irrigant activation techniques for cleaning root canal anastomosis
O. K. Montaser, D. M. Fayyad, N. Abdelsalam
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Heated distilled water with or without continuous ultrasonic irrigation improves final irrigation efficacy and reduces dentine erosion
Michelli Cássia dos Santos, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Bruno Henriques, Franklin R. Tay, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 103: 103507. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation during Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Petruţa E. Căpută, Anastasios Retsas, Lydwien Kuijk, Luis E. Chávez de Paz, Christos Boutsioukis
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 31. CrossRef - Irrigation effectiveness of continuous ultrasonic irrigation system: An ex vivo study
Ahmed JAMLEH, Hideaki SUDA, Carlos G. ADORNO
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure irrigation versus syringe irrigation: a systematic review of cleaning and disinfection of the root canal system
E. Konstantinidi, Z. Psimma, L. E. Chávez de Paz, C. Boutsioukis
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(11): 1034. CrossRef - Effect of Different Agitation Techniques on the Penetration of Irrigant and Sealer into Dentinal Tubules
Yu Gu, Hiran Perinpanayagam, David J.W. Jin, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Jin-Sun Jeong, Sang-Min Lim, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2017; 35(2): 71. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Sonic, Ultrasonic, and Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming Activation of NaOCl on Filling Material Removal Following Retreatment in Oval Canal Anatomy
Shan Jiang, Ting Zou, Dongxia Li, Jeffery W.W. Chang, Xiaojing Huang, Chengfei Zhang
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2016; 34(1): 3. CrossRef -
Efficacy of Needle, Ultrasonic, and Endoactivator Irrigation and Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming in Removing Calcium Hydroxide from the Main Canal and Isthmus: An
In Vitro
Micro-Computed Tomography and Scanning
Dongxia Li, Shan Jiang, Xingzhe Yin, Jeffrey Wen Wei Chang, Jie Ke, Chengfei Zhang
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2015; 33(6): 330. CrossRef - Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 143. CrossRef
- Efficacy of different irrigant activation techniques for cleaning root canal anastomosis
- 1,139 View
- 1 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Thermal irritation of teeth during dental treatment procedures
- Su-Jung Kwon, Yoon-Jung Park, Sang-Ho Jun, Jin-Soo Ahn, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Deog-Gyu Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):105-112. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub While it is reasonably well known that certain dental procedures increase the temperature of the tooth's surface, of greater interest is their potential damaging effect on the pulp and tooth-supporting tissues. Previous studies have investigated the responses of the pulp, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone to thermal irritation and the temperature at which thermal damage is initiated. There are also many
in vitro studies that have measured the temperature increase of the pulp and tooth-supporting tissues during restorative and endodontic procedures. This review article provides an overview of studies measuring temperature increases in tooth structures during several restorative and endodontic procedures, and proposes clinical guidelines for reducing potential thermal hazards to the pulp and supporting tissues.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Various Sleeve Materials on Temperature Variations During Guided Endodontic Access Cavity Preparation Utilizing Finite‐Element Analysis
Anna Muryani, Wandi Prasetia, Dudi Aripin, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Zainul Ahmad Rajion, Satrio Wicaksono
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of microcrack formation and fracture resistance of root dentin with the use of three different rotary files: An in vitro study
Paridhi Maheshwari, Sayantan Mukherjee, Ipsita Maity, Paromita Mazumdar
Journal of Oral Research and Review.2026; 18(1): 59. CrossRef - External Root Temperature and Its Relationship With Dentin Thickness During Gutta-Percha Removal Procedures With Ultrasound. An Ex Vivo Study
Juan Ramon Salazar-Silva, Carlos Emilio Paschoal, Daniela de Fatima Teixeira da Silva, Denise Maria Zezell, Fábio Luiz Cunha D'Assuncao, Celso Luiz Caldeira
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(3): 340. CrossRef - Temperature Changes of NaOCl after Irrigation Using Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation, Easy Clean, and XP-Endo Finisher: A Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial
Geraldo Edson Freitas Athayde de Moraes, Daniel Guimarães Pedro Rocha, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Índia Olinta De Azevedo Queiroz, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 660. CrossRef - Real‐Time Analysis of Changes in Internal and External Root Temperatures Using Different Systems for Activating the Irrigation Solution
Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Julia Menezes Savaris, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Tamer Ferreira Schmidt, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Behaviour of Teeth With Internal Root Resorption During Obturation and Enhancing Thermal Simulations: A Finite-Element Analysis
Alper Kabakci, Ayca Yilmaz, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(6): 103903. CrossRef - Determination of a safe protocol for using laser ablation with indocyanine green dye in endodontic treatment. In vitro, in vivo and human study
Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Mirtha Perdomo, Marcelo Costa Perdomo, María Betania Acevedo Giménez, Celso Kenji Nishiyama, Fernando Accorsi Orosco, Arturo Javier Aranda Garcia, Carolina Sayuri Wajima, Cristiane Cantiga-Silva, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Flávio
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial PEEK-Ag Surfaces: Development and In Vitro Evaluation Against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Flávio Rodrigues, Mariana Fernandes, Filipe Samuel Silva, Óscar Carvalho, Sara Madeira
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(10): 388. CrossRef - The effect of di̇fferent preheati̇ng methods on the intrapulpal temperature of bulk-fi̇ll composi̇te resi̇ns
Hilal Ateş, Merve İşcan Yapar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of increase in temperature on the external root surface of teeth during retrieval of broken NiTi instrument using two ultrasonic tips and two power settings: An in vitro study
Ashish K. Jain, Rishabhkumar Jain, Rahul Rao, Prajakta Rao, Pooja Yadav, Vinayak Thorat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 634. CrossRef - Dental health concerns for patients suffering from facial, peri-oral burns, and inhalation injury: A persistent yet underappreciated challenge
Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, Isabelle Rennekampff, Mayer Tenenhaus
Burns.2024; 50(9): 107224. CrossRef - Recent advances in the pathogenesis and prevention strategies of dental calculus
Yu Wei, Gao-peng Dang, Zhao-yang Ren, Mei-chen Wan, Chen-yu Wang, Hong-bo Li, Tong Zhang, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Root Surface Temperature Using Different Endodontic Filling Techniques
Lea Külzer, Theresia Saban, Andreas Braun, Johannes-S. Wenzler
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9830. CrossRef - Accuracy comparison of single- and double-sleeve endodontic guides for fiber post removal
Omid Dianat, Mandana Naseri, Yaser Safi, Ali Modaberi, Nazanin Zargar, Ove A. Peters, Mehran Farajollahi
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Water Coolant and Bur Type on Pulp Temperature When Removing Tooth Structure and Restorative Dental Materials
C Mafrici, M Kingston, R Grice, PV Abbott
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(1): 91. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Temperature Variations in Incisor Root Surfaces During Root Canal Preparation Using Various Rotary Systems and Irrigation Protocols
Mihai Paven, Adrian-George Marinescu, Osama Abuabboud, Laura-Elena Cirligeriu, Luminita Maria Nica, Vlad Tiberiu Alexa, Ruxandra Sava Rosianu, Atena Galuscan, Roxana Oancea
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(23): 7484. CrossRef - The Effect of Restoration Polymerization and Residual Dentine Thickness on Thermal Changes of Pulp Chamber of Immature Permanent Teeth
Kevser Kolçakoğlu, Merve Aksoy, Cenkhan Bal, Akif Demirel, Firdevs Tulga Öz
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of pulpotomy in managing irreversible pulpitis in mature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuanyuan Li, Wenying Wang, Qian Zeng, Michelle Tang, Joshua Massey, Brian E. Bergeron, Lisha Gu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 144: 104923. CrossRef - Evaluation of diamond rotary instruments marketed for removing zirconia restorations
Severin Hunziker, Lea Thorpe, Nicola U. Zitzmann, Nadja Rohr
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 131(5): 895. CrossRef - Influence of different cutting instruments and rotational speeds on heat generation and cutting efficiency when sectioning different types of zirconia
Lisa Türp, Frank Lehmann, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 160: 106715. CrossRef - Loss of pulp vitality correlated with the duration of the interim restoration and the experience of the dentist: A retrospective study
Göran Nilsson, Stefan Ellner, Liselott Arnebrant, Lars Brudin, Christel Larsson
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(6): 833. CrossRef - Thermal Sensing of Photo-Activated Dental Resin Composites Using Infrared Thermography
Turki A. Bakhsh, Abdulaziz Alfaifi, Yousef Alghamdi, Mohannad Nassar, Roaa A. Abuljadyel
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4117. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation acid solutions on cleaning and bond strength to post‐space dentin
C. de Melo Alencar, J. Ferrari Zaniboni, J. Felipe Besegato, A. Patricia Oliveira Barros, M. Bena Gélio, L Garcia Belizário, E. Maximiliano Fernandez Godoy, M. Carlos Kuga
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Intermediate Irrigation on Temperature Rise during Broken NiTi File Removal Using Ultrasonic Device
László Pintér, Károly Krajczár, Fanni Őry, József Szalma, Edina Lempel
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9761. CrossRef - Top tips for improving crown preparations
James Baker, Ewen McColl, Christopher Tredwin
British Dental Journal.2023; 234(1): 16. CrossRef - Evaluation of knowledge and awareness of pediatric oral health among school teachers of Hazaribag before and after oral health education.
Vipin Ahuja, Annapurna Ahuja, Nilima Thosar
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1292. CrossRef - Applications of single laser pulse from Nd:doped lasers for cleaning of small diameter carious lesions. Modelling and analytical study
T Uzunov, M Deneva, P Uzunova, M Nenchev
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2023; 2487(1): 012022. CrossRef - Accuracy of a 3D printed sleeveless guide system used for fiber post removal: An in vitro study
Siyi Mo, Yongwei Xu, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104367. CrossRef - Heat generated during dental treatments affecting intrapulpal temperature: a review
Xin Er Lau, Xiaoyun Liu, Helene Chua, Wendy Jingwen Wang, Maykon Dias, Joanne Jung Eun Choi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2277. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature rise in light-cure bonding of brackets with and without primer, in intact versus restored teeth
Gabriela Cenci SCHMITZ, Fernanda de Souza HENKIN, Mauricio MEZOMO, Mariana MARQUEZAN, Gabriela BONACINA, Maximiliano Schünke GOMES, Eduardo Martinelli Santayana de LIMA
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature Rise in Curing Modes of Two Different Dental Light-Curing Units: The Importance of Heating Rate
Ahmad Soori, Faezeh Soori, Farshad Kowsary, Shahin Kasraei
International Journal of Thermophysics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effective application of suitable single pulse of Nd:doped lasers for cleaning of initial carious lesions of human teeth. Experimental study
T Uzunov, M Deneva, V Kazakov, P Uzunova, N Kaimakanova, M Nenchev
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2023; 2487(1): 012021. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Intrapulpal Thermal Changes during the Polymerization of Different Adhesive Resin Materials: An In Vitro Study
Pavithra K Ramanna, Suneel V Vadavadagi, Konsam Bidya Devi, Pawankumar Kamalapurkar, Shreeshail Indi, Vineetha Chakravarthy Srinivas
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(5): 539. CrossRef - Anesthetic-, irrigation- and pain-free dentistry? The case for a femtosecond laser enabled intraoral robotic device
Ludovic Rapp, Steve Madden, Andrei V. Rode, Laurence J. Walsh, Heiko Spallek, Quan Nguyen, Van Dau, Peter Woodfield, Dzung Dao, Omar Zuaiter, Alaa Habeb, Timothy R. Hirst
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - 4D Printing of Shape‐Memory Semi‐Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Based On Aromatic Heterochain Polymers
Kseniia N. Bardakova, Bato Ch. Kholkhoev, Ivan A. Farion, Evgenii O. Epifanov, Olga S. Korkunova, Yuri M. Efremov, Nikita V. Minaev, Anna B. Solovieva, Peter S. Timashev, Vitaliy F. Burdukovskii
Advanced Materials Technologies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How does indirect air-cooling influence pulp chamber temperature in different volume teeth and absence/presence of resin-based composite during light curing?
Mathieu Mouhat, Lina Stangvaltaite-Mouhat, Emil Finnäs, Amani Andersen, Anneli Lirhus Evertsen, Bo W. Nilsen
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intrapulpal temperature changes during the cementation of ceramic veneers
Edina Lempel, Dóra Kincses, Donát Szebeni, Dóra Jordáki, Bálint Viktor Lovász, József Szalma
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Femtosecond laser dentistry for precise and efficient cavity preparation in teeth
Ludovic Rapp, Steve Madden, Julia Brand, Laurence J. Walsh, Heiko Spallek, Omar Zuaiter, Alaa Habeb, Timothy R. Hirst, Andrei V. Rode
Biomedical Optics Express.2022; 13(9): 4559. CrossRef - Three Dimensional mapping of the root apex: distances between apexes and anatomical structures and external cortical plates
Carlos Henrique FERRARI, Amjad ABU HASNA, Frederico Canato MARTINHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of 9,300 nm Carbon Dioxide Laser on Dental Hard Tissue: A Concise Review
Vicky Wenqing Xue, Irene Shuping Zhao, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, John Yun Niu, Edward Chin Man Lo, Chun Hung Chu
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2021; Volume 13: 155. CrossRef - PHOTOPOLYMERIZED COMPOSITIONS AND LIGHT SOURCES FOR DENTAL PRACTICE (REVIEW)
A. M. Lalatovich, M. A. Vaniev, N. V. Sidorenko, Y. A. Makedonova, D. Yu. Dyachenko, S. V. Dyachenko
IZVESTIA VOLGOGRAD STATE TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY.2021; (12(259)): 7. CrossRef - Spray mist reduction by means of a high-volume evacuation system—Results of an experimental study
Martin Koch, Christian Graetz, Essam Al-Moraissi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(9): e0257137. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature changes during orthodontic bonding – an in vitro study
Aysegul Ayhan Bani, Burcu Balos Tuncer, Cumhur Tuncer
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(2): 157. CrossRef - Thermal Behavior of Teeth During Restoration Procedure With Composite: Experimental Tests and Numerical Simulation
M. Potenza, P. Coppa, L. Cerroni, G. Bovesecchi
Journal of Heat Transfer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Thermal Alterations on External Root Surface during Mechanical Instrumentation and Thermoplasticized Gutta-percha Obturation: An Ex Vivo Study
Rohit Sharma, Atul Jain, Madhurima Sharma, Shivani Chauhan, Abhinay Agarwal
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(5): 367. CrossRef - Degree of conversion and in vitro temperature rise of pulp chamber during polymerization of flowable and sculptable conventional, bulk-fill and short-fibre reinforced resin composites
Edina Lempel, Zsuzsanna Őri, Dóra Kincses, Bálint Viktor Lovász, Sándor Kunsági-Máté, József Szalma
Dental Materials.2021; 37(6): 983. CrossRef - Pulp chamber temperature changes during orthodontic bonding – an in vitro study
Aysegul Ayhan Bani, Burcu Balos Tuncer, Cumhur Tuncer
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(2): 157. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature Dependence of Specific Heat of Human Enamel and Dentin: An Experimental Study
Ahmad Soori, Farshad Kowsary, Shahin Kasraei
International Journal of Thermophysics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prosthodontic Applications of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): An Update
Muhammad Sohail Zafar
Polymers.2020; 12(10): 2299. CrossRef - The effect of halogen bulb and light-emitting diode light curing units on temperature increase and fibroblast viability
Georgia Memari Trava, Juliane Almeida Santos, Lucas Paula Ramos, Pamela Beatriz Rosário Estevam dos Santos, Amjad Abu Hasna, Karen Cristina Yui, Adriano Bressane, Luciane Dias de Oliveira, Marianne Spalding
F1000Research.2020; 9: 1369. CrossRef - A Study on Temperature Changes during Bone Scaling and Cutting of Dental Ultrasonic Scaling/Surgery System
Min-Woo Sa, Tae-Jo Ko, Jong Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2020; 19(2): 1. CrossRef - Controlling In Vivo, Human Pulp Temperature Rise Caused by LED Curing Light Exposure
DC Zarpellon, P Runnacles, C Maucoski, U Coelho, FA Rueggeberg, CAG Arrais
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(3): 235. CrossRef - Pulp Temperature Rise Induced by Light-Emitting Diode Light-Curing Units Using an Ex Vivo Model
Alexandra Vinagre, João Ramos, Clara Rebelo, José Basto, Ana Messias, Nélia Alberto, Rogério Nogueira
Materials.2019; 12(3): 411. CrossRef - The cooling efficiency of different dental high-speed handpiece coolant port designs
Helene Chua, Joanne Jung Eun Choi, Rishi Sanjay Ramani, Ritu Ganjigatti, John Neil Waddell
Heliyon.2019; 5(8): e02185. CrossRef - Polymerisation Shrinkage Profiling of Dental Composites using Optical Fibre Sensing and their Correlation with Degree of Conversion and Curing Rate
Ginu Rajan, Raju Raju, Sagar Jinachandran, Paul Farrar, Jiangtao Xi, B. Gangadhara Prusty
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth sectioning for coronectomy: how to perform?
József Szalma, László Vajta, Lajos Olasz, Edina Lempel
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(2): 519. CrossRef - Dentistry Applications of Fiber Bragg Gratings: Irradiation Protocols for Bulk Fill Flow Dental Composites
Ana Paula Gebert de Oliveira Franco, Manoella Maria Machado Costa, Leandro Zen Karam, Osnara Maria Mongruel Gomes, Hypolito Jose Kalinowski
Journal of Lightwave Technology.2019; 37(18): 4881. CrossRef - In Vitro Analysis of Techniques that Alter the Surface Hardness of a Glass Ionomer Restorative Material
Riaan Mulder, Naeemah Noordien, Shaun Rossouw, Luzaan van Zyl
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(12): 1362. CrossRef - Changes in the radicular pulp-dentine complex in healthy intact teeth and in response to deep caries or restorations: A histological and histobacteriological study
Domenico Ricucci, Simona Loghin, Li-na Niu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 73: 76. CrossRef - Effect of Irradiance and Exposure Duration on Temperature and Degree of Conversion of Dual-Cure Resin Cement for Ceramic Restorations
JS Shim, SH Han, N Jha, ST Hwang, W Ahn, JY Lee, JJ Ryu
Operative Dentistry.2018; 43(6): E280. CrossRef - Protective Effects of Base Cements against Intrapulpal Temperature Rise during Curing of Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study by Pulpal Blood Microcirculation Model
Ihsan F Ertugrul, Basak Yazkan, Ceylan Ç Ertugrul
International Journal of Experimental Dental Science.2018; 7(2): 85. CrossRef - Thermal imaging of the pulp during residual adhesive removal
Gökmen Kurt, Nisa Gül, Özgür Er, Gülşen Çakmak, Emre Bendeş, Veysel Aslantaş
Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopädie.2017; 78(4): 330. CrossRef - Influence of the material for preformed moulds on the polymerization temperature of resin materials for temporary FPDs
Philipp-Cornelius Pott, Hans Schmitz-Wätjen, Meike Stiesch, Michael Eisenburger
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(4): 294. CrossRef - Light curing in dentistry and clinical implications: a literature review
Frederick Allen RUEGGEBERG, Marcelo GIANNINI, Cesar Augusto Galvão ARRAIS, Richard Bengt Thomas PRICE
Brazilian Oral Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Intrapulpal temperature changes during curing of different bulk-fill restorative materials
Elif YASA, Cigdem ATALAYIN, Gamze KARACOLAK, Tugrul SARI, L. Sebnem TURKUN
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(5): 566. CrossRef - Can Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Nanoparticulate EndoSequence Root Repair Material Produce Injurious Effects to Rat Subcutaneous Tissues?
Wafaa A. Khalil, Siham K. Abunasef
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1151. CrossRef - Comparison of photopolymerization temperature increases in internal and external positions of composite and tooth cavities in real time: Incremental fillings of microhybrid composite vs. bulk filling of bulk fill composite
Ryan Jin-Young Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Ji-Yun Hwang, In-Bog Lee, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1093. CrossRef - Real-Time Analysis of Temperature Changes in Composite Increments and Pulp Chamber during Photopolymerization
Ryan Jin-Young Kim, In-Bog Lee, Jin-Young Yoo, Su-Jung Park, Sin-Young Kim, Young-Ah Yi, Ji-Yun Hwang, Deog-Gyu Seo
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Maryam Khoroushi, Mohammadreza Moharreri, Mohammad Atai
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 155. CrossRef - Comparison of Exothermic Release during the Polymerization of Four Materials used to fabricate Provisional Restorations
Minu Raju
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2014; 4(1): 1. CrossRef
- Impact of Various Sleeve Materials on Temperature Variations During Guided Endodontic Access Cavity Preparation Utilizing Finite‐Element Analysis
- 4,697 View
- 22 Download
- 71 Crossref

- Review of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Su-Jeong Shin, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):180-187. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Introduction Eliminating the residual debris and bacteria in the root canal system is one of the main purposes of the endodontic treatment. However, the complexity on the anatomy of the root canal system makes it difficult to eliminate the bacterial biofilm existing along the root canal surface and necrotic pulp tissue by mechanical instrumentation and chemical irrigation. Recently, more effective irrigant delivery systems for root canal irrigation have been developed. The purpose of this review was to present an overview of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices available in endodontics.
Review The contents of this paper include as follows;
- syringe-needle irrigation, manual dynamic irrigation, brushes
- sonic and ultrasonic irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, rotary brush, RinsEndo, EndoVac, Laser
Conclusion Though technological advances during the last decade have brought to fruition new agitation devices that rely on various mechanisms, there are few evidence based study to correlate the clinical efficacy of these devices with improved outcomes except syringe irrigation with needle and ultrasonic irrigation.
The clinicians should try their best efforts to deliver antimicrobial and tissue solvent solutions in predictable volumes safely to working length.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
Gilhwan Sung, Jaeyong Sung, Myeong Ho Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Visualization.2016; 14(1): 40. CrossRef
- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
- 1,505 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
- Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):208-214. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.208
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the dye leakage of MTA (mineral trioxide aggregate) apical plug produced by two orthograde placement techniques (hand condensation technique and ultrasonically assisted hand condensation technique).
To simulate straight canal, 60 transparent acrylic blocks with straight canal were fabricated. These transparent acrylic blocks were divided into 2 groups (Group C; hand condensation technique (HC) and Group U; ultrasonically assisted hand condensation technique (UAHC)) of 30 blocks with each MTA application method. Each group was divided into 2 subgroups (n = 15) with different canal size of #70 (subgroup C70 and subgroup U70) and #120 (subgroup C120 and subgroup U120). After apical plug was created, a wet paper point was placed over the MTA plug and specimen was kept in a humid condition at room temperature to allow MTA to set. After 24 hours, remaining canal space was backfilled using Obtura II. All specimens were transferred to floral form socked by 0.2% rhodamine B solution and stored in 100% humidity at room temperature. After 48 hours, resin block specimens were washed and scanned using a scanner. The maximum length of microleakage was measured from the scanned images of four surfaces of each resin block using Photoshop 6.0.
Statistical analysis was performed with Mann-Whitney U test. Group U of UAHC had significantly lower leakage than Group C of HC in #70-size canal (subgroup U70) (p < 0.05).
- 886 View
- 2 Download

- Management of separated file in the root canal
- Hye-Jeong Kim, Hoon-Sang Jang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):161-168. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub During root canal preparation procedures, the potential for instrument separation is always present. Files, a lentulo, a Gates-Glidden (GG) bur or any manufactured obstruction can be left behind in the canal. Nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files are in common usage in these days. Despite their undeniable advantages, there is a potential risk of separation within the canals. It is very rapid, unpredictable, and creates a great deal of stress for the practitioner.
When an endodontic instrument separates, the best option is to remove it. Ultrasonic instruments and microscopes have improved the success rate for removing separated instruments. But it is difficult and not always possible. Therefore prevention is the key.
In this case report, several management methods of separated file in the canal are presented.
- 857 View
- 4 Download

-
An
in-vitro evaluation of sealer placement methods in simulated root canal extensions - Sung-Young Kim, Mi-Jeong Lee, Jang-Won Moon, Se-Joon Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):31-37. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of sealer placement in simulated root canal extensions. Forty resin blocks were attained from the Endo-training Bloc. In each block, the simulated root canal was made with #20, 08taper GT file. After each block was longitudinally split into two halves, a standardized groove was prepared on one canal wall of two halves to simulate the canal extensions with various irregularities. The two halves of each block were assembled and all simulated root canals were obturated by single cone method with AH26 sealer. Four different methods of sealer placement were used: group A, #20 K-file; group B, ultrasonic file; group C, lentulo spiral; group D, EZ-Fill bi-directional spiral. All obturated blocks were stored in 100% humidity at 37℃ for 1 week. Using a low speed saw, each block was sectioned horizontally. Images of the sections were taken using a stereomicroscope at × 30 magnification and a digital camera. The amount of the sealer in the groove was evaluated using a scoring system, a higher score indicated better sealing effectiveness. The data was statistically analysed by Fisher's Exact Test.
The sealing score was the lowest, specially at the middle area of canal extensions in group A, and that was statistically significant difference from other groups. In conclusion, the ultrasonic file, lentulo spiral and EZ-Fill bi-directional spiral were effective methods of sealer placement in simulated canal extensions. The K file was the least effective method, specially at the middle area of canal extensions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of apical sealing efficacies using different plugging depth in continuous wave of obturation technique
Sang-Jin Lee, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 491. CrossRef
- Comparison of apical sealing efficacies using different plugging depth in continuous wave of obturation technique
- 1,049 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


