Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of 3 different light-curing units on the physico-mechanical properties of bleach-shade resin composites
- Azin Farzad, Shahin Kasraei, Sahebeh Haghi, Mahboubeh Masoumbeigi, Hassan Torabzadeh, Narges Panahandeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e9. Published online February 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
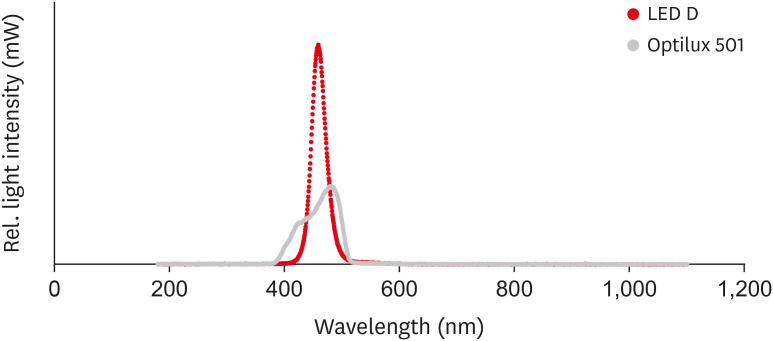
ePub Objectives This study investigated the microhardness, flexural strength, and color stability of bleach-shade resin composites cured with 3 different light-curing units.
Materials and Methods In this
in vitro experimental study, 270 samples were fabricated of bleach and A2 shades of 3 commercial resin composites (Point 4, G-aenial Anterior, and Estelite Sigma Quick). Samples (n = 5 for each trial) were cured with Bluephase N, Woodpecker LED.D, and Optilux 501 units and underwent Vickers microhardness and flexural strength tests. The samples were tested after 24 hours of storage in distilled water. Color was assessed using a spectrophotometer immediately after preparation and 24 hours after curing. Data were analyzed using 3-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test (p ≤ 0.001).Results Samples cured with Optilux exhibited the highest and those cured with LED.D exhibited the lowest microhardness (
p = 0.023). The bleach shade of Point 4 composite cured with Optilux displayed the highest flexural strength, while the same composite and shade cured with Sigma Quick exhibited the lowest (p ≤ 0.001). The color change after 24 hours was greatest for the bleach shade of G-aenial cured with Bluephase N and least for the A2 shade of Sigma Quick cured with Optilux (p ≤ 0.001).Conclusions Light curing with polywave light-emitting diode (LED) yielded results between or statistically similar to those of quartz-tungsten-halogen and monowave LED in the microhardness and flexural strength of both A2 and bleach shades of resin composites. However, the brands of light-curing devices showed significant differences in color stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
Ghada H. Naguib, Jumana Mazhar, Abeer Alnowaiser, Abdulghani Mira, Hisham Mously, Rabab Aljawi, Samar H. Abuzinadah, Mohamed T. Hamed
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1136. CrossRef - Repair Bond Strength of Aged Composite: Effect of Thermocycling and Surface Treatment
Sina Yarmoradian, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani, Elham Ahmadi, Niyousha Rafeie, Mahdi Abbasi, Nastaran Dabiri Shahabi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(3): 228. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Depth of Cure by Microhardness of Bulk-Fill Composites with Monowave and Polywave LED Light-Curing Units
Socratis Thomaidis, Dimitris Kampouropoulos, Maria Antoniadou, Afrodite Kakaboura
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11532. CrossRef - Effect of hard segment chemistry and structure on the self‐healing properties of UV‐curable coatings based on the urethane acrylates with built‐in Diels–Alder adduct
Paulina Bednarczyk, Karolina Mozelewska, Małgorzata Nowak, Joanna Klebeko, Joanna Rokicka, Paula Ossowicz‐Rupniewska
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dental Bleaching Agents on the Surface Roughness of Dental Restoration Materials
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Tuculina, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Cristiana Petcu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Ana Maria Rîcă, Ruxandra Voinea-Georgescu
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1067. CrossRef - Effect of Polywave and Monowave Light Curing Units on Color Change of Composites Containing Trime-thylbenzoyl-Diphenyl-Phosphine Before and After Aging
Negar Madihi, Maryam Hoorizad ganjkar, Negin Nasoohi, Ali Kaboudanian Ardestani
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 249. CrossRef
- Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
- 2,214 View
- 35 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Physicochemical characterization of two bulk fill composites at different depths
- Guillermo Grazioli, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Leina Nakanishi, Alejandro Francia, Rafael Ratto de Moraes
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e39. Published online July 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
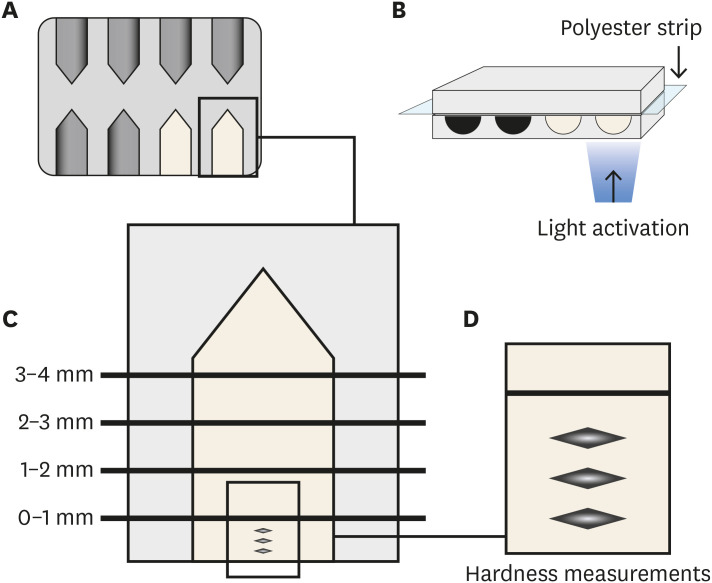
ePub Objectives This study analyzed the physical-chemical behavior of 2 bulk fill resin composites (BFCs; Filtek Bulk Fill [FBF], and Tetric-N-Ceram Bulk Fill [TBF]) used in 2- and 4-mm increments and compared them with a conventional resin composite (Filtek Z250).
Materials and Methods Flexural strength and elastic modulus were evaluated by using a 3-point bending test. Knoop hardness was measured at depth areas 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, and 3–4 mm. The translucency parameter was measured using an optical spectrophotometer. Real-time polymerization kinetics was analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
Results Flexural strength was similar among the materials, while TBF showed lower elastic modulus (Z250: 6.6 ± 1.3, FBF: 6.4 ± 0.9, TBF: 4.3 ± 1.3). The hardness of Z250 was similar only between 0–1 mm and 1–2 mm. Both BFCs had similar hardness until 2–3 mm, and showed significant decreases at 3–4 mm (FBF: 33.45 ± 1.95 at 0–1 mm to 23.19 ± 4.32 at 3–4 mm, TBF: 23.17 ± 2.51 at 0–1 mm to 15.11 ± 1.94 at 3–4 mm). The BFCs showed higher translucency than Z250. The polymerization kinetics of all the materials were similar at 2-mm increments. At 4-mm, only TBF had a similar degree of conversion compared with 2 mm.
Conclusions The BFCs tested had similar performance compared to the conventional composite when used in up to 2-mm increments. When the increment was thicker, the BFCs were properly polymerized only up to 3 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microhardness According to Surface, Distance and Time of Photopolymerization of a Bulk-Fill Resin: In Vitro Study
María José Loayza-Gallegos, Gino Hernan Vidalón-Romo, Julissa Amparo Dulanto-Vargas
Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 1(1): 384. CrossRef - Comparative In Vitro Analysis of Mechanical Properties in Three High-Viscosity Bulk-Fill Composite Resins
Carlos I. Santacruz, Jorge I. Fajardo, César A. Paltán, Ana del Carmen Armas-Vega, Eleonor Vélez León
Journal of Composites Science.2025; 9(11): 623. CrossRef - Translucency of bulk‐fill composite materials: A systematic review
Gaetano Paolone, Sofia Baldani, Niccolò De Masi, Mauro Mandurino, Giacomo Collivasone, Nicola Scotti, Enrico Gherlone, Giuseppe Cantatore
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 995. CrossRef - Can composite packaging and selective enamel etching affect the clinical behavior of bulk-fill composite resin in posterior restorations? 24-month results of a randomized clinical trial
Marcos de Oliveira BARCELEIRO, Chane TARDEM, Elisa Gomes ALBUQUERQUE, Leticia de Souza LOPES, Stella Soares MARINS, Luiz Augusto POUBEL, Roberta BARCELOS, Romina ÑAUPARI-VILLASANTE, Alessandro Dourado LOGUERCIO, Fernanda Signorelli CALAZANS
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - No-Cap Flowable Bulk-Fill Composite: Physico-Mechanical Assessment
Abdullah Alshehri, Feras Alhalabi, Ali Robaian, Mohammed A. S. Abuelqomsan, Abdulrahman Alshabib, Eman Ismail, Faisal Alzamil, Nawaf Alotaibi, Hamad Algamaiah
Polymers.2023; 15(8): 1847. CrossRef - The Microhardness and Surface Roughness Assessment of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites Treated with and without the Application of an Oxygen-Inhibited Layer and a Polishing System: An In Vitro Study
Ann Carrillo-Marcos, Giuliany Salazar-Correa, Leonor Castro-Ramirez, Marysela Ladera-Castañeda, Carlos López-Gurreonero, Hernán Cachay-Criado, Ana Aliaga-Mariñas, Alberto Cornejo-Pinto, Luis Cervantes-Ganoza, César Félix Cayo-Rojas
Polymers.2022; 14(15): 3053. CrossRef
- Microhardness According to Surface, Distance and Time of Photopolymerization of a Bulk-Fill Resin: In Vitro Study
- 2,216 View
- 20 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Influence of 10-MDP concentration on the adhesion and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Kazuhiko Shibuya, Naoko Ohara, Serina Ono, Kumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Yoshiyama
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e45. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e45
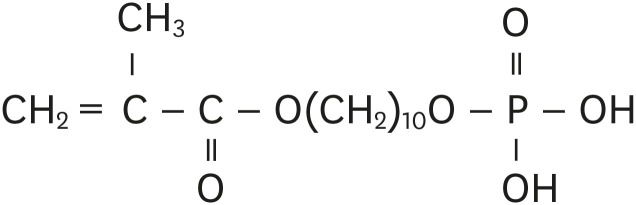
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Self-adhesive resin cements contain functional monomers that enable them to adhere to the tooth structure without a separate adhesive or etchant. One of the most stable functional monomers used for chemical bonding to calcium in hydroxyapatite is 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the10-MDP concentration on the bond strength and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods We used experimental resin cements containing 3 different concentrations of 10-MDP: 3.3 wt% (RC1), 6.6 wt% (RC2), or 9.9 wt% (RC3). The micro-tensile bond strength of each resin cement to dentin and a hybrid resin block (Estenia C&B, Kuraray Noritake Dental) was measured, and the fractured surface morphology was analyzed. Further, the flexural strength of the resin cements was measured using the three-point bending test. The water sorption and solubility of the cements following 30 days of immersion in water were measured.
Results The bond strength of RC2 was significantly higher than that of RC1. There was no significant difference between the bond strength of RC2 and that of RC3. The water sorption of RC3 was higher than that of any other cement. There were no significant differences in the three-point bending strength or water solubility among all three types of cements.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it is suggested that 6.6 wt% 10-MDP showed superior properties than 3.3 wt% or 9.9 wt% 10-MDP in self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Sofia Bignotto de Carvalho, Lívia Maiumi Uehara, João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104260. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Influence of temperature and curing modes on polymerization of self-adhesive resin cements
Hae-In Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(3): 143. CrossRef - Clinical Performance and Retention of Partial Implant Restorations Cemented with Fuji Plus® and DentoTemp™: A Retrospective Clinical Study with Mechanical Validation
Sergiu-Manuel Antonie, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Ioan-Achim Borsanu, Remus Christian Bratu, Emanuel-Adrian Bratu
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2183. CrossRef - A thorough assessment of 10-MDP primers in modern dental adhesive systems
Ahmed A Abduljawad, Harraa SM Salih, Omar F Tawfiq
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 79. CrossRef - Material properties and finite element analysis of adhesive cements used for zirconia crowns on dental implants
Megha Satpathy, Hai Pham, Shreya Shah
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Clinical reliability of self-adhesive luting resins compared to other adhesive procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammed Ahmed Alghauli, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 129: 104394. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization on bond strength between zirconia frameworks and Ti-base abutments using different resin cements
Reinhold Lang, Karl-Anton Hiller, Lena Kienböck, Katrin Friedl, Karl-Heinz Friedl
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(4): 617.e1. CrossRef - Varying 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP) level improves polymerisation kinetics and flexural strength in self-adhesive, remineralising composites
António H.S. Delgado, Nazanin Owji, Paul Ashley, Anne M. Young
Dental Materials.2021; 37(9): 1366. CrossRef - Investigating a Commercial Functional Adhesive with 12-MDPB and Reactive Filler to Strengthen the Adhesive Interface in Eroded Dentin
Madalena Belmar da Costa, António HS Delgado, Tomás Amorim Afonso, Luís Proença, Ana Sofia Ramos, Ana Mano Azul
Polymers.2021; 13(20): 3562. CrossRef
- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- 2,801 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The effect of thermocycling on the degree of conversion and mechanical properties of a microhybrid dental resin composite
- Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Melika Firouzmanesh, Hossein Bagheri, Tahereh S. Jafarzadeh Kashi, Fateme Razazpour, Marjan Behroozibakhsh
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e26. Published online April 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The purpose of this study was to investigate the degree of conversion (DC) and mechanical properties of a microhybrid Filtek Z250 (3M ESPE) resin composite after aging.
Method The specimens were fabricated using circular molds to investigate Vickers microhardness (Vickers hardness number [VHN]) and DC, and were prepared according to ISO 4049 for flexural strength testing. The initial DC (%) of discs was recorded using attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transforming infrared spectroscopy. The initial VHN of the specimens was measured using a microhardness tester under a load of 300 g for 15 seconds and the flexural strength test was carried out with a universal testing machine (crosshead speed, 0.5 mm/min). The specimens were then subjected to thermocycling in 5°C and 55°C water baths. Properties were assessed after 1,000–10,000 cycles of thermocycling. The surfaces were evaluated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance followed by the Tukey honest significant difference
post hoc test.Results Statistical analysis showed that DC tended to increase up to 4,000 cycles, with no significant changes. VHN and flexural strength values significantly decreased upon thermal cycling when compared to baseline (
p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between initial and post-thermocycling VHN results at 1,000 cycles. SEM images after aging showed deteriorative changes in the resin composite surfaces.Conclusions The Z250 microhybrid resin composite showed reduced surface microhardness and flexural strength and increased DC after thermocycling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026; 32(1): 94. CrossRef - Evaluation of surface roughness of PEEK and Laser-Sintered cobalt–chromium subjected to different polishing protocols and thermocycling (an in vitro study)
Marzia Kareem Ahmed, Aras Maruf Rauf
Oxford Open Materials Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative influence of triton and cavity conditioners on the surface characteristics and bond strength of dentin, indicating triton as a cavity conditioner
Lena Bal, Cangül Keskin, Aybüke Karaca Sakallı, Bilge Özcan
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2026; 9(1): 98. CrossRef - The Influence of Thermal and Mechanical Aging on the Flexural Properties of Conventional and 3D-Printed Materials Used in Occlusal Splints Manufacturing
Joanna Smardz, Katarzyna Kresse-Walczak, Heike Meißner, Klaus Böning, Joanna Weżgowiec, Andrzej Małysa, Mieszko Więckiewicz
Materials.2026; 19(2): 421. CrossRef - Failure mechanism analysis and machine learning-based residual strength prediction of CFRP with different ply orientations and loading types under six typical accelerated aging environments
Guofeng Qin, Chenglong Su, Peiwen Mi, Peng Huang, Qiuhan Fan, Ming Li, Wei Tan
Construction and Building Materials.2026; 516: 145630. CrossRef - Discoloration, radiopacity, and push-out bond strength of bismuth-based radiopacifiers in endodontic sealers
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Mina Shekarian, Amir Abdolmaleki, Michael Conte, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
Ömer Hatipoğlu, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Nessrin Taha, Thiyezen Abdullah Aldhelai, Daoud M. Ayyad, Ahmed A. Madfa, Benjamin Martin‐Biedma, Rafael Fernández‐Grisales, Bakhyt A. Omarova, Wen Yi Lim, Suha Alfirjani, Kacper Nijak
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 977. CrossRef - An In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Bioactive Liner's Effect on Marginal Adaptation of Class II Composite Restorations: A Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
Girija S Sajjan, Naveena Ponnada, Praveen Dalavai, Madhu Varma Kanumuri, Venkata Karteek Varma Penmatsa, B V Sindhuja
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 15(9): 749. CrossRef - Different contemporary resin cements for intracanal luting of glass fiber posts - Bonding and polymerization assessments
Anna Caroliny Detogni, Vitaliano Gomes de Araújo Neto, Caio Felipe de Almeida Nobre, Victor Pinheiro Feitosa, Mário Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 138: 103951. CrossRef - Effect of food-simulating liquids and polishing times on the color stability of microhybrid and nanohybrid resin composites
Muhammet Fidan, Nevin Çankaya
Discover Nano.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols for post space preparation on the bond of the resin luting agent and post to a hydraulic calcium silicate filled root: An in vitro study
Nuttanun Poeaim, Sirawut Hiran-us, Yanee Tantilertanant
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(4): 1039.e1. CrossRef - Influence of Different Adhesives and Surface Treatments on Shear and Tensile Bond Strength and Microleakage with Micro-CT of Repaired Bulk-Fill Composites
Handan Yıldırım-Işık, Mediha Büyükgöze-Dindar
Polymers.2025; 17(12): 1680. CrossRef - Effect of thermal ageing on physico-mechanical properties and self-healing potential of experimental 3D-printed denture base resin composites
Mariam Raza Syed, Amr Fawzy
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2025; 170: 107123. CrossRef - Effects of aging on the physicomechanical, antimicrobial, and cytotoxicity properties of flowable composite resin with strontium-modified phosphate-based glass
Seo-Hyun Kim, Hye-Bin Go, Myung-Jin Lee, Jae-Sung Kwon
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Colour Stability and Optical Properties of Provisional Crowns Fabricated With Milling, 3D Printing, and Direct Technique
Tommaso Rinaldi, Carlos Serrano Granger, Andrea Santamaría Laorden, Jaime Orejas-Perez, Pablo Gómez Cogolludo
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(6): 103932. CrossRef - EVALUATE DEGREE OF CONVERSION OF NEW BIOACTIVE ORTHODONTIC ADHESIVE WITH COLOR CHANGE & FLUORESCENCE PROPERTY
Mohammed Younis, Neam Fakhri Neam Fakhri
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 39. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity and physicochemical properties of light-curable fluoride varnishes containing strontium phosphate-based glass
Na-Yeon Kim, Mi-Sol Ryu, Ji-Min Lee, Soo-Yeon Jeong, Hye-Been Choi, Myung-Jin Lee, Song-Yi Yang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Review of Studies Comparing Microleakage After Restoration With Cention and Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement in Human Extracted Teeth
Rashmi Misra, Mansi Vandekar, Gayatri Pendse, Omkar Bhosale, Pauravi Hegde, Aashaka Vaishnav
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the radiopacity of different universal composite resins aged by thermocycling
Dilber Çölkesen, Alican Kuran, Neslihan Tekçe
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the sources and routes of micro- and nanoplastics from dental products and materials: their impact on human health - a systematic review
Vidhya Selvaraj, R. Saravanan, N. Raj Vikram, Uma revathi Gopalakrishnan, Ramsamy M
Next Research.2025; 2(4): 100925. CrossRef - Investigation of the mechanical response of MWCNTs infused carbon/glass fiber-based hybrid composites using digital image correlation
Somaiah Chowdary Mallampati, Ujendra Kumar Komal, Paladugu Rakesh, Parthapratim Barman
Construction and Building Materials.2025; 492: 143068. CrossRef - Mechanical, Surface and Physicochemical Properties of Nanozeolite‐Modified 3D Printed Hybrid Ceramics at Varying Concentrations: An In Vitro Study
Ahmed A. Holiel, Yomna M. Ibrahim, Noha Morsy
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Graphitic Carbon Nitride on Dental Composite’s Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties
Zainab Rafaqat, Saad Liaqat, Ahmed Bari, Warda Khan Yousafzai, Umar Nishan, Sandleen Feroz, Nawshad Muhammad
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Biological and Chemical Properties of Emerging 3D-Printed Dental Resin Composites Compared to Conventional Light-Cured Materials
Nikola Živković, Stefan Vulović, Miloš Lazarević, Anja Baraba, Aleksandar Jakovljević, Mina Perić, Jelena Mitrić, Aleksandra Milić Lemić
Materials.2025; 18(22): 5170. CrossRef - Awareness of possible complications associated with direct composite restorations: A multinational survey among dentists from 13 countries with meta-analysis
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Jakub Jankowski, David Donnermeyer, Paulo J. Palma, Milan Drobac, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Fatma Pertek Hatipoğlu, Indira Tulegenova, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Hamad Mohammad Alharkan, Olga Bekjanova, Sylvia Wyzga, Moataz
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 145: 105009. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of bond strength and color stability of polyetheretherketone and zirconia layered with indirect composite before and after thermocycling: An in vitro study
Pooja Singh, Subhabrata Maiti, Amrutha Shenoy
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2024; 24(3): 252. CrossRef - Biaxial flexural strength of hydrothermally aged resin-based materials
Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Mariana Miranda de Toledo Piza, Bruna de Mello Silva, Thalya Fernanda Horsth Maltarollo, Gustavo Sivieri-Araujo, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Estevam Augusto Bonfante, Henrico Badaoui Strazzi-Sahyon
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 155: 106568. CrossRef - Comparative Strength Study of Indirect Permanent Restorations: 3D-Printed, Milled, and Conventional Dental Composites
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Adelheid Veerman, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva
Clinics and Practice.2024; 14(5): 1940. CrossRef - Influencia del termociclado sobre la estabilidad del color de dos resinas compuestas
//Influence of thermocycling on the color stability of two composite resins
Verónica Lucía Ventrera, María Eugenia Alejandra Barrionuevo
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Efeito do protocolo de polimento e do armazenamento em meio úmido na variação de cor, massa e rugosidade superficial de resinas compostas
Leonardo Cruz Morais, Mateus Victória Gontijo, Gabriela Rodrigues Pires, Victor de Morais Gomes, Milton Carlos Kuga, Francisco Fernando Massola Filho, Amanda Gonçalves Franco, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2024; 16(6): e4556. CrossRef - A comparison of the mechanical properties of 3D-printed, milled, and conventional denture base resin materials
Hyeong-Ju YU, You-Jung KANG, Yeseul PARK, Hoon KIM, Jee-Hwan KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 813. CrossRef - Effect of aging and fiber‐reinforcement on color stability, translucency, and microhardness of single‐shade resin composites versus multi‐shade resin composite
Muhammet Fidan, Özhan Yağci
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(4): 632. CrossRef - Impact of Artificial Aging on the Physical and Mechanical Characteristics of Denture Base Materials Fabricated via 3D Printing
Ahmed Altarazi, Julfikar Haider, Abdulaziz Alhotan, Nick Silikas, Hugh Devlin, Weihao Yuan
International Journal of Biomaterials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis, monomer conversion, and mechanical properties of polylysine based dental composites
Saadia Bano Lone, Rabia Zeeshan, Hina Khadim, Muhammad Adnan Khan, Abdul Samad Khan, Anila Asif
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106398. CrossRef - Bond strength and surface roughness assessment of novel antimicrobial polymeric coated dental cement
Ghada Naguib, Hisham Mously, Jumana Mazhar, Ibrahim Alkanfari, Abdulelah Binmahfooz, Mohammed Zahran, Mohamed T. Hamed
Discover Nano.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness, degree of conversion, and abrasion resistance of nanoglass and multiwalled carbon nanotubes reinforced three‐dimensionally printed denture base resins
Pansai Ashraf Mohamed, Yomna Mohamed Ibrahim, Kenda Ibrahim Hisham Hanno, Mohamed Mahmoud Abdul‐Monem
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of CAD-CAM block thickness and translucency on the polymerization of luting materials
Bengü Doğu Kaya, Selinsu Öztürk, Ayşe Aslı Şenol, Erkut Kahramanoğlu, Pınar Yılmaz Atalı, Bilge Tarçın
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Simulation of oral environmental conditions through artificial aging of teeth for the assessment of enamel discoloration in orthodontics
Celal Irgın
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Do universal adhesive systems affect color coordinates and color change of single-shade resin composites compared with a multi-shade composite?
Muhammet FİDAN, Özhan YAĞCI
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 886. CrossRef - Fabrication, Evaluation, and Performance Ranking of Tri-calcium Phosphate and Silica Reinforced Dental Resin Composite Materials
Sonu Saini, Anoj Meena, Ramkumar Yadav, Amar Patnaik
Silicon.2023; 15(18): 8045. CrossRef - Can Modification with Urethane Derivatives or the Addition of an Anti-Hydrolysis Agent Influence the Hydrolytic Stability of Resin Dental Composite?
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Izabela M. Barszczewska-Rybarek, Marta W. Chrószcz-Porębska, Karolina Kopacz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Kinga Bociong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4336. CrossRef - Effect of veneering material type and thickness ratio on flexural strength of bi-layered PEEK restorations before and after thermal cycling
Ahmed Gouda, Ashraf Sherif, Mennatallah Wahba, Tarek Morsi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2629. CrossRef - 3D printed denture base material: The effect of incorporating TiO2 nanoparticles and artificial ageing on the physical and mechanical properties
Ahmed Altarazi, Julfikar Haider, Abdulaziz Alhotan, Nick Silikas, Hugh Devlin
Dental Materials.2023; 39(12): 1122. CrossRef - Influence of silane coupling agent and aging on the repair bond strength of dental composites
Gustavo Jusué-Esparza, José Alejandro Rivera-Gonzaga, Guillermo Grazioli, Ana Josefina Monjarás-Ávila, J. Eliezer Zamarripa-Calderón, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(5): 913. CrossRef - Degree of conversion of light‐polymerized composite resin in implant prosthesis screw access opening
Se‐Hyun Park, Yoon‐Hyuk Huh, Chan‐Jin Park, Lee‐Ra Cho, Kyung‐Ho Ko
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(9): 829. CrossRef - Investigation of the effect of matrix-interface formed with silane-based coupling agents on physico-chemical behavior and flow distance of dental composites
Zerin Yeşil Acar, Merve Tunç Koçyiğit, Meltem Asiltürk
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2023; 378: 121600. CrossRef - Evaluation of Water Sorption and Solubility of 3D-Printed, CAD/CAM Milled, and PMMA Denture Base Materials Subjected to Artificial Aging
Mariya Dimitrova, Angelina Vlahova, Ilian Hristov, Rada Kazakova, Bozhana Chuchulska, Stoyan Kazakov, Marta Forte, Vanja Granberg, Giuseppe Barile, Saverio Capodiferro, Massimo Corsalini
Journal of Composites Science.2023; 7(8): 339. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on internal microhardness of high and low viscosity bulk fill composite resins in class I cavities
Sâmara Luciana de Andrade LIMA, Lais Lemos CABRAL, Natália Russo CARLOS, Saulo André de Andrade LIMA, Kamila Rosamilia KANTOVITZ, Flávia Lucisano Botelho do AMARAL
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of an Acidic Environment on the Strength and Chemical Changes of Resin-based Composites
S Kang, B-H Cho
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(4): E81. CrossRef - Influence of compressive forces and aging through thermocycling on the strength of mono incremental dental composite resins
Cristian Roberto Sigcho Romero, Henry Fabricio Mejía Mosquera, Sandra Marcela Quisiguiña Guevara, Yudy Jacqueline Alvarado Aguayo
Bionatura.2023; 8(4): 1. CrossRef - Push-out Bond Strength of Two Fiber Posts in Composite Resin Using Different Types of Silanization
RM Novis, BLT Leon, FMG França, CP Turssi, RT Basting, FLB Amaral
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(2): 173. CrossRef - Penetration and Adaptation of the Highly Viscous Zinc-Reinforced Glass Ionomer Cement on Contaminated Fissures: An In Vitro Study with SEM Analysis
Galiah AlJefri, Sunil Kotha, Muhannad Murad, Reham Aljudaibi, Fatmah Almotawah, Sreekanth Mallineni
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 6291. CrossRef - Surface Characteristics and Color Stability of Dental PEEK Related to Water Saturation and Thermal Cycling
Liliana Porojan, Flavia Roxana Toma, Mihaela Ionela Bîrdeanu, Roxana Diana Vasiliu, Ion-Dragoș Uțu, Anamaria Matichescu
Polymers.2022; 14(11): 2144. CrossRef - Effects of aging and light-curing unit type on the volume and internal porosity of bulk-fill resin composite restoration
Afnan O. Al-Zain, Elaf A. Alboloshi, Walaa A. Amir, Maryam A. Alghilan, Eliseu A. Münchow
The Saudi Dental Journal.2022; 34(3): 243. CrossRef - An Evaluation of the Hydrolytic Stability of Selected Experimental Dental Matrices and Composites
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Karolina Kopacz, Malgorzata Iwona Szynkowska-Jozwik, Jerzy Sokolowski, Kinga Bociong
Materials.2022; 15(14): 5055. CrossRef - Comparison of the Mechanical Properties and Push-out Bond Strength of Self-adhesive and Conventional Resin Cements on Fiber Post Cementation
MR Santi, RBE Lins, BO Sahadi, JR Soto-Montero, LRM Martins
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 346. CrossRef - Effect of Different Polymerization Times on Color Change, Translucency Parameter, and Surface Hardness of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites
HY Gonder, M Fidan
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(10): 1751. CrossRef - Surface degradation and biofilm formation on hybrid and nanohybrid composites after immersion in different liquids
Gabriela Escamilla-Gómez, Octavio Sánchez-Vargas, Diana M. Escobar-García, Amaury Pozos-Guillén, Norma V. Zavala-Alonso, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, José E. Pérez-López, Gregorio Sánchez-Balderas, Gabriel F. Romo-Ramírez, Marine Ortiz-Magdaleno
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(4): 263. CrossRef - Effects of Different Adhesive Systems and Orthodontic Bracket Material on Enamel Surface Discoloration: An In Vitro Study
Ali Alqerban, Doaa R. M. Ahmed, Ali S. Aljhani, Dalal Almadhi, Amjad AlShahrani, Hussah AlAdwene, Abdulaziz Samran
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(24): 12885. CrossRef - Effects of Immediate Coating on Unset Composite with Different Bonding Agents to Surface Hardness
Nantawan Krajangta, Supissara Ninbanjong, Sunisa Khosook, Kanjana Chaitontuak, Awiruth Klaisiri
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(04): 828. CrossRef - Rational durability of optical properties of chameleon effect of Omnichroma and Essentia composite thermocycled in black dark drinks (in vitro study)
Bassma Abdelhamed, Asmaa Abdel-Hakeem Metwally, Heba A. Shalaby
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Nanohybrid Composite Restoration After the Placement of Flowable Compomer and Composite Using the Snowplow Technique
Meghna Dugar, Anuja Ikhar, Pradnya Nikhade, Manoj Chandak, Nidhi Motwani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The First Step in Standardizing an Artificial Aging Protocol for Dental Composites—Evaluation of Basic Protocols
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Magdalena Fronczek, Katarzyna Ranoszek-Soliwoda, Jarosław Grobelny, Jerzy Sokolowski, Kinga Bociong
Molecules.2022; 27(11): 3511. CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Long‐Term Repair Bond Strength of Aged Methacrylate‐Based Resin Composite Restorations: A Systematic Review and Network Meta‐analysis
Mahdi Hadilou, Amirmohammad Dolatabadi, Morteza Ghojazadeh, Hossein Hosseinifard, Parnian Alizadeh Oskuee, Fatemeh Pournaghi Azar, Victor Feitosa
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Edge chipping resistance of veneering composite resins
Parissa Nassary Zadeh, Bogna Stawarczyk, Rüdiger Hampe, Anja Liebermann, Felicitas Mayinger
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2021; 116: 104349. CrossRef - The effect of radiation exposure and storage time on the degree of conversion and flexural strength of different resin composites
Ragia M. Taher, Lamiaa M. Moharam, Amin E. Amin, Mohamed H. Zaazou, Farid S. El-Askary, Mokhtar N. Ibrahim
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Load of CAD/CAM Fabricated Cantilever Implant-Supported Zirconia Framework: An In Vitro Study
Ibraheem F. Alshiddi, Syed Rashid Habib, Muhammad Sohail Zafar, Salwa Bajunaid, Nawaf Labban, Mohammed Alsarhan
Molecules.2021; 26(8): 2259. CrossRef - A numerical, theoretical and experimental study of the effect of thermocycling on the matrix-filler interface of dental restorative materials
Yoan Boussès, Nathalie Brulat-Bouchard, Pierre-Olivier Bouchard, Yannick Tillier
Dental Materials.2021; 37(5): 772. CrossRef - Impact of polymerization and storage on the degree of conversion and mechanical properties of veneering resin composites
Felicitas MAYINGER, Marcel REYMUS, Anja LIEBERMANN, Marc RICHTER, Patrick KUBRYK, Henning GROẞEKAPPENBERG, Bogna STAWARCZYK
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(2): 487. CrossRef - Intrapulpal Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide of Teeth Restored With Bulk Fill and Conventional Bioactive Composites
DP Silva, BA Resende, M Kury, CB André, CPM Tabchoury, M Giannini, V Cavalli
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): E158. CrossRef - Silane content influences physicochemical properties in nanostructured model composites
Larissa Maria Cavalcante, Lucielle Guimarães Ferraz, Karinne Bueno Antunes, Isadora Martini Garcia, Luis Felipe Jochims Schneider, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Dental Materials.2021; 37(2): e85. CrossRef - AĞIZ GARGARALARI VE ANTİSEPTİKLERİNİN FARKLI KOMPOZİT REZİNLERİN RENK STABİLİTESİNE ETKİSİ
Turan Emre KUZU, Özcan KARATAŞ
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Immediate and Delayed Microleakage of Class V Cavities Restored with Chitosan-incorporated Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study
Roopa R Nadig, Veena Pai, Arpita Deb
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(5): 621. CrossRef - Influence of Diode Laser for the Treatment of Dentin Hypersensitivity on Microleakage of Cervical Restorations
Doaa R. M. Ahmed, Diana G. Shaath, Jomana B. Alakeel, Abdulaziz A. Samran, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Ageing of Dental Composites Based on Methacrylate Resins—A Critical Review of the Causes and Method of Assessment
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Jerzy Sokolowski, Joanna Kleczewska, Kinga Bociong
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 882. CrossRef - Flexural strength and surface microhardness of materials used for temporary dental disocclusion submitted to thermal cycling: An in vitro study
Tamires Borges de Lima, José Guilherme Neves, Ana Paula Terossi de Godoi, Ana Rosa Costa, Viviane Veroni Degan, Américo Bortolazzo Correr, Heloisa Cristina Valdrighi
International Orthodontics.2020; 18(3): 519. CrossRef - Evaluation of the repair capacities and color stabilities of a resin nanoceramic and hybrid CAD/CAM blocks
Hasibe Sevilay Bahadır, Yusuf Bayraktar
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments of Resin Relined Fiber Posts Cemented With Self-adhesive Resin Cement on Push-out and Microtensile Bond Strength Tests
RV Machry, PE Fontana, TC Bohrer, LF Valandro, OB Kaizer
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(4): E185. CrossRef - Influences of Successive Exposure to Bleaching and Fluoride Preparations on the Surface Hardness and Roughness of the Aged Resin Composite Restoratives
Khalid M. Abdelaziz, Shugufta Mir, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Suheel M. Baba, Saud S. Alshahrani, Eman A. Alshahrani, Zahra A. Alsafi
Medicina.2020; 56(9): 476. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Lithıum Disilicate, Indirect Resin Composite and Zirconıa by Using Dual Cure Resin Cements
Mohammed BADWAN, Erkut KAHRAMANOĞLU
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2020; 10(4): 435. CrossRef - Effect of Stress-decreasing Resin Thickness as an Intermediate Layer on Fracture Resistance of Class II Composite Restoration: An In Vitro Study
Dennis Dennis, Arwin Leonardy, Trimurni Abidin
World Journal of Dentistry.2020; 11(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of Thermocycling on Biaxial Flexural Strength of CAD/CAM, Bulk Fill, and Conventional Resin Composite Materials
EB Benalcázar Jalkh, CM Machado, M Gianinni, I Beltramini, MMT Piza, PG Coelho, R Hirata, EA Bonfante
Operative Dentistry.2019; 44(5): E254. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of hybrid computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials after aging treatments
Hae-Yong Jeong, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Yu-Sung Choi
Ceramics International.2018; 44(16): 19217. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 6,897 View
- 59 Download
- 83 Crossref

- Effect of water storage on flexural strength of silorane and methacrylate-based composite resins
- Narges Panahandeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Hani Naderi, Seyedeh Mahsa Sheikh-Al-Eslamian
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):309-315. Published online November 6, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study assessed the effect of water storage on the flexural strength (FS) of low shrinkage composites.
Materials and Methods A total of 165 bar-shaped specimens (2 × 2 × 25 mm) were fabricated of 2 low shrinkage composites (Filtek P90 [3M ESPE], GC Kalore [GC International]) and a conventional methacrylate-based composite (Filtek Z250 [3M ESPE]). The specimens were subjected to 3-point bending test at 6 time intervals, namely: immediately after curing, at 24 hours, 1 week, 1 month, 6 months, and 1 year following storage in wet and dry conditions. The FS of the specimens were measured by applying compressive load at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. Data was analyzed using 3-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test.
Results Three-way ANOVA revealed significant interactions between time, type of composite, and storage condition (
p = 0.001). Tukey's multiple comparison test revealed significant reductions in FS of all composites after 6 months and 1 year of storage in distilled water compared to dry condition.Conclusions Filtek P90 showed the highest and GC Kalore showed the lowest FS after 1 year storage in distilled water. The immediate high strength of Filtek Z250 significantly decreased at 1 year and its final value was lower than that of Filtek P90.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Graphene–Catechol Dental Sealant: Antibacterial and Mechanical Evaluation
Renata Pereira, Flávio H. B. Aguiar, Rodrigo B. E. Lins, Maria C. A. J. Mainairdi, Bruna G. Silva, Marcela A. Ferretti, Klaus Rischka
Advanced Engineering Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Bio-Aging on Mechanical Properties and Microbial Behavior of Different Resin Composites
Yuke Shou, Lanzhi Deng, Xiaoyu Huang, Xinyu Peng, Xinxuan Zhou, Zheng Wang, Yannan Huang, Bina Yang, Haohao Wang, Min Zhang, Lei Cheng
Biomolecules.2023; 13(7): 1125. CrossRef - Changes in color and contrast ratio of resin composites after curing and storage in water
Marlus da Silva Pedrosa, Fernando Neves Nogueira, Vitor de Oliveira Baldo, Igor Studart Medeiros
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(8): 1160. CrossRef - Ageing of Dental Composites Based on Methacrylate Resins—A Critical Review of the Causes and Method of Assessment
Agata Szczesio-Wlodarczyk, Jerzy Sokolowski, Joanna Kleczewska, Kinga Bociong
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 882. CrossRef - Color stability of nanohybrid composite resins in drinks
Juliana Jendiroba Faraoni, Isabela Barbosa Quero, Lívia Semedo Schiavuzzo, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 18: e191601. CrossRef - Mechanical Degradation of Different Classes of Composite Resins Aged in Water, Air, and Oil
Weber Adad Ricci, Priscila Alfano, Saulo Pamato, Carlos Alberto dos Santos Cruz, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Effects of water and microbial-based aging on the performance of three dental restorative materials
Xinxuan Zhou, Suping Wang, Xian Peng, Yao Hu, Biao Ren, Mingyun Li, Liying Hao, Mingye Feng, Lei Cheng, Xuedong Zhou
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2018; 80: 42. CrossRef
- Graphene–Catechol Dental Sealant: Antibacterial and Mechanical Evaluation
- 1,651 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Flexural strength and microstructure of two lithium disilicate glass ceramics for CAD/CAM restoration in the dental clinic
- Suk-Ho Kang, Juhea Chang, Ho-Hyun Son
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):134-140. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives There has been a growing interest in glass ceramic systems with good esthetics, high fracture resistance and bonding durability, and simplified fabrication techniques using CAD/CAM. The aim of this study is to compare flexural strength before and after heat treatment of two lithium disilicate CAD/CAM blocks, IPS e.max CAD (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Rosetta SM (Hass), and to observe their crystalline structures.
Materials and Methods Biaxial flexural strength was tested according to ISO 6872 with 20 disc form specimens sliced from each block before and after heat treatment. Also, the crystalline structures were observed using field-emission scanning microscopy (FE-SEM, Hitachi) and x-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku) analysis. The mean values of the biaxial flexural strength were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test at a significance level of
p = 0.05.Results There were no statistically significant differences in flexural strength between IPS e.max CAD and Rosetta SM either before heat treatment or after heat treatment. For both ceramics, the initial flexural strength greatly increased after heat treatment, with significant differences (
p < 0.05). The FE-SEM images presented similar patterns of crystalline structure in the two ceramics. In the XRD analysis, they also had similar patterns, presenting high peak positions corresponding to the standard lithium metasilicate and lithium disilicate at each stage of heat treatment.Conclusions IPS e.max CAD and Rosetta SM showed no significant differences in flexural strength. They had a similar crystalline pattern and molecular composition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lithium silicate glass‐ceramics for dental restoration: From fundamental properties to machine‐learning design
Shanshan Liu, Yan Yan, Pijun Gong, Feng He
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Translucency and Color Changes in Lithium Disilicate Ceramics After Sintering Modification and Artificial Aging
Mai Soliman, Raghad Alotaibi, Abrar Almutairi, Asma Alzahrani, Reem Abunyan, Aseel Rozi, Dalia Alamri, Shahad Almakenzi, Elzahraa Eldwakhly, Alhanoof Aldegheishem
Inorganics.2026; 14(2): 56. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Rehabilitation of a Missing Maxillary Lateral Incisor Using a Lithium Disilicate Cantilever Resin-Bonded Prosthesis: A Clinical Case Report
Mohanned M. Toras, Ossama Raffa, Hanaa Ashkar, Faris Alsufi, Loai Alsofi
Prosthesis.2026; 8(2): 17. CrossRef - A novel simplified method for assessing crystal length and crystalline content in dental ceramics
Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Lucas Nascimento Tavares, Isadora Aparecida Ribeiro Reis, William W. Brackett, Rafael Rocha Pacheco, Luís Henrique Araújo Raposo
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(1): 224. CrossRef - The Effect of Chewing Simulation on Flexural Strength of Different Lithium Disilicate Ceramics
Osamah Alsulimani, Salah Yousief, Raghad Al-Dabbagh, Esraa Attar, Dalea Bukhary, Hamad Algamaiah, Khadija Musawa, Awatif Subahi, Samar Abuzinadah, Abdulrahman Alhaddad, Waleed Alqahtani, Abdel Naser Emam, Mohammad Alqhtani, Ahmed Elmarakby
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2025; Volume 17: 67. CrossRef - The influence of thermal tempering on the fracture resistance, surface microstructure, elemental surface composition, and phase analysis of four heat-pressed lithia-based glass ceramic crowns
Khaled Nasser, Amr EL-Etreby, Soha Osama Nabih
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of color stability in polished and glazed CAD/CAM ceramics subjected to coffee thermal cycling: an in vitro study
Reza Nahidi, Azita Mazaheri, Shaghayegh Golalipour, Negin Youshaei, Sotude Khorshidi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the Effect of Precrystallization or Postcrystallization Adjustments on Fatigue Behavior of Lithium Disilicate‐Based Ceramics
Abdel Rahim Mohamad Abdel Salam Suleiman, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Vinícius Felipe Wandscher, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Jovito Adiel Skupien
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biaxial Flexural Strength of Lithium‐Based CAD/CAM Dental Glass‐Ceramics
Saleh Alhindi, Dayane Oliveira, Patricia Pereira, Ali A. Elkaffas, Mateus Rocha
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Zirconia Coping Overlapped by Lithium Disilicate on Esthetic Outcome: A Systematic Review
Mousa Alrashidy, Raghdah Abdullah Al Thubaiti, Najla Haif Alqahtani, Abdulrahman Kamal Habash, Ruba Abdullah Alkhalil
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Microstructure and mechanical properties of an experimental lithium disilicate dental glass-ceramic
Bruna de F. Vallerini, Laís D. Silva, Mariana de O.C. Villas-Bôas, Oscar Peitl, Edgar D. Zanotto, Lígia A.P. Pinelli
Ceramics International.2024; 50(1): 188. CrossRef - Effect of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing bleach shade ceramic thickness on its light transmittance and microhardness of light-cured resin cement
Pardis Sheibani, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenous, Behnaz Esmaeili, Ali Bijani
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of “fast”-crystallization and simultaneous glazing on physicochemical properties of lithium-disilicate CAD/CAM ceramic
Fabián Murillo-Gómez, Federico Murillo-Alvarado, Fabián Vásquez-Sancho, Esteban Avendaño, Roberto Urcuyo
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 148: 105257. CrossRef - Quantitative examination of factors influencing the colour reproduction ability of lithium disilicate glass-ceramics
József Saláta, Ferenc Szabó, Péter Csuti, Melinda Antal, Péter Márton, Péter Hermann, Judit Borbély, Emese Ábrám
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Flexural Strength of Modern CAD/CAM Restoratives After Artificial Aging
Thomas Melc, Thomas Attin, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan
Materials.2024; 17(21): 5178. CrossRef - Microstructural and flexural strength of various CAD‐CAM lithium disilicate ceramics
Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Amanda Soares Silva, Aryvelto Miranda Silva, João Felipe Besegato, Oscar Fernando Muñoz‐Chávez, Edson Alves de Campos
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface Roughness Evaluation of Pre- Versus Post-Crystallization Polish of Two High-Strength Silicate Ceramics for Chairside CAD/CAM Technology
Felipe Tarosso Rea, Andre Valcanaia, Pilar Herrera-Fierro, Manish Verma, Gisele de Faria Neiva
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2768. CrossRef - Influence of Finishing and Polishing Procedures on the Surface Characteristics and Flexural Strength of Monolithic Zirconia: An In Vitro Study
Lakshmi Shivasubramanian, Annapoorni Hariharan, Vyshnavi Devi Janagaraj, Vigneswaran Sekar
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 19. CrossRef - Effect of hydrofluoric acid concentration and aging on the bond strength ceramics to a resin cement
Bruno Delgado Clerot, Lourenço Correr-Sobrinho, Milena Bandini, Evaldo Pinheiro Beserra-Neto, Fernanda Midori Tsuzuki, Rafael Rocha Pacheco, Ana Rosa Costa
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biaxial flexural strength and Weibull characteristics of a resin ceramic material after thermal‐cycling
Elaheh Beyabanaki, Reza Eftekhar Ashtiani, Mehrnoosh Moradi, Mahshid Namdari, Delaram Mostafavi, Amirali Zandinejad
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(8): 721. CrossRef - Fit and fatigue behavior of CAD-CAM lithium disilicate crowns
William Garcia Alves, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Luiz Felipe Valandro, Myriam Pereira Kapczinski, Cristiane Machado Mengatto, Sara Fraga
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(2): 241.e1. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Five Esthetic Ceramic Materials Used for Monolithic Restorations: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Saleh N. Almohammed, Belal Alshorman, Layla A. Abu-Naba’a
Ceramics.2023; 6(2): 1031. CrossRef - The Light Reflection Changes of Monolithic Zirconia and Lithium Disilicate after Using Two External Staining Kits following by Thermocycling
Eran Dolve, Gil Ben-Izhack, Avi Meirowitz, Hadar Erel, Ofir Rosner, Ameer Biadsee, Diva Lugassy, Asaf Shely
Materials.2023; 16(5): 2057. CrossRef - Flexural Strength of CAD/CAM Lithium-Based Silicate Glass–Ceramics: A Narrative Review
Alvaro Munoz, Zejiao Zhao, Gaetano Paolone, Chris Louca, Alessandro Vichi
Materials.2023; 16(12): 4398. CrossRef - Effect of thickness of CAD/CAM materials on light transmission and resin cement polymerization using a blue light‐emitting diode light‐curing unit
Eduardo Fernandes de Castro, Bruna Marin Fronza, Jorge Soto‐Montero, Marcelo Giannini, Carlos Tadeu dos‐Santos‐Dias, Richard Bengt Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(2): 368. CrossRef - Fragile Effects of Mobile Phone Emitted Radiations on Agricultural Growth and Ecological Systems
Aqarab Husnain Gondal, Franklin Ore Areche, María Soledad Porras-Roque, Abel Alberto Muñiz Paucarmayta, Marco Herber Muñiz Paucarmayta, Guillermo Gomer Cotrina Cabello, Jorge Washington Rodriguez-Deza
Reviews in Agricultural Science.2023; 11: 137. CrossRef - Ceramics overview
Russell Giordano II
British Dental Journal.2022; 232(9): 658. CrossRef - Digital image analysis of fluorescence of ceramic veneers with different ceramic materials and resin cements
Jiao ZHANG, Qing YU
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 868. CrossRef - Microstructural considerations for novel lithium disilicate glass ceramics: A review
Jin‐Ho Phark, Sillas Duarte
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(1): 92. CrossRef - Biaxial flexure strength and physicochemical characterization of a CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramic: effect of etching time, silane, and adhesive applications
Sarah Emille Gomes da Silva, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Karina Barbosa Souza, Dayanne Monielle Duarte Moura, Iana Lamadrid Aurélio, Liliana Gressler May, Taciana Emília Leite Vila-Nova, Yu Zhang, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(11): 6753. CrossRef - Mechanical stability of dental CAD-CAM restoration materials made of monolithic zirconia, lithium disilicate, and lithium disilicate–strengthened aluminosilicate glass-ceramic with and without fatigue conditions
Nadin Al-Haj Husain, Tobias Dürr, Mutlu Özcan, Urs Brägger, Tim Joda
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(1): 73. CrossRef - In Vivo Evaluation of the Effects of Sintering Temperature on the Optical Properties of Dental Glass-Ceramics
Kuo-Cheng Fan, Yu-Ling Lin, Hao-Wei Tsao, Hsuan Chen, Sheng-Yang Lee, Yu-Chen Cheng, Hsiao-Ping Huang, Wei-Chun Lin
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(13): 2187. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of pressed ZLS crowns versus pressed LD crowns under thermo-mechanical cycling
Basma Osama Salem, Dina Magdy Elshehawi, Gihan Abdelhady Elnaggar
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(6): 103. CrossRef - Improving early running-in wear characteristics for dental lithium disilicate glass-ceramics by ion-exchange
T.J. Men, Z.G. Chai, X.C. Li, D. Li, F. Wang, L. He, S.F. Zhang, M. Meng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 126: 105037. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on the biaxial flexure strength, Weibull characteristics, roughness, and surface topography of bonded CAD/CAM silica-based ceramics
Camila Moreira Lima, Nathalia Ramos da Silva, Jordana Dias Martins, Jean Soares Miranda, Ricardo Tanaka, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza, Fabíola Pessôa Pereira Leite
Dental Materials.2021; 37(3): e151. CrossRef - Effects of multiple firing processes on the mechanical properties of lithium disilicate glass-ceramics produced by two different production techniques
Alper Ozdogan, Hatice Ozdemir
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 527.e1. CrossRef - The Influence of Surface Roughening and Polishing on Microbial Biofilm Development on Different Ceramic Materials
Mohamed Mahmoud Abdalla, Islam A.A. Ali, Khadija Khan, Nikos Mattheos, Sukhdeep Murbay, Jukka Pekka Matinlinna, Prasanna Neelakantan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(5): 447. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Load of the Four Translucent Zirconia Crowns
Suchada Kongkiatkamon, Kittipong Booranasophone, Apichat Tongtaksin, Valailuck Kiatthanakorn, Dinesh Rokaya
Molecules.2021; 26(17): 5308. CrossRef - The roles of microstructure and surface energy on subcritical crack growth in glass-ceramics
Pamela Ricco, Nathália de Carvalho Ramos, Tiago Moreira Bastos Campos, Viviane Oliveira Soares, Mariana de Oliveira Carlos Villas Boas, Renata Marques de Melo
Ceramics International.2021; 47(5): 6827. CrossRef - Comparative in-vitro study of marginal gap of four cad/cam all ceramic systems with thermal aging
Fatma A. Hasaneen, Marwa M. Mogahed
Tanta Dental Journal.2021; 18(1): 12. CrossRef - Stress Distribution in Modified Veneer Crowns: 3D Finite Element Analysis
Camila Ferreira Leite Madruga, Gabriela Freitas Ramos, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Guilherme de Siqueira Ferreira Anzaloni Saavedra, Rodrigo Othávio Souza, Renata Marques de Melo Marinho, Marcela Moreira Penteado
Oral.2021; 1(3): 272. CrossRef - Surface Characterization and Conductivity of Two Types of Lithium-Based Glass Ceramics after Accelerating Ageing
Marko Jakovac, Teodoro Klaser, Borna Radatović, Željko Skoko, Luka Pavić, Mark Žic
Materials.2020; 13(24): 5632. CrossRef - Biaxial flexural strength and translucent characteristics of dental lithium disilicate glass ceramics with different translucencies
Fu Wang, Tao Yu, Jihua Chen
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2020; 64(1): 71. CrossRef - Femtosecond laser micro-milling dental glass ceramics: An experimental analysis and COMSOL finite element simulation
Peixin Hu, Lu Yao, Mingji Zhang, Zilin Nie, Encai Ji, QiTao Lue, Zhengdi He
Ceramics International.2020; 46(14): 22146. CrossRef - Glass–Ceramics in Dentistry: A Review
Le Fu, Håkan Engqvist, Wei Xia
Materials.2020; 13(5): 1049. CrossRef - Effect of staining and repeated firing on the surface and optical properties of lithium disilicate
Jean S. Miranda, Aline S. P. Barcellos, Carolina M. MartinelliLobo, Taciana M. F. Caneppele, Marina Amaral, Estevão T. Kimpara
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2020; 32(1): 113. CrossRef - Effects of glazing methods on the optical and surface properties of silicate ceramics
Meral Kurt, Merve Bankoğlu Güngör, Seçil Karakoca Nemli, Bilge Turhan Bal
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2020; 64(2): 202. CrossRef - Microstructural and mechanical analysis of two CAD-CAM lithium disilicate glass-reinforced ceramics
Lucas do Nascimento TAVARES, Karla ZANCOPÉ, Anielle Christine Almeida SILVA, Luís Henrique Araújo RAPOSO, Carlos José SOARES, Flávio Domingues das NEVES
Brazilian Oral Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of New Metal-Free Materials Used for CAD-CAM Fabrication of Partial Posterior Restorations
Georgina García-Engra, Lucia Fernandez-Estevan, Javier Casas-Terrón, Antonio Fons-Font, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Juan Luis Román-Rodriguez
Medicina.2020; 56(3): 132. CrossRef - Surface Characterization and Optical Properties of Reinforced Dental Glass-Ceramics Related to Artificial Aging
Liliana Porojan, Roxana-Diana Vasiliu, Mihaela-Ionela Bîrdeanu, Sorin-Daniel Porojan
Molecules.2020; 25(15): 3407. CrossRef - Influence of Occlusal Thickness and Radicular Extension on the Fracture Resistance of Premolar Endocrowns from Different All-Ceramic Materials
Satheesh B. Haralur, Alaa Ali Alamri, Shatha Abdulrahman Alshehri, Danyah Saeed Alzahrani, Mohammed Alfarsi
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(8): 2696. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments and multimode adhesive application on the Weibull characteristics, wettability, surface topography and adhesion to CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramic
Karina Barbosa Souza, Dayanne Monielle Duarte Moura, Sarah Emille Gomes da Silva, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Rafael de Almeida Spinelli Pinto, Fabíola Pessôa Pereira Leite, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Splinting of the Anterior Maxillary Teeth Using Glass-Ceramic Materials: A Case Report
Vasilliki Roussou, Aspasia Pachiou, Stefanos Kourtis
The Open Dentistry Journal.2020; 14(1): 711. CrossRef - Influence of Computer-aided Design/Computer-aided Manufacturing Diamond Bur Wear on Marginal Misfit of Two Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Systems
LH Raposo, PS Borella, DC Ferraz, LM Pereira, MS Prudente, PC Santos-Filho
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(4): 416. CrossRef - Effect of thermal and mechanical cycles on shear bond strength of zirconia core to porcelain veneer under different surface treatments
Tahereh Ghaffari, Elnaz Moslehifard, Mehrnaz Motiei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(3): 227. CrossRef - Properties of hot-pressed lithium silicate glass-ceramics
Lubica Hallmann, Peter Ulmer, Mark-Daniel Gerngross, Justin Jetter, Michaël Mintrone, Frank Lehmann, Matthias Kern
Dental Materials.2019; 35(5): 713. CrossRef - Enhanced bonding strength between lithium disilicate ceramics and resin cement by multiple surface treatments after thermal cycling
Rui Li, Shi Qing Ma, Cheng Cheng Zang, Wen Yi Zhang, Zi Hao Liu, Ying Chun Sun, Yi Yu Feng, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(7): e0220466. CrossRef - Effect of Two Polishing Systems on Surface Roughness, Topography, and Flexural Strength of a Monolithic Lithium Disilicate Ceramic
Mahshid Mohammadibassir, Mohammad Bagher Rezvani, Hossein Golzari, Elham Moravej Salehi, Mohammad Amin Fahimi, Mohammad Javad Kharazi Fard
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Translucency, hardness and strength parameters of PMMA resin containing graphene-like material for CAD/CAM restorations
Shruti Vidhawan Agarwalla, Ritika Malhotra, Vinicius Rosa
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 100: 103388. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Monolithic Glass‐Ceramics Versus Bilayered Zirconia‐Based Restorations
Tamer A. Hamza, Rana M. Sherif
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Does the Translucency of Novel Monolithic CAD/CAM Materials Affect Resin Cement Polymerization with Different Curing Modes?
Yagmur Ozer Caprak, Pinar Turkoglu, Gokhan Akgungor
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the ceramic liner bonding effect between zirconia and lithium disilicate
Sung-Hoon Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Lee-Ra Cho, Yoon-Hyuk Huh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2018; 120(2): 282. CrossRef - The effect of adhesive failure and defects on the stress distribution in all-ceramic crowns
Yonggang Liu, Yuanzhi Xu, Bo Su, Dwayne Arola, Dongsheng Zhang
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 75: 74. CrossRef - Mechanical and optical properties of monolithic CAD-CAM restorative materials
Nazmiye Sen, Yesim Olcer Us
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2018; 119(4): 593. CrossRef - Effects of surface treatments on repair bond strength of a new CAD/CAM ZLS glass ceramic and two different types of CAD/CAM ceramics
Ayse Seda Ataol, Gulfem Ergun
Journal of Oral Science.2018; 60(2): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of the marginal and internal gaps of three different dental prostheses: comparison of the silicone replica technique and three-dimensional superimposition analysis
Jin-Young Park, So-Yeon Bae, Jae-Jun Lee, Ji-Hwan Kim, Hae-Young Kim, Woong-Chul Kim
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(3): 159. CrossRef - Dental ceramics: a review of new materials and processing methods
Lucas Hian da SILVA, Erick de LIMA, Ranulfo Benedito de Paula MIRANDA, Stéphanie Soares FAVERO, Ulrich LOHBAUER, Paulo Francisco CESAR
Brazilian Oral Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Bonding of the silane containing multi-mode universal adhesive for lithium disilicate ceramics
Hyun-Young Lee, Geum-Jun Han, Juhea Chang, Ho-Hyun Son
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 95. CrossRef - Tribological behaviour of unveneered and veneered lithium disilicate dental material
C.G. Figueiredo-Pina, N. Patas, J. Canhoto, R. Cláudio, S.M. Olhero, A.P. Serro, A.C. Ferro, M. Guedes
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2016; 53: 226. CrossRef - Survival of resin infiltrated ceramics under influence of fatigue
Moustafa N. Aboushelib, Mohamed H. Elsafi
Dental Materials.2016; 32(4): 529. CrossRef - Reliability Analysis of Lithium Disilicate Crowns: Effectof Veneering and Milling Production Workflow
Paolo Cardelli, Nicola Serafini, Bruna Sinjari, Giovanna Murmura, Mutlu Özcan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2016; 25(8): 623. CrossRef - Effects of pretreatments and hydrothermal aging on biaxial flexural strength of lithium di-silicate and Mg-PSZ ceramics
Maria André, Wen Kou, Göran Sjögren, Anders Sundh
Journal of Dentistry.2016; 55: 25. CrossRef - EFFECT OF PRE-CRYSTALLIZATION ON LITHIUM DISILICATE GLASS-CERAMICS FABRICATED BY DIFFERENT PROCESSES
Naruporn Monmaturapoj, Autcharaporn Sri-On, Thossapol Chunkiri
Phosphorus Research Bulletin.2016; 31: 24. CrossRef - Measurement of J-integral in CAD/CAM dental ceramics and composite resin by digital image correlation
Yanxia Jiang, Anna Akkus, Renato Roperto, Ozan Akkus, Bo Li, Lisa Lang, Sorin Teich
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2016; 62: 240. CrossRef - The Effect of Hydrofluoric Acid Etching Duration on the Surface Micromorphology, Roughness, and Wettability of Dental Ceramics
Ravikumar Ramakrishnaiah, Abdulaziz Alkheraif, Darshan Divakar, Jukka Matinlinna, Pekka Vallittu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(6): 822. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of monolithic zirconia molar crowns with reduced thickness
Keisuke Nakamura, Akio Harada, Ryoichi Inagaki, Taro Kanno, Yoshimi Niwano, Percy Milleding, Ulf Örtengren
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2015; 73(8): 602. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing ceramic crowns cemented on solid abutments
Deborah Stona, Luiz Henrique Burnett, Eduardo Gonçalves Mota, Ana Maria Spohr
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2015; 146(7): 501. CrossRef - Mechanical performance of implant-supported posterior crowns
Paul de Kok, Cornelis J. Kleverlaan, Niek de Jager, Ruud Kuijs, Albert J. Feilzer
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2015; 114(1): 59. CrossRef - Effect of Thermocycling on Flexural Strength and Weibull Statistics of Machinable Glass–Ceramic and Composite Resin
Chaimongkon Peampring, Sasiwimol Sanohkan
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2014; 14(4): 376. CrossRef - The effects of repeated heat-pressing on the mechanical properties and microstructure of IPS e.max Press
Xuehua Tang, Chengzhong Tang, Han Su, Huinan Luo, Takashi Nakamura, Hirofumi Yatani
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 40: 390. CrossRef - Flexural strength of a pressable lithium disilicate ceramic: influence of surface treatments
Tabata do Prado Sato, Caroline Cotes, Lígia Tiaki Yamamoto, Natalia Rivoli Rossi, Vanessa da Cruz Macedo, Estevão Tomomitsu Kimpara
Applied Adhesion Science.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Lithium silicate glass‐ceramics for dental restoration: From fundamental properties to machine‐learning design
- 5,224 View
- 32 Download
- 81 Crossref

-
Inhibitory effect on
Streptococcus mutans and mechanical properties of the chitosan containing composite resin - Ji-Sun Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):36-42. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the antibacterial effect and mechanical properties of composite resins (LCR, MCR, HCR) incorporating chitosan with three different molecular weights (L, Low; M, Medium; H, High).
Materials and Methods Streptococcus (S). mutans 100 mL and each chitosan powder were inoculated in sterilized 10 mL Brain-Heart Infusion (BHI) solution, and was centrifuged for 12 hr. Absorbance of the supernatent was measured at OD660 to estimate the antibacterial activities of chitosan. AfterS. mutans was inoculated in the disc shaped chitosan-containing composite resins, the disc was cleansed with BHI and diluted with serial dilution method.S. mutans was spread onMitis-salivarius bacitracin agar. After then, colony forming unit (CFU) was measured to verify the inhibitory effect onS. mutans biofilm. To ascertain the effect on the mechanical properties of composite resin, 3-point bending and Vickers hardness tests were done after 1 and 3 wk water storage, respectively. Using 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Scheffe test, statistical analysis was done with 95% significance level.Results All chitosan powder showed inhibition effect against
S. mutans . CFU number in chitosan-containing composite resins was smaller than that of control resin without chitosan. The chitosan containing composite resins did not show any significant difference in flexural strength and Vickers hardness in comparison with the control resin. However, the composite resin, MCR showed a slightly decreased flexural strength and the maximum load than those of control and the other composite resins HCR and LCR.Conclusions LCR and HCR would be recommended as a feasible antibacterial restorative due to its antibacterial nature and mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dental Resin Composites Modified with Chitosan: A Systematic Review
Wojciech Dobrzyński, Paweł J. Piszko, Jan Kiryk, Sylwia Kiryk, Mateusz Michalak, Agnieszka Kotela, Julia Kensy, Witold Świenc, Natalia Grychowska, Jacek Matys, Maciej Dobrzyński
Marine Drugs.2025; 23(5): 199. CrossRef - Bactericidal Effects of Ultraviolet-C Light-Emitting Diode Prototype Device Through Thin Optical Fiber
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Deog-Gyu Seo
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4504. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity, and microshear bond strength of an experimental adhesive system containing chitosan-based silver oxide particles
Hamideh Sadat Mohammadipour, Alireza Boruziniat, Seyedeh Azam Hoseini, Hosein Bagheri, Navid Ramezanian, Abbas Tanhaieian, Solmaz Pourgonabadi, Arsalan Shahri
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of a novel antibacterial nanocomposite resin restorative material
Rasha Abd El Rahman El Naggar, Manal A. ElEbiary, ElRefaie Kenawy, Gehan A. Elolimy
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(3): 439. CrossRef - The impact of chitosan in experimental resin with different photoinitiator systems
Isaías Donizeti Silva, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Bruno Vilela Muniz, Karina Cogo-Muller, Flávia Gonçalves, William Cunha Brandt
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106323. CrossRef - The effect of adding chitosan nanoparticles on different properties of the adhesive and high-filled composite resin
Mahan Masoumi, Sara Valizadeh, Ricardo M. Carvalho, Alireza Akbari Moghaddam, Safoura Ghodsi
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2024; 134: 103766. CrossRef - Prospective and applications of bacterial nanocellulose in dentistry
Yasmin Alimardani, Esmaeel Mirzakhani, Fereshteh Ansari, Hadi Pourjafar, Nadia Sadeghi
Cellulose.2024; 31(13): 7819. CrossRef - BNN/TiO2 nanocomposite system–modified dental flow resins and the mechanism of the enhancement of mechanical and antibacterial properties
Xinzi Kong, Qize Han, Axue Jiang, Yurui Wang, Ruizhi Li, Yuting Wang, Shengjie Xiao, Rong Wei, Yu Ma
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(8): 2775. CrossRef - Influence of the Loading with Newly Green Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Equisetum sylvaticum on the Antibacterial Activity and Surface Hardness of a Composite Resin
Ionuț Tărăboanță, Ana Flavia Burlec, Simona Stoleriu, Andreia Corciovă, Adrian Fifere, Denisa Batir-Marin, Monica Hăncianu, Cornelia Mircea, Irina Nica, Andra Claudia Tărăboanță-Gamen, Sorin Andrian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(8): 402. CrossRef - The Impact of Adding Chitosan Nanoparticles on Biofilm Formation, Cytotoxicity, and Certain Physical and Mechanical Aspects of Directly Printed Orthodontic Clear Aligners
Botan Barzan Taher, Tara Ali Rasheed
Nanomaterials.2023; 13(19): 2649. CrossRef - Synthesis of Submicrometric Chitosan Particles Loaded with Calcium Phosphate for Biomedical Applications
Diana Pereira Lopes, Selma Regina Muniz Freitas, Carina Baptiston Tanaka, Giovanne Delechiave, Lucia Nobuco Takamori Kikuchi, Roberto R. Braga, Jamie J. Kruzic, Maria Stella Moreira, Leticia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Luiz Henrique Catalani, Flávia Gonçalve
AAPS PharmSciTech.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodegradable Nonwoven Materials with Antipathogenic Layer
Longina Madej-Kiełbik, Karolina Gzyra-Jagieła, Jagoda Jóźwik-Pruska, Maria Wiśniewskia-Wrona, Marzena Dymel
Environments.2022; 9(7): 79. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of eighth-generation bonding agent modified with 7% arginine and 0.12% chitosan for antibacterial property and microtensile bond strength
HimaliRajan Desai, SanjyotA Mulay, RonitR Shinde, PradeepK Shetty, SoumyaS Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 440. CrossRef - Effects of the crosslinking of chitosan/DCPA particles in the antimicrobial and mechanical properties of dental restorative composites
Lucia Nobuco Takamori Kikuchi, Selma Regina Muniz Freitas, Aldo Ferreira Amorim, Giovanne Delechiave, Luiz Henrique Catalani, Roberto Ruggiero Braga, Maria Stella Moreira, Leticia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Flávia Gonçalves
Dental Materials.2022; 38(9): 1482. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of lactoferrin-chitosan-gellan nanoparticles and their influence on strawberry preservation
Larissa G.R. Duarte, Carolina S.F. Picone
Food Research International.2022; 159: 111586. CrossRef - Polyphenol-Enriched Extract of Lacquer Sap Used as a Dentine Primer with Benefits of Improving Collagen Cross-Linking and Antibacterial Functions
Ying Zhao, Xi He, Han Wang, Huimin Wang, Zuosen Shi, Song Zhu, Zhanchen Cui
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2022; 8(9): 3741. CrossRef - Evaluation of the changes in physical properties and mineral content of enamel exposed to radiation after treating with remineralization agent
Merve Pelin Dur, Neslihan Celik, Nilgun Seven
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(9): 5673. CrossRef - Evaluation of Immediate and Delayed Microleakage of Class V Cavities Restored with Chitosan-incorporated Composite Resins: An In Vitro Study
Roopa R Nadig, Veena Pai, Arpita Deb
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(5): 621. CrossRef - Evaluation of Microleakage of Micro Hybrid Composite Resins versus Chitosan-Incorporated Composite Resins When Restored in Class V Cavities Using Total Etch and Self-Etch Adhesives
Arpita Deb, Veena Pai, Aesha Akhtar, Roopa R. Nadig
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(4): 346. CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Orthodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Adam Lubojanski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 337. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect on Enterococcus Faecalis and Physical Properties of Chitosan Added Calcium Hydroxide Canal Filling Material
Sol Song, Yu-Jin Kim, Jung-Hwan Lee, Joonhaeng Lee, Jisun Shin, Jongbin Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(2): 198. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Bonding Properties of Universal Adhesive Dental Polymers Doped with Pyrogallol
Naji Kharouf, Ammar Eid, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Youri Arntz, Hamdi Jmal, Federico Foschi, Salvatore Sauro, Vincent Ball, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1538. CrossRef - Efficacy of chitosan-based chewing gum on reducing salivary S. mutans counts and salivary pH: a randomised clinical trial
Zahra Khamverdi, Fatemeh Farhadian, Salman Khazaei, Maryam Adabi
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2021; 79(4): 268. CrossRef - Effect of antiseptic gels in the microbiologic colonization of the suture threads after oral surgery
Samuel Rodríguez Zorrilla, Andrés Blanco Carrión, Abel García García, Pablo Galindo Moreno, Xabier Marichalar Mendía, Rafael Seoane Prado, Antonio J. Pérez Estévez, Mario Pérez-Sayáns
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating antibacterial and surface mechanical properties of chitosan modified dental resin composites
Shahid Ali, Laila Sangi, Naresh Kumar, Bharat Kumar, Zohaib Khurshid, Muhammad S. Zafar
Technology and Health Care.2020; 28(2): 165. CrossRef - Comparison of antibacterial effects of orthodontic composites containing different nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans at different times
Soghra Yassaei, Ali Nasr, Hengameh Zandi, Mohammad Nima Motallaei
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(2): 52. CrossRef - Development of novel dental restorative composites with dibasic calcium phosphate loaded chitosan fillers
Carina B. Tanaka, Diana P. Lopes, Lucia N.T. Kikuchi, Maria Stella Moreira, Luiz H. Catalani, Roberto R. Braga, Jamie J. Kruzic, Flávia Gonçalves
Dental Materials.2020; 36(4): 551. CrossRef - Effect of iodonium salt and chitosan on the physical and antibacterial properties of experimental infiltrants
Mariana Dias FLOR-RIBEIRO, Talita Signoreti GRAZIANO, Flávio Henrique Baggio AGUIAR, Rafael Nóbrega STIPP, Giselle Maria MARCHI
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan/Fluoride Nanoparticles for Preventing Dental Caries
Niousha Ebrahimi, Ali Asghar Soleimani, Jamal Rashidiani, Beheshteh Malekafzali, Fatemeh Abedini, Hossein Hosseinkhani
Current Dentistry.2019; 1(1): 61. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of model composites containing quaternary ammonium methacrylates
Marina Lermenn Vidal, Guilherme Ferreira Rego, Gil Mendes Viana, Lucio Mendes Cabral, Juliana Primo Basílio Souza, Nick Silikas, Luis Felipe Schneider, Larissa Maria Cavalcante
Dental Materials.2018; 34(1): 143. CrossRef - Chitosan—PRP nanosphere as a growth factors slow releasing device with superior antibacterial capability
Radyum Ikono, Etik Mardliyati, Iis Tentia Agustin, Muhammad Mufarrij Fuad Ulfi, Dimas Andrianto, Uswatun Hasanah, Boy Muchlis Bachtiar, Nofa Mardianingsih, Endang Winiati Bachtiar, Nurwenda Novan Maulana, Nurul Taufiqu Rochman, Li Xianqi, Hideaki Kagami,
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2018; 4(4): 045026. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Effect of Two Cavity Disinfectants against One of Cariogenic Pathogen: An In vitro Comparative Study
Hanaa M. Elgamily, Hoda S. El-Sayed, Ali Abdelnabi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2018; 9(3): 457. CrossRef - Chitosan-Properties and Applications in Dentistry
Kmiec M
Advances in Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine: Open Access.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the shelf life of chitosan stored in different types of packaging, using colorimetry and dentin microhardness
Antonio Miranda da Cruz-Filho, Angelo Rafael de Vito Bordin, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Débora Fernandes da Costa Guedes, Paulo César Saquy, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Jesus Djalma Pécora
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 87. CrossRef - Restorative materials containing antimicrobial agents: is there evidence for their antimicrobial and anticaries effects? A systematic review
GS do Amaral, T Negrini, M Maltz, RA Arthur
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(1): 6. CrossRef - Antibacterial capacity of cavity disinfectants against Streptococcus mutans and their effects on shear bond strength of a self-etch adhesive
Han-Sol CHA, Dong-Hoon SHIN
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(1): 147. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect and Physical-Mechanical Properties of Temporary Restorative Material Containing Antibacterial Agents
Amanda Mahammad Mushashe, Carla Castiglia Gonzaga, Paulo Henrique Tomazinho, Leonardo Fernandes da Cunha, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Janes Francio Pissaia, Gisele Maria Correr
International Scholarly Research Notices.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of conventional restorative filling materials and advances in antimicrobial properties of composite resins and glass ionomer cements—A literature review
Cher Farrugia, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2015; 31(4): e89. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Dental materials with antibiofilm properties
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Dental Materials.2014; 30(2): e1. CrossRef - Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles onStreptococcus mutansandLactobacillus
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 109. CrossRef - Antibakterielle fyllinger - hvor står vi i dag?
Nils Jacobsen
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2014; 124(8): 616. CrossRef
- Dental Resin Composites Modified with Chitosan: A Systematic Review
- 1,898 View
- 14 Download
- 42 Crossref

- Effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion and flexural strength
- Ji-A Yoo, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):324-335. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.324
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effects of the color components of light-cured composite resin before and after polymerization on degree of conversion (DC) and biaxial flexural strength (FS).
Materials and Methods Four enamel shades (A1, A2, A3, A4) and two dentin shades (A2O, A3O) of Premisa (Kerr Co.) and Denfil (Vericom Co.) were evaluated on their CIE L*, a*, b* color components using the spectrophotometer before curing, after curing and at 7 day. The DC of same specimens were measured with Near-infrared spectrometer (Nexus, Thermo Nicolet Co.) at 2 hr after cure and at 7 day. Finally, the FS was obtained after all the other measurements were completed at 7 day. The correlations between each color component and DC and FS were evaluated.
Results The light-curing of composite resin resulted in color changes of Premisa in red-blue direction and Denfil in green-blue direction. The DC and FS were affected by product, time and shade (3-way ANOVA,
p < 0.05) and product and shade (2-way ANOVA,p < 0.05), respectively. Premisa only showed a significant correlation between the DC and CIE a* component - before and after polymerization (Pearson product moment correlation,p < 0.05). The FS of Premisa showed significant negative correlations with CIE a* and CIE b* components.Conclusions The DC and FS of the light-curing composite resin were affected by the color components of the material before and after polymerization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Color Stability according to Shade of Temporary Crown Resin Using Digital Spectrophotometer: In Vitro Study
Hye-min Ku, Mi-Kyoung Jun
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2022; 22(3): 139. CrossRef - The properties of UDMA dental composite resin with novel photosensitizers
Gum Ju Sun
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2013; 35(3): 209. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Color Stability according to Shade of Temporary Crown Resin Using Digital Spectrophotometer: In Vitro Study
- 1,488 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of environment on the physical properties of core materials
- Yoo-Sook Hwang, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(2):86-94. Published online March 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to measure the flexural strength and hardness of four core materials in 4 different medias and to evaluate the relationship between the physical properties.
For the flexural strength, the specimens were prepared from each of the following materials: Bisfil Core, Core Max, Fuji IX GP, Miracle Mix and randomly divided into four groups and stored at 37 degree C in the following medias: distilled water for 24 hours (DW/1), distilled water for 30 days (DW/30). 2% NaF for 30 days (NF/30), 0.02N lactic acid for 30 days (LA/30). After storage, the specimens were subjected to flexural strength testing and calculated to flexural modulus.
For hardness testing, specimens were prepared from four materials and storaged in the uniform way. After storage, the specimens were subjected to Vicker's hardness testing.
1. The flexural strength of Core Max were the highest, and the flexural strength of Miracle Mix were the lowest.
2. The hardness of Bisfil Core were the highest.
3. The hardness of Core Max were the highest.
4. The hardness of Miracle Mix were the lowest.
5. 2% NaF and 0.02N lactic acid negatively affected the flexural strength and hardness of four core materials.
- 852 View
- 0 Download

- A study on the material properties of various composite resins for core build-up
- Soo-Il Shin, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):191-199. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purposes of this study were to estimate the material properties of the recently developed domestic composite resins for core filling material (Chemical, Dual A, Dual B; Vericom, Korea) and to compare them with other marketed foreign products (CorePaste, Den-Mat, USA; Ti-Core, Essential Dental Systems, USA; Support, SCI-Pharm, USA). Six assessments were made; working time, setting time, depth of polymerization, flexural strength, bonding strength, and marginal leakage. All items were compared to ISO standards.
All domestic products satisfied the minimum requirements from ISO standards (working time: above 90 seconds, setting time: within 5 minutes), and showed significantly higher flexural strength than Core Paste. Dual A and B could, especially, reduce the setting time to 60 seconds when cured with 600 mW/cm2 light intensity. All experimental materials showed 6 mm depth of polymerization.
Bond strengths of Ti-Core and Dual B materials were significantly higher than the other materials. Furthermore, three domestic products and Ti-Core could reduce the microleakage effectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
Hye-Jo Keum, Hyun-Mi Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 173. CrossRef
- Effect of surface treatments of fiber posts on bond strength to composite resin cores
- 1,243 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


