Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Phase transformation temperatures influence the reduction ratio of fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium reciprocating files at body temperature: an in vitro experimental study
- Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Lola Pedèches, Sylvie Lê, Marie Georgelin-Gurgel, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Franck Diemer
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e35. Published online November 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
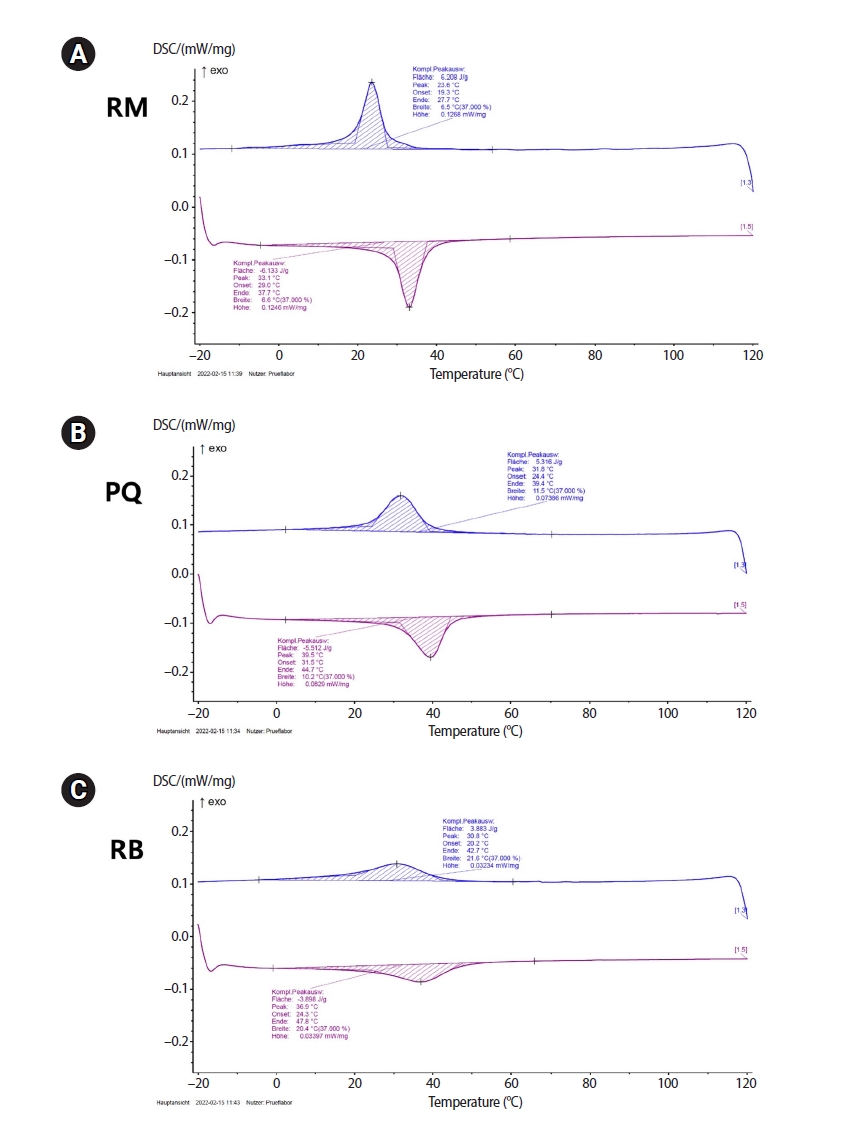
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of transformational temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance at body temperature of reciprocating file systems: R motion (RM), Procodile Q (PQ), and Reciproc Blue.
Methods
Resistance test was done in a custom-made device at room (20°C ± 1°C) and body (37°C ± 1°C) temperatures within a 60° angle of curvature and 5 mm radius of the artificial canal. The time to fracture (TTF) was recorded. The scanning electron microscope observation and differential scanning calorimetry analyses were performed. Two-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc comparison were applied at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
The results showed a significant influence of temperature on instrumental breakage, regardless of the file systems (p < 0.05). The TTF is significantly decreased at body temperature (p < 0.05). PQ showed the longest TTF in both temperature conditions (p < 0.05). RM demonstrated a significantly higher TTF reduction ratio compared to the other files (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Within the limitations of this study, the heat-treated files with reciprocating kinetics may have different reduction ratios of the fatigue resistance of the file systems under different temperature conditions. This characteristic is an important point of consideration when clinicians select the file system to reduce potential file fracture.
- 1,522 View
- 62 Download

- Isolating design variables by assessing the impact of cross-section geometry on the mechanical performance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a comparative in vitro study
- Anne Rafaella Tenório Vieira, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
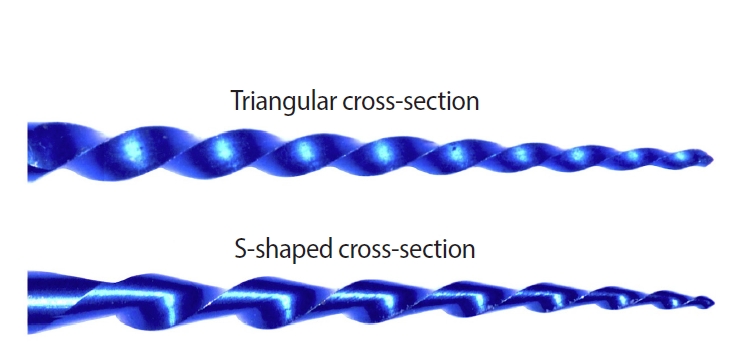
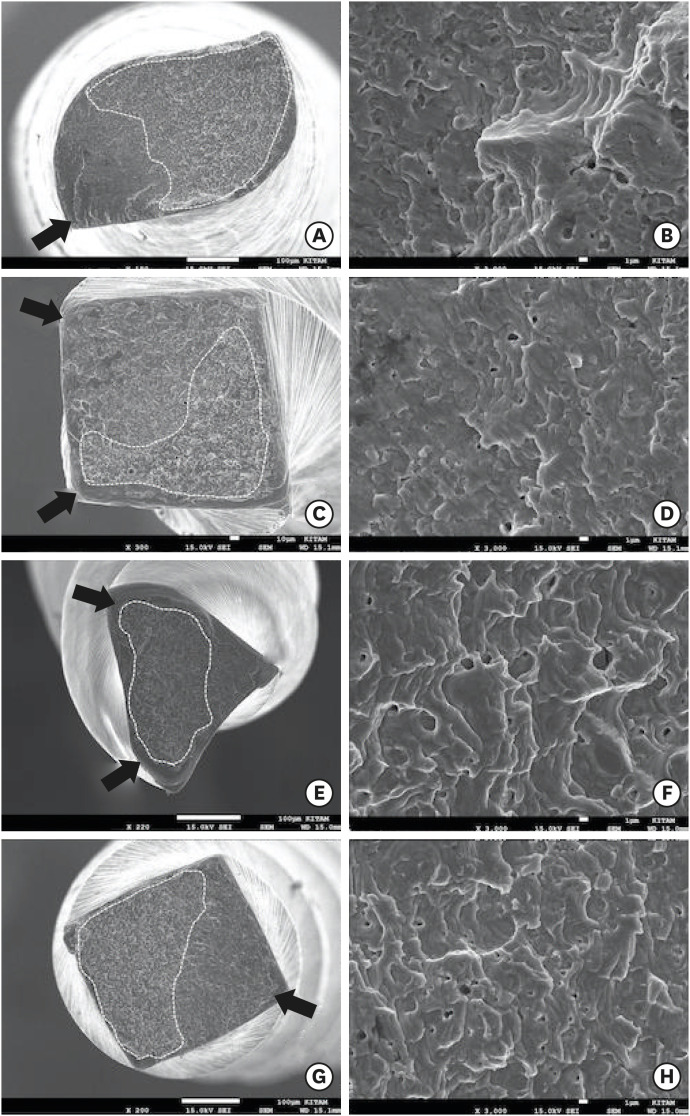
This study aimed to assess the effect of cross-section geometry on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments by comparing two instruments with identical tip size, taper, and thermal treatment but differing in cross-section design.
Methods
One hundred four NiTi rotary instruments, being S-shaped and triangular cross-section, manufactured with Blueish thermal treatment, were tested (n = 52 per group). Differential scanning calorimetry was employed, and the metal mass volume and cross-section area were assessed. The cyclic fatigue, torsional, and bending resistance tests were assessed. Data were analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Student t tests, and the level of significance was set at 5%.
Results
The instruments exhibited similar start and finish temperatures of phase transformation. The S-shaped instruments had significantly lower metal mass volume and cross-sectional area (p < 0.05). S-shaped instruments demonstrated superior cyclic fatigue resistance, greater angular deflection, and lower bending stiffness (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Cross-section geometry significantly influences the mechanical properties of NiTi rotary instruments.
- 2,453 View
- 91 Download

- Comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of One Curve, F6 Skytaper, Protaper Next, and Hyflex CM endodontic files
- Charlotte Gouédard, Laurent Pino, Reza Arbab-Chirani, Shabnam Arbab-Chirani, Valérie Chevalier
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e16. Published online March 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of One Curve (C wire) and F6 Skytaper (conventional austenite nickel-titanium [NiTi]), and 2 instruments with thermo-mechanically treated NiTi: Protaper Next X2 (M wire) and Hyflex CM (CM wire).
Materials and Methods Ten new instruments of each group (size: 0.25 mm, 6% taper in the 3 mm tip region) were tested using a rotary bending machine with a 60° curvature angle and a 5 mm curvature radius, at room temperature. The number of cycles until fracture was recorded. The length of the fractured instruments was measured. The fracture surface of each fragment was examined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and the
post hoc Tukey test. The significance level was set at 0.05.Results At 60°, One Curve, F6 Skytaper and Hyflex CM had significantly longer fatigue lives than Protaper Next X2 (
p < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were found in the cyclic fatigue lives of One Curve, F6 Skytaper, and Hyflex CM (p > 0.05). SEM images of the fracture surfaces of the different instruments showed typical features of fatigue failure.Conclusions Within the conditions of this study, at 60° and with a 5 mm curvature radius, the cyclic fatigue life of One Curve was not significantly different from those of F6 Skytaper and Hyflex CM. The cyclic fatigue lives of these 3 instruments were statistically significantly longer than that of Protaper Next.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Canal Shaping and Transportation Between the Protaper Next and Protaper Ultimate in Simulated Double-curved Canals
Seher Pelda Biçer, Betül Aycan Uysal
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2026; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Evaluation of cyclic fatigue in three pediatric endodontic rotary file systems in root canals of primary molars: A finite element analysis (FEA)
Monika sri S.S., K.C. Vignesh, K. Vivek, Kavitha Swaminathan, Selvakumar Haridoss
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(2): 310. CrossRef - Stress analysis of different experimental finite element models of rotary endodontic instruments
Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Nada Omar
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Cyclic Fatigue in Three Nickel–Titanium Pediatric Files: An In Vitro Study for Enhanced Patient Care
Alwaleed Abushanan, Rajashekhara Bhari Sharanesha, Fahd Aljarbou, Hadi Alamri, Mohammed Hamad Almasud, Abdulfatah AlAzmah, Sara Alghamdi, Mubashir Baig Mirza
Medicina.2025; 61(5): 830. CrossRef - Analyzing Surface Morphology Changes Induced by Cyclic Fatigue in Three Different Nickel–Titanium Rotary Files Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
Chintan Joshi, Mahima P Jain, Sweety M Thumar, Jay H Dave, Applu R Bhatt, Juhi I Dholani
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(7): 579. CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of Canal Shaping and Transportation Between the Protaper Next and Protaper Ultimate in Simulated Double-curved Canals
- 3,422 View
- 47 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of VDW.ROTATE, TruNatomy, 2Shape, and HyFlex CM nickel-titanium rotary files at body temperature
- Mustafa Gündoğar, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek, Gianluca Plotino
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e37. Published online June 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aims to compare the cyclic fatigue resistance of VDW.ROTATE, TruNatomy, 2Shape, and HyFlex CM nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files at body temperature.
Materials and Methods In total, 80 VDW.ROTATE (25/0.04), TruNatomy (26/0.04), 2Shape (25/0.04), and HyFlex CM (25/0.04) NiTi rotary files (
n = 20 in each group) were subjected to static cyclic fatigue testing at body temperature (37°C) in stainless-steel artificial canals prepared according to the size and taper of the instruments until fracture occurred. The number of cycles to fracture (NCF) was calculated, and the lengths of the fractured fragments were measured. The data were statistically analyzed using a 1-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tamhane tests at the 5% significance level (p < 0.05).Results There were significant differences in the cyclic fatigue resistance among the groups (
p < 0.05), with the highest to lowest NCF values of the files as follows: VDW.ROTATE, HyFlex CM, 2Shape, and TruNatomy. There was no significant difference in the lengths of the fractured fragments among the groups. The scanning electron microscope images of the files revealed typical characteristics of fracture due to cyclic fatigue.Conclusions The VDW.ROTATE files had the highest cyclic fatigue resistance, and the TruNatomy and 2Shape files had the lowest cyclic fatigue resistance in artificial canals at body temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multimethod Analysis of a Novel NiTi Rotary System: Cyclic Fatigue, Buckling Resistance, and Bending Tests
Alyne Rouse Rocha, Ana Grasiela Limoeiro, Iris Nogueira Seckler, Bárbara Rebeca Alves, Adriana Jesus Soares, Samuel Nogueira Lima, Victor Talarico Vieira, Marília Fagury Videira Marceliano-Alves, Wayne Martins Nascimento, Luis Cardoso Rasquin, Marcos Froz
European Journal of Dentistry.2026; 20(01): 061. CrossRef - Micro‐CT Evaluation of Dentin Preservation by ProTaper Gold and VDW.Rotate in Oval Mandibular Incisors
Wesley Viana de Sousa, Marina da Cunha Isaltino, Christianne Velozo, Silmara de Andrade Silva, Luiza de Almeida Souto Montenegro, Hugo Victor Dantas, Frederico Barbosa de Sousa, Diana Albuquerque, Cristiana Corsi
The Scientific World Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of dentinal microcrack formation in mesiobuccal canals of maxillary molars following instrumentation with heat-treated rotary and reciprocating systems
Fatemeh Soltaninejad, Yazdan Shantiaee, Babak Zandi, Arsham Moslemi, Seyed Sepehr Mirebeigi-Jamasbi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue and Physical Properties Testing of Different Small Taper Heat-Treated Reciprocating Files
Ahmed Altuwalah, Taher Al Omari, Riyadh Alroomy, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hamza Elfarraj, Rubén A. Domínguez-Pérez, Rashid El Abed
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance, number of uses, and morphological/chemical analysis of RCS Rainbow Files, VDW Rotate and ProTaper Ultimate: in vitro study
Tayná Lopes da Silva, Patrícia Carla Lopes, Mírian Galvão Bueno de Rezende, Amjad Abu Hasna
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Efficiency of Different Endodontic File Systems; Protaper Universal, MTWO, Protaper Next, Trunatomy, I-Race in Terms of Remaining Dentin Thickness: An In vitro CBCT Analysis
Anju Retnakaran, Faisal M. A. Gaffoor, Rethi Gopakumar, C Sabari Girish, N. C Sajeena, N Gokul Krishna
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1409. CrossRef - Analysis of Cutting Capacity, Surface Finishing, and Mechanical Properties of NiTi Instruments 25/.04: ROTATE and LOGIC 2
Ridalton Carlos de Morais, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Marcos Frozoni, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 982. CrossRef - Effect of Temperature on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Phase Transformation Behavior of Three Different NiTi Endodontic Instruments
Esra İrem Yi̇ği̇t, İrem Çetinkaya
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of a New TruNatomy Glider File after Different Cycles of Use
Lorena Ferreira Rego, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Alana Pinto Carôso Souza, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 619. CrossRef - Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite and Hypochlorous Acid Solutions on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Waveonegold, K3XF and Hyflex-EDM: A Study of Metallurgical Properties
D. A. Bozkurt, M. Akman, H. B. Karadag, Z. Ovalioglu, Ö.Küçük Keleş
Strength of Materials.2023; 55(1): 191. CrossRef - Effectiveness of conservative instrumentation in root canal disinfection
Sıla Nur Usta, Carmen Solana, Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Pilar Baca, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque, Monica Cabeo, Maria Teresa Arias-Moliz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 3181. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of different nickel‐titanium instruments in single and double curvature at room and body temperatures: A laboratory study
Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Maria Laura Leotta, Francesco Saverio Canova, Virginia Rosy Romeo, Gabriele Cervino, Luigi Generali, Eugenio Pedullà
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 592. CrossRef - Influence of NiTi Wire Diameter on Cyclic and Torsional Fatigue Resistance of Different Heat-Treated Endodontic Instruments
Eugenio Pedullà, Francesco Saverio Canova, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Luigi Generali, Walid Nehme
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6568. CrossRef - Impact of Different Access Cavity Designs and Ni–Ti Files on the Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal System: An In Vitro Study
Gizem Andac, Atakan Kalender, Buket Baddal, Fatma Basmaci
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(4): 2049. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportations and centering ability of rotary instrument systems with different heat-treated NiTi alloys: An in vitro CBCT study
Mukadder İnci BAŞER KOLCU, Gülter Devrim KAKİ
Turkish Journal of Health Science and Life.2022; 5(2): 81. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cutting efficiency, cyclic fatigue, corrosion resistance, and autoclave cycle effects of three different file systems: An in-vitro micro-CT and metallurgy analysis
KondasV Venkatesh, EldhoJ Varghese
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(6): 551. CrossRef - Influence of different heat treatments and temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments with the same design
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Maria Laura Leotta, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Eugenio Pedullà
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(4): 1793. CrossRef - Analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next rotary instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Andjelkovic-Apostolovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Radomir Barac, Marija Nikolic, Marko Igic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(3): 109. CrossRef - Influência do hipoclorito de sódio na resistência à fadiga cíclica em instrumentos rotatórios endodônticos de memória controlada de NiTi: uma avaliação experimental
Marcelo Leite MESQUITA, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira BUENO, Alexandre Sigrist DE MARTIN, Rina Andrea PELEGRINE, Carlos Eduardo FONTANA
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel TruNatomy Files with Conventional Endodontic Files: An In Vitro SEM Study
Sabari Murugesan, Vinoth Kumar, Bharath Naga Reddy, Syed Nahid Basheer, Rajeswary Kumar, Saravanan Selvaraj
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(11): 1243. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of TruNatomy Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument in Single and Double Curvature Canals: A Comparative Study
Sarah A Rashid, Hikmet A AI-Gharrawi
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 28. CrossRef
- Multimethod Analysis of a Novel NiTi Rotary System: Cyclic Fatigue, Buckling Resistance, and Bending Tests
- 3,246 View
- 45 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mayara Zanon, Fernanda Hecksher, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e25. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This systematic review evaluated the influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments.
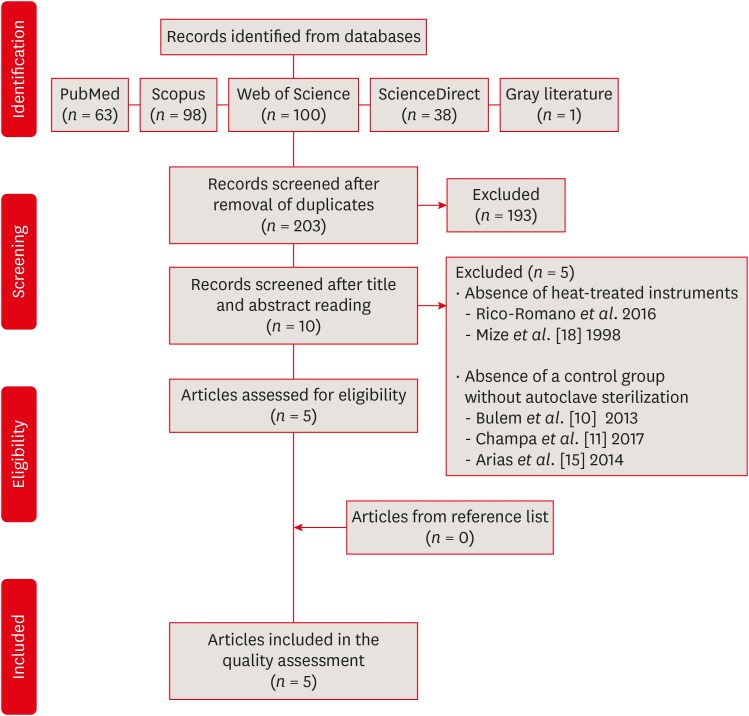
Materials and Methods A systematic search without restrictions was conducted in the following electronic databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and Open Grey. The hand search was also performed in the main endodontic journals. The eligible studies were submitted to the methodological assessment and data extraction.
Results From 203 abstracts, a total of 10 articles matched the eligible criteria. After reading the full articles, 2 were excluded because of the absence of the heat-treated instruments in the experimental design and 3 due to the lack of a control group using heat-treated instruments without autoclave sterilization. From the 5 included studies, 1 presented a low risk of bias, 3 presented moderate and 1 high risk. It was observed heterogeneous findings in the included studies, with autoclave sterilization cycles increasing, decreasing or not affecting the cyclic fatigue life of heat-treated NiTi instruments. However, the retrieved studies evaluating the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments presented different protocols and assessing outcomes, this variability makes the findings less comparable within and also between groups and preclude the establishment of an unbiased scientific evidence base.
Conclusions Considering the little scientific evidence and considerable risk of bias, it is still possible to conclude that autoclave sterilization procedures appear to influence the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated NiTi instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
Fatima Bardan, Mohamed El-Kishawi, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Saaid Al Shehadat, Rashid El Abed, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 292. CrossRef - Impact of Repeated Use on Cyclic and Torsional Fatigue of 3 Rotary Files: Implications for Clinical Safety
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Rafael da Rocha Tavares Duarte, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 954. CrossRef - EndoMagic Gold M06 Eğelerinde Boyut ve Konikliğin Döngüsel Yorgunluğa Etkisi: Bir İn Vitro Çalışma
Bircan Kuloğlu, Ayşe Çoban, Hatice Büyüközer Özkan
Akdeniz Diş Hekimliği Dergisi.2025; 4(3): 212. CrossRef - Effect of simulated clinical use and sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel titanium files
Mohammad Alajemi, Ammar AbuMostafa
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17418. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Michela Scorziello, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Massimo Pisano
Bioengineering.2024; 11(5): 499. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary versus Reciprocating Endodontic Files: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana De Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano, Patricia Sánchez-Llobet, José María Montiel-Company, Jesús Mena-Álvarez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 882. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeTaper Platinum, Protaper Gold, and TruNatomy Prime rotary files before and after autoclave sterilization
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal F. Alkadi
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14656. CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Effect of body temperature on the cyclic fatigue resistance of the nickel”titanium endodontic instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Selventhra Savitha, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Perumal Vanamail, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 338. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files After Usage and Autoclave Sterilization: An In Vitro Study
Rashid El Abed, Aisha Alshehhi, Yoo Jung Kang, Dana Al Raeesi, Amar H. Khamis, Mohamed Jamal, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(11): 1428. CrossRef - Effect of Autoclaving Cycles on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Race and Race Evo Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Rotary Files: An In Vitro Study
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem Barakat, Aroob Albakri, Manal Altamimi
Metals.2021; 11(12): 1947. CrossRef - Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Claudia Arena, Diego Sovereto, Riccardo Aiuto, Luigi Laino, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Antonio Dioguardi, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
- 2,701 View
- 47 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
- Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e22. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
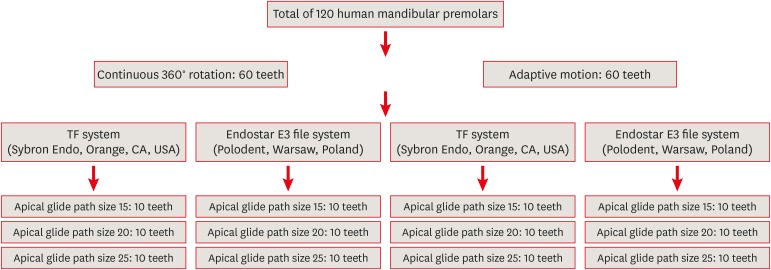
ePub Objectives This study investigated the influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on the time to reach the working length and the fracture resistance of Twisted File (TF) and Endostar E3 files.
Materials and Methods A total of 120 mandibular single-rooted premolars were selected. Two methods of kinetic motion (TF adaptive and continuous rotary motion) and file systems (TF and Endostar E3) were employed. The files were used in root canals prepared to apical glide path sizes of 15, 20, and 25. The time taken to reach the working length and the number of canals used before the instrument deformed or fractured were noted. Fractured instruments were examined with scanning electron microscopy.
Results The TF system took significantly more time to reach the working length than the Endostar E3 system. Both systems required significantly more time to reach the working length at the size 15 glide path than at sizes 20 and 25. A greater number of TFs than Endostar E3 files exhibited deformation, and a higher incidence of instrument deformation was observed in adaptive than in continuous rotary motion; more deformation was also observed with the size 15 glide path. One TF was fractured while undergoing adaptive motion.
Conclusions No significant difference was observed between continuous rotary and adaptive motion. The TF system and adaptive motion were associated with a higher incidence of deformation and fracture. Apical glide path sizes of 20 and 25 required significantly less time to reach the working length than size 15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Assessment of Different File Systems for Working Time Based on Glide Path, Operating Kinetics, and the Fracture Resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Divya Batra, Debkant Jena, Nandita Bansal, Alka Arora, Divya Gaurav Dudulwar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 69. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 1,866 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance of the WaveOne Gold Glider, ProGlider, and the One G glide path instruments in double-curvature canals
- Damla Kırıcı, Alper Kuştarcı
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e36. Published online September 9, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e36

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the cyclic fatigue resistance of the WaveOne Gold Glider, ProGlider and One G glide path instruments in artificial double-curvature canals.
Materials and Methods This study included 15 WaveOne Gold Glider (size 15/0.08), 15 ProGlider (size 16/0.08), and 15 One G (size 16/0.06) nickel titanium files. The files were used in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions until they were broken in artificial double-curvature canals made of stainless steel. The time to fracture was recorded via a digital stopwatch and the number of rotations until fracture was also calculated. The data were statistically analyzed via the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results The highest average number of rotations until fracture of the files was found for the WaveOne Gold Glider, followed by ProGlider and One G in order. Statistically significant differences were present between all groups of files (
p < 0.05).Conclusions In our study, the resistance of the WaveOne Gold Glider nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) file to cyclic fatigue in S-shaped curved canals was found to be higher than that of the ProGlider and One G Ni-Ti files.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of a New TruNatomy Glider File after Different Cycles of Use
Lorena Ferreira Rego, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Alana Pinto Carôso Souza, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 619. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Negotiability of mesiobuccal canals in maxillary first molars using different path file systems
Maryam Gharechahi, Mandana Khajehpour, Ali Hamedi, Maryam Peighoun
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Glide Path Rotary Files: A Systematic Review of in Vitro Studies
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6662. CrossRef - Evaluation of design, mechanical properties, and torque/force generation of heat-treated NiTi glide path instruments
Soram Oh, Ji-Yeon Seo, Ji-Eun Lee, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef
- Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
- 1,703 View
- 12 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of ProTaper Gold and EdgeEvolve files in canals with single- and double-curvature
- Wafaa A. Khalil, Zuhair S. Natto
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e19. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of EdgeEvolve (EdgeEndo) and ProTaper Gold (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties) nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files.
Materials and Methods The instruments (
n = 15/each) were tested for cyclic fatigue in single- (60° curvature, 5-mm radius) and double-curved (coronal curvature 60°, 5-mm radius, and apical curvature of 30° and 2-mm radius) artificial canals. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated. The bending resistance of both files were tested using a universal testing machine where the files were bent until reach 45°. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray energy-dispersive spectrometric analysis were used for imaging the fractured segments, while the atomic force microscope was used to quantify the surface roughness average (Ra).Results EdgeEvolve files exhibited higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in single- and double-curved canals (
p < 0.05) and both files were more resistant to cyclic fatigue in single-curved canals than double-curved canals (p < 0.05). EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly more flexibility than did ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05). Both files had approximately similar Ni and Ti contents (p > 0.05). EdgeEvolve files showed significantly lower Ra values than ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitation of this study, EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in both single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
Mert Unal, Elif Bahar Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2026; 89(1): 87. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of alterations in surface topographies of three different rotary files after root canal preparation with different irrigating solutions: Atomic force microscopic study
PremSai Parepalli, TB. V G. Raju, PKrishna Prasad, GowtamDev Dondapati, VenkataSrija Kintada, Alekhya Mediboyina
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 299. CrossRef - Assessment of surface topographic changes of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic file at repeated usage: An in vitro study
E. Viswas, VSS Krishna, E. Sridevi, A. J. Sai Sankar, K. Siva Sankar, B. Nagesh
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 149. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Influence of nickel-titanium rotary systems with varying cross-sectional, pitch, and rotational speed on deflection and cyclic fatigue: a finite element analysis study
Wignyo Hadriyanto, Lukita Wardani, Christina Nugrohowati, Ananto Alhasyimi, Rachmat Sriwijaya, Margareta Rinastiti, Widowati Siswomihardjo, Gunadi, T. Yamada, A.A.C. Pramana, Y. Ophinni, A. Gusnanto, W.A. Kusuma, J. Yunus, Afiahayati, R. Dharmastiti, T.
BIO Web of Conferences.2021; 41: 05005. CrossRef - Can the Separated Instrument be Removed From the Root Canal System out by Magnetism? A Hypothesis
Mohammad Daryaeian, Sanjay Miglani, AbdolMahmood Davarpanah, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Mohsen Ramazani
Dental Hypotheses.2019; 10(4): 108. CrossRef - Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis
Raymond Scott, Ana Arias, José C. Macorra, Sanjay Govindjee, Ove A. Peters
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(3): 400. CrossRef
- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,547 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance, torsional resistance, and metallurgical characteristics of M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold NiTi files
- Eugenio Pedullà, Fabio Lo Savio, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Gabriele Miccoli, Elena Bruno, Silvia Rapisarda, Seok Woo Chang, Ernesto Rapisarda, Guido La Rosa, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e25. Published online April 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the mechanical properties and metallurgical characteristics of the M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (United Dental).
Materials and Methods One hundred and sixty new M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (sizes 20/0.04 and 25/0.04) were used. Torque and angle of rotation at failure (
n = 20) were measured according to ISO 3630-1. Cyclic fatigue resistance was tested by measuring the number of cycles to failure in an artificial stainless steel canal (60° angle of curvature and a 5-mm radius). The metallurgical characteristics were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and the Student-Newman-Keuls test.Results Comparing the same size of the 2 different instruments, cyclic fatigue resistance was significantly higher in the M3 Pro Gold files than in the M3 Rotary files (
p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed between the files in the maximum torque load, while a significantly higher angular rotation to fracture was observed for M3 Pro Gold (p < 0.05). In the DSC analysis, the M3 Pro Gold files showed one prominent peak on the heating curve and 2 prominent peaks on the cooling curve. In contrast, the M3 Rotary files showed 1 small peak on the heating curve and 1 small peak on the cooling curve.Conclusions The M3 Pro Gold files showed greater flexibility and angular rotation than the M3 Rotary files, without decrement of their torque resistance. The superior flexibility of M3 Pro Gold files can be attributed to their martensite phase.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
Reyhaneh Shoorgashti, Marzie Jafari, Mohadeseh Alimohammadi, Niloofar Ebrahimi
Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Studies.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in Niti and Glide Path Rotary System: Preparation of Canal Centering and Transportation in Double-curved Root Canals
Calvin Reinnaldi, Wiena Widyastuti, Taufiq Ariwibowo, Sri Ratna Laksmiastuti
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Cleaning Efficacy of Neolix and M3 Immatural Rotary Files in Comparison with Hand Files in Primary Molar Root Canals
Shabnam Maleki, Effat Khodadadi, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Elham Mahmoudi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Instrumentation Time Among ProTaper Next, Neoniti, and M3‐Pro Gold Rotary Systems: An In Vitro Study
Robab Farhang, Bita Alizadeh, Saeedeh Galledar, Sara Noorolouny, Rashin Alyali, Bahareh Pouya, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Elango Natarajan
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Continuous Rotation and Optimal Torque Reverse Kinematics on the Cyclic Fatigue Strength of Endodontic NiTi Clockwise Cutting Rotary Instruments
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Marco A. Versiani
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 317. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The extended finite element method in endodontics: A scoping review and future directions for cyclic fatigue testing of nickel–titanium instruments
Philip Yuan‐Ho Chien, Laurence James Walsh, Ove Andreas Peters
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Characterization of the file‐specific heat‐treated ProTaper Ultimate rotary system
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Duarte Marques, Natasha Ajuz, Mário Rito Pereira, Rui Pereira da Costa, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 530. CrossRef - Influence of different heat treatments and temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments with the same design
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Maria Laura Leotta, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Eugenio Pedullà
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(4): 1793. CrossRef - Analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next rotary instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Andjelkovic-Apostolovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Radomir Barac, Marija Nikolic, Marko Igic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(3): 109. CrossRef - What Meaningful Information Are the Instruments Mechanical Testing Giving Us? A Comprehensive Review
Jorge N.R. Martins, Rui F. Martins, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(8): 985. CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Four different Contemporary NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files by Metallurgical and Mechanical Analysis with Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectrophotometry with FE-SEM and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance Evaluation
Akash Azad, Shraddha Chokshi
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 21. CrossRef - Impact of Peracetic Acid on the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Endodontic Instrument
Suhad Jabbar Hamed Al-Nasrawi, Zuha Ayad Jaber, Nibrass Talib Al-Quraine, Abtesam Imhemed Aljdaimi, Sattar Jabbar Abdul-Zahra Al-Hmedat, Saleh Zidan, Julfikar Haider, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Influence of shaft length on torsional behavior of endodontic nickel–titanium instruments
Gianluca Gambarini, Marco Seracchiani, Alessio Zanza, Gabriele Miccoli, Andrea Del Giudice, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 568. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments according to the Angle of File Access and Radius of Root Canal
Eugenio Pedullà, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Chiara Virgillito, Ernesto Rapisarda, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Luigi Generali
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 431. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
- 1,933 View
- 22 Download
- 19 Crossref

-
In vitro comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, One G, and ProGlider nickel titanium glide path instruments in single and double curvature canals - Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):282-289. Published online October 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It was aimed to compare the cyclic fatigue resistances of ProGlider (PG), One G (OG), and HyFlex EDM (HEDM) nickel titanium glide path files in single- and double-curved artificial canals.
Materials and Methods 40 PG (16/0.02), 40 OG (14/0.03), and 40 HEDM (10/0.05) single-file glide path files were used in the present study. Sixty files were subjected to cyclic fatigue test by using double-curved canals and 60 files by using single-curved canal (
n = 20). The number of cycles to fracture (NCF) was calculated and the length of the fractured fragment (FL) was determined by a digital micro-caliper. Twelve pieces of fractured files were examined with scanning electron microscope to determine fracture types of the files (n = 2). The NCF and the FL data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tukey test using SPSS 21 software (p < 0.05).Results In all of the groups, NCF values were significantly lower in double-curved canals when compared to single-curved canals (
p < 0.05). For both of single- and double-curved canals, NCF values of HEDM group in apical and coronal curvatures were found to be significantly higher than NCF values of PG and OG groups (p < 0.05). In both of single- and double-curved canals, NCF value of PG group was found significantly higher than OG group (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, HEDM glide path files were found to have the highest cyclic fatigue resistance in both of single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of canal curvature on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary instruments using different irrigation materials (in vitro study)
Mohammed Hamoudi Alsunboli, Sally Saad Ali Ihsan, Duha Qais Sabah
F1000Research.2024; 12: 449. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Static and Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in a Double-Curved Stainless Steel Artificial Canal
Hoang-Lan-Anh Le, Thuan-Loc Tran, Thu-Thuy Nguyen, Tran-Lan-Khue Pham, Van-Khoa Pham
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(4): 2687. CrossRef - The effect of canal curvature on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary instruments using different irrigation materials (in vitro study)
Mohammed Hamoudi Alsunboli, Sally Saad Ali Ihsan, Duha Qais Sabah
F1000Research.2023; 12: 449. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the efficacy of different Ni-Ti systems on acrylic blocks for correcting ledge formation
Osman Ünlü, Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, Faruk Haznedaroğlu
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain in single visit endodontics using heat-treated nickel − titanium file systems – A randomized clinical trial
Priyanka Unnikrishnan, Lalitagauri Mandke, Leena Padhye
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 94. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Glide Path Rotary Files: A Systematic Review of in Vitro Studies
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6662. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary First Molar with Tactile Controlled Activation Technique – A Case Report
Vijay Yadav, Rega Kumar, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar
Journal of Pierre Fauchard Academy (India Section).2022; : 67. CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of TruNatomy Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument in Single and Double Curvature Canals: A Comparative Study
Sarah A Rashid, Hikmet A AI-Gharrawi
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 28. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 188. CrossRef - Torsional fatigue strength of reciprocating and rotary pathfinding instruments manufactured from different NiTi alloys
Rodrigo Ricci VIVAN, Murilo Priori ALCALDE, George CANDEIRO, Giulio GAVINI, Celso Luis CALDEIRA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain intensity after using reciprocating and continuous rotary glide path systems: a randomized clinical trial
Mehmet Adıgüzel, Koray Yılmaz, Pelin Tüfenkçi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of the WaveOne Gold Glider, ProGlider, and the One G glide path instruments in double-curvature canals
Damla Kırıcı, Alper Kuştarcı
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef
- The effect of canal curvature on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary instruments using different irrigation materials (in vitro study)
- 1,536 View
- 9 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Comparison of cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium files: an examination using high-speed camera
- Taha Özyürek, Neslihan Büşra Keskin, Fatma Furuncuoğlu, Uğur İnan
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):224-231. Published online August 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.224
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the actual revolutions per minute (rpm) values and compare the cyclic fatigue life of Reciproc (RPC, VDW GmbH), WaveOne (WO, Dentsply Maillefer), and TF Adaptive (TFA, Axis/SybronEndo) nickel-titanium (NiTi) file systems using high-speed camera.
Materials and Methods Twenty RPC R25 (25/0.08), 20 WO Primary (25/0.08), and 20 TFA ML 1 (25/0.08) files were employed in the present study. The cyclic fatigue tests were performed using a dynamic cyclic fatigue testing device, which has an artificial stainless steel canal with a 60° angle of curvature and a 5-mm radius of curvature. The files were divided into 3 groups (group 1, RPC R25 [RPC]; group 2, WO Primary [WO]; group 3, TF Adaptive ML 1 [TFA]). All the instruments were rotated until fracture during the cyclic fatigue test and slow-motion videos were captured using high-speed camera. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated. The data were analyzed statistically using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA,
p < 0.05).Results The slow-motion videos were indicated that rpm values of the RPC, WO, and TFA groups were 180, 210, and 425, respectively. RPC (3,464.45 ± 487.58) and WO (3,257.63 ± 556.39) groups had significantly longer cyclic fatigue life compared with TFA (1,634.46 ± 300.03) group (
p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the mean length of the fractured fragments.Conclusions Within the limitation of the present study, RPC and WO NiTi files showed significantly longer cyclic fatigue life than TFA NiTi file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different axial speed patterns on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Shunsuke Kimura, Taro Nakatsukasa, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Kinematics of “Adaptive Motion” under Constant Torque Values
Ekim Onur Orhan, Duygu Bahadır, Ozgur Irmak
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(3): 355. CrossRef - COMPARISON OF FOUR DIFFERENT ENDODONTIC ROTARY SYSTEMS IN TERMS OF CYCLIC FATIGUE
Ahter ŞANAL ÇIKMAN, Tolga CEYHANLI
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(Supplement): 124. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilization on cyclic fatigue and torsional fracture resistance of NiTi rotary instruments
Wooyoung Kim, Soram Oh, Gil-Joo Ryu, Tae-Hwan Kim, Sung-Jae Kim, Dong-Hyung Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seok Woo Chang, Ji-Hyun Jang
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 194. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, Reciproc Blue, WaveOne Gold, and Twisted File Adaptive rotary files under different temperatures and ambient conditions
Mustafa Gündoğar, Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(3): 166. CrossRef
- Effect of different axial speed patterns on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary nickel-titanium instruments
- 1,542 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
- Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):216-223. Published online June 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the mechanical properties of various nickel-titanium (NiTi) files with similar tapers and cross-sectional areas depending on whether they were surface-treated.
Materials and Methods Three NiTi file systems with a similar convex triangular cross-section and the same ISO #25 tip size were selected for this study: G6 (G6), ProTaper Universal (PTU), and Dia-PT (DPT). To test torsional resistance, 5 mm of the straightened file's tip was fixed between polycarbonate blocks (
n = 15/group) and continuous clockwise rotation until fracture was conducted using a customized device. To evaluate cyclic fatigue resistance, files were rotated in an artificial curved canal until fracture in a dynamic mode (n = 15/group). The torsional data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukeypost-hoc comparison test, while the cyclic fatigue data were analyzed using the Mann-WhitneyU test at a significance level of 95%.Results PTU showed significantly greater toughness, followed by DPT and G6 (
p < 0.05). G6 showed the lowest resistance in ultimate torsional strength, while it showed a higher fracture angle than the other files (p < 0.05). In the cyclic fatigue test, DPT showed a significantly higher number of cycles to failure than PTU or G6 (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that the torsional resistance of NiTi files was affected by the cross-sectional area, while the cyclic fatigue resistance of NiTi files was influenced by the surface treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
Abdulkadir ÖZŞAHİN, Meltem DARTAR ÖZTAN, Emine ODABAŞI TEZER
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Heat Treatment and Surface Treatment of Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Ya Shen, He Liu, Zhejun Wang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Markus Haapasalo
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
- 1,321 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of air-abrasion pressure on the resin bond strength to zirconia: a combined cyclic loading and thermocycling aging study
- Eman Z. Al-Shehri, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Alaa H. Sabrah, Sarah S. Al-Angari, Laila Al Dehailan, George J. Eckert, Mutlu Özcan, Jeffrey A. Platt, Marco C. Bottino
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):206-215. Published online June 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the combined effect of fatigue cyclic loading and thermocycling (CLTC) on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a resin cement to zirconia surfaces that were previously air-abraded with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) particles at different pressures.
Materials and Methods Seventy-two cuboid zirconia specimens were prepared and randomly assigned to 3 groups according to the air-abrasion pressures (1, 2, and 2.8 bar), and each group was further divided into 2 groups depending on aging parameters (
n = 12). Panavia F 2.0 was placed on pre-conditioned zirconia surfaces, and SBS testing was performed either after 24 hours or 10,000 fatigue cycles (cyclic loading) and 5,000 thermocycles. Non-contact profilometry was used to measure surface roughness. Failure modes were evaluated under optical and scanning electron microscopy. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and χ2 tests (α = 0.05).Results The 2.8 bar group showed significantly higher surface roughness compared to the 1 bar group (
p < 0.05). The interaction between pressure and time/cycling was not significant on SBS, and pressure did not have a significant effect either. SBS was significantly higher (p = 0.006) for 24 hours storage compared to CLTC. The 2 bar-CLTC group presented significantly higher percentage of pre-test failure during fatigue compared to the other groups. Mixed-failure mode was more frequent than adhesive failure.Conclusions CLTC significantly decreased the SBS values regardless of the air-abrasion pressure used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
Yanru Shen, Xiang Wang, Chen Yang, Ying Jiang, Feng Wang, Li Peng, Yongsheng Zhou, Yuchun Sun
Surfaces and Interfaces.2024; 54: 105153. CrossRef - Multiscale analysis of the compressive behaviour of polymer-based composites reinforced by hybrid Al2O3/Al fibres
Hao Tang, Jiaqi Xu, Constantinos Soutis, Aleksey Yerokhin
Composites Science and Technology.2024; 255: 110718. CrossRef - An Advanced Surface Treatment Technique for Coating Three-Dimensional-Printed Polyamide 12 by Hydroxyapatite
Abdulaziz Alhotan, Saleh Alhijji, Sahar Ahmed Abdalbary, Rania E. Bayoumi, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Tamer M. Hamdy, Rasha M. Abdelraouf
Coatings.2024; 14(9): 1181. CrossRef -
Does incorporation of TiO
2
nanotubes in air-abraded high translucent zirconia influence shear bond strength?*
Bahadır Ezmek, Osman Cumhur Sipahi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(22): 3206. CrossRef - Effects of aging and light-curing unit type on the volume and internal porosity of bulk-fill resin composite restoration
Afnan O. Al-Zain, Elaf A. Alboloshi, Walaa A. Amir, Maryam A. Alghilan, Eliseu A. Münchow
The Saudi Dental Journal.2022; 34(3): 243. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and cyclic fatigue on subsurface defects and mechanical properties of zirconia frameworks
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Nikolaos Silikas, Moustafa Aboushelib
Dental Materials.2021; 37(5): 905. CrossRef - Effects of low-temperature degradation on the surface roughness of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hui Yang, Yi-Li Xu, Guang Hong, Hao Yu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(2): 222. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on repair strength, roughness and morphology in aged metal-free crowns
Yançanã Luizy Gruber, Thaís Emanuelle Bakaus, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, João Carlos Gomes, Alessandra Reis, Giovana Mongruel Gomes
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 19: e206155. CrossRef - Retentive Force of Glass-Ceramic Soldered Customized Zirconia Abutment Copings with Prefabricated Titanium Bases
Jeremias Hey, Monika Kasaliyska, Andreas Kiesow, Ramona Schweyen, Christin Arnold
Materials.2020; 13(14): 3193. CrossRef - Solvent-aided direct adhesion of a metal/polymer joint using micro/nano hierarchical structures
Gyosik Jun, Jeong-Won Lee, Younghun Shin, Kihwan Kim, Woonbong Hwang
Journal of Materials Processing Technology.2020; 285: 116744. CrossRef - Study of physicochemical properties and effects on bonding to zirconia ceramics of five resin cements
Xiuju Liu, Zhaoying Liu, Xuan Li, Han Wang, Gaigai Yu, Song Zhu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(18): 2031. CrossRef - The effect of air-particle abrasion and a zirconia primer application on resin cement bonding strength to zirconia
Alana M. Dantas, Fernanda Campos, Sarina M. Pereira, Elis J. dos Santos, Laudenice L. Pereira, Dayanne M. Moura, Rodrigo O. Souza
Minerva Stomatologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on Shear Bond Strength between Y-TZP and Self-Adhesive Resin Cement
Dae-Sung Kim, Jong-Ju Ahn, Eun-Bin Bae, Gyoo-Cheon Kim, Chang-Mo Jeong, Jung-Bo Huh, So-Hyoun Lee
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3321. CrossRef - Effect of airborne particle abrasion and sintering order on the surface roughness and shear bond strength between Y-TZP ceramic and resin cement
Yener OKUTAN, Munir Tolga YUCEL, Tugce GEZER, Mustafa Borga DONMEZ
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(2): 241. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
- 2,260 View
- 13 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue life of Tango-Endo, WaveOne GOLD, and Reciproc NiTi instruments
- Koray Yılmaz, Taha Özyürek
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):134-139. Published online April 11, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To compare the fatigue life of Tango-Endo, WaveOne GOLD, and Reciproc NiTi instruments under static model via artificial canals with different angles of curvature.
Materials and Methods Reciproc R25, WaveOne GOLD Primary, and Tango-Endo instruments were included in this study (
n = 20). All the instruments were rotated in artificial canals which were made of stainless steel with an inner diameter of 1.5 mm, 45°, 60°, and 90° angles of curvatures and a radius of curvature of 5 mm until fracture occurred, and the time to fracture was recorded in seconds using a digital chronometer. The data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis andpost-hoc Dunn tests were used for the statistical analysis of data in SPSS 21.0 software.Results Tango-Endo files were found to have significantly higher values than WaveOne GOLD and Reciproc files in terms of fatigue life (
p < 0.05). However, there was no statistically significant difference between fatigue life of Reciproc and WaveOne GOLD files (p > 0.05). It was determined that increasing the angle of curvature of the stainless canals caused significant decreases in fatigue life of all of three files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of the present study, the cyclic fatigue life of Tango-Endo in canals having different angles of curvature was statistically higher than Reciproc and WaveOne GOLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apically extruded debris of different file systems used with various kinematic movements during retreatment: An in vitro study
Tuğba Koşar, Davut Çelik, Tamer Taşdemir
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 33. CrossRef - Nickel-titanium files in endodontics: Development, improvement and modifications of nickel-titanium alloy
Slavoljub Zivkovic, Milica Jovanovic-Medojevic, Jelena Neskovic, Marijana Popovic-Bajic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2023; 80(3): 262. CrossRef - FATIGUE FAILURE OF NICKEL-TITANIUM INSTRUMENTS IN ENDODONTICS AND ITS INFLUENCING FACTORS
A Jusku, T Dodeková, J Staněk, B Özel, P Jirásek, V Polanská, Ľ Harvan
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2022; 122(2): 51. CrossRef - Reciproc Endodontic File Surface Defects After Single Use
Mohammed Howait
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2021; 11(1): 98. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of cyclic fatigue resistance of Reciproc Blue, WaveOne Gold and 2Shape nickel–titanium rotary files in different artificial canals
Ankita Grace Lall, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Vijay Alageshan, Parmeet Banga
Endodontology.2021; 33(1): 1. CrossRef - Cutting efficiency of heat‐treated nickel–titanium single‐file systems at different incidence angles
Eugenio Pedullà, Pietro La Paglia, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Anna Maria Gueli, Stefania Pasquale, David E. Jaramillo, Leopoldo Forner, Fabio Lo Savio, Guido La Rosa, Ernesto Rapisarda
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(1): 20. CrossRef - Influence of the type of reciprocating motion on the cyclic fatigue resistance of reciprocating files in a dynamic model
Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez, Carlos Falcão Costa, Norberto Quispe-López, Ruben Agustín-Panadero, Jesús Mena-Álvarez
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cutting efficiency of conventional and heat‐treated nickel–titanium rotary or reciprocating glide path instruments
E. Pedullà, G. Leanza, G. R. M. La Rosa, A. M. Gueli, S. Pasquale, G. Plotino, E. Rapisarda
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(3): 376. CrossRef - Influence of static and dynamic cyclic fatigue tests on the lifespan of four reciprocating systems at different temperatures
A. Keleş, A. Eymirli, O. Uyanık, E. Nagas
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(6): 880. CrossRef - Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of 5 Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Reciprocating Systems in Canals with Single and Double Curvatures
Mohammad I. Al-Obaida, Khalid Merdad, Mohammed S. Alanazi, Hesham Altwaijry, Mohammad AlFaraj, Ali A. Alkhamis, Ebtissam M. Al-Madi
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(10): 1237. CrossRef - Assessment of mechanical properties of WaveOne Gold Primary reciprocating instruments
Tong FANGLI, Keiichiro MAKI, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(3): 490. CrossRef - Comparison between Single-file Rotary Systems: Part 2—The Effect of Length of the Instrument Subjected to Cyclic Loading on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Adham A. Azim, Mohamed Tarrosh, Katharina A. Azim, Lucila Piasecki
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1837. CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of XP-endo Shaper, HyFlex CM, FlexMaster and Race instruments
Mehmet Adiguzel, Ipek Isken, Ismail Ilker Pamukcu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2018; 12(3): 208. CrossRef
- Apically extruded debris of different file systems used with various kinematic movements during retreatment: An in vitro study
- 1,707 View
- 10 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of adaptive motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of a nickel titanium instrument designed for retreatment
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):34-38. Published online December 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.34

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file (Dentsply Maillefer) under continuous and adaptive motion.
Materials and Methods Forty ProTaper Universal D1 files were included in this study. The cyclic fatigue tests were performed using a dynamic cyclic fatigue testing device, which had an artificial stainless steel canal with a 60° angle of curvature and a 5 mm radius of curvature. The files were randomly divided into two groups (Group 1, Rotary motion; Group 2, Adaptive motion). The time to failure of the files were recorded in seconds. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated for each group. The data were statistically analyzed using Student's
t -test. The statistical significant level was set atp < 0.05.Results The cyclic fatigue resistance of the adaptive motion group was significantly higher than the rotary motion group (
p < 0.05).Conclusion Within the limitations of the present study, the ‘Adaptive motion’ significantly increased the resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file to cyclic facture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
Anas Sira, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 64. CrossRef - Surface Alterations of Ni‐Ti Files After Retreatment of Root Canals Filled With Different Sealers: AFM and SEM Study
Duygu Aksoy, Sibel Koçak, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(10): 2704. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Assessment the impact of operator experience on cyclic fatigue resistance in reciprocating and rotary NiTi files: a comparative study between dental students and pediatric dentistry specialists
Hande Özyürek, Mesut Elbay, Taha Özyürek
Frontiers in Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef - Influences of Continuous Rotation and TF adaptive Motion on the Resistance of Different Retreatment File Systems to Deformation and Fracture: An In Vitro study
Divya Meena, Ramyadharshini LNU, V Nivedha, Anand Sherwood
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018; 3(2): 71. CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium files: an examination using high-speed camera
Taha Özyürek, Neslihan Büşra Keskin, Fatma Furuncuoğlu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 224. CrossRef
- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
- 1,586 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
- Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):31-35. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium (NiTi) files obtained in a conventional test using a simulated canal with a newly developed method that allows the application of constant fatigue load conditions.
Materials and Methods ProFile and K3 files of #25/.06, #30/.06, and #40/.04 were selected. Two types of testing devices were built to test their fatigue performance. The first (conventional) device prescribed curvature inside a simulated canal (C-test), the second new device exerted a constant load (L-test) whilst allowing any resulting curvature. Ten new instruments of each size and brand were tested with each device. The files were rotated until fracture and the number of cycles to failure (NCF) was determined. The NCF were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Duncan's
post-hoc test for each method. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was computed to examine any association between methods.Results Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (ρ = -0.905) showed a significant negative correlation between methods. Groups with significant difference after the L-test divided into 4 clusters, whilst the C-test gave just 2 clusters. From the L-test, considering the negative correlation of NCF, K3 gave a significantly lower fatigue resistance than ProFile as in the C-test. K3 #30/.06 showed a lower fatigue resistance than K3 #25/.06, which was not found by the C-test. Variation in fatigue test methodology resulted in different cyclic fatigue resistance rankings for various NiTi files.
Conclusions The new methodology standardized the load during fatigue testing, allowing determination fatigue behavior under constant load conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fracture Resistance of Heat-treated NiTi Instruments by the Load of Mechanical Preparation According to Tooth Type and Canal Number
Badria AlAli, Amre Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Fatemeh Ahmad, Amar H. Khamis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Rashid El Abed
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - File-Specific Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of NiTi Instruments After Repeated Use in Simulated Canals: Patterns Compatible with Potential Stress-Induced Martensite Transformation Effects
Hyeonu Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2026; 19(5): 866. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeFile X7, 2Shape, and F-one nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
ArkanH Al-Amidi, HikmetAbdul-Rahim Al-Gharrawi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 26. CrossRef - Investigation of cyclic fatigue of rotary endodontic instruments
Z. S. Khabadze, F. R. Ismailov
Endodontics Today.2022; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Instruments under Different Temperature Conditions
Hyo Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2021; 14(18): 5295. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 216. CrossRef - Effect from Rotational Speed on Torsional Resistance of the Nickel-titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung Kyo Kim, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 443. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Conditioning of root canal anatomy on static and dynamics of nickel-titanium rotary instruments
Italo Di Giuseppe, Davide Di Giuseppe, Vito Antonio Malagnino, Enrico Paolo Silla, Francesco Somma
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 58. CrossRef - Effect from surface treatment of nickel‐titanium rotary files on the fracture resistance
Bo Hoon Kim, Jung‐Hong Ha, Woo Cheol Lee, Sang‐Won Kwak, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of alloy type on the life‐time of torsion‐preloaded nickel‐titanium endodontic instruments
Jung‐Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Gary Shun‐Pan Cheung, Seong Hwa Jeong, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(3): 172. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Elastic Limits in Torsion of Reciprocating Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Seo-Ryeong Kim, Antheunis Versluis, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jin-Woon Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 715. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Safety of the Factory Preset Rotation Angle of Reciprocating Instruments
Jin-Woon Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Antheunis Versluis, Sang-Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(10): 1671. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals
Oscar Faciola Pessoa, Juliana Melo da Silva, Giulio Gavini
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(2): 117. CrossRef - Methods and models to study nickel–titanium instruments
Ya Shen, Gary S.P. Cheung
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 18. CrossRef - An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
Huimin Zhou, Bin Peng, Yu‐Feng Zheng
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 42. CrossRef
- Fracture Resistance of Heat-treated NiTi Instruments by the Load of Mechanical Preparation According to Tooth Type and Canal Number
- 1,605 View
- 5 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in .06 taper ProFile
- Hye-Rim Jung, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):79-83. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relation between intentionally induced internal stress and cyclic fatigue failure of .06 taper ProFile.
Materials and Methods Length 25 mm, .06 taper ProFile (Dentsply Maillefer), and size 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 were used in this study. To give the internal stress, the rotary NiTi files were put into the .02 taper, Endo-Training-Bloc (Dentsply Maillefer) until auto-stop by torque controlled motor. Rotary NiTi files were grouped by the number of induced internal stress and randomly distributed among one control group and three experimental groups (
n = 10, Stress 0 [control], Stress 1, Stress 2 and Stress 3). For cyclic fatigue measurement, time for separation of the rotary NiTi files was recorded. The fractured surfaces were observed by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, SU-70, Hitachi). The time for separation was statistically analyzed using two-way ANOVA andpost-hoc Scheffe test at 95% level.Results In .06 taper ProFile size 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40, there were statistically significant difference on time for separation between control group and the other groups (
p < 0.05).Conclusion In the limitation of this study, cyclic fatigue failure of .06 taper ProFile is influenced by internal stress accumulated in the files.
- 770 View
- 4 Download

- Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in K3
- Jun-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):74-78. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the cyclic fatigue of a K3 file and internal stress intentionally induced until the activation of the auto-stop function of the torque-controlled motor.
Materials and Methods K3 (Sybron Endo) .04 and .06 taper, size 25, 30, 35, 40 and 45 were used in this study. To give the internal stress, the K3 files were put into the .02 taper Endo-Training-Bloc (Dentsply Maillefer) until the activation of the auto-stop function of the torque-controlled motor. The rotation speed was 300 rpm and torque value was 1.0 N·cm. K3 were grouped by the number of induced internal stress and randomly distributed to 4 experimental groups (
n = 10, Stress 0 [control], Stress 1, Stress 2 and Stress 3). For measuring the cyclic fatigue failure, the K3 files were worked against a sloped glass block and time for file separation was recorded. Data was statistically analyzed Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA and Duncan post-hoc test atp < 0.05 level.Results Except .04 taper size 30 in Stress 1 group, there were statistically significant differences in time for file separation between control and all experimental groups. K3 with .04 taper showed higher cyclic fatigue resistance than those of .06 taper.
Conclusion In the limitation of this study, the cyclic fatigue of the K3 file was influenced by the accumulated internal stress from use until the auto-stop function was activated by the torque-controlled motor. Therefore, clinicians should avoid the reuse of the K3 file that has undergone auto-stops.
- 856 View
- 1 Download

- Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
- Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(5):424-429. Published online September 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.424
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to assess the influence of different cross-sectional area on the cyclic fatigue fracture of Ni-Ti rotary files using a fatigue tester incorporating cyclical axial movement. Six brands of Ni-Ti rotary files (ISO 30 size with .04 taper) of 10 each were tested: Alpha system (KOMET), HeroShaper (MicroMega), K3 (SybronEndo), Mtwo (VDW), NRT (Mani), and ProFile (Dentsply). A fatigue-tester (Denbotix) was designed to allow cyclic tension and compressive stress on the tip of the instrument. Each file was mounted on a torque controlled motor (Aseptico) using a 1:20 reduction contra-angle and was rotated at 300 rpm with a continuous, 6 mm axial oscillating motion inside an artificial steel canal. The canal had a 60° angle and a 5 mm radius of curvature. Instrument fracture was visually detected and the time until fracture was recorded by a digital stop watch. The data were analyzed statistically. Fractographic analysis of all fractured surfaces was performed to determine the fracture modes using a scanning electron microscope. Cross-sectional area at 3 mm from the tip of 3 unused Ni-Ti instruments for each group was calculated using Image-Pro Plus (Imagej 1.34n, NIH). Results showed that NRT and ProFile had significantly longer time to fracture compared to the other groups (p < .05). The cross-sectional area was not significantly associated with fatigue resistance. Fractographycally, all fractured surfaces demonstrated a combination of ductile and brittle fracture. In conclusion, there was no significant relationship between fatigue resistance and the cross-sectional area of Ni-Ti instruments under experimental conditions.
- 959 View
- 5 Download

- CYCLIC FATIGUE OF THE SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE TREATED AND /OR STEAM AUTOCLAVED NICKEL-TITANIUM ENDODONTIC FILES
- Hye-Young Cho, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):54-65. Published online January 14, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of sodium hypochlorite and steam autoclaving on the cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium endodontic files.
Two types of files with a .06 taper and #30 were used, K3® (SybronEndo, Glendora, California, USA) and Hero642®(Micro-Mega, Besançon, France).
The files were divided into 6 experimental groups containing 10 files each group depending the soaking time in 6% sodium hypochlorite solution and number of cycles of steam autoclave. After sterilization, a cyclic fatigue test was performed on each file, and the fracture time was recorded in seconds. The control group underwent the cyclic fatigue test only. After the test, the surface characteristics of the files were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
All groups containing the Hero 642® files showed a similar cyclic fatigue fracture time. However, the cyclic fatigue fracture time with the K3® files was significantly shorter in groups which were treated with sodium hypochlorite than in the control group (P < 0.05). SEM revealed both Hero642® and K3® files to have significant corrosion on the file surface in groups treated with sodium hypochlorite, compared with the sharp and regular blades of the control group. K3® files showed more corrosion than the Hero642® files. Bluntness of the blades of the K3® file was observed in groups treated with steam autoclave. Although there was no obvious destruction on the surface of steam autoclaved Hero642® files, slight bluntness was observed.
Sterilizing with a steam autoclave is much less destructive to K3® files than sodium hypochlorite. The longer time exposed to sodium hypochlorite, the more destructive pattern was shown on the blades of the files. Therefore, when using sodium hypochlorite solution, the exposure time should be as short as possible in order to prevent corrosion and increase the cyclic fatigue fracture time.
- 873 View
- 1 Download

- The Effect of Surface Defects on the Cyclic Fatigue Fracture of HEROShaper Ni-Ti rotary files in a Dynamic Model: A Fractographic Analysis
- Jung-Kyu Lee, Eui-Sung Kim, Myoung-Whai Kang, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):130-137. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.130
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This
in vitro study examined the effect of surface defects on cutting blades on the extent of the cyclic fatigue fracture of HEROShaper Ni-Ti rotary files using fractographic analysis of the fractured surfaces. A total of 45 HEROShaper (MicroMega) Ni-Ti rotary files with a #30/.04 taper were divided into three groups of 15 each. Group 1 contained new HEROShapers without any surface defects. Group 2 contained HEROShapers with manufacturing defects such as metal rollover and machining marks. Group 3 contained HEROShapers that had been clinically used for the canal preparation of 4-6 molars. A fatigue-testing device was designed to allow cyclic tension and compressive stress on the tip of the instrument whilst maintaining similar conditions to those experienced in a clinic. The level of fatigue fracture time was measured using a computer connected the system. Statistical analysis was performed using a Tukey's test. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used for fractographic analysis of the fractured surfaces. The fatigue fracture time between groups 1 and 2, and between groups 1 and 3 was significantly different (p < 0.05) but there was no significant difference between groups 2 and 3 (p > 0.05). A low magnification SEM views show brittle fracture as the main initial failure mode. At higher magnification, the brittle fracture region showed clusters of fatigue striations and a large number of secondary cracks. These fractures typically led to a central region of catastrophic ductile failure. Qualitatively, the ductile fracture region was characterized by the formation of microvoids and dimpling. The fractured surfaces of the HEROShapers in groups 2 and 3 were always associated with pre-existing surface defects. Typically, the fractured surface in the brittle fracture region showed evidence of cleavage (transgranular) facets across the grains, as well as intergranular facets along the grain boundaries. These results show that surface defects on cutting blades of Ni-Ti rotary files might be the preferred sites for the origin of fatigue fracture under experimental conditions. Furthermore, this work demonstrates the utility of fractography in evaluating the failure of Ni-Ti rotary files.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Canal Curvature and Different Manufacturing Processes of Five Different NiTi Rotary Files on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Panupat Phumpatrakom, Awiruth Klaisiri, Sukitti Techapatiphandee, Thippawan Saekow, Panuroot Aguilar
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 264. CrossRef - Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in .06 taper ProFile
Hye-Rim Jung, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 79. CrossRef - Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in K3
Jun-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 74. CrossRef - Stress distribution for NiTi files of triangular based and rectangular based cross-sections using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
Hyun-Ju Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of various corrosive environmental conditions for NiTi rotary files
Ji-Wan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 377. CrossRef
- The Effect of Canal Curvature and Different Manufacturing Processes of Five Different NiTi Rotary Files on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
- 1,569 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
- Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):96-102. Published online March 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.096
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are various factors affecting the fracture of NiTi rotary files. This study was performed to evaluate the effect of cross sectional area, pecking motion and pecking distance on the cyclic fatigue fracture of different NiTi files. Five different NiTi files-Profile®(Maillefer, Ballaigue, Switzerland), ProTaper™ (Maillefer, Ballaigue, Switzerland), K3® (SybronEndo, Orange, CA), Hero 642® (Micro-mega, Besancon, France), Hero Shaper®(Micro-mega, Besancon, France)-were used. Each file was embedded in temporary resin, sectioned horizontally and observed with scanning electron microscope. The ratio of cross-sectional area to the circumscribed circle was calculated. Special device was fabricated to simulate the cyclic fatigue fracture of NiTi file in the curved canal,. On this device, NiTi files were rotated (300rpm) with different pecking distances (3 mm or 6 mm) and with different motions (static motion or dynamic pecking motion). Time until fracture occurs was measured. The results demonstrated that cross-sectional area didn't have any effect on the time of file fracture. Among the files, Profile® took the longest time to be fractured. Between the pecking motions, dynamic motion took the longer time to be fractured than static motion. There was no significant difference between the pecking distances with dynamic motion, however with static motion, the longer time was taken at 3mm distance. In this study, we could suggest that dynamic pecking motion would lengthen the time for NiTi file to be fractured from cyclic fatigue.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study Assessing the Canal Cleanliness Using Automated Device and Conventional Syringe Needle for Root Canal Irrigation—An Ex-Vivo Study
Keerthika Rajamanickam, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Abdulaziz S. AbuMelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Khalid H. Almadi, Sarah Ahmed Bahammam, Krishnamachari Janani, Sahil Choudhari, Jerry Jose, Kumar Chandan Srivastava, Deepti Shrivastava, Shankarg
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6184. CrossRef - Vibrations Generated by Several Nickel-titanium Endodontic File Systems during Canal Shaping in an Ex Vivo Model
Dong-Min Choi, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(7): 1197. CrossRef - Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 424. CrossRef
- Comparative Study Assessing the Canal Cleanliness Using Automated Device and Conventional Syringe Needle for Root Canal Irrigation—An Ex-Vivo Study
- 1,220 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of surface defects and cross-sectional configuration on the fatigue fracture of NiTi rotary files under cyclic loading
- Yu-Mi Shin, Eui-Sung Kim, Kwang-Man Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):267-272. Published online May 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this in vitro study was to evaluate the effect of surface defects and cross-sectional configuration of NiTi rotary files on the fatigue life under cyclic loading. Three NiTi rotary files (K3™, ProFile®, and HERO 642®) with #30/.04 taper were evaluated. Each rotary file was divided into 2 subgroups: control (no surface defects) and experimental group (artificial surface defects). A total of six groups of each 10 were tested. The NiTi rotary files were rotated at 300rpm using the apparatus which simulated curved canal (40 degree of curvature) until they fracture. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated and the fractured surfaces were observed with a scanning electron microscope. The data were analyzed statistically. The results showed that experimental groups with surface defects had lower number of cycles to fracture than control group but there was only a statistical significance between control and experimental group in the K3™ (p<0.05). There was no strong correlation between the cross-sectional configuration area and fracture resistance under experimental conditions. Several of fractured files demonstrated characteristic patterns of brittle fracture consistent with the propagation of pre-existing cracks.
This data indicate that surface defects of NiTi rotary files may significantly decrease fatigue life and it may be one possible factor for early fracture of NiTi rotary files in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Torsional behavior and microstructure characterization of additively manufactured NiTi shape memory alloy tubes
Keyvan Safaei, Mohammadreza Nematollahi, Parisa Bayati, Hediyeh Dabbaghi, Othmane Benafan, Mohammad Elahinia
Engineering Structures.2021; 226: 111383. CrossRef - Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in K3
Jun-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 74. CrossRef - An evaluation of rotational stability in endodontic electronic motors
Se-Hee Park, Hyun-Woo Seo, Chan-Ui Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 246. CrossRef - Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 424. CrossRef - The Effect of Surface Defects on the Cyclic Fatigue Fracture of HEROShaper Ni-Ti rotary files in a Dynamic Model: A Fractographic Analysis
Jung-Kyu Lee, Eui-Sung Kim, Myoung-Whai Kang, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 96. CrossRef
- Torsional behavior and microstructure characterization of additively manufactured NiTi shape memory alloy tubes
- 1,204 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


