Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
- Statistical notes for clinical researchers: analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)
- Hae-Young Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e43. Published online October 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e43
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative methods to improve bivalirudin dosing in pediatric cardiac ICU patients
Lindsey Brinkley, Zasha Vazquez-Colon, Aashay Patel, Matthew S Purlee, Terry Vasilopoulos, Mark S Bleiweis, Jeffrey P Jacobs, Giles J Peek, Helen Moore
Perfusion.2025; 40(8): 1751. CrossRef - Soybean Reproductive Traits Evaluated in Response to Temperature Stress and Elevated Oxygen; Three Peroxidase Transgenes Reduce Seed Abortion
Bernard A. Hauser, Ya-Ying Wang, Kenneth J. Boote, Prachee Chaturvedi, Eric S. McLamore, Leon H. Allen
Oxygen.2025; 5(2): 5. CrossRef - Reutericyclin mitigates risperidone-induced suppression of anaerobic energy expenditure
Matthew A. Hadiono, Alexis B. Kazen, Fatima A. Aboulalazm, Colin M. L. Burnett, John J. Reho, Tammy L. Kindel, Justin L. Grobe, John R. Kirby
American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology.2025; 328(6): R741. CrossRef - Can Brain Volume-Driven Characteristic Features Predict the Response of Alzheimer’s Patients to Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation? A Pilot Study
Chandan Saha, Chase R. Figley, Brian Lithgow, Paul B. Fitzgerald, Lisa Koski, Behzad Mansouri, Neda Anssari, Xikui Wang, Zahra Moussavi
Brain Sciences.2024; 14(3): 226. CrossRef - Comparisons of the effects of two types of titratable mandibular advancement devices on respiratory parameters and upper airway dimensions in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a randomized controlled trial
Xiaoxin Shi, Frank Lobbezoo, Hui Chen, Boudewijn R. A. M. Rosenmöller, Erwin Berkhout, Jan de Lange, Ghizlane Aarab
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2013. CrossRef - Impact of carbamazepine and lacosamide on serum lipid levels
Prateek Kumar Panda, Indar Kumar Sharawat
Epilepsia.2021; 62(4): 1034. CrossRef - Whole Brain and Cranial Size Adjustments in Volumetric Brain Analyses of Sex- and Age-Related Trends
Marek Kijonka, Damian Borys, Krzysztof Psiuk-Maksymowicz, Kamil Gorczewski, Piotr Wojcieszek, Bartosz Kossowski, Artur Marchewka, Andrzej Swierniak, Maria Sokol, Barbara Bobek-Billewicz
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef The Impact of Virologic Parameters and Liver Fibrosis on Health-Related Quality of Life in Black African Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: Results from a High Endemic Area
Alassan Kouamé Mahassadi, Olga Team Machekam, Alain Koffi Attia
Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology.2020; Volume 13: 407. CrossRef- A Phase 2a, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Placebo-Controlled Trial of IBD98-M Delayed-Release Capsules to Induce Remission in Patients with Active and Mild to Moderate Ulcerative Colitis
Gionata Fiorino, Giacomo Carlo Sturniolo, Fabrizio Bossa, Andrea Cassinotti, Antonio Di Sabatino, Paolo Giuffrida, Silvio Danese
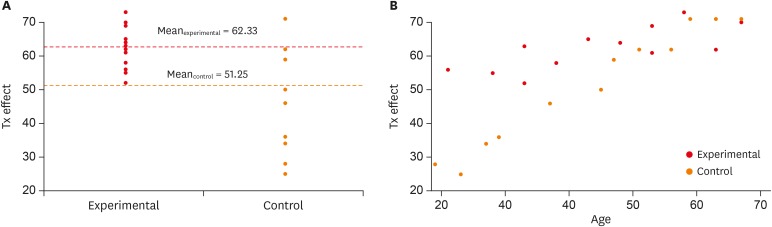
Cells.2019; 8(6): 523. CrossRef - Application of Student's t-test, Analysis of Variance, and Covariance
Prabhaker Mishra, Uttam Singh, Chandra M Pandey, Priyadarshni Mishra, Gaurav Pandey
Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia.2019; 22(4): 407. CrossRef - The Association of Body Mass Index and Body Composition with Pain, Disease Activity, Fatigue, Sleep and Anxiety in Women with Fibromyalgia
María Correa-Rodríguez, Jamal El Mansouri-Yachou, Antonio Casas-Barragán, Francisco Molina, Blanca Rueda-Medina, María Encarnación Aguilar-Ferrándiz
Nutrients.2019; 11(5): 1193. CrossRef
- Quantitative methods to improve bivalirudin dosing in pediatric cardiac ICU patients
- 4,468 View
- 77 Download
- 11 Crossref

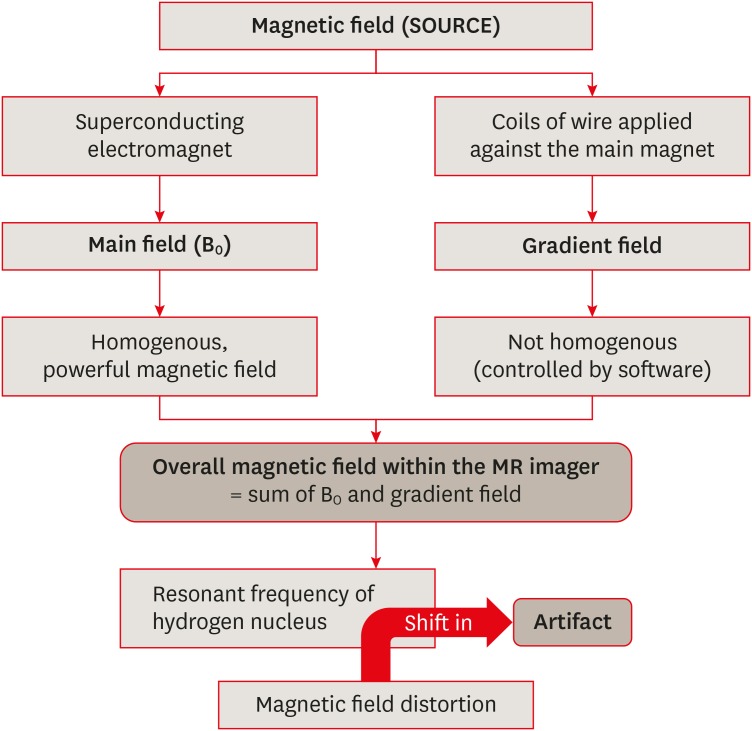
- Unwanted effects due to interactions between dental materials and magnetic resonance imaging: a review of the literature
- Sherin Jose Chockattu, Deepak Byathnal Suryakant, Sophia Thakur
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e39. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an advanced diagnostic tool used in both medicine and dentistry. Since it functions based on a strong uniform static magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses, it is advantageous over imaging techniques that rely on ionizing radiation. Unfortunately, the magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses generated within the magnetic resonance imager interact unfavorably with dental materials that have magnetic properties. This leads to unwanted effects such as artifact formation, heat generation, and mechanical displacement. These are a potential source of damage to the oral tissue surrounding the affected dental materials. This review aims to compile, based on the current available evidence, recommendations for dentists and radiologists regarding the safety and appropriate management of dental materials during MRI in patients with orthodontic appliances, maxillofacial prostheses, dental implants, direct and indirect restorative materials, and endodontic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postoperative MRI in cranio-maxillofacial and oral reconstruction: A prospective comparative pilot study on artifact reduction
Adib Al-Haj Husain, Sameena Sandhu, Maximilian Eberhard Hermann Wagner, Suen An Nynke Lie, Egon Burian, Daniel Zedler, Bernd Stadlinger, Peter Kessler, Harald Essig
Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery.2026; 54(6): 104522. CrossRef - Artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck: Unwanted effects caused by implant-supported restorations fabricated with different alloys
Lauren Bohner, Dieter Dirksen, Marcel Hanisch, Newton Sesma, Johannes Kleinheinz, Norbert Meier
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(6): 1574. CrossRef - The influence of preformed metal crowns versus zirconia crowns on the diagnostic quality of magnetic resonance images
O. Dalzell, P. Haghighi, J. Ho, T. Rayner, L. Vidarsson, G. A. Garisto
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2025; 26(1): 109. CrossRef - Interference of titanium and zirconia implants on dental-dedicated MR image quality: ex vivo and in vivo assessment
Katrine M Johannsen, Jennifer Christensen, Louise Hauge Matzen, Brian Hansen, Rubens Spin-Neto
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2025; 54(2): 132. CrossRef - Accuracy of Ionizing‐Radiation‐Based and Non‐Ionizing Imaging Assessments for the Diagnosis of Periodontitis: Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Nicola Discepoli, Isabella De Rubertis, Cecile Wasielewski, Giuseppe Troiano, Maria Clotilde Carra
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2025; 52(S29): 74. CrossRef - The Effect of MRI Exposure on the Shear Bond Strength and Adhesive Remnant Index of Different Bracket Types
Luka Šimunović, Jakov Stojanović, Katarina Tečić, Dijana Zadravec, Senka Meštrović
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 108. CrossRef - Impact of Artifacts Caused by Intraoral Dental Materials in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Divya Josephraj, Ravindranath Vineetha, Priya Pattath Sankaran, Prakashini Koteshwara, Mathangi Kumar, Kalyana Chakravarthy Pentapati
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Orthodontic appliances and their diagnostic impact to brain MRI
Lisa Latzko, Anna Schmit, Bernhard Glodny, Astrid E. Grams, Christoph Birkl, Adriano G. Crismani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Intra-Oral Dental Materials on Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Perspective Survey from Dental Professionals
Sejal Gupta, Mathangi Kumar, Kalyana C Pentapati, Ravindranath Vineetha, Vinu Thomas George, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal, Priya Pattath Sankaran
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S551. CrossRef - Beyond radiation: Emerging applications of MRI in dental diagnostics and clinical practice
Gerta Halilaj, Nebi Cemeta
Journal of Dentistry and Multidisciplinary Sciences.2025; 1(1): 31. CrossRef - Nonionizing diagnostic imaging modalities for visualizing health and pathology of periodontal and peri‐implant tissues
Andy Wai Kan Yeung, Abeer AlHadidi, Rutvi Vyas, Michael M. Bornstein, Hiroshi Watanabe, Ray Tanaka
Periodontology 2000.2024; 95(1): 87. CrossRef - Cortical thickness and grey-matter volume anomaly detection in individual MRI scans: Comparison of two methods
David Romascano, Michael Rebsamen, Piotr Radojewski, Timo Blattner, Richard McKinley, Roland Wiest, Christian Rummel
NeuroImage: Clinical.2024; 43: 103624. CrossRef - Association between dental restorations and artefacts on head magnetic resonance images in paediatric patients
Pitchaya Tunlayadechanont, Padcha Tunlayadechanont, Nantana Sriudomporn, Ploy Wisetsathon, Duangporn Duangthip, Varangkanar Jirarattanasopha
International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry.2024; 34(5): 546. CrossRef - Commercially Pure Titanium Implants With Selenium and Hyaluronic Acid Coating for Dental Applications
Soorya Ganesh, Gheena S, Kalaiyarasan Madhu
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multibraided Fixed Retainers with Different Diameters after Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): In Vitro Study Investigating Temperature Changes and Bonding Efficacy
Maria Francesca Sfondrini, Maurizio Pascadopoli, Paola Gandini, Lorenzo Preda, Domenico Sfondrini, Karin Bertino, Cinzia Rizzi, Andrea Scribante
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 255. CrossRef - Chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis of the mandible – orthodontic considerations and management: A case report
Saskia Andrea Schwabe, Sean Booth, Susi Caldwell
Journal of Orthodontics.2024; 51(4): 415. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of periodontal and periapical disease
Katrine Mølgaard Johannsen, João Marcus de Carvalho E Silva Fuglsig, Louise Hauge Matzen, Jennifer Christensen, Rubens Spin-Neto
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Surveillance of head neck cancer: Case for personalized and standardized surveillance
Shrikant B. Mali
Oral Oncology.2023; 139: 106354. CrossRef - Effect of Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 1.5 T and 3 T on Temperature and Bond Strength of Orthodontic Bands with Welded Tubes: An In Vitro Study
Maria Francesca Sfondrini, Simone Gallo, Maurizio Pascadopoli, Cinzia Rizzi, Andrea Boldrini, Simone Santagostini, Luca Anemoni, Maria Sole Prevedoni Gorone, Lorenzo Preda, Paola Gandini, Andrea Scribante
Materials.2023; 16(2): 651. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging artefacts caused by orthodontic appliances and/or implant-supported prosthesis: a systematic review
Katrine Mølgaard Johannsen, João Marcus de Carvalho E Silva Fuglsig, Brian Hansen, Ann Wenzel, Rubens Spin-Neto
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(2): 394. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging investigations in patients with metallic dental prosthesis: “The associated dilemma for medical fraternity and the dentist's role”
Ritika Bhambhani, SantanuSen Roy, Shubha Joshi
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2023; 23(2): 203. CrossRef - Recent advances in the application and biological mechanism of silicon nitride osteogenic properties: a review
Ziyi Liu, Ruijie Wang, Wenjing Liu, Yushan Liu, Xiaoli Feng, Fujian Zhao, Pei Chen, Longquan Shao, Mingdeng Rong
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(21): 7003. CrossRef - Techniques, Tricks, and Stratagems of Oral Cavity Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Davide Maraghelli, Michele Pietragalla, Linda Calistri, Luigi Barbato, Luca Giovanni Locatello, Martina Orlandi, Nicholas Landini, Antonio Lo Casto, Cosimo Nardi
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(3): 1473. CrossRef - GEÇICI VE DAIMI SIMANLARIN DENTINE OLAN BAĞLANMA DAYANIMI ÜZERINE MANYETIK REZONANS GÖRÜNTÜLEME İŞLEMININ ETKISININ ARAŞTIRILMASI
Melih ÜLGEY, Oğuzhan GÖRLER, İsmail ŞALK, Derya ÖZDEMİR DOĞAN
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Performance of PROPELLER FSE T2WI in reducing metal artifacts of material porcelain fused to metal crown: a clinical preliminary study
Wenjin Li, Jing Shi, Wenjin Bian, Jianting Li, Xiaoqing Chen, Juan Feng, Jiali Yu, Jun Wang, Jinliang Niu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tracking the Molecular Fingerprint of Head and Neck Cancer for Recurrence Detection in Liquid Biopsies
Araceli Diez-Fraile, Joke De Ceulaer, Charlotte Derpoorter, Christophe Spaas, Tom De Backer, Philippe Lamoral, Johan Abeloos, Tim Lammens
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(5): 2403. CrossRef - Review on Biocompatibility and Prospect Biomedical Applications of Novel Functional Metallic Glasses
Michał Biały, Mariusz Hasiak, Amadeusz Łaszcz
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 245. CrossRef - MRI compatibility of orthodontic brackets and wires: systematic review article
Adrienn Dobai, Fanni Dembrovszky, Tamás Vízkelety, Péter Barsi, Fanni Juhász, Csaba Dobó-Nagy
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The interaction and interference of preformed metal crowns on magnetic resonance imaging: a scoping review with a systematic methodology
O. Sumner, R. Goldsmith, N. Heath, G. D. Taylor
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2021; 22(6): 1023. CrossRef - An Evidence-based Protocol for the Management of Orthodontic Patients Undergoing MRI Scans
Rachael Shivam, Sheelagh Rogers, Nicholas Drage
Orthodontic Update.2021; 14(1): 32. CrossRef - Reversal of Osseointegration as a Novel Perspective for the Removal of Failed Dental Implants: A Review of Five Patented Methods
Rolf G. Winnen, Kristian Kniha, Ali Modabber, Faruk Al-Sibai, Andreas Braun, Reinhold Kneer, Frank Hölzle
Materials.2021; 14(24): 7829. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging as a diagnostic tool for periodontal disease: A prospective study with correlation to standard clinical findings—Is there added value?
Monika Probst, Egon Burian, Teresa Robl, Dominik Weidlich, Dimitrios Karampinos, Teresa Brunner, Claus Zimmer, Florian Andreas Probst, Matthias Folwaczny
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2021; 48(7): 929. CrossRef - An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review
Rodolfo Reda, Alessio Zanza, Alessandro Mazzoni, Andrea Cicconetti, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Journal of Imaging.2021; 7(5): 75. CrossRef - Implant-supported overdentures: part 1
David Gray, Jaymit Patel
British Dental Journal.2021; 231(2): 94. CrossRef - Oral and dental considerations in pediatric cancers
Priyanshi Ritwik, Tammuella E. Chrisentery-Singleton
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2020; 39(1): 43. CrossRef - Recent advances in bioelectronics chemistry
Yin Fang, Lingyuan Meng, Aleksander Prominski, Erik N. Schaumann, Matthew Seebald, Bozhi Tian
Chemical Society Reviews.2020; 49(22): 7978. CrossRef - Imaging of root canal treatment using ultra high field 9.4T UTE-MRI – a preliminary study
Maximilian Timme, Max Masthoff, Nina Nagelmann, Malte Masthoff, Cornelius Faber, Sebastian Bürklein
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2020; 49(1): 20190183. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging based computer‐guided dental implant surgery—A clinical pilot study
Florian Andreas Probst, Josef Schweiger, Maria Juliane Stumbaum, Dimitrios Karampinos, Egon Burian, Monika Probst
Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research.2020; 22(5): 612. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging artifacts produced by dental implants with different geometries
Lauren Bohner, Norbert Meier, Felix Gremse, Pedro Tortamano, Johannes Kleinheinz, Marcel Hanisch
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2020; 49(8): 20200121. CrossRef - Implications and Considerations of Dental Materials in MRI: A Case Report and Literature Review
Brenton J. Wilson, Phoebe E. O’hare, John Zacariah, Wen Lin Chai
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Postoperative MRI in cranio-maxillofacial and oral reconstruction: A prospective comparative pilot study on artifact reduction
- 6,869 View
- 61 Download
- 40 Crossref

- Effects of the exposure site on histological pulpal responses after direct capping with 2 calcium-silicate based cements in a rat model
- Panruethai Trongkij, Supachai Sutimuntanakul, Puangwan Lapthanasupkul, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Rebecca Wong, Danuchit Banomyong
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e36. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e36

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Direct pulp capping is a treatment for mechanically exposed pulp in which a biocompatible capping material is used to preserve pulpal vitality. Biocompatibility tests in animal studies have used a variety of experimental protocols, particularly with regard to the exposure site. In this study, pulp exposure on the occlusal and mesial surfaces of molar teeth was investigated in a rat model.
Materials and Methods A total of 58 maxillary first molars of Wistar rats were used. Forty molars were mechanically exposed and randomly assigned according to 3 factors: 1) the exposure site (occlusal or mesial), 2) the pulp-capping material (ProRoot White MTA or Bio-MA), and 3) 2 follow-up periods (1 day or 7 days) (
n = 5 each). The pulp of 6 intact molars served as negative controls. The pulp of 12 molars was exposed without a capping material (n = 3 per exposure site for each period) and served as positive controls. Inflammatory cell infiltration and reparative dentin formation were histologically evaluated at 1 and 7 days using grading scores.Results At 1 day, localized mild inflammation was detected in most teeth in all experimental groups. At 7 days, continuous/discontinuous calcified bridges were formed at exposure sites with no or few inflammatory cells. No significant differences in pulpal response according to the exposure site or calcium-silicate cement were observed.
Conclusions The location of the exposure site had no effect on rat pulpal healing. However, mesial exposures could be performed easily, with more consistent results. The pulpal responses were not significantly different between the 2 capping materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioactivity and biocompatibility of bioceramic-based pulp capping materials in laboratory and animal models
Rafiqul Islam, Md. Refat Readul Islam, Kenta Tsuchiya, Yu Toida, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The road map to proper dental pulp experiments in animal models
Nuha A Elmubarak
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 11(4): 163. CrossRef - Treatment outcomes of root perforations repaired by calcium silicate-based cements with or without an accelerator: A randomized controlled trial
Kanyarat Tungputsa, Danuchit Banomyong, Sittichoke Osiri, Supachai Sutimuntanakul
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 315. CrossRef - Biological evaluation of novel phosphorylated pullulan‐based calcium hydroxide formulations as direct pulp capping materials: An in vivo study on a rat model
Md Refat Readul Islam, Rafiqul Islam, Yunqing Liu, Yu Toida, Yasuhiro Yoshida, Hidehiko Sano, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Atsushi Tomokiyo
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(9): 1247. CrossRef - 3D-printed microgels supplemented with dentin matrix molecules as a novel biomaterial for direct pulp capping
Diana Cunha, Nayara Souza, Manuela Moreira, Nara Rodrigues, Paulo Silva, Cristiane Franca, Sivaporn Horsophonphong, Ashley Sercia, Ramesh Subbiah, Anthony Tahayeri, Jack Ferracane, Pamela Yelick, Vicente Saboia, Luiz Bertassoni
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1215. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Pulpal response to mineral trioxide aggregate containing phosphorylated pullulan-based capping material
Yu TOIDA, Shimpei KAWANO, Rafiqul ISLAM, Fu JIALE, AFM A CHOWDHURY, Shuhei HOSHIKA, Yasushi SHIMADA, Junji TAGAMI, Masahiro YOSHIYAMA, Satoshi INOUE, Ricardo M. CARVALHO, Yasuhiro YOSHIDA, Hidehiko SANO
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(1): 126. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium-Silicate Cements on Reparative Dentinogenesis Following Direct Pulp Capping on Animal Models
Mihai Andrei, Raluca Paula Vacaru, Anca Coricovac, Radu Ilinca, Andreea Cristiana Didilescu, Ioana Demetrescu
Molecules.2021; 26(9): 2725. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of a novel phosphorylated pullulan‐based pulp capping material: An in vivo study on rat molars
Rafiqul Islam, Yu Toida, Fei Chen, Toru Tanaka, Satoshi Inoue, Tetsuya Kitamura, Yasuhiro Yoshida, Abu Faem Mohammad Almas Chowdhury, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Hidehiko Sano
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(10): 1902. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - A strontium and amorphous calcium phosphate dipped premixed injectable calcium silicate-based ceramic for dental root canal sealing
Huimin Jin, Yuzhu Li, Qingqing Wang, Menglu Dong, Mengmeng Yang, Wendy Chen, Shengrui Wang, Heng Zhang, Shunli Zheng, Chris Ying Cao, Zheng Zhou, Quan-Li Li
Ceramics International.2021; 47(23): 33738. CrossRef - Bioactive tri/dicalcium silicate cements for treatment of pulpal and periapical tissues
Carolyn M. Primus, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2019; 96: 35. CrossRef
- Bioactivity and biocompatibility of bioceramic-based pulp capping materials in laboratory and animal models
- 2,124 View
- 20 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of CAD/CAM-fabricated polymer-ceramics to different adhesive resin cements
- Leyla Sadighpour, Farideh Geramipanah, Zahra Ghasri, Mehrnoosh Neshatian
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e40. Published online September 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of polymer-ceramic and indirect composite resin with 3 classes of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Two computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated polymer-ceramics (Enamic [ENA; Vita] and Lava Ultimate [LAV; 3M ESPE]) and a laboratory indirect composite resin (Gradia [GRA; GC Corp.]) were equally divided into 6 groups (
n = 18) with 3 classes of resin cements: Variolink N (VAR; Vivadent), RelyX U200 (RXU; 3M ESPE), and Panavia F2 (PAN; Kuraray). The μTBS values were compared between groups by 2-way analysis of variance and thepost hoc Tamhane test (α = 0.05).Results Restorative materials and resin cements significantly influenced µTBS (
p < 0.05). In the GRA group, the highest μTBS was found with RXU (27.40 ± 5.39 N) and the lowest with VAR (13.54 ± 6.04 N) (p < 0.05). Similar trends were observed in the ENA group. In the LAV group, the highest μTBS was observed with VAR (27.45 ± 5.84 N) and the lowest with PAN (10.67 ± 4.37 N) (p < 0.05). PAN had comparable results to those of ENA and GRA, whereas the μTBS values were significantly lower with LAV (p = 0.001). The highest bond strength of RXU was found with GRA (27.40 ± 5.39 N,p = 0.001). PAN showed the lowest µTBS with LAV (10.67 ± 4.37 N;p < 0.001).Conclusions When applied according to the manufacturers' recommendations, the µTBS of polymer-ceramic CAD/CAM materials and indirect composites is influenced by the luting cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
Mohamed F. Haridy, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Shehabeldin Saber, Edgar Schafer, Samar Elsayed Swelam, Youssef M. Haridy, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrofluoric acid and self-etch ceramic primers on the flexural strength and fatigue resistance of glass ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Paulo Matias Moreira, Gabriela Luiza Moreira Carvalho, Rodrigo de Castro Albuquerque, Carolina Bosso André
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 198. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on the mechanical properties of permanent composite-based CAD-CAM restorative materials produced by additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques
Tuğba Temizci, Hatice Nalan Bozoğulları
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on resin-matrix CAD/CAM ceramics bonding to dentin: in vitro study
Hanan Fathy, Hamdi H. Hamama, Noha El-Wassefy, Salah H. Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital image analysis of fluorescence of ceramic veneers with different ceramic materials and resin cements
Jiao ZHANG, Qing YU
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 868. CrossRef - Fatigue Behavior of Monolithic Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramic Restorations: Effects of Conditionings of the Intaglio Surface and the Resin Cements
F Dalla-Nora, LF Guilardi, CP Zucuni, LF Valandro, MP Rippe
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): 316. CrossRef
- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
- 2,113 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of the ability of Reciproc and Reciproc Blue instruments to reach the full working length with or without glide path preparation
- Mehmet Adıguzel, Pelin Tufenkci
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e41. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of the present study was to compare the mean preparation times and frequency with which Reciproc and Reciproc Blue instruments reached the full working length in mandibular molars, with or without glide path preparation.
Materials and Methods Previously untreated mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals with completely formed apices were randomly divided into 6 groups (
n = 50) depending on the usage of Reciproc (RC; VDW), Reciproc Blue (RC Blue; VDW), C-Pilot (CP; VDW), and R-Pilot (RP; VDW) files: RC, RC Blue, RC + C-Pilot (RC-CP), RC-Blue + C-Pilot (RC Blue-CP), RC+R-Pilot (RC-RP), and RC Blue + R-Pilot (RC Blue-RP). A glide path was prepared using the hand-operated C-Pilot or the machine-operated R-Pilot instruments, respectively. The χ2 test, analysis of variance, and the Tukeypost hoc test were used for statistical comparisons.Results No statistically significant differences were observed in the distribution of the frequency of reaching the full working length in the RC (94%), RC Blue (88%), RC-CP (94%), RC Blue-CP (90%), RC-RP (96%), and RC Blue-RP (92%) groups (
p > 0.05).Conclusions Preparation of a glide path did not have a significant effect on reaching the full working length using these systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Influence of the Brushing Motions on the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of the Reciproc Blue Instrument: In vitro Study
Juliana Borsoi Chicon, Vanessa Maria Fernandes Pavão, Maíra Henrique Gonçalves Cunha, Marcos Frozoni
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(9): 1340. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Nickel-titanium files in endodontics: Development, improvement and modifications of nickel-titanium alloy
Slavoljub Zivkovic, Milica Jovanovic-Medojevic, Jelena Neskovic, Marijana Popovic-Bajic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2023; 80(3): 262. CrossRef - Comparison of the incidence of postoperative pain in single sitting root canal treatment after using two reciprocating systems and two continuous rotary systems: An in vivo study
VijayKumar Vijayran, Ambica Khetarpal, Asit Vats, Monika Ahlawat, Neha Singhal, Harshita
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 12. CrossRef - Effect of mode of rotation on apical extrusion of debris with four different single‐file endodontic instrumentation systems: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Durre Sadaf, Marcy McCall MacBain, Khalid A. Merdad
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 202. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain intensity following the use of three different instrumentation techniques: A randomized clinical trial
Mehmet Adiguzel, Pelin Tufenkci, ismail Ilker Pamukcu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 133. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 2,717 View
- 11 Download
- 11 Crossref

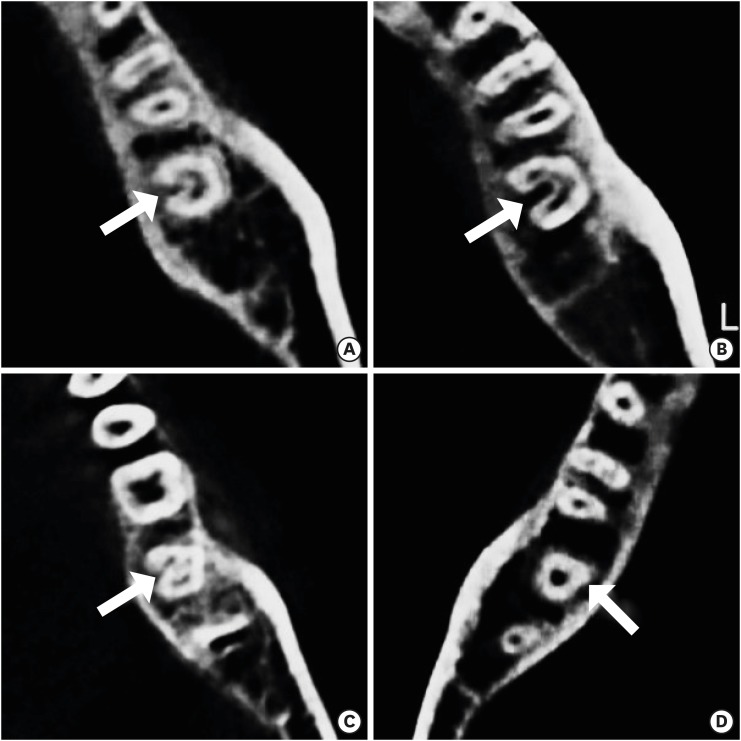
- C-shaped root canals of mandibular second molars in a Korean population: a CBCT analysis
- Hee-Sun Kim, Daun Jung, Ho Lee, Yoon-Sic Han, Sohee Oh, Hye-Young Sim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the C-shaped root canal anatomy of mandibular second molars in a Korean population.
Materials and Methods A total of 542 teeth were evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The canal shapes were classified according to a modified version of Melton's method at the level where the pulp chamber floor became discernible.
Results Of the 542 mandibular second molars, 215 (39.8%) had C-shaped canals, 330 (53%) had 3 canals, 17 (3.3%) had 2 canals, 12 (2.2%) had 4 canals, and 8 (1.7%) had 1 canal. The prevalence of C-shaped canals was 47.8% in females and 28.4% in males. Seventy-seven percent of the C-shaped canals showed a bilateral appearance. The prevalence of C-shaped canals showed no difference according to age or tooth position. Most teeth with a C-shaped canal system presented Melton's type II (45.6%) and type III (32.1%) configurations.
Conclusions There was a high prevalence of C-shaped canals in the mandibular second molars of the Korean population studied. CBCT is expected to be useful for endodontic diagnosis and treatment planning of mandibular second molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
Jacob John, Wei Cheong Ngeow, Ting-Chun Shen, Lih-Jyh Fuh, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Yen-Wen Shen, Jui-Ting Hsu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 21(1): 265. CrossRef - Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Amin Salem Milani, Shahin Namvar Asl Amirkhizi, Tahmineh Razi, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Pouya Sabanik, Nikhat Kaura
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of mandibular and maxillary second molar root canal anatomy in a Turkish subpopulation using CBCT: comparison of Briseno-Marroquin and Vertucci classifications
Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, İpek Öreroğlu, Kemal Çağlar, Kader Cesur Aydin
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e18. CrossRef - Prevalence of c-shaped canal morphology in premolar and molar teeth assessed by cone-beam computed tomography: systematic review and meta-analysis
Faezeh Yousefi, Younes Mohammadi, Elham Shokri
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging Findings of Clinical Significance in Endodontics During Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scanning of the Upper Airway—The Anterior, Bilateral, C-Shaped, Dual of Mandibular Root Canals: A Brief Case Report
Edgar García-Torres, Diana Laura Grissel Guerrero-Falcón, Hugo Alejandro Bojórquez-Armenta, Oscar Eduardo Almeda-Ojeda, Víctor Hiram Barajas-Pérez, Luis Javier Solís-Martínez
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3157. CrossRef - Frequency of C-Shaped Root Canals in Permanent Mandibular Second Molars in a Sample of Pakistani Population using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Syed Nabeel Ahmed, Muhammad Mansoor Majeed, Sakina Kazmi, Muhammad Omar Ansari
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2024; : 109. CrossRef - ANÁLISE DAS VARIAÇÕES ANATÔMICAS DE CANAIS C-SHAPED NOS MOLARES INFERIORES: UMA REVISÃO INTEGRATIVA DA LITERATURA
Larissa Eulália Pereira, Thayana Karla Guerra Lira dos Santos
Revista Contemporânea.2024; 4(5): e4264. CrossRef - External Validation of the Effect of the Combined Use of Object Detection for the Classification of the C-Shaped Canal Configuration of the Mandibular Second Molar in Panoramic Radiographs: A Multicenter Study
Sujin Yang, Kee-Deog Kim, Yoshitaka Kise, Michihito Nozawa, Mizuho Mori, Natsuho Takata, Akitoshi Katsumata, Yoshiko Ariji, Wonse Park, Eiichiro Ariji
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 627. CrossRef - A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of C‐Shaped Canal Configuration in Maxillary Molars Among an Iranian Population
Nafiseh Nikkerdar, Mohammad Moslehi, Amin Golshah, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Egyptian subpopulation: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Mohammed abou El Seoud, Shaimaa Mohamed Abu el Sadat, Nawar Naguib Nawar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al‑Zubaidi, Abdulmjeed S. Enizy, Ahmed A. Madfa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in kuwaiti sub-population
AbdullahJassim Alenezi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, MazenA Aldosimani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 283. CrossRef - Prevalence and morphology of C‐shaped and non‐C‐shaped root canal systems in mandibular second molars
T Fenelon, P Parashos
Australian Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars of a selected patient group using cone beam computed tomography: prevalence, configuration and radicular groove types
Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan, Güzide Pelin Sezgin
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 949. CrossRef - Prevalência estimada de canais “C- Shaped”: Uma revisão sistemática e meta-análise
Natália Pereira da Silva Falcão, Sandro Junio de Oliveira Tavares, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Katherine Azevedo Batistela Rodrigues Thuller, Leonardo dos Santos Antunes, Estefano Borgo Sarmento, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azevedo, Cinthya Cristina Gomes, Ca
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 91. CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Clinical and radiological assessment of the anatomical and topographic structure of the root canals of teeth in patients of different age groups
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, O.A. Boriskina, I.S. Berkutova, V.A. Venediktova, R.R. Saltovets
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(5): 32. CrossRef
- A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
- 2,349 View
- 13 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on fluoride release and micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement in caries-affected dentin
- Jamila Nuwayji Agob, Neven Saad Aref, Essam El Saeid Al-Wakeel
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e45. Published online October 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e45
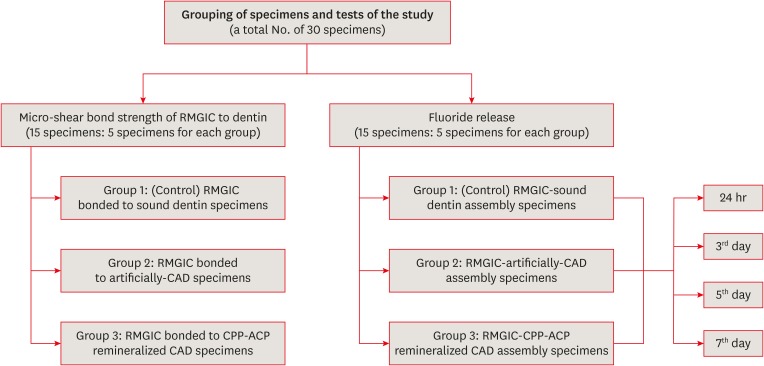
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate fluoride release and the micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) in casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP)-remineralized caries-affected dentin (CAD).
Materials and Methods Exposed dentin surfaces of 30 human third molar teeth were divided into 2 equal groups for evaluating fluoride release and the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC to CAD. Each group was subdivided into 3 equal subgroups: 1) control (sound dentin); 2) artificially demineralized dentin (CAD); 3) CPP-ACP remineralized dentin (remineralized CAD). To measure fluoride release, 15 disc-shaped specimens of RMGIC (4 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) were bonded on one flat surface of the dentin discs of each group. Fluoride release was tested using ion chromatography at different intervals; 24 hours, 3, 5, 7 days. RMGIC micro-cylinders were built on the flat dentin surface of the 15 discs, which were prepared according to the assigned group. Micro-shear bond strength was measured after 24 hours water storage. Data were analyzed using 1- and 2-way analysis of variance and the
post hoc least significant difference test (α = 0.05).Results Fluoride detected in solutions (at all intervals) and the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC bonded to CPP-ACP-remineralized dentin were significantly higher than those bonded to artificial CAD (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Demineralized CAD consumes more fluoride released from RMGIC into the solution for remineralization than CPP-ACP mineralized dentin does. CPP-ACP increases the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC to CAD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synergistic effect of nanosilver fluoride with L-arginine on remineralization of early carious lesions
Ahmad S. Albahoth, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jeong-Won Park
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the bond strength of glass ionomer cement modified with fluoride-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to caries-affected dentin
Hanife Altınışık, Merve Nezir, Hülya Erten Can, Necibe Başaran Mutlu Ağardan, Aysel Berkkan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-collagenous protein analog-induced biomimetic mineralization strategy to restore the dentin interface
Ruhua Chen, Yimeng Xie, Liang Ma, Bing Li, Wei Yao
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2024; 10(6): 062004. CrossRef - A Critical Review on the Factors Affecting the Bond Strength of Direct Restorative Material Alternatives to Amalgam
Zeynep Batu Eken, Nicoleta Ilie
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4853. CrossRef - ÇOCUK DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE GÜMÜŞ DİAMİN FLORÜR KULLANIMI
Zeynep UÇAR, Bahar Melis AKYILDIZ
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 652. CrossRef - Microshear Bond Strength of Nanoparticle-Incorporated Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer to Caries-Affected Dentin
Zahra Fattah, Zahra Jowkar, Safoora Rezaeian, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Synergistic effect of nanosilver fluoride with L-arginine on remineralization of early carious lesions
- 1,948 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Improved dentin disinfection by combining different-geometry rotary nickel-titanium files in preparing root canals
- Marwa M. Bedier, Ahmed Abdel Rahman Hashem, Yosra M. Hassan
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e46. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e46

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was to evaluate the antibacterial effect of different instrumentation and irrigation techniques using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) after root canal inoculation with
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ).Materials and Methods Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of extracted mandibular molars were apically enlarged up to a size 25 hand K-file, then autoclaved and inoculated with
E. faecalis . The samples were randomly divided into 4 main groups according to the system of instrumentation and irrigation: an XP-endo Shaper (XPS) combined with conventional irrigation (XPS/C) or an XP-endo Finisher (XPF) (XPS/XPF), and iRaCe combined with conventional irrigation (iRaCe/C) or combined with an XPF (iRaCe/XPF). A middle-third samplewas taken from each group, and then the bacterial reduction was evaluated using CLSM at a depth of 50 µm inside the dentinal tubules. The ratio of red fluorescence (dead cells) to green-and-red fluorescence (live and dead cells) represented the percentage of bacterial reduction. The data were then statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for comparisons across the groups and the Dunn test was used for pairwise comparisons.Results The instrumentation and irrigation techniques had a significant effect on bacterial reduction (
p < 0.05). The iRaCe/XPF group showed the strongest effect, followed by the XPS/XPF and XPS/C group, while the iRaCe/C group had the weakest effect.Conclusions Combining iRaCe with XPF improved its bacterial reduction effect, while combining XPS with XPF did not yield a significant improvement in its ability to reduce bacteria at a depth of 50 µm in the dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
Oksana A. Shuliatnikova, Mikhail V. Yakovlev, Anatoliy P. Godovalov
HERALD of North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.2025; 17(2): 89. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Shaping ability of non‐adaptive and adaptive core nickel–titanium single‐file systems with supplementary file in ribbon‐shaped canals analysed by micro‐computed tomography
Parichat Chinchiyanont, Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Nathamon Thongbai‐On
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - In vitro reduction in Enterococcus faecalis count following root canal preparation with Neolix and XP shaper rotary files
Mina Mehrjouei, Somayeh Teimoori, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Seyed Majed Mortazavi, Maryam Khorasanchi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 236. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite versus apple cider vinegar against Enterococcus faecalis in contracted endodontic cavity
Kaur Supreet, Karkala Venkappa Kishan, Nimisha Chinmay Shah
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 254. CrossRef - Ex vivo evaluation of the effectiveness of XP-endo Finisher on the removal of smear layer from the root canal
Sângela Maria PEREIRA, Ceci Nunes CARVALHO, Rudys Rodolfo TAVAREZ, Paulo NELSON-FILHO, Léa Assed Bezerra DA SILVA, Etevaldo Matos MAIA FILHO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biofilm elimination from infected root canals using four different single files
Sarah A. Hamed, Sarah Shabayek, Hayam Y. Hassan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adaptive, Rotary, and Manual Root Canal Instrumentation in Primary Molars: A Triple-Armed, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Bhaggyashri A. Pawar, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Anuj Bhardwaj, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Amelia Kristanti Rahardjo, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Zvi Metzger, Anda Kfir
Biology.2021; 10(1): 42. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Endodontic Access Cavity Design and Using XP-endo Finisher on the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal System
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Koray Yılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 419. CrossRef - Irrigation in Endodontics: a Review
Sarah Bukhari, Alaa Babaeer
Current Oral Health Reports.2019; 6(4): 367. CrossRef
- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
- 1,629 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Influence of thickness and incisal extension of indirect veneers on the biomechanical behavior of maxillary canine teeth
- Victória Luswarghi Souza Costa, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Eduardo Shigueyuki Uemura, Dayana Campanelli de Morais, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e48. Published online November 12, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To analyze the influence of thickness and incisal extension of indirect veneers on the stress and strain generated in maxillary canine teeth.
Materials and Methods A 3-dimensional maxillary canine model was validated with an
in vitro strain gauge and exported to computer-assisted engineering software. Materials were considered homogeneous, isotropic, and elastic. Each canine tooth was then subjected to a 0.3 and 0.8 mm reduction on the facial surface, in preparations with and without incisal covering, and restored with a lithium disilicate veneer. A 50 N load was applied at 45° to the long axis of the tooth, on the incisal third of the palatal surface of the crown.Results The results showed a mean of 218.16 µstrain of stress in the
in vitro experiment, and 210.63 µstrain in finite element analysis (FEA). The stress concentration on prepared teeth was higher at the palatal root surface, with a mean value of 11.02 MPa and varying less than 3% between the preparation designs. The veneers concentrated higher stresses at the incisal third of the facial surface, with a mean of 3.88 MPa and a 40% increase in less-thick veneers. The incisal cover generated a new stress concentration area, with values over 48.18 MPa.Conclusions The mathematical model for a maxillary canine tooth was validated using FEA. The thickness (0.3 or 0.8 mm) and the incisal covering showed no difference for the tooth structure. However, the incisal covering was harmful for the veneer, of which the greatest thickness was beneficial.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- On fracture modelling of implantable load-bearing bioceramic structures and its state of the art
Boyang Wan, Chi Wu, Ziyan Man, Zhongpu Zhang, Michael V Swain, Qing Li
Acta Biomaterialia.2025; 207: 83. CrossRef - Clinical Survival Rate and Laboratory Failure of Dental Veneers: A Narrative Literature Review
Tariq F. Alghazzawi
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(5): 131. CrossRef - Facettes en céramique
O. Etienne
EMC - Médecine buccale.2024; 17(3): 1. CrossRef - Canine guidance reconstruction with ceramic or composite resin: A 3D finite element analysis and in vitro wear study
Mírian Galvão Bueno, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(5): 765.e1. CrossRef - Effect of three different veneering techniques on the stress distribution and in vitro fatigue behavior of core-veneer all-ceramic fixed partial dentures
Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Anna Karina Figueiredo Costa, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Alana Barbosa Alves Pinto, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(3): 188. CrossRef Lithium Disilicate Crown, Zirconia Hybrid Abutment and Platform Switching to Improve the Esthetics in Anterior Region: A Case Report
Dario Adolfi, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Maurício Adolfi, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Guilherme de Siqueira Ferreira Anzaloni Saavedra, Marco Antonio Bottino
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2020; Volume 12: 31. CrossRef- Effect of the restorative technique on load-bearing capacity, cusp deflection, and stress distribution of endodontically-treated premolars with MOD restoration
Daniel Maranha da Rocha, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Milena Cerqueira da Rocha, Rebeca Di Nicoló, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- On fracture modelling of implantable load-bearing bioceramic structures and its state of the art
- 2,019 View
- 19 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Endocrown restorations for extensively damaged posterior teeth: clinical performance of three cases
- Konstantinos Tzimas, Maria Tsiafitsa, Paris Gerasimou, Effrosyni Tsitrou
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e38. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e38
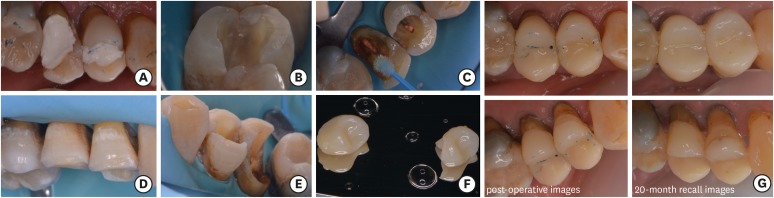
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restoration of endodontically treated teeth (ETT) with more than one cusp missing and thin remaining walls is challenging for the general practitioner. The use of posts combined with full coverage restorations is a well-established approach, yet not following the minimal invasive principles of adhesive dentistry. Endocrowns are indirect monoblock restorations that use the pulp chamber of the ETT for retention. In this study the fabrication of 4 endocrowns and their clinical performance will be discussed. Two clinical cases include computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing manufactured molar endocrowns (one feldspathic ceramic and one hybrid composite-ceramic restoration) and the other two are dental laboratory manufactured resin composite premolar endocrown restorations. The modified United States Public Health Service criteria were used to assess the clinical behavior of the restorations at different follow up periods. Endocrown restorations present a satisfactory clinical alternative, either by the use of resin composite or glass ceramic and hybrid materials. Specific guidelines with minimal alterations should be followed for an endocrown restoration to be successful. Due to limited evidence regarding the long term evaluation of this restorative technique, a careful selection of cases should be applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical performance of endocrown restorations in anterior teeth: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Julia Fehrenbach, Jéssica Lopes Soares de Soares, João Carlos Silva do Nascimento Foly, Leonardo Lamberti Miotti, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2025; 41(1): 28. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and mode of failure of modified Polyether-ether-ketone versus lithium disilicate endocrowns
Mohamed G. A. Kharboush, Hesham I. Othman, Mohamed F. Aldamaty, Ahmed M. L. Alameldin
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic assessment of composite CAD/CAM endocrowns and stainless steel crowns for endodontically treated first permanent molars in Egyptian children: randomized controlled pilot study
Basheer Ali Mabkhot, Sheriene Ezz Eldin Taha, Shaimaa Mohamed Sabry
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of cavity design on the mechanical behavior of endo-crown restorations: an ex-vivo study
Mohamed Gomaa Altamimi, Omaima El Mahallawi, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Mohammed Turky
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Microtensile Bonding Strength and Microleakage of Endocrowns Restorations Prepared With Two Different Materials
Emrah Ayna, Burcu Ayman, Cansel Belge
HRU International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Research.2025; 5(2): 66. CrossRef - Exploring the evolution of endocrowns: a bibliometric analysis (2010-2024)
Sanjana Jayakumar Nair, Jinesh Azhuvancheri, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Gopika Krishnan
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2025; 13(10): 4296. CrossRef - Beyond Traditional Restorations: Management With Endocrown in a Late Adolescent
Abdulaziz Binrayes, Abdullatif A AlGhazzi, Saud M Alotaibi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrown-retained fixed partial dentures: Revolutionizing tooth restoration or risky business? A finite element study
Nivedha Muthukumar, Parthasarathy Natarajan, Seenivasan Madhan Kumar, Shanmuganathan Natarajan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1234. CrossRef - Chinese dentists’ restorative preferences and choices for endodontically treated teeth: a representative survey
Wenhui Li, Ziting Zheng, Yuting Zeng, Zhiyan Zhou, Ping Xiao, Xincen Zhong, Wenjuan Yan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PHỤC HÌNH ENDOCROWN TRÊN RĂNG CỐI NHỎ ĐÃ NỘI NHA: BÁO CÁO MỘT CA LÂM SÀNG
Trịnh Minh Trí Trịnh Minh Trí, Lê Võ Thảo Phương Lê Võ Thảo Phương, Nguyễn Tấn Đạt Nguyễn Tấn Đạt, Phạm Nguyên Quân Phạm Nguyên Quân, Văn Hồng Phượng Văn Hồng Phượng
Tạp Chí Khoa Học Trường Đại Học Quốc Tế Hồng Bàng.2024; : 241. CrossRef - Application of one-piece endodontic crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM system to molars
Haruto Hiraba, Kensuke Nishio, Yoshimasa Takeuchi, Takashi Ito, Tetsuo Yamamori, Atsushi Kamimoto
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 81. CrossRef - Clinical performance and wear resistance of milled resin composite material versus direct nanohybrid bulk-fill resin composite in the restoration of endodontically treated posterior teeth over 1 year: Randomized clinical trial
Esraa Esmeail H. Elhaddad, Mohamed M. A. Mohsen, Dina Ezz Eldin Mohamed
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(4): 400. CrossRef - Roughness analysis on porcelain sectional surface of porcelain fused to Co-Cr alloy endocrowns
Xuesheng Li
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimal İnvaziv Protetik Tedavilerde CAD-CAM Kullanımı: İki Olgu Sunumu
Aynur Beyza Çavuşculu Güdül, Şükriye Ece Geduk, Gaye Sağlam
Journal of International Dental Sciences.2024; 10(3): 167. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Toughness and Marginal Adaptation of PEEK and Cast Metal Crowns for Restoring Posterior Teeth with Endocrown and Richmond Crown: An In Vitro Study
Lalit Kumar, Komalpreet Kaur, Shefali Singla, Charnpreet Singh, Sunint Singh
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 14(4): 234. CrossRef - Retrospective study on the evolution of teeth with endodontic treatment in a group of patients from Craiova – Romania
Mihaela-Roxana Boțilă, Mihaela Jana Țuculina , Oana Andreea Diaconu , Mihaela Ionescu , Petre Costin Mărășescu , Luana Corina Lascu , Veronica Mercut
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(2): 225. CrossRef - Criterios clínicos y radiológicos de los tratamientos endodónticos para rehabilitación Endocrown: meta análisis
Domenica Camila Astudillo Benavides, Rafael Bernardo Piedra Andrade, Amanda Isabel Pesantez Coronel, Jose Esteban Torrachi Carrasco
Anatomía Digital.2024; 7(4): 81. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Central Incisors Restored Using Different Post and Crown Materials
Nour Al-Deen Kharboutly, Mirza Allaf, Shaza Kanout
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of extended pulp chamber preparations on the clinical performance of endocrowns in Indian patients: A 1-year observational study
Preethi Duraisamy, Naveen Gopi Chander, Jetty Ramesh Reddy, Muthukumar Balasubramanium
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(5): 616. CrossRef - Endocrowns: Indications, Preparation Techniques, and Material Selection
Dalal S AlDabeeb, Nouf S Alakeel, Raneem M Al jfshar, Thakra K Alkhalid
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Awareness of Dental Practitioners About the Utilization of Endocrown in Post-endodontic Management
Ahmed A Madfa, Moazzy I Almansour, Asma F Alshammari, Nada M. Alenezi, Essa F. Alrashidi, Adel A. Aldhaban, Thoraya Aljohani, Faris A. Alshammari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Performance of Two CAD/CAM Fabricated Ceramic Restorations with Different Designs for MIH Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ayat G. Montaser, Sara N. Hashem, Menna-Allah S. Ali, Nour Alhoda Fathy, Hebatullah Ahmed Safwat, Alaa M. Eldehna
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrown as a restorative strategy in endodontically treated teeth: an integrative literature review
Robson de Lima GOMES, Andressa Cristina da Silva QUEIROZ, Viviane Maria Gonçalves de FIGUEIREDO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ENDOCROWN RESTORATION OF THE ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH BY USING CAD/CAM: CASE SERIES
Begüm ÜNLÜ KURŞUN, Ender AKAN
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(Suppl 1): 13. CrossRef - Clinical Evaluation of CAD/CAM Ceramic Endocrown Versus Prefabricated Zirconia Crown in the Restoration of Pulpotomized Primary Molars: A Two-Year Spilt-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial
Nagwa Mohmmad Ali Khattab, Yasmine Mohamed Farouk El Makawi, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 627. CrossRef - Hyperplastic Pulpitis Management with Endocrown: A Case Report
Pérez Jardón A, Otero Gayoso N, Otero. Rey E.M, Guerra Caamaño M, Chamorro-Petronacci C.M, Blanco Carrión A, Rivas Mundiña B
The Open Dentistry Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inner crown thickness on the bonding strength of porcelain fused to Co-Cr alloy endocrown
Xuesheng Li
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of pulp chamber depth on the accuracy of endocrown scans made with different intraoral scanners versus an industrial scanner: An in vitro study
Bahar Gurpinar, Onjen Tak
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(3): 430. CrossRef - Efectividad de las restauraciones en piezas con tratamiento de conducto: Una revisión clínica actual
Guiselle Andrea Verástegui Baldárrago
Revista Odontológica Basadrina.2022; 6(2): 41. CrossRef - “Conservative Bonded Restoration (An Alternative to Full Coverage Crown): A Case Report on Endocrown
Josey Mathew, Liza George, Sinju Paul, Aleesha Joy, Beulah M Bejoy, Sethuparvathi Anitha
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 42. CrossRef - Fractography of clinical failures of indirect resin composite endocrown and overlay restorations
Carlo M. Saratti, Giovanni T. Rocca, Stéphane Durual, Ulrich Lohbauer, Jack L. Ferracane, Susanne S. Scherrer
Dental Materials.2021; 37(6): e341. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - A Thorough Analysis of the Endocrown Restoration: A Literature Review
Dimokritos Papalexopoulos, Theodora-Kalliopi Samartzi, Aspasia Sarafianou
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(4): 422. CrossRef - Full‐Crown Versus Endocrown Approach: A 3D‐Analysis of Both Restorations and the Effect of Ferrule and Restoration Material
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Niek de Jager, Marco Antonio Bottino, Paul de Kok, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(4): 335. CrossRef - Monolithic Endocrown Vs. Hybrid Intraradicular Post/Core/Crown Restorations for Endodontically Treated Teeth; Cross-sectional Study
Mai Soliman, Lamar Alshamrani, Basma Yahya, Ghadah Alajlan, Alhanoof Aldegheishem, Elzahraa Eldwakhly
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(11): 6523. CrossRef - Which materials would account for a better mechanical behavior for direct endocrown restorations?
José Augusto Sedrez-Porto, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 103: 103592. CrossRef - Indications and Success Rate of Endo Crowns – A Systematic Review
Shahzeb Hasan Ansari, Abdullah Ahmed Alfaqeeh, Abdullah Al Buryk, Sara Ahmed Alfaqeeh, Abdullatif Yousif A. Almusharraf, Atheer Hussain N. Aljarullah
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(43): 3247. CrossRef
- Mechanical performance of endocrown restorations in anterior teeth: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- 5,727 View
- 115 Download
- 37 Crossref

- Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
- Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Ameya Parlikar
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e44. Published online October 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e44
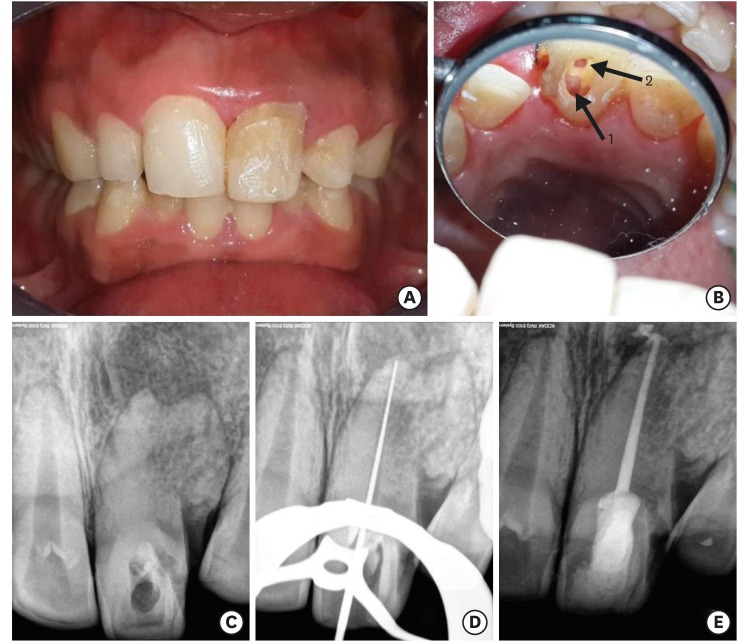
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Fusion and gemination are developmental anomalies of teeth that may require endodontic treatment. Fusion may cause various clinical problems related to esthetics, tooth spacing, and other periodontal complications. Additional diagnostic tools are required for the diagnosis and the treatment planning of fused tooth. The present case report describes a case of unilateral fusion of a supernumerary root to an upper permanent central incisor with large periapical lesion in which a conservative approach was used without extraction of supernumerary tooth and obturated with mineral trioxide aggregate to reach a favorable outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of fusion between a third molar and a distomolar: case report
G. M. Almeida, M.A. H. Duarte, J. R. Carvalho-Junior, R.M. C. Travassos, G. F. Silva, M.F. V. Marceliano-Alves, A. G. Limoeiro, M. P. Alcalde
Endodontics Today.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontics and Decompression-Based Management of Extensive Periapical Cystic-Like Lesions: A Comparative and Radiological Study with A Two-Year Follow-Up
Roxana Talpoș-Niculescu, Ioana Veja, Carina Sonia Neagu, Laura Cristina Rusu, Șerban Talpoș-Niculescu, Mălina Popa, Luminița Maria Nica
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(17): 6127. CrossRef - Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
Tatsuya Akitomo, Satoru Kusaka, Momoko Usuda, Mariko Kametani, Ami Kaneki, Taku Nishimura, Masashi Ogawa, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Children.2023; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Approche multidisciplinaire d’un cas de fusion incisive centrale maxillaire avec un « talon cusp »
Sonia Terbeche, Kheira Yousfi, Samia Saddat, Souad Larbi Messaoudi, Noureddine Ahmed Fouatih, G. Mer, O. Weissenbach
Revue d'Orthopédie Dento-Faciale.2022; 56(2): 205. CrossRef
- A rare case of fusion between a third molar and a distomolar: case report
- 2,670 View
- 23 Download
- 4 Crossref


 KACD
KACD



 First
First Prev
Prev


