-
Analysis of temperature change during polymerization according to resin thickness: an in vitro experimental study
-
Kkot-Byeol Bae, Eun-Young Noh, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e34. Published online November 12, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e34
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the temperature changes during the light curing of conventional flowable composite resin and bulk-fill composite resin of various thicknesses using an infrared thermographic camera.
Methods
Flowable composite resin (G-aenial Flo, GC Co.) and bulk-fill composite resin (SDR, Dentsply Caulk) were used. Specimens with thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 5.0 mm were prepared. The infrared thermographic camera measured the temperature changes at the maximum temperature rise point during light curing. The data were analyzed for maximum temperature, time to peak temperature, and temperature rise patterns.
Results
For G-aenial Flo, the maximum temperature tended to decrease with increasing thickness, whereas for SDR, the maximum temperature decreased up to 2.0 mm and then remained relatively consistent from 2.0 mm to 5.0 mm. At thicknesses of 1.5 mm or less, both resins showed a rapid temperature increase within the first 5 seconds, followed by a reduced rate of increase up to 80 seconds. At thicknesses of 2.0 mm or greater, the temperature peaked and then gradually decreased. Across all thicknesses, SDR was observed to reach peak temperature more rapidly than G-aenial Flo.
Conclusions
Observable differences in polymerization dynamics were identified between the two resin types, particularly at greater thicknesses. Although no statistical analysis was performed, these descriptive findings suggest that infrared thermographic cameras may be useful for indirectly assessing polymerization dynamics during resin polymerization.
-
Impact of post adhesion on stress distribution: an in silico study
-
Kkot-Byeol Bae, Jae-Yoon Choi, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e19. Published online May 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e19
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the stress distribution in teeth restored with different post materials and bonding conditions using finite element analysis (FEA).
Methods
A two-dimensional FEA model of a maxillary central incisor restored with IPS-Empress-2 crown (Ivoclar Vivadent), composite resin core, and posts were created. The model simulated bonded and non-bonded conditions for both fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) and titanium (Ti) posts. Stress distribution was analyzed using ANSYS 14.0 software under a 100-N load applied at a 45° angle to the long axis of the tooth.
Results
The results revealed that stress concentration was significantly higher in non-bonded posts compared to bonded ones. FRC posts exhibited stress values closer to those of dentin, whereas Ti posts demonstrated higher stress concentration, particularly in non-bonded states, increasing the potential risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
Conclusions
FRC posts, with elastic properties similar to dentin and proper adhesion, minimize stress concentration and potential damage to surrounding tissues. Conversely, materials with higher elastic modulus like Ti, can cause unfavorable stress concentrations if not properly bonded, emphasizing the importance of post adhesion in tooth restoration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Advances in Ecofriendly and High-Strength Dental Composites: Structural and Functional Perspectives
Sayem A. Mulla, Amit Patil, Himmat Jaiswal, Bhavani Sangala Nagendra, Ashima Jakhar, Waseem Z. Khan
European Journal of General Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,430
View
-
95
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effects of CTHRC1 on odontogenic differentiation and angiogenesis in human dental pulp stem cells
-
Jong-soon Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e18. Published online April 28, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e18
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to determine whether collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 (CTHRC1), which is involved in vascular remodeling and bone formation, can stimulate odontogenic differentiation and angiogenesis when administered to human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs). Materials and MethodsThe viability of hDPSCs upon exposure to CTHRC1 was assessed with the WST-1 assay. CTHRC1 doses of 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL were administered to hDPSCs. Reverse-transcription polymerase reaction was used to detect dentin sialophosphoprotein, dentin matrix protein 1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor 2. The formation of mineralization nodules was evaluated using Alizarin red. A scratch wound assay was conducted to evaluate the effect of CTHRC1 on cell migration. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance followed by the Tukey post hoc test. The threshold for statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. ResultsCTHRC1 doses of 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL had no significant effect on the viability of hDPSCs. Mineralized nodules were formed and odontogenic markers were upregulated, indicating that CTHRC1 promoted odontogenic differentiation. Scratch wound assays demonstrated that CTHRC1 significantly enhanced the migration of hDPSCs. ConclusionsCTHRC1 promoted odontogenic differentiation and mineralization in hDPSCs.
-
Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA in vivo
-
Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e17. Published online February 25, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
In recent in vitro study, it was reported that osteostatin (OST) has an odontogenic effect and synergistic effect with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) in human dental pulp cells. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate whether OST has a synergistic effect with MTA on hard tissue formation in vivo. Materials and MethodsThirty-two maxillary molars of Spraque-Dawley rats were used in this study. An occlusal cavity was prepared and the exposed pulps were randomly divided into 3 groups: group 1 (control; ProRoot MTA), group 2 (OST 100 μM + ProRoot MTA), group 3 (OST 10 mM + ProRoot MTA). Exposed pulps were capped with each material and cavities were restored with resin modified glass ionomer. The animals were sacrificed after 4 weeks. All harvested teeth were scanned with micro-computed tomography (CT). The samples were prepared and hard tissue formation was evaluated histologically. For immunohistochemical analysis, the specimens were sectioned and incubated with primary antibodies against dentin sialoprotein (DSP). ResultsIn the micro-CT analysis, it is revealed that OST with ProRoot MTA groups showed more mineralized bridge than the control (p < 0.05). In the H&E staining, it is showed that more quantity of the mineralized dentin bridge was formed in the OST with ProRoot MTA group compared to the control (p < 0.05). In all groups, DSP was expressed in newly formed reparative dentin area. ConclusionsOST can be a supplementary pulp capping material when used with MTA to make synergistic effect in hard tissue formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pulpal responses to mineral trioxide aggregate with and without zinc oxide addition in mature canine teeth after full pulpotomy
Behnam Bolhari, Neda Kardouni Khouzestani, Hadi Assadian, Saeed Farzad-Mohajeri, Mohammad Mehdi Dehghan, Soheil Niavarzi, Behnam Dorost, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Henry F. Duncan, Artak Heboyan, Antonio Signore, Stefano Benedicenti
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Advancements in Peptides for Promoting Reparative Dentin Regeneration in Direct Pulp Capping: A Narrative Review
Jiawen Wang, Shuwei Qiao, Tianjia Huang, Junjie Lian, Song Zhu
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and pro-mineralization effects of premixed calcium silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro and in vivo study
Nyein Chan KO, Sonoko NODA, Yamato OKADA, Kento TAZAWA, Nobuyuki KAWASHIMA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 729. CrossRef - Osteostatin, a peptide for the future treatment of musculoskeletal diseases
Daniel Lozano, Arancha R. Gortazar, Sergio Portal-Núñez
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 223: 116177. CrossRef - Comparison of bioactive material failure rates in vital pulp treatment of permanent matured teeth – a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Péter Komora, Orsolya Vámos, Noémi Gede, Péter Hegyi, Kata Kelemen, Adél Galvács, Gábor Varga, Beáta Kerémi, János Vág
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hard tissue formation in pulpotomized primary teeth in dogs with nanomaterials MCM-48 and MCM-48/hydroxyapatite: an in vivo animal study
Sahar Talebi, Nosrat Nourbakhsh, Ardeshir Talebi, Amir Abbas Nourbakhsh, Abbas Haghighat, Maziar Manshayi, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi, Razieh Karimi, Rahman Nazeri, Kenneth J.D. Mackenzie
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reparative Mineralized Tissue Characterization by Different Bioactive Direct Pulp-capping Agents
Mrunal Shinde, Varsha Pandit, Sarita Singh, Aniket Jadhav, Sarah Marium, Smita Patil
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Effects of barium titanate on the dielectric constant, radiopacity, and biological properties of tricalcium silicate-based bioceramics
Yoorina CHOI, Yun-Chan HWANG, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 55. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - A Breakthrough in the Era of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements: A Critical Review
Payal S Chaudhari, Manoj G Chandak, Akshay A Jaiswal, Nikhil P Mankar, Priyanka Paul
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef
-
2,972
View
-
38
Download
-
12
Web of Science
-
13
Crossref
-
Oral manifestation and root canal therapy of the patient with mucopolysaccharidosis
-
Ji-Hye Yoon, Hyo-Il Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e14. Published online April 4, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e14
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency in enzymes that participate in the degradation of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) such as heparin sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Left untreated, patients show progressive mental and physical deterioration due to deposition of GAGs in organs. Death often occurs due to cardiac or respiratory failure before patients reach their early twenties. MPS has several oral and dental manifestations. An enlarged head, short neck, and open mouth associated with a large tongue are major characteristics of MPS patients. Dental complications can be severe, including unerupted dentition, dentigerous cyst-like follicles, malocclusions, condylar defects, and gingival hyperplasia. A 21-year-old female patient with MPS was described in this article, with special emphasis on oral manifestations and dental treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pediatric Interventions in a Sanfilippo Syndrome Patient Under General Anesthesia: A Case Report
Ahmad Al Malak, Hassan Issawi, Mohammad Hassoun, Mohammad Al Halabi, Darko Macan
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioural disorders and sleep problems in Sanfilippo syndrome: overlaps with some other conditions and importance indications
Karolina Wiśniewska, Jakub Wolski, Paulina Anikiej-Wiczenbach, Magdalena Żabińska, Grzegorz Węgrzyn, Karolina Pierzynowska
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.2025; 34(6): 1795. CrossRef - Hurler syndrome: Oral and radiographic findings of a rare clinical case
W. Kabbassi, H. Hessissen, J. Hammouti
Medical Reports.2025; 14: 100325. CrossRef - Sanfilippo syndrome: consensus guidelines for clinical care
Nicole Muschol, Roberto Giugliani, Simon A. Jones, Joseph Muenzer, Nicholas J. C. Smith, Chester B. Whitley, Megan Donnell, Elise Drake, Kristina Elvidge, Lisa Melton, Cara O’Neill
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Manifestaciones bucales de pacientes con mucopolisacaridosis. Serie de casos
Andrea Verónica Ríos, Mariana Llorensi
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,712
View
-
7
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
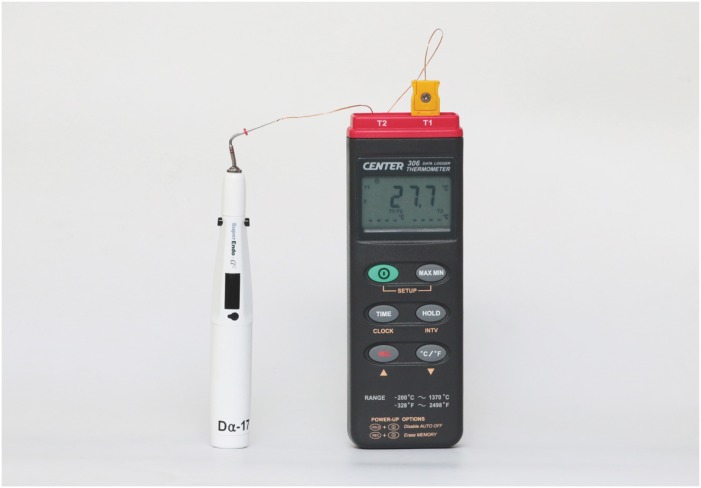
Plugger temperature of cordless heat carriers according to the time elapsed
-
Hoon-Sang Chang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e12. Published online February 7, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e12
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objective
The purpose of this study was to measure the temperature of the plugger tip of 3 cordless heat carriers set at 200°C. Materials and MethodsPluggers of the same taper (0.06, 0.08, 0.10) and similar tip sizes (sizes of 50 and 55) from 3 cordless heat carriers, namely SuperEndo-α2 (B & L Biotech), Friendo (DXM), and Dia-Pen (Diadent), were used and an electric heat carrier, System B (SybronEndo), was used as the control. The plugger tips were covered with customized copper sleeves, heated for 10 seconds, and the temperature was recorded with a computerized measurement system attached to a K-type thermometer at room temperature (n = 10). The data were analyzed with 2-way analysis of variance at a 5% level of significance. ResultsThe peak temperature of the plugger tips was significantly affected by the plugger taper and by the heat carrier brand (p < 0.05). The peak temperature of the plugger tips was between 177°C and 325°C. The temperature peaked at 207°C–231°C for the 0.06 taper pluggers, 195°C–313°C for the 0.08 taper pluggers, and 177°C–325°C for the 0.10 taper pluggers. Only 5 of the 12 plugger tips showed a temperature of 200°C ± 10°C. The time required to reach the highest temperature or 200°C ± 10°C was at least 4 seconds. ConclusionWhen using cordless heat carriers, clinicians should pay attention to the temperature setting and to the activation time needed to reach the intended temperature of the pluggers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Infrared thermographic evaluation of root surface during warm vertical compaction technique
Aysenur Oncu, Ecem Ozgur, Merve Sarı, Pelin Tufenkci, Berkan Celikten
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Temperature Variation with Three Continuous Wave Obturation Systems in Endodontics: An In Vitro Study
Jesús Mena-Álvarez, Maria Ruiz-Barrio, Norberto Quispe-López, Ana de Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6229. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Softening versus Ultrasonic Removal of Root-End Gutta-Percha on the Quality of Root-End Preparation for Endodontic Microsurgery
Zhiting Ling, Ziting Zheng, Yuting Zeng, Lifang Jiang, Yuan Wu, Buling Wu, Wenjuan Yan, Lavinia C. Ardelean
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
-
1,328
View
-
8
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Dental management of patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia
-
Bin-Na Lee, Hye-Yoon Jung, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):146-151. Published online January 6, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.146
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is a hereditary metabolic disease caused by the loss of phosphate through the renal tubules into the urine, and an associated decrease in serum calcium and potassium phosphate. Its dental features include spontaneous dental abscesses that occur in the absence of trauma or dental caries. The aim of this case report was to describe the dental problems of XLH patients and to evaluate limitations in their treatment. A 14 year old male and a 38 year old female with XLH were referred to the Department of Conservative Dentistry for endodontic treatment. The dental findings were periapical abscesses without obvious trauma or caries. Conservative endodontic treatment was performed in teeth with pulp necrosis and abscess. In case 1, the treated teeth showed improvements in bone healing, without clinical symptoms. However, in case 2, the implants and the treated tooth showed hypermobility, and the final restoration was therefore postponed. Early diagnosis, periodic examinations, and communication with the patient's pediatrician are important in the dental management of patients with XLH. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Oral Features in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets: An 8-Year Follow-Up Case Report
Soumaya Kachti, Manel Chalbi, Soumaya Boussaid, Faten Awled Brahim, Mohamed Ali Chemli
OBM Genetics.2025; 09(02): 1. CrossRef - Targeted Alkaline Phosphatase Therapy Enhances Alveolar Bone Healing in X‐Linked Hypophosphatemia in Mice
Aonjittra Phanrungsuwan, Bella Donnelly, José Luis Millán, Brian L. Foster
Journal of Periodontal Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental implant considerations in patients with systemic diseases: An updated comprehensive review
Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Sahar Talebi, Seied Omid Keyhan, Hamid Reza Fallahi, Mohammad Darvishi, Seyedeh Sara Aghili, Narges Tavahodi, Reza Abdollahi Namanloo, Artak Heboyan, Amirhossein Fathi
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 51(7): 1250. CrossRef - Inherited fibroblast growth factor 23 excess
Kripa Elizabeth Cherian, Thomas Vizhalil Paul
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 38(2): 101844. CrossRef - Dental abnormalities in rare genetic bone diseases: Literature review
Eiji Iwata, Shyam Kishor Sah, I‐Ping Chen, Ernst Reichenberger
Clinical Anatomy.2024; 37(3): 304. CrossRef - Implant Survival in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Case Report and Systematic Review of the Literature
Iris Alla, Felice Lorusso, Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, Francesco Inchingolo, Maristella Di Carmine, Antonio Scarano
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2401. CrossRef - X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: Orthodontic considerations and management. A case report
Clara Gibson, Suhaym Mubeen, Robert Evans
Journal of Orthodontics.2022; 49(2): 205. CrossRef - X-chromosomale Hypophosphatämie (XLH)/Phosphatdiabetes – Eine lebenslange Erkrankung
Adalbert Raimann, Roland Kocijan, Gabriel T. Mindler
Journal für Klinische Endokrinologie und Stoffwechsel.2022; 15(2): 63. CrossRef - Dental Manifestations and Oral Management of X-Linked Hypophosphatemia
Rena Okawa, Kazuhiko Nakano
Endocrines.2022; 3(4): 654. CrossRef - Prospective Analysis of Muscle Adiposity in Children With X-linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets vs Control Children
Virginie Nguyen-Khac, Aurore Bonnet-Lebrun, Agnès Linglart, Marine de Tienda, Jugurtha Berkenou, Inès Mannes, Catherine Adamsbaum, Philippe Wicart, Wafa Skalli
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental and periodontal features and management in XLH children and adults
Martin Biosse Duplan, Elvire Le Norcy, Frédéric Courson, Catherine Chaussain
International Journal of Bone Fragility.2021; 1(2): 74. CrossRef - Hiding in plain sight: Gene panel and genetic markers reveal 26-year undiagnosed tumor-induced osteomalacia of the rib concurrently misdiagnosed as X-linked hypophosphatemia
Juan M. Colazo, Joseph A. DeCorte, Erin A. Gillaspie, Andrew L. Folpe, Kathryn M. Dahir
Bone Reports.2021; 14: 100744. CrossRef - X-linked hypophosphatemia and burosumab: Practical clinical points from the French experience
Justine Bacchetta, Anya Rothenbuhler, Iva Gueorguieva, Peter Kamenicky, Jean-Pierre Salles, Karine Briot, Agnès Linglart
Joint Bone Spine.2021; 88(5): 105208. CrossRef - Presentation and non‐surgical endodontic treatment of two patients with X‐linked hypophosphatemia: a case report
H. Bradley, A. Dutta, R. Philpott
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1403. CrossRef - Periodontal status evaluation in adolescents with hereditary rickets-like diseases
E.V. Vislobokova, L.P. Kiselnikova, D.A. Lezhnev, S.S. Murtazaev, N.A. Sholokhova
Stomatologiya.2021; 100(6): 63. CrossRef - Diagnosis, treatment-monitoring and follow-up of children and adolescents with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH)
Anya Rothenbuhler, Dirk Schnabel, Wolfgang Högler, Agnès Linglart
Metabolism.2020; 103: 153892. CrossRef - Long-term outcomes for Asian patients with X-linked hypophosphataemia: rationale and design of the SUNFLOWER longitudinal, observational cohort study
Takuo Kubota, Seiji Fukumoto, Hae Il Cheong, Toshimi Michigami, Noriyuki Namba, Nobuaki Ito, Shin Tokunaga, Yoshimi Gibbs, Keiichi Ozono
BMJ Open.2020; 10(6): e036367. CrossRef - X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets Manifesting as Sclerotic Bone Disease and Enthesopathy
Hiya Boro, Shailendra Singh Naik, Charandeep Singh, Saurav Khatiwada, Rajesh Khadgawat
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - X-linked hypophosphatemia diagnosed after identification of dental symptoms
Kaoruko Wato, Rena Okawa, Saaya Matayoshi, Yuko Ogaya, Ryota Nomura, Kazuhiko Nakano
Pediatric Dental Journal.2020; 30(2): 115. CrossRef - X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: A New Era in Management
Kathryn Dahir, Mary Scott Roberts, Stan Krolczyk, Jill H Simmons
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prosthetic rehabilitation of a patient with X-linked hypophosphatemia using dental implants: a case report and review of the literature
Martin James, Reza Vahid Roudsari
International Journal of Implant Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral symptoms and oral health-related quality of life of individuals with x-linked hypophosphatemia
Marcel Hanisch, Lauren Bohner, Martin M. I. Sabandal, Johannes Kleinheinz, Susanne Jung
Head & Face Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of adult patients with X‐linked hypophosphatemia caused by PHEX gene mutations
Douglas Chesher, Michael Oddy, Ulpee Darbar, Parag Sayal, Adrian Casey, Aidan Ryan, Annalisa Sechi, Charlotte Simister, Aoife Waters, Yehani Wedatilake, Robin H. Lachmann, Elaine Murphy
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease.2018; 41(5): 865. CrossRef
-
2,940
View
-
16
Download
-
23
Crossref
-
Evaluation of reparative dentin formation of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine and BioAggregate using micro-CT and immunohistochemistry
-
Jia Kim, Young-Sang Song, Kyung-San Min, Sun-Hun Kim, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):29-36. Published online January 4, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.29
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of two new calcium silicate-based pulp-capping materials (Biodentine and BioAggregate) to induce healing in a rat pulp injury model and to compare them with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). Materials and MethodsEighteen rats were anesthetized, cavities were prepared and the pulp was capped with either of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine, or BioAggregate. The specimens were scanned using a high-resolution micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) system and were prepared and evaluated histologically and immunohistochemically using dentin sialoprotein (DSP). ResultsOn micro-CT analysis, the ProRoot MTA and Biodentine groups showed significantly thicker hard tissue formation (p < 0.05). On H&E staining, ProRoot MTA showed complete dentin bridge formation with normal pulpal histology. In the Biodentine and BioAggregate groups, a thick, homogeneous hard tissue barrier was observed. The ProRoot MTA specimens showed strong immunopositive reaction for DSP. ConclusionsOur results suggest that calcium silicate-based pulp-capping materials induce favorable effects on reparative processes during vital pulp therapy and that both Biodentine and BioAggregate could be considered as alternatives to ProRoot MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of microhardness, monomer conversion, and antibacterial properties of an experimental pulp-capping material containing collagen–hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and/or chlorhexidine
Hacer Balkaya, Sezer Demirbuğa, Fatih Duman, Ahmet Ceylan, Ömer Aydın
Odontology.2026; 114(1): 204. CrossRef - Clinical applications and classification of calcium silicate-based cements based on their history and evolution: a narrative review
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diode laser irradiation along with Biodentine on dental pulp stem cell proliferation and pluripotent gene expression
Ladan Alborzy, Sedighe Sadat Hashemikamangar, Mahshid Hodjat, Nasim Chiniforush, Behnaz Behniafar
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different treatment methods on apical closure and treatment success in immature permanent first molars with reversible pulpitis
Muhammed ALAGOZ, Sera SIMSEK DERELIOĞLU
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Novelties in pulp capping materials
Vani Grover, Namith Rai, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2025; 41(91): 3086. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of pulp response to alendronate and Biodentine as pulp capping agents: an animal study
Thangavel Boopathi, Sekar Manimaran, Joseline Charles Kerena, Mathew Sebeena, Kumaravadivel Karthick, Natesan Thangaraj Deepa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Clinical and Radiographic Success Rate of Bioceramic Premix vs Biosilicate-based Medicament as Indirect Pulp Treatment Materials in Primary Molars: A Double-blind Randomized Trial with a Follow-up of 12 Months
Aditi Mathur, Meenakshi Nankar, Sunnypriyatham Tirupathi, Payal Kothari, Rashmi Chauhan, Ashrita Suvarna
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(7): 748. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Evaluation of biocompatibility and bioactive potential of Well-Root PT by comparison with ProRoot MTA and Biodentine
Yong Kwon Chae, Ju Ri Ye, Ok Hyung Nam
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2218. CrossRef - Dentine Remineralisation Induced by “Bioactive” Materials through Mineral Deposition: An In Vitro Study
Marta Kunert, Ireneusz Piwonski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Francesco Inchingolo, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2024; 14(3): 274. CrossRef - Different pulp capping agents and their effect on pulp inflammatory response: A narrative review
Mustafa Tariq Mutar, Anas F Mahdee
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1295. CrossRef - Clinical application of calcium silicate-based bioceramics in endodontics
Xinyuan Wang, Yizhi Xiao, Wencheng Song, Lanxiang Ye, Chen Yang, Yuzhen Xing, Zhenglin Yuan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the pulp response following direct pulp capping with exogenous nitric oxide and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) a histologic study
Amirah Alnour, Ghassan Almohammad, Anas Abdo, Kinda Layous
Heliyon.2023; 9(7): e17458. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of dental pulp response to Biodentine, enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain), and mineral trioxide aggregate as direct pulp-capping agents – A randomized clinical trial
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ngairangbam Sanjeeta
Journal of Medical Society.2023; 37(3): 107. CrossRef - Effect of Intracoronal Sealing Biomaterials on the Histological Outcome of Endodontic Revitalisation in Immature Sheep Teeth—A Pilot Study
Elanagai Rathinam, Sivaprakash Rajasekharan, Heidi Declercq, Christian Vanhove, Peter De Coster, Luc Martens
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(4): 214. CrossRef - Restorative management of the posterior tooth that has undergone a pulpotomy
Nicholas N Longridge, James S Hyde, Fadi Jarad, Sondos Albadri
Dental Update.2023; 50(11): 932. CrossRef - Direct pulp capping procedures – Evidence and practice
Rafiqul Islam, Md Refat Readul Islam, Toru Tanaka, Mohammad Khursheed Alam, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Hidehiko Sano
Japanese Dental Science Review.2023; 59: 48. CrossRef - A novel analysis of the formation and resorption changes in dental hard tissue using longitudinal in vivo micro computed tomography
Yeon-Jee YOO, Joonil HWANG, So-Hyun PARK, Jaehong HWANG, Seungryong CHO, Sun-Young KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(5): 708. CrossRef - Evaluation of pH and Calcium Ion Diffusion from Intracanal MTA and Bioaggregate to Simulated External Resorption Cavities Through Dentinal Tubules
Umut AKSOY, Kaan POLATOĞLU, Feridun ŞAKLAR
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(3): 108. CrossRef - Pulpa Kuafajı ve Kuafaj Materyallerine Güncel Bir Bakış: Derleme
Dilek AKIN, Çiğdem ATALAYIN ÖZKAYA
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 617. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - Evaluation of shear bond strength of e-mineral trioxide aggregate and biodentine with glass ionomer cement
Hemalatha Hiremath, Aishwarya Singh Solanki, Shivangi Trivedi, Devansh Verma
Endodontology.2022; 34(2): 127. CrossRef - Multiple growth factors accommodated degradable submicron calcium sulfate hemihydrate/porous hydroxyapatite for dentin-pulp regeneration
Chih-Wen Chi, Bharathi Priya Lohanathan, Ching-Ching Wong, Che-Lun Chen, Hsun-Chang Lin, Yu-Chih Chiang
Biomaterials Advances.2022; 140: 213045. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF BLOOD CONTAMINATION ON SHEAR BOND STRENGTH OF CALCIUM SILICATE-BASED PULP CAPPING MATERIALS
Hasan Fatih YAVUZ, Güneş BULUT EYÜBOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 24(4): 371. CrossRef - Comparison of Four Dental Pulp-Capping Agents by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological Techniques—A Split-Mouth Design Ex Vivo Study
Jayanandan Muruganandhan, Govindarajan Sujatha, Saravanan Poorni, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Nezar Boreak, Ahmed Al-Kahtani, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hitesh Chohan, Shilpa Bhandi, A. Thirumal Raj, Alessio Zanza, Luca Testarelli, Shankargouda Patil
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3045. CrossRef - Effect of Naturally Occurring Biogenic Materials on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells (hDPSC): an In Vitro Study.
Prasanna T. Dahake, Vinod V. Panchal, Yogesh J. Kale, Mahesh V. Dadpe, Shrikant B. Kendre, Vijay M. Kumbar
Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine.2021; 7(4): 506. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Tailored 70S30C Bioactive glass induces severe inflammation as pulpotomy agent in primary teeth: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial
Yasmine Elhamouly, Rania M. El Backly, Dalia M. Talaat, Samia S. Omar, Maha El Tantawi, Karin M. L. Dowidar
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(6): 3775. CrossRef - Response of dental pulp capped with calcium-silicate based material, calcium hydroxide and adhesive resin in rabbit teeth
Cynthia Kassis, Pierre Khoury, Karim Corbani, Charbel Mansour, Louis Hardan, Ghassan Yared, Carole Chakar
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical expression of non-collagenous extracellular matrix molecules involved in tertiary dentinogenesis following direct pulp capping: a systematic review
C. Călin, M. Sajin, V.T. Moldovan, C. Coman, S.I. Stratul, A.C. Didilescu
Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger.2021; 235: 151674. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Indirect Pulp Treatment Materials for Primary Teeth: A Literature Review
Omar AES El Meligy, Afnan M Saber, Sumer M Alaki
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(6): 795. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Histological evaluation of the regenerative potential of a novel treated dentin matrix hydrogel in direct pulp capping
Ahmed A. Holiel, Elsayed M. Mahmoud, Wegdan M. Abdel-Fattah, Khadiga Y. Kawana
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(4): 2101. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential of tailored amorphous multiporous calcium silicate glass for pulp capping regenerative endodontics—A preliminary assessment
Jie Liu, Chao-An Chen, Xiaofei Zhu, Brian R. Morrow, Ukrit Thamma, Tia J. Kowal, Hassan M. Moawad, Matthias M. Falk, Himanshu Jain, George T.-J. Huang
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 109: 103655. CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of direct pulp capping using a novel injectable treated dentin matrix hydrogel: a 2-year randomized controlled clinical trial
Ahmed A. Holiel, Elsayed M. Mahmoud, Wegdan M. Abdel-Fattah
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4621. CrossRef - Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA in vivo
Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydraulic cements for various intra-coronal applications: Part 1
Stephen J Bonsor, Josette Camilleri
Dental Update.2021; 48(8): 653. CrossRef - In vivo Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Calcium Silicate-Based Bioceramics in Endodontics
Wencheng Song, Wei Sun, Lili Chen, Zhenglin Yuan
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of dentinogenesis inducer biomaterials: an in vivo study
Anabela B. Paula, Mafalda Laranjo, Carlos-Miguel Marto, Siri Paulo, Ana M. Abrantes, Bruno Fernandes, João Casalta-Lopes, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Bio-Inductive Materials in Direct and Indirect Pulp Capping—A Review Article
Marta Kunert, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Materials.2020; 13(5): 1204. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Release of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 from Human Tooth Dentin after Application of Either ProRoot MTA or Biodentine as a Coronal Barrier
Kunlada Wattanapakkavong, Tanida Srisuwan
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(6): 701. CrossRef - Effect of Leptin on Odontoblastic Differentiation and Angiogenesis: An In Vivo Study
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Ji-Hyun Jang, Jeong-Tae Koh, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(11): 1332. CrossRef - Análise da composição química dos cimentos MTA Angelus® branco, cinza e HP Repair® através de Microscopia Eletrônica de Varredura (MEV) acoplada a Espectrômetro de Energia Dispersiva (EDS)
Gabriela Duarte Rocha SARZEDA, Marcelo Santos BAHIA, Paulo Victor Teixeira DORIGUÊTTO, Karina Lopes DEVITO, Anamaria Pessoa Pereira LEITE
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct Pulp Capping: Which is the Most Effective Biomaterial? A Retrospective Clinical Study
Anabela Paula, Eunice Carrilho, Mafalda Laranjo, Ana M. Abrantes, João Casalta-Lopes, Maria Filomena Botelho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel M. Ferreira
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3382. CrossRef - Characterization of Odontoblast-like Cell Phenotype and Reparative Dentin Formation In Vivo: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 241. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effects of calcium silicate cements on dental pulp cells: A systematic review
Ramy Emara, Karim Elhennawy, Falk Schwendicke
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 77: 18. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - The Relationship of Surface Characteristics and Antimicrobial Performance of Pulp Capping Materials
Cher Farrugia, Christie Y.K. Lung, Pierre Schembri Wismayer, Maria Teresa Arias-Moliz, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1115. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - Influence of Biodentine® - A Dentine Substitute - On Collagen Type I Synthesis in Pulp Fibroblasts In Vitro
Frangis Nikfarjam, Kim Beyer, Anke König, Matthias Hofmann, Manuel Butting, Eva Valesky, Stefan Kippenberger, Roland Kaufmann, Detlef Heidemann, August Bernd, Nadja Nicole Zöller, Dimitrios Karamichos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167633. CrossRef - Effect of an Experimental Direct Pulp-capping Material on the Properties and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Fan Yu, Yan Dong, Yan-wei Yang, Ping-ting Lin, Hao-han Yu, Xiang Sun, Xue-fei Sun, Huan Zhou, Li Huang, Ji-hua Chen
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,416
View
-
37
Download
-
57
Crossref
-
Treatment of non-vital immature teeth with amoxicillin-containing triple antibiotic paste resulting in apexification
-
Hyon-Beom Park, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):322-327. Published online August 28, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.322
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
A recent treatment option for non-vital immature teeth in young patients is revascularization with triple antibiotic paste (TAP). However, tooth discoloration was reported with the use of conventional minocycline-containing TAP. In this case report, amoxicillin-containing TAP was used for revascularization of non-vital immature teeth to prevent tooth discoloration. At the 1 yr follow up, the teeth were asymptomatic on clinical examination and showed slight discoloration of the crown due to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) filling rather than amoxicillin-containing TAP. Radiographic examination revealed complete resolution of the periapical radiolucency, and closed apex with obvious periodontal ligament space. However, the root growth was limited, and the treatment outcome was more like apexification rather than revascularization. These results may be due to unstable blood clot formation which could not resist the condensation force of MTA filling, whether or not a collagen matrix was in place. These cases showed that although revascularization was not successful, apexification could be expected, resulting in the resolution of the periapical radiolucency and the closure of the apex. Therefore, it is worthwhile attempting revascularization of non-vital immature teeth in young patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
Aparna Palekar, Piyush Mantri, Minal Awinashe, Basawaraj Biradar, Mukund Singh
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing of Large Endodontic Lesions Using Long‐Term Application of a New Combination of Triple Antibiotics: A Series of Cases
Saeed Asgary, Ardavan Parhizkar, Maria Beatriz Duarte Gavião
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Antibiotic Pastes for Root Canal Disinfection
Sadhna Sharma, Urvashi Bhushan, Mridula Goswami, CP Baveja
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S1): S12. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics as the Future Treatment of Immature Permanent Teeth
Justyna Zbańska, Katarzyna Herman, Piotr Kuropka, Maciej Dobrzyński
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(13): 6211. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste in teeth with primary endodontic infection: A systematic review
Rhythm Bains, Aseem P. Tikku, Promila Verma, Pragya Pandey
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2021; 11: 2. CrossRef - Effectiveness of MTA apical plug in dens evaginatus with open apices
Khoa Van Pham, Thu Anh Tran
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair: A Literature Review
Ankit Rawat, Jyoti Nagpal, Shreeya Mehta, Divya Vyas, Abhishek Kumar, Fathima Amal
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 6. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric assessment of Tooth discoloration induced by various Antibiotic pastes
Ravi Gupta, Radhika Kewalramani, Dishant Patel
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2021; : 1979. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of calcium release of the apical plugs formed by mineral trioxide aggregate, Biodentine, and EndoSequence root repair material with and without 2% triple antibiotic powder: An in vitro study
PoojaNitin Mapara, ND Shashikiran, Sachin Gugawad, Namrata Gaonkar, Savita Hadakar, Swapnil Taur, Dhanshri Khade
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2020; 38(2): 132. CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic loaded apatitic nanocarriers on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm – An In vitro study
S. Nagarathinam, V. Sujatha, K. Madhumathi, S. Mahalaxmi, P.Pranav Vanajassun, T.S.Sampath Kumar
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2019; 51: 499. CrossRef - Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month ex vivo study
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Alternative to Avoid Tooth Discoloration after Regenerative Endodontic Procedure: A Systematic Review
Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Luiz Alexandre Chisini, Camila Guerner Springmann, Beatriz Dulcineia Mendes de Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Flávio Fernando Demarco, Mara Cristina Santos Felippe, Wilson Tadeu Felippe
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(5): 409. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment or Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apical Plug in Teeth with Necrotic Pulps and Open Apices: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mahmoud Torabinejad, Ali Nosrat, Prashant Verma, Oyoyo Udochukwu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1806. CrossRef - Revascularization in Immature Permanent Teeth with Necrotic Pulp and Apical Pathology: Case Series
López Carmen, Mendoza Asunción, Solano Beatriz, Yáñez-Vico Rosa, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,189
View
-
9
Download
-
16
Crossref
-
A review of the regenerative endodontic treatment procedure
-
Bin-Na Lee, Jong-Wook Moon, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):179-187. Published online March 16, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.179
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Traditionally, apexification has been used to treat immature permanent teeth that have lost pulp vitality. This technique promotes the formation of an apical barrier to close the open apex so that the filling materials can be confined to the root canal. Because tissue regeneration cannot be achieved with apexification, a new technique called regenerative endodontic treatment was presented recently to treat immature permanent teeth. Regenerative endodontic treatment is a treatment procedure designed to replace damaged pulp tissue with viable tissue which restores the normal function of the pulp-dentin structure. After regenerative endodontic treatment, continued root development and hard tissue deposition on the dentinal wall can occur under ideal circumstances. However, it is difficult to predict the result of regenerative endodontic treatment. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to summarize multiple factors effects on the result of regenerative endodontic treatment in order to achieve more predictable results. In this study, we investigated the features of regenerative endodontic treatment in comparison with those of other pulp treatment procedures and analyzed the factors that have an effect on regenerative endodontic treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures Using Autologous Platelet Concentrate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elnaz Mousavi, Navid Nasrabadi, Samira Jamali, Arian Haddadi
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial 3D printed gelatin scaffolds for root canal disinfection in regenerative endodontics procedures
Mateo Dallos Ortega, Jenny Aveyard, Raghda Magdy Abdelgawad, Reem El-Gendy, Alexander Ciupa, David Whetnall, Julia Behnsen, Robert J. Poole, Raechelle A. D'Sa
Biomaterials Science.2025; 13(14): 3795. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Therapies: Harnessing Stem Cells, Scaffolds, and Growth Factors
Rosana Farjaminejad, Samira Farjaminejad, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
Polymers.2025; 17(11): 1475. CrossRef - Effects of combining hyaluronic acid hydrogel with injectable platelet rich fibrin on apical papilla stem cells proliferation and differentiation
Azal H. Al-Masoody, Nasrin Asadi, Hadiseh Mohammadpour, Mahshid Hodjat, Tahereh Sadat Jafarzadeh Kashi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Experts consensus on management of tooth luxation and avulsion
Ruijie Huang, Chenchen Zhou, Ling Zhan, Yuan Liu, Xian Liu, Qin Du, Jun Wang, Wei Zhao, Guangtai Song, Li-an Wu, Beizhan Jiang, Yanhong Li, Hongmei Zhang, Jing Zou
International Journal of Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A review of tissue engineering in regenerative endodontic treatment
Eric Priyo Prasetyo, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Galih Sampoerno, Wilson Sukandar, Shafy Shariz Bin Sharizal, Nurfahira Paidal, Menza Fadiyan Amriel, Nathania Elita Gunawan, Ketut Suardita, Evelyn Tjendronegoro
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2024; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Innovative Paradigms and Established Strategies in Tooth Revitalization: A Review
Ahmad Shah Khan, Zahid Mehmood Khan, Palwasha Ishaque, Muhammad Zubair, Syeda Fatima Tu Zahra, Sana Ashfaq
Dental Update.2024; 51(8): 570. CrossRef - Explore the most recent developments and upcoming outlooks in the field of dental nanomaterials
Ali Alsuraifi, Zainab M. Sulaiman, Noor Alhuda R. Mohammed, Jassim Mohammed, Sarah Kareem Ali, Yousef Husam Abdualihamaid, Fatimah Husam, Abdullah Ayad
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Regenerative Endodontics: A Review of Current Techniques and Future Directions
Firas A Alothman, Lamia S Hakami, Ali Alnasser, Faris M AlGhamdi, Abdullah A Alamri, Basel M Almutairii
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Response to a Bioceramic Dental Sealer and Photobiomodulation: An In Vitro Study
Hamed A Alshawkani, Mohamed Mansy, Mahmoud Al Ankily, Mohamed Shamel
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(4): 313. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - GelMA‐based hydrogel biomaterial scaffold: A versatile platform for regenerative endodontics
Lei Huang, Xuan Chen, XiaoXia Yang, Yinchun Zhang, Xiaoling Qiu
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Dentinogenesis Imperfecta‐Induced Apical Periodontitis
Ying Liao, Ting Pan, Xianghui Xing, Sivakumar Nuvvula
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro and in vivo evaluation of iRoot BP Plus as a coronal sealing material for regenerative endodontic procedures
Ning Yang, Wenxiao Yang, Rou Shen, Shengcai Zhang, Tianchi Ma, Yao Liu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of pH and Ca+ ion release from MTA on interaction with platelet-rich fibrin and blood clot: an in vitro study
Sonia Khatri, Sylvia Mathew, Shruthi Nagaraja, Swaroop Hegde, Soumyadeep Ghosh, Kavimalar Ravichandran
F1000Research.2023; 12: 364. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Therapy and Pulp-Regenerative Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Jiawen Yong, Sabine Gröger, Zuping Wu, Sabine Ruf, Yuer Ye, Xiaoyan Chen
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 371. CrossRef - Efficacy of disinfection procedures performed prior to regenerative endodontic therapy: An integrative review
Ketillyn da Silva Magalhães, Ana Clara Kuerten Gil, Taynara Santos Goulart, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Daniela de Rossi Figueiredo, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(2): 418. CrossRef - Newer Prospects of Regenerative Endodontics: A Comprehensive and Updated Review of Literature
Mohammad Kamran Khan, Mahendra Kumar Jindal
Journal of the Scientific Society.2023; 50(3): 299. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of pH and Ca+ ion release from MTA on interaction with platelet-rich fibrin and blood clot: an in vitro study
Sonia Khatri, Sylvia Mathew, Shruthi Nagaraja, Swaroop Hegde, Soumyadeep Ghosh, Kavimalar Ravichandran
F1000Research.2023; 12: 364. CrossRef - Effects of CEM cement and emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla: a comparative in vitro study
Elham Khoshbin, Leila Ghasemi, Rezvan Najafi, Hamed Karkehabadi
Biotechnology Letters.2023; 45(1): 69. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Regenerative Potential of Blood Clot and Platelet-rich Fibrin in Young Permanent Teeth Based on the Revised American Academy of Endodontics Clinical Considerations for Regenerative Procedure: 2016
Saraswathi V Naik, Prabhakar Attiguppe, Aarathi J Prakash
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S149. CrossRef - Biomechanical characterization of a fibrinogen–blood hydrogel for human dental pulp regeneration
Sofia Silvia Piglionico, Bela Varga, Orsolya Pall, Olivier Romieu, Csilla Gergely, Frédéric Cuisinier, Bernard Levallois, Ivan Vladislavov Panayotov
Biomaterials Science.2023; 11(20): 6919. CrossRef - Intracellular bacterial eradication using a novel peptide in vitro
Wing Nok Isaac Ng, Shanthini Kalimuthu, Carmen Oi Kwan Law, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Terrence Chi Kong Lau, Yiu Yan Leung, Gary Shun Pan Cheung, Prasanna Neelakantan
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(11): 1360. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of Previously Treated Mature Permanent Tooth: A Case Report with 3-year Follow Up
Myung-Jin Lee
The Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2023; 47(6): 133. CrossRef - Clinical Outcome and Comparison of Regenerative and Apexification Intervention in Young Immature Necrotic Teeth—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Pratima Panda, Lora Mishra, Shashirekha Govind, Saurav Panda, Barbara Lapinska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3909. CrossRef - Evaluation of Attitude and Knowledge of Endodontic, Pedodontic and SBARD Residents in Saudi Arabia toward Regenerative Endodontics—A National Survey
Ali A. Assiry, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Roshan Noor Mohamed, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohammed Zameer
Medicina.2022; 58(4): 545. CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Antimicrobials on Viability and Differentiation of Stem Cells From the Apical Papilla: An In Vitro Study
Gavin Raddall, Isabel Mello, Brendan M. Leung
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(7): 880. CrossRef - Awareness and Acceptance of Vital Pulp Therapy and Regenerative Endodontic Procedures among Dental Professionals in India: A Web-based Survey
Saloni Rathi, Priya Chauhan, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Rolly Agarwal, Simar Kaur Manocha, Mrinali Chaddha
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 10. CrossRef - Exosomes as Biochemistry Tools for Stem Cell Differentiation: A Novel Cell-Based Treatment for Diseases
Saeed Azandeh, Darioush Bijan Nejad, Samaneh Karimi, Fereshtesadat Fakhredini
Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of biodentine coated with emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla
Hamed Karkehabadi, Erfan Ahmadyani, Rezvan Najafi, Elham Khoshbin
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 3685. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Laser‐Assisted Bleaching of the Teeth Discolored due to Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Paste: A Suitable Medicament for Intracanal Disinfection
Krutika Malu, Monika Khubchandani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Microhardness and Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentin with Two Combinations of TAP and MTAP: An In Vitro Study
P Niharika, Saigeeta Kondamadugu, Nagireddy Venugopal Reddy, Muthumula Daneswari, Annie P Chris, Nikhila V Reddy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(S2): S151. CrossRef - Comparing Antibiotic Pastes with Electrospun Nanofibers as Modern Drug Delivery Systems for Regenerative Endodontics
Nura Brimo, Dilek Çökeliler Serdaroğlu, Busra Uysal
Current Drug Delivery.2022; 19(9): 904. CrossRef - The Advances of Blood Clots Used as Biomaterials in Regenerative Medicine
Eliza VanZweden, Rachael Tolsma, Victor Hung, Peter Awad, Robert Sawyer, Yong Li
Regenerative Medicine.2022; 17(12): 957. CrossRef - Microstructure and color stability of calcium silicate-based dental materials exposed to blood or platelet-rich fibrin
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Ibrahim Abu Tahun, Shima Saber Tahan, Fatemeh Mohandes, Mohammad H. Nekoofar, Paul M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1193. CrossRef - Results of “proroot mta” application in treatment of chronic periodontitis in teeth with incomplete root formation
N.M. Korneeva, E.A. Novikova, D.S. Popova, K.S. Rabadanova, L.Ya Rzaeva
Stomatology for All / International Dental review.2022; (2(99)): 10. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Combined with Electrolyzed Superoxidized Solution at Neutral pH on Enterococcus faecalis Growth
Héctor Armando Jimenez-Gonzalez, María Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Sergio Eduardo Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Víctor Hugo Urrutia-Baca, Myriam Angélica De La Garza-Ramos, Juan Manuel Solis-Soto, Ricardo Gomez-Flores, Patricia Tamez-Guerra, Yeliz Guven
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Unpredictable Outcomes of a Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Zahra Mohammadi, Hadi Assadian, Behnam Bolhari, Mohammadreza Sharifian, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Nazanin Chitsaz, Andrea Scribante
Case Reports in Dentistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Revascularization of nonvital immature incisor with asymptomatic apical periodontitis
Ema Mulyawati, Pribadi Santosa, Tunjung Nugraheni
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(3): 134. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of calcium hydroxide apexification and regenerative endodontic procedure for root dentine growth stimulation in immature incisors with pulp necrosis
M.S. Rakhmanova, M.V. Korolenkova
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(6): 55. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of a Novel Antibiotic‐Eluting Injectable Platelet‐Rich Fibrin Scaffold against a Dual‐Species Biofilm in an Infected Immature Root Canal Model
Azade Rafiee, Mahtab Memarpour, Yasaman Najibi, Bahman Khalvati, Sedigheh Kianpour, Mohammad Hossein Morowvat, Sung-Hwan Choi
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exosomes Derived from Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla Promote Dentine-Pulp Complex Regeneration by Inducing Specific Dentinogenesis
Xueying Zhuang, Lingli Ji, Huan Jiang, Yao Liu, Xuemei Liu, Jing Bi, Weidong Zhao, Zhenjiang Ding, Xu Chen
Stem Cells International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Injectable Biomaterials for Dental Tissue Regeneration
Håvard Jostein Haugen, Poulami Basu, Mousumi Sukul, João F Mano, Janne Elin Reseland
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(10): 3442. CrossRef - Viability and Stimulation of Human Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla (hSCAPs) Induced by Silicate-Based Materials for Their Potential Use in Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review
José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, Alicia Almudéver, Julia Guerrero-Gironés, Carmen Llena
Materials.2020; 13(4): 974. CrossRef - An Innovative Drug Delivery System Loaded with a Modified Combination of Triple Antibiotics for Use in Endodontic Applications
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Fahimeh Tabatabaei, Saeed Asgary
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Defining Endodontic Residents' Clinical Experiences: A National Survey
Jonathan D. Blacher, Kamran E. Safavi, Robert H. Aseltine, Blythe M. Kaufman
Journal of Dental Education.2019; 83(5): 504. CrossRef - Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month ex vivo study
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Study between Revitalization of Necrotic Immature Permanent Anterior Teeth with and without Platelet Rich Fibrin: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Rasha Adel Ragab, Amr Ezzat Abd El Lattif, Norhan Abd El Wahab El Dokky
Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2019; 43(2): 78. CrossRef - Biomaterials and Scaffold Design Strategies for Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
Gavin Raddall, Isabel Mello, Brendan M. Leung
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Iloprost Induces Dental Pulp Angiogenesis in a Growth Factor–free 3-Dimensional Organ Culture System
Sonntana Seang, Prasit Pavasant, Chalida N. Limjeerajarus
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 759. CrossRef - Ratio and Rate of Induced Root Growth in Necrotic Immature Teeth
Eun Jung Sang, Ji-Soo Song, Teo Jeon Shin, Young-Jae Kim, Jung-Wook Kim, Ki-Taeg Jang, Sang-Hoon Lee, Hong-Keun Hyun
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(2): 225. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Traumatic avulsion and delayed replantation of maxillary incisors in an eleven-year-old child
Gokcen Deniz Bayrak
Edorium Journal of Dentistry.2018; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Diameter on the Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Teeth with Pulp Necrosis: A Review
Yanjun Fang, Xinhuan Wang, Jingjing Zhu, Chaonan Su, Ying Yang, Liuyan Meng
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 414. CrossRef - Assessment of Regaining Pulp Sensibility in Mature Necrotic Teeth Using a Modified Revascularization Technique with Platelet-rich Fibrin: A Clinical Study
Mohamed Nageh, Geraldine M. Ahmed, Alaa A. El-Baz
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1526. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics
Kristina Feigin, Bonnie Shope
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2017; 34(3): 161. CrossRef - Intentional Replantation of an Avulsed Immature Permanent Incisor: A Case Report
Claudio Maniglia-Ferreira, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Marcelo de Morais Vitoriano
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1383. CrossRef - Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 12. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef - Effects of a Bioactive Scaffold Containing a Sustained Transforming Growth Factor-β1–releasing Nanoparticle System on the Migration and Differentiation of Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla
Craig Bellamy, Suja Shrestha, Calvin Torneck, Anil Kishen
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(9): 1385. CrossRef - Effects of Novel 3-dimensional Antibiotic-containing Electrospun Scaffolds on Dentin Discoloration
Margaret Louise A. Porter, Eliseu A. Münchow, Maria T.P. Albuquerque, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Anderson T. Hara, Marco C. Bottino
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(1): 106. CrossRef
-
7,145
View
-
117
Download
-
63
Crossref
-
Changes in SIRT gene expression during odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp cells
-
Young-Eun Jang, Su-Hee Go, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):223-228. Published online July 15, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.223
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of 7 different sirtuin genes (SIRT1-SIRT7) in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs), and to determine the role of SIRTs in the odontoblastic differentiation potential of HDPCs. Materials and MethodsHDPCs were isolated from freshly extracted third molar teeth of healthy patients and cultulred in odontoblastic differentiation inducing media. Osteocalcin (OCN) and dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) expression was analyzed to evaluate the odontoblastic differentiation of HDPCs by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), while alizarin red staining was used for the mineralization assay. To investigate the expression of SIRTs during odontoblastic differentiation of HDPCs, real time PCR was also performed with RT-PCR. ResultsDuring the culture of HDPCs in the differentiation inducing media, OCN, and DSPP mRNA expressions were increased. Mineralized nodule formation was also increased in the 14 days culture. All seven SIRT genes were expressed during the odontogenic induction period. SIRT4 expression was increased in a time-dependent manner. ConclusionsOur study identified the expression of seven different SIRT genes in HDPCs, and revealed that SIRT4 could exert an influence on the odontoblast differentiation process. Further studies are needed to determine the effects of other SIRTs on the odontogenic potential of HDPCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Biodegradable Zn‐5Dy Alloy with Enhanced Osteo/Angio‐Genic Activity and Osteointegration Effect via Regulation of SIRT4‐Dependent Mitochondrial Function
Yue Han, Xian Tong, Runqi Zhou, Yilin Wang, Yuge Chen, Liang Chen, Xinhua Hong, Linmei Wu, Zhiqiang Lin, Yichi Zhang, Xuejia Zhang, Chaoming Hu, Bin Li, Yifan Ping, Zelin Cao, Zhou Ye, Zhongchen Song, Yuncang Li, Cuie Wen, Yongsheng Zhou, Jixing Lin, Shen
Advanced Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Histone Acetylation Modification in Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Odontogenesis
Haoling Chen, Zijing Huang, Chuxiao Chen
Cellular Reprogramming.2023; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Metabolic Remodeling Impacts the Epigenetic Landscape of Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Haiyun Luo, Yachuan Zhou, Wenjing Liu, Jun Wang
Stem Cells International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - SIRT4 regulates rat dental papilla cell differentiation by promoting mitochondrial functions
Haoling Chen, Jun Kang, Fuping Zhang, Tong Yan, Wenguo Fan, Hongwen He, Fang Huang
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology.2021; 134: 105962. CrossRef - Sirtuins as Interesting Players in the Course of HIV Infection and Comorbidities
Karolina Jurkowska, Beata Szymańska, Brygida Knysz, Amadeusz Kuźniarski, Agnieszka Piwowar
Cells.2021; 10(10): 2739. CrossRef - Robust expression of SIRT6 inhibits pulpitis via activation of the TRPV1 channel
Jia Hu, Weiran Chen, Zailing Qiu, Hongbing Lv
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2020; 38(5): 676. CrossRef - Downregulation of microRNA‐143‐5p is required for the promotion of odontoblasts differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through the activation of the mitogen‐activated protein kinases 14‐dependent p38 mitogen‐activated protein kinases signaling pa
Bao‐Liang Wang, Zhi Wang, Xi Nan, Qing‐Cai Zhang, Wei Liu
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(4): 4840. CrossRef - A potential role for the silent information regulator 2 homologue 1 (SIRT1) in periapical periodontitis
H. Kudo, O. Takeichi, K. Hatori, K. Makino, K. Himi, B. Ogiso
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(7): 747. CrossRef - Overexpressed Sirt1 in MSCs Promotes Dentin Formation in Bmi1-Deficient Mice
H. Wang, C. Lv, Y. Gu, Q. Li, L. Xie, H. Zhang, D. Miao, W. Sun
Journal of Dental Research.2018; 97(12): 1365. CrossRef - Expression of silent information regulator 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1) in periapical granulomas
Hiroshi Kudo, Osamu Takeichi, Kosuke Makino, Keisuke Hatori, Bunnai Ogiso
Journal of Oral Science.2018; 60(3): 411. CrossRef - TET1 knockdown inhibits the odontogenic differentiation potential of human dental pulp cells
Li-Jia Rao, Bai-Cheng Yi, Qi-Meng Li, Qiong Xu
International Journal of Oral Science.2016; 8(2): 110. CrossRef
-
1,762
View
-
6
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
-
Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):89-94. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.89
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the cytotoxicity, setting time and compressive strength of MTA and two novel tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials, Bioaggregate (BA) and Biodentine (BD). Materials and MethodsCytotoxicity was evaluated by using a 2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-5-((phenylamino)carbonyl)-2H-tetrazolium hydroxide (XTT) assay. Measurements of 9 heavy metals (arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, manganese, nickel, and zinc) were performed by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) of leachates obtained by soaking the materials in distilled water. Setting time and compressive strength tests were performed following ISO requirements. ResultsBA had comparable cell viability to MTA, whereas the cell viability of BD was significantly lower than that of MTA. The ICP-MS analysis revealed that BD released significantly higher amount of 5 heavy metals (arsenic, copper, iron, manganese, and zinc) than MTA and BA. The setting time of BD was significantly shorter than that of MTA and BA, and the compressive strength of BA was significantly lower than that of MTA and BD. ConclusionsBA and BD were biocompatible, and they did not show any cytotoxic effects on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. BA showed comparable cytotoxicity to MTA but inferior physical properties. BD had somewhat higher cytotoxicity but superior physical properties than MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the physical properties of bromelain-modified biodentine for direct pulp capping
Paridhi Agrawal, Manoj Chandak, Aditya Patel, Jay Bhopatkar
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
H.K. Abd El-Hamid, A.M. Fayad, R.L. Elwan
Ceramics International.2024; 50(14): 25322. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Strength of a cement-based dental material: Early age testing and first micromechanical modeling at mature age
Petr Dohnalík, Christian Hellmich, Gilles Richard, Bernhard L. A. Pichler
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Biomimetic Approaches in Clinical Endodontics
Naresh Kumar, Nazrah Maher, Faiza Amin, Hani Ghabbani, Muhammad Sohail Zafar, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Ricardo E. Oñate-Sánchez
Biomimetics.2022; 7(4): 229. CrossRef - Effect of different manipulations on the physical, chemical and microstructural characteristics of Biodentine
Mariana Domingos Pires, Joana Cordeiro, Isabel Vasconcelos, Mariana Alves, Sérgio André Quaresma, António Ginjeira, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2021; 37(7): e399. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Material Pulp Cells and Tissue Interactions
Nastaran Meschi, Biraj Patel, Nikita B. Ruparel
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): S150. CrossRef - Biological Effects of Tricalcium Silicate Nanoparticle-Containing Cement on Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth
Yoonsun Jung, Ji-Young Yoon, Kapil Dev Patel, Lan Ma, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jongbin Kim, Jung-Hwan Lee, Jisun Shin
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1373. CrossRef - Physicochemical, mechanical and cytotoxicity evaluation of chitosan-based accelerated portland cement
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2020; 9(5): 11574. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cements: osteogenic and angiogenic responses of human bone marrow stem cells
Mohamed R. W. Ali, Manal Mustafa, Asgeir Bårdsen, Athanasia Bletsa
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 127(3): 261. CrossRef - Bioactive tri/dicalcium silicate cements for treatment of pulpal and periapical tissues
Carolyn M. Primus, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2019; 96: 35. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on the setting times and tensile strengths of calcium silicate‐based cements
Ozgur Uyanik, Emre Nagas, Selen Kucukkaya Eren, Zafer C. Cehreli, Pekka K. Vallittu, Lippo V.J. Lassila
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 241. CrossRef - Effects of four novel root-end filling materials on the viability of periodontal ligament fibroblasts
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Pembegul Uyar Arpaci, Ayce Unverdi Eldeniz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Root perforations: a review of diagnosis, prognosis and materials
Carlos Estrela, Daniel de Almeida Decurcio, Giampiero Rossi-Fedele, Julio Almeida Silva, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Álvaro Henrique Borges
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of chelating agent and acids on Biodentine
V Ballal, JN Marques, CN Campos, CO Lima, RA Simão, M Prado
Australian Dental Journal.2018; 63(2): 170. CrossRef - Biological interactions of a calcium silicate based cement (Biodentine™) with Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous teeth
Eirini Athanasiadou, Maria Paschalidou, Anna Theocharidou, Nikolaos Kontoudakis, Konstantinos Arapostathis, Athina Bakopoulou
Dental Materials.2018; 34(12): 1797. CrossRef - Retention of BioAggregate and MTA as coronal plugs after intracanal medication for regenerative endodontic procedures: an ex vivo study
Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin, Shaimaa Ismail Gawdat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Dens Invaginatus Type II Associated with Immature Apex and Large Periradicular Lesion Using Platelet-rich Fibrin and Biodentine
Shruti Goel, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1750. CrossRef - Brain aluminium accumulation and oxidative stress in the presence of calcium silicate dental cements
K Demirkaya, B Can Demirdöğen, Z Öncel Torun, O Erdem, E Çırak, YM Tunca
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2017; 36(10): 1071. CrossRef - Calcium silicate‐based cements: composition, properties, and clinical applications
Alaa E. Dawood, Peter Parashos, Rebecca H.K. Wong, Eric C. Reynolds, David J. Manton
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological response of commercially available different tricalcium silicate‐based cements and pozzolan cement
Serhat Köseoğlu, Tuğba Pekbağr?yan?k, Ebru Kucukyilmaz, Mehmet Sağlam, Sukru Enhos, Ayşe Akgün
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(9): 994. CrossRef - Modified tricalcium silicate cement formulations with added zirconium oxide
Xin Li, Kumiko Yoshihara, Jan De Munck, Stevan Cokic, Pong Pongprueksa, Eveline Putzeys, Mariano Pedano, Zhi Chen, Kirsten Van Landuyt, Bart Van Meerbeek
Clinical Oral Investigations.2017; 21(3): 895. CrossRef - Cytotoxic effects of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium enrichedmixture cement, Biodentine and octacalcium pohosphate onhuman gingival fibroblasts
Eshagh A. Saberi, Narges Farhadmollashahi, Faroogh Ghotbi, Hamed Karkeabadi, Roholla Havaei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2016; 10(2): 75. CrossRef - The effect of working time on the displacement of Biodentine™ beneath prefabricated stainless steel crown: a laboratory study
Alaa E. Dawood, David J. Manton, Peter Parashos, Rebecca H. K. Wong
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2016; 7(4): 391. CrossRef - Evaluation of reparative dentin formation of ProRoot MTA, Biodentine and BioAggregate using micro-CT and immunohistochemistry
Jia Kim, Young-Sang Song, Kyung-San Min, Sun-Hun Kim, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 29. CrossRef
-
1,925
View
-
6
Download
-
30
Crossref
-
Autogenous tooth transplantation for replacing a lost tooth: case reports
-
Ji-Youn Kang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Bin-Na Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):48-51. Published online February 26, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.48
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The autogenous tooth transplantation is an alternative treatment replacing a missing tooth when a suitable donor tooth is available. It is also a successful treatment option to save significant amount of time and cost comparing implants or conventional prosthetics. These cases, which required single tooth extraction due to deep caries and severe periodontal disease, could have good results by transplanting non-functional but sound donor tooth to the extraction site. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Autogenous tooth transplantation of canines: a prospective clinical study on the influence of extraoral storage time-guided adjunctive antibiotic therapy and patient-related risk factors affecting success, survival, and prognosis after two years of follow
Sebastian Meinzer, Dirk Nolte, Karin Christine Huth
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Autogenous Tooth Transplantation of Canines—A Prospective Clinical Study on the Influence of Adjunctive Antibiosis and Patient-Related Risk Factors During Initial Healing
Sebastian Meinzer, Dirk Nolte, Karin Christine Huth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(3): 821. CrossRef - 13-year follow-up of autotransplantation using an immature third molar: a case report
Hojin Moon
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 72. CrossRef - Template-Guided Autogenous Tooth Transplantation Using a CAD/CAM Dental Replica in a Complex Anatomical Scenario: A Case Report
Michael Alfertshofer, Florian Gebhart, Dirk Nolte
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 281. CrossRef - Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Dental autotransplantation: case report and follow-up
Kassandra García Covarrubias, Erika Etcheverry Doger, Jennifer Antón Sarabia, Mario Alberto Lagunes López
Revista Odontología Pediátrica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and evaluation of the effectiveness of autotransplantation of teeth
Filipp V. Dulov, Roman B. Gurkin, Ekaterina S. Derbentsova, Ulia V. Budanova
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2023; 27(3): 193. CrossRef - Pre- and peri-operative factors influence autogenous tooth transplantation healing in insufficient bone sites
Thanapon Suwanapong, Aurasa Waikakul, Kiatanant Boonsiriseth, Nisarat Ruangsawasdi
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Third molar autotransplantation: An alternative to dental implant - 9 years follow up of a case
Sanjay Kumar, Mansi Jain, Suma Sogi, Prinka Shahi, Saru Dhir, Swati Rana
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2020; 10(2): 529. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef - Post-Odontoma autotransplantation of an impacted tooth: A case report
Waikhom Robindro Singh, Kirankumar Aheibam, Anthopia Nameirakpam
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2015; 5(2): 120. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of a Mandibular Third Molar: A Case Report with 5 Years of Follow-up
Mauro Henrique Chagas e Silva, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Maria das Gracas Afonso Miranda Chaves, Celso Neiva Campos
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 289. CrossRef
-
2,074
View
-
6
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
-
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):130-135. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.130
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to enhance curing light penetration through resin inlays by modifying the thicknesses of the dentin, enamel, and translucent layers. Materials and MethodsTo investigate the layer dominantly affecting the power density of light curing units, resin wafers of each layer with 0.5 mm thickness were prepared and power density through resin wafers was measured with a dental radiometer (Cure Rite, Kerr). The dentin layer, which had the dominant effect on power density reduction, was decreased in thickness from 0.5 to 0.1 mm while thickness of the enamel layer was kept unchanged at 0.5 mm and thickness of the translucent layer was increased from 0.5 to 0.9 mm and vice versa, in order to maintain the total thickness of 1.5 mm of the resin inlay. Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays was measured. ResultsPower density measured through 0.5 mm resin wafers decreased more significantly with the dentin layer than with the enamel and translucent layers (p < 0.05). Power density through 1.5 mm resin inlays increased when the dentin layer thickness was reduced and the enamel or translucent layer thickness was increased. The highest power density was recorded with dentin layer thickness of 0.1 mm and increased translucent layer thickness in all light curing units. ConclusionsTo enhance the power density through resin inlays, reducing the dentin layer thickness and increasing the translucent layer thickness would be recommendable when fabricating resin inlays.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of layering technique on the shade of resin overlays and the microhardness of dual cure resin cement
Hoon-Sang Chang, Sung-Ok Hong
Brazilian Oral Research.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Hardness and Shear Bond Strength of Dual-cure Resin Cement Light Cured Through Resin Overlays With Different Dentin-layer Thicknesses
H-S Chang, J-W Kim
Operative Dentistry.2014; 39(4): 398. CrossRef - Light curing of dual cure resin cement
Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 266. CrossRef
-
1,347
View
-
1
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Colorimetric comparison of single layered dental composite with double layered dental composite
-
Young-Sang Song, Ja-Hyun Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):84-89. Published online May 18, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.84
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study analyzed the difference in color caused by different thickness in enamel layer of composite resins when applied with single and layering placement technique, and evaluated if the results agreed with the shade guide from the manufacturers to verify reliability of the color matching process of the manufacturers.
Materials and Methods
For single composite resin samples, 6 mm diameter and 4 mm thickness cylindrical samples were fabricated using Ceram-X mono (DENTSPLY DeTrey) and CIE L*a*b* values were measured with spectrophotometer. Same process was done for layering composite resin samples, making 3 dentinal shade samples, 4 mm thickness, for each shade using Ceram-X duo (DENTSPLY DeTrey) and enamel shade resins were layered in 2 mm thickness and CIE L*a*b* values were measured. These samples were ground to 0.2 mm thickness each time, and CIE L*a*b* values were measured to 1 mm thickness of enamel shade resin.
Results
Color difference (ΔE*) between single and layering composite resin was 1.37 minimum and 10.53 maximum when layering thicknesses were between 1 mm and 2 mm and 6 out of 10 same shade groups suggested by manufacturer showed remarkable color difference at any thickness (ΔE* > 3.3).
Conclusion
When using Ceram-X mono and duo for composite resin restoration, following the manufacturer's instructions for choosing the shade is not appropriate, and more accurate information for Ceram-X duo is needed on the variation and expression of the shades depending on the thickness of the enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Improvement of mechanical strength and water repellency of Hanji (traditional Korean paper) through acetylation in supercritical CO2
Seungmok Shin, Hwi-Sung Lee, Hee Suk Woo, Mulugeta G. Aregay, Tae Jun Yoon, Youn-Woo Lee
The Journal of Supercritical Fluids.2022; 190: 105735. CrossRef - Color Change in Tooth Induced by Various Calcium Silicate-Based Pulp-Capping Materials
Jiyoon Jeon, Namki Choi, Seonmi Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(3): 280. CrossRef
-
1,105
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
-
Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):490-497. Published online November 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.490
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study examined the effect of the uncured dentin adhesives on the bond interface between the resin inlay and dentin.
Materials and Methods
Dentin surface was exposed in 24 extracted human molars and the teeth were assigned to indirect and direct resin restoration group. For indirect resin groups, exposed dentin surfaces were temporized with provisional resin. The provisional restoration was removed after 1 wk and the teeth were divided further into 4 groups which used dentin adhesives (OptiBond FL, Kerr; One-Step, Bisco) with or without light-curing, respectively (Group OB-C, OB-NC, OS-C and OS-NC). Pre-fabricated resin blocks were cemented on the entire surfaces with resin cement. For the direct resin restoration groups, the dentin surfaces were treated with dentin adhesives (Group OB-D and OS-D), followed by restoring composite resin. After 24 hr, the teeth were assigned to microtensile bond strength (µTBS) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), respectively.
Results
The indirect resin restoration groups showed a lower µTBS than the direct resin restoration groups. The µTBS values of the light cured dentin adhesive groups were higher than those of the uncured dentin adhesive groups (p < 0.05). CLSM analysis of the light cured dentin adhesive groups revealed definite and homogenous hybrid layers. However, the uncured dentin adhesive groups showed uncertain or even no hybrid layer.
Conclusions
Light-curing of the dentin adhesive prior to the application of the cementing material in luting a resin inlay to dentin resulted in definite, homogenous hybrid layer formation, which may improve the bond strength.
-
Microtensile bond strength of resin inlay bonded to dentin treated with various temporary filling materials
-
Tae-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Young-Jung Choi, So-Young Yang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):419-424. Published online September 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.419
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study was aimed to determine the effects of temporary sealing materials on microtensile bond strength between resin-coated dentin and resin inlay and to compare the bonding effectiveness of delayed dentin sealing and that of immediate dentin sealing.
Materials and Methods
The teeth were divided into 4 groups: group 1, specimens were prepared using delayed dentin sealing after temporary sealing with zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE); group 2, specimens were prepared using immediate dentin sealing and ZOE sealing; group 3, specimens were prepared using immediate dentin sealing and Dycal (Dentsply) sealing; group 4, specimens were prepared using immediately sealed, and then temporarily sealed with a resin-based temporary sealing material.
After removing the temporary sealing material, we applied resin adhesive and light-cured. Then the resin inlays were applied and bonded to the cavity with a resin-based cement. The microtensile bond strength of the sectioned specimens were measured with a micro-tensile tester (Bisco Inc.). Significance between the specimen groups were tested by means of one-way ANOVA and multiple Duncan's test.
Results
Group 1 showed the lowest bond strength, and group 4 showed the highest bond strength (p < 0.01). When temporary sealing was performed with ZOE, immediate dentin sealing showed a higher bonding strength than delayed dentin sealing (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
Based on these results, immediate dentin sealing is more recommended than delayed dentin sealing in bonding a resin inlay to dentin. Also, resin-based temporary sealing materials have shown the best result.
-
The effects of short-term application of calcium hydroxide on dentin fracture strength
-
Eun-Jung Shin, Yeong-Joon Park, Bin-Na Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):425-430. Published online September 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.425
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This in vitro study investigated whether short-term application of calcium hydroxide in the root canal system for 1 and 4 wk affects the fracture strength of human permanent teeth.
Materials and Methods
Thirty two mature human single rooted mandibular premolars in similar size and dentin thickness without decay or restorations were hand and rotary instrumented and 16 teeth vertically packed with calcium hydroxide paste and sealed coronally with caviton to imitate the endodontic procedure and the other 16 teeth was left empty as a control group. The apicies of all the samples were sealed with resin, submerged in normal saline and put in a storage box at 37℃ to mimic the oral environment. After 1 and 4 wk, 8 samples out of 16 samples from each group were removed from the storage box and fracture strength test was performed. The maximum load required to fracture the samples was recorded and data were analysed statistically by the two way ANOVA test at 5% significance level.
Results
The mean fracture strengths of two groups after 1 wk and 4 wk were similar. The intracanal placement of calcium hydroxide weakened the fracture strength of teeth by 8.2% after 4 wk: an average of 39.23 MPa for no treatment group and 36.01 MPa for CH group. However there was no statistically significant difference between experimental groups and between time intervals.
Conclusions
These results suggest that short term calcium hydroxide application is available during endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of niobium pentoxide incorporated calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament on fracture resistance of root canal dentin
Nadimpalli Teja Varma, Venkatappan Sujatha, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(12): 1211. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide as an Intracanal Medication on Dentine Fracture Resistance: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Chayanit Sunlakawit, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Natchalee Srimaneekarn, Sittichoke Osiri
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(12): 1714. CrossRef
-
3,382
View
-
25
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The evaluation of color and color difference according to the layering placement of Incisal shade composites on the body composites of the indirect resin restoration
-
Su-Jung Park, Han-Young Lee, Myong-Yun Nah, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):37-49. Published online January 14, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
Objectives:
The aim of this study was to evaluate the surface color of indirect resin restoration according to the layering placement of different shade of incisal composite.
Materials and Methods:
In this study, CIE L*a*b* value of 16 Body composite of Tescera ATL (Bisco, Schaumburg IL, USA) was measured by spectrophotometer (NF999, Nippon Denshuku, Japan), and compared to CIE L*a*b* value of Vitapan shade guide. Nine shade Incisal composite of Tescera ATL were buildup to 1 mm thickness on Body composites inlay block, and CIE L*a*b* value was measured. Incisal composite was ground to 0.5 mm thickness and CIE L*a*b* value was re-measured. Color difference between Body composite and Incisal composites layered on Body composite was calculated as a function of thickness.
Results:
Color difference between corresponding shade of Tescera Body composite and Vitapan shade guide was from 6.88 to 12.80.
L* and b*value was decreased as layering thickness of Incisal composite on Body composite was increased. But, a* value did not show specific change tendency.
Conclusions:
Surface color difference between Body composites and Incisal composites layered on Body composite was increased as the layering thickness of Incisal composite increased (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Color stability of esthetic restorative materials after application of fluoride varnishes
Chul-Hoon Jang, Dong-Gil Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2021; 48(3): 147. CrossRef - Color Change in Tooth Induced by Various Calcium Silicate-Based Pulp-Capping Materials
Jiyoon Jeon, Namki Choi, Seonmi Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(3): 280. CrossRef - Discrimination between FRC-post and core according to the color difference
Jou-Hwe Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2015; 31(2): 75. CrossRef - Optical characteristics of resin composite before and after polymerization
Ah-Hyang Eom, Duck-Su Kim, Soo-Hee Lee, Chang-Won Byun, Noh-Hoon Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 219. CrossRef
-
1,205
View
-
2
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
-
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):353-358. Published online September 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.353
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to measure the power density of light curing units transmitted through resin inlays fabricated with direct composite (Filtek Z350, Filtek Supreme XT) and indirect composite (Sinfony).
Materials and Methods
A3 shade of Z350, A3B and A3E shades of Supreme XT, and A3, E3, and T1 shades of Sinfony were used to fabricate the resin inlays in 1.5 mm thickness. The power density of a halogen light curing unit (Optilux 360) and an LED light curing unit (Elipar S10) through the fabricated resin inlays was measured with a hand held dental radiometer (Cure Rite). To investigate the effect of each composite layer consisting the resin inlays on light transmission, resin specimens of each shade were fabricated in 0.5 mm thickness and power density was measured through the resin specimens.
Results
The power density through the resin inlays was lowest with the Z350 A3, followed by Supreme XT A3B and A3E. The power density was highest with Sinfony A3, E3, and T1 (p < 0.05). The power density through 0.5 mm thick resin specimens was lowest with dentin shades, Sinfony A3, Z350 A3, Supreme XT A3B, followed by enamel shades, Supreme XT A3E and Sinfony E3. The power density was highest with translucent shade, Sinfony T1 (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Using indirect lab composites with dentin, enamel, and translucent shades rather than direct composites with one or two shades could be advantageous in transmitting curing lights through resin inlays.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of polymerization shrinkage of dual-cure core build-up resin according to shade and curing mode
Yoorina Choi, Karl Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(4): 243. CrossRef - Early Hardness and Shear Bond Strength of Dual-cure Resin Cement Light Cured Through Resin Overlays With Different Dentin-layer Thicknesses
H-S Chang, J-W Kim
Operative Dentistry.2014; 39(4): 398. CrossRef - Effects of layering technique on the shade of resin overlays and the microhardness of dual cure resin cement
Hoon-Sang Chang, Sung-Ok Hong
Brazilian Oral Research.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Light curing of dual cure resin cement
Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 266. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef
-
1,220
View
-
2
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Effect of infection control barrier thickness on light curing units
-
Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Ryun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Chang-Kyu Song, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):368-373. Published online September 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.368
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study investigated the effect of infection control barrier thickness on power density, wavelength, and light diffusion of light curing units.
Materials and Methods
Infection control barrier (Cleanwrap) in one-fold, two-fold, four-fold, and eight-fold, and a halogen light curing unit (Optilux 360) and a light emitting diode (LED) light curing unit (Elipar FreeLight 2) were used in this study. Power density of light curing units with infection control barriers covering the fiberoptic bundle was measured with a hand held dental radiometer (Cure Rite). Wavelength of light curing units fixed on a custom made optical breadboard was measured with a portable spectroradiometer (CS-1000). Light diffusion of light curing units was photographed with DSLR (Nikon D70s) as above.
Results
Power density decreased significantly as the layer thickness of the infection control barrier increased, except the one-fold and two-fold in halogen light curing unit. Especially, when the barrier was four-fold and more in the halogen light curing unit, the decrease of power density was more prominent. The wavelength of light curing units was not affected by the barriers and almost no change was detected in the peak wavelength. Light diffusion of LED light curing unit was not affected by barriers, however, halogen light curing unit showed decrease in light diffusion angle when the barrier was four-fold and statistically different decrease when the barrier was eight-fold (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
It could be assumed that the infection control barriers should be used as two-fold rather than one-fold to prevent tearing of the barriers and subsequent cross contamination between the patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Light curing infection control barriers: do some types jeopardize the concept of conventional bulk-fill composites?
Dalia I. Sherief, Mohamed M. Kandil, Dina Ahmed El-Refai
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Infection Control Barriers on Light Output from a Dental Light-Curing Unit Used in Various Positions
Jitte van der Zee, Andrew Tawse-Smith, Sunyoung Ma
Oral.2023; 3(2): 166. CrossRef - Evaluation of irradiance and spectral output of visible light curing units used in the laboratory
Yoorina Choi, Su-Beom Choi, Ji-Hye Jung, Hoon-Sang Chang
Oral Biology Research.2021; 45(4): 201. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Clinical Sterilization Methods in Dental Air/water Syringes
Seyoung Shin, Yeonmi Yang, Miah Kim, Jaegon Kim, Byeongju Baik
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2013; 40(4): 268. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef - Effect of a multi-layer infection control barrier on the micro-hardness of a composite resin
In-Nam Hwang, Sung-Ok Hong, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2012; 20(5): 576. CrossRef
-
1,149
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Infection control of light curing units
-
Hoon-Sang Chang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):235-237. Published online July 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.235
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
When curing the composite restorations with light curing units, the light guides are often in direct contact with oral tissues, therefore contamination of light guides is inevitable. Curing light guides fall into the "semicritical" instrument category according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and must be heat or vapor-sterilized or at a minimum, these semicritical instruments must be sterilized in a liquid chemical agent. Currently, most common methods of maintaining sterility of the light guides are wiping the guide with a disinfectant, such as glutaraldehyde, after each patient use; using autoclavable guides; using presterilized, single-use plastic guides; and using translucent disposable barriers to cover the guide. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of a multi-layer infection control barrier on the micro-hardness of a composite resin
In-Nam Hwang, Sung-Ok Hong, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2012; 20(5): 576. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef
-
1,082
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Clinical diagnosis of herpes zoster presenting as odontogenic pain
-
Seong-Hak Yang, Dong-Ho Jung, Hae-Doo Lee, Yoon Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):452-456. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.452
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Herpes zoster, an acute viral infection produced by the varicella zoster virus, may affect any of the trigeminal branches. This case report presents a patient with symptoms mimicking odontogenic pain. No obvious cause of the symptoms could be found based on clinical and radiographic examinations. After a dermatologist made a diagnosis of herpes zoster involving the third trigeminal branch, the patient was given antiviral therapy. Two months later, the facial lesions and pain had almost disappeared, and residual pigmented scars were present. During the diagnostic process, clinicians should keep in mind the possibility that orofacial pain might be related to herpes zoster. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Herpes Zoster Accompanying Odontogenic Inflammation: A Case Report with Literature Review
Soyeon Lee, Minsik Kim, Jong-Ki Huh, Jae-Young Kim
Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain.2021; 46(1): 9. CrossRef - Recurrent Herpetic Stomatitis Mimicking Post-Root Resection Complication
Sung-Ok Hong, Jae-Kwan Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2013; 29(4): 418. CrossRef - Diagnostic challenges of nonodontogenic toothache
Hyung-Ok Park, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 170. CrossRef
-
3,139
View
-
14
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Microleakage of endodontic temporary restorative materials under dynamic loading
-
Dong-Ho Jung, Young-Sin Noh, Hae-Doo Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):198-203. Published online May 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.198
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to compare the sealing abilities of four endodontic temporary restorative materials using a methylene blue dye penetration test under dynamic loading. Standardized access cavities were prepared in forty-four intact human permanent molar teeth, and the cavities were restored with Caviton, MD-Temp, IRM, or ZOE. After thermocycling, an intermittent load of 98 N at 1 Hz was applied for 1,000 cycles to the long axis of the functional cusp of each of the teeth, which were immersed in a 1% methylene blue solution. The teeth were split in half, and the linear depth of dye penetration was evaluated according to the criteria. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (p = 0.05) and Duncan's multiple range test. The results demonstrated that Caviton and MD-Temp showed significantly lower microleakage than IRM and ZOE. It was concluded that Caviton and MD-Temp exhibited better sealing ability than IRM and ZOE under dynamic loading. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 29. CrossRef
-
2,087
View
-
18
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The palato-gingival groove - anatomical anomaly occurred in maxillary lateral incisors: case reports
-
Hyun-Il Kim, Young-Shin Noh, Hoon-Sang Chang, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):483-490. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.483
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This report describes clinical cases of a palato-gingival groove on a maxillary lateral incisor with associated localized periodontal disease and pulp necrosis. The tooth of the first case was extracted because of severe bone destruction. The palato-gingival groove of the second case was eliminated using a round bur, and the resulting defect was filled with synthetic graft and covered by an absorbable membrane. Both diagnosis and treatment of palato-gingival groove were very difficult and usually extraction of the involved tooth is the treatment of choice, but combined endodontic-periodontic treatment allowed the tooth to be saved. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Exploring anatomical uniqueness: A rare case report of the buccomesial groove variation in maxillary lateral incisor and its management
Shubhangi Kadoo, Pallav Mahesh Patni, Sanket Hans Pandey, Rahul Vaswani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 394. CrossRef - Radicular lingual groove: A contributory factor in periodontal pathology
Gaurav Didhra, Jagjit Singh, Rajan Gupta, Parveen Dahiya
Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences.2019; 7(2): 240. CrossRef - Management of a Palatal Gingival Groove in a Maxillary Lateral Incisor: A Case Report
Ashkan Salari, Maosumeh Faramarzi, Seyedeh Fereshteh Naser alavi
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry.2016; 7(2): 66. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
-
1,690
View
-
5
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Evaluation of the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of resinous root canal sealers
-
Chang-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Hoon-Sang Chang, Byung-Do Lee, Kyung-San Min, Chan-Ui Hong
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(5):419-425. Published online September 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.5.419
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of three resin-based (AH 26, EZ fill and AD Seal), a zinc oxide-eugenol-based (ZOB Seal), and a calcium hydroxide-based (Sealapex) root canal sealers. Specimens, 10 mm in diameter and 1 mm in thickness, were radiographed simultaneously with an aluminum step wedge using occlusal films, according to ISO 6876/2001 standards. Radiographs were digitized, and the radiopacity of sealers was compared to the different thicknesses of the aluminum step wedge, using the Scion image software. Using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, the cytotoxicity of each material was determined in immortalized human periodontal ligament (IPDL) cells.
The results demonstrated that EZ fill was the most radiopaque sealer, while Sealapex was the least radiopaque (p < 0.05). AH 26, AD Seal and ZOB Seal presented intermediate radiopacity values. All the materials evaluated, except for Sealapex, presented the minimum radiopacity required by ISO standards. The cell viabilities of resin-based root canal sealers were statistically higher than that of other type of root canal sealers through the all experimental time. Further, EZ fill showed statistically lower cell viability in 24 and 48 hours compared to AD Seal and in 72 hours compared to all other resin-based root canal sealers. However, there was no correlation between the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of three resin-based root canals sealers (p > 0.05).
These results indicate that resin-based root canal sealer is more biocompatible and has advantage in terms of radiopacity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Comparative Evaluation of Two Commonly Used GP Solvents on Different Epoxy Resin-based Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Sakshi Tyagi, Ekta Choudhary, Rajat Chauhan, Ashish Choudhary
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(1): 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of cytotoxicity of root canal sealers: anin vitrostudy
Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Manjusha Madhukar Warhadpande, Ganesh Kothiramji Meshram, Rakesh Namdeoraoji Bahadure, Shubha Gopal Tawani, Gopal Tawani, Shital Gautam Badole
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 204. CrossRef - Evaluation of radiopacity and discriminability of various fiber reinforced composite posts
Eun-Hye Lee, Hang-Moon Choi, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 188. CrossRef - A comparative study on radiopacity of root canal sealers
Tae-Min Kim, Seo-Kyoung Kim, In-Nam Hwang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Byung-Cheol Kang, Suk-Ja Yoon, Jae-Seo Lee, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 61. CrossRef - A comparative study on radiopacity of canal filling and retrograde root-end filling materials
Yong-Sang Kim, Seo-Kyong Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(2): 107. CrossRef
-
1,958
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
The instrument-centering ability of four Nickel-Titanium instruments in simulated curved root canals
-
Jae-Hoon Ku, Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Woo Chang, Hwan-Hee Cho, Ji-Myung Bae, Kyung-San Min
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):113-118. Published online March 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.113
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the ability of newly marketed NRT instruments to maintain the original root canal configuration and curvature during preparation in comparison with the three existing instruments in simulated root canals.
Simulated canals in resin blocks were prepared with ProFile, K3, ProTaper, and NRT instrument (n = 10 canals in each case). Pre- and post-operative images were recorded, and assessment of canal shape was completed with a computer image analysis program. The data were analyzed statistically using the One-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test.
The ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1-, 2-mm levels was significantly better in ProFile groups than in other groups (p < 0.05). The change of centering ratio in NRT groups at 5-mm level was significantly greater than ProFile group and at 6- and 7-mm level than all other groups (p < 0.05).
Although the NRT system was comparable to other systems in regards to its ability to maintain the canal configuration of apical portion, this system was more influenced by the mid-root curvature due to its stainless-steel files for coronal preflaring. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A comparison of the shaping ability of reciprocating NiTi instruments in simulated curved canals
Young-Sil Yoo, Yong-Bum Cho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 220. CrossRef - Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 424. CrossRef
-
1,263
View
-
0
Download
-
2
Crossref
|