-
Accidental injury of the inferior alveolar nerve due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide in endodontic treatment: a case report
-
Yooseok Shin, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yemi Kim, Taehyeon Kim, Hyungjun Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):63-67. Published online January 6, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.63
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
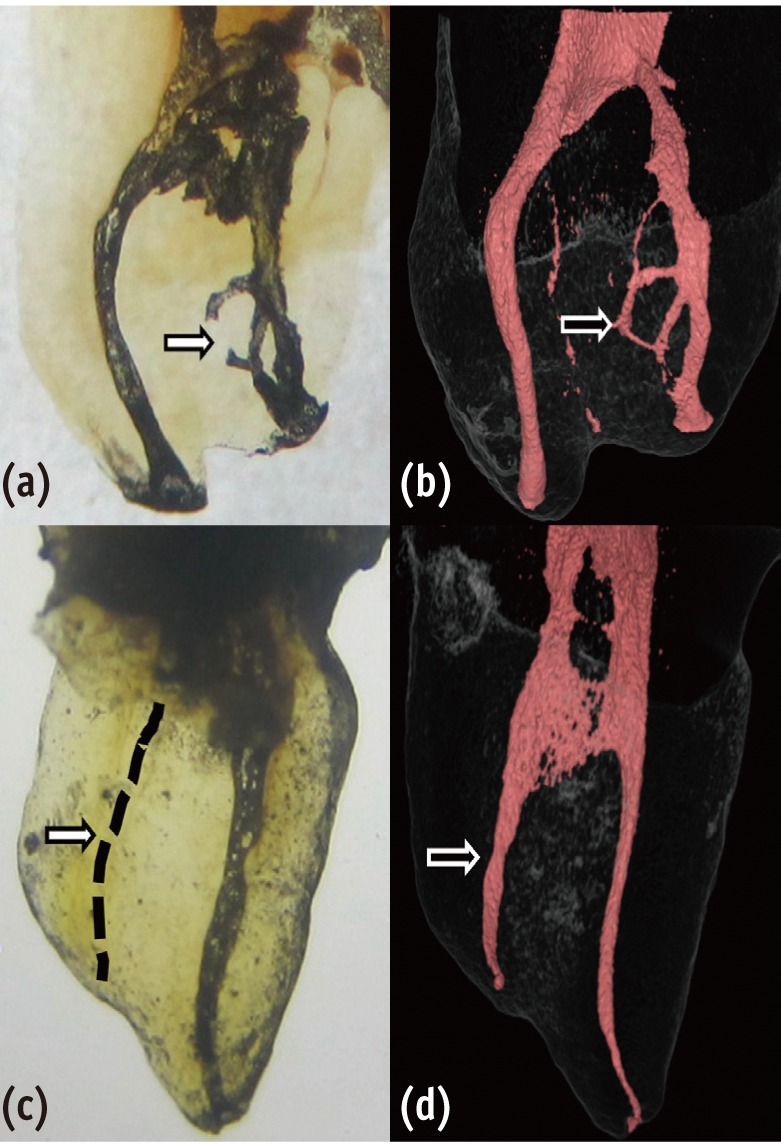
During clinical endodontic treatment, we often find radiopaque filling material beyond the root apex. Accidental extrusion of calcium hydroxide could cause the injury of inferior alveolar nerve, such as paresthesia or continuous inflammatory response. This case report presents the extrusion of calcium hydroxide and treatment procedures including surgical intervention. A 48 yr old female patient experienced Calcipex II extrusion in to the inferior alveolar canal on left mandibular area during endodontic treatment. After completion of endodontic treatment on left mandibular first molar, surgical intervention was planned under general anesthesia. After cortical bone osteotomy and debridement, neuroma resection and neurorrhaphy was performed, and prognosis was observed. But no improvement in sensory nerve was seen following surgical intervention after 20 mon. A clinician should be aware of extrusion of intracanal medicaments and the possibility of damage on inferior alveolar canal. Injectable type of calcium hydroxide should be applied with care for preventing nerve injury. The alternative delivery method such as lentulo spiral was suggested on the posterior mandibular molar. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nicolau syndrome in endodontics: A narrative review on calcium hydroxide extrusion and its therapeutic risks
Manisha Chaudhary, Akash Kumar Giri, Ashok Ayer
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 12. CrossRef - Invasion of Calcium Hydroxide Preparations Leading to Severe Chemical Nerve Injury Treated Through Nerve Repair Using Artificial Nerve Conduit: A Case Report
Akihiro Nishiyama, Andreas Neff, Takahiro Nakada, Takaharu Ariizumi, Akira Iwasaki, Keisuke Sugahara, Akira Katakura, Hannah Wesley
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Automatic localization of inferior alveolar nerve canal in panoramic dental images
Uma Maheswari Pandyan, Banumathi Arumugam, Ulaganathan Gurunathan, Shahul Hameed Kopuli Ashkar Ali
Signal, Image and Video Processing.2022; 16(5): 1389. CrossRef - Inferior alveolar nerve injury due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide during endodontic treatment: A case report
Metin Berk Kasapoğlu, Gülce Ecem Doğancalı
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 342. CrossRef - Inferior alveolar nerve canal segmentation by local features based neural network model
P. Uma Maheswari, A. Banumathi, G. Ulaganathan, R. Yoganandha
IET Image Processing.2022; 16(3): 703. CrossRef - Microsurgical Repair of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injuries Associated With Endodontic Treatment: Results on Sensory Function and Relief of Pain
Keith A. Sonneveld, Kristopher L. Hasstedt, Roger A. Meyer, Shahrokh C. Bagheri
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2021; 79(7): 1434. CrossRef - The significance of diagnosis and treatment planning in periapical lesion overfilled with calcium hydroxide paste
Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Eun-Young Kwon, Youn-Kyung Choi, So-Yeun Kim, Hye-Mi Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(2): 95. CrossRef - The anatomical relationship between the roots of erupted permanent teeth and the mandibular canal: a systematic review
Michał Puciło, Mariusz Lipski, Magdalena Sroczyk-Jaszczyńska, Aleksandra Puciło, Alicja Nowicka
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2020; 42(5): 529. CrossRef - Massive extrusion of calcium hydroxide paste containing barium sulphate during endodontic treatment
Jéssica Montenegro Fonsêca, Natália Rangel Palmier, Gleyson Kleber Amaral‐Silva, Lady Paola Aristizabal Arboleda, José Flávio Affonso Almeida, Mario Fernando de Goes, Pablo Agustin Vargas, Marcio Ajudarte Lopes, Alan Roger Santos‐Silva
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(2): 257. CrossRef - The double-edged sword of calcium hydroxide in endodontics
Alan H. Gluskin, Gordon Lai, Christine I. Peters, Ove A. Peters
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(5): 317. CrossRef - Endodontic-related inferior alveolar nerve injuries: A review and a therapeutic flow chart
R. Castro, M. Guivarc'h, J.M. Foletti, J.H. Catherine, C. Chossegros, L. Guyot
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 119(5): 412. CrossRef - Relationship between Root Apices and the Mandibular Canal: A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Comparison of 3 Populations
Alex Lvovsky, Shir Bachrach, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Ajinkya Pawar, Oleg Levinzon, Joe Ben Itzhak, Michael Solomonov
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 555. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef - Oral dysesthesia
Christopher J. Spencer, Gary D. Klasser
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2017; 148(12): 941. CrossRef - Microsurgical Decompression of Inferior Alveolar Nerve After Endodontic Treatment Complications
Bernardo Bianchi, Andrea Ferri, Andrea Varazzani, Michela Bergonzani, Enrico Sesenna
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2017; 28(5): 1365. CrossRef
-
3,697
View
-
43
Download
-
15
Crossref
-
A study on the compatibility between one-bottle dentin adhesives and composite resins using micro-shear bond strength
-
Minju Song, Yooseok Shin, Jeong-Won Park, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):30-36. Published online September 26, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.30
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study was performed to determine whether the combined use of one-bottle self-etch adhesives and composite resins from same manufacturers have better bond strengths than combinations of adhesive and resins from different manufacturers. Materials and Methods25 experimental micro-shear bond test groups were made from combinations of five dentin adhesives and five composite resins with extracted human molars stored in saline for 24 hr. Testing was performed using the wire-loop method and a universal testing machine. Bond strength data was statistically analyzed using two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's post hoc test. ResultsTwo way ANOVA revealed significant differences for the factors of dentin adhesives and composite resins, and significant interaction effect (p < 0.001). All combinations with Xeno V (Dentsply De Trey) and Clearfil S3 Bond (Kuraray Dental) adhesives showed no significant differences in micro-shear bond strength, but other adhesives showed significant differences depending on the composite resin (p < 0.05). Contrary to the other adhesives, Xeno V and BondForce (Tokuyama Dental) had higher bond strengths with the same manufacturer's composite resin than other manufacturer's composite resin. ConclusionsNot all combinations of adhesive and composite resin by same manufacturers failed to show significantly higher bond strengths than mixed manufacturer combinations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
Stefan Dačić, Milan Miljković, Aleksandar Mitić, Goran Radenković, Marija Anđelković‐Apostolović, Milica Jovanović
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(6): 1212. CrossRef - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef - Dentin bond strengths of all-in-one adhesives combined with different manufacturers’ flowable resin composites
Koichi SHINKAI, Daiki YOSHII, Akira KOIDE, Masaya SUZUKI, Shiro SUZUKI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(5): 1094. CrossRef - DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE ADEZİV SİSTEMLER
Elmas TÜRKER, Buket AYNA
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of EDC on Dentin-Resin Shear Bond Strength and Demineralized Dentin Thermal Properties
Lin Tang, Yi Zhang, Yuhua Liu, Yongsheng Zhou
Materials.2016; 9(11): 920. CrossRef
-
1,473
View
-
7
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
-
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):79-88. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.79
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Appropriate use of local hemostatic agent is one of the important factors on the prognosis of endodontic microsurgery. However, most investigations to date focus on the hemostatic efficacy of the agents, whereas their biologic characteristics have not received enough attention. The purpose of this paper was to review the biologic response of local hemostatic agents, and to provide clinical guidelines on their use during endodontic microsurgery. Electronic database (PUBMED) was screened to search related studies from 1980 to 2013, and 8 clinical studies and 18 animal studies were identified. Among the materials used in these studies, most widely-investigated and used materials, epinephrine, ferric sulfate (FS) and calcium sulfate (CS), were thoroughly discussed. Influence of these materials on local tissue and systemic condition, such as inflammatory and foreign body reaction, local ischemia, dyspigmentation, delayed or enhanced bone and soft tissue healing, and potential cardiovascular complications were assessed. Additionally, biological property of their carrier materials, cotton pellet and absorbable collagen, were also discussed. Clinicians should be aware of the biologic properties of local hemostatic agents and their carrier materials, and should pay attention to the potential complications when using them in endodontic microsurgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A drug-carrying, multiscene, absorbable biological suture from fish swim bladder
Peng Sun, Hao Cui, Jinwei Zhang, Jingan Li, Changwei Ren, Yongqiang Lai
International Journal of Surgery.2025; 111(10): 6663. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of apicoectomy without retrograde filling in treating periapical inflammatory cysts
Jeong-Kui Ku, Woo-Young Jeon, Seung-O Ko, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2024; 50(3): 140. CrossRef - Functional and structural neurodegenerative activities of Ankaferd BloodStopper in a mouse sciatic nerve model
Ramazan Üstün, Elif Oğuz, Ayşe Şeker, Filiz Taspinar
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Local and Systemic Hemostatic Agents: A Comprehensive Review
Bardia Jamali, Saeed Nouri, Salimeh Amidi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PLGA Nanoparticle Rapamycin- or Necrostatin-1-Coated Sutures Inhibit Inflammatory Reactions after Arterial Closure in Rats
Liwei Zhang, Wang Wang, Boao Xie, Peng Sun, Shunbo Wei, Haoliang Wu, Cong Zhang, Jingan Li, Zhuo Li, Hualong Bai
ACS Applied Bio Materials.2022; 5(4): 1501. CrossRef - COMPARING THE CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES OF PULPOTOMIES IN PRIMARY MOLARS USING BIOACTIVE ENDODONTIC MATERIALS AND FERRIC SULFATE – A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIALS
VELLORE KANNAN GOPINATH, SHAJU JACOB PULIKKOTIL, SAJESH K VEETTIL, LALLI DHARMARAJAN, PONNUDURAI SAMUEL GNANA PRAKASH, VINEET DHAR, JAYAKUMAR JAYARAMAN
Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice.2022; 22(4): 101770. CrossRef - Perioperative Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Management with Endodontic Microsurgical Techniques
Anita Aminoshariae, Mark Donaldson, Michael Horan, James C. Kulild, Dale Baur
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(10): 1557. CrossRef - Effect of blood contamination and various hemostatic procedures on the push-out bond strength of Biodentine when used for furcation perforation repair
Shanthana Reddy, Ramya Shenoy, LohithReddy Mandadi, Ishani Saluja, ManuelS Thomas
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 260. CrossRef - Endodontic Perforation Closure by Five Mineral Oxides Silicate-Based Cement with/without Collagen Sponge Matrix
Talal Al-Nahlawi, Maisour Ala Rachi, Amjad Abu Hasna, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Hemostatic agents in periapical surgery: The systematic review
Z. S. Khabadze, D. A. Nazarova, E. S. Shilyaeva, A. P. Kotelnikova, Yu. A. Bakayev, S. M. Abdulkerimova, Kh. O. Omarova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(3): 184. CrossRef - An Innovative Bioceramic Bone Graft Substitute for Bone Defect Treatment: In Vivo Evaluation of Bone Healing
Syamsiah Syam, Yung-Chieh Cho, Chung-Ming Liu, Mao-Suan Huang, Wen-Chien Lan, Bai-Hung Huang, Takaaki Ueno, Chi-Hsun Tsai, Takashi Saito, May-Show Chen, Keng-Liang Ou
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(22): 8303. CrossRef - Trial finds better haemostasis with aluminium chloride during periapical surgery
Niall Mc Goldrick, Carly Ross, James Nelson
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2017; 18(2): 50. CrossRef - Comparison of the Hemostatic Activity of Quercus persica Jaub. & Spach. (Oak) With Ferric Sulfate in Bony Crypts
Mohammad Reza Nabavizadeh, Arman Zargaran, Fariborz Moazami, Fatemeh Askari, Safoora Sahebi, Alireza Farhadpoor, Pouya Faridi
Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine.2016; 21(1): 34. CrossRef - Effect of the plant-based hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper® on the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate
Muzaffer Emir Dinçol, Hakan Ozbas, Bulent Yılmaz, Handan Ersev, Selcuk Gokyay, Vakur Olgac
BMC Oral Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,777
View
-
17
Download
-
15
Crossref
-
Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation on composite resins containing ursolic acid
-
Soohyeon Kim, Minju Song, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):65-72. Published online May 28, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.65
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the inhibitory effect of ursolic acid (UA)-containing composites on Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) biofilm. Materials and MethodsComposite resins with five different concentrations (0.04, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 wt%) of UA (U6753, Sigma Aldrich) were prepared, and their flexural strengths were measured according to ISO 4049. To evaluate the effect of carbohydrate source on biofilm formation, either glucose or sucrose was used as a nutrient source, and to investigate the effect of saliva treatment, the specimen were treated with either unstimulated whole saliva or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). For biofilm assay, composite disks were transferred to S. mutans suspension and incubated for 24 hr. Afterwards, the specimens were rinsed with PBS and sonicated. The colony forming units (CFU) of the disrupted biofilm cultures were enumerated. For growth inhibition test, the composites were placed on a polystyrene well cluster, and S. mutans suspension was inoculated. The optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was recorded by Infinite F200 pro apparatus (TECAN). One-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction were used for the data analyses. ResultsThe flexural strength values did not show significant difference at any concentration (p > 0.01). In biofilm assay, the CFU score decreased as the concentration of UA increased. The influence of saliva pretreatment was conflicting. The sucrose groups exhibited higher CFU score than glucose group (p < 0.05). In bacterial growth inhibition test, all experimental groups containing UA resulted in complete inhibition. ConclusionsWithin the limitations of the experiments, UA included in the composite showed inhibitory effect on S. mutans biofilm formation and growth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Environmental Stress Induces Altered Composition of Streptococcus mutans Membrane Vesicles: pH‐Driven Changes in Membrane Vesicle Production and Composition
Taylor C. Boone, Swetha K. Shankar, Melodie L. Weller
Molecular Oral Microbiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-cariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid using dental microcosm biofilm
Jonghyun Jo, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Sun Kyu Park, Su-Jung Shin, Baek-il Kim, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105447. CrossRef - Rapid specific detection of oral bacteria using Cas13-based SHERLOCK
Jett Liu, Camden Carmichael, Hatice Hasturk, Wenyuan Shi, Batbileg Bor
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Bioactive Nanocomposites Containing Calcium Fluoride and Calcium Phosphate with Antibacterial and Low-Shrinkage-Stress Capabilities to Inhibit Dental Caries
Abdullah Alhussein, Rashed Alsahafi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Lamia Mokeem, Abraham Schneider, Mary-Ann Jabra-Rizk, Radi Masri, Gary D. Hack, Thomas W. Oates, Jirun Sun, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H. K. Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(9): 991. CrossRef - Quorum sensing inhibition and antibiofilm action of triterpenoids: An updated insight
Sudipta Paul Bhattacharya, Snigdha Karmakar, Kusumita Acharya, Arijit Bhattacharya
Fitoterapia.2023; 167: 105508. CrossRef - The Application of Small Molecules to the Control of Typical Species Associated With Oral Infectious Diseases
Sirui Yang, Xiaoying Lyu, Jin Zhang, Yusen Shui, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Planktonic and Anti-Biofilm Properties of Pentacyclic Triterpenes—Asiatic Acid and Ursolic Acid as Promising Antibacterial Future Pharmaceuticals
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska, Dorota Wojnicz
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 98. CrossRef - Development and Physicochemical Characterization of Eugenia brejoensis Essential Oil-Doped Dental Adhesives with Antimicrobial Action towards Streptococcus mutans
Maury Luz Pereira, Danyelle Cristina Pereira Santos, Carlos Alberto Mendes Soares Júnior, Tamyris Alicely Xavier Nogueira Bazan, Clovis Macêdo Bezerra Filho, Márcia Vanusa da Silva, Maria Tereza dos Santos Correia, Andres Felipe Millan Cardenas, Fabiana S
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(3): 149. CrossRef - Does Secondary Plant Metabolite Ursolic Acid Exhibit Antibacterial Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Living in Single- and Multispecies Biofilms?
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Wojnicz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(8): 1691. CrossRef - Prolonged Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Growth and Biofilm Formation by Sustained Release of Chlorhexidine from Varnish Coated Dental Abutments: An in Vitro Study
Mark Feldman, Walid Shaaban Moustafa Elsayed, Michael Friedman, Irith Gati, Doron Steinberg, Hesham Marei, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interkingdom Signaling Interference: The Effect of Plant-Derived Small Molecules on Quorum Sensing in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria
Janak Raj Joshi, Netaly Khazanov, Amy Charkowski, Adi Faigenboim, Hanoch Senderowitz, Iris Yedidia
Annual Review of Phytopathology.2021; 59(1): 153. CrossRef - Small Molecule Compounds, A Novel Strategy against Streptococcus mutans
Sirui Yang, Jin Zhang, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Pathogens.2021; 10(12): 1540. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide nanotubes added to glass ionomer cements affect S. mutans viability and mechanisms of virulence
Isaac Jordão de Souza ARAÚJO, Mariana Gallante RICARDO, Orisson Ponce GOMES, Priscila Alves GIOVANI, Júlia PUPPIN-RONTANI, Vanessa Arias PECORARI, Elizabeth Ferreira MARTINEZ, Marcelo Henrique NAPIMOGA, Francisco Humberto NOCITI JUNIOR, Regina Maria PUPPI
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ursolic and Oleanolic Acids on Lipid Membranes: Studies on MRSA and Models of Membranes
Sandrine Verstraeten, Lucy Catteau, Laila Boukricha, Joelle Quetin-Leclercq, Marie-Paule Mingeot-Leclercq
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1381. CrossRef - Ursolic acid inhibits multi-species biofilms developed by Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguinis, and Streptococcus gordonii
Xiaoying Lyu, Liang Wang, Yusen Shui, Qingsong Jiang, Lan Chen, Wen Yang, Xiaoya He, Jumei Zeng, Yuqing Li
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 125: 105107. CrossRef - The physical properties and anticariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid
Hyunkyung Yoo, So Youn Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 641. CrossRef - Ursolic acid: A systematic review of its pharmacology, toxicity and rethink on its pharmacokinetics based on PK-PD model
Qiang Sun, Man He, Meng Zhang, Sha Zeng, Li Chen, Lijuan Zhou, Haibo Xu
Fitoterapia.2020; 147: 104735. CrossRef - Effects of UVB and UVC irradiation on cariogenic bacteria in vitro
Shigeki Uchinuma, Yasushi Shimada, Khairul Matin, Keiichi Hosaka, Masahiro Yoshiyama, Yasunori Sumi, Junji Tagami
Lasers in Medical Science.2019; 34(5): 981. CrossRef - Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential
Dharambir Kashyap, Hardeep Singh Tuli, Anil K. Sharma
Life Sciences.2016; 146: 201. CrossRef - Protective Effects on Gastric Lesion of Ursolic acid
Sun Whoe Kim, In Young Hwang, Sun Yi Lee, Choon Sik Jeong
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2016; 31(4): 286. CrossRef - Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities
Łukasz Woźniak, Sylwia Skąpska, Krystian Marszałek
Molecules.2015; 20(11): 20614. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Dental materials with antibiofilm properties
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Dental Materials.2014; 30(2): e1. CrossRef - Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles onStreptococcus mutansandLactobacillus
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 109. CrossRef - Synergistic effect of xylitol and ursolic acid combination on oral biofilms
Yunyun Zou, Yoon Lee, Jinyoung Huh, Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 288. CrossRef - The virulence of Streptococcus mutans and the ability to form biofilms
W. Krzyściak, A. Jurczak, D. Kościelniak, B. Bystrowska, A. Skalniak
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.2014; 33(4): 499. CrossRef
-
1,948
View
-
5
Download
-
26
Crossref
-
Invasive cervical resorption: treatment challenges
-
Yookyung Kim, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):228-231. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.228
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Invasive cervical resorption is a relatively uncommon form of external root resorption. It is characterized by invasion of cervical region of the root by fibrovascular tissue derived from the periodontal ligament. This case presents an invasive cervical resorption occurring in maxillary lateral incisor, following damage in cervical cementum from avulsion and intracoronal bleaching procedure. Flap reflection, debridement and restoration with glass ionomer cement were performed in an attempt to repair the defect. But after 2 mon, more resorption extended apically. Considering root stability and recurrence potential, we decided to extract the tooth. Invasive cervical resorption in advanced stages may present great challenges for clinicians. Therefore, prevention and early detection must be stressed when dealing with patients presenting history of potential predisposing factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Outcome of Decoronation in Severe Cases of External Cervical Root Resorption in Young Patients
Dina Moss, Eyal Nuni, Hagay Slutzky, Daniel Moreinos, Iris Slutzky-Goldberg
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical repair of external cervical resorption - Prognosis and prognostic factors
Po-Yuan Jeng, Shu-Hui Chang, Chen-Ying Wang, Li-Deh Lin, Jiiang-Huei Jeng, Yi-Ling Tsai
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 377. CrossRef - The Disease Process, Diagnosis and Treatment of Invasive Cervical Resorption: A Review
Olivia Rotondi, PhiAnh Waldon, Sahng G. Kim
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(3): 64. CrossRef - Combined endodontic and periodontal management of a class 3 invasive cervical resorption in a mandibular first molar
Takayoshi Nagahara, Katsuhiro Takeda, Yusuke Aida, Tomoyuki Iwata, Ryoichi Yagi, Hidemi Kurihara, Hideki Shiba
Clinical Case Reports.2018; 6(10): 2005. CrossRef - External cervical resorption: a three‐dimensional classification
S. Patel, F. Foschi, F. Mannocci, K. Patel
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 206. CrossRef - Invasive cervical resorption and the oro-facial cleft patient: a review and case series
A. O'Mahony, C. McNamara, A. Ireland, J. Sandy, J. Puryer
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(9): 677. CrossRef - Characteristics and treatment of invasive cervical resorption in vital teeth. A narrative review and a report of two cases
P. Tsaousoglou, E. Markou, N. Efthimiades, I. Vouros
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(6): 423. CrossRef - Fifteen-year Clinical Follow-up of Restoration of Extensive Cervical Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor
EG Reston, RPR Bueno, LQ Closs, J Zettermann
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(2): E55. CrossRef - The Assessment and Management of External Cervical Resorption with Periapical Radiographs and Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Clinical Study
Kreena Patel, Francesco Mannocci, Shanon Patel
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1435. CrossRef - Management of invasive cervical resorption in a maxillary central incisor
SSenthil Kumar, NS Mohan Kumar, JV Karunakaran, S Nagendran
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2015; 7(6): 712. CrossRef
-
2,359
View
-
14
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Pre-prosthetic minor tooth movement with elastic separating ring & provisional restoration modification: case report
-
Haneol Shin, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yoo-Seok Shin, Chan-Young Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):114-118. Published online May 18, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.114
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Proximal caries or coronal defect in posterior teeth may result in the loss of proximal space and drifting of neighboring teeth, which makes restoration difficult. Inability to restore proper contours and to align tooth axis properly are commonly encountered problems when planning tooth restoration. Moreover, tilted teeth aggravate periodontal tissue breakdown, such as pseudo-pocket, and angular osseous defect. The purpose of this case presentation is to describe a simple technique for inducing minor tooth movement with orthodontic separating ring and provisional restoration modification. This method was used to create crown placement space on mesially tilted molar. This method is easy, simple and efficient technique which could be used in interproximal space gaining in selected situation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three cases with long-term follow ups
Jae-Hyung Lim, Ji-Hyun Lee, Su-Jung Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 56. CrossRef
-
1,297
View
-
8
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Influence of three different preparation designs on the marginal and internal gaps of CEREC3 CAD/CAM inlays
-
Deog-Gyu Seo, Young-Ah Yi, Yoon Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):177-183. Published online May 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.177
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the marginal and internal gaps in CEREC3 CAD/CAM inlays of three different preparation designs. CEREC3 Inlays of three different preparation designs (n = 10) were fabricated according to Group I-conventional functional cusp capping/shoulder preparation, Group II-horizontal reduction of cusps and Group III-complete reduction of cusps/shoulder preparation. After cementation of inlays, the bucco-lingual cross section was performed through the center of tooth. Cross section images of 20 magnifications were obtained through the stereomicroscope. The gaps were measured using the Leica application suite software at each reference point. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey's test (α<0.05).
The marginal gaps ranged from 80.0 to 97.8 µm for Group I, 42.0 to 194.8 µm for Group II, 51.0 to 80.2 µm for Group III. The internal gaps ranged from 90.5 to 304.1 µm for Group I, 80.0 to 274.8 µm for Group II, 79.7 to 296.7 µm for Group III. The gaps of each group were the smallest on the margin and the largest on the horizontal wall. For the CEREC3 CAD/CAM inlays, the simplified designs (groups II and III) did not demonstrate superior results compared to the traditional cusp capping design (group I). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of preparation design on fit and ceramic thickness of CEREC 3 partial ceramic crowns after cementation
Jae-Hoon Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Jin-Hee Lee, Soo-Jung Kwon, Young-Ah Yi, Yooseok Shin, Byoung-Duck Roh, Deog-Gyu Seo
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2015; 73(2): 107. CrossRef
-
1,337
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The influence of cavity configuration on the microtensile bond strength between composite resin and dentin
-
Yemi Kim, Jeong-won Park, Chan young Lee, Yoon jung Song, Deok Kyu Seo, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):472-480. Published online September 30, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.472
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This study was conducted to evaluate the influence of the C-factor on the bond strength of a 6th generation self-etching system by measuring the microtensile bond strength of four types of restorations classified by different C-factors with an identical depth of dentin.
Eighty human molars were divided into four experimental groups, each of which had a C-factor of 0.25, 2, 3 or 4. Each group was then further divided into four subgroups based on the adhesive and composite resin used. The adhesives used for this study were AQ Bond Plus (Sun Medical, Japan) and Xeno III (DENTSPLY, Germany). And composite resins used were Fantasista (Sun Medical, Japan) and Ceram-X mono (DENTSPLY, Germany).
The results were then analyzed using one-way ANOVA, a Tukey's test, and a Pearson's correlation test and were as follows.
There was no significant difference among C-factor groups with the exception of groups of Xeno III and Ceram-X mono (p < 0.05).
There was no significant difference between any of the adhesives and composite resins in groups with C-factor 0.25, 2 and 4.
There was no correlation between the change in C-factor and microtensile bond strength in the Fantasista groups.
It was concluded that the C-factor of cavities does not have a significant effect on the microtensile bond strength of the restorations when cavities of the same depth of dentin are restored using composite resin in conjunction with the 6th generation self-etching system. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of different chlorhexidine application times on microtensile bond strength to dentin in Class I cavities
Hyun-Jung Kang, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 9. CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Effect of Chlorhexidine Application Methods on Microtensile Bond Strength to Dentin in Class I Cavities
Y-E. Chang, D-H. Shin
Operative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 618. CrossRef - Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef
-
1,098
View
-
1
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
In vitro evaluation of the consistency of two electronic apex locators
-
Gyu-Young Hwang, Byoung-Duck Roh, Eui-Sung Kim, Seung-Jong Lee
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):20-27. Published online January 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.020
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the consistency of two electronic apex locators in vitro model.
Materials consisted of fifty two extracted premolars and two electronic apex locators; Root ZX (J. Morita, Osaka, Japan) and E-Magic Finder Deluxe (S-Denti, Cheonan, Korea). After access preparation, the teeth were embedded in a saline-mixed alginate model. Canal lengths of each tooth were measured at "0.5" and "Apex" mark of the apex locators, respectively so that each tooth had two measurements from 0.5 and Apex points. The file was fixed at final measurement using a glass ionomer cement. The apical 4 mm from the apex was exposed to measure the distance from the file tip to the major apical foramen of each tooth. Average distances and standard deviations were used to evaluate the consistency.
Results showed that all measurements of both Root ZX and E-Magic Finder located the major foramen the range of ± 0.5 mm level. Both apex locators showed better consistency at Apex mark than at 0.5 mark. The average distance of file tip-major foramen was - 0.18 mm at 0.5 mark and - 0.07 mm at Apex mark in Root ZX, - 0.25 mm at 0.5 mark and - 0.02 mm at Apex mark in E-Magic Finder. Standard deviation was 0.21 at 0.5 mark and 0.12 at Apex mark in Root ZX, 0.12 at 0.5 mark and 0.09 at Apex mark in E-Magic Finder. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Variations in the morphology of apical constriction affecting electronic readings: An in vitro investigation using 3D‐printed tooth models
Juhee Nam, Lucila Piasecki, Doun Kwak, Jung Hwa Hong, Il‐Young Jung, Sung‐Ho Park, Sin‐Yeon Cho
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 245. CrossRef - In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
Chien-Yun Pi, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 453. CrossRef
-
1,164
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The influence of pH and lactic acid concentration on the formation of artificial root caries in acid buffer solution
-
Hyun-Suk Oh, Byoung-Duck Roh, Chan-Young Lee
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):47-60. Published online January 31, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.047
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study is to compare and to evaluate the effect of pH and lactic acid concentration on the progression of artificial root caries lesion using polarizing microscope, and to evaluate the morphological changes of hydroxyapatite crystals of the demineralized area and to investigate the process of demineralization using scanning electron microscope.
Artificial root caries lesion was created by dividing specimens into 3 pH groups (pH 4.3, 5.0, 5.5), and each pH group was divided into 3 lactic acid concentration groups (25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM). Each group was immersed in acid buffer solution for 5 days and examined. The results were as follows:
1. Under polarized microscope, the depth of lesion was more effected by the lactic acid concentration rather than the pH.
2. Under scanning electron microscope, dissolution of hydroxyapatite crystals were increased as the lactic acid concentration increased and the pH decreased.
3. Demineralized hydroxyapatite crystals showed peripheral dissolution and decreased size and number within cluster of hydroxyapatite crystals and widening of intercluster and intercrystal spaces as the pH decreased and the lactic acid concentration increased.
4. Under scanning electron microscope evaluation of the surface zone, clusters of hydroxyapatite crystals were dissolved, and dissolution and reattachment of crystals on the surface of collagen fibrils were observed as the lactic acid concentration increased.
5. Under scanning electron microscope, demineralization of dentin occurred not only independently but also with remineralization simultaneously.
In conclusion, the study showed that pH and lactic acid concentration influenced the rate of progression of the lesion in artificial root caries. Demineralization process was progressed from the surface of the cluster of hydroxyapatite crystals and the morphology of hydroxyapatite crystals changed from round or elliptical shape into irregular shape as time elapsed.
-
The comparison of relative reliability on biaxial and three point flexural strength testing methods of light curing composite resin
-
Deog-Gyu Seo, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):58-65. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.058
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The possibility of applying a bi-axial flexure strength test on composite resin was examined using three point and bi-axial flexure strength tests to measure the strength of the light-cured resin and to compare the relative reliability using the Weibull modulus.
The materials used in this study were light-curing restorative materials, MICRONEW™, RENEW® (Bisco, Schaumburg, USA). The bi-axial flexure strength measurements used the piston-on-3-ball test according to the regulations of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 6872 and were divided into 6 groups, where the radius of the specimens were 12 mm (radius connecting the 3-balls: 3.75 mm), 16 mm (radius connecting the 3-balls: 5 mm), and the thickness were 0.5 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm for each radius.
The bi-axial flexure strength of the MICRONEW™ and RENEW® were higher than the three point flexure strength and the Weibull modulus value were also higher in all of the bi-axial flexure strength groups, indicating that the bi-axial strength test is relatively less affected by experimental error.
In addition, the 2 mm thick specimens had the highest Weibull modulus values in the bi-axial flexure strength test, and the MICRONEW™ group showed no significant statistical difference (p > 0.05). Besides the 2 mm MICRONEW™ group, each group showed significant statistical differences (p < 0.05) according to the thickness of the specimen and the radius connecting the 3-balls.
The results indicate that for the 2 mm group, the bi-axial flexure strength test is a more reliable testing method than the three point flexure strength test. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Remineralization of demineralized teeth enamel with nHAp and nHAp-NaF-PEO nanocomposite
Nazifa Zaman Khan, S. Manjura Hoque, Harinarayan Das, Arup Kumar, Rafiqul Islam, Mozammal Hossain
Biomedical Engineering Advances.2025; 10: 100192. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of CAD/CAM polylactic acid as a material for interim restoration
Won-Il Choi, Lee-gang Yoo, Yu-ri Kim, Bock-Young Jung
Heliyon.2023; 9(4): e15314. CrossRef - The comparisons of layers and the effect of additional firings on flexural strength and translucency of 5Y-ZP
Hyung-Joon Kim, Soo-Yeon Shin
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(3): 111. CrossRef - Effect of coloring liquids on biaxial flexural strength of monolithic zirconia
Chaeyul Jung, Min-Jeong Kim, Jae-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2021; 59(2): 190. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties and Reliability of Sand Casting 3D Printing Materials
Hyeon Jin Son, Seongwan Jang, Hwan Jong Lee, Jeong Jik Yang, Yeong Geun Jeong, Chang-Jun Bae
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(1): 38. CrossRef - Comparison analysis of fracture load and flexural strength of provisional restorative resins fabricated by different methods
Won-Tak Cho, Jae-Won Choi
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2019; 57(3): 225. CrossRef - Effect of Two Polishing Systems on Surface Roughness, Topography, and Flexural Strength of a Monolithic Lithium Disilicate Ceramic
Mahshid Mohammadibassir, Mohammad Bagher Rezvani, Hossein Golzari, Elham Moravej Salehi, Mohammad Amin Fahimi, Mohammad Javad Kharazi Fard
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics according to the Amount of HAp Added in Resin for Tooth Repair
Sungu Hwang, Jinhyuck Lim, Suchak Ryu
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2019; 56(6): 521. CrossRef - Flexural strength and microstructure of two lithium disilicate glass ceramics for CAD/CAM restoration in the dental clinic
Suk-Ho Kang, Juhea Chang, Ho-Hyun Son
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 134. CrossRef
-
1,262
View
-
4
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
IN VITRO MICRO-SHEAR BOND STRENGTH OF FIVE COMPOSITE RESINS TO DENTIN WITH FIVE DIFFERENT DENTIN ADHESIVES
-
Jin-Ho Chung, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):353-364. Published online January 14, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.353
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- ABSTRACT
The purpose of this study was to compare and to evaluate the combination use of 5 kinds of dentin adhesive systems and 5 kinds of composite resins using micro-shear bond test. Five adhesive systems (Prime & Bond NT (PBN), Onecoat bond (OC), Excite (EX), Syntac (SY), Clearfil SE bond (CS)) and five composite resins (Spectrum (SP), Synergy Compact (SC), Tetric Ceram (TC), Clearfil AP-X (CA), Z100 (Z1)) were used for this study (5 × 5 = 25group, n = 14/group). The slices of horizontally sectioned human tooth were bonded with each bonding system and each composite resin, and tested by a micro-shear bond strength test. These results were analyzed statistically. The mean micro-shear bond strength of dentin adhesive systems were in order of CS (22.642 MPa), SY (18.368 MPa), EX (14.599 MPa), OC (13.702 MPa), PBN (12.762 MPa). The mean bond strength of self-etching primer system group (CS, SY) in dentin was higher than that of self-priming adhesive system groups (PBN, EX, OC) significantly (P<0.05). The mean bond strength of composite resins was in order of SP (19.008 MPa), CA (17.532 MPa), SC (15.787 MPa), TC (15.068 MPa), Z1 (14.678 MPa). Micro-shear bond strength of SP was stronger than those of other composite resins significantly (P < 0.05). And those of TC and Z1 were weaker than other composite resins significantly (P < 0.05). No difference was found in micro-shear bond strength of composite resin in self-etching primer adhesive system groups (CS, SY) statistically. However, there was significant difference of micro-shear bond strength of composite resin groups in self-priming adhesive systems group (PBN, EX, OC). The combination of composite resin and dentin adhesive system recommended by manufacturer did not represent positive correlation. It didn’t seem to be a significant factor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 30. CrossRef - Correlation Between the Amount of Linear Polymerization Shrinkage and Cuspal Deflection
S-Y. Lee, S-H. Park
Operative Dentistry.2006; 31(3): 364. CrossRef - Correlation between Linear polymerization shrinkage & tooth cuspal deflection
Soon-Young Lee, Sung-Ho Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(6): 442. CrossRef
-
1,136
View
-
5
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
In vivo quantitative analysis of remineralization effect of remineralization solution "R" of incipient enamel dental caries
-
Myung-Eun Kim, Il-young Jung, Kee-Yeon Kum, Chang-young Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):175-182. Published online March 31, 2002
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.175
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Dental caries is a chronic disease that causes the destruction of tooth structure by the interaction of plaque bacteria, food debris, and saliva.
There has been attempts to induce remineralization by supersaturating the intra-oral environment around the surface enamel, where there is incipient caries.
In this study, supersaturated remineralized solution "R" was applied to specimens with incipient enamel caries, and the quantitative ananlysis of remineralization was evaluated using microradiography. Thirty subjects volunteered to participate in this study. Removable appliances were constructed for the subjects, and the enamel specimen with incipient caries were embedded in the appliances. The subjects wore the intra-oral appliance for 15 days except while eating and sleeping.
The removable appliance were soaked in supersaturated solution "R", saline, or Senstime® to expose the specimen to those solutions three times a day, 5 minutes each time. After 15 days, microradiography was retaken to compare and evaluate remineralization.
The results were as the following:
1. The ratio of remineralized area to demineralized area was significantly higher in the supersaturated solution "R" and Senstime® than in the saline. (p<0.05)
2. Remineralization in the supersaturated buffer solution "R" occurred in the significantly deeper parts of the tooth, compared to the Senstime® group containing high concentration of fluoride.(p<0.05)
As in the above results, the remineralization effect of remineralized buffer solution "R" on incipient enamel caries has been proven. For clinical utilization, further studies on soft tissue reaction and the effect on dentin and cementum are necessary.
In conclusion compared to commercially available fluoride solution, remineralization solution "R" showed better remineralization effect on early enamel caries lesion, so it is considered as effecient solution for clinical application. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 90. CrossRef - Changes in surface content and crystal structure after fluoride gel or hydroxyapatite paste application on stripped enamel
Sang-Cheol Kim, Hyun-Sil Hong, Young-Cheol Hwang
The Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2008; 38(6): 407. CrossRef
-
1,234
View
-
9
Download
-
2
Crossref
|