Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
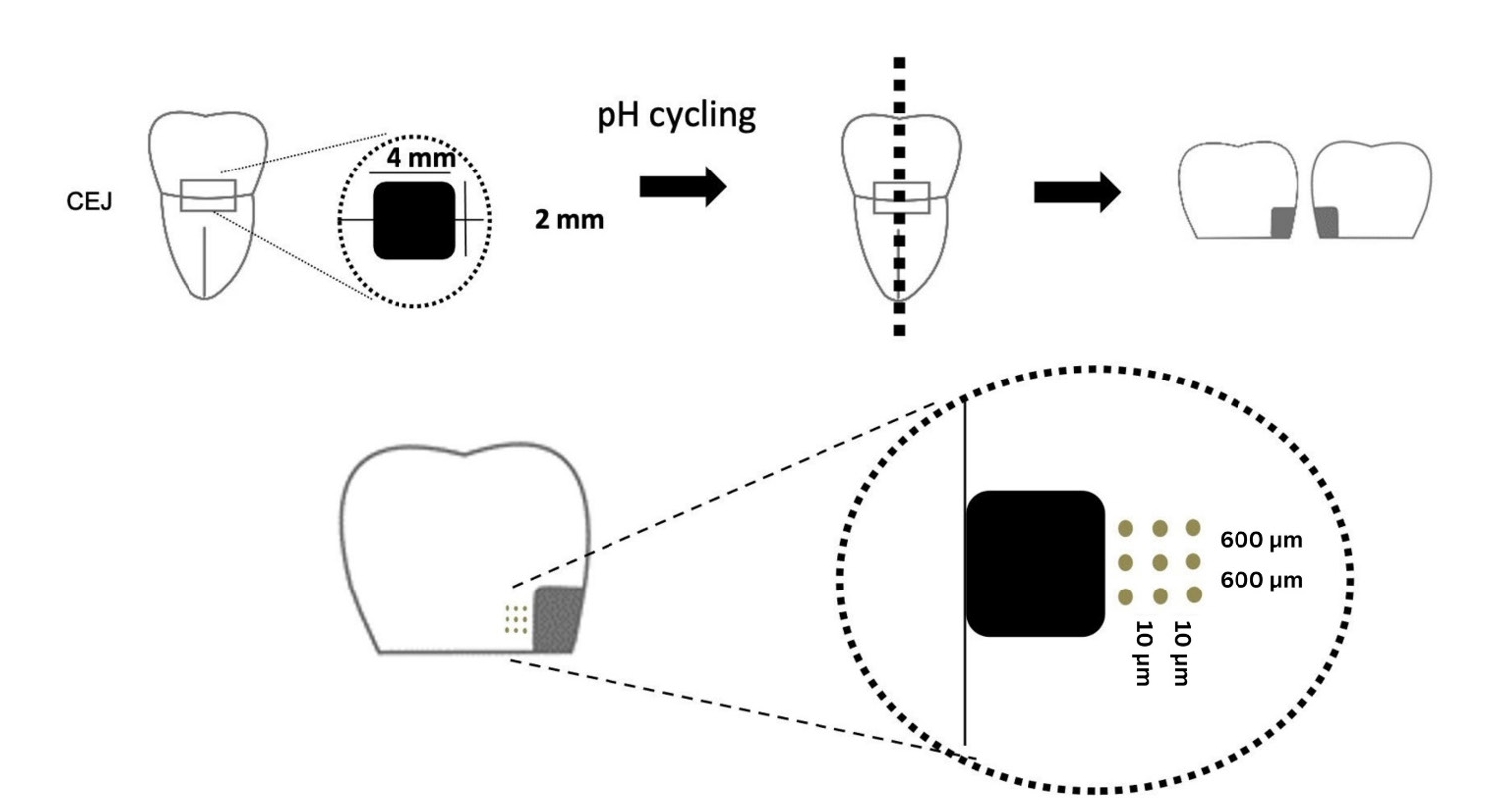
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,806 View
- 213 Download

- The influence of bioactive glass (BGS-7) on enamel remineralization: an in vitro study
- Chaeyoung Lee, Eunseon Jeong, Kun-Hwa Sung, Su-Jung Park, Yoorina Choi
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e33. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to compare the remineralizing capacity of bioactive glass (BGS-7, CGBIO) with other agents.
Methods
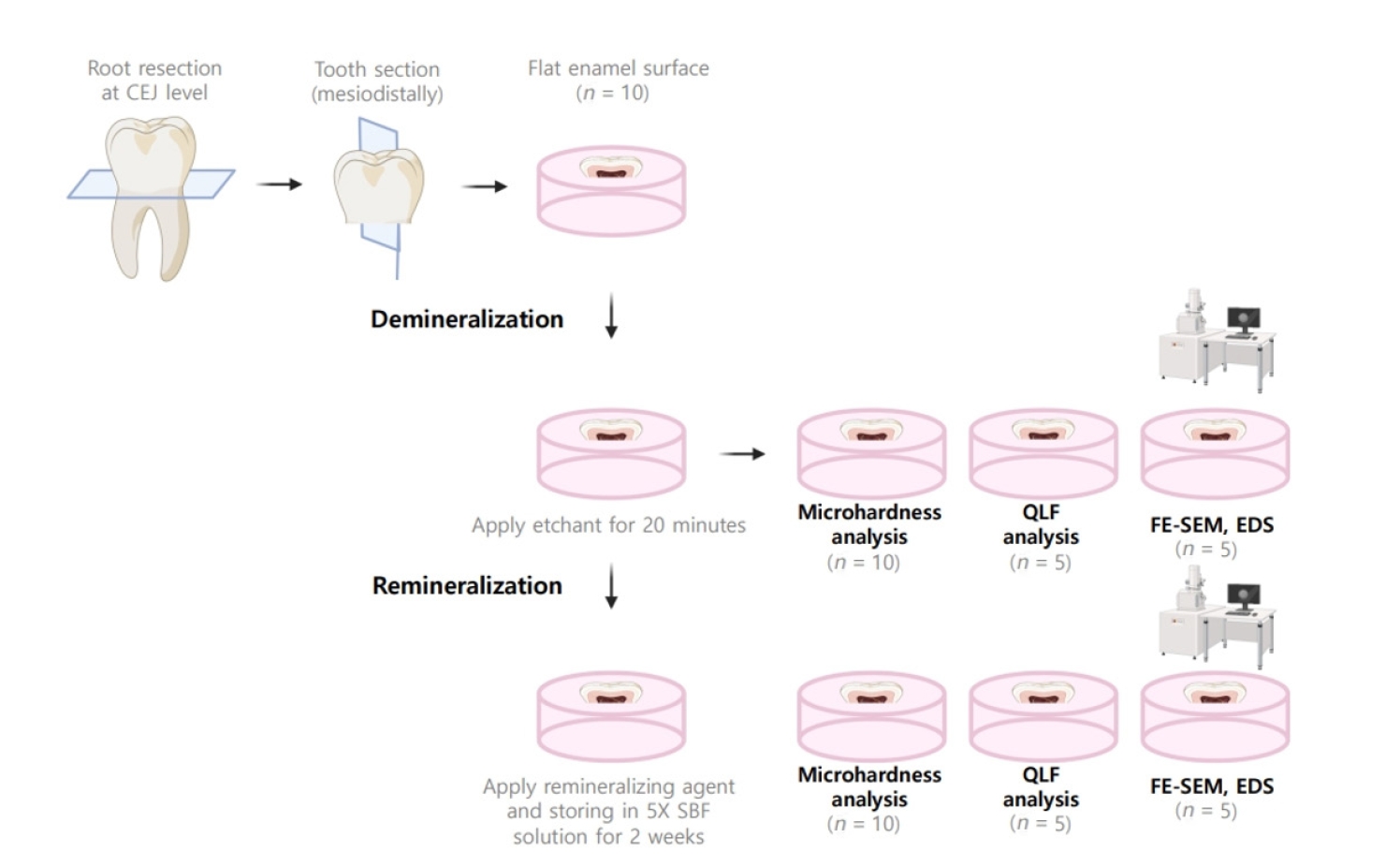
Twenty caries-free third molars were sectioned and demineralized. Specimens were divided into four groups: (1) control, (2) Clinpro XT varnish (Solventum), (3) 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel, and (4) a new type of CaO-SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 system of bioactive glass ceramics (BGS-7). Agents were applied and stored in simulated body fluid at 37℃ for 2 weeks. Microhardness was measured using the Vickers hardness testing method. Five specimens per group were analyzed using quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF) to assess mineral loss. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) were used to examine the surface morphology and elemental composition. Data were analyzed using paired t-test and one-way analysis of variance (p < 0.05).
Results
BGS-7 showed the highest microhardness values and the greatest recovery in QLF analysis (p < 0.05). FE-SEM revealed granular precipitates on demineralized enamel in the BGS-7 group. EDS confirmed the presence of newly formed silicon and fluoride layers.
Conclusions
BGS-7 demonstrated superior remineralization capacity compared to other agents, suggesting its potential as an effective remineralizing material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
Helal F. Hetta, Ibraheem M. Mwafey, Noura H. Abd Ellah, Fawaz E. Alanazi, Yasmin N. Ramadan
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
- 1,627 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of different fluoride application methods on the remineralization of initial carious lesions
- Seon Mi Byeon, Min Ho Lee, Tae Sung Bae
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):121-129. Published online May 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of single and combined applications of fluoride on the amount of fluoride release, and the remineralization and physical properties of enamel.
Materials and Methods Each of four fluoride varnish and gel products (Fluor Protector, FP, Ivoclar Vivadent; Tooth Mousse Plus, TM, GC; 60 Second Gel, A, Germiphene; CavityShield, CS, 3M ESPE) and two fluoride solutions (2% sodium fluoride, N; 8% tin(ii) fluoride, S) were applied on bovine teeth using single and combined methods (10 per group), and then the amount of fluoride release was measured for 4 wk. The electron probe microanalysis and the Vickers microhardness measurements were conducted to assess the effect of fluoride application on the surface properties of bovine teeth.
Results The amount of fluoride release was higher in combined applications than in single application (
p < 0.05). Microhardness values were higher after combined applications of N with FP, TM, and CS than single application of them, and these values were also higher after combined applications of S than single application of A (p < 0.05). Ca and P values were higher in combined applications of N with TM and CS than single application of them (p < 0.05). They were also increased after combined applications of the S with A than after single application (p < 0.05).Conclusions Combined applications of fluoride could be used as a basis to design more effective methods of fluoride application to provide enhanced remineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
Soumyashri Das, Mansi Jain, HP Suma Sogi, Sonali Sukesh K, Apurva Gambhir, FNU Gagandeep
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(11): 1365. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of ozone gel on the initial carious lesions
Maha A. Alsharqawy, Wedad M Etman, Mirvat M Salama, Reda G. Saleh
Tanta Dental Journal.2023; 20(3): 203. CrossRef - Evaluation of Remineralization Potential of Natural Substances on Artificially Induced Carious Lesions in Primary Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Kavitha Ramar, Pooja V Ravi, Rajakumar Sekar
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(2): 244. CrossRef - Upaya Preventif Kesehatan Gigi dan Mulut dengan Aplikasi Fluor pada Gigi Siswa SMPN 77 Jakarta
Agus Ardinansyah, Mochammad Atmaji Windrianto, Nur Hidayati Nosi Prastiyani
Info Abdi Cendekia.2023; 6(2): 74. CrossRef - Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Enamelast® and Fluor defender® fluoride varnishes against Streptococcus mutans biofilm: an in vitro study in primary teeth
M. A. Matar, S. S. Darwish, R. S. Salma, W. A. Lotfy
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(5): 549. CrossRef - In-vitro evaluation of the anti-cariogenic effect of a hybrid coating associated with encapsulated sodium fluoride and stannous chloride in nanoclays on enamel
Sávio José Cardoso BEZERRA, Ítallo Emídio Lira VIANA, Idalina Vieira AOKI, Simone DUARTE, Anderson Takeo HARA, Taís SCARAMUCCI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Salivary Fluoride Concentration after Topical Application of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Sodium Fluoride: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nidhi Agarwal, V Vishnu Priya, Zohra Jabin, Iffat Nasim
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(3): 371. CrossRef - Release and Recharge of Fluoride Ions from Acrylic Resin Modified with Bioactive Glass
Zbigniew Raszewski, Danuta Nowakowska, Wlodzimierz Wieckiewicz, Agnieszka Nowakowska-Toporowska
Polymers.2021; 13(7): 1054. CrossRef - Enamel remineralisation-inducing materials for caries prevention
Sri Kunarti, Widya Saraswati, Dur Muhammad Lashari, Nadhifa Salma, Tasya Nafatila
Dental Journal.2021; 54(3): 165. CrossRef - Fluoride Concentration in Saliva following Professional Topical Application of 2% Sodium Fluoride Solution
Manjit Talwar, Amrit Tewari, H. S. Chawla, Vinod Sachdev, Suresh Sharma
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 423. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory evaluation of the Elgydium Protection caries toothpaste effectiveness in patients with high intensity of dental caries
O. A. Zorina, N. B. Petruhina, A. Z. M, O. A. Boriskina, A. A. Tupicin, V. A. Prohodnaja
Stomatologiya.2019; 98(3): 21. CrossRef - Bleaching of simulated stained-remineralized caries lesions in vitro
Sarah S. Al-Angari, Frank Lippert, Jeffrey A. Platt, George J. Eckert, Carlos González-Cabezas, Yiming Li, Anderson T. Hara
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(4): 1785. CrossRef - Short-Time Antibacterial Effects of Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate on Oral Multispecies Biofilm In Vitro
Yujie Zhou, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Yiran Zou, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Hockin H. K. Xu, Michael D. Weir, Lei Cheng, Yu Chen, Qi Han
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the Application of Different Fluoride Supplements on Enamel Demineralization Adjacent to Orthodontic Brackets: An In Vitro Study
Arman Mohammadi Shayan, Monireh Rassouli, Soodabeh Kimyai, Hadi Valizadeh, Mohammad Hossein Ahangar Atashi, Sahand Rikhtegaran
Iranian Journal of Orthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of nicomethanol hydrofluoride on dental enamel and synthetic apatites: a role for anti-caries protection
N. Sharkov
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2017; 18(6): 411. CrossRef - Intérêt prophylactique et thérapeutique des chewing-gums sans sucre en orthodontie. Une étude menée auprès de professionnels de santé et de patients
Pauline Ferney, François Clauss, Damien Offner, Delphine Wagner
L'Orthodontie Française.2017; 88(3): 275. CrossRef - Silver Diamine Fluoride Has Efficacy in Controlling Caries Progression in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana Cláudia Chibinski, Letícia Maíra Wambier, Juliana Feltrin, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio, Denise Stadler Wambier, Alessandra Reis
Caries Research.2017; 51(5): 527. CrossRef - Dental Caries Management of a Patient with a High Caries Risk Based on the Caries Risk Assessment: a Case Peport
Dong-Hyun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(3): 231. CrossRef
- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
- 2,250 View
- 13 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Comparative efficacy of photo-activated disinfection and calcium hydroxide for disinfection of remaining carious dentin in deep cavities: a clinical study
- Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani, Naseem Shah
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):195-200. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To comparatively evaluate the efficacy of photo-activated disinfection (PAD), calcium hydroxide (CH) and their combination on the treatment outcome of indirect pulp treatment (IPT).
Materials and Methods Institutional ethical clearance and informed consent of the patients were taken. The study was also registered with clinical registry of India. Sixty permanent molars exhibiting deep occlusal carious lesion in patients with the age range of 18 - 22 yr were included. Clinical and radiographic evaluation and set inclusion and exclusion criteria's were followed. Gross caries excavation was accomplished. In group I (
n = 20) PAD was applied for sixty seconds. In group II (n = 20), CH was applied to the remaining carious dentin, while in group III (n = 20), PAD application was followed by CH placement. The teeth were permanently restored. They were clinically and radiographically followed-up at 45 day, 6 mon and 12 mon. Relative density of the remaining affected dentin was measured by 'Radiovisiography (RVG) densitometric' analysis.Results Successful outcome with an increase in radiographic grey values were observed in all three groups. However, on inter-group comparison, this change was not significant (
p > 0.05).Conclusions PAD and CH both have equal disinfection efficacy in the treatment of deep carious dentin. PAD alone is as effective for treatment of deep carious lesion as calcium hydroxide and hence can be used as an alternative to CH. They can be used independently in IPT, since combining both does not offer any additional therapeutic benefits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation between Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Gel-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in Indirect Pulp Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Yusuf Chunawala, BK Vanishree, Supriya S Dighe, Rooposhi Saha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 17(12): 1383. CrossRef - Potentialities of photoactivated disinfection in dentistry
E.I. Utkina, M.A. Gorbatova, A.M. Grjibovski, L.N. Gorbatova, A.A. Simakova
Stomatology.2023; 102(2): 84. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic evaluation of diode laser and chemical disinfection in comparison to selective caries removal in management of patients with deep carious lesions
Mohamed Bahgat AbdelHamid, Ahmed Fawzy Abo Elezz, Ola M. Ibrahim Fahmy
Lasers in Dental Science.2022; 6(4): 219. CrossRef - Commercially Available Ion-Releasing Dental Materials and Cavitated Carious Lesions: Clinical Treatment Options
Amel Slimani, Salvatore Sauro, Patricia Gatón Hernández, Sevil Gurgan, Lezize Sebnem Turkun, Ivana Miletic, Avijit Banerjee, Hervé Tassery
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6272. CrossRef - Radiological Appraisal of Biodentine and Pulpotec Individually or in Combination with Photo-activated Disinfection as Pulp-capping Cements in Mature Teeth
Pratik Agrawal, Gaurav Patri, Surabhi Soumya, Prasanti K Pradhan, Vijeta Patri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1014. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic evaluation of indirect pulp treatment of young permanent molars using photo-activated oral disinfection versus calcium hydroxide: a randomized controlled pilot trial
Marwa Aly Elchaghaby, Dalia Mohamed Moheb, Osama Ibrahim El Shahawy, Ahmed Mohamed Abd Alsamad, Mervat Abdel Moniem Rashed
BDJ Open.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Guidelines for the selection, use, and maintenance of LED light-curing units - Part 1
A. C. Shortall, R. B. Price, L. MacKenzie, F. J. T. Burke
British Dental Journal.2016; 221(8): 453. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation between Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Gel-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in Indirect Pulp Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- 1,626 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Crossref

-
How to design
in situ studies: an evaluation of experimental protocols - Young-Hye Sung, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):164-171. Published online May 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Designing
in situ models for caries research is a demanding procedure, as both clinical and laboratory parameters need to be incorporated in a single study. This study aimed to construct an informative guideline for planningin situ models relevant to preexisting caries studies.Materials and Methods An electronic literature search of the PubMed database was performed. A total 191 of full articles written in English were included and data were extracted from materials and methods. Multiple variables were analyzed in relation to the publication types, participant characteristics, specimen and appliance factors, and other conditions. Frequencies and percentages were displayed to summarize the data and the Pearson's chi-square test was used to assess a statistical significance (
p < 0.05).Results There were many parameters commonly included in the majority of
in situ models such as inclusion criteria, sample sizes, sample allocation methods, tooth types, intraoral appliance types, sterilization methods, study periods, outcome measures, experimental interventions, etc. Interrelationships existed between the main research topics and some parameters (outcome measures and sample allocation methods) among the evaluated articles.Conclusions It will be possible to establish standardized
in situ protocols according to the research topics. Furthermore, data collaboration from comparable studies would be enhanced by homogeneous study designs.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- What is the effectiveness of titanium tetrafluoride to prevent or treat dental caries and tooth erosion? A systematic review
Ana Beatriz Chevitarese, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Guido A. Marañón-Vásquez, Danielle Masterson, Matheus Pithon, Lucianne Cople Maia
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2022; 80(6): 441. CrossRef - Effect of fluoride group on dental erosion associated or not with abrasion in human enamel: A systematic review with network metanalysis
Bruna Machado da Silva, Daniela Rios, Gerson Aparecido Foratori-Junior, Ana Carolina Magalhães, Marília Afonso Rabelo Buzalaf, Silvia De Carvalho Sales Peres, Heitor Marques Honório
Archives of Oral Biology.2022; 144: 105568. CrossRef - Multimodal Human and Environmental Sensing for Longitudinal Behavioral Studies in Naturalistic Settings: Framework for Sensor Selection, Deployment, and Management
Brandon M Booth, Karel Mundnich, Tiantian Feng, Amrutha Nadarajan, Tiago H Falk, Jennifer L Villatte, Emilio Ferrara, Shrikanth Narayanan
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2019; 21(8): e12832. CrossRef - Evaluation of an antibacterial orthodontic adhesive incorporated with niobium-based bioglass: an in situ study
Felipe Weidenbach DEGRAZIA, Aline Segatto Pires ALTMANN, Carolina Jung FERREIRA, Rodrigo Alex ARTHUR, Vicente Castelo Branco LEITUNE, Susana Maria Werner SAMUEL, Fabrício Mezzomo COLLARES
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the Common Models Used in Mechanistic Studies on Demineralization-Remineralization for Cariology Research
Ollie Yiru Yu, Irene Shuping Zhao, May Lei Mei, Edward Chin-Man Lo, Chun-Hung Chu
Dentistry Journal.2017; 5(2): 20. CrossRef - Effects of rinsing with arginine bicarbonate and urea solutions on initial enamel lesions in situ
Y Yu, X Wang, C Ge, B Wang, C Cheng, Y‐H Gan
Oral Diseases.2017; 23(3): 353. CrossRef - The cariogenicity of commercial infant formulas: a systematic review
S. F. Tan, H. J. Tong, X. Y. Lin, B. Mok, C. H. Hong
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2016; 17(3): 145. CrossRef - In situ antibiofilm effect of glass-ionomer cement containing dimethylaminododecyl methacrylate
Jin Feng, Lei Cheng, Xuedong Zhou, Hockin H.K. Xu, Michael D. Weir, Markus Meyer, Hans Maurer, Qian Li, Matthias Hannig, Stefan Rupf
Dental Materials.2015; 31(8): 992. CrossRef
- What is the effectiveness of titanium tetrafluoride to prevent or treat dental caries and tooth erosion? A systematic review
- 1,493 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of matrix metallproteinases on dentin bonding and strategies to increase durability of dentin adhesion
- Jung-Hyun Lee, Juhea Chang, Ho-Hyun Son
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):2-8. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The limited durability of resin-dentin bonds severely compromises the longevity of composite resin restorations. Resin-dentin bond degradation might occur via degradation of water-rich and resin sparse collagen matrices by host-derived matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This review article provides overview of current knowledge of the role of MMPs in dentin matrix degradation and four experimental strategies for extending the longevity of resin-dentin bonds. They include: (1) the use of broad-spectrum inhibitors of MMPs, (2) the use of cross-linking agents for silencing the activities of MMPs, (3) ethanol wet-bonding with hydrophobic resin, (4) biomimetic remineralization of water-filled collagen matrix. A combination of these strategies will be able to overcome the limitations in resin-dentin adhesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Remineralization Effects of Silver Fluoride, Silver Diamine Fluoride, and Sodium Fluoride Varnish
Jihyeon Lee, Hwalim Lee, Jongsoo Kim, Joonhaeng Lee, Jongbin Kim, Jisun Shin, Miran Han
International Journal of Clinical Preventive Dentistry.2024; 20(1): 19. CrossRef
- Remineralization Effects of Silver Fluoride, Silver Diamine Fluoride, and Sodium Fluoride Varnish
- 1,374 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The remineralization aspect of enamel according to change of the degree of saturation of the organic acid buffering solution in pH 5.5
- Jin-Sung Park, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):96-105. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.096
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to observe and compare the remineralization tendencies of artificial enamel caries lesion by remineralization solutions of different degree of saturations at pH 5.5, using a polarizing microscope and computer programs (Photoshop, Image pro plus, Scion Image, Excel).
For this study, 48 sound permanent teeth with no signs of demineralization, cracks, or dental restorations were used. The specimens were immersed in lactic acid demineralization solution for 2 days in order to produce artificial dental caries that consist of surface and subsurface lesions. Each of 9 or 10 specimens was immersed in pH 5.5 lactic acid buffering remineralization solution of four different degrees of saturation (0.507, 0.394, 0.301, and 0.251) for 12 days. After the demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by a polarizing microscope (×100). The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens, and using computer programs, the density of caries lesions were estimated.
While the group with the lowest degree of saturation (0.251) showed total remineralization feature from the surface to the subsurface of the lesion, the group with the highest degree of saturation (0.507) showed demineralization mainly on the surface of the lesion at the constant organic acid concentration 0.01 M and pH 5.5.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of a Mouthwash Containing Glycyrrhiza uralensis Extract for Preventing Dental Caries
Yu-Rin Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 242. CrossRef - Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
- A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of a Mouthwash Containing Glycyrrhiza uralensis Extract for Preventing Dental Caries
- 1,129 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effects of the fluoride concentration of acidulated buffer solutions on dentine remineralization
- Won-Sub Han, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):526-536. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.526
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this vitro-study is to evaluate the effects of fluoride on remineralization of artificial dentine caries. 10 sound permanent premolars, which were extracted for orthodontic reason within 1 week, were used for this study. Artificial dentine caries was created by using a partially saturated buffer solution for 2 days with grounded thin specimens and fractured whole-body specimens. Remineralization solutions with three different fluoride concentration (1 ppm, 2 ppm and 4 ppm) were used on demineralized-specimens for 7 days. Polarizing microscope and scanning electron microscope were used for the evaluation of the mineral distribution profile and morphology of crystallites of hydroxyapatite.
The results were as follows :
When treated with the fluoride solutions, the demineralized dentine specimens showed remineralization of the upper part and demineralization of the lower part of the lesion body simultaneously.
As the concentration of fluoride increased, the mineral precipitation in the caries dentine increased. The mineral precipitation mainly occurred in the surface layer in 1 and 2 ppm-specimens and in the whole lesion body in 4 ppm-specimens.
When treated with the fluoride solution, the hydroxyapatite crystals grew. This crystal growth was even observed in the lower part of the lesion body which had shown the loss of mineral.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infant Oral Health Care Concerning Education of Mothers – Part 2
Lehya Mounica Kadali, Viddyasagar Mopagar, Shilpa Shetty, Shridhar Shetty, Venkatesh Kodgi, Shantanu Chaudhari
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(31): 2538. CrossRef
- Infant Oral Health Care Concerning Education of Mothers – Part 2
- 1,140 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- THE DYNAMIC CHANGE OF ARTIFICIALLY DEMINERALIZED ENAMEL BY DEGREE OF SATURATION OF REMINERALIZATION SOLUTION AT pH 4.3
- Ji-Sook Yi, Bung-Duk Roh, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Hyung-Kyu Gong, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):20-29. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.020
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study is to observe and compare the dynamic change of artificially demineralized enamel by remineralization solutions of different degrees of saturation at pH 4.3.
In this study, 30 enamel specimens were demineralized artificially by lactic acid buffered solution. Each of 10 specimens was immersed in pH 4.3 remineralization solution of three different degrees of saturation (0.22, 0.30, 0.35) for 10 days. After demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by a polarizing microscope (× 100). The density of lesion were determined from images taken after demineralization and remineralization.
During remineralization process, mineral deposition and mineral loss occurred at the same time. After remineralization, total mineral amount and width of surface lesion increased in all groups. The higher degree of saturation was, the more mineral deposition occurred in surface lesion and the amount of mineral deposition was not much in subsurface lesion. Total demineralized depth increased in all groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
- 1,214 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of lactic acid concentration and ph of lactic acid buffer solutions on enamel remineralization
- Jung-Won Kwon, Duk-Gyu Suh, Yun-Jung Song, Yun Lee, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):507-517. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.507
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are considerable in vitro and in vivo evidences for remineralization and demineralization occurring simultaneously in incipient enamel caries. In order to "heal"the incipient dental caries, many experiments have been carried out to determine the optimal conditions for remineralization. It was shown that remineralization is affected by different pH, lactic acid concentrations, chemical composition of the enamel, fluoride concentrations, etc.
Eighty specimens from sound permanent teeth without demineralization or cracks, 0.15 mm in thickness, were immersed in lactic acid buffered demineralization solutions for 3 days. Dental caries with a surface zone and subsurface lesion were artificially produced. Groups of 10 specimens were immersed for 10 or 12 days in lactic acid buffered remineralization solutions consisting of pH 4.3 or pH 6.0, and 100, 50, 25, or 10 mM lactic acid. After demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by polarizing microscopy (x100) and micro-computed tomography. The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens and the density of the caries lesions was determined.
As the lactic acid concentration of the remineralization solutions with pH 4.3 was higher, the surface zone of the carious enamel increased and an isotropic zone of the subsurface lesion was found. However, the total decalcification depth increased at the same time.
In the remineralization solutions with pH 6.0, only the surface zone increased slightly but there was no significant change in the total decalcification depth and subsurface zone.
In the lactic acid buffer solutions with the lower pH and higher lactic acid concentration, there were dynamic changes at the deep area of the dental carious lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
- 1,598 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The remineralizing features of pH 5.5 solutions of different degree of saturations on artificially demineralized enamel
- Young-Jun Kwak, Eui-seoug Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Hyung Kyu Gong, Yoon Lee, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):481-492. Published online September 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.481
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to observe and compare the remineralization tendencies of artificially demineralized enamel by remineralization solutions of different degree of saturations at pH 5.5, using a polarizing microscope and computer programs (Photoshop, Image pro plus, Scion Image, Excel).
For this study, 36 sound permanent teeth with no signs of demineralization, cracks, or dental restorations were used. The specimens were immersed in lactic acid demineralization solution for 3 days in order to produce dental caries artificially that consist of surface and subsurface lesions. Each of 9 or 10 specimens was immersed in pH 5.5 lactic acid buffered remineralization solution of three different degrees of saturation (0.25, 0.30, 0.35) for 12 days. After the demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by a polarizing microscope (× 100). The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens, and using computer programs, the density of caries lesions were determined.
In conclusion, in the group with the lowest degree of saturation, remineralization occurred thoroughly from the surface to the subsurface lesion, whereas in the groups with greater degree of saturation showed no significant change in the subsurface lesion, although there was corresponding increase in the remineralization width on the surface zones.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
- 1,287 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The change of the configuration of hydroxyapatite crystals in enamel by changes of pH and degree of saturation of lactic acid buffer solution
- Young-Eui Chon, Il-Young Jung, Bung-Duk Roh, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):498-513. Published online November 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.498
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Since it was reported that incipient enamel caries can be recovered, previous studies have quantitatively evaluated that enamel artificial caries have been remineralized with fluoride, showing simultaneously the increase of width of surface layer and the decrease of width of the body of legion. There is, however, little report which showed that remineralization could occur without fluoride. In addition, the observations on the change of hydroxyapatite crystals also have been scarcely seen.
In this study, enamel caries in intact premolars or molars was induced by using lactic acidulated buffering solutions over 2 days. Then decalcified specimens were remineralized by seven groups of solutions using different degree of saturation (0.212, 0.239, 0.301, 0.355) and different pH (5.0, 5.5, 6.0) over 10 days. A qualitative comparison to changes of hydroxyapatite crystals after fracturing teeth was made under SEM (scanning electron microscopy) and AFM (atomic force microscopy).
The results were as follows:
1. The size of hydroxyapatite crystals in demineralized area was smaller than the normal ones. While the space among crystals was expanded, it was observed that crystals are arranged irregularly.
2. In remineralized enamel area, the enlarged crystals with various shape were observed when the crystals were fused and new small crystals in intercrystalline spaces were deposited.
3. Group 3 and 4 with higher degree of saturation at same pH showed the formation of large clusters by aggregation of small crystals from the surface layer to the lesion body than group 1 and 2 with relatively low degree of saturation at same pH did. Especially group 4 showed complete remineralization to the body of lesions. Group 5 and 6 with lower pH at similar degree of saturation showed remineralization to the body of lesions while group 7 didn't show it. Unlike in Group 3 and 4, Group 5 and 6 showed that each particle was densely distributed with clear appearance rather than crystals form clusters together.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anticariogenic Sanative Effect of Aluminum Gallium Arsenide Crystals on Hydroxyapatite Crystals
Sonali Sharma, Mithra N. Hegde, Sindhu Ramesh
Crystals.2022; 12(12): 1841. CrossRef
- Anticariogenic Sanative Effect of Aluminum Gallium Arsenide Crystals on Hydroxyapatite Crystals
- 1,699 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of the pH of remineralized buffer solutions on dentin remineralization
- Sung-Chul Kim, Bung-Duk Roh, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):151-161. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental caries is the most common disease in the oral cavity. However, the mechanism and treatment of dental caries is not completely understood since many complex factors are involved. Especially the effect of pH on remineralization of early stage of dental caries is still controversial.
In this study, dental caries in dentin was induced by using lactic acidulated buffering solutions and the loss of inorganic substance was measured. Also decalcified specimens were remineralized by three groups of solution with different pH (group of pH 4.3, 5.0, and 5.5). Then, the amount and the area of inorganic substance precipitation was quantitatively analyzed with microradiograph. Also a qualitative comparison of the normal phase, the demineralized phase, and the remineralized phase of hydroxyapatite crystal was made under SEM.
The results were as follows;
In microradiograghic analysis, as the pH increased, the amount of remineralization in decalcified dentin tended to increase significantly. As the pH decreaced, deeper decalcification, however, occurred along with remineralization. The group of pH 5.5 had a tendency to be remineralized without demineralization (p < 0.05).
In SEM view, the remineralization in dentine caries occurred from the hydroxyapatite crystal surface surrounding the mesh of organic matrix, and eventually filled up the demineralized area.
5 days after remineralization, hydroxyapatite crystal grew bigger with deposition of inorganic substance in pH 4.3 and 5.0 group, and the crystal in the remineralized area appeared to return to normal. After 10 days, the crystals in group of pH 4.3 and 5.0, which grew bigger after 5 days of remineralization, turned back to their normal size, but in group of pH 5.5, some crystals were found to double their size.
In according to the results of this experiment, the decalcifying and remineralizing process of dentine is neither simple nor independent, but a dynamic process in which decalcification and remineralization occur simultaneously. The remineralization process occurred from the hydroxyapatite crystal surface.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Remineralization Effects of Silver Fluoride, Silver Diamine Fluoride, and Sodium Fluoride Varnish
Jihyeon Lee, Hwalim Lee, Jongsoo Kim, Joonhaeng Lee, Jongbin Kim, Jisun Shin, Miran Han
International Journal of Clinical Preventive Dentistry.2024; 20(1): 19. CrossRef - The remineralizing features of pH 5.5 solutions of different degree of saturations on artificially demineralized enamel
Young-Jun Kwak, Eui-seoug Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Hyung Kyu Gong, Yoon Lee, Chan-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(5): 481. CrossRef
- Remineralization Effects of Silver Fluoride, Silver Diamine Fluoride, and Sodium Fluoride Varnish
- 1,131 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
In vivo quantitative analysis of remineralization effect of remineralization solution "R" of incipient enamel dental caries - Myung-Eun Kim, Il-young Jung, Kee-Yeon Kum, Chang-young Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):175-182. Published online March 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.175
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental caries is a chronic disease that causes the destruction of tooth structure by the interaction of plaque bacteria, food debris, and saliva.
There has been attempts to induce remineralization by supersaturating the intra-oral environment around the surface enamel, where there is incipient caries.
In this study, supersaturated remineralized solution "R" was applied to specimens with incipient enamel caries, and the quantitative ananlysis of remineralization was evaluated using microradiography. Thirty subjects volunteered to participate in this study. Removable appliances were constructed for the subjects, and the enamel specimen with incipient caries were embedded in the appliances. The subjects wore the intra-oral appliance for 15 days except while eating and sleeping.
The removable appliance were soaked in supersaturated solution "R", saline, or Senstime® to expose the specimen to those solutions three times a day, 5 minutes each time. After 15 days, microradiography was retaken to compare and evaluate remineralization.
The results were as the following:
1. The ratio of remineralized area to demineralized area was significantly higher in the supersaturated solution "R" and Senstime® than in the saline. (p<0.05)
2. Remineralization in the supersaturated buffer solution "R" occurred in the significantly deeper parts of the tooth, compared to the Senstime® group containing high concentration of fluoride.(p<0.05)
As in the above results, the remineralization effect of remineralized buffer solution "R" on incipient enamel caries has been proven. For clinical utilization, further studies on soft tissue reaction and the effect on dentin and cementum are necessary.
In conclusion compared to commercially available fluoride solution, remineralization solution "R" showed better remineralization effect on early enamel caries lesion, so it is considered as effecient solution for clinical application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 90. CrossRef - Changes in surface content and crystal structure after fluoride gel or hydroxyapatite paste application on stripped enamel
Sang-Cheol Kim, Hyun-Sil Hong, Young-Cheol Hwang
The Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2008; 38(6): 407. CrossRef
- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
- 1,210 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


