Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Ingestion and surgical retrieval of an endodontic file: a case report
- Devon Marta Ptak, Elinor Alon, Robert Bruce Amato, Julia Tassinari, Adrian Velasquez
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e32. Published online September 2, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
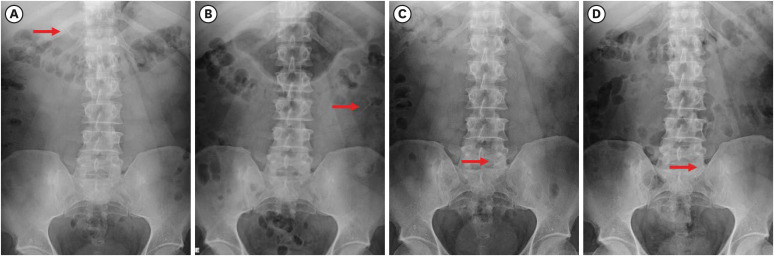
ePub Ingestions and aspirations of foreign bodies are rare, but do occasionally occur during dental treatment. Although reports exist, few include photos demonstrating the extensive surgical intervention that may be necessary to manage such events. Perhaps this lack of visualization, and associated lack of awareness, is one of the reasons some clinicians still provide non-surgical root canal therapy (NSRCT) without a rubber dam. This case report outlines the medical treatment of a 30-year-old male who initially presented to a general dentist’s office (not associated with the authors) for NSRCT of their mandibular right first molar. A rubber dam was not used for this procedure, during which the accidental ingestion of an endodontic K-file occurred. The patient was subsequently hospitalized for evaluation and treatment, consisting of numerous imaging studies, endoscopic evaluation, and surgical removal of the file from his small intestine. The ingestion of foreign bodies, and the associated complications, can be reduced through the routine use of a rubber dam, which is considered the standard of care for NSRCT. This case graphically illustrates the potential consequences associated with deviating from the standard of care and should remind clinicians that a rubber dam is necessary for all cases of NSRCT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dental Dam Isolation for Crown Removal, Atraumatic Tooth Extraction, Immediate Implant Placement, and Restoration Cementation: A Case Study
G Guzman-Perez, S Rojas-Rueda, F Floriani, A Unnadkat, C-C Fu, CA Jurado
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(1): 5. CrossRef - Patient and Operator Experiences with Conventional Rubber Dam and OptiDam: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Rashed F. Binqali, Abdulwahab M. Alghamdi, Mishal S. Aloufi, Suliman A. Alharbi, Omair M. Bukhari, Reham M. Alsamman
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(6): 554. CrossRef
- Dental Dam Isolation for Crown Removal, Atraumatic Tooth Extraction, Immediate Implant Placement, and Restoration Cementation: A Case Study
- 4,462 View
- 98 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
- Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e33. Published online August 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
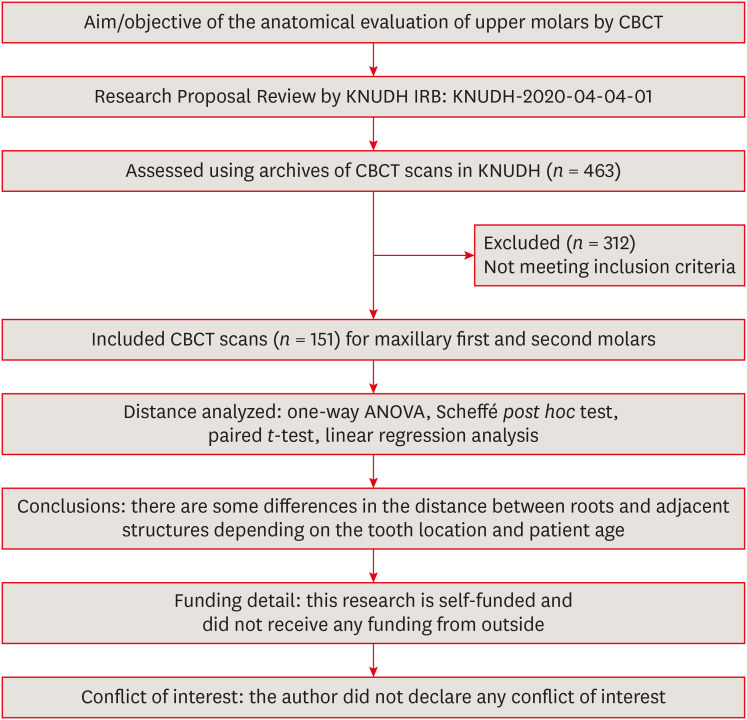
ePub Objectives This study aimed to analyze the proximity of maxillary molar roots to their overlying cortical bone surfaces and the maxillary sinus.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomographic images of 151 patients with completely erupted upper molars that had 3 separate roots were studied. The following distances were measured: from the root apex to the cortical plate and maxillary sinus floor, and from the apical 3-mm level of the root to the cortical plate. Differences between groups were analyzed with 1-way analysis of variance and the Scheffé
post hoc test, the significance of differences between cone-beam computed tomography views with the pairedt -test, and the significance of differences among age groups with linear regression analysis. The significance level was set atp < 0.05.Results The mesiobuccal and distobuccal root apexes of maxillary second molars were more distant from the buccal cortical plate than the maxillary first molars (
p < 0.05). The apical 3-mm level of the mesiobuccal root of the first molar was closer to the buccal cortical bone than the second molar (p < 0.05). In the maxillary first molars, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone decreased in all roots with age (p < 0.05). In all root apexes of both molars, the difference in the vertical level between the maxillary sinus floor and the root apex increased with age (p < 0.05).Conclusions Awareness of the anatomical profile of maxillary molar apices in relation to the cortical bones and maxillary sinus will be beneficial for apical surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Xiaoxiang Huang, Jun Xu, Benxiang Hou, Ying Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Periapical bone loss configuration in sub-Saudi patients afflicted with periapical abscesses: A 3D cone-beam computed tomography analysis
Swati A. Srivastava, Rahaf A. Alawajy, Rehab Abdelaziz, Elzahraa A. Eldwakhly, Selma A. Saadaldin, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Fahda Nabeel Algahtani, Mai Salah Soliman, Manal M. Abdelhafeez
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 144. CrossRef
- Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
- 3,247 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin in endodontic microsurgery: a report of 2 cases
- Mariana Domingos Pires, Jorge N. R. Martins, Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Beatriz Pereira, António Ginjeira
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e17. Published online March 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
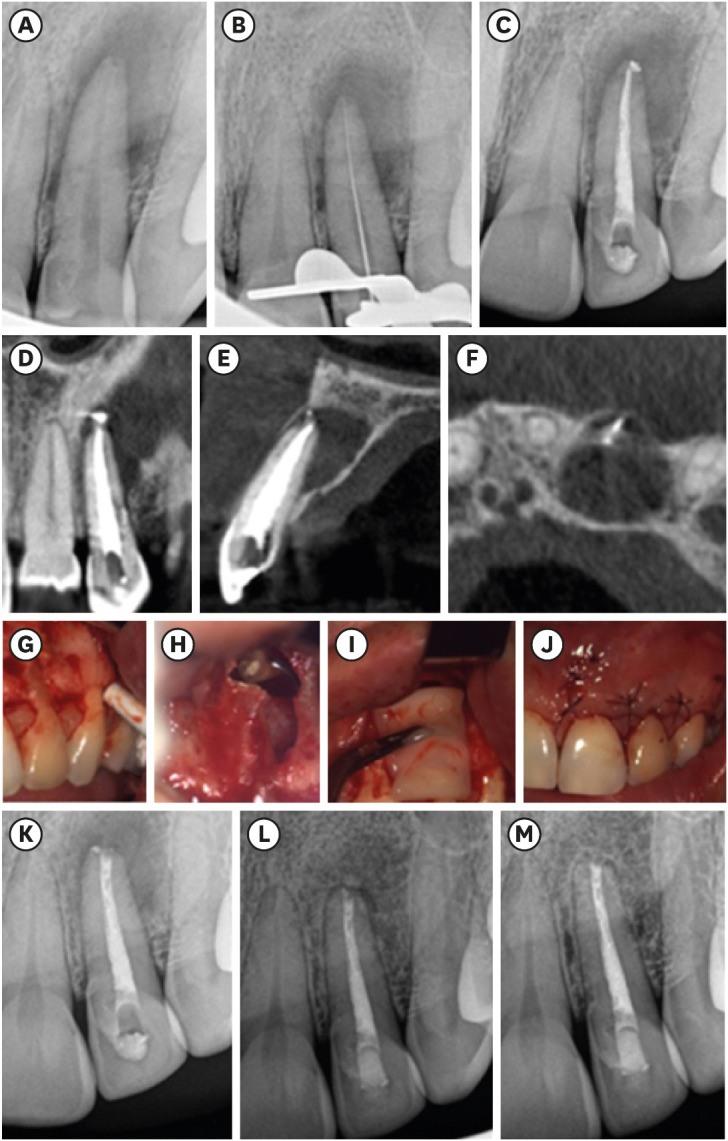
ePub Endodontic microsurgery is a predictable treatment option when orthograde treatment or retreatment is unsuccessful or unfeasible. However, when there is a gross compromise of periapical bone, achievement of bone regeneration after the surgical procedure may be hampered. In such cases, the application of guided tissue regeneration principles, with adjunctive use of leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin to fill the bone defect as a bone substitute and as a membrane to cover the site, provides a cost-effective solution with the benefits of accelerated physiological healing and reduced post-surgical pain and discomfort. This case report presents 2 cases of endodontic microsurgery of the upper lateral incisors with loss of buccal cortical plate, where platelet-rich fibrin was successfully applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Focuses and Trends of Research on Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
Ying Zhao, Chen Dong, Liumeizi Fan, Ting Lei, Xin Ge, Zhou Yu, Sheng Hu
Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery.2024; 57(05): 356. CrossRef
- Focuses and Trends of Research on Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
- 1,720 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The application of “bone window technique” using piezoelectric saws and a CAD/CAM-guided surgical stent in endodontic microsurgery on a mandibular molar case
- Ukseong Kim, Sunil Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e27. Published online May 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
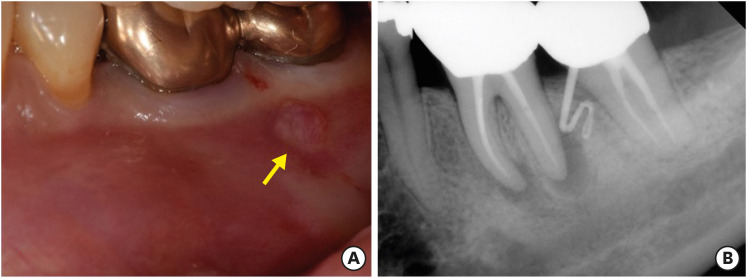
ePub Apical surgery for a mandibular molar is still challenging for many reasons. This report describes the applications of computer-guided cortical ‘bone-window technique’ using piezoelectric saws that prevented any nerve damage in performing endodontic microsurgery of a mandibular molar. A 49-year-old woman presented with gumboil on tooth #36 (previously endodontically treated tooth) and was diagnosed with chronic apical abscess. Periapical lesions were confirmed using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Endodontic microsurgery for the mesial and distal roots of tooth #36 was planned. Following the transfer of data of the CBCT images and the scanned cast to an implant surgical planning program, data from both devices were merged. A surgical stent was designed, on the superimposed three-dimensional model, to guide the preparation of a cortical window on the buccal side of tooth #36. Endodontic microsurgery was performed with a printed surgical template. Minimal osteotomy was required and preservation of the buccal cortical plate rendered this endodontic surgery less traumatic. No postoperative complications such as mental nerve damage were reported. Window technique guided by a computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacture based surgical template can be considerably useful in endodontic microsurgery in complicated cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimising Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: Evidence, Uncertainties and Future Directions
Ukseong Kim, Euiseong Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy of Guided Dual Technique in Esthetic Crown Lengthening: A Prospective Case‐Series Study
Meritxell Enfedaque‐Prat, Albert González‐Barnadas, Adrià Jorba‐García, Javi Vilarrasa, Jorge Toledano‐Serrabona, Rui Figueiredo, Eduard Valmaseda‐Castellón, Octavi Camps‐Font
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1284. CrossRef - Guided endodontics in the application of personalized mini-invasive treatment in clinical cases: a literature review
Shuangshuang Ren, Wanping Wang, Mingyue Cheng, Wenyue Tang, Yue Zhao, Leiying Miao
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Accurately Defining the Location and Dimension of the Bony Lid Under the Guidance of Dynamic Navigation: Report on Three Cases
Kailiang Tang, Xiaole Zhang, Qibao Wang, Xinyu Zhao, Xijiao Yu, Yi Du
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 785. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Vertical Incision Subperiosteal Tunnelling Technique for Targeted Endodontic Surgery: Technical Overview and a Case Report
Francesc Abella Sans, Jaime Barragán Montes, Tomasz Zbozen, Nandini Suresh, Lalli Dharmarajan, Paul M. H. Dummer, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1799. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of a Mandibular Molar Using a Dynamic Navigation System (DNS) and Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Gustavo Castillo, Silvia Restrepo-Méndez, Oscar Zuluaga, Paola Escobar-Villegas
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2024; 3: 1. CrossRef - The bone lid technique in endodontic microsurgery
Min Zhang, He Liu, Ya Shen
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024; 47(7): 3126. CrossRef - Guided Periradicular Surgery with Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Osteotomy: A Case Report
Julian Torres Celeita, Johanna Hernández la Rotta, Amdie Chirinos Salazar, Jorge Fandiño Rodríguez, Laura López Rincón, Mauren Orduz Solorzano, Diana Parra Galvis, Oscar Jiménez Peña
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Piezoelectric Endodontic Microsurgery with Modified Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Rojas, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 34. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiological outcomes of dynamic navigation in endodontic microsurgery: a prospective study
Chen Chen, Rui Zhang, Wei Zhang, Fangzhe Li, Zan Wang, Li Qin, Yun Chen, Zhuan Bian, Liuyan Meng
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(9): 5317. CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Failure case analysis during each stage of endodontic microsurgery: A retrospective study based on clinical databases
Changwoo Ryu, Sooil Shin, Yong-Bum Cho, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 160. CrossRef - Piezoelectric Device and Dynamic Navigation System Integration for Bone Window-Guided Surgery
Frederico C. Martinho, Ina L. Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(12): 1698. CrossRef - Bone Window Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery – Report of Two Cases
Spyros Floratos, Vasileios Molonis, Apostolos Tsolakis, Stylianos Kykalos, Konstantinos Kontzoglou
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022; 2: 24. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef
- Optimising Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: Evidence, Uncertainties and Future Directions
- 2,259 View
- 40 Download
- 17 Crossref

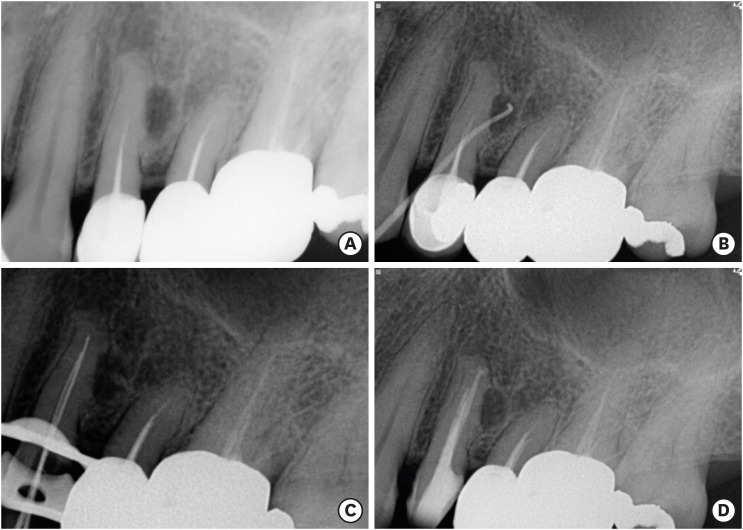
- Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
- Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e30. Published online July 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub We report the surgical endodontic treatment of a maxillary first premolar with a lateral lesion that originated from an accessory canal. Although lesions originating from accessory canals frequently heal with simple conventional endodontic therapy, some lesions may need additional and different treatment. In the present case, conventional root canal retreatment led to incomplete healing with the need for further treatment (
i.e. , surgery). Surgical endodontic management with a fast-setting calcium silicate cement was performed on the accessory canal using a dental operating microscope. At the patient's 9-month recall visit, the lesion was resolved upon radiography.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictive analysis of root canal morphology in relation to root canal treatment failures: a retrospective study
Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan, P. J. Nagarathna, Sudhir Rama Varma, Jayaraj Kodangattil Narayanan, Santosh R. Patil
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of internal replacement resorption of two maxillary central incisors with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography as the diagnostic tool: a case report and review of literature
Fatemeh Eskandari, Safoora Sahebi, Negar Ghorbani Jahandizi, Hossein Mofidi
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
- Predictive analysis of root canal morphology in relation to root canal treatment failures: a retrospective study
- 1,664 View
- 17 Download
- 4 Crossref

-
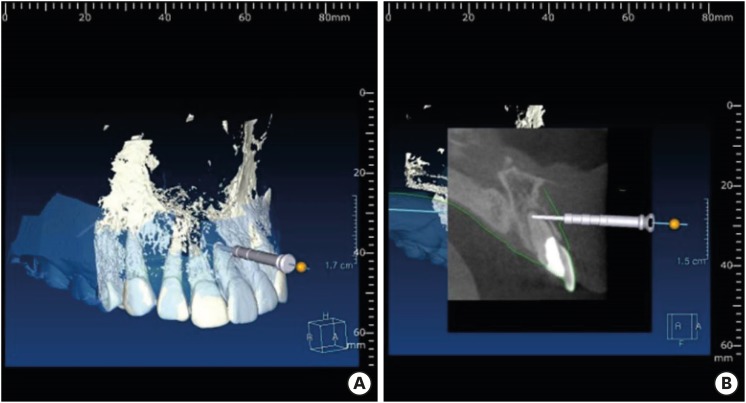
A new minimally invasive guided endodontic microsurgery by cone beam computed tomography and 3-dimensional printing technology

- Jong-Eun Kim, June-Sung Shim, Yooseok Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e29. Published online July 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Endodontic microsurgery is defined as the treatment performed on the root apices of an infected tooth, which was unresolved with conventional root canal therapy. Recently, the advanced technology in 3-dimensional model reconstruction based on computed tomography such as cone beam computed tomography has opened a new avenue in application of personalized, accurate diagnosis and has been increasingly used in the field of dentistry. Nevertheless, direct intra-oral localization of root apex based on the 3-dimensional information is extremely difficult and significant amount of bone removal is inevitable when freehand surgical procedure was employed. Moreover, gingival flap and alveolar bone fenestration are usually required, which leads to prolonged time of surgery, thereby increasing the chance of trauma as well as the risk of infection. The purpose of this case report is to present endodontic microsurgery using the guide template that can accurately target the position of apex for the treatment of an anterior tooth with calcified canal which was untreatable with conventional root canal therapy and unable to track the position of the apex due to the absence of fistula.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
Yinghua Fu, Zhixin Zhang, Xiaoping Tang, Jiangling Su
Medicine.2025; 104(3): e41033. CrossRef - Segmentation algorithms of dental CT images: A comprehensive review from classical to deep learning trend
Dianhao Wu, Jingang Jiang, Jinke Wang, Zhuming Bi, Guang Yu
Expert Systems with Applications.2025; 275: 126853. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Removal of Extraradicular Separated Instrument by Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery Using the 3D‐Printed Guide and Trephine: A Case Report
Lin Yang, Liang Chen
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Augmented Reality-Assisted Micro-Invasive Apicectomy with Markerless Visual–Inertial Odometry: An In Vivo Pilot Study
Marco Farronato, Davide Farronato, Federico Michelini, Giulio Rasperini
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12588. CrossRef - 3D finite element analysis of stress distribution on the shape of resected root-end or with/without bone graft of a maxillary premolar during endodontic microsurgery
Aein Mon, Mi-El Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Ho-Beom Kwon
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 837. CrossRef - TREATMENT OF YATROGENIC POST-TRAUMATIC NEUROPATHY ASSOCIATED WITH
ENDODONTIC THERAPY USING 3D TECHNOLOGIES
Karen Sevterteryan, Vladislav Tarasenok, Lyudmila Tatintsyan
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2024; : 73. CrossRef - Advancements in guided surgical endodontics: A scoping review of case report and case series and research implications
Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Matteo Peditto, Andrea Venticinque, Antonia Marcianò, Alberto Bianchi, Eugenio Pedullà
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 397. CrossRef - Comparison of a Novel Static Computer-aided Surgical and Freehand Techniques for Osteotomy and Root-end Resection
Kyle Westbrook, Corey Rollor, Sara A. Aldahmash, Guadalupe G. Fay, Elias Rivera, Jeffery B. Price, Ina Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik, Frederico C. Martinho
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(5): 528. CrossRef - Comparison of the Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Guided Apicoectomy Performed with a Drill or a Trephine: An In Vitro Study
Ramóna Kiscsatári, Eszter Nagy, Máté Szabó, Gábor Braunitzer, József Piffkó, Márk Fráter, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9642. CrossRef - Review of “Outcome of Endodontic Surgery: A Meta- Analysis of the Literature—Part 1: Comparison
of Traditional Root-End Surgery and Endodontic Microsurgery” by Setzer and Colleagues in J Endod 36(11):1757-1765, 2010
Oleksandr Nozhenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 41. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Exploratory In Vitro Microcomputed Tomographic Investigation of the Efficacy of Semicircular Apicoectomy Performed with Trephine Bur
Eszter Nagy, Brigitta Vőneki, Lívia Vásárhelyi, Imre Szenti, Márk Fráter, Ákos Kukovecz, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(16): 9431. CrossRef - The Time Has Come: Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery: A First Peer-Reviewed Open Access Publication Focused on Microsurgery in Endodontics
Ievgen Fesenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prefabricated Grid-guided Endodontic Microsurgery: A Pilot Study
Cruz Nishanthine, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Ravi Devi, Kadhar Begam Farjana, Dasarathan Duraivel
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022; 6(2): 58. CrossRef - Guided osteotomy
Saini Rashmi, Saini V Kr
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(3): 172. CrossRef - Accuracy of digitally planned, guided apicoectomy with a conventional trephine and a custom-made endodontic trephine: An in vitro comparative study
Eszter Nagy, Gábor Braunitzer, Dániel Gerhard Gryschka, Ibrahim Barrak, Mark Adam Antal
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 123(4): 388. CrossRef - Stress Distribution on Trephine-Resected Root-end in Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery: A Finite Element Analysis
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Miel Kim, Qiang Zhu, Seung-Ho Baek, Ho-Beom Kwon, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(12): 1517. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef - When to consider the use of CBCT in endodontic treatment planning in adults
Nisha Patel, Andrew Gemmell, David Edwards
Dental Update.2021; 48(11): 932. CrossRef
- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
- 2,442 View
- 31 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Comparing the effect of a desensitizing material and a self-etch adhesive on dentin sensitivity after periodontal surgery: a randomized clinical trial
- Hila Hajizadeh, Atefeh Nemati-Karimooy, Sara Majidinia, Amir Moeintaghavi, Marjaneh Ghavamnasiri
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):168-175. Published online July 21, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.168
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the ability of a desensitizing agent and a self-etch adhesive on cervical dentin sensitivity (CDS) after periodontal surgery.
Materials and Methods Ninety hypersensitive teeth of 13 subjects were included in the study. After periodontal surgery, the teeth of each posterior sextant treated with one of the following materials: G1: Clearfil S3 Bond (Kuraray Dental), G2: Gluma Desensitizer (Heraeus Kulzer), and G3: placebo (water). The sensitivity was assessed using evaporative stimuli before treatment (baseline, T0), 1 day after treatment (T1), after 1 week (T2), and after 1 month (T3) according to visual analog scale (VAS).
Results Following the treatment, all the 3 groups showed significant reduction of CDS in T1 compared to T0. Reduction of CDS between T1 and T2 was observed only in G1 but there was no significant difference between T2 and T3 in this group. Although we observed a significant difference in T3 compared to T1 and T2 in G2 and G3, comparison of treatment groups in each assessment time showed a significant difference only in T3. According to paired comparison, this was due to the difference between G2 and G3.
Conclusions Dentin sensitivity following periodontal surgery will decrease spontaneously over time, but treating the sensitive teeth with Gluma Desensitizer and Clearfil S3 Bond can have some benefits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomineralization reaction from nanosized calcium silicate: A new method for reducing dentin hypersensitivity
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Jeong-Kil Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Yu-Chih Chiang, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(1): 428. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self-etching Adhesive Only Versus in Combination with Gluma Desensitizer for Preventing Post-composite Sensitivity - A Prospective Study
Hemamalini Rath, Shilpa Mahapatra, Sri Priya Narayanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(1): 32. CrossRef - Efficacy of seventh generation bonding agents as desensitizers in patients with dentin hypersensitivity: a randomized clinical trial
Sumaiya Shabbir, Shahbaz Ahmed, Syed Jaffar Abbas Zaidi, Sania Riaz, Huma Sarwar, Muhammad Taqi, Zia ur Rahman Khan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the crystal formation from calcium silicate in human dentinal tubules and the effect of phosphate buffer saline concentration
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jin-Soo Ahn, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2278. CrossRef - The effect of fluoride iontophoresis on seal ability of self-etch adhesive in human dentin in vitro
Kanittha Kijsamanmith, Parintorn Wallanon, Chanya Pitchayasatit, Poonnapha Kittiratanaviwat
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The study of toothpaste desensitizing properties
S. B. Ulitovskiy, O. V. Kalinina, A. A. Leontev, O. V. Khabarova, L. I. Pankrateva, E. S. Soloveva, N. K. Fok
Parodontologiya.2022; 27(1): 81. CrossRef - Effectiveness and cytotoxicity of two desensitizing agents: a dentin permeability measurement and dentin barrier testing in vitro study
Ruodan Jiang, Yongxiang Xu, Feilong Wang, Hong Lin
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A randomized clinical trial of dentin hypersensitivity reduction over one month after a single topical application of comparable materials
Samar Hatem Abuzinadah, Abdulrahman Jafar Alhaddad
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between effectiveness of dentine desensitizer and one bottle self-etch adhesive on dentine hypersensitivity
Muhammad Zohaib Younus, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Azeem Ul Yaqin Syed, Jiand Malik Baloch, Muhammad Ali, Abubakar Sheikh
Technology and Health Care.2021; 29(6): 1153. CrossRef - A long-term evaluation of experimental potassium oxalate concentrations on dentin hypersensitivity reduction: A triple-blind randomized clinical trial
Alexia da Mata Galvão, Livia Fávaro Zeola, Guilherme Faria Moura, Daniela Navarro Ribeiro Teixeira, Ramon Corrêa de Queiroz Gonzaga, Gisele Rodrigues da Silva, Paulo Vinícius Soares
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 89: 103180. CrossRef
- Biomineralization reaction from nanosized calcium silicate: A new method for reducing dentin hypersensitivity
- 2,406 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
- Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT.
Results The second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (
p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01).Conclusions For apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
- 2,223 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Microsurgical re-treatment of an endodontically treated tooth with an apically located incomplete vertical root fracture: a clinical case report
- Silvio Taschieri, Massimo Del Fabbro, Ahmed El Kabbaney, Igor Tsesis, Eyal Rosen, Stefano Corbella
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):316-321. Published online June 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although it is challenging, the early diagnosis of a vertical root fracture (VRF) is crucial in order to ensure tooth preservation. The purpose of this clinical case report was to describe reparative surgery performed to treat a tooth affected by an incomplete VRF. A 26 year old male patient was suspected to have a VRF in a maxillary left central incisor, and an exploratory flap was performed in order to confirm the diagnosis. After detecting the fracture, the lesion was surgically treated, the fracture and the infected root-end were removed, and a platelet-rich plasma membrane was used to cover the defect in order to prevent bacterial migration. A 24 month clinical and radiological follow-up examination showed that the tooth was asymptomatic and that the healing process was in progress. The surgical approach described here may be considered an effective treatment for a combined endodontic-periodontal lesion originating from an incomplete VRF and a recurrent periapical lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical perspectives on dentine cracks and fractures: Implications in their clinical management
Sishi Chen, Dwayne Arola, Domenico Ricucci, Brian E. Bergeron, John A. Branton, Li-sha Gu, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 130: 104424. CrossRef - Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review of Human Studies
Joanna Metlerska, Irini Fagogeni, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 20. CrossRef - The preservation of teeth with root-originated fractures
Eyal Rosen, Ilan Beitlitum, Igor Tsesis
Evidence-Based Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Biomechanical perspectives on dentine cracks and fractures: Implications in their clinical management
- 2,429 View
- 25 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A combined approach to non-carious cervical lesions associated with gingival recession
- SungEun Yang, HyeJin Lee, Sung-Ho Jin
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):218-224. Published online May 2, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.218
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Non-carious cervical lesions (NCCLs) with gingival recession require specific consideration on both aspects of hard and soft tissue lesion. In the restorative aspect, careful finishing and polishing of the restorations prior to mucogingival surgery is the critical factor contributing to success. Regarding surgery, assessment of the configuration of the lesion and the choice of surgical technique are important factors. The precise diagnosis and the choice of the proper treatment procedure should be made on the basis of both restorative and surgical considerations to ensure the successful treatment of NCCLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting clinical decision-making for the management of non-carious cervical lesions - a qualitative analysis
Wai Ling TSE, Johnson Chun Ming LEE, Tong Wah LIM, Michael George BOTELHO
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 164: 106225. CrossRef - Effect of different material protocols on the control of dentin hypersensitivity: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
Júlia Marques Martins, Maria Fernanda Ferreira Nogueira, Guilherme José Pimentel Lopes de Oliveira, Alexandre Coelho Machado, Paulo César de Freitas Santos Filho, Hugo Lemes Carlo, Carlos José Soares, Gisele Rodrigues da Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The link between Noncarious Cervical Lesions (NCCL) and gingival recession. Etiology and treatment. A narrative review.
Luminița Lazăr, Zsigmond-Loránd Makkai, Timea Dakó, Mircea Suciu, Ana-Petra Lazăr
Acta Stomatologica Marisiensis Journal.2023; 6(1): 5. CrossRef - Treatment efficacy of gingival recession defects associated with non-carious cervical lesions: a systematic review
Lívia Maria Lopes de Oliveira, Camila Agra Souza, Sinara Cunha, Rafael Siqueira, Bruna de Carvalho Farias Vajgel, Renata Cimões
Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science.2022; 52(2): 91. CrossRef - Clinical Behavior of the Gingival Margin following Conservative “Coronally Dynamic” Restorations in the Presence of Non-Carious Cervical Lesions Associated with Gingival Recession: A Pilot Study
Felice Femiano, Rossella Sorice, Rossella Femiano, Luigi Femiano, Ludovica Nucci, Vincenzo Grassia, Marco Annunziata, Andrea Baldi, Nicola Scotti, Livia Nastri
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(7): 132. CrossRef - Effects of cervical restorations on the periodontal tissues: 5-year follow-up results of a randomized clinical trial
Morgana Favetti, Anelise Fernandes Montagner, Silvia Terra Fontes, Thiago Marchi Martins, Alexandre Severo Masotti, Patricia dos Santos Jardim, Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Francisco Wilker Mustafa Gomes Muniz
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 106: 103571. CrossRef
- Factors affecting clinical decision-making for the management of non-carious cervical lesions - a qualitative analysis
- 3,659 View
- 82 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Cutting efficiency of apical preparation using ultrasonic tips with microprojections: confocal laser scanning microscopy study
- Sang-Won Kwak, Young-Mi Moon, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):276-281. Published online July 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the cutting efficiency of a newly developed microprojection tip and a diamond-coated tip under two different engine powers.
Materials and Methods The apical 3-mm of each root was resected, and root-end preparation was performed with upward and downward pressure using one of the ultrasonic tips, KIS-1D (Obtura Spartan) or JT-5B (B&L Biotech Ltd.). The ultrasonic engine was set to power-1 or -4. Forty teeth were randomly divided into four groups: K1 (KIS-1D / Power-1), J1 (JT-5B / Power-1), K4 (KIS-1D / Power-4), and J4 (JT-5B / Power-4). The total time required for root-end preparation was recorded. All teeth were resected and the apical parts were evaluated for the number and length of cracks using a confocal scanning micrscope. The size of the root-end cavity and the width of the remaining dentin were recorded. The data were statistically analyzed using two-way analysis of variance and a Mann-Whitney test.
Results There was no significant difference in the time required between the instrument groups, but the power-4 groups showed reduced preparation time for both instrument groups (
p < 0.05). The K4 and J4 groups with a power-4 showed a significantly higher crack formation and a longer crack irrespective of the instruments. There was no significant difference in the remaining dentin thickness or any of the parameters after preparation.Conclusions Ultrasonic tips with microprojections would be an option to substitute for the conventional ultrasonic tips with a diamond coating with the same clinical efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
- 1,516 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
- Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):79-88. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Appropriate use of local hemostatic agent is one of the important factors on the prognosis of endodontic microsurgery. However, most investigations to date focus on the hemostatic efficacy of the agents, whereas their biologic characteristics have not received enough attention. The purpose of this paper was to review the biologic response of local hemostatic agents, and to provide clinical guidelines on their use during endodontic microsurgery. Electronic database (PUBMED) was screened to search related studies from 1980 to 2013, and 8 clinical studies and 18 animal studies were identified. Among the materials used in these studies, most widely-investigated and used materials, epinephrine, ferric sulfate (FS) and calcium sulfate (CS), were thoroughly discussed. Influence of these materials on local tissue and systemic condition, such as inflammatory and foreign body reaction, local ischemia, dyspigmentation, delayed or enhanced bone and soft tissue healing, and potential cardiovascular complications were assessed. Additionally, biological property of their carrier materials, cotton pellet and absorbable collagen, were also discussed. Clinicians should be aware of the biologic properties of local hemostatic agents and their carrier materials, and should pay attention to the potential complications when using them in endodontic microsurgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A drug-carrying, multiscene, absorbable biological suture from fish swim bladder
Peng Sun, Hao Cui, Jinwei Zhang, Jingan Li, Changwei Ren, Yongqiang Lai
International Journal of Surgery.2025; 111(10): 6663. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of apicoectomy without retrograde filling in treating periapical inflammatory cysts
Jeong-Kui Ku, Woo-Young Jeon, Seung-O Ko, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2024; 50(3): 140. CrossRef - Functional and structural neurodegenerative activities of Ankaferd BloodStopper in a mouse sciatic nerve model
Ramazan Üstün, Elif Oğuz, Ayşe Şeker, Filiz Taspinar
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Local and Systemic Hemostatic Agents: A Comprehensive Review
Bardia Jamali, Saeed Nouri, Salimeh Amidi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PLGA Nanoparticle Rapamycin- or Necrostatin-1-Coated Sutures Inhibit Inflammatory Reactions after Arterial Closure in Rats
Liwei Zhang, Wang Wang, Boao Xie, Peng Sun, Shunbo Wei, Haoliang Wu, Cong Zhang, Jingan Li, Zhuo Li, Hualong Bai
ACS Applied Bio Materials.2022; 5(4): 1501. CrossRef - COMPARING THE CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES OF PULPOTOMIES IN PRIMARY MOLARS USING BIOACTIVE ENDODONTIC MATERIALS AND FERRIC SULFATE – A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIALS
VELLORE KANNAN GOPINATH, SHAJU JACOB PULIKKOTIL, SAJESH K VEETTIL, LALLI DHARMARAJAN, PONNUDURAI SAMUEL GNANA PRAKASH, VINEET DHAR, JAYAKUMAR JAYARAMAN
Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice.2022; 22(4): 101770. CrossRef - Perioperative Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Management with Endodontic Microsurgical Techniques
Anita Aminoshariae, Mark Donaldson, Michael Horan, James C. Kulild, Dale Baur
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(10): 1557. CrossRef - Effect of blood contamination and various hemostatic procedures on the push-out bond strength of Biodentine when used for furcation perforation repair
Shanthana Reddy, Ramya Shenoy, LohithReddy Mandadi, Ishani Saluja, ManuelS Thomas
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 260. CrossRef - Endodontic Perforation Closure by Five Mineral Oxides Silicate-Based Cement with/without Collagen Sponge Matrix
Talal Al-Nahlawi, Maisour Ala Rachi, Amjad Abu Hasna, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Hemostatic agents in periapical surgery: The systematic review
Z. S. Khabadze, D. A. Nazarova, E. S. Shilyaeva, A. P. Kotelnikova, Yu. A. Bakayev, S. M. Abdulkerimova, Kh. O. Omarova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(3): 184. CrossRef - An Innovative Bioceramic Bone Graft Substitute for Bone Defect Treatment: In Vivo Evaluation of Bone Healing
Syamsiah Syam, Yung-Chieh Cho, Chung-Ming Liu, Mao-Suan Huang, Wen-Chien Lan, Bai-Hung Huang, Takaaki Ueno, Chi-Hsun Tsai, Takashi Saito, May-Show Chen, Keng-Liang Ou
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(22): 8303. CrossRef - Trial finds better haemostasis with aluminium chloride during periapical surgery
Niall Mc Goldrick, Carly Ross, James Nelson
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2017; 18(2): 50. CrossRef - Comparison of the Hemostatic Activity of Quercus persica Jaub. & Spach. (Oak) With Ferric Sulfate in Bony Crypts
Mohammad Reza Nabavizadeh, Arman Zargaran, Fariborz Moazami, Fatemeh Askari, Safoora Sahebi, Alireza Farhadpoor, Pouya Faridi
Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine.2016; 21(1): 34. CrossRef - Effect of the plant-based hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper® on the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate
Muzaffer Emir Dinçol, Hakan Ozbas, Bulent Yılmaz, Handan Ersev, Selcuk Gokyay, Vakur Olgac
BMC Oral Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 2,740 View
- 16 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
- Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):187-193. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Epinephrine is one of the most widely-used vasoconstrictors in dental treatment including endodontic microsurgery. However, the systemic safety of epinephrine has been in debate for many years because of its potential risk to cause cardiovascular complications. The purpose of this review was to assess the cardiovascular effect of epinephrine use in endodontic microsurgery. Endodontic microsurgery directly applies epinephrine into the bone cavity, and the amount is reported to be much larger than other dental surgeries. Moreover, when considering that systemic potency of intraosseous application is reported to be comparable to intravenous application, the systemic influence of epinephrine could be increased in endodontic microsurgery. Besides, pre-existing cardiovascular complications or drug interactions can enhance its systemic influence, resulting in increased susceptibility to cardiovascular complications. Although clinical studies have not reported significant complications for patients without severe systemic complications, many epinephrine-induced emergency cases are warning the cardiovascular risk related with pre-existing systemic disease or drug interactions. Epinephrine is a dose-sensitive drug, and its hypersensitivity reaction can be fatal to patients when it is related to cardiovascular complications. Therefore, clinicians should recognize the risk, and the usage of pre-operative patient evaluation, dose control and patient monitoring are required to ensure patient's safety during endodontic microsurgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Local Hemostatic Agents in Minor Oral Surgical Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Kshitija Patil, Jay N Goyal, Saurabh Dudhe, Janice John, Simona Joseph, Sanchi Kadbe, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacological Interactions of Epinephrine at Concentrations Used in Dental Anesthesiology: An Updated Narrative Review
Maria Aikaterini Saraga, Ioannis Fotopoulos, Vasileios Zisis, Athanasios Poulopoulos, Nikolaos Dabarakis, Theodoros Lillis
Reports.2025; 8(4): 224. CrossRef - Effects of nasal desmopressin spray versus topical epinephrine on surgical field clarity and hemodynamics in endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: a randomized clinical study
Mohamed G.M. El Sayed, Marwa M. Medhat, Dina A.E. Salem, Marwa A.M. Khedr, Alshaimaa A.F. Kamel
Research and Opinion in Anesthesia & Intensive Care.2024; 11(1): 1. CrossRef - Is 1:1000 adrenaline as a topical haemostat an effective alternative to control bleeding in dentistry and oral surgery?
Raj D. Aslam, Jonathan Liew, Eleni Besi
British Dental Journal.2023; 235(1): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Flumazenil on Emergence Agitation after Orthognathic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Young Hyun Koo, Geun Joo Choi, Hyun Kang, Yong Hun Jung, Young Cheol Woo, Young-Jun Choi, Chong Wha Baek
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(3): 416. CrossRef - Hemostatic agents in periapical surgery: The systematic review
Z. S. Khabadze, D. A. Nazarova, E. S. Shilyaeva, A. P. Kotelnikova, Yu. A. Bakayev, S. M. Abdulkerimova, Kh. O. Omarova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(3): 184. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON DYNAMICS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM INDICES IN RATS
S. Shkurashivska, H. Ersteniuk
Visnyk of Lviv University. Biological series.2017; (75): 151. CrossRef - The Correlation between the Blood Sugar and Allergy of the Trauma Patient
Jeong Soo Lee, Sung Hee Hyun, Ji-Sook Lee, In Sik Kim
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2014; 46(1): 22. CrossRef - Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 1,994 View
- 7 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
- Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):113-118. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Nowadays, oral anticoagulants are commonly prescribed to numerous patients for preventing cardiovascular accident such as thromboembolism. An important side effect of anticoagulant is anti-hemostasis. In a major surgery, the oral anticoagulant therapy (OAT) regimen must be changed before the surgery for proper post-operative bleeding control. However, in a minor dental surgery and endodontic surgery, the necessity for changing or discontinuing the OAT is open to debate. In this study, risks of the consequences were weighed and analyzed. In patients who stop the OAT, the occurrence of thromboembolic complication is rare but the result is fatal. In patients who continuing the OAT, post-operative bleeding can be controlled well with the local hemostatic measures. In the endodontic surgery, there are almost no studies about this issue. The intra-operative bleeding control is particularly important in the endodontic surgery because of its delicate and sensitive procedures such as inspection of resected root surface using dental microscope and retrograde filling. Further studies are necessary about this issue in the viewpoint of endodontic surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Patients Receiving Anticoagulation Therapy in Dental Practice: A Systematic Review
Francesco Inchingolo, Angelo Michele Inchingolo, Fabio Piras, Laura Ferrante, Antonio Mancini, Andrea Palermo, Alessio Danilo Inchingolo, Gianna Dipalma
Healthcare.2024; 12(15): 1537. CrossRef - Hemostatic Alginate/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Aerogel Loaded with Tranexamic Acid for the Potential Protection against Alveolar Osteitis
Mai El Halawany, Randa Latif, Mohamed H. H. AbouGhaly
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(10): 2255. CrossRef - Perioperative Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Management with Endodontic Microsurgical Techniques
Anita Aminoshariae, Mark Donaldson, Michael Horan, James C. Kulild, Dale Baur
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(10): 1557. CrossRef - Administration of Coagulation-Altering Therapy in the Patient Presenting for Oral Health and Maxillofacial Surgery
Thomas M. Halaszynski
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America.2016; 28(4): 443. CrossRef - Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 187. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 2,165 View
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref

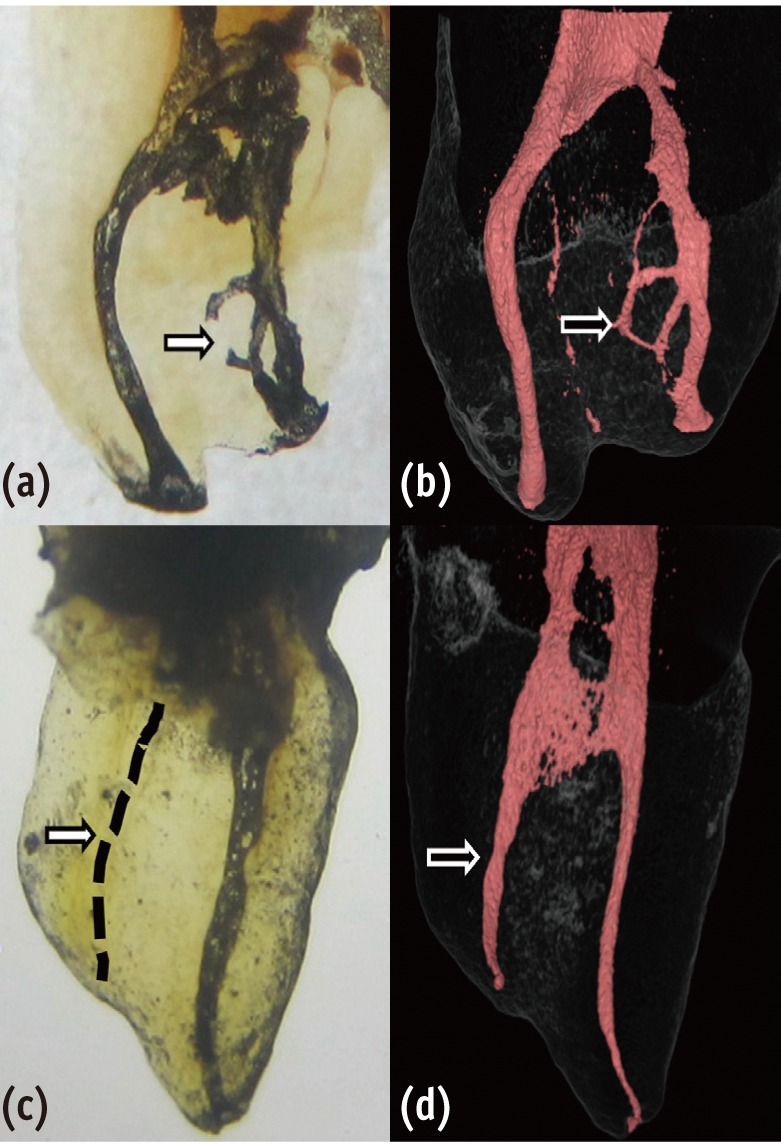
- Does apical root resection in endodontic microsurgery jeopardize the prosthodontic prognosis?
- Sin-Yeon Cho, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):59-64. Published online May 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Apical surgery cuts off the apical root and the crown-to-root ratio becomes unfavorable. Crown-to-root ratio has been applied to periodontally compromised teeth. Apical root resection is a different matter from periodontal bone loss. The purpose of this paper is to review the validity of crown-to-root ratio in the apically resected teeth. Most roots have conical shape and the root surface area of coronal part is wider than apical part of the same length. Therefore loss of alveolar bone support from apical resection is much less than its linear length.The maximum stress from mastication concentrates on the cervical area and the minimum stress was found on the apical 1/3 area. Therefore apical root resection is not so harmful as periodontal bone loss. Osteotomy for apical resection reduces longitudinal width of the buccal bone and increases the risk of endo-perio communication which leads to failure. Endodontic microsurgery is able to realize 0 degree or shallow bevel and precise length of root resection, and minimize the longitudinal width of osteotomy. The crown-to-root ratio is not valid in evaluating the prosthodontic prognosis of the apically resected teeth. Accurate execution of endodontic microsurgery to preserve the buccal bone is essential to avoid endo-perio communication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Approaches in apical microsurgery: conventional vs. guided. A systematic review
Germán Sánchez-Herrera, Matteo Facchera, Cristina Palma-Carrió, Martín Pérez-Leal
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of apical root resection level and filling technique on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth: a biomechanical study
Guilherme Pauletto, Sidnei Flores de Pellegrin, Yasmin Padoin, Andressa Weber Vargas, Duvan Cala Castillo, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Renata Dornelles Morgental
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of horizontal bone loss and dehiscence with the bundle and conventional fiber post: a finite element analysis
Deniz Yanık, Nurullah Türker, Ahmet Mert Nalbantoğlu
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - The tooth survival of non‐surgical root‐filled posterior teeth and the associated prognostic tooth‐related factors: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
S. R. Patel, F. Jarad, E. Moawad, A. Boland, J. Greenhalgh, Maria Liu, Michelle Maden
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(10): 1404. CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multifactorial Analysis of Endodontic Microsurgery Using Finite Element Models
Raphael Richert, Jean-Christophe Farges, Jean-Christophe Maurin, Jérôme Molimard, Philippe Boisse, Maxime Ducret
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(6): 1012. CrossRef - Mid‐term outcomes and periodontal prognostic factors of autotransplanted third molars: A retrospective cohort study
Ernest Lucas‐Taulé, Marc Llaquet, Jesús Muñoz‐Peñalver, José Nart, Federico Hernández‐Alfaro, Jordi Gargallo‐Albiol
Journal of Periodontology.2021; 92(12): 1776. CrossRef - Effect of length of apical root resection on the biomechanical response of a maxillary central incisor in various occlusal relationships
S. J. Ran, X. Yang, Z. Sun, Y. Zhang, J. X. Chen, D. M. Wang, B. Liu
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(1): 111. CrossRef - Changes of Root Length and Root-to-Crown Ratio after Apical Surgery: An Analysis by Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Thomas von Arx, Simon S. Jensen, Michael M. Bornstein
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(9): 1424. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Root Resection on the Biomechanical Response of a Single-rooted Tooth—Part 2: Apical Root Resection Combined with Periodontal Bone Loss
Youngjune Jang, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Heoung-Jae Chun, Byoung-Duck Roh
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(3): 412. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Root Resection on the Biomechanical Response of a Single-rooted Tooth: A 3-dimensional Finite Element Analysis
Youngjune Jang, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Byoung-Duck Roh, Heoung-Jae Chun
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(9): 1489. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 2,215 View
- 15 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Success and failure of endodontic microsurgery
- Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):465-476. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In current endodontic practice, introduction of operating microscope, ultrasonic instruments, and microinstruments has induced a big change in the field of surgical retreatment. In this study, we aimed to offer key steps of endodontic microsurgery procedure compared with traditional root-end surgery, and to evaluate factors influencing success and failure based on published articles.
Endodontic microsurgery is a surgical procedure performed with the aid of a microscope, ultrasonic instruments and modern microsurgical instruments. The microscope provides magnification and illumination - essential for identifying minute details of the apical anatomy. Ultrasonic instruments facilitate the precise root-end preparation that is within the anatomical space of the canal. Modern endodontics can therefore be performed with precision and predictability, thus eliminating the disadvantages inherent in traditional periapical surgery such as large osteotomy, beveled apicoectomy, inaccurate root-end preparation and the inability to observe isthmus.
Factors influencing the outcomes of endodontic microsurgery may be diverse, but standardization of procedures can minimize its range. Among patient and tooth-related factors, periodontal status and tooth position are known to be prognostic, but there are only few articles concerning this matter. High-evidence randomized clinical trials or prospective cohort studies are needed to confirm these findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jarosław Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6382. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jaroslaw Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(14): 3991. CrossRef - Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Microsurgery: 1 Year versus Long-term Follow-up
Minju Song, Taekjin Nam, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(4): 490. CrossRef - The Influence of Bone Tissue Deficiency on the Outcome of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(11): 1341. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors of Clinical Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Baekil Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1491. CrossRef - Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 113. CrossRef
- Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
- 2,429 View
- 33 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


