Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Influence of modeling agents on the surface properties of an esthetic nano-hybrid composite
- Zeynep Bilge Kutuk, Ecem Erden, Damla Lara Aksahin, Zeynep Elif Durak, Alp Can Dulda
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e13. Published online January 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e13
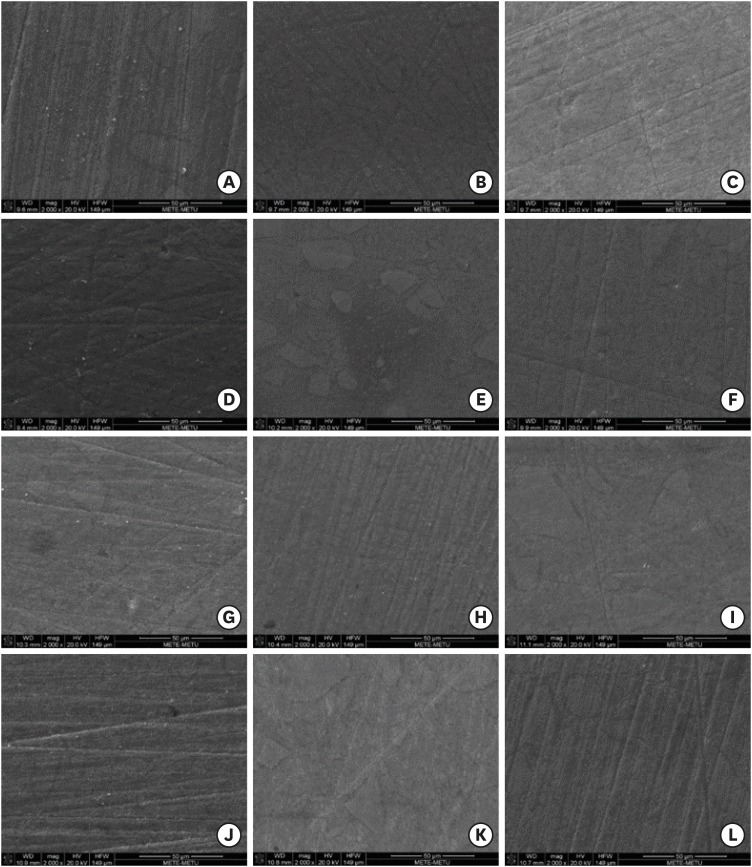
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of different modeling agents on the surface microhardness (Vickers hardness number; VHN), roughness (Ra), and color change (ΔE) of a nano-hybrid composite with or without exposure to discoloration by coffee.
Materials and Methods Sixty-four cylinder-shaped nano-hybrid composite specimens were prepared using a Teflon mold. The specimens' surfaces were prepared according to the following groups: group 1, no modeling agent; group 2, Modeling Liquid; group 3, a universal adhesive (G-Premio Bond); and group 4, the first step of a 2-step self-adhesive system (OptiBond XTR). Specimens were randomly allocated into 2 groups (
n = 8) according to the storage medium (distilled water or coffee). VHN, Ra, and ΔE were measured at 24 hours, 1 week, and 6 weeks. The Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Bonferroni correction for pairwise comparisons was used for statistical analysis (α = 0.05).Results Storage time did not influence the VHN of the nano-hybrid composite in any group (
p > 0.05). OptiBond XTR Primer application affected the VHN negatively in all investigated storage medium and time conditions (p < 0.05). Modeling Liquid application yielded improved Ra values for the specimens stored in coffee at each time point (p < 0.05). Modeling Liquid application was associated with the lowest ΔE values in all investigated storage medium and time conditions (p < 0.05).Conclusion Different types of modeling agents could affect the surface properties and discoloration of nano-hybrid composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do modeling liquid and glycerin gel compromise the color stability of one-shade composites
Ezgi Erden Kayalidere, Merve Sahin
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Placement Techniques on Marginal Integrity, Wear Behavior, and Clinical Efficiency of a Bulk-Fill Resin Composite
Kerem Can Işık, Handan Yıldırım-Işık, Uğur Tuna Sazlıkoğlu, Mediha Büyükgöze-Dindar
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(3): 108. CrossRef - The Impact of Modeling Liquids on Surface Roughness and Color Properties of Bulkfill Resin Composites After Simulated Tooth Brushing: An in Vitro Study. Part I
Camila Falconí‐Páez, Claudia González‐Vaca, Juliana Guarneri, Newton Fahl, Paulina Aliaga‐Sancho, Maria Lujan Mendez‐Bauer, Cesar Augusto Galvão Arrais, Andrés Dávila‐Sánchez
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(2): 514. CrossRef - Coating Agents for Resin Composites: Effect on Color Stability, Roughness, and Surface Micromorphology Subjected to Brushing Wear
FR Hojo, TC Martins, WF Vieira-Junior, FMG França, CP Turssi, RT Basting
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(1): 101. CrossRef - Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
Melek Güven Bekdaş, Ihsan Hubbezoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of modeling liquids on the color adaptation and optical properties of single and simply shade resin composites
Bengü Doğu Kaya, Mehmet Buldur, Burcu Gözetici-Çil
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of modeling liquids on Vickers microhardness, flexural strength and color stability of resin-based composites
Ahmed Alshawi, Benin Dikmen, Sevda Ozel Yildiz, Ugur Erdemir
Materials Research Express.2025; 12(11): 115402. CrossRef - Does composite repair time affect repair protocol, immediate or delayed?
Murat Can Ersen, Nevin Cobanoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of combining dental composite brushes with modeling resins on the color stability and topographic features of composites
Abdulrahman A Balhaddad, Faisal Alharamlah, Alhanoof Aldossary, Wejdan Almutairi, Turki Alshehri, Mary Anne S Melo, Afnan O Al-Zain, Eman H Ismail
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the Degree of Monomer Conversion in Dental Composites through Various Methods: An In Vitro Study
Musa Kazim Ucuncu, Ozge Celiksoz, Emine Sen, Yasemin Yucel Yucel, Bircan Dinc
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(11): 4406. CrossRef - EFEITO DOS LÍQUIDOS MODELADORES NA SUPERFÍCIE DA RESINA COMPOSTA – UMA REVISÃO DE LITERATURA
Samuel Silva Dias, Matheus Fernando Lopes, Jeffison Teles Dias, Caio Junji Tanaka, Jose Augusto Rodrigues
RECIMA21 - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar - ISSN 2675-6218.2024; 5(2): e524899. CrossRef - Effect of Instrument Lubricant on Mechanical Properties of Restorative Composite
G Pippin, D Tantbirojn, M Wolfgang, JS Nordin, A Versluis
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 475. CrossRef - Full analysis of the effects of modeler liquids on the properties of direct resin-based composites: a meta-analysis review of in vitro studies
Eduardo Trota Chaves, Lisia Lorea Valente, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3289. CrossRef - Influence of Modeling Liquids and Universal Adhesives Used as Lubricants on Color Stability and Translucency of Resin-Based Composites
Gaetano Paolone, Claudia Mazzitelli, Giacomo Zechini, Salvatore Scolavino, Cecilia Goracci, Nicola Scotti, Giuseppe Cantatore, Enrico Gherlone, Alessandro Vichi
Coatings.2023; 13(1): 143. CrossRef - Influence of Instrument Lubrication on Properties of Dental Composites
Juliusz Kosewski, Przemysław Kosewski, Agnieszka Mielczarek
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(04): 719. CrossRef - Effect of Modelıng Liquid Use on Color and Whiteness Index Change of Composite Resins
Numan AYDIN, Serpil KARAOĞLANOĞLU, Bilge ERSÖZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(Supplement): 119. CrossRef - Effects of Immediate Coating on Unset Composite with Different Bonding Agents to Surface Hardness
Nantawan Krajangta, Supissara Ninbanjong, Sunisa Khosook, Kanjana Chaitontuak, Awiruth Klaisiri
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(04): 828. CrossRef - Modeling Liquids and Resin-Based Dental Composite Materials—A Scoping Review
Gaetano Paolone, Claudia Mazzitelli, Uros Josic, Nicola Scotti, Enrico Gherlone, Giuseppe Cantatore, Lorenzo Breschi
Materials.2022; 15(11): 3759. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of Composite Diluted with Composite-Handling Agents on Dentin and Enamel
Mijoo Kim, Deuk-Won Jo, Shahed Al Khalifah, Bo Yu, Marc Hayashi, Reuben H. Kim
Polymers.2022; 14(13): 2665. CrossRef - Effect of Modeling Resins on Microhardness of Resin Composites
Ezgi T. Bayraktar, Pinar Y. Atali, Bora Korkut, Ezgi G. Kesimli, Bilge Tarcin, Cafer Turkmen
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(03): 481. CrossRef
- Do modeling liquid and glycerin gel compromise the color stability of one-shade composites
- 2,219 View
- 35 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Finishing and polishing effects of multiblade burs on the surface texture of 5 resin composites: microhardness and roughness testing
- Elodie Ehrmann, Etienne Medioni, Nathalie Brulat-Bouchard
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e1. Published online November 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e1

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to test the effect of 2 finishing–polishing sequences (QB, combining a 12/15-fluted finishing bur and an EVO-Light polisher; QWB, adding a 30-fluted polishing bur after the 12/15-fluted finishing bur used in the QB sequence) on 5 nanotech-based resin composites (Filtek Z500, Ceram X Mono, Ceram X Duo, Tetric Evoceram, and Tetric Evoceram Bulk Fill) by comparing their final surface roughness and hardness values to those of a Mylar strip control group (MS).Materials and Methods Twelve specimens of each nanocomposite were prepared in Teflon moulds. The surface of each resin composite was finished with QB (5 samples), QWB (5 samples), or MS (2 samples), and then evaluated (60 samples). Roughness was analysed with an optical profilometer, microhardness was tested with a Vickers indenter, and the surfaces were examined by optical and scanning electron microscopy. Data were analysed using the Kruskal-Wallis test (
p < 0.05) followed by the Dunn test.Results For the hardness and roughness of nanocomposite resin, the QWB sequence was significantly more effective than QB (
p < 0.05). The Filtek Z500 showed significantly harder surfaces regardless of the finishing–polishing sequence (p < 0.05).Conclusions QWB yielded the best values of surface roughness and hardness. The hardness and roughness of the 5 nanocomposites presented less significant differences when QWB was used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
Melek Güven Bekdaş, Ihsan Hubbezoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different charcoal-containing whitening toothpastes on color and surface roughness of a supra-nanofilled composite resin
Meltem Nermin Polan, Sevil Gurgan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different polishing techniques on surface roughness, gloss, and microhardness of zirconium oxide reinforced flowable bulk-fill resin composite: an in vitro study
Amr Elsayed Elnahas, Mohamed Elshirbeny Elawsya, Abeer ElSayed ElEmbaby
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tek Renkli Monokromatik Kompozit Rezinlerle İlgili Bir Durum Değerlendirmesi
Kubra Nur Yeşilova, Sebnem Turkun
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(2): 331. CrossRef - Effect of different finishing and polishing systems on surface properties of universal single shade resin-based composites
Ghada Alharbi, Hend NA Al Nahedh, Loulwa M. Al-Saud, Nourah Shono, Ahmed Maawadh
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative study of polishing systems on optical properties and surface roughness of additively manufactured and conventional resin based composites
Ayse Tugba Erturk-Avunduk, Sevim Atılan-Yavuz, Hande Filiz, Esra Cengiz-Yanardag
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Instrument Lubricant on Mechanical Properties of Restorative Composite
G Pippin, D Tantbirojn, M Wolfgang, JS Nordin, A Versluis
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 475. CrossRef - An In Vitro Study regarding the Wear of Composite Materials Following the Use of Dental Bleaching Protocols
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Ţuculină, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Andrei Osman, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Smaranda Adelina Bugălă, Mihaela Ionescu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Bogdan Dimitriu
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(10): 532. CrossRef - Akıllı Kromatik Teknolojili Kompozit Rezinlerin Farklı pH Değerlerindeki Sıvılarda Bekletilmesi Sonrası Oluşan Yüzey Pürüzlülüğü ve Renk Değişimlerinin Değerlendirilmesi
Fatih ÖZNURHAN, Aylin ÖZEL
Farabi Tıp Dergisi.2023; 2(4): 17. CrossRef - Enamel surface roughness evaluation after debonding and residual resin removal using four different burs
Rapeti Madhu Vanya, Anil Chirla, Uday Kumar Digumarthi, Tarakesh Karri, Bommareddy Radhika, Sanapala Manojna
Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics.2023; 7(3): 173. CrossRef - Finishing and Polishing of Composite Restoration: Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Among Various Dental Professionals in India
Sankar Vishwanath, Sadasiva Kadandale, Senthil kumar Kumarappan, Anupama Ramachandran, Manu Unnikrishnan, Honap manjiri Nagesh
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of different composite resin finishing and polishing protocols by confocal laser scan microscopy
Kayo Matheus Rodrigues de Souza, Roberto Victor de Melo Silva, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Paulo Cardoso Lins-Filho, Claudio Heliomar Vicente da Silva, Renata Pedrosa Guimarães
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2022; 21: e225334. CrossRef - Laboratory methods to simulate the mechanical degradation of resin composite restorations
Veronica P. Lima, Jaqueline B. Machado, Yu Zhang, Bas A.C. Loomans, Rafael R. Moraes
Dental Materials.2022; 38(1): 214. CrossRef - FARKLI POLİSAJ SİSTEMLERİNİN POSTERİOR BÖLGEDE KULLANILAN KOMPOZİT REZİNLERİN YÜZEY PÜRÜZLÜLÜĞÜ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİ
Meltem Nermin DURSUN, Cansu ATALAY
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Additional Finishing and Polishing Sequences on Hardness and Roughness of Two Different Dental Composites: An In Vitro Study
Kıvanç Dülger
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 216. CrossRef - Effect of immediate and delayed finishing and polishing procedure on Streptococcal mutans adhesion and micro-hardness of composite resin surface: An in-vitro study
Tushar Kanti Majumdar, Moumita Khatua, Paromita Mazumdar, Sayantan Mukherjee
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2022; 10(1): 5. CrossRef - Comparison of Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Resin Based Composites Containing Different Monomers
Marina Gullo Augusto, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Ingrid Fernandes Mathias-Santamaria, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Journal of Composites Science.2022; 6(5): 146. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF PH-CYCLING AND TOOTHBRUSHING SIMULATIONS ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF BULK-FILL COMPOSITES
Tuğba MİSİLLİ, Nihan GONULOL, Özge Gizem CABADAĞ, Lena ALMASIFAR, Derya DİNÇ
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(3): 487. CrossRef - A three-year randomized clinical trial evaluating direct posterior composite restorations placed with three self-etch adhesives
Joseph Sabbagh, Layal El Masri, Jean Claude Fahd, Paul Nahas
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2021; 8(1): 92. CrossRef - Press-On Force Effect on the Efficiency of Composite Restorations Final Polishing—Preliminary In Vitro Study
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Natalia Potempa, Paweł Sieradzki, Mateusz Król, Olaf Czyż, Agnieszka Radziszewska, Anna Surdacka
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 705. CrossRef - Surface evaluations of a nanocomposite after different finishing and polishing systems for anterior and posterior restorations
Riccardo Monterubbianesi, Vincenzo Tosco, Giulia Orilisi, Simone Grandini, Giovanna Orsini, Angelo Putignano
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(12): 2922. CrossRef - Wear, roughness and microhardness analyses of single increment restorative materials submitted to different challenges in vitro
L. C. Oliveira, P. H. dos Santos, F. S. S. Ramos, M. D. Moda, A. L. F. Briso, T. C. Fagundes
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2021; 22(2): 247. CrossRef - Neurotic personality trait as a predictor in the prognosis of composite restorations: A 24-month clinical follow up study
Sulthan Ibrahim Raja Khan, Dinesh Rao, Anupama Ramachandran, Bhaskaran Veni Ashok, Jagan Kumar Baskaradoss
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces
Ksenia Babina, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Marianna Arakelyan, Nina Novozhilova
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1339. CrossRef - Surface Geometry of Four Conventional Nanohybrid Resin‐Based Composites and Four Regular Viscosity Bulk Fill Resin‐Based Composites after Two‐Step Polishing Procedure
Mateusz Granat, Janusz Cieloszyk, Urszula Kowalska, Jadwiga Buczkowska-Radlińska, Ryta Łagocka, Ali Nokhodchi
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
- 2,456 View
- 24 Download
- 25 Crossref

- The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
- Ye-Mi Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Min-Ju Song, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):119-124. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate four different polishing systems of their polishability and polishing time.
Materials and Methods 4 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness Teflon mold was made. Z-250 (3M ESPE) hybrid composite resin was slightly overfilled and pressed with slide glass and cured with Optilux 501 for 40 sec each side. Then the surface roughness (glass pressed: control group) was measured with profilometer. One surface of the specimen was roughened by #320 grit sand paper and polished with one of the following polishing systems; Sof-Lex (3M ESPE), Jiffy (Ultradent), Enhance (Dentsply/Caulk), or Pogo (Dentsply/Caulk). The surface roughness and the total polishing time were measured. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
Results The surface roughness was lowest in Pogo, and highest in Sof-Lex. Polishing times were shortest with Pogo, and followed by the Sof-Lex, Enhance and Jiffy.
Conclusions One-step polishing system (Pogo) is very effective to get the smooth surface in a short time, therefore it can be recommended for final polishing system of the restoration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of surface characteristic changes in a dental Co-Cr alloy with the automatic polishing time
Yeong-cheol Jeong, Byung-Wook Jeon, Sungmin Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2025; 47(4): 232. CrossRef - Observation of surface roughness on three types of resin based on grinding time of dental automatic barrel finishing
An-Na Jung, Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(2): 56. CrossRef - Observations of surface roughness of Co-Cr alloys according to grinding time of dental barrel finishing
Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(3): 93. CrossRef - Component and surface residue observation of barrel finishing media for grinding dental resins
An-Na Jung, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(4): 145. CrossRef - Performance of a novel polishing rubber wheel in improving surface roughness of feldspathic porcelain
Geum-Jun HAN, Jae-Hoon KIM, Mi-Ae LEE, So-Yeon CHAE, Yun-Hee LEE, Byeong-Hoon CHO
Dental Materials Journal.2014; 33(6): 739. CrossRef
- Evaluation of surface characteristic changes in a dental Co-Cr alloy with the automatic polishing time
- 1,609 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Surface roughness of experimental composite resins using confocal laser scanning microscope
- JH Bae, MA Lee, BH Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a new resin monomer, filler size and polishing technique on the surface roughness of composite resin restorations using confocal laser scanning microscopy. By adding new methoxylated Bis-GMA (Bis-M-GMA, 2,2-bis[4-(2-methoxy-3-methacryloyloxy propoxy) phenyl] propane) having low viscosity, the content of TEGDMA might be decreased. Three experimental composite resins were made: EX1 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 40 mm nanofillers); EX2 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 20 mm nanofillers); EX3 (Bis-GMA/TEGDMA = 70/30 wt%, 40 mm nanofillers). Filtek Z250 was used as a reference.
Nine specimens (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) for each experimental composite resin and Filtek Z250 were fabricated in a teflon mold and assigned to three groups. In Mylar strip group, specimens were left undisturbed. In Sof-lex group, specimens were ground with #1000 SiC paper and polished with Sof-lex discs. In DiaPolisher group, specimens were ground with #1000 SiC paper and polished with DiaPolisher polishing points. The Ra (Average roughness), Rq (Root mean square roughness), Rv (Valley roughness), Rp (Peak roughness), Rc (2D roughness) and Sc (3D roughness) values were determined using confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data were statistically analyzed by Two-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons test (p = 0.05).
The type of composite resin and polishing technique significantly affected the surface roughness of the composite resin restorations (p < 0.001). EX3 showed the smoothest surface compared to the other composite resins (p < 0.05). Mylar strip resulted in smoother surface than other polishing techniques (p < 0.05).
Bis-M-GMA, a new resin monomer having low viscosity, might reduce the amount of diluent, but showed adverse effect on the surface roughness of composite resin restorations.
- 1,159 View
- 3 Download

- Surface roughness and color stability of various composite resins
- Sung-Yi Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):542-549. Published online November 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.542
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the difference in the surface roughness after polishing and to evaluate the difference in color stability after immersion in a dye solution among four types of composite resin materials. Four light-polymerized composite resins (Shade A2) with different sized filler content (a nanofilled, a hybrid, a microfilled, a flowble) were used. Average surface roughness (Ra) was measured with a surface roughness tester (Surftest Formtracer) before and after polishing with aluminum oxide abrasive discs (Super-Snap). Color of specimens before and after staining with 2% methylene blue solution were measured using spectrophotometer (CM-3700d) with SCI geometries. The results of Ra and ΔE were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), a Scheffe multiple comparison test and Student t-test (p = 0.05). After polishing, Ra values were decreased regardless of type of composite resins. In surface roughness after polishing and color stability after staining, nanofilled composite resin was not different with other composite resins except flowable resins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of contemporary polishing systems on hardness and roughness of one-shaded dental composites
Kivanc Dulger, Gencaga Purcek
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2025; 61(3): 841. CrossRef - Physicomechanical properties and polymerization shrinkage of the newly developed radiopaque flowable composite derived from rice husk
Nor Ain Fatihah Azlisham, Yanti Johari, Dasmawati Mohamad, Mohd Firdaus Yhaya, Zuliani Mahmood
Polymer Composites.2025; 46(7): 5924. CrossRef - Highly Filled Flowable Composite Resins as Sole Restorative Materials: A Systematic Review
Konstantinos Tzimas, Eftychia Pappa, Maria Fostiropoulou, Efstratios Papazoglou, Christos Rahiotis
Materials.2025; 18(14): 3370. CrossRef - Effect of immersion and thermocycling in different beverages on the surface roughness of single- and multi-shade resin composites
Aiah A. El-Rashidy, Omar Shaalan, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Nour A. Habib
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Degree of conversion and physicomechanical properties of newly developed flowable composite derived from rice husk using urethane dimethacrylate monomer
Nor Ain Fatihah Azlisham, Yanti Johari, Dasmawati Mohamad, Mohd Firdaus Yhaya, Zuliani Mahmood
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2023; 237(12): 1339. CrossRef - Translucency and Color Stability of a Simplified Shade Nanohybrid Composite after Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing
Ksenia Babina, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Alexandr Zaytsev, Elena E. Nikonova, Gleb S. Budylin, Evgeny A. Shirshin, Christian Tantardini, Nina Novozhilova
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(24): 4465. CrossRef - Surface properties and color stability of dental flowable composites influenced by simulated toothbrushing
Guangyun LAI, Liya ZHAO, Jun WANG, Karl-Heinz KUNZELMANN
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(5): 717. CrossRef - Topography and surface roughness of fluid resins used as bioprotectors of mini-implants
Rogério Lacerda-Santos, Mirella de Fátima Liberato de Moura, Fabíola Galbiatti Carvalho, Hugo Lemes Carlo, Matheus Melo Pithon, Bruno Alessandro Silva Guedes de Lima, Tibério Andrade dos Passos
Applied Adhesion Science.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of contemporary polishing systems on hardness and roughness of one-shaded dental composites
- 2,509 View
- 19 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Surface roughness of composite resin according to finishing methods
- Jeong-Bum Min, Kong-Chul Cho, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):138-150. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the difference of surface roughness of composite resin according to composite resin type, polishing methods, and use of resin sealant.
Two hundred rectangular specimens, sized 8 × 3 × 2 mm, were made of Micro-new (Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A) and Filtek Supreme (3M ESPE Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.), and divided into two groups; Micronew-M group, Filtek Supreme-S group. Specimens for each composite group were subdivided into five groups by finishing and polishing instruments used; M1 & S1 (polyester strip), M2 & S2 (Sof-Lex disc), M3 & S3 (Enhance disc and polishing paste), M4 & S4 (Astropol), and M5 & S5 (finishing bur). Polished groups were added letter B after the application of resin surface sealant (Biscover), eg, M1B and S1B.
After specimens were stored with distilled water for 24 hr, average surface roughness (Ra) was taken using a surface roughness tester. Representative specimens of each group were examined by FE-SEM (S-4700: Hitachi High Technologies Co., Tokyo, Japan). The data were analysed using paired t-test, ANOVA and Duncan's tests at the 0.05 probability level. The results of this study were as follows;
The lowest Ra was achieved in all groups using polyester strip and the highest Ra was achieved in M5, S5 and M5B groups using finishing bur. On FE-SEM, M1 and S1 groups provided the smoothest surfaces, M5 and S5 groups were presented the roughest surfaces and voids by debonding of filler on the polished specimens.
There was no significant difference in Ra between Micronew and Filtek Supreme before the application of resin sealant, but Micronew was smoother than Filek Supreme after the application of resin sealant.
There was significant corelation between Ra of type of composite resin and polishing methods before the application of resin sealant (p = 0.000), but no significant interaction between them after the application of resin sealant. On FE-SEM, most of composite resin surfaces were smooth after the application of resin sealant on the polished specimens.
Compared with before and after the application of resin sealant in group treated in the same composite and polishing methods, Ra of M4B and M5B was statistically lower than that of M4 and M5, and S5B was lower than that of S5, respectively (p < 0.05).
In conclusion, surface roughness by polishing instruments was different according to type of composite resin. Overall, polyester strip produced the smoothest surface, but finishing bur produced the roughest surface. Application of resin sealant provided the smooth surfaces in specimens polished with Enhance, Astropol and finishing bur, but not provided them in specimens polished with Sof-Lex disc.
- 1,427 View
- 7 Download

- EVALUATION ON THE ABRASION RESISTANCE OF A SURFACE SEALANT
- Soo-Mee Kim, Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):180-190. Published online January 14, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the abrasion resistance of surface penetrating sealant which was applied on a composite resin restoration and to provide proper time to reapply sealant on composite resin surface.
Two hundred rectangular specimens, sized 8 × 3 × 2 mm, were made of Micronew (Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A) and divided into two groups; F group (n = 10) was finished with coarse and medium grit of Sof-Lex discs and BisCoverwas applied B group (n = 190) after finishing with discs. B group was again subdivided into nineteen subgroups. From B-1 group to B-18 group were subjected to toothbrush abrasion test using a distilled water-dentifrice slurry and toothbrush heads. B-IM group was not subjected to toothbrush abrasion test.
Average surface roughness (Ra) of each group was calculated using a surface roughness tester (Surfcorder MSE-1700: Kosaka Laboratory Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). A representative specimen of each group was examined by FE-SEM (S-4700: Hitachi High Technologies Co., Tokyo, Japan). The data were analysed using cluster analysis, paired t-test, and repeated measure ANOVA. The results of this study were as follows;
Ra of F group was 0.898 ± 0.145 μm and B-IM group was 0.289 ± 0.142 μm. Ra became higher from B-1 group (0.299 ± 0.48 μm) to B-18 group (0.642 ± 0.313 μm).
Final cluster center of Ra was 0.361 μm in cluster 1 (B-IM ∼ B-7), 0.511 μm in cluster 2 (B-8 ∼ B-14) and 0.624 μm in cluster 3 (B-15 ∼ B-18). There were significant difference among Ra of three clusters.
Ra of B-IM group was decreased 210.72% than Ra of F group. Ra of B-8 group and B-15 group was increased 35.49% and 51.35% respectively than Ra of B-IM group.
On FE-SEM, B-IM group showed the smoothest resin surface. B-8 group and B-15 group showed vertically shallow scratches, and wide and irregular vertical scratches on composite resin surface respectively.
Within a limitation of this study, finished resin surface will be again smooth and glazy if BisCover would be reapplied within 8 to 14 months after applying to resin surface.
- 978 View
- 3 Download

- Influence of the Surface roughness on translucency and surface color of the dental composite resins
- Kyu-Jeong Cho, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):312-322. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.312
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effect of surface roughness on the surface color and translucency of the composite resins.
Two composite resins (Esthet-X, Dentsply, Milford, USA and Charisma, Kulzer, Domagen, Germany) were used to investigate the surface color. Charisma was used to investigate the translucency. 40 disc samples (diameter: 8 mm, thickness: 5 mm) were made by each product to measure the surface color. Polymerized each sample's one side was treated by Sof-Lex finishing and polishing system (Group C, M, F, SF). 40 disc samples (diameter: 6 mm, thickness: 1 mm) were prepared to measure the opacity. 1 mm samples were ground one side with #600, #1000, #1500 and #2000 sandpapers. CIE L*a*b* values of each 5 mm thickness samples, and XYZ values of 1 mm thickness samples on the white and black background were measured with spectrophotometer (Spectrolino, GretagMacbeth, Regensdorf, Switzerland).
Mean surface roughness (Ra) of all samples before and after surface treatment was measured using the Surface Roughness Tester SJ-301 (Mytutoyo, Tokyo, Japan).
Regardless of type and shade of the composite resin, L* values measured in group C were higher than others (p < 0.05), and L* value decreased as the Ra value decreased except B3 shade of Esthet-X. But there were no significant difference in a* values among groups. In control group and SF, highest b* values were measured (p < 0.05), except B1 shade of Esthet-X.
Contrast ratio decreased as the Ra value decreased (p < 0.05).
With the above results, difference of surface roughness has influence on surface color and translucency of dental composite resins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Smokeless Tobacco on Color Stability and Surface Roughness of 3D-Printed, CAD/CAM-Milled, and Conventional Denture Base Materials: An In Vitro Study
Maryam H. Mugri, Saurabh Jain, Mohammed E. Sayed, Amjad Hussain Asiri Halawi, Safa Ahmed Ibrahim Hamzi, Raniya Abdulaziz Saad Aljohani, Zainab Mousa Ali Madkhali, Asaad Khalid, Hossam F. Jokhadar, Mai Almarzouki, Ghaida A. Alhumaidan, Ahid Amer Alshahrani
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 491. CrossRef - Optical characteristics of resin composite before and after polymerization
Ah-Hyang Eom, Duck-Su Kim, Soo-Hee Lee, Chang-Won Byun, Noh-Hoon Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 219. CrossRef - Surface roughness and color stability of various composite resins
Sung-Yi Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 542. CrossRef
- Effects of Smokeless Tobacco on Color Stability and Surface Roughness of 3D-Printed, CAD/CAM-Milled, and Conventional Denture Base Materials: An In Vitro Study
- 1,517 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Surface roughness and microleakage of class V composite restorations : Effect of surface sealing
- Min-Jeong Kim, Mi-Jeong Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Soo-Joung Park, Kwang-Won Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):22-30. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.022
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of surface sealing materials on microleakage and surface roughness in Class V composite restorations.
Twenty five standardized Class V cavity preparations were made on the facial surface of human premolars and were randomly assigned to 5 groups. The teeth were restored with Z-250 after applying Single Bond. Following 7 days storage in distilled water at 37℃, the restorations were sealed as following systems : No sealing ; Single Bond Adhesive ; Biscover ; Fortify ; Optiguard. Then, toothbrush abrasion test was conducted using a wear testing machine.
Surface roughness was measured by means of profilometer before and after toothbrushing and the results were statistically analysed by using a paired t-test and ANOVA. The bonded interfaces and the changes of surface roughness were examined by SEM.
For microleakage test, specimens were stained in a 2% methylene blue solution, then longitudinally sectioned and analyzed for leakage at occlusal and cervical interfaces using stereomicroscope. The results were statistically analysed by using a Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U test.
Surface roughness was increasing in all groups after toothbrushing, but no statistically significant differences. In SEM observation, surface sealant was partially retained and partially detached in bonded interfaces. Especially, microgap was identified in cervical margins. In microleakage test, there was better seal in the enamel region and a significant difference between groups at occlusal margin. Control group and Single Bond group had significantly better marginal seal at enamel margin than cervical margin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microleakage of 2-step adhesive systems in diamond-prepared cavity
Myung-Goo Lee, Kwon-Hwan Cho, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 437. CrossRef
- Microleakage of 2-step adhesive systems in diamond-prepared cavity
- 1,007 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surface roughness of universal composites after polishing procedures
- Jae-Yong Lee, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):369-377. Published online September 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.369
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of two polishing methods and chemical conditioning on the surface of hybrid composites.
Ninety cylindrical specimens (diameter: 8 mm, depth: 2 mm) were made with three hybrid composites - Filtek Z250, Tetric Ceram, DenFil. Specimens for each composite were randomly divided into three treatment subgroups - ① Mylar strip (no treatment), ② Sof-Lex XT system, ③ PoGo system. Average surface roughness(Ra) was taken using a surface profilometer at the time of setting and after immersion into 0.02N lactic acid for 1 week and 1 month. Representative specimens were examined by scanning electron microscopy. The data were analyzed using ANOVA and Scheffe's tests at 0.05% significance level.
The results were as follows:
Mylar strip resulted in smoother surface than PoGo and Sof-Lex system(p<0.001). Sof-Lex system gave the worst results.
Tetric Ceram was smoother than DenFil and Z250 when cured under only mylar strip. However, it was significantly rougher than other materials when polished with PoGo system.
All materials showed rough surface after storage in 0.02N lactic acid, except groups polished with a PoGo system.
The PoGo system gave a superior polish than Sof-Lex system for the three composites. However, the correlation to clinical practice may be limited, since there are several processes, such as abrasive, fatigue, and corrosive mechanisms. Thus, further studies are needed for polishing technique under in vivo conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
Ye-Mi Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Min-Ju Song, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 119. CrossRef - Surface roughness of experimental composite resins using confocal laser scanning microscope
JH Bae, MA Lee, BH Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation on the abrasion resistance of a surface sealant
Soo-Mee Kim, Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(3): 180. CrossRef - Surface roughness of composite resin according to finishing methods
Jeong-Bum Min, Kong-Chul Cho, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 138. CrossRef - Influence of the Surface roughness on translucency and surface color of the dental composite resins
Kyu-Jeong Cho, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(4): 312. CrossRef
- The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
- 1,101 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


