Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 32(2); 2007 > Article
- Original Article Surface roughness of composite resin according to finishing methods
- Jeong-Bum Min, Kong-Chul Cho, Young-Gon Cho
-
2007;32(2):-150.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.138
Published online: March 31, 2007
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Young-Gon Cho. Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, 421 Seosuk-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju, 501-825, Korea. Tel: 82-62-220-3840, 3845, Fax: 82-62-232-9064, ygcho@chosun.ac.kr
Copyright © 2007 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,422 Views
- 7 Download
Abstract
-
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the difference of surface roughness of composite resin according to composite resin type, polishing methods, and use of resin sealant.Two hundred rectangular specimens, sized 8 × 3 × 2 mm, were made of Micro-new (Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, U.S.A) and Filtek Supreme (3M ESPE Dental Products, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.), and divided into two groups; Micronew-M group, Filtek Supreme-S group. Specimens for each composite group were subdivided into five groups by finishing and polishing instruments used; M1 & S1 (polyester strip), M2 & S2 (Sof-Lex disc), M3 & S3 (Enhance disc and polishing paste), M4 & S4 (Astropol), and M5 & S5 (finishing bur). Polished groups were added letter B after the application of resin surface sealant (Biscover), eg, M1B and S1B.After specimens were stored with distilled water for 24 hr, average surface roughness (Ra) was taken using a surface roughness tester. Representative specimens of each group were examined by FE-SEM (S-4700: Hitachi High Technologies Co., Tokyo, Japan). The data were analysed using paired t-test, ANOVA and Duncan's tests at the 0.05 probability level. The results of this study were as follows;
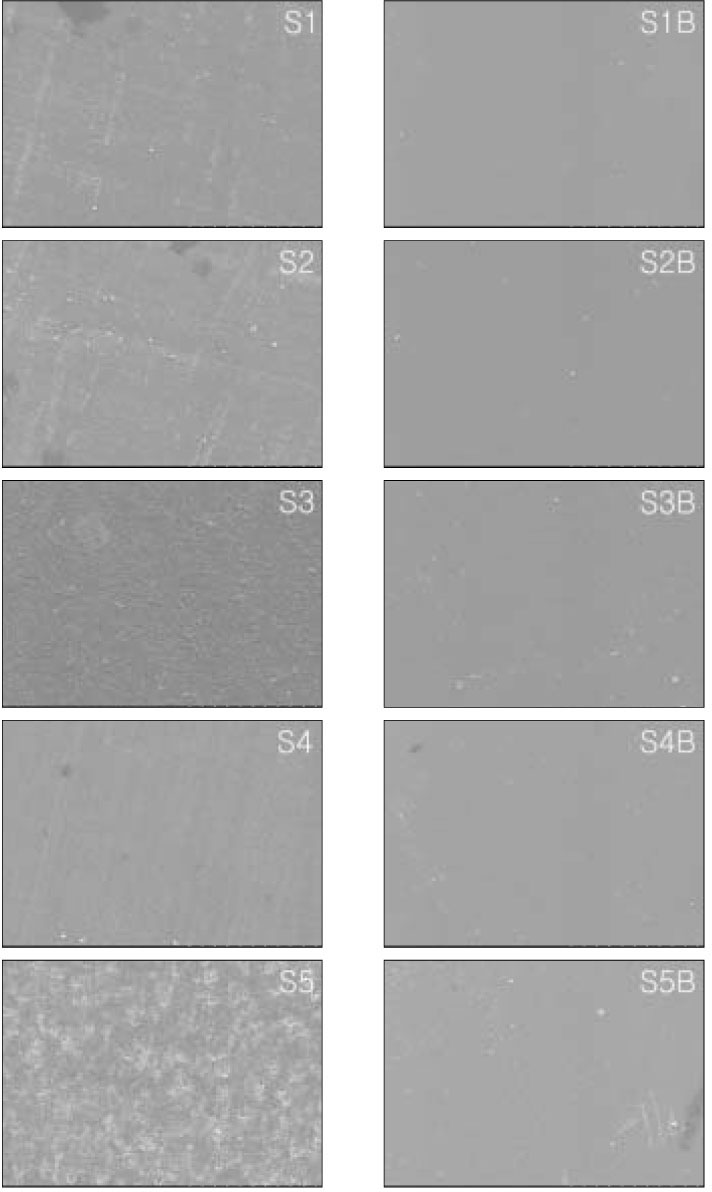
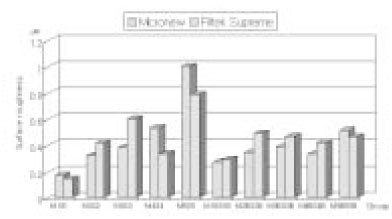
The lowest Ra was achieved in all groups using polyester strip and the highest Ra was achieved in M5, S5 and M5B groups using finishing bur. On FE-SEM, M1 and S1 groups provided the smoothest surfaces, M5 and S5 groups were presented the roughest surfaces and voids by debonding of filler on the polished specimens.
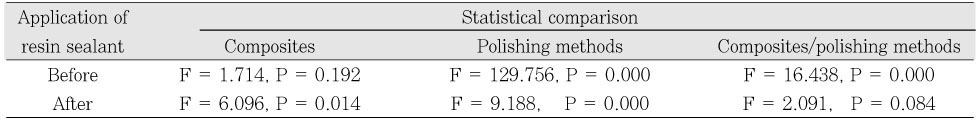
There was no significant difference in Ra between Micronew and Filtek Supreme before the application of resin sealant, but Micronew was smoother than Filek Supreme after the application of resin sealant.
There was significant corelation between Ra of type of composite resin and polishing methods before the application of resin sealant (p = 0.000), but no significant interaction between them after the application of resin sealant. On FE-SEM, most of composite resin surfaces were smooth after the application of resin sealant on the polished specimens.
Compared with before and after the application of resin sealant in group treated in the same composite and polishing methods, Ra of M4B and M5B was statistically lower than that of M4 and M5, and S5B was lower than that of S5, respectively (p < 0.05).
In conclusion, surface roughness by polishing instruments was different according to type of composite resin. Overall, polyester strip produced the smoothest surface, but finishing bur produced the roughest surface. Application of resin sealant provided the smooth surfaces in specimens polished with Enhance, Astropol and finishing bur, but not provided them in specimens polished with Sof-Lex disc.
- 1. Lu H, Roeder LB, Powers JM. Effect of polishing systems on the surface roughness of microhybrid composites. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2003;15: 297-304.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Joniot SB, Gregoire GL, Auther AM, Roques YM. Three-dimensional optical profilometry analysis of surface states obtained after finishing sequences for three composite resins. Oper Dent. 2000;25: 311-315.PubMed
- 3. Tate WH, Powers JM. Surface roughness of composites and hybrid ionomers. Oper Dent. 1996;21: 53-58.PubMed
- 4. Yap AUJ, Yap SH, Teo CK, Ng JJ. Finishing/polishing of composite and compomer restoratives: effectiveness of one-step systems. Oper Dent. 2004;29: 275-279.PubMed
- 5. Turssi CP, Saad JRC, Duarte SLL, Rodrigues AL. Composite surfaces after finishing and polishing techniques. Am J Dent. 2000;13: 136-138.PubMed
- 6. Marigo L, Rizzi M, La Torre G, Rumi G. 3-D surface profile analysis: different finishing methods for resin composites. Oper Dent. 2001;26: 562-568.PubMed
- 7. Reis AF, Giannini M, Lovadino JR, Ambrosano GM. Effects of various finishing systems on the surface roughness and staining susceptibility of packable composite resins. Dent Mater. 2003;19: 12-18.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Reis AF, Giannini M, Lovadino JR, dos Santos Dias CT. The effect of six polishing systems on the surface roughness of two packable resin-based composites. Am J Dent. 2002;15: 193-197.PubMed
- 9. Roeder LB, Tate WH, Powers JM. Effect of finishing and polishing procedures on the surface roughness of packable composites. Oper Dent. 2000;25: 534-543.PubMed
- 10. Yap AUJ, Yap SH, Teo CK, Ng JJ. Comparison of surface finish of new aesthetic restorative materials. Oper Dent. 2004;29: 100-104.PubMed
- 11. Fruits TJ, Miranda FJ, Coury TL. Effects of equivalent abrasive grit sizes utilizing different polishing motions on selected restorative materials. Quintessence Int. 1996;27: 279-285.PubMed
- 12. Ryba TM, Dunn WJ, Murchison DF. Surface roughness of various packable composites. Oper Dent. 2002;27: 243-247.PubMed
- 13. Schmidlin PR, Sener B, Lutz F. Cleaning and polishing efficacy of abrasive-bristle brushes and a prophylaxis paste on resin composite material in vitro. Quintessence Int. 2002;33: 691-699.PubMed
- 14. Turkun LS, Turkun M. The effect of one-step polishing system on the surface roughness of three esthetic resin composite materials. Oper Dent. 2004;29: 203-211.PubMed
- 15. Jung M, Voit S, Klinek J. Surface geometry of three packable and one hybrid composite after finishing. Oper Dent. 2003;28: 53-59.PubMed
- 16. van Dijken JW, Ruyter IE. Surface characteristics of posterior composites after polishing and tooth brushing. Acta Odontol Scand. 1987;45: 337-346.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Ferracane JL, Condon JR, Mitchem JC. Evaluation of subsurface defects created during the finishing of composites. J Dent Res. 1992;71: 1628-1632.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Yap AUJ, Lye KW, Sau CW. Surface characteristics of tooth-colored restoratives polished utilizing different polishing systems. Oper Dent. 1997;22: 260-265.PubMed
- 19. Hoelscher DC, Neme AML, Pink FE, Hughes PJ. The effect of three finishing systems on four esthetic restorative materials. Oper Dent. 1998;23: 36-42.PubMed
- 20. O'Brien WJ, Yee J. Microstructure of posterior restoration of composite resin after clinical wear. Oper Dent. 1980;5: 90-94.PubMed
- 21. Shinkai K, Suzuki S, Leinfelder KF, Katoh Y. Effect of surface-penetrating sealant on resistance of luting agents. Quintessence Int. 1994;25: 767-771.PubMed
- 22. Dickinson GL, Leinfelder KF. Assessing the long-term effect of a surface penetrating sealant. J Am Dent Assoc. 1993;124: 68-72.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Erhardt MCG, Magalhaes CS, Serra MC. The effect of rebonding on microleakage of class V aesthetic restorations. Oper Dent. 2002;27: 396-402.PubMed
- 24. Nagem Filho H, D'Azevedo MTFS, Nagem HD, Marsola FP. Surface roughness of composite resins after finishing and polishing. Braz Dent J. 2003;14: 37-41.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Ramos RP, Chinelatti MA, Chimello DT, Dibb RGP. Assessing microleakage in resin composite restorations rebonded with a surface sealant and three low-viscosity resin systems. Quintessence Int. 2002;33: 450-456.PubMed
- 26. Barghi N, Alexander C. A new surface sealant for polishing composite resin restorations. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2003;24: 30-33.PubMed
- 27. Suh BI. A new resin technology: a glaze/composite sealant that cures without forming an oxygen-inhibited layer. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2003;24: 27-29.PubMed
- 28. Lee JY, Shin DH. Surface roughness of universal composites after polishing procedures. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2003;28: 369-377.Article
- 29. Setcos JC, Tarim B, Suzuki S. Surface finish produced on resin composites by new polishing systems. Quintessence Int. 1999;30: 169-173.PubMed
- 30. Bertrand MF, Leforestier E, Muller M, Lupi-Pegurier L, Bolla M. Effect of surface penetrating sealant on surface texture and microhardness of composite resins. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;53: 658-663.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Weitman RT, Eames WB. Plaque accumulation on composite surface after various finishing procedures. J Am Dent Assoc. 1975;91: 101-106.PubMed
REFERENCES

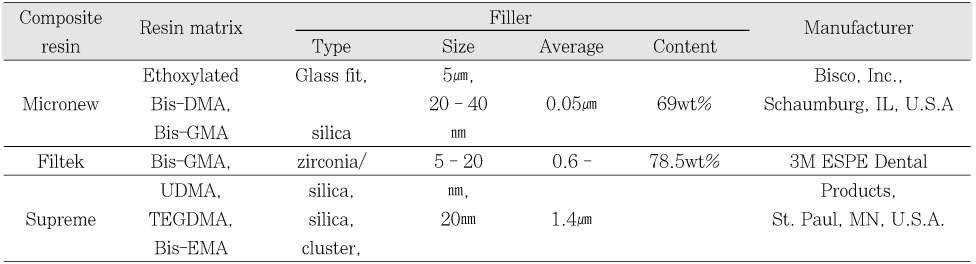
Bis-DMA: bisphenol A dimethacrylate, Bis-GMA: bisphenol A diglycidylmethacrylate,
UDMA: urethan dimethacrylate, TEGDMA: triethylene glycol dimethacrylate,
Bis-EMA: bisphenol A polyethylene glycol diether dimethacrylate
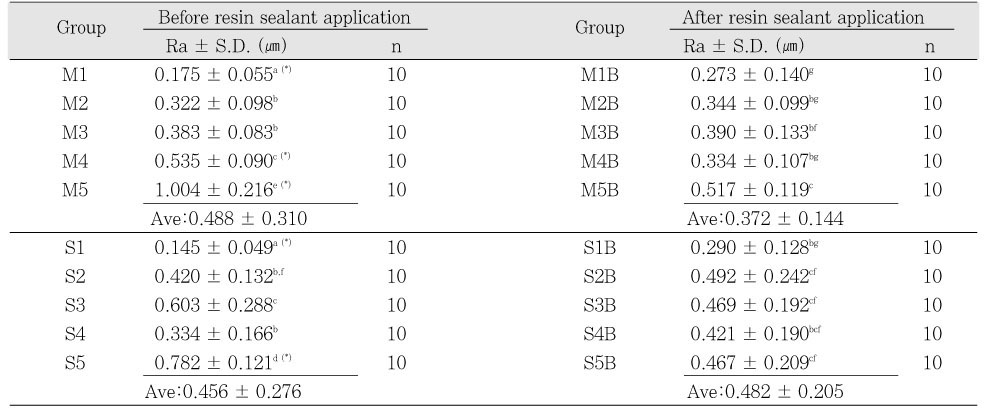
Superscripts of the other letter indicate values of statistical significant difference
(p < 0.05, Duncan,s multiple comparison test). Ave: Average roughness
(*): statistical significant difference between groups in the same composite and polishing method before and after resin sealant application (p < 0.05, paired t-test).
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

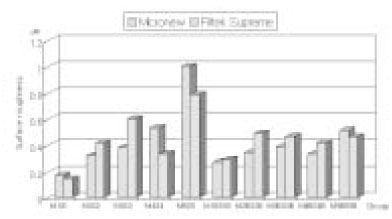
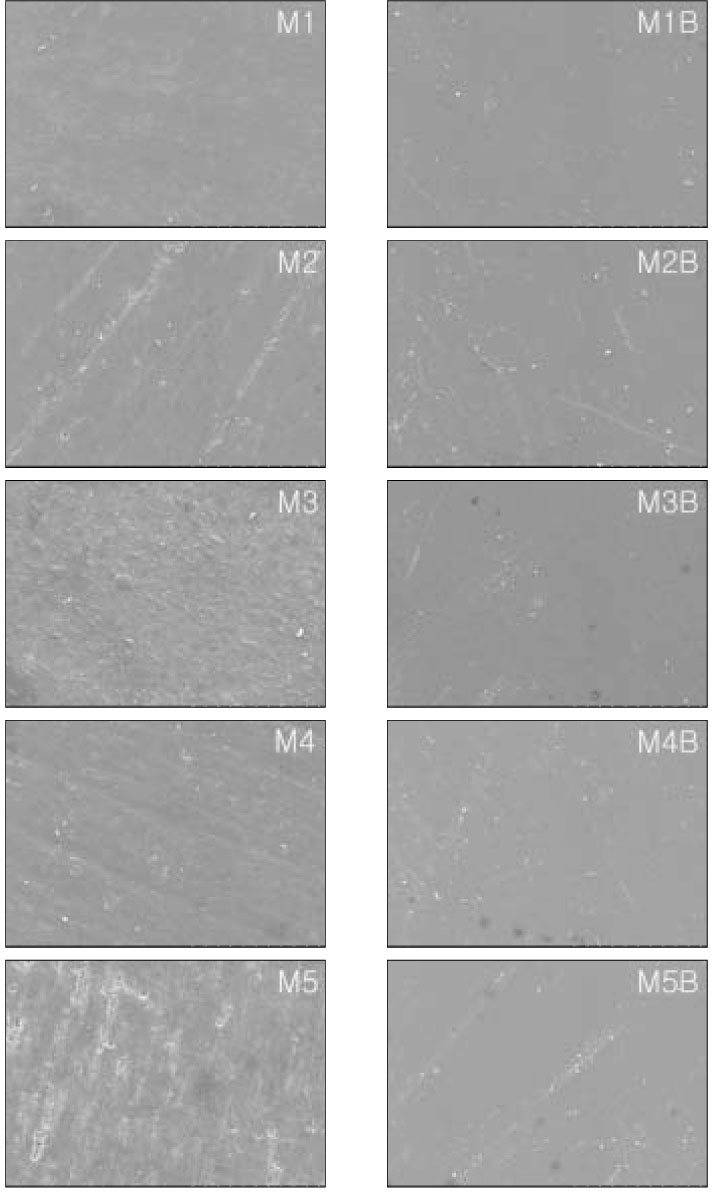
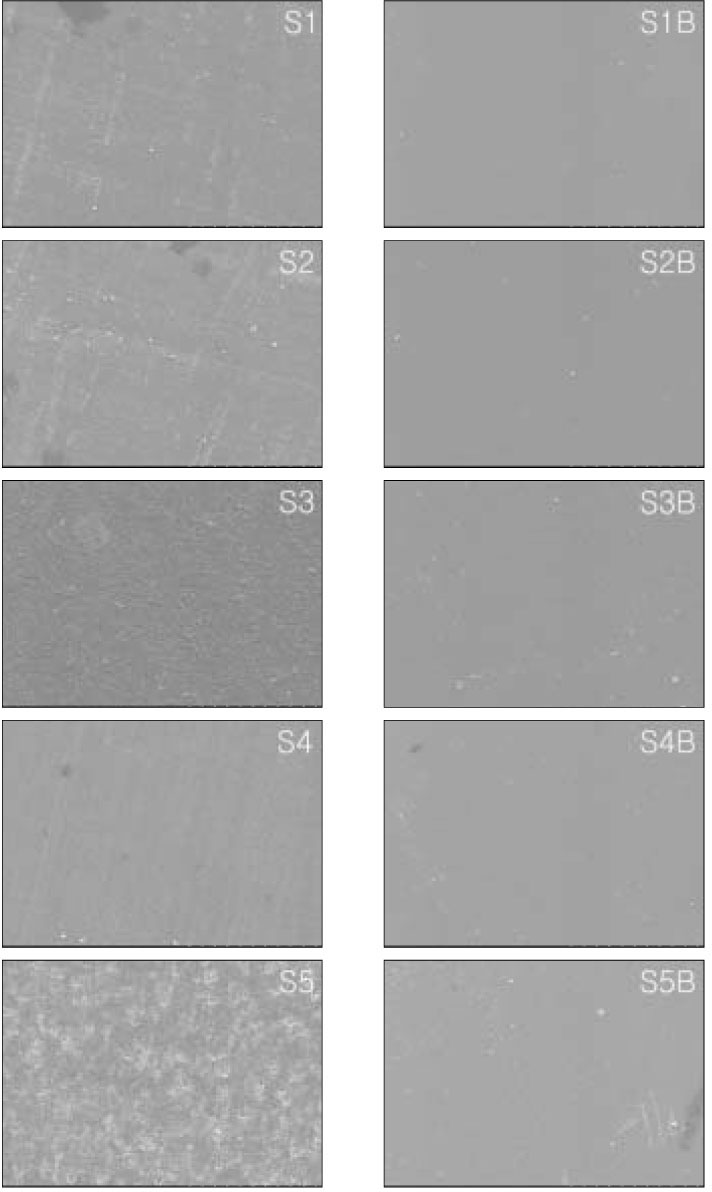
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Resin matrix and filler of composite resins used
Bis-DMA: bisphenol A dimethacrylate, Bis-GMA: bisphenol A diglycidylmethacrylate,
UDMA: urethan dimethacrylate, TEGDMA: triethylene glycol dimethacrylate,
Bis-EMA: bisphenol A polyethylene glycol diether dimethacrylate
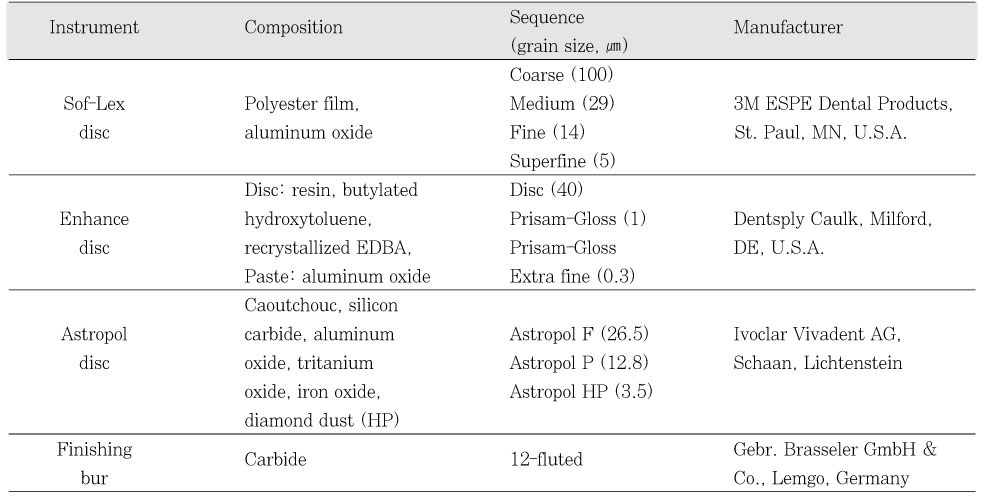
Composition and sequence of finishing and polishing instruments used
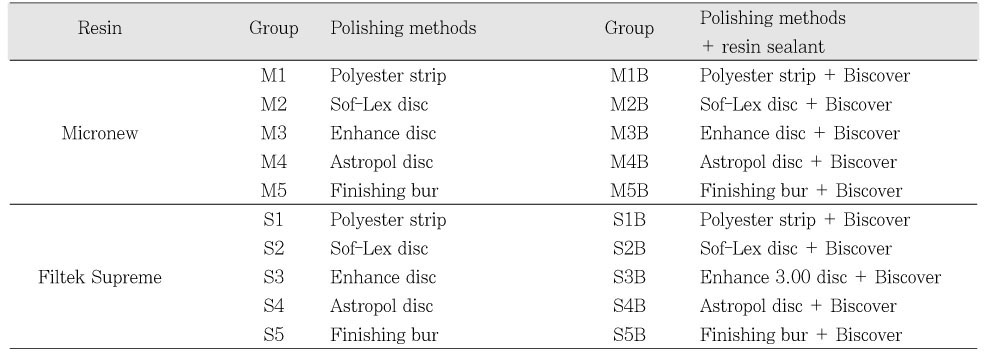
Group classification by composite type, polishing methods and resin sealant application
M: Micronew, S: Filtek Supreme, B: Biscover
Average surface roughness (Ra) of each group before and after resin sealant application
Superscripts of the other letter indicate values of statistical significant difference
(p < 0.05, Duncan,s multiple comparison test). Ave: Average roughness
(*): statistical significant difference between groups in the same composite and polishing method before and after resin sealant application (p < 0.05, paired t-test).
Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA
Bis-DMA: bisphenol A dimethacrylate, Bis-GMA: bisphenol A diglycidylmethacrylate, UDMA: urethan dimethacrylate, TEGDMA: triethylene glycol dimethacrylate, Bis-EMA: bisphenol A polyethylene glycol diether dimethacrylate
M: Micronew, S: Filtek Supreme, B: Biscover
Superscripts of the other letter indicate values of statistical significant difference (p < 0.05, Duncan,s multiple comparison test). Ave: Average roughness (*): statistical significant difference between groups in the same composite and polishing method before and after resin sealant application (p < 0.05, paired t-test).

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

