Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
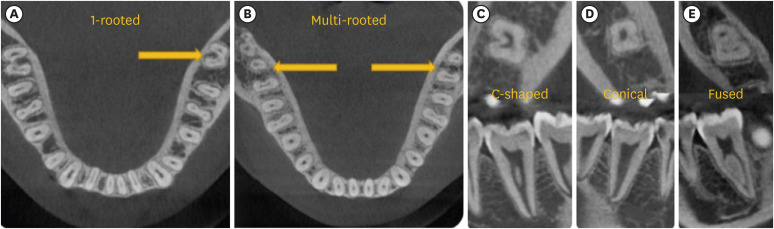
- Predictor factors of 1-rooted mandibular second molars on complicated root and canal anatomies of other mandibular teeth
- Hakan Aydın, Hatice Harorlı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e2. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to determine the effects of 1-rooted mandibular second molar (MnSM) teeth on root canal anatomy complexities of the mandibular central incisor (MnCI), mandibular lateral incisor (MnLI), mandibular canine (MnCn), mandibular first premolar (MnFP), mandibular second premolar (MnSP), and mandibular first molar (MnFM) teeth.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography images of 600 patients with full lower dentition were examined. Individuals with 1-rooted MnSMs were determined, and the complexity of root canal anatomy of other teeth was compared with individuals without 1-rooted MnSMs (Group-1; subjects with at least one 1-rooted MnSM, Group-2; subjects with more than a single root in both MnSMs). A second canal in MnCIs, MnLIs, MnCns, MnFPs, and MnSPs indicated a complicated root canal. The presence of a third root in MnFMs was recorded as complicated.
Results The prevalence of 1-rooted MnSMs was 12.2%, with the C-shaped root type being the most prevalent (9%). There were fewer complicated root canals in MnCIs (
p = 0.02), MnLIs (p < 0.001), and MnFPs (p < 0.001) in Group 1. The other teeth showed no difference between the groups (p > 0.05). According to logistic regression analysis, 1-rooted right MnSMs had a negative effect on having complex canal systems of MnLIs and MnFPs. Left MnSMs were explanatory variables on left MnLIs and both MnFPs.Conclusions In individuals with single-rooted MnSMs, a less complicated root canal system was observed in all teeth except the MnFMs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
Ariana Esperanza Apolo Aguilar, Maria Soledad Peñaherrera Manosalvas, Henry Paul Valverde Haro
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1007. CrossRef
- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
- 1,957 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

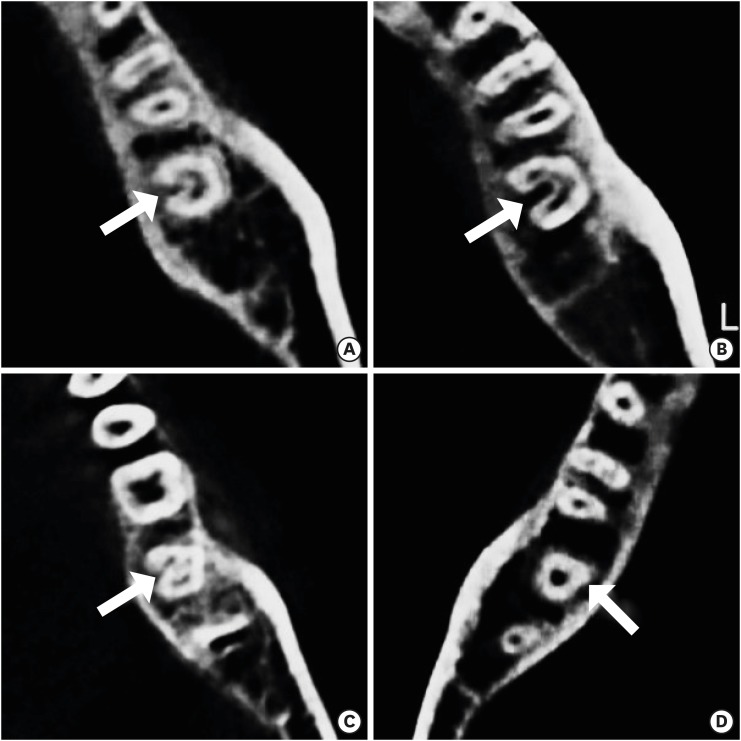
- C-shaped root canals of mandibular second molars in a Korean population: a CBCT analysis
- Hee-Sun Kim, Daun Jung, Ho Lee, Yoon-Sic Han, Sohee Oh, Hye-Young Sim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the C-shaped root canal anatomy of mandibular second molars in a Korean population.
Materials and Methods A total of 542 teeth were evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The canal shapes were classified according to a modified version of Melton's method at the level where the pulp chamber floor became discernible.
Results Of the 542 mandibular second molars, 215 (39.8%) had C-shaped canals, 330 (53%) had 3 canals, 17 (3.3%) had 2 canals, 12 (2.2%) had 4 canals, and 8 (1.7%) had 1 canal. The prevalence of C-shaped canals was 47.8% in females and 28.4% in males. Seventy-seven percent of the C-shaped canals showed a bilateral appearance. The prevalence of C-shaped canals showed no difference according to age or tooth position. Most teeth with a C-shaped canal system presented Melton's type II (45.6%) and type III (32.1%) configurations.
Conclusions There was a high prevalence of C-shaped canals in the mandibular second molars of the Korean population studied. CBCT is expected to be useful for endodontic diagnosis and treatment planning of mandibular second molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
Jacob John, Wei Cheong Ngeow, Ting-Chun Shen, Lih-Jyh Fuh, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Yen-Wen Shen, Jui-Ting Hsu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 21(1): 265. CrossRef - Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Amin Salem Milani, Shahin Namvar Asl Amirkhizi, Tahmineh Razi, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Pouya Sabanik, Nikhat Kaura
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of mandibular and maxillary second molar root canal anatomy in a Turkish subpopulation using CBCT: comparison of Briseno-Marroquin and Vertucci classifications
Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, İpek Öreroğlu, Kemal Çağlar, Kader Cesur Aydin
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e18. CrossRef - Prevalence of c-shaped canal morphology in premolar and molar teeth assessed by cone-beam computed tomography: systematic review and meta-analysis
Faezeh Yousefi, Younes Mohammadi, Elham Shokri
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging Findings of Clinical Significance in Endodontics During Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scanning of the Upper Airway—The Anterior, Bilateral, C-Shaped, Dual of Mandibular Root Canals: A Brief Case Report
Edgar García-Torres, Diana Laura Grissel Guerrero-Falcón, Hugo Alejandro Bojórquez-Armenta, Oscar Eduardo Almeda-Ojeda, Víctor Hiram Barajas-Pérez, Luis Javier Solís-Martínez
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3157. CrossRef - Frequency of C-Shaped Root Canals in Permanent Mandibular Second Molars in a Sample of Pakistani Population using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Syed Nabeel Ahmed, Muhammad Mansoor Majeed, Sakina Kazmi, Muhammad Omar Ansari
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2024; : 109. CrossRef - ANÁLISE DAS VARIAÇÕES ANATÔMICAS DE CANAIS C-SHAPED NOS MOLARES INFERIORES: UMA REVISÃO INTEGRATIVA DA LITERATURA
Larissa Eulália Pereira, Thayana Karla Guerra Lira dos Santos
Revista Contemporânea.2024; 4(5): e4264. CrossRef - External Validation of the Effect of the Combined Use of Object Detection for the Classification of the C-Shaped Canal Configuration of the Mandibular Second Molar in Panoramic Radiographs: A Multicenter Study
Sujin Yang, Kee-Deog Kim, Yoshitaka Kise, Michihito Nozawa, Mizuho Mori, Natsuho Takata, Akitoshi Katsumata, Yoshiko Ariji, Wonse Park, Eiichiro Ariji
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 627. CrossRef - A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of C‐Shaped Canal Configuration in Maxillary Molars Among an Iranian Population
Nafiseh Nikkerdar, Mohammad Moslehi, Amin Golshah, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Egyptian subpopulation: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Mohammed abou El Seoud, Shaimaa Mohamed Abu el Sadat, Nawar Naguib Nawar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al‑Zubaidi, Abdulmjeed S. Enizy, Ahmed A. Madfa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in kuwaiti sub-population
AbdullahJassim Alenezi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, MazenA Aldosimani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 283. CrossRef - Prevalence and morphology of C‐shaped and non‐C‐shaped root canal systems in mandibular second molars
T Fenelon, P Parashos
Australian Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars of a selected patient group using cone beam computed tomography: prevalence, configuration and radicular groove types
Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan, Güzide Pelin Sezgin
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 949. CrossRef - Prevalência estimada de canais “C- Shaped”: Uma revisão sistemática e meta-análise
Natália Pereira da Silva Falcão, Sandro Junio de Oliveira Tavares, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Katherine Azevedo Batistela Rodrigues Thuller, Leonardo dos Santos Antunes, Estefano Borgo Sarmento, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azevedo, Cinthya Cristina Gomes, Ca
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 91. CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Clinical and radiological assessment of the anatomical and topographic structure of the root canals of teeth in patients of different age groups
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, O.A. Boriskina, I.S. Berkutova, V.A. Venediktova, R.R. Saltovets
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(5): 32. CrossRef
- A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
- 2,433 View
- 14 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Healing outcomes of root canal treatment for C-shaped mandibular second molars: a retrospective analysis
- Hye-Ra Ahn, Young-Mi Moon, Sung-Ok Hong, Min-Seock Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):262-270. Published online August 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the healing rate of non-surgical endodontic treatment between C-shaped and non-C-shaped mandibular second molars.
Materials and Methods Clinical records and radiological images of patients who had undergone endodontic treatment on mandibular second molars between 2007 and 2014 were screened. The periapical index scoring system was applied to compare healing outcomes. Information about preoperative and postoperative factors as well as the demographic data of the patients was acquired and evaluated using chi-square and multinomial logistic regression tests.
Results The total healing rate was 68.4%. Healing rates for the mandibular second molar were 70.9% in C-shaped canals (
n = 79) and 66.6% in non-C-shaped ones (n = 117). The difference was not statistically significant.Conclusions The presence of a C-shaped canal in the mandibular second molar did not have a significantly negative effect on healing after treatment. Instead, proper pulpal diagnosis and final restoration were indicated as having significantly greater influence on the healing outcomes of C-shaped and non-C-shaped canals, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting early endodontic treatment failure following primary root canal treatment
Young-Eun Jang, Yemi Kim, Sin-Young Kim, Bom Sahn Kim
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Non-Surgical Root Canal Treatment Outcomes in Mandibular Second Molars: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Da-Min Park, Woo-Hyun Seok, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(10): 2931. CrossRef - Retrospective Assessment of Healing Outcome of Endodontic Treatment for Mandibular Molars with C-shaped Root Canal
Kishore Kumar Majety, Basanta Kumar Choudhury, Anika Bansal, Achla Sethi, Jaina Panjabi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(7): 591. CrossRef
- Predicting early endodontic treatment failure following primary root canal treatment
- 1,977 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
- Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):132-136. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The presence of radix entomolaris (RE) in a mandibular first molar is a common occurrence in certain ethnic groups, but the presence of RE in a mandibular second molar is a rare occurrence. In the present case, RE was identified from preoperative radiographs and confirmed using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The access cavity was modified to locate the RE. Cleaning and shaping were performed with nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Obturation was completed with gutta-percha cones using AH Plus (Dentsply Detrey GmbH) as sealer. From the CBCT axial images, the RE was determined to have a Type III curvature by the De Moor classification, Type B separate RE by the Carlsen and Alexandersen classification, and radiographically, a Type i image by the Wang classification. The presence of RE in the mandibular second molar makes it essential to anticipate and treat the distolingual root canal. This case report highlights the usefulness of CBCT for assessing RE in the mandibular second molar, which can help the clinician in making a confirmatory diagnosis and assessing the morphology of the root canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Three-Dimensional Observation and Classification of Root and Root Canal Morphology in Japanese Mandibular Third Molars
Tomoyuki Inose, Satoru Matsunaga, Norio Kasahara, Masashi Yamada, Shinichi Abe, Masahiro Furusawa
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2026; 35(1): 7. CrossRef - Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular Second Molar Featuring Vertucci Type V Configuration in the Distal Root: A Case Report
He Liu, Ya Shen
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of a case of radix entomolaris: A case report
Priyanka Shorey, Kitty Sidhu
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2022; 7(1): 39. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of tooth with morphological anomalies using cone-beam computed tomography
Sung-Hyeon Choi, Na-Kyung Yoon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Bin-Na Lee
Oral Biology Research.2018; 42(1): 53. CrossRef - Unusual root morphology in second mandibular molar with a radix entomolaris, and comparison between cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiography: a case report
Elisardo López-Rosales, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Roland De Moor, Manuel Ruíz-Piñón, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, Purificación Varela-Patiño
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Three-Dimensional Observation and Classification of Root and Root Canal Morphology in Japanese Mandibular Third Molars
- 2,238 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Asymmetry in mesial root number and morphology in mandibular second molars: a case report
- Gurudutt Nayak, Shashit Shetty, Rhitu Shekhar
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):45-50. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Ambiguity in the root morphology of the mandibular second molars is quite common. The most common root canal configuration is 2 roots and 3 canals, nonetheless other possibilities may still exist. The presence of accessory roots is an interesting example of anatomic root variation. While the presence of radix entomolaris or radix paramolaris is regarded as a typical clinical finding of a three-rooted mandibular second permanent molar, the occurrence of an additional mesial root is rather uncommon and represents a possibility of deviation from the regular norms. This case report describes successful endodontic management of a three-rooted mandibular second molar presenting with an unusual accessory mesial root, which was identified with the aid of multiangled radiographs and cone-beam computed tomography imaging. This article also discusses the prevalence, etiology, morphological variations, clinical approach to diagnosis, and significance of supernumerary roots in contemporary clinical dentistry.
- 2,051 View
- 6 Download

- Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
- Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):172-177. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The mesiobuccal root of the maxillary molars is well known to pose a hindrance during endodontic therapy. Presented here is a case of a maxillary left second molar where three canals were located in its mesiobuccal root with the use of visual and diagnostic aids. Difficulties encountered during the process of unveiling the tooth's internal anatomy were discussed. The dilemmas encountered pertained to the root canal configuration, the nomenclature of the extra canals, and the justification for the presence of a third canal. The root canal configuration of 3-2-1 was confirmed for the mesiobuccal root using information gained from clinical, radiographic, and multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) scan findings. This case demonstrates the need for efforts to locate extra canals in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary molars as their internal anatomy remains a mystery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Somayeh Majidi, Vlaho Brailo
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A case report on endodontic management of the rarest Vertucci's Type VIII configuration in maxillary second molar with three mesiobuccal canals
ShrustiAjay Govil, Geeta Asthana, Shikha Kanodia, Abhishek Parmar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 404. CrossRef - The MB3 canal in maxillary molars: a micro-CT study
Ronald Ordinola-Zapata, Jorge N. R. Martins, Hugo Plascencia, Marco A. Versiani, Clovis M. Bramante
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(11): 4109. CrossRef - Three Root Canals in the Mesiobuccal Root of Maxillary Molars: Case Reports and Literature Review
Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Anas Al-Jadaa
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(12): 2087. CrossRef
- Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
- 1,738 View
- 8 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A retrospective study of the intentionally replanted mandibular second molars with C-shaped root canal configurations
- Won-Jun Shon, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Woo-Cheol Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):19-25. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the success rate of intentionally replanted mandibular second molar with C-shaped canal configurations and to access the impact of preoperative periapical lesion on the success of intentional replantation procedure.
Materials and Methods This retrospective chart review study evaluated 52 intentionally replanted mandibular second molar teeth treated at Seoul National University Dental Hospital Department of Conservative Dentistry from January 2005 to December 2007. Seventeen teeth were lost for the follow-up, and another 6 teeth did not meet inclusion criteria of C-shaped root canal configurations. Healing outcome such as success, uncertain healing, and failure after follow-up was evaluated by clinical criteria and radiographs.
Results The overall success rate was 72.4% for the 29 intentionally replanted C-shaped mandibular second molars. The success rate of replanted teeth with preoperative periapical lesions was similar to that of replanted teeth which have no periapical lesions.
Conclusions Therefore, root canal treatment failure on C-shaped mandibular second molar can be predictably treated by intentional replantation regardless of the presence of periapical lesion.
- 1,258 View
- 6 Download

- A retrospective study on incidence of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars
- Hee-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(4):346-349. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mandibular second molars have many variations in canal configuration. Technical modifications in cleaning, shaping and obturation are required. The purpose of this study was to investigate the root canal anatomy of mandibular second molars. 86 teeth of 85 patients were accessed and evaluated with taking radiographs for working length determination. 27 teeth(31.4%) had C-shaped canals, 43 teeth(50%) had 3 canals, 11 teeth(12.7%) had 4 canals, 5 teeth(5.8%) had 2 canals. Incidence of C-shaped canal was 31.7% in male and 31.1% in female. 30.9% of left mandibular second molar and 31.8% of right mandibular second molar showed C-shaped canals.
- 818 View
- 1 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


