Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Does the use of different root canal sealers and adhesive resin cements impact the bond strength of glass fiber posts?
- Ália Regina Neves de Paula Porto, Rudá França Moreira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e29. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
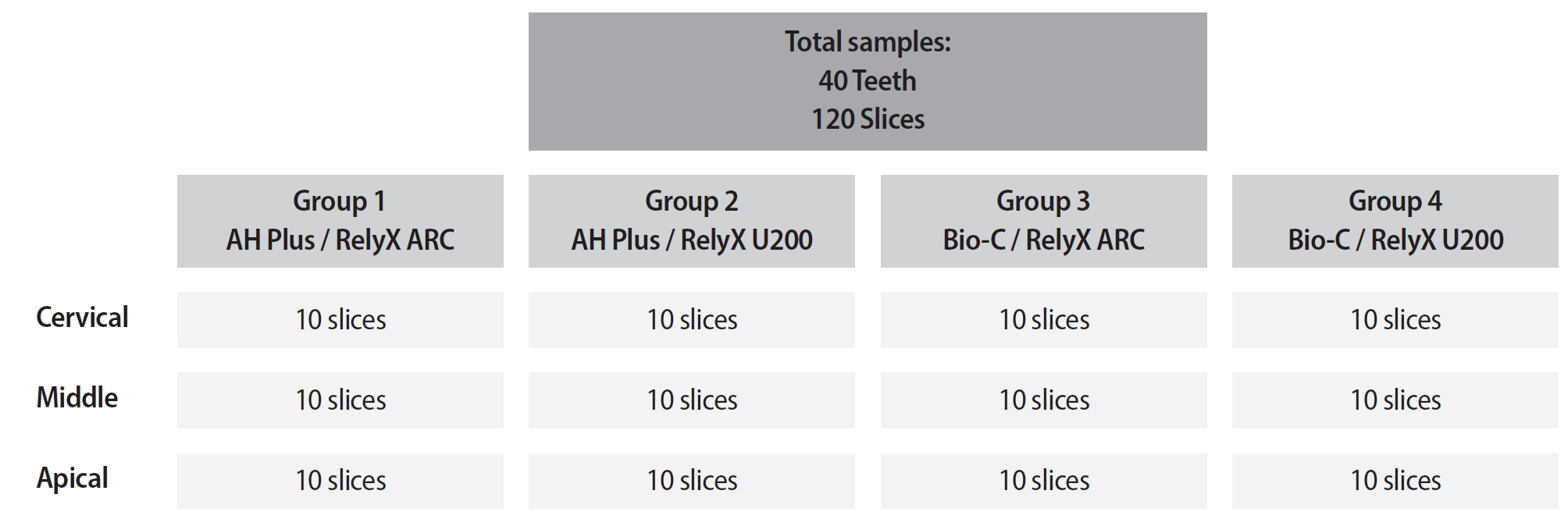
This study aimed to assess the influence of two endodontic sealers on the bond strength of glass fiber posts using conventional and self-adhesive resin cement through a push-out test. Methods: Forty central human incisors were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) based on sealer (epoxy resin- based or calcium silicate-based) and cement (conventional and self-adhesive resin) types: AH Plus (Dentsply De- Trey)/RelyX ARC (3M ESPE), AH Plus/RelyX U200 (3M ESPE), Bio-C Sealer (Angelus)/RelyX ARC, and Bio-C Sealer/RelyX U200. After canal filling and post cementation, roots were sectioned to obtain one specimen per root third. A pushout test and failure pattern assessment were conducted, with bond strength analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test. Results: AH Plus/RelyX ARC showed the highest bond strength values, with a significant difference in the middle third. The most common failure was mixed (55%), while adhesive failures made up 45%, with 23.5% at the cement/post interface and 21.5% at the cement/dentin interface. Conclusions: AH Plus/RelyX ARC provided the highest bond strength values for glass fiber posts to dentin.
- 1,819 View
- 146 Download

- Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
- Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e18. Published online March 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of relined and non-relined fiberglass posts when cemented to root canal dentin using a conventional dual-cure resin cement or a self-adhesive resin cement.
Materials and Methods Two types of resin cements were utilized: conventional and self-adhesive. Additionally, 2 cementation protocols were employed, involving relined and non-relined fiberglass posts. In total, 72 bovine incisors were cemented and subjected to push-out bond strength testing (
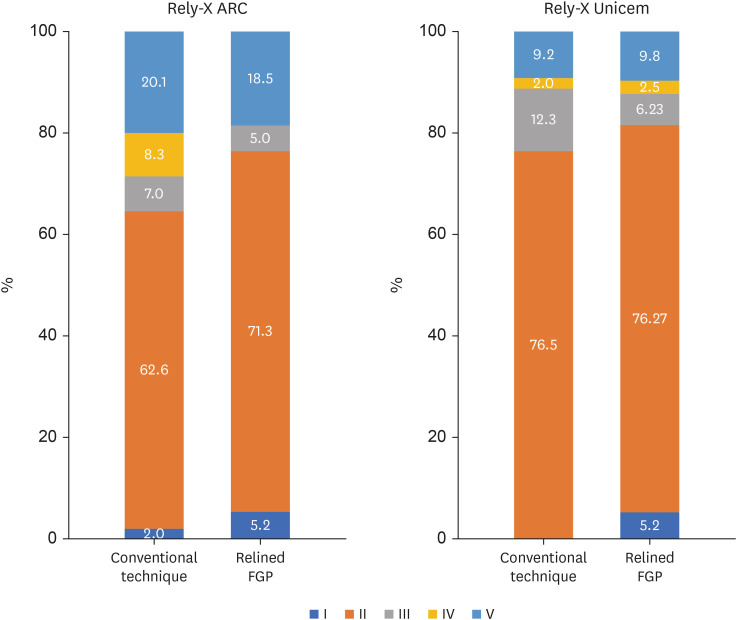
n = 10) followed by failure mode analysis. The cross-sectional microhardness (n = 5) was assessed along the root canal, and interface analyses (n = 3) were conducted using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data from the push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness tests were analyzed via 3-way analysis of variance and the Bonferronipost-hoc test (α = 0.05).Results For non-relined fiberglass posts, conventional resin cement exhibited higher push-out bond strength than self-adhesive cement. Relined fiberglass posts yielded comparable results between the resin cements. Type II failure was the most common failure mode for both resin cements, regardless of cementation protocol. The use of relined fiberglass posts improved the cross-sectional microhardness values for both cements. SEM images revealed voids and bubbles in the incisors with non-relined fiberglass posts.
Conclusions Mechanical properties were impacted by the cementation protocol. Relined fiberglass posts presented the highest push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness values, regardless of the resin cement used (conventional dual-cure or self-adhesive). Conversely, for non-relined fiberglass posts, the conventional dual-cure resin cement yielded superior results to the self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 5,100 View
- 133 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Giovanna Corrêa Denucci, Gabriela Soffner, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e32. Published online July 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements (SARCs).
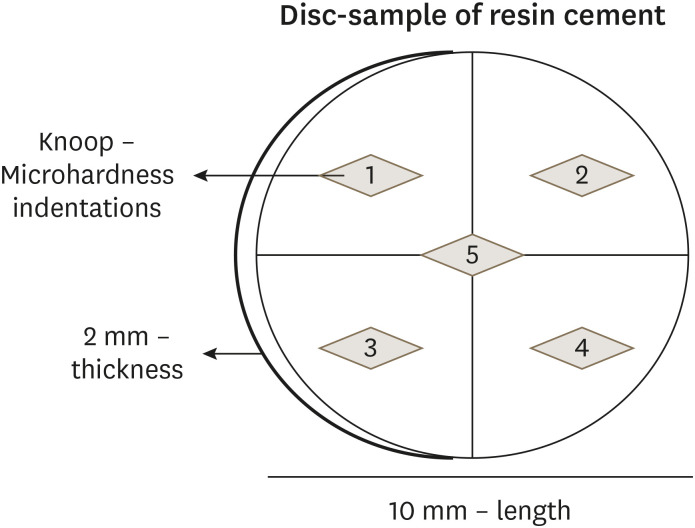
Materials and Methods Three SARCs including RelyX Unicem-2 (RUN), Maxcem Elite (MAX), and Calibra Universal (CAL) were tested. Rectangular bar-shaped specimens were prepared for flexural strength (FS) and flexural modulus (FM) and determined by a 3-point bending test. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and top/bottom microhardness ratio (%KHN) were conducted on the top and bottom faces of disc-shaped samples. Sorption (Wsp) and solubility (Wsl) were evaluated after 24 hours of water immersion. Filler morphology was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). FS, FM, %KHN, Wsp, Wsl, and EDS results were submitted to 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s
post-hoc test, and KHN also to pairedt -test (α = 0.05).Results SARC-CAL presented the highest FS value, and SARC-RUN presented the highest FM. SARC-MAX and RUN showed the lowest Wsp and Wsl values. KHN values decreased from top to bottom and the SARCs did not differ statistically. Also, all resin cements presented carbon, aluminum, and silica in their composition. SARC-MAX and RUN showed irregular and splintered particles while CAL presented small and regular size particles.
Conclusions A higher mechanical strength can be achieved by a reduced spread in grit size and the filler morphology can influence the KHN, as well as photoinitiators in the composition. Wsp and Wsl can be correlated with ions diffusion of inorganic particles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Assessment of fit accuracy and retentive strength of additively manufactured zirconia crowns luted to Ti‐base abutments with different resin cements: An in vitro study
Rafat Sasany, Sultan Merve Uçar, Burak Yilmaz
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Resin Cement Color Stability and Restoration Thickness as Determinants of the Final Shade in a Glass–Ceramic CAD/CAM Material
Hanin E. Yeslam, Alaa Turkistani
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 319. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Resin-Based Luting Materials—Review
Aleksandra Maletin, Milica Jeremić Knežević, Daniela Đurović Koprivica, Tanja Veljović, Tatjana Puškar, Bojana Milekić, Ivan Ristić
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4156. CrossRef - A Scoping Review on the Polymerization of Resin-Matrix Cements Used in Restorative Dentistry
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Orlanda Torres, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva, Susana O. Catarino, Mutlu Özcan, Júlio C. M. Souza
Materials.2023; 16(4): 1560. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
- 2,189 View
- 23 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Influence of 10-MDP concentration on the adhesion and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Kazuhiko Shibuya, Naoko Ohara, Serina Ono, Kumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Yoshiyama
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e45. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e45
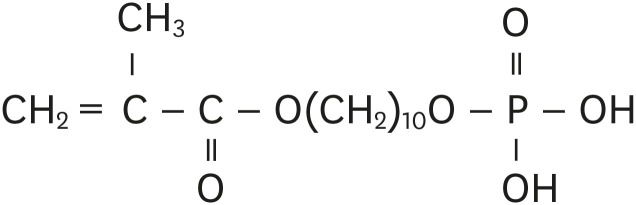
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Self-adhesive resin cements contain functional monomers that enable them to adhere to the tooth structure without a separate adhesive or etchant. One of the most stable functional monomers used for chemical bonding to calcium in hydroxyapatite is 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the10-MDP concentration on the bond strength and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods We used experimental resin cements containing 3 different concentrations of 10-MDP: 3.3 wt% (RC1), 6.6 wt% (RC2), or 9.9 wt% (RC3). The micro-tensile bond strength of each resin cement to dentin and a hybrid resin block (Estenia C&B, Kuraray Noritake Dental) was measured, and the fractured surface morphology was analyzed. Further, the flexural strength of the resin cements was measured using the three-point bending test. The water sorption and solubility of the cements following 30 days of immersion in water were measured.
Results The bond strength of RC2 was significantly higher than that of RC1. There was no significant difference between the bond strength of RC2 and that of RC3. The water sorption of RC3 was higher than that of any other cement. There were no significant differences in the three-point bending strength or water solubility among all three types of cements.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it is suggested that 6.6 wt% 10-MDP showed superior properties than 3.3 wt% or 9.9 wt% 10-MDP in self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Sofia Bignotto de Carvalho, Lívia Maiumi Uehara, João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104260. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Influence of temperature and curing modes on polymerization of self-adhesive resin cements
Hae-In Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(3): 143. CrossRef - Clinical Performance and Retention of Partial Implant Restorations Cemented with Fuji Plus® and DentoTemp™: A Retrospective Clinical Study with Mechanical Validation
Sergiu-Manuel Antonie, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Ioan-Achim Borsanu, Remus Christian Bratu, Emanuel-Adrian Bratu
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2183. CrossRef - A thorough assessment of 10-MDP primers in modern dental adhesive systems
Ahmed A Abduljawad, Harraa SM Salih, Omar F Tawfiq
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 79. CrossRef - Material properties and finite element analysis of adhesive cements used for zirconia crowns on dental implants
Megha Satpathy, Hai Pham, Shreya Shah
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Clinical reliability of self-adhesive luting resins compared to other adhesive procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammed Ahmed Alghauli, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 129: 104394. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization on bond strength between zirconia frameworks and Ti-base abutments using different resin cements
Reinhold Lang, Karl-Anton Hiller, Lena Kienböck, Katrin Friedl, Karl-Heinz Friedl
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(4): 617.e1. CrossRef - Varying 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP) level improves polymerisation kinetics and flexural strength in self-adhesive, remineralising composites
António H.S. Delgado, Nazanin Owji, Paul Ashley, Anne M. Young
Dental Materials.2021; 37(9): 1366. CrossRef - Investigating a Commercial Functional Adhesive with 12-MDPB and Reactive Filler to Strengthen the Adhesive Interface in Eroded Dentin
Madalena Belmar da Costa, António HS Delgado, Tomás Amorim Afonso, Luís Proença, Ana Sofia Ramos, Ana Mano Azul
Polymers.2021; 13(20): 3562. CrossRef
- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- 2,802 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of CAD/CAM-fabricated polymer-ceramics to different adhesive resin cements
- Leyla Sadighpour, Farideh Geramipanah, Zahra Ghasri, Mehrnoosh Neshatian
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e40. Published online September 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e40
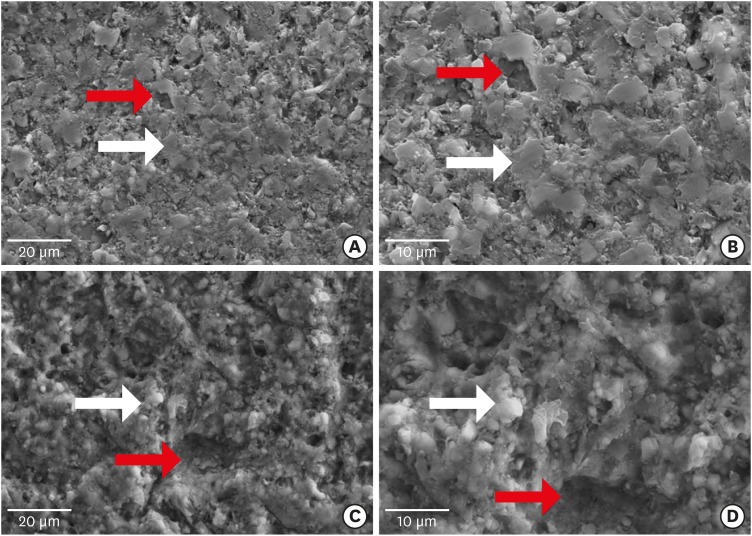
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of polymer-ceramic and indirect composite resin with 3 classes of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Two computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated polymer-ceramics (Enamic [ENA; Vita] and Lava Ultimate [LAV; 3M ESPE]) and a laboratory indirect composite resin (Gradia [GRA; GC Corp.]) were equally divided into 6 groups (
n = 18) with 3 classes of resin cements: Variolink N (VAR; Vivadent), RelyX U200 (RXU; 3M ESPE), and Panavia F2 (PAN; Kuraray). The μTBS values were compared between groups by 2-way analysis of variance and thepost hoc Tamhane test (α = 0.05).Results Restorative materials and resin cements significantly influenced µTBS (
p < 0.05). In the GRA group, the highest μTBS was found with RXU (27.40 ± 5.39 N) and the lowest with VAR (13.54 ± 6.04 N) (p < 0.05). Similar trends were observed in the ENA group. In the LAV group, the highest μTBS was observed with VAR (27.45 ± 5.84 N) and the lowest with PAN (10.67 ± 4.37 N) (p < 0.05). PAN had comparable results to those of ENA and GRA, whereas the μTBS values were significantly lower with LAV (p = 0.001). The highest bond strength of RXU was found with GRA (27.40 ± 5.39 N,p = 0.001). PAN showed the lowest µTBS with LAV (10.67 ± 4.37 N;p < 0.001).Conclusions When applied according to the manufacturers' recommendations, the µTBS of polymer-ceramic CAD/CAM materials and indirect composites is influenced by the luting cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
Mohamed F. Haridy, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Shehabeldin Saber, Edgar Schafer, Samar Elsayed Swelam, Youssef M. Haridy, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrofluoric acid and self-etch ceramic primers on the flexural strength and fatigue resistance of glass ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Paulo Matias Moreira, Gabriela Luiza Moreira Carvalho, Rodrigo de Castro Albuquerque, Carolina Bosso André
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 198. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on the mechanical properties of permanent composite-based CAD-CAM restorative materials produced by additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques
Tuğba Temizci, Hatice Nalan Bozoğulları
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on resin-matrix CAD/CAM ceramics bonding to dentin: in vitro study
Hanan Fathy, Hamdi H. Hamama, Noha El-Wassefy, Salah H. Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital image analysis of fluorescence of ceramic veneers with different ceramic materials and resin cements
Jiao ZHANG, Qing YU
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 868. CrossRef - Fatigue Behavior of Monolithic Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramic Restorations: Effects of Conditionings of the Intaglio Surface and the Resin Cements
F Dalla-Nora, LF Guilardi, CP Zucuni, LF Valandro, MP Rippe
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): 316. CrossRef
- Enhancing severely compromised premolar strength: role of cusp reduction design in CAD/CAM composite restorations
- 2,114 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Light transmittance of CAD/CAM ceramics with different shades and thicknesses and microhardness of the underlying light-cured resin cement
- Zahra Jafari, Homayoon Alaghehmand, Yasaman Samani, Mina Mahdian, Soraya Khafri
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e27. Published online June 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the effects of the thickness and shade of 3 types of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials.Materials and Methods A total of 120 specimens of 2 shades (A1 and A3) and 2 thicknesses (1 and 2 mm) were fabricated using VITA Mark II (VM; VITA Zahnfabrik), IPS e.max CAD (IE; IvoclarVivadent), and VITA Suprinity (VS; VITA Zahnfabrik) (
n = 10 per subgroup). The amount of light transmission through the ceramic specimens was measured by a radiometer (Optilux, Kerr). Light-cured resin cement samples (Choice 2, Bisco) were fabricated in a Teflon mold and activated through the various ceramics with different shades and thicknesses using an LED unit (Bluephase, IvoclarVivadent). In the control group, the resin cement sample was directly light-cured without any ceramic. Vickers microhardness indentations were made on the resin surfaces (KoopaPazhoohesh) after 24 hours of dark storage in a 37°C incubator. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance followed by the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05).Results Ceramic thickness and shade had significant effects on light transmission and the microhardness of all specimens (
p < 0.05). The mean values of light transmittance and microhardness of the resin cement in the VM group were significantly higher than those observed in the IE and VS groups. The lowest microhardness was observed in the VS group, due to the lowest level of light transmission (p < 0.05).Conclusion Greater thickness and darker shades of the 3 types of CAD/CAM ceramics significantly decreased the microhardness of the underlying resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
Shervin Reybod, Fariba Ezoji, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenouz, Behnaz Esmaeili
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Ultrasonic Scaling on Microleakage in Lithium Disilicate Crowns Luted With Different Resin Cements
Waleed AL-Mutairi, Marwa Eltayeb I. Elagra, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Polymerization through Glass-ceramics: Influence of Light-polymerizing Unit’s Emitted Power and Restoration Parameters (Shade, Translucency, and Thickness) on Transmitted Radiant Power
Ra’fat I. Farah, Ibrahim A. Alblihed, Alhareth A. Aljuoie, Bandar Alresheedi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 35. CrossRef - Effect of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing bleach shade ceramic thickness on its light transmittance and microhardness of light-cured resin cement
Pardis Sheibani, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenous, Behnaz Esmaeili, Ali Bijani
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of shade and thickness on the translucency parameter of anatomic-contour zirconia, transmitted light intensity, and degree of conversion of the resin cement
Noppamath Supornpun, Molly Oster, Kamolphob Phasuk, Tien-Min G. Chu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 129(1): 213. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Color Stabilities of Lithium Disilicate Material
Onur Doğan DAĞ, Göknil ALKAN DEMETOĞLU, Ayşegül KURT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(2): 395. CrossRef - Effect of thickness of CAD/CAM materials on light transmission and resin cement polymerization using a blue light‐emitting diode light‐curing unit
Eduardo Fernandes de Castro, Bruna Marin Fronza, Jorge Soto‐Montero, Marcelo Giannini, Carlos Tadeu dos‐Santos‐Dias, Richard Bengt Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(2): 368. CrossRef - Effect of Optical Properties of Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramics and Light-Curing Protocols on the Curing Performance of Resin Cement
Kejing Meng, Lu Wang, Jintao Wang, Zhuoqun Yan, Bin Zhao, Bing Li
Coatings.2022; 12(6): 715. CrossRef - Effect of the thickness of CAD‐CAM materials on the shear bond strength of light‐polymerized resin cement
Yener Okutan, Banucicek Kandemir, Mustafa Borga Donmez, Munir Tolga Yucel
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inhomogeneity of the polymerization light beam on the microhardness of resin cement under a CAD-CAM block
Yu-Ra Go, Kwang-Man Kim, Sung-Ho Park
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(5): 802.e1. CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness and water sorption/solubility of dual-cure resin cement through monolithic zirconia in different shades
Elham Ansarifard, Zahra Panbehzan, Rashin Giti
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(1): 50. CrossRef - Comparison between Different Shades of Monolithic Zirconia over Microhardness and Water Solubility and Sorption of Dual-cure Resin Cement
Sarika Sharma, Soni Kumari, Nikita Raman, Ashish K Srivastava, Gunja LNU, Arunendra S Chauhan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1019. CrossRef - Effect of light intensity, light-curing unit exposure time, and porcelain thickness of ips e.max press and vintage LD press on the hardness of resin cement
Silvia Naliani, Suzan Elias, Rosalina Tjandrawinata
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(1): 21. CrossRef
- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
- 2,047 View
- 8 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of radiant exposure and wavelength spectrum of light-curing units on chemical and physical properties of resin cements
- Adriano Fonseca Lima, Stephanie Ellen Ferreira Formaggio, Lígia França Aires Zambelli, Alan Rodrigo Muniz Palialol, Giselle Maria Marchi, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Marcelo Tavares de Oliveira
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):271-277. Published online September 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we evaluated the influence of different radiant exposures provided by single-peak and polywave light-curing units (LCUs) on the degree of conversion (DC) and the mechanical properties of resin cements.
Materials and Methods Six experimental groups were established for each cement (RelyX ARC, 3M ESPE; LuxaCore Dual, Ivoclar Vivadent; Variolink, DMG), according to the different radiant exposures (5, 10, and 20 J/cm2) and two LCUs (single-peak and polywave). The specimens were made (7 mm in length × 2 mm in width × 1 mm in height) using silicone molds. After 24 hours of preparation, DC measurement was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. The same specimens were used for the evaluation of mechanical properties (flexural strength, FS; elastic modulus,
E ) by a three-point bending test. Data were assessed for normality, after which two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey's test were performed.Results No properties of the Variolink cement were influenced by any of the considered experimental conditions. In the case of the RelyX ARC cement, DC was higher when polywave LCU was used; FS and E were not influenced by the conditions evaluated. The LuxaCore cement showed greater sensitivity to the different protocols.
Conclusions On the basis of these results, both the spectrum of light emitted and the radiant exposure used could affect the properties of resin cements. However, the influence was material-dependent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
Eduardo Fernández Godoy, Alain Chaple Gil, Rodrigo Caviedes Thomas, Cristian Bersezio Miranda, Javier Martín Casielles, Gonzalo Rodríguez Martínez, Pablo Angel Aguirre
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Transmittance and Depth of Cure of a Bulk Fill Composite Based on the Exposure Reciprocity Law
Mateus Garcia Rocha, Jean-François Roulet, Mario Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Américo Bortolazzo Correr, Dayane Oliveira
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(1): 78. CrossRef
- Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
- 1,834 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to composite submitted to different surface pretreatments
- Victor Hugo dos Santos, Sandro Griza, Rafael Ratto de Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):12-16. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Extensively destroyed teeth are commonly restored with composite resin before cavity preparation for indirect restorations. The longevity of the restoration can be related to the proper bonding of the resin cement to the composite. This study aimed to evaluate the microshear bond strength of two self-adhesive resin cements to composite resin.
Materials and Methods Composite discs were subject to one of six different surface pretreatments: none (control), 35% phosphoric acid etching for 30 seconds (PA), application of silane (silane), PA + silane, PA + adhesive, or PA + silane + adhesive (
n = 6). A silicone mold containing a cylindrical orifice (1 mm2 diameter) was placed over the composite resin. RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE) or BisCem (Bisco Inc.) self-adhesive resin cement was inserted into the orifices and light-cured. Self-adhesive cement cylinders were submitted to shear loading. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's test (p < 0.05).Results Independent of the cement used, the PA + Silane + Adhesive group showed higher microshear bond strength than those of the PA and PA + Silane groups. There was no difference among the other treatments. Unicem presented higher bond strength than BisCem for all experimental conditions.
Conclusions Pretreatments of the composite resin surface might have an effect on the bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to this substrate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
Yugandhar Garlapati, Sampath Krishna Veni, Jashva Vamsi Kogila, Polisetty Siva Krishna, K. N. Anand Kumar
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2025; 59(3): 279. CrossRef - Effect of Cement Type on Marginal Microleakage of Zirconia Crowns with or without Cervical Margin Relocation: An In Vitro Study
RI Farah
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(2): 194. CrossRef - Challenges faced when masking a single discoloured tooth - Part 2: indirect restoration procedures
May Aljanahi, Argwan Alhussin, Haitham Elbishari
British Dental Journal.2025; 239(1): 25. CrossRef - Influence of mechanochemical treatment and oxygen inhibited layer on the adhesion of self-adhesive resin cement to bulk-fill composite resin
Sreya Dutta, Samikhya Priyadarsani Sahu, Anushka Arora, Srikant Natarajan, Abhishek Parolia, Manuel Thomas
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2024; 27(2): 79. CrossRef - Substrate Rigidity Effect on CAD/CAM Restorations at Different Thicknesses
César Rogério Pucci, Ana Paula Valente Pinho Mafetano, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Cornelis J. Kleverlaan, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(04): 1020. CrossRef - Microgap Formation between a Dental Resin-Matrix Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing Ceramic Restorative and Dentin after Various Surface Treatments and Artificial Aging
Alexandros Galanopoulos, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Constantinos Papadopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Kosmas Tolidis
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(4): 2335. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef - Effect of full-step versus simplified resin cement luting strategies on the push-out bond strength of indirect resin composite restorations bonded to dentin
Bianca Cristina Dantas da Silva, Isabelle Helena Gurgel de Carvalho, Taciana Emília Leite Vila-Nova, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges, Marília Regalado Galvão Rabelo Caldas, Isauremi Vieira de Assunção, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(24): 3552. CrossRef - Effect of various polymerization protocols on the cytotoxicity of conventional and self-adhesive resin-based luting cements
Ece Irem Oguz, Ufuk Hasanreisoglu, Sadullah Uctasli, Mutlu Özcan, Mehmet Kiyan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1161. CrossRef - Repair bond strength of resin composite to three aged CAD/CAM blocks using different repair systems
Pinar Gul, Latife Altınok-Uygun
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 131. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Surface Characteristics of Dental CAD/CAM Materials after Different Surface Treatments
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Kimon Pahinis, Kyriaki Saltidou, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Effrosyni Tsitrou
Materials.2020; 13(4): 981. CrossRef - Adhesive Systems Used in Indirect Restorations Cementation: Review of the Literature
Cristian Abad-Coronel, Belén Naranjo, Pamela Valdiviezo
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(3): 71. CrossRef - Effects of different etching methods and bonding procedures on shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets applied to different CAD/CAM ceramic materials
S. Kutalmış Buyuk, Ahmet Serkan Kucukekenci
The Angle Orthodontist.2018; 88(2): 221. CrossRef - Ceramic repairs with resins: silanization protocols
Teresa Cristina Vasconcelos dos Santos
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different surface treatments on bond strength of novel CAD/CAM restorative materials to resin cement
Meltem Bektaş Kömürcüoğlu, Elçin Sağırkaya, Ayça Tulga
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(6): 439. CrossRef - Adhesive bonding to polymer infiltrated ceramic
Judith SCHWENTER, Fredy SCHMIDLI, Roland WEIGER, Jens FISCHER
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(5): 796. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of Silanization on Microtensile Bond Strength of Different Resin Cements to a Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramic
Cristina Parise Gré, Renan C de Ré Silveira, Shizuma Shibata, Carlo TR Lago, Luiz CC Vieira
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2016; 17(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of air abrasion with alumina or glass beads on surface characteristics of CAD/CAM composite materials and the bond strength of resin cements
ARAO Nobuaki, YOSHIDA Keiichi, SAWASE Takashi
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2015; 23(6): 629. CrossRef - Resin cement to indirect composite resin bonding: Effect of various surface treatments
Omer Kirmali, Cagatay Barutcugil, Osman Harorli, Alper Kapdan, Kursat Er
Scanning.2015; 37(2): 89. CrossRef - Impact of different adhesives on work of adhesion between CAD/CAM polymers and resin composite cements
Christine Keul, Manuel Müller-Hahl, Marlis Eichberger, Anja Liebermann, Malgorzata Roos, Daniel Edelhoff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Journal of Dentistry.2014; 42(9): 1105. CrossRef - Effect of Plasma Deposition Using Low-Power/Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Promoting Adhesion of Composite Resin to Enamel
Geum-Jun Han, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2014; 34(4): 933. CrossRef - Bonding efficacy of a self-adhesive resin cement to enamel and dentin
Linhu Wang, Haixing Xu, Songyang Li, Bin Shi, Rong Li, Mingfu Ye, Jing Yang
Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed..2014; 29(6): 1307. CrossRef
- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
- 1,787 View
- 8 Download
- 23 Crossref

- EFFECT OF DENTIN SURFACE WETNESS ON TENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
- Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):113-119. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to compare the tensile bond strength of several self-adhesive resin cements bonded to dentin surfaces with different wet conditions.
Three self-adhesive resin cements; Rely-X Unicem (3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA), Embrace Wetbond (Pulpdent, Oakland, MA, USA), Maxcem (Kerr, Orange, CA, USA) were used. Extracted sixty human molars were used. Each self-adhesive resin cement was adhered to the dentin specimens (two rectangular sticks from each molar) in different wet conditions.
Tensile bond strength were measured using universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu corporation, Kyoto, Japan) at a crosshead speed of 1.0mm/min. After the testing, bonding failures of specimens were observed by Operative microscope (OPMI pro, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). T-test was used to evaluate the effect of dentin surface wetness. One-way ANOVA test was used to evaluate the tensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements in the same condition. Scheffe's test was used for statistical analyzing at the 95% level of confidence.
The result showed that wetness of dentin surface didn't affect tensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements and Maxcem showed the lowest tensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overdried Preparation and Thermocycling on the Fracture of CAD–CAM Hybrid Ceramic Occlusal Veneer Restorations
Daranee Tantbirojn, Antheunis Versluis, Paul D Edgerley, David R Cagna
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 9(2): 38. CrossRef - Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 234. CrossRef - 'Wet or Dry tooth surface?' - for self-adhesive resin cement
Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 249. CrossRef
- Impact of Overdried Preparation and Thermocycling on the Fracture of CAD–CAM Hybrid Ceramic Occlusal Veneer Restorations
- 1,343 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


