Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Contemporary research trends on nanoparticles in endodontics: a bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles
- Sıla Nur Usta, Zeliha Uğur-Aydın, Kadriye Demirkaya, Cumhur Aydın
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e27. Published online July 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Advancements in nanotechnology have led to the widespread usage of nanoparticles in the endodontic field. This bibliometric study aimed to determine and analyze the top 100 most-cited articles about nanoparticles in endodontics from 2000 to 2022.
Materials and Methods A detailed electronic search was conducted on the “Clarivate Analytics Web of Science, All Databases” to receive the most-cited articles related to the topic. Articles were ranked in descending order based on their citation counts, and the first 100 were selected for bibliometric analysis. Parameters such as citation density, publication year, journal, country, institution, author, study design, study field, evidence level, and keywords were analyzed.
Results The top 100 most-cited articles received 4,698 citations (16–271) with 970.21 (1.91–181) citation density in total. Among decades, citations were significantly higher in 2011–2022 (
p < 0.001).Journal of Endodontics had the largest number of publications. Canada and the University of Toronto made the highest contribution as country and institution, respectively. Anil Kishen was the 1 who participated in the largest number of articles. The majority of the articles were designedin vitro . The main study field was “antibacterial effect.” Among keywords, “nanoparticles” followed by “Enterococcus faecalis ” were used more frequently.Conclusions Developments in nanotechnology had an impact on the increasing number of studies in recent years. This bibliometric study provides a comprehensive view of nanoparticle advances and trends using citation analysis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research trends and mapping knowledge for maxillary sinus augmentation in oral and maxillofacial surgery
Özlem Saraç Atagün, Şeyma Çardakcı Bahar, Seval Ceylan Şen, Gülbahar Ustaoğlu
Journal of Stomatology Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025; 126(4): 102116. CrossRef - Visualized bibliometric panorama of ureteral stents (1975–present): trends and hotspots revealed
Renjie Wei, Fudong Liu, Xinjie Ji, Xu Luo, Chunyu Gong, Ruitu Ran
World Journal of Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue in NiTi files: a bibliometric and science mapping analysis
Huda Melike Bayram, Emre Bayram
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic antibiofilm activity of methylene blue and silver nanoparticle-mediated photothermal therapy against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm
Eman M. Fouad, Hossam Tawfiq, Soha Abdelrahman Elhady, Ali M. Saafan
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring vital pulp Therapies: A bibliometric analysis of the most cited articles
Gustavo Henrique Sousa, Rodolfo Lima Gonçalves, Barbara Figueiredo, Vilton Cardozo Moreira Dias, Ana Carolina Soares Mendes, Valéria de Cássia Bueno Melo, Adriana Guimarães Rodrigues, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(5): 778. CrossRef - The cutting-edge roles of lasers in endodontics: A bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the 100 most-cited articles
Sıla Nur Usta, Pablo Betancourt, Alper Ceylan, Cangül Keskin
Lasers in Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research trends and mapping knowledge for maxillary sinus augmentation in oral and maxillofacial surgery
- 2,365 View
- 33 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Physicochemical properties of a calcium aluminate cement containing nanoparticles of zinc oxide
- Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Thuany Schmitz Amaral, Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Taynara Santos Goulart, Hebert Luís Rossetto, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e3. Published online December 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of different nanoparticulated zinc oxide (nano-ZnO) and conventional-ZnO ratios on the physicochemical properties of calcium aluminate cement (CAC).
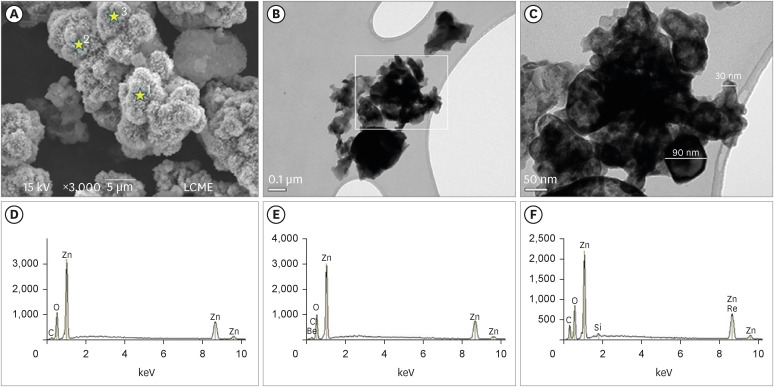
Materials and Methods The conventional-ZnO and nano-ZnO were added to the cement powder in the following proportions: G1 (20% conventional-ZnO), G2 (15% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO), G3 (12% conventional-ZnO + 3% nano-ZnO) and G4 (10% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO). The radiopacity (Rad), setting time (Set), dimensional change (Dc), solubility (Sol), compressive strength (Cst), and pH were evaluated. The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO were also assessed using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Radiopacity data were analyzed by the 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni tests (
p < 0.05). The data of the other properties were analyzed by the ANOVA, Tukey, and Fisher tests (p < 0.05).Results The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO powders presented particles with few impurities and nanometric and micrometric sizes, respectively. G1 had the highest Rad mean value (
p < 0.05). When compared to G1, groups containing nano-ZnO had a significant reduction in the Set (p < 0.05) and lower values of Dc at 24 hours (p < 0.05). The Cst was higher for G4, with a significant difference for the other groups (p < 0.05). The Sol did not present significant differences among groups (p > 0.05).Conclusions The addition of nano-ZnO to CAC improved its dimensional change, setting time, and compressive strength, which may be promising for the clinical performance of this cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
Sara Ghorbani, Rahim Naghizadeh, Ebrahim Ghasemi, Hamidreza Rezaie
Advances in Cement Research.2025; 37(4): 269. CrossRef - Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design
Hongyin Hu, Fufei Wu, Jiao Chen, Shuangshuang Guan, Peng Qu, Hongqin Zhang, Yuyi Chen, Zirun Xu, Chuanteng Huang, Shuang Pu
Materials.2025; 18(7): 1515. CrossRef - Radiographic, mechanical, and chemical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate from nanosilica and clam shell calcium carbonate
Leny Yuliatun, Muhammad Adly Rahandi Lubis, Muhammad Khaliim Jati Kusala, Lia Destiarti, Ratna Betriani, Jolang Budiarta, Mariyam Mariyam
Polyhedron.2025; 278: 117590. CrossRef - Application of Calcium Aluminate-Based Materials for Direct Pulp Capping – In Vivo Study
Ognjenka Janković, Smiljana Paraš, Tijana Adamović, Ljiljana Tadić Latinović, Radmila Arbutina, Igor Đukić, Saša Marin, Marko Bulajić, Karolina Vukoje, Vukoman Jokanović, Verica Pavlić
Acta Veterinaria.2025; 75(2): 212. CrossRef - Nanotechnology for calcium aluminate cement: thematic analysis
Lapyote Prasittisopin
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
- 2,137 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
- Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e38. Published online October 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the cytotoxicity, radiopacity, pH, and dentinal tubule penetration of a paste of 1.0% calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals (ZnO:1.0Ca) combined with propylene glycol (PRG) or polyethylene glycol and propylene glycol (PEG-PRG).
Materials and Methods The pastes were prepared by mixing calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] or ZnO:1.0Ca with PRG or a PEG-PRG mixture. The pH was evaluated after 24 and 96 hours of storage in deionized water. Digital radiographs were acquired for radiopacity analysis and bubble counting of each material. The materials were labeled with 0.1% fluorescein and applied to root canals, and images of their dentinal tubule penetration were obtained using confocal laser scanning microscopy. RAW264.7 macrophages were placed in different dilutions of culture media previously exposed to the materials for 24 and 96 hours and tested for cell viability using the MTT assay. Analysis of variance and the Tukey test (
α = 0.05) were performed.Results ZnO:1.0Ca materials showed lower viability at 1:1 and 1:2 dilutions than Ca(OH)2 materials (
p < 0.0001). Ca(OH)2 had higher pH values than ZnO:1.0Ca at 24 and 96 hours, regardless of the vehicle (p < 0.05). ZnO:1.0Ca pastes showed higher radiopacity than Ca(OH)2 pastes (p < 0.01). No between-material differences were found in bubble counting (p = 0.0902). The ZnO:1.0Ca pastes had a greater penetration depth than Ca(OH)2 in the apical third (p < 0.0001).Conclusions ZnO:1.0Ca medicaments presented higher penetrability, cell viability, and radiopacity than Ca(OH)2. Higher values of cell viability and pH were present in Ca(OH)2 than in ZnO:1.0Ca.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Nano calcium zincate-assisted synthesis of benzo[
d
]thiazol-2-yl phenylisoxazoles: quantum computational,
in silico
molecular docking simulations and DNA interaction
A. K. Smitha, V. Srinivasa Murthy, B. Vinay Kumar, M. Sennappan, A. H. Shridhar, Lohit Naik, K. Yogendra, N. Madhusudhana
Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids.2026; 45(3): 261. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-Enhanced Dentistry: A Clinical Perspective
Selvam Manoj, Radhakrishnan Sreena, Rajkumar Divya, Starlin Ebinesh, Shenbagaraman Akshaya, Srikumar Sugantha Angel, Arputharaj Joseph Nathanael
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2025; 11(8): 4671. CrossRef
-
Nano calcium zincate-assisted synthesis of benzo[
d
]thiazol-2-yl phenylisoxazoles: quantum computational,
in silico
molecular docking simulations and DNA interaction
- 2,108 View
- 24 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The effect of using nanoparticles in bioactive glass on its antimicrobial properties
- Maram Farouk Obeid, Kareim Moustafa El-Batouty, Mohammed Aslam
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e58. Published online October 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e58
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study addresses the effect of using nanoparticles (np) on the antimicrobial properties of bioactive glass (BAG) when used in intracanal medicaments against
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) biofilms.Materials and Methods E. faecalis biofilms, grown inside 90 root canals for 21 days, were randomly divided into 4 groups according to the antimicrobial regimen followed (n = 20; BAG-np, BAG, calcium hydroxide [CaOH], and saline). After 1 week, residual live bacteria were quantified in terms of colony-forming units (CFU), while dead bacteria were assessed with a confocal laser scanning microscope.Results Although there was a statistically significant decrease in the mean CFU value among all groups, the nano-group performed the best. The highest percentage of dead bacteria was detected in the BAG-np group, with a significant difference from the BAG group.
Conclusions The reduction of particle size and use of a nano-form of BAG improved the antimicrobial properties of the intracanal treatment of
E. faecalis biofilms-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Size matters: Radiation shielding superiority of borate glasses with nano vs. micro ZnO
Aljawhara H. Almuqrin, M.I. Sayyed, M. Elsafi
Nuclear Engineering and Technology.2025; 57(9): 103614. CrossRef - Effect of Chitosan and bioactive glass nanomaterials as intracanal medicaments on TGF-β1 release from intraradicular dentin
Sarah Salah Hashem, Mohammed M. Khalefa, Mahmoud Hassan Mohamed, Hemat M. ELSheikh, Fatma Abd El-Rahman Taher
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG laser, phthalocyanine activated photodynamic therapy, and bioactive glass nanoparticles on smear layer removal and push out bond strength of quartz fiber posts to canal dentin: a SEM assessment
Okba Mahmoud, Erum Zain
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Root Canal Therapy: Translational Innovations and the Role of Nanoparticles in Endodontic Treatment
Noha M. Badawi, Mohamed M. Kataia, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mozhgan Afshari
Journal of Nanotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propolis in Endodontics—Unveiling Its Therapeutic Potential: A Narrative Review
Poorani Durai, Santha Devy A, Mithila Mohan, Harish Ramalingam, Shasidharan P, Rahul Chaurasia M
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 16(10): 959. CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Endodontics
Farzaneh Afkhami, Yuan Chen, Laurence J. Walsh, Ove A. Peters, Chun Xu
BME Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal Atiya Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effects of Formulations of Various Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide as Intra-canal Medications Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review
Seema H Bukhari, Dax Abraham, Shakila Mahesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of nanoparticles on antibacterial efficacy of intracanal medicament: A scoping review
Alpa Gupta, Arundeep Singh, Vivek Aggarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 283. CrossRef - Physical properties, marginal adaptation and bioactivity of an experimental mineral trioxide aggregate-like cement modified with bioactive materials
Abigailt Flores-Ledesma, Adriana Tejeda-Cruz, María A. Moyaho-Bernal, Ana Wintergerst, Yoshamin A. Moreno-Vargas, Jacqueline A. Rodríguez-Chávez, Carlos E. Cuevas-Suárez, Kenya Gutiérrez-Estrada, Jesús A. Arenas-Alatorre
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(2): 141. CrossRef - Nanopartículas antimicrobianas en endodoncia: Revisión narrativa
Gustavo Adolfo Tovar Rangel , Fanny Mildred González Sáenz , Ingrid Ximena Zamora Córdoba , Lina María García Zapata
Revista Estomatología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Size matters: Radiation shielding superiority of borate glasses with nano vs. micro ZnO
- 1,677 View
- 26 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Silver nanoparticles in endodontics: recent developments and applications
- Aysenur Oncu, Yan Huang, Gulin Amasya, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Kaan Orhan, Berkan Celikten
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e38. Published online July 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The elimination of endodontic biofilms and the maintenance of a leak-proof canal filling are key aspects of successful root canal treatment. Several materials have been introduced to treat endodontic disease, although treatment success is limited by the features of the biomaterials used. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been increasingly considered in dental applications, especially endodontics, due to their high antimicrobial activity. For the present study, an electronic search was conducted using MEDLINE (PubMed), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Google Scholar, and EMBASE. This review provides insights into the unique characteristics of AgNPs, including their chemical, physical, and antimicrobial properties; limitations; and potential uses. Various studies involving different application methods of AgNPs were carefully examined. Based on previous clinical studies, the synthesis, means of obtaining, usage conditions, and potential cytotoxicity of AgNPs were evaluated. The findings indicate that AgNPs are effective antimicrobial agents for the elimination of endodontic biofilms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
Laila Mohamed Mohamed Kenawi, Mohamed Fattouh, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Abla Arafa
The Open Dentistry Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Advanced nanoparticle-based antibacterial delivery for endodontic disinfection: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kanwalpreet Kaur, Seerat Kaura, Ravinder S Saini, Maurya Manjunath, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Mario Alberto Alarcón-Sánchez, Javier Flores-Fraile, Artak Heboyan
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106347. CrossRef - Scoping review on the genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in endodontics: therapeutic saviors or genetic saboteurs?
Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Widya Lestari, Mohd Haikal Muhamad Halil, Mohd Syafiq Abd Aziz
Odontology.2025; 113(2): 457. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Recent advances in antibacterial nanoformulations for endodontic applications
Tiago Dionísio, Pedro Brandão, Vanessa Machado, João Botelho, José João Mendes, Pedro Fonte
Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2025; 22(8): 1117. CrossRef - Systematic review of silver and vanadium-based antibiofilm agents: mechanisms and efficacy in oral biofilms
João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
Future Microbiology.2025; 20(10): 639. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-Enhanced Dentistry: A Clinical Perspective
Selvam Manoj, Radhakrishnan Sreena, Rajkumar Divya, Starlin Ebinesh, Shenbagaraman Akshaya, Srikumar Sugantha Angel, Arputharaj Joseph Nathanael
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2025; 11(8): 4671. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effects of Formulations of Various Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide as Intra-canal Medications Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review
Seema H Bukhari, Dax Abraham, Shakila Mahesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Push-Out Bond Strength, Surface Roughness, and Antimicrobial Properties of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealers Supplemented with Silver Nanoparticles
Karla Navarrete-Olvera, Nereyda Niño-Martínez, Idania De Alba-Montero, Nuria Patiño-Marín, Facundo Ruiz, Horacio Bach, Gabriel-Alejandro Martínez-Castañón
Molecules.2024; 29(18): 4422. CrossRef - Synergistic bactericidal activity of chlorhexidine loaded on positively charged ionic liquid-protected silver nanoparticles as a root canal disinfectant against Enterococcus faecalis: An ex vivo study
Abbas Abbaszadegan, Elham Tayebikhorami, Ahmad Gholami, Nazanin Bonyanpour, Bahar Asheghi, Sara Nikmanesh
Journal of Ionic Liquids.2024; 4(2): 100117. CrossRef - Improving the Antimicrobial Potency of Berberine for Endodontic Canal Irrigation Using Polymeric Nanoparticles
Célia Marques, Liliana Grenho, Maria Helena Fernandes, Sofia A. Costa Lima
Pharmaceutics.2024; 16(6): 786. CrossRef - A narrative review on application of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in endodontics
Roohollah Sharifi, Ahmad Vatani, Amir Sabzi, Mohsen Safaei
Heliyon.2024; 10(15): e34673. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Silver Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcium Hydroxide against Candida albicans: An Ex Vivo Analysis
Maha Alghofaily, Jood Alfraih, Aljohara Alsaud, Norah Almazrua, Terrence S. Sumague, Sayed H. Auda, Fahd Alsalleeh
Microorganisms.2024; 12(2): 289. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy of a novel disinfecting material on the surface topography of gutta-percha: An in vitro study
KHanisha Reddy, Lekshmi Chandran, TMurali Mohan, K Sudha, DL Malini, Bonney Dominic
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 94. CrossRef - Silver Nanoparticles and Their Therapeutic Applications in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Farzaneh Afkhami, Parisa Forghan, James L. Gutmann, Anil Kishen
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(3): 715. CrossRef - Nanopartículas antimicrobianas en endodoncia: Revisión narrativa
Gustavo Adolfo Tovar Rangel , Fanny Mildred González Sáenz , Ingrid Ximena Zamora Córdoba , Lina María García Zapata
Revista Estomatología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Functionalized Nanoparticles: A Paradigm Shift in Regenerative Endodontic Procedures
Vinoo Subramaniam Ramachandran, Mensudar Radhakrishnan, Malathi Balaraman Ravindrran, Venkatesh Alagarsamy, Gowri Shankar Palanisamy
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 6,014 View
- 100 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Can silver diamine fluoride or silver nanoparticle-based anticaries agents to affect enamel bond strength?
- Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Yana Cosendey Toledo de Mello Peixoto, Omar Geha, Flaviana Alves Dias, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e7. Published online January 12, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
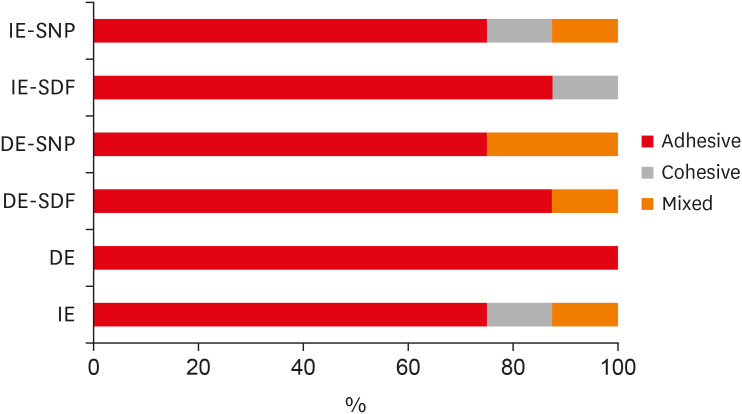
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study is to investigate the effect of different anticaries agents, such as experimental agents based on silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and silver diamine fluoride (SDF), on the micro-shear bond strength (μ-SBS) of composite resin applied to intact enamel (IE) or demineralized enamel (DE).
Materials and Methods Sixty dental enamel fragments were collected from human third molars and categorized into 6 groups (
n = 10): positive control (IE), negative control (DE), IE + SDF, DE + SDF, IE + SNP and DE + SNP. Samples from DE, DE + SDF and DE + SNP groups were subjected to pH cycling; superficial microhardness test was performed to confirm demineralization. Resin composite build-ups were applied to the samples (0.75-mm diameter and 1-mm height) after the treatments (except for IE and DE groups); μ-SBS was also evaluated. Samples were analyzed under a stereomicroscope at 40× magnification to identify failure patterns. Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's and Dunnett's tests (p < 0.05).Results There was no significant difference among the IE, IE + SNP, DE + SDF, and DE + SNP groups. The IE + SDF and DE groups recorded the highest and the lowest μ-SBS values, respectively. Adhesive-type failures were the most frequent for all treatments.
Conclusions Anticaries agents did not have a negative effect on the μ-SBS of composite resin when it was used on IE or DE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
Naif Almosa
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 89. CrossRef - Preventing white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets: efficacy of pre-reacted glass-ionomer barrier coat versus silver diamine fluoride: an in vitro study
Enas A. Elshenawy, Safa B. Alawy, Wafaa Yahia Alghonemy, Ahmed Ibrahime El dosoky
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Status of Silver Nanoparticles for Dental Applications
Yanyan Guo, Xiaomei Hou, Sanjun Fan, Chanyuan Jin
Inorganics.2025; 13(5): 168. CrossRef - The use of silver diamine fluoride to prevent/treat enamel carious lesions: a narrative review
Rasha N. AlSheikh
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17897. CrossRef - Phosphoric Acid Etch Partially Restores the Initial Bond Strength of Composite to Silver Diamine Fluoride–Treated Enamel Using Universal Adhesives
Zaher Jabbour, Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Reuben Kim
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(7): 161. CrossRef - Efficacy of Nano Silver Fluoride and/or Diode Laser In Enhancing Enamel Anticariogenicity around orthodontic brackets
Aya Anwar Alsherif, Mohamed Ali Farag, Mai Badreldin Helal
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Amelioration Strategies for Silver Diamine Fluoride: Moving from Black to White
Amjad Almuqrin, Inder Preet Kaur, Laurence J. Walsh, Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne, Sobia Zafar
Antibiotics.2023; 12(2): 298. CrossRef - The Effect of Loading Time on Color Stability of Various Restorative Materials Bonded to Silver Diamine Fluoride-Treated Demineralized Dentin
Mohammed M Aldosari, Fares S Al-Sehaibany
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2022; Volume 14: 123. CrossRef - In vitro study of the effect of nanosilver fluoride on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and demineralization of enamel
Mariam H. El-Toukhy, Eman M. El-Shourbagy, Neveen M. Fakhry
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(4): 281. CrossRef
- Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
- 1,952 View
- 26 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

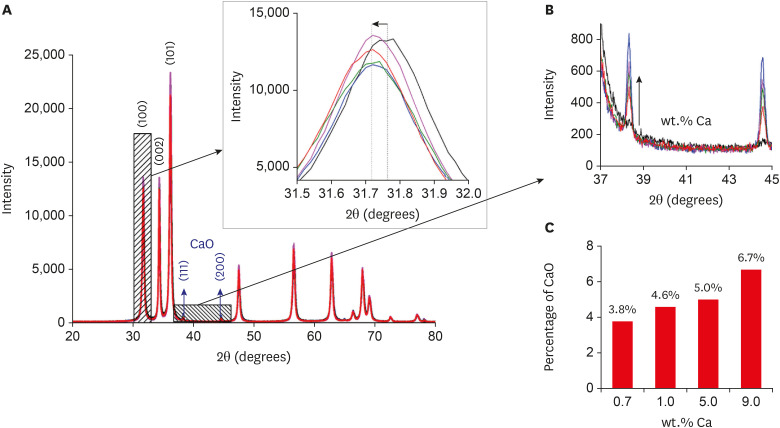
- Effects of zinc oxide and calcium–doped zinc oxide nanocrystals on cytotoxicity and reactive oxygen species production in different cell culture models
- Gabriela Leite de Souza, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Juliane Zacour Marinho, Thaynara Rodrigues Silva, Noelio Oliveira Dantas, Jéssica Fernanda Sena Bonvicini, Ana Paula Turrioni
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e54. Published online October 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e54
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to synthesize nanocrystals (NCs) of zinc oxide (ZnO) and calcium ion (Ca2+)-doped ZnO with different percentages of calcium oxide (CaO), to evaluate cytotoxicity and to assess the effects of the most promising NCs on cytotoxicity depending on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation.
Materials and Methods Nanomaterials were synthesized (ZnO and ZnO:xCa, x = 0.7; 1.0; 5.0; 9.0) and characterized using X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and methylene blue degradation. SAOS-2 and RAW 264.7 were treated with NCs, and evaluated for viability using the MTT assay. NCs with lower cytotoxicity were maintained in contact with LPS-stimulated (+LPS) and nonstimulated (−LPS) human dental pulp cells (hDPCs). Cell viability, nitric oxide (NO), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were evaluated. Cells kept in culture medium or LPS served as negative and positive controls, respectively. One-way analysis of variance and the Dunnett test (α = 0.05) were used for statistical testing.
Results ZnO:0.7Ca and ZnO:1.0Ca at 10 µg/mL were not cytotoxic to SAOS-2 and RAW 264.7. +LPS and −LPS hDPCs treated with ZnO, ZnO:0.7Ca, and ZnO:1.0Ca presented similar NO production to negative control (
p > 0.05) and lower production compared to positive control (p < 0.05). All NCs showed reduced ROS production compared with the positive control group both in +LPS and −LPS cells (p < 0.05).Conclusions NCs were successfully synthesized. ZnO, ZnO:0.7Ca and ZnO:1.0Ca presented the highest percentages of cell viability, decreased ROS and NO production in +LPS cells, and maintenance of NO production at basal levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Waste-derived Ca and Zn-based bimetallic (Ca/Zn) nanorods encapsulated chitosan-based haemostatic dressing bandage: A step towards waste to bandages
Pooja Thakur, Rishabh Anand Omar, Neetu Talreja, Divya Chauhan, Mohammad Ashfaq
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 143: 327. CrossRef - Europium and calcium-co-doped TiO2 nanocrystals: tuning the biocompatibility and luminescence traceability of Drosophila melanogaster
Jerusa Maria de Oliveira, Larissa Iolanda M. de Almeida, Francisco Rubens Alves dos Santos, João Paulo S. de Carvalho, Amanda I. dos S. Barbosa, Marcus Andrei R. F. da Costa, Vanessa Tomaz Maciel, Gabriela L. de Souza, Alysson N. Magalhães, Marcos V. Verm
Environmental Science: Nano.2025; 12(1): 835. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of capsules loaded with red propolis extract and metallic nanoparticles using the ionic gelation method
Ilza Fernanda Barboza Duarte Rodrigues, Jéssica Maria Pereira, Lívia Maria Santos de Lima, Kathleen Gomes Lins Silva, Melissa Rosa Silva, Valdemir da Costa Silva, Salvana Priscylla Manso Costa, Ticiano Gomes do Nascimento, Adeildo Junior de Oliveira, John
Journal of Apicultural Research.2025; 64(4): 1151. CrossRef - Structural, optical, and magnetic behavior and the nucleation of a Griffiths-like phase in (Ca,V)-doped ZnO nanoparticles
S. Mrabet, N. Ihzaz, M. N. Bessadok, C. Vázquez-Vázquez, M. Alshammari, O. M. Lemine, D. Ananias, L. El Mir
Dalton Transactions.2025; 54(18): 7400. CrossRef - The effect of iron oxide synergism on the structural and magnetic properties of iron-doped ZnO
Adenilson F. dos Santos, Angela Marta da Silva, Thaís Karine de Lima, Noelio O. Dantas, Marcio A. Correa, Anielle Christine A. Silva
Next Materials.2025; 9: 101047. CrossRef - IN VITRO EVALUATION OF THE ANTI-LEISHMANIAL ROLE OF MILTEFOSINE-LOADED MESOPORUSZNO NANOPARTICLES IN RAW 264.7 MACROPHAGES
PARAG GHOSH, DILEEP KUMAR BHARATI, DIBYA DAS, SUBAS CHANDRA DINDA, ANIRBANDEEP BOSE
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.2025; : 231. CrossRef - Development of antibacterial dual-cure dental resin composites via tetrapod-shaped zinc oxide incorporation
Hwalim Lee, Yu-Jin Kim, Ye-Jin Yang, Jung-Hwan Lee, Hae-Hyoung Lee
Dental Materials.2024; 40(11): 1762. CrossRef - Investigation on the non-linear behaviour of silicon nanowires and assessment of the biosensing potential
M M A Hakim
Engineering Research Express.2023; 5(2): 025017. CrossRef - Evaluation of Cytotoxicity, Cell Attachment, and Elemental Characterization of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Anahi de Paula Melo, Camila Maria Peres de Rosatto, Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Gabriela Leite de Souza, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Materials.2023; 16(20): 6705. CrossRef - Metallic Nanoparticles: A New Frontier in the Fight Against Leishmaniasis
Rhanoica Oliveira Guerra, José Rodrigues do Carmo Neto, Tarcísio de Albuquerque Martins, Thaís Soares Farnesi de-Assunção, Virmondes Rodrigues Junior, Carlo José Freire de Oliveira, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Marcos Vinicius da Silva
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 29(26): 4547. CrossRef - In situ synthesis of zinc oxide/selenium composite for UV blocker application
Chaoqun Xia, Shi Liu, Baining Cui, Mingjun Li, Hongshui Wang, Chunyong Liang, Phong A. Tran, Yan Wang, Huan Zhou, Lei Yang
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and Connectivity of Semiconductor Nanostructures for Cardiac Tissue Engineering Applications
Roberto Gaetani, Yuriy Derevyanchuk, Andrea Notargiacomo, Marialilia Pea, Massimiliano Renzi, Elisa Messina, Fabrizio Palma
Bioengineering.2022; 9(11): 621. CrossRef - Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Waste-derived Ca and Zn-based bimetallic (Ca/Zn) nanorods encapsulated chitosan-based haemostatic dressing bandage: A step towards waste to bandages
- 2,130 View
- 13 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Influence of silver nanoparticles on resin-dentin bond strength durability in a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive system
- Zahra Jowkar, Fereshteh Shafiei, Elham Asadmanesh, Fatemeh Koohpeima
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e13. Published online March 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of dentin pretreatment with silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and chlorhexidine (CHX) on the microshear bond strength (µSBS) durability of different adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods Occlusal surfaces of 120 human molars were ground to expose flat dentin surfaces. The specimens were randomly assigned to six groups (
n = 20). Three groups (A, B, and C) were bonded with Adper Single Bond 2 (SB) and the other groups (D, E, and F) were bonded with Clearfil SE Bond (SEB). Dentin was pretreated with CHX in groups B and E, and with SNPs in groups C and F. The specimens were restored with Z250 composite. Half of the bonded surfaces in each group underwent µSBS testing after 24 hours and the other half was tested after 6 months of water storage.Results SNP application was associated with a higher µSBS than was observed in the CHX and control groups for SEB after 24 hours (
p < 0.05). A significantly lower µSBS was observed when no dentin pretreatment was applied compared to dentin pretreatment with CHX and SNPs for SB after 24 hours (p < 0.05). The µSBS values of the 6-month specimens were significantly lower than those obtained from the 24-hour specimens for all groups (p < 0.05). This decrease was much more pronounced when both adhesives were used without any dentin pretreatment (p < 0.05).Conclusions SNPs and CHX reduced the degradation of resin-dentin bonds over a 6-month period for both adhesive systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Nanoparticle-enhanced dental adhesives: improving dentin bond strength through multifunctional nanotechnology
Suleiman Ibrahim Mohammad, Asokan Vasudevan, Lashin Saad Ali, Wenchang Chen
The Journal of Adhesion.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer: An In Vitro Study
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Dalal AlDabeeb
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9817. CrossRef - Performance of self-etching adhesives on caries-affected primary dentin treated with glutaraldehyde or silver diamine fluoride
Marcelly Tupan Christoffoli Wolowski, Andressa Mioto Stabile Grenier, Victória Alícia de Oliveira, Caroline Anselmi, Mariana Sversut Gibin, Lidiane Vizioli de Castro-Hoshino, Francielle Sato, Cristina Perez, Régis Henke Scheffel, Josimeri Hebling, Mauro L
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106293. CrossRef - The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles on Dentinal Tubule Penetration of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealer
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Amal Almohaimede, Nourah Alkhayatt, Shahad Alsulaiman, Salma Alohali
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11639. CrossRef - Effect of silver diamine fluoride on the longevity of the bonding properties to caries-affected dentine
LP Muniz, M Wendlinger, GD Cochinski, PHA Moreira, AFM Cardenas, TS Carvalho, AD Loguercio, A Reis, FSF Siqueira
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 143: 104897. CrossRef - Evaluation of Chitosan-Oleuropein Nanoparticles on the Durability of Dentin Bonding
Shuya Zhao, Yunyang Zhang, Yun Chen, Xianghui Xing, Yu Wang, Guofeng Wu
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2023; Volume 17: 167. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on the resin-dentin bond strength and antibacterial activity of a self-etch adhesive system
Jia Wang, Wei Jiang, Jingping Liang, Shujun Ran
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(6): 1363.e1. CrossRef - Marginal Integrity of Composite Restoration with and without Surface Pretreatment by Gold and Silver Nanoparticles vs Chlorhexidine: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Aya AEM Nemt-Allah, Shereen H Ibrahim, Amira F El-Zoghby
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1087. CrossRef - Effect of Cavity Disinfectants on Dentin Bond Strength and Clinical Success of Composite Restorations—A Systematic Review of In Vitro, In Situ and Clinical Studies
Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Beatriz Rascão, Inês Marcelino, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 22(1): 353. CrossRef
- An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
- 1,569 View
- 13 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Chelating and antibacterial properties of chitosan nanoparticles on dentin
- Aldo del Carpio-Perochena, Clovis Monteiro Bramante, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marcia Regina de Moura, Fauze Ahmad Aouada, Anil Kishen
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):195-201. Published online March 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The use of chitosan nanoparticles (CNPs) in endodontics is of interest due to their antibiofilm properties. This study was to investigate the ability of bioactive CNPs to remove the smear layer and inhibit bacterial recolonization on dentin.
Materials and Methods One hundred bovine dentin sections were divided into five groups (
n = 20 per group) according to the treatment. The irrigating solutions used were 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 20 min, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 3 min and 1.29 mg/mL CNPs for 3 min. The samples were irrigated with either distilled water (control), NaOCl, NaOCl-EDTA, NaOCl-EDTA-CNPs or NaOCl-CNPs. After the treatment, half of the samples (n = 50) were used to assess the chelating effect of the solutions using portable scanning electronic microscopy, while the other half (n = 50) were infected intra-orally to examine the post-treatment bacterial biofilm forming capacity. The biovolume and cellular viability of the biofilms were analysed under confocal laser scanning microscopy. The Kappa test was performed for examiner calibration, and the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests (p < 0.05) were used for comparisons among the groups.Results The smear layer was significantly reduced in all of the groups except the control and NaOCl groups (
p < 0.05). The CNPs-treated samples were able to resist biofilm formation significantly better than other treatment groups (p < 0.05).Conclusions CNPs could be used as a final irrigant during root canal treatment with the dual benefit of removing the smear layer and inhibiting bacterial recolonization on root dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of experimental dentifrices containing epigallocatechin-3-gallate–loaded chitosan nanoparticles on permeability, tubule occlusion, microhardness, and wear in eroded dentin
Karen Pintado-Palomino, Letícia de Sousa Franco, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Luiza Araújo Gusmão, Antonio Claudio Tedesco, Mario Sadaiti Ogasawara, Raissa Manoel Garcia, Tais Scaramucci, Silmara Aparecida Corona
JADA Foundational Science.2026; 5: 100057. CrossRef - Advanced nanoparticle-based antibacterial delivery for endodontic disinfection: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kanwalpreet Kaur, Seerat Kaura, Ravinder S Saini, Maurya Manjunath, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Mario Alberto Alarcón-Sánchez, Javier Flores-Fraile, Artak Heboyan
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106347. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength at Resin Interface after Pretreatment with Three Dentine Biomodifiers on Primary Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Sangeetha K Maheshappa, Anandamoy Bagchi, Praveen K Bankur, Anil P Melitt, Randa MF Ibrahim, Thiyezen A AlDhelai
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2026; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparison of Various Irrigation Techniques for the Removal of Silicone Oil-Based Calcium Hydroxide Intracanal Medicament from the Apical Third: An SEM Study
Shalin Ann Saji, Chitharanjan Shetty, Gurmeen Kaur, Sunheri Bajpe, Chandraprabha Chandraprabha, Rashi Shroff, Shazeena Qaiser, Surabhi Gupta
Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU.2025; 15(01): 103. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of smear layer removal and dentin wettability using 1% phytic acid with and without 0.2% chitosan nanoparticles: An in vitro study
Rahul Halkai, Kiran R. Halkai, Syeda Uzma Mahveen
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(1): 38. CrossRef - Chitosan’s Ability to Remove the Smear Layer—A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Ana Ferreira-Reguera, Inês Ferreira, Irene Pina-Vaz, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, José Martín-Cruces
Medicina.2025; 61(1): 114. CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Optimization of chitosan nanoparticle dentin pretreatment with different concentrations and application times to improve bonding at resin-dentin interface
Rinki Meher, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi, Amit Jena, Shradha Suman, Gaurav Sharma
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(3): 248. CrossRef - Innovative strategy for chitosan nanoparticles biosynthesis using Gelidium amansii, statistical optimization, characterization, cytotoxicity and molecular docking against hepatocellular carcinoma
Noura El-Ahmady El-Naggar, Naglaa Elshafey, Hagar I. Alafifi, Manar A. Eltahy, Reem I. Haikl, Hagar A. ElShazly, Yasmin W. Ahmed, Hossam I. Hassan, Mohamed M. Safo, S.A. Haroun, Asmaa A. El-Sawah
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 311: 143687. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effect of chitosan and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the pushout bond strength of mineral trioxide aggregate: An in vitro comparative study
Garima Poddar, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Rolly S. Agarwal, Geetika Pable, Affrin Shaikh, Shakti Singh
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 289. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of chitosan nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis in planktonic and biofilm forms
Raras Ajeng Enggardipta, Minato Akizuki, Kazumitsu Sekine, Kenichi Hamada, Tomoko Sumitomo, Hiromichi Yumoto
Journal of Applied Microbiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Corrosion Inhibition Properties of Chitosan Doped With Fe, Cu, Zn, and Co on the Fe(110) Surface: A Combined DFT and Monte Carlo Simulation Study
D. M. Mamand, Peshawa O. Hama, Rebaz Anwar Omer, Rebaz Obaid Kareem, Dana S. Muhammad, Sarkawt A. Hussen, Yousif Hussein Azeez
Surface and Interface Analysis.2025; 57(12): 936. CrossRef -
Er:YAG Laser Activated Chlorhexidine and Nano Chitosan Against
Enterococcus faecalis
-An In Vitro Study
Manimozhi M, Kiran Kumar N, Biji Brigit, Abhishek M, Swetha Geervani V
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2025; 43(10): 498. CrossRef - Comparison of penetration depth of chitosan, zinc oxide, and silica-doped titanium novel nanoparticle irrigant solutions – A confocal laser scanning microscopic in vitro study
Sree Laksmi Bademela, T. B. V. G. Raju, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, Abitha Seshadri, Nadimpalli Mahendra Varma, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 280. CrossRef - Combined use of XP-Endo Finisher and different chelating agents on the smear layer
Meenu Elizabeth Saju, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Lekha Santhosh, Subhashini Rajasekhara, Priya C. Yadav
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic efficacy of chitosan-based hybrid nanomaterials to treat microbial biofilms and their infections – A review
Anisha Salim, Palanivel Sathishkumar
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 283: 137850. CrossRef - Local and systemic adverse effects of nanoparticles incorporated in dental materials- a critical review
Harini Karunakaran, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta, Mukesh Doble
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(1): 158. CrossRef - Effect of final irrigation protocols with chitosan nanoparticle and genipin on dentine against collagenase degradation: An ex‐vivo study
S. N. Şengül, S. Ozturk, K. Ulubayram, N. Pekel Bayramgil, S. Kucukkaya Eren
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(4): 477. CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Endodontics
Farzaneh Afkhami, Yuan Chen, Laurence J. Walsh, Ove A. Peters, Chun Xu
BME Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - In vitro analysis of compressive strength of root dentin on application of intracanal medicaments for different time periods
Kushal Kumar Ghosh, Sayantan Mukherjee, Paromita Mazumdar, Sahil Ali, Lovely Das
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1289. CrossRef - The comparative of chitosan and chitosan nanoparticle versus ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the smear layer removal: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro study
Hasan İlhan, Elif Bahar Cakici, Fatih Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(2): 181. CrossRef - Final Irrigant Temoporfin, Femtosecond Laser, and Chitosan Nanoparticles on Extrusion Bond Strength of Glass Fiber Post, Microhardness, and Modulus of Elasticity of Canal Dentin
Lujain Ibrahim N. Aldosari
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2024; 14(2): 78. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of an epoxy resin-based and a premixed calcium silicate-based sealer’s push-out bond strength with and without incorporation of chitosan nanoparticles: An in vitro investigation
S. Harishma, K. B. Jeyalakshmi, K. Shibani Shetty, S. Harshini
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(9): 970. CrossRef - Chitosan: A Versatile Biomaterial Revolutionizing Endodontic Therapy
Akash Thakare, Shweta Sedani, Simran Kriplani , Aditya Patel, Utkarsh Umre
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Farnesol and/or Chitosan as a Final Irrigation on Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm; An In-vitro Study
Ardavan Moinafshar, Hanieh Paik, Rashid Ramazanzadeh, Amjad Ahmadi, Mohammad Rastegar Khosravi
Scientific Journal of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences.2024; 29(1): 85. CrossRef - Bionanomaterials an emerging field of nanotechnology
A.R. Shelin, S. Meenakshi
Archives of Materials Science and Engineering.2023; 121(1): 33. CrossRef - Bonding of chitosan and nanochitosan modified universal adhesive to dentin
Yasmin Ezz El-Din, Ahmed El-Banna, Tarek Salah Hussein
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2023; 125: 103432. CrossRef - Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Application in Endodontics
Nicoletta Capuano, Alessandra Amato, Federica Dell’Annunziata, Francesco Giordano, Veronica Folliero, Federica Di Spirito, Pragati Rajendra More, Anna De Filippis, Stefano Martina, Massimo Amato, Massimiliano Galdiero, Alfredo Iandolo, Gianluigi Franci
Antibiotics.2023; 12(12): 1690. CrossRef - In vitro techniques for evaluating smear layer removal by root canal irrigants: a literature review
Luis Hernán Carrillo Varguez, Aracely Serrano-Medina, Eduardo Alberto López Maldonado, Eustolia Rodríguez Velázquez, José Manuel Cornejo-Bravo
Horizon Interdisciplinary Journal.2023; 1(2): 58. CrossRef - Applicability of a Natural Nano-derivative as a Mouth Rinse on Salivary pH and S. mutans Count: An Ex Vivo Study
Raja S Prathigudupu, Deepthi N Gavarraju, Sai S Kallam, Sai Sankar J Avula, Chaitanya M Sattenapalli, Amrutha Valli Audipudi
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(3): 207. CrossRef - Nanopartículas antimicrobianas en endodoncia: Revisión narrativa
Gustavo Adolfo Tovar Rangel , Fanny Mildred González Sáenz , Ingrid Ximena Zamora Córdoba , Lina María García Zapata
Revista Estomatología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantification of Calcium Ions From the Irrigants Activated With Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser in the Root Dentin: An In Vitro Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer Study
Dhanalakshmi P, Kiran Kumar N, K Rashmi, Biji Brigit, Shwetha R S, Sourabh T J
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of chelating effect of chitosan as intracanal lubricant and an irrigant on smear layer removal – An in-vitro scanning electron microscope study
Thati Jyotsnanjali, M. A. Ranjini, G. R. Krishna Kumar, D. V. Swapna, S. N. Joshi, Roopa R. Nadig
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 254. CrossRef - Assessment of the Effectiveness of Two Different Dentin Biomodifiers on Shear Bond Strength of Dentin and Resin Interface: A Comparative Study
Narendra V Penumatsa, AlWaleed Abushanan, Uthman S Uthman, Abdulhamid Al Ghwainem, Adel S Alqarni, Abdulfatah Alazmah
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(1): 16. CrossRef - Scanning electron microscopy evaluation of smear layer removal using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, etidronic acid, and chitosan nanoparticle solution as root canal irrigants
Sunheri Bajpe, Chitharanjan Shetty, Aditya Shetty, Gurmeen Kaur, Shalin Ann Saji, Chandra Prabha
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 48. CrossRef - Green fabrication of chitosan nanoparticles using Lavendula angustifolia, optimization, characterization and in‑vitro antibiofilm activity
Noura El-Ahmady El-Naggar, Marwa Eltarahony, Elsayed E. Hafez, Shimaa I. Bashir
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanobiotechnology: Synthesis components and a few approaches for controlling plant diseases
Malavika Ram A K, Ramji Singh, Meenakshi Rana, S.A. Dwivedi, Kshitij Parmar, Abha Sharma, Chitranjan Kumar, Vineeta Pandey, Vikash Kumar, Shashank Mishra, Ajay Tomar
Plant Nano Biology.2023; 4: 100038. CrossRef - Physicochemical and biological properties of a biostimulating membrane (BBio) for pulp capping
Natalino Lourenço Neto, Luciana Lourenço Ribeiro Vitor, Silgia Aparecida da Costa, Sirlene Maria da Costa, Thiago Cruvinel, Thais Marchini Oliveira, Rodrigo Cardoso Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Andrade Moreira Machado
Materials Letters.2022; 308: 131186. CrossRef - In Vitro Study of Irrigation solution of Chitosan Nanoparticles to Inhibit the Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal
Imelda Darmawi, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2691. CrossRef - Nanoparticles in Endodontics Disinfection: State of the Art
Xavier Roig-Soriano, Eliana B. Souto, Firas Elmsmari, Maria Luisa Garcia, Marta Espina, Fernando Duran-Sindreu, Elena Sánchez-López, Jose Antonio González Sánchez
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(7): 1519. CrossRef - An In Vitro Study Comparing the Antimicrobial Efficacy of 0.2% Chitosan, 3% Sodium Hypochlorite, 2% Chlorhexidine against Enterococcus faecalis, Alone and in Conjunction with Diode Laser
Sameer Makkar, Tamanpreet Kaur, Pallavi Goel, Virat Galhotra, Jatinder Mohan, Neetu Bala
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(1): 109. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots with Applied Aspects: New Frontiers of International Interest in a Material of Marine Origin
Angel M. Villalba-Rodríguez, Reyna Berenice González-González, Manuel Martínez-Ruiz, Elda A. Flores-Contreras, María Fernanda Cárdenas-Alcaide, Hafiz M. N. Iqbal, Roberto Parra-Saldívar
Marine Drugs.2022; 20(12): 782. CrossRef - The Effect of Final Irrigation Protocols on the Apical Sealing Ability of Epoxy Resin-based and Bioceramic-based Root Canal Sealers
Anan Medhat, Angie Ghoneim, Nehal Nabil Roshdy
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(D): 458. CrossRef - Molecular docking reveals Chitosan nanoparticle protection mechanism for dentin against Collagen-binding bacteria
Ziliang Zhou, Yanyan Yang, Lu He, Junmei Wang, Jie Xiong
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Free Available Chlorine of Sodium Hypochlorite When Admixed with 0.2% Chitosan: A Preliminary Study
Rupali Karale, Nithin K Shetty, Prashanth Bytarahosalli Rajachar, Mythreyee S Vidhya, Vinay Kumar Govindaraju
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1171. CrossRef - Effect of chitosan irrigant solutions on the release of bioactive proteins from root dentin
Sara Quijano-Guauque, Lilia J. Bernal-Cepeda, Félix G. Delgado, Jaime E. Castellanos, Claudia García-Guerrero
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(2): 691. CrossRef - Chemical and morphological characterization of self-etch primers incorporated with nanochitosan
Pâmella Coelho Dias, Isabela Barbosa Quero, Juliana Jendiroba Faraoni, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2022; 118: 103215. CrossRef - The effects of different root canal irrigation protocols and artificial aging procedures on the bond strength between dentin and hybrid ceramic posts
Celalettin Topbaş, Şevki Çınar, Bike Altan, Dursun Ali Şirin, Mehmet Ali Fildişi
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of two different concentrations of chitosan irrigation on smear layer removal during root canal treatment
Doaa M. Abd El-latif, Abeer M. Darrag, Dalia A. Sherif
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(4): 204. CrossRef - Impact of Dentin Conditioning and Sealer Modification With Chitosan-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomplexes on the Antibacterial and Mechanical Characteristics of Root Dentin
Aldo del Carpio-Perochena, Eric Nicholson, Chandra Veer Singh, Josette Camilleri, Anil Kishen
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(10): 1319. CrossRef - Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Nano Chitosan, Chlorhexidine, Chlorhexidine/Nano Chitosan Combination versus Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigation in Patients with Necrotic Mandibular Premolars: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Maha Nasr, Alaa Diab, Nehal Roshdy, Amira Farouk
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 235. CrossRef - Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
Shashirekha Govind, Amit Jena, Satabdi Pattanaik, Mahaprasad Anarasi, Satyajit Mohapatra, Vinay Shivagange
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Biomaterial, Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine for Potential Use as Intracanal Medication
Bruna de Siqueira Nunes, Rosana Araújo Rosendo, Abrahão Alves de Oliveira Filho, Marcus Vinícius Lia Fook, Wladymyr Jefferson Bacalhau de Sousa, Rossemberg Cardoso Barbosa, Hermano de Vasconcelos Pina, João Emídio da Silva Neto, Solomon Kweku Sagoe Amoah,
Materials.2021; 14(3): 488. CrossRef - Nanostructures as Targeted Therapeutics for Combating Oral Bacterial Diseases
Shima Afrasiabi, Nasim Chiniforush, Hamid Reza Barikani, Alireza Partoazar, Ramin Goudarzi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(10): 1435. CrossRef - Microbiological Aspects of Root Canal Infections and Disinfection Strategies: An Update Review on the Current Knowledge and Challenges
Jasmine Wong, Daniel Manoil, Peggy Näsman, Georgios N. Belibasakis, Prasanna Neelakantan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Endodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzyński, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Adam Lubojański, Wojciech Dobrzyński, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafał Jakub Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak
Materials.2021; 14(18): 5296. CrossRef - Preparation and application of chitosan biomaterials in dentistry
Chenxi Zhang, Didi Hui, Colin Du, Huan Sun, Wei Peng, Xiaobing Pu, Zhengyong Li, Jianxun Sun, Changchun Zhou
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 167: 1198. CrossRef - The Potential Translational Applications of Nanoparticles in Endodontics
Jasmine Wong, Ting Zou, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Chengfei Zhang
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2021; Volume 16: 2087. CrossRef - Chitosan Enhances the Anti-Biofilm Activity of Biodentine against an Interkingdom Biofilm Model
Sumaya Abusrewil, Jason L. Brown, Christopher Delaney, Mark C. Butcher, Mohammed Tiba, J. Alun Scott, Gordon Ramage, William McLean
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1317. CrossRef - Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Activity of Mouthrinses Containing Tannic Acid or Chitosan on Dentin In Situ
Anton Schestakow, Moritz S. Guth, Tobias A. Eisenmenger, Matthias Hannig
Molecules.2021; 26(5): 1351. CrossRef - An All-inclusive Estimation of Antibacterial and Antifungal Efficiencies of Propolis and Cetrimide Root Canal Irrigants against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans: An In vitro (Original Research) Study
Sumita Giri Nishad
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2021; 12(5): 185. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-containing nanoparticles as vaccine adjuvants
Xinyuan Zhang, Zhigang Zhang, Ningshao Xia, Qinjian Zhao
Expert Review of Vaccines.2021; 20(7): 797. CrossRef - RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL OF ANTIMICROBIAL EFFICACY OF TWO HERBAL PRODUCTS AS ROOT CANAL IRRIGANTS IN PRIMARY ENDODONTIC INFECTIONS.
Sonam Dhall, Rakesh Mittal, Monika Tandan
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preparation methods and applications of chitosan nanoparticles; with an outlook toward reinforcement of biodegradable packaging
Murat Yanat, Karin Schroën
Reactive and Functional Polymers.2021; 161: 104849. CrossRef -
Effect of the Incorporation of Chitosan and TiO
2
Nanoparticles on the Shear Bond Strength of an Orthodontic Adhesive: An In Vitro Study
Fahimeh Farzanegan, Hooman Shafaee, Majid Darroudi, Abdolrasoul Rangrazi
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2021; 12(2): 261. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of hyaluronan/chitosan nanofilm in the initial adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa wild type, and IV pili and LPS mutant strains
Jacobo Hernandez-Montelongo, Gianlucca G. Nicastro, Thays de O. Pereira, Mariana Zavarize, Marisa M. Beppu, Waldemar A.A. Macedo, Regina L. Baldini, Monica A. Cotta
Surfaces and Interfaces.2021; 26: 101415. CrossRef - Randomized Clinical Trial of Antimicrobial Effi cacy of two Herbal Products as Root Canal Irrigants in Primary Endodontic Infections
Sonam Dhall, Rakesh Mittal, Monika Tandan
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation Of Fracture Resistance Of Root Dentin To Different Intracanal Medicaments: In-Vitro Study
Anita Sanap-Tandale, Nikhil Borse, Kunal Kunjir, Karan Bhargava
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(2): 86. CrossRef - Engineering Polymeric Nanosystems against Oral Diseases
Valeria Mercadante, Edoardo Scarpa, Valeria De Matteis, Loris Rizzello, Alessandro Poma
Molecules.2021; 26(8): 2229. CrossRef - Chelation capability of chitosan and chitosan derivatives: Recent developments in sustainable corrosion inhibition and metal decontamination applications
Chandrabhan Verma, M.A. Quraishi
Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry.2021; 4: 100184. CrossRef - Comparative effects of final canal irrigation with chitosan and EDTA
Polliana Vilaça Silva Antunes, Luis Eduardo Souza Flamini, Jardel Francisco Mazzi Chaves, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Antonio Miranda da Cruz Filho
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial property of chitosan against E. faecalis standard strain and clinical isolates
Apimon SUPOTNGARMKUL, Anchana PANICHUTTRA, Chootima RATISOONTORN, Mettachit NAWACHINDA, Oranart MATANGKASOMBUT
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(3): 456. CrossRef - Polymeric and inorganic nanoscopical antimicrobial fillers in dentistry
Pooyan Makvandi, Jun Ting Gu, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Behnaz Ashtari, Arash Moeini, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2020; 101: 69. CrossRef - A chitosan-based irrigant improves the dislocation resistance of a mineral trioxide aggregate-resin hybrid root canal sealer
Esin Ozlek, Priti Pragati Rath, Anil Kishen, Prasanna Neelakantan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(1): 151. CrossRef - Detection, treatment and prevention of endodontic biofilm infections: what’s new in 2020?
Sumaya Abusrewil, Om Alkhir Alshanta, Khawlah Albashaireh, Saeed Alqahtani, Christopher J. Nile, James Alun Scott, William McLean
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2020; 46(2): 194. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of Chelating Agents Used In Endodontics and Their Influence on MMPs of Cell Membranes
Kellin Pivatto, Fabio Luis Miranda Pedro, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Evandro Piva, Thiago Machado Pereira, Welligton Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Brazilian Dental Journal.2020; 31(1): 32. CrossRef - The Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticle as A Final Irrigation Solution on The Smear Layer Removal, Micro-hardness and Surface Roughness of Root Canal Dentin
Diatri Nari Ratih, Raras Ajeng Enggardipta, Aqilla Tiara Kartikaningtyas
The Open Dentistry Journal.2020; 14(1): 19. CrossRef - Time-Dependent Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticles as Final Irrigation on the Apical Sealing Ability and Push-Out Bond Strength of Root Canal Obturation
Diatri Nari Ratih, Nikita Ika Sari, Pribadi Santosa, Nofa Mardia Ningsih Kaswati
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Targeting tuberculosis infection in macrophages using chitosan oligosaccharide nanoplexes
Uday Koli, Kayzad Nilgiriwala, Kalpana Sriraman, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Journal of Nanoparticle Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry
Wenjing Song, Shaohua Ge
Molecules.2019; 24(6): 1033. CrossRef - Assessment of antibacterial activity of 2.5% NaOCl, chitosan nano-particles against Enterococcus faecalis contaminating root canals with and without diode laser irradiation: an in vitro study
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Engy M. Kataia, Neveen A. Helmy
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(1): 39. CrossRef - In Vitro Antimicrobial Effect of Bioadhesive Oral Membrane with Chlorhexidine Gel
Annelyze Podolan Kloster, Natalino Lourenço Neto, Silgia Aparecida da Costa, Thais Marchini Oliveira, Rodrigo Cardoso de Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Andrade Moreira Machado
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(4): 354. CrossRef - How to improve root canal filling in teeth subjected to radiation therapy for cancer
Fabiana de Góes Paiola, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves, Rodrigo Dantas Pereira, Harley Francisco Oliveira, Alexandra Mussolino de Queiroz, Manoel Damião de Sousa-Neto
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of toxicity and oxidative DNA damage of sodium hypochlorite, chitosan and propolis on fibroblast cells
Zeliha Uğur Aydin, Kerem Engin Akpinar, Ceylan Hepokur, Demet Erdönmez
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent developments in the use of nanoparticles for treatment of biofilms
Chendong Han, Nicholas Romero, Stephen Fischer, Julia Dookran, Aaron Berger, Amber L. Doiron
Nanotechnology Reviews.2017; 6(5): 383. CrossRef - Assessment of the Amount of Calcium Ions Released after the use of Different Chelating Agents and Agitation Protocols
Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Laura Maria Amorim Santana Costa, Gilberto Siebert Filho, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Thiago Machado Pereira, Alvaro Henrique Borges
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 133. CrossRef - Wettability and surface morphology of eroded dentin treated with chitosan
Mirian Saavedra Ururahy, Fabiana Almeida Curylofo-Zotti, Rodrigo Galo, Lucas Fabricio Bahia Nogueira, Ana Paula Ramos, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Archives of Oral Biology.2017; 75: 68. CrossRef - Biophysical and biological characterization of intraoral multilayer membranes as potential carriers: A new drug delivery system for dentistry
Mariana dos Santos Silva, Natalino Lourenço Neto, Silgia Aparecida da Costa, Sirlene Maria da Costa, Thais Marchini Oliveira, Rodrigo Cardoso de Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Andrade Moreira Machado
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2017; 71: 498. CrossRef - Antibacterial Properties of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Propolis Associated with Calcium Hydroxide against Single- and Multispecies Biofilms: An In Vitro and In Situ Study
Aldo del Carpio-Perochena, Anil Kishen, Rafael Felitti, Anjali Y. Bhagirath, Manoj R. Medapati, Christopher Lai, Rodrigo S. Cunha
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1332. CrossRef - Analysis of the shelf life of chitosan stored in different types of packaging, using colorimetry and dentin microhardness
Antonio Miranda da Cruz-Filho, Angelo Rafael de Vito Bordin, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Débora Fernandes da Costa Guedes, Paulo César Saquy, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Jesus Djalma Pécora
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 87. CrossRef - Does nanobiotechnology create new tools to combat microorganisms?
Marlena K. Zielińska-Górska, Ewa Sawosz, Konrad Górski, André Chwalibog
Nanotechnology Reviews.2017; 6(2): 171. CrossRef - New frontiers for anti-biofilm drug development
Suzana M. Ribeiro, Mário R. Felício, Esther Vilas Boas, Sónia Gonçalves, Fabrício F. Costa, Ramar Perumal Samy, Nuno C. Santos, Octávio L. Franco
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2016; 160: 133. CrossRef - The effect of combined use of chitosan and PIPS on push-out bond strength of root canal filling materials
Ugur Aydin, Fatih Aksoy, Samet Tosun, Abdul Semih Ozsevik
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(18): 2024. CrossRef - Organic Nanomaterials and Their Applications in the Treatment of Oral Diseases
Maria Virlan, Daniela Miricescu, Radu Radulescu, Cristina Sabliov, Alexandra Totan, Bogdan Calenic, Maria Greabu
Molecules.2016; 21(2): 207. CrossRef
- Effect of experimental dentifrices containing epigallocatechin-3-gallate–loaded chitosan nanoparticles on permeability, tubule occlusion, microhardness, and wear in eroded dentin
- 3,108 View
- 44 Download
- 97 Crossref

-
Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles on
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus - Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):109-114. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Recurrent caries was partly ascribed to lack of antibacterial properties in composite resin. Silver and zinc nanoparticles are considered to be broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the antibacterial properties of composite resins containing 1% silver and zinc-oxide nanoparticles on
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus .Materials and Methods Ninety discoid tablets containing 0%, 1% nano-silver and 1% nano zinc-oxide particles were prepared from flowable composite resin (
n = 30). The antibacterial properties of composite resin discs were evaluated by direct contact test. Diluted solutions ofStreptococcus mutans (PTCC 1683) andLactobacillus (PTCC 1643) were prepared. 0.01 mL of each bacterial species was separately placed on the discs. The discs were transferred to liquid culture media and were incubated at 37℃ for 8 hr. 0.01 mL of each solution was cultured on blood agar and the colonies were counted. Data was analyzed with Kruskall-Wallis and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results Composites containing nano zinc-oxide particles or silver nanoparticles exhibited higher antibacterial activity against
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The effect of zinc-oxide onStreptococcus mutans was significantly higher than that of silver (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the antibacterial activity againstLactobacillus between composites containing silver nanoparticles and those containing zinc-oxide nanoparticles.Conclusions Composite resins containing silver or zinc-oxide nanoparticles exhibited antibacterial activity against
Streptococcus mutans andLactobacillus .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabricated modified compomer bearing CF/SBA-15 nanomaterials: Physicochemical and antibacterial properties
Fatma Nur Kızılay, Mustafa Aydınbelge, Sezer Demirbuğa, Kevser Kolçakoğlu, Nilay Ildız, Serkan Dayan
Dental Materials.2026; 42(3): 451. CrossRef - Physicochemical and antibacterial evaluation of novel nano α-TCP–AgNPs biocomposites for direct pulp-capping applications
Selviana Wulansari, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Nasrul Wathoni, Rosalina Tjandrawinata, Arief Cahyanto, Moehamad Orliando Roeslan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental plaque biofilm-targeting composite nanomaterials: advances and outlook
Jiaxuan Zhao, Shengyuan Huang, Yongjia Yang, Jilei Wang, Qianqian Guo, Yueming Xu, Bingyin Jiang, Jiang Lin
Biomaterials Science.2026; 14(4): 952. CrossRef - Next-Gen Restorative Materials to Revolutionise Smiles
John Yun Niu, Kelsey Xingyun Ge, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Olivia Lili Zhang, Irene Shuping Zhao, Chun Hung Chu
Bioengineering.2026; 13(2): 143. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of tricalcium silicate-based cements with different antibacterial additives
Reda Banon, Luc Martens, Peter De Coster, Jakob van Acker, Jerina Boelens, Elanagai Rathinam, Sivaprakash Rajasekharan
Scientific Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Roles of Nanoparticles in Orthodontic Bonding Materials
Maria Arampatzi, Ellas Spyratou, Iosif Sifakakis, Efstathios P. Efstathopoulos
Applied Sciences.2026; 16(4): 1996. CrossRef - The effect of photoinitiator systems on resin-based composite containing ZnO-nanoparticles
Abdulaziz Alayed, Nikolaos Silikas, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2025; 41(2): 220. CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant effects of propolis nanoparticles and cinnamon nanostructures in preventive dentistry: Experimental and theoretical approaches
Faeze Hamze, Mahnaz Amiri, Zeinab Sadat Islami, Tayebeh Shamspur, Razieh Razavi, Payam Khazaeli
Phytochemical Analysis.2025; 36(8): 2236. CrossRef - Synthesis of boron nitride@copper oxide‐based light‐curing resin composites: Investigating mechanical and antibacterial properties
Shuya Li, Dawei Liu, Zegang Shi, Wenyi Yu, Tingting Yang, Yufeng Bai, Tianlu He, Tai Peng
Polymer Composites.2025; 46(3): 2073. CrossRef - Long-lasting antimicrobial effect of multipurpose ZnO nanoparticle-loaded dental resins enhanced by blue light photodynamic therapy
Maria Luisa Leite, Patricia Comeau, Ala Zaghwan, Ya Shen, Adriana Pigozzo Manso
Dental Materials.2025; 41(3): 347. CrossRef - Use of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles for the Management of Dental Diseases
Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Anjaneyulu Udduttulla, Veena Wenqing Xu, Kitty Jieyi Chen, Monica Yuqing Zhang, Chun Hung Chu
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(3): 209. CrossRef - Assessment of cytotoxicity of clear aligners coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles
Indu Ravi, Vignesh Kailasam
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(2): 262. CrossRef - Emerging developments in plant-based metal nanomaterials for diverse versatile applications - A review
Garima Rana, Vivek Kumar Dhiman, Syed Kashif Ali, Ankush Chauhan, Majid S. Jabir, Suresh Ghotekar
Results in Chemistry.2025; 15: 102231. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Assessment of the Antimicrobial Properties of Mesoporous Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Against Streptococcus mutans: An In Vitro Investigation
Zahra Jowkar, Shima Askarzadeh, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi, Zahra Fattah, Ali Moaddeli, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of theranostic nanoparticles in dental infectious diseases: A review
Mitra Rostami, Pouria Farahani, Moslem Karimzadeh, Samar Esmaelian, Abbas Fadel Hussein, Kamyar Nasiri, Hareth A. Alrikabi, Naghmeh Shenasa
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2025; 112: 107223. CrossRef - Effect on hygroscopic characteristics of n‐ZnO additions to resin composite
Abdulaziz Alayed, Nikolaos Silikas, David C. Watts
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Applications of Nanoparticles in Endodontics as an Antibacterial Agent: A Mini-review
Mina Saliminasab
Advances in Applied NanoBio-Technologies.2025; 6(2): 46. CrossRef - Effect of Nanohydroxyapatite and Silver Nanoparticle Incorporation on the Flexural Strength of Resin Composites
Marzie Moradaian, Maryam Saadat, Shahab Agharezaei, Zahra Khorshidi Asl, Baisakhi Banerjee
BioMed Research International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage and Microhardness of Omnichroma and Silver Nanoparticles- incorporated Omnichroma
Mrithyunjay Satish Mendon, Mansi Jain, Suma Sogi, Gulbar Shah, Gagandeep Bhagat, Simran Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(10): 1181. CrossRef - EVOLUTION OF DENTAL IMPLANT AND IMPLANT SURFACE TREATMENTS- A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Wamiq Fareed, Hossam Mossa, Medhat Mohamed, Malik Almutairi, Rashed Alfehaid, Yousef Ahmad
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 303. CrossRef - Comprehensive review on zinc oxide nanoparticle production and the associated antibacterial mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Aeshah M. Mohammed, Mohammed Mohammed, Jawad K. Oleiwi, Falah H. Ihmedee, Tijjani Adam, Bashir O. Betar, Subash C.B. Gopinath
Nano Trends.2025; 11: 100145. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy and surface roughness of orthodontic brackets coated with silver–copper hybrid or zinc oxide nanoparticles: An in-vitro study
Aseem Sharma, Tanushree Sharma, Nambi. Rammohan. Shrinivaasan, Geetika Tomer, Nisha Gupta, Pramada Kishore, Prashant Babaji, Azhar Mohammed, Ananya Neralla
Journal of Orthodontic Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy, antibiofilm effect, and resistance to biodegradation of a novel composite against Streptococcus mutans
S. Pallavi, A. Devadathan, Lizymol Philipose Pampadykandathil, Vibha Chandrababu, N J Nagaraj, Arvind Kumar Alexander
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1001. CrossRef - Cymbopogon citratus essential oil infused zinc oxide nanoparticles for eco-friendly anticariogenic action
Preeti Pallavi, Saswat Aryan, Pragnya Paramita Sahoo, Adyasha Anapurba Sahoo, Sangeeta Raut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Computational Insights Into Antimicrobial Peptide‐Enhanced Dental Resin Composites: Targeting Porphyromonas gingivalis Heme‐Binding Proteins and Biofilms
Ravinder S. Saini, Doni Dermawan, Abdulkhaliq Ali F. Alshadidi, Rayan Ibrahim H. Binduhayyim, Rajesh Vyas, Fahad Hussain Alhamoudi, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Mohamed Saheer Kuruniyan, Lujain Ibrahim N. Aldosari, Artak Heboyan
MicrobiologyOpen.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The formation of cariogenic plaque to contemporary adhesive restorative materials: an in vitro study
Anna Lehrkinder, Olivia Rydholm, Anna Wänström, Keisuke Nakamura, Ulf Örtengren
Odontology.2024; 112(4): 1090. CrossRef - The Impact of Incorporating Five Different Boron Materials into a Dental Composite on Its Mechanical Properties
Mehmet Kutluhan Ucuk, Musa Kazim Ucuncu
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(3): 1054. CrossRef - Albumin nanoparticles are a promising drug delivery system in dentistry
Mohammad Kiarashi, Saman Yasamineh
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Three Antibacterial Nanoparticle Coatings on the Surface Characteristics of Stainless Steel
Ahmed Al-Mayali, Ammar Kadhum, Thair Alzubaydi
Metals.2024; 14(8): 853. CrossRef - Bioresponsive nanotechnology in pediatric dental drug delivery
Seyed Ebrahim Alavi, Lieba Malik, Raghad Matti, Farah Al-Najafi, Hasan Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, Lavanya A. Sharma
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2024; 93: 105436. CrossRef - Visible light-activated curcumin-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles integrated into orthodontic adhesive on Micro-tensile bond strength, degree of conversion, and antibacterial effectiveness against Staphylococcus Aureus. An investigation using scanning elect
Abdullah A. Alnazeh, Muhammad Abdullah Kamran, Salem Almoammar, Mohammed Mohsen Al Jearah, Muhammad Qasim, Ibrahim Alshahrani
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology.2024; 253: 112888. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of PMMA enriched with nano-clay loaded with metronidazole and chlorhexidine
Eduardo Buozi Moffa, Samuel Santana Malheiros, Larissa Tavares Sampaio Silva, Delcio Ildefonso Branco, Regis Cléo Fernandes Grassia Junior, William Cunha Brandt, Flavia Goncalves, Valentim Adelino Ricardo Barao, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating Antibacterial Frontiers: A Panoramic Exploration of Antibacterial Landscapes, Resistance Mechanisms, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Krittika Ralhan, Kavita A. Iyer, Leilani Lotti Diaz, Robert Bird, Ankush Maind, Qiongqiong Angela Zhou
ACS Infectious Diseases.2024; 10(5): 1483. CrossRef - Use of nanotechnology-based nanomaterial as a substitute for antibiotics in monogastric animals
Abdul Qadeer, Aamir Khan, Noor Muhammad Khan, Abdul Wajid, Kaleem Ullah, Sylvie Skalickova, Pompido Chilala, Petr Slama, Pavel Horky, Mohammed S. Alqahtani, Maha Awjan Alreshidi
Heliyon.2024; 10(11): e31728. CrossRef - Local and systemic adverse effects of nanoparticles incorporated in dental materials- a critical review
Harini Karunakaran, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta, Mukesh Doble
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(1): 158. CrossRef - Determining the cytotoxicity of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles in ESBL and carbapenemase producing Proteus mirabilis isolated from clinical samples in Shiraz, Southwest Iran
Farshad Kakian, Esmaeil Mirzaei, Afagh Moattari, Sara Takallu, Abdollah Bazargani
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New insights into nanotherapeutics for periodontitis: a triple concerto of antimicrobial activity, immunomodulation and periodontium regeneration
Jiaxin Li, Yuxiao Wang, Maomao Tang, Chengdong Zhang, Yachen Fei, Meng Li, Mengjie Li, Shuangying Gui, Jian Guo
Journal of Nanobiotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of silver and calcium fluoride nanoparticles on antibacterial activity of composite resin against Streptococcus mutans: An in vitro study
Mehdi Fathi, Zahra Hosseinali, Tina Molaei, Somayeh Hekmatfar
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Flowable resin-based composites modified with chlorhexidine-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles induce superior antibiofilm properties
Barsha Shrestha, Sultan Aati, Sheetal Maria Rajan, Amr Fawzy
Journal of Nanoparticle Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Temporary Acrylic Soft Denture Lining Material Enriched with Silver-Releasing Filler-Cytotoxicity, Mechanical and Antifungal Properties
Grzegorz Chladek, Igor Kalamarz, Wojciech Pakieła, Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Zenon Czuba, Anna Mertas
Materials.2024; 17(4): 902. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Properties of a Reinforced Zinc Oxide Eugenol Combined with Cloisite 5A Nanoclay: An In-Vitro Study
Bahareh Nazemisalman, Shaghayegh Niaz, Shayan Darvish, Ayda Notash, Ali Ramazani, Ionut Luchian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(7): 198. CrossRef - Assessing the physico-mechanical, anti-bacterial, and anti-demineralization properties of orthodontic resin composite containing different concentrations of photoactivated zinc oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans biofilm around ceramic and metal o
Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Rashin Bahrami, Maryam Pourhajibagher
International Orthodontics.2024; 22(4): 100901. CrossRef - Biosynthesis of a Novel Composite Resin Incorporating Gamma Radiation Synthesized Pomegranate Extract–Coated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and In Vitro Assessment Against Streptococcus mutans Causing Dental Caries
Amany Badr El-Deen Abd El-Aziz, Mehreshan El-Mokadem, Hoda Hassan Abo-Ghalia, Zakaria Ahmed Mattar, Abdelrazq Ibrahim Sallam
BioNanoScience.2024; 14(5): 5017. CrossRef - Global trend and hotspot of resin materials for dental caries repair: a bibliometric analysis
Baodi Han, Lian Wang
Frontiers in Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Studying the Application of Nanoparticles in Orthodontics: A Review Study
Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafal J. Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Adam Lubojanski, Karolina Kurek, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Zakrzewski
Annals of Dental Specialty.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs): Photocatalysis, antibacterial, toxicity and genotoxicity
Olcay Gençyılmaz, Fahriye Zemheri Navruz, Sinan İnce, Abdulsattar Ali Abbas, Abdullah Hüssein Salim Salim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2024; 456: 115847. CrossRef - Advancements in Nanoparticle-Based Strategies for Enhanced Antibacterial Interventions
Madineh Moradialvand, Nastaran Asri, Mahtab Jahdkaran, Maryam Beladi, Hamidreza Houri
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics.2024; 82(4): 3071. CrossRef - Performance evaluation of carbon quantum dots impregnated glass ionomer cement to avoid peri-implant disease
Febina Josephraj, Ashwin Kumar N, Vidyashree Nandini V, Sujatha S, Varshini Karthik
Biomedical Materials.2024; 19(3): 035040. CrossRef - Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensor for periodontitis detection
Mohammad Hosseini Hooshiar, Masoud Amiri Moghaddam, Mohammad Kiarashi, Athraa Y. Al-Hijazi, Abbas Fadel Hussein, Hareth A.Alrikabi, Sara Salari, Samar Esmaelian, Hassan Mesgari, Saman Yasamineh
Journal of Biological Engineering.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the antibacterial properties of Resin cements with and without the addition of nanoparticles: a systematic review
Ravinder Saini, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Masroor Ahmed Kanji, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Saeed Awod Bin Hassan, Sukumaran Anil, Deepti Shrivastava, Kumar Chandan Srivastava
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanotecnologia aplicada a Biomateriais em técnicas preventivas e restauradoras
Lucas Mateus Do Nascimento, Ricardo Felipe Ferreira Da Silva
Revista Sociedade Científica.2024; 7(1): 2326. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetration of Various Nano-sized Intra-canal Medicaments: An In Vitro Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Mounika Veeraiyan, Chikine Yashas Chandhar, Deepa Mastammanavar, Kantheti Kavya, Deepa Jarupula, Gangishetti Sairam
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1690. CrossRef - Preparation and characterization of nano silver antibacterial gel for gynecolog
Qiuqun Xiao, Jingnan Zhu, Tao Fang, Ruyi Peng, Jiayi Chen, Kailan Liu, Yanshi Ceng, Meng Yuan, Yunrui Hu
Ferroelectrics.2024; 618(13-14): 2249. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their biocompatibility in L929 fibroblasts
Zahra Jowkar, Ali Moaddeli, Fereshteh Shafiei, Tara Tadayon, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Nanoparticles on Dental Composites: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dhruv Ahuja, M. R. Akhila, Ashish Kumar Singh, Puneet Batra
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 439. CrossRef - Nanotechnology in Orthodontics: Current Applications and Future Perspectives
Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafal J. Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Adam Lubojanski, Karolina Kurek, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Zakrzewski
Asian Journal of Periodontics and Orthodontics.2024; 4(1): 24. CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Nanoparticles on Addition to Orthodontic
Materials- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Crystal Runa Soans, Deesha Kumari, Shalin Shersha, Rahila Mansoor, M.S. Ravi
Nanoscience & Nanotechnology-Asia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inorganic nanoparticles on dental materials’ mechanical properties. A narrative review
Ghada Naguib, Abdulrahman A. Maghrabi, Abdulghani I. Mira, Hisham A. Mously, Maher Hajjaj, Mohamed T. Hamed
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Restorative Dentistry
Rutvik Mandhalkar, Priyanka Paul, Amit Reche
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The germicidal effect, biosafety and mechanical properties of antibacterial resin composite in cavity filling
Jiamu Ren, Xinwei Guo
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19078. CrossRef - Influence of the Loading with Newly Green Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Equisetum sylvaticum on the Antibacterial Activity and Surface Hardness of a Composite Resin
Ionuț Tărăboanță, Ana Flavia Burlec, Simona Stoleriu, Andreia Corciovă, Adrian Fifere, Denisa Batir-Marin, Monica Hăncianu, Cornelia Mircea, Irina Nica, Andra Claudia Tărăboanță-Gamen, Sorin Andrian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(8): 402. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Ocimum tenuiflorum and Stevia rebaudiana-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles – An In vitro Study
Indumathy Pandiyan, Meignana Indiran Arumugham, Sri Sakthi Doraikannan, Pradeep Kumar Rathinavelu, Jayashri Prabakar, S. Rajeshkumar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2023; 14(2): 109. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Properties of an Orthodontic Composite Containing Silver and Amor-phous Tricalcium Phosphate Nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans: An In Vitro Study
Zahra Tavakolinejad, Mahmood Sheikh Fathollahi, farzaneh Mirzaei, Farzaneh Mirzaei, Elham Mirzaei
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 257. CrossRef - Effect of incorporating silica-hydroxyapatite-silver hybrid nanoparticles into the resin-modified glass ionomer on the adhesive remnant index score and shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets: An in vitro study
Nazila Biglar, Elahe Chaychi Raghimi, Somayeh Sadighian, Farzaneh Karamitanha, Elham Zajkani, Azin Nourian
International Orthodontics.2023; 21(3): 100761. CrossRef - Method development for the intraoral release of nanoparticles from dental restorative materials
Laura Kleinvogel, Gregor Wemken, Cosima Reidelbach, Manuel Garcia-Käufer, Kirstin Vach, Elmar Hellwig, Benedikt C. Spies, Olga Polydorou
Dental Materials.2023; 39(8): 693. CrossRef - Recent advancements in blended and reinforced polymeric systems as bioscaffolds
Jasmin Joseph, Ramesh Parameswaran, Unnikrishnan Gopalakrishna Panicker
International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials.2023; 72(11): 834. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Copper-Doped Phosphate Glass on Pathogenic Bacteria
Sunaina Shetty, Priyadharshini Sekar, Raghavendra M. Shetty, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel
Molecules.2023; 28(7): 3179. CrossRef - Effect of Zinc Oxide Incorporation on the Antibacterial, Physicochemical, and Mechanical Properties of Pit and Fissure Sealants
Ji-Won Choi, Song-Yi Yang
Polymers.2023; 15(3): 529. CrossRef - Novel bioactive dental restorations to inhibit secondary caries in enamel and dentin under oral biofilms
Wen Zhou, Hong Chen, Michael D. Weir, Thomas W. Oates, Xuedong Zhou, Suping Wang, Lei Cheng, Hockin H.K. Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 133: 104497. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of glass-ionomer cement incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles against mutans streptococci and lactobacilli under orthodontic bands: An in vivo split-mouth study
Maryam Shirazi, Fatemeh Fotoohi Qazvini, Saeed Mohamadrezaie
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the cell viability and antimicrobial effects of orthodontic bands coated with silver or zinc oxide nanoparticles: An in vitro study
Rashin Bahrami, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Alireza Badiei, Reza Masaeli, Behrad Tanbakuchi
Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2023; 53(1): 16. CrossRef - Evaluation and comparison of the effect of incorporating zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the bond strength and microleakage of two orthodontic fixed retainer adhesives
Leila Jazi, Ahmad Sodagar, Sepehr Sobhani Kazemi, Amirhossein Mirhashemi
Journal of the World Federation of Orthodontists.2023; 12(1): 22. CrossRef - Bioactive Materials for Caries Management: A Literature Review
Olivia Lili Zhang, John Yun Niu, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Ollie Yiru Yu, May Lei Mei, Chun Hung Chu
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(3): 59. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of zinc oxide nanoparticle-coated aligners on Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans
Prathima Anita, Haritha Pottipalli Sathyanarayana, Kennedy Kumar, Krishnapriya Ramanathan, Vignesh Kailasam
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2023; 163(3): 338. CrossRef - The Impact of Adhesive-Containing Nanoparticles of ZrO2and TiO2 on Antimicrobial Effectiveness, the Strength of Bonding, and the Extent of Microleakage in Dentin Affected by Caries
Fayez Hussain Niazi, Shadi El Bahra, Nisren Ansary, Zeeshan Qamar, Hajar Albahkaly, Badr Bamousa, Ahlam Smran, Ahmed Al Ahmari, Saleh Wael S. Al-Akki, Abdulaziz Samran
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2023; 13(9): 946. CrossRef - Comparitive evaluation of antimicrobial effectiveness of silver oxide coatings on different types of ceramic brackets against Streptococcus mutans
S. V. Ramesh Goud, K. Raja Sigamani, Bhaskar, Kurinchi Kumaran, Mohammed Arafat, S.N Reddy Duvvuri
The Journal of Dental Panacea.2022; 4(2): 75. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial and mechanical features of dental adhesives containing colloidal gold nanoparticles
Sara Dadkan, Mehrdad Khakbiz, Lida Ghazanfari, Meizi Chen, Ki-Bum Lee
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2022; 365: 119824. CrossRef - Preparation of electrospun silver/poly(vinyl alcohol) fibrous membranes and characterization of the effect of sterilization processes on the antibacterial activity
Wen-Cheng Chen, Chia-Ying Ko, Kai-Chi Chang, Chih-Hua Chen, Dan-Jae Lin
Journal of Industrial Textiles.2022; 51(4_suppl): 7205S. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-Based Zinc Ion Interference Therapy to Combat Bacterial Infections
Yongbin Wei, Jiaming Wang, Sixuan Wu, Ruixue Zhou, Kaixiang Zhang, Zhenzhong Zhang, Junjie Liu, Shangshang Qin, Jinjin Shi
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative Investigation of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Used in Dentistry
Ajay Kumar Tiwari, Saket Jha, Abhimanyu Kumar Singh, Sheo Kumar Mishra, Ashok Kumar Pathak, Rudra Prakash Ojha, Raghvendra Singh Yadav, Anupam Dikshit
Crystals.2022; 12(8): 1063. CrossRef - Efficient Route for the Preparation of Composite Resin Incorporating Silver Nanoparticles with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties
Drake Beery, Mohammad Abdul Mottaleb, Mohammed J. Meziani, James Campbell, Isabella Pires Miranda, Michael Bellamy
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(3): 471. CrossRef - Antibacterial performance of composite containing quaternary ammonium silica (QASi) filler – A preliminary study
Michal Dekel-Steinkeller, Ervin I. Weiss, Trudi Lev-Dor Samovici, Itzhak Abramovitz
Journal of Dentistry.2022; 123: 104209. CrossRef - Therapeutic Applications of Antimicrobial Silver-Based Biomaterials in Dentistry
Qiyu Wang, Yu Zhang, Qiang Li, Li Chen, Hui Liu, Meng Ding, Heng Dong, Yongbin Mou
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2022; Volume 17: 443. CrossRef - In-vitro Comparative Assessment of Antibacterial and Anti-adherent Effect of Two Types of Surface Modificants on Stainless Steel Orthodontic Brackets Against Streptococcus mutans
Mrunmaye Math, Alok G. Shah, Parag Gangurde, Anita G. Karandikar, Anjali Gheware, Bhagyashree S. Jadhav
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2022; 56(3): 282. CrossRef - Dental Composites with Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Prevent Secondary Caries in the Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Model
Tahreem Tanweer, Nosheen Fatima Rana, Iqra Saleem, Iqra Shafique, Sultan M. Alshahrani, Hanadi A. Almukhlifi, Amenah S. Alotaibi, Sohad Abdulkaleg Alshareef, Farid Menaa
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15926. CrossRef - Effect of Different Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles on the Quality of the Chemical Bond of Glass Ionomer Cement Dentine in Primary Teeth
Faisal Mohammed Abed, Sunil Babu Kotha, Haneen AlShukairi, Fatmah Nasser Almotawah, Rwan Abdulali Alabdulaly, Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity of Dental Composite with Ciprofloxacin Loaded Silver Nanoparticles
Wafa Arif, Nosheen Rana, Iqra Saleem, Tahreem Tanweer, Muhammad Khan, Sohad Alshareef, Huda Sheikh, Fatima Alaryani, Manal AL-Kattan, Hanan Alatawi, Farid Menaa, Aroosa Nadeem
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7182. CrossRef - Experimental composite containing silicon dioxide-coated silver nanoparticles for orthodontic bonding: Antimicrobial activity and shear bond strength
Rogéria Christina de Oliveira AGUIAR, Larissa Pereira NUNES, Eduardo Silva BATISTA, Marina Mariante VIANA, Marcela Charantola RODRIGUES, Bruno BUENO-SILVA, Marina Guimarães ROSCOE
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - DEAE-Dextran Coated AgNPs: A Highly Blendable Nanofiller Enhances Compressive Strength of Dental Resin Composites
Shabia Azhar, Nosheen Fatima Rana, Amer Sohail Kashif, Tahreem Tanweer, Iqra Shafique, Farid Menaa
Polymers.2022; 14(15): 3143. CrossRef - Synthesis of a Novel, Biocompatible and Bacteriostatic Borosiloxane Composition with Silver Oxide Nanoparticles
Denis N. Chausov, Veronika V. Smirnova, Dmitriy E. Burmistrov, Ruslan M. Sarimov, Alexander D. Kurilov, Maxim E. Astashev, Oleg V. Uvarov, Mikhail V. Dubinin, Valery A. Kozlov, Maria V. Vedunova, Maksim B. Rebezov, Anastasia A. Semenova, Andrey B. Lisitsy
Materials.2022; 15(2): 527. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties, Biocompatibility and Anti-Bacterial Adhesion Property Evaluation of Silicone-Containing Resin Composite with Different Formulae
Muzi Liao, Hui Tong, Xiangya Huang, Fang Liu, Jingwei He, Sui Mai
Journal of Renewable Materials.2022; 10(12): 3201. CrossRef - Current trends and future perspectives on dental nanomaterials – An overview of nanotechnology strategies in dentistry
Vidhya Rekha Umapathy, Prabhu Manickam Natarajan, C. SumathiJones, Bhuminathan Swamikannu, W.M.S. Johnson, V. Alagarsamy, Ashequr Rahman Milon
Journal of King Saud University - Science.2022; 34(7): 102231. CrossRef - Boron nitride nanosheets modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles as novel fillers of dental resin composite
Ameenah Saad Alansy, Thekra Ali Saeed, Reem Al-Attab, Yuqing Guo, Yanwei Yang, Bin Liu, Zengjie Fan
Dental Materials.2022; 38(10): e266. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review on Its Applications in Dentistry
C Pushpalatha, Jithya Suresh, VS Gayathri, SV Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Antibacterial Activity of Nano Titania-Enriched Alkasite Restorative Material: An In Vitro Study
Neven S. Aref, Reham M. Abdallah
The Open Dentistry Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Properties of a Methacrylate-Based Dental Material Loaded with ZnO Nanoparticles
Patricia Comeau, Julia Burgess, Niknaz Malekafzali, Maria Luisa Leite, Aidan Lee, Adriana Manso
Materials.2022; 15(14): 5075. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef - Development of Direct Immobilization Technique of Ag Nanoparticles on Resin Substrates Imparting High Antibacterial and Antiviral Activities
Satoshi Seino, Yuji Ohkubo, Tomonari Magara, Hiroki Enomoto, Eri Nakajima, Tomoki Nishida, Yasuo Imoto, Takashi Nakagawa
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(17): 3046. CrossRef - Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
Pooja Jain, Uzma Farooq, Nazia Hassan, Mohammed Albratty, Md. Shamsher Alam, Hafiz A. Makeen, Mohd. Aamir Mirza, Zeenat Iqbal
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 1935. CrossRef - Impact of Different Antibacterial Substances in Dental Composite Materials: A Comprehensive Review
Badr Soliman AlHussain, Abdulrahman Abdulaziz AlFayez, Abdullah Abdulrahman AlDuhaymi, Essam Abdulaziz AlMulhim, Mohammad Yahya Assiri, Shahzeb Hasan Ansari
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2022; 2(1): 1. CrossRef - Chlorhexidine in operative dentistry - A review
TanviSanjay Satpute, SanjyotA Mulay
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 80. CrossRef - Nanotechnology-based materials as emerging trends for dental applications
Tejas Barot, Deepak Rawtani, Pratik Kulkarni
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2021; 60(1): 173. CrossRef - A Brief Review on the Evolution of Metallic Dental Implants: History, Design, and Application
Sumanth Ratna Kandavalli, Qingge Wang, Mahmoud Ebrahimi, Ceren Gode, Faramarz Djavanroodi, Shokouh Attarilar, Shifeng Liu
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans, antioxidant property and cytotoxicity of novel nano-zinc oxide varnish
Manali Deb Barma, Indumathy Muthupandiyan, Srinivasan Raj Samuel, Bennett T. Amaechi
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 126: 105132. CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Orthodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Adam Lubojanski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 337. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of new denture base material modified with gold nanoparticles
Adamović Tijana, Veselinović Valentina, Trtić Nataša, Hadži-Mihailović Miloš, Gotovac Atlagić Suzana, Balaban Milica, Hattori Yoshiyuki, Sugiyama Hironori, Andrej Ivanič, Rudolf Rebeka
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2021; 65(2): 155. CrossRef - Dynamics of different ion release from denture-base acrylic resins and their mechanical properties after the addition of bioactive materials
Zbigniew Raszewski
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(8): 1071. CrossRef - Genotoxic assay of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by leaf extract of Garcinia livingstonei T. Anderson: A comparative study
AzharuddinB Daphedar, SiddappaB Kakkalameli, Govindappa Melappa, TarikereChandrashekharappa Taranath, Chandrashekar Srinivasa, Chandan Shivamallu, Asad Syed, Najat Marraiki, AbdallahM Elgorban, Ravindra Veerapur, SharangoudaS Patil, ShivaPrasad Kollur
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2021; 17(5): 114. CrossRef - Nanostructures as Targeted Therapeutics for Combating Oral Bacterial Diseases
Shima Afrasiabi, Nasim Chiniforush, Hamid Reza Barikani, Alireza Partoazar, Ramin Goudarzi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(10): 1435. CrossRef - Well-Orientation Strategy Biosynthesis of Cefuroxime-Silver Nanoantibiotic for Reinforced Biodentine™ and Its Dental Application against Streptococcus mutans
Sanaa M. F. Gad El-Rab, Amal A. Ashour, Sakeenabi Basha, Amal Ahmed Alyamani, Nayef H. Felemban, Enas Tawfik Enan
Molecules.2021; 26(22): 6832. CrossRef - Application of Selected Nanomaterials and Ozone in Modern Clinical Dentistry
Adam Lubojanski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Nicole Nowak, Justyna Rewak-Soroczynska, Klaudia Sztyler, Wojciech Zakrzewski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Katarzyna Wiglusz, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 259. CrossRef - Nanomaterials as drug delivery systems with antibacterial properties: current trends and future priorities
Khatereh Khorsandi, Reza Hosseinzadeh, Homa Sadat Esfahani, Saeedeh Keyvani-Ghamsari, Saeed Ur Rahman
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy.2021; 19(10): 1299. CrossRef - Synthesis and antibacterial activity of polymer–antibiotic conjugates incorporated into a resin-based dental adhesive
Ziwen Zhang, Megan M. Jones, Camila Sabatini, Stephen T. Vanyo, Ming Yang, Abhishek Kumar, Yancheng Jiang, Mark T. Swihart, Michelle B. Visser, Chong Cheng
Biomaterials Science.2021; 9(6): 2043. CrossRef - Effect Of Various Antibacterial Materials In Dental Composites: A Systematic Review
Abdulrahman Abdulaziz Alfayez, Abdullah Abdulrahman Alduhaymi, Essam Abdulaziz Almulhim, Mohammad Yahya Assiri, Shahzeb Hasan Ansari
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(3): 39. CrossRef - Low-temperature flow-synthesis-assisted urethane-grafted zinc oxide-based dental composites: physical, mechanical, and antibacterial responses
Jaffar Hussain Bukhari, Abdul Samad Khan, Kashif Ijaz, Shahreen Zahid, Aqif Anwar Chaudhry, Muhammad Kaleem
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of nano‐technology applications in resin‐based restorative materials
Natalia Almeida Bastos, Sandro Basso Bitencourt, Emerson Alves Martins, Grace Mendonca De Souza
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(4): 567. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Therapies for the Management of Dental Caries—A Literature Review
Hetal Desai, Cameron Stewart, Yoav Finer
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 147. CrossRef - In-vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles and Its Indigenous Mouthwash
Lichi. A. Solanki, KK Shantha Sundari, S Rajeshkumar
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2021; 15(2): 735. CrossRef - Antibacterial response of oral microcosm biofilm to nano-zinc oxide in adhesive resin
Isadora Martini Garcia, AbdulRahman A. Balhaddad, Maria S. Ibrahim, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dental Materials.2021; 37(3): e182. CrossRef - Toxic mechanisms of Roth801, Canals, microparticles and nanoparticles of ZnO on MG-63 osteoblasts
Mei-Chi Chang, Chia-Mei Tang, Yu-Heng Lin, Hsin-Cheng Liu, Tong-Mei Wang, Wen-Chien Lan, Ru-Hsiu Cheng, Yan-Ru Lin, Hsiao-Hua Chang, Jiiang-Huei Jeng
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 119: 111635. CrossRef - Initial Mechanical Stabilization of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cements with Different Active Principles
Caroline Santos Ribeiro, Mayra Manoella Perez, Pablo Lenin Benitez-Sellan, Renata de Oliveira Guaré, Eduardo Bresciani, Michele Baffi Diniz
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinc oxide nanoparticles inhibit bacterial biofilm formation via altering cell membrane permeability
Tanvir Kaur, Chayanika Putatunda, Ashish Vyas, Gaurav Kumar
Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology.2021; 51(4): 309. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, mechanical, and bonding properties of a dental adhesive modified with antibacterial monomer and cross-linker
Hoda Moussa, Megan M. Jones, Ningbo Huo, Runsheng Zhang, Mayuresh Keskar, Michelle B. Visser, Mark T. Swihart, Chong Cheng, Camila Sabatini
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2877. CrossRef - The Benefits of Smart Nanoparticles in Dental Applications
Silvia Vasiliu, Stefania Racovita, Ionela Aurica Gugoasa, Maria-Andreea Lungan, Marcel Popa, Jacques Desbrieres
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(5): 2585. CrossRef - Microshear Bond Strength of Nanoparticle-Incorporated Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer to Caries-Affected Dentin
Zahra Fattah, Zahra Jowkar, Safoora Rezaeian, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - An Insight in to Various Metallic Oxide Nanoparticles as Antimicrobials and Their Applications in Dentistry
Hema Kanathila, Ashwin M. Pangi, Suvidha Patil, Shilpa Shirlal, Rahul Jaiswal
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(33): 2803. CrossRef - Innovative Strategies in Minimally Invasive Dentistry for Caries Management: A Literature Synthesis
Mariana Vega, Hugo Fuentes, Valeria Cordero, Luis Silva, Regina Cabrera
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2021; 1(2): 66. CrossRef - Nanoparticle technology and its implications in endodontics: a review
Natasha Raura, Anirudh Garg, Arpit Arora, M. Roma
Biomaterials Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Use of Silver Nanomaterials for Caries Prevention: A Concise Review
Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Irene Shuping Zhao, May Lei Mei, Quanli Li, Ollie Yiru Yu, Chun Hung Chu
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 3181. CrossRef- Study on a novel antibacterial light-cured resin composite containing nano-MgO
Zhongyuan Wu, Haiping Xu, Wei Xie, Meimei Wang, Cunjin Wang, Cheng Gao, Fang Gu, Jie Liu, Jing Fu
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces.2020; 188: 110774. CrossRef - Effect of Addition of Nano-TiO2, Nano-SiO2, and a Combination of Both, on Antimicrobial Activity of an Orthodontic Composite
Abbas Bahador, Mohammad J Kharazifard, Nazanin Kiomarsi, Paniz Zamani, Sedighe S Hashemikamangar, Maryam Pourhajibagher
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(8): 857. CrossRef - Biomimetic Aspects of Oral and Dentofacial Regeneration
Akshaya Upadhyay, Sangeeth Pillai, Parisa Khayambashi, Hisham Sabri, Kyungjun T. Lee, Maryam Tarar, Stephanie Zhou, Ingrid Harb, Simon D. Tran
Biomimetics.2020; 5(4): 51. CrossRef Dental Materials Incorporated with Nanometals and Their Effect on the Bacterial Growth of Staphylococcus aureus
Rabeah Yousef Rawashdeh, Reyad Sawafta, Hanan I Malkawi
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 4325. CrossRef- Does the Addition of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Improve the Antibacterial Properties of Direct Dental Composite Resins? A Systematic Review
Divya Arun, Dulanja Adikari Mudiyanselage, Rumana Gulam Mohamed, Michael Liddell, Nur Mohammad Monsur Hassan, Dileep Sharma
Materials.2020; 14(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on broilers’ performance and health status
Usama T. Mahmoud, Hosnia S. Abdel-Mohsein, Manal A. M. Mahmoud, Omar A. Amen, Rasha I. M. Hassan, Ashraf M. Abd-El-Malek, Sohair M. M. Rageb, Hanan S. A. Waly, Aly A. Othman, Mohamed A. Osman
Tropical Animal Health and Production.2020; 52(4): 2043. CrossRef - The potential anti‐infective applications of metal oxide nanoparticles: A systematic review
Yasmin Abo‐zeid, Gareth R. Williams
WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - ZnO Modulates Swine Gut Microbiota and Improves Growth Performance of Nursery Pigs When Combined with Peptide Cocktail
Xiaoyuan Wei, Tsungcheng Tsai, Joshua Knapp, Kristopher Bottoms, Feilong Deng, Robert Story, Charles Maxwell, Jiangchao Zhao
Microorganisms.2020; 8(2): 146. CrossRef - Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial activity of silica-coated silver nanoparticles for esthetic dental applications
Marcela Charantola Rodrigues, Wallace Rosado Rolim, Marina Mariante Viana, Thaís Rodrigues Souza, Flavia Gonçalves, Caio Junji Tanaka, Bruno Bueno-Silva, Amedea Barozzi Seabra
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 96: 103327. CrossRef - Advances of Anti-Caries Nanomaterials
Hui Chen, Lisha Gu, Binyou Liao, Xuedong Zhou, Lei Cheng, Biao Ren
Molecules.2020; 25(21): 5047. CrossRef - Antibacterial Properties of Nanoparticles in Dental Restorative Materials. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elena Ferrando-Magraner, Carlos Bellot-Arcís, Vanessa Paredes-Gallardo, José Manuel Almerich-Silla, Verónica García-Sanz, Mercedes Fernández-Alonso, José María Montiel-Company
Medicina.2020; 56(2): 55. CrossRef - Polymeric and inorganic nanoscopical antimicrobial fillers in dentistry
Pooyan Makvandi, Jun Ting Gu, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Behnaz Ashtari, Arash Moeini, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2020; 101: 69. CrossRef - The effect of incorporation Nano Cinnamon powder on the shear bond of the orthodontic composite (an in vitro study)
Saba N. Yaseen, Amer A. Taqa, Ali R. Al-Khatib
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 128. CrossRef - Synthesis of an anti-cariogenic experimental dental composite containing novel drug-decorated copper particles
Mehwish Pasha, Nawshad Muhammad, Maleeha Nayyer, Jaffar Hussain Bokhari, Hina Ashraf, Sher Zaman Safi, Muhammad Kaleem
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2020; 114: 111040. CrossRef The Effects of Silver, Zinc Oxide, and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Used as Dentin Pretreatments on the Microshear Bond Strength of a Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement to Dentin
Zahra Jowkar, Zahra Fattah, Saeedreza Ghanbarian, Fereshteh Shafiei
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 4755. CrossRef- Metal‐Based Nanomaterials in Biomedical Applications: Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity Aspects
Pooyan Makvandi, Chen‐yu Wang, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Assunta Borzacchiello, Li‐na Niu, Franklin R. Tay
Advanced Functional Materials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Biomedical Materials
Maria P. Nikolova, Murthy S. Chavali
Biomimetics.2020; 5(2): 27. CrossRef - Comparison of antibacterial effects of orthodontic composites containing different nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans at different times
Soghra Yassaei, Ali Nasr, Hengameh Zandi, Mohammad Nima Motallaei
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(2): 52. CrossRef - Nanoparticles as Anti-Microbial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Remineralizing Agents in Oral Care Cosmetics: A Review of the Current Situation
Florence Carrouel, Stephane Viennot, Livia Ottolenghi, Cedric Gaillard, Denis Bourgeois
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(1): 140. CrossRef - Nanometals in Dentistry: Applications and Toxicological Implications—a Systematic Review
Rupali Agnihotri, Sumit Gaur, Sacharia Albin
Biological Trace Element Research.2020; 197(1): 70. CrossRef - Ex vivo investigation on internal tunnel approach/internal resin infiltration and external nanosilver-modified resin infiltration of proximal caries exceeding into dentin
Andrej M. Kielbassa, Marlene R. Leimer, Jens Hartmann, Stephan Harm, Markus Pasztorek, Ina B. Ulrich, Yogendra Kumar Mishra
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(1): e0228249. CrossRef - Nanocomposites based on low density polyethylene filled with carbon nanotubes prepared by high energy ball milling and their potential antibacterial activity
Erika Benigno, Miguel A Lorente, Dania Olmos, Gustavo González‐Gaitano, Javier González‐Benito
Polymer International.2019; 68(6): 1155. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide and modified titanium dioxide by silver nanoparticles as an anti biofilm filler content for composite resins
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Taís Maria Bauab, Antônio Carlos Hernandes, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): e36. CrossRef - Synthesis, characterization and application of Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles in a composite resin
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Valéria Spolon Marangoni, Adilson César de Abreu Bernardi, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli, Antônio Carlos Hernandes
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 96: 391. CrossRef - The effect of silver nanoparticles incorporation in the self-etch adhesive system on its antibacterial activity and degree of conversion: an in-vitro study
Heba F. Mohammed, Mona I. Riad
F1000Research.2019; 8: 244. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on resin-dentin bond strength durability in a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive system
Zahra Jowkar, Fereshteh Shafiei, Elham Asadmanesh, Fatemeh Koohpeima
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and status of resin composite as dental restorative materials
Xinxuan Zhou, Xiaoyu Huang, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Lei Cheng
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticle solution on the mechanical properties of resin cements and intrarradicular dentin
Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, Juno Gallego, Wirley Gonçalves Assunção, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Chun-Pin Lin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(6): e0217750. CrossRef - Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole
Yasaman Delaviz, Timothy W. Liu, Ashley R. Deonarain, Yoav Finer, Babak Shokati, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): 229. CrossRef - Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry
Wenjing Song, Shaohua Ge
Molecules.2019; 24(6): 1033. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of a tissue conditioner used in complete dentures after incorporation of ZnO‒Ag nanoparticles
Seyed Amin Mousavi, Reza Ghotaslou, Abolfazl Akbarzadeh, Niloufar Azima, Ali Aeinfar, Azin Khorramdel
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(1): 11. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Mechanical Properties of Pit and Fissure Sealants Containing Zinc Oxide and Calcium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Dara Lakshmi Swetha, C. Vinay, K. S. Uloopi, Kakarla Sri RojaRamya, Rayala Chandrasekhar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 477. CrossRef - Addition of antibacterial agent effect on color stability of composites after immersion of different beverages
Makbule T. Tuncdemir, Nilgun Gulbahce
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 31(5): 508. CrossRef - Toward dental caries: Exploring nanoparticle-based platforms and calcium phosphate compounds for dental restorative materials
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Anmar A. Kansara, Denise Hidan, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Bioactive Materials.2019; 4: 43. CrossRef - Antibacterial effects of polymeric PolymP-n Active nanoparticles. An in vitro biofilm study
M.C. Sánchez, M. Toledano-Osorio, J. Bueno, E. Figuero, M. Toledano, A.L. Medina-Castillo, R. Osorio, D. Herrera, M. Sanz
Dental Materials.2019; 35(1): 156. CrossRef - Potencial antimicrobiano de diferentes retentores intrarradiculares frente a Enterococcus faecalis: uma avaliação in vitro
Nicole Hoffmann FINGER, Marília PAULUS, Alexandra Flávia GAZZONI
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomedicine for anticancer and antimicrobial treatment: an overview
Shatavari Kulshrestha, Asad U. Khan
IET Nanobiotechnology.2018; 12(8): 1009. CrossRef - Effect of Silver Nanoparticles, Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Microshear Bond Strength to Enamel and Dentin
Fatemeh Koohpeima, Zahra Jowkar, Nazbanoo Farpour, Mohammad J Mokhtari, Fereshteh Shafiei
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(11): 1405. CrossRef - Studies on the Curing Efficiency and Mechanical Properties of Bis-GMA and TEGDMA Nanocomposites Containing Silver Nanoparticles
Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Grzegorz Chladek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(12): 3937. CrossRef - Properties of Experimental Dental Composites Containing Antibacterial Silver-Releasing Filler
Robert Stencel, Jacek Kasperski, Wojciech Pakieła, Anna Mertas, Elżbieta Bobela, Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Grzegorz Chladek
Materials.2018; 11(6): 1031. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial properties on polysulfone composite membranes using synthesized biogenic silver nanoparticles with Ulva compressa (L.) Kütz. and Cladophora glomerata (L.) Kütz. extracts
Fozia T. Minhas, Gulsin Arslan, I. Hilal Gubbuk, Cengiz Akkoz, Betul Yılmaz Ozturk, Baran Asıkkutlu, Ugur Arslan, Mustafa Ersoz
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2018; 107: 157. CrossRef - Human In Situ Study of the effect of Bis(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl) Dimethylammonium Bromide Immobilized in Dental Composite on Controlling Mature Cariogenic Biofilm
Mary Anne S. Melo, Michael D. Weir, Vanara F. Passos, Juliana P. M. Rolim, Christopher D. Lynch, Lidiany K. A. Rodrigues, Hockin H. K. Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(11): 3443. CrossRef - A systematic review on antibacterial activity of zinc against Streptococcus mutans
Manal Mohamed Almoudi, Alaa Sabah Hussein, Mohamed Ibrahim Abu Hassan, Nurhayati Mohamad Zain
The Saudi Dental Journal.2018; 30(4): 283. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and diametrical tensile strength of an interim cement modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles and terpenes: An in vitro study
Verónica Andrade, Alejandra Martínez, Ninón Rojas, Helia Bello-Toledo, Paulo Flores, Gabriela Sánchez-Sanhueza, Alfonso Catalán
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2018; 119(5): 862.e1. CrossRef - Developing a New Generation of Therapeutic Dental Polymers to Inhibit Oral Biofilms and Protect Teeth
Ke Zhang, Bashayer Baras, Christopher Lynch, Michael Weir, Mary Melo, Yuncong Li, Mark Reynolds, Yuxing Bai, Lin Wang, Suping Wang, Hockin Xu
Materials.2018; 11(9): 1747. CrossRef - Do quaternary ammonium monomers induce drug resistance in cariogenic, endodontic and periodontal bacterial species?
Suping Wang, Haohao Wang, Biao Ren, Hao Li, Michael D. Weir, Xuedong Zhou, Thomas W. Oates, Lei Cheng, Hockin H.K. Xu
Dental Materials.2017; 33(10): 1127. CrossRef - Antimicrobial nanomaterials against biofilms: an alternative strategy
Chunhua Liu, Jing Guo, Xiaoqing Yan, Yongbing Tang, Asit Mazumder, Shikai Wu, Yan Liang
Environmental Reviews.2017; 25(2): 225. CrossRef - Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future
Azhwar Raghunath, Ekambaram Perumal
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.2017; 49(2): 137. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Polymers in the Nano-World
Marta Álvarez-Paino, Alexandra Muñoz-Bonilla, Marta Fernández-García
Nanomaterials.2017; 7(2): 48. CrossRef - Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles on Orthodontic Elastomeric Modules: Evaluation of Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties
Alma Hernández-Gómora, Edith Lara-Carrillo, Julio Robles-Navarro, Rogelio Scougall-Vilchis, Susana Hernández-López, Carlo Medina-Solís, Raúl Morales-Luckie
Molecules.2017; 22(9): 1407. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Influence Microflora in Ileal Digesta and Correlate Well with Blood Metabolites
Yanni Feng, Lingjiang Min, Weidong Zhang, Jing Liu, Zhumei Hou, Meiqiang Chu, Lan Li, Wei Shen, Yong Zhao, Hongfu Zhang
Frontiers in Microbiology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial activity of glass ionomer cement modified by zinc oxide nanoparticles
Patrícia Petromilli Nordi Sasso Garcia, Mariana Florian Bell Cardia, Renata Serignoli Francisconi, Lívia Nordi Dovigo, Denise Madalena Palomari Spolidório, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli, Ana Carolina Botta
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(5): 456. CrossRef - Effects on cytotoxicity and antibacterial properties of the incorporations of silver nanoparticles into the surface coating of dental alloys
Xiao-ting Shen, Yan-zhen Zhang, Fang Xiao, Jing Zhu, Xiao-dong Zheng
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2017; 18(7): 615. CrossRef - Nanosilver coated orthodontic brackets:in vivoantibacterial properties and ion release
Gamze Metin-Gürsoy, Lale Taner, Gülçin Akca
The European Journal of Orthodontics.2017; 39(1): 9. CrossRef - Prenatal Exposure to Nanosized Zinc Oxide in Rats: Neurotoxicity and Postnatal Impaired Learning and Memory Ability
Feng Xiaoli, Wu Junrong, Lai Xuan, Zhang Yanli, Wei Limin, Liu Jia, Shao Longquan
Nanomedicine.2017; 12(7): 777. CrossRef - Heat-Polymerized Resin Containing Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate Inhibits Candida albicans Biofilm
Hui Chen, Qi Han, Xuedong Zhou, Keke Zhang, Suping Wang, Hockin Xu, Michael Weir, Mingye Feng, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Lei Cheng
Materials.2017; 10(4): 431. CrossRef - Zinc oxide 3D microstructures as an antimicrobial filler content for composite resins
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Matheus Aparecido dos Santos Ramos, Tamara Carolina Trevisan, Taís Maria Bauab, Antônio Carlos Hernandes, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(6): 634. CrossRef - Polymer-Ceramic Bionanocomposites for Dental Application
Jung-Hwan Lee, Hae-Won Kim, Seog-Jin Seo
Journal of Nanomaterials.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of nanosilver-coated orthodontic brackets: an in vivo study
Gamze Metin-Gürsoy, Lale Taner, Emre Barış
Progress in Orthodontics.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Restorative materials containing antimicrobial agents: is there evidence for their antimicrobial and anticaries effects? A systematic review
GS do Amaral, T Negrini, M Maltz, RA Arthur
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(1): 6. CrossRef - Evaluation of Bond Strength and Microleakage of a Novel Metal-titanate Antibacterial Agent
S Deng, KH Chung, DCN Chan, C Spiekerman
Operative Dentistry.2016; 41(3): E48. CrossRef - Investigation of optical, structural, morphological and antimicrobial properties of carboxymethyl cellulose capped Ag-ZnO nanocomposites prepared by chemical and mechanical methods
Magdalena-Valentina Lungu, Eugeniu Vasile, Mariana Lucaci, Delia Pătroi, Natalia Mihăilescu, Florentina Grigore, Virgil Marinescu, Alexandra Brătulescu, Sorina Mitrea, Arcadie Sobetkii, Arcadii A. Sobetkii, Marcela Popa, Mariana-Carmen Chifiriuc
Materials Characterization.2016; 120: 69. CrossRef - Substantivity of Ag–Ca–Si mesoporous nanoparticles on dentin and its ability to inhibit Enterococcus faecalis
Wei Fan, Yujie Wu, Tengjiao Ma, Yanyun Li, Bing Fan
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomaterials for Tissue Engineering In Dentistry
Manila Chieruzzi, Stefano Pagano, Silvia Moretti, Roberto Pinna, Egle Milia, Luigi Torre, Stefano Eramo
Nanomaterials.2016; 6(7): 134. CrossRef - Alternative Antimicrobial Approach: Nano-Antimicrobial Materials
Nurit Beyth, Yael Houri-Haddad, Avi Domb, Wahid Khan, Ronen Hazan
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Advances in Dental Materials through Nanotechnology: Facts, Perspectives and Toxicological Aspects
Gislaine C. Padovani, Victor P. Feitosa, Salvatore Sauro, Franklin R. Tay, Gabriela Durán, Amauri J. Paula, Nelson Durán
Trends in Biotechnology.2015; 33(11): 621. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of conventional restorative filling materials and advances in antimicrobial properties of composite resins and glass ionomer cements—A literature review
Cher Farrugia, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2015; 31(4): e89. CrossRef - Biofilm and Dental Biomaterials
Marit Øilo, Vidar Bakken
Materials.2015; 8(6): 2887. CrossRef - Antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles as a vehicle for calcium hydroxide medicament against Enterococcus faecalis
Farzaneh Afkhami, Seyyed Jalal Pourhashemi, Mona Sadegh, Yasaman Salehi, Mohammad Javad Kharrazi Fard
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(12): 1573. CrossRef - Physical Properties of an Ag-Doped Bioactive Flowable Composite Resin
Hiba Kattan, Xanthippi Chatzistavrou, James Boynton, Joseph Dennison, Peter Yaman, Petros Papagerakis
Materials.2015; 8(8): 4668. CrossRef - Effect of sterilization techniques prior to antimicrobial testing on physical properties of dental restorative materials
Cher Farrugia, Glenn Cassar, Vasilis Valdramidis, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(6): 703. CrossRef - The effects of gold coated and uncoated zinc oxide nanohexagons on the photophysicochemical properties of the low symmetry zinc phthalocyanine
Sarah D'Souza, Racheal Ogbodu, Tebello Nyokong
Journal of Molecular Structure.2015; 1099: 551. CrossRef - In Vitro Activity of Curcumin and Silver Nanoparticles Against Blastocystis hominis
Mona Abdel-Fattah Ahmed, Khadiga Ahmed Ismail, Sabah Abd-El-Ghany Ahmed, Ayman Nabil Ibrahim, Yousry Mahmoud Gohar
Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice.2015; 23(3): 135. CrossRef - Development and characterization of novel ZnO-loaded electrospun membranes for periodontal regeneration
Eliseu A. Münchow, Maria Tereza P. Albuquerque, Bianca Zero, Krzysztof Kamocki, Evandro Piva, Richard L. Gregory, Marco C. Bottino
Dental Materials.2015; 31(9): 1038. CrossRef - Review of Nanomaterials in Dentistry: Interactions with the Oral Microenvironment, Clinical Applications, Hazards, and Benefits
Alexandros Besinis, Tracy De Peralta, Christopher J. Tredwin, Richard D. Handy
ACS Nano.2015; 9(3): 2255. CrossRef - Study on the Bactriostasis of Nano-Silver against Penicillium
Lu Qiu, Mei Hua Xie, Jia Yan Lv, Shu Guo Fan, Jian Hui Gao
Advanced Materials Research.2014; 1051: 62. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Satureja hortensis Extract on Isolated Bacillus cereus from Soil of Sistan Plain
Ebrahim Shirmohammadi, Saeide Saeidi, Taher Mohasseli, Ali Rahimian Boogar
International Journal of Infection.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Strategies to Improve Biocompatibility of Dental Materials
Gottfried Schmalz
Current Oral Health Reports.2014; 1(4): 222. CrossRef
- Fabricated modified compomer bearing CF/SBA-15 nanomaterials: Physicochemical and antibacterial properties
- 5,977 View
- 59 Download
- 209 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


