Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of combined application of premixed bioceramic paste and diode laser in vital pulp therapy: an immunohistochemical randomized controlled split-mouth in vivo animal experiment
- Mo’men A. Salama, Dalia M. Fayyad, Mohamed I. Rabie, Manar A. A. Selim, Mahmoud F. Ahmed
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e4. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
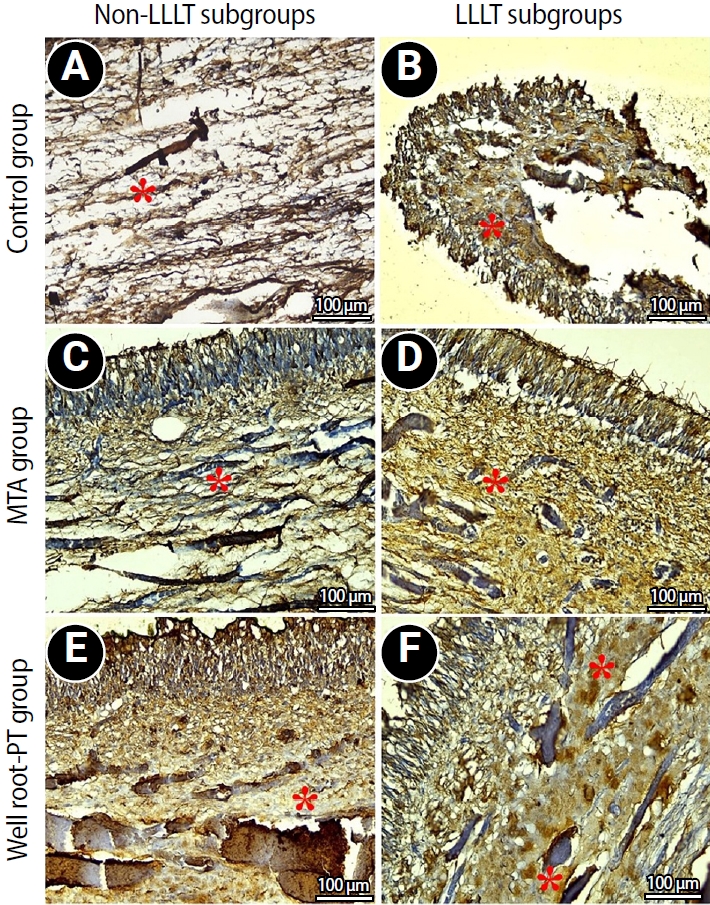
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of premixed bioceramic paste (Well-Root PT; Vericom) compared to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on the expression of the mineralization-related marker dentin sialoprotein (DSP) in dental pulp following direct pulp capping, with or without prior diode laser application.
Methods
Direct pulp exposures were performed in the upper and lower incisors of eight dogs (n = 96 teeth). Cavities (Class V) were created and received pulp capping with either Well-Root PT (n = 32), MTA (n = 32), or no capping material (polytetrafluoroethylene disc only) (n = 32), with or without the application of a diode laser. Immunohistochemical analysis of DSP expression was conducted and quantified as the mean area percentage using ImageJ software at 2 and 8 weeks posttreatment.
Results
Both the Well-Root PT and MTA groups showed significantly increased DSP expression compared to the control group at both 2 and 8 weeks (p < 0.05). No significant difference in the mean area percentage of DSP expression was found between the Well-Root PT and MTA groups. The diode laser application did not produce a significant effect on DSP expression. Within-group comparison revealed a significant increase in DSP expression between the 2- and 8-week follow-up periods (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Well-Root PT demonstrated comparable efficacy to MTA in promoting DSP expression, supporting its use as an effective direct pulp capping material. Diode laser application prior to capping had no effect on DSP expression in this experimental model.
- 549 View
- 30 Download

- Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
- Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
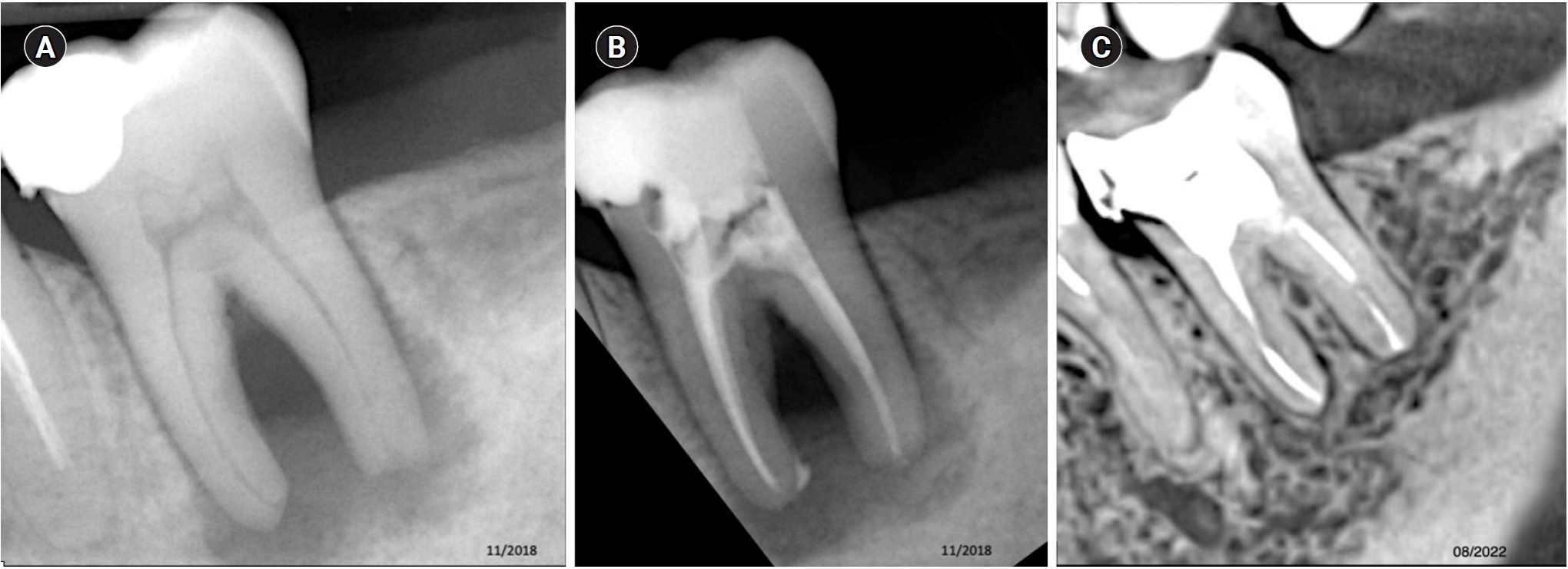
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
- 4,011 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
- Seda Falakaloğlu, Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Betül Güneş, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mustafa Gündoğar, Burcu Güçyetmez Topal
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e25. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
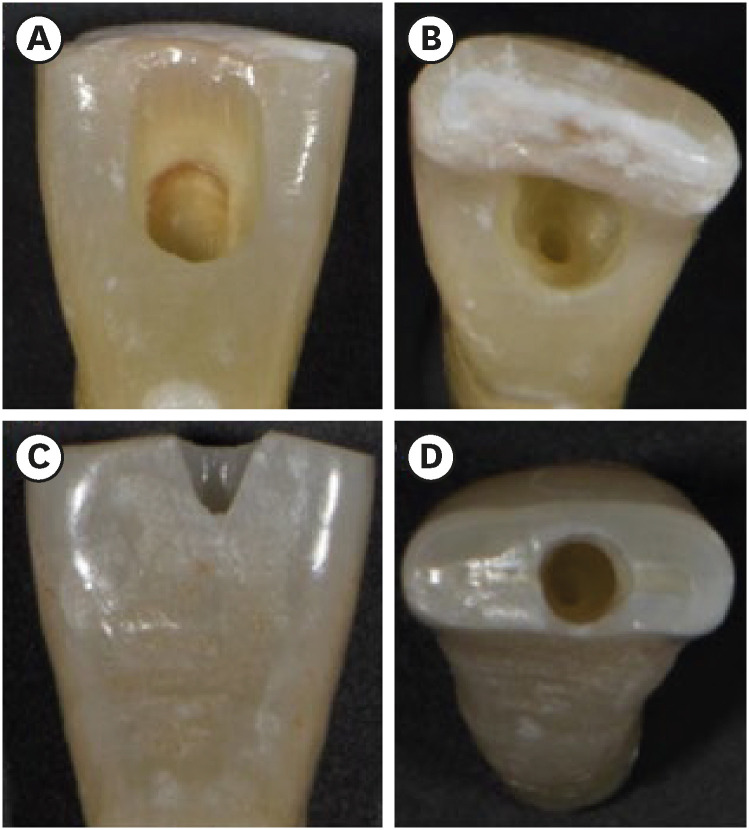
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of endodontic access cavities design on the removal of calcium hydroxide medication of the apical third of mandibular incisor root canal walls and dentinal tubules with different cleaning protocols: EDDY sonic activation, Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation, or conventional irrigation with IrriFlex.
Materials and Methods Seventy-eight extracted human mandibular incisors were assigned to 6 experimental groups (
n = 13) according to the endodontic access cavity and cleaning protocol for calcium hydroxide removal: traditional access cavity (TradAC)/EDDY; ultraconservative access cavity performed in the incisal edge (UltraAC.Inc)/EDDY; TradAC/Er,Cr:YSGG; UltraAC.Inc/Er,Cr:YSGG; TradAC/IrriFlex; or UltraAC.Inc/IrriFlex. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were used to measure the non-penetration percentage, maximum residual calcium hydroxide penetration depth, and penetration area at 2 and 4 mm from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed using Shapiro-Wilk and WRS2 package for 2-way comparison of non-normally distributed parameters (depth of penetration, area of penetration, and percentage of non-penetration) according to cavity and cleaning protocol with the significance level set at 5%.Results The effect of cavity and cleaning protocol interactions on penetration depth, penetration area and non-penetration percentage was not found statistically significant at 2 and 4 mm levels (
p > 0.05).Conclusions The present study demonstrated that TradAC or UltraAC.Inc preparations with different cleaning protocols in extracted mandibular incisors did not influence the remaining calcium hydroxide at 2 and 4 mm from the apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
Rania Lebbos, Naji Kharouf, Deepak Mehta, Jamal Jabr, Cynthia Kamel, Roula El Hachem, Youssef Haikel, Marc Krikor Kaloustian
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 678. CrossRef - Combination of Chitosan Nanoparticles, EDTA, and Irrigation Activation Enhances TGF-β1 Release from Dentin: A Laboratory Study
Sıla Nur Usta, Emre Avcı, Ayşe Nur Oktay, Cangül Keskin
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(8): 1081. CrossRef
- Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
- 3,022 View
- 73 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Does photobiomodulation on the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth? A systematic review of animal studies
- Theodoro Weissheimer, Karolina Frick Bischoff, Carolina Horn Troian Michel, Bruna Barcelos Só, Manoela Domingues Martins, Matheus Albino Souza, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e24. Published online June 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This review aimed to answer the following question “Does photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth?” Electronic searches were performed in the MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Grey Literature Report databases. Risk of bias was evaluated using SYRCLE Risk of Bias tool. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) tool was used to assess the certainty of evidence. In total, 6 studies were included. Five studies reported a reduced occurrence of root resorption in teeth that received photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation. Only 1 study reported contradictory results. The photobiomodulation parameters varied widely among studies. GRADE assessment showed a low certainty of evidence. It can be inferred that photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation of teeth can reduce the occurrence of root resorption. Nonetheless, further clinical studies are needed.
Trial Registration PROSPERO Identifier: CRD42022349891
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
Noriaki Yoshihashi
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 85. CrossRef - Evidence Mapping and Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews in Dental Traumatology: A 54 Months Update
Nitesh Tewari, Pavithra Devi, Hemlata Nehta, Ekta Wadhwani, Rigzen Tamchos, Georgios Tsilingaridis, Vijay Prakash Mathur, Morankar Rahul
Dental Traumatology.2025; 41(6): 727. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Literature Watch September 2023
James D. Carroll
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(7): 498. CrossRef
- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
- 2,872 View
- 44 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The effect of using nanoparticles in bioactive glass on its antimicrobial properties
- Maram Farouk Obeid, Kareim Moustafa El-Batouty, Mohammed Aslam
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e58. Published online October 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e58
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study addresses the effect of using nanoparticles (np) on the antimicrobial properties of bioactive glass (BAG) when used in intracanal medicaments against
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) biofilms.Materials and Methods E. faecalis biofilms, grown inside 90 root canals for 21 days, were randomly divided into 4 groups according to the antimicrobial regimen followed (n = 20; BAG-np, BAG, calcium hydroxide [CaOH], and saline). After 1 week, residual live bacteria were quantified in terms of colony-forming units (CFU), while dead bacteria were assessed with a confocal laser scanning microscope.Results Although there was a statistically significant decrease in the mean CFU value among all groups, the nano-group performed the best. The highest percentage of dead bacteria was detected in the BAG-np group, with a significant difference from the BAG group.
Conclusions The reduction of particle size and use of a nano-form of BAG improved the antimicrobial properties of the intracanal treatment of
E. faecalis biofilms-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Size matters: Radiation shielding superiority of borate glasses with nano vs. micro ZnO
Aljawhara H. Almuqrin, M.I. Sayyed, M. Elsafi
Nuclear Engineering and Technology.2025; 57(9): 103614. CrossRef - Effect of Chitosan and bioactive glass nanomaterials as intracanal medicaments on TGF-β1 release from intraradicular dentin
Sarah Salah Hashem, Mohammed M. Khalefa, Mahmoud Hassan Mohamed, Hemat M. ELSheikh, Fatma Abd El-Rahman Taher
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG laser, phthalocyanine activated photodynamic therapy, and bioactive glass nanoparticles on smear layer removal and push out bond strength of quartz fiber posts to canal dentin: a SEM assessment
Okba Mahmoud, Erum Zain
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Root Canal Therapy: Translational Innovations and the Role of Nanoparticles in Endodontic Treatment
Noha M. Badawi, Mohamed M. Kataia, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mozhgan Afshari
Journal of Nanotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propolis in Endodontics—Unveiling Its Therapeutic Potential: A Narrative Review
Poorani Durai, Santha Devy A, Mithila Mohan, Harish Ramalingam, Shasidharan P, Rahul Chaurasia M
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 16(10): 959. CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Endodontics
Farzaneh Afkhami, Yuan Chen, Laurence J. Walsh, Ove A. Peters, Chun Xu
BME Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal Atiya Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effects of Formulations of Various Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide as Intra-canal Medications Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review
Seema H Bukhari, Dax Abraham, Shakila Mahesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of nanoparticles on antibacterial efficacy of intracanal medicament: A scoping review
Alpa Gupta, Arundeep Singh, Vivek Aggarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 283. CrossRef - Physical properties, marginal adaptation and bioactivity of an experimental mineral trioxide aggregate-like cement modified with bioactive materials
Abigailt Flores-Ledesma, Adriana Tejeda-Cruz, María A. Moyaho-Bernal, Ana Wintergerst, Yoshamin A. Moreno-Vargas, Jacqueline A. Rodríguez-Chávez, Carlos E. Cuevas-Suárez, Kenya Gutiérrez-Estrada, Jesús A. Arenas-Alatorre
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(2): 141. CrossRef - Nanopartículas antimicrobianas en endodoncia: Revisión narrativa
Gustavo Adolfo Tovar Rangel , Fanny Mildred González Sáenz , Ingrid Ximena Zamora Córdoba , Lina María García Zapata
Revista Estomatología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Size matters: Radiation shielding superiority of borate glasses with nano vs. micro ZnO
- 1,653 View
- 26 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Improved dentin disinfection by combining different-geometry rotary nickel-titanium files in preparing root canals
- Marwa M. Bedier, Ahmed Abdel Rahman Hashem, Yosra M. Hassan
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e46. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e46

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was to evaluate the antibacterial effect of different instrumentation and irrigation techniques using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) after root canal inoculation with
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ).Materials and Methods Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of extracted mandibular molars were apically enlarged up to a size 25 hand K-file, then autoclaved and inoculated with
E. faecalis . The samples were randomly divided into 4 main groups according to the system of instrumentation and irrigation: an XP-endo Shaper (XPS) combined with conventional irrigation (XPS/C) or an XP-endo Finisher (XPF) (XPS/XPF), and iRaCe combined with conventional irrigation (iRaCe/C) or combined with an XPF (iRaCe/XPF). A middle-third samplewas taken from each group, and then the bacterial reduction was evaluated using CLSM at a depth of 50 µm inside the dentinal tubules. The ratio of red fluorescence (dead cells) to green-and-red fluorescence (live and dead cells) represented the percentage of bacterial reduction. The data were then statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for comparisons across the groups and the Dunn test was used for pairwise comparisons.Results The instrumentation and irrigation techniques had a significant effect on bacterial reduction (
p < 0.05). The iRaCe/XPF group showed the strongest effect, followed by the XPS/XPF and XPS/C group, while the iRaCe/C group had the weakest effect.Conclusions Combining iRaCe with XPF improved its bacterial reduction effect, while combining XPS with XPF did not yield a significant improvement in its ability to reduce bacteria at a depth of 50 µm in the dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
Oksana A. Shuliatnikova, Mikhail V. Yakovlev, Anatoliy P. Godovalov
HERALD of North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.2025; 17(2): 89. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Shaping ability of non‐adaptive and adaptive core nickel–titanium single‐file systems with supplementary file in ribbon‐shaped canals analysed by micro‐computed tomography
Parichat Chinchiyanont, Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Nathamon Thongbai‐On
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - In vitro reduction in Enterococcus faecalis count following root canal preparation with Neolix and XP shaper rotary files
Mina Mehrjouei, Somayeh Teimoori, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Seyed Majed Mortazavi, Maryam Khorasanchi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 236. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite versus apple cider vinegar against Enterococcus faecalis in contracted endodontic cavity
Kaur Supreet, Karkala Venkappa Kishan, Nimisha Chinmay Shah
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 254. CrossRef - Ex vivo evaluation of the effectiveness of XP-endo Finisher on the removal of smear layer from the root canal
Sângela Maria PEREIRA, Ceci Nunes CARVALHO, Rudys Rodolfo TAVAREZ, Paulo NELSON-FILHO, Léa Assed Bezerra DA SILVA, Etevaldo Matos MAIA FILHO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biofilm elimination from infected root canals using four different single files
Sarah A. Hamed, Sarah Shabayek, Hayam Y. Hassan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adaptive, Rotary, and Manual Root Canal Instrumentation in Primary Molars: A Triple-Armed, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Bhaggyashri A. Pawar, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Anuj Bhardwaj, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Amelia Kristanti Rahardjo, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Zvi Metzger, Anda Kfir
Biology.2021; 10(1): 42. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Endodontic Access Cavity Design and Using XP-endo Finisher on the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal System
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Koray Yılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 419. CrossRef - Irrigation in Endodontics: a Review
Sarah Bukhari, Alaa Babaeer
Current Oral Health Reports.2019; 6(4): 367. CrossRef
- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
- 1,629 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Antifungal effects of synthetic human β-defensin 3-C15 peptide
- Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Christine Kim, Jong-Won Kum, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yu Gu, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seok Woo Chang, Seung Hyun Han, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):91-97. Published online March 17, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
ex vivo study was to compare the antifungal activity of a synthetic peptide consisting of 15 amino acids at the C-terminus of human β-defensin 3 (HBD3-C15) with calcium hydroxide (CH) and Nystatin (Nys) againstCandida albicans (C. albicans ) biofilm.Materials and Methods C. albicans were grown on cover glass bottom dishes or human dentin disks for 48 hr, and then treated with HBD3-C15 (0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 300 µg/mL), CH (100 µg/mL), and Nys (20 µg/mL) for 7 days at 37℃. On cover glass, live and dead cells in the biomass were measured by the FilmTracer Biofilm viability assay, and observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). On dentin, normal, diminished and ruptured cells were observed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The results were subjected to a two-tailedt -test, a one way analysis variance and apost hoc test at a significance level ofp = 0.05.Results C. albicans survival on dentin was inhibited by HBD3-C15 in a dose-dependent manner. There were fewer aggregations ofC. albicans in the groups of Nys and HBD3-C15 (≥ 100 µg/mL). CLSM showedC. albicans survival was reduced by HBD3-C15 in a dose dependent manner. Nys and HBD3-C15 (≥ 100 µg/mL) showed significant fungicidal activity compared to CH group (p < 0.05).Conclusions Synthetic HBD3-C15 peptide (≥ 100 µg/mL) and Nys exhibited significantly higher antifungal activity than CH against
C. albicans by inhibiting cell survival and biofilm.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-fungal peptides: an emerging category with enthralling therapeutic prospects in the treatment of candidiasis
Jyoti Sankar Prusty, Ashwini Kumar, Awanish Kumar
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2025; 51(5): 755. CrossRef - Current status of antimicrobial peptides databases and computational tools for optimization
Madhulika Jha, Akash Nautiyal, Kumud Pant, Navin Kumar
Environment Conservation Journal.2025; 26(1): 281. CrossRef - Harnessing antimicrobial peptides in endodontics
Xinzi Kong, Vijetha Vishwanath, Prasanna Neelakantan, Zhou Ye
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(7): 815. CrossRef - Human β-defensins and their synthetic analogs: Natural defenders and prospective new drugs of oral health
Mumian Chen, Zihe Hu, Jue Shi, Zhijian Xie
Life Sciences.2024; 346: 122591. CrossRef - Candida albicans Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity for Endodontic Infections
Yeon-Jee Yoo, A Reum Kim, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Seung Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
Microorganisms.2020; 8(9): 1300. CrossRef - Innate Inspiration: Antifungal Peptides and Other Immunotherapeutics From the Host Immune Response
Derry K. Mercer, Deborah A. O'Neil
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Human salivary proteins and their peptidomimetics: Values of function, early diagnosis, and therapeutic potential in combating dental caries
Kun Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Wei Li, Linglin Zhang
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 99: 31. CrossRef - Endodontic biofilms: contemporary and future treatment options
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Soram Oh, A-Reum Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Peptides Against Fungal Biofilms
Karen G. N. Oshiro, Gisele Rodrigues, Bruna Estéfani D. Monges, Marlon Henrique Cardoso, Octávio Luiz Franco
Frontiers in Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Anticandidal Potential of Stem Bark Extract from Schima superba and the Identification of Its Major Anticandidal Compound
Chun Wu, Hong-Tan Wu, Qing Wang, Guey-Horng Wang, Xue Yi, Yu-Pei Chen, Guang-Xiong Zhou
Molecules.2019; 24(8): 1587. CrossRef - Synthetic Human β Defensin-3-C15 Peptide in Endodontics: Potential Therapeutic Agent in Streptococcus gordonii Lipoprotein-Stimulated Human Dental Pulp-Derived Cells
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Jue-Yeon Lee, Soram Oh, Yu Gu, A-Reum Kim, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 21(1): 71. CrossRef - Candida Infections and Therapeutic Strategies: Mechanisms of Action for Traditional and Alternative Agents
Giselle C. de Oliveira Santos, Cleydlenne C. Vasconcelos, Alberto J. O. Lopes, Maria do S. de Sousa Cartágenes, Allan K. D. B. Filho, Flávia R. F. do Nascimento, Ricardo M. Ramos, Emygdia R. R. B. Pires, Marcelo S. de Andrade, Flaviane M. G. Rocha, Cristi
Frontiers in Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Perspectives for clinical use of engineered human host defense antimicrobial peptides
María Eugenia Pachón-Ibáñez, Younes Smani, Jerónimo Pachón, Javier Sánchez-Céspedes
FEMS Microbiology Reviews.2017; 41(3): 323. CrossRef - The synthetic human beta-defensin-3 C15 peptide exhibits antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus mutans, both alone and in combination with dental disinfectants
Ki Bum Ahn, A. Reum Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2017; 55(10): 830. CrossRef - Antibiofilm peptides against oral biofilms
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2017; 9(1): 1327308. CrossRef - Humanβ-Defensin 3 Reduces TNF-α-Induced Inflammation and Monocyte Adhesion in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Tianying Bian, Houxuan Li, Qian Zhou, Can Ni, Yangheng Zhang, Fuhua Yan
Mediators of Inflammation.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Antifungal Effects of Synthetic Human Beta-defensin-3-C15 Peptide on Candida albicans –infected Root Dentin
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Ikyung Kwon, So-Ram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Yoon Lee, Seung-Hyun Han, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1857. CrossRef - A 15-amino acid C-terminal peptide of beta-defensin-3 inhibits bone resorption by inhibiting the osteoclast differentiation and disrupting podosome belt formation
Ok-Jin Park, Jiseon Kim, Ki Bum Ahn, Jue Yeon Lee, Yoon-Jeong Park, Kee-Yeon Kum, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Molecular Medicine.2017; 95(12): 1315. CrossRef
- Anti-fungal peptides: an emerging category with enthralling therapeutic prospects in the treatment of candidiasis
- 1,760 View
- 5 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
- Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):143-148. Published online February 11, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the maximum depth and percentage of irrigant penetration into dentinal tubules by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human teeth were instrumented and divided into three groups. According to final irrigation regimen, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (Group A, NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine (Group B, CHX) and saline solution (Group C, control group) were applied with Irrisafe 20 tips (Acteon) and PUI. Irrigant was mixed with 0.1% rhodamine B. Sections at 2 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm from the apex were examined with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The percentage and maximum depth of irrigant penetration were measured. Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test were performed for overall comparison between groups at each level and for pairwise comparison, respectively. Within a group, Wilcoxon test was performed among different levels.
p values less than 0.05 were considered significant.Results In all groups, highest penetration depth and percentage of penetration were observed at the 8 mm level. At 2 mm level, Groups A and B had significantly greater depths and percentages in penetration than Group C (
p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences between Groups A and B. At 5 mm level, penetration depths and percentage of penetration was not significantly different among the groups.Conclusions NaOCl and CHX applied by PUI showed similar depth and percentage of penetration at all evaluated levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
Anjali Meena, Nidhi Sharma, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Sarita Singh, Anu Dhawan, Neha Verma
Endodontology.2025; 37(1): 80. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Sonic versus ultrasonic activation for the cleaning of the root canal after post space preparation: an in vitro study.
René Carrasco, Ricardo Román, Makarena Ojeda, Carolina Vergara
Journal Oral Of Research.2015; 4(4): 255. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
- 1,613 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Bond strength of resin cement to CO2 and Er:YAG laser-treated zirconia ceramic
- Shahin Kasraei, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Bijan Heidari, Fariborz Vafaee
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):296-302. Published online August 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.296
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It is difficult to achieve adhesion between resin cement and zirconia ceramics using routine surface preparation methods. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of CO2 and Er:YAG laser treatment on the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics.
Materials and Methods In this
in-vitro study 45 zirconia disks (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) were assigned to 3 groups (n = 15). In control group (CNT) no laser treatment was used. In groups COL and EYL, CO2 and Er:YAG lasers were used for pretreatment of zirconia surface, respectively. Composite resin disks were cemented on zirconia disk using dual-curing resin cement. Shear bond strength tests were performed at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min after 24 hr distilled water storage. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA andpost hoc Tukey's HSD tests.Results The means and standard deviations of shear bond strength values in the EYL, COL and CNT groups were 8.65 ± 1.75, 12.12 ± 3.02, and 5.97 ± 1.14 MPa, respectively. Data showed that application of CO2 and Er:YAG lasers resulted in a significant higher shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics (
p < 0.0001). The highest bond strength was recorded in the COL group (p < 0.0001). In the CNT group all the failures were adhesive. However, in the laser groups, 80% of the failures were of the adhesive type.Conclusions Pretreatment of zirconia ceramic via CO2 and Er:YAG laser improves the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic, with higher bond strength values in the CO2 laser treated samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Er:YAG Laser Irradiation on the Flexural Fatigue Strength of a 4YSZ Ceramic
Duvan Cala Castillo, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Gabriela Carrão Aragonez, Bibiana Vogel Peres Riesgo, Natália de Freitas Daudt, Marilia Pivetta Rippe, Mutlu Özcan, Liliana Gressler May, Luiz Felipe Valandro, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Sandblasting, Tribochemical Silica Coating, CO2 Laser, and Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition on Surface Characteristics and Shear Bond Strength of 3Y-TZP Zirconia
Mohammed A. Alrabiah, Fahad Alkhudhairy
Crystals.2026; 16(1): 59. CrossRef - The Impact of Surface Roughness and Different Pre-treatments on the Shear Bond Strength of Super-translucent Multi-layered Zirconia to Adhesive Resin Cement: An In Vitro Study
Manar Almousli
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Surface Roughening Techniques on Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Monolithic Zirconia: In Vitro Study
Nehal F Albelasy, Ahmad M Hafez, Abdullah S Alhunayni
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(12): 1104. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of etching with ytterbium fiber laser on the bond strength, color stability, and fracture analysis of lithium disilicate ceramics to bovine teeth: an in vitro study
Göknil Alkan Demetoğlu, Esra Talay Çevlïk
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear bond strength of multilayered zirconia to adhesive resin cement after CO2 laser surface treatment (an in vitro study)
Abdelrahman Badran, Reem Gabr
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Different surface treatments and adhesive monomers for zirconia-resin bonds: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Xinyang Li, Shengjie Liang, Masanao Inokoshi, Shikai Zhao, Guang Hong, Chenmin Yao, Cui Huang
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 175. CrossRef - The impact of CO2 laser on the bond strength of translucent zirconia and traditional zirconia with the resin cement: In vitro study
Rima Saker, Bashar Zleik
Balkan Journal of Dental Medicine.2024; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Evaluation of Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Prepared with Different Surface Roughening Methods: An In Vitro Study
Marwa A Tawfik, Abdullah M Fayyadh, Mohammed A Elbialy
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(8): 766. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser and sllica-coating on zirconia framework-veneering ceramic bonding, surface chemistry and crystallographic changes
Tevfik Yavuz, Muhammed Ali Aslan, Yusuf Ziya Akpinar, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Nadin Al-Haj Husain, Mutlu Özcan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(6): 1059. CrossRef - In vitro comparative study between adhesion forces obtained on zirconia ceramic micromechanically treated with femtosecond laser (1027 nm), carbon dioxide laser (10,600 nm), and aluminum-oxide particles
Ignasi Piulachs, Luis Giner-Tarrida, Antoni España-Tost, Josep Arnabat-Dominguez, Camilo Florian
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating in Combination with Physical Modifications on Microshear Bond Strength of Zirconia to Resin Cement
Faezeh Atri, Vanya Rasaie, Sakineh Nikzad Jamnani, Saba Mohammadi, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Zirconia Surface Treatment with CO2 and Nd:YAG Lasers on Shear Bond Strength between Zirconia Frameworks and Porcelain Veneers
Bijan Heidari, Hadi Ranjzad, Farzane Ostovar Rad, Amirreza Hendi, Zahra Ghorbani
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(10): 1026. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Three Surface Treatments on the Bond Strength of Zirconia to Resin-luting Agents: An In Vitro Study
Abhinav Sharma, Arka Swarnakar, Angana Pal Swarnakar, Himadri Sekhar Pal, Shivani Tyagi, Pragati Rawat
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 883. CrossRef - Surface modification of zirconia or lithium disilicate-reinforced glass ceramic by laser texturing to increase the adhesion of prosthetic surfaces to resin cements: an integrative review
Júlio C. M. Souza, Angelo Raffaele-Esposito, Oscar Carvalho, Filipe Silva, Mutlu Özcan, Bruno Henriques
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3331. CrossRef - A Shift to Synergistic Surface Treatment Using Laser to Enhance the Bonding of Zirconia to Veneering Ceramic: An In Vitro Study
N Kiran Kumar, Anoop Nair, Savitha B Naik, Annie Swathisha, CH Laxmi Priya, HS Preetham, V Shylaja
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(1): 37. CrossRef - Effects of cold atmospheric plasma treatment on resin bonding to high-translucency zirconia ceramics
Xin-Yi YE, Ming-Yue LIU, Jing LI, Xiao-Qiang LIU, Yu LIAO, Ling-Lu ZHAN, Xiao-Ming ZHU, He-Ping LI, Jianguo TAN
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 896. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser zirconia surface treatment on cement shear bond strength
Elif Yeğin, Tevfik Yavuz, Muhammed Ali Aslan, Mustafa Hayati Atala, John A. Sorensen, Hamdi Şükür Kılıç
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2022; 36(18): 1951. CrossRef - Effects of different frequencies of Er:YAG laser on the bonding properties of zirconia ceramic
Hong Zhu, Hui-hui Tao, Meng Wei, Pan Liu, Lu Yuan, Yan-nan Zhang, Bo Wang, Jian-feng Chen
Lasers in Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on Repair Bond Strength of CAD/CAM Resin-Matrix Ceramics
Semih Arkoy, Mutahhar Ulusoy
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6314. CrossRef - Effect of different laser treatments on the shear bond strength of zirconia ceramic to resin cement
Mahnaz Hatami, Mohammadhossein Lotfi-Kamran, Abdolrahim Davari, Meisam Molazem
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 56. CrossRef - Effect of laser irradiation on bond strength between zirconia and resin cement or veneer ceramic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
SandroBasso Bitencourt, LetíciaChaves Ferreira, LeticiaCerri Mazza, DanielaMicheline dos Santos, AldierisAlves Pesqueira, LeticiaHelena Theodoro
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(2): 125. CrossRef - Effect of laser irradiation on the adhesion of resin-based materials to zirconia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato, Oscar Carvalho, Mutlu Özcan, Márcio Celso Fredel, Filipe Samuel Silva
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(10): 1035. CrossRef - Laser surface texturing of zirconia-based ceramics for dental applications: A review
Jide Han, Fei Zhang, Bart Van Meerbeek, Jozef Vleugels, Annabel Braem, Sylvie Castagne
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 123: 112034. CrossRef - Effect of Nd:YAG, Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation, and Adjunctive Photodynamic Therapy on Push‐Out Bond Strength of Zirconia Posts to Radicular Dentin
Freah Alshammary, Mohmed I. Karobari, Ali A. Assiry, Anand Marya, Gul M. Shaikh, Ammar A. Siddiqui, Mohammad K. Alam, Iole Vozza
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser and silica coating on the bond strength of zirconia ceramic
Hongbo Zhou, Chen Yu, Cheng Qi, Dingxiang Qiu, Shusen Zhang, Jilin Li, Youwang Hu
Advances in Applied Ceramics.2020; 119(5-6): 276. CrossRef - Laser-Milled Microslits Improve the Bonding Strength of Acrylic Resin to Zirconia Ceramics
Saiji Shimoe, Tzu-Yu Peng, Yuki Wakabayashi, Hiroto Takenaka, Shogo Iwaguro, Masato Kaku
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 817. CrossRef - Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal/resin luting agent bond strength: Influence of Titanium dioxide nanotubes addition in both materials
Ana Paula Rodrigues Magalhães, Carla Müller Ramos-Tonello, Mateus Zamora Galli, Orisson Ponce Gomes, Leandro Edgar Pacheco, Carlos Alberto Fortulan, Paulo Noronha Lisboa-Filho, Rafael Francisco Lia Mondelli, Adilson Yoshio Furuse, Ana Flávia Sanches Borge
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2020; 64(4): 408. CrossRef - Exploring the use of pulsed erbium lasers to retrieve a zirconia crown from a zirconia implant abutment
Ahmed Elkharashi, Kinga Grzech-Leśniak, Janina Golob Deeb, Aous A. Abdulmajeed, Sompop Bencharit, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(6): e0233536. CrossRef - Evaluation of zirconia surface roughness after aluminum oxide airborne-particle abrasion and the erbium-YAG, neodymium-doped YAG, or CO2 lasers: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Felipe V. Martins, Cláudia T. Mattos, Wayne J.B. Cordeiro, Edgard M. Fonseca
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(6): 895. CrossRef - Effect of thermal and mechanical cycles on shear bond strength of zirconia core to porcelain veneer under different surface treatments
Tahereh Ghaffari, Elnaz Moslehifard, Mehrnaz Motiei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(3): 227. CrossRef - Ultrashort-pulse laser as a surface treatment for bonding between zirconia and resin cement
Mahmood Abu Ruja, Grace M. De Souza, Yoav Finer
Dental Materials.2019; 35(11): 1545. CrossRef - Adhesion behavior of conventional and high‐translucent zirconia: Effect of surface conditioning methods and aging using an experimental methodology
Edwin Ruales‐Carrera, Paulo F. Cesar, Bruno Henriques, Márcio C. Fredel, Mutlu Özcan, Claudia A. M. Volpato
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 31(4): 388. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Resin Cement and Glass Ionomer to Nd:YAG Laser‐Treated Zirconia Ceramics
Nafiseh Asadzadeh, Foojan Ghorbanian, Farzaneh Ahrary, Hamidreza Rajati Haghi, Reza Karamad, Amir Yari, Abdollah Javan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Zirconia and Glass Fiber Posts with Radicular Dentin
Raneem S. Alofi, Ibraheem F. Alshiddi, Yasser F. AlFawaz, Abdulaziz Alsahhaf, Khulud Abdulrahman Al-Aali, Tariq Abduljabbar, Fahim Vohra
International Journal of Biomaterials.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG Laser, Sandblast and Several Types of Universal Bonding on Shear Bond Strength of Zirconia Ceramic to Composite Resin
Mahdi Akbarzadeh, Loghman R Sofi, Reza Fekrazad, Marjan Maleki
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(10): 1246. CrossRef - The effects of lasers on bond strength to ceramic materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Verónica García-Sanz, Vanessa Paredes-Gallardo, Omel Mendoza-Yero, Miguel Carbonell-Leal, Alberto Albaladejo, José María Montiel-Company, Carlos Bellot-Arcís, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(1): e0190736. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on the shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic and metal alloy
Munir Tolga Yucel, Ismail Kilic, Yener Okutan, Elif Sumeyye Tobi, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Abdullah Kepceoglu, Mustafa Borga Donmez
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2018; 32(20): 2232. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser beam angle and formed shape on surface roughness and shear bond strength between zirconia and resin cement
Munir Tolga Yucel, Ismail Kilic, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Yasemin Gundogdu, Yener Okutan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2018; 32(12): 1265. CrossRef - The effect of subpressure on the bond strength of resin to zirconia ceramic
Yong-Mei Li, Rui-Shen Zhuge, Zu-Tai Zhang, Yue-Ming Tian, Ning Ding, Dengshun Miao
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(6): e0179668. CrossRef - Effects of Laser Treatment on the Bond Strength of Differently Sintered Zirconia Ceramics
Doğu Ömür Dede, Murat Yenisey, Nergiz Rona, Figen Öngöz Dede
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2016; 34(7): 276. CrossRef - Zirconia based ceramics, some clinical and biological aspects: Review
Ossama Saleh Abd El-Ghany, Ashraf Husein Sherief
Future Dental Journal.2016; 2(2): 55. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - The Effect of Femtosecond Laser Treatment on the Effectiveness of Resin-Zirconia Adhesive: An In Vitro Study
María Vicente Prieto, Ana Luisa Caseiro Gomes, Javier Montero Martín, Alfonso Alvarado Lorenzo, Vicente Seoane Mato, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2016; 7(4): 214. CrossRef - Adhesion to Zirconium Dioxide Used for Dental Reconstructions: Surface Conditioning Concepts, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Mutlu Özcan, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
Current Oral Health Reports.2015; 2(4): 190. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of MDP-Containing Self-Adhesive Resin Cement and Y-TZP Ceramics: Effect of Phosphate Monomer-Containing Primers
Jin-Soo Ahn, Young-Ah Yi, Yoon Lee, Deog-Gyu Seo
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Preliminary studies on the effects of in situ synthesized polycrystalline particulates on the bonding strength of resin to zirconia ceramic surface
Yueming Tian, Lingling Zhang, Zutai Zhang, Ning Ding, Yan Liu, Guozhong Tian
Applied Surface Science.2015; 357: 961. CrossRef
- Effect of Er:YAG Laser Irradiation on the Flexural Fatigue Strength of a 4YSZ Ceramic
- 1,917 View
- 12 Download
- 47 Crossref

- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):180-186. Published online May 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the microleakage and penetration of fissure sealant in permanent molar teeth with fluorosis after pretreatment of the occlusal surface.Materials and Methods A total of 120 third molars with mild dental fluorosis were randomly divided into 6 groups (
n = 20). The tooth surfaces were sealed with an unfilled resin fissure sealant (FS) material. The experimental groups included: 1) phosphoric acid etching (AE) + FS (control); 2) AE + One-Step Plus (OS, Bisco) + FS; 3) bur + AE + FS; 4) bur + AE + OS + FS; 5) Er:YAG laser + AE + FS; and 6) Er:YAG laser + AE + OS + FS. After thermocycling, the teeth were immersed in 0.5% fuchsin and sectioned. Proportions of mircoleakage (PM) and unfilled area (PUA) were measured by digital microscope.Results Overall, there were significant differences among all groups in the PM (
p = 0.00). Group 3 showed the greatest PM, and was significantly different from groups 2 to 6 (p < 0.05). Group 6 showed the lowest PM. Pretreatment with Er:YAG with or without adhesive led to less PM than bur pretreatment. There were no significant differences among groups in PUA.Conclusions Conventional acid etching provided a similar degree of occlusal seal in teeth with fluorosis compared to those pretreated with a bur or Er:YAG laser. Pretreatment of pits and fissures with Er:YAG in teeth with fluorosis may be an alternative method before fissure sealant application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Retention Rates of Composite Resin Pit and Fissure Sealants Placed on Permanent Molars Treated with Air Abrasion and Acid Etching: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Vishal Raut, Deepak Sharma, Ashish K Jain, Rahul Rao, Laresh N Mistry, Supriya Solanke
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2026; 19(2): 271. CrossRef - Effects of Er: YAG laser and acid etching on bond strength of clear aligner attachments to fluorotic enamel
Rui Xia, Jie Lei, Maoxuan Luo, Yao Xiao, Rawaa A. Faris
PLOS One.2025; 20(8): e0328937. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetrative and Adaptive Properties of Unfilled and Filled Resin-Based Sealants When Placed using Conventional acid Etching, Lasing, and Fissurotomy Bur Technique of Enamel Preparation
Poonam Ramrao Shingare, Vishwas Chaugule, Neha Pankey, Pallavi Kakade
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 349. CrossRef - Laser Tooth Preparation for Pit and Fissure Sealing
Yair Schwimmer, Nurit Beyth, Diana Ram, Eitan Mijiritsky, Esti Davidovich
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 7813. CrossRef - The clinical effects of laser preparation of tooth surfaces for fissure sealants placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yunhan Zhang, Yan Wang, Yandi Chen, Yang Chen, Qiong Zhang, Jing Zou
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of laser preparation on adhesion of a self‐adhesive flowable composite resin to primary teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Faranak Razmjoei, Nasrin Kianimanesh
Microscopy Research and Technique.2016; 79(4): 334. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Retention Rates of Composite Resin Pit and Fissure Sealants Placed on Permanent Molars Treated with Air Abrasion and Acid Etching: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- 1,651 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Review of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Su-Jeong Shin, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):180-187. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Introduction Eliminating the residual debris and bacteria in the root canal system is one of the main purposes of the endodontic treatment. However, the complexity on the anatomy of the root canal system makes it difficult to eliminate the bacterial biofilm existing along the root canal surface and necrotic pulp tissue by mechanical instrumentation and chemical irrigation. Recently, more effective irrigant delivery systems for root canal irrigation have been developed. The purpose of this review was to present an overview of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices available in endodontics.
Review The contents of this paper include as follows;
- syringe-needle irrigation, manual dynamic irrigation, brushes
- sonic and ultrasonic irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, rotary brush, RinsEndo, EndoVac, Laser
Conclusion Though technological advances during the last decade have brought to fruition new agitation devices that rely on various mechanisms, there are few evidence based study to correlate the clinical efficacy of these devices with improved outcomes except syringe irrigation with needle and ultrasonic irrigation.
The clinicians should try their best efforts to deliver antimicrobial and tissue solvent solutions in predictable volumes safely to working length.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
Gilhwan Sung, Jaeyong Sung, Myeong Ho Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Visualization.2016; 14(1): 40. CrossRef
- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
- 1,715 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
- Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):134-142. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation with hypersensitivity mode on microtensile bond strength of composite resin. Twenty extracted permanent molars were randomly assigned to six groups, according to the irradiation of Er,Cr:YSGG laser, adhesive system (Optibond FL or Clearfil SE bond) and application time of etchant (15 sec or 20 sec). Then composite resin was build up on each conditioned surface. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 h and twelve specimens for each group were prepared. All specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength and the fracture modes were evaluated. Also, the prepared dentin surface and laser irradiated dentin surface were examined under SEM.
The results were as follows:
The microtensile bond strength of laser irradiated group was lower than that of no laser irradiated group.
Regardless of laser irradiation, the microtensile bond strength of Optibond FL was higher than that of Clearfil SE bond. And the microtensile bond strength of 20 sec etching group was higher than that of 15 sec etching group when using Optibond FL.
The SEM image of laser irradiated dentin surface showed prominent peritubular dentin, opened dentinal tubules and no smear layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 180. CrossRef
- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- 1,510 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surface roughness of experimental composite resins using confocal laser scanning microscope
- JH Bae, MA Lee, BH Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a new resin monomer, filler size and polishing technique on the surface roughness of composite resin restorations using confocal laser scanning microscopy. By adding new methoxylated Bis-GMA (Bis-M-GMA, 2,2-bis[4-(2-methoxy-3-methacryloyloxy propoxy) phenyl] propane) having low viscosity, the content of TEGDMA might be decreased. Three experimental composite resins were made: EX1 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 40 mm nanofillers); EX2 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 20 mm nanofillers); EX3 (Bis-GMA/TEGDMA = 70/30 wt%, 40 mm nanofillers). Filtek Z250 was used as a reference.
Nine specimens (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) for each experimental composite resin and Filtek Z250 were fabricated in a teflon mold and assigned to three groups. In Mylar strip group, specimens were left undisturbed. In Sof-lex group, specimens were ground with #1000 SiC paper and polished with Sof-lex discs. In DiaPolisher group, specimens were ground with #1000 SiC paper and polished with DiaPolisher polishing points. The Ra (Average roughness), Rq (Root mean square roughness), Rv (Valley roughness), Rp (Peak roughness), Rc (2D roughness) and Sc (3D roughness) values were determined using confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data were statistically analyzed by Two-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons test (p = 0.05).
The type of composite resin and polishing technique significantly affected the surface roughness of the composite resin restorations (p < 0.001). EX3 showed the smoothest surface compared to the other composite resins (p < 0.05). Mylar strip resulted in smoother surface than other polishing techniques (p < 0.05).
Bis-M-GMA, a new resin monomer having low viscosity, might reduce the amount of diluent, but showed adverse effect on the surface roughness of composite resin restorations.
- 1,151 View
- 3 Download

- REGULATION OF PULPAL MICROCIRCULATION BY CALCITONIN GENE-RELATED PEPTIDE
- Sung-Kyo Kim, Young-Kyung Kim, Myoung-Uk Jin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):470-476. Published online January 14, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.470
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to investigate the function of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in regulatory mechanism of pulpal microcirculation with the aim of elucidating neurogenic inflammation.
Experiments were performed on twelve cats under general anesthesia. CGRP was administered through the femoral vein to see the systemic influence and through the external carotid artery to see the local effect. Sympathetic nerve to the dental pulp was stimulated electrically and pulpal blood flow (PBF) was measured with a laser Doppler flowmeter on the canine teeth to the drug administration. The paired variables of control and experimental data were compared by paired
t -test and differences withp < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.Systemic administration of CGRP (0.3 μg/kg) exerted decreases in systemic blood pressure and caused changes in PBF with an initial increase followed by decrease and a more marked second increase and decrease.
Close intra-arterial (i.a.) injection of CGRP (0.03 μ/kg) resulted in slight PBF increase. The effect of CGRP resulted in no significant increase in PBF in the presence of CGRP8-37.
The electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve alone resulted in PBF decreases. The i.a. administration of CGRP following the electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve compensated the decreased PBF. Therefore, CGRP effectively blocked the sympathetic nerve stimulation-induced PBF decrease.
Results of the present study have provided evidences that even though the local vasodilatory function of CGRP are weak, CGRP is effectively involved in blocking the vasoconstriction caused by sympathetic nerve stimulation in the feline dental pulp.
- 854 View
- 0 Download

- THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE APPLICATION ON MICROTENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF ALL-IN-ONE DENTIN ADHESIVE SYSTEMS
- Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):423-429. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of multiple application of all-in-one dentin adhesive system on microtensile bond strength using confocal laser scanning microscope and microtensile bond strength test. Flat occlusal dentin surfaces were prepared using low-speed diamond saw. In group I, Scotchbond Multipurpose (SM) was applied by manufacturer’s recommendation. In group II, after Adper Prompt L-Pop was applied for 15s and light cured for 10s, the second coat was re-applied and light-cured. In group III, after light-curing the second layer, the third coat was re-applied and light-cured. Specimens bonded with a resin-composite were sectioned into resin-dentin stick for measuring the adhesive layer thickness by confocal laser scanning microscope and evaluating micro-tensile bond strength. The adhesive layers of three-step dentin adhesive system, 3 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop had significantly thicker than SM, 2 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop (p < 0.05). However, there was no significant differences in bond strengths between SM and 3 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop (p > 0.05). And SM, 3 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop had significantly higher than 2 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop in bond strengths (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 203. CrossRef
- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- 1,087 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of hybrid layer thickness on microtensile bond strength of three-step and self-etching dentin adhesive systems
- Hye-Jung Lee, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):491-497. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.491
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between hybrid layer thickness and bond strength using confocal laser scanning microscope and microtensile bond strength test of two adhesive systems.
The dentin surface of human molars, sectioned to remove the enamel from the occlusal surface. Either Scotchbond Multi-Purpose(3M Dental Product, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A) or Clearfil SE Bond(Kuraray, Osaka, Japan) was bonded to the surface, and covered with resin-composite. The resin-bonded teeth were serially sliced perpendicular to the adhesive interface to measure the hybrid layer thickness by confocal laser scanning microscope. The specimen were trimmed to give a bonded cross-sectional surface area of 1mm2, then the micro-tensile bone test was performed at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. All fractured surfaces were also observed by stereomicroscope.
There was no significant differences in bond strengths the materials(p>0.05). However, the hybrid layers of three-step dentin adhesive system, SM, had significantly thicker than self-etching adhesive system, CS(p<0.05). Pearson's correlation coefficient showed no correlation between hybrid layer thickness and bond strengths(p>0.05). Bond strengths of dentin adhesive systems were not dependent on the thickness of hybrid layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Techniques for the restorative management of localized and generalized tooth wear
Alex Milosevic
Dental Update.2023; 50(10): 842. CrossRef
- Techniques for the restorative management of localized and generalized tooth wear
- 1,337 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The influence of epinephrine concentration in local anesthetics on pulpal and gingival blood flows
- Jae-Sang Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):475-484. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.475
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 187. CrossRef - Effect of local anesthesia on pulpal blood flow in mechanically stimulated teeth
Wan-Sik Chu, Seung-Ho Park, Dong-Kuk Ahn, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(4): 257. CrossRef
- Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
- 2,196 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of dentinal tubules orientation on penetration pattern of dentin adhesives using confocal laser scanning microscopy
- Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Ho Kim, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):392-401. Published online September 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the penetration pattern of dentin adhesives according to the orientation of dentinal tubules with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Specimens having perpendicular, parallel and oblique surface to dentinal tubules were fabricated. The primer of dentin adhesives (ALL BOND® 2, CLEARFIL™ SE BOND and PQ1) was mixed with fluorescent material, rhodamine B isothiocyanate (Aldrich Chem. CO., Milw., USA). It was applied to the specimens according to the instructions of manufactures. The specimens were covered with composite resin (Estelite, shade A2) and then cut to a thickness of 500 µm with low speed saw (Isomet™, Buehler, USA). The adhesive pattern of dentin adhesives were observed by fluorescence image using confocal laser scanning microscopy.
The results were as follows.
For the groups with tubules perpendicular to bonded surface, funnel shape of resin tag was observed in all specimen. However, resin tags were more prominent in phosphoric acid etching system (ALL BOND® 2 and PQ1) than self etching system (CLEARFIL™ SE BOND).
For the groups with tubules parallel to bonded surface, rhodamine-labeled primer penetrated into peritubular dentin parallel to the orientation of dentinal tubules. But rhodamine-labeled primer of PQ1 diffused more radially into surrounding intertubular dentin than other dentin adhesive systems.
For the groups with tubules oblique to bonded surface, resin tags appeared irregular and discontinuous. But they penetrated deeper into dentinal tubules than other groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 490. CrossRef
- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
- 1,263 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effects of EDTA and pulsed Nd:YAG laser on apical leakage of canal obturation
- Jin-Soo Kwon, Hee-Joo Lee, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):50-56. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.050
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of EDTA and pulsed Nd:YAG laser on apical leakage of canal obturation. Forty-eight single-rooted teeth were used in this study. The teeth were instrumented up to a size 40 K-file and irrigated with 2.5% NaOCl between each file size. And the teeth were divided into 4 groups. In group A, the root canals were irrigated with a final flush of 5ml 2.5% NaOCl as a control group. The teeth in group B were irrigated with a final flush of 5ml 17% EDTA. The teeth in group C and D were irradiated by pulsed Nd:YAG laser(laser parameters were set at 1W, 100mJ, 10Hz, and 2W, 100mJ, 20Hz respectively).
The results were as follows:
1. Apical leakage was observed in 50% of samples in group A, 30% of samples in group B, 20% of samples in group C, and 10% of samples in group D.
2. The teeth in group B had less leakage than group A, but there was no statistically significant differences(p>0.05).
3. The teeth in group C, D had less leakage than group A, and there was statistically significant differences(p<0.05).
4. The teeth in group C, D had less leakage than group B, but there was no statistically significant differences(p>0.05).
5. There was no significant differences in apical leakage between group C and group D(p>0.05).
- 801 View
- 1 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


