Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A global overview of enamel microabrasion for white spot lesions: a bibliometric review
- Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Karina Cardoso, Michely Cristina Goebel, Pablo Silveira Santos, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Juliana Silva Ribeiro, Carla Miranda Santana, Mariane Cardoso
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e29. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
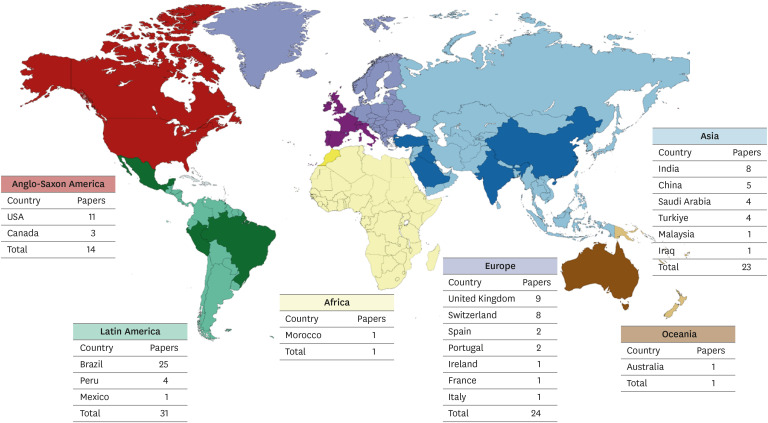
ePub This study aimed to identify and analyze articles on enamel microabrasion for the treatment of white spot lesions. A search was conducted on the Web of Science. The following parameters were recorded and analyzed: number of citations, year, journal, impact factor, study design, theme, country and continent, institution, authors, and keywords. Data was analyzed using VOSviewer software. The initial search resulted in 1,126 documents, of which 94 articles were included. The highest number of citations an article received was 65. The oldest article was published in 1975, and the most recent in 2023. The most frequent study design was case report (
n = 42). Regarding the themes, it was observed that the main objective of the studies was to evaluate the clinical performance of enamel microabrasion (n = 75), primarily using Opalustre (Ultradent Products Inc., South Jordan, UT, USA) (n = 37) for treating white stains caused by dental fluorosis (n = 41). Most articles originated from Latin America (n = 31), mainly from Brazil (n = 26). The most frequent author was Sundfeld RH (n = 10). This study reveals research trends in the field of enamel microabrasion. The publications were mainly case reports/series using Opalustre for the removal of fluorosis stains.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
Michael Willian Favoreto, Leticia Condolo, Camila Mendes Camargo, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Karol Carrillo, Abraham Lincoln Calixto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105655. CrossRef - Micro- and Macroabrasion in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review and Case Study
Jose Villalobos-Tinoco, Carlos A. Jurado, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Nechama S. Citrin, Staley Colvert, Jose Luis Gutierrez-Quintero, Salwa Mekled
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(5): 183. CrossRef - Evaluation of demineralization changes in molar tissues in vitro using electrical impedance spectroscopy
V. D. Goncharov, M. A. Gorelikova, K. V. Shadrina, L. Yu. Orekhova, V. D. Berezkin, E. S. Nemovskaya, A. A. Petrov
Parodontologiya.2025; 30(3): 254. CrossRef
- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
- 5,549 View
- 149 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of surrounding and underlying shades on the color adjustment potential of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer
- Mariana Silva Barros, Paula Fernanda Damasceno Silva, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e7. Published online December 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
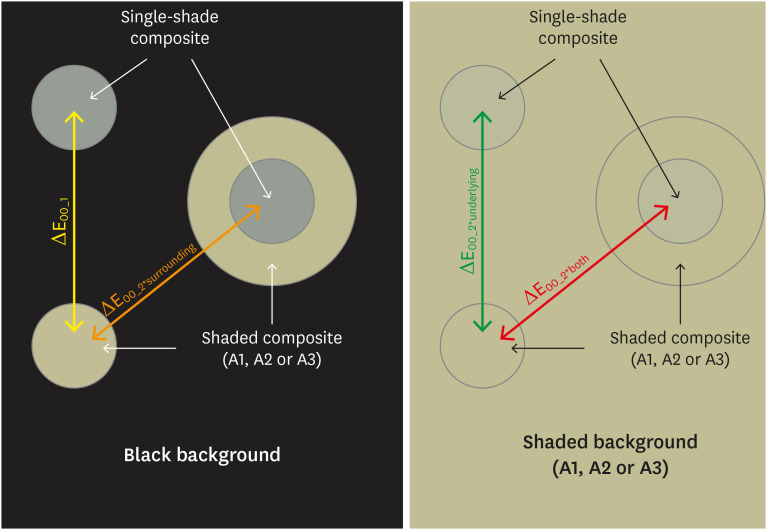
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the surrounding and underlying shades’ effect on the color adjustment potential (CAP) of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer.
Materials and Methods Cylinder specimens (1.0 mm thick) were built with the Vittra APS Unique composite, surrounded (dual specimens) or not (simple specimens) by a control composite (shade A1, A2, or A3). Simple specimens were also built only with the control composites. Each specimen’s color was measured against white and black backgrounds or the simple control specimens with a spectrophotometer (CIELAB system). The whiteness index for dentistry (WID) and translucency parameters (TP00) were calculated for simple specimens. Differences (ΔE00) in color between the simple/dual specimens and the controls were calculated. The CAP was calculated based on the ratios between data from simple and dual specimens.
Results The Vittra APS Unique composite showed higher WID and TP00 values than the controls. The highest values of ΔE00 were observed among simple specimens. The color measurements of Vittra APS Unique (simple or dual) against the control specimens presented the lowest color differences. Only surrounding the single-shade composite with a shaded composite barely impacted the ΔE00. The highest CAP values were obtained using a shaded composite under simple or dual specimens.
Conclusions The CAP of Vittra APS Unique was strongly affected by the underlying shade, while surrounding this composite with a shaded one barely affected its color adjustment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of water absorption on the translucency of single-shade and conventional resin composites: an in vitro comparative study
Ceyda Sari, Elifnur Aydemir Aydın
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline color-matching in anterior non-carious cervical lesions of patients of two single-shade resin composites: a randomized clinical trial
Ayşe Nur Doğan, Soley Arslan
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
Luciana Vasconcelos Ramos, Dayana Fernandes Rocha Aparicio, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva, Maíra do Prado, Andréa Vaz Braga Pintor, Marcela Baraúna Magno
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1567. CrossRef - Evaluation of color matching of three single-shade composites employing simulated 3D printed cavities with different thicknesses using CIELAB and CIEDE2000 color difference formulae
Engin Kariper, Aylin Cilingir
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of kombucha, coffee, and turmeric beverages on the color stability of a single-shade versus a multi-shade resin-based composite
Hanin E. Yeslam, Abdulaziz F. Bakhsh
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19759. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Esthetic Outcome of Pedo Shades of Composite Resin—A Randomized Controlled Trial: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
Priyanka Raj, Shikha Choubey, Divya Doneria, Diksha Bhat, Shivani Mathur, Shailja Sinha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(S1): S22. CrossRef - Influence of cavity wall thickness on the color adjustment potential of single-shade resin composites
Fabrício Luscino Alves de Castro, Letícia Brandão Durand
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2024; 155(7): 605. CrossRef - Assessing color mismatch in single-shade composite resins for enamel replacement
Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Diana Leyva Del Rio, Luiz Alves Oliveira-Neto, William Michael Johnston
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 132(3): 613.e1. CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Is It Possible for Single-shade Composites to Mimic the Color, Lightness, Chroma, and Hue of Other Single-shade Composites? An In Vitro Study
M Buldur, G Ayan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 691. CrossRef - Color evaluation of a one-shade used for restoration of non-carious cervical lesions: an equivalence randomized clinical trial
Michael Willian Favoreto, Amanda de Oliveira de Miranda, Thalita P. Matos, Andrea dos Santos de Castro, Mylena de Abreu Cardoso, Julia Beatriz, Jenny Collantes-Acuña, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Thickness on the Translucency Parameter and Whiteness Index of Single-Shade Resin Composites
Ö Yağcı, M Fidan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(2): 189. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Ishihara Test With Various Displays
Thomas Klinke, Wolfgang Hannak, Klaus Böning, Holger Jakstat
International Dental Journal.2024; 74(4): 892. CrossRef - Color match evaluation using instrumental method for three single-shade resin composites before and after in-office bleaching
Aylin Cilingir, Engin Kariper
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of interface distance and underlying substrate on the color adjustment potential of single‐shade composites
Gabriella Jesus Santos de Livi, Tauan Rosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, Rosa Maria Viana de Bragança Garcez, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1279. CrossRef
- Impact of water absorption on the translucency of single-shade and conventional resin composites: an in vitro comparative study
- 4,777 View
- 102 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
- Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e8. Published online February 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
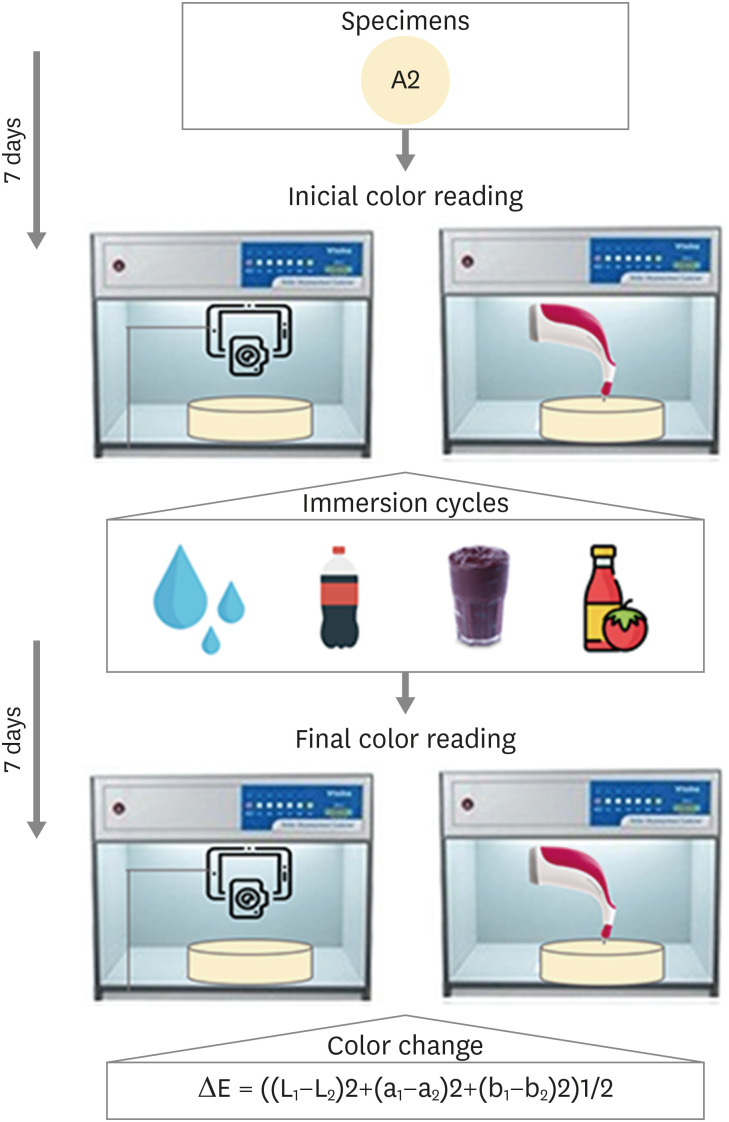
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the color change of the Giomer resin composite (Beautifil-Bulk) by using photographs obtained with a smartphone (iPhone 6S) associated with Adobe Photoshop software (digital method), with the spectrophotometric method (Vita Easyshade) after immersion in different pigment solutions.
Materials and Methods Twenty resin composite samples with a diameter of 15.0 mm and thickness of 1.0 mm were confectioned in A2 color (
n = 5). Photographs and initial color readings were performed with a smartphone and spectrophotometer, respectively. Then, samples were randomly divided and subjected to cycles of immersion in distilled water (control), açai, Coke, and tomato sauce, 3 times a day, 20 minutes for 7 days. Later, new photographs and color readings were taken.Results The analysis (2-way analysis of variance, Holm-Sidak,
p < 0.05) demonstrated no statistical difference (p < 0.005) between the methods in all groups. Similar color changes were observed for all pigment solutions when using the spectrophotometric method. For the digital method, all color changes were clinically unacceptable, with distilled water and tomato sauce similar to each other and with statistical differences (p < 0.005) for Coke and açai.Conclusions Only the tomato sauce produced a color change above the acceptability threshold using both methods of color assessment. The spectrophotometric and digital methods produce different patterns of color change. According to our results, the spectrophotometric method is more recommended in color change assessment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
Jamieson Wong, Constance Yeo, Michelle The, Filip Taneski, Uros Josic, Lorenzo Breschi, Vesna Miletic
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026; 38(1): 70. CrossRef - The effects of mechanical and chemical degradation on the surface roughness, gloss, and color stability of bulk-fill resin composites
Merve Nezir, Hanife Altınışık, Esra Özyurt, Naz Bayar, Mediha Büyükgöze Dindar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef
- Are Sculptable Bulk‐Fill Composites Susceptible to Color Change: A Systematic Review
- 2,786 View
- 40 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Spectrophotometric evaluation of restorative composite shades and their match with a classical shade guide
- Rafael Melara, Luciana Mendonça, Fábio Herrmann Coelho-de-Souza, Juliana Nunes Rolla, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e60. Published online November 12, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to verify the match between 5 shades of composites from different manufacturers with a shade guide and among the systems using a portable spectrophotometer.
Materials and Methods Shade measurements were performed on specimens of Z350 XT (3M ESPE), Charisma Diamond (Heraeus Kulzer GmbH), Esthet X-HD (Dentsply Caulk), and Empress Direct (Ivoclar-Vivadent) for shades A1, A2, A3, B1, and C3 using a Vita Easyshade spectrophotometer (Vita Zahnfabrik) against a white background. Corresponding shades of Vitapan Classical (Vita Zahnfabrik) guide were measured likewise and shade variation (ΔE) was calculated based on International Commission on Illumination L*a*b* parameters. The ΔE of the composites in each shade was compared by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's
post hoc test (α = 0.05).Results All composites presented ΔE > 3.7 compared with the shade guide. Variation in shades A3, B1, and C3 was significantly different for all composites. ΔE of Z350 XT was significantly lower for A1 than for the other shades, whereas ΔE of Z350 XT and Charisma Diamond were significantly lower for A2 than for the other shades.
Conclusions No composite shade matched with the shade guide. Equivalent shades of the restorative composite from different manufacturers may show clinically noticeable ΔE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Análise espectrofotométrica da cor de resinas compostas e sua correspondência com a escala de referência VITA Classical
Gardenia Mascarenhas de Oliveira, Marta Conceição Oliveira Silva, Natan dos Anjos Nery de Oliveira, Maria Fernanda Moreira Carvalho Caxico, Lucas Gomes Pereira, Leandro do Rozário Teixeira, Marcus Vinícius Santos da Silva, Iuri Muniz Pepe
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2026; 18(1): e10592. CrossRef - Instrumental and visual evaluation of the color adjustment potential of a recently introduced single‑shade composite resin versus multishade composite resins
Jiakang Zhu, Yue Xu, Mengxun Li, Cui Huang
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(3): 832. CrossRef - Evaluation of the roughness, color match, and color stability of two monochromatic composite resins: a randomized controlled laboratory study
Iara Campos Santana, Sabrina Sobral de Oliveira, Karolina Pena Botelho, Renan Leonardi de Oliveira Rigotti, José Cristiano Ramos Glória, Adriana Maria Botelho, Dhelfeson Willya Douglas-de-Oliveira, Karine Taís Aguiar Tavano
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different finishing and polishing protocols of composite CAD CAM blocks on surface roughness and biological response of gingival mesenchymal stem cells
Mohamed F. Haridy, Mohamed Shamel, Raghda A. Khalil, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Hoda Fouda, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Instrumental and Visual Evaluation of the Chameleon Effect of Single-shaded Composite Resins
RM Adiguzel, LK Kose, N Arhun
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 432. CrossRef - Color Stability of Bioactive Restorative Material vs Nanohybrid Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
Esraa H Saber, Mohsen H Abielhassan, Yasser A Abed, Shereen E Fahim
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(3): 221. CrossRef - A system for reliable composite shade matching: Custom shade tabs and an intra‐oral mockup
Adamo Notarantonio, Amanda Seay
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(5): 787. CrossRef - Color Stability of Bioactive Restorative Materials After Immersion in Various Media
Shara I Sajini, Ali B Mushayt, Talal A Almutairi, Roaa Abuljadayel
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2022; 12(4): 418. CrossRef
- Análise espectrofotométrica da cor de resinas compostas e sua correspondência com a escala de referência VITA Classical
- 2,116 View
- 30 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

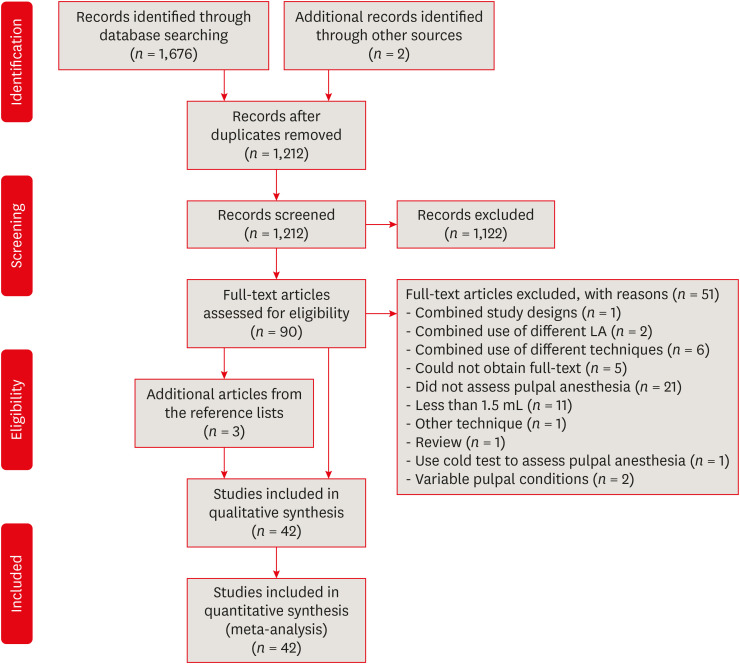
- Anesthetic efficacy in vital asymptomatic teeth using different local anesthetics: a systematic review with network meta-analysis
- Amy Kia Cheen Liew, Yi-Chun Yeh, Dalia Abdullah, Yu-Kang Tu
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e41. Published online July 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of various local anesthesia (LA) in vital asymptomatic teeth.
Materials and Methods Randomized controlled trials comparing pulpal anesthesia of various LA on vital asymptomatic teeth were included in this review. Searches were conducted in the Cochrane CENTRAL, MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE, ClinicalTrials.gov, Google Scholar and 3 field-specific journals from inception to May 3, 2019. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessment using Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool were done by 2 independent reviewers in duplicate. Network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed within the frequentist setting using STATA 15.0. The LA was ranked, and the surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) line was plotted. The confidence of the NMA estimates was assessed using the CINeMA web application.
Results The literature search yielded 1,678 potentially eligible reports, but only 42 were included in this review. For maxillary buccal infiltration, articaine 4% with epinephrine 1:100,000 was more efficacious than lidocaine 2% with epinephrine 1:100,000 (odds ratio, 2.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.14–3.89). For mandibular buccal infiltration, articaine 4% with epinephrine 1:100,000 was more efficacious than various lidocaine solutions. The SUCRA ranking was highest for articaine 4% with epinephrine when used as maxillary and mandibular buccal infiltrations, and lidocaine 2% with epinephrine 1:80,000 when used as inferior alveolar nerve block. Inconsistency and imprecision were detected in some of the NMA estimates.
Conclusions Articaine 4% with epinephrine is superior when maxillary or mandibular infiltration is required in vital asymptomatic teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical Basis of the Palatal Injection Technique for Pulpal Anesthesia of Maxillary Teeth
Sergey Kabak, Joe Iwanaga, Yuliya Melnichenko, Ruslan Mekhtiev, Nina Savrasova
Clinical Anatomy.2026; 39(2): 134. CrossRef - Adrenaline in pulp capping treatment of reversible pulpitis
Si-Yun Yang, Jin-Zhu Wang, Hao Fan, Min Chen
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(22): 5024. CrossRef - Effect of 810 nm Diode Laser Irradiation on the Time of Initiation and Depth of Anesthesia for Endodontic Treatment of Mandibular First Molars with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Clinical Trial
Elham Khoshbin, Leila Ghasemi, Rooholah Behroozi, Zahra Khosravi, Afsaneh Rahmati, Loghman Rezaeisoufi, Hamed Karkehabadi
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2023; 41(9): 475. CrossRef - The potential of articaine as new generation of local anesthesia in dental clinics: A review
Wen Luo, Kaiyue Zheng, Huifang Kuang, Zhixin Li, Jinrong Wang, Jie Mei
Medicine.2022; 101(48): e32089. CrossRef
- Anatomical Basis of the Palatal Injection Technique for Pulpal Anesthesia of Maxillary Teeth
- 4,306 View
- 39 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

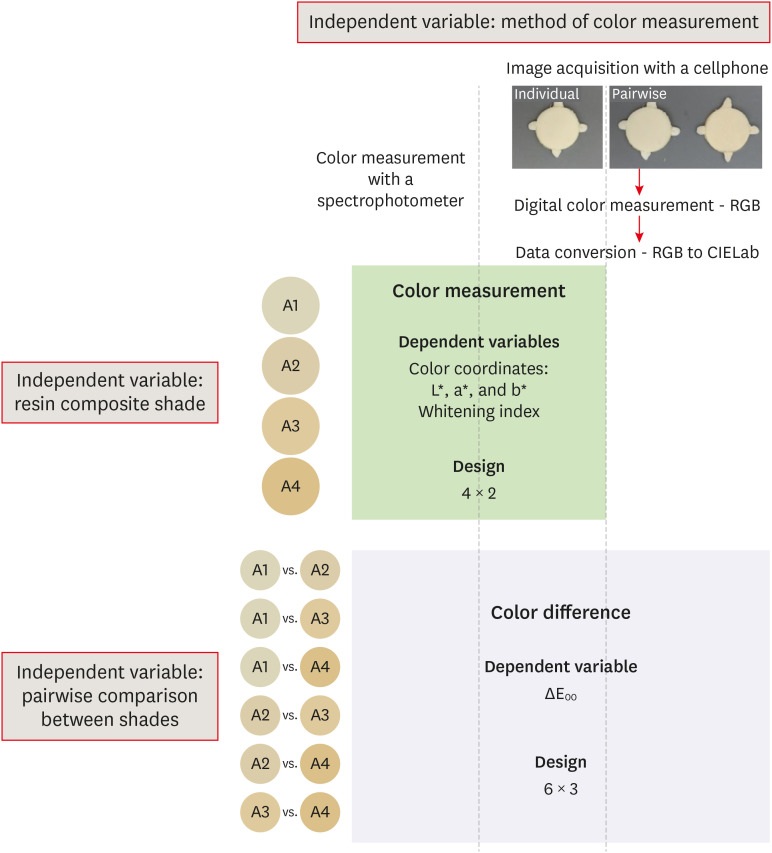
- Color assessment of resin composite by using cellphone images compared with a spectrophotometer
- Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Ratto Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e23. Published online April 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study assessed the reliability of digital color measurements using images of resin composite specimens captured with a cellphone.
Materials and Methods The reference color of cylindrical specimens built-up with the use of resin composite (shades A1, A2, A3, and A4) was measured with a portable spectrophotometer (CIELab). Images of the specimens were obtained individually or pairwise (compared shades in the same photograph) under standardized parameters. The color of the specimens was measured in the images using RGB system and converted to CIELab system using image processing software. Whiteness index (WID) and color differences (ΔE00) were calculated for each color measurement method. For the cellphone, the ΔE00 was calculated between the pairs of shades in separate images and in the same image. Data were analyzed using 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05). Linear regression models were used to predict the reference ΔE00 values of those calculated using color measured in the images.
Results Images captured with the cellphone resulted in different WID values from the spectrophotometer only for shades A3 and A4. No difference to the reference ΔE00 was observed when individual images were used. In general, a similar ranking of ΔE00 among resin composite shades was observed for all methods. Stronger correlation coefficients with the reference ΔE00 were observed using individual than pairwise images.
Conclusions This study showed that the use of cellphone images to measure the color difference seems to be a feasible alternative providing outcomes similar to those obtained with the spectrophotometer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How the Translucency and Color Stability of Single-Shade Universal Resin Composites Are Affected by Coffee?
Büşra Özdemir, Betül Kübra Kurucu Karadeniz, Seyit Bilal Özdemir, Ömer Akbulut
Current Research in Dental Sciences.2024; 34(4): 270. CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of VITA Shade Guide and Various Composite Shades Using Spectrophotometer, Digital Single-lens Reflex, and Cellphone: An In Vitro Study
Aman Verma, Sonali Taneja, Surabhi Ghosh
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 803. CrossRef - Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,655 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

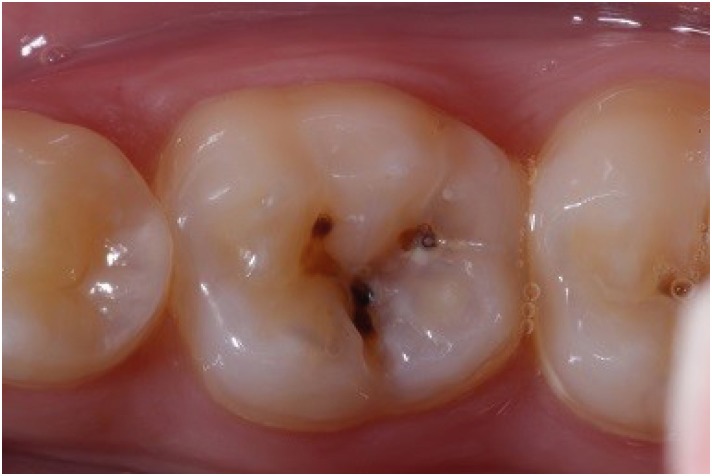
- Functional and aesthetic rehabilitation in posterior tooth with bulk-fill resin composite and occlusal matrix
- Luciana Fávaro Francisconi-dos-Rios, Johnny Alexandre Oliveira Tavares, Luanderson Oliveira, Jefferson Chaves Moreira, Flavia Pardo Salata Nahsan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e9. Published online January 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative procedure in posterior teeth involves clinical steps related to professional skill, especially when using the incremental technique, which may fail in the long term. A recent alternative is bulk-fill resins, which can reduce polymerization shrinkage, decreasing clinical problems such as marginal leakage, secondary caries, and fracture. This scientific study aims to report a clinical case using bulk-fill resin with an occlusal matrix. As determined in the treatment plan, an acrylic resin matrix was produced to establish an improved oral and aesthetic rehabilitation of the right mandibular first molar, which presented a carious lesion with dentin involvement. The occlusal matrix is a simple technique that maintains the original dental anatomy, showing satisfactory results regarding function and aesthetic rehabilitation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
Yu. Kolenko
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2025; (2): 67. CrossRef - Color stability of bulk‐fill compared to conventional resin‐based composites: A scoping review
Gaetano Paolone, Mauro Mandurino, Nicola Scotti, Giuseppe Cantatore, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(4): 657. CrossRef - Evaluation of Abfraction Lesions Restored with Three Dental Materials: A Comparative Study
Bogdan Constantin Costăchel, Anamaria Bechir, Alexandru Burcea, Laurența Lelia Mihai, Tudor Ionescu, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Edwin Sever Bechir
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(5): 1043. CrossRef - Aesthetic restoration of posterior teeth using different occlusal matrix techniques
Elsa Reis Carneiro, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Eunice Carrilho
British Dental Journal.2021; 231(2): 88. CrossRef
- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
- 1,703 View
- 22 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Criteria for clinical translucency evaluation of direct esthetic restorative materials
- Yong-Keun Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):159-166. Published online June 28, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this review was to suggest practical criteria for the clinical translucency evaluation of direct esthetic restorative materials, and to review the translucency with these criteria. For the evaluation of reported translucency values, measuring instrument and method, specimen thickness, background color, and illumination should be scrutinized. Translucency parameter (TP) of 15 to 19 could be regarded as the translucency of 1 mm thick human enamel. Visual perceptibility threshold for translucency difference in contrast ratio (ΔCR) of 0.07 could be transformed into ΔTP value of 2. Translucency differences between direct and indirect resin composites were perceivable (ΔTP > 2). Universal and corresponding flowable resin composites did not show perceivable translucency differences in most products. Translucency differed significantly by the product within each shade group, and by the shade group within each product. Translucency of human enamel and perceptibility threshold for translucency difference may be used as criteria for the clinical evaluation of translucency of esthetic restorative materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bio-inspired nacre-like glass flake/polymer composites with antibacterial function and translucent appearance
Huijun Sun, Aukrit Luangpattarawong, Parinaz Tabrizian, Aqsa Qambrani, Tan Sui, Angela H. Nobbs, Tony Ireland, Bo Su
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106327. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Carving Materials Used in Dental Anatomy Courses on Students' Preferences and Performance
Hilal Şiriner Gümüş, Nazik İrem Onugoren, Mesut Tuzlalı, Nazlı Totik Dogan
Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 1(1): 667. CrossRef - Determining the perceptibility and acceptability threshold of the relative translucency parameter‐ A pilot study
Yale Cho, Soni Prasad, Judy Chia‐Chun Yuan, Cortino Sukotjo, William M. Johnston, Alvin G. Wee
Journal of Prosthodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive characterization of tobacco-induced changes in enamel surface topography
Tamanna Kaur, Ramya Ramadoss, Nitya Krishnasamy, Sandhya Sundar, Suganya Panneer Selvam, Hema Shree K
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(1): 97. CrossRef - Impact of Artificial Aging on the Optical Properties of High-translucent Zirconia and Lithium Disilicate: An In Vitro Analysis
Ahmed N Abdelaziz, Shereen A Amin, Mahmoud A Aboulhawa
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 15(1): 3. CrossRef - Color and Translucency Compatibility Among Various Resin-Based Composites and Layering Strategies
Elena Bianca Varvara, Cristina Gasparik, Javier Ruiz-López, Alexandra Iulia Aghiorghiesei, Bogdan Culic, Diana Dudea
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 173. CrossRef - Influence of Acidic Storage and Simulated Toothbrushing on the Translucency and Color Stability of 3D-Printed Resins for Prosthodontic Applications
Sarah M. Alnafaiy, Nawaf Labban, Alhanoof Saleh Aldegheishem, Saleh Alhijji, Refal Saad Albaijan, Saad Saleh AlResayes, Rafa Abdulrahman Alsultan, Abeer Mohammed Alrossais, Rahaf Farhan Alanazi
Materials.2025; 18(17): 3942. CrossRef - Color Stability Assessment of Single- and Multi-Shade Composites Following Immersion in Staining Food Substances
Vittorio Checchi, Eleonora Forabosco, Giulia Della Casa, Shaniko Kaleci, Luca Giannetti, Luigi Generali, Pierantonio Bellini
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(9): 285. CrossRef - Effects of multiple firings on the translucency, crystalline phase, and mechanical strength of highly translucent zirconia
Haruko KATADA, Masanao INOKOSHI, Singo KAMIJO, Hengyi LIU, Kaiqi XU, Masakazu KAWASHITA, Taishi YOKOI, Masaya SHIMABUKURO, Shunsuke MINAKUCHI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(2): 294. CrossRef - Effect of Repolishing on Color Stability, Translucency, and Surface Roughness of Aged Monochromatic Dental Composites
Mohamed M. Abdul-Monem, Mohamed A. Hussein, Mona G. Abdelrehim
European Journal of General Dentistry.2024; 13(03): 240. CrossRef - The optical property measuring methods for resin composite using multiple spectrophotometers
Ji-Hun YOUM, Il Jun JEONG, Jae-Sung KWON, Bum-Soon LIM, Myung-Hwan OH, Kwang-Mahn KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(4): 525. CrossRef - Translucency and Polymerization Ability of Contemporary Resin Composites
Bianca Alves Barata Mills, Cristian Sbardelotto, Mario Couto Neto, Vladi Oliveira Guimaraes Junior, Larissa Maria Cavalcante, Luis Felipe Jochims Schneider
Biomaterials Connect.2024; 1(1): 1. CrossRef - The Dependence on Hue, Value and Opacity of Real-Time- and Post-Curing Light Transmission in a Nano-Hybrid Ormocer
Nicoleta Ilie
Materials.2024; 17(2): 496. CrossRef - Flexural strength and translucency of barium‐silicate‐filled resin nanoceramics for additive manufacturing
Geun‐Taek Park, Kyung‐Ho Ko, Yoon‐Hyuk Huh, Chan‐Jin Park, Lee‐Ra Cho
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 445. CrossRef - Color and translucency of enamel in vital maxillary central incisors
Alvin G. Wee, Damian A. Winkelmann, David J. Gozalo, Masayasu Ito, William M. Johnston
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(6): 878. CrossRef - Performance of two-flux and four-flux models for predicting the spectral reflectance and transmittance factors of flowable dental resin composites
Vincent Duveiller, Raphaël Clerc, Julien Eymard, Jean-Pierre Salomon, Mathieu Hébert
Dental Materials.2023; 39(8): 743. CrossRef - Effect of thickness on the translucency of resin-based composites and glass-ceramics
Sumi KANG, Seung-Yeon RYU, Kwang-Mahn KIM, Sung-Ho PARK
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 30. CrossRef - Evaluation of fracture strength and translucency of 3D printing resin crown for carious primary anterior tooth
Young-Jun Ham, Joon-Haeng Lee, Jong-Su Kim, Jong-Bin Kim, Mi-Ran Han, Ji-Sun Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2023; 47(1): 40. CrossRef - Digital Light Processing of Zirconia Suspensions Containing Photocurable Monomer/Camphor Vehicle for Dental Applications
Seo-Young Yang, Young-Hag Koh, Hyoun-Ee Kim
Materials.2023; 16(1): 402. CrossRef - Translucency of CAD/CAM and 3D Printable Composite Materials for Permanent Dental Restorations
Alessandro Vichi, Dario Balestra, Nicola Scotti, Chris Louca, Gaetano Paolone
Polymers.2023; 15(6): 1443. CrossRef - Translucency and Radiopacity of Dental Resin Composites – Is There a Direct Relation?
LPL Rosado, EA Münchow, ELS de Oliveira, R Lacerda-Santos, DQ Freitas, HL Carlo, FS Verner
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(3): E61. CrossRef - Light Transmission Characteristics and Cytotoxicity within A Dental Composite Color Palette
Nicoleta Ilie, Andrei Cristian Ionescu, Karin Christine Huth, Marioara Moldovan
Materials.2023; 16(10): 3773. CrossRef - Layer characteristics in strength-gradient multilayered yttria-stabilized zirconia
Masanao Inokoshi, Hengyi Liu, Kumiko Yoshihara, Mao Yamamoto, Watcharapong Tonprasong, Yasuhiko Benino, Shunsuke Minakuchi, Jef Vleugels, Bart Van Meerbeek, Fei Zhang
Dental Materials.2023; 39(4): 430. CrossRef - Manufacturing and Characterization of Dental Crowns Made of 5-mol% Yttria Stabilized Zirconia by Digital Light Processing
Jae-Min Jung, Gyu-Nam Kim, Young-Hag Koh, Hyoun-Ee Kim
Materials.2023; 16(4): 1447. CrossRef - Effect of artificial aging on the translucency of monolithic zirconia materials sintered at different temperatures
Burcu Kanpalta, Defne Burduroğlu, Özlem Kara
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(1): 91.e1. CrossRef - The Influence of Two Curing Protocols on the Colour Stability and Translucency of Resin Luting Agents
Riccardo Monterubbianesi, Flavia Vitiello, Vincenzo Tosco, Rim Bourgi, Angelo Putignano, Giovanna Orsini
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(21): 11120. CrossRef - Optical characteristics of experimental dental composite resin materials
Diana Leyva del Rio, William Michael Johnston
Journal of Dentistry.2022; 118: 103949. CrossRef - In Vivo Evaluation of the Effects of Sintering Temperature on the Optical Properties of Dental Glass-Ceramics
Kuo-Cheng Fan, Yu-Ling Lin, Hao-Wei Tsao, Hsuan Chen, Sheng-Yang Lee, Yu-Chen Cheng, Hsiao-Ping Huang, Wei-Chun Lin
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(13): 2187. CrossRef - Translucency and masking ability of translucent zirconia; comparison with conventional zirconia and lithium disilicate
Joon Hee Park, Hyun Ji Bang, Nak-Hyun Choi, Eun-Jin Park
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2022; 14(5): 324. CrossRef - Color and optical properties of 3D printing restorative polymer‐based materials: A scoping review
Cristina Espinar, Alvaro Della Bona, María M. Pérez, Rosa Pulgar
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(6): 853. CrossRef - Effects of Aging on the Color and Translucency of Monolithic Translucent Y‐TZP Ceramics: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis of In Vitro Studies
Chang-yuan Zhang, Check Agingu, James Kit Hon Tsoi, Hao Yu, Fernanda Faot
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Conventional and Electronic Cigarettes Smoking on the Color Stability and Translucency of Tooth Colored Restorative Materials: An In Vitro Analysis
Hamad A. Alnasser, Ahmed A. Elhejazi, Abdalrahman A. Al-Abdulaziz, Saad S. Alajlan, Syed Rashid Habib
Coatings.2021; 11(12): 1568. CrossRef - Color interaction between resin composite layers: An overview
Eman Hani Ismail
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(8): 1105. CrossRef - Translucency parameter of conventional restorative glass‐ionomer cements
Joana Yumi Teruya Uchimura, Francielle Sato, Rosangela Getirana Santana, Rafael Menezes‐Silva, Ligia S. Bueno, Ana Flávia Sanches Borges, Maria Fidela de Lima Navarro, John W. Nicholson, Sharanbir K. Sidhu, Renata Corrêa Pascotto
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(6): 935. CrossRef - Comparison between translucencies of anterior resin composites and natural dental tissues
Melin Balci, Zeynep Ergucu, Esra Uzer Çelik, Lezize Sebnem Turkun
Color Research & Application.2021; 46(3): 635. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Translucency and Color Stability of CAD/CAM Polymer‐Infiltrated Ceramic Materials after Accelerated Aging
Mohammad D. Al Amri, Nawaf Labban, Saleh Alhijji, Hassan Alamri, Mounir Iskandar, Jeffrey A. Platt
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(4): 318. CrossRef - The Thickness and Opacity of Aesthetic Materials Influence the Restoration of Discolored Teeth
I Durães, A Cavalcanti, P Mathias
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(5): 559. CrossRef - Bulk-Fill Direct Restorative Materials: An In Vitro Assessment of Their Physio-Mechanical Properties
Hui Woon Yeo, May Yeh Loo, Mariam Alkhabaz, Kai Chun Li, Joanne Jung Eun Choi, Abdullah Barazanchi
Oral.2021; 1(2): 75. CrossRef - Color and Translucency Stability of Three-Dimensional Printable Dental Materials for Crown and Bridge Restorations
Jong-Eun Kim, Won-Huy Choi, Dasun Lee, Yooseok Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Byoung-Duck Roh, Dohyun Kim
Materials.2021; 14(3): 650. CrossRef - Effect of Veneering and Hydrothermal Aging on the Translucency of Newly Introduced Extra Translucent and High Translucent Zirconia with Different Thicknesses
Sevki Cinar, Bike Altan, Victor Feitosa
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro optical characterization of dental resin composite aged in darkness
Sarah S. Mikhail, William M. Johnston
Color Research & Application.2020; 45(2): 345. CrossRef - Color Stability of Dental Reinforced CAD/CAM Hybrid Composite Blocks Compared to Regular Blocks
Yeong-Ah Kang, Han-Ah Lee, Joseph Chang, Wonjoon Moon, Shin Hye Chung, Bum-Soon Lim
Materials.2020; 13(21): 4722. CrossRef - Highly translucent dental resin composites through refractive index adaption using zirconium dioxide nanoparticles and organic functionalization
Carina Kolb, Katrin Gumpert, Herbert Wolter, Gerhard Sextl
Dental Materials.2020; 36(10): 1332. CrossRef - Spatial Distribution of the Micro-Mechanical Properties in High-Translucent CAD/CAM Resin-Composite Blocks
Nicoleta Ilie
Materials.2020; 13(15): 3352. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Light Transmission by Various Dental Restorative Materials and the Tooth Structure
N Ilie, G Furtos
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(4): 442. CrossRef - The Effect of Surface Treatments on the Mechanical and Optical Behaviors of CAD/CAM Restorative Materials
Sevcan Kurtulmus‐Yilmaz, Esra Cengiz, Salim Ongun, Izgen Karakaya
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of accelerated artificial aging on the translucency and color stability of monolithic ceramics with different surface treatments
Meral Kurt, Bilge Turhan Bal
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(4): 712.e1. CrossRef - Translucency thresholds for dental materials
Marianne Salas, Cristina Lucena, Luis Javier Herrera, Ana Yebra, Alvaro Della Bona, María M. Pérez
Dental Materials.2018; 34(8): 1168. CrossRef - Color and Translucency of Resin-based Composites: Comparison of A-shade Specimens Within Various Product Lines
D Kim, S-H Park
Operative Dentistry.2018; 43(6): 642. CrossRef - Effect of 2 Bleaching Agents with a Content of High Concentrated Hydrogen Peroxide on Stained 2 CAD/CAM Blocks and a Nanohybrid Composite Resin: An AFM Evaluation
İzgen Karakaya, Esra Cengiz
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Effects of glass chemistry on the optical properties of highly translucent alumina-glass biocomposites for dental restorations
Afonso Chimanski, Paulo Francisco Cesar, Humberto Naoyuki Yoshimura
Ceramics International.2017; 43(16): 13970. CrossRef - Relative Translucency of a Multilayered Ultratranslucent Zirconia Material
Loubna Shamseddine, Zeina Majzoub
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(12): 1099. CrossRef
- Bio-inspired nacre-like glass flake/polymer composites with antibacterial function and translucent appearance
- 2,325 View
- 20 Download
- 52 Crossref

- Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry
- Hee-Jin Kim, Lorena Karanxha, Su-Jung Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):236-239. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although several methods including composite resin restoration and microabrasion have been used for management of white spot lesion, tooth jewelry can be considered as another noninvasive option. This case report describes the management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry. This report also highlights the patients' preference for tooth jewelry as an esthetic concern.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Putting the mouth back in the body – the neglected area of dental and oral travel health
Irmgard L Bauer
Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth adornments, gems, and grills
Harpuneet Kaur
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2022; 12(2): 50. CrossRef - Gold Enamel Choumps – A Case report
Sargam D. Kotecha, Y. Deepa Hedge, Kalpna Chaudhry, Ramakrishna Yeluri, Updesh Masih, Chanchal Singh
Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences.2016; 6(3): 303. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef
- Putting the mouth back in the body – the neglected area of dental and oral travel health
- 1,494 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Hypoesthesia after IAN block anesthesia with lidocaine: management of mild to moderate nerve injury
- Sungjoo Moon, Seung-Jong Lee, Euiseong Kim, Chan-Young Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):232-235. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Hypoesthesia after an inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) block does not commonly occur, but some cases are reported. The causes of hypoesthesia include a needle injury or toxicity of local anesthetic agents, and the incidence itself can cause stress to both dentists and patients. This case presents a hypoesthesia on mental nerve area followed by IAN block anesthesia with 2% lidocaine. Prescription of steroids for a week was performed and periodic follow up was done. After 1 wk, the symptoms got much better and after 4 mon, hypoesthesia completely disappeared. During this healing period, only early steroid medication was prescribed. In most cases, hypoesthesia is resolved within 6 mon, but being aware of etiology and the treatment options of hypoesthesia is important. Because the hypoesthesia caused by IAN block anesthesia is a mild to moderate nerve injury, early detection of symptom and prescription of steroids could be helpful for improvement of the hypoesthesia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Botulinum Toxin-A, Generating a Hypothesis for Orofacial Pain Therapy
Yair Sharav, Rafael Benoliel, Yaron Haviv
Toxins.2025; 17(8): 389. CrossRef - Intranasal CRMP2-Ubc9 inhibitor regulates NaV1.7 to alleviate trigeminal neuropathic pain
Santiago I. Loya-Lopez, Heather N. Allen, Paz Duran, Aida Calderon-Rivera, Kimberly Gomez, Upasana Kumar, Rory Shields, Rui Zeng, Akshat Dwivedi, Saumya Saurabh, Olga A. Korczeniewska, Rajesh Khanna
Pain.2024; 165(3): 573. CrossRef - İMPLANT CERRAHİSİ SONRASI HİPOESTEZİ-6 AYLIK TAKİP: VAKA SERİSİ
Sefa AYDINDOĞAN, Emine Elif MUTAFCİLAR VELİOĞLU, Yunus Emre BALABAN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(4): 350. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of Post-Traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain
Olga A. Korczeniewska, Divya Kohli, Rafael Benoliel, Sita Mahalakshmi Baddireddy, Eli Eliav
Biomolecules.2022; 12(12): 1753. CrossRef - Shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen to the mandibular premolars in an Indian sub-population: a retrospective CBCT analysis
Komal Sheth, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, James L. Gutmann, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain (atypical facial pain)
Gary W. Jay, Robert L. Barkin
Disease-a-Month.2022; 68(6): 101302. CrossRef - Differential roles of NMDAR subunits 2A and 2B in mediating peripheral and central sensitization contributing to orofacial neuropathic pain
Yan-Yan Zhang, Fei Liu, Zhong-Han Fang, Yue-Ling Li, Hong-Lin Liao, Qin-Xuan Song, Cheng Zhou, Jie-Fei Shen
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.2022; 106: 129. CrossRef - Visualization of Inferior Alveolar and Lingual Nerve Pathology by 3D Double-Echo Steady-State MRI: Two Case Reports with Literature Review
Adib Al-Haj Husain, Daphne Schönegg, Silvio Valdec, Bernd Stadlinger, Thomas Gander, Harald Essig, Marco Piccirelli, Sebastian Winklhofer
Journal of Imaging.2022; 8(3): 75. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of painful traumatic trigeminal neuropathy—Evidence from animal research and clinical correlates
Olga A. Korczeniewska, Junad Khan, Eli Eliav, Rafael Benoliel
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2020; 49(6): 580. CrossRef - Behavioral changes in calves 11 days after cautery disbudding: Effect of local anesthesia
Sarah J.J. Adcock, Danielle M. Cruz, Cassandra B. Tucker
Journal of Dairy Science.2020; 103(9): 8518. CrossRef - Frequency of Lower Lip Paresthesia in Patients Receiving Implant-Supported Mandibular Dentures in Tabriz, Iran in 2017-2018
Farrokh Farhadi, Reza Khorshidi-Khiavi, Fereshteh Taheri, Milad Ghanizadeh
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2019; 11(1): 26. CrossRef - Persistent idiopathic facial pain
Rafael Benoliel, Charly Gaul
Cephalalgia.2017; 37(7): 680. CrossRef - Painful Traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathy
Rafael Benoliel, Sorin Teich, Eli Eliav
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America.2016; 28(3): 371. CrossRef - Neuropathy of Trigeminal Nerve Branches After Oral and Maxillofacial Treatment
Jimoh Olubanwo Agbaje, Elke Van de Casteele, Marjolein Hiel, Ciska Verbaanderd, Ivo Lambrichts, Constantinus Politis
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2016; 15(3): 321. CrossRef - The Enigma of the Mental Foramen as It Relates to Plastic Surgery
Raphael Alves Chu, Fabio Xerfan Nahas, Marcello Di Martino, Fernanda Abibi Soares, Neil Ferreira Novo, Ricardo Luiz Smith, Lydia Masako Ferreira
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2014; 25(1): 238. CrossRef - Mental nerve paresthesia secondary to initiation of endodontic therapy: a case report
Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi, Sharique Alam, Afaf Zia, Masood Hasan Khan, Ashok Kumar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 215. CrossRef - Pain Sensation and Postsurgical Complications in Posterior Mandibular Implant Placement Using Ridge Mapping, Panoramic Radiography, and Infiltration Anesthesia
Ali Saad Thafeed AlGhamdi
ISRN Dentistry.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef
- Botulinum Toxin-A, Generating a Hypothesis for Orofacial Pain Therapy
- 2,599 View
- 8 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Proposal of new dental color-space for aesthetic dental materials
- Yun-Jeong Oh, Su-Jung Park, Dong-Jun Kim, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):19-27. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to develope new dental color-space system. Twelve kinds of dental composites and one kind of dental porcelain were used in this study. Disk samples (15 mm in diameter, 4 mm in thickness) of used materials were made and sample's CIE L*a*b* value was measured by Spectrocolorimeter (MiniScan XE plus, Model 4000S, diffuse/8° viewing mode, 14.3 mm Port diameters, Hunter Lab. USA). The range of measured color distribution was analyzed. All the data were applied in the form of T### which is expression unit in CNU Cons Dental Color Chart.
The value of L* lies between 80.40 and 52.70. The value of a* are between 10.60 and 3.60 and b* are between 28.40 and 2.21. The average value of L* is 67.40, and median value is 67.30. The value of a* are 2.89 and 2.91 respectively. And for the b*, 14.30 and 13.90 were obtained. The data were converted to T### that is the unit count system in CNU-Cons Dental Color Chart. The value of L* is converted in the first digit of the numbering system. Each unit is 2.0 measured values. The second digit is the value of a* and is converted new number by 1.0 measured value. For the third digit b* is replaced and it is 2.0 measured unit apart. T555 was set to the value of L* ranging from 66.0 to 68.0, value of a* ranging from 3 to 4 and b* value ranging from 14 to 16.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Difference in color and translucency according to dental zirconia A3 colorant
Joo-Hee Lee, Jin-Young Park
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2022; 44(4): 118. CrossRef
- Difference in color and translucency according to dental zirconia A3 colorant
- 1,128 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of local anesthesia on pulpal blood flow in mechanically stimulated teeth
- Wan-Sik Chu, Seung-Ho Park, Dong-Kuk Ahn, Sung Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):257-262. Published online January 14, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.257
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The aims of the study were to evaluate the effect of epinephrine-containing local anesthetics on pulpal blood flow (PBF) and to investigate its effect on cavity preparation-induced PBF change. PBF was recorded using a laser Doppler flowmeter (Perimed Co., Sweden) from canines of nine cats under general anesthesia before and after injection of local anesthetics and after cavity preparation. 2% lidocaine hydrochloride with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine was administered by local infiltration given apical to the mandibular canine at the vestibular area and the same volume of isotonic saline was injected on the contralateral tooth as a control. A round carbide bur was operated at slow speed with isotonic saline flushing to grind spherical cavities with increasing depth through the enamel and into the dentin on both teeth. The obtained data was analyzed with paired
t -test.Cavity preparation caused significant increase of PBF (
n = 9,p < 0.05). Local infiltration of lidocaine with epinephrine resulted in decreases of PBF (n = 9,p < 0.05), whereas there was no significant change of PBF with the physiologic saline as a control. Cavity preparation on tooth anesthetized with lidocaine with epinephrine caused significantly less increase of PBF than in control tooth (p < 0.05).Therefore, the result of the present study demonstrates that local infiltration of 2% lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine effectively reduces PBF increase caused by cavity preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Systematic Injection Patterned-Technique of One-Per-Mil Tumescent Solution for Perforator-Based Skin Flap: Is it Better Than the Random Patterned-Technique?
Theddeus O. H. Prasetyono, Sweety Pribadi
International Surgery.2015; 100(9-10): 1308. CrossRef - Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Change in Pulpal Blood Flow of Heat-induced Neurogenic Inflammation in Feline Dental Plup
Min-Kyoung Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(12): 6340. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 187. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,924 View
- 19 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The influence of epinephrine concentration in local anesthetics on pulpal and gingival blood flows
- Jae-Sang Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):475-484. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.475
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 187. CrossRef - Effect of local anesthesia on pulpal blood flow in mechanically stimulated teeth
Wan-Sik Chu, Seung-Ho Park, Dong-Kuk Ahn, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(4): 257. CrossRef
- Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
- 2,265 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


